NSC LMV341MGX, LMV342MMX, LMV342MAX, LMV342MA, LMV342MM Datasheet
March 2003
LMV341/LMV342/LMV344
Single with Shutdown/Dual/Quad General Purpose, 2.7V,
Rail-to-Rail Output, 125˚C, Operational Amplifiers
General Description
The LMV341/342/344 are single, dual, and quad low voltage, and low power Operational Amplifiers. They are designed specifically for low voltage portable applications.
Other important product characteristics are low input bias
current, rail-to-rail output, and wide temperature range.
The patented class AB turnaround stage significantly reduces the noise at higher frequencies, power consumption,
and offset voltage. The PMOS input stage provides the user
with ultra-low input bias current of 20fA (typical) and high
input impedance.
The industrial-plus temperature range of -40˚C to 125˚C
allows the LMV341/342/344 to accommodate a broad range
of extended environment applications. LMV341 expands National Semiconductor’s Silicon Dust
fering enhancements in size, speed, and power savings. The
LMV341/342/344 are guaranteed to operate over the voltage
range of 2.7V to 5.0V and all have rail-to-rail output.
The LMV341 offers a shutdown pin that can be used to
disable the device. Once in shutdown mode, the supply
current is reduced to 45pA (typical). The LMV341/342/344
have 29nV Voltage Noise at 10KHz, 1MHz GBW, 1.0V/µs
Slew Rate, 0.25mVos, and 0.1µA shutdown current
(LMV341.)
The LMV341 is offered in the tiny SC70-6L package, the
LMV342 in space saving MSOP-8 and SOIC-8, and the
LMV344 in TSSOP-14 and SOIC-14. These small package
amplifiers offer an ideal solution for applications requiring
™
amplifier portfolio of-
minimum PC board footprint. Applications with area constrained PC board requirements include portable electronics
such as cellular handsets and PDAs.
Features
(Typical 2.7V Supply Values;Unless Otherwise Noted)
n Guaranteed 2.7V and 5V specifications
n Input referred voltage noise (
n Supply current (per amplifier) 100µA
n Gain bandwidth product 1.0MHz
n Slew rate 1.0V/µs
n Shutdown Current (LMV341) 45pA
n Turn-on time from shutdown (LMV341) 5µs
n Input bias current 20fA
@
10kHz) 29nV/
Applications
n Cordless/cellular phones
n Laptops
n PDAs
n PCMCIA/Audio
n Portable/battery-powered electronic equipment
n Supply current monitoring
n Battery monitoring
n Buffer
n Filter
n Driver
LMV341/LMV342/LMV344 Single with Shutdown/Dual/Quad General Purpose, 2.7V, Rail-to-Rail
Output, 125˚C, Operational Amplifiers
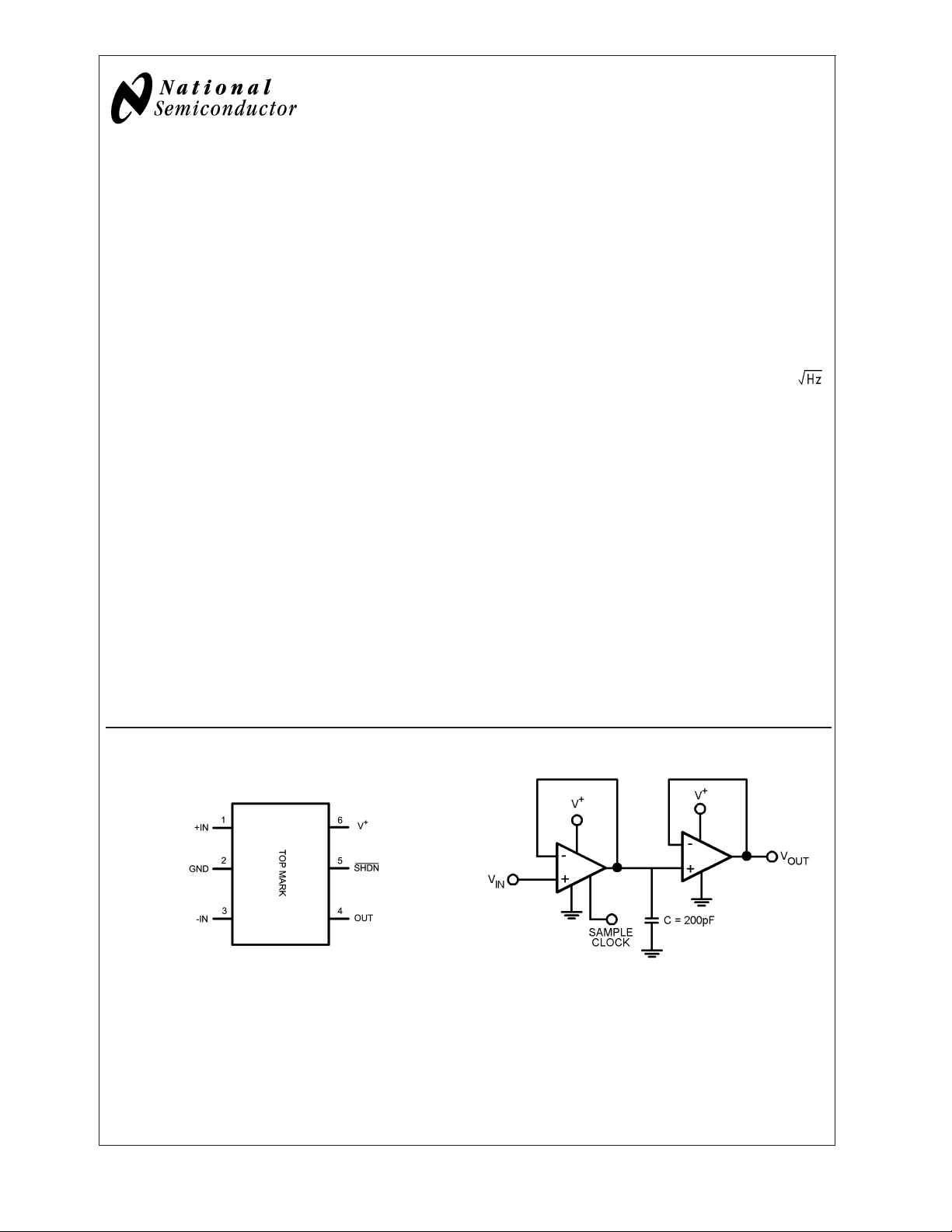
Connection Diagram
SC70-6L
20030441
Top View
Order Number
LMV341MG, LMV341MGX
LMV342MM, LMV342MMX
LMV342MA, LMV342MAX
LMV344MT, LMV344MTX
LMV344MA, LMV344MAX
© 2003 National Semiconductor Corporation DS200304 www.national.com
Sample and Hold Circuit
20030444
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Infrared or Convection Reflow
(20 sec.) 235˚C
Wave Soldering Lead Temp.
(10 sec.) 260˚C
ESD Tolerance (Note 2)
Machine Model 200V
Human Body Model 2000V
Differential Input Voltage
LMV341/LMV342/LMV344
Supply Voltage (V
Output Short Circuit to V
Output Short Circuit to V
+-V−
) 5.5V
+
−
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to 150˚C
Junction Temperature (Note 5) 150˚C
Mounting Temperature
±
Supply Voltage
(Note 3)
(Note 4)
Operating Ratings (Note 1)
Temperature Range −40˚C to 125˚C
Thermal Resistance (θ
6-Pin SC70 414˚C/W
8-Pin SOIC 190˚C/W
8-Pin MSOP 235˚C/W
14-Pin TSSOP 155˚C/W
14-Pin SOIC 145˚C/W
)
JA
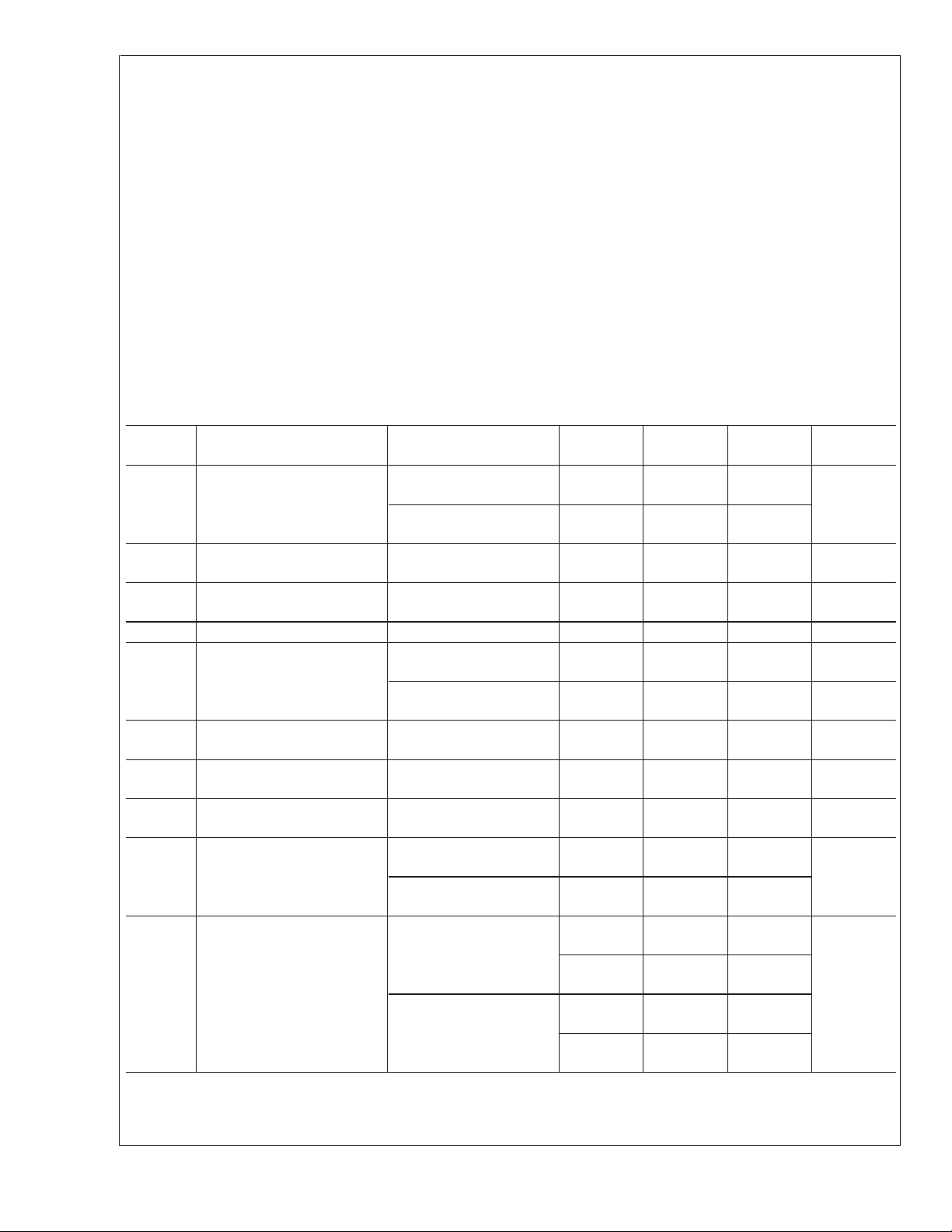
2.7V DC Electrical Characteristics (Note 10)
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for TJ= 25˚C, V+= 2.7V, V−= 0V, VCM=V+/2, VO=V+/2 and R
Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions
V
OS
Input Offset Voltage LMV341 0.25 4
LMV342/LMV344 0.55 5
TCV
Input Offset Voltage Average
OS
Drift
I
B
I
OS
I
S
Input Bias Current 0.02 120
Input Offset Current 6.6 fA
Supply Current Per Amplifier 100 170
Shutdown Mode, VSD=0V
(LMV341)
CMRR Common Mode Rejection
Ratio
0V ≤ V
0V ≤ V
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio 2.7V ≤ V
V
CM
A
V
Input Common Mode Voltage For CMRR ≥ 50dB 0 −0.2 to 1.9
Large Signal Voltage Gain RL= 10kΩ to 1.35V 78
≤ 1.7V
CM
≤ 1.6V
CM
+
≤ 5V 65
RL=2kΩ to 1.35V 72
V
O
Output Swing RL=2kΩ to 1.35V 24 60
= 10kΩ to 1.35V 5.0 30
R
L
Min
(Note 7)
56
50
60
70
64
60
95
30
40
Typ
(Note 6)
1.7 µV/˚C
45pA 1µA
80 dB
82 dB
(Range)
113
103
26
5.3
>
1MΩ.
L
Max
(Note 7) Units
4.5
mV
5.5
pA
250
µA
230
1.5µA
1.7 V
dB
95
mV
40
www.national.com 2
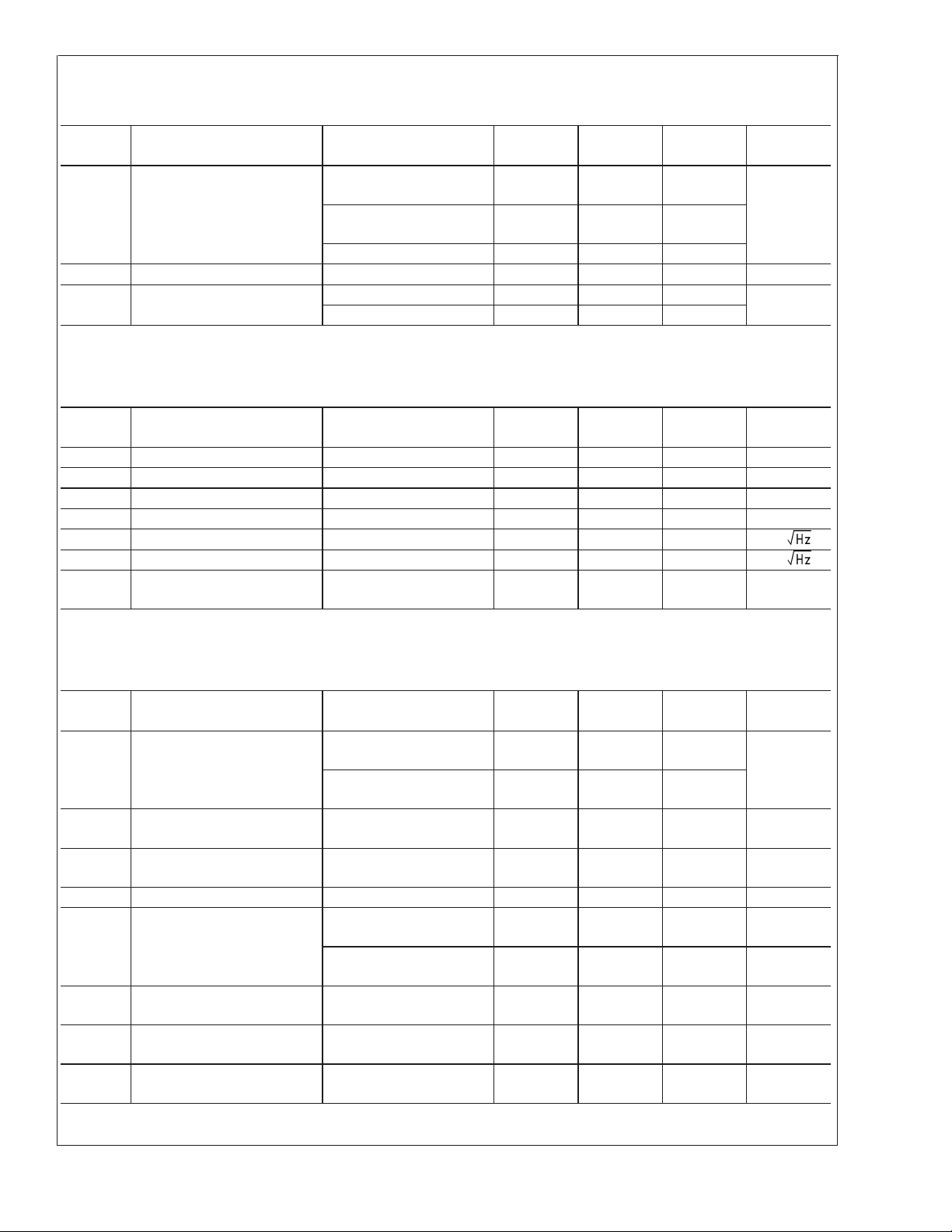
2.7V DC Electrical Characteristics (Note 10) (Continued)
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for TJ= 25˚C, V+= 2.7V, V−= 0V, VCM=V+/2, VO=V+/2 and R
Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions
I
O
Output Short Circuit Current Sourcing
Min
(Note 7)
20 32
Typ
(Note 6)
Max
(Note 7) Units
LMV341/LMV342
18 24
LMV344
Sinking 15 24
t
on
V
SD
Turn-on Time from Shutdown (LMV341) 5 µs
Shutdown Pin Voltage Range ON Mode (LMV341) 1.7 to 2.7 2.4 to 2.7
Shutdown Mode (LMV341) 0 to 1 0 to 0.8
2.7V AC Electrical Characteristics (Note 10)
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for TJ= 25˚C, V+= 2.7V, V−= 0V, VCM=V+/2, VO=V+/2 and R
Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
(Note 7)
SR Slew Rate R
GBW Gain Bandwidth Product R
Φ
m
G
m
e
n
i
n
Phase Margin RL= 100kΩ 72 deg
Gain Margin RL= 100kΩ 20 dB
Input-Referred Voltage Noise f = 1kHz 40 nV/
Input-Referred Current Noise f = 1kHz 0.001 pA/
= 10kΩ, (Note 9) 1.0 V/µs
L
= 100kΩ,CL= 200pF 1.0 MHz
L
THD Total Harmonic Distortion f = 1kHz, AV=+1
= 600Ω,VIN=1V
R
L
PP
Typ
(Note 6)
Max
(Note 7)
0.017 %
LMV341/LMV342/LMV344
>
1MΩ.
L
mASourcing
V
>
1MΩ.
L
Units
5V DC Electrical Characteristics (Note 10)
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for TJ= 25˚C, V+= 5V, V−= 0V, VCM=V+/2, VO=V+/2 and R
Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions
V
OS
Input Offset Voltage LMV341 0.025 4
LMV342/LMV344 0.70 5
TCV
Input Offset Voltage Average
OS
Drift
I
B
I
OS
I
S
Input Bias Current 0.02 200
Input Offset Current 6.6 fA
Supply Current Per Amplifier 107 200
Shutdown Mode, V
(LMV341)
CMRR Common Mode Rejection
Ratio
0V ≤ V
0V ≤ V
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio 2.7V ≤ V
V
CM
Input Common Mode Voltage For CMRR ≥ 50dB 0 −0.2 to 4.2
≤ 4.0V
CM
≤ 3.9V
CM
+
≤ 5V 65
SD
Min
(Note 7)
=0V
56
50
60
Typ
(Note 6)
Max
(Note 7) Units
1.9 µV/˚C
375
260
0.033 1
86 dB
82 dB
(Range)
>
1MΩ.
L
4.5
mV
5.5
pA
µA
µA
1.5
4V
www.national.com3
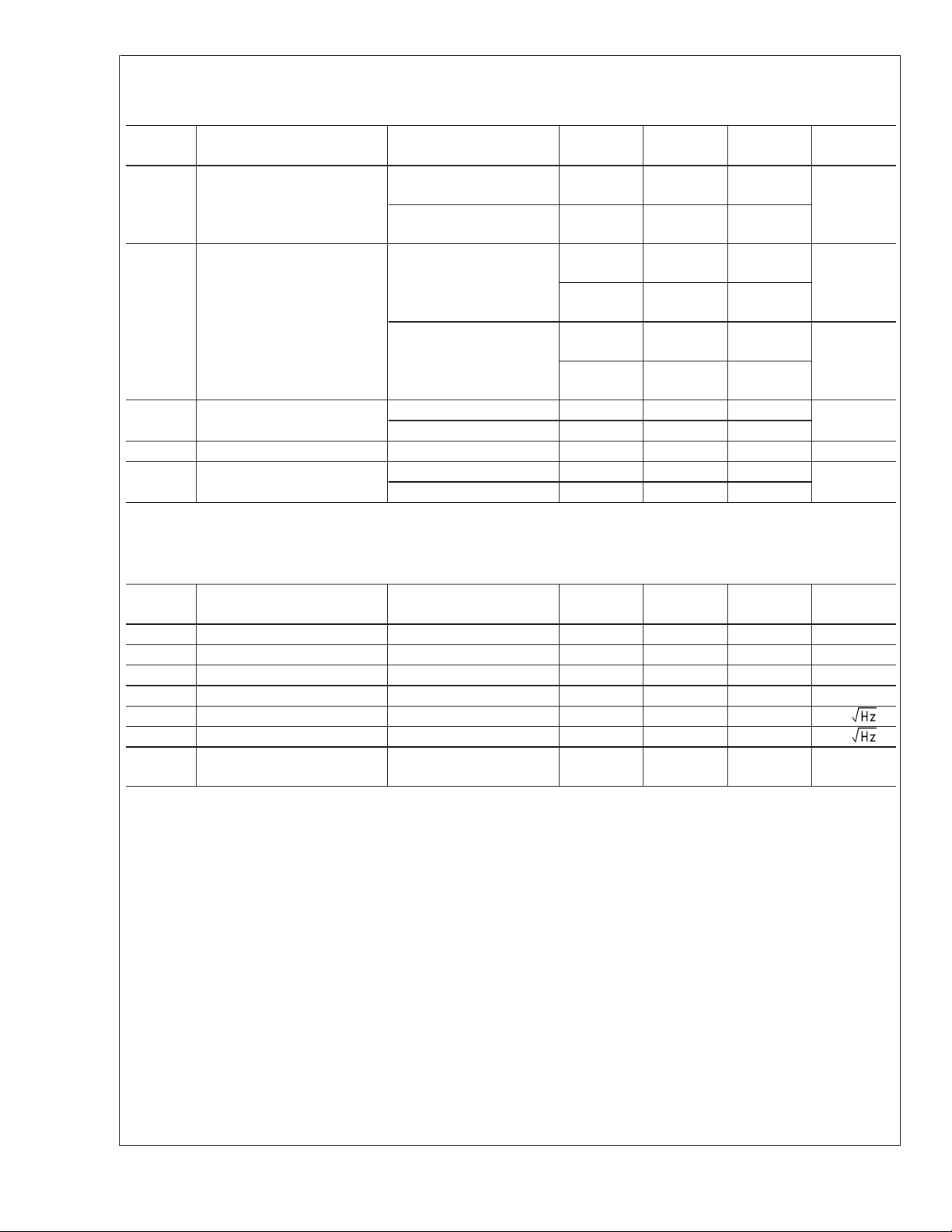
5V DC Electrical Characteristics (Note 10) (Continued)
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for TJ= 25˚C, V+= 5V, V−= 0V, VCM=V+/2, VO=V+/2 and R
Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions
A
V
Large Signal Voltage Gain
RL= 10kΩ to 2.5V 78
(Note 8)
RL=2kΩ to 2.5V 72
LMV341/LMV342/LMV344
V
O
I
O
t
on
V
SD
Output Swing RL=2kΩ to 2.5V 32 60
= 10kΩ to 2.5V 7 30
R
L
Output Short Circuit Current Sourcing 85 113
Sinking 50 75
Turn-on Time from Shutdown (LMV341) 5 µs
Shutdown Pin Voltage Range ON Mode (LMV341) 3.1 to 5 4.5 to 5.0
Shutdown Mode (LMV341) 0 to 1 0 to 0.8
Min
(Note 7)
70
64
60
95
30
40
Typ
(Note 6)
116
107
34
7
>
1MΩ.
L
Max
(Note 7) Units
dB
95
40
mV
mV
mA
V
5V AC Electrical Characteristics (Note 10)
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for TJ= 25˚C, V+= 5V, V−= 0V, VCM=V+/2, VO=V+/2 and R
Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
(Note 7)
SR Slew Rate R
GBW Gain-Bandwidth Product R
Φ
m
G
m
e
n
i
n
Phase Margin RL= 100kΩ 70 deg
Gain Margin RL= 100kΩ 20 dB
Input-Referred Voltage Noise f = 1kHz 39 nV/
Input-Referred Current Noise f = 1kHz 0.001 pA/
= 10kΩ, (Note 9) 1.0 V/µs
L
= 10kΩ,CL= 200pF 1.0 MHz
L
THD Total Harmonic Distortion f = 1 kHz, AV=+1
= 600Ω,VIN=1V
R
L
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is
intended to be functional, but specific performance is not guaranteed. For guaranteed specifications and the test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics.
Note 2: Human body model, 1.5kΩ in series with 100pF. Machine model, 0Ω in series with 200pF.
Note 3: Shorting output to V
Note 4: Shorting output to V
Note 5: The maximum power dissipation is a function of T
(T
J(MAX)–TA
Note 6: Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm.
Note 7: All limits are guaranteed by testing or statistical analysis.
Note 8: R
Note 9: Connected as voltage follower with 2V
Note 10: Electrical Table values apply only for factory testing conditions at the temperature indicated. Factory testing conditions result in very limited self-heating
of the device such that T
)/θJA. All numbers apply for packages soldered directly into a PC board.
is connected to mid-supply. The output voltage is GND + 0.2V ≤ VO≤ V+−0.2V
L
+
will adversely affect reliability.
-
will adversely affect reliability.
, θJA, and TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is PD=
J(MAX)
step input. Number specified is the slower of the positive and negative slew rates.
PP
. No guarantee of parametric performance is indicated in the electrical tables under conditions of internal self heating where T
J=TA
PP
Typ
(Note 6)
Max
(Note 7)
0.012 %
>
1MΩ.
L
Units
>
TA.
J
www.national.com 4
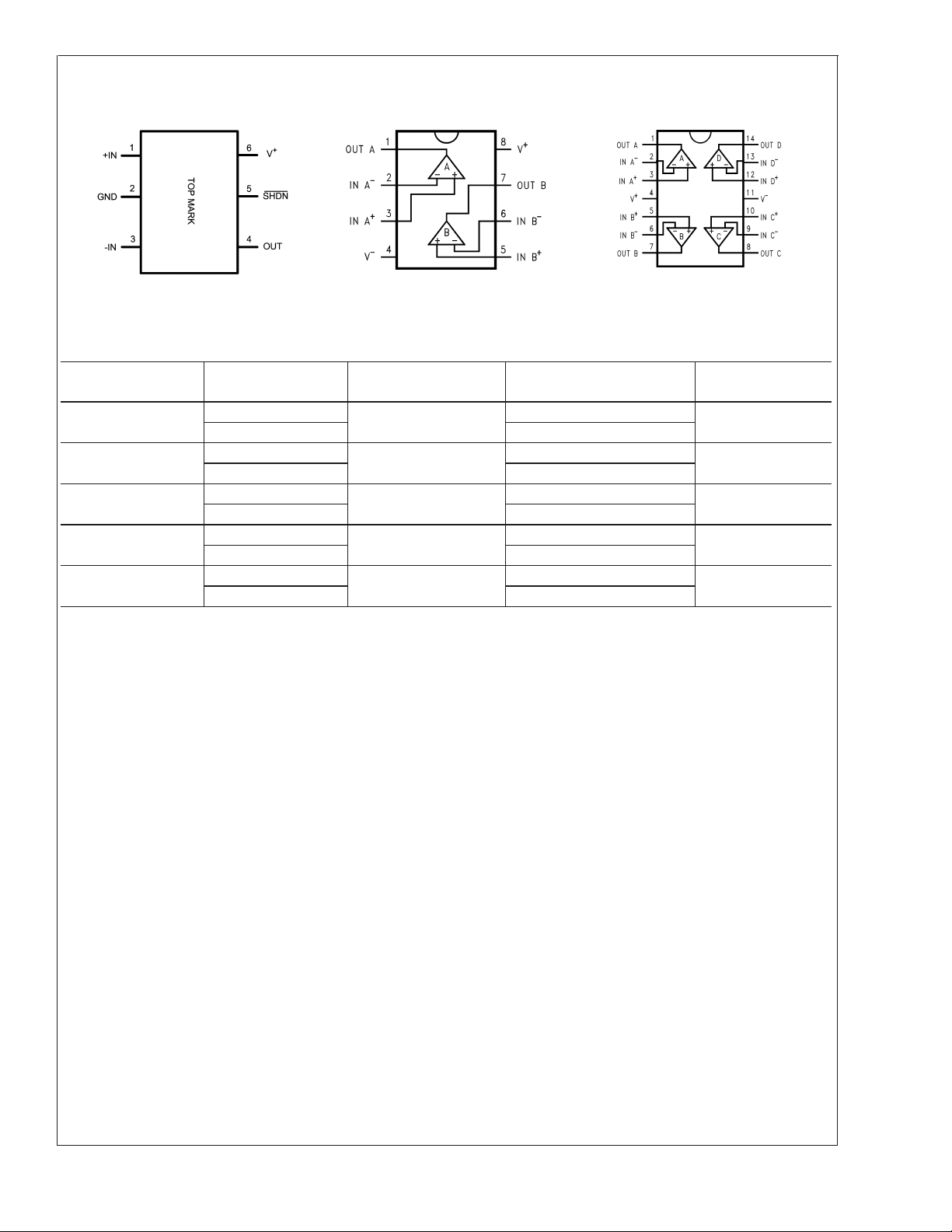
Connection Diagrams
SC70-6L 8-Pin MSOP/SOIC 14-Pin TSSOP/SOIC
LMV341/LMV342/LMV344
20030451
Top View
Top View
20030441
Top View
Ordering Information
Package Part Number Package Marking Transport Media NSC Drawing
6-Pin SC70
8-Pin MSOP
8-Pin SOIC
14-Pin TSSOP
14-Pin SOIC
LMV341MG
LMV341MGX 3k Units Tape and Reel
LMV342MM
LMV342MMX 3.5k Units Tape and Reel
LMV342MA
LMV342MAX 2.5k Units Tape and Reel
LMV344MT
LMV344MTX 2.5k Units Tape and Reel
LMV344MA
LMV344MAX 2.5k Units Tape and Reel
A78
A82A
LMV342MA
LMV344MT
LMV344MA
1k Units Tape and Reel
1k Units Tape and Reel
95 Units/Rail
Rails
55 Units/Rail
20030452
MAA06A
MUA08A
M08A
MTC14
M14A
www.national.com5
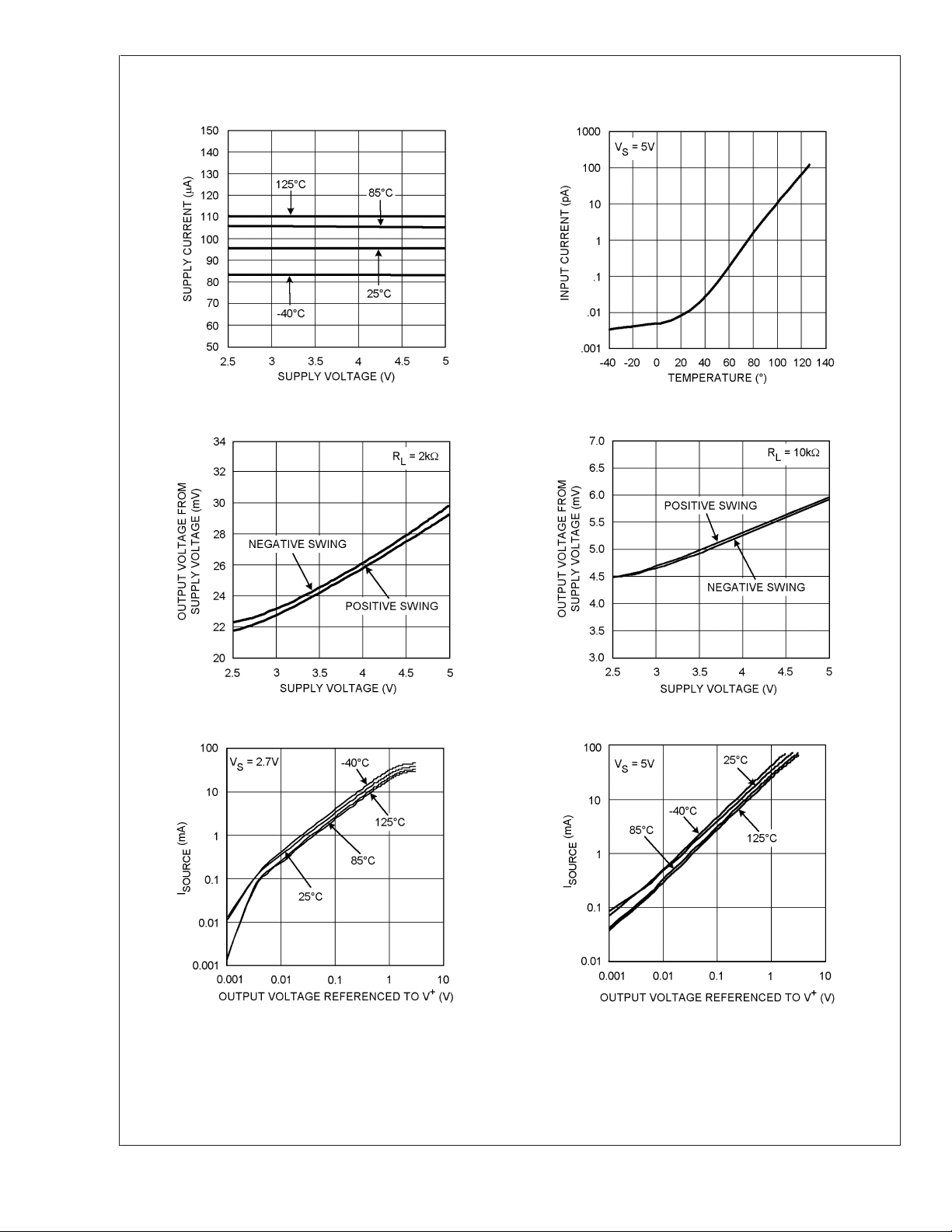
Typical Performance Characteristics
Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage (LMV341) Input Current vs. Temperature
LMV341/LMV342/LMV344
20030428
20030446
Output Voltage Swing vs. Supply Voltage Output Voltage Swing vs. Supply Voltage
20030426 20030427
I
SOURCE
vs. V
OUT
I
SOURCE
vs. V
OUT
20030429
www.national.com 6
20030430
 Loading...
Loading...