NSC LP2954IS, LP2954IMX, LP2954IM, LP2954IT, LP2954ISX Datasheet
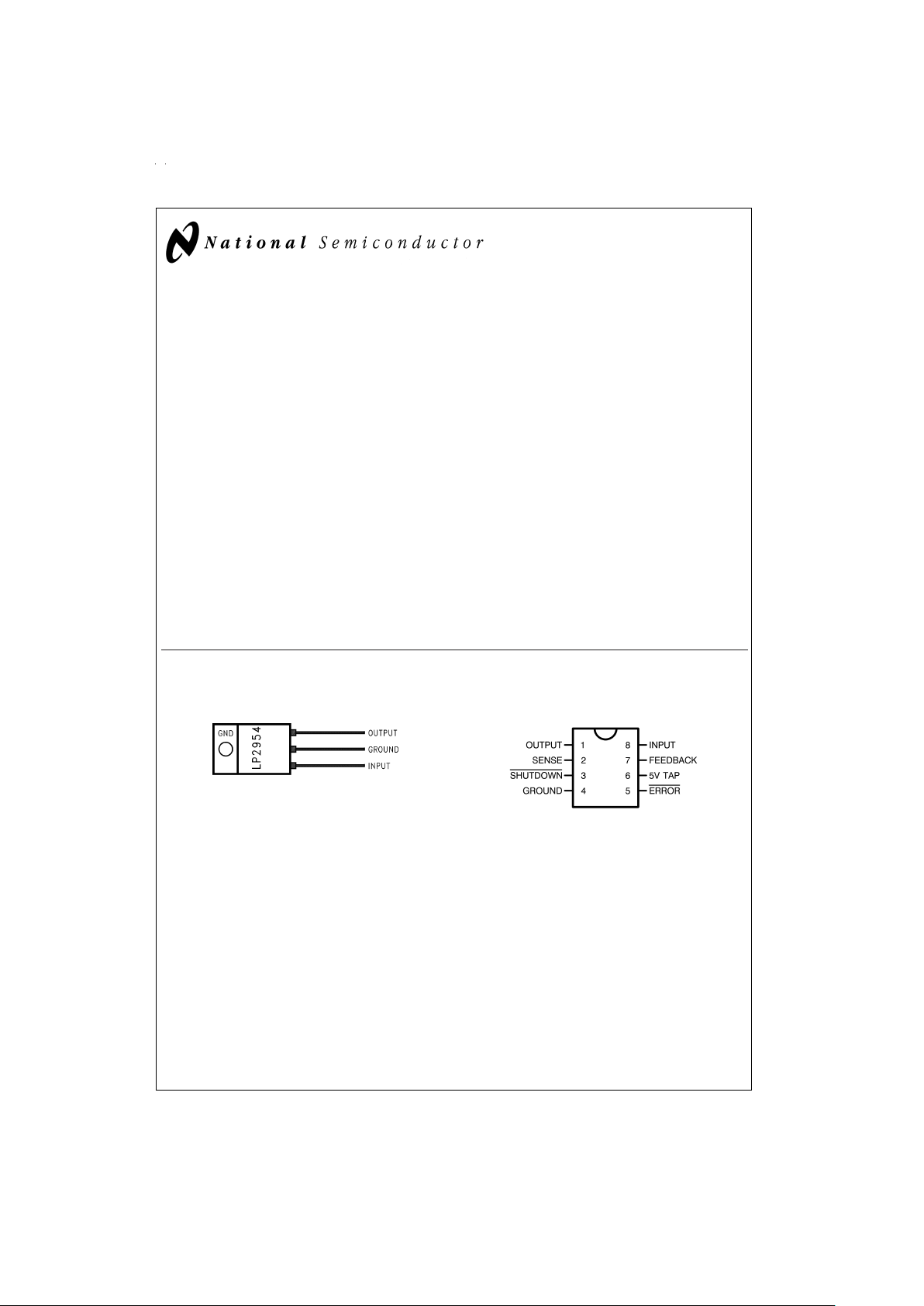
LP2954/LP2954A
5V and Adjustable Micropower Low-Dropout Voltage
Regulators
General Description
The LP2954 is a 5V micropower voltage regulator with very
low quiescent current (90 µA typical at 1 mA load) and very
low dropout voltage (typically 60 mV at light loads and
470 mV at 250 mA load current).
The quiescent current increases only slightly at dropout
(120 µA typical), which prolongs battery life.
The LP2954 with a fixed 5V output is available in the
three-lead TO-220 and TO-263 packages. The adjustable
LP2954 isprovided in an 8-lead surface mount, small outline
package. The adjustable version also provides a resistor network which can be pin strapped to set the output to 5V.
Reverse battery protection is provided.
The tight line and load regulation (0.04%typical), as well as
very low output temperature coefficient make the LP2954
well suited for use as a low-power voltage reference.
Output accuracy is guaranteed at both room temperature
and over the entire operating temperature range.
Features
n 5V output within 1.2%over temperature (A grade)
n Adjustable 1.23 to 29V output voltage available
(LP2954IM and LP2954AIM)
n Guaranteed 250 mA output current
n Extremely low quiescent current
n Low dropout voltage
n Reverse battery protection
n Extremely tight line and load regulation
n Very low temperature coefficient
n Current and thermal limiting
n Pin compatible with LM2940 and LM340 (5V version
only)
n Adjustable version adds error flag to warn of output drop
and a logic-controlled shutdown
Applications
n High-efficiency linear regulator
n Low dropout battery-powered regulator
Package Outline and Ordering Information
TO-220 3–Lead Plastic Package
DS011128-2
Front View
Order Number LP2954AIT or LP2954IT
See NS Package T03B
SO-8 Small Outline Surface Mount
DS011128-33
Top View
Order Number LP2954AIM or LP2954IM
See NS Package M08A
June 1999
LP2954/LP2954A 5V and Adjustable Micropower Low-Dropout Voltage Regulators
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS011128 www.national.com
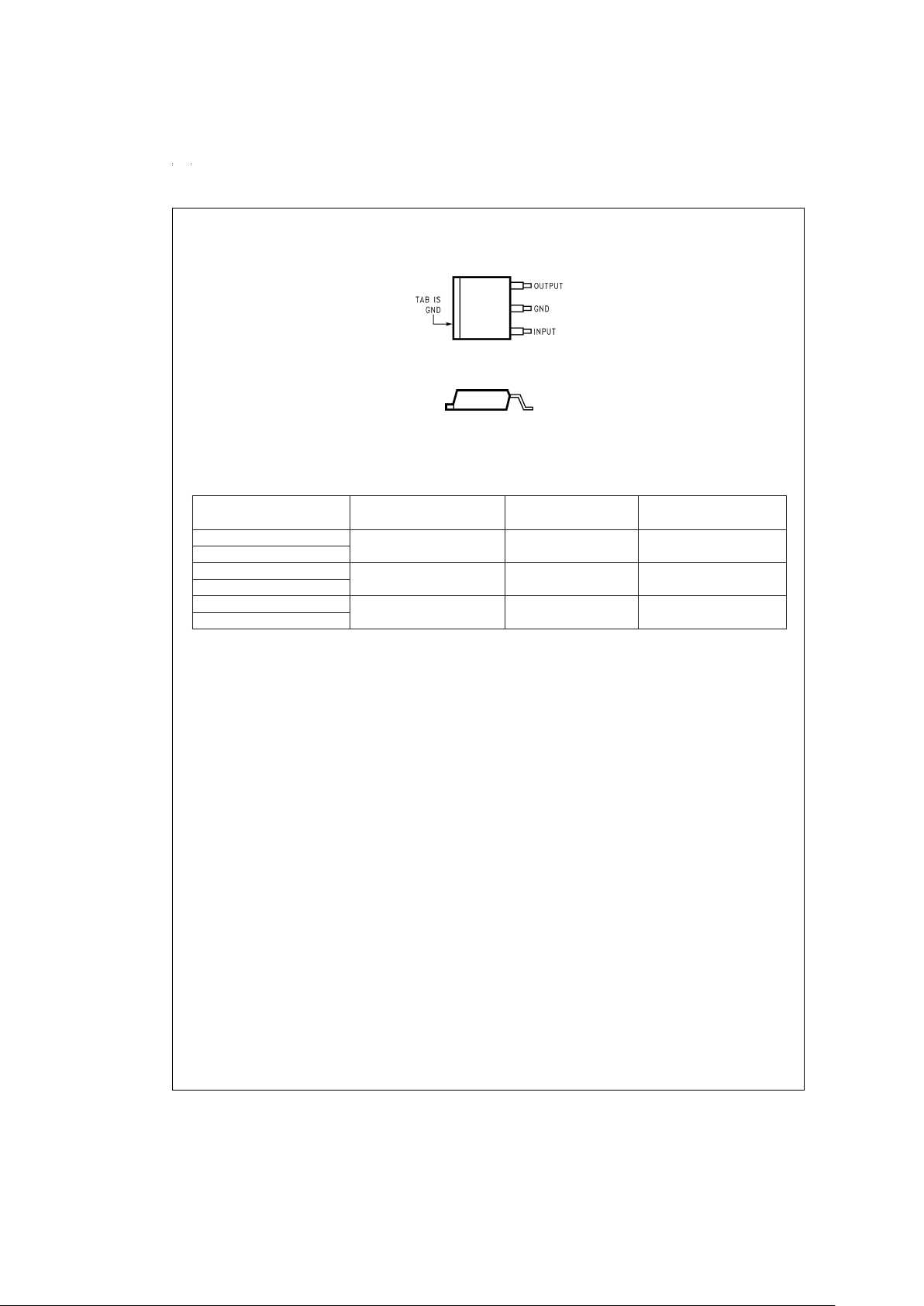
Package Outline and Ordering Information (Continued)
Ordering Information
Order Number Temp. Range Package NS Package
(T
J
) ˚C (JEDEC) Number
LP2954AIT −40 to +125 TO-220 TO3B
LP2954IT
LP2954AIS −40 to +125 TO-263 TS3B
LP2954IS
LP2954AIM −40 to +125 SO-8 M08A
LP2954IM
TO-263 3-Lead Plastic Surface-Mount Package
DS011128-9
Top View
DS011128-10
Side View
Order Number LP2954AIS or LP2954IS
See NS Package TS3B
www.national.com 2
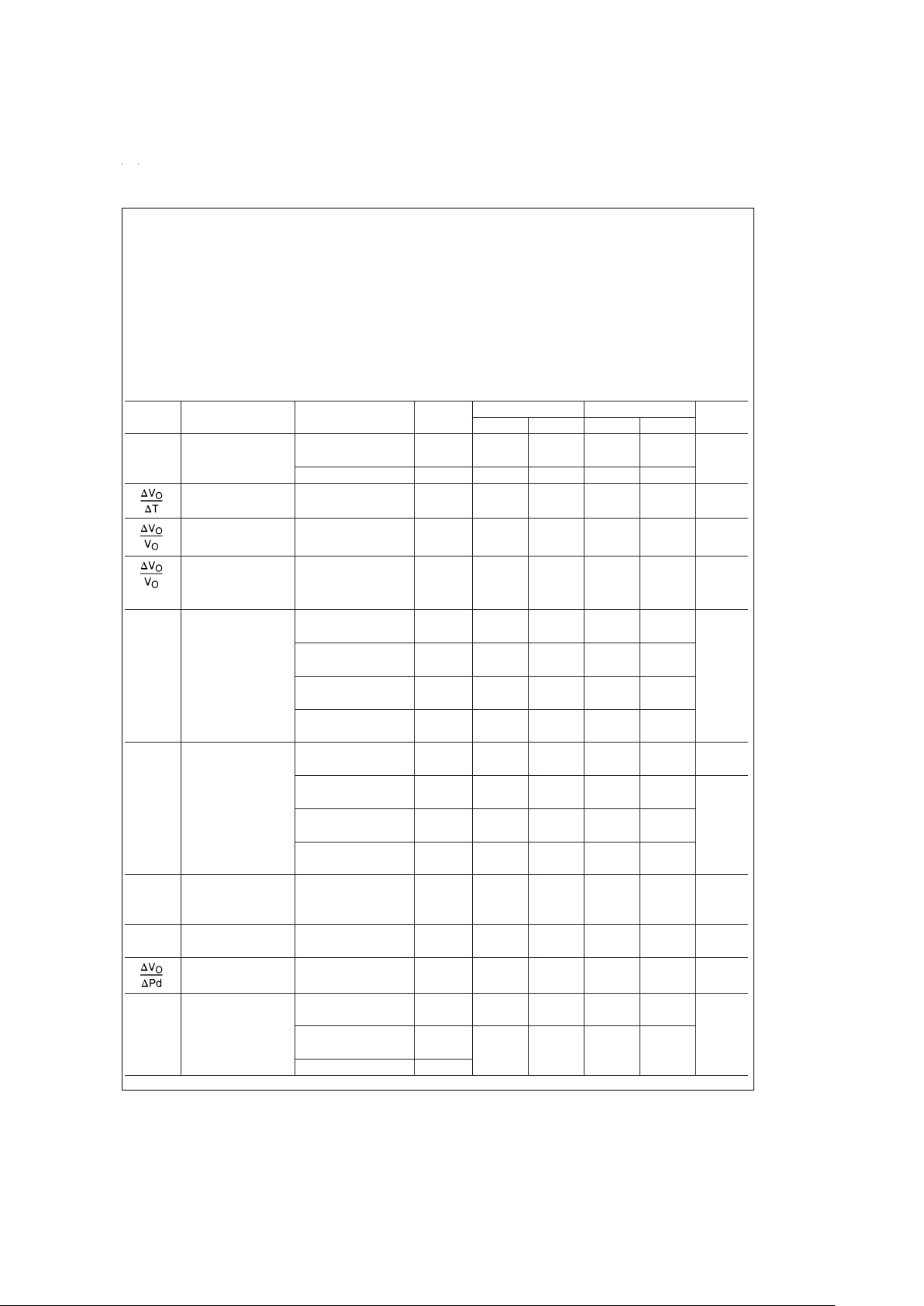
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Operating Junction Temperature
Range
LP2954AI/LP2954I −40˚C to +125˚C
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temperature
(Soldering, 5 seconds) 260˚C
Power Dissipation (Note 2) Internally Limited
Input Supply Voltage −20V to +30V
ESD Rating 2 kV
Electrical Characteristics
Limits in standard typeface are for T
J
=
25˚C, bold typeface applies over the −40˚C to +125˚C temperature range. Limits
are guaranteed by production testing or correlation techniques using standard Statistical Quality Control (SQC) methods. Unless otherwise noted: V
IN
=
6V, I
L
=
1 mA, C
L
=
2.2 µF.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical 2954AI 2954I Units
Min Max Min Max
V
O
Output Voltage 5.0 4.975 5.025 4.950 5.050 V
4.940 5.060 4.900 5.100
1mA≤I
L
≤250 mA 5.0 4.930 5.070 4.880 5.120
Output Voltage (Note 3)
20 100 150 ppm/˚C
Temp. Coefficient
Line Regulation V
IN
=
6V to 30V 0.03 0.10 0.20
%
0.20 0.40
Load Regulation I
L
=
1 to 250 mA
0.16 0.20
I
L
=
0.1 to 1 mA 0.04
0.20 0.30
%
(Note 4)
V
IN–VO
Dropout Voltage I
L
=
1 mA 60 100 100 mV
(Note 5) 150 150
I
L
=
50 mA 240 300 300
420 420
I
L
=
100 mA 310 400 400
520 520
I
L
=
250 mA 470 600 600
800 800
I
GND
Ground Pin Current I
L
=
1 mA 90 150 150 µA
(Note 6) 180 180
I
L
=
50 mA 1.1 2 2 mA
2.5 2.5
I
L
=
100 mA 4.5 6 6
88
I
L
=
250 mA 21 28 28
33 33
I
GND
Ground Pin V
IN
=
4.5V 170 170
Current at Dropout 120 210 210 µA
(Note 6)
I
LIMIT
Current Limit V
OUT
=
0V 380 500 500 mA
530 530
Thermal Regulation (Note 7)
0.05 0.2 0.2
%
/W
e
n
Output Noise C
L
=
2.2 µF 400 µV RMS
Voltage
(10 Hz to 100 kHz) C
L
=
33 µF 260
I
L
=
100 mA
C
L
=
33µF(Note 9) 80
www.national.com3
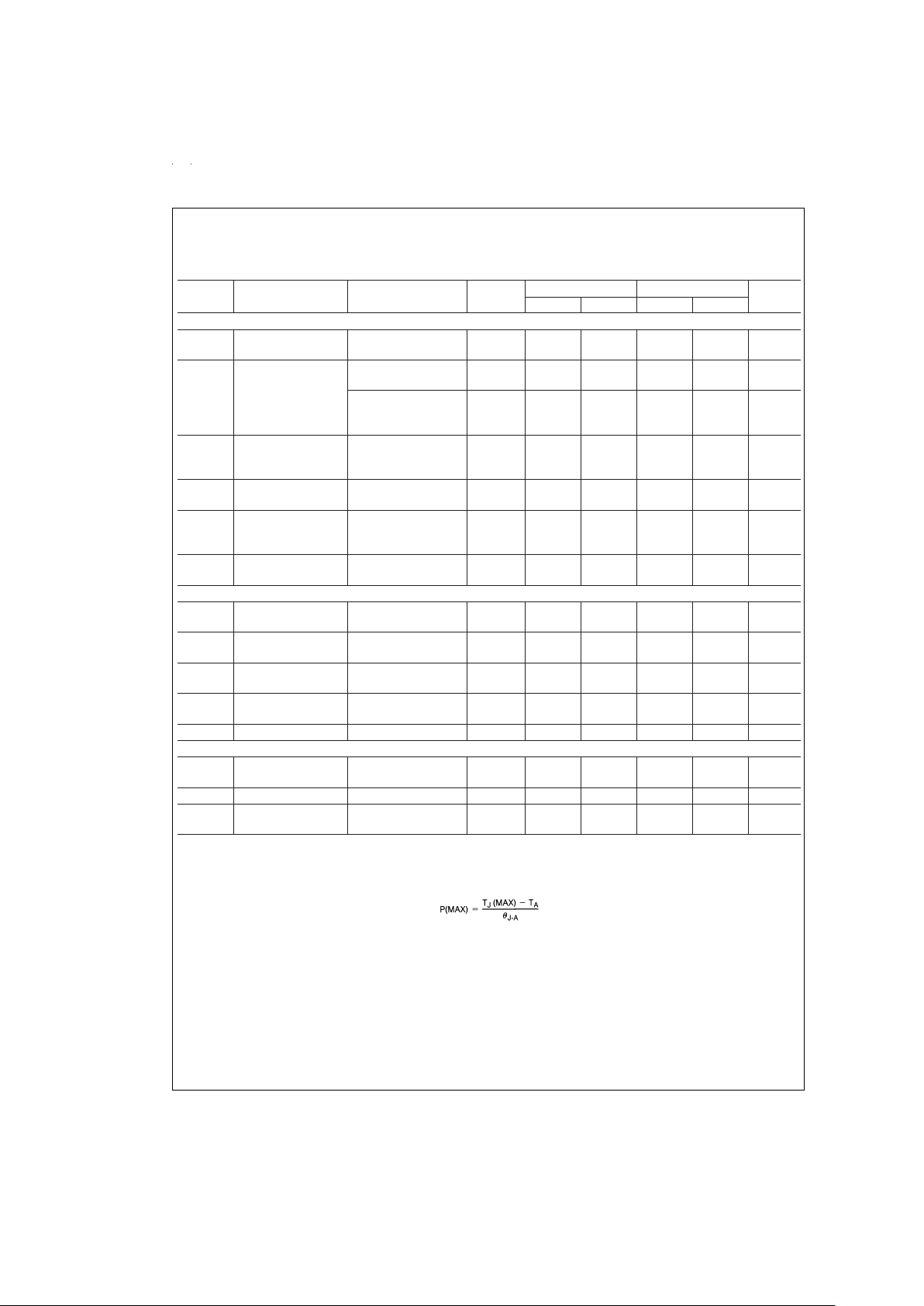
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Limits in standard typeface are for T
J
=
25˚C, bold typeface applies over the −40˚C to +125˚C temperature range. Limits
are guaranteed by production testing or correlation techniques using standard Statistical Quality Control (SQC) methods. Unless otherwise noted: V
IN
=
6V, I
L
=
1 mA, C
L
=
2.2 µF.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical 2954AI 2954I Units
Min Max Min Max
Additional Specifications for the Adjustable Device (LP2954AIM and LP2954IM)
V
REF
Reference Voltage (Note 10) 1.230 1.215
1.205
1.245
1.255
1.205
1.190
1.255
1.270
V
∆V
REF
/
V
REF
Reference Voltage
Line Regulation
V
IN
=
2.5V to
VO(NOM)+1V
0.03 0.1 0.2
V
IN
=
2.5V to
VO(NOM)+1V to 30V
(Note 11)
0.2 0.4
∆V
REF
/∆T Reference Voltage
Temperature
Coefficient
(Note 3) 20 ppm/˚C
I
B
(FB) Feedback Pin Bias
Current
20 40
60
40
60
nA
I
GND
Ground Pin Current
at Shutdown (Note
6)
V
SHUTDOWN
≤1.1V 105 140 140 µA
I
O
(SINK) Output ″OFF″
Pulldown Current
(Note 12) 30
20
30
20
mA
Dropout Detection Comparator
I
OH
Output ″HIGH″
Leakage Current
V
OH
=
30V 0.01 1
2
1
2
µA
V
OL
Output ″LOW″
Voltage
V
IN
=
V
O
(NOM)−0.5V
I
O
(COMP)=400µA
150 250
400
250
400
mV
V
THR
(MAX) Upper Threshold
Voltage
(Note 13) −60 −80
−95
−35
−25
−80
−95
−35
−25
mV
V
THR
(MIN) Lower Threshold
Voltage
(Note 13) −85 −110
−160
−55
−40
−110
−160
−55
−40
mV
HYST Hysteresis (Note 13) 15 mV
Shutdown Input
V
OS
Input Offset Voltage (Referred to V
REF
)
±
3 −7.5
−10
7.5
10
−7.5
−10
7.5
10
mV
HYST Hysteresis 6 mV
I
B
Input Bias Current VIN(S/D)=0V to 5V 10 −30
−50
30
50
−30
−50
30
50
nA
Note 1: Absolute maximum ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the component may occur. Electrical specifications do not apply when operating the device outside of its rated operating conditions.
Note 2: The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of the maximum junction temperature, T
J
(MAX), the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, θ
J-A
,
and the ambient temperature, T
A
. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is calculated using:
.
Exceeding the maximum allowable power dissipation will result in excessive die temperature, and the regulator will gointothermal shutdown.The junction-to-ambient
thermal resistance of the TO-220 (without heatsink) is 60˚C/W, 73˚C/W for the TO-263, and 160˚C/W for the SO-8. If the TO-263 package is used, the thermal resistance can be reduced by increasing the P.C. board copper area thermally connected to the package: Using 0.5 square inches of copper area, θ
JA
is 50˚C/W; with
1 square inch of copper area, θ
JA
is 37˚C/W; and with 1.6 or more square inches of copper area, θJAis 32˚C/W. The junction-to-case thermal resistance is 3˚C/W.
If an external heatsink is used, the effective junction-to-ambient thermal resistance is the sum of the junction-to-case resistance (3˚C/W), the specified thermal resistance of the heatsink selected, and the thermal resistance of the interface between the heatsink and the LP2954. Some typical values are listed for interface materials used with TO-220:
www.national.com 4
 Loading...
Loading...