Page 1

B6200/B6300 SERIES
network print environment user's guide
Page 2

NetWare is a registered trademark of Novell, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
All product/brand names are trademarks or registered trademarks of the respective holders.
Important
This manual is copyrighted with all rights reserved. Under the copyright laws, this manual may not be copied
or modified in whole or part, without the written consent of the publisher.
Parts of this manual are subject to change without prior notice.
We welcome any comments on ambiguities, errors, omissions, or missing pages.
Page 3

E
n
g
l
i
s
hEn
g
l
i
s
hEn
g
l
i
s
hEn
g
l
i
s
h
Preface
Thank you for choosing this printer.
This User Guide provides all the necessary information about installing and operating this
printer on the network.
Please read this guide in detail to ensure full and efficient use of this product on a network
and keep it handy for a quick reference should you encounter any difficulties when using
the machine.
Preface 3
Page 4

Contents
1 Overview .................................................................................................... 9
1.1 Supported Environment ........................................................................................... 9
2 Printing Through LPD or Port9100 ........................................................... 10
2.1 Installation Procedure for Printing Through LPD or Port9100 ............................... 10
2.2 Setting Up the Computer ....................................................................................... 11
3 Internet Printing........................................................................................ 13
3.1 Installation Procedure for Internet Printing ............................................................ 13
3.2 Installing the Printer Driver .................................................................................... 14
System Configuration ............................................................................................10
Target Computers ..................................................................................................10
Set Up Procedure ..................................................................................................11
Creating a Shared Printer ......................................................................................11
System Configuration ............................................................................................13
Target Computers ..................................................................................................13
Set Up Procedure ..................................................................................................13
Installation Procedure (Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003) .......14
Installation Procedure (Windows Me) ....................................................................15
4 Printing Through SMB .............................................................................. 16
4.1 Installation Procedure for Printing through SMB ................................................... 16
System Configuration ............................................................................................16
Target Computers ..................................................................................................16
Set Up Procedure ..................................................................................................17
4.2 Setting/Changing SMB Using the [Config.txt] File ................................................. 17
4.3 Auto Driver Downloading....................................................................................... 20
Preparation for Auto Driver Downloading ..............................................................20
Auto Downloading of Printer Driver .......................................................................22
5 Printing Through NetWare........................................................................ 23
5.1 Installation Procedure for Printing Through NetWare............................................ 23
System Configuration ............................................................................................23
Target Computers ..................................................................................................23
IPX/SPX Frame Types ..........................................................................................24
Set Up Procedure ..................................................................................................24
6 Printing From UNIX .................................................................................. 25
6.1 For Printing From UNIX ......................................................................................... 25
System Configuration ............................................................................................25
Target Computers ..................................................................................................25
Interface .................................................................................................................25
Set Up Procedure ..................................................................................................26
6.2 Setting Up the Workstation.................................................................................... 26
Before Setup ..........................................................................................................26
Print Language/Mode ............................................................................................26
Examples of Settings for SunOS 4.1.4 ..................................................................27
Examples of Settings for Solaris 2.X .....................................................................28
Examples of Settings for HP-UX 11.0 ...................................................................29
6.3 Printing (SunOS) ................................................................................................... 29
Print (lpr) ................................................................................................................29
Delete (lprm) ..........................................................................................................31
Inquiry (lpq) ............................................................................................................32
4 Contents
Page 5

6.4 Printing (HP-UX/Solaris)........................................................................................ 33
Print (lp) .................................................................................................................33
Delete (Cancel) ......................................................................................................34
Inquiry (lpstat) ........................................................................................................35
6.5 -C Option (lpr Command) ...................................................................................... 36
Function .................................................................................................................36
Printing ..................................................................................................................39
7 Printing From a Macintosh Computer....................................................... 40
7.1 Printing From a Macintosh Computer.................................................................... 40
System Configuration ............................................................................................40
Target Computers ..................................................................................................40
Set Up Procedure ..................................................................................................40
8 Network Utility Software ........................................................................... 41
8.1 IP Address Setting Tool......................................................................................... 41
8.2 NetWare Setup Wizard.......................................................................................... 41
8.3 Simple Status Notification...................................................................................... 41
Operating Requirements .......................................................................................42
Using SSN .............................................................................................................42
SSN Features ........................................................................................................44
9 Precautions and Limitations ..................................................................... 46
9.1 On Using TCP/IP................................................................................................... 46
Setting Up ..............................................................................................................46
Switching the Power On/Off ..................................................................................47
Printing From Windows .........................................................................................47
Printing From UNIX ...............................................................................................47
9.2 On Using SMB....................................................................................................... 49
Setting Up ..............................................................................................................49
Switching the Power On/Off ..................................................................................49
Printing ..................................................................................................................50
9.3 On Using NetWare ................................................................................................ 51
Setting Up the Printer ............................................................................................51
Setting Up the Server ............................................................................................52
Printing ..................................................................................................................52
About Printing Control ...........................................................................................53
10 Troubleshooting........................................................................................ 54
10.1 Using TCP/IP......................................................................................................... 54
When Using Windows 95/Windows 98/Windows Me ............................................54
When Using Windows NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003 .
55
When Using UNIX .................................................................................................56
10.2 Using SMB............................................................................................................. 57
The Printer Is Not Found .......................................................................................57
The Printer Is Not Printing .....................................................................................57
Cannot Delete Documents From the Printer Window ............................................58
Cannot Perform Auto Driver Downloading ............................................................58
10.3 Using NetWare ...................................................................................................... 59
The Printer Is Not Printing .....................................................................................59
When “Please reboot printer” Appears ..................................................................61
Unable to Obtain Desired Print Results .................................................................61
No Notification .......................................................................................................61
10.4 Using EtherTalk..................................................................................................... 61
Contents 5
Page 6

A Appendix .................................................................................................. 64
A.1 Using Telnet .......................................................................................................... 64
Settings for Using the Telnet .................................................................................64
Using the Telnet ....................................................................................................64
The Items That Can Be Set Using the Telnet ........................................................66
A.2 Setting IP Address................................................................................................. 67
Index ............................................................................................................... 69
6 Contents
Page 7
E
n
g
l
i
s
hEn
g
l
i
s
hEn
g
l
i
s
hEn
g
l
i
s
h
Using This Guide
Prerequisite Knowledge
Read this guide in detail before using this printer. If you are not familiar with the printer to
which the printer is to be connected or the basic operations or concepts of the software,
read the relevant manuals first.
Machines and software to which the printer is to be connected refer to personal computers,
workstations, networks, and the respective operating systems and applications on which
these machines run.
Organization
The following is a summary of each chapter.
1. Overview
This chapter contains information on using the printer as a network printer.
2. Printing Through LPD or Port9100
This chapter explains the installation procedure for printing from a Windows NT 4.0/
Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003 computer through LPD or Port9100.
This chapter also explains the installation procedure for printing from another Windows
computer by creating a shared printer on a Windows NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP/
Windows Server 2003 computer.
3. Internet Printing
This chapter explains the installation procedure for printing using the Internet Printing
Protocol (IPP).
4. Printing Through SMB
This chapter explains the installation procedure for connecting a printer to the Windows
network through SMB.
5. Printing Through NetWare
This chapter explains the installation procedure for connecting a printer to the NetWare
network.
6. Printing From UNIX
This chapter explains the procedure for printing from a UNIX computer.
7. Printing From a Macintosh Computer
This chapter explains the procedure for printing from a Macintosh computer.
8. Network Utility Software
This chapter explains instructions on how to use the Network Utility Software.
9. Precautions and Limitations
This chapter explains the operational precautions and limitations under each network
environment.
10. Troubleshooting
This chapter explains instructions on how to solve a problem under each network
environment.
Appendix
This chapter explains instructions on how to use Telnet and how to manually set the
printer’s IP address.
Using This Guide 7
Page 8

Conventions
1. In this guide, “computer” refers to both the personal computer and workstation.
2. The following icons are used in this guide:
3. The following conventions are used in this guide:
Important Indicates important information which you should read.
Note Indicates additional information on operations or features.
Refer to Indicates reference sources.
Refer to “xxx” : The cross-reference is within this guide.
Refer to YYY : The cross-reference is not within this guide.
[ ] : Indicates items displayed on the computer and the printer control
panel. Also indicates the title of printed reports/lists from the printer.
< > : Indicates items such as hard buttons and indicators on the keyboard
and printer.
8 Using This Guide
Page 9
E
n
g
l
i
s
hEn
g
l
i
s
hEn
g
l
i
s
hEn
g
l
i
s
h
1 Overview
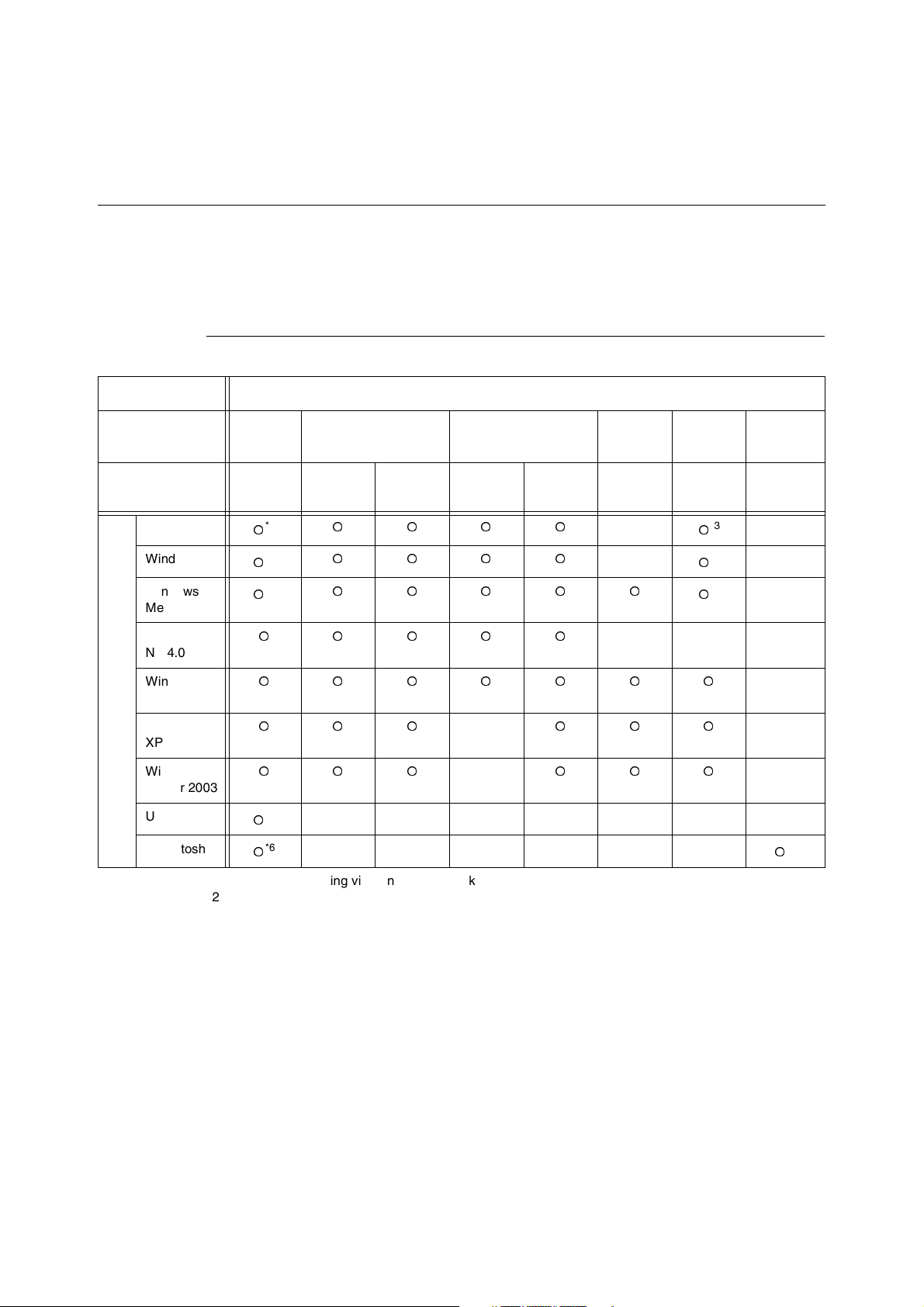
1.1 Supported Environment
This printer can be connected to a network through the Ethernet interface.
The printer supports multiple protocols. As a result, one printer can be shared even from
different network environments.
Supported OS and Environment
Connection Network
Port LPD NetWare
Protocol TCP/IP TCP/IP IPX/SPX
*3
*3
*3
*4
*6
OS
Windows 95
Windows 98
Windows
Me
Windows
NT 4.0
Windows
2000
Windows
XP
Windows
Server 2003
UNIX
Macintosh
Net
BEUI
*1
SMB
TCP/IP TCP/IP TCP/IP
IPP
*2
Port
9100
*3
*3
*3
EtherTalk
Apple
Talk
*5
*1: Used when printing via Windows network.
*2: Used when printing via Internet. For Windows Me, install the IPP port.
*3: When using Windows 95/98/Me, use OKI LPR.
*4: UNIX Filter are required to print PostScript data. UNIX Filter is compatible with the OSs in Solaris, HP-
UX and Linux (Redhat, SuSE).
*5: Supports Mac OS 8.6 or later.
*6: Supports only Mac OS X.
Important
• The NetWare, IPP, and EtherTalk port settings in this printer are disabled by default. To use these ports,
enable the settings on the control panel.
1.1 Supported Environment 9
Page 10
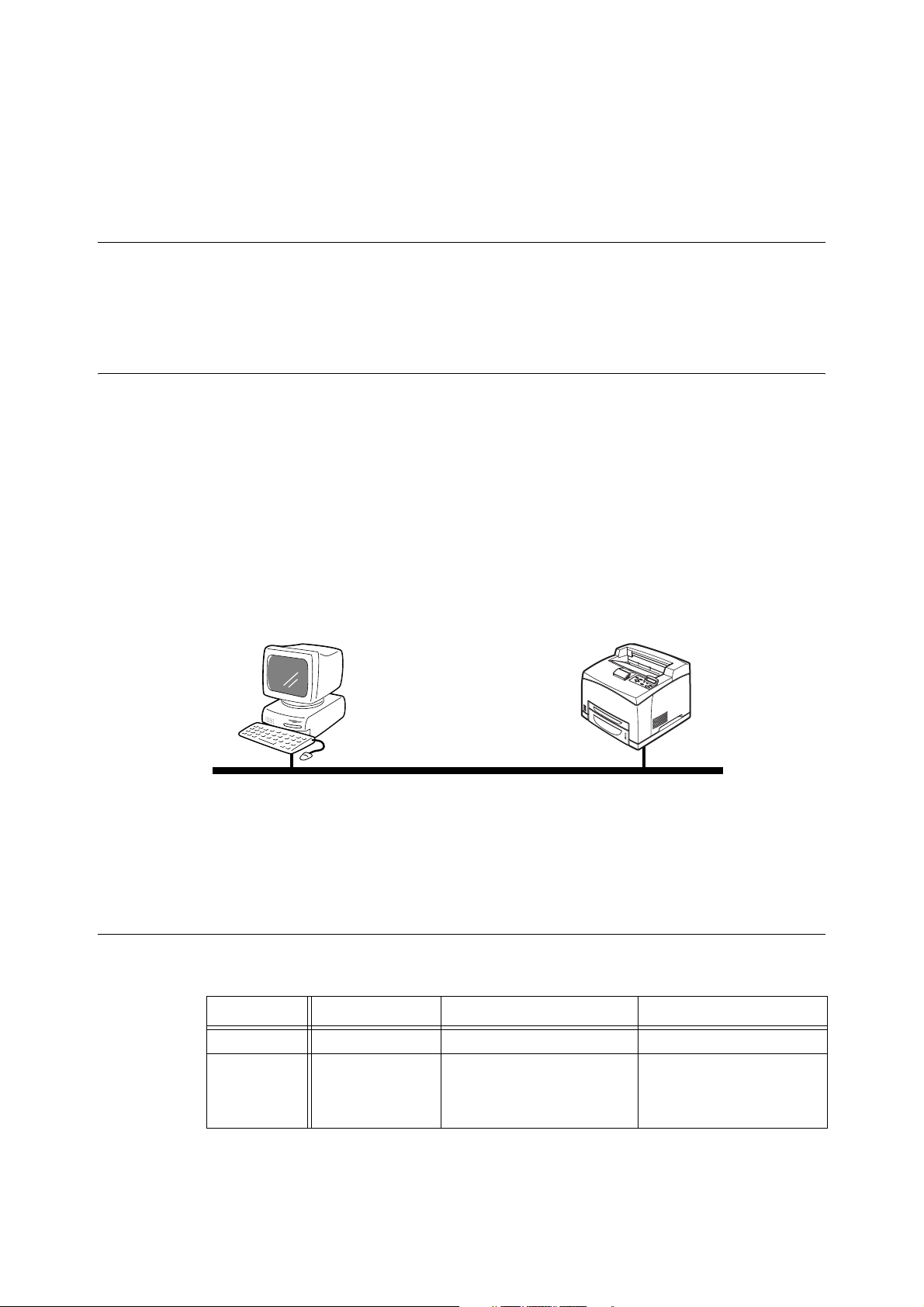
2 Printing Through LPD or Port9100
2.1 Installation Procedure for Printing Through LPD or Port9100
This section explains the installation procedure for printing from a Windows NT® 4.0/
Windows
Port9100.
®
2000/Windows®XP/Windows Server™ 2003 computer through LPD or
System Configuration
As the printer supports the LPD and Port9100 protocol, you can print directly from Windows
NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003 computer through the OS
standard LPR port (standard TCP/IP port for Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server
2003).
The transport protocol for LPD and Port9100 can be TCP/IP.
You will need to set up the IP address on the printer and the Windows NT 4.0/Windows
2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003 computer. And once the printer registered on the
Windows NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003 computer is shared,
you can also print from Windows 95/Windows 98/Windows Me computers through this
printer.
Windows NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP/
Windows Server 2003
Note
• Only Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003 support printing through Port 9100.
• When the LPD port is used, the printer can limit print instructions by IP addresses. For details, refer to
the User Guide.
Target Computers
The following computers support printing through LPD or Port9100:
Connection OS Service/Client Protocol
LPD port Windows NT 4.0 Microsoft TCP/IP Printing TCP/IP
LPD port
Port9100 port
LPD or Port9100 (TCP/IP)
Windows 2000
Windows XP
Windows Server
2003
- Internet protocol (TCP/IP)
10 2 Printing Through LPD or Port9100
Page 11

Set Up Procedure
The setting procedure is as follows:
1. Setting up the printer
Set the IP address on the printer control panel.
Use the printer control panel or OkiWebRemote to set the following ports to [Enable].
• Printing through LPD: LPD port (default: [Enable])
• Printing through Port9100: Port9100 port (default: [Enable])
Note
• Before activating the LPD or Port9100 port, set the IP address of the printer.
For details on how to set the IP address and the port, refer to the Setup and Quick Reference Guide.
• OkiWebRemote allows more detailed settings.
2. Setting up the computer
Install the printer driver for Windows NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows
Server 2003.
If necessary, set sharing.
Refer to
• “2.2 Setting Up the Computer” (P. 11)
2.2 Setting Up the Computer
This section explains the setup procedure for creating a shared printer and printing from the
Windows 95/Windows 98/Windows Me computer.
Creating a Shared Printer
Create a shared printer as required.
Settings of Windows NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003
The following procedure explains how to do the settings, using Windows XP as an example.
1. Click [Start], and then select [Printers and Faxes].
The [Printers and Faxes] window appears.
2. Select the icon of a printer to set, and then select [Sharing] from the right-click menu.
Then the printer properties dialog box is displayed.
3. Click [Share this printer] and enter a share name.
4. Click [Additional Drivers] and select a substitute driver to install, and then click [OK].
5. When installing a substitute driver, an input screen is displayed for the printer driver
file location. Insert the attached CD-ROM and specify the appropriate folder.
2.2 Setting Up the Computer 11
Page 12

Settings of Windows 95/Windows 98/Windows Me
1. Click [Start], and then select [Settings], followed by [Printers].
The [Printers] window appears.
2. Double click [Add Printer].
The [Add Printer Wizard] dialog box appears.
3. Install the printer driver according to the on-screen instructions.
Select [Network Printer] for the printer connection, then specify the shared printer
created on Windows NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003 in the
previous section.
12 2 Printing Through LPD or Port9100
Page 13
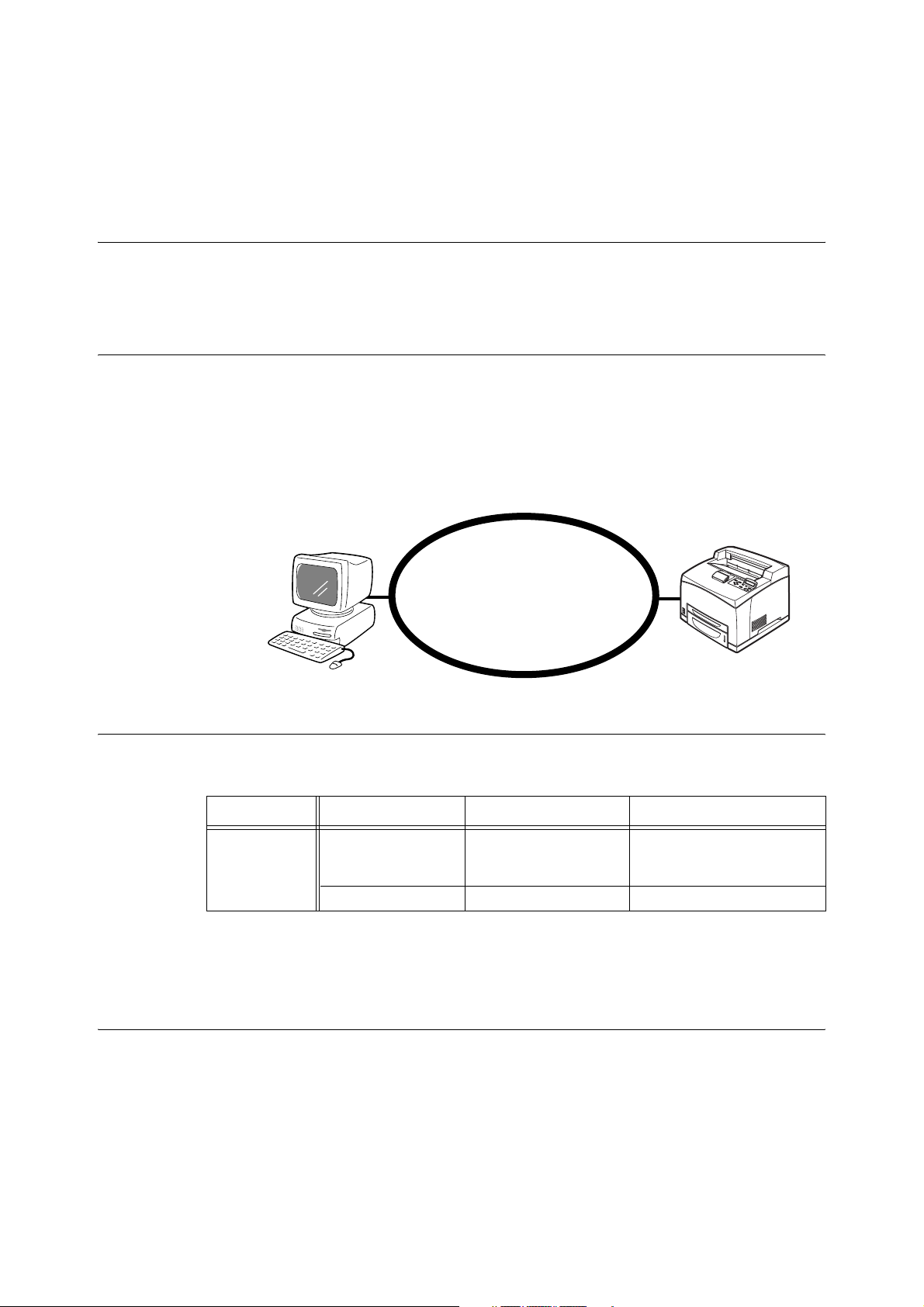
3 Internet Printing
3.1 Installation Procedure for Internet Printing
This section explains the installation procedure for printing using the Internet Printing
Protocol (IPP).
System Configuration
The printer supports Internet Printing Protocol (IPP). As Windows 2000/Windows XP/
Windows Server 2003/Windows Me is installed with the client software needed to output to
IPP printer, you can specify the printer to support IPP using the [Add Printer Wizard]. Using
IPP, you can print to a remote printer through the Internet or intranet.
The transport protocol for IPP can be TCP/IP.
IPP client
(Windows Me/Windows 2000/Windows XP/
Windows Server 2003)
Target Computers
The following computers support Internet printing:
Connection OS Service/Client Protocol
IPP port
(TCP/IP)
Important
• For Internet printing from a Windows Me computer, the IPP port should be installed. For the IPP port
installation method, refer to the Windows Me manual.
Set Up Procedure
Internet
Windows 2000
Windows XP
Windows Server 2003
Windows Me IPP port monitor TCP/IP protocol
IPP port monitor Internet protocol (TCP/IP)
The setting procedure is as follows:
1. Setting up the printer
Set the IP address on the printer control panel.
Use the printer control panel or OkiWebRemote to set the IPP port to [Enable] (default:
[Disable]).
3.1 Installation Procedure for Internet Printing 13
Page 14

Note
• Before activating the IPP port, set the IP address of the printer.
For details on how to set the IP address and the port, refer to the Setup and Quick Reference Guide.
• OkiWebRemote allows more detailed settings.
2. Setting up the computer
Install the printer driver for Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003/
Windows Me.
Refer to
• “3.2 Installing the Printer Driver” (P. 14)
3.2 Installing the Printer Driver
This section explains instructions on how to install the printer driver in the computer.
Note
• Before installing the printer driver on the computer, check that Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) or TCP/IP
protocol has been installed. If it has not been installed, refer to the Windows 2000/Windows XP/
Windows Server 2003/Windows Me manual to install it.
• When using the internet printing through the proxy server, an error message, “Cannot be connected to
the internet” may appear when setting the printer. When this happens, change the setting of the IP
address without going through the proxy server by selecting [Internet Options] on the [Control Panel]
window. For details on how to do this setting, refer to the Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server
2003/Windows Me manual.
Installation Procedure (Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server
2003)
We will install the PCL printer driver on Windows XP here as an example.
The procedure is as follows:
1. Click [Start], and then select [Printers and Faxes].
The [Printers and Faxes] window appears.
2. Click [Add a printer].
The [Add Printer Wizard] dialog box appears.
3. Install the printer driver by following the on-screen instructions.
Select [A network printer, or a printer attached to another computer] for the printer
connection. Then select [Connect to a printer on the Internet or on a home or office
network] at [Specify a Printer] and enter the following URL:
“http://printer IP address/ipp”
When the printer manufacturer and model selection screen is displayed, insert the
attached CD-ROM, click [Have disk], and specify the appropriate folder.
4. At the end of installation, the printer icon is added to the [Printers and Faxes] window.
Make settings for the options mounted on the printer.
Refer to
• Online Help for the printer driver
14 3 Internet Printing
Page 15

Installation Procedure (Windows Me)
The procedure is as follows:
1. Click [Start], and then select [Settings], followed by [Printers].
The [Printers] window appears.
2. Double-click [Add Printer].
The [Add Printer Wizard] dialog box appears.
3. Install the printer driver by following the on-screen instructions.
Select [Network Printer] for the printer connection, then enter the following URL for the
network path or queue:
“http://printer IP address/ipp”
When the printer manufacturer and model selection screen is displayed, insert the
attached CD-ROM, click [Have disk], and specify the appropriate folder.
4. At the end of installation, the printer icon is added to the [Printers] window.
Make settings for the options mounted on the printer.
Refer to
• Online Help for the printer driver
3.2 Installing the Printer Driver 15
Page 16
4 Printing Through SMB
4.1 Installation Procedure for Printing through SMB
Server Message Block (SMB) is a protocol for sharing files or printers on a Windows OS.
This section explains the installation procedure for connecting a printer to the Windows
network through SMB.
System Configuration
As the printer supports SMB protocol, you can print by sending print data directly to the
printer on the same network without going through the server.
You can use either NetBEUI or TCP/IP, or even both as the transport protocol for SMB. You
will need to set up the IP address on the printer and the computer if you are using TCP/IP.
Windows 95/Windows 98/Windows Me/
Windows NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP/
Windows Server 2003
Note
• Windows XP/Windows Server 2003 does not support NetBEUI.
Target Computers
The following computers support printing through SMB:
Connection OS Protocol
SMB port
(Windows
network)
SMB (NetBEUI or TCP/IP)
Windows 95
Windows 98
Windows Me
Windows NT 4.0 NetBEUI
Windows 2000 Internet protocol (TCP/IP)
Windows XP
Windows Server 2003
NetBEUI
TCP/IP
TCP/IP
NetBEUI protocol
Internet protocol (TCP/IP)
16 4 Printing Through SMB
Page 17

Set Up Procedure
The setting procedure is as follows:
1. Setting up the printer
• When using NetBEUI
Use the printer control panel or OkiWebRemote to set the SMB port to [Enable]
(default: [Enable]).
• When using TCP/IP
Set the IP address on the printer control panel.
Use the printer control panel or OkiWebRemote to set the SMB port to [Enable]
(default: [Enable]).
Note
• For details on how to set the IP address and the port, refer to the Setup and Quick Reference Guide.
• OkiWebRemote allows more detailed settings.
• By rewriting the [config.txt] file of the printer, SMB can be set or changed on a Windows computer. For
details, refer to “4.2 Setting/Changing SMB Using the [Config.txt] File” (P. 17).
2. Setting up the computer
Install the printer driver to the computer.
Refer to
• “4.3 Auto Driver Downloading” (P. 20)
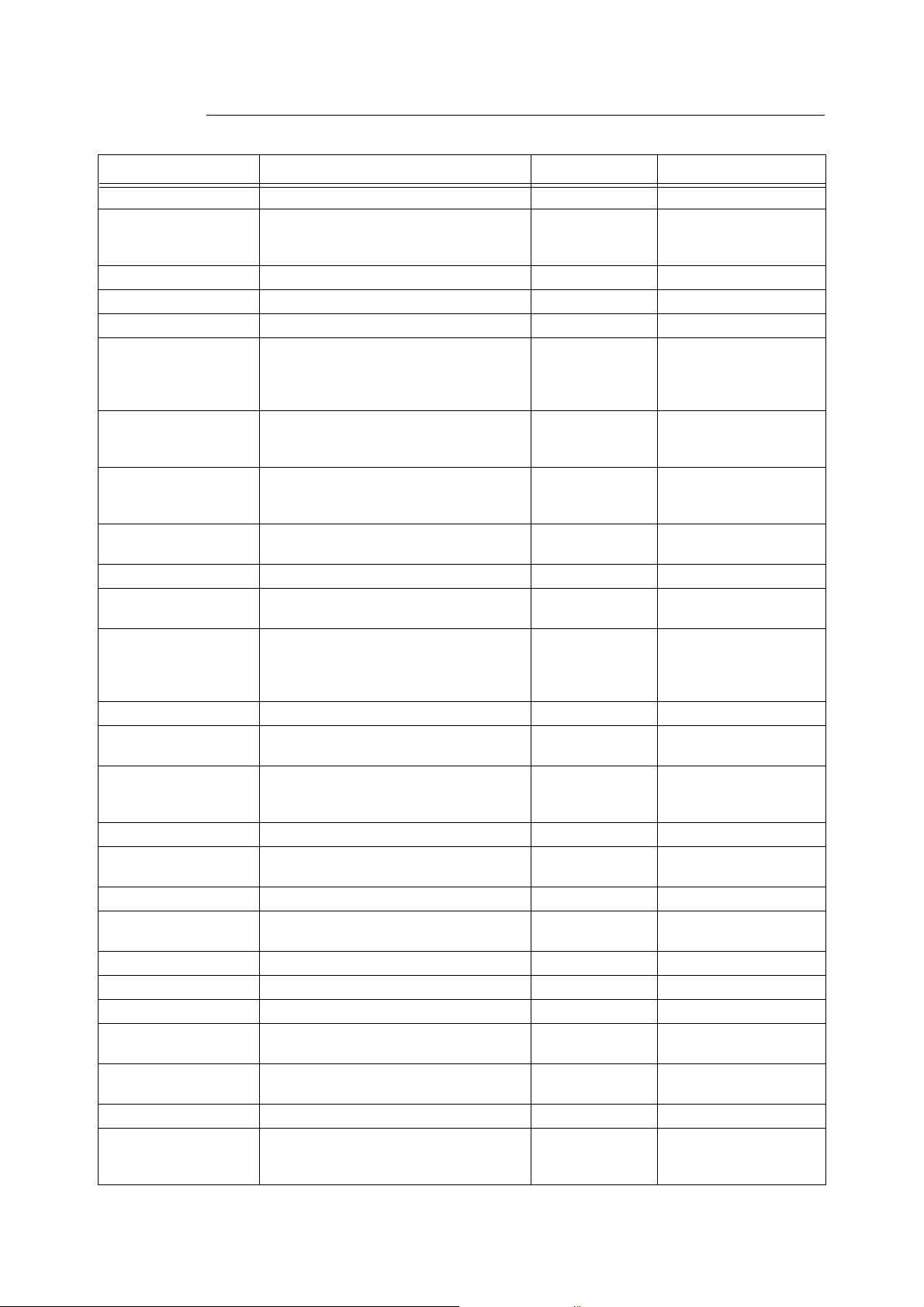
4.2 Setting/Changing SMB Using the [Config.txt] File
You can change the SMB setting by accessing the setting file (config.txt) in the printer
through the Windows network from the computer. However, only the administrator is
allowed to do this.
The procedure below explains how to overwrite the [config.txt] file.You will need to know the
following items that have been set: SMB Host Name, Workgroup, Administrator Name, and
Administrator Password. The procedure here explains with Windows XP as an example.
1. Open [My Network Places] from the Windows computer, followed by [Workgroup]
(default: [Workgroup]) and then the printer.
Note
• The factory default of the host name of the printer is “OKI-xxxxxx” (where xxxxxx is the last six
characters of the printer MAC address). You can confirm the name by referring to SMB Host Name on
the [System Settings List].
Important
• This method does not enable printer search across subnets. For printer search across subnets, you
should set the WINS server or edit LMHOSTS. For details about LMHOSTS, refer to the Windows
manual.
2. Click the [admintool] folder.
The [Connect to Oki-xxxxxx] dialog box will be displayed.
3. For Windows 95/Windows 98/Windows Me, enter only the password (SMB
Administrator Password) and for Windows NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP/
Windows Server 2003, enter the user name (SMB Administrator Name) and password
(SMB Administrator Password).
Then, click [OK].
4.2 Setting/Changing SMB Using the [Config.txt] File 17
Page 18

Note
• The factory default of Administrator Name is “
six characters of the printer MAC address).
root” and Administrator Password is “xxxxxx” (the last
4. Using a text editor like Notepad, open the [config.txt] file.
5. If necessary, change each item , and then overwrite and close the [config.txt] file.
The [message.txt] file is created inside the [admintool] folder.
Refer to
• Details on the [config.txt] file: “Setting Format of [config.txt] File” (P. 19)
6. Open the [message.txt] file and check that it displays the following information.
Note
• If the [message.txt] file is not displayed, select [Refresh] from the [View] menu. If an error message
appears, check the contents that have been set again.
7. Close the [message.txt] file.
8. Switch off the printer, then switch on it again.
Note
• The setting changes you have made will be enabled when switching off and on the power switch or
saving [config.txt] file with its [Reboot] set to [Yes].
18 4 Printing Through SMB
Page 19
Setting Format of [config.txt] File
Item Remarks Value Factory default
Printer Language Language to be used. English English
Host Name Host name of the printer. Maximum 15 bytes OKI-xxxxxx (xxxxxx: last 6
characters of the printer
MAC address)
Workgroup Name of workgroup of printer. Maximum 15 bytes WORKGROUP
NETBEUI Activation of NetBEUI protocol. On/Off Off
TCP/IP Activation of TCP/IP protocol. On/Off On
Spool Activation of spool function.
Can select from Disk, Memory, and Off.
If Disk is not recognised when it is selected,
it will become Memory.
Max Spool Size The maximum receive buffer size during
spooling.
Can be set in 256 kbyte units.
Max Receive Buffer Size The maximum receive buffer size during
non-spooling.
Can be set in 32 kbyte units.
Auto Driver Download Activation of the automatic downloading of
printer driver.
JCL Activation of JCL. On/Off On
Print Mode Set the printer language. AUTO/PS/HPGL/
Auto Master Mode Activation of the automatic browse master
feature.
Not available when Wins server is
designated.
Encrypt Password Activation of the encrypt password feature. On/Off On
Time Zone Set the time zone in units of minutes. -720 to 720 (unit:
Daylight Savings Set the period of summer time. hour-start-end (h-
Maximum Session Maximum connections of printer. 3 - 10 5
Unicode Support Set whether to use unicode or local code
(Shift JIS).
DHCP Activation of the DHCP protocol. On/Off Off
Get WINS DHCP Set whether or not to get WINS from the
DHCP server.
IP Address Set the IP address. ----- 0.0.0.0
Subnet Mask Set the subnet mask. ----- 0.0.0.0
Gateway Address Set the gateway address. ----- 0.0.0.0
WINS Primary Server IP
Address
WINS Secondary Server
IP Address
Administrator Name Name Administrator name. Maximum 20 bytes ADMIN
Administrator Password Password of administrator.
Set the WINS primary server IP address. ----- 0.0.0.0
Set the WINS secondary server IP address. ----- 0.0.0.0
Current setting not displayed.
Disk/Memory/ Off Off
512 - 32768 (unit:
kbyte)
64 - 1024 (unit:
kbyte)
Enabled/Disabled Enabled
PCL/ESCP/TIFF
On/Off On
minutes)
hhddmmhhddmm)
Enabled/Disabled Disabled
Ye s/ No No
Maximum 14 bytes xxxxxx (the last six
1024 kbyte
256 kbyte
AUTO
0 (England)
characters of the printer’s
MAC address)
4.2 Setting/Changing SMB Using the [Config.txt] File 19
Page 20

Item Remarks Value Factory default
Location Specify the information about the printer’s
location.
Reboot Printer will be rebooted after the editing of
the config.txt parameter setting file if set to
Ye s.
Usually set to No when activated.
Machine will not be rebooted even if it is set
to Yes if there is an error in the setting.
Example of [Config.txt] File
Maximum 48 bytes
Ye s/ No No
4.3 Auto Driver Downloading
When installing printer driver to Windows 95/Windows 98/Windows Me computer, you can
define the settings to use the auto driver downloading feature.
Note
• This feature is not applicable to Windows NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003.
• Installation of the hard disk (optional) is required to use the auto driver downloading feature.
Preparation for Auto Driver Downloading
The following procedure explains the preparations needed in order to use the auto driver
downloading feature. Only the administrator can define this setting. The procedure here
explains with Windows XP as an example.
1. Open [My Network Places] from the Windows computer, followed by [Workgroup]
(default: [Workgroup]) and then the printer.
Note
• The factory default of the host name of the printer is “OKI-xxxxxx” (where xxxxxx is the last six
characters of the printer Mac address). Ask your system administrator for the current setting.
20 4 Printing Through SMB
Page 21

2. By referring to “4.2 Setting/Changing SMB Using the [Config.txt] File” (P. 17), open
the [config.txt] file inside the [admintool] folder, and then check that [Auto Driver
Download] is set to [Enabled] (default: [Enabled]).
3. Close the [config.txt] file and then open the [drivers] folder.
4. Create a folder for each OS in the drivers folder. For example, create the [Win98]
folder in the drivers folder.
Note
• You can specify a folder name with a maximum of eight alphanumeric characters.
• You can create a maximum of two levels of folders.
5. Insert the CD-ROM bundled with this printer into the CD-ROM drive.
6. Copy all the files for the printer driver from the appropriate folder in the CD-ROM to
the folder you have just created (here, [win98]).
7. Close the [drivers] folder.
8. Switch off the power to the printer, then switch it on again.
9. Open [My Network Places] from the Windows computer, followed by [Workgroup]
(default: [Workgroup]) and then the printer.
You notice that a printer icon of the printer driver has been added.
You are now ready for auto driver downloading.
4.3 Auto Driver Downloading 21
Page 22

Auto Downloading of Printer Driver
The following procedure explains how to use this auto driver downloading feature to install
the printer driver to the computer. We will install the PCL printer driver to Windows 98 as an
example.
1. Open [Network Neighborhood] from the Windows computer, followed by [Workgroup]
(default: [Workgroup]) and the printer. Then, select the new printer icon that has been
added.
Note
• The factory default of Workgroup is “Workgroup” and host name of the printer is “OKI-xxxxxx” (where
xxxxxx is the last six characters of the printer Mac address). Ask your system administrator for the
current setting.
2. When the message to confirm whether or not to continue the operation is displayed,
select [Yes].
3. Follow the on-screen messages to complete installation of the printer driver.
4. The printer icon of the newly installed printer is added to the [Printers] window and the
printer is now ready for use.
Make settings for the options mounted on the printer.
Refer to
• Online Help for the printer driver
22 4 Printing Through SMB
Page 23

5 Printing Through NetWare
5.1 Installation Procedure for Printing Through NetWare
This section explains the installation procedure for connecting a printer to the Novell
NetWare network.
System Configuration
This printer is compatible with Novell NetWare 3.12/3.2/4.1/4.11/4.2/5/6 and by the bindery
services or the directory service (NDS) (NetWare 4.11 and above) supports the print server
(PServer) mode only.
In the PServer mode, the printer will function as a print server and retrieve print jobs from
the print queue for printing. This printer uses one user license of the file server.
NetWare client NetWare server
Important
• This printer does not support RPrinter mode.
Target Computers
The NetWare server and NetWare client computers require the following environments:
• NetWare server
Novell-accredited computer which can be installed with NetWare 3.12/3.2/4.1/4.11/4.2/5/
6
• NetWare client
Novell-accredited computer which can run Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows Me,
Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, or Windows XP.
NetWare (IPX/SPX or TCP/IP)
5.1 Installation Procedure for Printing Through NetWare 23
Page 24

IPX/SPX Frame Types
The printer supports the following types of Ethernet interface:
• 10Base-T (Twisted Pair Cable)
• 100Base-TX (Twisted Pair Cable)
The following frame types are supported:
• Ethernet II specification
• IEEE802.3 specification
• IEEE802.3/802.2 specification
• IEEE802.3/802.2/SNAP specification
The printer will send out packets of each frame type on the connected network and activate
automatically to the frame type which responds first.
However, if other protocols are running simultaneously on the same network, use the frame
type that the NetWare server is using.
Note
• Some network components (such as the hub) may not support automatic setup for frame type. If the
data link indicator light of the port which is connected to the printer of the network component does not
light up, match the setting ([IPX/SPX FrameType]) of the printer to the frame type of the file server.
Set Up Procedure
The setting procedure is as follows:
1. Setting up the printer
Use the printer control panel or OkiWebRemote to set the NetWare port to [Enable]
(default: [Disable]).
Print the [System Settings List] and check the device name and network address that
listed in the Netware.
Refer to
• Setup and Quick Reference Guide
2. Settings for the NetWare Environment
Using PCONSOLE or NetWare Administrator (NWADMIN), create print queue, print
server and printer, and assign the respective objects.
By using OkiWebRemote, transfer the set NetWare environment to the printer.
Important
• When setting up for the PCONSOLE or NWADMIN, use the device name checked in Step 1 for the print
server name. Set Printer Location as Auto Load (Local).
• For information on how to use PCONSOLE or NWADMIN, refer to the manual which comes with
NetWare. NWADMIN can be used on NetWare 5 or later.
Note
• OkiWebRemote allows more detailed settings.
• By using the NetWare Setup Wizard, you can set the printing environments for the NetWare server or
printer. For details about the NetWare Setup Wizard, refer to “8.2 NetWare Setup Wizard” (P. 41).
3. Setting up the computer
Install the printer driver to the NetWare client computer.
24 5 Printing Through NetWare
Page 25

6 Printing From UNIX
6.1 For Printing From UNIX
This section explains the installation procedure for printing from a UNIX computer.
System Configuration
The printer uses the Line Printer Daemon Protocol (LPD) that supports TCP/IP as the
transport protocol. With the LPD, use the printer under a UNIX network environment.
The printer LPD supports Spool Mode where print jobs from clients are spooled once before
output and Non-spool Mode where print jobs are sequentially output without spooling.
UNIX
Note
• When the LPD port is used, the printer can limit print instructions by IP addresses. For details, refer to
the User Guide.
Target Computers
The target computers are as follows:
• Workstation or personal computer with RFC 1179 Line Printer Daemon Protocol
Interface
The printer LPD is available on the following interfaces:
• Ethernet 100BaseTX
• Ethernet 10Base-T
The applicable frame types conform to Ethernet II.
LPD (TCP/IP)
6.1 For Printing From UNIX 25
Page 26

Set Up Procedure
The setting procedure is as follows:
1. Setting up the printer
Set the IP address on the printer control panel.
Use the printer control panel or OkiWebRemote to set the LPD port to [Enable] (default:
[Enable]).
When necessary, set the following items using the printer control panel:
• Print Mode (default: [Auto])
• PJL (default: [Enable])
• Buffer Size (default: [Off])
Note
• Before activating the LPD port, set the IP address of the printer.
For details on how to set the IP address and the port, refer to the Setup and Quick Reference Guide.
• OkiWebRemote allows more detailed settings.
2. Settings of the workstation
Set the printer in the workstation.
Refer to
• “6.2 Setting Up the Workstation” (P. 26)
6.2 Setting Up the Workstation
This section explains the settings of SunOS 4.1.4, HP-UX 11.0 workstation and Solaris 2.x
for printing.
Before Setup
Before setting up the workstation, check the following:
• The setup procedures and commands may vary according to different versions of OS.
Refer to the manuals that came with the workstation for details.
• To setup the printer, the user must be a superuser. Contact your network administrator
to perform the setup if you do not have the authority of a superuser.
• Check the IP address set up for the printer in advance. Be cautious as an incorrect IP
address may cause severe errors.
• Before performing any network setup (such as the IP address) to a host running under
NIS (Network Information Service), consult the NIS administrator.
Print Language/Mode
When setting the printer in a workstation, a printer name should be specified on the remote
host (printer).
The printer name depends on the print language/mode used for printing. The relationship
between printer name and print language/mode is as follows:
PS PostScript
PSASC/PSA PostScript
26 6 Printing From UNIX
Printer name Print language/mode
Page 27

Printer name Print language/mode
PSBIN/PSB PostScript
PS%n PostScript (%n: Input the number of the logical printer (1 - 10) that is
registered on the OkiWebRemote*.)
PCL PCL
ESCP/ESC ESC/P
HPGL/HPG HP-GL
PLT%nH HP-GL (%n: Input the number of the logical printer (1 - 10) that is
registered on the control panel or the OkiWebRemote*.)
LP Print mode set in OkiWebRemote
AUTO/ATO Auto discrimination mode
*: When printing a PostScript or HP-GL file, you can register logical printers whose output style is preset
using OkiWebRemote.
Important
• If a printer name other than the above is specified at printing, the printer mode set in OkiWebRemote is
used.
• When setting print languages/modes from the same workstation to a single printer, it is recommended to
set one kind each. If two or more kinds of languages/modes are set, the workstation may display the
same job number for some queries (lpq).
• To print an ASCII-format PostScript file, specify PSASC for data processing with TBCP enabled.
• To print a binary-format PostScript file, specify PSBIN for data processing with TBCP disabled.
• When PS is specified, the printer operates as if PSBIN is specified (factory shipping).
Note
• Lowercase characters may be used for a printer name.
• When outputting the PostScript file, using the UNIX filter is recommended.
Examples of Settings for SunOS 4.1.4
The examples below show printer settings for SunOS 4.1.4 where the printer host name is
printer1.
1. Registering a printer (printer name: P001) supporting the PostScript language
#
##chosen PS decomposer on printer
##
P001 | printerPS | Auto select PS:\
:lp=:rp=PS:rm=printer1:\
:sd=/usr/spool/P001lpd:\
:lf=/usr/adm/printer1-errs:mx#0
2. Registering a printer (printer name: P002) supporting the Postscript language that
feeds paper from an A4-size paper tray for duplex printing
#
##chosen PS decomposer on printer
##
P002 | printerPS:\
:lp=:rp=PS_A4:rm=printer1:\
:sd=/usr/spool/P002lpd:\
:lf=/usr/adm/printer1-errs:mx#0
6.2 Setting Up the Workstation 27
Page 28

3. Registering PS01 set using OkiWebRemote
#
##chosen PS decomposer on printer
##
P003 | printerPS:\
:lp=:rp=PS01:rm=printer1:\
:sd=/usr/spool/P003lpd:\
:lf=/usr/adm/printer1-errs:mx#0
Important
• To specify multiple entries for the logical printer, make sure each printer entry is assigned its unique
spool directory. If a single spool directory is used for multiple printer entries, the printer select option may
not function correctly.
Note
• Add the printer name to the initial field of /etc/printcap. To specify multiple printer names, separate them
by “|”.
• lp: The connected port device. No need to specify.
• rp: This is the printer name of the remote host. The printer name corresponds to the print
language/mode.
The output style may be specified at the same time. The parameters for specifying a style
are the same as those available for the -C option. As the example of (2) shows, insert “_ ”
between the printer name and output parameters. You can enter up to 14 characters.
If PS%n or PLT%nH is specified for the printer name as in the example of (3), however,
the printer does not operate normally with an output style different from the preset one.
Set a printer name corresponding to the print language/mode and output style.
• rm: This is the host name of the remote printer. Input the host name registered with /etc/hosts.
• sd: This is the spool directory. Specify the absolute path of the spool directory which must be
created.
• lf: This is the error log file. Create one if it does not already exist.
• mx#0: The spool size limit is cancelled.
Refer to
• Manuals, such as online manuals, that came with various workstations
• For details about the -C option: “6.5 -C Option (lpr Command)” (P. 36).
Examples of Settings for Solaris 2.X
The examples below show printer settings for Solaris 2.6 where the printer host name is
printer1.
1. Registering a printer (printer name: P001) supporting the PostScript language
#lpadmin -p P001 -s printer1\!PS
2. Registering a printer (printer name: P002) supporting the PostScript language that
feeds paper from an A4-size paper tray for duplex printing
#lpadmin -p P002 -s printer1\!PS_A4_DUP
3. Registering a logical PostScript printer PS01 set using OkiWebRemote
#lpadmin -p P003 -s printer1\!PS01
Note
• Enter the host name and printer name of the remote host after -s by linking with !. The printer name
corresponds to the print language/mode.
• The output style may be specified at the same time. The parameters for specifying a style are the same
as those available for the -C option. As the example of (2) shows, insert “_” between the printer name
and output parameters. You can enter up to 14 characters.
• If PS%n or PLT%nH is specified for the printer name as in the example of (3), however, the printer does
not operate normally with an output style different from the preset one.
• Set a printer name corresponding to the print language/mode and output style.
28 6 Printing From UNIX
Page 29

Refer to
• Manuals, such as online manuals, that came with various workstations
• For details about the -C option: “6.5 -C Option (lpr Command)” (P. 36)
Examples of Settings for HP-UX 11.0
The examples below show printer settings for HP-UX 11.0 where the printer host name is
printer1.
1. Registering a printer (printer name: P001) supporting the PostScript language
#lpadmin -pP001 -mrmodel -v/dev/null -ocmrcmodel
-ormprinter1 -osmrsmodel -orpPS -ob3
2. Registering a printer (printer name: P002) supporting the PostScript language that
feeds paper from an A4-size paper tray for duplex printing
#lpadmin -pP002 -mrmodel -v/dev/null -ocmrcmodel
-ormprinter1 -osmrsmodel -orpPS_A4_DUP -ob3
3. Registering a logical PostScript printer PS01 set using OkiWebRemote
#lpadmin -pP003 -mrmodel -v/dev/null -ocmrcmodel
-ormprinter1 -osmrsmodel -orpPS01 -ob3
Note
• Enter the host name of the printer after -orm.
• Enter the printer name of the remote host after -orp. The printer name corresponds to the print language/
mode.
• The output style may be specified at the same time. The parameters for specifying a style are the same
as those available for the -C option. As the example of (2) shows, insert “_” between the printer name
and output parameters. You can enter up to 14 characters.
• If PS%n or PLT%nH is specified for the printer name as in the example of (3), however, the printer does
not operate normally with an output style different from the preset one.
• Set a printer name corresponding to the print language/mode and output style.
Refer to
• Manuals, such as online manuals, that came with various workstations
• For details about the -C option: “6.5 -C Option (lpr Command)” (P. 36)
6.3 Printing (SunOS)
This section describes the procedure for printing from workstations running SunOS.
Refer to
• Manuals that came with the workstations
Print (lpr)
The “lpr” command is used to print.
Command Format
/usr/ucb/lpr [-P Printer name] [-# No. of copies] [-C Option] File name
6.3 Printing (SunOS) 29
Page 30

Command Options
The following command options are available:
-P Printer name
This option specifies the printer name registered at “/etc/printcap”. If this option is omitted,
print data will be output to the default printer lp.
-# No. of copies
This option specifies the number of copies. If one “lpr” command is issued to print multiple
files, the number of copies specified by this option will apply to all the files.
This option is valid when the printer is in the spool mode.
-C option
Use the -C option to specify the form of output.
This option is valid when the printer is in the spool mode. In the non-spool mode, the client
must be a Windows NT machine to use this option.
Important
• When the PostScript logical printer that was configured on the OkiWebRemote and -C option of “lpr”
command have been specified simultaneously, some of the actions cannnot be guaranteed to work.
Also, when specifying the PostScript logical printer as a default printer on Unix, it is recommended not to
user the -C option by “lpr” command.
Refer to
• “6.5 -C Option (lpr Command)” (P. 36)
Precautions
• Among options not listed above (e.g. -m option), those not processed by the workstation
that sends the print instructions will not be valid.
• In the spool mode, up to 32 files can be printed by one “lpr” command. Files that come
after the 32nd file will be ignored.
Sample
To print a file named “file1” to a printer set up as “P001”, enter the following command:
%lpr -P P001 file1
To output 3 copies of “file1” and “file2” to “P001”, enter the following:
%lpr -P P001 -#3 file1 file2
To print a file named “file1” to a printer set up as “P001” as a A4-sized duplex job, enter the
following command
%lpr -P P001 -C,DUP,A4 file1
30 6 Printing From UNIX
Page 31

Delete (lprm)
This “lprm” command is used to delete print data which has been sent to print.
Command Format
/usr/ucb/lprm [-P Printer name] Job number
Command Options
The following command options are available:
-P Printer name
This option specifies the printer name registered with /etc/printcap. If this option is omitted,
the default printer “lp” will be specified.
Job Number
This option specifies the job number of the print data to be deleted. A job number is a serial
number between 1-999 determined by the workstation. These numbers can be checked by
issuing a “lpq” command.
Instead of a job number, you can specify a user name or “-”.
This option is invalid in the non-spool mode.
User name
This option is only valid when the user logs in as a superuser. When this option is executed,
all the print data specified by the user who logged in as superuser will be deleted.
This option is invalid in the non-spool mode.
-
A user can delete all his print data by specifying this option. If this option is issued by a
superuser, all the print data received by the printer can be deleted.
This option is invalid in the non-spool mode.
Precautions
• Print data which consists of multiple files sent in one print instruction, cannot be deleted
file by file. All the files will be deleted at one go.
• This command will become invalid if it is executed without options having been specified
or if there is no print data which matches the option.
• A workstation can only delete print data it has sent. It cannot delete print data sent by
other workstations.
• When a command to delete print data is received, the file concerned will be deleted even
if it is in the process of being printed. The outcome of the printing will only consist of the
print data available before the file is deleted.
Sample
To cancel the print data related to the files of printer “fxPS” (Job number: 351), enter the
following command:
%lprm -P P001 351
6.3 Printing (SunOS) 31
Page 32

Inquiry (lpq)
The “lpq” command is used to inquire about the status of the printer.
Important
• In the non-spool mode, this function is available to Windows NT clients but not to SunOS clients.
Command Format
/usr/ucb/lpq [-P Printer name] [-l] [User name] [+interval]
Command Options
The following command options are available:
-P Printer name
This option specifies the printer name registered at /etc/printcap. If this option is omitted, the
default printer “lp” will be specified.
-l
This option displays workstation information, which sends print instructions, in the long
format.
User name
This option displays print data information already received from a specified user.
+interval
This option specifies the interval for which inquiries are sent and information is displayed
regularly on the client for the duration of printing until the print data received by the printer
has been printed. The interval is set up in seconds.
This option clears the display each time the information is displayed.
Precautions
• Long file names will be truncated.
• Up to 64 print instructions can be displayed.
• If two or more types of print languages/modes are set up on a single workstation, identical
job numbers may be displayed when an inquiry command (lpq) is issued.
Sample
To inquire about the print data received by a printer set up as “P001”, enter the following
command:
%lpq -P P001
To display a printer set up as “P001” in the long format, enter the following command:
%lpq -P P001 -l
32 6 Printing From UNIX
Page 33

6.4 Printing (HP-UX/Solaris)
This section describes the procedure for printing from workstations running HP-UX or
Solaris.
Refer to
• Manuals that came with the workstations
Print (lp)
The “lp” command is used for printing.
Command Format
lp [-d Printer name] [-n No. of copies] File name
Command Options
The following command options are available:
-d Printer name
Specify the printer name registered by the “lpadmin” command as the -d option. If this option
is omitted, the default printer lp will be specified.
-n No. of copies
This option specifies the number of copies. If one “lp” command is issued to print multiple
files, the number of copies specified by this option will apply to all the files.
However, this option is effective when the printer is in the spool mode. In the non-spool
mode, the client must be a Windows NT machine to use this option.
Precautions
• Among options not listed above (e.g. -m option), those not processed by the workstation
which sends the print instructions will not be effective.
• In the spool mode, up to 32 files can be printed by one “lp” command. Files that come
after the 32nd files will be ignored.
Sample
To print a file named “file1” to a printer set up as “P001”, enter the following command:
%lp -d P001 file1
To output three copies of “file1” and “file2” to “P001”, enter the following:
%lp -d P001 -n3 file1 file2
6.4 Printing (HP-UX/Solaris) 33
Page 34

Delete (Cancel)
This cancel command is used to delete print data which has been sent to print.
Command Format
cancel [Printer name] [Job Number]
Command Options
The following command options are available:
Printer name
This option specifies the printer name. The “cancel” command can be effectively used with
the combined use of -a, -e and -u as shown below. This option is invalid in the non-spool
mode.
-a Deletes all the print data, sent by a user who issues this command, from the data
-e Deletes all the print data received by a specified printer.
-u user name Deletes all the print data sent by a specified user and received by a specified
which has been received by a specified printer.
printer.
Job Number
This option specifies the job number of the print data to be deleted. These numbers can be
checked by issuing a “lpstat” command.
This option is invalid in the non-spool mode.
Precautions
• Print data that consists of multiple files sent in one print instruction cannot be deleted file
by file. All the files will be deleted at one go.
• This command will become invalid if it is executed without options having been specified
or if there is no print data which matches the option.
• A workstation can only delete print data it has sent. It cannot delete print data sent by
other workstations.
• When a command to delete print data is received, the file concerned will be deleted even
if it is in the process of being printed. Only the print data available prior to file deletion will
be printed.
Sample
To cancel the print data related to the files of printer “P001” (Job number: P001-27), enter
the following command:
%cancel P001-27
To cancel all the printer data of printer “P001”, enter the following command:
%cancel P001 -e
34 6 Printing From UNIX
Page 35

Inquiry (lpstat)
The “lpstat” command is used to inquire about the status of the printer.
Important
• In the non-spool mode, this function is available to Windows NT clients but not to HP-UX/Solaris clients.
Command Format
lpstat [Option]
Command Options
The following command options are available:
If no option is specified, all the print data-related information will be displayed.
The sequence of the options does not affect the outcome.
To use more than one argument at the same time, separate them by commas and enclose
all the arguments with “ ”.
E.g. %lpstat -u “user1,user2,user3”
-o [Printer name]
This option displays the print data received. The printer name is specified in the argument.
-t
This option displays all the information.
-u [User name]
This option displays received print data information on users of specified user names.
-v [Printer name]
This option displays the printer name and the device path name. The printer name is
specified in the argument.
Precautions
• Long file names will be truncated.
• Up to 64 print instruction information can be displayed.
• If two or more types of print languages/modes are set up on a single workstation, identical
job numbers may be displayed when an inquiry command (lpstat) is issued.
Sample
To inquire about the print data received by a printer set up as “P001”, enter the following
command:
%lpstat -o P001
6.4 Printing (HP-UX/Solaris) 35
Page 36

6.5 -C Option (lpr Command)
This section explains the functions which can be specified and printing operations which will
be affected by the -C option.
The -C option is available only when the SunOS directs the printer to enter the spool mode.
Important
• When the PostScript logical printer that was configured on the OkiWebRemote and -C option of “lpr”
command have been specified simultaneously, some of the actiions cannnot be guaranteed to wprk.
Also, when specifying the PostScript logical printer as a default printer on Unix, it is recommended not to
user the -C option by “lpr” command.
Function
The following items can be set up by using the -C option:
Note
• Any parameter other than below becomes invalid if specified.
Selecting a Paper Tray
When selecting a paper tray, either the paper size or the tray itself is specified. If the paper
size is specified, the printer automatically searches and selects the tray where the specified
paper is loaded.
The following parameters can be specified:
Parameter Description
INTRAY1/intray1 Selects Tray 1.
INTRAY2/intray2 Selects Tray 2.
INTRAY3/intray3 Selects Tray 3 (option).
INTRAY4/intray4 Selects Tray 4 (option).
A4/a4 Selects the tray where A4 paper is loaded.
B5/b5 Selects the tray where B5 paper is loaded.
A5/a5 Selects the tray where A5 paper is loaded.
LETTER/letter Selects the letter size.
LEGAL/legal Selects the legal size (8.5 × 14).
Note
• If several parameters are specified in one “lpr” command, data may not be printed correctly.
• The system default is used if no tray number is specified, a specified tray is not loaded, or paper of a
specified size is not loaded.
• This option is for specifying a paper size only. Paper is selected but the document size is not corrected
according to the paper size.
• If the print data specifies a paper tray, the tray specification by the data becomes valid and that by the -C
option becomes invalid.
• If an unacceptable combination is specified, the printer may not operate correctly.
• For some print language, the specification may be invalid.
36 6 Printing From UNIX
Page 37

Selecting a Paper Output Tray
The following parameters can be specified:
Parameter Description
OUTUP/outup Ejects prints to the rear tray (option).
OUTDOWN/outdown Ejects prints to the center tray.
Selecting a Paper Type
The following parameters can be specified:
Parameter Description
PTS/pts Selects Plain paper.
PT1/pt1 Selects Heavy weight paper 1.
PT2/pt2 Selects Heavy weight paper 2.
POH/poh Selects Transparency.
PRC/prc Selects Recycled paper.
Specifying 2 sided Printing
The following parameters can be specified:
Parameter Description
DUP/dup 2 sided printing as follows:
TUMBLE/tumble 2 sided printing as follows:
SIMP/simp 1 sided printing
Note
• If several parameters are specified in one “lpr” command, data may not be printed correctly.
• The system default is used if no parameter is specified.
• If the print data specifies 2 sided or 1 sided printing, the specification by the data becomes valid and
overrides that by -C option.
6.5 -C Option (lpr Command) 37
Page 38

Specifying Paper Size and 2 sided Printing
Select a paper size and a binding type. The following parameters can be specified:
Parameter Description
A4D/a4d 2 sided printing on A4 paper and long-side binding
A4T/a4t 2 sided printing on A4 paper and short-side binding
A5D/a5d 2 sided printing on A5 paper and long-side binding
A5T/a5t 2 sided printing on A5 paper and short-side binding
B5D/b5d 2 sided printing on B5 paper and long-side binding
B5T/b5t 2 sided printing on B5 paper and short-side binding
Note
• If several parameters are specified in one “lpr” command, data may not be printed correctly.
• The system default is used if no parameter is specified.
• If the print data specifies 2 sided or 1 sided printing, the specification by the data becomes valid and
overrides that by -C option.
Specifying Collation
The following parameter can be specified:
Parameter Description
COLLATE/collate Sorts prints electronically.
Note
• For some print language, the specification may be invalid.
Specifying Color and Print Modes
The following color and print mode parameters can be specified:
Parameter Description
CC/cc Selects color for color mode and quality priority for print mode.
CB/cb Selects color for color mode and speed priority for print mode.
GC/gc Selects monochrome for color mode and quality priority for print mode.
GB/gb Selects monochrome for color mode and speed priority for print mode.
AC/ac Selects auto (color/monochrome) for color mode and quality priority for
print mode.
AB/ab Selects auto (color/monochrome) for color mode and speed priority for
print mode.
Note
• If several parameters are specified in one “lpr” command, data may not be printed.
• For some print language, the specification may be invalid.
• The system default is used if no parameter is specified.
• The color setting is not available on this printer.
38 6 Printing From UNIX
Page 39

Printing
To specify the output format of printing, enter the following command:
-C, [Parameter], [Parameter]
Enter a “,” (comma) after -C followed by the parameters which specify the output format. To
specify multiple parameters, separate them with “,”.
For example, to output a file named “file1” 2-sided on A4 to printer “P001”, enter the
following command:
%lpr -P P001 -C,DUP,A4 file1
Important
• If the command specified by the -C option exceeds 64 characters, the operation may not function
correctly.
6.5 -C Option (lpr Command) 39
Page 40

7 Printing From a Macintosh
Computer
7.1 Printing From a Macintosh Computer
This section explains the installation procedure for printing from a Macintosh computer.
System Configuration
As the printer supports EtherTalk and LPD protocol, you can print from Macintosh.
Note
• Printing using the LPD protocol is available only with the Mac OS X.
Target Computers
The printer supports a Macintosh or Power Macintosh with the following OS:
• Mac OS 8.6 through 9.2.2
•Mac OS X
Refer to
• User Guide (PostScript Driver)
Set Up Procedure
The setting procedure is as follows:
1. Setting up the printer
Use the printer control panel or OkiWebRemote to set the following port to [Enable].
• Printing through LPD: LPD port (default: [Enable])
• Printing through EtherTalk: EtherTalk port (default: [Disable])
Note
• For details on how to set the port, refer to the Setup and Quick Reference Guide.
• OkiWebRemote allows more detailed settings.
2. Setting up the Macintosh
Install the printer driver(Adobe PS) for Macintosh. Install the screen font if necessary.
Refer to
• User Guide (PostScript Driver)
40 7 Printing From a Macintosh Computer
Page 41

8 Network Utility Software
8.1 IP Address Setting Tool
You can set the printer’s IP address by using the IP Address Setting tool. You can easily
connect the printer to a network with a TCP/IP environment. This tool searches a network
for a printer that has been assigned an IP address by a server such as a DHCP server, then
sets the printer’s IP address. Also, this tool enables you to set a printer that is connected to
a network without a DHCP server by specifying the MAC address.
This tool can be used by starting it from the CD-ROM.
Refer to
• For details about how to use the IP Address Setting Tool: Online Help for the tool
8.2 NetWare Setup Wizard
You can set or change the initial settings for the NetWare server and the printer by using
the NetWare Setup Wizard. This tool can be used when setting the printing environment by
using the NetWare server.
This tool can be used by starting it from the CD-ROM.
Note
• This tool cannot be used on Windows NT Server 4.0, Windows 2000 Server, and Windows Server 2003.
Refer to
• For details about how to use the NetWare Setup Wizard: Online Help for the tool
8.3 Simple Status Notification
Simple Status Notification (hereinafter called SSN) is a tool that enables users to monitor
the network printer status by an icon or a dialog box on the computer.
SSN can be used by installing it to your computer from the CD-ROM that is bundled with
this printer.
8.1 IP Address Setting Tool 41
Page 42

Operating Requirements
The following is a list of computer operating systems of the computer where SSN can be
installed and the printers that can be monitored.
OS Printer
Using SSN
Windows 95
WIndows 98
Windows Me
Windows NT 4.0
Windows 2000
Windows XP
Windows Server 2003
Important
• Here, it is assumed that the network client setting in the computer has been completed.
• The factory setting of the SNMP prot is set to [Enable], and the transport protocol is set to [UDP].
Note
• For details on how to set the IP address, refer to the Setup and Quick Reference Guide.
• When you install SSN, read the readme file in the CD-ROM.
• Printer with TCP/IP environment being setup, IP address set, and SNMP
port (transport protocol : UDP) activated.
• Printer with NetWare environment setup and SNMP port (transport port:
IPX) activated.
The procedure here explains with Windows XP as an example.
1. Click [Okidata] > [Simple Status Notification] > [Simple Status Notification] from [All
Programs] on the [Start] menu.
The [Simple Status Notification] dialog box appears.
2. Enter IP address of the printer that you want to monitor.
3. Click [Start].
The dialog box to confirm the printer name is displayed.
4. Click [OK].
The printer icon is displayed at the bottom right corner of the task bar on the computer
desktop. The icon color,
Refer to
• “Color of the Icon and Printer Status”
42 8 Network Utility Software
changes according to the printer status.
Page 43

5. Place the cursor on the icon and the status of the printer is displayed.
Note
• The dialog box to indicate the printer information is displayed by double-clicking the icon.
• The printer status is updated by left-clicking the icon.
6. To exit SSN, right-click on the icon and then click [Close] from the menu displayed.
Color of the Icon and Printer Status
The color of the icon, indicates the following status.
Color Display Printer Status
Blue Printing is possible
Green Printing
Yellow Printing is possible -User Intervention Required.
Red Printing is not possible due to a printer error.
Grey No response from the printer.
Monitoring a Specific Printer Automatically when Windows Starts
Prepare the following settings and you can monitor the printer status by activating SSN
automatically after you have started Windows.
1. From the [Simple Status Notification] folder, create an [Ssn.exe] shortcut and copy to
the [Startup] folder.
Note
• If [Ssn.exe] is not changed during installation, it will be stored in the \Program Files\
Okidata\Simple Status Notification folder.
• The [Startup] folder is located in the following destination depending on the OS that you are using.
Windows 95/Windows 98/Windows Me: Windows\Start menu\Programs\Startup
Windows NT 4.0: Winnt\profiles\(user name)\Start menu\Programs\Startup
Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003:Documents and Settings\(user name)\Start
menu\Programs\Startup
2. Select the shortcut icon that you have created and click [Properties] from [File] menu.
8.3 Simple Status Notification 43
Page 44

3. Click the [Shortcut] tab and enter in the [Target], the File name, a space and then the
address of the printer you want to monitor.
Example: “C:\Program Files\Okidata\Simple Status Notification\
Ssn.exe” 129.249.242.179 ( indicates spacing)
4. Click [OK].
SSN Features
This section explains the overview of SSN features.
Simple Status Notification dialog box
You can specify the target printer and the monitoring interval here.
Enter IP
address of
the printer
This completes the installation. Restart Windows to confirm that SSN start
automatically.
If you are in TCP/IP environment,
you can search the printer
address from this dialog box.
The default value is
255.255.255.255, search from the
entire subnet connected to the
computer.
Set the monitoring interval of the printer
status in the range of 10-9999 seconds.
The defalut value is 60 seconds.
The [Simple Status Notification] dialog box is displayed during startup.
You can also display this dialog box after startup by right-clicking on the printer icon and
clicking [Simple Status Notification Dialog display] from the displayed menu. Click [Cancel]
to close this dialog box.
44 8 Network Utility Software
Page 45

Menu
After you have right-clicked on the printer icon, you can do the following on the displayed
menu.
Activate
OkiWebRemote
Display the [Simple Status
Notification] dialog box.
Show the printer
status
8.3 Simple Status Notification 45
Page 46

9 Precautions and Limitations
9.1 On Using TCP/IP
This section explains the precautions and limitations of using this printer with TCP/IP.
Setting Up
Setting Up the Printer
• Be very careful in setting up IP addresses which are controlled as an entire system.
Consult your network administrator before performing any setup on IP addresses.
• Depending on the network environments, some require subnet mask and gateway to be
set up. Consult your network administrator and set up the necessary items.
• If setting the port to [Enable] leads to insufficient memory, a message to that effect will be
displayed on the printer control panel and the port status may be set to [Disable]
automatically. If this happens, set the ports which are not in use to [Disable], change the
memory size or add more memory.
• Set up the size for the receive buffer memory as required by the environment.
If the size of the receive buffer memory is smaller than the file data to be received, data
will not be received.
Setting Up the Computer
• Be very careful in setting up IP addresses which are controlled as an entire system.
Consult your network administrator before performing any setup on IP addresses.
• Before performing any network setup (such as the IP address) to a host running under
NIS (Network Information Service), consult the NIS administrator.
When setting a UNIX workstation, note the following also:
• The setup procedures and commands may vary according to different versions of OS.
Refer to the manuals that came with the workstation for the details.
• To setup the printer, the user must be a superuser. Contact your network administrator
to perform the setup if you do not have the authority of a superuser.
• The print language/mode is determined by the printer model and configuration. Before
setting a UNIX workstation, check the available languages/modes.
• To specify multiple entries for the logical printer, make sure each printer entry is assigned
its own unique spool directory. If a single spool directory is used for multiple printer
entries, the printer select option may not function correctly.
46 9 Precautions and Limitations
Page 47

Switching the Power On/Off
Take note of the following when switching off the printer:
When LPD Spool Is Set to [Memory] (Spool Mode)
All the print data spooled in the printer memory, including print data which is being output,
will be deleted. When the printer is switched on again, the print data will not be found.
However, if the printer is switched off immediately after the print data has been sent, the
data may be stored on the computer. In this case, when it is switched on again, the stored
print data will be printed first even if new print data has been instructed.
When LPD Spool Is Set to [Hard Disk] (Spool Mode)
All the spooled print data, including print data which is being printed, will be saved. When
the power is switched on again, the stored print data will be printed first even if new print
data has been instructed.
When LPD Spool Is Set to [Off] (Non-spool Mode)
All the print data spooled in the printer receive buffer, including print data which is being
output, will be deleted. When the printer is switched on again, the print data will not be
found.
However, if the power is switched off immediately after the print data has been sent, the
data may be stored on the computer. In this case, when the power is switched on again, the
stored print data will be printed first even if new print data has been sent.
Printing From Windows
Take note of the following when printing from Windows:
• In the spool mode, if the print data is bigger than the remaining capacity of the hard disk
or the memory at the point of receiving, the data will not be received by the printer.
Note
• Some client computers may re-send immediately when the print data has exceeded the receiving
capacity. When this occurs, the client appears as if it has crashed.
To rectify this situation, the client computer must be stopped from sending print data.
• In the non-spool mode, printing will commence once data starts to be received by the
printer. Therefore, if the printer has accepted a print request from a computer, it will not
receive another print request from another computer.
• For PCL and DUMP, the specification for the number of copies is invalid.
Printing From UNIX
Take note of the following when printing from UNIX:
• In the spool mode, up to 32 files can be printed by one command. Files that come after
the 32nd file will be ignored. An instruction with more than 32 files will be treated by the
printer as a print request of up to 32 files.
• In the spool mode, if the print data is bigger than the remaining capacity of the hard disk
or the memory at the point of receiving, the data will not be received by the printer.
9.1 On Using TCP/IP 47
Page 48

Note
• Some client workstations may re-send immediately when the print data has exceeded the receiving
capacity. When this occurs, the client workstation appears as if it has crashed.
To rectify this situation, the client must be stopped from sending print data.
• In the non-spool mode, multiple files can be printed by issuing one command.
Furthermore, the number of files is not limited.
• In the non-spool mode, printing will commence once the data starts to be received by the
printer. Therefore, if the printer has accepted a print request from a client workstation, it
will not receive another print request from another client workstation.
• Options, such as -m option, not processed by the workstation which sends the print
instructions will not be valid.
• For PCL and DUMP, the specification for the number of copies is invalid.
Delete
• Print data which consists of multiple files sent in one print instruction, cannot be deleted
file by file. All the files will be deleted at one go.
• This command will become invalid if it is executed without options having been specified
or if there is no print data which matches the option.
• A workstation can only delete print data it has sent. It cannot delete print data sent by
other workstations.
• Print data which is in the process of printing may not be deleted.
Inquiry
• Long file names will be truncated.
• Up to 64 print instructions can be displayed.
• If two or more types of print languages/modes are set up on a single workstation, identical
job numbers may be displayed when an inquiry command is issued.
• In the non-spool mode, the client must be a Windows NT machine to use this option.
Others
• When the IP address or the computer name of a workstation is changed, the printer may
not process inquiries or deletions correctly. Make sure the printer is free of all spooled
data and switch off/on the printer.
Note
• The function to stop/eject print data spooled to the printer spool can be operated from the printer control
panel. Refer to the Setup and Quick Reference Guide for information on this operation.
48 9 Precautions and Limitations
Page 49

9.2 On Using SMB
This section explains the precautions and limitations of using this printer with SMB.
Setting Up
Setting Up the Printer
• Be very careful in setting up IP addresses which are controlled as an entire system.
Consult your network administrator before defining any IP address.
• Depending on the network environment used, it may be necessary to set up the subnet
mask and gateway. Consult your network administrator to set up the necessary items.
• If setting the port to [Enable] leads to insufficient memory, a message to that effect will be
displayed on the control panel and the port status may be set to [Disable] automatically.
When this happens, set the ports which are not in use to [Disable], change the memory
size, or install more memories.
• Specify the size for the receive buffer memory (SMB spool) as required by the
environment. If the size of the receive buffer memory (SMB spool) is smaller than the file
data to be received, the data may not be received.
Setting Up the Computer
• Be very careful in setting up IP addresses which are controlled as an entire system.
Consult your network administrator before defining any IP address.
• Before setting any network (such as the IP address) to a host being used under Network
Information Service (NIS), consult the NIS administrator.
Switching the Power On/Off
Take note of the following when switching off the printer:
When SMB Spool Is Set to [Memory] (Spool Mode)
All the print data spooled to the printer memory, including print data which is being output,
will be deleted. When the printer is switched on again, the print data will not be found.
However, if the printer is switched off immediately after the print data has been sent, the
data may be stored on the computer. In this case, when it is switched on again, the stored
print data will be printed first even if new print data has been specified.
When SMB Spool Is Set to [Hard Disk] (Spool Mode)
All the spooled print data, including print data which is being printed, will be saved. When
the power is switched on again, the stored print data will be printed first even if new print
data has been specified.
9.2 On Using SMB 49
Page 50

Printing
When SMB Spool Is Set to [Off] (Non-spool Mode)
All the print data spooled in the printer receive buffer, including print data which is being
output, will be deleted. When the printer is switched on again, the print data will not be
found.
However, if the power is switched off immediately after the print data has been sent, the
data may be stored in the computer. In this case, when the power is switched on again, the
stored print data will be printed first even if new print data has been specified.
Take note of the following when printing:
When SMB Spool Is Set to [Hard Disk] or [Memory] (Spool Mode)
If the print data is larger than the hard disk or the remaining memory capacity at the point
of receiving data, the data will not be received by the printer.
Note
• Some client computers may re-send immediately when the print data has exceeded the receiving
capacity. When this occurs, the client computer appears as if it has crashed. To rectify this situation, the
client computer must be stopped from sending print data.
When SMB Spool Is Set to [Off] (Non-spool Mode)
The printer will process print data as soon as data is being received. If the printer has
accepted a print request from a computer, it will not receive another print request from
another computer.
When the IP Address or Computer Name Is Changed
When the IP address or computer name of a computer is changed, it may not be able to
process enquiries or deletion requests from the printer correctly. Make sure the printer is
free of all spooled data and then switch off/on the printer.
Note
• The function to stop/eject print data spooled to the printer spool can be operated from the printer control
panel. Refer to the Setup and Quick Reference Guide for information on the operation.
When Printer Is in Offline Mode
If the printer receives print request from a computer when it is in offline mode, it will not
receive the data and an error message dialog box will be displayed on the computer.
However, with SMB, print data will be sent from the computer even in offline mode.
Deleting Jobs
For Windows NT 4.0, you cannot delete jobs if Service Pack 4 and other items noted above
are not installed. If you delete jobs while the computer is receiving data, an error message
will be displayed. When this happens, the Retry button on the error message is not effective.
50 9 Precautions and Limitations
Page 51

9.3 On Using NetWare
This section explains the precautions and limitations of using this printer with NetWare.
Setting Up the Printer
• If there is not enough memory after the port status is set to [Enable], the display might
display a message indicating insufficient memory and the port status might be set to
[Disable] automatically. When this happens, either set the port status of ports not in use
to [Disable] or increase the memory size.
• Take note of the following limitations on the names:
Item Limitation
Device Name Use only single-byte alphanumeric characters.
Cannot use mathematical symbol (+ =), dot (.), backslash (\), tilde (~).
There is no difference between underscore(_) and space( ).*
There is no difference between the capital and small letters of half-width
alphanumeric characters.
Tree Use only single-byte alphanumeric characters.
Cannot use mathematical symbol (+ =), dot (.), backslash (\), tilde (~).
There is no difference between underscore(_) and space( ).
There is no difference between the capital and small letters of half-width
alphanumeric characters.
File Server Name Use only single-byte alphanumeric characters.
Cannot use mathematical symbol (+ =), dot (.), backslash (\), tilde (~).
There is no difference between underscore(_) and space( ).*
There is no difference between the capital and small letters of half-width
alphanumeric characters.
Context Use only single-byte alphanumeric characters.
Cannot use mathematical symbol (+ =), dot (.), backslash (\), tilde (~).
There is no difference between underscore(_) and space( ).*
There is no difference between the capital and small letters of half-width
alphanumeric characters.
Print Server Name Use only single-byte alphanumeric characters.
Cannot use mathematical symbol (+ =), dot (.), backslash (\), tilde (~).
There is no difference between underscore(_) and space( ).*
There is no difference between the capital and small letters of half-width
alphanumeric characters.
*1: The following characters cannot be used in the present Netware file server when it is operating in
bindery mode but in order to standardise the directory service and the limitations, there is no
limitation at the printer without taking into consideration the type of operating mode:
semicolon (;), colon (:), asterisk (*), question mark (?), comma (,), double quotation ("), greater
than/less than symbol (<>), bracket ([ ]), pipe (|)
*2: Mathematical symbol (=) and dot (.) cannot be used as context and can be only used as delimiters.
1
1
2
1
9.3 On Using NetWare 51
Page 52

Setting Up the Server
For NDS
Take note of the following when setting up an environment in NDS:
Item For Pserver Mode
No. of file server Up to 16 servers per tree
No. of print queue Up to 48 queues
No. of notifying candidates Up to 48 users
No. of password characters Up to 32 characters*
*: If 33 or more characters are used to set the password, printing cannot be carried out.
For Bindery
Take note of the following when setting up an environment in bindery:
Item For Pserver Mode
No. of file server Up to 16 servers per tree
No. of print queue Up to 48 queues
No. of notifying candidates Up to 48 users
No. of password characters Up to 32 characters*
*: If 33 or more characters are used to set the password, printing cannot be carried out.
Printing
Workload of Bindery Reference Queue (for Directory Service/Pserver Mode)
This printer does not support bindery reference queue. As such, printing with bindery
reference queue is not allowed.
Using TCP/IP
Packet burst is invalid. The printing speed becomes lower than IPX/SPX.
Using NetWare 5.1
This printer does not support XeroxPrinterGateway.
Printing From Windows Application
For printing from a Windows application, note the following:
• If the setting of [Fast Print] is not valid, data may not be printed correctly. For printing from
a Windows application, set the machine to make [Fast Print] valid.
52 9 Precautions and Limitations
Page 53

About Printing Control
The following printer features are applicable when using NWADMIN or PCONSOLE:
Parameter Port status
Interrupt Print Job A
Stop Printer A
Pause Printer A
Activate Printer A
Paper Edge mark NA
Form feed NA
Printer rewind A
Mount paper A
Stop print server A
Note
• NA: Not Available; A: Available
9.3 On Using NetWare 53
Page 54

10 Troubleshooting
10.1 Using TCP/IP
This section provides information on the possible causes, verifying methods and
recommended actions pertaining to errors which may occur when the printer is used with
TCP/IP.
When Using Windows 95/Windows 98/Windows Me
Cause Treatment
The printer and the computer are
connected to different networks.
An error has occurred on the
network between the computer
and the printer. Connection cannot
be established.
The printer is switched off after the
print instruction has been sent
from the computer. Or the print
instruction is sent to the printer
which is switched off.
Print instructions from multiple
computers are sent to the printer
at the same time.
Printing files cannot be spooled
due to insufficient disk capacity of
the computer.
Status Display Unable to print (Network Error)
Verification Check with the system administrator of the network to verify
that the network connecting the computer and that connecting
the printer are linked by a router or a gateway.
Action Connect the printer directly to the network connecting the
computer.
Status Display Unable to print (Network Error)
Verification -
Action Ask the system administrator of the network to check the
network for errors.
Status Display Unable to print (Network Error)
Verification Check whether or not the printer is switched on.
Action Switch on the printer.
Status Display Unable to print (Network Error)
Verification -
Action - (Printing will be reprocessed automatically.)
Status Display Unable to print (Spool Error)
Verification Double click [My Computer] and right click the disk installed
with Windows 95/98/Me (e.g. C-drive).
Select [Properties] from the menu displayed and check the
free space available.
54 10 Troubleshooting
Action After erasing unnecessary files to increase the free space
available, select [Pause Printing] from the [Document] menu of
the printer window to enable printing to restart.
Page 55

When Using Windows NT 4.0/Windows 2000/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003
The Printer Is Not Printing
Cause Verification Action
Incorrect IP address. Ask the network administrator to check that
the IP address is correct.
If LPD spool is set to
[Memory], the print data
sent by the user in a single
print instruction has
exceeded the upper limit
of the receiving capacity
set up by the printer
control panel of the printer.
An irrecoverable error has
occurred during printing.
The data format of the
print data to be processed
by the printer and that
sent by the computer are
different.
Check the upper limit of the receiving
capacity from the printer control panel and
compare it with the print data which was sent
in the single print instruction.
Check the error message on the printer
control panel.
- Disable the output function of Ctrl-D.
Unable to Obtain the Desired Print Results
Cause Verification Action
The specified print
language and that of the
print data are different.
The printer driver for this
printer is not used. (The
printer driver of another
company is used)
Check the specified print language and that
of the print data.
Check that the printer driver which came with
this printer has been selected.
Set up the correct IP address for the printer.
1. If a single file of print data has exceeded
the upper limit of the receiving capacity,
split the file into smaller ones to keep
them below the upper limit of the
receiving capacity.
2. If multiple files have exceeded the upper
limit of the receiving capacity, reduce the
number of files which can be sent at one
go.
Switch off the printer, then switch it on again.
Specify the print language consistent with
that used in the print data.
Select the printer driver which came with this
printer. If it does not appear on the selection
list, install and select the printer driver.
If a printer driver from another maker is used,
the printer may not print properly.
10.1 Using TCP/IP 55
Page 56

When Using UNIX
The Printer Is Not Printing
Causes Verification Action
Incorrect IP address. Ask the network administrator to check if the
IP address is correct.
Error occurs on the
network connecting the
workstation and the
printer.
Unable to set the correct
printer entry on the
workstation.
The printer is in the offline
status.
If LPD spool is set to
[Memory], the print data
sent by the user in a single
print instruction has
exceeded the upper limit
of the receiving capacity
set up by the printer
control panel of the printer.
An irrecoverable error has
occurred during printing.
The data format of the
print job does not conform
to the printing
environment of the
workstation. (Print data
from the client contains
TBCP.)
The data format of the
print job does not conform
to the printing
environment of the
workstation. (Print data
from the client is of a
binary format.)
The printer has run out of
paper.
Activate the network test mode (ping) on the
workstation to check the communication
status.
Check and correct the printer entry settings
on the workstation. Check the /etc/printcap
file on the workstation or use the “lpstat”
command to troubleshoot.
Check whether “Off-line” is displayed on the
printer control panel.
Check the upper limit of the receiving
capacity from the printer control panel and
compare it with the print data which was sent
in the single print instruction.
Check the error message on the printer
control panel.
- Specify PSASC on the client side to print data
- Specify PSBIN on the client side for the
Check the message on the printer control
panel.
Set up the correct IP address for the printer.
Ask the network administrator to look into the
network failure.
Re-enter the correct printer entry.
Press the <ON LINE> button.
1. If a single file of print data has exceeded
the upper limit of the receiving capacity,
split the file into smaller ones to keep
them below the upper limit of the
receiving capacity.
2. If multiple files have exceeded the upper
limit of the receiving capacity, reduce the
number of files which can be sent at one
go.
Switch off the printer, then switch it on again.
containing TBCP by the PostScript language.
printer name on the remote host to print a
binary file in the PostScript language.
Load paper into the paper tray.
Unable to Obtain Desired Print Results
Causes Verification Action
The indicated print
language and the print
language used in the print
data are different.
56 10 Troubleshooting
Check that the print language specified is the
print language used in the print data.
Specify the print language consistent with
that used in the print data.
Page 57

10.2 Using SMB
This section provides information on the possible causes, verifying methods and
recommended actions pertaining to errors which may occur when the printer is used with
SMB.
The Printer Is Not Found
Cause Verification Action
The transport protocol
used by the client
computer and printer is
different.
There are multiple
browsers.
The network (subnet) is
wrong.
Name search of the host
name is not working
correctly (for TCP/IP)
The host name specified
already exists in the
printer.
On the client computer, you can find the
printer when searching it as another
computer ([Start] > [Find] > [Other computer])
but not when searching for it in the Network
Neighborhood.
(same as above) When there are multiple client computers
(same as above) When the printer and the client computer are
When specifying the printer IP address and
the relevant Host Name do not respond to the
PING command issued.
Check if Status of SMB on the [System
Settings List] indicates that the host name is
repetitive.
The Printer Is Not Printing
Specify similar transport protocol for SMB in
the printer and every client computer.
within the same workgroup, change the [Auto
Master Mode] in the [config.txt] file to [Off],
and then reboot the printer.
in different networks, contact your system
administrator.
Check the settings of the [config.txt] file
(WINS Primary Server, WINS Secondary
Server, Subnet Mask) with the settings on the
client computer (e.g. WINS, DNS, LMHOST).
Change the [Host Name] of the [config.txt] file
to another name not in use.
Or, change the host name used by
OkiWebRemote to another name not in use.
Or, reset the printer settings to default values.
Cause Verification Action
The printer is processing
print instructions from
other client computers.
(only for non-spool mode)
The printer has exceeded
the maximum number of
connections allowed.
Check if the printer is processing print
instructions. (An error message about
insufficient memory for waiting print jobs is
displayed.)
Check if the printer is processing requests
(e.g. print instruction, status enquiry) from
multiple client computers at the same time.
(An error message about remote computer
cannot be used is displayed.)
After the printer has processed the print
instructions, send a print job to the printer or
at the printer, change the mode to spool
mode.
Wait for a while, then send the print
instruction again.
Or, increase the value of [Maximum
Sessions] on the [config.txt] file, and then
reboot the printer.
10.2 Using SMB 57
Page 58

Cannot Delete Documents From the Printer Window
Cause Verification Action
Tried to delete all
documents displayed in
the printer window.
(only possible for printer
administrator)
The owner of the
document is not correct.
Service Pack 3 and above
is not installed.
(for Windows NT 4.0)
Check if you are trying to delete documents
from the Printer menu on the printer window.
Check if owner of the selected document is
similar to the name used for login in to
Windows.
Check the version of Service Pack displayed
when Windows NT 4.0 is activated.
Cannot Perform Auto Driver Downloading
Cause Verification Action
The auto driver
downloading feature is not
working.
Different types of printer
drivers are saved.
The printer driver is not
saved within two levels
from the drivers’ folder.
The printer driver is not
saved in a folder which
has more than eight
alphanumeric characters
in its name.
Check the setting of [Auto Driver Download]
in the [config.txt] file.
(only for printer administrator)
Check the printer type, and then check if the
correct printer driver is saved.
Check if the folder containing the printer
driver is within two levels from the drivers’
folder.
Open [driver.txt] of the [drivers] folder, and
check if there is a message about the folder
that has more than eight alphanumeric
characters in its name.
Select the document you want to delete, and
then select [Cancel Printing] from the
[Document] menu.
Log in to Windows again using the name of
the owner of the document, and then delete
the document.
Install Service Pack 3 or above.
Set [Auto Driver Download] to [Enabled] in
the [config.txt] file, and then reboot the
printer.
After saving the correct printer driver, reboot
the printer.
Save the printer driver inside a folder within
two levels from the drivers’ folder, and then
reboot the printer.
Change the folder name to a name with eight
alphanumeric characters, and then reboot the
printer.
58 10 Troubleshooting
Page 59

10.3 Using NetWare
This section provides information on the possible causes, verifying methods and
recommended actions pertaining to errors which may occur when the printer is used with
NetWare.
The Printer Is Not Printing
Cause Verification Action
The network component
(such as the hub) is not
compatible with the auto
setup of the frame type.
There is a breakdown in
the network from the
computer to the printer.
The user name and group
name are not registered in
User of the print queue.
Jobs cannot be sent to the
print queue.
Jobs cannot be sent to the
print queue.
The user name and group
name are not registered in
the print server user of the
print server.
The print queue to which
the job is sent is not
assigned to the printer.
The print queue has
exceeded the maximum
number of supported
queues of the printer (in
the print server mode).
The slave file server is not
set up (in the bindery
service mode).
Check if the data link lamp of the network
component board connected to the printer is
on.
Check if the frame type of the file server in
the network is the same.
Using NWADMIN from the computer, check if
the target printer object can be seen.*
Using NWADMIN from the computer, and
referring to the target queue object, check if
the user name and group name are
registered in User*.
Using PCONSOLE, check if [Yes] is set for
“User can register with the queue” at the
Current Queue Status of Print Queue
Information.
Using NWADMIN from the computer, check if
the operator flag is checked for Recognition
of the target print queue.*
Using NWADMIN from the computer, check if
the user name and group name are
registered with the User of the target print
server.*
Using NWADMIN from the computer, check if
the target printer is assigned to the serviced
printer in the list under User of the target print
server.*
Using NWADMIN from the computer, check if
the desired print queue is assigned to the
assigned print queue of the target print
queue.*
Using PCONSOLE from the computer, check
if the slave file server is registered in the
Service NetWare Server by the print server of
the Print Server Information. *
From the printer, set up the frame type
specified to the file server to which you want
to connect.
Switch the network cable between the
computer and printer that cannot be used for
transmitting.
1. Re-send the print jobs to a print queue
which is correctly registered with the user
name or group name at User of Print
Queue Information.
2. Using NWADMIN from the computer,
register the user name and group name
at User of Print Queue Information.*
Using PCONSOLE, set it to [Yes].
Using NWADMIN from the computer, check if
each item of the operator flag is checked for
Recognition of the target print queue. *
1. Re-send the print jobs to a print queue
which is correctly registered with the user
name or group name at User of Print
Server Information.
2. Using NWADMIN from the computer,
register the user name and group name
at User of the target print server.*
1. Re-send the job to a print queue
registered with user name and group
name at User of Print Server
Information.*
2. Using NWADMIN from the computer,
check if the user name and group name
are registered at User of the target print
server.*
Re-send the job to a print queue assigned to
the printer.*
Using PCONSOLE from the computer, reflect
the setting parameter after having registered
the slave file server.
10.3 Using NetWare 59
Page 60

Cause Verification Action
The print type is incorrect. Using PCONSOLE from the computer, check
if Printer:
Parallel, Port: LPT1, Position: Auto mode
(local) is defined for [Printer Information] >
[Printer] > [Printer xxx Environment].*
The setting for the slave
file server is incorrect (in
the bindery service mode).
The number of paper
definitions specified at the
print server is not the
same as that of paper
definitions set at the print
queue.
Print job data format and
computer print
environment setting are
not similar.
The level setting for the
IPX checksum is incorrect.
The level setting for the
NCP packet signature is
incorrect.
The default printer name
is incorrect.
The directory tree name is
not set.
Context is not set. Print the [System Settings List] and check if
Connected to another
printer object.
NetWare port cannot be
activated.
File server is down. Search for the target file server in Network
There are printers with the
same device name on the
network.
Network port is not
activated.
* Refer to NetWare online documentation for details on the way to set and check.
Using PCONSOLE from the computer, check
if the printer type has been set up as Defined
at the [Print Server Information] > [Printer] >
[Printer xxx Environment Setting].*
Using PCONSOLE from the computer, check
if the number of paper definitions specified at
the print server is same as that of paper
definitions set at the print queue.*
- When printing bindery-format file using
At the console screen of the file server,
execute a set command and check if the IPX
checksum is set to level 2.
At the console screen of the file server,
execute a set command and check if the NCP
packet signature is set to level 3.
Print the [System Settings List] and check the
last six characters (3 bytes) of the MAC
address.
Print the [System Settings List] and check if
the tree name is specified.
the context is specified.
Using NWADMIN from the computer, check if
the object is correctly assigned by the layout
information of the desired print server.*
Print the [System Settings List] and
the NetWare port is activated.
Neighborhood on Windows.
Switch off the printer, using NWADMIN from
the computer, check that the status of the
concerned printer object is job waiting.
Print the [System Settings List], check if the
network number when using IPX/SPX is at
00000000 (NetWare server down). Also,
check if the IP address when using TCP/IP is
at 0.0.0.0 (fixed IP not set or address supply
server (DHCP) is down).
check if
Using PCONSOLE from the computer, set
Printer: Parallel, Port: LPT1, Position: Auto
mode (local) and reflect the parameter.*
If it is not [Defined], change it to [Defined] and
reflect the parameter.*
Using PCONSOLE from the computer,
specify the same number of paper definitions
at the print server as that of paper definitions
set at the print queue.*
PostScript language, enable TBCP at the
printer. When using Windows at the
computer, set do not output Ctrl-D.
At the console screen of the file server, enter
the following command and set the IPX
checksum to level 0 or 1.
set Enable IPX Checksum=X
(X: 0 or 1)
At the console screen of the file server, enter
the following command, and after setting the
NCP packet signature to either level 0, 1 or 2,
restart the file server:
set NCP Packet Signature Option=X (X: 0,
1 or 2)
1. Set up a printer name which uses the
2. Set up any printer name except the
Set the tree name.
Set the context.
1. Using the NWADMIN from the
2. Using OkiWebRemote from the
Activate the NetWare port.
Activate the file server.
Using the NWADMIN from the computer, set
another device name.
For IPX/SPX, activate NetWare server.
For TCP/IP, set the fixed IP address or
activate the address supply server (DHCP).
correct MAC address.
default.
computer,
set the file server name, tree, context,
active mode correctly.
computer, set the file server name, tree,
context, active mode correctly.
60 10 Troubleshooting
Page 61

When “Please reboot printer” Appears
Cause Verification Action
An error occurs in the
NetWare interface.
- Switch off the printer, then switch it on again.
Unable to Obtain Desired Print Results
Cause Verification Action
The print language of the
print job and that set up at
the printer are different.
Check the print language of the printer. Set the same print language for the print job
No Notification
This section provides information on the possible causes, verifying methods and
recommended actions when there are no messages on the computers which have been
sent print instructions.
No Notification of Printer Errors
Cause Verification Action
and the printer.
Not registered in the Notify
Candidate List of the print
server.
Using PCONSOLE from the
if the user name and
registered in [Print
[Printer] > [Printer
> [Notify].
group name are
Server Information] >
xxx Environment Settings]
No End-of-job Notification
Cause Verification Action
When sending jobs from
the computer, the NOTIFY
option has not been
specified.
The NetWare CASTOFF
utility is executed on the
computer.
Check if the NOTIFY option is specified when
jobs are sent.
- Execute the NetWare CASTON utility on the
10.4 Using EtherTalk
This section provides information on the possible causes, verifying methods and
recommended actions pertaining to errors which may occur when the printer is used with
EtherTalk.
computer, check
Register the user name and group name in
[Notify].
When jobs are sent, specify the NOTIFY
option.
computer.
10.4 Using EtherTalk 61
Page 62

Problem Treatment
The name (or the default name) of
the printer has been changed.
The printer does not appear in
Chooser.
Unable to obtain desired print
results.
Cause The AppleTalk function of the printer changes the printer name
if it detects that a printer of the same name exists on the
network.
Verification Check Chooser to confirm that the printer name has been
changed.
Action Change the name of the printer or change the name of the
other printer to avoid duplicate printer names on the network.
Cause 1 In Chooser, only the NBP entity name of which entity type is
LaserWriter is displayed.
The printer is set up as a slave of the Apple Share Print Server
or the Windows NT Server and the NBP entity name of the
printer has been changed from LaserWriter.
Verification 1 Use of a network management application software, such as
Apple InterPole, and check that the type of the NBP entity
name of the printer has been changed from LaserWriter.
Action 1 If the type of NBP entity name of the printer has been changed
from LaserWriter, the printer cannot be selected in the
Chooser. If the printer must be selected, open the printer using
the Apple Share Print Server or the Windows NT Server.
Cause 2 The Macintosh printer driver searches for a printer with the
printer name specified in the Chooser and the zone name of
AppleTalk.
If the network is not connected correctly, the printer cannot be
found.
Verification 2 Use of a network management application software, such as
Apple InterPole, and check that the printer exists on the
network.
Check that the network is connected correctly.
Action 2 If the printer cannot be found on the network, the printer may
be off or the network cable may be faulty.
If the printer is on and the network cable normal, contact our
Printer Support Desk.
Cause 1 The print language of the printer and that of the printer driver
are different.
Verification 1 Check the print language set up for the printer and that for the
printer driver for Macintosh.
Action 1 Ensure that PostScript and AdobePS are set up as the print
language for the printer and printer driver respectively.
If the print language of the printer is the dump mode, the print
data sent from the Macintosh will be output in hexadecimal
notations.
Cause 2 The printer driver which came with the printer is not set up on
the Macintosh. A printer driver of another maker has been
used instead.
Verification 2 Check the installation procedure for the printer driver which
came with the printer again and confirm that the printer driver is
installed on the Macintosh.
Check that the printer driver which came with the printer
appears in the Chooser.
Action 2 If garbled characters are still printed after the printer driver for
the printer has been selected, contact our Printer Support
Desk.
If a printer driver of another maker is used, the printer may not
print properly.
62 10 Troubleshooting
Page 63

Problem Treatment
The printer is not connected. Cause 1 On the Macintosh, the printer is not selected correctly in the
Chooser. Or, the printer is processing another job.
Verification 1 Check that the printer is selected correctly on the Macintosh.
If the printer is processing another job, the job must be
completed before the printer can be connected.
Action 1 If the printer is still not connected though it is selected
correctly and is not processing another job, check the
following causes.
Cause 2 The EtherTalk port of the printer is set to [Disable].
Or, the Start/Stop setting for EtherTalk has been set to Off by
the PostScript command.
Or, the printer is in the offline status.
Verification 2 Check that the port used is set to [Enable] and that the Start/
Stop setting is set to [Start].
Check whether “Off-line” is displayed on the printer control
panel.
Action 2 If the printer still cannot be connected although all the above
conditions are normal, contact our Printer Support Desk.
Although it is connected, the printer
does not print.
“Please reboot printer” is displayed
on the printer control panel.
Cause 1 The printer is in the offline status.
Verification 1 Check whether “Off-line” is displayed on the printer control
panel.
Action 1 Press the <ON LINE> button.
Cause 2 The print language of the printer and that of the printer driver
are different.
Verification 2 Check the print language set up for the printer and that for the
printer driver for Macintosh.
Action 2 If the print language of the printer and that of the printer driver
are different, set the same language for them. If the problem
remains, check the following causes.
Cause 3 After the Macintosh was connected to the printer, the power to
the printer was shut off.
Or, paper jam has occurred in the printer.
Or, the network is faulty.
Verification 3 Check that the printer is switched on.
Select the printer again from Macintosh and reprint.
Action 3 If the problem remains, contact our Printer Support Desk.
Cause The AppleTalk function of the printer has failed.
Verification Switch off the printer, then switch it on again.
Action If “Please reboot printer” still appears on the printer control
panel, contact our Printer Support Desk.
10.4 Using EtherTalk 63
Page 64

A Appendix
A.1 Using Telnet
You can set the settings about the port and protocol for each network by using the Telnet.
Settings for Using the Telnet
Here explains the environment to set the printer by using the Telnet and the procedure to
set the Telnet.
Clients
Telnet client compatible with VT100 (such as Microsoft Windows telnet or SunOS telnet)
Settings on the Printer
When using Telnet, it is required that the printer’s IP address is set and the [Telnet] port is
set to [Enable] (default: [Enable]).
Using the Telnet
Here, we use the Solalis 2.x as an example.
1. Start the Telnet and log in. (Example: when the printer’s IP address is set to
“192.168.1.100”)
When you log in successfully, the main menu is displayed.
% telnet 129.168.1.100
login: root
‘root’ user needs password to login.
password:
User ‘root’ logged in.
Unable to enter Administrator Mode. Control panel in use or job
in progress
No. Message Value (level.2)
------------------------------------------------ ---------------
1 : Machine Details
2 : Port Status
3 : Protocol Settings
4 : Display status
5 : IP Filtering Setup
6 : Internet Services Settings
98 : Set default (Network)
99 : Exit setup
Please select (1 - 99)?
64 A Appendix
Note
• When logging in as “root” (administrator), you can check and change the settings. In that case, you need
to input the password. The default password is set as the last 6 digits of the MAC address. The
password can be changed in the [Protocol Settings] menu.
• When logging in to the Telnet as a user other than “root”, you can only confirm the settings.
• You cannot log in to the Telnet as “root” while operating the printer’s control panel or executing a print
job.
Page 65

2. Input the number of the item to set. Detailed information about the selected item is
displayed.
Please select (1 - 99)? 2
No. Message Value (level.2)
------------------------------------------------ -------------------
1 : AppleTalk : Enable
2 : SMB : Enable, TCP/IP, NetBEUI
3 : NetWare : Enable, TCP/IP IPX/SPX,
4 : LPD : Enable
5 : SNMP : Enable, UDP, IPX
6 : IPP : Enable
7 : Port9100 : Enable
8 : UPnP : Enable
9 : Receive Mail : Enable
10 : Mail Notification : Enable
11 : Internet Services : Enable
12 : Telnet : Enable
99 : Back to prior menu
Please select (1 - 99)?
Note
• Each menu is configured with some levels. Set the settings by selecting the menus and items of each
level. For details about the items of each menu, refer to “The Items That Can Be Set Using the Telnet”
(P. 66).
3. After completing the settings, select [Back to prior menu] to return to the main menu.
Please select (1 - 99)? 99
No. Message Value (level.2)
------------------------------------------------ ---------------
1 : Machine Details
2 : Port Status
3 : Protocol Settings
4 : Display status
5 : IP Filtering Setup
6 : Internet Services Settings
98 : Set default (Network)
99 : Exit setup
Please select (1 - 99)?
4. Select [Exit setup] in the main menu, and then select [Save and Reset].
When the items needed to restart the printer are changed, the printer restarts.
Please select (1 - 99)? 99
No. Message Value (level.2)
------------------------------------------------ ---------------
1 : Save and Reset
2 : Exit without Saving
99 : Back to prior menu
Please select (1 - 99)? 1
Connection closed by foreign host.
%
A.1 Using Telnet 65
Page 66

Note
• To exit the Telnet without saving the settings you have made, select [Exit without Saving].
The Items That Can Be Set Using the Telnet
Menu Description
Machine Details You can confirm and change the settings of the details of the printer.
The following items can be set:
• Machine Model
•Serial No.
• Machine Name
•Location
• Contact Person
• Administrator E-mail Address
• Machine Mail Address
• Comment
Port Status You can confirm and change each port status settings.
Protocol Settings You can confirm and change the protocol settings.
The following items can be set:
•TCP/IP
•LPD
•SNMP
•IPP
•Port9100
•UPnP
• HTTP
• Telnet
Display Status The TCP/IP status is displayed.
IP Filtering Setup You can confirm and set the IP filter setting and permitted IP address list.
The following items can be set:
• IP Filter
• IP Filter (n)
• Permitted IP Address
•IP Mask
Internet Services
Settings
Set Default
(Network)
You can set the Internet Services. The following items can be set:
• Auto Refresh Interval
• Administrator Password
Reset the settings to the default settings.
This menu can be used when you log in as “root”.
66 A Appendix
Page 67

A.2 Setting IP Address
When the printer is connected to the network, it retrieves the IP address automatically from
the DHCP server once it is switched on.
If the DHCP server is not available or not in use, use one of the following methods to retrieve
and set the IP address.
• Set the IP address from the control panel
• Use the IP address Setup Tool in the CD-ROM bundled with this printer.
Important
• When using the DHCP server, use WINS (Windows Internet Name Service) server at the same time.
• The address information can also be retrieved automatically via the BOOTP or RARP servers. For such
cases, change the [Get IP Address] selection on the control panel to [BOOTP] or [RARP].
• Depending on the network environment, you may need to set the subnet mask and gateway address.
• Please check with your network administrator if you have any questions concerning your network
environment.
Refer to
• Details on retrieving IP address: Reference Guide, Chapter 4 “Admin Menu” (P. 64, 74, 85)
• IP Address Setup Tool: Network Print Environment User Guide, Chapter 8
• Web browser: Reference Guide, 6.3 “Setting Printer Configurations Via Web Browser” (P. 119)
Note
• You can change the IP address using a web browser.
• You can check the current IP address, subnet mask and gateway address settings from the [System
Settings List]. Refer to Reference Guide, 6.2 “Printing Reports/Lists” (P. 116) on how to print the [System
Settings List].
This section explains how to set IP address from the control panel.
Note
• If you have made a mistake when operating the control panel, press the <MENU> button to restart.
Setting IP Address
1. Press the <MENU> button to display the Menu screen.
2. Press the < > or < > button until [Admin Menu] is displayed, then press the < >
button.
3. Check that [Network/Port] is displayed, then press the < > button.
4. Press the < > or < > button until [TCP/IP Settings] is displayed, then press the < >
button.
5. Check that [Get IP Address] is displayed, then press the < > button.
6. Press the < > or < > button until [Manual] is displayed, then press the <FEED/
SELECT> button.
7. Proceed to step 10 when the IP address input screen is displayed.
Proceed to step 8 when [Manual*] is displayed.
8. Press the < > button to return to [Get IP Address].
9. Press the < > button to display [IP Address], then press the < > button.
10. Press the < > < > < > < > buttons to enter the IP address, then press the
<FEED/SELECT> button. To set the subnet mask and gateway address, press the < >
button and proceed to "Setting Subnet Mask/Gateway Address" (P. 68).
11. Press the <MENU> button. The printer reboots.
A.2 Setting IP Address 67
Page 68

Setting Subnet Mask/Gateway Address
Note
• When “Ready to print” is displayed, follow steps 1 to 4 in the previous section, then proceed to the next
step.
1. When [Get IP Address] or [IP Address] is displayed, press the < > or < > button to
display [Subnet Mask], then press the < > button.
2. Press the < > < > < > < > buttons to enter the subnet mask, then press the
<FEED/SELECT> button.
3. Press the < > button to return to [Subnet Mask].
4. Press the < > or < > button until [Gateway Address] is displayed, then press the
< > button.
5. Press the < > < > < > < > buttons to enter the gateway address, then press the
<FEED/SELECT> button.
6. Press the <MENU> button. The printer reboots.
68 A Appendix
Page 69

Index
A
AppleTalk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
auto driver downloading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
C
Checking Printer Status With SSN . . . . . . . . 42
config.txt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
E
EtherTalk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9, 40, 61
H
HP-UX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29, 33
I
IPP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9, 13
IPX/SPX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
L
LPD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
lpr Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
M
Simple Status Notification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
SMB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9, 16, 49, 57
Solaris . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28, 33
spool mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47, 49, 50
SSN Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
SunOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27, 29
T
TCP/IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9, 25, 46, 54
U
UNIX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25, 56
UNIX Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
W
Workgroup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Macintosh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
N
NetBEUI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
NetWare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9, 23, 51, 59
NWADMIN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24, 53, 59
O
OKI LPR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
P
PCONSOLE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24, 53, 59
Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
EtherTalk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
IPP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
LPD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
NetWare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Port9100 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
SMB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Port9100 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
AppleTalk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
IPX/SPX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
NetBEUI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
TCP/IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
S
Setting Gateway Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Setting IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Setting Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Index 69
Page 70

B6200/B6300 series
central house
balfour road, hounslow
TW3 1HY
united kingdom
tel +44 (0) 20 8219 2190
Fax +44 (0) 20 8219 2199
07047501 Iss.02
 Loading...
Loading...