Oakton C401, C301, C201, C101, C102 Instruction Manual
...
Instruction Manual
gyM
sy...
C401 / 301 / 201 / 101 / 102 / 103 / 104 / 105
Waterproof Portable Colorimeter
68X357704
Rev 2 05/08
Technolo
adeEa
Part of Thermo Fisher Scientific


Preface
This manual functions in two ways: first as a step by step guide to help
you operate the waterproof C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105
Colorimeter; second, it serves as a handy reference guide.
It contains basic instructions that you must follow during the operation,
care and maintenance of the instrument. The safety protection provided by
this equipment may be impaired if it is used in a manner not described in
this manual. It is recommended that all operators should read this manual
prior to working with this instrument.
Eutech Instruments/ Oakton Instruments cannot accept any responsibility
for damage or malfunction to the meter caused by improper use of the
instrument.
The information presented in this manual is subject to change without
notice as improvements are made, and does not represent a commitment
on the part of Eutech Instruments Pte Ltd/ Oakton Instruments.
Note: Eutech Instruments Pte Ltd/ Oakton Ins truments reserves the
right to make improvements in design, construct ion, and appe arance
of our products without notice.
Copyright © 2004 All rights reserved.
Eutech Instruments Pte Ltd
Oakton Instruments
Rev. 2 05/08


TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 UNPACKING C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 COLORIMETER AND ACCESSORIES............................. 2
1.2 DISPLAY................................................................................................................................................. 3
1.3 KEYS AND FUNCTIONS ............................................................................................................................4
1.4 BATTERY INSTALLATION.......................................................................................................................... 5
2 MEASUREMENT....................................................................................................................... 6
2.1 GENERAL INFORMATION.......................................................................................................................... 6
2.2 PREPARATION OF SAMPLE VIAL .............................................................................................................. 7
2.3 MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE .................................................................................................................. 7
2.4 CHLORINE, FREE & TOTAL (0 – 6PPM CL2)............................................................................................... 9
Chlorine, Free & Total Measuring Hints & Tips........................................................................................... 11
2.4.1 Sample Collection..........................................................................................................................11
2.4.2 Sample Measurement.................................................................................................................... 11
2.4.3 Interferences.................................................................................................................................. 11
2.4.4 Accuracy Check / User Calibration................................................................................................ 13
2.4.5 Chemistry....................................................................................................................................... 14
2.5 CYANURIC ACID (5-90 PPM).................................................................................................................. 15
Cyanuric Acid Measuring Hints & Tips........................................................................................................ 17
2.5.1 Sample Collection..........................................................................................................................17
2.5.2 Sample Measurement.................................................................................................................... 17
2.5.3 Interferences.................................................................................................................................. 17
2.5.4 Accuracy Check / User Calibration................................................................................................ 17
2.5.5 Chemistry....................................................................................................................................... 18
2.6 PH (5.9-8.2 PH UNITS).......................................................................................................................... 19
pH Measuring Hints & Tips.......................................................................................................................... 21
2.6.1 Sample Collection..........................................................................................................................21
2.6.2 Sample Measurement.................................................................................................................... 21
2.6.3 Interferences.................................................................................................................................. 21
2.6.4 Accuracy Check / User Calibration................................................................................................ 21
2.6.5 Chemistry....................................................................................................................................... 22
2.7 CHORINE DIOXIDE (0 – 11.4 PPM CLO2) ................................................................................................23
Chlorine Dioxide Measuring Hints & Tips....................................................................................................25
2.7.1 Sample Collection..........................................................................................................................25
2.7.2 Sample Measurement.................................................................................................................... 25
2.7.3 Interferences.................................................................................................................................. 25
2.7.4 Accuracy Check / User Calibration................................................................................................ 27
2.8 BROMINE (0 – 13.5PPM BR2)................................................................................................................. 29
Bromine Measuring Hints & Tips.................................................................................................................31
2.8.1 Sample Collection..........................................................................................................................31
2.8.2 Sample Measurement.................................................................................................................... 31
2.8.3 Interferences.................................................................................................................................. 31
2.8.4 Accuracy Check / User Calibration................................................................................................ 33
2.9 OZONE (0 – 4.1 PPM O3)....................................................................................................................... 34
Ozone Measuring Hints & Tips.................................................................................................................... 36
2.9.1 Sample Collection..........................................................................................................................36
2.9.2 Sample Measurement.................................................................................................................... 36
2.9.3 Interferences.................................................................................................................................. 36
2.9.4 Accuracy Check / User Calibration................................................................................................ 38
3 CALIBRATION......................................................................................................................... 39
3.1 CALIBRATION PROCEDURE.................................................................................................................... 39
3.2 CHLORINE, FREE & TOTAL, CHLORINE DIOXIDE, BROMINE AND OZONE .................................................. 40
3.3 CYANURIC ACID.................................................................................................................................... 43
3.4 PH .......................................................................................................................................................46
3.5 RESTORING FACTORY CALIBRATION ...................................................................................................... 49
4 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE.................................................................................................51
5 ROUTINE MAINTENANCE...................................................................................................... 52
5.1 VIALS – HANDLING, CLEANING AND CARE.............................................................................................. 52
6 ACCESSORIES .......................................................................................................................53
7 SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................................................... 54
8 WARRANTY............................................................................................................................. 56
9 RETURN OF ITEMS.................................................................................................................56


C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter
Introduction
1 INTRODUCTION
Thank you for selecting the waterproof portable C401/301/201/101/
102/103/104/105 Colorimeter. Depending on the model selected, the
C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter series allows you to
measure up to seven parameters - namely the Free Chlorine, Total
Chlorine, Cyanuric Acid, pH, Chlorine Dioxide, Bromine and Ozone of an
aqueous sample in the field. You have one of the following models:
• C101: pH measurement
• C102: Cyanuric Acid measurement
• C103: Chlorine Dioxide measurement
• C104: Bromine measurement
• C105: Ozone measurement
• C201: Free Chlorine and Total Chlorine measurement
• C301: Free Chlorine, Total Chlorine and pH measurement
• C401: Free Chlorine, Total Chlorine, Cyanuric Acid and pH
measurement
1
C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter
Introduction
1.1 Unpacking C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter
and Accessories
The table below indicates the items that you should find in your
Colorimeter shipment.
Item
1. Colorimeter with 4 “AAA”
batteries
2. Instruction Manual
3. Instrument Carrying Case
4. Empty Vial
5. pH Indicator (Phenol Red)
Kit
6. Cyanuric Acid Reagent Kit 1
7. Chlorine, Free (DPD)
Reagent Kit
8. Chlorine, Total (DPD)
Reagent Kit
9. Chlorine Dioxide (Glycine)
Reagent Kit
Qty C401 C301 C201 C101 C102 C103 C104 C105
1
1
1
4
1
1
1
1
●
● ● ● ● ● ●
●
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ●
●
● ● ●
● ● ●
●
●
●
●
● ●
Remove C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter from the
packing carton. Carefully inspect all items to ensure that no visible
damage has occurred during shipment. If the items you received do not
match your order, please contact your nearest distributor immediately.
WARNING: Extra care should be taken when unpacking, opening, and
handling the sample vials. Surface scratches or finger smudges on t he vial
surface may cause measurement errors. Handle these items by their caps
only.
Batteries provided with the meter package are to be installed prior to use.
See Section 1.4 Battery Installation on page 5.
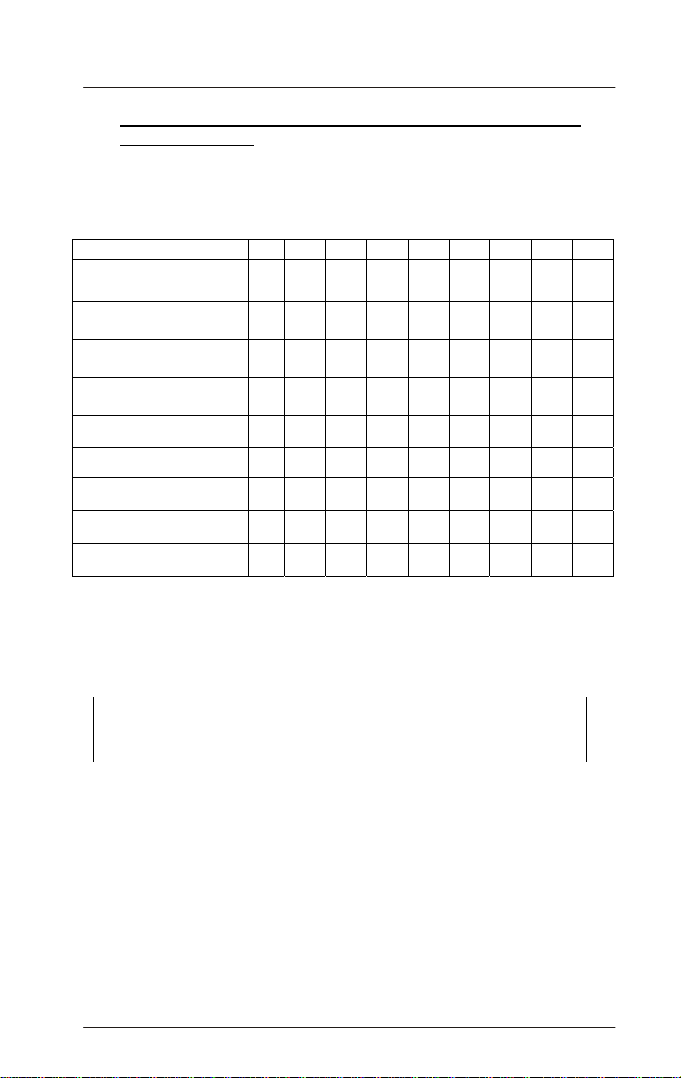
In the next page, Figure 1 depicts the meter. The three main components
of the instrument are the sample well, the display, and the keypad. The
following sections will describe the functionality of the display and the
keypad. The proper use of the instrument will be discussed in later
sections.
2
Sample Well
C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter
Introduction
Sample Vial
Liquid Crystal
Display
Meter Index
Marking
Keypad
Figure 1: Parts of C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter
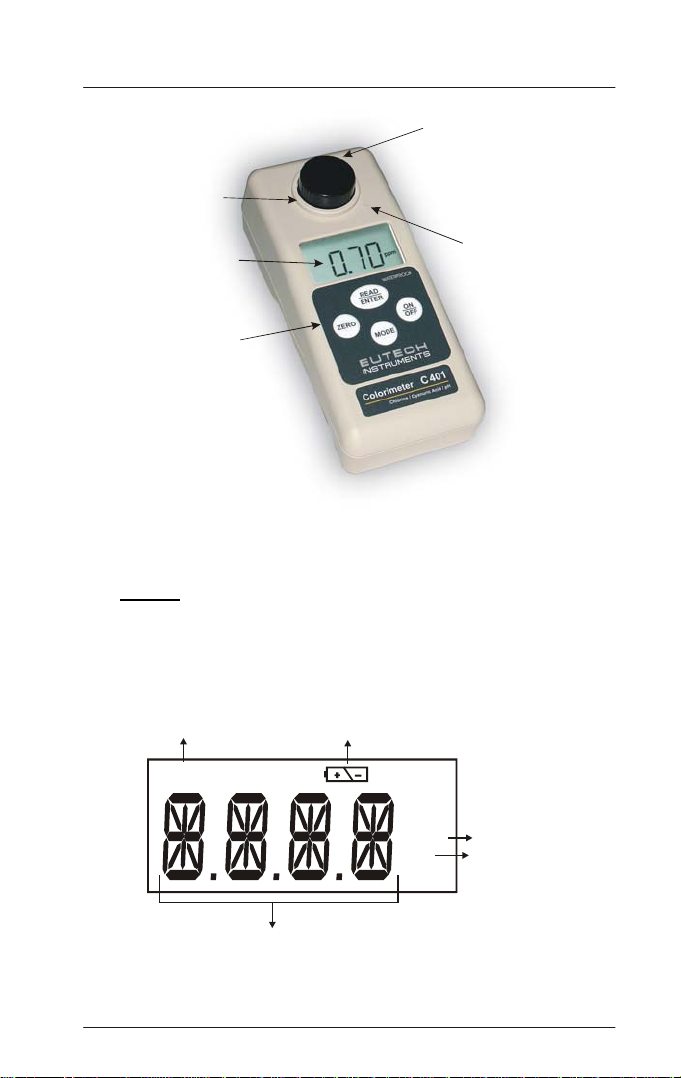
1.2 Display
All the LCD segments and annunciators that can appear on the display are
shown in Figure 2. The display is used for reporting the colorimeter
reading, communicate error messages and provide guidance for the
operation of the instrument.
Calibration Mode
Annunciator
Battery Indicator
CAL
ppm
pH
14-segment Liquid Crystal Display
Figure 2: Customized LCD when switched on
3
Units of
Measure
C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter
Introduction
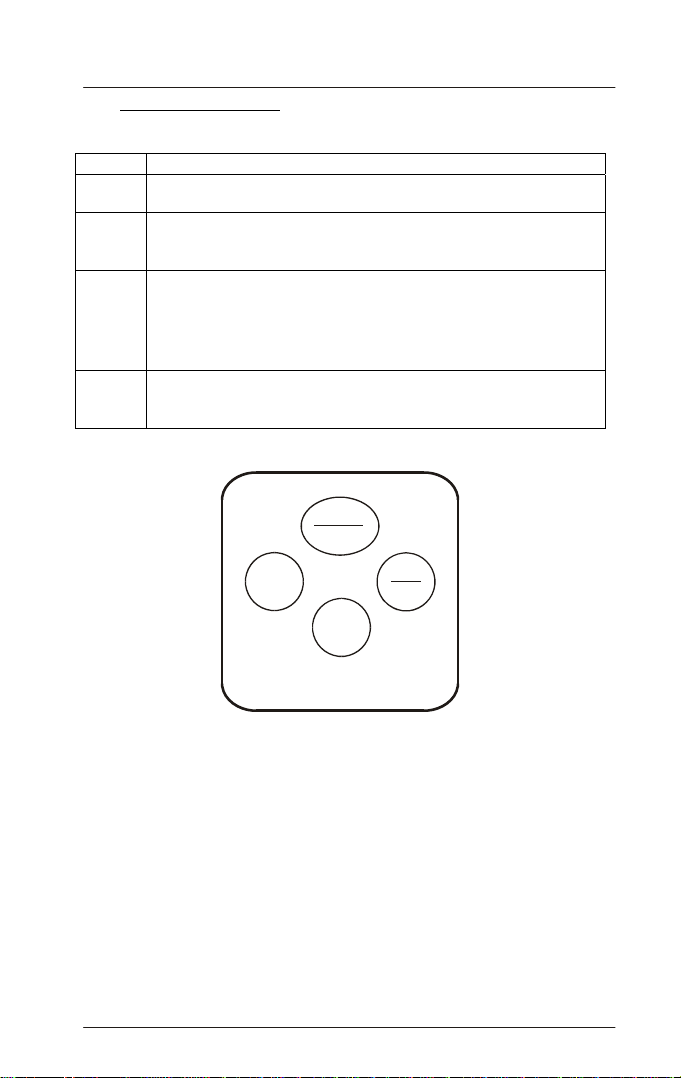
1.3 Keys and Functions
The keypad has four keys: ON/OFF, MODE, ZERO and READ/ENTER.
Keys Functions
ON/OFF
MODE
ZERO
READ /
ENTER
- Powers on and shuts off the meter. With the auto switch-off feature
the meter automatically shuts off 10 minutes after last key press.
- Selects the test to be performed.
- Selects the calibration point in an incremental circular manner during
calibration.
- Blanks the instrument (sets the meter to zero) before chemical
reagent is added.
- Initiates the calibration mode when used with the ON/OFF key.
- Aborts the calibration process without saving.
- Exits the calibration mode.
- Initiates the measurement of the sample after the chemical reagent
has been added.
- Confirms the test selection.
WATERPROOF
READ
ENTER
ZERO
ON
OFF
MODE
Figure 3: C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Keypad
4
C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter
Introduction
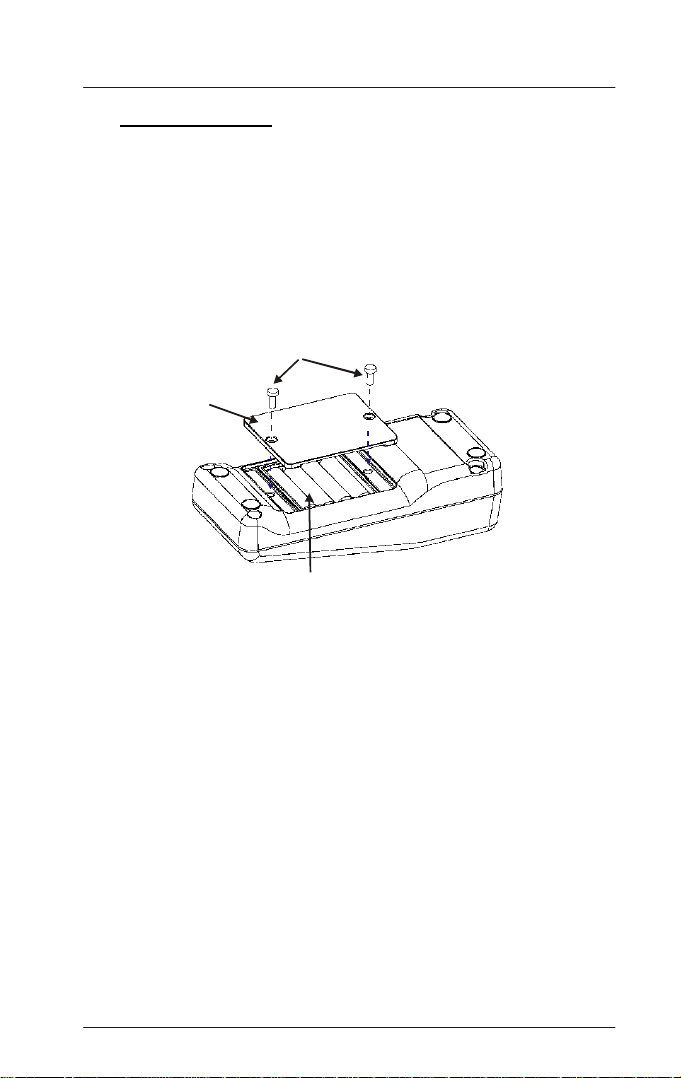
1.4 Battery Installation
Four AAA-sized batteries are included in your meter’s packaging:
1. Use a Philips screwdriver to remove the two screws holding the
battery cover. See Figure 4 : Battery Installation.
2. Remove the battery cover.
3. Insert the batteries. Follow the diagram inside the cover for correct
polarity.
4. Replace the battery cover onto its original position using the two
screws removed earlier.
5. The meter is now ready to operate.
Philips Screws
Battery cover
Four 'AAA'-sized batteries
Figure 4 : Battery Installation
NOTE: Dispose used batteries in accordance with your local regulations.
5
C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter
Measurement
2 MEASUREMENT
2.1 General Information
The waterproof C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter allows
you to measure up to seven parameters - namely the pH, Cyanuric acid,
Free Chlorine, Total Chlorine, Chlorine Dioxide, Bromine and Ozone of a
sample and reports the results in appropriate units (ppm or pH). Each
specific measurement has its own range as listed in the specifications.
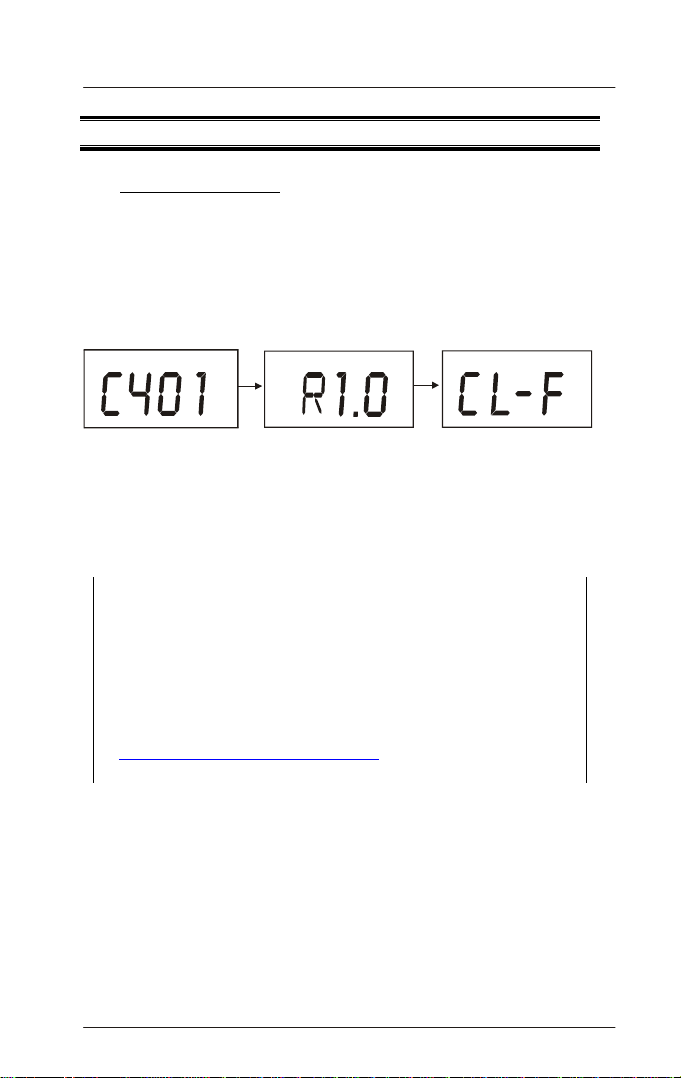
The meter will go through a power sequence as shown below.
Meter’s Model Number
Figure 5: Example of C401 Colorimeter power up sequence
Meter’s Revision Number
Measurement M ode Selecti on
An accurate colorimeter measurement depends on good measurement
techniques. Factors such as clean sample vials, positioning of vial in the
sample well, using a vial with a light shield cap, meter calibration, handling
of meter, and others, have to be taken into consideration.
NOTE: Do not pour liquid directly into the sample well of t he instrument.
Always use a vial. The instrument will only accurately measure the sample
when vials sealed with the black caps are used. The black cap serves as
both seal and a light shield.
NOTE: Do not attempt to clean the sample well. The optics may be
damaged.
NOTE: This instrument is designed to measure solutions containe d in the
custom made glass vials and therefore the use of other type of sample vials
or sample cells may result in inaccurate measurements.
NOTE: Reagents’ MSDS can be obtained from
http://www.eutechinst.com/techtips/msds.htm
6
C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter
p
Measurement
2.2 Preparation of Sample Vial
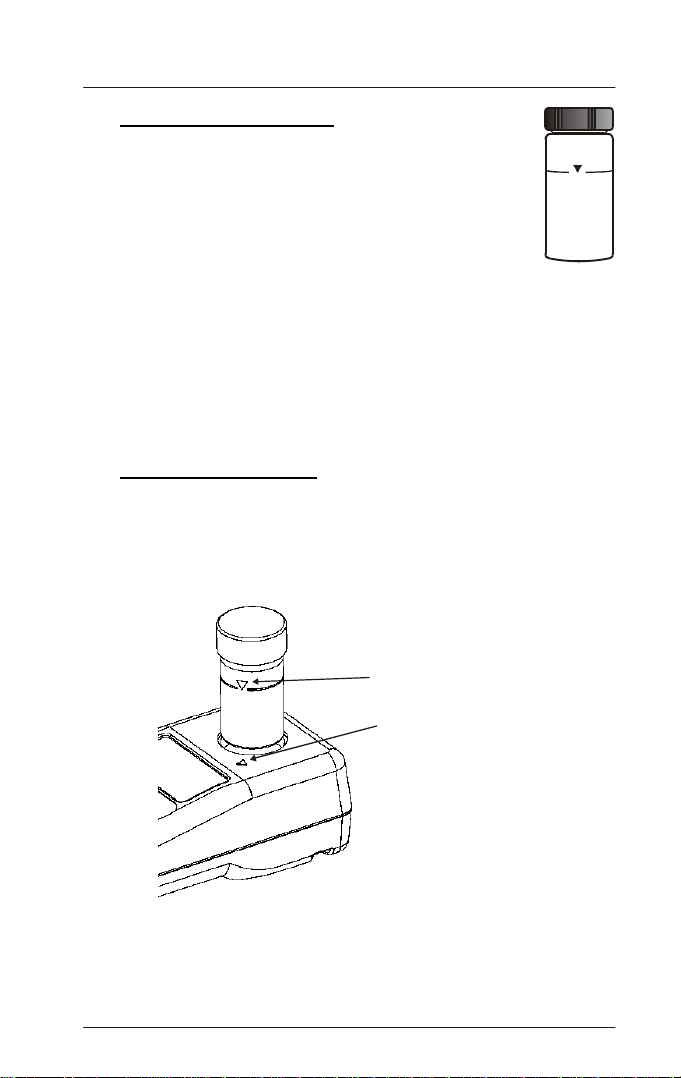
1. Obtain a clean and dry sample vial (Figure 6).
2. Take care to handle the sample vial by the top.
3. Rinse the vial with approximately 10 ml of the sample
water, capping the vial with the black screw cap and gently
inverting it several times. Discard the used sample and
repeat the rinsing procedure two more times.
Figure 6:
Sam
4. Fill the rinsed vial with the remaining portion (approximately
le Vial
10 ml) of the grab sample up to the mark indicated in the
vial. Cap the vial with the supplied black screw cap.
5. Wipe the vial with a soft, lint-free cloth. Ensure that the outside of the
vial is dry, clean and free from smudges.
6. You are now ready to place the vial into the meter for measurement.
2.3
Measurement Procedure
1. Place C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter on a flat and
level surface.
2. Place the sample vial inside the sample well and align the vial’s mark
with the meter’s index mark. See Figure 8.
Figure 8: Sample vial index alignment to the meter's index mark
3. Push the vial until it is fully snapped in.
Align index mark on
the sample vial with
the index mark on
the colorimeter and
push till it is fully
snapped in
IMPORTANT
Place me t e r o n a flat
and leve l s urface.
DO NOT hold it on
hands while operating
the meter. It may lead to
inaccurate readings
7
:

C401/301/201/101/102/103/104/105 Colorimeter
Measurement
4. Turn on the meter by pressing the ON/OFF key.
5. For the single-parameter colorimeter, the display will momentarily
show the test to be performed before switching directly to [STbY] as
that of step 6. For the multi-parameter colorimeter, the display will
indicate the last test performed. Press the MODE key to make
selection on the desired test to be performed.
6. Press the READ/ENTER key to confirm your selection. The meter will
display [STbY] indicating it is ready to accept a measurement or a
blanking.
7. Press the ZERO key to perform the blanking of the meter. If the user
chooses to skip this step, the meter will use the last value of the
blank for the next calculation.
8. Remove the sample vial used for blanking from the instrument and
add the appropriate reagent to it. Cap the vial and follow the
appropriate instructions (including the time required to develop the
color) for each type of reagents.
9. Place the vial with the developed color into the sample well and align
the ▼ mark on the vial with the ▲ mark on the instrument, and press
it down until it snaps fully into the optical holder.
10. Press the READ/ENTER key. The meter will display the reading in
appropriate units within 3 seconds.
11. To repeat the measurement of the same sample, repeat steps 7-11.
Ideally, step 7 should not be skipped, but the user may do so if
testing the same sample.
8
Measurement: Chlorine, Free & Total
C401/301/201Colorimeter
2.4 Chlorine, Free & Total (0 – 6ppm Cl
• DPD method
1
for Free Chlorine - applicable to water, treated w ater,
)
2
estuary water and seawater.
• DPD method
1
for Total Chlorine - applicable to water, treated
water, wastewater, estuary water and seawater.
The DPD Method is USEPA accepted for reporting drinking water
analyses (Free and Total Chlorine) and wastewater analyses
2
(Total
Chlorine only).
Note: 1Adapted from “Standard methods for the Examination of W ater and
Wastewater.”
Note: 2Procedure is equivalent to USEPA method 330.5 for wastewater and
Standard Method 4500-Cl G for drinking water.
1. Switch the meter on by pressing the ON/OFF key.
2. Press the MODE key repeatedly until [CL – F] is displayed (for Free
Chlorine determination) or [CL – T] is displayed (for Total Chlorine
determination).
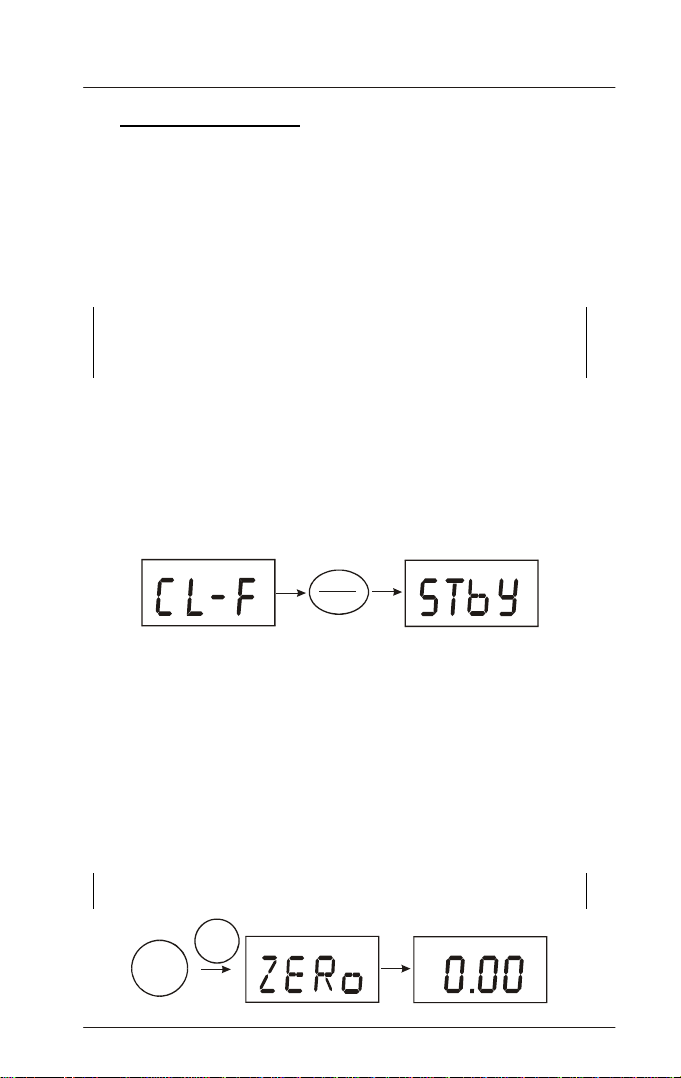
3. Press the READ/ENTER key to confirm the desired test parameter.
The meter will read [STbY] indicating it is in stand-by mode, waiting
for either blanking or measurement.
READ
ENTER
Free Chlorine test se lection
4. Select a clean and dry vial, un-screw the cap and fill with sample
water to the line on the vial. Replace the cap, ensuring it is screwed
on finger tight to the vial.
5. Ensure the outside of the vial is clean, dry and absent of any marks
or finger-prints. Gently push the vial fully into the sample well of the
instrument, whilst aligning the ▼ mark on the vial with the ▲ mark on
the meter.
6. Press the ZERO key to initiate blanking of the meter. The display will
show [ZERo] while blanking is taking place.
Note: The meter will store and use the last blanking (or zero) value, even if it
is turned off, or if the batteries are removed.
Blanking
Sample
ZERO
ppm
9
Measurement: Chlorine, Free & Total
C401/301/201Colorimeter
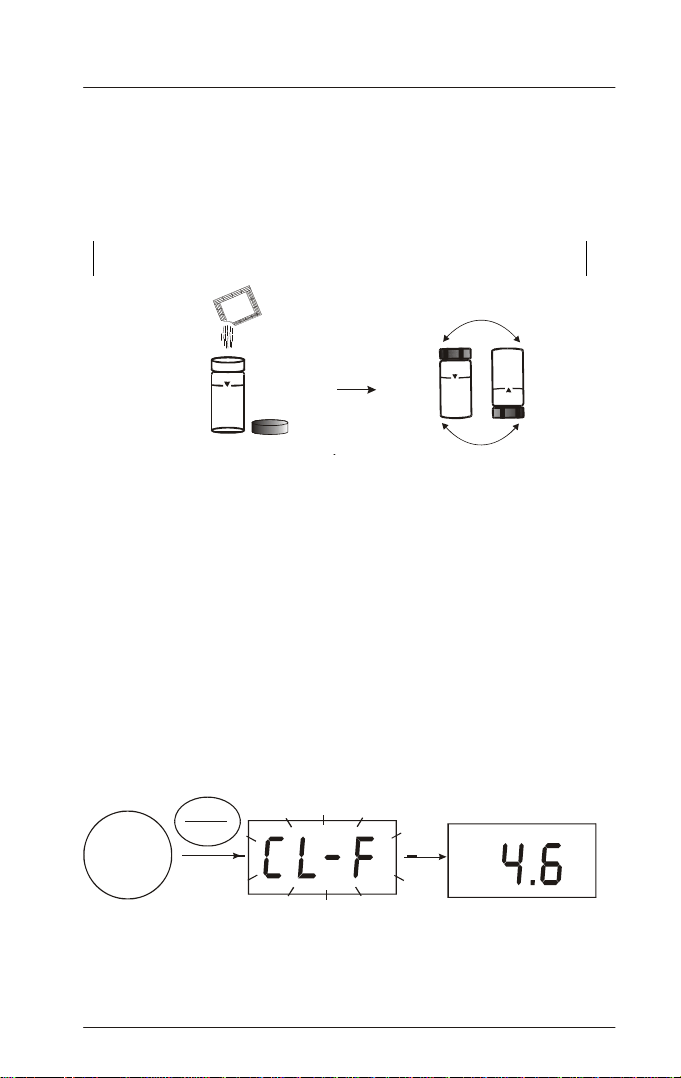
7. Remove the vial from the meter and add into it the content of one
Chlorine, Free (DPD) Reagent Sachet (for Free Chlorine
determination) or the content of one Chlorine, Total (DPD) Reagent
Sachet (for Total Chlorine determination).
8. Replace the cap, ensuring it is screwed on finger tight to the vial.
Invert the vial repeatedly for approximately 20 seconds, until the
powder has dissolved.
Note: A small amount of the powder may remain un-di ssolved in the vial, but
this will not affect the measurement.
Add content of one Chlorine, Free (DPD) Reagent Sachet
(for Free Chlorine determination) or one
(DPD) Reagent Sac het
(for Total Chlorine determination).
Chlorine, Total
Invert vial approximately 20
seconds until powder dissolves
9. Gently push the vial back fully into the sample well of the meter,
whilst again aligning the ▼ mark on the vial with the ▲ mark on the
meter.
10. For Free Chlorine determination, press the READ/ENTER key within
two minutes from the time the DPD Free reagent was added to the
vial.
11. For Total Chlorine determination, wait for two minutes and then press
the READ/ENTER key within four minutes from the time the DPD
Total reagent was added to the vial.
12. The meter will flash either [CL-F] or [CL-T], depending on which test
is being performed, whilst the measurement is taken. It will then
display the Chlorine concentration in parts per million (ppm) Cl
READ
Free
ENTER
Chlorine
Sample
Free Chlorine determination
10
.
2
ppm

Measurement: Chlorine, Free & Total
C401/301/201Colorimeter
Chlorine, Free & Total Measuring Hints & Tips
2.4.1 Sample Collection
Chlorine determination must take place as soon as possible after the
sample is taken or else low results may be obtained.
Plastic containers should not be used to collect the sample because these
may have a high chlorine demand which will lead to low reading results. It
is advisable to wash the container with sample water before the sample is
collected.
Avoid agitating the sample excessively as this may also lead to low
results.
2.4.2 Sample Measurement
If the pink color forms and then rapidly fades, this is an indication that the
chlorine concentration may be very high. If this is the case, dilute the
sample with de-ionized water and retest. Multiply the result by the dilution
factor used.
Example: if the sample was diluted 2:1 with de-ionized water (i.e. 1 part
sample water to 1 part de-ionized water), the result is multiplied by 2 to
give the true concentration of the original sample.
Note: Results obtained by this method will not be as accurate as stated in
this manual because some chlorine will be lost in the dilution process.
After use, the vial should be cleaned thoroughly to avoid contaminating the
next sample. Do not use household cleaners as these may have a
chlorine demand which will lead to low results on subsequent tests.
After testing Total Chlorine, give extra attention to cleaning the vial as any
residual reagent will affect any subsequent Free Chlorine tests. It is
advisable to use separate vials for Free and Total Chlorine.
2.4.3 Interferences
Acidity:
Greater than 250ppm CaCO3 may cause interference. To remove this
interference, neutralise a separate sample to pH6-7 using 1N Sodium
Hydroxide. Record the volume used and add the same volume of 1N
Sodium Hydroxide to the sample before carrying out the above test
procedure. Use a multiplication factor to correct for the dilution of the
sample.
11

Measurement: Chlorine, Free & Total
C401/301/201Colorimeter
Alkalinity:
Greater than 250ppm CaCO3 may cause interference. To remove this
interference, neutralise a separate sample to pH6-7 using 1N Sulphuric
Acid. Note the volumes used and add the same volume of 1N Sulphuric
Acid to the sample before carrying out the above test procedure. Use a
multiplication factor to correct for the dilution of the sample.
Hardness:
No effect at less than 2000ppm CaCO
.
3
Monochloramine:
Monochloramine will cause a gradual increase in the Free Chlorine result
over time. Take the test result within 1 minute of adding the reagent
sachet to avoid these errors.
Oxidants, including Bromine, Chlorine Dioxide, Iodine and Ozone:
These will interfere with the test method at all levels. It is recommended
that an alternative test method is used if more than any two of these
species are present.
Oxidised Manganese or Oxidised Chromium:
All levels will cause interference. To remove this interference:
1. Test a 10ml sample as described in the above procedure.
2. Adjust the pH of a separate 10ml sample to pH6-7 using 1N Sodium
Hydroxide or 1N Sulphuric Acid.
3. Add 1 drop of 20% Potassium Iodide Solution; swirl to mix and then
wait 60 seconds.
4. Add 3 drop of 5g/l Sodium Arsenite Solution and swirl to mix.
5. Use this as the sample in the above test procedure and make a note
of the result. Use a multiplication factor to correct for the dilution of
the sample.
6. Subtract the result obtained in step 5 from the result obtained in step
1 to give the true result.
7. Correcting for dilution: To correct for any reagent added to the
sample to neutralise it, a dilution correction factor must be used:
Final Volume ÷ Initial Sample Volume = Correction Factor
The final volume can be calculated by adding together the initial
12

Measurement: Chlorine, Free & Total
C401/301/201Colorimeter
sample volume and the volume of neutralising reagent used:
Final Volume = Initial Sample Volume + Volume of Neutralising
Reagent.
The result from a test can then be multiplied by the Correction Factor
to give the true result.
If reagents are added from the supplied dropper bottles, then 25
drops is equal to 1ml.
Example:
50ml sample is neutralised using 50 drops of 1N Sulphuric Acid, and
each drop is 0.04 ml.
Initial Sample Volume = 50ml
Volume of Neutralising Reagent added = 50drops X 0.04 ml= 2ml
Final Volume = 50ml + 2ml = 52ml
Correction Factor = 52/50 = 1.04
A test result of 1.00ppm would then become 1.00ppm X 1.04 =
1.04ppm
2.4.4 Accuracy Check / User Calibration
Producing chlorine standards is a difficult procedure that should only be
attempted by trained laboratory staff. Details of preparation techniques are
not provided in this document.
The prepared chlorine standard may be used to check the accuracy of the
meter or to re-calibrate the meter. In almost all cases it is recommended
to use the default factory calibration.
To check the accuracy of the meter: Prepare a standard solution of
known concentration within the range of the instrument. It is advisable to
prepare a standard near to the concentration value usually tested with the
meter. Use this standard in place of the sample water in the above test
method. Repeat the measurement 5-7 times with different sachets and
average the results. The result obtained should be approximately the
value of the standard used (please refer to instrument’s specifications for
data on meter precision and accuracy).
To re-calibrate the meter: All instruments are factory calibrated and user
calibration is not recommended. However, if a Chlorine standard can be
prepared, measured accurately and qualified by a different method
(titration, for example) or another instrument of higher precision and
accuracy, then a Chlorine standard in the 4.1-5.0 ppm Cl
range can be
2
used. Please refer to Section 3.2 Chlorine, Free & Total, Chlorine Dioxide,
13

Measurement: Chlorine, Free & Total
C401/301/201Colorimeter
Bromine and Ozone, for details.
2.4.5 Chemistry
Chlorine exists in water as Un-Combined (Free) Chlorine and Combined
Chlorine. The concentration of Free Chlorine can be determined directly
and the concentration of Combined Chlorine may be calculated by
subtracting the concentration of Free Chlorine from that of Total Chlorine.
In the Free Chlorine test method Un-Combined Chlorine reacts directly
with DPD (N,N-diethyl-p-phenylenediamine) in a conditioned sample to
give a pink color. In the Total Chlorine test method Combined Chlorine
reacts with potassium iodide to form tri-iodide ions. The tri-iodide ions and
the Free Chlorine present react with DPD in a conditioned sample to give
a pink color.
The depth of the pink color produced is proportional to the concentration of
Chlorine. The amount of 525nm light absorbed by the pink color is
accurately measured by the meter and then converted into the Chlorine
concentration.
14
 Loading...
Loading...