Page 1

Magnetoresistive sensors for rotational,
angle and weak-fi eld measurement
The sixth sense for
automotive applications
Page 2

Accuracy and reliability
are key to NXP sensors
Engine management and ABS, variable valve timing and electronic throttle
control, active suspension and electronic steering – just some of automotive
applications vital in ensuring today’s cars are safer, more comfortable and
less fuel hungry. The majority of these systems depend on an accurate
and reliable supply of information and NXP Semiconductors provides an
extensive portfolio of high-performance sensor solutions to deliver just that.
Additionally, as you would expect from a leading supplier of automotive
semiconductors, all NXP’s sensors have the ruggedness and reliability needed
to meet the exacting automotive quality standards.
You can choose from a proven range of magnetoresistive (MR) sensors
for angle, rotation and weak-field measurements. They all offer precise
measurement, reliable operation and long lifetimes – exactly the qualities
needed for automotive use. With numerous options available to match a
wide variety of applications, you are sure to find the perfect part for your
application.
Page 3
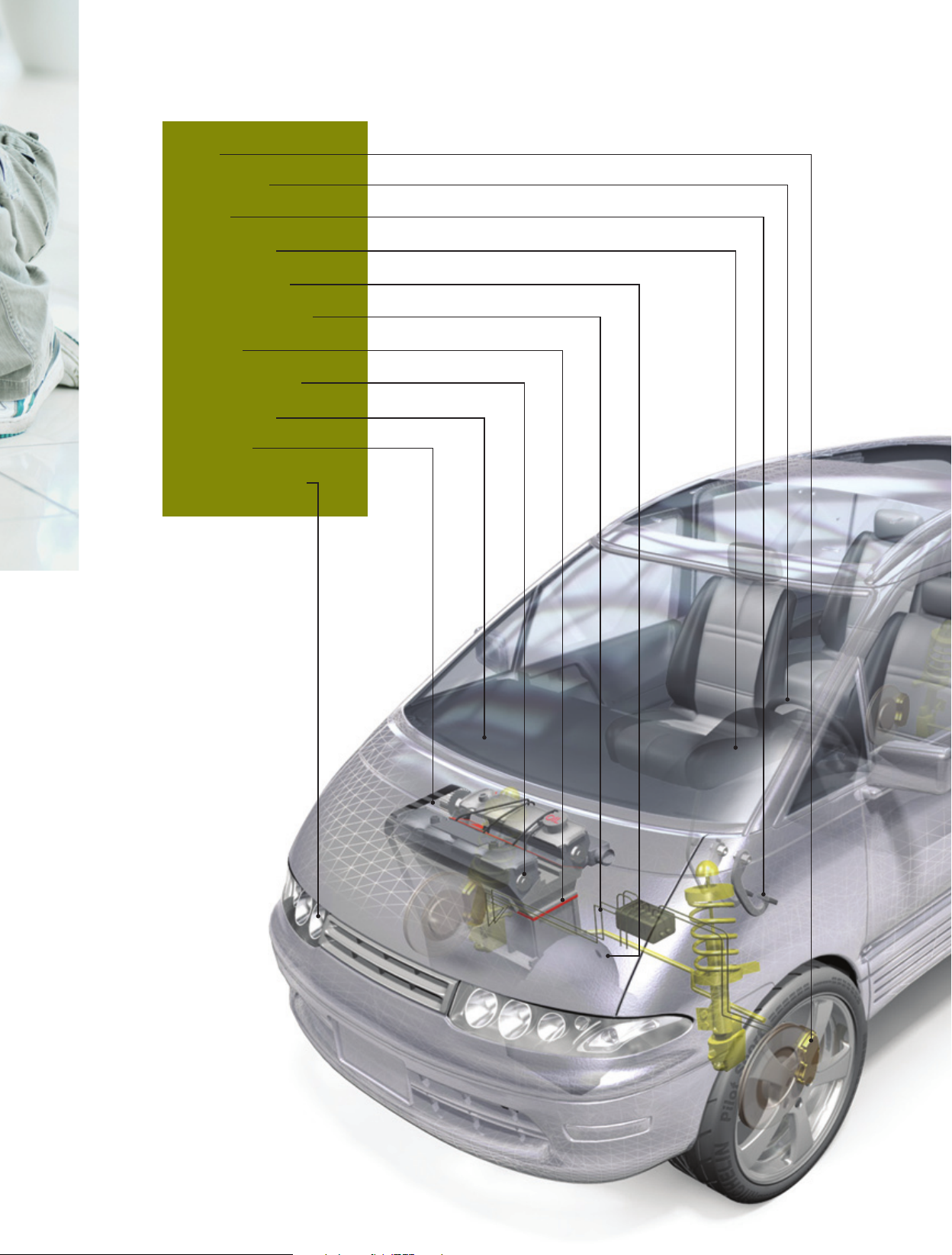
Magnetoresistive sensors - suited to a host of applications
ABS
Steering angle
E-Gas
Steering torsion
Active transmision
EPAS motor positioning
E-throttle
Variable Valve Timing
Window wipers
Crankshaft
Headlight adjustment
Page 4

Page 5

Page 6

Page 7

NXP’s automotive sensors portfolio
Magnetoresistive rotational speed sensors
Compact and easy to design in, our KMI rotational speed sensors
provide a simple and cost-effective rotational sensing solution.
They are ready to use and include the sensor,
an advanced signal conditioning IC and a choice of three
back-biasing magnets, all housed in a special multi-chip package.
Magnetoresistive angle sensors
Highly accurate, NXP’s angle sensors are ideal for a variety of
demanding automotive and industrial applications.
These easy-to-use devices provide an output signal virtually
independent of magnet tolerances, magnet temperature
coefficients, magnet-sensor distance and positioning tolerances,
guaranteeing reliability and simplifying your manufacturing
process.
Magnetoresistive weak field detection sensors
Capable of detecting weak magnetic fields such as the Earth’s,
the KMZ5x range are ideal for navigation and traffic detection
applications. These devices consist of four magnetically sensitive
permalloy resistors arranged in a Wheatstone bridge configuration,
maximizing sensitivity while minimizing temperature influences.
Page 8

www.nxp.com
NXP Semi conduc tors is i n th e pr ocess of being esta blished as a separa te le gal entity in
vari ous coun tries wo rldwid e. This pro cess wil l be fi nalized in the cou rse of 20 06.
© 20 06 Konink lijke Phi lips Elec tronic s N.V.
All rights reserv ed. Repr oducti on in w hole or in par t is pro hibited withou t the pr ior wri tten
cons ent of the cop yright ow ner. The infor mation pre sented in t his docum ent does not
form part of any quotat ion or contra ct, is believe d to b e accur ate and reliab le and may be
chan ged wit hout not ice. No l iabilit y will be accept ed by the publish er for a ny conse quence
of it s use. P ublicat ion the reof doe s not co nvey nor imply an y licens e under patent- o r other
indu strial o r intelle ctual p ropert y right s.
Date o f release: Septemb er 200 6
Docu ment ord er numbe r: 9397 750 15728
Prin ted in the N etherla nds
Page 9

Magnetoresistive angle
Rotating shaft
S N
A
sensor systems
Cover all the angles in your
automotive systems
NXP’s magnetoresistive sensor technology is the superior choice for automotive measurement systems.
Features such as lack of wear, long term stability and direct measurement combine to deliver highly
accurate and robust sensors. With stand-alone sensors, companion signal conditioning ICs and complete
single-package sensing solutions our range of cost-effective angle sensors covers all your application needs.
Key benefi ts
Ñ
Contactless angle measurement up to 180°
Ñ
Measurement independent of magnetic drift caused by life
time and temperature changes
Ñ
Operation independent of mechanical tolerances and magnet
shifts caused by thermal stress
Ñ
High temperature range
Ñ
Automotive qualifi cation
Ñ
Highly fl exible solutions that measure any automotive angle
effectively
Ñ
Fully stable operation over long life-cycle
Key applications
Ñ
Electronic throttle control (ETC)
Ñ
Variable valve control (VVC)
Ñ
Pedal and wiper positioning
Ñ
Active suspension
Ñ
Automatic headlight adjustment
Ñ
Electronic steering
Ñ
Seat positioning
Offering many technical benefi ts over other technologies, our
magnetoresistive (MR) angle sensors provide car manufacturers
with a more reliable and accurate solution for automotive angle
measurement – reducing the risk of mechanical breakdown and
improving overall vehicle safety. This is an increasingly important
area within automotive electronics as the industry moves closer to
incorporating advanced X-by-wire networks and control systems,
such as FlexRay, that rely on accurate measurement data.
MR sensors use magnetic fi elds to
conduct measurement information
between physical value and sensor.
This contactless principle allows isolation
of all rotating components, making the
entire sensing system robust with respect
to pollution and mechanical degradation.
Also, MR sensors evaluate the direction
of the magnetic fi eld and not the fi eld
strength. As a result, MR sensors can
tolerate variations in fi eld strength caused
by ageing, mechanical fl uctuations or
temperature sensitivity of the magnet.
Rotating shaft
MR-sensor set-up
Page 10

Magnetoresistive angle sensors KMZ41/KMZ43 and UZZ900x
14
bra159
KMZ41 UZZ9000
ADC1
14
ALGORITHM
RC-OSCILLATOR &
CLOCK GENERATOR
TEST AND TRIM
MODE
RESET
DAC V
out
ADJUSTMENT
OF
OUTPUT CURVE
CHARACTERISTIC
+ V
O1
- V
O1
+ V
O2
- V
O2
ADC2
BUFFER
BUFFER
13 13
Our KMZ41 and KMZ43 sensor bridges contain eight MR resistors, connected as two individual Wheatstone bridges aligned at 45°.
Possessing different sensitivities, our KMZ41 and KMZ43 angle sensors are designed to work with the UZZ900x conditioning ICs.
Ensuring maximum flexibility, we offer MR sensor bridges both as standalone devices in SO8 package and as bare die for spacecritical solutions.
KMZ41, KMZ43T and X3T-KMZ43
(bare die) key specifications
Property KMZ41
Operating voltage max. 9 V max. 9 V
Angle range 180° 180°
Output signal sin/cos sin/cos
KMZ43T
X3T-KMZ43
Saturation field
strength
Operating
temperature range
100 kA/m 25 kA/m
-40 ....+150 °C -40 ....+150 °C
KMZ43T chip layout, showing the two 45º aligned bridges
Companion signal conditioning ICs for sensor bridges
Designed and developed specifically to complement the KMZ family of angle sensors, the UZZ9000 series provides optimized
single-chip signal conditioning solutions with either analog or 13-bit SPI interfacing. Incorporating all conditioning electronics they
also offer an adjustable measurement range and zero point to maximize design flexibility.
UZZ9000 and UZZ9001 key specifications
Property UZZ9000 UZZ9001
Supply voltage 5 V +/- 10 % 5 V +/- 10 %
KMZ4x and UZZ900x
Maximum angle
range
Angle range
variation
Zero point offset
cancellation
Output
Measurement
resolution
Accuracy
(ideal input)
0° to 180° 0° to 180°
0°- 30 °... 0°- 180° in
10° steps
fixed to 0°- 180°
+/- 5° in 0.5° steps fixed to 0
ratiometric analog
voltage
digital (SPI) with 13-Bit
< 0.1° < 0.05°
< +/- 0.4° < +/- 0.3°
Package SO24 (SOT137-1) SO24 (SOT137-1)
range
Temperature
-40°C to +150°C -40°C to +150°C
Page 11

Single package angle sensor systems with on-chip diagnostics - KMA200 and KMA199
bra900
EEPROM
ONLINE
DIAGNOSIS
R-DAC
DIGITAL PART
HV-
Protection
V
DD
Out1/Data
Buffer
Out2/CLK
GND
CS
MC
Amplifier $3-ADC
TEMP
SENSOR
SERIAL
INTERFACE
MR-
Bridges
bra901
V
DD
V
SS
V
out
EEPROM
DIGITAL PART (STATE MACHINE)
ONE-WIREINTERFACE
MPX
SAR-ADC
R-DAC Buffer
Protection
OFFSET
CALCULATION
ANGULAR/
RANGE
ADJUSTMENT
CORDIC
ALGORITHM
LOW-PASS
DIGITAL
FILTER
4 V-REGULATOR
MR-
Bridges
Amplifier
The KMA200 and KMA199 are pre-aligned, ready-to-use sensor systems. They consist of a magnetoresistive element
containing two independent MR sensor bridges and a signal conditioning IC in a special multi-chip package that allows
90º bending of the MR-element.
Magnetoresistive MR-element
Angle Sensor Chip
Signal Processing IC
The KMA 200 sensor system
KMA200 key features
Ñ
Digital SPI for programming (customer settings and calibration)
Ñ
4 analog and 2 digital output modes, selectable
Ñ
Reverse supply voltage protection up to 16.5 V
Ñ
Over voltage protection up to 26.5 V (32 V for 400 ms)
Ñ
On-line diagnosic of all main functional blocks
Magnetoresistive MR-element
Angle Sensor Chip
Signal Processing IC
The KMA199 sensor system
KMA199 key features
Ñ
Single-wire digital interface for programming
Ñ
3-lead device with analog output
Ñ
Transient protection circuit
Ñ
Active power-loss functionality
KMA200 sensor system KMA199 sensor system
Key specifications
Property KMA200 KMA199
Angular measurement range 180º 180º
Output mode 4 analog/2 digital, selectable ratiometric analog
Maximum error from reference line -1.65º…+1.65º
Linearity error ± 1º
Temperature drift (-25…+125 ºC) -0.64º…+0.64º
Temperature drift related to room temperature 0.55º
Microlinearity -0.1º…+0.1º -0.1º…+0.1º
Temperature range -40…+160 ºC -40…+140 ºC
Supply voltage 5 V + - 10% 5 V + - 10%
Page 12

Magnetoresistive angle sensors and conditioning ICs
Portfolio overview
Type Product Package
Supply
voltage (V)
Angle
range
Output value Output type
Operating
temperatures °C
KMZ41 sensor SO8 5.0 ... 9.0 180° 78 mV peak (5 V) sin/cos -40 ...+150
KMZ43 sensor SO8 5.0 ... 9.0 180° 67 mV peak (5 V) sin/cos -40 ...+150
X3T-KMZ43 sensor die 5.0 ... 9.0 180° 67 mV peak (5 V) sin/cos -40 ...+150
UZZ9000 signal conditioning unit SO24 4.5 ... 5.5 180° 0.5 ... 4.5 V analog linear -40 ...+150
UZZ9001 signal conditioning unit SO24 4.5 ... 5.5 180° 0.5 ... 4.5 V digital -40 ...+150
KMA199 sensor system SOT880 4.5 ... 5.5 180° 0.5 ... 4.5 V analog linear -40 ...+140
KMA200 sensor system SOT637 4.5 ... 5.5 180° 0.5 ... 4.5 V 4 analog linear/2 digital -40 ...+160
www.nxp.com
NXP Sem iconducto rs is in the proc ess of being e stablishe d as a separate l egal entit y in various co untries wor ldwide. Thi s process will b e finalized in th e course of 20 06.
© 2006 Konin klijke Philip s Electroni cs N.V.
All rights r eserved. Reproduc tion in whole or in pa rt is prohibited withou t the pr ior wri tten con sent of the cop yright o wner. The
infor mation pr esented i n this d ocument does no t form p art of any quot ation or contrac t, is b elieved to be acc urate an d reliable
and may be chang ed with out no tice. No liabil ity wi ll be accepted by the pu blisher for an y cons equence of it s use. Public ation
there of does not conv ey nor imply any l icense unde r patent- or othe r industria l or intellec tual proper ty right s.
Date of rel ease: Septem ber 2006
Docum ent order num ber: 9397 750 1572 9
Printe d in the Nether lands
Page 13

Rotational speed sensor
Constantly aware of that
speed sensation
Compact and easy to design in, our KMI magnetoresistive sensors provide simple and
cost-effective solutions for all your rotational speed measurement needs. They meet the high
EMC, reliability and temperature range requirements of the automotive sector, and are available
in a range of options to maximize design freedom.
Key benefi ts
Ñ
Wide air gap between sensor and target
Ñ
Speed detection down to 0 Hz
Ñ
Very low jitter
Ñ
Wide frequency range
Ñ
Insensitive to vibrations
Ñ
Temperature range: -40 to +150 ºC
Ñ
Prepared for injection moulding
Key applications
Ñ
ABS
Ñ
Engine management
Ñ
Gearbox
Ñ
Transmission systems
Ñ
Vehicle speed
Ñ
DC motor commutation
Accurate rotational speed measurement is a vital component
in maintaining performance, safety and reliability in modern
vehicles. It forms the basis of numerous applications from anti-lock
braking to engine management systems, and opens the way for
embedding intelligence throughout the car with the introduction
of advanced X-by-wire networks and control systems.
NXP’s KMI family of magnetoresistive (MR) rotational speed
sensors provides a solution for all applications. Designed
specifi cally to meet the needs of automotive systems,
they are complete, ready-to-use modules comprising sensor,
back-biasing magnet and advanced signal conditioning IC.
Enabling maximum design fl exibility, the devices are available
with a choice of output signals and individually magnetized
back-biasing magnets.
“ Ears “ to fi x the position
of the sensor chip during
moulding process
Extra thick leadframe material
for robustness, bendable
Conditioning IC
Component detail of the KMI20
MR-sensor
Conditioning IC
Page 14

How to measure rotation with MR sensors
gear wheel or rack
(a)
V
(b) (c) (d)
t
MBE073
magnet
sensor
magnetic field lines direction of motion
amplifier,
comparator
sensor
magnetic field lines
magnetized target
msc655
position
current
14 mA
7 mA
N
N
S
S
mbh777
KMIXY/2
mbh779
KMIXY/4
mbh778
KMIXY/1
The KMI sensors are designed to sense the motion of ferrous gear wheels or of magnetized targets. A periodic magnetic field
stemming from the effect of flux bending by ferrous gear wheels or directly from magnetized targets will be transformed by
a MR sensor into an analog electrical signal. The frequency of this signal is proportional to the rotational speed of the target.
A subsequent integrated circuit transforms the analogue into a digital output signal. The output level is independent of the sensing distance within the
measurement range.
Back-biasing magnets, individually magnetized
for each sensor
Ñ
Large (8.0 x 8.0 x 4.5 mm) – for maximum air gap
between sensor and ferrous targets
Ñ
Medium (5.5 x 5.5 x 3.0 mm) – for use with ferrous
targets where space is limited
Ñ
Small (3.8 x 2.0 x 0.8 mm) – for magnetized targets,
stabilizing the inherently bi-stable MR sensor
Output signals
For high flexibility in the design of the subsequent signal
conditioning electronics, the KMI sensors are available
with:
Ñ
a digital current output signal (2-wire)
Ñ
an open collector output signal (3-wire)
Page 15

mbl238
SMART
COMPARATOR
OFFSET
CANCELLATION
Fc = 0 Hz
ADJUSTABLE
AMPLIFIER
SENSOR
DIGITAL CONTROL UNIT
ON-CHIP
OSCILLATOR
VOLTAGE CONTROL
SWITCHABLE
CURRENT
SOURCE
VCC
V-
CONSTANT
CURRENT
SOURCE
SCHMITT
TRIGGER
AMPLIFIERSENSOR
VOLTAGE CONTROL
V
CC
mra958
SWITCHABLE
CURRENT
SOURCE
V-
CONSTANT
CURRENT
SOURCE
SCHMITT
TRIGGER
AMPLIFIERSENSOR
VOLTAGE CONTROL
V
CC
GND
V
out
open collector
output
mgl348
I
CC
T
t
p
mra960
14 mA
7 mA
KMI15 – 7/14 mA current output (2-wire)
KMI18 – open collec tor output (3-wire)
The MR sensor signal is amplified, temperature compensated and passed to a Schmitt trigger.
KMI20 – 7/14 mA current output (2-wire), extended air gap
The MR sensor signal is fed into the conditioning IC. The of fset, gain and
7/14 mA output signal as a func tion of time
hysteresis are digitally adapted to ensure an exceptional air gap capability.
Product overview
Sensor type typ. sensing distance (mm) Tooth frequency (Hz) Target Interface Magnet size (mm)
KMI15/1 0.9 - 2.9 0 - 25.000 note 1 Current 8 x 8 x 4.5
KMI15/2 0.5 - 2.7 0 - 25.000 note 2 Current 3.8 x 2 x 0.8
KMI15/4 0.5 - 2.3 0 - 25.000 note 1 Current 5.5 x 5.5 x 3
KMI18/1 0.9 - 2.9 0 - 25.000 note 1 Open collector 8 x 8 x 4.5
KMI18/2 0.5 - 2.7 0 - 25.000 note 2 Open collector 3.8 x 2 x 0.8
KMI18/4 0.5 - 2.3 0 - 25.000 note 1 Open collector 5.5 x 5.5 x 3
KMI20/1 0.9 - 3.5* 0 - 2.500 note 1 Current 8 x 8 x 4.5
KMI20/2 0.5 - 3.2* 0 - 2.500 note 2 Current 3.8 x 2 x 0.8
KMI20/4 0.5 - 2.8* 0 - 2.500 note 1 Current 5.5 x 5.5 x 3
* + 1 mm dynamic reserve | note 1 - ferrous target | note 2 - magnetized target
Page 16

mlc127
I
Magnetization
Permalloy
H
Current
A
R = R0 $ R0cos2A
Advantages by design
The magnetoresistive ef fect in permalloy
The MR sensor consists of four sensitive resistors in a
Wheatstone bridge configuration, with each resistor arranged
to maximize sensitivity and minimize temperature influences.
Such a Wheatstone bridge design along with the inherent
benefits of MR technology provides several advantages:
Ñ
reduction of temperature drift
Ñ
independent of mechanical assembly tolerances / shifts
Ñ
maximum signal output
Ñ
reduction of non-linearity
MR sensors offer a uniquely versatile combination of features
and important cost benefits. Based on the MR effect,
specifically designed sensors for angle and linear displacement
measurements are also available from NXP, as are solutions for
weak field detection.
NXP sensors are based on the MR effect, where the resistance
of a current-carrying magnetic material, for example a permalloy
(19% Fe, 81% Ni) changes under the influence of an external
magnetic field. If an external field is applied, in the plane of the
current flow, the internal magnetization vector will rotate by the
angle of this field, changing the resistance of the material.
www.nxp.com
Tipical sensor bridge structure
NXP Sem iconducto rs is in the proc ess of being e stablishe d as a separate l egal entit y in various co untries wor ldwide. Thi s process will b e finalized in th e course of 20 06.
© 2006 Konin klijke Philip s Electroni cs N.V.
All rights r eserved. Reproduc tion in whole or in pa rt is prohibited withou t the pr ior wri tten con sent of the cop yright o wner. The
infor mation pr esented i n this d ocument does no t form p art of any quot ation or contrac t, is b elieved to be acc urate an d reliable
and may be chang ed with out no tice. No liabil ity wi ll be accepted by the pu blisher for an y cons equence of it s use. Public ation
there of does not conv ey nor imply any l icense unde r patent- or othe r industria l or intellec tual proper ty right s.
Date of rel ease: Septem ber 2006
Docum ent order num ber: 9397 750 15731
Printe d in the Nether lands
 Loading...
Loading...