Okidata OKIOFFICE 1200, OKIOFFICE 1600 Parts list

OKIOFFICE 1200 1600
FIELD ENGINEERING MANUAL
Version 2.0
(11 June 2002)
Safety Information
LED Safety Label
A LED safety label is attached to the outside of the machine as shown below.
Battery Precautions
CAUTION
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer.
Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Important: Muratec does not recommend the independent replacement of this battery.
The battery is sold only as a component part of the main control PCB and Battery
PCB, and cannot be purchased separately from Muratec.
Il y a un danger d'explosion s'il y a un remplacement incorrect de la batterie.
Remplacer uniquement avec une batterie du même type ou d'un type recommandé par le
constructeur. Mettre au rebut les batteries usagées conformement aux instructions du fabricant.
Germany only
VORSICHT!
Explosinsgefahr bei unsachgemäßen austausch der batterie.
Ersatz nur durch denselben oder einen vom hersteller empfohlenen ähnlichen typ. Entsorgung
gebrauchter batterien nach angaben des herstellers.
Denmark only
ADVARSEL!
Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering
Udskiftning må kun ske med batteri af samme fabrikat og type.
Levér det brugte batteri tilbage til leverandøren.
Norway only
ADVARSEL
Eksplosjonsfare ved feilaktig skifte av batteri.
Benytt samme batteritype eller en tilsvarende type anbefalt av apparatfabrikanten.
Brukte batterier kasseres i henhold til fabrikantens instruksjoner.
Sweden only
VARNING
Explosionsfara vid felaktigt batteribyte.
Använd samma batterityp eller en ekvivalent typ som rekommenderas av apparattillverkaren.
Kassera använt batteri enligt fabrikantens instruktion.

Finland only
ALL Areas
“Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer.
Germany only
gleichwertigen typ. Entsorgung gebrauchter Batterien nach Angaben des Herstellers.
VAROlTUS
Paristo voi räjähtää, los se on virheellisesti asennettu.
Vaihda paristo ainoastaan laitevalmistajan suosittelemaan tyyppiin.
Hävitä Käytetty paristo valmistajan ohjeiden mukaisesti.
CAUTION
Dispose of used IC Package according to the manufacturer’s instructions.”
VORSICHT!
⇒”Austausch nur durch denselben oder einen vom Hersteller empfohlenen,

Table of Contents
Safety Information..........................................................................................................................................1
LED Safety Label.................................................... .................................. .................................................1
Battery Precautions...................................................................................................................................1
Section 1 General Description
1.1 Product Description..............................................................................................................................1-1
1.2 Specifications....... .................................. ................................. ..............................................................1-2
Section2 Machine Composition
2.1 OKIOFFICE 1200 In te r connect Block Diagra m ( 1 /2 )........................................ .................................. ..2-1
OKIOFFICE 1600 Interconnect Block Diagram (1/2).......................................................... ... ..... ..... .. . ..... ...2-3
2.2 Main Control PCB... .. ................................................. .................................. .........................................2-5
2.3 Network Control Unit (NCU) PCB............ .................................. ................................. ..........................2-7
2.4 Power Supply Unit (PSU) .....................................................................................................................2-8
2.5 Sensors ................................ ................................................. ................................. .. .............................2-9
2.5.1 Sensor Locations...........................................................................................................................2-9
2.5.2 Sensor Descriptions ....................................................................................................................2-10
2.6 Document Scanning Sequence....................................................................................... ..... ..... .........2-11
2.6.1 Document Detection....................................................................................................................2-11
2.6.2 Document Separation..................................................................................................................2-11
2.6.3 Document Transport....................................................................................................................2-11
2.6.4 Document Scanning....................................................................................................................2-11
2.6.5 Document Discharge...................................................................................................................2-12
2.7 Recording Section .............. ... ................................................. .................................. ..........................2-13
2.7.1 Recording Paper Feed Path........................................................................................................2-13
2.8 Image Processing...............................................................................................................................2-13
2.8.1 Drum Charge...............................................................................................................................2-14
2.8.2 Drum Exposure ...........................................................................................................................2-14
2.8.3 Development ...............................................................................................................................2-14
2.8.4 Image Transfer............................................................................................................................2-15
2.8.5 Residual toner distribute............................................ ... .. ... ......................................... ... ..............2-15
2.8.6 Fusing..........................................................................................................................................2-16
Section3 Adjustment Procedures
3.1 Field Service Program Modes .......................... . ..... ..... ... .... . ..... ..... ... .... . ..... ... ..... .... . ..... ... ..... ................3-1
3.2 Machine Parameter Ad j us tment .............. .................................. ................................. ..........................3-2
3.2.1 Setting the Machine Parameters...................................................................................................3-2
3.2.2 Clearing the Machine Parameters.................................................................................................3-2
3.3 Memory Switch Adjustment ................................................................................................................3-18
3.3.1 Setting the Memory Switches......................................................................................................3-18
3.3.2 Clearing the Memory Switches....................................................................................................3-18
3.4 Clear Programmed D a ta / Use r Settings..................................... .................................. .....................3-35
3.5 All RAM Clear .................................................. .................................. .................................................3-36
3.6 Setting Individual Autodialer Attributes...............................................................................................3-36
3.7 Unique Switch Adjustment............................................................. ... .......... ... ..... ..... ..... ... ...................3-40
3.7.1 Setting the Unique Switches........................................................................................................3-40
3.7.2 Clearing the Unique Switches............................................................................. ..... ..... ..... .........3-40
Unique Switch a:0 — Dialer...................................... .. ... ..... ... ..... ..... ... .... . ..... ... ..... ..... ..... .. . ..... ..............3-41
3.8 Printer maintenance mode..... .................................. ................................. ..........................................3-62
3.9 Print Program Mode List ....................................... .................................. ............................................3-63
3.10 Test Modes.......................................................................................................................................3-63
3.10.1 Life Monitor................................................................................................................................3-64
i

3.10.2 Printer Test................................................................................................................................3-65
3.10.3 Feeder test............................................................ ..... .. ... ..... .. . ..... .... . ... .... . ..... ...........................3-66
3.10.4 Backgrou nd Level Test. .................. ................................................. ..........................................3-66
3.10.5 Set Background Level ...............................................................................................................3-66
3.11 Print Machine Parameters, Memory Switch and Unique Switch Settings........................................ .3-67
3.12 Factory Functions .............................................................................................................................3-67
3.12.1 Function List..............................................................................................................................3-67
3.12.2 LED Test....................................................................................................................................3-67
3.12.3 LCD Test ...................................................................................................................................3-68
3.12.4 Key Panel Test..........................................................................................................................3-68
3.12.5 SRAM Check.............................................................................................................................3-69
3.12.6 DRAM Check.............................................................................................................................3-69
3.12.7 RTC(real time clock) Test..........................................................................................................3-70
3.12.8 RS-232C Test............................................................................................................................3-70
3.13 Line Tests .........................................................................................................................................3-71
3.13.1 Relay Test .................................................................................................................................3-71
3.13.2 Tonal Signal Test.......................................................................................................................3-72
3.13.3 DTMF Output Test.....................................................................................................................3-74
3.14 Mirror Carriage Transfer Mode...................................................................... ... ..... ..... ... ...................3-75
3.15 Consumable order sheet ..................................................................................................................3-75
3.15.1 Set consumable order sheet .....................................................................................................3-75
3.15.2 Print consumable order sheet ............................ .. ... ... ..... .... . ... ..... .... . ..... ... ................................3-76
3.15.3 Clear consumable order sheet ..................................................................................................3-76
3.16 DRAM Clear......................................................................................................................................3-77
3.17 Clear Life Monitor .............................................................................................................................3-77
3.18 Clear Optional Data..........................................................................................................................3-77
3.19 Set Service Code.............. .................................................. ................................. .............................3-78
3.20 Life monitor maintenance .................................................................................................................3-78
3.21 JP1, JP2 Battery Backup..................................................................................................................3-79
3.22 Update the software..........................................................................................................................3-80
Section4 Troubleshooting Procedures
4.1 Troubleshoot in g O ut line......... .................................. ................................................. ............................4-1
4.2 Recording Paper Jam...........................................................................................................................4-2
4.3 Document Feeder Jam.......................................................................... ..... ..........................................4-2
4.4 Document Feeder Multi-feeding or Skew ............................................................................. .. ... ... ........4-3
4.5 Mirror Carriage Error...................................................................... ... ..... ..... ... ..... ..... ..... ........................4-3
4.6 Transmit Erro r............................................... .................................. ......................................................4-3
4.7 Transmit Black Lines ............................................................................................................................4-3
4.8 Cannot transmi t ................... ................................. ................................................. ...............................4-4
4.9 Receive Erro r s..... .................................. ................................. ..............................................................4-4
4.10 Will not Auto-Answer ..........................................................................................................................4-4
4.11 Clearing Jammed Pap er ................ .................................. .................. .................................................4-5
If the original document jams..................................................................................................................4-5
To remove the document: ............... .................................. ................................. .................. ..................4-6
If a printout jams inside your machine....................................................................................................4-7
4.12. The Image Quality Problems . ................................. .................................. .........................................4-9
4.12.1 Blank pages.................................................................................................................................4-9
4.12.2 Black pages.................................................................................................................................4-9
4.12.3 Printout too light.........................................................................................................................4-10
4.12.4 Printout too dark........................................................................................................................4-10
4.12.5 Blurred background...................................................................................................................4-10
4.12.6 Uneven print density .................. .................................. ................................. .............................4-11
4.12.7 Irregularities...............................................................................................................................4-11
4.12.8 White (Black) Line .....................................................................................................................4-12
ii

4.12.9 Toner Smudges....................................... . ..... .... . ..... .. . ..... .... . ... ..................................................4-12
4.13 LCD Error Messages ........................................................................................................................4-13
LCD error messa g es ( Alp h ab e tic list)...... ................................................. ................................. ...........4-13
4.14 Error Codes ....................................... . ..... ..... ... ..... ..... .. . ..... ..... ..... ... ..... .. ... ... ..... ..... ...........................4-18
Dialing errors ........................................................................................................................................4-18
Reception errors...................................................................................................................................4-18
Transmission errors..............................................................................................................................4-19
Communication Error Messages......................................... .................. .................................. .............4-20
4.15 Service Call Error..............................................................................................................................4-21
4.15.1 Call For Service......................... .................................. ................................. .............................4-21
4.15.2 Please Call Service ...................................................................................................................4-21
4.16 LCD Failure.......................................................................................................................................4-24
4.17 General Power Failure......................................................................................................................4-24
4.18 Cleaning the Unit.................................................. ..... .. ... ... .... . ..... .. . ..... .... . ..... ...................................4-25
Curing frequent jams in the ADF..........................................................................................................4-25
Cleaning the FBS glass, Contact glass and white pad.........................................................................4-26
Cleaning the LED print head ........................ ................................. ................... ....................................4-26
Section5 Maintenance & Adjustment
5.1 Maintenance schedule..........................................................................................................................5-2
5.2 Re/Disass embl e........... .................. ................................. .................................. ....................................5-3
5.2.1 Covers ...........................................................................................................................................5-5
5.2.2 PCBs ...........................................................................................................................................5-13
5.2.3 Sensors .......................................................................................................................................5-24
5.2.4 Scanning section.........................................................................................................................5-25
5.2.5 Printer section..............................................................................................................................5-37
5.3 Adjustment................ .................................. ................................................. .......................................5-49
5.3.1 Adjustment of Retard roller pressure...........................................................................................5-49
Section 6 Options
6.1 Memory Upgrade.... .................. ................................. .................. .................................. .. .....................6-1
Packaging contents:........... .................................. ................................. .................................................6-1
Installation ..............................................................................................................................................6-1
6.2 Attaching an optional handset ..............................................................................................................6-3
Packaging contents:........... .................................. ................................. .................................................6-3
Installation ..............................................................................................................................................6-3
6.3 RS-232C interfa ce...................................... ................................. .................................. . ......................6-4
Packaging contents:........... .................................. ................................. .................................................6-4
Installation ..............................................................................................................................................6-4
RS-232C interface cable ........................................................................................................................6-6
Signal direction.......................................................................................................................................6-6
RS-232C Test.........................................................................................................................................6-6
6.3 Page Counter........................................................................................................................................6-7
Packaging contents:........... .................................. ................................. .................................................6-7
Installation ..............................................................................................................................................6-7
6.4 AL-200 (only for OKIOFFICE 1600)......................................................................................................6-8
Packaging contents:........... .................................. ................................. .................................................6-8
Installation ..............................................................................................................................................6-8
6.5 OP-100/NP- 200 ............. .................................. .................................. .................................................6-12
Packaging contents:........... .................................. ................................. ...............................................6-12
Attaching the OP-100 (and NP-200) ........................ ..... ... .. ... ..... ..........................................................6-13
Installing the Printer driver............ ... ................................................. ....................................................6-16
6.6 Attaching the 2-Bin tr a y ................................ .................................. ....................................................6-17
Packaging contents:........... .................................. ................................. ...............................................6-17
Installation ............................................................................................................................................6-17
6.7 Second paper cassette.......................................................................................................................6-22
iii

Packaging contents:........... .................................. ................................. ...............................................6-22
Installation ............................................................................................................................................6-22
Setting of the Paper Size......................................................................................................................6-25
iv
Section 1
General Description
1.1 Product Description
The OKIOFFICE 1200 and OKIOFFICE 1600 is Multi-function product with flat bed scanner and Group
3 and V.34 HDX modem facsimile machine. Documents are printed on plain paper using dry
electrophotographic printing.
1-1
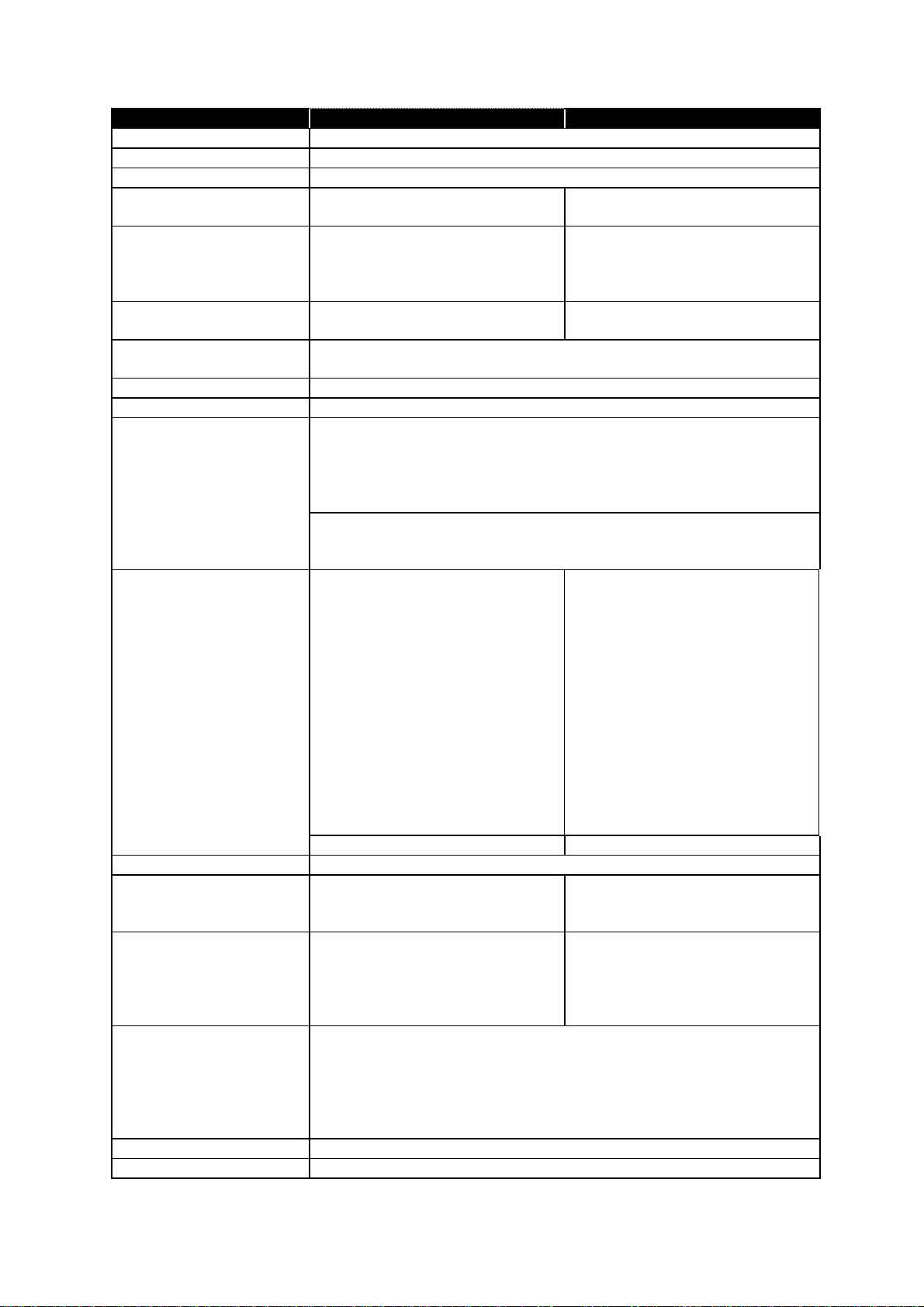
1.2 Specifications
Item 1200 1600
Type Desktop type
Telephone network PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) or equivalent.
Compatibility ITU-T T.4 and T.30
Coding method ITU-T-standard MH, MR, MMR and
Murata-proprietary MSE.
Modem speed 14400, 12000, 9600, 7200, 4800
and 2400 bps
Dual Access Allows up to two simultaneous
operations.
Display LCD: 2 lines, 20 characters per line.
Language: English, French, Spanish, Germany
Scanning method Flatbed CCD
Recording method Dry electrophotographic (LED) printer
Acceptable document size
Scanning resolution <Transmission>
<Copy> 300 dpi 400 dpi
Effective Scanning width 208 mm(Fax), 210 mm(Copy)
Transmission speed Approx. 6 seconds
Document Memory Standard:
Document memory backup (Total memory capacity : Backup time)
Printing resolution 600 dpi
Warm-up time Less than 20 seconds at 68° F (20° C)
<ADF>
Single sheet Two or more sheets
Max: 216 mm (W) × 900 mm (L) 210 mm (W) × 330 mm (L)
Min: 120 mm (W) × 100 mm (L) 148 mm (W) × 105 mm (L)
Paper weight: 30.2 – 104.7g/m2 52.3 – 80 g/m2
<FBS glass>
Max: 210 mm (W) × 330 mm (L)
Min: No limit
horizontal × vertical
(in dots/mm × in lines/mm)
Normal: 8 × 3.85
Fine: 8 × 7.7
Super fine: 8 × 15.4
Greyscale: 8 × 7.7
Based on transmission of ITU-T
Test Document 1.
8 MB (630 pages)
Upgrade option:
plus 8MB (680 pages)
8 MB: 72 hours
16 MB: 36 hours
32 MB: 18 hours (1600 only)
The backup battery requires about 24 hours to reach full charge after
power to the fax unit is restored.
ITU-T-standard MH, MR, MMR,
JBIG and Murata-proprietary MSE.
33600, 31200, 28800, 26400,
24000, 21600, 19200, 16800,
14400, 12000, 9600, 7200, 4800
and 2400 bps
Allows up to three simultaneous
operations.
<Transmission>
horizontal × vertical
(in dots/mm × in lines/mm)
Normal: 8 × 3.85
Fine: 8 × 7.7
Super fine: 16 × 15.4*
Greyscale: 8 × 7.7(Memory Tx)
16 × 15.4*(Rea l t i m e T x )
*: In the case that the remote fax
has the ability of “16 × 15.4”.
If not, the superfine resolution is
“8 × 15.4“, and the greyscale
resolution in real time transmission
is “8 × 7.7”.
Approx. 2 seconds
Based on transmission of ITU-T
Test Document 1.
Standard:
8 MB (630 pages)
Upgrade option:
plus 8MB (680 pages)
plus 24MB (2040 pages)
1-2
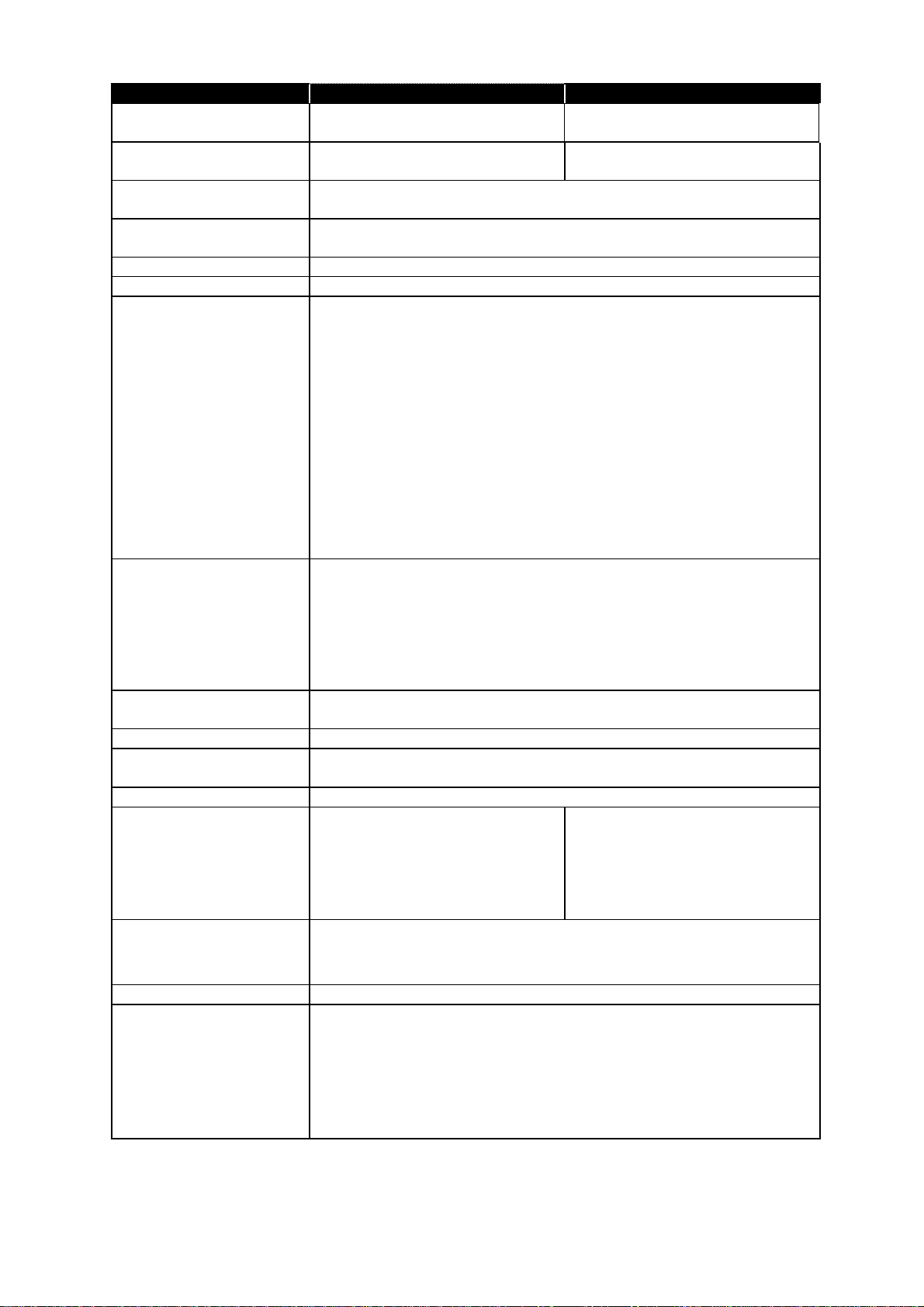
Item 1200 1600
First copy time 12 seconds (using A4-sized paper
in 1st paper cassette)
Printing speed 12 ppm (When loading A4-sized
paper from 1st paper cassette.)
10 seconds (using A4-sized paper
in 1st paper cassette)
16 ppm (When loading A4-sized
paper from 1st paper cassette.)
Toner yield Approx. 8,000 pages (A4, 6 % document coverage under 2-pages
interval printing.)
Drum yield Approx. 16,000 pages (A4, 6 % document coverage under 2-pages
interval printing.)
Smoothing Yes
Print margin Reading edge, Trailing edge, Left edge and Right edge: 3 ± 2 mm
Acceptable recording
paper size
<Paper cassette>
Plain paper: A4(SEF), A5(LEF), F4(SEF)
Paper weight: 60 – 90g/m
2
<Bypass tray>
Plain paper: A4(SEF), A5(LEF)(SEF), A6(SEF), F4(SEF),
Letter(SEF), Legal(SEF), Half letter(LEF),
Executive(SEF)
Envelopes: DL(SEF), COM10(SEF), Monarch(SEF)
Postcard: 100 mm (W) × 148 mm (L)
Transparency: A4(SEF)
Custom size*: (105 – 216 mm) × (148 – 356 mm) (Width × Length)
*Custom sized paper is available only when the optional printer controller
kit has been installed.
Recording paper capacity <Paper cassette>
1st cassette: 500 sheets
2nd cassette (option): 500 sheets
<Bypass tray>
Plain paper: 50 sheet
Postcard/Transparency: 20 sheets
Envelopes 1 sheet
Receive paper tray
capacity
Approx. 300 sheets
with optional 2-bin tray: Upper approx. 100, Lower approx. 150 sheets
Printouts exit Face up
Environmental conditions
Ambient temperature: 10 °C to 32 °C (50 °F to 89.6 °F)
Relative humidity: 20 % to 80 % with no condensation
Power requirements 230 VAC ± 10 %; 50/60 Hz
Power consumption Sleep mode (Heater off) 19.8 W
Standby: 20.6 W
Memory Transmission: 21.3 W
Reception: 21.5 W
Copying: 1020 W
Maximum: 1060 W
Dimensions
2WAY: 510 (W) × 492 (D)
3WAY: 510 (W) × 492 (D)
× 376 (H) mm
× 483 (H) mm
Sleep mode (Heater off) 22.2 W
Standby (Heater off): 24.2 W
Memory Transmission: 25.0 W
Reception: 25.2 W
Copying: 1200 W
Maximum: 1210 W
When the Extension paper tray and Bypass tray are retracted.
Weight Approx. 23.3 Kg (51.4 lbs) without consumables and trays.
Optional products
• Optional telephone handset
• 2nd paper cassette
• Printer controller kit
• Network interface card
• Second phone line kit (only for OKIOFFICE 1600)
• RS-232C interface kit
• Mechanical page counter
1-3
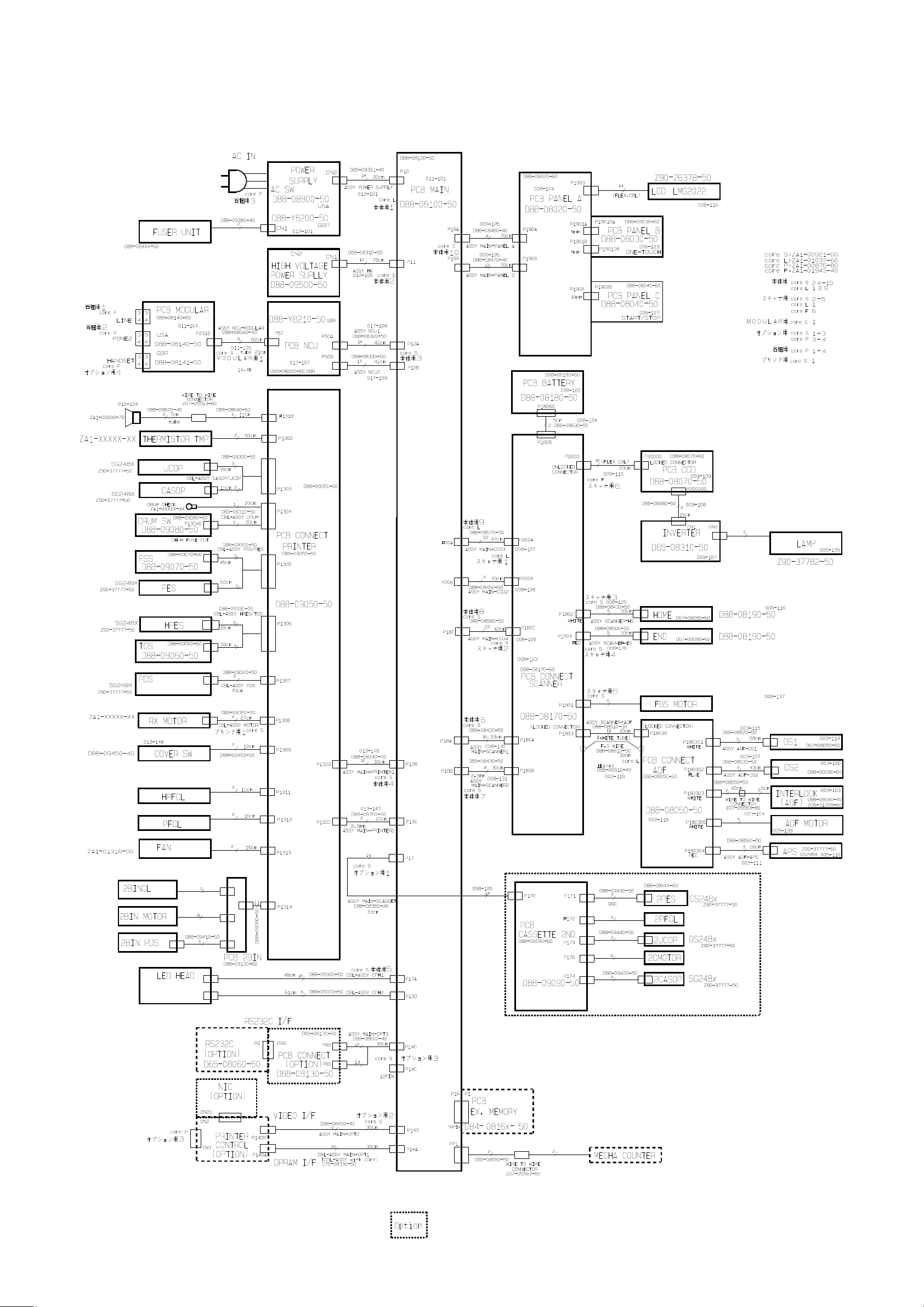
Section2
Machine Composition
2.1 OKIOFFICE 1200 Interconnect Block Diagram (1/2)
2-1
OKIOFFICE 1200
Connection Diagram (1/2)
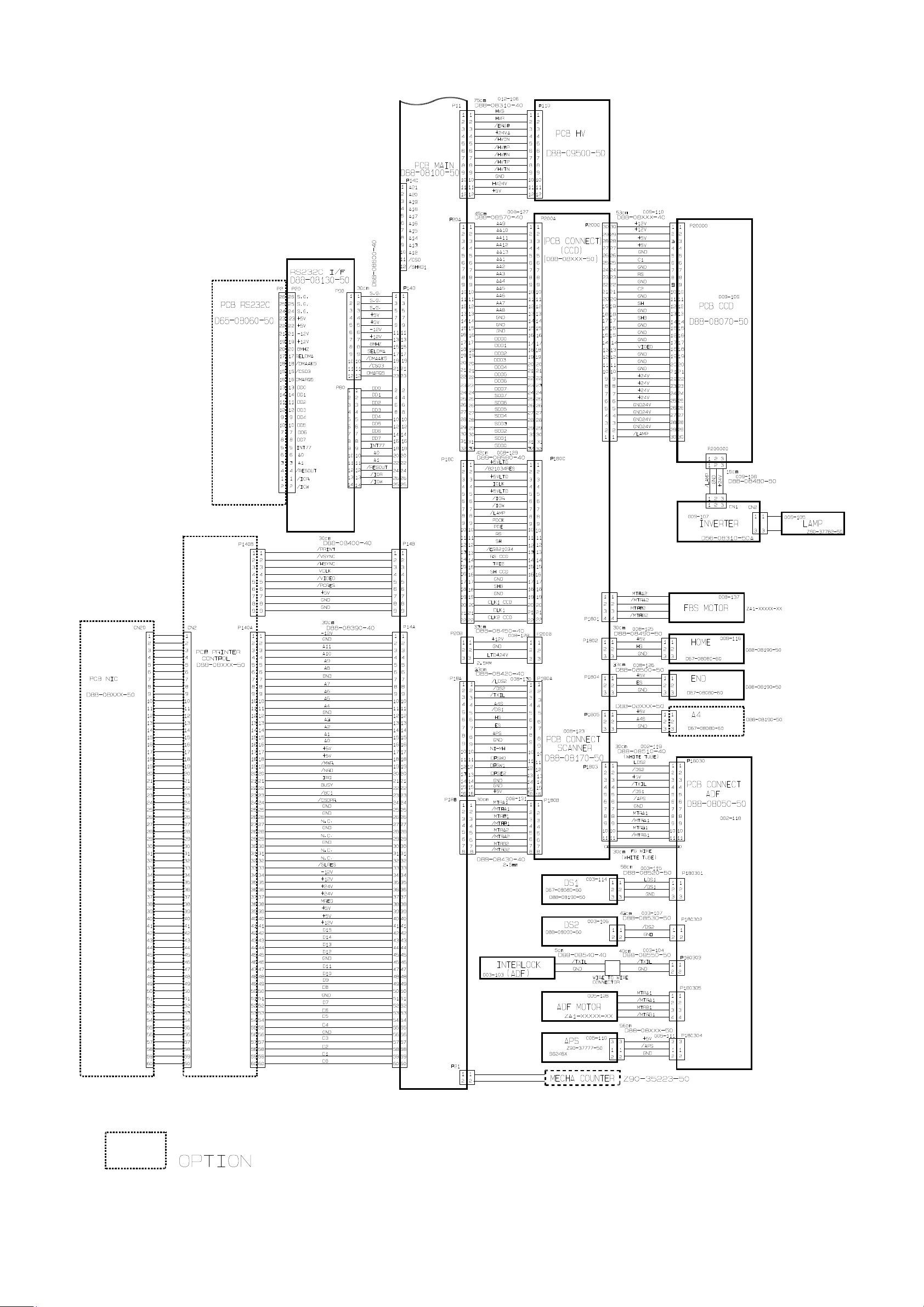
OKIOFFICE 1200 Interconnect Block Diagram (2/2)
OKIOFFICE 1200
Connection Diagram (2/2)
2-2
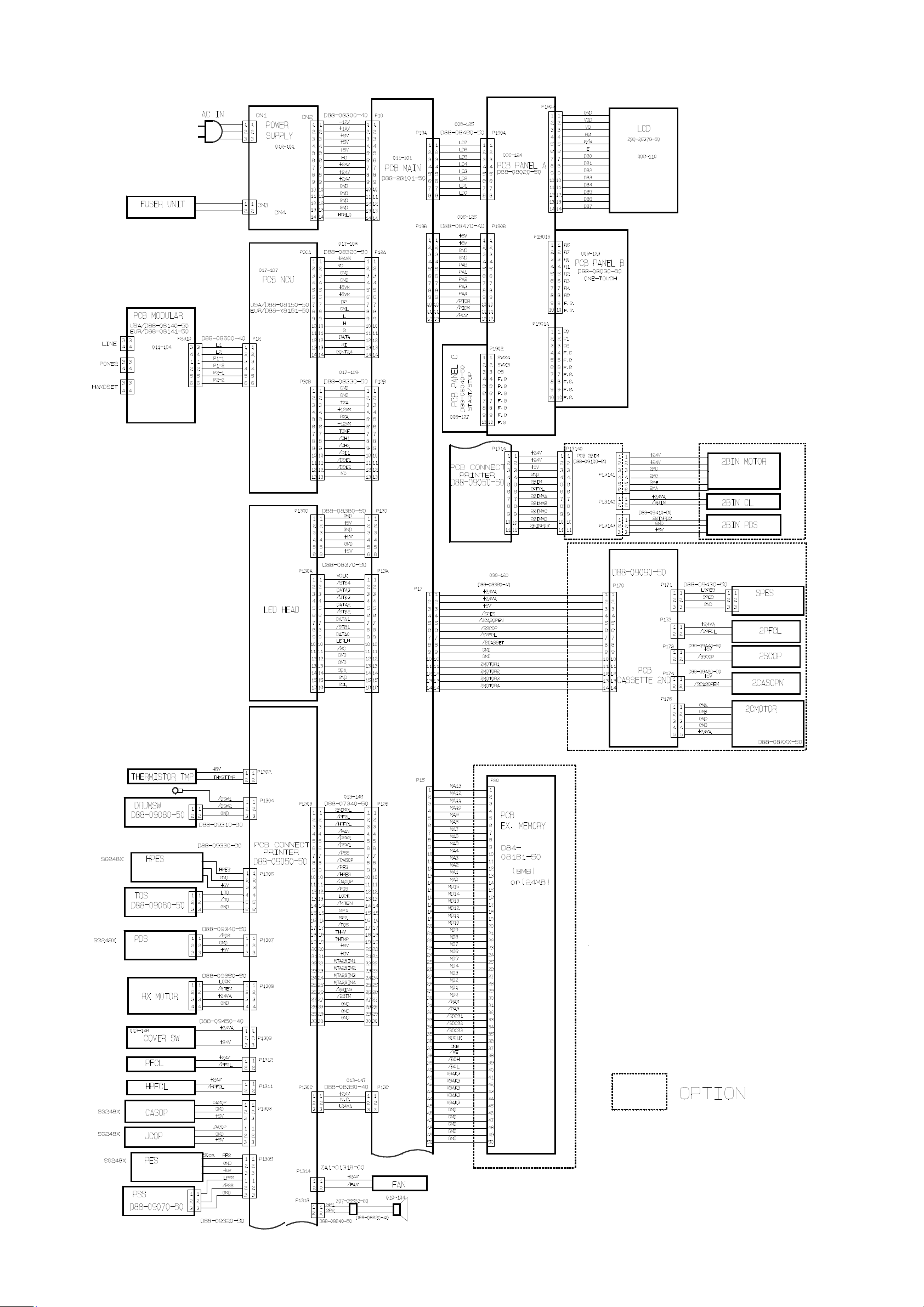
OKIOFFICE 1600 Interconnect Block Diagram (1/2)
2-3
OKIOFFICE 1600
Connection Diagram (1/2)
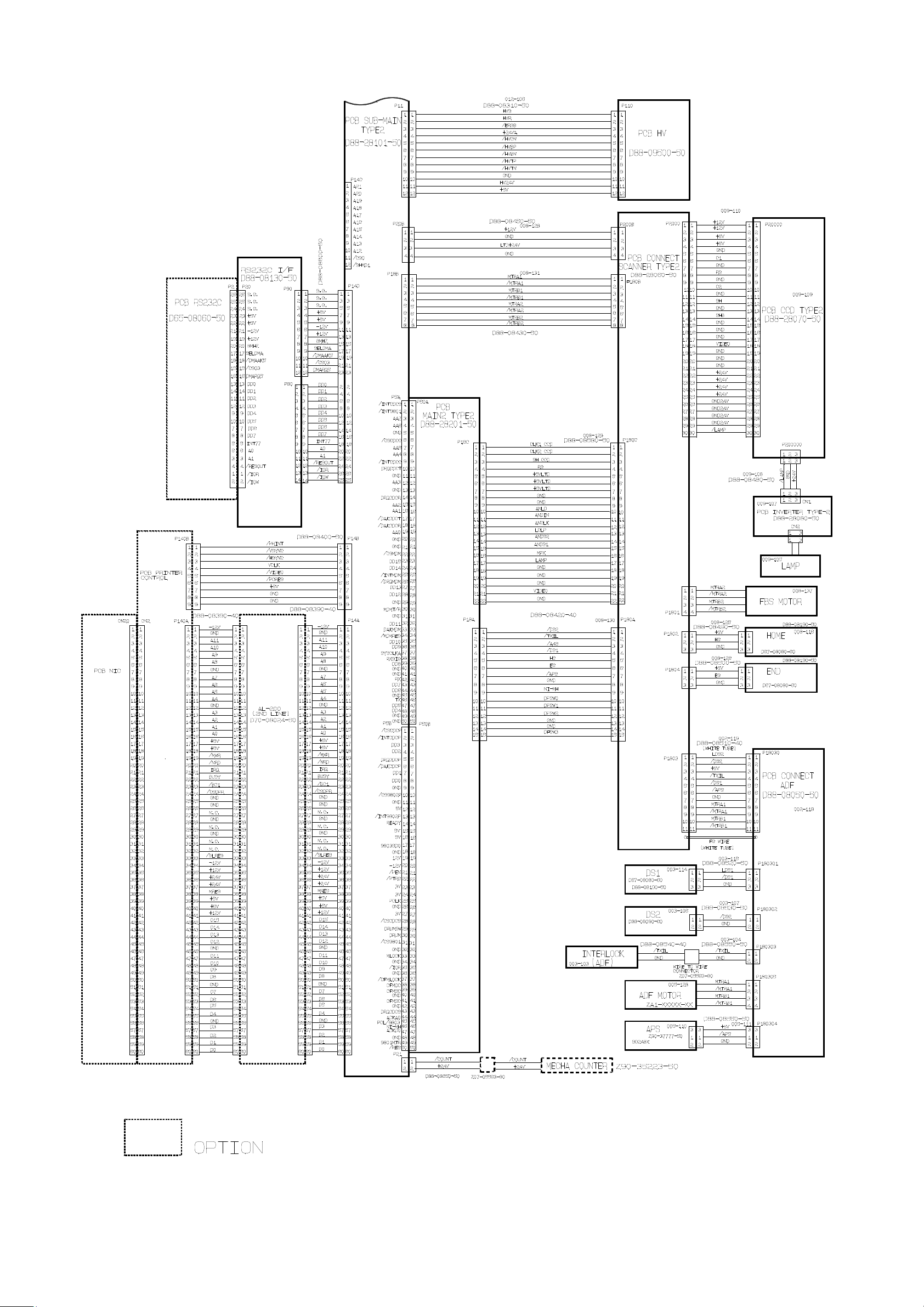
OKIOFFICE 1600 Interconnect Block Diagram (2/2)
OKIOFFICE 1600
Connection Diagram (2/2)
2-4
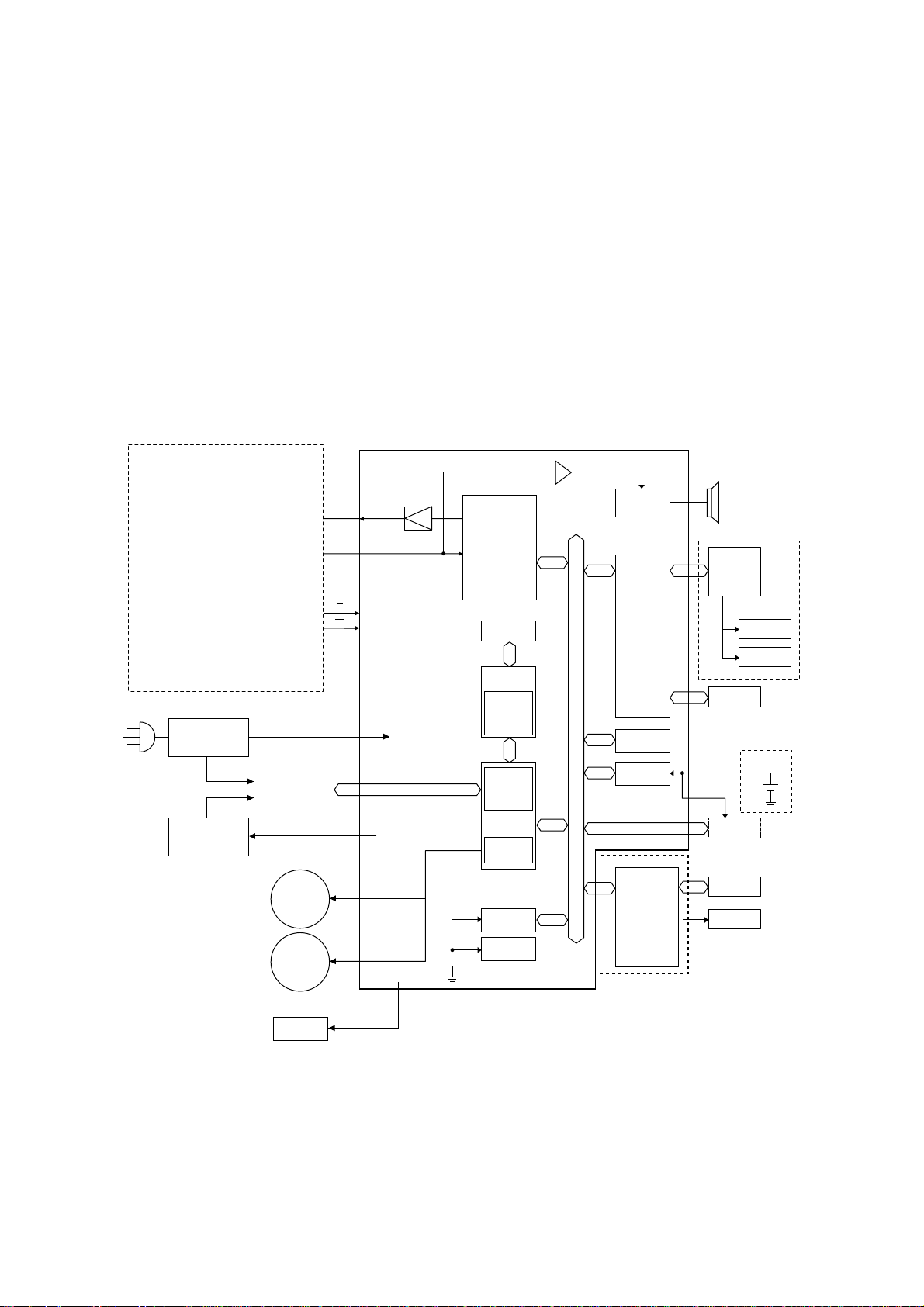
2.2 Main Control PCB
The main control PCB controls the operations of all machine functions.
Jumper JP2 on the main control PCB is used for battery back-up of the SDRAM. Removing JP2 will
initialize the SDRAM. If the power is turned off, the battery will provide up to 72 hours (8MB) of backup when fully charged.
Jumper JP1 on the main control PCB is used for battery back-up of the SRAM. All user programmed
data and internal memory switch settings are held in SRAM. Removing JP1 will initialize the SRAM.
If the power is turned off, the battery will provide up to five years of back-up when fully charged.
NOTE: JP1, JP2 should remain in the "ON" position at all times.
Memory (FLASH MEMORY, SRAM, SDRAM)
FLASH MEMORY --- T he FL A SH ME M OR Y co n t a in s al l p r og r am in s tr u c t io n s f o r u ni t operation.
SRAM --- T he S RA M, w hi c h i s b a ck e d- u p b y a l it hi u m b at t er y is us e d t o st o re us e r p r og r am me d
information.
SDRAM --- T he S DR AM i s u s ed fo r bu f fe r, w hi c h i s b a ck e d- u p b y a b at t er y i s us e d t o s t or e
memorized documents.
MAIN CONTROL PCB
NCU PCB
POWER SUPPLY
UNIT
AC 220V
HIGHT VOLTAGE
POWER SUPPLY
UNIT
TXA
RXA
TONE
OH
+24V, +12V, -12V,
+5V, GND
PRINTER
UNIT
+24V, +5V, GND
ADF MOTOR
FBS MOTOR
BUFFER
LPF
MODEM
IC
CI
SRAM
SYSTEM
G/A2
PRINTER
CONTROL
2
PRINTER
CONTROL
1
SYSTEM
G/A1
MOTOR
CONTROL
SDRAM
SDRAM
Lithium Battery
Monitor
Control
CPU
FLASH ROM
SDRAM
IMAGE
PROCESSING
IC
CONNECTOR (SCANNER) PCB
Speaker
PANEL PCB
LOGIC IC
RS232C
Battery PCB
SDRAM
Extension Memory
CCD
LED LAMP
LCD
KEY
Ni-MH
Battery
SDRAM
OKIOFFICE 1200 Main control PCB block diagram
2-5
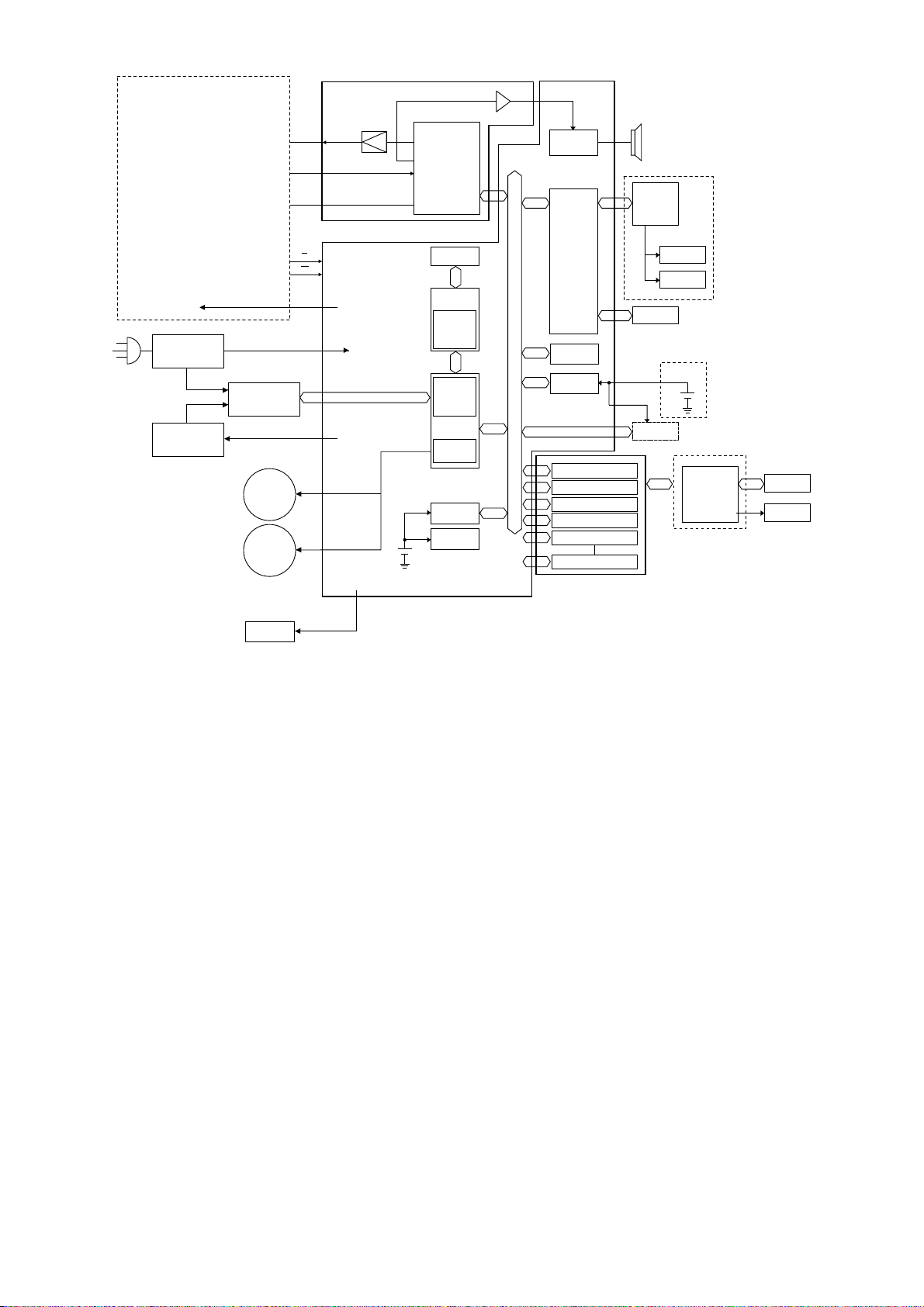
NCU PCB
POWER SUPPLY
UNIT
AC 220V
HIGHT VOLTAGE
POWER SUPPLY
UNIT
+24V, +5V, GND
+12V, -12V
+24V, +12V, -12V,
+5V, GND
PRINTER
UNIT
+24V, +5V, GND
ADF MOTOR
FBS MOTOR
PCB MAIN 2 for MFX-1600
TXA
RXA
TONE
LPF
PCB MAIN 1 for MFX-1600
CI
OH
MODEM
IC
SRAM
SYSTEM
G/A2
PRINTER
CONTROL
2
PRINTER
CONTROL
1
SYSTEM
G/A1
MOTOR
CONTROL
SDRAM
SDRAM
Lithium Battery
BUFFER
Monitor
Control
PANEL PCB
LOGIC IC
CPU
RS232C
FLASH ROM
SDRAM
SDRAM
Extension Memory
Image Processing IC
CODEC
CODEC
CODEC
Memory CTR IC
SDRAM
PCB MAIN 2 for MFX-1600
Speaker
LCD
KEY
Battery PCB
Ni-MH
Battery
AFG
CONNECTOR (SCANNER) PCB
CCD
LED LAMP
SDRAM
OKIOFFICE 1600 Main control PCB block diagram
2-6

2.3 Network Control Unit (NCU) PCB
The NCU PCB provides the connection to the telephone line. It consists of the interface circuit, dial
pulse generator, ring signal detector and telephone control circuit.
MODULAR
PCB
Major components of the NCU
CML relay
Connects the telephone line to the phone or fax.
S relay
Used to send dial pulse signals in pulse dialing.
OH & Tone detector
Detects the On-hook condition of the second telephone unit.
H relay
Connects the Tel1 and Tel2 line to the fax machine.
24V generator
Supplies 24 volts to the relays.
Ring signal detector
A photo coupler that detects an incoming ring.
NCU PCB
TXA
RXA
S
DP
GENERATOR
TONE
OH
CI
+24V, +5V, GND
+12V, -12V
NCU PCB block diagram
2-7
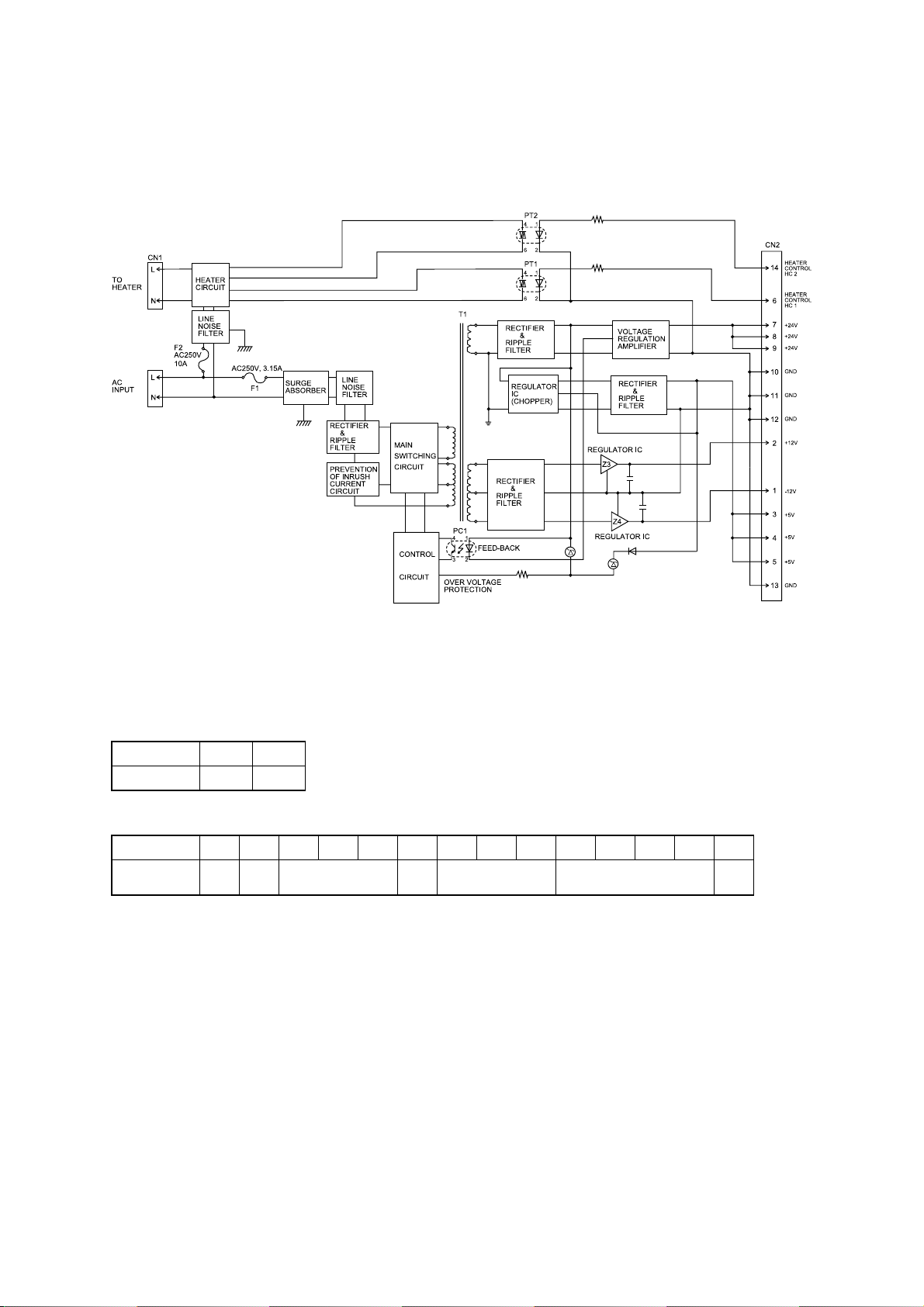
2.4 Power Supply Unit (PSU)
The power supply unit receives the input line voltage and currents it to output voltages of +5 VDC, +24
VDC, +12 VDC, and -12 VDC.
The heater circuit controls output voltage to the fuser heater according to instructions received from
the heater control circuit.
If an over-current is sensed in the secondary circuit, power is interrupted.
Power supply unit block diagram
The power supply unit has two output connectors.
The following table shows the connector outputs:
CN1 -- to the Fuser Heater
Pin No. 1 2
Output L N
CN2 -- to the Main Control PCB.
Pin No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Output
voltage
–12V +12V +5V HC1 +24V GND HC2
2-8
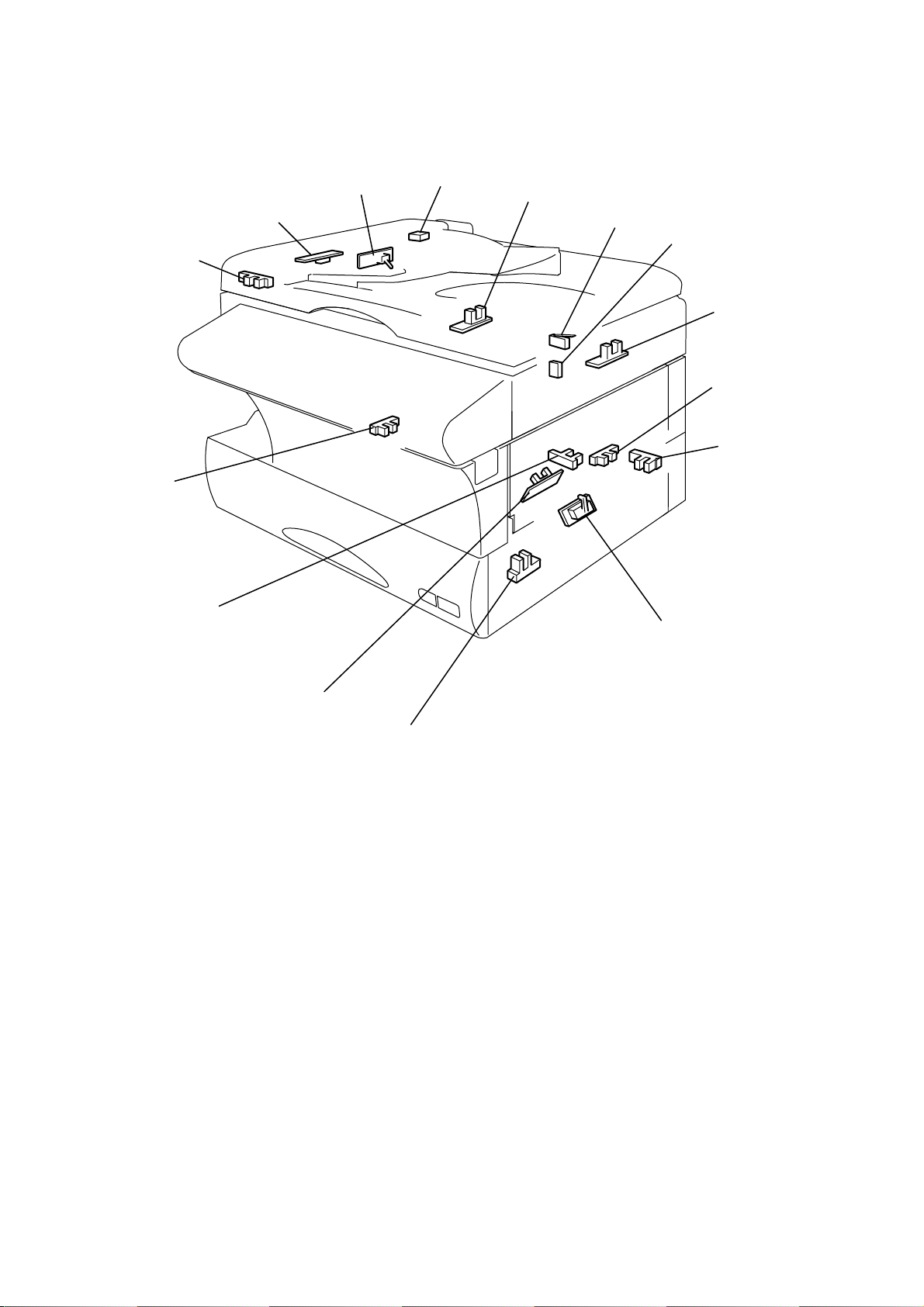
2.5 Sensors
2.5.1 Sensor Locations
The following illustration shows the relative positions of the machine’s sensors.
DS2
DS1
APS
PDS
TXIL
END
COVER SW
DRUM SW
HOME
HPES
CASOP
PES
PSS
TOS
JCOP
2-9
2.5.2 Sensor Descriptions
The following table gives a brief description of each sensor and its function.
Code Name Detects Sensor Type
DS1 Document sensor 1 P res ence of document in feeder Photo interrupter
DS2 Document sensor 2 Leading and trailing edge of doc ument Mechanical Switch
HOME Mirror carriage home
position sensor
END Mirror carriage end
position sensor
APS ADF permit sensor Platen c over quite close or not Photo interrupter
TXIL
(ADF)
PSS Paper set sensor Detects paper feeding out of
PDS Paper disc harge sensor Detects paper pass at paper ex i t . P hoto interrupter
PES Paper empty sensor Detect s presence of recording paper in
HPES Hand paper empty
TOS Toner sensor Detects the toner empty and toner
CASOP Paper cassette open
JCOP Jam access cover (side
COVERSW
DRUM
SW
Interlock switc h (A DF) Scanner cover open or close Micro switch
sensor
sensor
cover) open sensor
Cover switch Detects top cover open or c l ose Micro swit ch
Drum switch Detects drum cartridge is set or not Electrical terminal
Mirror carriage position Photo interrupter
Mirror carriage position Photo interrupter
Photo interrupter
cassette/tray.
Photo interrupter
the 1st paper cassette
Detects presence of rec ordi ng paper i n
the bypass tray
cartridge set.
Detects the 1st paper c as sette open or
close
Detects the side cover open or close Photo interrupter
Photo interrupter
Photo interrupter
Photo interrupter
2-10
2.6 Document Scanning Sequence
2.6.1 Document Detection
When a document is placed into the document feeder, Document Sensor 1 (DS1) is activated and you
will hear the short beep.
2.6.2 Document Separation
Document separation is the process that allows a multi-page document to go through the scanner one
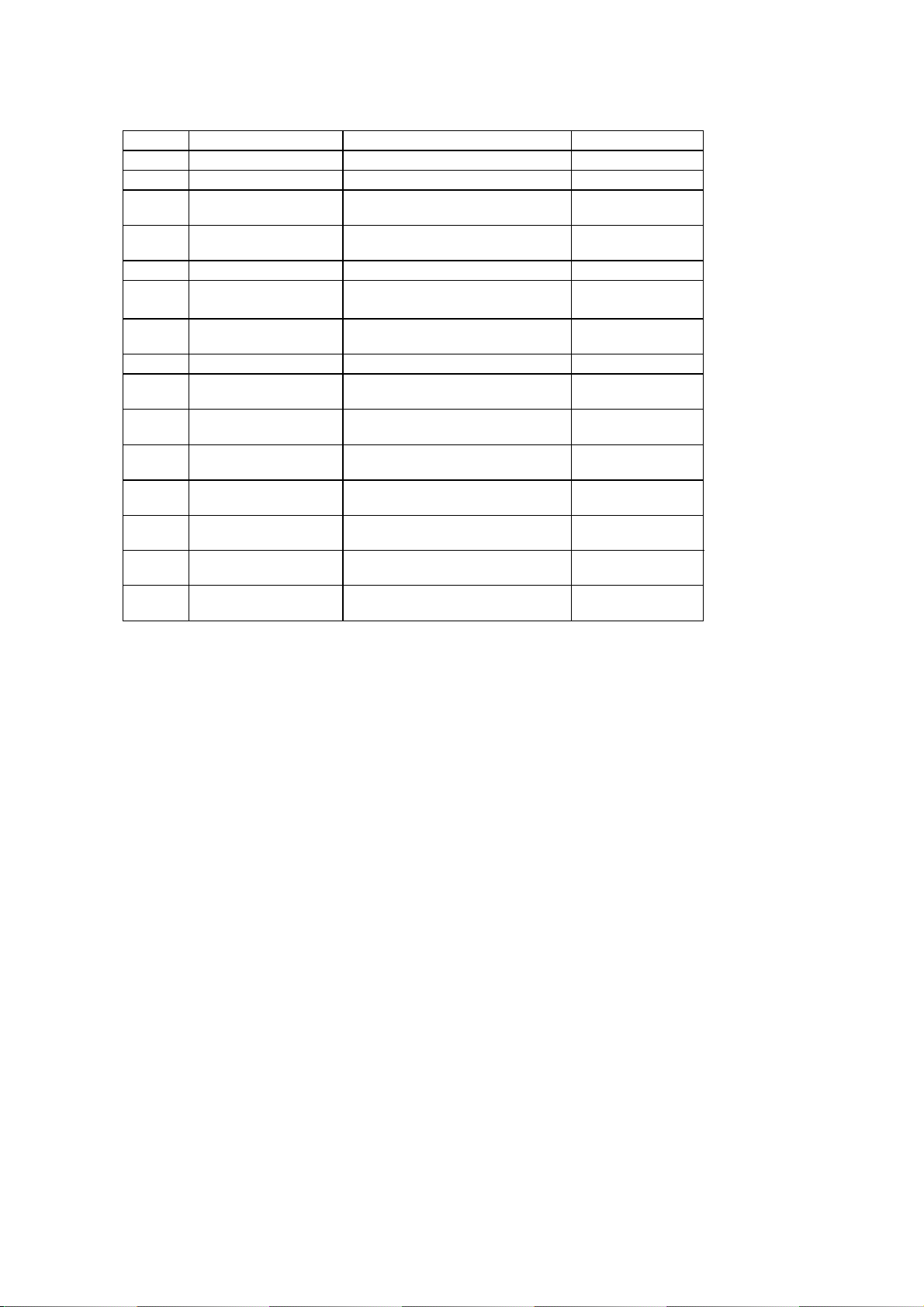
page at a time. Separation occurs through the action of the separator roller and retard roller.
As shows in the illustrations, documents in the feeder are pressed against the separator roller. The
bottom document is separated from the remaining documents by the friction of the retard roller.
2.6.3 Document Transport
Following document separation, the feed roller causes the document to advance. As it advances, the
leading edge of the document activates the Document Sensor 2 (DS2) sensor. Once DS2 is activated,
the feed roller continues to rotate until the document reaches the scan wait position. The machine
uses the distance from DS2 to the scan wait position and the diameter of the feed roller to determine
the number of rotations necessary to feed the document to the scan wait position.
2.6.4 Document Scanning
When the document reaches the scan wait position, the machine waits for the next command. It will
start scanning the document when either the START key is pressed. The light from the scanner lamp
strikes the face of the document and is reflected into the lens through mirrors A, B, and C. In case the
light intensity along the length of the scanner lamp is not uniform, shading compensation is provided to
ensure even illumination.
As the reflected image passes through the lens, it is focused onto the charged coupled device(CCD).
The CCD then converts the dark and light areas of the image into electrical impulses, or image data.
Circuits on the main control PCB encode the image data and send it to the modem where it is
modulated. The modulated signal is then placed onto the telephone line by the NCU.
2-11
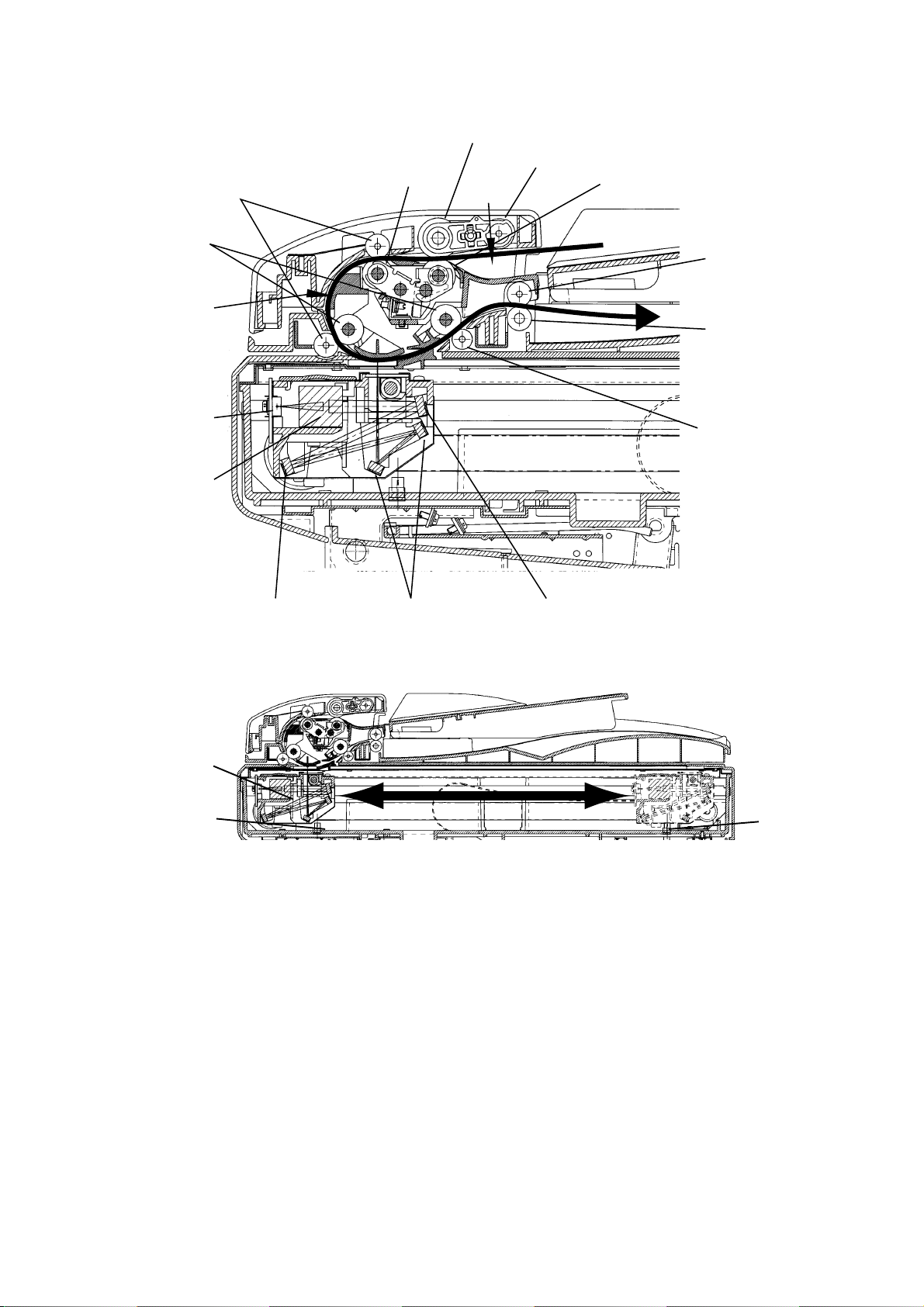
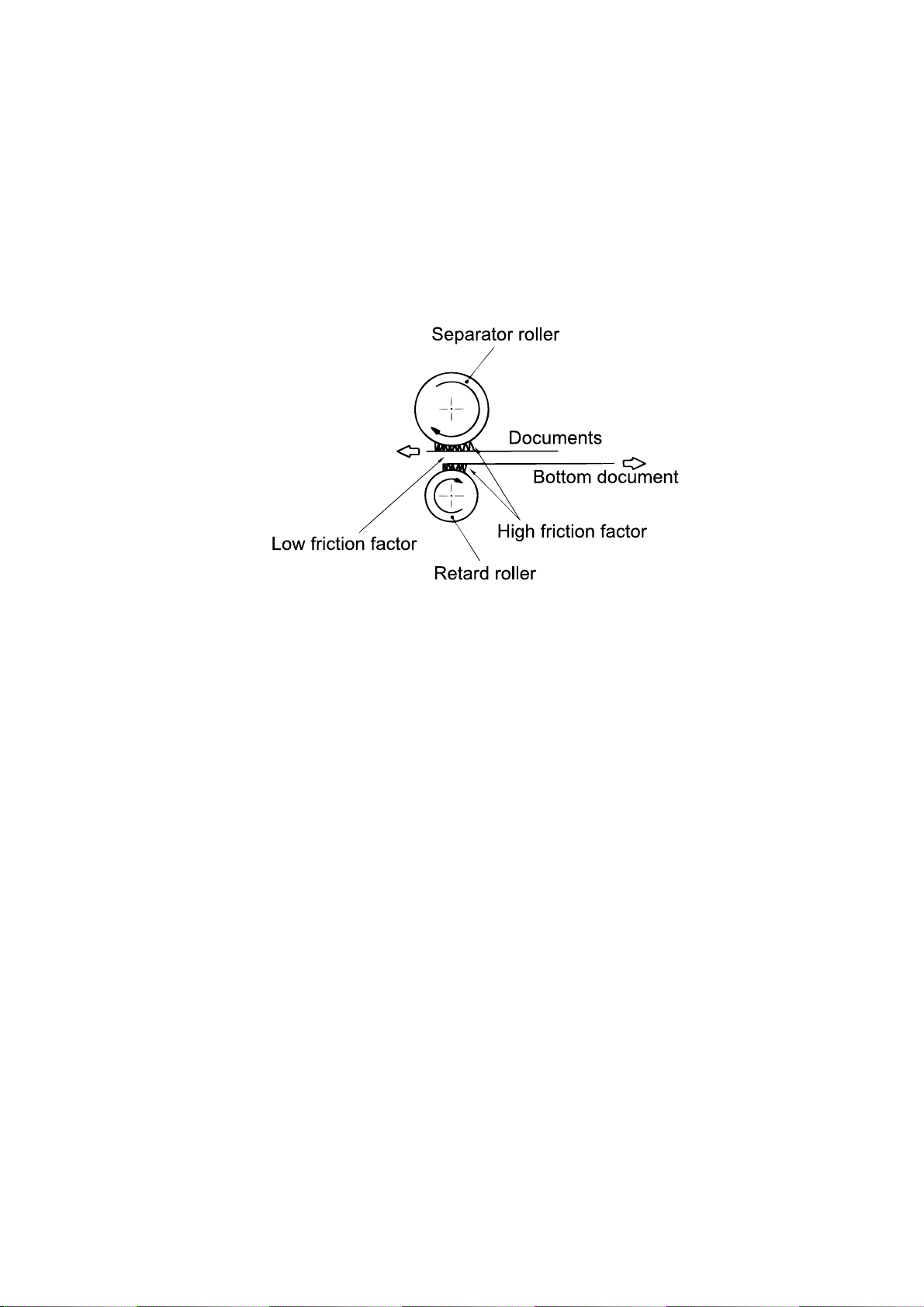
When DS2 detects the trailing edge of the document, the image signal output is turned off. The
scanner continues to remain active for a few more seconds in case there is another document to
follow.
Separator roller
Pick up roller
Press roller A
Feed roller B
DS2
Feed roller A
DS1
Retard roller
Press roller A
Exit roller
CCD
Lens
Scanner unit
End sensor
Mirror AMirror B Mirror C
Document scanning in ADF section
Document scanning in FBS section
Press roller B
Home sensor
2.6.5 Document Discharge
The scanned document is discharged through the document exit by the exit roller
2-12
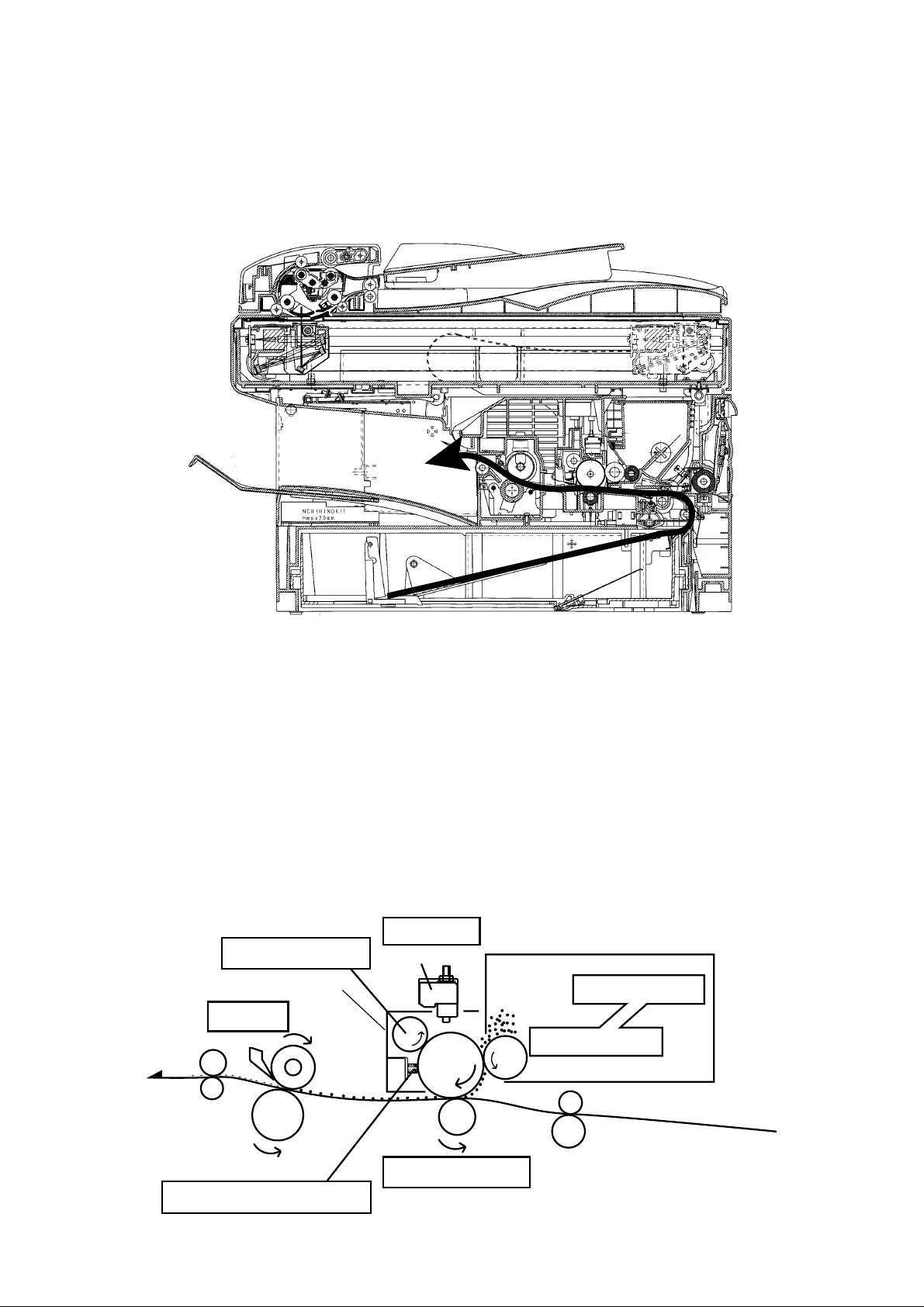
2.7 Recording Section
2.7.1 Recording Paper Feed Path
A sheet of the recording paper is separated from the remaining paper by the friction of the pickup
roller.
The paper is moved along the paper guide until it reaches the platen roller. Is then fed by the rotation
of the platen roller.
2.8 Image Processing
Incoming data is received from the telephone line by the NCU and sent to the main control PCB. The
modem, located on the main control PCB, demodulates the data.
The data is then sent to the printer for image processing.
The image processing is roughly divide into the following steps:
1. Drum Charging
2. Drum Exposure
3. Development
4. Image transfer
5. Fusing
6. Distributing the toner
Drum charging
Drum cartridge
Fusing
Exposure
LED print head
Development
Toner cartridge
Toner agitate
Image transfer
Distributing the toner
2-13
2.8.1 Drum Charge
• The Drum is charged with static electricity before LED exposure. The Rotating Charge Brush is
used for the charging method.
• The rotating brush charging generate little ozone in the printer. Because the charge is directly given
to the Drum, the Drum can be charged by low voltage. At the same time, the Drum can be charged
stably and evenly.
2.8.2 Drum Exposure
An invisible static image is made by the light from the LED print head.
The LED print head, located inside the printer cover, closes down over the drum and projects light
onto the drum surface. When the document is to be printed, individual elements in the LED print head
turn on and expose the drum where ever a dark area should appear in the document.
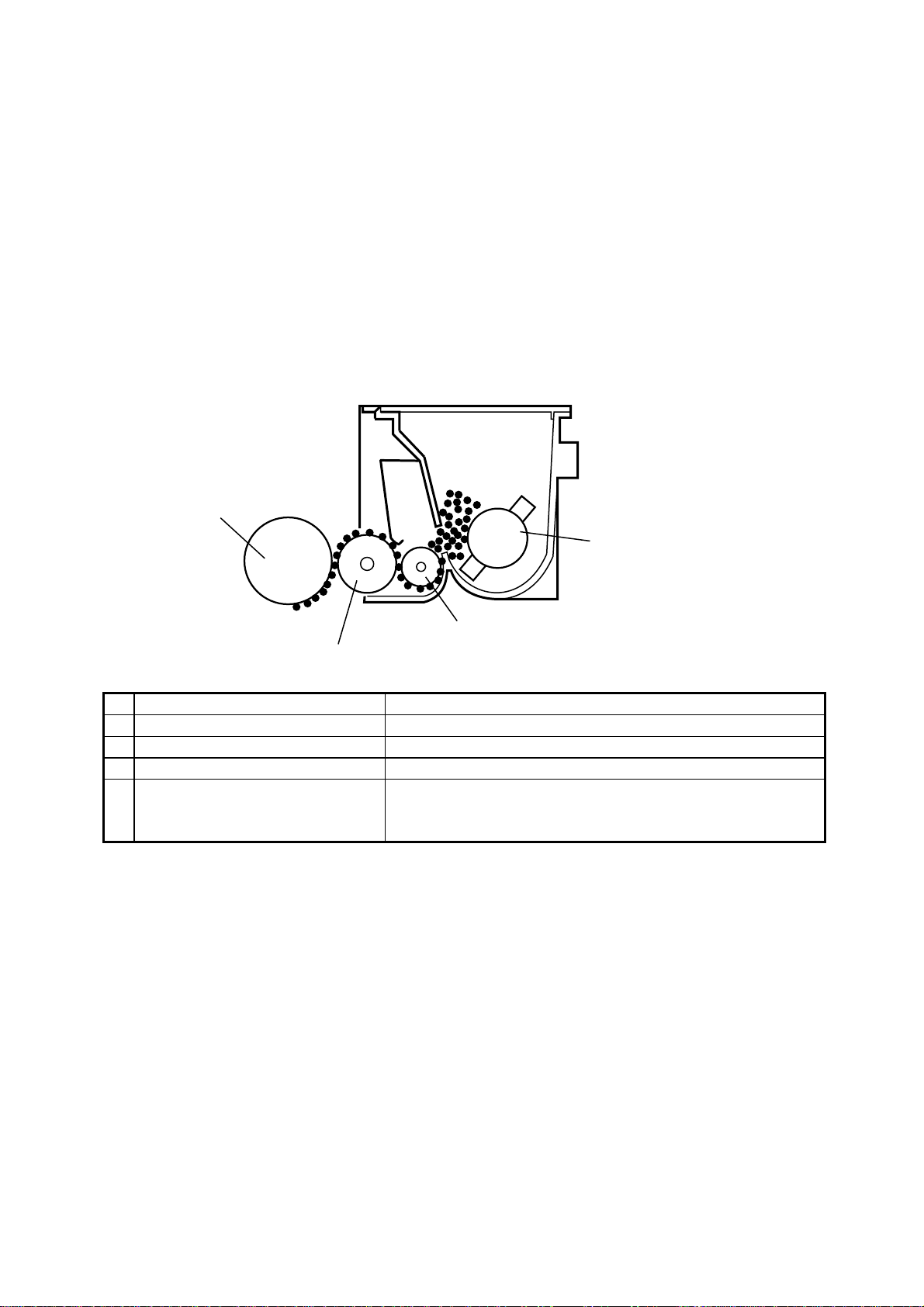
2.8.3 Development
Toner is applied to the invisible static image on the Drum and a toner image is created on the surface.
Drum
Toner agitator
Toner supply roller
Developing roller
Part Name Function
1 Toner Agit at or Contains toner.
2 Toner supply Roller Transports the toner to t he developing r oller.
3 Developing Roller Carries the toner to the Drum surf ace for development.
4 Dr um Exposed to LED right to create an invisible image and
rotates to carry the developed image to t he paper
surface.
2-14
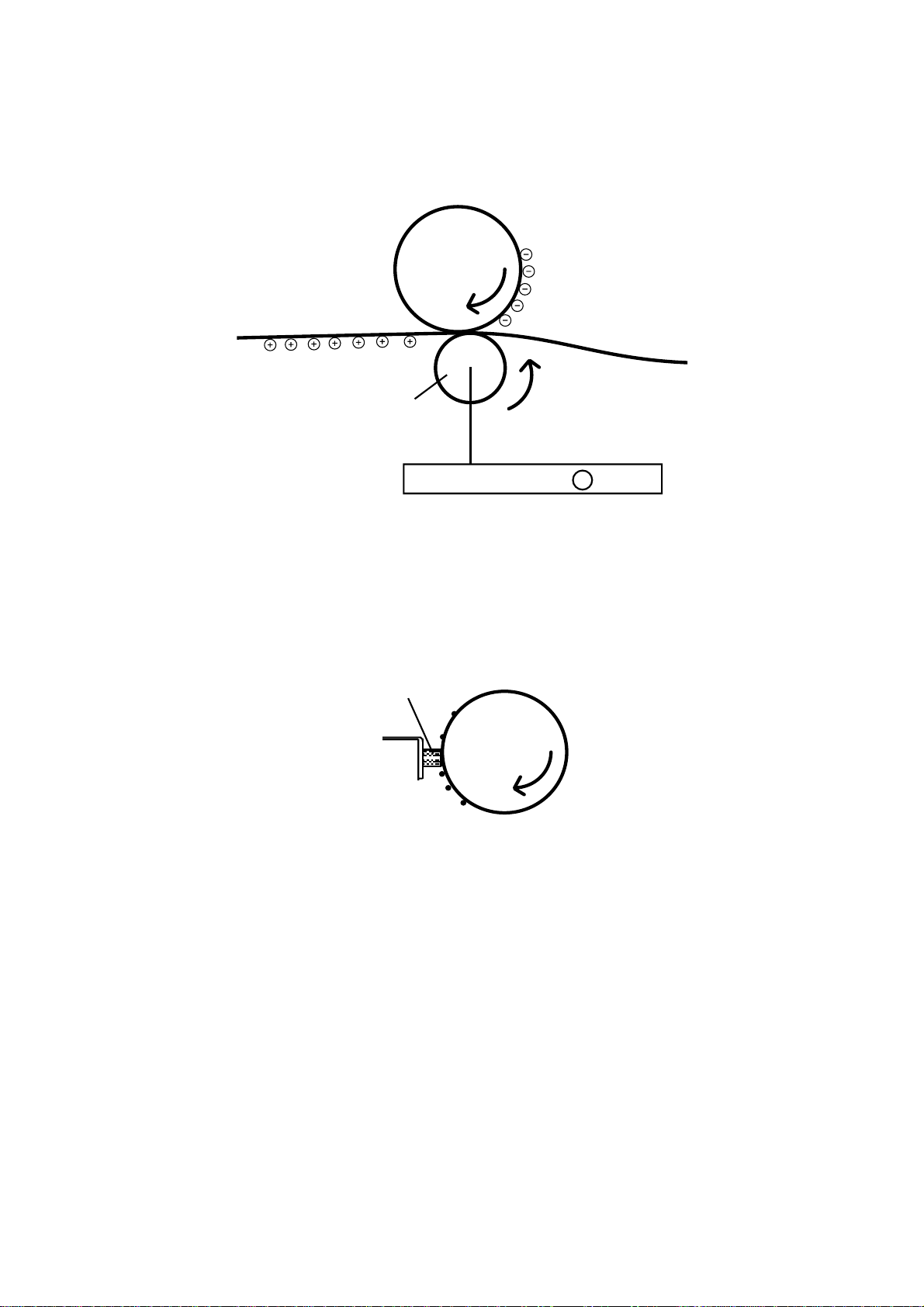
2.8.4 Image Transfer
Image transfer is the process of transferring the toner image created on the Drum in the developing
process to paper. We use the Roller Image Transfer instead of the Corona Image Transfer, as the
image transfer method. In the Roller Image Transfer, there is little generation of ozone due to corona
discharge. Also, there is no blur of toner because the paper is always pressed by the Drum and the
Image Transfer Roller.
PC Drum
Image transfer roller
Hight voltage unit + output
2.8.5 Residual toner distribute
The residual toner must be removed from the drum. This step does not actually remove the residual
toner from the drum surface. Instead, a “Eraser brush” is used to evenly distribute the remaining toner
over the drum surface. When the drum surface is charged in preparation for printing the next
document the remaining toner is also charged. Any residual toner that is not exposed in the
subsequent drum exposure process is attached back onto the developing roller.
Eraser brush
PC drum
2-15
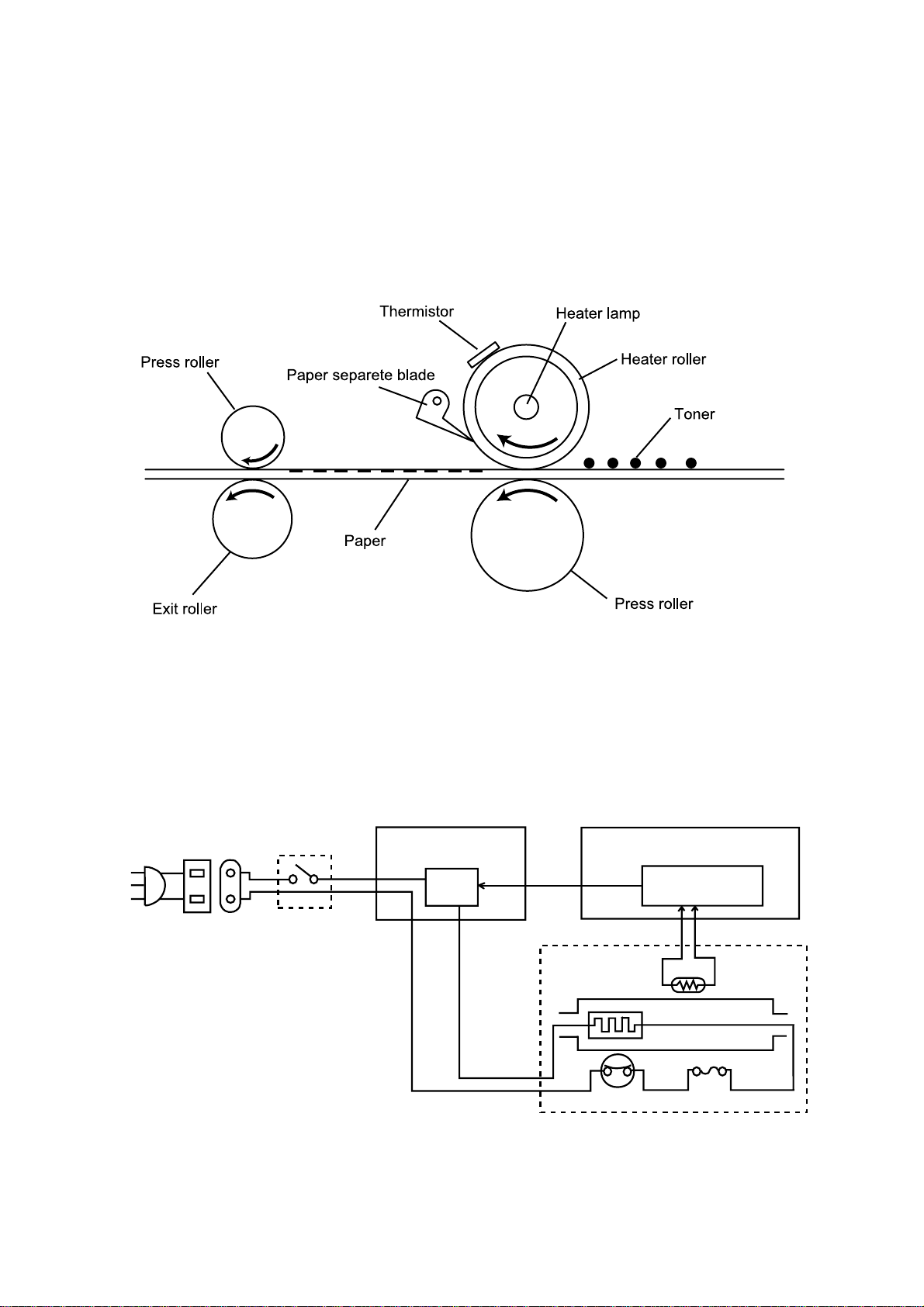
2.8.6 Fusing
An Overview
The toner image transferred on to the paper is securely fixed.
A heat roller system is used as the fusing system. The toner image is fused by Heater Roller heated
by the Heater Lamp, and securely fixed by the pressure between the Heater roller and Press rollers.
A Thermistor detects and controls the Heater Roller temperature.
The Thermostat functions when the Heater Lamp is not turned OFF even if the Thermistor detects a
high temperature malfunction.
Fusing Temperature Control Circuit
The Thermistor detects the surface temperature of the Heater Roller and inputs that analog voltage
into the Main Control PCB. Corresponding to this data, the Heater Lamp ON/OFF signal is output to
the Heater ON/OFF switch of the power supply unit, causing the Heater Lamp to turn ON or OFF to
control the fusing temperature.
When the Heater Lamp is not turned OFF even if the Thermistor detects a high temperature
malfunction, the thermostat shuts down the power to the heater lamp. When the thermostat is
malfunction, the thermal cut-off shuts down the power to the heater lamp.
AC Inlet
L
N
Main switch
Power supply unit
Heater
on/off
switch
Main Control PCB
Fusing unit
Fusing temperture
control circuit
Thermistor
Heater Lamp
Thermostat Thermal cut-off
2-16
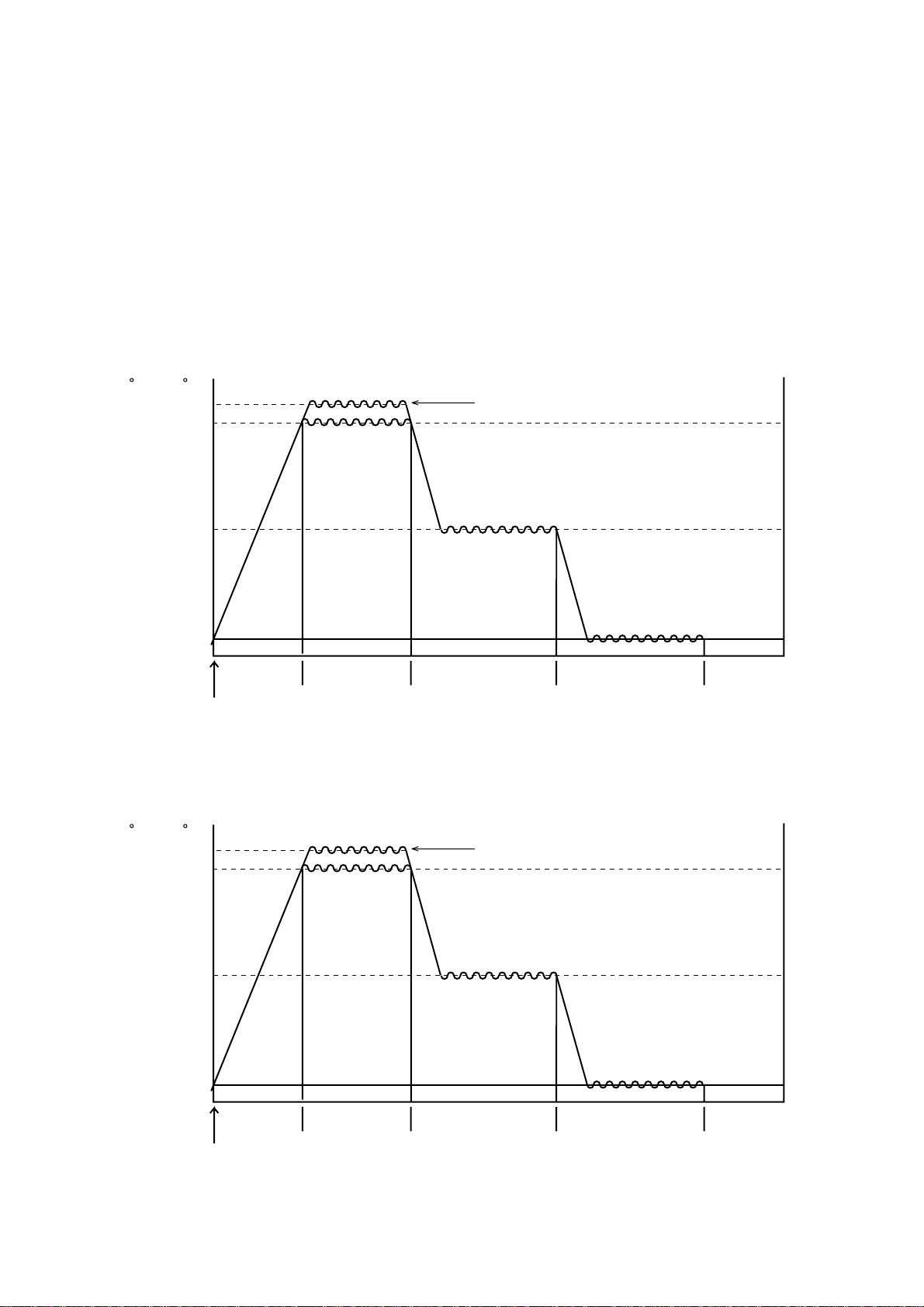
Fusing temperature
1) Warming Up After the initialization of the printer, warming up of the printer starts and the
Heater Lamp turns ON until the temperature of the Heater Roller reaches
approx. 185 °C.
2) Printing When the printer obtains the printing command from its controller, the Heater
Roller is maintained at 185 °C.
After printing, the printer turns to standby mode. The fuser kept at low
temperature.
3) Standby mode The Heater Roller maintained at approx. 100 °C.
4) Sleep mode In this mode, saving the power.
OKIOFFICE 1200:
Temperature
( F) ( C)
392
356
200
180
Post card printing only
320
160
Warming up
Power ON
OKIOFFICE 1600:
Temperature
( F) ( C)
401
374
338
205
190
170
Printing
Standby mode
Post card printing only
Sleep mode
Time
Warming up
Power ON
Printing
Standby mode
Sleep mode
Time
2-17

Section3
Adjustment Procedures
3.1 Field Service Program Modes
The fax machine feature maintenance modes for machine adjustment. Each mode is listed below
along with the command used to activate the mode and a brief functional description.
Note: When you press “ * ”, you will hear short beeps. However continue the operation, as it is no
problem.
Set or Clear Machine Parameters.............................................................................. Program key, *, 0
Used to set or clear machine parameters.
Set or Clear Memory Switches.................................................................................. Program key, *, 1
Used to set or clear memory switches.
Clear Programmed Data / User Se ttings.................................................................. Program key, *, 2
Erases user-programmed information (date, time, TTI, autodialer, etc.) and any documents
stored in memory.
All RAM Clear.............................................................................................................. Program key, *, 3
Erases same information as “Clear Programmed Data / User Settings” function along with
resetting all of the machine parameters, memory switches and unique switches to factory
defaults.
Set or Clear Unique Switches.................................................................................... Program key, *, 4
Used to set or clear Unique switches.
Printer maintenance mode........................................................................................ Program key, *, 6
Access the printer maintenance mode.
Print Program Mode List............................................................................................ Program key, *, 8
Prints a list of the unit’s programming modes.
Test Modes.................................................................................................................. Program key, *, 9
Allows the technician to perform a series of diagnostic tests.
Print Machine Parameters, Memory Switches and
Unique Switches List ......................................................................................... Program key, *, A (01)
Prints a list of the machine switch settings showing the default settings and current
settings.
Factory Functions .............................................................................................. Program key, *, B (02)
Allows the technician to perform a series of diagnostic tests.
Telephone Circuit Test Modes .......................................................................... Program key, *, C (03)
Allows the technician to perform a series of diagnostic tests.
Mirror Carriage Transfer Mode...........................................................................Program key, *, E (05)
Perform it before installing the fax machine.
Set or clear the consumable order sheet..........................................................Program key, *, F (06)
Used to set or clear the consumable order sheet.
DRAM Clear......................................................................................................... Program key, *, G (07)
Used to clear a DRAM.
Clear Life Monitor............................................................................................... Program key, *, H (08)
Used to clear a Life monitor keeps a count of the pages scanned, etc.
Clear option module’s SRAM..............................................................................Program key, *, I (09)
Used to clear a SRAM of option module.
Set Service Code .................................................................................................Program key, *, J (10)
Used to protect to clear a Life monitor.
Life Monitor Maintenance ...................................................................................Program key, *, K (11)
Used to protect to clear a Life monitor.
3-1
3.2 Machine Parameter Adjustment
3.2.1 Setting the Machine Parameters
These switches are used to program internal machine parameters. The primary back up battery maintains
these settings if power is lost.
1. From standby, press Program key, *, 0.
Set Parameters
/ /Enter
2. Press ENTER.
A0: 00000000
/ /Enter
3. Select the desired parameter by pressing a one-touch key plus a number on the keypad. For example,
to access parameter B:1, press one-touch “B” plus the number “1” on the numeric keypad.
B1: 00101011
/ /Enter
4. Press ENTER.
Set Parameters
B1 0
Bit No. 76543210
(The bits are numbered 7 through 0 --- b it 7 i s l ef t m os t. )
5. To navigate through the machine parameter settings:
• Press
• Press
• Press the 0 or 1 on the numeric keypad to change the bit value.
• Press ENTER to save the setting of the displayed parameter and advance to the next
parameter.
(Continue pressing ENTER until the desired parameter is shown in the display. Be sure to press
ENTER after each parameter is programmed to save the new setting.)
• Press STOP to return the unit to standby.
Note: You can confirm the initial setting of each Machine parameter by the Machine Parameters List.
The Machine Parameters List will be printed by pressing Program key, *, A(01).
key to move the cursor to the left.
to move the cursor to the right.
0101011
3.2.2 Clearing the Machine Parameters
Resets the machine parameters to factory defaults.
1. From standby, press Program key, *, 0,
.
Clear Parameters
/ /Enter
2. Press ENTER.
Clear Parameters
Check Enter/Cancel
3. Press ENTER. The machine parameters will reset to factory defaults.
Note: To finish the operation without clearing the parameters, press CANCEL.
3-2
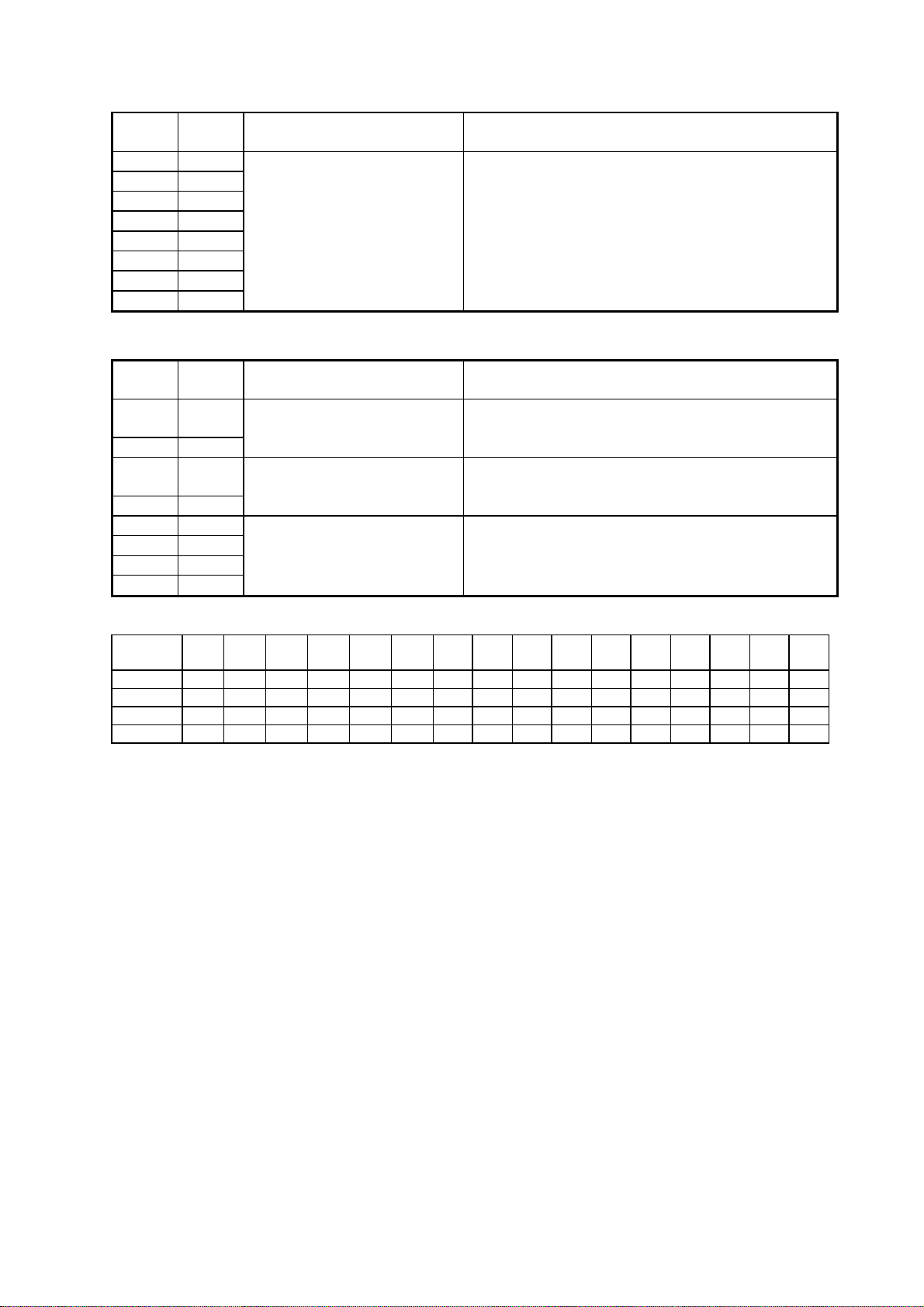
Machine Parameter A:0
Switch
7 0
6 0
5 0
4 0
3 0
2 0
1 0
0 0
Initial
Setting
Adjust Usage/Comments
Country code The country code enables the ROM to output the
correct programming information for the respective
country.
Machine Parameter A:1
Switch
7 0 Non-loaded cable
6 1 0: 1: 0: 1:
5 0 Non-loaded cable
4 1 0: 1: 0: 1:
3 *
2 *
1 *
0 *
Machine Parameter A:1…Output attenuation
Switch -15
3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0
0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
Initial
Setting
dB
Adjust Usage/Comments
0: 0: 1: 1:
compensation (TX)
0 db 4 db 8 db 12 db
0: 0: 1: 1:
compensation (RX)
0 db 4 db 8 db 12 db
Output attenuation See table below
Note: The setting of this switch is available only
when setting other than 0 dB and this setting is
used instead of Memory Switch B:1, bit 3-0.
-14
-13
-12
-11
-10
-9
-8
-7
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
-6
dB
-5
dB
-4
dB
-3
dB
-2
dB
-1
dB
-0
dB
3-3
 Loading...
Loading...