
Front Cover
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 0 Introduction
OKIPAGE 8w
LED PAGE PRINTER
Adobe Acrobat printable reference copy
of the OKIDATA Service Training Manual.
05/17/99
Note: This Adobe Acrobat version of the Okidata Service Training Manual was built with the pictures
rendered at 300 dpi, which is ideal for printing, but does not display well on most displays.
Table of Contents Page
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
0 Introduction
Preface 1
1 Configuration
Configuration 2
....1.1 System Configuration 3
....1.2 Printer Configuration 4
....1.3 Specification 5
....1.4 Safety Standards 6
........1.4.1 Certification Label 7
........1.4.2 Warning Label 8
2 Operation Description
2.0 Operation Description 9
2.1 Main Control Board 10
2.2 Power Supply Unit 11
2.3 High-Voltage Power Supply Board 12
2.4 Electro-Photographic Processor 13
2.5 Electro-Photographic Process 14
....2.5.1 Explanation of Each Process Operation 15
2.6 Paper Jam Detection 16
2.7 Toner Low Detection 17
2.8 Cover Open 18
2.9 Detecting ID existence 19
3 Parts Replacement
Parts Replacements 20
....3.1 Precautions for Parts Replacement 21
....3.2 Parts Layout 22
........Upper Cover Assy 23
........Base Frame Unit 24
........Base Plate Unit 25
....3.3 Replacing Parts 26
........3.3.1 Hopper Plate 27
........3.3.2 LED Head and Head Spring 28
........3.3.3 Transfer Roller 29
........3.3.4 Upper Cover Assy 30
........3.3.5 High-Voltage Power Supply Board (P2H/P6L) 31
........3.3.6 Top Cover Assy and Flat Cable Assy 32
........3.3.7 Paper Holder 33
........3.3.8 Side Plate M and Idle Gear 34
........3.3.9 Heat Assy 35
........3.3.10 Drive Shaft E (Eject) and Eject Roller 36
........3.3.11 Pressure Roller B (Back Up Roller) 37
........3.3.12 Separator Guide 38
........3.3.13 Pulse Motor (Main) 39
........3.3.14 Hopping Shaft Assy 40
........3.3.15 Resist Roller 41
........3.3.16 Paper Sensor E, Paper Sensor Exit and Toner
Sensor Assy
........3.3.17 Base Plate 43
4 Adjustment
42
Table of Contents Page
4.0 Adjustment 44
....4.1 Adjustment Types and Functions 45
........4.1.1 Printer Driver 46
........4.1.2 Engine Maintenance Utility 47
....4.2 Adjustment When Replacing a Part 48
........4.2.1 Setting LED Head Drive Time 49
........4.2.2 Uploading and Downloading EEPROM Data 50
5 Periodical Maintenance
5.1 Periodical Replacement Parts 51
5.2 Cleaning 52
....5.2.1 Cleaning the LED Lens Array 53
6 Troubleshooting Procedures
6.1 Troubleshooting Tips 54
6.2 Check Points Before Correcting Image Problems 55
6.3 Notes When Correcting Image Problems 56
6.4 Preparation Before Troubleshooting 57
6.5 Troubleshooting 58
....6.5.1 Status Monitor Message List 59
....6.5.2 Status Message Troubleshooting 60
....6.5.3 Image Troubleshooting 61
........(1) An image is light or blurred entirely 62
........(2) Dark background density 63
........(3) A blank paper is output 64
........(4) Vertical black belt/stripe 65
........(5) Cyclic defect 66
........(6) A blank paper is output 67
........(7) Poor fusing 68
........(8) Vertical white belt/stripe 69
........Contents - Figure 6-4 70
........Contents - Figure 6-5 71
7 Wiring Diagram
7.1 Interconnect Signal Diagram 72
7.2 PCB Layout 73
....7.2.1 Main Control Board (HBY PCB) 74
....7.2.2 High-Voltage Power Supply Board 75
8 Parts List
Cover Assy Upper 76
Base Frame Unit 77
Heat Assy 78
Base Plate Unit 79
A Local Printing
Local Printing 80
B Parallel Interface
Parallel Interface 81
C Maintenance Utility
Outline of Maintenance Utility 82
Detail of Each Function 83
....4.1 Engine Menu Setting 84
....4.2 Engine Counter 85
....4.3 Printer Status 86
Table of Contents Page
....4.4 Test Print 87
....4.5 Option 88
....4.6 About 89
....4.7 Reload 90
.... 4.8 Exit 91

Page: 1
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 0 Introduction
Preface
This Service Handbook describes the field maintenance procedures for the OKIPAGE 8w.
This manual is written for use by service persons. Please note that you should refer to the Printer User's Manual for
operating procedures.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 1 Configuration
Configuration
System Configuration
Printer Configuration
Specification
Safety Standards
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 2
Page: 3
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 1 Configuration
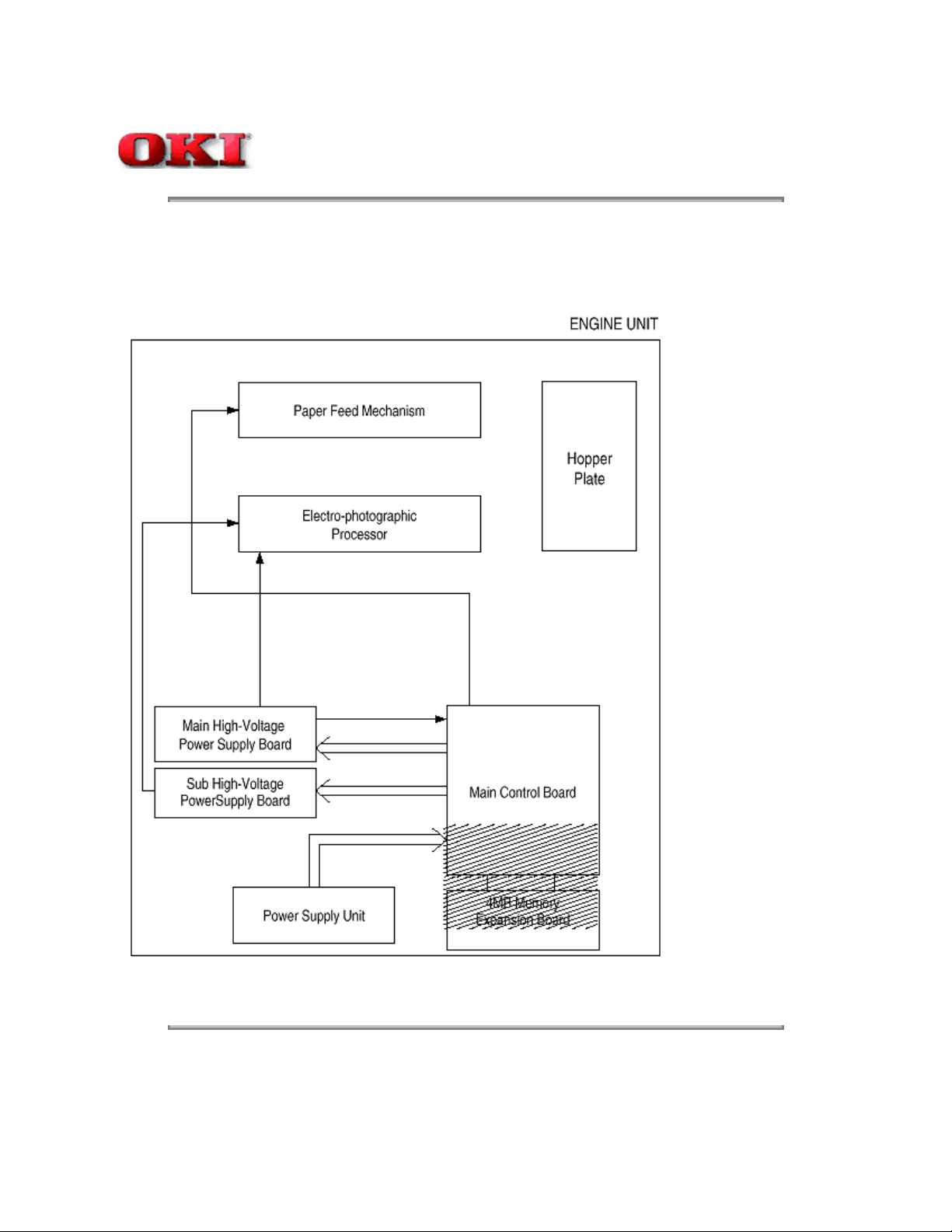
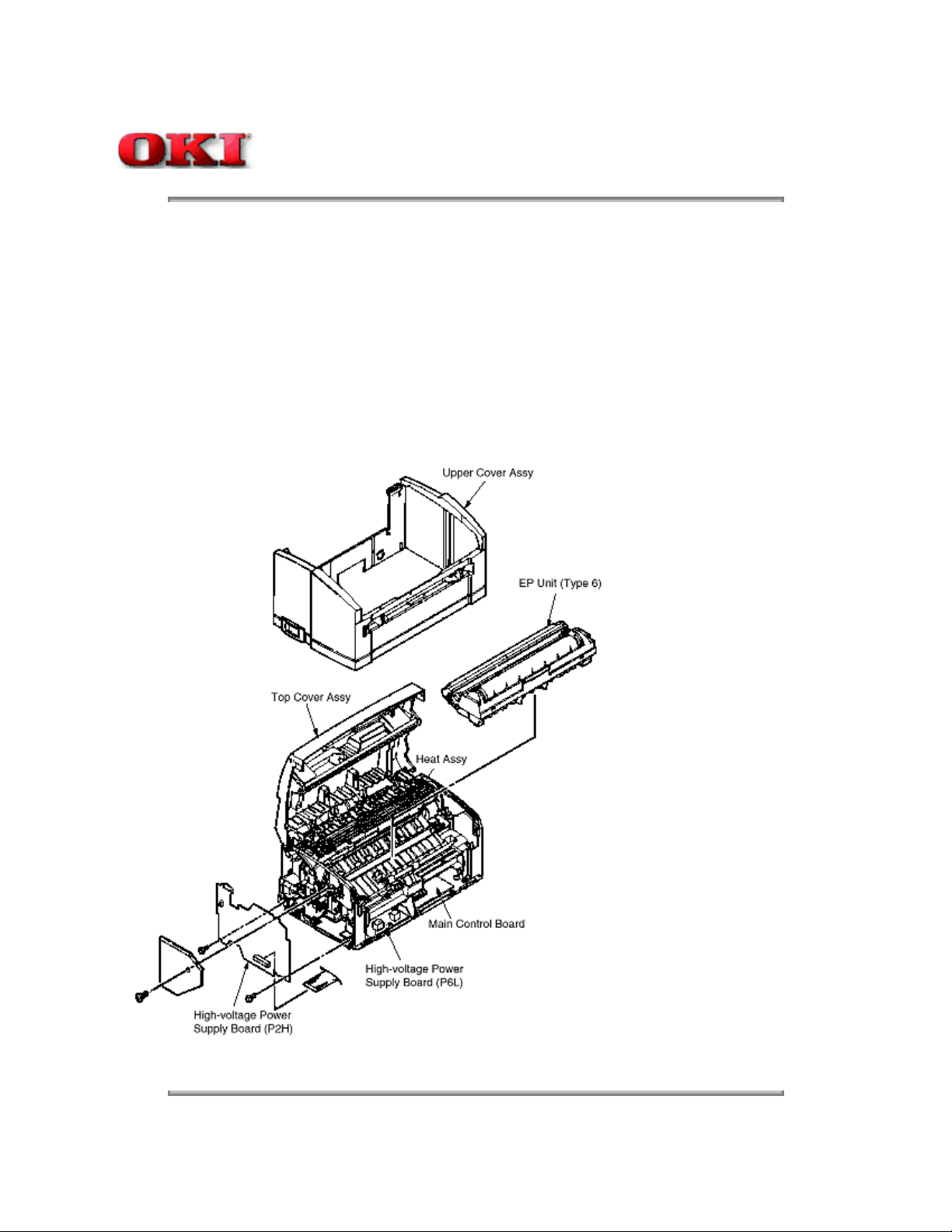
1.1 System Configuration
The OKIPAGE 8w consists of a control block, a power supply unit, and an engine block. (See Figure 1-1
below.)
Figure 1-1
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 1 Configuration
1.2 Printer Configuration
The printer unit consists of the following five hardware components:
Electro-Photographic Processor l
Paper Feeder l
Main Control Board l
High-Voltage Power Supply Board l
Power Supply Unitl
Figure 1-2 is the configuration of the printer unit.
Page: 4
Figure 1-2

Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

1.3 Specification
(1) Type: Desktop
Page: 5
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 1 Configuration
(2) Outside dimensions
(excludes protruding
portion)
(3) Weight 9.3 lbs. (4.2 kg)
(4) Development method
Exposure method
(5) Paper used <Type>
(6) Printing speed: First print: 23 seconds (A4) (after warm-up)
Height: 5.9" (150 mm)
Width 12.2" (310 mm)
Depth 7.5" (191mm)
Dry non-magnetic development system
LED stationary head
Standard paperl
- Xerox 4200 (20 lbs)
Application paper (manual face-up feed)l
- Label
- Envelope
- OHP paper (Transparency)
<Size>
14" (355.6 mm) (Max.) x 8.5" (215.9 mm)
<Thickness>
Automatic feed: 16 to 28 lbs (60 to 105 g/m2)
- Manual feed: Label, Envelope, OHP paper (transparency)
Continuous print: 8 sheets/minute (A4)
Warm-up time: 40 seconds (120 VAC for ODA, 230 VAC for
OEL/INT) (at room temperature 77o F (25o C)
(7) Paper feeding method Automatic paper feed or manual paper feed
(8) Paper delivery
method
(9) Resolution 600 dpi x 600 dpi (true)
(10) Power input 230 VAC +/-10% (for OEL/INT)
(11) Power consumption Peak: Approx. 450W
(12) Temperature and
humidity
Face down
120 VAC +/-15% for (ODA)
Typical operation: Approx. 100W
Idle: Approx. 30W
Power save mode: Approx. 5W

Temperature Humidity
During operation
In storage
10 to 32o C
-10 to +43o C
20 to 80% RH (relative humidity)
10 to 90% RH (relative humidity)
No condensation is permissible.
Caution: Temperature and humidity in storage are measured with the OKIPAGE 8w being packed; they
are valid for one year.
(13) Noise During operation: 48 dB (A) or less
Standby: 38 dB (A) or less
(14) Consumables Toner cartridge kit - 1,500 (5% duty) ---- 45g cartridge kit
Image drum cartridge - 10,000 (at continuous printing)
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 1 Configuration
1.4 Safety Standards
1.4.1 Certification Label
1.4.2 Warning Label
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 6
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 1 Configuration
1.4.1 Certification Label
The safety certification label is affixed to the following location of the OKIPAGE 8w:
Page: 7
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 1 Configuration
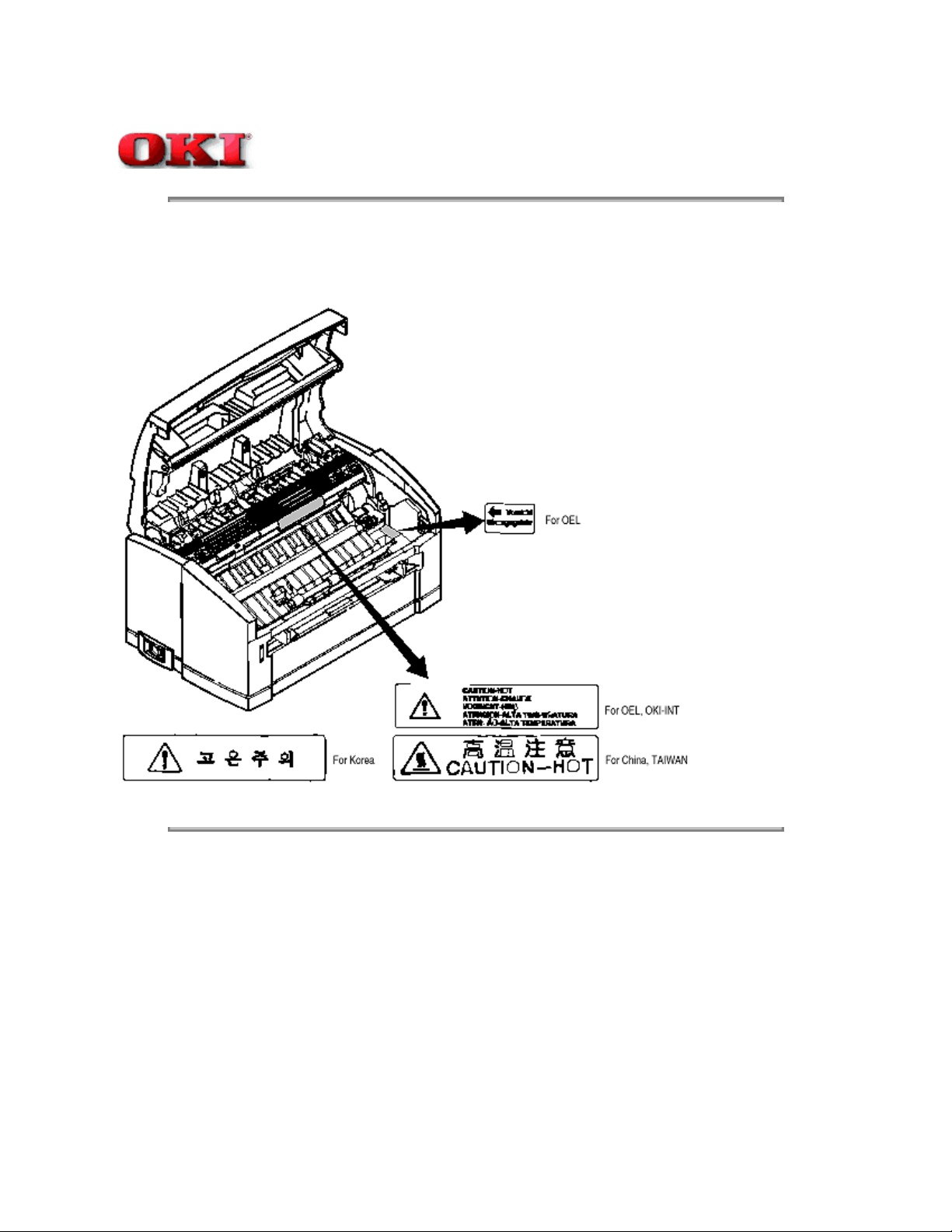
1.4.2 Warning Label
Warning labels are affixed to the locations that may cause bodily injury.
During maintenance, do work with enough care while following instructions on these warning labels.
Page: 8
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 9
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.0 Operation Description
The OKIPAGE 8w consists of a main control board, a high-voltage power supply board, a power supply
unit, and an electro-photographic processor. The OKIPAGE 8w receives print data from a higher-level
interface and sequentially stores it in memory. The OKIPAGE 8w decodes and edits the received data
while storing print data from the interface in memory. It sequentially transfers the edited data to the LED
head for each dot line. The electro-photographic processor then prints the data on sheets of paper.
The display of the higher-level host is used for device operation and status display.
Figure 2-1 is the block diagram of the OKIPAGE 8w.
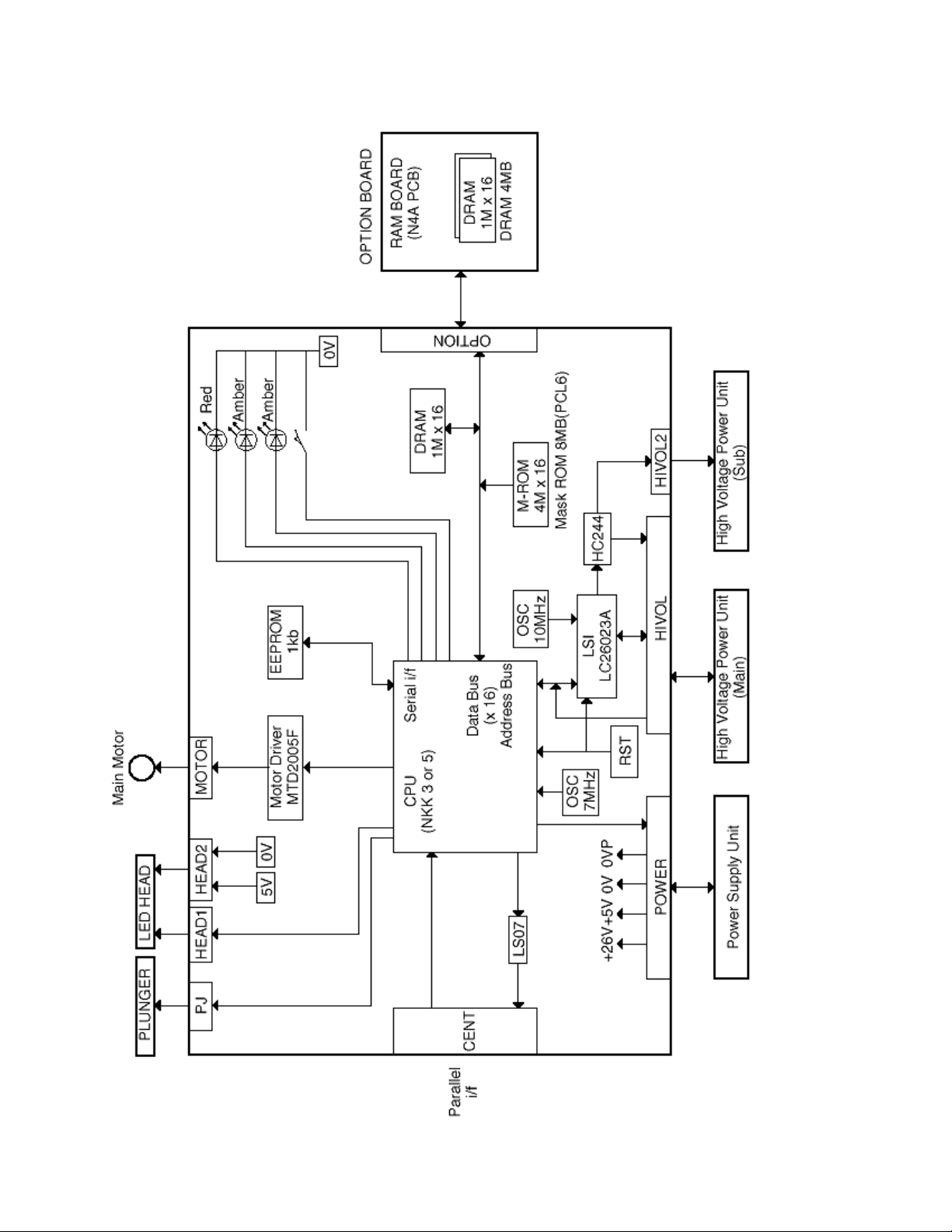

Figure 2-1 Block Diagram
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 10
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.1 Main Control Board
The main control board consists of a one-chip CPU, a program ROM, a DRAM, an EEPROM, a host
interface circuit, and a mechanism driving circuit. The mechanism driving circuit consists of an LED
head, a main motor, and an electromagnetic clutch.
(1) One-chip CPU
The one-chip CPU is a custom CPU (8-bit internal bus, 8-bit external bus, 10-MHz clock) incorporating
mask ROM and CPU peripheral devices. This CPU has the functions listed in the table below.
Built-in Device Function
DRAM controller Controls DRAM.
DMA controller Transfers image data from Parallel I/F to DRAM, from
DRAM to a video output port and between CPU and DRAM.
Parallel interface controller Controls the parallel interface.
Video output port
LED STB output port
Timer Generates various control timings for monitoring paper
I/O Port Inputs and outputs the sensor signals and motor signals,
A/D converter Inputs the feedback signals from a high-voltage generation
(2) Program ROM
Program ROM contains a program for the equipment. EPROM is used as program ROM. When mask
ROM in the one-chip CPU explained in (1) above is valid, the EPROM is not mounted. (For details on
short wiring setting, see Section 7.2.)
(3) DRAM
DRAM is used as resident memory.
(4) EEPROM
Controls LED head.
feeding and a paper size.
etc. Also performs I/O for EEPROM.
circuit and thermistor signal.
EEPROM holds the following data:
Menu data l
Counter value l

Adjustment valuel
(5) Parallel interface
The parallel interface receives parallel data from the host; it conforms to the IEEE1284 specification.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.2 Power Supply Unit
The power supply unit supplies +5 V and +26 V to the main control board according to 230 VAC / 120 VAC.
Output voltage Application
+5 V Used to generate a logic circuit and a high voltage.
+26 V used to drive the motor and electromagnetic clutch.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 11

Page: 12
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.3 High-Voltage Power Supply Board
(1) High-Voltage power supply circuit
The high-voltage power supply circuit generates the following voltages required for the electro-photographic processor
from +5 V according to the control sequence from the main control board. When the cover is open, +5 V supply is
automatically interrupted to stop high-voltage output.
Output Voltage Application
CH -1.3 KV Voltage to be applied to charge roller.
DB -265 V/+265 V Voltage to be applied to a developing roller.
SB -520 V/ 0 V Voltage to be applied to a sponge roller.
CB +400 V/-1.3 KV Voltage to be applied to a cleaning roller.
TR +500 V ~ +3.5 KV/-750 V Voltage to be applied to a transfer roller.
Caution: The TR voltage varies with medium and transfer roller impedance.
(2) Sensors
The high-voltage power supply board consists of the high-voltage power supply circuit that supplies power to the
electro-photographic processor system and the photosensor that detects a paper feeding system and toners.
Figure 2-2 shows the sensor layout drawing.
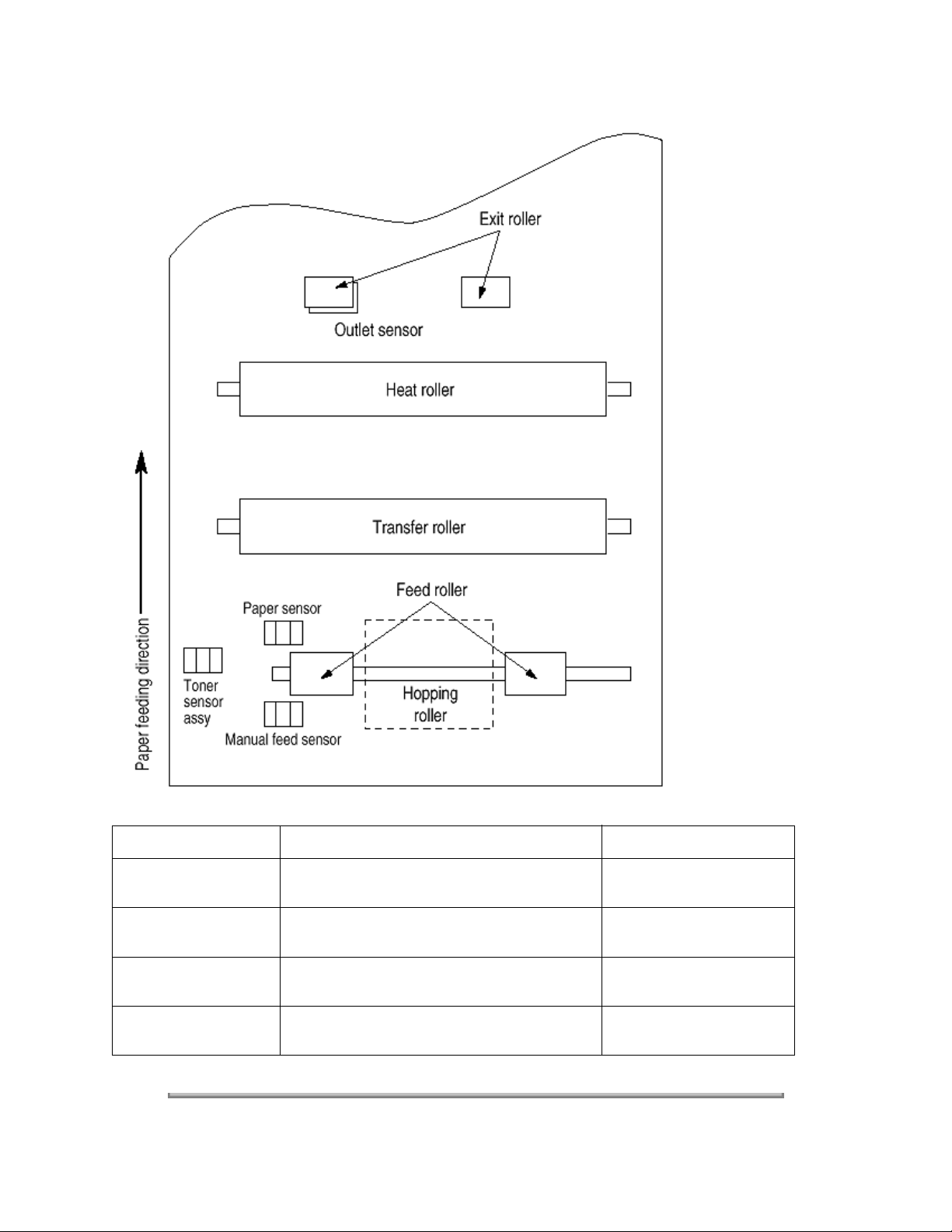
Sensor Function Sensing State
Manual feed sensor Monitors whether paper was inserted into the
manual feed sensor section.
Paper sensor Detects the leading part of the paper. Monitors
paper feeding.
Output sensor Monitors paper feeding and the paper size
according to the paper sensor arrival and passing
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
time.
Toner sensor Detects the low toner status. ON (long): Toner low.
OFF (short): Toner high.

Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 13
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.4 Electro-Photographic Processor
The electro-photographic processor prints out the image data to be sent from the main control board on sheets of paper.
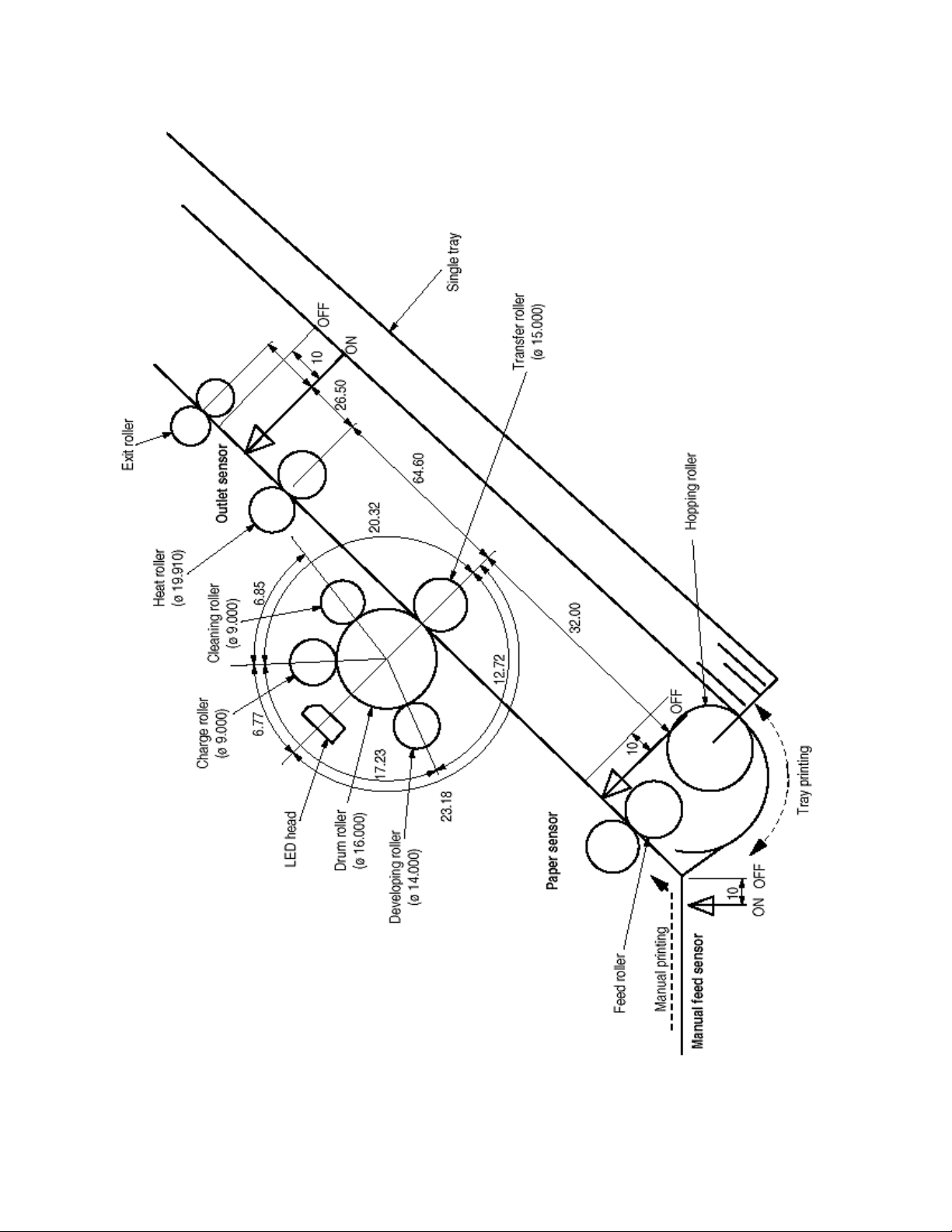
Figure 2-3 shows the layout drawing of the electro-photographic processor.
(1) Image drum unit
The image drum unit makes a toner adhere to the formed electrostatic latent image with static electricity. This
electrostatic latent image is formed by the lights irradiated from LED heads.
(2) Electromagnetic clutch
The electromagnetic clutch controls the rotation of the hopping roller according to signals from the control block.
(3) Pulse motor (Main)
This pulse motor of 48 steps/rotation is two-phase excited by the signal from the main control board; it performs feeding

control by switching normal rotation to reverse rotation or vice versa and turning on/off the electromagnetic clutch. The
relationship between the main motor, electromagnetic clutch, resist gear, drum gear, hopping roller is shown in the table
below and on the subsequent pages.
Main Motor Electromagnetic
Clutch
Hopping Roller Regist Gear Drum Gear Operation
Normal rotation OFF Non-rotation Non-rotation Rotation Warm-up
Reverse rotation ON Rotation Rotation Rotation Hopping
Reverse rotation OFF Non-rotation Rotation Rotation Printing
(4) LED head
The shift and latch registers receive image data from the main control board for each dot line. 4,992 LEDs are driven to
radiate the image drum.
(5) Heat Assy
The heat Assy consists of a heater, a heat roller, a thermistor, and a thermostat.
The power supply unit supplies AC voltage to the heater according to the HEATON signal from the main control board to
heat the heat roller. The main control board monitors the heat roller temperature via the thermistor and keeps the
temperature constant by turning on/off the heater AC voltage supply.
If the heat roller temperature rises abnormally, the thermostat of the heater voltage supply circuit functions to forcibly
suspend the AC voltage supply.
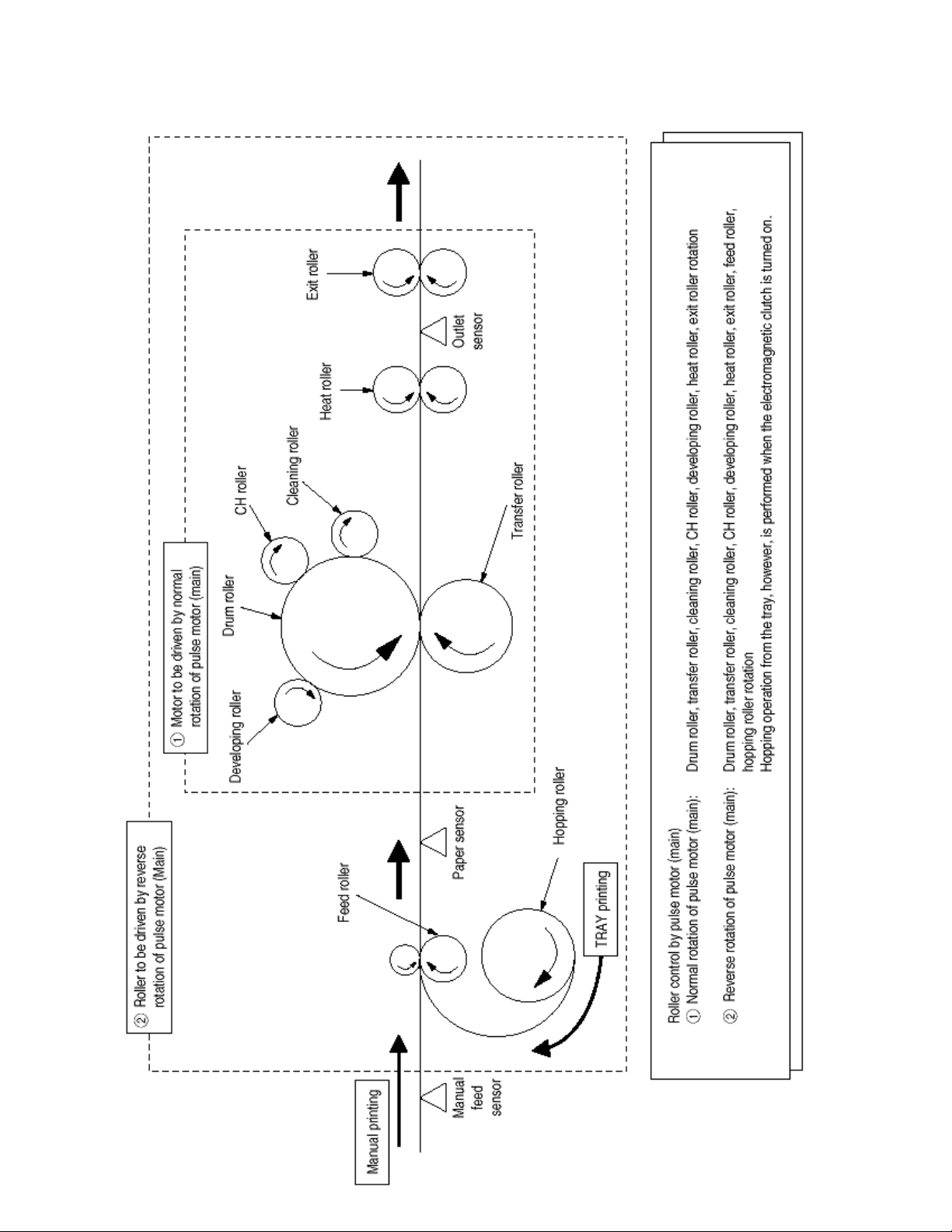
Roller control by pulse motor (main)
(1) Normal rotation of pulse motor (main): Drum roller, transfer roller, cleaning roller, CH roller,
developing roller, heat roller, exit roller rotation.
(2) Reverse rotation of pulse motor (main): Drum roller, transfer roller, cleaning roller, CH roller,
developing roller, heat roller, exit roller, feed roller,
hopping roller rotation.
Hopping operation from the tray, however, is
performed when the electromagnetic clutch is turned
on.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.5 Electro-Photographic Process
(1) Charging - The surface of the OPC drum is charged negatively and uniformly by applying the DC
voltage to the CH roller.
(2) Exposure - Light emitted from the LED head irradiates the negatively charged surface of the OPC
drum. The surface potential of the irradiated surface attenuates to form the electrostatic latent image
corresponding to the image signal.
(3) Development and residual toner recovery - The negatively charged toner is brought into contact with
the OPC drum, adhering to the electrostatic latent image on the OPC drum by static electricity. This
adhesion causes the electrostatic latent image to change to a visible image. At the same time, the
residual toner on the OPC drum is attracted to the developing rollerby static electricity.
(4) Transfer - When paper is placed over the image drum surface, the positive charge which is opposite
in polarity to that of the toner, is applied to the reverse side by the transfer roller. The toner is
attracted by the positive charge and is transferred onto the paper. This results in the transfer of the
toner image formed on the image drum onto the paper.
(5) Cleaning - The cleaning roller temporarily attracts the residual toner on the transferred OPC drum
with static electricity, then returns the toner to the OPC drum.
Page: 14
(6) Fusing - The transferred unfused toner image is fused to a sheet of paper by applying heat and
pressure to the image.
Figure 2-5 shown below is a flow for the electro-photographic process.
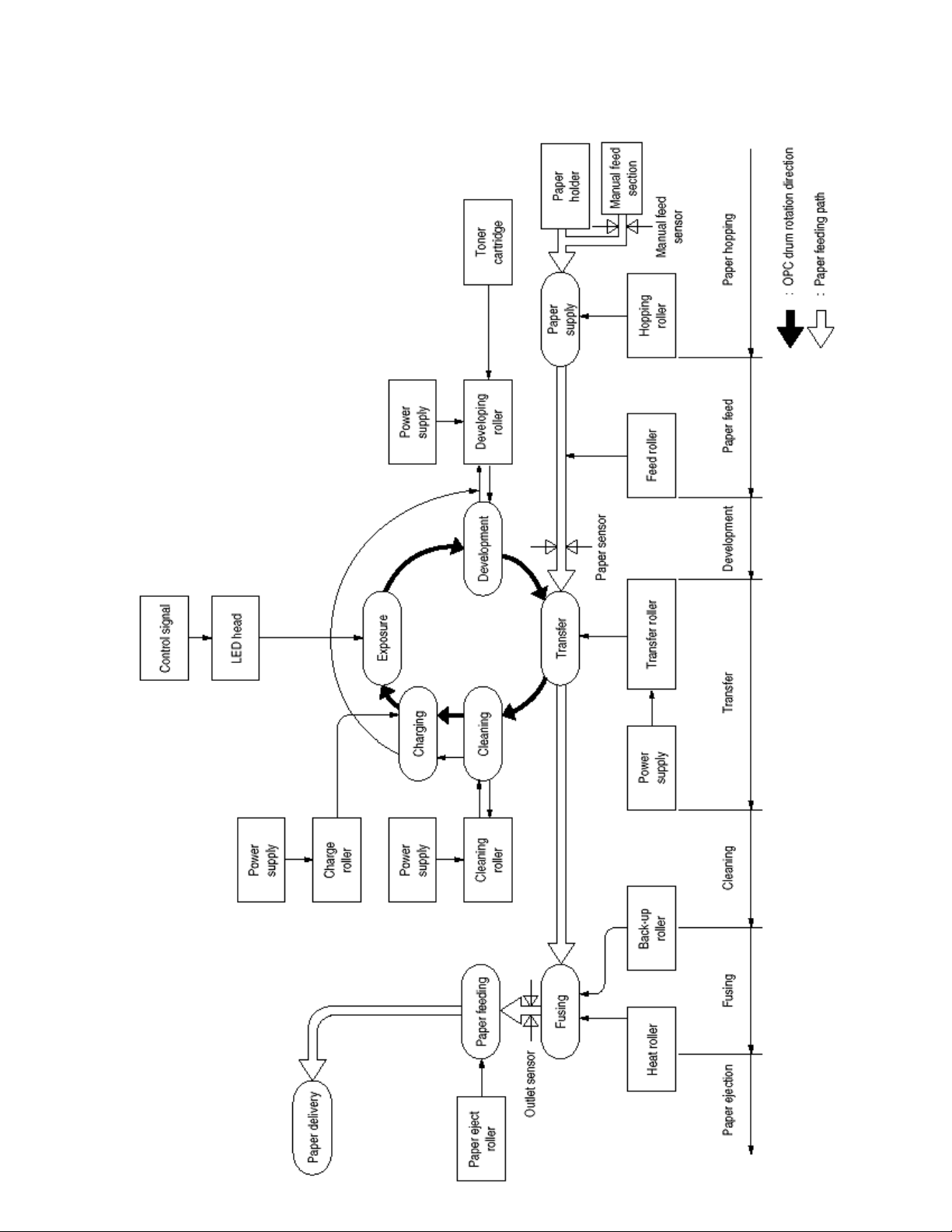

Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.5.1 Explanation of Each Process Operation
(1) Hopping
As shown in the figure below, the clutch for hopping is turned on/off according to current ON/OFF to a coil.
When the clutch is OFF
Page: 15
When the clutch is ON

When the clutch is on, the hopping gear engages with the clutch plate to rotate the hopping roller.
When the clutch is off, the hopping gear is separated from the clutch plate by the spring for resetting, disabling the
rotation of the hopping roller.
(2) Printing and warm-up
At warm-up
Rotate the pulse motor (main) in the a direction. The planetary gear rotates in the a' direction, dislocating its position in
the a" direction. This causes the planetary gear to be separated from gear A. The hopping gear will not rotate. The triple
gear and transfer gear rotate via the idle gear to drive the EP unit.

At printing
The paper is further advanced in synchronization to the print data.
(3) Charging
Charging is performed by applying DC voltage to the charge roller that is in contact with the surface of the OPC drum.
(4) Exposure

Light emitted from the LED head irradiates the negatively charged surface of the OPC drum. The surface potential of the
irradiated surface attenuates to form the electrostatic latent image corresponding to the image signal.
(5) Development
The electrostatic latent image on the surface of the OPC drum is changed to a visible toner image by applying a toner to
it. Development is performed in the contact part between the OPC drum and developing roller.
1 The sponge roller negatively charges a toner and applies it to the developing roller.
2 The toner applied to the developing roller is thin-coated by the developing blade.
3 A toner adheres to the exposure part of the OPC drum in the contact part between the OPC drum and
developing roller. This causes the electrostatic latent image to be changed to a visible image.

(6) Transfer
The transfer roller is composed of conductive sponge material. This roller is set so that the surface of the OPC drum and
sheets of paper will adhere closely.
A sheet of paper is placed on the surface of the OPC drum and the positive charge opposite to the negative charge of a
toner is applied from the reverse side by the transfer roller.
When a high negative voltage is applied from the power supply to the transfer roller, the positive charge induced on the
surface of the transfer roller moves to the paper side at the contact part between the transfer roller and the sheet of
paper. The positive charge on the lower side of the sheet of paper then causes the negatively charged toner adhering to
the surface of the OPC drum to move to the upper side of the sheet. This enables transfer to the sheet of paper.
(7) Fusing
The transferred unfused toner image is fused to a sheet of paper because heat and pressure are applied when it passes
between the heat roller and back-up roller.
The Teflon-coated heat roller contains a 400 W heater (Halogen lamp) that heats the heat roller. The thermistor on the
surface of the heat roller keeps the temperature of the heat roller constant. A thermostat is also installed for safety. If
temperature rises abnormally, this thermostat opens to suspend voltage supply to the heater.
The back-up roller is pressurized to the heat roller by the pressure spring on each side.

(8) Cleaning
After transfer has terminated, the cleaning roller temporarily draws in the untransferred residual toner adhering to the
OPC drum with static electricity and then returns it to the OPC drum.

Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 16
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.6 Paper Jam Detection
The OKIPAGE 8w monitors the paper status when the power supply is on and during printing. In the following cases, the
OKIPAGE 8w interrupts the printing process as a paper jam. Printing can be recovered by opening the cover, removing
the jammed paper, and closing the cover.
Error Cause of Error
Paper inlet jam - Only the manual feed sensor detects "Paper exists" when the power
supply is on.
- The leading part of the paper does not reach the paper sensor
although hopping operation was performed three time.
Paper feed jam - The leading part of the paper does not reach the outlet sensor within a
fixed time after it has passed the paper sensor.
Paper outlet jam - The trailing part of the paper does not pass the outlet sensor within L
mm after the leading part of the paper has passed the outlet sensor.
2.52" (64 mm) <= L <= 15.77" (400.6 mm)
Paper size error - The trailing part of the paper does not pass the paper sensor within L
mm after the leading part of the paper has passed the paper sensor.
2.52" (64 mm) <= L <= 15.77" (400.6 mm)
Paper Feed Check List
Type of Error Supervisory
Sensor
Paper feed error Electromagnetic
Reference Value Error
Plus Minus
69.8 35 _
clutch ON/Paper
sensor ON
Paper feed jam 1 Paper sensor ON/
122.9 20.0 _
Outlet sensor ON
Paper size error Paper sensor ON/
Paper sensor OFF
2.52" (64 mm) <= L
<=
_ _
15.77" (400.56 mm)
Paper outlet jam Outlet sensor ON/
Outlet sensor OFF
2.52" (64 mm) <= L
<=
45.0 45.0
15.77" (400.56 mm)
Paper feed jam 2 Outlet sensor OFF/
Outlet sensor OFF
121.9 20.0 20.0

Unit: mm
Timing Chart for Paper Feed (Tray Feed)
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.7 Toner Low Detection
Hardware configuration of toner sensorl
The figure below shows the hardware configuration of the toner sensor.
Page: 17
Hardware Configuration of Toner Sensor
Toner detection methodl
(1) Toner sensor monitoring conditions are shown in the figure below.
Caution: The toner sensor is not monitored when the drum is inactive.
(a) When the toner-low state continues twice, Toner Low occurs. (This state is monitored at a cycle of 40 milliseconds.)
(b) When the toner-full state continues twice, Toner Low is released. (This state is monitored at a cycle of 40
milliseconds.)
(c) When the toner sensor does not change over two cycles (T x 2), the toner sensor alarm state occurs.

(d) After the EP unit has been replaced (after the drum counter has been reset), Toner Low is not detected when the
drum counter indicates 1 to 100 counts.
(2) The basic rotation cycle of the toner sensor is as follows:
T time
Basic rotation cycle of toner sensor 2.5 sec.
Toner low time t1 > 0.6 sec.
Toner full time 0.6 > t1 > 0.14 sec.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 18
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.8 Cover Open
Opening the stacker cover turns off the microswitch on the high-voltage power supply board to suspend +5 V supply to
the high voltage power supply. This results in the stop of all high-voltage outputs. At the same time, the CVOPN signal is
issued to notify the main control board of the switch status and cover open processing is executed.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 19
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.9 Detecting ID existence
In this model, a micro switch may be activated, applying a high voltage to the machine under a state where the cover is
slightly opened. In this case, there is a fear that, when a user insert his hand through the opening, he may be shocked
unless an ID has been installed. (Safety standard measures EN60950: 1992)
Therefore, with mechanism, an interlock system for micro switch shall be added if a machine has no mechanism with ID
inside. Also, for control, ID existence detection shall be implemented according to the following method.
<Conditions for judging ID existence>
If a toner sensor does not change for 1.2 cycle of toner sensor basic rotation cycle soon after powering on or closing
cover, no installed ID shall be judged, stopping Warming Up motion to shift the machine mode to light malfunction. But
this error can be recovered by cover open and close operation after installing ID.
T time Remarks
ID existence detection time 3.04 sec. As the toner sensor monitors at intervals of 40 msec. the
fractional part should be rounded down.
The conditions for enabling this error should be as follows.
Valid condition In the case of 31 pages or more in total drum counter
Invalid condition In the case of 30 pages or less in total drum counter, a significant malfunction
toner sensor error shall occur.
But when the toner sensor breaks down with 31 or more counted in total at the drum, ID not Install will be displayed
without fail at power on. Even in this case, the machine should be in printable state so that printing can be guaranteed
until the completion of toner repair. (See the drawing below).

Image Drum (ID) not Installed / Toner Sensor Error
Specification
1. Toner sensor error/ID not Installed state should not be stored in the EEPROM.

2. A shift to ID not Installed and Toner Sensor Error shall be made at cover open or close.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Parts Replacements
This chapter explains how to replace parts, assemblies, and units in the field.
The replacement procedures to be explained here include dismounting, not mounting. When mounting parts,
assemblies, and units, reverse the dismounting steps.
3.1 Precautions for Parts Replacement
3.2 Parts Layout
3.3 Replacing Parts
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 20

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
3.1 Precautions for Parts Replacement
(1) Be sure to disconnect the AC cord and interface cable before replacing parts.
(a) Be sure to disconnect the AC cord in the following procedures:
i) Turn off the POWER switch ("0").
ii) Disconnect the AC plug from the power outlet.
iii) Disconnect the AC cord and interface cable from the printer.
(b) Be sure to reconnect the printer using the following procedures:
i) Connect the AC cord and interface cable to the printer.
ii) Connect the AC cord to the power outlet.
iii) Turn on the printer's POWER switch (|).
Page: 21
(2) Do not disassemble parts as long as the printer is operating normally.
(3) Minimize disassembling. (Only the parts indicated in the parts replacement procedures can be
disassembled.)
(4) Use only the specified maintenance tools.
(5) Disassemble parts in the specified sequence; otherwise, parts may be damaged.
(6) Temporarily tighten small parts such as screws and collars to the original locations because they tend
to be lost easily.
(7) When handling ICs such as CPUs, ROM, and RAM and PC boards, do not wear gloves that can
generate static electricity.
(8) Do not place PC boards directly on devices or floors.
[Maintenance Tools]

Table 3-1 lists the maintenance tools necessary for parts replacement.
[Maintenance Utility]
Table 3-2 Maintenance Utility
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
3.2 Parts Layout
This section explains the layout of main parts.
Upper Cover Assy
Base Frame Unit
Base Plate Unit
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 22

Upper Cover Assy
Page: 23
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Base Frame Unit
Page: 24
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement

Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Base Plate Unit
Page: 25
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
3.3 Replacing Parts
This section explains how to replace parts and assemblies.
3.3.1 Hopper Plate
3.3.2 LED Head and Head Spring
3.3.3 Transfer Roller
3.3.4 Upper Cover Assy
3.3.5 High-Voltage Power Supply Board (P2H/P6L)
3.3.6 Top Cover Assy and Flat Cable Assy
3.3.7 Paper Holder
3.3.8 Side Plate M and Idle Gear
3.3.9 Heat Assy
3.3.10 Drive Shaft E (Eject) and Eject Roller
Page: 26
3.3.11 Pressure Roller B (Back Up Roller)
3.3.12 Separator Guide
3.3.13 Pulse Motor (Main)
3.3.14 Hopping Shaft Assy
3.3.15 Resist Roller
3.3.16 Paper Sensor E, Paper Sensor Exit, and toner Sensor Assy
3.3.17 Base Plate
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

3.3.1 Hopper Plate
Remove two claws and dismount hopper plate (1).1.
Page: 27
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

3.3.2 LED Head and Head Spring
Open top cover assy (1).1.
Dismount the left clamp and LED head (2). Then, dismount flat cable assy (3).2.
Dismount two head springs (4).3.
Page: 28
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

3.3.3 Transfer Roller
Open top cover assy (1) and dismount the image drum unit (Type 6) (2).1.
Remove the right claw. Then, dismount transfer roller (3), two regist bearings (4), and gear T (5).2.
Page: 29
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

3.3.4 Upper Cover Assy
Turn off the power switch and unplug the AC cord from the AC socket.1.
Disconnect interface cable (1).2.
Open top cover assy (2) and dismount the image drum unit (Type 6) (3).3.
Move paper guide (L) (4) and paper guide (R) (5) on the rear of the printer to the center.4.
Remove two front claws of upper cover assy (6) and lift upper cover assy (6).5.
Dismount spur gear (A) (7), guide slide (L) (8), and guide slide (R) (9).6.
Dismount lamp (10).7.
Page: 30
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
3.3.5 High-Voltage Power Supply Board (P2H/P6L)
Dismount upper cover assy. (See Section 3.3.4.)1.
Remove three screws (1) and remove the cover (2) and draw out high-voltage power supply board (3).2.
Disconnect all the cables (4) from high-voltage power supply board (3) and dismount high-voltage power supply 3.
board (3).
Caution: Note the following when assembling the high-voltage power supply board:
Mount the high-voltage power supply board with top cover assy removed or open.l
Take care that cable 4 will not interfere with the paper sensor exit when it is connected.l
Page: 31
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

3.3.6 Top Cover Assy and Flat Cable Assy
Dismount the upper cover assy. (See Section 3.3.4.)1.
Dismount the LED head. (See Section 3.3.2.)2.
Press the left clamp outward and dismount the engagement and top cover assy (1). (Tension spring (2) also comes 3.
off at the same time.)
Disconnect connector CN6 and dismount flat cable assy (3).4.
Page: 32
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

3.3.7 Paper Holder
Dismount the upper cover assy.(See Section 3.3.4.)1.
Dismount paper holder (1).2.
Unlock and dismount paper guide (L) (2) and paper guide (R) (3).3.
Remove the claw and dismount hopper spring (4).4.
Remove the claw and dismount stopper spring (5).5.
Page: 33
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
3.3.8 Side Plate M and Idle Gear
Perform parts replacement while making the base frame assy stand so that side plate M will face upward.
Dismount the upper cover assy. (See Section 3.3.4.)1.
Remove two screws (1) and two claws, then dismount plate side M(2).2.
Dismount earth plate (3), two idle gears P (4), idle gear M (5), idle gear 3R (6), idle gear 2R (7), idle gear heat (8), 3.
idle gear R (9) and Gear R (10).
Page: 34
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 35
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
3.3.9 Heat Assy
This section explains how to dismount the heat assy and parts in the assy.
<Dismounting the heat assy>
1. Dismount the upper cover assy. (See Section 3.3.4.)
2. Dismount the high-voltage power supply board. (See Section 3.3.5.)
3. Remove two screws (1), disconnect connector (2), and dismount heat assy (3).
<Dismounting parts in heat assy>
4. Dismount heat separator (14).
5. Remove screw (4) and dismount terminal plate (6). (Handle heat assy (3) carefully because Halogen lamp (7) comes
off.)
6. Turn left and right heat bearings (8) in the arrow direction to unlock. Then, dismount Halogen lamp (7), heat bearing
(8), heat roller (9), and heat gear (13) together. (Take care not to drop Halogen lamp (7).)
7. Dismount thermistor (10).
8. Dismount the clamp, then thermostat (11), heat contact (12), and heat cord (5) together.
9. Dismount heat contact (12) and heat cord (5) from thermostat (11).
Caution: Take care not to bend the claw when dismounting heat bearing (8).


Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

3.3.10 Drive Shaft E (Eject) and Eject Roller
Dismount the upper cover assy. (See Section 3.3.4.)1.
Dismount top cover assy. (See Section 3.3.6.)2.
Remove two screws (1) from heat assy (Section 3.3.9), life the heat assy, and dismount idle gear E (A) (2) and idle 3.
gear E (B) (3).
Unlock and dismount drive shaft E (Eject) (4).4.
Dismount two eject rollers (5).5.
Page: 36
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

3.3.11 Pressure Roller B (Back Up Roller)
Dismount the upper cover assy. (See Section 3.3.4.)1.
Dismount the high-voltage power supply board. (See Section 3.3.5.)2.
Dismount the heat assy. (Section 3.3.9)3.
Dismount the engagement with the left ground, then pressure roller B (1). (Two bearing BUs (2) and two bias 4.
springs (3) also come off at the same time.)
Page: 37
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 38
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
3.3.12 Separator Guide
1. Dismount the upper cover assy. (See Section 3.3.4.)
2. Dismount the high-voltage power supply board. (See Section 3.3.5.)
3. Remove four screws (1).
4. Dismount inlet (2) from base frame (3).
<Dismounting inlet (2)>
Insert a screwdriver into the hole on the side of base frame (3), remove the inlet claw from base frame (8), and dismount
inlet (2).
5. Disconnect three cables (4) and connector (11) and dismount base frame (3). Then, remove screw (10).
<Disconnecting connector (11), (12)>
Dismount connector (11) by drawing it upward while pushing the clamp lever with a standard screwdriver.
6. Dismount the paper holder assy. (See Section 3.3.7.)
7. Dismount two engagements and sheet guide (5).
8. Dismount friction pad (6), compression spring S(7), and separator guide (8).
9. Dismount paper sensor E(9).

Dismount Inlet Disconnecting Connector Disconnecting Connector
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

3.3.13 Pulse Motor (Main)
Dismount the upper cover assy. (See Section 3.3.4.)1.
Dismount the high-voltage power supply board. (See Section 3.3.5.)2.
Dismount side plate M. (See Section 3.3.8.)3.
Dismount the base frame. (See Section 3.3.12.)4.
Remove two screws (1) and dismount pulse motor (main) (2).5.
Page: 39
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
3.3.14 Hopping Shaft Assy
Dismount the upper cover assy. (See Section 3.3.4.)1.
Dismount the high-voltage power supply board. (See Section 3.3.5.)2.
Dismount the base frame. (See Section 3.3.12.)3.
Dismount the paper holder assy. (See Section 3.3.7.)4.
Dismount the sheet guide. (See Section 3.3.12.)5.
Dismount side plate M. (See Section 3.3.8.)6.
Raise up roller holder (3), slide hopping shaft assy (1), and dismount roller holder (3) and hopping roller (4). (Knock 7.
pin (5) also comes off at the same time. Take care not to lose it.)
Draw out hopping shaft assy (1) to the right and dismount magnet H (6).8.
Page: 40
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

3.3.15 Resist Roller
Dismount the upper cover assy. (See Section 3.3.4.)1.
Dismount Idle gear R (3) and Gear R (4).2.
Move resist roller (1) to the right and dismount it by lifting. (Two resist bearings (2) also come off at the same time. 3.
Take care not to lose them.)
Page: 41
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
3.3.16 Paper Sensor E, Paper Sensor Exit and Toner Sensor Assy
Dismount the upper cover assy. (See Section 3.3.4.)1.
Dismount the high-voltage power supply board. (See Section 3.3.5.)2.
Dismount the base frame. (See Section 3.3.12.)3.
Dismount the paper holder assy. (See Section 3.3.7.)4.
Dismount the sheet guide. (See Section 3.3.12.)5.
Dismount the heat assy. (Section 3.3.9)6.
Dismount drive shaft E. (See Section 3.3.10.)7.
Dismount paper sensor E (1).8.
Dismount paper sensor exit (2).9.
Dismount toner sensor assy (3).10.
Page: 42
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

3.3.17 Base Plate
Dismount the upper cover assy. (See Section 3.3.4.)1.
Dismount the base frame. (See Section 3.3.12.)2.
Remove two screws (1), disconnect connector (2), and dismount power supply unit (3).3.
Dismount insulation sheet (4).4.
Remove five screws (5) and dismount main control board (6).5.
Remove screw (7) , disconnect connector (8) and dismount P6L board (9) from base plate (10).6.
Dismount insulation sheet (11).7.
Page: 43
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 3 Parts Replacement
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 44
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 4 Adjustment
4.0 Adjustment
This chapter explains adjustment necessary when a part is replaced.
This adjustment is made by changing the parameters values set in EEPROM on the main control board. The printer
driver or maintenance utility can be used to change these values.
Only servicemen and maintenance personnel can use the maintenance utility. This utility cannot be made public for
printer end users.
4.1 Adjustment Types and Functions
4.2 Adjustment When Replacing a Part
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 4 Adjustment
4.1 Adjustment Types and Functions
4.1.1 Printer Driver
4.1.2 Engine Maintenance Utility
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 45

4.1.1 Printer Driver
(For Microsoft Windows)
This printer driver has the following functions:
Drum counter resetl
Charge roller cleaningl
Page: 46
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 4 Adjustment
Figure 4-1
(1) Drum counter reset
This function resets the life of the drum counter when the image drum unit is replaced. Clicking the "clear" button resets
the life.
(2) Charge roller cleaning
This function cleans the charge roller of the image drum unit; it is used when printing is unclear. For details on how to
operate this function, refer to "User's Manual."
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 4 Adjustment
4.1.2 Engine Maintenance Utility
See Appendix C.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 47

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 4 Adjustment
4.2 Adjustment When Replacing a Part
The table below lists the parts that requires adjustment when they are replaced:
Parts to be Replaced Adjustment
LED head Set the LED head drive time.
Set the LED head dot count. (OKIPAGE 8w only)
Image Drum Unit Reset the drum counter. (Refer to User's Manual)
Main control board Upload or download EEPROM data.
4.2.1 Setting LED Head Drive Time
4.2.2 Uploading and Downloading EEPROM Data
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 48

Page: 49
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 4 Adjustment
4.2.1 Setting LED Head Drive Time
Caution: When the luminous intensity of a new LED head is the same as that of the old LED head, do not set the LED
head drive time.
Use "LED Head Making No." in the engine menu tab of the maintenance driver to set the luminous intensity displayed on
the LED head as the LED head drive time. (See Figure 4-2 below.)
Luminous intensity of LED headl
Figure 4-2
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 50
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 4 Adjustment
4.2.2 Uploading and Downloading EEPROM Data
When the main control board is replaced, EEPROM data must be reflected on a new main control board. Use
"EEPROM Operations" in the option tab of the maintenance utility to reflect EEPROM data on the new main control
board.
Reflect EEPROM data on the new main control board in the following procedures:
(1) Check that the printer and PC are connected by the parallel I/F, then execute the maintenance utility.
(2) Click the "Option" button in "Main Menu Dialog".
(3) Click the "Upload" button (Upload EEPROM Data) in "EEPROM Operations." (EEPROM data read is completed.)
(4) The read EEPROM data is displayed in "Dialog" of the maintenance driver.
(5) Leave the display of the maintenance driver as is and replace the main control board.
(6) Click the "Download" button (Download EEPROM Data) in "EEPROM Operations". (EEPROM data write is
completed.)
Depending on the level of a main control board failure (parallel I/O failure, etc.), however, EEPROM data may be unable
to be uploaded.
In such a case, use the maintenance utility to perform the following adjustment after replacing the main control board:
Setting the LED head drive time (Section 4.2.1)l
Setting the LED head count (OKIPAGE 8w only)l
Setting specifications (ODA/OEL/INT-A/INT-L)l
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 5 Periodical Maintenance
5.1 Periodical Replacement Parts
Table 5-1 lists the part and unit to be replaced periodically.
Table 5-1 Routine Replacement Parts
Page: 51
Part Name Replacement Time Part to be Checked
Simultaneously
Toner cartridge (Type 6) When "Toner Low" is displayed. Clean LED head Consumables
Image drum unit (Type 6) When "Change Drum" is displayed. See 5.2 Consumables
Caution: Also reset the drum counter when replacing the image drum unit.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Remarks

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 5 Periodical Maintenance
5.2 Cleaning
Remove any toner or dirt and clean the circumference and inside of the printer with a waste cloth.
Caution: Do not touch the image drum unit, LED lens array, and connector block of the LED head.
5.2.1 Cleaning the LED Lens Array
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 52

Page: 53
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 5 Periodical Maintenance
5.2.1 Cleaning the LED Lens Array
When a white belt or a white stripe (void, light printing) occurs in the vertical direction of the print surface, clean the LED
lens array or replace the toner cartridge.
Caution: Be sure to use an LED head cleaner to clean the LED lens array.
(1) Set the LED head cleaner in the LED lens array, as shown in the figure below, and slide the cleaner left and right
several time to clean the head.
Caution: Do not press the LED head cleaner against the LED lens array.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner

Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Procedures
6.1 Troubleshooting Tips
Check the basic check points written in the user's manual.1.
Gather detailed failure information as much as possible from the customer.2.
Check the printer under the condition close to that under which the failure occurred.3.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 54

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Procedures
6.2 Check Points Before Correcting Image Problems
Is the printer running in proper ambient conditions?1.
Are consumables (toner and EP image drum unit) replaced correctly?2.
Are sheets of paper normal?3.
Is the EP image drum unit set correctly?4.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 55

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Procedures
6.3 Notes When Correcting Image Problems
Do not touch the surface of the image drum nor place foreign matter on it.1.
Do not expose the image drum to direct sunlight.2.
Do not touch the fuser because it heats up during operation.3.
Do not expose the image drum to light for more than five minutes at room temperature.4.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 56

Page: 57
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Procedures
6.4 Preparation Before Troubleshooting
1. Message display
The failure status of the OKIPAGE 4w Plus /4m is displayed on the status monitor of the PC. Take proper action
according to the message displayed on the status monitor.
2. LED display
The OKIPAGE 8w is equipped with only one LED. This LED indicates one of the following status:
Printer Status LED Indication
Ready Lighting
Printing in progress Blink (*1)
Recoverable alarm Blink (*2)
Unrecoverable alarm Blink (*3)
*1: The LED blinks at a cycle of 1 second (0.5s ON) from data reception to printing end.
*2: The LED blinks at a cycle of 0.24 second (0.12s ON).
*3: The LED blinks at a cycle of 0.24 second (012s ON)
Status Error (red) Manual Feed
(amber)
Ready Undefined OFF ON
During suspending data
processing (in OFF-LINE) (Data
is left in the buffer)
During receiving data or
processing data
Manual request OFF Flash 2 Undefined
Low toner Flash 1 OFF Undefined
Warning Change drum, toner
low, toner sensor (total page >
30 sheets)
Error
(printing Error)
Buffer Overflow, Print Overrun
Error
Paper out, Input Jam
Error
Paper Jam (Paper Size Check
Error, Feed Jam, Exit Jam)
Error Cover Open Flash 2 Flash 2 Flash 2 Re-power on
Hardware error (fatal error)
(ROM/RAM error, fuser error,
thermister error and toner
sensor error) (total page < 30)
During printer resetting. OFF OFF Flash 2
During initializing. ON and then
During initializing EEPROM Flash 2 until
Undefined OFF Flash 1 Printing contents of buffer by
Undefined OFF Flash 2
Flash 1 Undefined Undefined
Flash 2 OFF OFF Recovered by pressing and
Flash 2 OFF OFF Recovered by pressing a switch
Flash 2 OFF OFF The printing can be continued
Flash 3 Flash 3 Flash 3 Service call even if the printer
ON and then
OFF
Ready
OFF
Flash 2 until
Ready
Ready
(amber)
ON and then
OFF
Flash 2 until
Ready
Remarks
pressing switch two seconds.
Clearing buffer by pressing
switch five seconds.
releasing a switch
and the printing can be
continued.
by cover open/close
cannot recover from one of
these errors.
Flash 1: Slow blinking

Flash 2: Blinking
Flash 3: Fast blinking
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

6.5 Troubleshooting
6.5.1 Status Monitor Message List
Page: 58
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Procedures
6.5.2 Status Message Troubleshooting
6.5.3 Image Troubleshooting
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Procedures
6.5.1 Status Monitor Message List
Table 6-1 lists the statuses and troubles to be displayed on the status monitor in the message format.
Table 6-1
Page: 59
Category Status Message Status
Code
Normal status Warming Up 18 00 Warming-up status. Normal operation.
Normal status Online (Ready) 00 10 Online (ready) status. Normal operation.
Normal status Power Save Mode 00 20 Power save status. Normal operation.
Normal status Toner Low 10 00 The toner amount of the
Normal status Toner Sensor 10 01 The image drum is not
Normal status Change Drum 10 02 Image drum is nearing
Normal status Manual Paper In 12 20 The paper is in the manual
Normal status Printing In Progress 14 20 Printing in progress. Normal operation.
Explanation Remedy
Normal
toner cartridge is small.
installed or the toner
sensor is faulty.
end of life.
feed mode.
operation/replace
the toner cartridge.
Install the image
drum or replace the
toner sensor.
Replace the image
drum. Note: Be sure
to reset the drum
counter after
replacing the image
drum).
Normal operation.
Normal status Ejection in Progress 14 30 Ejection in progress. Normal operation.
Normal status Manual Request
Executive
Letter
Legal 14
Legal 13
A6
A5
A4
B5
Monarch
COM-10
DL
C5
COM-9
16 01
16 02
16 03
16 04
16 18
16 19
16 1A
16 21
16 50
16 51
16 5A
16 5B
16 7F
Request the paper to be
set in the manual feed
mode.
The paper sizes are as
follows: Executive, Letter,
Legal 14, Legal 13, A4,
A5, A6, B5, Monarch, DL,
C5, COM-10, COM-9.
Set the requested
paper in the manual
feed mode.

Paper size error Paper Size Error 30 00 Paper of improper size
was fed. 2.52" (64 mm) L
15.77" (400.56 mm)
Check the paper.
Also check whether
more than one sheet
of paper were fed
simultaneously. To
clear the error
display, open the
cover, then close it.
Paper jam Paper Input Jam 31 00 A paper jam occurred
when sheets of paper
were being supplied.
Paper jam Paper Feed Jam 32 00 A paper jam occurred
during paper feeding.
Paper Jam Paper Exit Jam 33 00 A paper jam occurred
during paper ejection.
Cover Open Cover Open 4F 00 The upper cover is open. To clear the error
Check the paper. To
release the error
display, open the
cover, then close it.
Open the cover,
then remove the
jammed paper. To
clear the error
display, close the
cover.
Open the cover,
then remove the
jammed paper. To
clear the error
display, close the
cover. If this error
occurs frequently,
see Section 6.5.2
2-2.
display, close the
cover. If this error
occurs frequently,
replaced the power
supply board.
Buffer overflow Page Buffer
Overflow
Buffer overflow Print Over Run 40 10 A print overrun occurred
Device
configuration error
Program ROM
Check Error
40 01 The page buffer
overflowed because there
are a large number of print
data.
because print data is
complicated.
60 10 An error occurred during
program ROM check.
To release the error
display, press the
reset button on the
status monitor of the
printer driver. Install
option RAM or
reduce the number
of print data.
To clear the error
display, press the
reset button on the
status monitor of the
printer driver.
Simplify the print
data format.
Replace program
ROM or the main
control board.
(When replacing the
main control board,
also adjust
EEPROM data).

Device
configuration error
Resident RAM
Check Error
60 30 An error occurred during
resident RAM check.
Replace the main
control board.
(When replacing the
main control board,
also adjust
EEPROM data).
Device
configuration error
Device
configuration error
Device
configuration error
Device
configuration error
Device
configuration error
Device
configuration error
EEPROM Check
Error
Option RAM Check
Error
Fuser Error 60 80 A heater timeout error
Thermistor Error 60 90 A thermistor error
Thermistor Open
Check Error
Thermistor Short
Check Error
60 40 An error occurred during
EEPROM check.
60 60 An error occurred during
option RAM check.
occurred.
occurred.
60 91 The thermistor is open. Replace the
60 92 A thermistor short
occurred.
Replace the main
control board.
(When replacing the
main control board,
also adjust
EEPROM data).
Check the
connection of the
Option RAM PC
board. If the option
RAM PC board is
faulty, replace it.
See Section 6.52 4.
Replace the
thermistor of the
heater Assy.
thermistor of the
heater Assy.
Replace the
thermistor of the
heater Assy.
Device
configuration error
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Watch Dog Timeout
Error
60 00 A watchdog timeout
occurred.
To clear the error
display, turn on the
power supply again.
Replace the main
control board.

Page: 60
Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Procedures
6.5.2 Status Message Troubleshooting
Some failures cannot be corrected according to the status message trouble list. Troubleshoot these failures according
to the following troubleshooting flowcharts.
Caution: When replacing the main control board troubleshooted according to the troubleshooting flowcharts, also
adjust EEPROM data.
(1) The OKIPAGE 8w malfunctions after the power supply has been turned on.
Turn the power supply off, then on again.
Is the LED lamp on?
No - Is the AC cable connected correctly?
No - Connect the AC cable correctly.
Yes - Is +5 V supplied between CN1 Pin 7 and CN1 Pin 13 of the high-voltage power supply board? (Pin 7:
+5 V, Pin 13: 0 V)
No - Are the CN1 connectors of the high-voltage power supply board and main control board
connected correctly?
No - Connect the CN1 connectors correctly.
Yes - Is +5 V supplied between CN2 Pin 2 and CN2 Pin 3 of the main control board? (Pin 2: +5 V, Pin
3: 0 V)
No - Replace the power supply board.
Yes - Replace the main control board.
Yes - Is 1-2 V voltage supplied between CN1 Pin 2 and CN1 Pin 13 of the high-voltage power supply
board?
No - Replace the main control board.
Yes - Replace the high-voltage power supply board.
Yes - Replace the main control board.
[JAM error]
(2)-1 paper input jam
Does a paper input jam occur when the power supply is turned on?

Yes - Is the jammed paper on paper sensor E?
Yes - Remove the jammed paper.
No - Is paper sensor E (manual feed/paper) operating normally?
No - Replace paper sensor E (manual feed or paper).
Yes - Replace the high-voltage power supply board.
No - Does a paper input jam occur during paper loading?
Yes - Is the paper already fed to paper sensor E (manual feed)?
Yes - Is paper sensor E (manual feed) operating normally?
Yes - Check the gear block or replace high-voltage power supply board.
No - Is the paper already fed to paper sensor E (paper)?
Yes - Is paper sensor E (paper) operating normally?
Yes - Replace high-voltage power supply board.
No - Replace the stepping roller or friction pad.
No - Is the hopping roller rotating?
Yes - Check the coil resistance of magnet H. Is the resistance normal (about 120 W)?
No - Replace magnet H.
Yes - Is +26 V supplied between CN8 Pin 1 and CN8 Pin 2 of the main control board?
No - Replace the main control board.
No - Check the gear block or replace the hopping shaft assy.
No - Are the CN7 connectors of the pulse motor (main) and main control board connected?
No - Connect the CN7 connectors correctly.
Yes - Measure the resistance of the pulse motor (main). Is the resistance normal (about 3.8 W)?
No - Replace the pulse motor (main).
Yes - Replace the main control board.
[JAM error]
2-2 Paper feed jam
Does a paper feed jam occur when the power supply is turned on?
Yes - Is the jammed paper on paper sensor E (paper/exit)?
Yes - Remove the jammed paper.
No - Is paper sensor E (exit/paper) operating normally?
No - Replace paper sensor E (exit or paper).
Yes - Replace the high-voltage power supply board.
No - Has the paper arrived at paper sensor E (paper)?
No - Is the feed roller rotating?
No - Check the gear block.
Yes - Is the EP image drum unit set correctly?
No - Set the EP image drum unit correctly.
Yes - Check the gear block.
Yes - Has the paper arrived at the paper sensor (exit)?
Yes - Is the paper sensor (exit) operating normally?
No - Replace paper sensor E (manual feed).
No - Replace paper sensor E (paper).

No - Replace the paper sensor (exit).
Yes - Replace the high-voltage power supply board.
No - Check the gear block.
(2)-3 Paper exit jam
Does a paper exit jam occur when the power supply is turned on?
Yes - Is the jammed paper on the paper sensor (exit)?
Yes - Remove the jammed paper.
No - Is the paper sensor (exit) operating normally?
No - Replace the paper sensor (exit).
Yes - Replace the high-voltage power supply board.
No - Check the gear block or replace the eject roller.
(3) Paper size error
Is the paper of the specified size being use?
No - Use paper of the specified size.
Yes - Is paper sensor E (paper) operating normally?
No - Replace paper sensor E (paper) or clean the inlet sensor on the high-voltage power supply board.
Yes - Is the paper sensor (exit) operating normally?
No - Replace the paper sensor (exit) or clean the outlet sensor on the high-voltage power supply board.
Yes - Replace the high-voltage power supply board.
Paper feeding direction

(4) Heat assy error
Turn the power supply off, then on again.
Does the Halogen lamp of the heat assy go on?
No - Is the Halogen lamp or thermostat disconnected?
Yes - Replace the heat assy, Halogen lamp, or thermostat.
No - Replace the power supply unit.
Yes - Are the CN2 connectors of the power supply unit and main control board connected correctly?
No - Connect the CN2 connectors correctly.
Yes - Replace the main control board.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OKIPAGE8w
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Procedures
6.5.3 Image Troubleshooting
Procedures for troubleshooting for the cases of abnormal image printouts are explained below.
Figure 6-3 below shows typical abnormal images.
Problem Flowchart number
Images are light or blurred entirely (Figure 6-3, A ) (1)
Dark background density (Figure 6-3, B ) (2)
Blank paper is output (Figure 6-3, C ) (3)
Vertical block belt/black stripe (Figure 6-3, D ) (4)
Cyclical defect (Figure 6-3, E ) (5)
Print void (6)
Poor fusing (images are blurred or peeled off when touched by hands) (7)
Vertical white belt/white stripe (Figure 6-3, F ) (8)
Page: 61
A Light or blurred images entirely B Dark background density C Blank paper
D Black vertical stripes E Cyclical defect F White vertical belts
or streaks
Figure 6-3 Image Problems
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business Partner
Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
 Loading...
Loading...