Page 1
QN908x
DK User Guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
DK User Guide
Document information
Info
Content
Keywords
QN9080-DK, QN9080, QN9083, BLE, USB Dongle
Abstract
This document is an introduction to the QN908x DK V1.2 board
Page 2
NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP Semiconductors B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
2 of 28
Contact information
For more information, please visit: http://www.nxp.com
Revision history
Rev
Date
Description
0.1
20160818
Initial release.
0.2
20160908
Updated the figures, schematics, and PCB layout according to the QN908x DK board V1.0
and added the QN9080 QFN module board information.
0.3
20161110
Updated pictures and schematics according to the QN908x DK board V1.1, added the
current test using the DC power analyzer. Added notes about using a battery as the power
supply for the QN9080 module.
0.4
20170117
Updated pictures and schematics according to the QN908x DK board V1.2 and changed
the jumper default settings.
1.0
20170613
Public release.
Page 3

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
3 of 28
1. Introduction
The QN908x DK board is designed for the QN908x HVQFN and WLCSP package IC
evaluation and development. It is easy to evaluate QN908x’s functions and performance.
There are also some useful peripherals like the GPIOs, PMod, and Arduino interface.
The J-Link and J-Trace functions are supported for the QN908x debugging. The ISP
download function is also supported and very easy to use.
1.1 Purpose
This document introduces all functions of the QN908x DK V1.2 board and describes all
its parts in detail.
1.2 Kit contents
QN908x DK includes the following:
QN908x DK board
QN9080 USB dongle
USB cable
Page 4

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
4 of 28
2. Hardware description
The QN908x DK board provides easy access to peripherals, such as the buttons and
LED. The board also provides useful interfaces, such as the USB port for UART
communication and CMSIS-DAP debugger, and the standard Arduino & Pmod
connector. The USB dongle is a Bluetooth device powered by QN9080. It acts as a
master/slave when communicating with the QN908x devices.
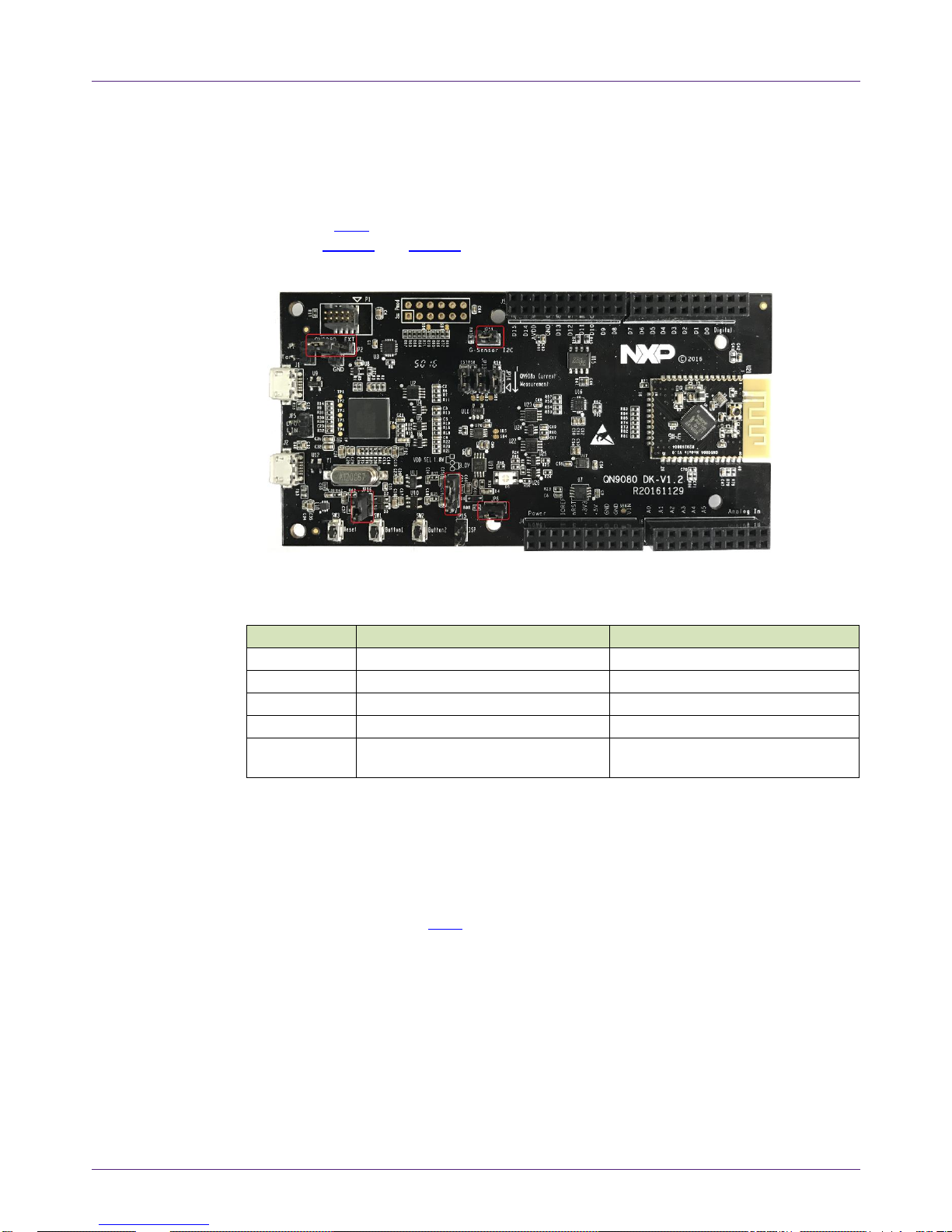
2.1 Hardware overview
The QN908x DK V1.2 board is shown in Fig 1. The detailed information is listed in Table
1.
Fig 1. Board overview
Page 5
NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
5 of 28
Table 1. QN908x DK V1.2 board’s mark information list
Number
Name
Description
1
QN908x USB port
The QN908x USB port provides power supply to the whole
board and the USB signal path to the QN908x module.
2
LPC4322 USB port
The LPC4322 USB port provides power supply to the
whole board and the USB signal path is connected to
LPC4322.
3
LPC4322
LPC4322 works as the JTAG/SWD link bridge.
4
QN908x module
The QN908x module boards come in two types, according
to the QN908x chip package: HVQFN and WLCSP.
5
Jumper JP1
This jumper sets the JTAG/SWD link bridge target:
• Open: on-board target (default)
• Short: off-board target
6
Jumper JP5
This jumper sets the LPC4322 DFU mode:
• Short: DFU mode enabled
• Open: normal mode (default)
7
Jumper JP7
This jumper sets the QN908x module power supply
voltage:
• 1-2: 1.8 V power supply
• 2-3: 3.0 V power supply
8
Jumper JP8
This jumper sets the QN908x ISP UART path mode:
• Short: UART path enabled (default)
• Open: UART path disabled
9
Jumper JP11
This jumper sets the QN908x external I2C path mode,
• Short: I2C path enabled (default)
• Open: I2C path disabled
10
Header J5 and J7
QN908x GPIO for testing and compatible with the Arduino
board interface.
11
Header J4 and J6
QN908x GPIO for testing and compatible with the Arduino
board interface.
12
Jumper JP12, JP13,
JP14
These jumpers are used for the power consumption test.
13
Header J8
PMod interface connector, compatible with PMod.
14
Debugger
connector
Used to offer the JTAG/SWD interfaces to the off-board
target.
15
Jumper JP2
This jumper sets the QN908x power supply source;
on-board power or EXT power.
16
Button3 SW3
Button3 resets the QN908x chip.
17
Button1 SW1
Button1 is a function button defined by the user.
18
Button2 SW2
Button2 is a function button defined by the user.
19
Jumper JP15
Jumper used to enable the QN908x chip mode function.
20
GND Pin
GND pin used as the test ground pin.
21
Jumper JP16
Jumper used to cut off the USB leakage, when the DK
board is powered by a battery.
Page 6
NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
6 of 28
2.2 Default jumper settings on the DK board
As shown in Fig 2, the power, JTAG/SWD, UART, and I2C enable jumpers are connected
by default. Table 2 and Table 3 show the jumpers’ functions and how to set them.
Fig 2. Board jumper default settings
Table 2. QN9080A MINIDK board’s default jumper settings
Jumper
Jumper setting
Function
JP2
Pin 1, 2 shorted
QN908x’s on-board power
JP7
Pin 2, 3 shorted
QN908x’s power (3 V)
JP8
Pin 1, 2 shorted
UART path enabled
JP11
Pin 1, 2 shorted
I2C path enabled
JP16
Pin 1, 2 shorted
When the DK board is powered by a
battery, leave it open.
2.3 CMSIS-DAP debugger
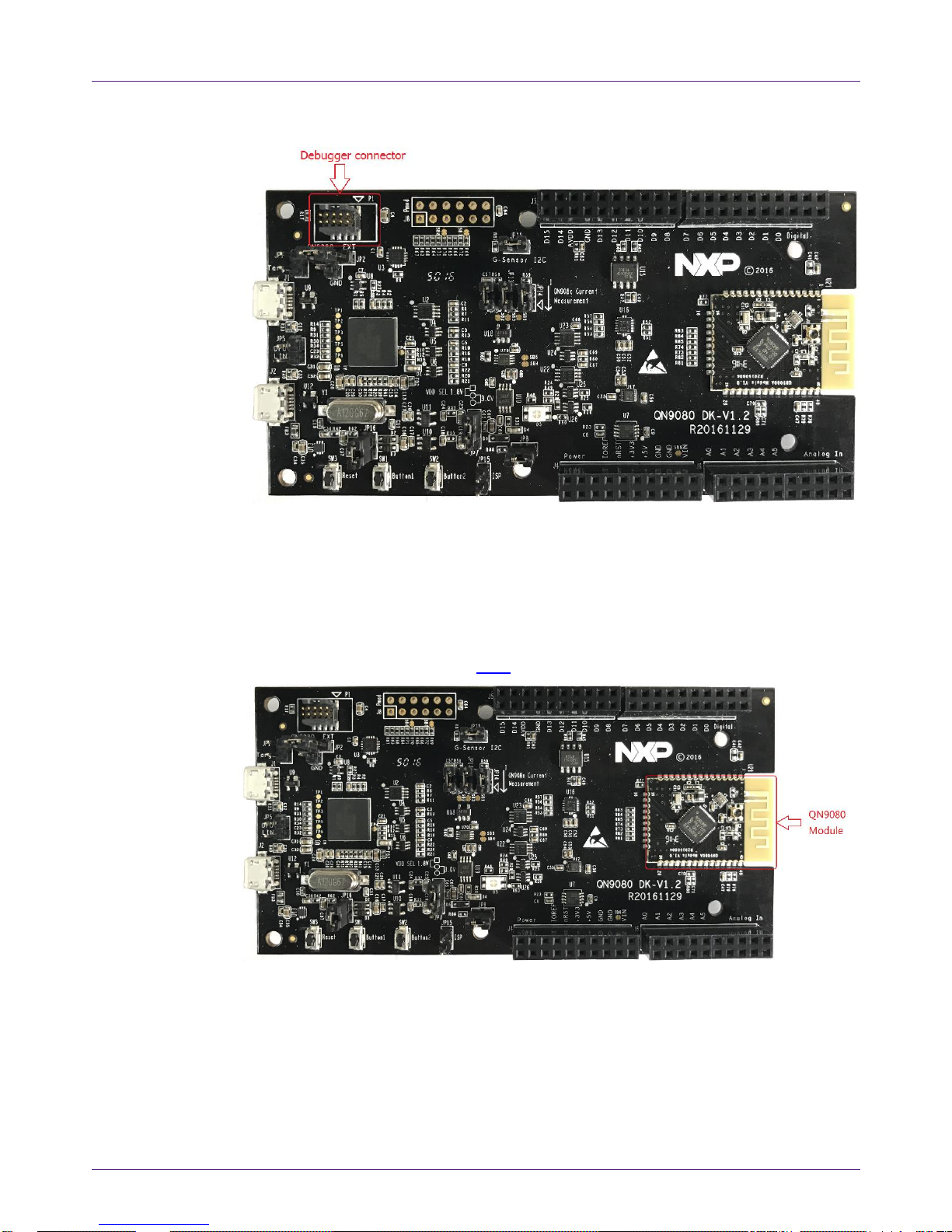
The CMSIS-DAP debugger provides both the SWD/JTAG and UART interfaces. You
may download or update the firmware into the QN908x device using the UART or
JTAG/SWD interfaces. There is a debugger connector to program and debug an
off-board target (shown in Fig 3).
Page 7
NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
7 of 28
Fig 3. J-Link connector
2.4 QN9080 module
The QN908x IC integrates the BLE radio, controller, protocol stack, and profile software
on a single chip, which provides a flexible and easy way to use the BLE SoC solution. It
also includes a high-performance MCU (32-bit ARM® Cortex®-M4F), on-chip memory,
and peripherals for users to develop a truly single-chip wireless MCU solution.
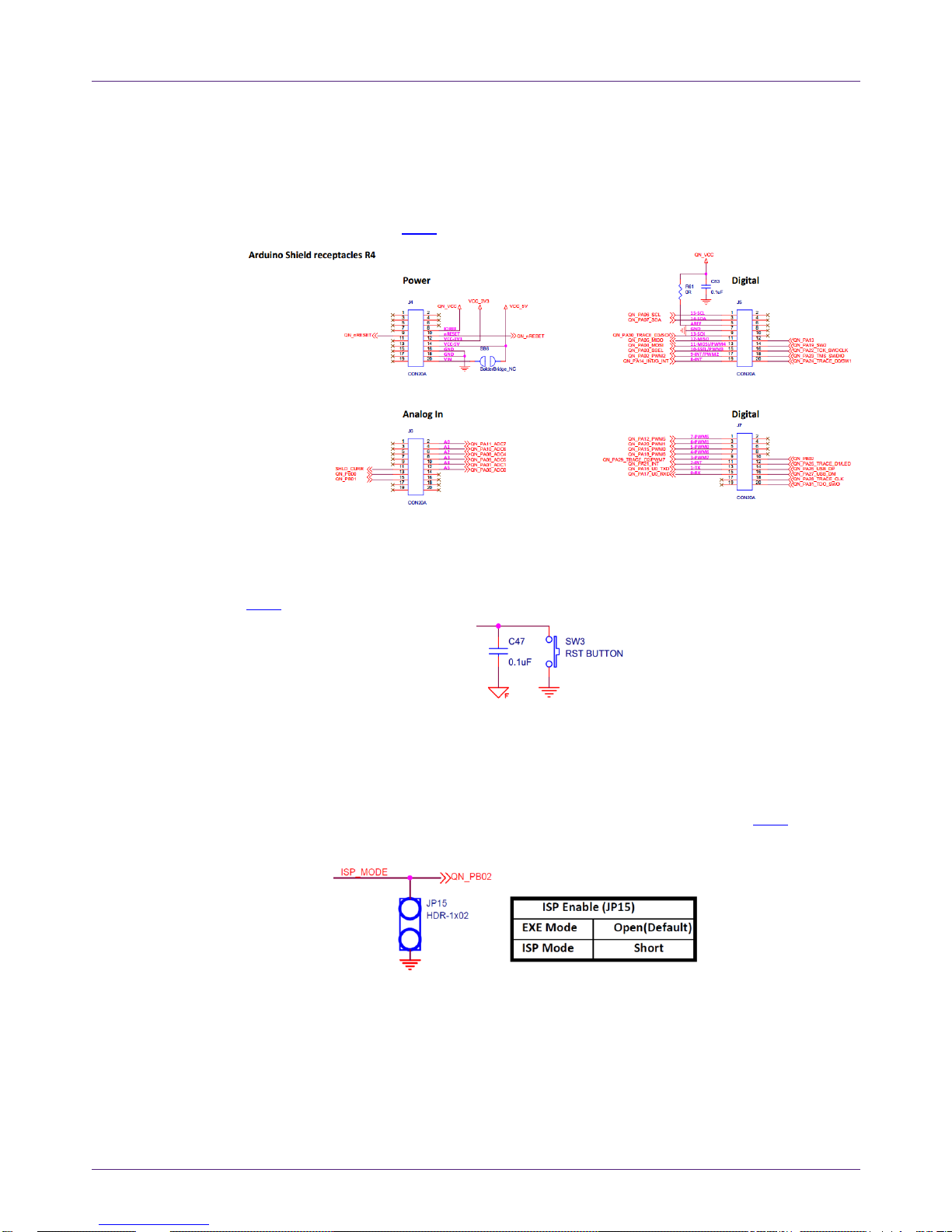
The QN9080 module is shown in Fig 4.
Fig 4. QN9080 module board
The QN908x module has a MIFA antenna on the front side of the board. Therefore, it can
work without an external antenna. There is a RF connector that has a switch on the RF
front-end. You can easily perform the RF test by connecting an RF cable to the RF
connector.
Page 8
NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
8 of 28
2.5 GPIO and Arduino interfaces
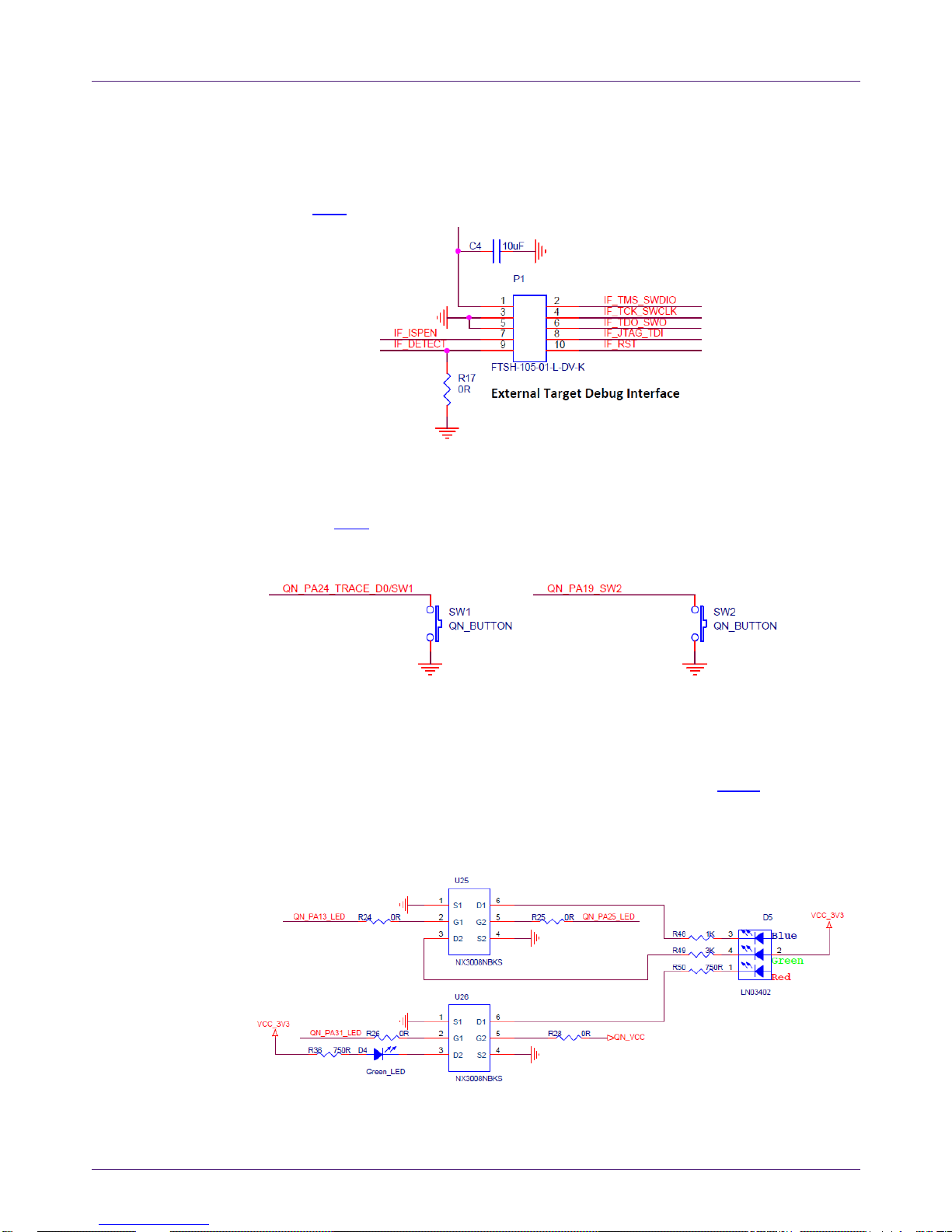
On the QN908x DK board, the J4, J5, J6, and J7 connectors all provide GPIO connection
outputs. The board is also compatible with the Arduino board interface. The interface
schematic is shown in Fig 5.
Fig 5. QN908x DK board GPIO and Arduino interface
2.6 QN908x reset button
The reset button is used to provide a hardware reset to the QN908x device, as shown in
Fig 6).
Fig 6. Reset button
2.7 ISP mode jumper
JP15 is the ISP mode jumper used to set the QN908x ISP mode. When the jumper is
shorted, the PB02 chip mode pin is connected to GND and this function is enabled.
When the jumper is open, the ISP mode function is disabled, as shown in Fig 7.
Fig 7. Chip mode jumper
Page 9
NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
9 of 28
2.8 JTAG interface
The board provides a SWD/JTAG interface to be used by an external debugger, as
shown in Fig 8.
Fig 8. JTAG interface
2.9 Buttons
As shown in Fig 9, the DK board offers three buttons. When using the SW1 and SW2
buttons, the GPIO must be configured as the input. The logic LOW input is applied to the
GPIO when a button is pressed.
Fig 9. Buttons
The SW3 button is used to reset the QN908x chip. Press the button to reset the QN908x.
2.10 LED
The board offers a 3-color RGB LED. The connections are shown in Fig 10. The LED
lights up when the corresponding GPIO outputs switch to the logic high level. The GPIO
control pins are QN_PA13, QN_PA25, and QN_PA31. The GPIO QN_PA13 can work in
the PWM out mode. Therefore, the brightness of the LED can change with the PWM
pulse width.
Fig 10. LED
Page 10

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
10 of 28
3. DK board application function
3.1 CMSIS-DAP interface
The QN908x DK V1.2 board offers the JTAG/SWD interface either to the on-board or
off-board QN908x targets. It also provides the USB-to-UART interface for QN908x.
3.1.1 CMSIS-DAP to on-board QN908x
When programing or debugging a QN908x device using the CMSIS-DAP interface, JP1
and JP2 must be configured according to Table 3.
Table 3. ISP mode jumper setting
JP1
Open, CMSIS-DAP target is on-board QN9080
JP2
Short pin 1, 2, QN908x power enable
When downloading firmware into the QN908x with the ISP mode, enable the UART path
and set the chip mode pin to ground. The jumper setting is shown in Table 4.
Table 4. ISP mode jumper setting
JP8
Short, UART path enable
JP15
Short, ISP mode enable
The ISP download operation flow is shown in Fig 11.
Fig 11. ISP download operation flow
After the ISP download operation, move the jumper cap on JP15 away and leave JP15
open. Then, the QN908x chip can go into the normal mode normally.
3.1.2 CMSIS-DAP to off-board target
When using the QN908x DK board to program or debug off-board targets by the
JTAG/SWD interface, JP1 and JP2 must be configured according to Table 5.
Table 5. ISP mode jumper setting
JP1
Short, CMSIS-DAP target is off-board target
JP2
Short pin 2,3, 3 V power disable on JTAG/SWD connector
3.2 Current consumption test
The QN908x DK board provides two ways to measure the QN908x chip current
consumption. One way is to measure the current by the on-board precise resistor used
for the I-to-V conversion. The small voltage signal is amplified by the operation amplifier
and fed to the ADC. Then, it can be calculated by LPC4322 and shown in the
MCUXpresso IDE. Another way is to measure the current by an external ammeter on
jumper JP14.
UART
Enable
Short ISP
Jumper
ISP
Loading
Press QN908x
RST Button
Page 11

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
11 of 28
3.2.1 Current test using LPC4322
The QN908x DK board has an on-board current measurement circuit consisting of the
MAX9634T (U18) current monitor chip and the 12-bit ADC (ADC122S021, U19) with a
12-bit sampling from 50 ksps to 200 ksps. The on-board MAX9634T current monitor
measures the voltage across the QN908x VCC V-sense resistors; either 8.24 Ω or
4.12 Ω if JP13 is installed. MAX9634 multiplies the sense voltage 25 times to provide a
voltage range suitable for the ADC to measure.
A 2-input analog mux is used to select the channel to be measured; either the QN9080 or
the devices from the expansion board on the DK extension connectors. The current
measurement circuit is controlled by the Link2 processor and is not user-programmable.
The power-measurement utilities with this feature are available only after installing the
MCUXpresso IDE.
Due to the input offset voltage variations in MAX9634, the current measurement circuit is
not recommended for measuring currents below 150 A.
The QN908x current can be measured by the voltage across a sense resistor in series
with the supply. The voltage across a series 4.12-Ω resistor with the target QN908x VCC
can be manually measured at JP12 on the PCB. Use the Ohm’s law to calculate the
current (QN908x current = measured voltage / 4.12 Ω). As an example, if the measured
voltage is 10 mV, then 10e-3 / 4.12 Ω = 2.44 mA. Note that the current consumed by
MAX9634 used in the on-board current measurement is included in the voltage
measured on this resistor. The detailed schematic is shown in Fig 12.
Fig 12. Current test using the LPC processor
When performing the current test using the Link2 processor, jumpers JP12, JP13, and
JP14 must be set according to Table 6 .
Table 6. Current test jumper setting
JP12
Open when used for the Link2 processor current test
JP13
Open when used for the Link2 processor current test
JP14
Short when no digital ammeter series in
Page 12

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
12 of 28
3.2.1 Current test using a digital ammeter
When performing the current test using an external digital ammeter, jumpers JP12, JP13,
and JP14 must be set according to Table 7. Use a jumper cap to short the pins. The
schematic is shown in Fig 13.
Fig 13. Current test using an ammeter
When performing the current test using an ammeter, jumpers JP12, JP13, and JP14
must be set according to Table 7.
Table 7. Current test jumper setting
JP12
Short, when used for Ammeter current test
JP13
Short, when used for Ammeter current test
JP14
Need an ammeter series in
3.2.2 Current test using a DC power analyzer
Measure the current using a DC power analyzer in these two ways: one way is to use the
DC power analyzer as an ammeter that shares the same settings as the ammeter test,
and the other way is to use the DC power analyzer as the power supply for the DUT.
In this case, the QN9080 module is powered by the DC power analyzer. The QN_VCC
power pin is on jumper JP14, where a triangle symbol indicates the pin. The GND pin
near jumper JP2 can be also used as the power ground.
Fig 14. QN_VCC power pin
Page 13

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
13 of 28
3.3 RF connective test with CBT
The QN908x module RF signal can be tested by the on-trace RF connector. This RF
connector is manufactured by Murata. When performing the RF test with the CBT
instruments system, you may need an expansion board to match the signal voltage level
from UART to the RS232 interface. The RS232 expansion board can be powered from
the QN908x DK Board through connectors. The connection of the two boards is shown in
Fig 15.
Fig 15. RF CBT test with the expansion board
Before the RF test, download the Controller Mode binary file to the QN908x module to
put the QN908x into the DTM mode. Connect an RF cable from the QN908x module to
the CBT and set the CBT RS232 baud rate to 115200 bit/s. After that, start the RF test.
4. QN9080 USB dongle
4.1 Dongle hardware
Fig 16. Dongle hardware
The USB dongle works together with the QTool and behaves either as a master or as a
slave when talking to the QN908x DK or other devices. As shown in Fig 17, the USB
dongle receives commands from QTool via a virtual COM port, which initializes the
QN9080 dongle either as a master or slave device. All tests can be performed by QTool
after the initialization.
Page 14

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
14 of 28
4.2 Dongle connection
The QN9080 USB dongle is a USB-interfaced device with the QN9080 built in. With the
driver and SDK installed on your computer (see the QN9080 quick start guide), use the
QTool in SDK to control the QN9080 in the dongle to work as a central/peripheral device.
The DK board is supplied from the USB port and works as a peripheral/central device.
The dongle connection is illustrated in the below figure. See the QTool User Manual for
information about the QTool usage.
5. Appendix
5.1 Schematics
5.1.1 QN908x DK main board
The QN908x DK V1.22 board schematic has five parts: power, LPC processor,
QN908x-BLE, QN908x-function, and Arduino interface.
Fig 17. Power schematic of the QN908x DK board
Page 15

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
15 of 28
Fig 18. LPC processor schematic of the QN908x DK board
Fig 19. QN908x-BLE schematic of the QN908x DK board
Page 16

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
16 of 28
Fig 20. QN908x-function schematic of the QN908x DK board
Fig 21. Arduino interface schematic of the QN908x DK board
Page 17

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
17 of 28
5.1.2 QN9080 module board
Fig 22. QN9080 QFN module board
5.2 PCB layout
5.2.1 QN908x DK main board
Fig 23. Top etch
Page 18

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
18 of 28
Fig 24. GND plane
Fig 25. PWR plane
Page 19

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
19 of 28
Fig 26. Bottom etch
Fig 27. Top silkscreen
Page 20

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
20 of 28
Fig 28. Bottom silkscreen
5.2.2 QN9080 QFN board
Fig 29. Top etch
Page 21

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
21 of 28
Fig 30. GND plane
Fig 31. PWR plane
Page 22

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
22 of 28
Fig 32. Bottom etch
Fig 33. Top silkscreen
Page 23

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
23 of 28
5.3 Dimensions of the PCB board
5.3.1 QN908x DK board
Fig 34. Dimensions of the QN908x DK board
Page 24

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
24 of 28
5.3.2 QN9080 QFN module
Fig 35. Dimensions of the QN9080 QFN module board
5.4 Notes for using a lithium battery
When using a lithium battery as the power supply for the QN9080 module, pay attention
to the following:
To avoid current leakage from the QN9080 USB data line, leave the JP16 open.
To avoid current leakage from the 3-color LED, remove resistors R48, R49, and
R50.
Fig 36. Lithium battery on the QN908x DK board
Page 25

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
25 of 28
5.5 Statements
5.5.1 FCC compliance statement
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which
can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
IC Compliance Statement
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation
is subject to the following conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and (2)
this device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause
undesired operation of the device.
Page 26

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
QN908x-DK
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
User guide
Rev. 1.0 — June 2017
26 of 28
6. Legal information
6.1 Definitions
Draft — The document is a draft version only. The content is still under
internal review and subject to formal approval, which may result in
modifications or additions. NXP Semiconductors does not give any
representations or warranties as to the accuracy or completeness of
information included herein and shall have no liability for the consequences
of use of such information.
6.2 Disclaimers
Limited warranty and liability — Information in this document is believed to
be accurate and reliable. However, NXP Semiconductors does not give any
representations or warranties, expressed or implied, as to the accuracy or
completeness of such information and shall have no liability for the
consequences of use of such information. NXP Semiconductors takes no
responsibility for the content in this document if provided by an information
source outside of NXP Semiconductors.
In no event shall NXP Semiconductors be liable for any indirect, incidental,
punitive, special or consequential damages (including - without limitation lost profits, lost savings, business interruption, costs related to the removal or
replacement of any products or rework charges) whether or not such
damages are based on tort (including negligence), warranty, breach of
contract or any other legal theory.
Notwithstanding any damages that customer might incur for any reason
whatsoever, NXP Semiconductors’ aggregate and cumulative liability
towards customer for the products described herein shall be limited in
accordance with the Terms and conditions of commercial sale of NXP
Semiconductors.
Right to make changes — NXP Semiconductors reserves the right to make
changes to information published in this document, including without
limitation specifications and product descriptions, at any time and without
notice. This document supersedes and replaces all information supplied prior
to the publication hereof.
Suitability for use — NXP Semiconductors products are not designed,
authorized or warranted to be suitable for use in life support, life-critical or
safety-critical systems or equipment, nor in applications where failure or
malfunction of an NXP Semiconductors product can reasonably be expected
to result in personal injury, death or severe property or environmental
damage. NXP Semiconductors and its suppliers accept no liability for
inclusion and/or use of NXP Semiconductors products in such equipment or
applications and therefore such inclusion and/or use is at the customer’s own
risk.
Applications — Applications that are described herein for any of these
products are for illustrative purposes only. NXP Semiconductors makes no
representation or warranty that such applications will be suitable for the
specified use without further testing or modification.
Customers are responsible for the design and operation of their applications
and products using NXP Semiconductors products, and NXP
Semiconductors accepts no liability for any assistance with applications or
customer product design. It is customer’s sole responsibility to determine
whether the NXP Semiconductors product is suitable and fit for the
customer’s applications and products planned, as well as for the planned
application and use of customer’s third party customer(s). Customers should
provide appropriate design and operating safeguards to minimize the risks
associated with their applications and products.
NXP Semiconductors does not accept any liability related to any default,
damage, costs or problem which is based on any weakness or default in the
customer’s applications or products, or the application or use by customer’s
third party customer(s). Customer is responsible for doing all necessary
testing for the customer’s applications and products using NXP
Semiconductors products in order to avoid a default of the applications and
the products or of the application or use by customer’s third party
customer(s). NXP does not accept any liability in this respect.
Export control — This document as well as the item(s) described herein
may be subject to export control regulations. Export might require a prior
authorization from competent authorities.
Translations — A non-English (translated) version of a document is for
reference only. The English version shall prevail in case of any discrepancy
between the translated and English versions.
Evaluation products — This product is provided on an “as is” and “with all
faults” basis for evaluation purposes only. NXP Semiconductors, its affiliates
and their suppliers expressly disclaim all warranties, whether express,
implied or statutory, including but not limited to the implied warranties of noninfringement, merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. The entire
risk as to the quality, or arising out of the use or performance, of this product
remains with customer.
In no event shall NXP Semiconductors, its affiliates or their suppliers be
liable to customer for any special, indirect, consequential, punitive or
incidental damages (including without limitation damages for loss of
business, business interruption, loss of use, loss of data or information, and
the like) arising out the use of or inability to use the product, whether or not
based on tort (including negligence), strict liability, breach of contract, breach
of warranty or any other theory, even if advised of the possibility of such
damages.
Notwithstanding any damages that customer might incur for any reason
whatsoever (including without limitation, all damages referenced above and
all direct or general damages), the entire liability of NXP Semiconductors, its
affiliates and their suppliers and customer’s exclusive remedy for all of the
foregoing shall be limited to actual damages incurred by customer based on
reasonable reliance up to the greater of the amount actually paid by
customer for the product or five dollars (US$5.00). The foregoing limitations,
exclusions and disclaimers shall apply to the maximum extent permitted by
applicable law, even if any remedy fails of its essential purpose.
6.3 Licenses
Purchase of NXP <xxx> components
<License statement text>
6.4 Patents
Notice is herewith given that the subject device uses one or more of the
following patents and that each of these patents may have corresponding
patents in other jurisdictions.
<Patent ID> — owned by <Company name>
6.5 Trademarks
Notice: All referenced brands, product names, service names and
trademarks are property of their respective owners.
<Name> — is a trademark of NXP Semiconductors N.V.
Page 27

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
Please be aware that important notices concerning this document and the product(s)
described herein, have been included in the section 'Legal information'.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
For more information, visit: http://www.nxp.com
Date of release: June 2017
Document identifier: QN908x-DK
7. Contents
1. Introduction ......................................................... 3
1.1 Purpose .............................................................. 3
1.2 Kit contents ........................................................ 3
2. Hardware description .......................................... 4
2.1 Hardware overview ............................................ 4
2.2 Default jumper settings on the DK board ........... 6
2.3 CMSIS-DAP debugger ....................................... 6
2.4 QN9080 module ................................................. 7
2.5 GPIO and Arduino interfaces ............................. 8
2.6 QN908x reset button .......................................... 8
2.7 ISP mode jumper ............................................... 8
2.8 JTAG interface ................................................... 9
2.9 Buttons ............................................................... 9
2.10 LED .................................................................... 9
3. DK board application function ......................... 10
3.1 CMSIS-DAP interface ...................................... 10
CMSIS-DAP to on-board QN908x .................... 10
CMSIS-DAP to off-board target ........................ 10
3.2 Current consumption test ................................. 10
Current test using LPC4322 ............................. 11
Current test using a digital ammeter ................ 12
Current test using a DC power analyzer .......... 12
3.3 RF connective test with CBT ............................ 13
4. QN9080 USB dongle .......................................... 13
4.1 Dongle hardware .............................................. 13
4.2 Dongle connection ........................................... 14
5. Appendix ................................ ............................ 14
5.1 Schematics....................................................... 14
QN908x DK main board ................................... 14
QN9080 module board ..................................... 17
5.2 PCB layout ....................................................... 17
QN908x DK main board ................................... 17
QN9080 QFN board ......................................... 20
5.3 Dimensions of the PCB board .......................... 23
QN908x DK board ............................................ 23
Page 28

NXP Semiconductors
QN908x
DK User Guide
Please be aware that important notices concerning this document and the product(s)
described herein, have been included in the section 'Legal information'.
© NXP B.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
For more information, visit: http://www.nxp.com
Date of release: June 2017
Document identifier: QN908x-DK
QN9080 QFN module ...................................... 24
5.4 Notes for using a lithium battery ....................... 24
5.5 Statements ....................................................... 25
FCC compliance statement .............................. 25
6. Legal information .............................................. 26
6.1 Definitions ........................................................ 26
6.2 Disclaimers....................................................... 26
6.3 Licenses ........................................................... 26
6.4 Patents ............................................................. 26
6.5 Trademarks ...................................................... 26
7. Contents ............................................................. 27
 Loading...
Loading...