Okidata OKIPAGE 8cn, OKIPAGE 8c Service Manual

Front Cover
Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
Chapter
0 Introduction
OKIPAGE 8c / OKIPAGE 8cn
LED PAGE COLOR PRINTER PRODUCTS
Adobe Acrobat printable reference copy
of the OKIDATA Service Training Manual.
11/02/98 Rev. 2.0
Note: This Adobe Acrobat version of the Okidata Service Training Manual was built with
the pictures rendered at 72 dpi, which is ideal for screen viewing. For future updates
to this manual, and more on-line information visit our
(BPX) at http://bpx.okidata.com
.
Business Partner Exchange

Table of Contents Page
Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
0 Introduction
Preface 2
1 Specifications
1.1 Basic System Configuration 3
1.2 Printer Specifications 4
1.3 Option Specifications 5
1.4 Basic Specifications 6
2 Operation
2. Operation 7
2.1 Main Control Board (PCR PCB) 8
2.2 Engine Control Board (PX4 PCB) 9
2.3 Power/Board 10
2.4 Mechanical Processes 11
....2.4.1 Electrophotographic processing mechanism 12
....2.4.2 Paper running process 13
2.5 Sensors 14
....2.5.1 Paper Related Sensors 15
....2.5.2 Other sensors 16
2.6 Correction of Color Deviation 17
2.7 Transfer Control according to Environmental Changes 18
2.8 Form Jam Detection 19
2.9 Cover Opening 20
2.10 Toner Lower Detection 21
2.11 Page Size Detection 22
2.12 Power-on Processing 23
3 Disassembly
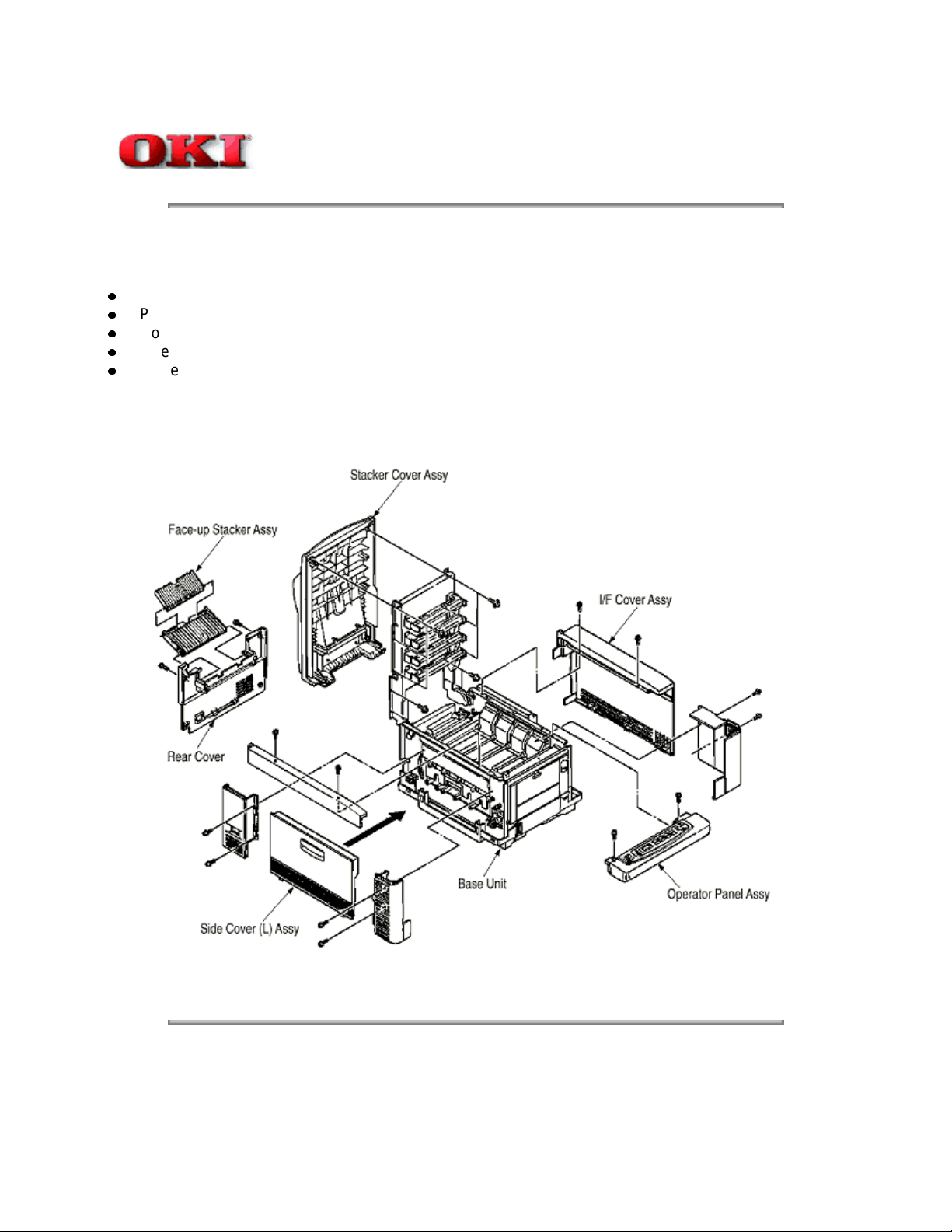
3.0 Parts Replacement 24
3.1 Precautions for Parts Replacement 25
3.2 Parts Layout 26
3.3 How to Change Parts 27
....3.3.1 Cover Assy Rear 28
....3.3.2 Motor-Fan (80-25) 29
....3.3.3 Paper Eject Assy 30
....3.3.4 Cover Assy Stacker, Guide Eject FD Assy 31
....3.3.5 Upper Frame Assy 32
....3.3.6 Plate Support Assemblies 33
....3.3.7 Limiter 2way (L), (R) / Plate Guide (L), (R) 34
....3.3.8 Cover 35
....3.3.9 PCR PCB Assy 36
....3.3.10 Motor Fan 37
....3.3.11 PXF PCB/PX4 PCB 38
....3.3.12 Gear Heat Assy 39

Table of Contents Page
....3.3.13 Main Motor (A), (B) Assy 40
....3.3.14 Gear One-way (Z30) 41
....3.3.15 Motor Assy Belt 42
....3.3.16 Power Supply Unit, Holder Inlet, Sheet Insulation 43
....3.3.17 Sensor Assy Box Toner 44
....3.3.18 Square-shaped Connector 45
....3.3.19 Motor - Pulse (ID) 46
....3.3.20 One-way Gears 47
....3.3.21 Feeder Unit Front 48
....3.3.22 Manual Feed Hopper Assy 49
....3.3.23 Guide Paper Input Assy 50
....3.3.24 Two Lever Input Sensors, Lever 2nd Feed Sensor 51
....3.3.25 Roller Registration, Roller Assy Hopping 52
....3.3.26 Hopping Roller Assy 53
....3.3.27 PXU PCB/PXM PCB, Lever Resist Sensor 54
....3.3.28 Paper End Lever 55
....3.3.29 PCO PCB (Operator Panel) 56
....3.3.30 Holder Gear Toner Assy 57
....3.3.31 Plate Latch Lever (FD), Spring Latch Lever (FD) 58
....3.3.32 Transfer Belt 59
....3.3.33 High Voltage Power Supply Unit, Bracket HV (BT)
Assy
....3.3.34 Eraser Bracket Assy, Eraser Bracket (KCM) Assy 61
....3.3.35 Shaft Link 62
....3.3.36 Contact Bracket (BL-R) Assy, Contact Bracket (CL-R)
Assy
....3.3.37 Contact (BL-L) Assy, Contact (CL-L) Assy 64
....3.3.38 Contact SB Assy 65
....3.3.39 PXC PCB 66
....3.3.40 Heat Unit Assy (Fuser unit and oil roller) 67
....3.3.41 Oil Roller Kit 68
....3.3.42 Lever Lock Heat (L)/(R), Guide Side Heat, Spring Lock 69
....3.3.43 PXL PCB 70
....3.3.44 Heat Unit Guide Assy 71
....3.3.45 Holder LED Assy, LED Head 72
4 Adjustments
4. Adjustments 73
4.1 Maintenance Modes and Their Functions 74
....4.1.1 User maintenance mode 75
....4.1.2 System maintenance mode 76
....4.1.3 Engine maintenance mode 77
4.2 Adjustments after Parts Replacement 78
....4.2.1 Confirm the LED head driving time 79
60
63

Table of Contents Page
....4.2.2 Color Registration Using the Operator Panel (Color
deviation correction)
5 Maintenance
Preventive Maintenance 81
....5.1 Periodically Replaced Parts 82
....5.2 Cleaning 83
....5.4 Cleaning the Pickup Roller 84
6 Troubleshooting Procedures
6.0 Troubleshooting Procedures 85
....6.1 Troubleshooting Tips 86
....6.2 Points to Check before Correcting Image Problems 87
....6.4 Preparation for Troubleshooting 88
....6.5 Troubleshooting Flow 89
........6.5.1 LCD status message/problem list 90
........6.5.2 LCD message troubleshooting 91
........6.5.3 Image Troubleshooting 92
............Blank paper 93
............Vertical black 94
............Vertical white 95
............Poor fusing (Images are blurred or peeled off when
touched)
............Evenly spaced, repeating marks 97
............Missing characters or colors 98
............Poor synthesization Color 99
............Printout colors different from original colors
7 Wiring Diagram
7.1 Resistance Check 100
7.2 Program/Font ROM Location 101
8 Centronics Parallel Interface
Centronics Parallel Interface 102
A Illustrated Parts List
Diagram A1: Covers (Top & Sides) 103
Diagram A2: Printer Unit 104
Diagram A3: Main Chassis Unit (1) 105
Diagram A4: Main Chassis Unit (2) 106
Diagram A5: Main Chassis Motor/PCB 107
Diagram A6: Frame Upper Assy 108
Diagram A7: Guide Cassette (R) Assy 109
Diagram A8: Main Motor (A) Assy 110
Diagram A9: Main Motor (B) Assy 111
Product Accessory: I. Second Paper Feed
Preface 112
1.0 Outline 113
80
96

Table of Contents Page
....1.1 Functions 114
....1.2 External View and Component Names 115
2.0 Mechanism Description 116
....2.1 General Mechanism 117
....2.2 Hopper Mechanism 118
3.0 PARTS REPLACEMENT 119
....3.1 Precautions Concerning Parts Replacement 120
....3.2 Parts Layout 121
....3.3 Parts Replacement Methods 122
........3.3.1 Idle rollers 123
........3.3.2 AOLT-PCB 124
........3.3.3 Hopping motor 125
........3.3.4 Feed roller 126
........3.3.5 Hopping roller 127
........3.3.6 Side frame (L) assy 128
........3.3.7 Side frame (R) assy 129
4.0 Troubleshooting 130
....4.1 Precautions Prior to the Troubleshooting 131
....4.2 Preparations Prior to the Troubleshooting 132
....4.3 Troubleshooting Method 133
........4.3.1 LCD Status Message List 134
........4.3.2 Troubleshooting Flow 135
5.0 CONNECTION DIAGRAM 136
....5.1 Interconnection Diagram 137
....5.2 PCB Layout 138
6. PARTS LIST 139
....High Capacity Second Paper Feeder 140
....2nd Tray Assembly 141

Page: 2
Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
Chapter 0 Introduction
Preface
This manual provides procedures and techniques for the troubleshooting, maintenance, and repair of
OKIPAGE 8c.
This manual is written for maintenance personnel, but it should always be accompanied with the
OKIPAGE 8c User's Manual for procedures for handling and operating OKIPAGE 8c. For repairing each
component of OKIPAGE 8c, see the Troubleshooting Manual.
[Notices]
The contents of this manual are subject to change without prior notice. Although reasonable efforts have
been taken in the preparation of this manual to assure its accuracy, this manual may still contain some
errors and omissions. OKI will not be liable for any damage caused or alleged to be caused, by the
customer or any other person using this maintenance manual to repair, modify, or alter OKIPAGE 8c in
any manner.
[Warning]
Many parts of OKIPAGE 8c are very sensitive and can be easily damaged by improper servicing. We
strongly suggest that OKIPAGE 8c be serviced by OKI's authorized technical service engineers.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
Chapter 1 Specifications
1.1 Basic System Configuration
This diagram shows the basic system configuration of OKIPAGE 8c.
Page: 3
Basic System Configuration Diagram
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
Chapter 1 Specifications
1.2 Printer Specifications
This printer unit is composed of the following hardware.
Electro-photographic processor
z
z
Paper feeder
z
Controller (CU part / PU Part)
z
Operator panel
z
Power board (High voltage part / PU part)
This diagrams shows the printer unit configuration.
Page: 4
Printer Unit Configuration Diagram
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
Chapter 1 Specifications
1.3 Option Specifications
The OKIPAGE 8c options are listed below.
(1) Second Paper Feeder
(2) RAMM SIMM module (72 pin SIMM, 4MB/8MB/16MB/32MB)
Page: 5
Make sure to use a set of 2 of the same volume size modules.
z
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

1.4 Basic Specifications
Page: 6
Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
Chapter 1 Specifications
(1) Dimensions
(2) Weight
(3) Form
Type:
Sizes:
Reams:
(4) Printing speed:
(5) Resolution
(6) Input voltage
(7) Power
consumption
(8) Frequency
(9) Noises
(10) Expendables and
service life
(11) Periodically
replaced parts
Width: 18.8"
Approx. 91 lbs. without box
Ordinary paper (Hammermill xx lb.) and Transparency (Only CG3710)
Recommended paper (for color printing)
Note: the printout color tones are dependent upon the whiteness of the
print paper.
Letter, Legal (13" or 14"), Executive, A4, A5, B5, and B6 (1st tray and front
feeder)
1st tray - 20 lbs. to 28 lbs.
2nd tray - 20 lbs. to 28 lbs.
Front feeder - 20 lbs. to 44 lbs.
8 pages per minute (5 pages per minute: Transparency / 34 lb. ~ 44 lb.,
123g/m
2
~ 166g/m2)
600 dots per inch x 600 dots per inch
120VAC +5.5%, -15%
230VAC to 240VAC +10%, -14%
Peak: Approx. 980W
Typical operation: Approx 230W
Idle: Approx 70W
Power save mode: Approx 32W
50Hz or 60Hz +2%, -2%
Operating: 54 decibels (without 2nd tray), 55 decibels (with 2nd tray)
Standby: 45 decibels
Power-saving: 43 decibels
Toner Cartridge: Approx. 1800 pages (5% density) (each of Y, M, C, and
K)
Image Drum: Up to 12,000 pages (5% density, continuous) (each of Y, M,
C and K)
Waste Toner Box: Up to 25,000 sheets (under typical printout conditions:
Single images of 5% density, equivalent to printout using 14 toner
cartridges)
Oil Roller Unit: Up to 10,000 sheets (Life defined in the number of actual
printed paper sheets)
Y=Yellow, M=Magenta, C=Cyan, K=Black
Note:
Fuser Heat Unit Assy: 60,000 pages
Transfer Belt Cassette Assy: 50,000 pages
(12) Temperatures and relative humidities
Temperature
Temperature conditions
Fahrenheit Celsius Remarks

Operating 50 to 89.6 10 to 32 17 Celsius to 27 Celsius (for assurance of
full-color printout quality)
Non-operating 32 to 109.4 0 to 43 Power off
Storage (1 year max.) -14 to 109.4 -10 to 43 with drum and toner
Delivery (1 month max.) -20 to 122 -29 to 50 without drum and toner and Belt Cassette
Assy
Delivery (1 month max.) -20 to 122 -29 to 50 with drum and toner
Humidity
Humidity condition
Fahrenheit Celsius Remarks
Operating 20 to 80 5 50% to 70% (for assurance of full-color
printout quality)
Non-operating 10 to 90 26.8 Power off
Storage 10 to 90 35
Delivery 10 to 90 40
(13) Printer life - 3,000,000 (A4) pages or 5 years
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 7
Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
Chapter 2 Operation
2. Operation
OKIPAGE 8c is a tandem color electrophotographic page printer, using 4992 Pixel-LED technologies,
OPC, dry single-component non-magnetic developing, roller transfer, heat-compression fixing (fusing).
The printing method used is a Black Writing method which applies light beams to printout areas.
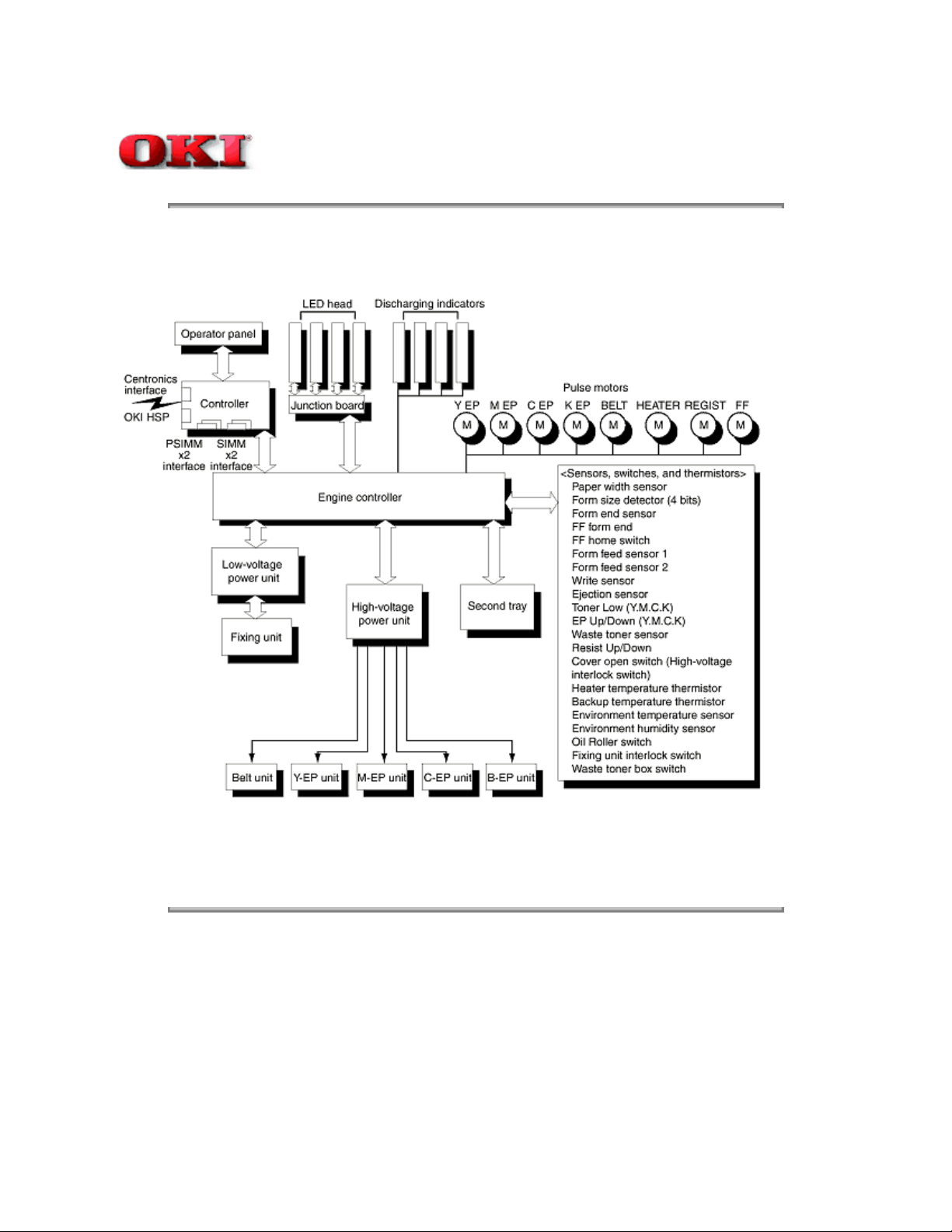
Here is the Functional Block Diagram of OKIPAGE 8c.
Functional Block Diagram
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 8
Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
Chapter 2 Operation
2.1 Main Control Board (PCR PCB)
The control board consists of a CPU (NR4700) block, a memory control LSI block, an interface control
LSI block, a DRAM block, an EEPROM block, a mask ROM block, and an interface block.
Here is the Functional Block Diagram of the main control board (PCR PCB).
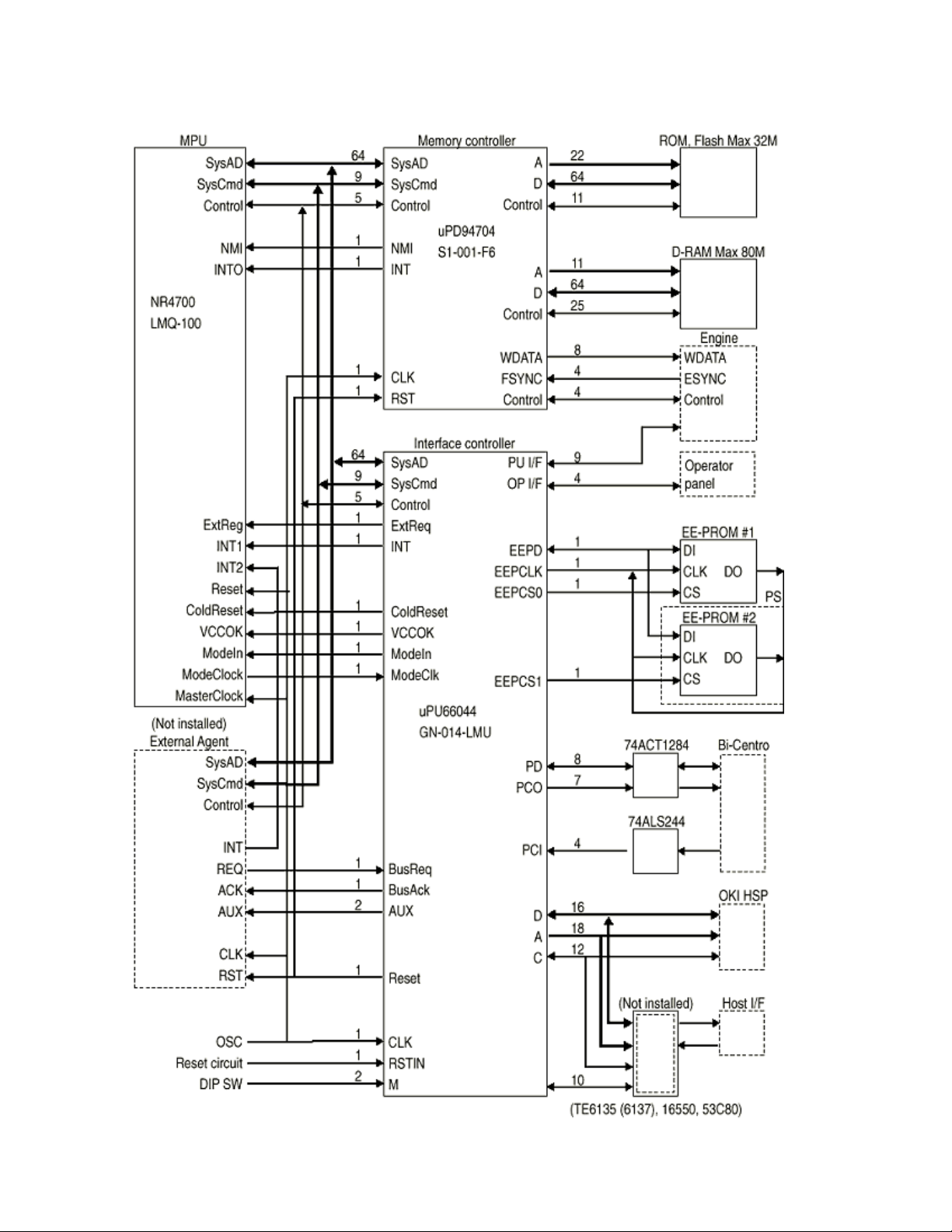

Functional Block Diagram of Main Control Board
(1) CPU
The CPU is a 64-bit RISC architecture processor (provided y NKK). It inputs a frequency
of 50 MHz and runs at 100 MHz. It transfers data to a from memory at 50 MHz.
(2) Mask ROM
The mask ROM block consists of four 16 Mbit (1M x 16 bits) chips and its total size is 8M
bytes. The chips are mounted on the PCR-PCB by means of IC sockets and store
programs and character fonts.
(3) DRAM
The DRAM block consists of eight 16 Mbit (1M x 16bits) chips and its total size is 16M
bytes. The chips are mounted on the PCR-PCB and can be expanded up to 80M bytes
by adding the 32M byte SIMMs to the SIMM slots on the PCR-PCB.
(4) EEPROM
The EEPROM block consists of 1K-bit chips mounted on a board by means of IC sockets
and stores the following:
z
Menu data
z
Counter values
z
Adjustment values
(5) Flash ROM
The Flash ROM block consists of four 4M bit (256K x 16bits) chips and its total size is 2M
bytes. The chips are mounted on the PCR-PCB and are used for storing fonts, macro
and demo pages.
(6) Memory control LSI
This block mainly consists of memory control, CPU control, compression and
decompression, and video interface functions.
(7) Interface control LSI
This block mainly consists of PU interface control, operator panel interface control,
EEPROM control, parallel interface control, and HSP control functions.
(8) Host interface
The printer has the following interfaces to the host.
Centronics bi-directional parallel interface
OKI HSP interface (Option)
The single effective interface or the automatic interface select mode can be selected
using the menu. If the busy state of the printer continues for a long time period, the buffer
near-full control releases the busy status at constant intervals even if the host side is
busy so as not to cause interface time-out at the host side.
(a) Centronics bi-directional parallel interface
This is an interface confirming to IEEE-1284 and provides either unidirectional ad
bi-directional communications according to each of the following communication modes.
Compatibility mode - Unidirectional communications from the host to the printer.
z
z
Nibble mode - This mode transfers 4-bit wide data from the printer to the host. In
z
z
this mode, each bit of 1-byte data transmits in the form of two nibbles using
ERROR, BUSY, FAULT, and SELECT signal leads. This mode can provide
bi-directional operation in combination with the compatibility mode.
ECP mode - This mode provides the asynchronous bi-directional interface and
z
z
transmits and receives 1-byte data using eight data signal leads under semi-duplex
control by the host.
When the power is turned on, the compatibility mode is automatically selected. The
change to another mode form the compatibility mode is made through negotiation. (When
the BI-DIRECTION is set to ENABLE in the menu, this change can be performed.) (For
the electrical/physical characteristics of this interface, see APPENDIX B).
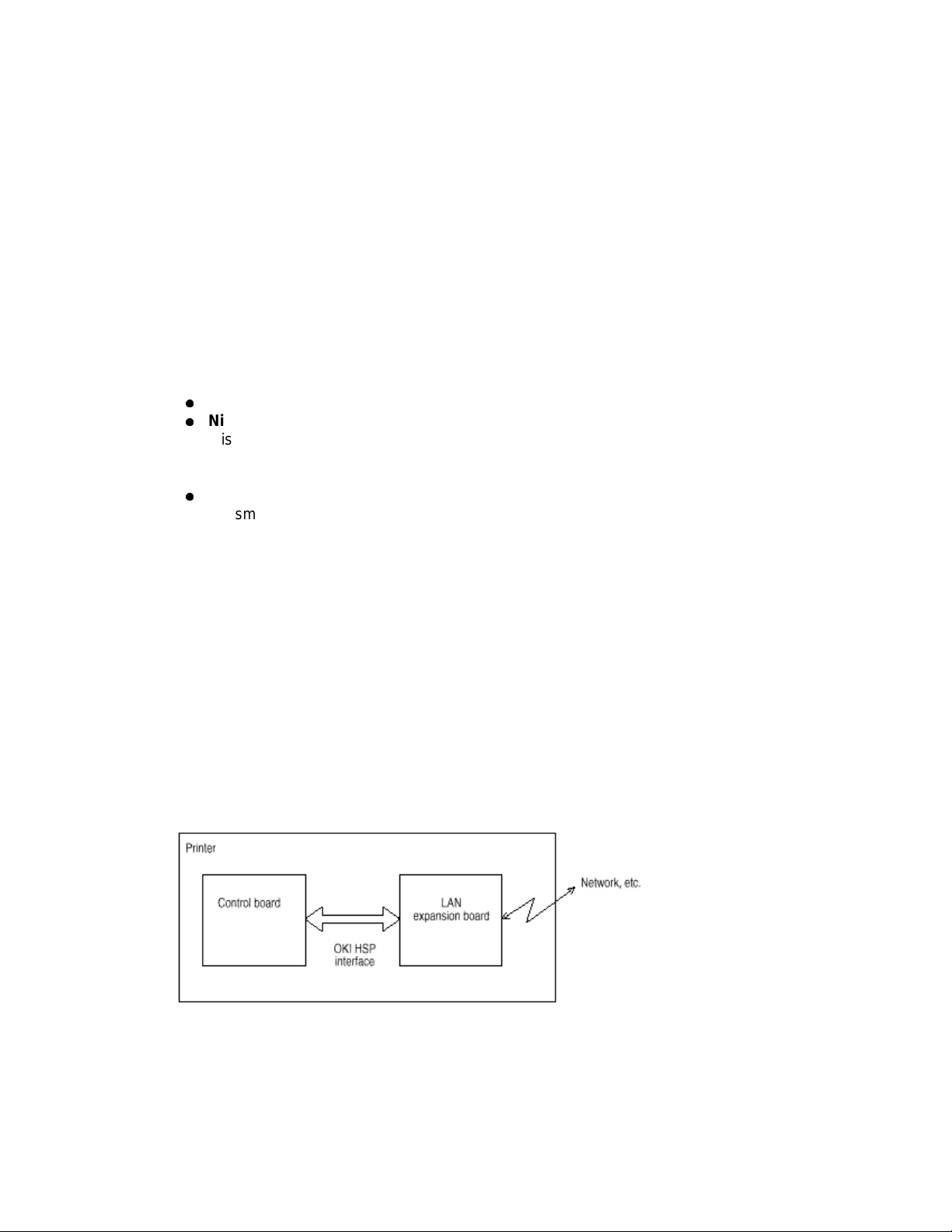
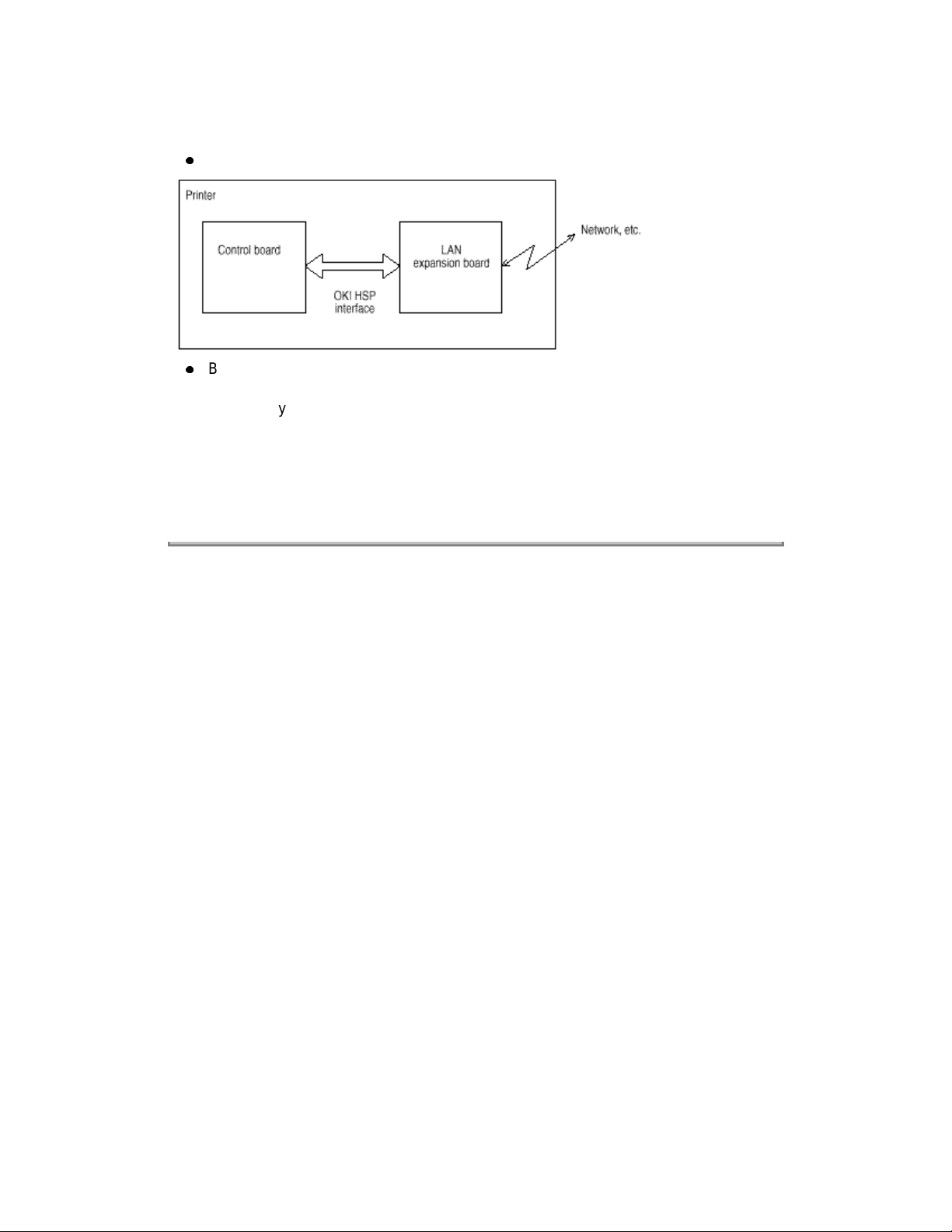
(b) OKI HSP interface (Option)
This interface (slot) is an OKI unique universal interface that provides the platform to
connect various boards (including those supplied by third vendors) such as the LAN
connection expansion board and SCSI expansion board.
Any expansion boards compatible with this interface can be mounted on the Control
board the piggyback board from without modifying the program at the printer side. Refer
to the Conceptual Diagram of the OKI HSP interface.
Conceptual Diagram of OKI HSP Interface
(9) RAM module
z
Pin layout
z
Basic specification
Type:
Access time: 72 pins SIMM (32 bits buss width)
Capacity: 60ns, 70ns, 80ns
Parity: 4, 8, 16 32 or 64MB
None
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
Chapter 2 Operation
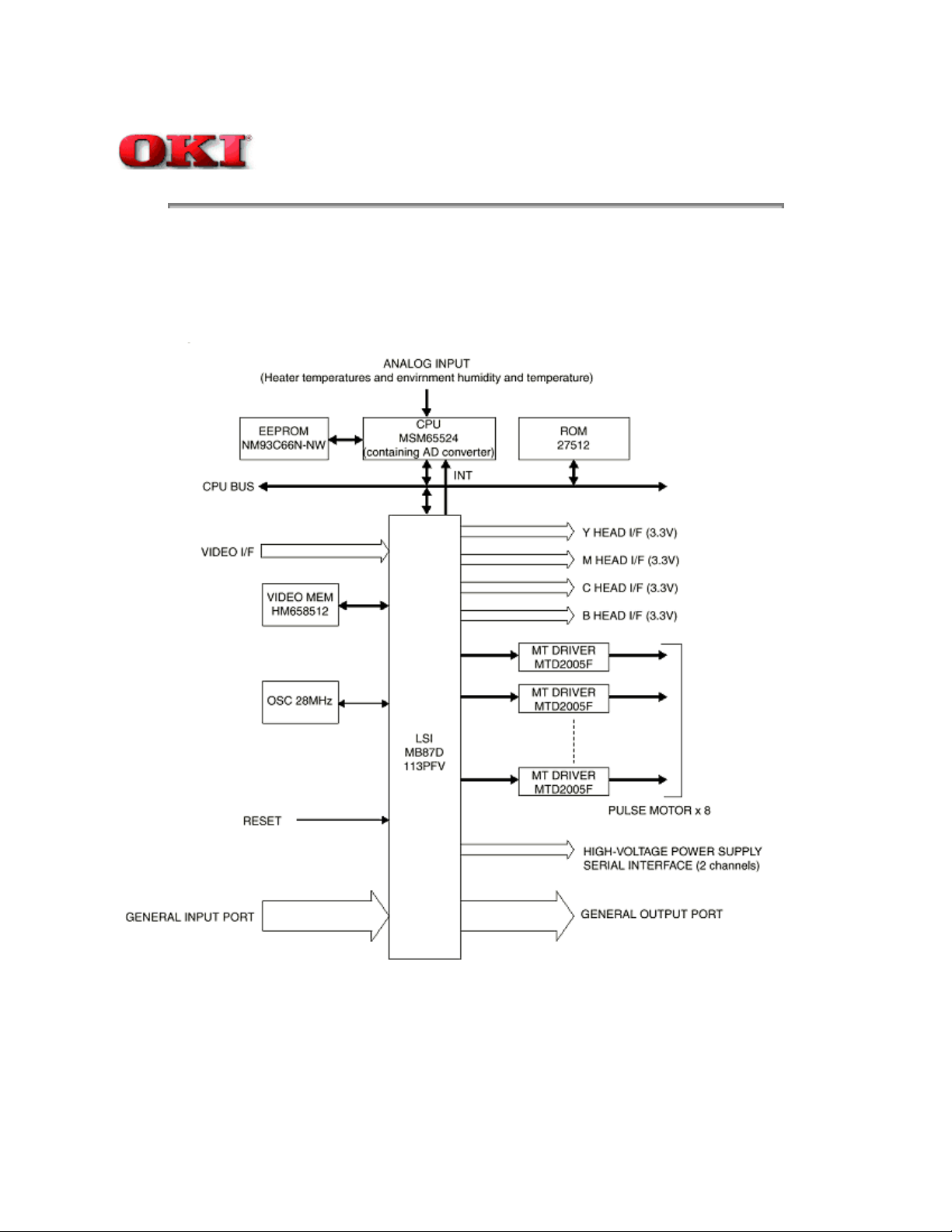
2.2 Engine Control Board (PX4 PCB)
ANALOG INPUT
(Heater temperatures and environmental humidity and temperature)
Yellow (Y), Magenta (M), Cyan (C), Black (B)
Page: 9
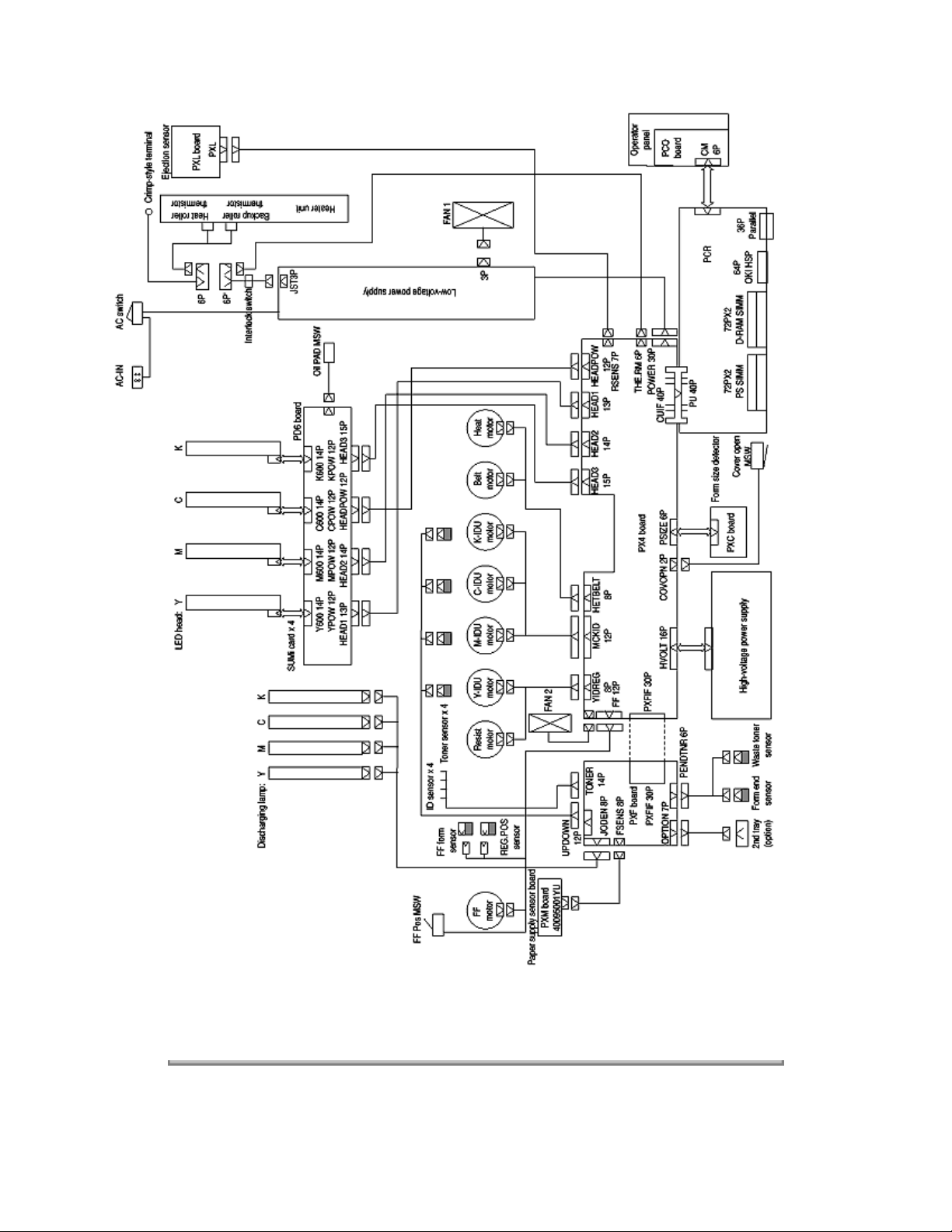
Engine Control Board Block Diagram
The engine control block (PU) is controlled by the engine control board (PX4 PCB) which consists of a
CPU (MSM65524), general purpose LSI chips, EPROM, EEPROM, pulse motor drivers, and video
memory. Refer to the Engine Control Board Block Diagram.

(1) CPU
This is an 8-bit CPU (OKI MSM65524) containing the AD converter and controls the whole
system.
(2) General-purpose LSI
This LSI (MB87D113PFV) is provided in the printer engine control block and has
controller-engine video interface, LED interface, motor control, sensor input, video memory
control, main scanning color correction, skew correction, high-voltage power control, and
OST-EX2 functions.
(3) EPROM
This EPROM (275C512-150) has a storage capacity of 512K bits and stores programs for
the PU block.
(4) EEPROM
This EEPROM (NM93C66N-NW) has a storage capacity of 4K bits. It is mounted on the
board by means of IC socket and stores adjustment values.
(5) Pulse motor drivers
These drivers (MTD2005F) drive eight pulse motors for moving up and down the image
drum (EP) and transferring medium.
(6) Video memory
This SRAM received print data through video interface and stores it.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 10
Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
Chapter 2 Operation
2.3 Power/Board
The power board consists of an AC filter circuit, a low voltage power supply circuit, a high voltage power
supply circuit, and heater drive circuit, and photo sensors.
(1) Low voltage power supply circuit.
This circuit generates the following voltages.
Output voltage
+3.3 V CU Unit CPU, LED HEAD
+5 V Logic circuit supply voltage
+32 V Motor and fan drive voltage and source voltage for high-voltage supply,
discharge lamp
+12 V HSP, OP Amp, high voltage power supply
-12 V HSP
(2) High voltage power supply circuit
This circuit generates the following voltages necessary for electro-photographic processing from +32 V in
accordance with the control sequence from the control board. When cover open state is detected, +32 V
supply is automatically interrupted to stop the supply of all high-voltage outputs.
YMCK = Yellow, Magenta, Cyan, Black
Output
CH -1.35 KV ±50V Voltage applied to charging
DB Normal paper
Y.M.C.K.: -250V/+300V, -232V/+300V
(First paper: Y only)
Voltage Use Remarks
Use
roller
Voltage applied to
developing roller
K.: -270V/+300V
Transparency
Y.M.C.: -200V/+300V, K.:
-250V/+300V
SB Y.M.C.K.: -650V/0V Voltage applied to toner
supply roller
TR 0 to 4 KV Voltage applied to transfer
roller
FIX 0 to 2.5 KV Voltage applied to transfer
roller
Variable
Variable

Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
Chapter 2 Operation
2.4 Mechanical Processes
Here is the Mechanical Process Diagram of OKIPAGE 8c.
Page: 11
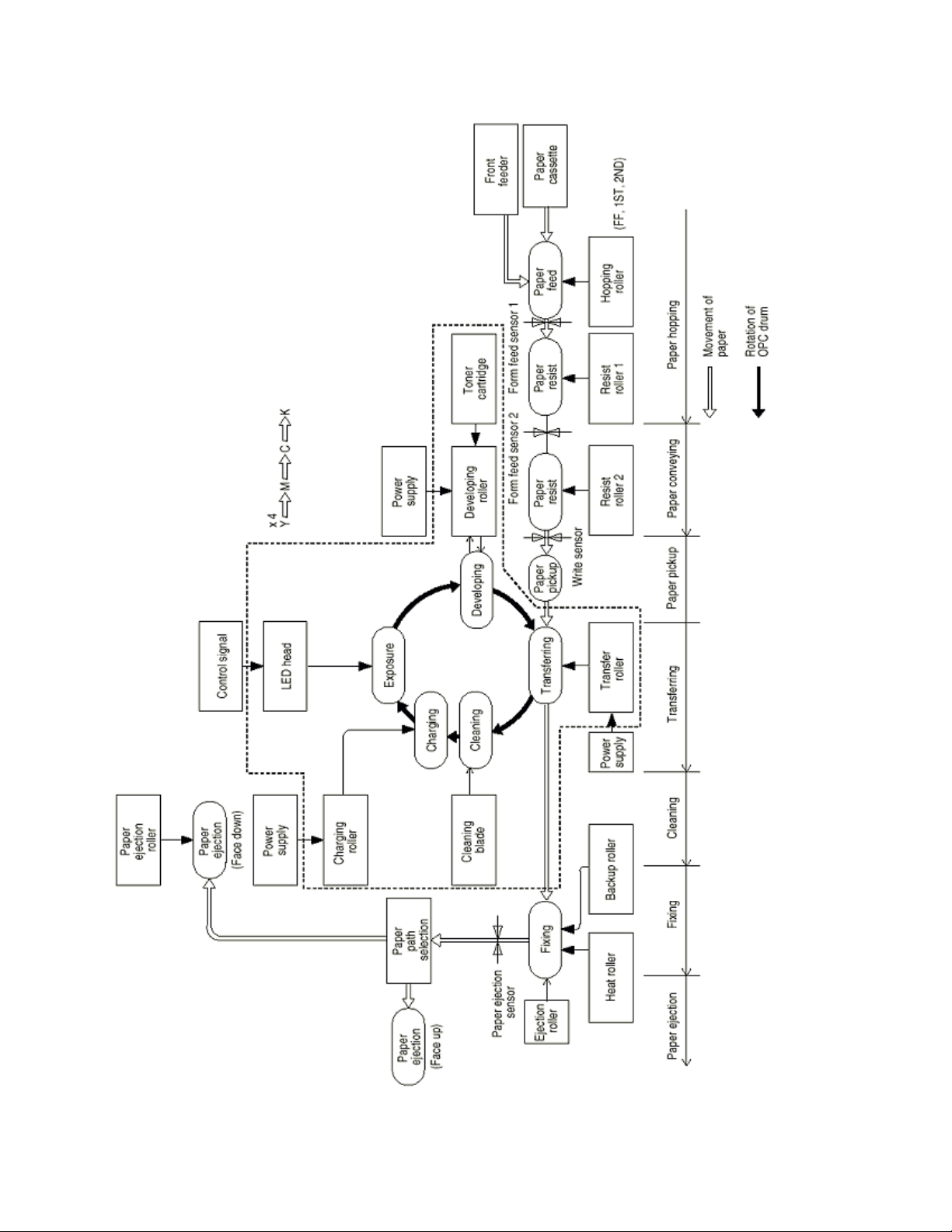

Mechanical Process Diagram (Figure 2.5)
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
2.4.1 Electrophotographic processing mechanism
Page: 12
Chapter 2 Operation
(1) Electrophotographic processed
mechanism is outlined below.
(1) Paper pickup
resulting in a negative charge. With this negative charge, the paper is electrostatically
attracted to the roller.
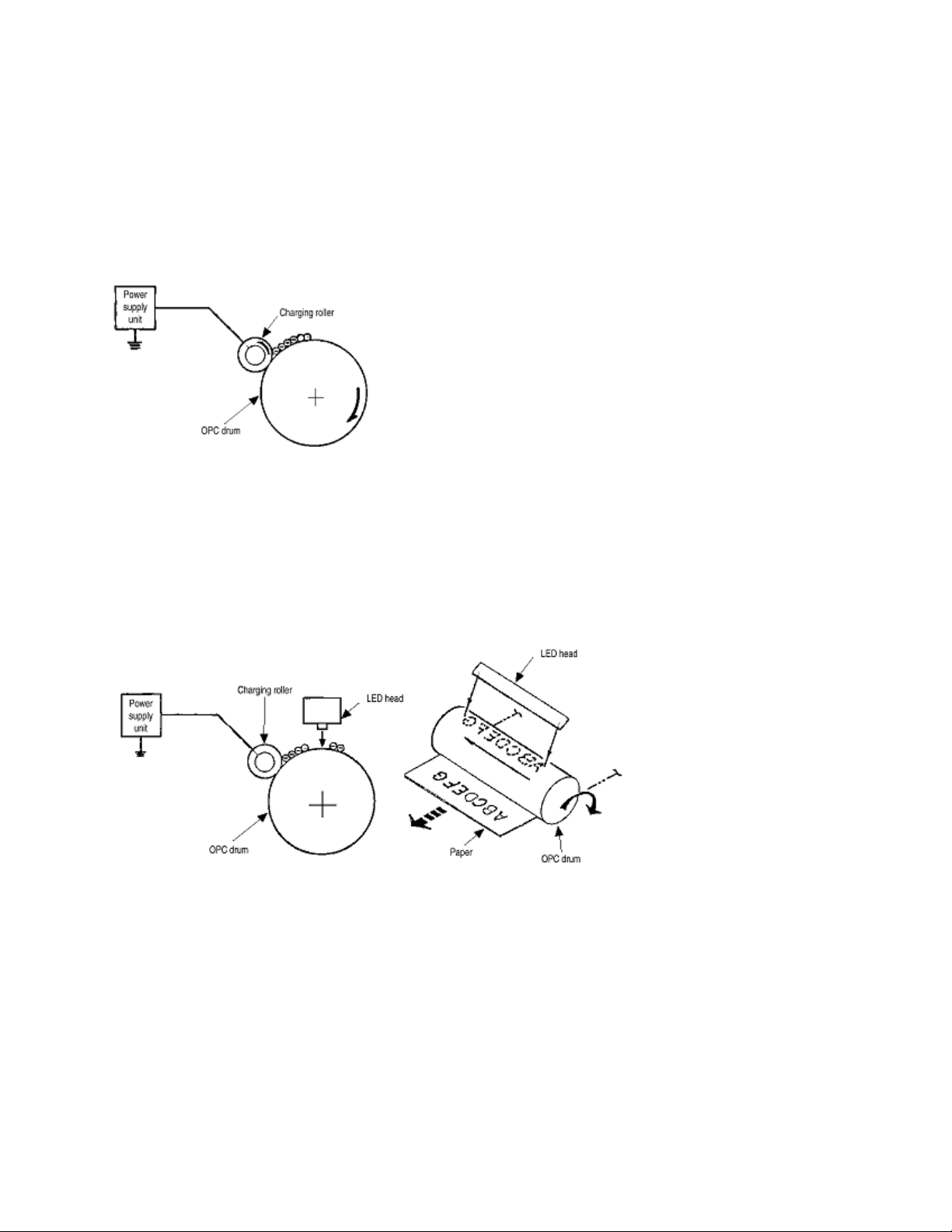
(2) Charging
drum may have a uniform negative charge on its surface.
(3) Exposure
image signals to the negatively-charged surface of the image drum. The negative charge
on the illuminated surface of the image drum is reduced according to magnitudes of the
light beams. Thus, a latent image is formed on the surface of the image drum according
to the resulting surface potentials.
(4) Developing and recovery of excessive toner
negatively-charged toner to the surface of the image drum. The toner is electrostatically
attracted to the latent image to form a visible image on the surface of the image drum.
Simultaneously, this process electrostatically transfers excessive toner from the image
drum to the developing roller.
(5) Transferring
positive charge (opposite to the charge of the toner) to the back side of the paper from
the transfer roller. The toner image is transferred to the paper.
(6) Cleaning
has been used to transfer the image drum the drum to the paper.
(7) Fixing
image.
(2) Paper pickup
- This process fixes the toner image on the paper by pressing the fusing the
- This process causes the roller to give a DC voltage to the paper,
- This process gives a DC voltage to the charge roller so that the image
- This process causes the LED head to apply light beams according to
- This process fits paper to the surface of the image drum and applies
- Cleaning blade scrapes off the remaining toner of any image drum, which
- Each process of the electrophotographic processing
- This process applies
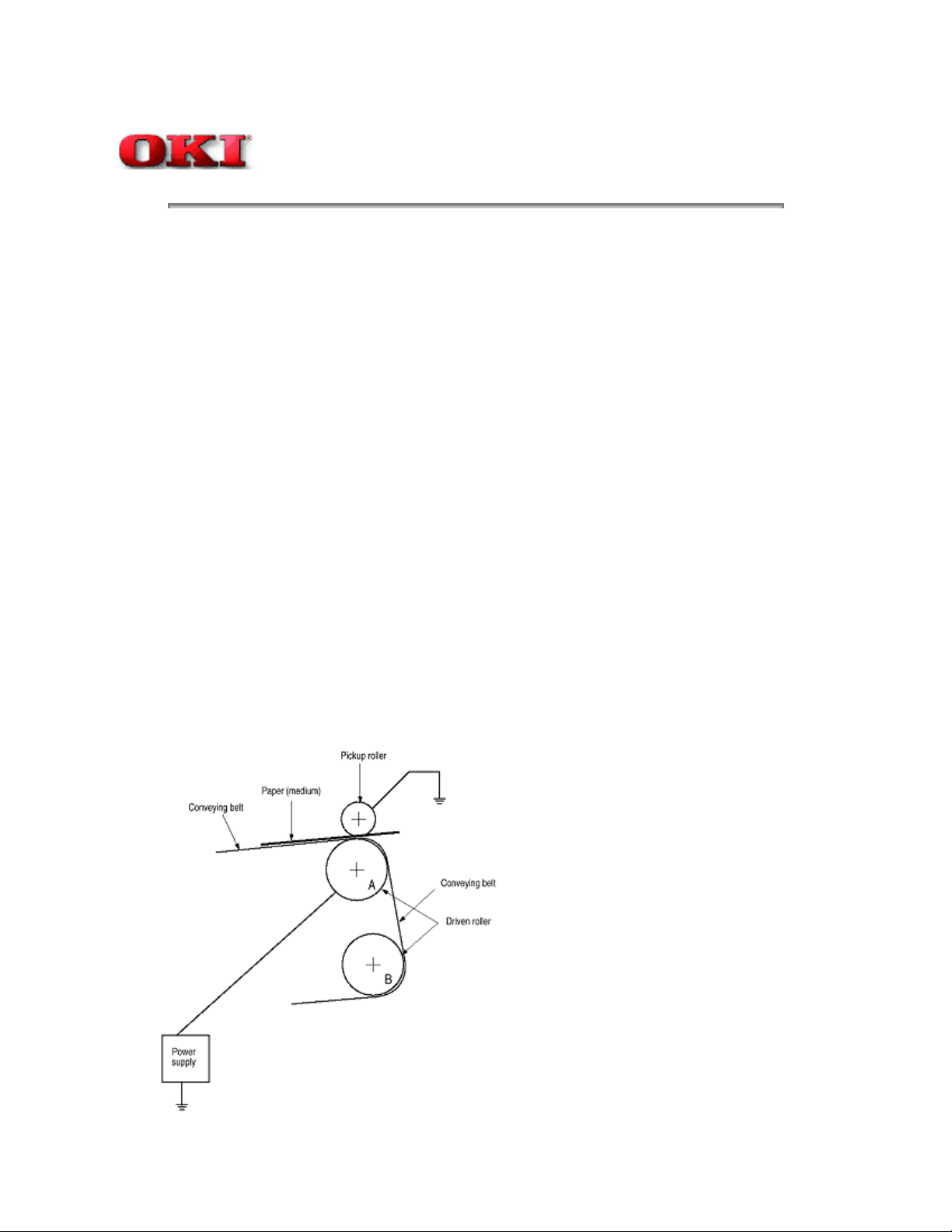
A DC voltage (0V to 2KV) is applied to the driven roller A, to create a positive charge on the lower surface
of the paper. The
kept in charged paper is electrostatically attracted to the pickup roller. The paper is in close contact with
the conveying Belt
and moves steadily.
(3) Charging - This process applies a DC voltage to the charging roller in contact with the surface of the
image drum.
(4) Exposure - The light beams from the LED head are applied to the surface of the image drum which is
charged
negatively. The negative charge on the illuminated surface f the image drum is reduced according to the
magnitude of the
light beams and a latent image is formed on the surface of the image drum according to the resulting
surface potentials.
(5) Developing - This process applies toner to the latent image on the surface of the drum to create a
toner image.
Developing is carried out on the surface of the image drum at where the image contacts with the
developing roller.
(1) The sponge roller transfers toner to the developing roller. The toner is charged negatively.
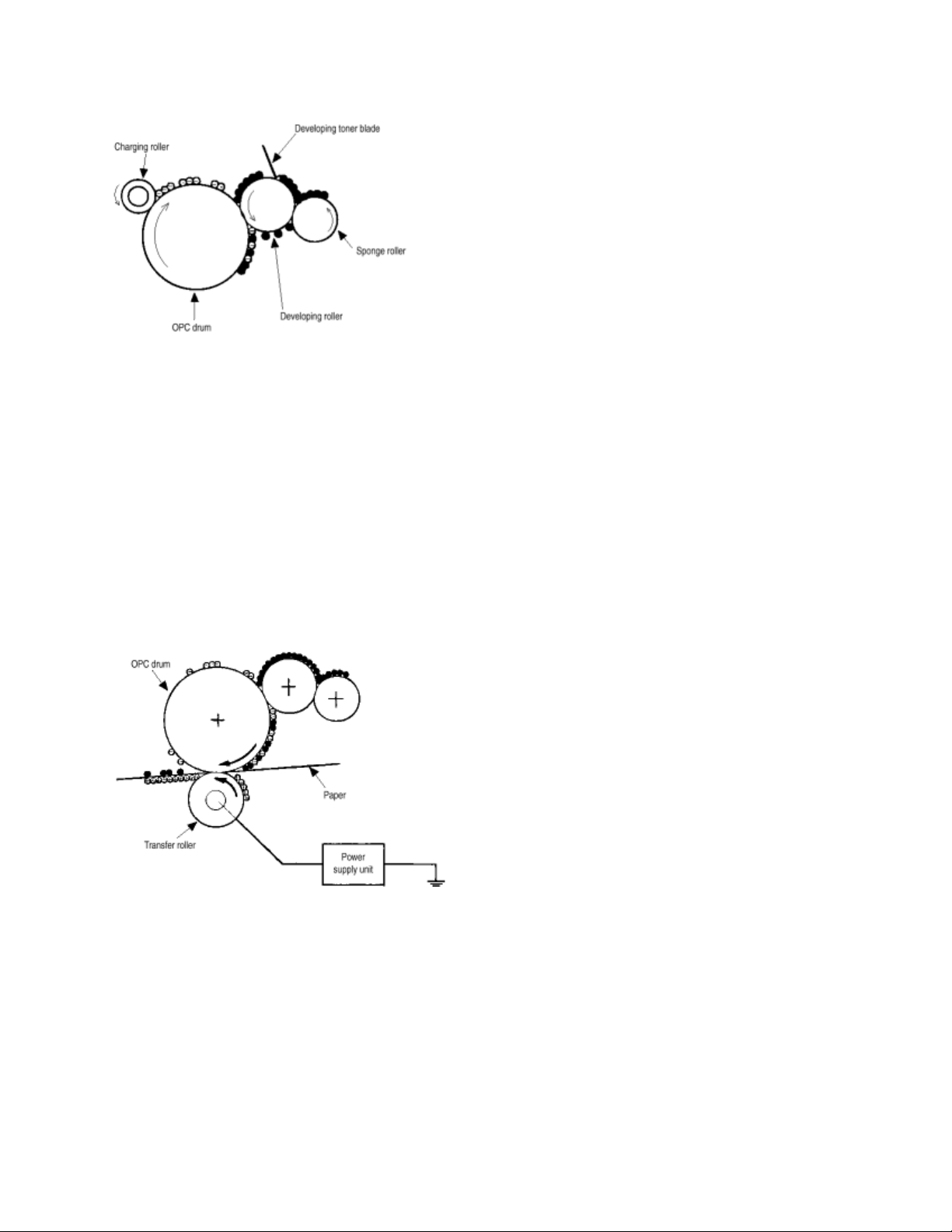
(2) The toner blade scrapes away excess toner from the developing roller, leaving a thin film of toner
on the surface of
the developing roller.
(3) The toner is attracted to the latent image on the surface of the image drum, where the image
drum contacts the
developing roller. The latent image on the surface of the image drum is made visible with the toner.
(6) Transferring - The transfer roller made of conductive sponge presses the paper against the surface
of the image drum. The paper will make close contact with the surface of the image drum. This process
fits the paper to the surface of the image drum (using the transfer roller) and applies a positive charge
(opposite to the charge of the toner) from under the paper. When a positive high voltage is applied to the
transfer roller from the power supply, the positive charge induced on the transfer roller jumps to the upper
surface of the paper (where the transfer roller touches the paper) and attracts the negatively-charged
toner from the surface of the image drum onto the surface of the paper.
(7) Fixing - The toner image just transferred to the paper is fused and fixed to the paper while the paper
is passing through the gap between the heat roller and the backup roller. The teflon-coated surface of
the heat roller is heated by the 800-watt heater (or a halogen lamp) in the heat roller. The temperature of
the heat roller surface is controlled by a thermistor in contact with the surface of the heat roller. A
thermostat is provided for safety. When the heat roller temperature rises above the preset temperature,
the thermostat opens and shuts off power to the heater in the heat roller. The backup roller is evenly
pushed against the heat roller by two end springs.
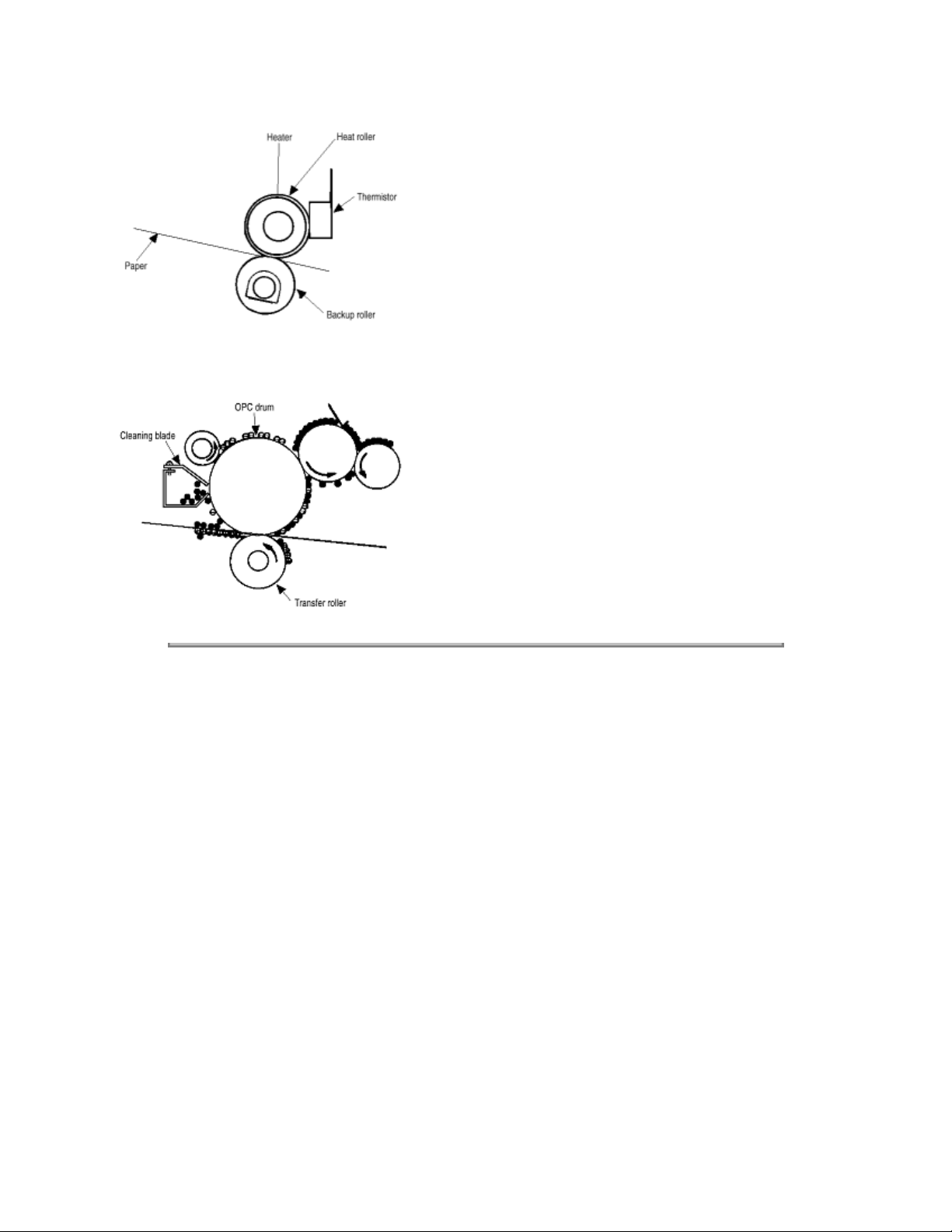
(8) Cleaning - The toner which remains on the (OPC) Image Drum without being fused is scraped by a
cleaning blade and discarded in the waste toner tank.
Copyright 1998, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide - OKIPAGE 8c
Chapter 2 Operation
2.4.2 Paper running process
How paper moves through the OKIPAGE 8c is shown in the Paper Route Diagram.
Y=Yellow; M=Magenta; C=Cyan; K=Black
Page: 13
 Loading...
Loading...