Page 1

LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit Arm Cortex®-M3 microcontroller; up to 512 kB flash and
64 kB SRAM with Ethernet, USB 2.0 Host/Device/OTG, CAN
Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 Product data sheet
1. General description
The LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63 are ARM Cortex-M3 based microcontrollers for
embedded applications featuring a high level of integration and low power consumption.
The Arm Cortex-M3 is a next generation core that offers system enhancements such as
enhanced debug features and a higher level of support block integration.
The LPC1768/67/66/65/64/63 operate at CPU frequencies of up to 100 MHz. The
LPC1769 operates at CPU frequencies of up to 120 MHz. The Arm Cortex-M3 CPU
incorporates a 3-stage pipeline and uses a Harvard arc hit ec tu re with s eparate loca l
instruction and data buses as well as a third bus for peripher als. The Arm Cortex-M3 CPU
also includes an internal prefetch unit that supports speculative branching.
The peripheral complement of the LPC1769/68/67 /66/65/64/63 includes up to 512 kB of
flash memory, up to 64 kB of data memory, Ethernet MAC, USB Device/Host/OTG
interface, 8-channel general purpose DMA controller, 4 UARTs, 2 CAN channels, 2 SSP
controllers, SPI interface, 3 I
8-channel 12-bit ADC, 10-bit DAC, motor control PWM, Quadrature Encoder interface,
four general purpose timers, 6-output general purpose PWM, ultra-low power Real-Time
Clock (RTC) with separate battery supply, and up to 70 general purpose I/O pins.
The LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63 are pin-co mpatible to the 100-pi n LPC236x Arm7-base d
microcontroller series.
For additional documentation, see Section 19 “
2. Features and benefits
Arm Cortex-M3 processor, running at frequencies of up to 100 MHz
(LPC1768/67/66/65/64/63) or of up to 120 MHz (LPC1769) . A Memory Pro tection Unit
(MPU) supporting eight regions is included.
Arm Cortex-M3 built-in Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC).
Up to 512 kB on-chip flash programming memory. Enhanced flash memory accelerator
enables high-speed 120 MHz operation with zero wait states.
In-System Programming (ISP) and In-Application Programming (IAP) via on-chip
bootloader software.
On-chip SRAM includes:
32/16 kB of SRAM on the CPU with local code/data bus for high-performance CPU
access.
2
C-bus interfaces, 2-input plus 2-output I2S-bus interface,
References”.
Page 2

NXP Semiconductors
Eight channel General Purpose DMA controller (GPDMA) on the AHB multilayer
Multilayer AHB matrix interconnect provides a separate bus for each AHB master.
Split APB bus allows high throughput with few stalls between the CPU and DMA.
Serial interfaces:
Other peripherals:
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Two/one 16 kB SRAM blocks with separate access paths for higher throughput.
These SRAM blocks may be used for Ethernet, USB, and DMA memory, as well as
for general purpose CPU instruction and data storage.
matrix that can be used with SSP, I
Digital-to-Analog converter peripherals, timer match signals, and for
memory-to-memory transfers.
AHB masters include the CPU, General Purpose DMA controller, Ethernet MAC, and
the USB interface. This interconnect provides communication with no arbitration
delays.
Ethernet MAC with RMII interface and dedicated DMA controller. (Not available on
all parts, see Table 2
.)
USB 2.0 full-speed device/Host/OTG controller with de dic at ed DMA contr o ller and
on-chip PHY for device, Host, and OTG functions. (Not available on all parts, see
Table 2
.)
Four UARTs with fractional baud rate generation, internal FIFO, and DMA support.
One UART has modem control I/O and RS-485/EIA-485 support, and one UART
has IrDA support.
CAN 2.0B controller with two channels. (Not available on all parts, see Table 2
SPI controller with synchronous, serial, full duplex communication and
programmable data length.
Two SSP controllers with FIFO and multi-protocol capabilities. The SSP interfaces
can be used with the GPDMA controller.
Three enhanced I
2
I
C specification and Fast mode plus with data rates of 1 Mbit/s, two with standard
2
C bus interfaces, one with an open-drain output supporting full
port pins. Enhancements include multiple address recognition and monitor mode.
2
I
S (Inter-IC Sound) interface for digital audio input or output, with fractional rate
control. The I
2
S-bus interface can be used with the GPDMA. The I2S-bus interface
supports 3-wire and 4-wire data transmit and receive as well as master clock
input/output. (Not available on all parts, see Table 2
70 (100 pin package) General Purpose I/O (GPIO) pins with configurable
pull-up/down resistors. All GPIOs support a new , configurable o pen-drain operating
mode. The GPIO block is accessed through the AHB multilayer bus for fast access
and located in memory such that it supports Cortex-M3 bit banding and use by the
General Purpose DMA Controller.
12-bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) with input multiplexing among eight pins,
conversion rates up to 200 kHz, and multiple result registers. The 12-bit ADC can
be used with the GPDMA controller.
10-bit Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) with dedicated conversion timer and DMA
support. (Not available on all parts, see Table 2
Four general purpose timers/counters, with a total of eight capture inputs and ten
compare outputs. Each timer block has an external count input. Specific timer
events can be selected to generate DMA requests.
One motor control PWM with support for three-phase motor control.
2
S-bus, UART, Analog-to-Digital and
.)
)
.)
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 2 of 93
Page 3

NXP Semiconductors
Standard JTAG debug interface for compatibility with existing tools. Serial Wire Debug
Emulation trace module enables non-intrusive, high-speed real-time tracing of
Integrated PMU (Power Management Unit) automatically adjusts internal regulators to
Four reduced power modes: Sleep, Deep-sleep, Power-down, and Deep power-down.
Single 3.3 V power supply (2.4 V to 3.6 V).
Four external interrupt inputs configurable as edge/level sensitive. All pins on Port 0
Non-maskable Interrupt (NMI) input.
Clock output function that can reflect the main oscillator clock, IRC clock, RTC clock,
The Wake-up Interrupt Controller (WIC) allows the CPU to automatically wake up from
Processor wake-up from Power-down mode via any interrupt able to operate during
Brownout detect with separate threshold for interrupt and forced reset.
Power-On Reset (POR).
Crystal oscillator with an operating range of 1 MHz to 25 MHz.
4 MHz internal RC oscillator trimmed to 1 % accuracy that can optionally be used as a
PLL allows CPU operation up to the maximum CPU rate without the need for a
USB PLL for added flexibility.
Code Read Protection (CRP) with different security levels.
Unique device serial number for identification purposes.
Available as LQFP100 (14 mm 14 mm 1.4 mm), TFBGA100
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Quadrature encoder interface that can monitor one external quadrature encoder.
One standard PWM/timer block with external count input.
RTC with a separate power domain and dedicated RTC oscillator. The RTC block
includes 20 bytes of battery-powered backup registers.
WatchDog Timer (WDT). The WDT can be clocked from the internal RC oscillator,
the RTC oscillator, or the APB clock.
Arm Cortex-M3 system tick timer, including an external clock input option.
Repetitive interrupt timer provides programmable and repeating timed interrupts.
Each peripheral has its own clock divider for further power savings.
and Serial Wire Trace Port options. Boundary Scan Description Language (BSDL) is
not available for this device.
instruction execution.
minimize power consumption during Sleep, Deep sleep, Power-down, and Deep
power-down modes.
and Port 2 can be used as edge sensitive interrupt sources.
CPU clock, and the USB clock.
any priority interrupt that can occur while the clocks are stopped in deep sleep,
Power-down, and Deep power-down modes.
Power-down mode (includes external interrupts, RTC interrupt, USB activity, Ethernet
wake-up interrupt, CAN bus activity, Port 0/2 pin interrupt, and NMI).
system clock.
high-frequency crystal. May be run from the main oscillator, the internal RC oscillator,
or the RTC oscillator.
1
(9 mm 9 mm 0.7
mm), and WLCSP100 (5.07 5.07 0.53 mm) package.
1. LPC1768/65 only.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 3 of 93
Page 4

NXP Semiconductors
3. Applications
eMetering Alarm systems
Lighting White goods
Industrial networking Motor control
4. Ordering information
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 1. Ordering information
Type number Package
LPC1769FBD100 LQFP100 plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 14 1.4 mm SOT407-1
LPC1768FBD100 LQFP100 plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 14 1.4 mm SOT407-1
LPC1768FET100 TFBGA100 plastic thin fine-pitch ball grid array package; 100 balls; body 9 9 0.7 mm SOT926-1
LPC1768UK WLCSP100 wafer level chip-scale package; 100 balls; 5.07 5.07 0.53 mm LPC1767FBD100 LQFP100 plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 14 1.4 mm SOT407-1
LPC1766FBD100 LQFP100 plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 14 1.4 mm SOT407-1
LPC1765FBD100 LQFP100 plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 14 1.4 mm SOT407-1
LPC1765FET100 TFBGA100 plastic thin fine-pitch ball grid array package; 100 balls; body 9 9 0.7 mm SOT926-1
LPC1764FBD100 LQFP100 plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 14 1.4 mm SOT407-1
LPC1763FBD100 LQFP100 plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 14 1.4 mm SOT407-1
Name Description Version
4.1 Ordering options
Table 2. Ordering options
SRAM in kB
S
Typ e number
LPC1769FBD100 LPC1769FBD100,551 512 32 16 16 64 yes Device/Host/OTG 2 yes yes 70 120
LPC1768FBD100 LPC1768FBD100/CP32 512 32 16 16 64 yes Device/Host/OTG 2 yes yes 70 100
LPC1768FET100 LPC1768FET100Z 512 32 16 16 64 yes Device/Host/OTG 2 yes yes 70 100
LPC1768UK LPC1768UKZ 512 32 16 16 64 yes Device/Host/OTG 2 yes yes 70 100
LPC1767FBD100 LPC1767FBD100,551 512 32 16 16 64 yes no no yes yes 70 100
LPC1766FBD100 LPC1766FBD100,551 256 32 16 16 64 yes Device/Host/OTG 2 yes yes 70 100
LPC1765FBD100 LPC1765FBD100/3271 256 32 16 16 64 no Device/Host/OTG 2 yes yes 70 100
LPC1765FET100 LPC1765FET100,551 256 32 16 16 64 no Device/Host/OTG 2 yes yes 70 100
LPC1764FBD100 LPC1764FBD100,551 128 16 16 - 32 yes Device only 2 no no 70 100
LPC1763FBD100 LPC1763FBD100K 256 32 16 16 64 no no no yes yes 70 100
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 4 of 93
Device order
part number
Flash (kB)
CPU
AHB SRAM0
Total
Ethernet
AHB SRAM1
USB
CAN
2
I
DAC
GPIO
Maximum CPU
operating frequency
(MHz)
Page 5

NXP Semiconductors
5. Marking
The LPC176x devices typically have the following top-side marking:
LPC176xxxx
xxxxxxx
xxYYWWR[x]
The last/second to last letter in the third line (field ‘R’) will identify the device revision. This
data sheet covers the following revisions of the LPC176x:
Table 3. Devic e revision table
Revision identifier (R) Revision description
‘-’ Initial device revision
‘A’ Second device revision
‘B’ Third device revision
Field ‘YY’ states the year the device was manufactured. Field ‘WW’ states the week the
device was manufactured during that year.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 5 of 93
Page 6

NXP Semiconductors
SRAM 32/64 kB
ARM
CORTEX-M3
TEST/DEBUG
INTERFACE
EMULATION
TRACE MODULE
FLASH
ACCELERATOR
FLASH
512/256/128 kB
DMA
CONTROLLER
ETHERNET
CONTROLLER
WITH DMA
(1)
USB HOST/
DEVICE/OTG
CONTROLLER
WITH DMA
(1)
I-code
bus
D-code
bus
system
bus
AHB TO
APB
BRIDGE 0
HIGH-SPEED
GPIO
AHB TO
APB
BRIDGE 1
CLOCK
GENERATION,
POWER CONTROL,
SYSTEM
FUNCTIONS
XTAL1
XTAL2
RESET
clocks and
controls
JTAG
interface
debug
port
USB PHY
SSP0
UART2/3
I2S
(1)
I2C2
RI TIMER
TIMER2/3
EXTERNAL INTERRUPTS
SYSTEM CONTROL
MOTOR CONTROL PWM
QUADRATURE ENCODER
SSP1
UART0/1
CAN1/2
(1)
I2C0/1
SPI0
TIMER 0/1
WDT
PWM1
12-bit ADC
PIN CONNECT
GPIO INTERRUPT CONTROL
RTC
BACKUP REGISTERS
32 kHz
OSCILLATOR
APB slave group 1
APB slave group 0
DAC
(1)
RTC POWER DOMAIN
LPC1769/68/67/
66/65/64/63
master master master
002aad944
slaveslave slave
slave
slave
ROM
slave
MULTILAYER AHB MATRIX
P0 to
P4
SDA2
SCL2
SCK0
SSEL0
MISO0
MOSI0
SCK1
SSEL1
MISO1
MOSI1
RXD2/3
TXD2/3
PHA, PHB
INDEX
EINT[3:0]
AOUT
MCOA[2:0]
MCOB[2:0]
MCI[2:0]
MCABORT
4 × MAT2
2 × MAT3
2 × CAP2
2 × CAP3
3 × I2SRX
3 × I2STX
TX_MCLK
RX_MCLK
RTCX1
RTCX2
VBAT
PWM1[7:0]
2 × MAT0/1
2 × CAP0/1
RD1/2
TD1/2
SDA0/1
SCL0/1
AD0[7:0]
SCK/SSEL
MOSI/MISO
8 × UART1
RXD0/TXD0
P0, P2
PCAP1[1:0]
RMII pins
USB pins
CLKOUT
MPU
= connected to DMA
6. Block diagram
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 1. Block diagram
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 6 of 93
(1) Not available on all parts. See Table 2.
Page 7

NXP Semiconductors
LPC176xFBD100
50
1
25
75
51
26
76
100
002aad945
002aaf723
LPC1768/65FET100
Transparent top view
J
G
K
H
F
E
D
C
B
A
24681013579
ball A1
index area
7. Pinning information
7.1 Pinning
Fig 2. Pin configuration LQFP100 package
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 3. Pin configuration TFBGA100 package
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 7 of 93
Page 8

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
bump A1
index area
1
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
LPC1768UK
2345678910
aaa-009522
Transparent top view
Fig 4. Pin configuration WLCSP100 package
Table 4. Pin allocation table TFBGA100
Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol
Row A
1 TDO/SWO 2 P0[3]/RXD0/AD0[6] 3 V
5 P1[10]/ENET_RXD1 6 P1[16]/ENET_MDC 7 V
DD(3V3)
DD(REG)(3V3)
4 P1[4]/ENET_TX_EN
8 P0[4]/I2SRX_CLK/
RD2/CAP2[0]
9 P0[7]/I2STX_CLK/
SCK1/MAT2[1]
10 P0[9]/I2STX_SDA/
MOSI1/MAT2[3]
11 - 12 -
Row B
1 TMS/SWDIO 2 RTCK 3 V
5 P1[9]/ENET_RXD0 6 P1[17]/
7V
ENET_MDIO
SS
SS
4 P1[1]/ENET_TXD1
8 P0[6]/I2SRX_SDA/
SSEL1/MAT2[0]
9 P2[0]/PWM1[1]/TXD1 10 P2[1]/PWM1[2]/RXD1 11 - 12 -
Row C
1TCK/SWDCLK 2TRST
5 P1[8]/ENET_CRS 6 P1[15]/
ENET_REF_CLK
9V
SS
10 V
DD(3V3)
3 TDI 4 P0[2]/TXD0/AD0[7]
7 P4[28]/RX_MCLK/
MAT2[0]/TXD3
8 P0[8]/I2STX_WS/
MISO1/MAT2[2]
11 - 12 -
Row D
1 P0[24]/AD0[1]/
I2SRX_WS/CAP3[1]
5 P1[0]/ENET_TXD0 6 P1[14]/ENET_RX_ER 7 P0[5]/I2SRX_WS/
9 P2[4]/PWM1[5]/
DSR1/TRACEDATA[1]
2 P0[25]/AD0[2]/
I2SRX_SDA/TXD3
10 P2[5]/PWM1[6]/
DTR1/TRACEDATA[0]
3 P0[26]/AD0[3]/
4n.c.
AOUT/RXD3
8 P2[2]/PWM1[3]/
TD2/CAP2[1]
11 - 12 -
CTS1/TRACEDATA[3]
Row E
1V
SSA
5 P0[23]/AD0[0]/
I2SRX_CLK/CAP3[0]
2V
DDA
6 P4[29]/TX_MCLK/
MAT2[1]/RXD3
3VREFP 4n.c.
7 P2[3]/PWM1[4]/
DCD1/TRACEDATA[2]
8 P2[6]/PCAP1[0]/
RI1/TRACECLK
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 8 of 93
Page 9

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 4. Pin allocation table TFBGA100
…continued
Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol
9 P2[7]/RD2/RTS1 10 P2[8]/TD2/TXD2 11 - 12 -
Row F
1 VREFN 2 RTCX1 3 RESET
4 P1[31]/SCK1/
AD0[5]
5 P1[21]/MCABORT
PWM1[3]/SSEL0
9 P0[17]/CTS1/
MISO0/MISO
/
6 P0[18]/DCD1/
MOSI0/MOSI
10 P0[15]/TXD1/
SCK0/SCK
7 P2[9]/USB_CONNECT/
8 P0[16]/RXD1/
RXD2
11 - 12 -
SSEL0/SSEL
Row G
1 RTCX2 2 VBAT 3 XTAL2 4 P0[30]/USB_D
5 P1[25]/MCOA1/
MAT1[1]
6 P1[29]/MCOB2/
PCAP1[1]/MAT0[1]
7V
SS
8 P0[21]/RI1/RD1
9 P0[20]/DTR1/SCL1 10 P0[19]/DSR1/SDA1 11 - 12 -
Row H
1 P1[30]/V
BUS
AD0[4]
5 P1[24]/MCI2/
PWM1[5]/MOSI0
9V
DD(3V3)
/
2 XTAL1 3 P3[25]/MAT0[0]/
4 P1[18]/USB_UP_LED/
PWM1[2]
6V
DD(REG)(3V3)
7 P0[10]/TXD2/
8P2[11]/EINT1/
SDA2/MAT3[0]
10 P0[22]/RTS1/TD1 1 1 - 12 -
PWM1[1]/CAP1[0]
I2STX_CLK
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 9 of 93
Page 10

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 4. Pin allocation table TFBGA100 …continued
Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol
Row J
1 P0[28]/SCL0/
USB_SCL
5 P1[22]/MCOB0/
USB_PWRD/
MAT1[0]
9 P2[13]/EINT3
/
I2STX_SDA
Row K
1 P3[26]/STCLK/
MAT0[1]/PWM1[3]
5 P1[23]/MCI1/
PWM1[4]/MISO0
9 P0[11]/RXD2/
SCL2/MAT3[1]
2 P0[27]/SDA0/
3 P0[29]/USB_D+ 4 P1[19]/MCOA0/
USB_SDA
6V
SS
7 P1[28]/MCOA2/
8 P0[1]/TD1/RXD3/SCL1
PCAP1[0]/
MAT0[0]
10 P2[10]/EINT0/NMI 11 - 12 -
2V
DD(3V3)
6 P1[26]/MCOB1/
PWM1[6]/CAP0[0]
3V
SS
7 P1[27]/CLKOUT
/USB_OVRCR
4 P1[20]/MCI0/
8 P0[0]/RD1/TXD3/SDA1
/
CAP0[1]
10 P2[12]/EINT2
/
11 - 12 -
I2STX_WS
USB_PPWR
CAP1[1]
PWM1[2]/SCK0
/
7.2 Pin description
Table 5. Pin description
Symbol Pin/ball Type Description
P0[0] to P0[31] I/O Port 0: Port 0 is a 32-bit I/O port with individual direction controls for
P0[0]/RD1/TXD3/
SDA1
P0[1]/TD1/RXD3/
SCL1
P0[2]/TXD0/AD0[7] 98 C4 B1
P0[3]/RXD0/AD0[6] 99 A2 C3
LQFP100
TFBGA100
WLCSP100
46 K8 H10
47 J8 H9
each bit. The operation of port 0 pins depends upon the pin function
selected via the pin connect block. Pins 12, 13, 14, and 31 of this
port are not available.
[1]
I/O P0[0] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I RD1 — CAN1 receiver input. (LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only).
O TXD3 — Transmitter output for UART3.
2
I/O SDA1 — I
C1 data input/output. (This is not an I2C-bus compliant
open-drain pin).
[1]
I/O P0[1] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O TD1 — CAN1 transmitter output. (LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only).
I RXD3 — Receiver input for UART3.
2
I/O SCL1 — I
C1 clock input/output. (This is not an I2C-bus compliant
open-drain pin).
[2]
I/O P0[2] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O TXD0 — Transmitter output for UART0.
I AD0[7] — A/D converter 0, input 7.
[2]
I/O P0[3] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I RXD0 — Receiver input for UART0.
I AD0[6] — A/D converter 0, input 6.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 10 of 93
Page 11

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 5. Pin description
…continued
Symbol Pin/ball Type Description
LQFP100
TFBGA100
WLCSP100
P0[4]/
I2SRX_CLK/
RD2/CAP2[0]
81 A8 G2
[1]
I/O P0[4] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I/O I2SRX_CLK — Receive Clock. It is driven by the master and
received by the slave. Corresponds to the signal SCK in the I
specification. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
I RD2 — CAN2 receiver input. (LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only).
I CAP2[0] — Capture input for Timer 2, channel 0.
[1]
P0[5]/
I2SRX_WS/
TD2/CAP2[1]
80 D7 H1
I/O P0[5] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I/O I2SRX_WS — Receive Word Select. It is driven by the master and
received by the slave. Corresponds to the signal WS in the I
specification. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
O TD2 — CAN2 transmitter output. (LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only).
I CAP2[1] — Capture input for Timer 2, channel 1.
[1]
P0[6]/
I2SRX_SDA/
SSEL1/MAT2[0]
79 B8 G3
I/O P0[6] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I/O I2SRX_SDA — Receive data. It is driven by the transmitter and read
by the receiver. Corresponds to the signal SD in the I
specification. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
I/O SSEL1 — Slave Select for SSP1.
O MAT2[0] — Match output for Timer 2, channel 0.
[1]
P0[7]/
I2STX_CLK/
SCK1/MAT2[1]
78 A9 J1
I/O P0[7] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I/O I2STX_CLK — Transmit Clock. It is driven by the master and
received by the slave. Corresponds to the signal SCK in the I
specification. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
I/O SCK1 — Serial Clock for SSP1.
O MAT2[1] — Match output for Timer 2, channel 1.
[1]
P0[8]/
I2STX_WS/
MISO1/MAT2[2]
77 C8 H2
I/O P0[8] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I/O I2STX_WS — Transmit Word Select. It is driven by the master and
received by the slave. Corresponds to the signal WS in the I
specification. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
I/O MISO1 — Master In Slave Out for SSP1.
O MAT2[2] — Match output for Timer 2, channel 2.
[1]
P0[9]/
I2STX_SDA/
MOSI1/MAT2[3]
76 A10 H3
I/O P0[9] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I/O I2STX_SDA — Transmit data. It is driven by the transmitter and
read by the receiver. Corresponds to the signal SD in the I
specification. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
I/O MOSI1 — Master Out Slave In for SSP1.
O MAT2[3] — Match output for Timer 2, channel 3.
[1]
P0[10]/TXD2/
SDA2/MAT3[0]
48 H7 H8
I/O P0[10] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O TXD2 — Transmitter output for UART2.
I/O SDA2 — I
O MAT3[0] — Match output for Timer 3, channel 0.
2
S-bus
2
2
C2 data input/output (this is not an open-drain pin).
2
S-bus
2
S-bus
2
S-bus
2
S-bus
S-bus
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 11 of 93
Page 12

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 5. Pin description
…continued
Symbol Pin/ball Type Description
LQFP100
TFBGA100
WLCSP100
P0[11]/RXD2/
SCL2/MAT3[1]
49 K9 J10
[1]
I/O P0[11] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I RXD2 — Receiver input for UART2.
I/O SCL2 — I
O MAT3[1] — Match output for Timer 3, channel 1.
[1]
P0[15]/TXD1/
SCK0/SCK
62 F10 H6
I/O P0[15] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O TXD1 — Transmitter output for UART1.
I/O SCK0 — Serial clock for SSP0.
I/O SCK — Serial clock for SPI.
[1]
P0[16]/RXD1/
SSEL0/SSEL
63 F8 J5
I/O P0[16] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I RXD1 — Receiver input for UART1.
I/O SSEL0 — Slave Select for SSP0.
I/O SSEL — Slave Select for SPI.
[1]
P0[17]/CTS1/
MISO0/MISO
61 F9 K6
I/O P0[17] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I CTS1 — Clear to Send input for UART1.
I/O MISO0 — Master In Slave Out for SSP0.
I/O MISO — Master In Slave Out for SPI.
[1]
P0[18]/DCD1/
MOSI0/MOSI
60 F6 J6
I/O P0[18] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I DCD1 — Data Carrier Detect input for UART1.
I/O MOSI0 — Master Out Slave In for SSP0.
I/O MOSI — Master Out Slave In for SPI.
[1]
P0[19]/DSR1/
SDA1
59 G10 K7
I/O P0[19] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I DSR1 — Data Set Ready input for UART1.
I/O SDA1 — I
open-drain pin).
[1]
P0[20]/DTR1/SCL1 58 G9 J7
I/O P0[20] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O DTR1 — Data Termina l Ready output for UART1. Can also be
configured to be an RS-485/EIA-485 output enable signal.
I/O SCL1 — I
open-drain pin).
[1]
P0[21]/RI1/RD1 57 G8 H7
I/O P0[21] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I RI1 — Ring Indicator input for UART1.
I RD1 — CAN1 receiver input. (LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only).
[1]
P0[22]/RTS1/TD1 56 H10 K8
I/O P0[22] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O RTS1 — Request to Send output for UART1. Can also be
configured to be an RS-485/EIA-485 output enable signal.
O TD1 — CAN1 transmitter output. (LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only).
2
C2 clock input/output (this is not an open-drain pin).
2
C1 data input/output (this is not an I2C-bus compliant
2
C1 clock input/output (this is not an I2C-bus compliant
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 12 of 93
Page 13

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 5. Pin description
…continued
Symbol Pin/ball Type Description
LQFP100
TFBGA100
WLCSP100
P0[23]/AD0[0]/
I2SRX_CLK/
CAP3[0]
9E5D5
[2]
I/O P0[23] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I AD0[0] — A/D converter 0, input 0.
I/O I2SRX_CLK — Receive Clock. It is driven by the master and
received by the slave. Corresponds to the signal SCK in the I
specification. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
I CAP3[0] — Capture input for Timer 3, channel 0.
[2]
P0[24]/AD0[1]/
I2SRX_WS/
CAP3[1]
8D1B4
I/O P0[24] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I AD0[1] — A/D converter 0, input 1.
I/O I2SRX_WS — Receive Word Select. It is driven by the master and
received by the slave. Corresponds to the signal WS in the I
specification. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
I CAP3[1] — Capture input for Timer 3, channel 1.
[2]
P0[25]/AD0[2]/
I2SRX_SDA/
TXD3
7D2A3
I/O P0[25] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I AD0[2] — A/D converter 0, input 2.
I/O I2SRX_SDA — Receive data. It is driven by the transmitter and read
by the receiver. Corresponds to the signal SD in the I
specification. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
O TXD3 — Transmitter output for UART3.
[3]
P0[26]/AD0[3]/
AOUT/RXD3
6D3C5
I/O P0[26] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I AD0[3] — A/D converter 0, input 3.
O AOUT — DAC output (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
I RXD3 — Receiver input for UART3.
[4]
P0[27]/SDA0/
USB_SDA
25 J2 C8
I/O P0[27] — General purpose digital inpu t/output pin. Output is
open-drain.
I/O SDA0 — I
compliance).
I/O USB_SDA — USB port I
LPC1769/68/66/65 only).
[4]
P0[28]/SCL0/
USB_SCL
24 J1 B9
I/O P0[28] — General purpose digital inpu t/output pin. Output is
open-drain.
I/O SCL0 — I
compliance).
I/O USB_SCL — USB port I
LPC1769/68/66/65 only).
[5]
P0[29]/USB_D+ 29 J3 B10
I/O P0[29] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I/O USB_D+ — USB bidirectional D+ line. (LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only).
[5]
P0[30]/USB_D 30 G4 C9
I/O P0[30] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I/O USB_D — USB bidirectional D line. (LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only).
2
2
S-bus
2
C0 data input/output. Open-drain output (for I2C-bus
2
C serial data (OTG transceiver,
2
C0 clock input/output. Open-drain output (for I2C-bus
2
C serial clock (OTG transceiver,
2
S-bus
S-bus
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 13 of 93
Page 14

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 5. Pin description
…continued
Symbol Pin/ball Type Description
LQFP100
TFBGA100
WLCSP100
P1[0] to P1[31] I/O Port 1: Port 1 is a 32-bit I/O port with individual direction controls for
each bit. The operation of port 1 pins depends upon the pin function
selected via the pin connect block. Pins 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 11, 12, and 13
of this port are not available.
[1]
P1[0]/
ENET_TXD0
95 D5 C1
I/O P1[0] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O ENET_TXD0 — Ethernet transmit data 0. (LPC1769/68/67/66/64
only).
[1]
P1[1]/
ENET_TXD1
94 B4 C2
I/O P1[1] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O ENET_TXD1 — Ethernet transmit data 1. (LPC1769/68/67/66/64
only).
[1]
P1[4]/
ENET_TX_EN
93 A4 D2
I/O P1[4] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O ENET_TX_EN — Ethernet transmit data enable.
(LPC1769/68/67/66/64 only).
[1]
P1[8]/
ENET_CRS
P1[9]/
ENET_RXD0
92 C5 D1
91 B5 D3
I/O P1[8] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I ENET_CRS — Ethernet carrier sense. (LPC1769/68/67/66/64 only).
[1]
I/O P1[9] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I ENET_RXD0 — Ethernet receive data. (LPC1769/68/67/66/64
only).
[1]
P1[10]/
ENET_RXD1
90 A5 E3
I/O P1[10] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I ENET_RXD1 — Ethernet receive data. (LPC1769/68/67/66/64
only).
[1]
P1[14]/
ENET_RX_ER
89 D6 E2
I/O P1[14] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I ENET_RX_ER — Ethernet receive error. (LPC1769/68/67/66/64
only).
[1]
P1[15]/
ENET_REF_CLK
88 C6 E1
I/O P1[15] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I ENET_REF_CLK — Ethernet reference clock.
(LPC1769/68/67/66/64 only).
[1]
P1[16]/
ENET_MDC
P1[17]/
ENET_MDIO
87 A6 F3
86 B6 F2
I/O P1[16] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O ENET_MDC — Ethernet MIIM clock (LPC1769/68/67/66/64 only).
[1]
I/O P1[17] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I/O ENET_MDIO — Ethernet MIIM data input and output.
(LPC1769/68/67/66/64 only).
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 14 of 93
Page 15

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 5. Pin description
…continued
Symbol Pin/ball Type Description
LQFP100
TFBGA100
WLCSP100
P1[18]/
USB_UP_LED/
PWM1[1]/
CAP1[0]
32 H4 D9
[1]
I/O P1[18] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O USB_UP_LED — USB GoodLink LED indicator. It is LOW when the
device is configured (non-control endpoints enabled), or when the
host is enabled and has detected a device on the bus. It is HIGH
when the device is not configured, or when host is enabled and has
not detected a device on the bus, or during global suspend. It
transitions between LOW and HIGH (flashes) when the host is
enabled and detects activity on the bus. (LPC1769/68/66/65/64
only).
O PWM1[1] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, channel 1 output.
I CAP1[0] — Capture input for Timer 1, channel 0.
P1[19]/MCOA0/
USB_PPWR
/
CAP1[1]
33 J4 C10
[1]
I/O P1[19] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O MCOA0 — Motor control PWM channel 0, output A.
O USB_PPWR
(LPC1769/68/66/65 only).
I CAP1[1] — Capture input for Timer 1, channel 1.
[1]
P1[20]/MCI0/
PWM1[2]/SCK0
34 K4 E8
I/O P1[20] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I MCI0 — Motor control PWM channel 0, input. Also Quadrature
Encoder Interface PHA input.
O PWM1[2] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, channel 2 output.
I/O SCK0 — Serial clock for SSP0.
P1[21]/MCABORT
PWM1[3]/
SSEL0
/
35 F5 E9
[1]
I/O P1[21] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O MCABORT
O PWM1[3] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, channel 3 output.
I/O SSEL0 — Slave Select for SSP0.
[1]
P1[22]/MCOB0/
USB_PWRD/
MAT1[0]
36 J5 D10
I/O P1[22] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O MCOB0 — Motor control PWM channel 0, output B.
I USB_PWRD — Power Status for USB port (host power switch,
LPC1769/68/66/65 only).
O MAT1[0] — Match output for Timer 1, channel 0.
[1]
P1[23]/MCI1/
PWM1[4]/MISO0
37 K5 E7
I/O P1[23] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I MCI1 — Motor control PWM channel 1, input. Also Quadrature
Encoder Interface PHB input.
O PWM1[4] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, channel 4 output.
I/O MISO0 — Master In Slave Out for SSP0.
[1]
P1[24]/MCI2/
PWM1[5]/MOSI0
38 H5 F8
I/O P1[24] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I MCI2 — Motor control PWM channel 2, input. Also Quadrature
Encoder Interface INDEX input.
O PWM1[5] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, channel 5 output.
I/O MOSI0 — Master Out Slave in for SSP0.
— Port Power enable signal for USB port.
— Motor control PWM, LOW-active fast abort.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 15 of 93
Page 16

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 5. Pin description
…continued
Symbol Pin/ball Type Description
LQFP100
TFBGA100
WLCSP100
P1[25]/MCOA1/
MAT1[1]
39 G5 F9
[1]
I/O P1[25] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O MCOA1 — Motor control PWM channel 1, output A.
O MAT1[1] — Match output for Timer 1, channel 1.
[1]
P1[26]/MCOB1/
PWM1[6]/CAP0[0]
40 K6 E10
I/O P1[26] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O MCOB1 — Motor control PWM channel 1, output B.
O PWM1[6] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, channel 6 output.
I CAP0[0] — Capture input for Timer 0, channel 0.
P1[27]/CLKOUT
/USB_OVRCR
CAP0[1]
43 K7 G9
/
[1]
I/O P1[27] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O CLKOUT — Clock output pin.
I USB_OVRCR
— USB port Over-Current status. (LPC1769/68/66/65
only).
I CAP0[1] — Capture input for Timer 0, channel 1.
[1]
P1[28]/MCOA2/
PCAP1[0]/
MAT0[0]
44 J7 G10
I/O P1[28] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O MCOA2 — Motor control PWM channel 2, output A.
I PCAP1[0] — Capture input for PWM1, channel 0.
O MAT0[0] — Match output for Timer 0, channel 0.
[1]
P1[29]/MCOB2/
PCAP1[1]/
MAT0[1]
45 G6 G8
I/O P1[29] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O MCOB2 — Motor control PWM channel 2, output B.
I PCAP1[1] — Capture input for PWM1, channel 1.
O MAT0[1] — Match output for Timer 0, channel 1.
P1[30]/V
AD0[4]
BUS
/
21 H1 B8
[2]
I/O P1[30] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I V
— Monitors the presence of USB bus power.
BUS
(LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only).
Note: This signal must be HIGH for USB reset to occur.
I AD0[4] — A/D converter 0, input 4.
[2]
P1[31]/SCK1/
AD0[5]
20 F4 C7
I/O P1[31] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I/O SCK1 — Serial Clock for SSP1.
I AD0[5] — A/D converter 0, input 5.
P2[0] to P2[31] I/O Port 2: Port 2 is a 32-bit I/O port with individual direction controls for
each bit. The operation of port 2 pins depends upon the pin function
selected via the pin connect block. Pins 14 through 31 of this port
are not available.
[1]
P2[0]/PWM1[1]/
TXD1
75 B9 K1
I/O P2[0] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O PWM1[1] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, channel 1 output.
O TXD1 — Transmitter output for UART1.
[1]
P2[1]/PWM1[2]/
RXD1
74 B10 J2
I/O P2[1] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O PWM1[2] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, channel 2 output.
I RXD1 — Receiver input for UART1.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 16 of 93
Page 17

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 5. Pin description
…continued
Symbol Pin/ball Type Description
LQFP100
TFBGA100
WLCSP100
P2[2]/PWM1[3]/
CTS1/
TRACEDATA[3]
73 D8 K2
[1]
I/O P2[2] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O PWM1[3] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, channel 3 output.
I CTS1 — Clear to Send input for UART1.
O TRACEDATA[3] — Trace data, bit 3.
[1]
P2[3]/PWM1[4]/
DCD1/
TRACEDATA[2]
70 E7 K3
I/O P2[3] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O PWM1[4] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, channel 4 output.
I DCD1 — Data Carrier Detect input for UART1.
O TRACEDATA[2] — Trace data, bit 2.
[1]
P2[4]/PWM1[5]/
DSR1/
TRACEDATA[1]
69 D9 J3
I/O P2[4] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O PWM1[5] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, channel 5 output.
I DSR1 — Data Set Ready input for UART1.
O TRACEDATA[1] — Trace data, bit 1.
[1]
P2[5]/PWM1[6]/
DTR1/
TRACEDATA[0]
68 D10 H4
I/O P2[5] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O PWM1[6] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, channel 6 output.
O DTR1 — Data Termina l Ready output for UART1. Can also be
configured to be an RS-485/EIA-485 output enable signal.
O TRACEDATA[0] — Trace data, bit 0.
[1]
P2[6]/PCAP1[0]/
RI1/TRACECLK
67 E8 K4
I/O P2[6] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I PCAP1[0] — Capture input for PWM1, channel 0.
I RI1 — Ring Indicator input for UART1.
O TRACECLK — Trace Clock.
[1]
P2[7]/RD2/
RTS1
66 E9 J4
I/O P2[7] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I RD2 — CAN2 receiver input. (LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only).
O RTS1 — Request to Send output for UART1. Can also be
configured to be an RS-485/EIA-485 output enable signal.
[1]
P2[8]/TD2/
TXD2
65 E10 H5
I/O P2[8] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O TD2 — CAN2 transmitter output. (LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only).
O TXD2 — Transmitter output for UART2.
[1]
P2[9]/
USB_CONNECT/
RXD2
64 F7 K5
I/O P2[9] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O USB_CONNECT — Signal used to switch an external 1.5 k
resistor under software control. Used with the SoftConnect USB
feature. (LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only).
I RXD2 — Receiver input for UART2.
P2[10]/EINT0
/NMI 53 J10 K9
[6]
I/O P2[10] — General purpose digital input/output pin. A LOW level on
this pin during reset starts the ISP command handler.
I EINT0
— External interrupt 0 input.
I NMI — Non-maskable interrupt input.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 17 of 93
Page 18

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 5. Pin description
…continued
Symbol Pin/ball Type Description
LQFP100
TFBGA100
WLCSP100
P2[11]/EINT1/
I2STX_CLK
52 H8 J8
[6]
I/O P2[11] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I EINT1
— External interrupt 1 input.
I/O I2STX_CLK — Transmit Clock. It is driven by the master and
2
received by the slave. Corresponds to the signal SCK in the I
S-bus
specification. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
P2[12]/EINT2
I2STX_WS
/
51 K10 K10
[6]
I/O P2[12] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I EINT2
— External interrupt 2 input.
I/O I2STX_WS — Transmit Word Select. It is driven by the master and
2
received by the slave. Corresponds to the signal WS in the I
S-bus
specification. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
P2[13]/EINT3
I2STX_SDA
/
50 J9 J9
[6]
I/O P2[13] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I EINT3
— External interrupt 3 input.
I/O I2STX_SDA — Transmit data. It is driven by the transmitter and
2
read by the receiver. Corresponds to the signal SD in the I
S-bus
specification. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63 only).
P3[0] to P3[31] I/O Port 3: Port 3 is a 32-bit I/O port with individual direction controls for
each bit. The operation of port 3 pins depends upon the pin function
selected via the pin connect block. Pins 0 through 24, and 27
through 31 of this port are not available.
[1]
P3[25]/MAT0[0]/
PWM1[2]
27 H3 D8
I/O P3[25] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
O MAT0[0] — Match output for Timer 0, channel 0.
O PWM1[2] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, output 2.
[1]
P3[26]/STCLK/
MAT0[1]/PWM1[3]
26 K1 A10
I/O P3[26] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
I STCLK — System tick timer clock input. The maximum STCLK
frequency is 1/4 of the Arm processor clock frequency CCLK.
O MAT0[1] — Match output for Timer 0, channel 1.
O PWM1[3] — Pulse Width Modulator 1, output 3.
P4[0] to P4[31] I/O Port 4: Port 4 is a 32-bit I/O port with individual direction controls for
each bit. The operation of port 4 pins depends upon the pin function
selected via the pin connect block. Pins 0 through 27, 30, and 31 of
this port are not available .
[1]
P4[28]/RX_MCLK/
MAT2[0]/TXD3
82 C7 G1
I/O P4[28] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
2
O RX_MCLK — I
S receive master clock. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65
only).
O MAT2[0] — Match output for Timer 2, channel 0.
O TXD3 — Transmitter output for UART3.
[1]
P4[29]/TX_MCLK/
MAT2[1]/RXD3
85 E6 F1
I/O P4[29] — General purpose digital input/output pin.
2
O TX_MCLK — I
S transmit master clock. (LPC1769/68/67/66/65
only).
O MAT2[1] — Match output for Timer 2, channel 1.
I RXD3 — Receiver input for UART3.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 18 of 93
Page 19

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 5. Pin description
…continued
Symbol Pin/ball Type Description
LQFP100
TFBGA100
WLCSP100
TDO/SWO 1 A1 A1
[7]
O TDO — Test Data out for JTAG interface.
O SWO — Serial wire trace output.
[1][8]
TDI 2 C3 C4
TMS/SWDIO 3 B1 B3
I TDI — Test Data in for JTAG interface.
[1][8]
I TMS — Test Mode Select for JTAG interface.
I/O SWDIO — Serial wire debug data input/output.
TRST
4C2A2
TCK/SWDCLK 5 C1 D4
[1][8]
I TRST — Test Reset for JTAG interface.
[7]
I TCK — Test Clock for JTAG interface.
I SWDCLK — Serial wire clock.
[7]
RTCK 100 B2 B2
RSTOUT
14 - - - O RSTOUT — This is a 3.3 V pin. LOW on this pin indicates the
O RTCK — JTAG interface control signal.
microcontroller being in Reset state.
RESET
17 F3 C6
[9]
I External reset input: A LOW-going pulse as short as 50 ns on this
pin resets the device, causing I/O ports and peripherals to take on
their default states, and processor execution to begin at address 0.
TTL with hysteresis, 5 V tolerant.
[10][11]
XTAL1 22 H2 D7
XTAL2 23 G3 A9
RTCX1 16 F2 A7
RTCX2 18 G1 B7
V
SS
V
SSA
31,
B3,
E5,
41,
B7,
F5,
55,
C9,
F6,
72,
G7,
G5,
83,
J6,
G6,
97
K3
G7
11 E1 B5
I Input to the oscillator circuit and internal clock generator circuits.
[10][11]
O Output from the oscillator amplifier .
[10][11]
I Input to the RTC oscillator circuit.
[10]
O Output from the RTC oscillator circuit.
[10]
I ground: 0 V reference.
[10]
I analog ground: 0 V reference. This should nominally be the same
voltage as VSS, but should be isolated to minimize noise and error.
V
DD(3V3)
V
DD(REG)(3V3)
V
DDA
28,
K2,
54,
H9,
71,
C10
96
, A3
42, 84H6, A7F4,
10 E2 A4
E4,
E6,
F7,
G4
F10
[10]
I 3.3 V supply voltage: This is the power supply voltage for the I/O
ports.
[10]
I 3.3 V voltage regulator supply volt a ge: This is the supply voltage
for the on-chip voltage regulator only.
[10]
I analog 3.3 V pad supply voltage: This should be nominally the
same voltage as V
and error. This voltage is used to power the ADC and DAC. This pin
should be tied to 3.3 V if the ADC and DAC are not used.
[10]
VREFP 12 E3 A5
I ADC positive reference voltage: This should be nominally the
same voltage as V
error. Level on this pin is used as a reference for ADC and DAC.
This pin should be tied to 3.3 V if the ADC and DAC are not used.
but should be isolated to minimize noise
DD(3V3)
but should be isolated to minimize noise and
DDA
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 19 of 93
Page 20

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 5. Pin description
…continued
Symbol Pin/ball Type Description
LQFP100
TFBGA100
WLCSP100
VREFN 15 F1 A6 I ADC negative reference voltage: This should be nominally the
same voltage as VSS but should be isolated to minimize noise and
error. Level on this pin is used as a reference for ADC and DAC.
[10][12]
VBAT 19 G2 A8
I RTC pin power supply: 3.3 V on this pin supplies the power to the
RTC peripheral.
n.c. 13 D4, E4B6,
- not connected.
D6
[1] 5 V tolerant pad providing digital I/O functions with TTL levels and hysteresis. This pin is pulled up to a voltage level of 2.3 V to 2.6 V.
[2] 5 V tolerant pad providing digital I/O functions (with TTL levels and hysteresis) and analog input. When configured as a ADC input,
digital section of the pad is disabled and the pin is not 5 V tolerant. This pin is pulled up to a voltage level of 2.3 V to 2.6 V.
[3] 5 V tolerant pad providing digital I/O with TTL levels and hysteresis and analog output function. When configured as the DAC output,
digital section of the pad is disabled. This pin is pulled up to a voltage level of 2.3 V to 2.6 V.
[4] Open-drain 5 V tolerant digital I/O pad, compatible with I
output functionality. When power is switched off, this pin connected to the I
Open-drain configuration applies to all functions on this pin.
[5] Pad provides digital I/O and USB functions. It is designed in accordance with the USB specification, revision 2.0 (Full-speed and
Low-speed mode only). This pad is not 5 V tolerant.
[6] 5 V tolerant pad with 10 ns glitch filter providing digital I/O functions with TTL levels and hysteresis. This pin is pulled up to a voltage
level of 2.3 V to 2.6 V.
[7] 5 V tolerant pad with TTL levels and hysteresis. Internal pull-up and pull-down resistors disabled.
[8] 5 V tolerant pad with TTL levels and hysteresis and internal pull-up resistor.
[9] 5 V tolerant pad with 20 ns glitch filter providing digital I/O function with TTL levels and hysteresis.
[10] Pad provides special analog functionality. A 32 kHz crystal oscillator must be used with the RTC.
[11] When the system oscillator is not used, connect XTAL1 and XTAL2 as follows: XTAL1 can be left floating or can be grounded (grounding
is preferred to reduce susceptibility to noise). XTAL2 should be left floating.
[12] When the RTC is not used, connect VBAT to V
DD(REG)(3V3)
2
C-bus 400 kHz specification. This pad requires an external pull-up to provide
and leave RTCX1 floating.
2
C-bus is floating and does not disturb the I2C lines.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 20 of 93
Page 21

NXP Semiconductors
8. Functional description
8.1 Architectural overview
Remark: In the following, the notation LPC17xx refers to all parts:
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63.
The Arm Cortex-M3 includes three AHB-Lite buses: the system bus, the I-code bus, and
the D-code bus (see Figure 1
system bus and are used similarly to TCM interfaces: one bus dedicated for instruction
fetch (I-code) and one bus for data access (D-c ode). The use of two core buses allows for
simultaneous operations if concurrent operations target different devices.
The LPC17xx use a multi-layer AHB matrix to connect the Arm Cortex-M3 buses and
other bus masters to peripherals in a flexible mann e r tha t op tim ize s pe rfo rm a nc e by
allowing peripherals that are on different slaves ports of the matrix to be accessed
simultaneously by different bus masters.
8.2 Arm Cortex-M3 processor
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
). The I-code and D-code core buses are faster than the
The Arm Cortex-M3 is a general purpose, 32-bit microprocessor, which offers hig h
performance and very low power consumption. The Arm Cortex-M3 offers many new
features, including a Thumb-2 instruction set, low interrupt latency, hardware divide,
interruptible/continuable multiple load and store instructions, automatic state save and
restore for interrupts, tightly integrated interrupt controller with wake-up interrupt
controller, and multiple core buses capable of simultaneous accesses.
Pipeline techniques are employed so that all part s of the pro cessing and memory systems
can operate continuously. Typically, while one instruction is being executed, its successor
is being decoded, and a third instruction is being fetched from memory.
The Arm Cortex-M3 processor is described in detail in the Cortex-M3 Technical Reference
Manual that can be found on official Arm website.
8.3 On-chip flash program memory
The LPC17xx contain up to 512 kB of on-chip flash memory. A new two-port flash
accelerator maximizes performance for use with the two fast AHB-Lite buses.
8.4 On-chip SRAM
The LPC17xx contain a total of 64 kB on-chip st atic RAM memory. This includes the main
32 kB SRAM, accessible by the CPU and DMA controller on a higher-speed bus, and two
additional 16 kB each SRAM blocks situated on a separate slave port on the AHB
multilayer matrix.
This architecture allows CPU and DMA accesses to be spread over three separate RAMs
that can be accessed simultaneously.
8.5 Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
The LPC17xx have a Memory Protection Unit (MPU) which can be used to improve the
reliability of an embedded system by protecting critical data within the user application.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 21 of 93
Page 22

NXP Semiconductors
The MPU allows separating processing tasks by disallowing access to each other's data,
disabling access to memory regions, allowing memory regions to be defined as re ad -onl y
and detecting unexpected memory accesses that could potentially break the system.
The MPU separates the memory into distinct regions and implements protection by
preventing disallowed accesses. The MPU supports up to 8 regions each of which can be
divided into 8 subregions. Accesses to memory locations that are not defined in the MPU
regions, or not permitted by the region settin g , will ca use the Memory Management Fault
exception to take place.
8.6 Memory map
The LPC17xx incorporates several distinct memory regions, shown in the following
figures. Figure 5
program viewpoint following reset. The interrupt vector area supports address remapping.
The AHB peripheral area is 2 MB in size and is divided to allow for up to 128 peripherals.
The APB peripheral area is 1 MB in size and is divided to allow for up to 64 peripherals.
Each peripheral of either type is allocated 16 kB of space. This allows simplifying the
address decoding for each peripheral.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
shows the overall map of the entire address space from the user
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 22 of 93
Page 23

Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 23 of 93
0x5000 0000
0x5000 4000
0x5000 8000
0x5000 C000
0x5020 0000
0x5001 0000
AHB peripherals
Ethernet controller
(1)
USB controller
(1)
reserved
127- 4 reserved
GPDMA controller
0
1
2
3
APB0 peripherals
0x4000 4000
0x4000 8000
0x4000 C000
0x4001 0000
0x4001 8000
0x4002 0000
0x4002 8000
0x4002 C000
0x4003 4000
0x4003 0000
0x4003 8000
0x4003 C000
0x4004 0000
0x4004 4000
0x4004 8000
0x4004 C000
0x4005 C000
0x4006 0000
0x4008 0000
0x4002 4000
0x4001 C000
0x4001 4000
timer 0
timer 1
UART0
UART1
reserved
I2C0
SPI
RTC + backup registers
GPIO interrupts
pin connect
SSP1
ADC
CAN AF RAM
(1)
CAN AF registers
(1)
CAN common
(1)
CAN1
(1)
CAN2
(1)
22 - 19 reserved
I2C1
31 - 24 reserved
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
23
reserved
reserved
32 kB local SRAM (LPC1769/8/7/6/5/3)
16 kB local SRAM (LPC1764)
reserved
reserved
private peripheral bus
0.5 GB
4 GB
1 GB
0x0004 0000
0x0002 0000
0x0008 0000
0x1000 4000
0x1000 0000
0x1000 8000
0x1FFF 0000
0x1FFF 2000
0x2008 0000
0x2007 C000
0x2008 4000
0x2200 0000
0x200A 0000
0x2009 C000
0x2400 0000
0x4000 0000
0x4008 0000
0x4010 0000
0x4200 0000
0x4400 0000
0x5000 0000
0x5020 0000
0xE000 0000
0xE010 0000
0xFFFF FFFF
reserved
reserved
GPIO
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
APB0 peripherals
AHB peripherals
APB1 peripherals
AHB SRAM bit-band alias addressing
peripheral bit-band alias addressing
16 kB AHB SRAM1 (LPC1769/8/7/6/5)
16 kB AHB SRAM0
256 kB on-chip flash (LPC1766/65/63)
512 kB on-chip flash (LPC1769/8/7)
PWM1
8 kB boot ROM
0x0000 0400
active interrupt vectors
+ 256 words
I-code/D-code
memory space
APB1 peripherals
0x4008 0000
0x4008 8000
0x4009 0000
0x4009 4000
0x4009 8000
0x400A 0000
0x400A 4000
0x400A 8000
0x4010 0000
SSP0
DAC
(1)
timer 2
timer 3
UART2
UART3
reserved
I2S
(1)
I2C2
1 - 0 reserved
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
reserved
repetitive interrupt timer
11
12
reserved
motor control PWM
30 - 16 reserved
13
14
15
system control31
QEI
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx xxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
NXP Semiconductors
(1) Not available on all parts. See Table 2.
Fig 5. LPC17xx memory map
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Page 24

NXP Semiconductors
8.7 Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC)
The NVIC is an integral part of the Cortex-M3. The tight coup ling to the CPU allows for low
interrupt latency and efficient processing of late arriving interrupts.
8.7.1 Features
• Controls system exceptions and peripheral interrupts
• In the LPC17xx, the NVIC supports 33 vectored interrupts
• 32 programmable interrupt priority levels, with hardware priority level masking
• Relocatable vector table
• Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI)
• Software interrupt generation
8.7.2 Interrupt sources
Each peripheral device has one interrupt line con nected to the NVIC but may have several
interrupt flags. Individual interrupt flags may also represent more than one interrupt
source.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Any pin on Port 0 and Port 2 (total of 42 pins) regardless of the selected function, can be
programmed to generate an interrupt on a rising edge, a falling edge, or both.
8.8 Pin connect block
The pin connect block allows selected pins of the microcontroller to have more than one
function. Configuration registers control the multiplexers to allow connection between the
pin and the on-chip peripherals.
Peripherals should be connected to the appropriate pins prior to being activated and prior
to any related interrupt(s) being enabled. Activity of any enabled peripheral function that is
not mapped to a related pin should be considered undefined.
Most pins can also be configured as open-drain outpu ts or to have a pull-up, pull- down, or
no resistor enabled.
8.9 General purpose DMA controller
The GPDMA is an AMBA AHB compliant peripheral allowing selected peripherals to have
DMA support.
The GPDMA enables peripheral-to-memory, memory-to-peripheral,
peripheral-to-peripheral, and memory-to-memory transactions. The source and
destination areas can each be either a memory region or a peripheral, and can be
accessed through the AHB master. The GPDMA controller allows data transfers between
the USB and Ethernet controllers and the various on-chip SRAM areas. The supported
APB peripherals are SSP0/1, all UARTs, the I
Two match signals for each timer can be used to trigger DMA transfers.
2
S-bus interface, the ADC, and the DAC.
Remark: The Ethernet controller is available on parts LPC1769/68/67/66/64. The USB
controller is available on parts LPC1769/68/66/65/64. The I
parts LPC1769/68/67/66/65. The DAC is available on parts LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 24 of 93
2
S-bus interface is available on
Page 25

NXP Semiconductors
8.9.1 Features
• Eight DMA channels. Each channel can support an unidirectional transfer.
• 16 DMA request lines.
• Single DMA and burst DMA request signals. Each peripheral connected to the DMA
• Memory-to-memory, memory-to-peripheral, peripheral-to-memory, and
• Scatter or gather DMA is supported through the use of linked lists. This means that
• Hardware DMA channel priority.
• AHB slave DMA programming interface. The DMA Controller is programmed by
• One AHB bus master for transferring data. The interface transfers data when a DMA
• 32-bit AHB master bus width.
• Incrementing or non-incrementing addressing for source and destination.
• Programmable DMA burst size. The DMA burst size can be programmed to more
• Internal four-word FIFO per channel.
• Supports 8, 16, and 32-bit wide tra n sactions.
• Big-endian and little-endian support. The DMA Controller defaults to little-endian
• An interrupt to the processor can be generated on a DMA completion or when a DMA
• Raw interrupt status. The DMA error and DMA count raw interrupt status can be read
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Controller can assert either a burst DMA request or a single DMA request. The DMA
burst size is set by programming the DMA Controller.
peripheral-to-peripheral transfers are supported.
the source and destination areas do not have to occupy contiguous areas of memory.
writing to the DMA control registers over the AHB slave interface.
request goes active.
efficiently transfer data.
mode on reset.
error has occurred.
prior to masking.
8.10 Fast general purpose parallel I/O
Device pins that are not connected to a specific peripheral function are controlled by the
GPIO registers. Pins may be dynamically configured as inputs or outputs. Separate
registers allow setting or clearing any nu mber of outputs simultaneously. The value of the
output register may be read back as well as the current state of the port pins.
LPC17xx use accelerated GPIO functions:
• GPIO registers are ac ce sse d th ro ug h the AHB mu ltilaye r bu s so th at th e fa ste st
possible I/O timing can be achieved.
• Mask registers allow treating sets of port bits as a group, leaving other bits
unchanged.
• All GPIO registers are byte and half-word addressable.
• Entire port value can be written in one instruction.
• Support for Cortex-M3 bit banding.
• Support for use with the GPDMA controller.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 25 of 93
Page 26

NXP Semiconductors
Additionally, any pin on Port 0 and Port 2 (total of 42 pins) providing a digital function can
be programmed to generate an interrupt on a rising edge, a falling edge, or both. The
edge detection is asynchronous, so it may operate when clocks are not present such as
during Power-down mode. Each enabled interrupt can be used to wake up the chip from
Power-down mode.
8.10.1 Features
• Bit level set and clear registers allow a single instruction to set or clear any number of
• Direction control of individual bits.
• All I/O default to inputs after reset.
• Pull-up/pull-down resistor configuration and open-drain configuration can be
8.11 Ethernet
Remark: The Ethernet controller is available on part s LPC1769/68/67/66/64. The
Ethernet block supports bus clock rates of up to 100 MHz (LPC1768/67/66/64) or 120
MHz (LPC1769). See Table 2
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
bits in one port.
programmed through the pin connect block for each GPIO pin.
.
The Ethernet block contains a full featured 10 Mbit/s or 100 Mbit/s Ethernet MAC
designed to provide optimized performance through the use of DMA hardware
acceleration. Features include a generous suite of control registers, half or full duplex
operation, flow control, control frames, hardware acceleration for transmit retry, receive
packet filtering and wake-up on LAN activity. Automatic frame transmission and reception
with scatter-gather DMA off-loads many operations from the CPU.
The Ethernet block and the CPU share the Arm Cortex-M3 D-code and system bus
through the AHB-multilayer matrix to access the various on-chip SRAM blocks for
Ethernet data, control, and status information.
The Ethernet block interfaces between an off-chip Ethernet PHY using the Reduced MII
(RMII) protocol and the on-chip Media Independent Interface Management (MIIM) serial
bus.
8.11.1 Features
• Ethernet standards support:
– Supports 10 Mbit/s or 100 Mbit/s PHY devices including 10 Base-T, 100 Base-TX,
100 Base-FX, and 100 Base-T4.
– Fully compliant with IEEE standard 802.3.
– Fully compliant with 802.3x full duplex flow control and half duplex back pressure.
– Flexible transmit and receive frame options.
– Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) frame support.
• Memory management:
– Independent transmit and receive buffer s memory mapped to shared SRAM.
– DMA managers with scatter/gather DMA and arrays of frame descriptors.
– Memory traffic optimized by buffering and pre-fetching.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 26 of 93
Page 27

NXP Semiconductors
• Enhanced Ethernet features:
• Physical interface:
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
– Receive filtering.
– Multicast and broadcast frame support for both transmit and receive.
– Optional automatic Frame Check Sequence (FCS) insertion with Cyclic
Redundancy Check (CRC) for transmit.
– Selectable automatic transmit frame padding.
– Over-length frame support for both transmit and receive allows any length frames.
– Promiscuous receive mode.
– Automatic collision back-off and frame retransmission.
– Includes power management by clock switching.
– Wake-on-LAN power management support allows system wake-up: using the
receive filters or a magic frame detection filter.
– Attachment of external PHY chip through stan dard RMII interface.
– PHY register access is available via the MIIM interface.
8.12 USB interface
Remark: The USB controller is available as device/Host/OTG controller on parts
LPC1769/68/66/65 and as device-only controller on part LPC1764.
The Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a 4-wire bus that supports communication between a
host and one or more (up to 127) peripherals. The host controller allocates the USB
bandwidth to attached devices through a token-based protocol. The bus supports hot
plugging and dynamic configuration of the devices. All transactions are initiated by the
host controller.
The USB interface includes a device, Host, and OTG controller with on-chip PHY for
device and Host functions. The OTG switching protocol is supported through the use of an
external controller. Details on typical USB interfacing solutions can be found in
Section 15.1
8.12.1 USB device controller
The device controller enables 12 Mbit/s data exchange with a USB Host controller. It
consists of a register interface, serial interface engine, endpoint buffer memory, and a
DMA controller. The seria l interface eng ine decod es the USB dat a strea m and writes dat a
to the appropriate endpoint buffer. The status of a completed USB transfer or error
condition is indicated via status registers. An interrupt is also generated if enabled. When
enabled, the DMA controller transfers data between the endpoint buffer and the on-chip
SRAM.
.
8.12.1.1 Features
• Fully compliant with USB 2.0 specification (full speed).
• Supports 32 physical (16 logical) endpoints with a 4 kB endpoint buffer RAM.
• Supports Control, Bulk, Interrupt and Isochronous endpoints.
• Scalable realization of endpoints at run time.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 27 of 93
Page 28

NXP Semiconductors
• Endpoint Maximum packet size selection (up to USB maximum specification) by
• Supports SoftConnect and GoodLink features.
• While USB is in the Suspend mode, the part can ente r one of the re du ce d power
• Supports DMA transfers with all on-c hip SRAM blo cks on all non-control endpoints.
• Allows dynamic switching between CPU-controlled slave and DMA modes.
• Double buffer implementation for Bulk and Isochronous endpoints.
8.12.2 USB host controller
The host controller enables full- and low-speed dat a exchange with USB devices attached
to the bus. It consists of a register interface, a serial interface engine, and a DMA
controller. The register interface complies with the OHCI specification.
8.12.2.1 Features
• OHCI compliant.
• One downstream port.
• Supports port power switchin g .
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
software at run time.
modes and wake up on USB activity.
8.12.3 USB OTG controller
USB OTG is a supplement to the USB 2.0 specification that augments the capability of
existing mobile devices and USB peripherals by adding host functionality for connection to
USB peripherals.
The OTG Controller integrates the host controller, device controller, and a master-only
2
C-bus interface to implement OTG dual-role device functionality. The dedicated I2C-bus
I
interface controls an external OTG transceiver.
8.12.3.1 Features
• Fully compliant with On-The-Go supplement to the USB 2.0 Specification, Revision
1.0a.
• Hardware support for Host Negotiation Protocol (HNP).
• Includes a programmable timer required for HNP and Session Request Protocol
(SRP).
• Supports any OTG transceiver compliant with the OTG Transceiver Specification
(CEA-2011), Rev. 1.0.
8.13 CAN controller and acceptance filters
Remark: The CAN controllers are available on parts LPC1769/68/66/65/64. See Table 2.
The Controller Area Network (CAN) is a serial communications protocol which efficiently
supports distributed real-time control with a very high level of security. Its domain of
application ranges from high-speed networks to low cost multiplex wiring.
The CAN block is intended to support multiple CAN buses simultaneously, allowing the
device to be used as a gateway, switch, or router among a number of CAN buses in
industrial or automotive applications.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 28 of 93
Page 29

NXP Semiconductors
8.13.1 Features
• Two CAN controllers and buses.
• Data rates to 1 Mbit/s on each bus.
• 32-bit register and RAM access.
• Compatible with CAN specification 2.0B, ISO 11898-1.
• Global Acceptance Filter recognizes standard (11-bit) and extended-frame (29-bit)
• Acceptance Filter can provide FullCAN- s tyle automatic reception for selected
• FullCAN messages can generate interrupts.
8.14 12-bit ADC
The LPC17xx contain a single 12-bit successive approximation ADC with eight channels
and DMA support.
8.14.1 Features
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
receive identifiers for all CAN buses.
Standard Identifiers.
• 12-bit successive approximation ADC.
• Input multiplexing among 8 pins.
• Power-down mode.
• Measurement range VREFN to VREFP.
• 12-bit conversion ra te : 200 kH z.
• Individual channels can be selected for conversion.
• Burst conversion mode for single or multiple inputs.
• Optional conversion on transition of input pin or Timer Match signal.
• Individual result registers for each ADC channel to reduce interrupt overhead.
• DMA support.
8.15 10-bit DAC
The DAC allows to generate a variable analog output. The maximum output value of the
DAC is VREFP.
Remark: The DAC is available on parts LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63. See Table 2
8.15.1 Features
• 10-bit DAC
• Resistor string architecture
• Buffered output
• Power-down mode
• Selectable output drive
• Dedicated conversion timer
• DMA support
.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 29 of 93
Page 30

NXP Semiconductors
8.16 UARTs
The LPC17xx each contain four UARTs. In addition to standard transmit and receive data
lines, UART1 also provides a full modem control handshake interface and support for
RS-485/9-bit mode allowing both software address detection and automatic address
detection using 9-bit mode.
The UARTs include a fractional baud rate generator. Standard baud rates such as
115200 Bd can be achieved with any crystal frequency above 2 MHz.
8.16.1 Features
• Maximum UART data bit rate of 6.25 Mbit/s.
• 16 B Receive and Transmit FIFOs.
• Register locations conform to 16C550 industry standard.
• Receiver FIFO trigger points at 1 B, 4 B, 8 B, and 14 B.
• Built-in fractional baud rate generator covering wide range of baud rates without a
• Auto baud capabilities and FIFO control mechanism that enables software flow
• UART1 equipped with standard modem interface signals. This module also provides
• Support for RS-485 /9 -b it/EIA-485 mode (UART1).
• UART3 includes an IrDA mode to support infrared communication.
• All UARTs have DMA support.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
need for external crystals of particular values.
control implementation.
full support for hardware flow control (auto-CTS/RTS).
8.17 SPI serial I/O controller
The LPC17xx contain one SPI controller. SPI is a full duplex serial interface designed to
handle multiple masters and slaves connected to a given bus. Only a single maste r and a
single slave can communicate on the interface during a given data transfer. During a data
transfer the master always sends 8 bits to 16 bits of data to the slave, and the slave
always sends 8 bits to 16 bits of data to the master.
8.17.1 Features
• Maximum SPI data bit rate of 12.5 Mbit/s
• Compliant with SPI specification
• Synchronous, serial, full duplex communication
• Combined SPI master and slave
• Maximum data bit rate of one eighth of the input clock rate
• 8 bits to 16 bits per transfer
8.18 SSP serial I/O controller
The LPC17xx contain two SSP controllers. The SSP controller is capable of operation on
a SPI, 4-wire SSI, or Microwire bus. It can interact with multiple masters and slaves on the
bus. Only a single master and a single slave can communicate on the bus during a given
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 30 of 93
Page 31

NXP Semiconductors
data transfer. The SSP supports full duplex transfers, with frames of 4 bits to 16 bits of
data flowing from the master to the slave and from the slave to the master. In practice,
often only one of these data flows carries meaningful data.
8.18.1 Features
• Maximum SSP speed of 33 Mbit/s (master) or 8 Mbit/s (slave)
• Compatible with Motorola SPI, 4-wire Texas Instruments SSI, and National
• Synchronous serial communication
• Master or slave operation
• 8-frame FIFOs for both transmit and receive
• 4-bit to 16-bit frame
• DMA transfers supporte d by GP DMA
8.19 I2C-bus serial I/O controllers
The LPC17xx each contain three I2C-bus controllers.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Semiconductor Microwire buses
2
C-bus is bidirectional for inter-IC control using only two wires: a Serial Clock line
The I
(SCL) and a Serial DAta line (SDA). Each device is recognized by a unique address and
can operate as either a receiver-only device (e.g., an LCD driver) or a tra nsmitter with the
capability to both receive and send information (such as memory). Transmitters and/or
receivers can operate in either master or sla ve mode, de pendin g on wheth er the chip has
to initiate a data transfer or is only addressed. The I
controlled by more than one bus master connected to it.
8.19.1 Features
2
• I
C0 is a standard I2C compliant bus interface with open-drain pins. I2C0 also
supports Fast mode plus with bit rates up to 1 Mbit/s.
2
• I
C1 and I2C2 use standard I/O pins with bit rates of up to 400 kbit/s (Fast I2C-bus).
• Easy to configure as master, slave, or master/slave.
• Programmable clocks allow versatile rate control.
• Bidirectional data transfer between masters and slaves.
• Multi-master bus (no central master).
• Arbitration between simultaneously transmitting masters without corruption of serial
data on the bus.
• Serial clock synchronization allows devices with different bit rates to communicate via
one serial bus.
• Serial clock synchronization can be used as a handshake mechanism to suspend and
resume serial transfer.
• The I
2
• All I
2
C is a multi-master bus and can be
2
C-bus can be used for test and diagnostic purposes.
C-bus controllers support multiple address recognition and a bus monitor mode.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 31 of 93
Page 32

NXP Semiconductors
8.20 I2S-bus serial I/O controllers
Remark: The I2S-bus interface is available on parts LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63. See
Table 2
The I
The I
and one word select signal. The basic I
always the master , and one sla ve. The I
receive channel, each of which can operate as either a master or a slave.
8.20.1 Features
• The interface has separate input/output channels each of which can operate in master
• Capable of handling 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32-bit word sizes.
• Mono and stereo audio data supported.
• The sampling frequency can range from 16 kHz to 96 kHz (16, 22.05, 32, 44.1, 48,
• Support for an audio ma st er clock.
• Configurable word select period in master mode (separately for I
• Two 8-word FIFO data buffers are provided, one for transmit and one for receive.
• Generates interrupt requests when buffer levels cross a programmable boundary.
• Two DMA requests, controlled by programmable buffer levels. These are connected
• Controls include reset, stop and mute options separately for I
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
.
2
S-bus provides a standard communication interface for digital audio applications.
2
S-bus specification defines a 3-wire serial bus using one data line, one clock line,
or slave mode.
96) kHz.
output).
to the GPDMA block.
output.
2
S-bus connection has one master, which is
2
S-bus interface provides a separate transmit and
2
S-bus input and
2
S-bus input and I2S-bus
8.21 General purpose 32-bit timers/external event counters
The LPC17xx include four 32-bit timer/counters. The timer/counter is designed to count
cycles of the system derived clock or an externally-supplied clock. It can optionally
generate interrupts, generate timed DMA requests, or perform other actions at specified
timer values, based on four match registers. Each timer/counter also includes two capture
inputs to trap the timer value when an input signal transitions, optionally generating an
interrupt.
8.21.1 Features
• A 32-bit timer/counter with a programmable 32-bit prescaler.
• Counter or timer oper a tion .
• Two 32-bit capture channels per timer, that can take a snapshot of the timer value
when an input signal transitions. A capture event may also generate an interrupt.
• Four 32-bit match re gist er s tha t allo w:
– Continuous operation with optional interrupt generation on match.
– St op timer on match with optional interrupt generation.
– Reset timer on match with optional interrupt generation.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 32 of 93
Page 33

NXP Semiconductors
• Up to four external outputs corresponding to match registers, with the following
• Up to two match registers can be used to generate timed DMA requests.
8.22 Pulse width modulator
The PWM is based on the standard Timer block and inherits all of its features, although
only the PWM function is pinned out on the LPC17xx. The Timer is designed to count
cycles of the system derived clock and optionally switch pins, generate interrupts or
perform other actions when specified timer values occur , based on se ven match registers.
The PWM function is in addition to these features, and is based on match register events.
The ability to separately control rising and falling edge locations allows the PWM to be
used for more applications. For instance, multi-phase motor control typically requires
three non-overlapping PWM outputs with individual control of all three pulse widths and
positions.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
capabilities:
– Set LOW on match.
– Set HIGH on match.
– Toggle on match.
– Do nothing on match.
Two match registers can be used to provide a single edge controlled PWM output. One
match register (PWMMR0) controls the PWM cycle rate, by resetting the count upon
match. The other match register controls the PWM edge position. Additional single edge
controlled PWM outputs require only one match re gister each, since the repetition rate is
the same for all PWM outputs. Multiple single edge controlled PWM outputs will all have a
rising edge at the beginning of each PWM cycle, when an PWMMR0 match occurs.
Three match registers can be used to provide a PWM output with both edges controlled.
Again, the PWMMR0 match register controls the PWM cycle rate. The other match
registers control the two PWM edge positions. Additional double edge controlled PWM
outputs require only two match registers each, since the repetition rate is the same for all
PWM outputs.
With double edge controlled PWM outputs, specific match registers control the rising and
falling edge of the output. This allows both positive going PWM pulses (when the rising
edge occurs prior to the falling edge), and negative going PWM pulses (when the falling
edge occurs prior to the rising edge).
8.22.1 Features
• One PWM block with Counter or Timer ope ration (may use the peripheral clock or on e
of the capture inputs as the clock source).
• Seven match registers allow up to 6 single edge controlled or 3 double edge
controlled PWM outputs, or a mix of both types. The match registers also allow:
– Continuous operation with optional interrupt generation on match.
– St op timer on match with optional interrupt generation.
– Reset timer on match with optional interrupt generation.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 33 of 93
Page 34

NXP Semiconductors
• Supports single edge controlled and/or double edge controlled PWM outputs. Single
• Pulse period and width can be any number of timer counts. This allows complete
• Double edge controlled PWM outputs can be programmed to be either positive going
• Match register updates are synchronized with pulse outputs to prevent generation of
• May be used as a standard 32-bit timer/counter with a programma ble 32-bit pre scaler
8.23 Motor control PWM
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
edge controlled PWM outputs all go high at the beginning of each cycle unless the
output is a constant low. Double edge controlled PWM outputs can have either edge
occur at any position within a cycle. This allows for both positive going and negative
going pulses.
flexibility in the trade-off between resolution and repetition rate. All PWM outputs will
occur at the same repetition rate.
or negative going pulses.
erroneous pulses. Software must ‘release’ new match values before they can b ecome
effective.
if the PWM mode is not enabled.
The motor control PWM is a specialized PWM supporting 3-phase motors and other
combinations. Feedback inputs are provided to automatically sense rotor position and use
that information to ramp speed up or down. An abort input is also provided that causes the
PWM to immediately release all motor drive outputs. At the same time, the motor control
PWM is highly configurable for other generalized timing, counting, capture, and compare
applications.
8.24 Quadrature Encoder Interface (QEI)
A quadrature encoder, also known as a 2-channel incremental encoder, converts angular
displacement into two pulse signals. By monitoring both the number of pulses and the
relative phase of the two signals, the user ca n tr ack th e position, d ire ction of r otation, and
velocity. In addition, a third channel, or index signal, can be used to reset the position
counter. The quadrature encoder interface decodes the digital pulses from a quadrature
encoder wheel to integrate position over time and determine direction of rotation. In
addition, the QEI can capture the velocity of the encoder wheel.
8.24.1 Features
• Tracks encoder position.
• Increments/decrements depending on direction.
• Programmable for 2 or 4 position counting.
• Velocity capture using built-in timer.
• Velocity compare function with “less than” interrupt.
• Uses 32-bit register s for pos ition an d ve locity.
• Three position compare regis te rs with inte rr up ts.
• Index counter for revolution counting.
• Index compare register w ith int er ru p ts.
• Can combine index and position interrupts to produce an interrupt for whole and
partial revolution displacement.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 34 of 93
Page 35

NXP Semiconductors
• Digital filter with programmable delays for encoder input signals.
• Can accept decoded signal inputs (clk and direction).
• Connected to APB.
8.25 Repetitive Interrupt (RI) timer
The repetitive interrupt timer provides a free-running 32-bit counter which is compared to
a selectable value, generating an interrupt when a match occurs. Any bits of the
timer/compare can be masked such that they do no t contribute to the match detection.
The repetitive interrupt timer can be used to create an interrupt that repeats at
predetermined intervals.
8.25.1 Features
• 32-bit counter running from PCLK. Counter can be free-running or be reset by a
• 32-bit compare value.
• 32-bit compare mask. An interrupt is generated when the counter value equals the
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
generated interrupt.
compare value, after masking. This allows for combinations not possible with a simple
compare.
8.26 Arm Cortex-M3 system tick timer
The Arm Cortex-M3 includes a system tick timer (SYSTICK) that is intended to generate a
dedicated SYSTICK exception at a 10 ms interval. In the LPC17xx, this timer can be
clocked from the internal AHB clock or from a device pin.
8.27 Watchdog timer
The purpose of the watchdog is to reset the microcontroller within a reasonable amoun t of
time if it enters an erroneous state. When enabled, the watchdog will generate a system
reset if the user program fails to ‘feed’ (or reload) the watchdog within a predetermined
amount of time.
8.27.1 Features
• Internally resets chip if not periodically reloaded.
• Debug mode.
• Enabled by software but requires a hardware reset or a watchdog reset/interrupt to be
disabled.
• Incorrect/Incomplete feed sequence causes reset/interrupt if enabled.
• Flag to indicate watchdog reset.
• Programmable 32-bit timer with internal prescaler.
• Selectable time period from (T
multiples of T
cy(WDCLK)
4.
cy(WDCLK)
• The Watchdog Clock (WDCLK) source can be selected from the Internal RC (IRC)
oscillator, the RTC oscillator, or the APB peripheral clock. This gives a wide range of
potential timing choices of Watchdog operation under different power reduction
256 4) to (T
cy(WDCLK)
232 4) in
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 35 of 93
Page 36

NXP Semiconductors
• Includes lock/safe feature.
8.28 RTC and backup registers
The RTC is a set of counters for measuring ti me when system power is on, and op tionally
when it is off. The RTC on the LPC17xx is designed to have extremely low power
consumption, i.e. less than 1 A. The RTC will typically run from the main chip power
supply, conserving battery power while the rest of the device is powered up. When
operating from a battery, the RTC will continue working down to 2.1 V. Battery power can
be provided from a standard 3 V Lithium button cell.
An ultra-low power 32 kHz oscillator will provide a 1 Hz clock to the time counting portion
of the RTC, moving most of the power consumption out of the time counting function.
The RTC includes a calibration mechanism to allow fine-tuning the count rate in a way
that will provide less than 1 second per day error when operated at a constant voltage and
temperature. A clock output function (see Section 8.29.4
rate easy and accurate.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
conditions. It also provides the ability to run the WDT from an entirely internal source
that is not dependent on an external cryst al and it s associated component s and wiring
for increased reliability.
) makes measuring the oscillator
The RTC contains a small set of backup registers (20 bytes) for holding data while the
main part of the LPC17xx is powered off.
The RTC includes an alarm function that can wake up the LPC17xx from all reduced
power modes with a time resolution of 1 s.
8.28.1 Features
• Measures the passage of time to maintain a calendar and clock.
• Ultra low power design to support battery powered systems.
• Provides Seconds, Minutes, Hours, Day of Month, Month, Year, Day of Week, and
Day of Year.
• Dedicated power supply pin can be connected to a battery or to the main 3.3 V.
• Periodic interrupts can be generated from increment s of a ny field of th e time registe rs.
• Backup registers (20 by te s) po we re d by VBAT.
• RTC power supply is isolated from the rest of the chip.
8.29 Clocking and power control
8.29.1 Crystal oscillators
The LPC17xx include three independent oscillators. These are the main oscillator , the IRC
oscillator, and the RTC oscillator. Each oscillator can be used for more than one purpose
as required in a particular application. Any of the three clock sources can be chosen by
software to drive the main PLL and ultimately the CPU.
Following reset, the LPC17xx will operate from the Internal RC oscillator until switched by
software. This allows systems to operate without any external crystal and the bootloader
code to operate at a known frequency.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 36 of 93
Page 37

NXP Semiconductors
MAIN
OSCILLATOR
INTERNAL
RC
OSCILLATOR
RTC
OSCILLATOR
MAIN PLL
WATCHDOG
TIMER
REAL-TIME
CLOCK
CPU
CLOCK
DIVIDER
PERIPHERAL
CLOCK
GENERATOR
USB BLOCK
ARM
CORTEX-M3
ETHERNET
BLOCK
DMA
GPIO
NVIC
USB
CLOCK
DIVIDER
system
clock
select
(CLKSRCSEL)
USB clock config
(USBCLKCFG)
CPU clock config
(CCLKCFG)
pllclk
CCLK/8
CCLK/6
CCLK/4
CCLK/2
CCLK
pclk
WDT
rtclk = 1Hz
usbclk
(48 MHz)
cclk
USB PLL
USB PLL enable
main PLL enable
32 kHz
APB peripherals
LPC17xx
002aad947
See Figure 6 for an overview of the LPC17xx clock generation.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 6. LPC17xx clocking generation block diagram
8.29.1.1 Internal RC oscillator
The IRC may be used as the clock source for the WDT, and/or as the clock that drives the
PLL and subsequently the CPU. The nominal IRC frequency is 4 MHz. The IRC is
trimmed to 1 % accuracy over the entire voltage and temperature range.
Upon power-up or any chip reset, the LPC17xx use the IRC as the clock sour ce. Sof tware
may later switch to one of the other available clock sources.
8.29.1.2 Main oscillator
The main oscillator can be used as the clock source for the CPU, with or without using the
PLL. The main oscillator also provides the clock source for the dedicated USB PLL.
The main oscillator operates at frequencies of 1 MHz to 25 MHz. This frequency can be
boosted to a higher frequency, up to the maximum CPU operating frequency, by the main
PLL. The clock selected as the PLL input is PLLCLKIN. The Arm processor clock
frequency is referred to as CCLK elsewhere in this document. The frequencies of
PLLCLKIN and CCLK are the same value unless the PLL is active and connected. The
clock frequency for each peripheral can be selected individually and is referred to as
PCLK. Refer to Section 8.29.2
8.29.1.3 RTC oscillator
The RTC oscillator can be used as the clock source for the RTC block, the main PLL,
and/or the CPU.
for additional information.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 37 of 93
Page 38

NXP Semiconductors
8.29.2 Main PLL (PLL0)
The PLL0 accepts an input clock frequency in the range of 32 kHz to 25 MHz. The input
frequency is multiplied up to a high frequency, then divided down to provide the actual
clock used by the CPU and/or the USB block.
The PLL0 input, in the range of 32 kHz to 25 MHz, may initially be divided down by a
value ‘N’, which may be in the range of 1 to 256. This input division provides a wide range
of output frequencies from the same input frequency.
Following the PLL0 input divider is the PLL0 multiplier . This can multiply the input divider
output through the use of a Current Controlled Oscillator (CCO) by a value ‘M’, in the
range of 1 through 32768. The resulting frequency must be in the range of 275 MHz to
550 MHz. The multiplier works by dividing the CCO output by the value of M, then using a
phase-frequency detector to compare the divided CCO output to the multiplier input. The
error value is used to adjust the CCO frequency.
The PLL0 is turned off and bypassed following a chip Reset and by entering Power -down
mode. PLL0 is enabled by software only. The program must configure and activate the
PLL0, wait for the PLL0 to lock, and then connect to the PLL0 as a clock source.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
8.29.3 USB PLL (PLL1)
The LPC17xx contain a second, dedicated USB PLL1 to provide clocking for the USB
interface.
The PLL1 receives its clock input from the main oscillator only and provides a fixed
48 MHz clock to the USB block only. The PLL1 is disabled and powered of f on reset. If the
PLL1 is left disabled, the USB clock will be supplied by the 48 MHz clock from the main
PLL0.
The PLL1 accepts an input clock frequency in the range of 10 MHz to 25 MHz only. The
input frequency is multiplied up the range of 48 MHz for the USB clock using a Current
Controlled Oscillators (CCO). It is insured that the PLL1 output has a 50 % duty cycle.
8.29.4 RTC clock output
The LPC17xx feature a clock output function intended for synchronizing with external
devices and for use during system development to allow checking the internal clocks
CCLK, IRC clock, main crystal, RTC clock, and USB clock in the outside world. The RTC
clock output allows tuning the RTC frequency without probing the pin, which would distort
the results.
8.29.5 Wake-up timer
The LPC17xx begin operation at power-up and when awakened from Power-down mode
by using the 4 MHz IRC oscillator as the clock source. This allows chip operation to
resume quickly . If the main oscillator or the PLL is needed by the application, sof tware will
need to enable these features and wait for them to stabilize before they are used as a
clock source.
When the main oscillator is initially activated, the wake-up timer allows sof twa re to ensure
that the main oscillator is fully functional before the processor uses it as a clock source
and starts to execute instructions. This is important at power on, all types of Reset, and
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 38 of 93
Page 39

NXP Semiconductors
whenever any of the aforementioned functions are turned off for any rea son. Since the
oscillator and other functions are turned off during Power-down mode, any wake-up of the
processor from Power-down mode makes use of the wake-up timer.
The Wake-up Timer monitors the crystal oscillator to check whether it is safe to begin
code execution. When power is applied to the chip, or when some event caused the chip
to exit Power-down mode, some time is required for the oscillator to produce a signal of
sufficient amplitude to drive the clock logic. The amount of time depends on man y factors,
including the rate of V
electrical characteristics (if a quartz cryst al is used) , as well as any other external circuitry
(e.g., capacitors), and the characteristics of the oscillator itself under the existing ambient
conditions.
8.29.6 Power control
The LPC17xx support a variety of power control features. Th ere are four special modes of
processor power reduction: Sleep mode, Deep-sleep mode, Power-down mode, and
Deep power-down mode. The CPU clock rate may also be controlled as needed by
changing clock sources, reconfiguring PLL values, and/or altering the CPU clock divider
value. This allows a trade-off of power versus processing speed based on application
requirements. In addition, Peripheral Power Control allows shutting down the clocks to
individual on-chip peripherals, allowing fine tuning of power consumption by eliminating all
dynamic power use in any peripherals that are not required for th e application. Each of the
peripherals has its own clock divider which provides even better power control.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
ramp (in the case of power on), the type of crystal and its
DD(3V3)
Integrated PMU (Power Management Unit) automatically adjust internal regulators to
minimize power consumption during Sleep, Deep sleep, Power-down, and Deep
power-down modes.
The LPC17xx also implement a separate power domain to allow turning of f power to the
bulk of the device while maintaining operation of the RTC and a small set of registers for
storing data during any of the power-down modes.
8.29.6.1 Sleep mode
When Sleep mode is entered, the clock to the core is stopped. Resumption from the Sleep
mode does not need any special sequence but re-enabling th e clock to the Arm core.
In Sleep mode, execution of instructions is suspended until either a Reset or interrupt
occurs. Peripheral functions continue operation during Sleep mode and may generate
interrupts to cause the processor to resume execution. Sleep mode eliminates dynamic
power used by the processor itself, memory systems and related controllers, and internal
buses.
8.29.6.2 Deep-sleep mode
In Deep-sleep mode, the oscillator is shut down and the chip receives no internal clocks.
The processor state and registers, peripheral registers, and internal SRAM values are
preserved throughout Deep-sleep mode and the logic levels of chip pins remain static.
The output of the IRC is disabled but the IRC is not powered down for a fast wake-up later.
The RTC oscillator is not stopped because the RTC interrupts may be used as the
wake-up source. The PLL is automatically turned off and disconnected. The CCLK and
USB clock dividers automatically get reset to zero.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 39 of 93
Page 40

NXP Semiconductors
The Deep-sleep mode can be terminated and normal operation resumed by either a
Reset or certain specific interrupts that are able to function without clocks. Since all
dynamic operation of the chip is suspended, Deep-sleep mode reduces chip power
consumption to a very low value. Power to the flash memory is left on in Deep-sleep
mode, allowing a very quick wake-up.
On wake-up from Deep-sleep mode, the code execution and peripherals activities will
resume after 4 cycles expire if the IRC was used before entering Deep-sleep mode. If the
main external oscillator was used, the code execution will resume when 4096 cycles
expire. PLL and clock dividers need to be reconfigured accordingly.
8.29.6.3 Power-down mode
Power-down mode does everything that Deep-sleep mode does, but also turns off the
power to the IRC oscillator and the flash memory. This saves more power but requires
waiting for resumption of flash operation before execution of code or data access in the
flash memory can be accomplished.
On the wake-up of Power-down mode, if the IRC was used before entering Power-down
mode, it will take IRC 60 s to start-up. After this 4 IRC cycles will expire before the code
execution can then be resumed if the code was running from SRAM. In the meantime, the
flash wake-up timer then counts 4 MHz IRC clock cycles to make the 100 s flash start-up
time. When it times out, access to the flash will be allowed. Users need to reconfigure the
PLL and clock dividers accordingly.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
8.29.6.4 Deep power-down mode
The Deep power-down mode can only be entered from the RTC block. In Deep
power-down mode, power is shut off to the entire chip with the exception of the RTC
module and the RESET
The LPC17xx can wake up from Deep power-down mode via the RESET
match event of the RTC.
8.29.6.5 Wake-up interrupt controller
The Wake-up Interrupt Controller (WIC) allows the CPU to automatically wake up from
any enabled priority interrupt that can occur while the clocks are stopped in Deep sleep,
Power-down, and Deep power-down modes.
The WIC works in connection with the Nested Vectored Interrupt Cont roller (NVIC). When
the CPU enters Deep sleep, Power-down, or Deep power-down mode, the NVIC sends a
mask of the current interrupt situation to the WIC.This mask includes all of the interrupts
that are both enabled and of sufficient priority to be serviced immediately. With this
information, the WIC simply notices when one of the interrupts has occurred and then it
wakes up the CPU.
The WIC eliminates the need to periodically wake up the CPU and poll the interrupts
resulting in additional power savings.
pin.
8.29.7 Peripheral power control
pin or an alarm
A Power Control for Peripherals feature allows individual peripherals to be turned off if
they are not needed in the application, resulting in additional power savings.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 40 of 93
Page 41

NXP Semiconductors
8.29.8 Power domains
The LPC17xx provide two independent power domains that allow the bulk o f the device to
have power removed while maintaining operation of the RTC and the backup Regi sters.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
On the LPC17xx, I/O pads are powered by the 3.3 V (V
V
DD(REG)(3V3)
pin powers the on-chip voltage regulator which in turn provides po wer to the
) pins, while the
DD(3V3)
CPU and most of the peripherals.
Depending on the LPC17xx application, a design can use two power options to manage
power consumption.
The first option assumes that power consumption is not a concern and the design ties the
V
DD(3V3)
and V
DD(REG)(3V3)
pins together. This app roach requires only one 3.3 V power
supply for both pads, the CPU, and peripherals. While this solution is simple, it does not
support powering down the I/O pad ring “on the fly” while keeping the CPU and
peripherals alive.
The second option uses two power supplies; a 3.3 V supply for the I/O pads (V
a dedicated 3.3 V supply for the CPU (V
DD(REG)(3V3)
). Having the on-chip voltage regulator
DD(3V3)
) and
powered independently from the I/O pad ring enables shutting down of the I/O p a d power
supply “on the fly”, while the CPU and peripherals stay active.
The VBAT pin supplies power only to the RTC domain. The RTC requires a minimum of
power to operate, which can be supplied by an external battery. The device core power
(V
DD(REG)(3V3)
there is no power drain from the RTC battery when V
) is used to operate the RTC whenever V
DD(REG)(3V3)
DD(REG)(3V3)
is present. Therefore,
is available.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 41 of 93
Page 42

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
LPC17xx
V
DD(3V3)
V
DD(REG)(3V3)
VBAT
RTCX1
RTCX2
V
VREFP
VREFN
V
V
SS
DDA
SSA
to I/O pads
REGULATOR
MAIN POWER DOMAIN
POWER
SELECTOR
32 kHz
OSCILLATOR
RTC POWER DOMAIN
ADC POWER DOMAIN
to core
to memories,
peripherals,
oscillators,
PLLs
ULTRA LOW-POWER
REGULATOR
BACKUP REGISTERS
REAL-TIME CLOCK
DAC
ADC
002aad978
Fig 7. Power distribution
8.30 System control
8.30.1 Reset
Reset has four sources on the LPC17xx: the RESET pin, the Watchdog reset, power-on
reset (POR), and the BrownOut Detection (BOD) circuit. The RESET
trigger input pin. Assertion of chip Reset by any source, once the operating voltag e attains
a usable level, causes the RSTOUT
description in Section 8.29.5
). The wake-up timer ensures that reset remains asserted
pin to go LOW and starts the wake-up timer (see
until the external Reset is de-asserted, the oscillator is running, a fixed number of clocks
have passed, and the flash controller has completed its initialization. Once reset is
de-asserted, or, in case of a BOD-triggered reset, once the voltage rises above the BOD
threshold, the RSTOUT
pin goes HIGH.
When the internal Reset is removed, the processor begins executing at address 0, which
is initially the Reset vector mapped from the Boot Block. At that point, all of the processor
and peripheral registers have been initialized to predetermined values.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 42 of 93
pin is a Schmitt
Page 43

NXP Semiconductors
8.30.2 Brownout detection
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
The LPC17xx include 2-stage monitoring of the voltage on the V
voltage falls below 2.2 V, the BOD asserts an interrupt signal to the Vectored Interrupt
Controller. This signal can be enabled for interrupt in the Interrupt Enable Register in the
NVIC in order to cause a CPU interrupt; if not, software can monitor the signal by reading
a dedicated status register.
The second stage of low-voltage detection asserts reset to inactivate the LPC17xx when
the voltage on the V
DD(REG)(3V3)
pins falls below 1.85 V. This reset prevents alteration of
the flash as operation of the various elements of the chip would otherwise become
unreliable due to low voltage. The BOD circuit maintains this reset down below 1 V, at
which point the power-on reset circuitry maintains the overall reset.
Both the 2.2 V and 1.85 V thresholds include some hysteresis. In normal operation, this
hysteresis allows the 2.2 V detection to reliably interrupt, or a regularly executed event
loop to sense the condition.
8.30.3 Code security (Code Read Protection - CRP)
This feature of the LPC17xx allows user to enable dif ferent levels of securi ty in the system
so that access to the on-chip flash and use of the JTAG and ISP can be restricted. When
needed, CRP is invoked by programming a specific pattern into a dedicated flash location.
IAP commands are not affected by the CRP.
There are three levels of the Code Read Protection.
CRP1 disables access to chip via the JTAG and allows partial flash update (excluding
flash sector 0) using a limited set of the ISP commands. This mode is useful when CRP is
required and flash field updates are needed but all sectors can not be erased.
DD(REG)(3V3)
pins. If this
CAUTION
CRP2 disables access to chip via the JTAG and only allows full flash erase and update
using a reduced set of the ISP commands.
Running an application with level CRP3 selected fully disables any access to chip via the
JT AG pins and the ISP. This mode effectively disables ISP override using P2[10] pin, too.
It is up to the user’s application to provide (if needed) flash update mechanism using IAP
calls or call reinvoke ISP command to enable flash update via UART0.
If level three Code Read Protection (CRP3) is selected, no future factory testing can be
performed on the device.
8.30.4 APB interface
The APB peripherals are split into two separate APB buses in order to distribute the bus
bandwidth and thereby reducing stalls caused by contention between the CPU and the
GPDMA controller.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 43 of 93
Page 44

NXP Semiconductors
8.30.5 AHB multilayer matrix
The LPC17xx use an AHB multilayer matrix. This matrix connects the instruction (I-code)
and data (D-code) CPU buses of the Arm Cortex-M3 to the flash memory, the main
(32 kB) static RAM, and the Boot ROM. The GPDMA can also access all of these
memories. The peripheral DMA controllers, Ethernet, and USB can access all SRAM
blocks. Additionally, the matrix connects the CPU system bus and all of the DMA
controllers to the various peripheral function s.
8.30.6 External interrupt inputs
The LPC17xx include up to 46 edge sensitive interrupt inputs combined with up to four
level sensitive external interrupt inputs as selectable pin functions. The external interrupt
inputs can optionally be used to wake up the processor from Power-down mode.
8.30.7 Memory mapping control
The Cortex-M3 incorporates a mechanism that allows remapping the interrupt vector table
to alternate locations in the memory map. This is controlled via the Vector Table Offset
Register contained in the NVIC.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
The vector table may be located anywhere within the bottom 1 GB of Cortex-M3 address
space. The vector table must be located on a 128 word (512 byte) boundary because the
NVIC on the LPC17xx is configured for 128 total interrupts.
8.31 Emulation and debugging
Debug and trace functions are integrated into the Arm Cortex-M3. Serial wire debug and
trace functions are supported in addition to a standard JTAG debug and parallel trace
functions. The Arm Cortex-M3 is configured to support up to eight breakpoints and four
watch points.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 44 of 93
Page 45

NXP Semiconductors
9. Limiting values
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 6. Limiting values
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
[1]
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
V
DD(3V3)
V
DD(REG)(3V3)
V
DDA
supply voltage (3.3 V) external rail
regulator supply voltage (3.3 V)
analog 3.3 V pad supply
[2]
0.5 +4.6 V
[2]
0.5 +4.6 V
[2]
0.5 +4.6 V
voltage
V
i(VBAT)
V
i(VREFP)
V
IA
V
I
input voltage on pin VBAT for the RTC
input voltage on pin VREFP
analog input voltage on ADC related pins
input voltage 5 V tolerant digital I/O pins;
2.4 V
V
DD
[2]
0.5 +4.6 V
[2]
0.5 +4.6 V
[2][3]
0.5 +5.1 V
[2][4]
0.5 +5.5 V
VDD = 0 V 0.5 +3.6
[2][5]
5 V tolerant open-drain pins
0.5 +5.5
PIO0_27 and PIO0_28
I
DD
I
SS
I
latch
T
stg
T
j(max)
P
tot(pack)
supply current per supply pin - 100 mA
ground current per ground pin - 100 mA
I/O latch-up current (0.5V
(1.5V
storage temperature
DD(3V3)
DD(3V3)
); Tj < 125 C
) < VI <
-100mA
[6]
65 +150 C
maximum junction temperature 150 C
total power dissipation (per
package)
based on package heat
transfer, not device power
-1.5W
consumption
V
ESD
electrostatic discharge voltage human body model; all pins
[7]
4000 +4000 V
I
[1] The following applies to the limiting values:
a) This product includes circuitry specifically designed for the protection of its internal devices from the damaging effects of excessive
static charge. Nonetheless, it is suggested that conventional precautions be taken to avoid applying greater than the rated
maximum.
b) Parameters are valid over operating temperature range unless otherwise specified. All voltages are with respect to V
otherwise noted.
c) The limiting values are stress ratings only. Operating the part at these values is not recommended, and proper operation is not
guaranteed. The conditions for functional operation are specified in Table 8
[2] Maximum/minimum voltage above the maximum operating voltage (see Table 8
(< 10 ms) to a device without leading to irrecoverable failure. Failure includes the loss of reliability and shorter lifetime of the device.
[3] See Table 19
[4] Including voltage on outputs in 3-state mode.
[5] V
[6] The maximum non-operating storage temperature is different than the temperature for required shelf life which should be determined
[7] Human body model: equivalent to discharging a 100 pF capacitor through a 1.5 k series resistor.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 45 of 93
present or not present. Compliant with the I2C-bus standard. 5.5 V can be applied to this pin when VDD is powered down.
DD
based on required shelf lifetime. Please refer to the JEDEC spec (J-STD-033B.1) for further details.
for maximum operating voltage.
.
) and below ground that can be applied for a short time
unless
SS
Page 46

NXP Semiconductors
TjT
amb
PDR
th j a–
+=
10. Thermal characteristics
The average chip junction temperature, Tj (C), can be calculated using the following
equation:
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
(1)
• T
• R
• P
The internal power dissipation is the product of I
= ambient temperature (C)
amb
= the package junction-to-ambient thermal resistance (C/W)
th(j-a)
= sum of internal and I/O power dissipation
D
and VDD. The I/O power dissipation of
DD
the I/O pins is often small and many times can be n egligible. However it can be significant
in some applications.
Table 7. Thermal resistance (15 %)
Symbol Parameter Conditions Max/Min Unit
LQFP100
R
th(j-a)
R
th(j-c)
TFBGA100
R
th(j-a)
R
th(j-c)
thermal resistance from
junction to ambient
thermal resistance from
junction to case
thermal resistance from
junction to ambient
thermal resistance from
junction to case
JEDEC (4.5 in 4 in); still air 38.01 C/W
Single-layer (4.5 in 3 in); still air 55.09 C/W
9.065 C/W
JEDEC (4.5 in 4 in); still air 55.2 C/W
Single-layer (4.5 in 3 in); still air 45.6 C/W
9.5 C/W
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 46 of 93
Page 47

NXP Semiconductors
11. Static characteristics
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 8. Static characteristics
=40C to +85C, unless otherwise specified.
T
amb
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ
Supply pins
V
DD(3V3)
V
DD(REG)(3V3)
supply voltage (3.3 V) external rail
regulator supply voltage
[2]
2.4 3.3 3.6 V
2.4 3.3 3.6 V
(3.3 V)
V
DDA
analog 3.3 V pad supply
[3][4]
2.5 3.3 3.6 V
voltage
V
i(VBAT)
input voltage on pin
[5]
2.1 3.3 3.6 V
VBAT
V
i(VREFP)
input voltage on pin
[3]
2.5 3.3 V
VREFP
I
DD(REG)(3V3)
regulator supply current
(3.3 V)
active mode; code
while(1){}
executed from flash; all
peripherals disabled;
PCLK =
CCLK
⁄
8
CCLK = 12 MHz; PLL
[6][7]
-7-mA
disabled
CCLK = 100 MHz; PLL
[6][7]
-42-mA
enabled
[6][8]
CCLK = 100 MHz; PLL
-50-mA
enabled (LPC1769)
[6][8]
CCLK = 120 MHz; PLL
-67-mA
enabled (LPC1769)
sleep mode
deep sleep mode
power-down mode
deep power-down mode;
[6][9]
-2-mA
[6][10]
-240-A
[6][10]
-31-A
[11]
-630-nA
RTC running
I
BAT
battery supply current deep power-down mode;
RTC running
[12]
-530-nA
[13]
-
1.1 - A
[14][15]
-40-nA
[14][15]
-40-nA
[14]
-10-nA
I
DD(IO)
V
DD(REG)(3V3)
V
DD(REG)(3V3)
present
not
present
I/O supply current deep sleep mode
power-down mode
deep power-down mode
[1]
Max Unit
DDA
V
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 47 of 93
Page 48

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 8. Static characteristics …continued
T
=40C to +85C, unless otherwise specified.
amb
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ
I
DD(ADC)
I
I(ADC)
ADC supply current active mode;
ADC input current on pin VREFP
Standard port pins, RESET
I
IL
I
IH
LOW-level input current VI= 0 V; on-chip pull-up
HIGH-level input
current
I
OZ
OFF-state output
current
V
I
V
O
V
IH
input voltage pin configured to provide
output voltage output active 0 - V
HIGH-level input
voltage
V
IL
V
hys
V
OH
LOW-level input voltage - - 0.3V
hysteresis voltage 0.4 - - V
HIGH-level output
voltage
V
OL
LOW-level output
voltage
I
OH
HIGH-level output
current
I
OL
LOW-level output
current
I
OHS
HIGH-level short-circuit
output current
I
OLS
LOW-level short-circuit
output current
I
pd
I
pu
pull-down current VI=5V 10 50 150 A
pull-up current VI=0V 15 50 85 A
, RTCK
ADC powered
ADC in Power-down
mode
deep sleep mode
power-down mode
deep power-down mode
deep sleep mode
power-down mode
deep power-down
mode
resistor disabled
VI=V
DD(3V3)
; on-chip
pull-down resistor
disabled
VO=0V; VO=V
DD(3V3)
on-chip pull-up/down
resistors disabled
a digital function
IOH= 4 mA V
IOL=4 mA --0.4V
VOH=V
0.4 V 4--mA
DD(3V3)
VOL=0.4V 4--mA
VOH=0V
VOL=V
V
DD(3V3)
DD(3V3)<VI
<5V 000A
[16][17]
-1.95-mA
[16][18]
-<0.2-A
[16]
-38-nA
[16]
-38-nA
[16]
-24-nA
[19]
-100-nA
[19]
-100-nA
[19]
-100-nA
- 0.5 10 nA
- 0.5 10 nA
;
- 0.5 10 nA
[20][21]
0- 5.0V
[22]
0.7V
DD(3V3)
DD(3V3)
--V
--V
0.4
[23]
--45 mA
[23]
--50mA
[1]
Max Unit
DD(3V3)
DD(3V3)
V
V
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 48 of 93
Page 49

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 8. Static characteristics
T
=40C to +85C, unless otherwise specified.
amb
…continued
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ
I2C-bus pins (P0[27] and P0[28])
V
IH
HIGH-level input
0.7V
DD(3V3)
--V
voltage
V
IL
V
hys
LOW-level input voltage - - 0.3V
hysteresis voltage - 0.05
V
V
OL
LOW-level output
I
=3 mA --0.4V
OLS
voltage
I
LI
input leakage current VI=V
=5V - 10 22 A
V
I
DD(3V3)
[24]
-24A
Oscillator pins
V
i(XTAL1)
input voltage on pin
0.5 1.8 1.95 V
XTAL1
V
o(XTAL2)
output voltage on pin
0.5 1.8 1.95 V
XTAL2
V
i(RTCX1)
input voltage on pin
0.5 - 3.6 V
RTCX1
V
o(RTCX2)
output voltage on pin
0.5 - 3.6 V
RTCX2
USB pins (LPC1769/68/66/65/64 only)
I
OZ
OFF-state output
0V<VI<3.3V
[2]
--10 A
current
V
V
BUS
DI
bus supply voltage
differential input
(D+) (D)
[2]
--5.25V
[2]
0.2--V
sensitivity voltage
V
CM
differential common
includes VDI range
[2]
0.8 - 2.5 V
mode voltage range
V
th(rs)se
single-ended receiver
[2]
0.8 - 2.0 V
switching threshold
voltage
V
OL
LOW-level output
RL of 1.5 k to 3.6 V
[2]
--0.18V
voltage for
low-/full-speed
V
OH
HIGH-level output
RL of 15 k to GND
[2]
2.8 - 3.5 V
voltage (driven) for
low-/full-speed
C
Z
trans
DRV
transceiver capacitance pin to GND
driver output
impedance for driver
with 33 series resistor;
steady state drive
[2]
--20pF
[2][25]
36 - 44.1
which is not high-speed
capable
[1]
DD(3V3)
Max Unit
DD(3V3)
V
-V
[1] Typical ratings are not guaranteed. The values listed are at room temperature (25 C), nominal supply voltages.
[2] For USB operation 3.0 V V
[3] V
[4] V
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 49 of 93
and VREFP should be tied to V
DDA
for DAC specs are from 2.7 V to 3.6 V.
DDA
3.6 V. Guaranteed by design.
DD((3V3)
if the ADC and DAC are not used.
DD(3V3)
Page 50

NXP Semiconductors
002aaf568
temperature (°C)
−40 853510 60−15
250
350
300
400
I
DD(Reg)(3V3)
(μA)
200
3.6 V
3.3 V
2.4 V
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
[5] The RTC typically fails when V
[6] V
DD(REG)(3V3)
= 3.3 V; T
=25C for all power consumption measurements.
amb
drops below 1.6 V.
i(VBAT)
[7] Applies to LPC1768/67/66/65/64/63.
[8] Applies to LPC1769 only.
CCLK
[9] IRC running at 4 MHz; main oscillator and PLL disabled; PCLK =
⁄8.
[10] BOD disabled.
. I
[11] On pin V
DD(REG)(3V3)
[12] On pin VBAT; I
[13] On pin VBAT; V
DD(REG)(3V3)
BAT
= 530 nA. V
BAT
= 630 nA; V
= 3.0 V; T
amb
DD(REG)(3V3)
DD(REG)(3V3)
=25C.
[14] All internal pull-ups disabled. All pins configured as output and driven LOW. V
= 3.0 V; V
= 3.0 V; V
= 3.0 V; T
BAT
= 3.0 V; T
BAT
amb
amb
=25C.
=25C.
DD(3V3)
= 3.3 V; T
amb
=25C.
[15] TCK/SWDCLK pin needs to be externally pulled LOW.
[16] On pin V
DDA
=3.3V; T
DDA
=25C. The ADC is powered if the PDN bit in the AD0CR register is set to 1 and in Power-down mode
amb
; V
of the PDN bit is set to 0.
[17] The ADC is powered if the PDN bit in the AD0CR register is set to 1. See LPC17xx user manual UM10360_1.
[18] The ADC is in Power-down mode if the PDN bit in the AD0CR register is set to 0. See LPC17xx user manual UM10360_1.
[19] V
i(VREFP)
= 3.3 V; T
amb
=25C.
[20] Including voltage on outputs in 3-state mode.
[21] V
supply voltages must be present.
DD(3V3)
[22] 3-state outputs go into 3-state mode in Deep power-down mode.
[23] Allowed as long as the current limit does not exceed the maximum current allowed by the device.
[24] To V
.
SS
[25] Includes external resistors of 33 1 % on D+ and D.
1 1.1 Power consumption
Conditions: BOD disabled.
Fig 8. Deep-sleep mode: typical regulato r supply current I
temperature
DD(Reg)(3V3)
versus
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 50 of 93
Page 51

NXP Semiconductors
002aaf569
40
80
120
0
temperature (°C)
−40 853510 60−15
I
DD(Reg)(3V3)
(μA)
3.6 V
3.3 V
2.4 V
002aag119
1.0
1.4
1.8
0.6
temperature (°C)
-40 853510 60-15
I
BAT)
(μA)
V
i(VBAT)
= 3.6 V
3.3 V
3.0 V
2.4 V
Fig 9. Power-down mode: Typical regulator supply current I
Conditions: BOD disabled.
temperature
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
DD(Reg)(3V3)
versus
Conditions: V
DD(REG)(3V3)
floating; RTC running.
Fig 10. Deep power-down mode: Typical battery supply current I
versus temperature
BAT
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 51 of 93
Page 52

NXP Semiconductors
002aag120
temperature (°C)
-40 853510 60-15
0.8
1.6
0.4
1.2
2.0
0
I
DD(REG)(3V3)
I
BAT
I
DD(REG)(3V3)/IBAT
(µA)
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Conditions: V
= 3.0 V; V
BAT
DD(REG)(3V3)
= 3.0 V; RTC running.
Fig 11. Deep power-down mode: T ypi cal regulator supply c urrent I
supply current I
versus temperature
BAT
DD(REG)(3V3)
and battery
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 52 of 93
Page 53

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
1 1.2 Peripheral power consumption
The supply current per peripheral is measured a s the difference in supply current between
the peripheral block enabled and the peripheral block disabled in the PCONP register. All
other blocks are disabled and no code is executed. Measured on a typical sample at
T
=25C. The peripheral clock PCLK = CCLK/4.
amb
Table 9. Power consumption for individual analog and digital blocks
Peripheral Conditions Typical supply current in mA;
12 MHz 48 MHz 100 MHz
Timer 0.03 0.11 0.23 Average current per timer
UART 0.07 0.26 0.53 Average current per UART
PWM 0.05 0.20 0.41
Motor control
PWM
I2C 0.02 0.08 0.16 Average current per I2C
SPI 0.02 0.06 0.13
SSP1 0.04 0.16 0.32
ADC PCLK = 12 MHz for CCLK = 12 MHz
CAN PCLK = CCLK/6 0.13 0.49 1.00 Average current per CAN
CAN0, CAN1,
acceptance filter
DMA PCLK = CCLK 1.33 5.10 10.36
QEI 0.05 0.20 0.41
GPIO 0.33 1.27 2.58
I2S 0.09 0.34 0.70
USB and PLL1 0.94 1.32 1.94
Ethernet Ethernet block ena bled in the PCONP
Ethernet
connected
Notes
CCLK =
0.05 0.21 0.42
2.12 2.09 2.07
and 48 MHz; PCLK = 12.5 MHz for
CCLK = 100 MHz
PCLK = CCLK/6 0.22 0.85 1.73 Both CAN blocks and
acceptance filter
0.49 1.87 3.79
register; Ethernet not connected.
Ethernet initialized, connected to
network, and running web server
example.
- - 5.19
[1]
[1] The combined current of several peripherals running at the same time can be less than the sum of each individual peripheral current
measured separately.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 53 of 93
Page 54

NXP Semiconductors
IOH (mA)
0 24168
002aaf112
2.8
2.4
3.2
3.6
V
OH
(V)
2.0
T = 85 °C
25 °C
−40 °C
VOL (V)
0 0.60.40.2
002aaf111
5
10
15
I
OL
(mA)
0
T = 85 °C
25 °C
−40 °C
11.3 Electrical pin characteristics
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Conditions: V
DD(REG)(3V3)=VDD(3V3)
= 3.3 V; standard port pins.
Fig 12. Typical HIGH-level output voltage VOH versus HIGH-level output source current
I
OH
Conditions: V
DD(REG)(3V3)=VDD(3V3)
Fig 13. Typical LOW-level output current IOL versus LOW-level output voltage V
= 3.3 V; standard port pins.
OL
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 54 of 93
Page 55

NXP Semiconductors
0 54231
002aaf108
−30
−50
−10
10
I
pu
(μA)
−70
T = 85 °C
25 °C
−40 °C
VI (V)
002aaf109
VI (V)
0 53241
10
70
50
30
90
I
pd
(μA)
−10
T = 85 °C
25 °C
−40 °C
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Conditions: V
DD(REG)(3V3)=VDD(3V3)
= 3.3 V; standard port pins.
Fig 14. Typical pull-up current Ipu versus input voltage V
Conditions: V
DD(REG)(3V3)=VDD(3V3)
= 3.3 V; standard port pins.
Fig 15. Typical pull-down current Ipd versus input voltage V
I
I
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 55 of 93
Page 56

NXP Semiconductors
t
CHCL
t
CLCX
t
CHCX
T
cy(clk)
t
CLCH
002aaa907
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
12. Dynamic characteristics
12.1 Flash memory
Table 10. Flash characteristics
T
=40C to +85C, unless otherwise specified.
amb
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
N
endu
t
ret
t
er
t
prog
[1] Number of program/erase cycles.
[2] Programming times are given for writing 256 bytes from RAM to the flash. Data must be written to the flash in blocks of 256 bytes.
12.2 External clock
Table 11 . Dynamic characteristic: external clock
T
=40C to +85C; V
amb
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ
f
osc
T
cy(clk)
t
CHCX
t
CLCX
t
CLCH
t
CHCL
endurance
[1]
10000 100000 - cycles
retention time powered 10 - - years
unpowered 20 - - years
erase time sector or multiple
95 100 105 ms
consecutive sectors
programming time
over specified ranges.
DD(3V3)
[1]
[2]
0.95 1 1.05 ms
[2]
Max Unit
oscillator frequency 1 - 25 MHz
clock cycle time 40 - 1000 ns
clock HIGH time T
clock LOW time T
0.4 - - ns
cy(clk)
0.4 - - ns
cy(clk)
clock rise time - - 5 ns
clock fall time - - 5 ns
[1] Parameters are valid over operating temperature range unless otherwise specified.
[2] Typical ratings are not guaranteed. The values listed are at room temperature (25 C), nominal supply voltages.
Fig 16. External clock timing (with an amplitude of at least V
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 56 of 93
i(RMS)
= 200 mV)
Page 57
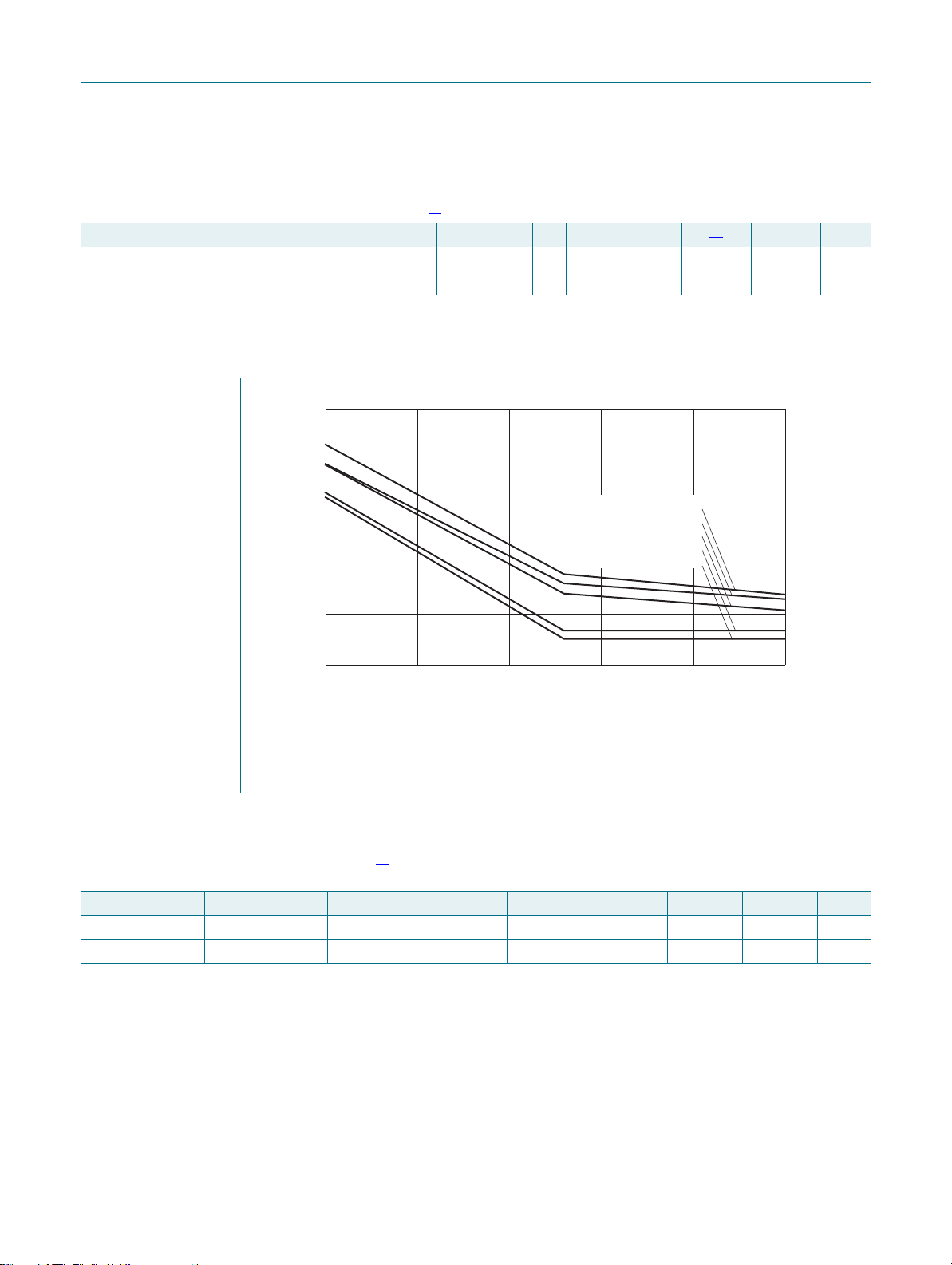
NXP Semiconductors
002aaf107
temperature (°C)
-40 853510 60-15
4.024
4.032
4.020
4.028
4.036
f
osc(RC)
(MHz)
4.016
V
DD(REG)(3V3)
= 3.6 V
3.3 V
3.0 V
2.7 V
2.4 V
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
12.3 Internal oscillators
Table 12. Dynamic characteristic: internal oscillators
T
=40C to +85C; 2.7 V V
amb
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ
f
osc(RC)
f
i(RTC)
[1] Parameters are valid over operating temperature range unless otherwise specified.
[2] Typical ratings are not guaranteed. The values listed are at room temperature (25 C), nominal supply voltages.
DD(REG)(3V3)
3.6 V.
[1]
[2]
internal RC oscillator frequency - 3.96 4.02 4.04 MHz
RTC input frequency - - 32.768 - kHz
Max Unit
Conditions: Frequency values are typical values. 4 MHz 1 % accuracy is guaranteed for
2.7 V V
DD(REG)(3V3)
3.6 V and T
= 40 Cto+85C. Variations between parts may cause
amb
the IRC to fall outside the 4 MHz 1 % accuracy specification for voltages below 2.7 V.
Fig 17. Internal RC oscillator frequency versus temperature
12.4 I/O pins
Table 13. Dynamic characteristic: I/O pins
T
=40C to +85C; V
amb
DD(3V3)
over specified ranges.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
t
r
t
f
[1] Applies to standard I/O pins.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 57 of 93
rise time pin configured as output 3.0 - 5.0 ns
fall time pin configured as output 2.5 - 5.0 ns
[1]
Page 58

NXP Semiconductors
12.5 I2C-bus
Table 14. Dynamic characteristic: I2C-bus pins
T
amb
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
f
SCL
t
f
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
HD;DAT
t
SU;DAT
=40C to +85C.
SCL clock
frequency
fall time
LOW period of
the SCL clock
HIGH period of
the SCL clock
data hold time
data set-up
time
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
[1]
[2]
Standard-mode 0 100 kHz
Fast-mode 0 400 kHz
Fast-mode Plus 0 1 MHz
[3][4][5][6]
[3][7][8]
[9][10]
of both SDA and
- 300 ns
SCL signals
Standard-mode
Fast-mode 20 + 0.1 Cb300 ns
Fast-mode Plus - 120 ns
Standard-mode 4.7 - s
Fast-mode 1.3 - s
Fast-mode Plus 0.5 - s
Standard-mode 4.0 - s
Fast-mode 0.6 - s
Fast-mode Plus 0.26 - s
Standard-mode 0 - s
Fast-mode 0 - s
Fast-mode Plus 0 - s
Standard-mode 250 - ns
Fast-mode 100 - ns
Fast-mode Plus 50 - ns
[1] See the I2C-bus specification UM10204 for details.
[2] Parameters are valid over operating temperature range unless otherwise specified.
[3] A device must internally provide a hold time of at least 300 ns for the SDA signal (with respect to the
(min) of the SCL signal) to bridge the undefined region of the falling edge of SCL.
V
IH
[4] C
= total capacitance of one bus line in pF.
b
[5] The maximum t
output stage t
SDA and the SCL pins and the SDA/SCL bus lines without exceeding the maximum specified t
[6] In Fast-mode Plus, fall time is specified the same for both output stage and bus timing. If series resistors
are used, designers should allow for this when considering bus timing.
[7] tHD;DA T is the data hold time that is measured from the falling edge of SCL; applies to data in transmission
and the acknowledge.
[8] The maximum t
the maximum of t
maximum must only be met if the device does not stretch the LOW period (t
clock stretches the SCL, the data must be valid by the set-up time before it releases the clock.
[9] tSU;DAT is the data set-up time that is measured with respect to the rising edge of SCL; applies to data in
transmission and the acknowledge.
[10] A Fast-mode I
250 ns must then be met. This will automatically be the case if the device does not stretch the LOW period
of the SCL signal. If such a device does stretch the LOW period of the SCL signal, it must output the next
data bit to the SDA line t
specification) before the SCL line is released. Also the acknowledge timing must meet this set-up time.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 58 of 93
for the SDA and SCL bus lines is specified at 300 ns. The maximum fall time for the SDA
f
is specified at 250 ns. This allows series protection resistors to be connected in between the
f
could be 3.45 s and 0.9 s for Standard-mode and Fast-mode but must be less than
HD;DAT
or t
VD;DAT
2
C-bus device can be used in a Standard-mode I2C-bus system but the requirement t
r(max)
by a transition time (see the I2C-bus specification UM10204). This
VD;ACK
+ t
= 1000 + 250 = 1250 ns (according to the Standard-mode I2C-bus
SU;DAT
) of the SCL signal. If the
LOW
f
.
SU;DAT
=
Page 59

NXP Semiconductors
002aaf425
t
f
70 %
30 %
SDA
t
f
70 %
30 %
S
70 %
30 %
70 %
30 %
t
HD;DAT
SCL
1 / f
SCL
70 %
30 %
70 %
30 %
t
VD;DAT
t
HIGH
t
LOW
t
SU;DAT
Fig 18. I2C-bus pins clock timing
12.6 I2S-bus interface
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Remark: The I2S-bus interface is available on parts LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63. See
Table 2
Table 15. Dynamic characteristics: I2S-bus interface pins
T
=40C to +85C.
amb
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
common to input and output
t
t
t
t
r
f
WH
WL
rise time
fall time
pulse width HIGH on pins I2STX_CLK and
pulse width LOW on pins I2STX_CLK and
output
t
v(Q)
data output valid time on pin I2STX_SDA
input
t
su(D)
t
h(D)
[1] CCLK = 20 MHz; peripheral clock to the I2S-bus interface PCLK =
data input set-up time on pin I2SRX_SDA
data input hold time on pi n I2SRX_SDA
signal in the I
2
S-bus specification.
.
I2SRX_CLK
I2SRX_CLK
on pin I2STX_WS
[1]
--35ns
[1]
--35ns
[1]
0.495 T
[1]
- - 0.505 T
[1]
--30ns
[1]
--30ns
[1]
3.5 - - ns
[1]
4.0 - - ns
CCLK
⁄4; I2S clock cycle time T
-- -
cy(clk)
= 1600 ns, corresponds to the SCK
cy(clk)
cy(clk)
ns
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 59 of 93
Page 60

NXP Semiconductors
002aad992
I2STX_CLK
I2STX_SDA
I2STX_WS
T
cy(clk)
t
f
t
r
t
WH
t
WL
t
v(Q)
t
v(Q)
002aae159
T
cy(clk)
t
f
t
r
t
WH
t
su(D)
t
h(D)
t
su(D)
t
su(D)
t
WL
I2SRX_CLK
I2SRX_SDA
I2SRX_WS
Fig 19. I2S-bus timing (output)
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 20. I
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
2
S-bus timing (input)
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 60 of 93
Page 61

NXP Semiconductors
SCK (CPOL = 0)
MOSI
MISO
T
cy(clk)
t
DS
t
DH
t
v(Q)
DATA VA L ID D ATA VA L ID
t
h(Q)
SCK (CPOL = 1)
DATA VALID
DATA VALID
MOSI
MISO
t
DS
t
DH
DATA VA L ID D ATA VA L ID
t
h(Q)
DATA VALID
DATA VALID
t
v(Q)
CPHA = 1
CPHA = 0
002aae829
12.7 SSP interface
The maximum SSP speed is 33 Mbit/s in master mode or 8 Mbit/s in slave mod e. In slave
mode, the maximum SSP clock rate must be 1/12 of the SSP PCLK clock rate.
Table 16. Dynamic characteristics: SSP pins in SPI mode
= 30 pF for all SSP pins; T
C
L
sampled at 10 % and 90 % of the signal level. Values guaranteed by design.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
SSP master
t
DS
t
DH
t
v(Q)
t
h(Q)
SSP slave
t
DS
t
DH
t
v(Q)
t
h(Q)
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
=40C to 85C; V
amb
data set-up time in SPI mode 16.1 - ns
data hold time in SPI mode 0 - ns
data output valid time in SPI mode - 2.5 ns
data output hold time in SPI mode 0 - ns
data set-up time in SPI mode 16.1 - ns
data hold time in SPI mode 0 - ns
data output valid time in SPI mode - 3*T
data output hold time in SPI mode 0 - ns
= 3.3 V to 3.6 V; input slew = 1 ns;
DD(3V3)
+ 2.5 ns
cy(PCLK)
Fig 21. SSP master timing in SPI mode
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 61 of 93
Page 62

NXP Semiconductors
SCK (CPOL = 0)
SCK (CPOL = 1)
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
T
cy(clk)
t
DS
t
DH
MOSI
MISO
MOSI
MISO
DATA VALID
DATA VA L ID D ATA VA L ID
DATA VALID
DATA VA L ID D ATA VA L ID
t
v(Q)
Fig 22. SSP slave timing in SPI mode
t
v(Q)
t
DS
t
DH
DATA VALID
DATA VALID
t
h(Q)
t
h(Q)
CPHA = 1
CPHA = 0
002aae830
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 62 of 93
Page 63

NXP Semiconductors
002aab561
T
PERIOD
differential
data lines
crossover point
source EOP width: t
FEOPT
receiver EOP width: t
EOPR1
, t
EOPR2
crossover point
extended
differential data to
SE0/EOP skew
n × T
PERIOD
+ t
FDEOP
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
12.8 USB interface
Remark: The USB controller is available as a device/Host/OTG controller on parts
LPC1769/68/66/65 and as device-only controller on part LPC1764.
Table 17. Dynamic characteristics: USB pins (full-speed)
= 50 pF; Rpu = 1.5 k on D+ to V
C
L
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
t
r
t
f
t
FRFM
V
CRS
t
FEOPT
t
FDEOP
t
JR1
t
JR2
t
EOPR1
t
EOPR2
DD(3V3)
; 3.0 V V
DD(3V3)
3.6 V.
rise time 10 % to 90 % 8.5 - 13.8 ns
fall time 10 % to 90 % 7.7 - 13.7 ns
differential rise and fall time
tr/t
f
--109%
matching
output signal crossover voltage 1.3 - 2.0 V
source SE0 interval of EOP see Figure 23 160 - 175 ns
source jitter for differential transition
see Figure 23 2-+5ns
to SE0 transition
receiver jitter to next transition 18.5 - +18.5 ns
receiver jitter for paired transitions 10 % to 90 % 9-+9ns
EOP width at receiver must reject as
[1]
40 --ns
EOP; see
Figure 23
EOP width at receiver must accept as
[1]
82 --ns
EOP; see
Figure 23
[1] Characterized but not implemented as production test. Guaranteed by design.
Fig 23. Differential data -to-EOP transition skew and EOP width
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 63 of 93
Page 64

NXP Semiconductors
SCK (CPOL = 0)
MOSI
MISO
002aad986
T
SPICYC
t
SPICLKH
t
SPICLKL
t
SPIDSU
t
SPIDH
t
SPIQV
DATA V ALID DATA VALID
t
SPIOH
SCK (CPOL = 1)
DATA V ALID
DATA V ALID
12.9 SPI
Table 18. Dynamic characteristics of SPI pins
T
amb
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
T
cy(PCLK)
T
SPICYC
t
SPICLKH
t
SPICLKL
SPI master
t
SPIDSU
t
SPIDH
t
SPIQV
t
SPIOH
SPI slave
t
SPIDSU
t
SPIDH
t
SPIQV
t
SPIOH
[1] T
[2] Timing parameters are measured with respect to the 50 % edge of the clock SCK and the 10 % (90 %)
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
=40C to +85C.
PCLK cycle time 10 - - ns
SPI cycle time
SPICLK HIGH time 0.485 T
SPICLK LOW time - 0.515 T
SPI data set-up time
SPI data hold time
SPI data output valid time
SPI output data hold time
SPI data set-up time
SPI data hold time
SPI data output valid time
SPI output data hold time
= (T
SPICYC
processor clock CCLK.
edge of the data signal (MOSI or MISO).
n) 0.5 %, n is the SPI clock divider value (n 8); PCLK is derived from the
cy(PCLK)
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
[1]
79.6 - - ns
-- ns
SPICYC
ns
SPICYC
[2]
0--ns
[2]
2 T
[2]
2 T
[2]
2 T
[2]
0--ns
[2]
2 T
[2]
2 T
[2]
2 T
5 - - ns
cy(PCLK)
+ 30 - - ns
cy(PCLK)
+ 5 - - ns
cy(PCLK)
+ 5 - - ns
cy(PCLK)
+ 35 - - ns
cy(PCLK)
+ 15 - - ns
cy(PCLK)
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 64 of 93
Fig 24. SPI master timing (CPHA = 1)
Page 65

NXP Semiconductors
SCK (CPOL = 0)
MOSI
MISO
002aad987
T
SPICYC
t
SPICLKH
t
SPICLKL
t
SPIDSU
t
SPIDH
DATA V ALID DATA VALID
t
SPIOH
SCK (CPOL = 1)
DATA V ALID
DATA V ALID
t
SPIQV
SCK (CPOL = 0)
MOSI
MISO
002aad988
T
SPICYC
t
SPICLKH
t
SPICLKL
t
SPIDSU
t
SPIDH
t
SPIQV
DATA V ALID DATA VALID
t
SPIOH
SCK (CPOL = 1)
DATA V ALID
DATA V ALID
Fig 25. SPI master timing (CPHA = 0)
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 26. SPI slave timing (CPHA = 1)
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 65 of 93
Page 66

NXP Semiconductors
SCK (CPOL = 0)
MOSI
MISO
002aad989
T
SPICYC
t
SPICLKH
t
SPICLKL
t
SPIDSU
t
SPIDH
t
SPIQV
DATA V ALID DATA VALID
t
SPIOH
SCK (CPOL = 1)
DATA V ALID
DATA V ALID
Fig 27. SPI slave timing (CPHA = 0)
13. ADC electrical characteristics
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 19. ADC characteristics (full resolution)
= 2.5 V to 3.6 V; T
V
DDA
=40C to +85C unless otherwise specified; ADC frequency 13 MHz; 12-bit resolution.
amb
[1]
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
C
E
E
E
E
E
R
IA
ia
D
L(adj)
O
G
T
vsi
analog input voltage 0 - V
DDA
analog input capacitance - - 15 pF
differential linearity error
integral non-linearity
offset error
gain error
absolute error
voltage source interface
[2][3]
--1LSB
[4]
--3LSB
[5][6]
--2LSB
[7]
--0.5%
[8]
--4LSB
[9]
--7.5k
V
resistance
f
clk(ADC)
f
c(ADC)
[1] V
DDA
[2] The ADC is monotonic, there are no missing codes.
[3] The differential linearity error (E
[4] The integral non-linearity (E
appropriate adjustment of gain and offset errors. See Figure 28
[5] The offset error (E
ideal curve. See Figure 28
[6] ADCOFFS value (bits 7:4) = 2 in the ADTRM register. See LPC17xx user manual UM10360.
[7] The gain error (E
error, and the straight line which fits the ideal transfer curve. See Figure 28
[8] The absolute error (E
ADC and the ideal transfer curve. See Figure 28
[9] See Figure 29
[10] The conversion frequency corresponds to the number of samples per second.
ADC clock frequency - - 13 MHz
ADC conversion frequency
and VREFP should be tied to V
) is the difference between the actual step width and the ideal step width. See Figure 28.
D
) is the peak difference between the center of the steps of the actual and the ideal transfer curve after
L(adj)
.
) is the absolute difference between the straight line which fits the actual curve and the straight line which fits the
O
) is the relative difference in percent between the straight line fitting the actual transfer curve after removing offset
G
) is the maximum difference between the center of the steps of the actual transfer curve of the non-calibrated
T
.
DD(3V3)
if the ADC and DAC are not used.
.
.
[10]
--200kHz
.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 66 of 93
Page 67

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 20. ADC characteristics (lower resolution)
T
=40C to +85C unless otherwise specified; 12-bit ADC used as 10-bit resolution ADC.
amb
[1]
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
E
D
E
L(adj)
E
O
E
G
f
clk(ADC)
f
c(ADC)
[1] V
[2] The ADC is monotonic, there are no missing codes.
[3] The differential linearity error (E
[4] The integral non-linearity (E
[5] The offset error (E
[6] The gain error (E
[7] The conversion frequency corresponds to the number of samples per second.
differential linearity error
integral non-linearity
offset error
gain error
ADC clock frequency 3.0 V V
2.7 V V
ADC conversion frequency 3 V V
2.7 V V
and VREFP should be tied to V
DDA
) is the difference between the actual step width and the ideal step width. See Figure 28.
D
) is the peak difference between the center of the steps of the actual and the ideal transfer curve after
appropriate adjustment of gain and offset errors. See Figure 28
ideal curve. See Figure 28
error, and the straight line which fits the ideal transfer curve. See Figure 28
O
) is the relative difference in percent between the straight line fitting the actual transfer curve after removing offset
G
L(adj)
) is the absolute difference between the straight line which fits the actual curve and the straight line which fits the
.
if the ADC and DAC are not used.
DD(3V3)
3.6 V - - 33 MHz
DDA
< 3.0 V - - 25 MHz
DDA
3.6 V
DDA
< 3.0 V
DDA
.
[2][3]
- 1- LSB
[4]
- 1.5 - LSB
[5]
- 2- LSB
[6]
- 2- LSB
[7]
-- 500 kHz
[7]
-- 400 kHz
.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 67 of 93
Page 68

NXP Semiconductors
002aad948
4095
4094
4093
4092
4091
(2)
(1)
40964090 4091 4092 4093 4094 4095
7123456
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
4090
(5)
(4)
(3)
1 LSB
(ideal)
code
out
VREFP − VREFN
4096
offset
error
E
O
gain
error
E
G
offset error
E
O
VIA (LSB
ideal
)
1 LSB =
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
(1) Example of an actual transfer curve.
(2) The ideal tr ansfer curve.
L(adj)
).
D
).
(3) Differential linearity error (E
(4) Integral non-linearity (E
(5) Center of a step of the actual transfer curve.
Fig 28. 12-bit ADC characteristics
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 68 of 93
Page 69

NXP Semiconductors
LPC17xx
AD0[n]
750 fF
65 fF
C
ia
2.2 pF
R
vsi
R
i2
100 Ω - 600 Ω
R
i1
2 kΩ - 5.2 kΩ
V
SS
V
EXT
002aaf197
ADC
COMPARATOR
BLOCK
C1
C3
C2
Fig 29. ADC interface to pins AD0[n]
Table 21. ADC interface components
Component Range Description
R
i1
R
i2
C1 750 fF Parasitic capacitance from the ADC block level.
C2 65 fF Parasitic capacitance from the ADC block level.
C3 2.2 pF Sampling capacitor.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
The values of resistor components Ri1 and Ri2 vary with temperature and input voltage and are
process-dependent (see Table 21
Parasitic resistance and capacitance from the pad are not included in this figure.
2 k to 5.2 k Switch-on resistance for channel selection switch. V aries with
100 to 600 Switch-on resistance for the comparator input switch. Varies
).
temperature, input voltage, and process.
with temperature, input voltage, and process.
14. DAC electrical characteristics
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 69 of 93
Remark: The DAC is available on parts LPC1769/68/67/66/65/63. See Table 2.
Table 22. DAC electrical characteristics
= 2.7 V to 3.6 V; T
V
DDA
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
E
D
E
L(adj)
E
O
E
G
C
L
R
L
differential linearity error - 1-LSB
integral non-linearity - 1.5 - LSB
offset error - 0.6 - %
gain error - 0.6 - %
load capacitance - 200 - pF
load resistance 1 - - k
=40C to +85C unless otherwise specified
amb
Page 70

NXP Semiconductors
LPC17xx
V
DD(3V3)
R1
1.5 kΩ
R2
USB_UP_LED
002aad940
USB-B
connector
USB_D+
USB_D−
V
BUS
V
SS
RS = 33 Ω
RS = 33 Ω
15. Application information
15.1 Suggested USB interface solutions
Remark: The USB controller is available as a device/Host/OTG controller on parts
LPC1769/68/66/65 and as device-only controller on part LPC1764.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
If the LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63 V
V
pin can be connected directly to the V
BUS
This applies to bus powered devices where the USB cable supplies the system power. For
systems where V
can be 0 V and V
DD
must be taken to reduce the voltage to below 3.6 V.
Fig 30. USB interface on a bus-powered device
is always greater than 0 V while V
DD
pin on the USB connector.
BUS
is directly applied to the V
BUS
= 5 V, the
BUS
pin, precautions
BUS
The maximum allowable voltage on the V
divider to connect the V
pin to the V
BUS
The voltage divider ratio should be such that the V
pin is 3.6 V. One method is to use a voltage
BUS
on the USB connector.
BUS
pin will be greater than 0.7VDD to
BUS
indicate a logic HIGH while below the 3.6 V allowable maximum voltage.
Use the following operating conditions:
VBUS
V
DD
= 5.25 V
max
= 3.6 V
The voltage divider would need to provide a reduction of 3.6 V/5.25 V or ~0.686 V.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 70 of 93
Page 71

NXP Semiconductors
LPC17xx
V
DD
R1
1.5 kΩ
R2
R3
USB-B
connector
USB_D+
USB_D-
V
BUS
V
SS
RS = 33 Ω
RS = 33 Ω
aaa-008962
R2
USB_UP_LED
LPC17xx
USB-B
connector
USB_D+
USB_CONNECT
SoftConnect switch
USB_D−
V
BUS
V
SS
V
DD(3V3)
R1
1.5 kΩ
RS = 33 Ω
002aad939
RS = 33 Ω
USB_UP_LED
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 31. USB interface on a bus-powered device where V
= 5 V, VDD not present
BUS
Fig 32. USB interface with soft-connect
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 71 of 93
Page 72

NXP Semiconductors
USB_D+
USB_D−
USB_SDA
USB_SCL
RSTOUT
LPC17xx
Mini-AB
connector
33 Ω
33 Ω
V
DD
V
DD
002aad941
EINTn
RESET_N
ADR/PSW
SPEED
SUSPEND
OE_N/INT_N
SCL
SDA
INT_N
VBUS
ID
DP
DM
ISP1302
V
SS
USB_UP_LED
V
DD
USB_UP_LED
USB_D+
USB_D−
USB_PWRD
15 kΩ 15 kΩ
LPC17xx
USB-A
connector
33 Ω
33 Ω
002aad942
V
DD
USB_OVRCR
USB_PPWR
LM3526-L
ENA
IN
5 V
FLAGA
OUTA
V
DD
D+
D−
V
BUS
V
SS
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 33. USB OTG port configuration
Fig 34. USB host port configuration
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 72 of 93
Page 73

NXP Semiconductors
LPC17xx
USB-B
connector
33 Ω
33 Ω
002aad943
USB_UP_LED
USB_CONNECT
V
DD
V
DD
D+
D−
USB_D+
USB_D−
V
BUS
V
BUS
V
SS
LPC1xxx
XTAL1
C
i
100 pF
C
g
002aae835
Fig 35. USB device port configuration
15.2 Crystal oscillator XTAL input and component selection
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
The input voltage to the on-chip oscillators is limited to 1.8 V . If the oscillator is driven by a
clock in slave mode, it is recommended that the input be coupled thro ugh a cap acitor wi th
C
= 100 pF. To limit the input voltage to the specified range, choose an additional
i
capacitor to ground C
which attenuates the input voltage by a factor Ci/(Ci + Cg). In slave
g
mode, a minimum of 200 mV(RMS) is needed.
Fig 36. Slave mode operation of the on-chip oscillator
In slave mode the input clock signal should be coupled by means of a capacitor of 100 pF
(Figure 36
), with an amplitude between 200 mV(RMS) and 1000 mV(RMS). This
corresponds to a square wave signal with a signal swing of between 280 mV and 1.4 V.
The XTALOUT pin in this configuration can be left unconnected.
External components and models used in oscillation mode are shown in Figure 37
Table 23
and the capacitances C
fundamental mode oscillation (the fundamental frequency is represented by L, C
R
not be larger than 7 pF. Parameters F
manufacturer.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 73 of 93
and in
and Table 24. Since the feedback resistance is integrated on chip, only a crystal
and CX2 need to be connected externally in case of
X1
and
L
). Capacitance CP in Figure 37 represents the parallel p ackage cap acitance and should
S
, CL, RS and CP are supplied by the crystal
OSC
Page 74

NXP Semiconductors
002aaf424
LPC1xxx
XTALIN XTALOUT
C
X2
C
X1
XTAL
=
C
L
C
P
R
S
L
Fig 37. Oscillator modes and models: oscillation mode of operation and external crystal
T able 23. Recommended values for C
Fundamental oscillation
frequency F
1 MHz to 5 MHz 10 pF < 300 18 pF, 18 pF
5 MHz to 10 MHz 10 pF < 300 18 pF, 18 pF
10 MHz to 15 MHz 10 pF < 160 18 pF, 18 pF
15 MHz to 20 MHz 10 pF < 80 18 pF, 18 pF
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
model used for CX1/CX2 evaluation
in oscillation mode (crystal and external
components parameters): low frequency mode
Crystal load
OSC
capacitance C
20 pF < 300 39 pF, 39 pF
30 pF < 300 57 pF, 57 pF
20 pF < 200 39 pF, 39 pF
30 pF < 100 57 pF, 57 pF
20 pF < 60 39 pF, 39 pF
X1/CX2
L
Maximum crystal
series resistance R
External load
capacitors CX1/C
S
X2
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 74 of 93
T able 24. Recommended values for C
in oscillation mode (crystal and external
X1/CX2
components parameters): high frequency mode
Fundamental oscillation
frequency F
OSC
Crystal load
capacitance C
Maximum crystal
series resistance R
L
External load
capacitors C
S
15 MHz to 20 MHz 10 pF < 180 18 pF, 18 pF
20 pF < 100 39 pF, 39 pF
20 MHz to 25 MHz 10 pF < 160 18 pF, 18 pF
20 pF < 80 39 pF, 39 pF
15.3 XTAL and RTCX Printed Circuit Board (PCB) layout guidelines
The crystal should be connected on the PCB as close as possible to the oscillator input
and output pins of the chip. Take care that the load capacitors C
third overtone crystal usage have a common ground plane. The external components
must also be connected to the ground plain. Loops must be made as small as possible in
, Cx2, and Cx3 in case of
x1
X1
, C
X2
Page 75

NXP Semiconductors
PIN
V
DD
V
DD
ESD
V
SS
ESD
strong
pull-up
strong
pull-down
V
DD
weak
pull-up
weak
pull-down
open-drain enable
output enable
repeater mode
enable
pull-up enable
pull-down enable
data output
data input
analog input
select analog input
002aaf272
pin configured
as digital output
driver
pin configured
as digital input
pin configured
as analog input
order to keep the noise coupled in via the PCB as small as possible. Also parasitic s
should stay as small as possible. Values of C
accordingly to the increase in parasitics of the PCB layout.
15.4 Standard I/O pin configuration
Figure 38 shows the possible pin modes for standard I/O pins with analog input function:
• Digital output driver: Open-dra in mo d e en ab le d/ disa b led
• Digital input: Pull-up enabled/disabled
• Digital input: Pull-down enabled/disabled
• Digital input: Repeater mode enabled/disabled
• Analog input
The default configuration for standard I/O pins is input with pull-up enabled. The weak
MOS devices provide a drive capability equivalent to pull-up and pull-down resistors.
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
and Cx2 should be chosen smaller
x1
Fig 38. Standard I/O pin configuration with analog input
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 75 of 93
Page 76

NXP Semiconductors
V
SS
reset
002aaf274
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
R
pu
ESD
ESD
20 ns RC
GLITCH FILTER
PIN
15.5 Reset pin configuration
Fig 39. Reset pin configuration
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 76 of 93
Page 77

NXP Semiconductors
15.6 ElectroMagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Radiated emission measurements according to the IEC61967-2 standard using the
TEM-cell method are shown for part LPC1768.
Table 25. ElectroMagnetic Compatibility (EMC) for part LPC1768 (TEM-cell method)
V
DD
Parameter Frequency band System clock = Unit
Input clock: IRC (4 MHz)
maximum
peak level
IEC level
Input clock: crystal oscillator (12 MHz)
maximum
peak level
IEC level
= 3.3 V; T
[1]
[1]
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
= 25 C.
amb
12 MHz 24 MHz 48 MHz 72 MHz 100 MHz
150 kHz to 30 MHz 7 6 4 7 7dBV
30 MHz to 150 MHz +1 +5 +11 +16 +9 dBV
150 MHz to 1 GHz 2 +4 +11 +12 +19 dBV
- OONML -
150 kHz to 30 MHz 5 4 4 7 8dBV
30 MHz to 150 MHz 1+5+10+15+7dBV
150 MHz to 1 GHz 1 +6 +11 +10 +16 dBV
- OONMM-
[1] IEC levels refer to Appendix D in the IEC61967-2 Specification.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 77 of 93
Page 78

NXP Semiconductors
UNIT
A
max.
A1A2A3bpcE
(1)
eHELL
p
Zywv θ
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC JEDEC JEITA
mm
1.6
0.15
0.05
1.45
1.35
0.25
0.27
0.17
0.20
0.09
14.1
13.9
0.5
16.25
15.75
1.15
0.85
7
0
o
o
0.08 0.080.21
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
0.75
0.45
SOT407-1 136E20 MS-026
00-02-01
03-02-20
D
(1) (1)(1)
14.1
13.9
H
D
16.25
15.75
E
Z
1.15
0.85
D
b
p
e
θ
E
A
1
A
L
p
detail X
L
(A )
3
B
25
c
D
H
b
p
E
H
A
2
v M
B
D
Z
D
A
Z
E
e
v M
A
X
1
100
76
75
51
50
26
y
pin 1 index
w M
w M
0 5 10 mm
scale
LQFP100: plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 x 14 x 1.4 mm
SOT407-1
16. Package outline
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 40. Package outline SOT407-1 (LQFP100)
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 78 of 93
Page 79

NXP Semiconductors
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC JEDEC JEITA
SOT926-1 - - - - - - - - -
SOT926-1
05-12-09
05-12-22
UNIT
A
max
mm 1.2
0.4
0.3
0.8
0.65
0.5
0.4
9.1
8.9
9.1
8.9
A
1
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
TFBGA100: plastic thin fine-pitch ball grid array package; 100 balls; body 9 x 9 x 0.7 mm
A
2
b D E e
2
7.2
e
0.8
e
1
7.2
v
0.15w0.05y0.08
y
1
0.1
0 2.5 5 mm
scale
b
e
2
e
1
e
e
1/2 e
1/2 e
AC
B
∅ v
M
C∅ w
M
ball A1
index area
A
B
C
D
E
F
H
K
G
J
24681013579
ball A1
index area
B A
E
D
C
y
C
y
1
X
detail X
A
A
1
A
2
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 41. Package outline SOT926-1 (TFBGA100)
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 79 of 93
Page 80

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 42. Package outline SOT1450-2 LPC1768UK (WLCSP100)
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 80 of 93
Page 81

NXP Semiconductors
SOT407-1
DIMENSIONS in mm
occupied area
Footprint information for reflow soldering of LQFP100 package
Ax
Bx
Gx
Gy
Hy
Hx
AyBy
P1P2
D2 (8×) D1
(0.125)
Ax Ay Bx By D1 D2 Gx Gy Hx HyP1 P2 C
sot407-1
solder land
C
Generic footprint pattern
Refer to the package outline drawing for actual layout
17.300 17.300 14.300 14.3000.500 0.560 0.2801.500 0.400 14.500 14.500 17.550 17.550
17. Soldering
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 43. Reflow soldering for the LQFP100 package
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 81 of 93
Page 82

NXP Semiconductors
DIMENSIONS in mm
PSLSPSRHxHy
Hx
Hy
SOT926-1
solder land plus solder paste
occupied area
Footprint information for reflow soldering of TFBGA100 package
solder land
solder paste deposit
solder resist
P
P
SL
SP
SR
Generic footprint pattern
Refer to the package outline drawing for actual layout
detail X
see detail X
sot926-1_fr
0.80 0.330 0.400 0.480 9.400 9.400
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 44. Reflow soldering of the TFBGA100 package
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 82 of 93
Page 83

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 45. Reflow soldering of the WLCSP100 package (part 1)
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 83 of 93
Page 84

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 46. Reflow soldering of the WLCSP100 package (part 2)
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 84 of 93
Page 85

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Fig 47. Reflow soldering of the WLCSP100 package (part 3)
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 85 of 93
Page 86

NXP Semiconductors
18. Abbreviations
Table 26. Abbreviations
Acronym Description
ADC A nalog-to-Digital Converter
AHB Advanced High-performance Bus
AMBA Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture
APB Advanced Peripheral Bus
BOD BrownOut Detection
CAN Controller Area Network
DAC Digital-to-Analog Converter
DMA Direct Memory Access
EOP End Of Packet
GPIO General Purpose Input/Output
IRC Internal RC
IrDA Infrared Data Association
JTAG Joint Test Action Group
MAC Media Access Control
MIIM Media Independent Interface Management
OHCI Open Host Controller Interface
OTG On-The-Go
PHY Physical Layer
PLL Phase-Locked Loop
PWM Pulse Width Modulator
RIT Repetitive Interrupt Timer
RMII Reduced Media Independent Interface
SE0 Single Ended Zero
SPI Serial Peripheral Interface
SSI Serial Synchronous Interface
SSP Synchronous Serial Port
TCM Tightly Coupled Memory
TTL Transistor-Transisto r Lo g i c
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
USB Universal Serial Bus
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
19. References
[1] LPC176x/5x User manual UM10360:
http://www.nxp.com/documents/user_manual/UM10360.pdf
[2] LPC176x Errata sheet:
http://www.nxp.com/documents/errata_sheet/ES_LPC176X.pdf
[3] Technical note ADC design guidelines:
http://www.nxp.com/documents/technical_note/TN00009.pdf
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 86 of 93
Page 87

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
20. Revision history
Table 27. Revision history
Document ID Release
date
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.9.8 20180504 Product da ta sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.9.7
Modifications: • Added Figure 45 “Reflow soldering of the WLCSP100 package (part 1)”, Figure
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.9.7 20170501 Product da ta sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.9.6
Modifications:
• Updated Table 2 “Ordering options”: WLCSP100 with body size 100 balls, 5.07
• Updated Figure 42 “Package outline SOT1450-2 LPC1768UK (WLCSP100)”.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.9.6 20150818 Product da ta sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.9.5
Modifications:
• Changed max value of t
• Updated Section 2 “Features and ben efits”: Added Bounda ry scan Description
• Updated Figure 5 “LPC17xx memory map”: APB0 slot 7 (0x4001C000) was
• Changed pins for V
• Removed footnote 1: “5 V tolerant pad providing digital I/O functions with TTL
• Added a column for GPIO pins and device order part number to the ordering
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.9.5 <tbd> Product data sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.9.4
Modifications:
• SSP timing diagram updated. SSP timing parameters t
• Parameter T
• SSP maximum bit rate in master mode corrected to 33 Mbit/s.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.9.4 20140404 Product da ta sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.9.3
Modifications:
• Added LPC1768UK.
• Table 5 “Pin description”: Changed RX_MCLK and TX_MCLK type from INPUT
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.9.3 20140108 Product da ta sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.9.2
Modifications:
• Table 7 “Thermal resistance (±15 %)”:
Data sheet status Change
notice
46 “Reflow soldering of the WLCSP100 package (part 2)”, and Figure 47
“Reflow soldering of the WLCSP100 package (part 3)”.
x 5.07 x 0.53mm; was 5.074 x 5.074 x 0.6mm.
(data output valid time) in SPI mode to 3*T
2.5 ns. See Table 16 “Dynamic characteristics: SSP pins in SPI mode”.
Language (BSDL) is not available for this device.
"reserved" and changed it to I2C0.
description”.
levels and hysteresis. This pin is pulled up to a voltage level of 2.3 V to 2.6 V”
from TDO/SWO, TCK/SWDCLK, and RTCK, pins. See T able 5 “Pin description”.
options table. See Table 2 “Ordering options”.
added. See Section 12.7 “SSP interface”.
j(max)
to OUTPUT .
– Added TFBGA100.
– Added 15 % to table title.
v(Q)
DD(REG)(3V3)
added in Table 6 “Limiting values”.
from F4 and F0 to F4 and F10. See Table 5 “Pin
Supersedes
v(Q)
, t
, tDS, and tDH
h(Q)
cy(PCLK)
+
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 87 of 93
Page 88

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 27. Revision history
Document ID Release
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.9.2 20131021 Product da ta sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.9.1
Modifications:
…continued
date
Data sheet status Change
notice
Supersedes
• T ab l e 8 “Static characteristics”:
– Added Table note 3 “VDDA and VREFP should be tied to VDD(3V3) if the
ADC and DAC are not used.”
– Added Table note 4 “VDDA for DAC specs are from 2.7 V to 3.6 V.”
– V
/VREFP spec changed from 2.7 V to 2.5 V.
DDA
• Table 19 “ADC characteristics (full resolution)”:
– Added Table note 1 “VDDA and VREFP should be tied to VDD(3V3) if the
ADC and DAC are not used.”
– V
changed from 2.7 V to 2.5 V.
DDA
• Table 20 “ADC characteristics (lower resolution)”: Added Table note 1 “VDDA
and VREFP should be tied to VDD(3V3) if the ADC and DAC are not used.”
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.9.1 20130916 Product data sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.9
Modifications:
• Added Table 7 “Thermal resistance”.
• Table 6 “Limiting values”:
– Updated min/max values for V
– Updated conditions for VI.
– Updated table notes.
DD(3V3)
and V
DD(REG)(3V3)
.
• Table 8 “Static characteristics”: Added Table note 15 “TCK/SWDCLK pin needs
to be externally pulled LOW.”
• Updated Section 15.1 “Suggested USB interfac e solutions”.
• Added Section 5 “Marking”.
• Changed title of Figure 31 from “USB interface on a self-powered device” to
“USB interface with soft-connect”.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.9 20120810 Product data sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.8
Modifications:
• Remove table note “The peak current is limited to 25 times the corresponding
maximum current.” from Table 5 “Limiting values”.
• Change V
DD(3V3)
to V
DD(REG)(3V3)
in Section 11.3 “Internal oscillators”.
• Glitch filter constant changed to 10 ns in Table note6 in Table 4.
• Description of RESET function updated in Table 4.
• Pull-up value added for GPIO pins in Table 4.
• Pin configuration diagram for LQFP100 package corrected (Figure 2).
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.8 20111114 Product data sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.7
Modifications:
• Pin description of USB_UP_LED pin updated in Table 4.
• R
and Ri2 labels in Figure 27 updated.
i1
• Part LPC1765FET100 added.
• Table note10 updated in Table 4.
• Table note 1 updated in Table 12.
• Pin description of STCLK pin updated in Table 4.
• Electromagnetic compatibility data added in Section 14.6.
• Section 16 added.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 88 of 93
Page 89

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Table 27. Revision history
Document ID Release
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.7 20110405 Product data sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.6
Modifications:
…continued
date
Data sheet status Change
notice
Supersedes
• Pin description of pins P0[29] and P0[30] updated in Table note 5 of Table 4.
Pins are not 5 V tolerant.
• Typical value for Parameter N
• Parameter V
Table 7.
• Condition 3.0 V V
for I2C bus pins: typical value corrected V
hys
DD(3V3)
• Typical values for parameters I
power-down mode corrected in Table 7 and Table note 9, Table note 10, and
Table note 11 updated.
added in Table 9.
endu
3.6 V added in Table 16.
DD(REG)(3V3)
and I
with condition Deep
BAT
= 0.05V
hys
DD(3V3)
• For Deep power-down mode, Figure 9 updated and Figure 10 added.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.6 20100825 Product data sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.5
Modifications:
• Part LPC1768TFBGA added.
• Section 7.30.2; BOD level corrected.
• Added Section 10.2.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 v.5 20100716 Product data sheet - LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.4
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64 v.4 20100201 Product data sheet - LPC1768_67_66_65_64 v.3
LPC1768_67_66_65_64 v.3 20091119 Product data sheet - LPC1768_66_65_64 v.2
LPC1768_66_65_64 v.2 20090211 Objective data sheet - LPC1768_66_65_64 v.1
LPC1768_66_65_64 v.1 20090115 Objective data sheet - -
in
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 89 of 93
Page 90

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
21. Legal information
21.1 Data sheet status
Document status
Objective [short] data sheet Development This document contains data from the objective specification for product development.
Preliminary [short] data sheet Qualification This document contains data from the preliminary specification.
Product [short] data sheet Production This document contains the product specification.
[1] Please consult the most recently issued document before initiating or completing a design.
[2] The term ‘short data sheet’ is explained in section “Definitions”.
[3] The product status of device(s) d escribed i n this docume nt may have changed since this docume nt was publis hed and ma y dif fer in case of multiple devices. The latest product statu s
information is available on the Internet at URL http://www.nxp.com.
[1][2]
Product status
[3]
Definition
21.2 Definitions
Draft — The document is a draft version only. The content is still under
internal review and subject to formal approval, which may result in
modifications or additions. NXP Semiconductors does not give any
representations or warranties as to the accuracy or completeness of
information included herein and shall have no liability for the consequences of
use of such information.
Short data sheet — A short data sheet is an extract from a full data sheet
with the same product type number(s) and title. A short data sheet is intended
for quick reference only and should not be relied u pon to co nt ain det ailed and
full information. For detailed and full information see the relevant full data
sheet, which is available on request via the local NXP Semiconductors sales
office. In case of any inconsistency or conflict with the short data sheet, the
full data sheet shall prevail.
Product specification — The information and data provided in a Product
data sheet shall define the specification of the product as agreed between
NXP Semiconductors and its customer, unless NXP Semiconductors and
customer have explicitly agreed otherwise in writing. In no event however,
shall an agreement be valid in which the NXP Semiconductors product is
deemed to offer functions and qualities beyond those described in the
Product data sheet.
21.3 Disclaimers
Limited warranty and liability — Information in this document is believed to
be accurate and reliable. However, NXP Semiconductors does not give any
representations or warranties, expressed or implied, as to the accuracy or
completeness of such information and shall have no liability for the
consequences of use of such information. NXP Semiconductors takes no
responsibility for the content in this document if provided by an information
source outside of NXP Semiconductors.
In no event shall NXP Semiconductors be lia ble for any indirect, incidental,
punitive, special or consequential damages (including - without limitation - lost
profits, lost savings, business interruption, costs related to the removal or
replacement of any products or rework charges) whether or not such
damages are based on tort (including negligence), warranty, breach of
contract or any other legal theory.
Notwithstanding any damages that customer might incur for any reason
whatsoever, NXP Semi conductors’ aggregat e and cumulative liabil ity towards
customer for the products described herein shall be limited in accordance
with the Terms and conditions of commercial sale of NXP Semiconductors.
Right to make changes — NXP Semiconductors reserves the right to make
changes to information published in this document, including without
limitation specifications and product descriptions, at any time and without
notice. This document supersedes and replaces all information supplied prior
to the publication hereof.
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Suitability for use — NXP Semiconductors products are not designed,
authorized or warranted to be suitable for use in life support, life-critical or
safety-critical systems or equipment, nor in applications where failure or
malfunction of an NXP Semiconductors product can reasonabl y be expected
to result in personal injury, death or severe property or environmental
damage. NXP Semiconductors and its suppliers accept no liability for
inclusion and/or use of NXP Semiconductors products in such equipment or
applications and therefore such inclusion and/or use is at the cu stomer’s own
risk.
Applications — Applications that are described herein for any of these
products are for illustrative purposes only. NXP Semiconductors makes no
representation or warranty that such applications will be suitable for the
specified use without further testing or modification.
Customers are responsible for the design and operation of their applications
and products using NXP Semiconductors products, and NXP Semiconductors
accepts no liability for any assistance with applications or customer product
design. It is customer’s sole responsibility to determine whether the NXP
Semiconductors product is suitable and fit for the customer’s applications and
products planned, as well as for the planned application and use of
customer’s third party customer(s). Customers should provide appropriate
design and operating safeguards to minimize the risks associated with their
applications and products.
NXP Semiconductors does not accept any liability related to any default ,
damage, costs or problem which is based on any weakness or default in the
customer’s applications or products, or the application or use by customer’s
third party customer(s). Customer is responsible for doing all necessary
testing for the customer’s applications and products using NXP
Semiconductors products in order to avoid a default of the applications and
the products or of the application or use by customer’s third part y
customer(s). NXP does not accept any liability in this respect.
Limiting values — Stress above one or more limiting values (as defined in
the Absolute Maximum Ratings System of IEC 60134) will cause permanent
damage to the device. Limiting values are stress ratings only and (proper)
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those given in
the Recommended operating conditions section (if present) or the
Characteristics sections of this document is not warranted. Constant or
repeated exposure to limiting values will permanently and irreversibly affect
the quality and reliability of the device.
Terms and conditions of commercial sale — NXP Semiconductors
products are sold subject to the general terms and conditions of commercial
sale, as published at http://www.nxp.com/profile/terms
agreed in a valid written individual agreement. In case an individual
agreement is concluded only the terms and conditions of the respective
agreement shall apply. NXP Semiconductors hereby expressly objects to
applying the customer’s general terms and conditions with regard to the
purchase of NXP Semiconductors products by customer.
No offer to sell or license — Nothing in this document may be interpreted or
construed as an offer to sell product s that is ope n for accept ance or the gr ant,
conveyance or implication of any license under any copyrights, patents or
other industrial or intellectual property rights.
, unless otherwise
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 90 of 93
Page 91

NXP Semiconductors
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Export control — This document as well as the item(s) described herein
may be subject to export control regulations. Export might require a prior
authorization from competent authorities.
Non-automotive qualified products — Unless this data sheet expressly
states that this specific NXP Semiconductors product is automotive qualified,
the product is not suitable for automotive use. It i s neither qua lif ied nor test ed
in accordance with automotive testing or application requirements. NXP
Semiconductors accepts no liability for inclusion and/or use of
non-automotive qualified products in automotive equ ipment or applications.
In the event that customer uses the product for design-in and use in
automotive applications to automotive specifications and standards, customer
(a) shall use the product without NXP Semiconductors’ warranty of the
product for such automotive applications, use and specifications, and (b)
whenever customer uses the product for automotive applications beyond
NXP Semiconductors’ specifications such use shall be solely at customer’s
own risk, and (c) customer fully indemnifies NXP Semiconductors for any
liability, da mages or failed produ ct cl aims resulting from custome r design and
use of the product for automotive applications beyond NXP Semiconductors’
standard warranty and NXP Semiconductors’ product specifications.
21.4 Trademarks
Notice: All referenced brands, prod uct names, service names and trad emarks
are the property of their respective owners.
2
I
C-bus — logo is a trademark of NXP B.V.
22. Contact information
For more information, please visit: http://www.nxp.com
For sales office addresses, please send an email to: salesaddresses@nxp.com
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 91 of 93
Page 92

NXP Semiconductors
23. Contents
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
1 General description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2 Features and benefits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
3 Applications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
4 Ordering information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
4.1 Ordering options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
5 Marking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
6 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
7 Pinning information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
7.1 Pinning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
7.2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
8 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8.1 Architectural overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8.2 ARM Cortex-M3 processor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8.3 On-chip flash program memory . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8.4 On-chip SRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8.5 Memory Protection Unit (MPU). . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8.6 Memory map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
8.7 Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC) . 24
8.7.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
8.7.2 Interrupt sources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
8.8 Pin connect block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
8.9 General purpose DMA controller . . . . . . . . . . 24
8.9.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
8.10 Fast general purpose parallel I/O . . . . . . . . . . 25
8.10.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
8.11 Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
8.11.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
8.12 USB interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
8.12.1 USB device controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
8.12.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
8.12.2 USB host controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
8.12.2.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
8.12.3 USB OTG controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
8.12.3.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
8.13 CAN controller and acceptance filters . . . . . . 28
8.13.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
8.14 12-bit ADC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
8.14.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
8.15 10-bit DAC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
8.15.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
8.16 UARTs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
8.16.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
8.17 SPI serial I/O controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
8.17.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
8.18 SSP serial I/O controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
8.18.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2
8.19 I
8.19.1 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
8.20 I
8.20.1 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
8.21 General purpose 32-bit timers/external event
8.21.1 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
8.22 Pulse width modulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
8.22.1 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
8.23 Motor control PWM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
8.24 Quadrature Encoder Interface (QEI) . . . . . . . 34
8.24.1 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
8.25 Repetitive Interrupt (RI) timer. . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.25.1 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.26 ARM Cortex-M3 system tick timer . . . . . . . . . 35
8.27 Watchdog timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.27.1 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.28 RTC and backup registers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.28.1 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.29 Clocking and power control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.29.1 Crystal oscillators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.29.1.1 Internal RC oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
8.29.1.2 Main oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
8.29.1.3 RTC oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
8.29.2 Main PLL (PLL0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
8.29.3 USB PLL (PLL1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
8.29.4 RTC clock output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
8.29.5 Wake-up timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
8.29.6 Power control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.29.6.1 Sleep mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.29.6.2 Deep-sleep mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.29.6.3 Power-down mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.29.6.4 Deep power-down mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.29.6.5 Wake-up interrupt controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.29.7 Peripheral power control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.29.8 Power domains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
8.30 System control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
8.30.1 Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
8.30.2 Brownout detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
8.30.3 Code security (Code Read Protection - CRP) 43
8.30.4 APB interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
8.30.5 AHB multilayer matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
8.30.6 External interrupt inputs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
8.30.7 Memory mapping control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
8.31 Emulation and debugging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9 Limiting values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
10 Thermal characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
C-bus serial I/O controllers . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2
S-bus serial I/O controllers . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
counters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
continued >>
LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 9.8 — 4 May 2018 92 of 93
Page 93

NXP Semiconductors
11 Static characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
11.1 Power consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
11.2 Peripheral power consumption. . . . . . . . . . . . 53
11.3 Electrical pin characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
12 Dynamic characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
12.1 Flash memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
12.2 External clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
12.3 Internal oscillators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
12.4 I/O pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
12.5 I
12.6 I2S-bus interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
12.7 SSP interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
12.8 USB interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
12.9 SPI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
13 ADC electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
14 DAC electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
15 Application information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
15.1 Suggested USB interface solutions . . . . . . . . 70
15.2 Crystal oscillator XTAL input and component
15.3 XTAL and RTCX Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
15.4 Standard I/O pin configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
15.5 Reset pin configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
15.6 ElectroMagnetic Compatibility (EMC). . . . . . . 77
16 Package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
17 Soldering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
18 Abbreviations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
19 References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
20 Revision history. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
21 Legal information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
21.1 Data sheet status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
21.2 Definitions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
21.3 Disclaimers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
21.4 Trademarks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
22 Contact information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
23 Contents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
2
C-bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
layout guidelines. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
LPC1769/68/67/66/65/64/63
32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 microcontroller
Please be aware that important notices concerning this docum ent and the product(s)
described herein, have been included in section ‘Legal information’.
© NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2018. All rights reserved.
For more information, please visit: http://www.nxp.com
For sales office addresses, please send an email to: salesaddresses@nxp.com
Document identifier: LPC1769_68_67_66_65_64_63
Date of release: 4 May 2018
 Loading...
Loading...