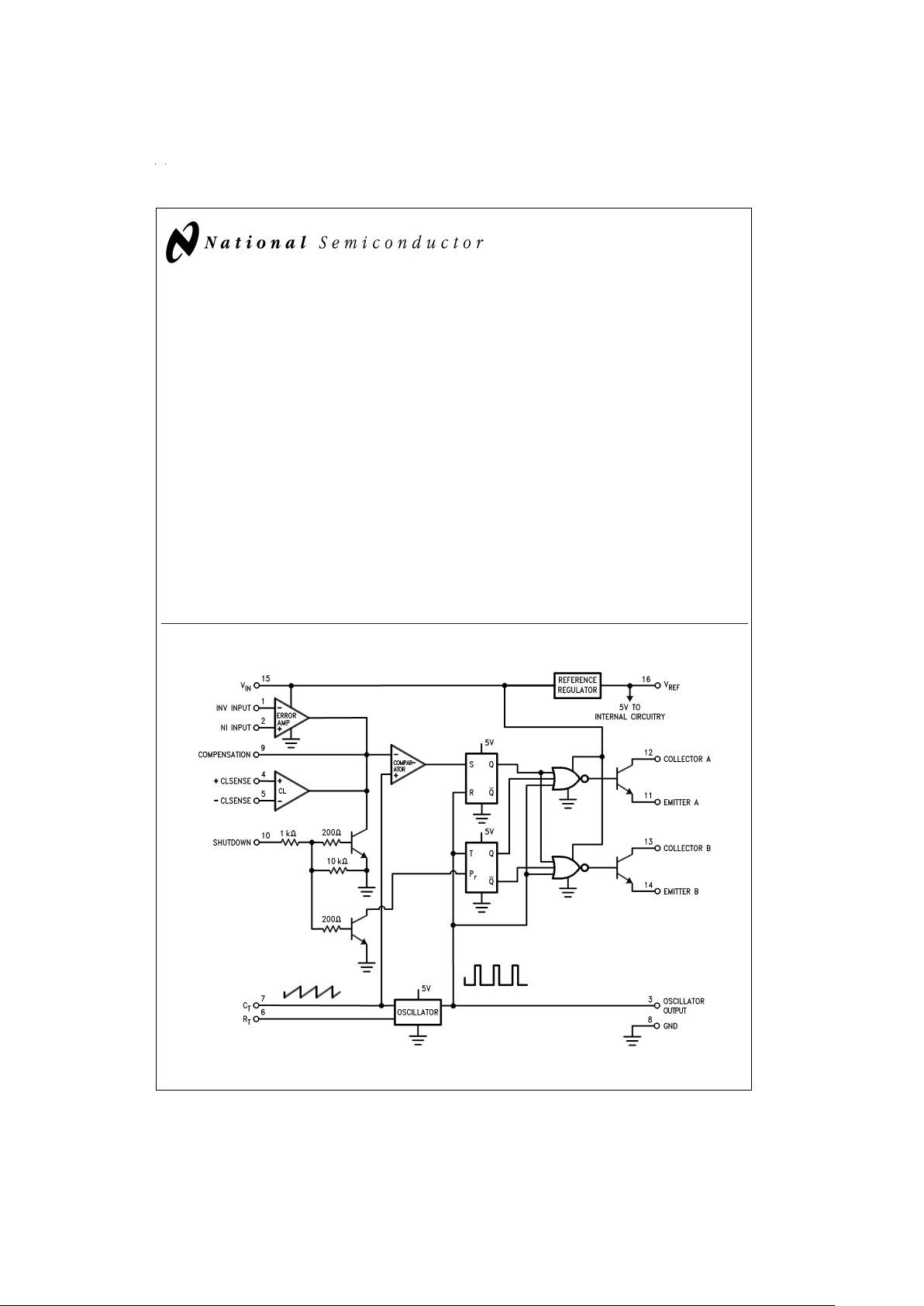
LM2524D/LM3524D
Regulating Pulse Width Modulator
General Description
The LM3524D family is an improved version of the industry
standard LM3524. It has improved specifications and additional featuresyet is pin for pin compatible with existing 3524
families. New features reduce the need for additional external circuitry often required in the original version.
The LM3524D has a
±
1%precision 5V reference. The current carrying capability of the output drive transistors has
been raised to 200 mAwhile reducing V
CEsat
and increasing
V
CE
breakdown to 60V. The common mode voltage range of
the error-amp has been raised to 5.5V to eliminate the need
for a resistive divider from the 5V reference.
In the LM3524D the circuit bias line has been isolated from
the shut-down pin. This prevents the oscillator pulse amplitude andfrequency from beingdisturbed by shut-down.Also
at high frequencies (
≅
300 kHz) the max. duty cycle per output has been improved to 44%compared to 35%max. duty
cycle in other 3524s.
In addition, the LM3524D can now be synchronized externally, through pin 3. Also a latch has been added to insure
one pulse per period even in noisy environments. The
LM3524D includes double pulse suppression logic that insures when a shut-down condition is removed the state of
the T-flip-flop will change only after the first clock pulse has
arrived. This feature prevents the same output from being
pulsed twice in a row, thus reducing the possibility of core
saturation in push-pull designs.
Features
n Fully interchangeable with standard LM3524 family
n
±
1%precision 5V reference with thermal shut-down
n Output current to 200 mA DC
n 60V output capability
n Wide common mode input range for error-amp
n One pulse per period (noise suppression)
n Improved max. duty cycle at high frequencies
n Double pulse suppression
n Synchronize through pin 3
Block Diagram
DS008650-1
June 1999
LM2524D/LM3524D Regulating Pulse Width Modulator
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS008650 www.national.com

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 5)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage 40V
Collector Supply Voltage
(LM2524D) 55V
(LM3524D) 40V
Output Current DC (each) 200 mA
Oscillator Charging Current (Pin 7) 5 mA
Internal Power Dissipation 1W
Operating Junction Temperature
Range (Note 2)
LM2524D −40˚C to +125˚C
LM3524D 0˚C to +125˚C
Maximum Junction Temperature 150˚
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temperature (Soldering 4 sec.)
M, N Pkg. 260˚C
Electrical Characteristics
(Note 1)
LM2524D LM3524D
Symbol Parameter Conditions Tested Design Tested Design Units
Typ Limit Limit Typ Limit Limit
(Note 3) (Note 4) (Note 3) (Note 4)
REFERENCE SECTION
V
REF
Output Voltage 5 4.85 4.80 5 4.75 V
Min
5.15 5.20 5.25 V
Max
V
RLine
Line Regulation V
IN
=
8V to 40V 10 15 30 10 25 50 mV
Max
V
RLoad
Load Regulation I
L
=
0mAto20mA 10 15 25 10 25 50 mV
Max
Ripple Rejection f=120 Hz 66 66 dB
I
OS
Short Circuit V
REF
=
0 25 25 mA Min
Current 50 50
180 200 mA Max
N
O
Output Noise 10 Hz ≤ f ≤ 10 kHz 40 100 40 100 µV
rms Max
Long Term T
A
=
125˚C 20 20 mV/kHr
Stability
OSCILLATOR SECTION
f
OSC
Max. Freq. R
T
=
1k, C
T
=
0.001 µF 550 500 350 kHz
Min
(Note 7)
f
OSC
Initial R
T
=
5.6k, C
T
=
0.01 µF 17.5 17.5 kHz
Min
Accuracy (Note 7) 20 20
22.5 22.5 kHz
Max
R
T
=
2.7k, C
T
=
0.01 µF 34 30 kHz
Min
(Note 7) 38 38
42 46 kHz
Max
∆f
OSC
Freq. Change V
IN
=
8 to 40V 0.5 1 0.5 1.0
%
Max
with V
IN
∆f
OSC
Freq. Change T
A
=
−55˚C to +125˚C
with Temp. at 20 kHz R
T
=
5.6k, 5 5
%
C
T
=
0.01 µF
V
OSC
Output Amplitude R
T
=
5.6k, C
T
=
0.01 µF 3 2.4 3 2.4 V
Min
(Pin 3) (Note 8)
t
PW
Output Pulse R
T
=
5.6k, C
T
=
0.01 µF 0.5 1.5 0.5 1.5 µs
Max
Width (Pin 3)
Sawtooth Peak R
T
=
5.6k, C
T
=
0.01 µF 3.4 3.6 3.8 3.8 V
Max
Voltage
Sawtooth Valley R
T
=
5.6k, C
T
=
0.01 µF 1.1 0.8 0.6 0.6 V
Min
Voltage
ERROR-AMP SECTION
V
IO
Input Offset V
CM
=
2.5V 2 8 10 210 mV
Max
Voltage
I
IB
Input Bias V
CM
=
2.5V 1 8 10 110 µA
Max
www.national.com 2
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
(Note 1)
LM2524D LM3524D
Symbol Parameter Conditions Tested Design Tested Design Units
Typ Limit Limit Typ Limit Limit
(Note 3) (Note 4) (Note 3) (Note 4)
ERROR-AMP SECTION
Current
I
IO
Input Offset V
CM
=
2.5V 0.5 1.0 1 0.5 1 µA
Max
Current
I
COSI
Compensation V
IN(I)−VIN(NI)
=
150 mV 65 65 µA
Min
Current (Sink) 95 95
125 125 µA
Max
I
COSO
Compensation V
IN(NI)−VIN(I)
=
150 mV −125 −125 µA
Min
Current (Source) −95 −95
−65 −65 µA
Max
A
VOL
Open Loop Gain R
L
=
∞
,V
CM
=
2.5 V 80 74 60 80 70 60 dB
Min
VCMR Common Mode 1.5 1.4 1.5 V
Min
Input Voltage Range 5.5 5.4 5.5 V
Max
CMRR Common Mode 90 80 90 80 dB
Min
Rejection Ratio
G
BW
Unity Gain A
VOL
=
0 dB, V
CM
=
2.5V 3 2 MHz
Bandwidth
V
O
Output Voltage R
L
=
∞
0.5 0.5 V
Min
Swing 5.5 5.5 V
Max
PSRR Power Supply V
IN
=
8 to 40V 80 70 80 65 db
Min
Rejection Ratio
COMPARATOR SECTION
Minimum Duty Pin 9=0.8V,
00 0 0
%
Max
Cycle [R
T
=
5.6k, C
T
=
0.01 µF]
Maximum Duty Pin 9=3.9V,
49 45 49 45
%
Min
Cycle [R
T
=
5.6k, C
T
=
0.01 µF]
Maximum Duty Pin 9=3.9V,
44 35 44 35
%
Min
Cycle [R
T
=
1k, C
T
=
0.001 µF]
V
COMPZ
Input Threshold Zero Duty Cycle 1 1 V
(Pin 9)
V
COMPM
Input Threshold Maximum Duty Cycle 3.5 3.5 V
(Pin 9)
I
IB
Input Bias −1 −1 µA
Current
CURRENT LIMIT SECTION
V
SEN
Sense Voltage V
(Pin 2)−V(Pin 1)
≥ 180 180 mV
Min
150 mV 200 200
220 220 mV
Max
TC-V
sense
Sense Voltage T.C. 0.2 0.2 mV/˚C
Common Mode −0.7 −0.7 V
Min
Voltage Range V5−V
4
=
300 mV 1 1 V
Max
SHUT DOWN SECTION
V
SD
High Input V
(Pin 2)−V(Pin 1)
≥ 1 0.5 1 0.5 V
Min
Voltage 150 mV 1.5 1.5 V
Max
I
SD
High Input I
(pin 10)
11 mA
Current
OUTPUT SECTION (EACH OUTPUT)
V
CES
Collector Emitter IC≤ 100 µA 55 40 V
Min
Voltage Breakdown
www.national.com3
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
(Note 1)
LM2524D LM3524D
Symbol Parameter Conditions Tested Design Tested Design Units
Typ Limit Limit Typ Limit Limit
(Note 3) (Note 4) (Note 3) (Note 4)
OUTPUT SECTION (EACH OUTPUT)
I
CES
Collector Leakage V
CE
=
60V
Current V
CE
=
55V 0.1 50 µA
Max
V
CE
=
40V 0.1 50
V
CESAT
Saturation I
E
=
20 mA 0.2 0.5 0.2 0.7 V
Max
Voltage I
E
=
200 mA 1.5 2.2 1.5 2.5
V
EO
Emitter Output I
E
=
50 mA 18 17 18 17 V
Min
Voltage
t
R
Rise Time V
IN
=
20V,
I
E
=
−250 µA 200 200 ns
R
C
=
2k
t
F
Fall Time R
C
=
2k 100 100 ns
SUPPLY CHARACTERISTICS SECTION
V
IN
Input Voltage After Turn-on 8 8 V
Min
Range 40 40 V
Max
T Thermal Shutdown (Note 2) 160 160 ˚C
Temp.
I
IN
Stand By Current V
IN
=
40V (Note 6) 5 10 5 10 mA
Note 1: Unless otherwise stated, thesespecificationsapply for T
A
=
T
J
=
25˚C. Boldface numbers applyover the rated temperaturerange: LM2524D is −40˚to85˚C
and LM3524D is 0˚C to 70˚C. V
IN
=
20V and f
OSC
=
20 kHz.
Note 2: For operation at elevated temperatures,devices in the N package must be derated based on a thermal resistance of 86˚C/W, junction to ambient. Devices
in the M package must be derated at 125˚C/W, junction to ambient.
Note 3: Tested limits are guaranteed and 100%tested in production.
Note 4: Design limits are guaranteed (but not 100%production tested) over the indicated temperature and supply voltage range. These limits are not used to cal-
culate outgoing quality level.
Note 5: Absolute maximum ratings indicate limitsbeyond which damage to the device mayoccur. DC andAC electrical specifications do notapply when operating
the device beyond its rated operating conditions.
Note 6: Pins 1, 4, 7, 8, 11, and 14 are grounded; Pin 2=2V.All other inputs and outputs open.
Note 7: The value of a C
t
capacitor can vary with frequency. Careful selection of this capacitor must be made for high frequency operation. Polystyrene was used
in this test. NPO ceramic or polypropylene can also be used.
Note 8: OSC amplitude is measured open circuit. Available current is limited to 1 mAso care must be exercised to limit capacitive loading of fast pulses.
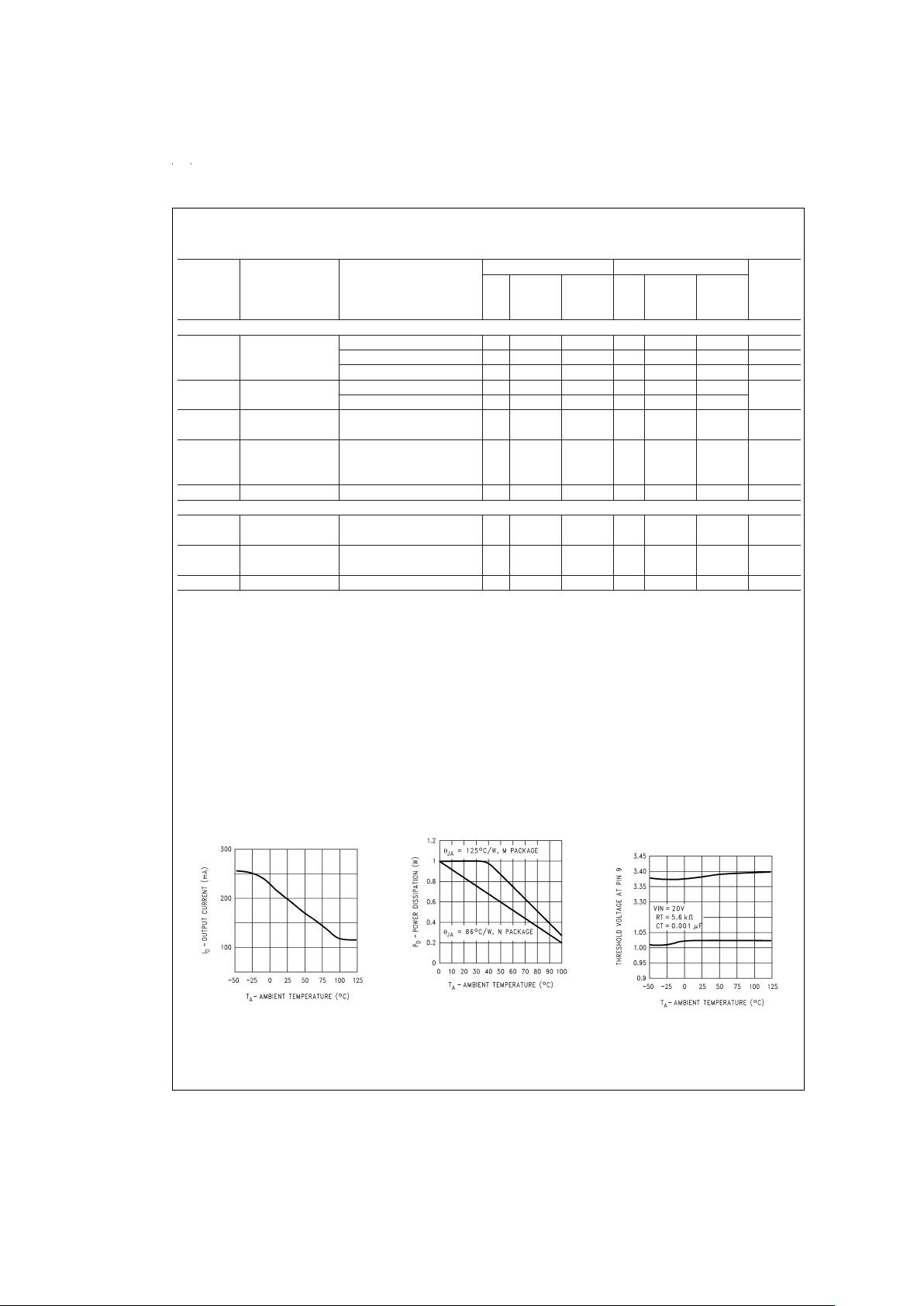
Typical Performance Characteristics
Switching Transistor
Peak Output Current
vs Temperature
DS008650-28
Maximum Average Power
Dissipation (N, M Packages)
DS008650-29
Maximum & Minimum
Duty Cycle Threshold
Voltage
DS008650-30
www.national.com 4
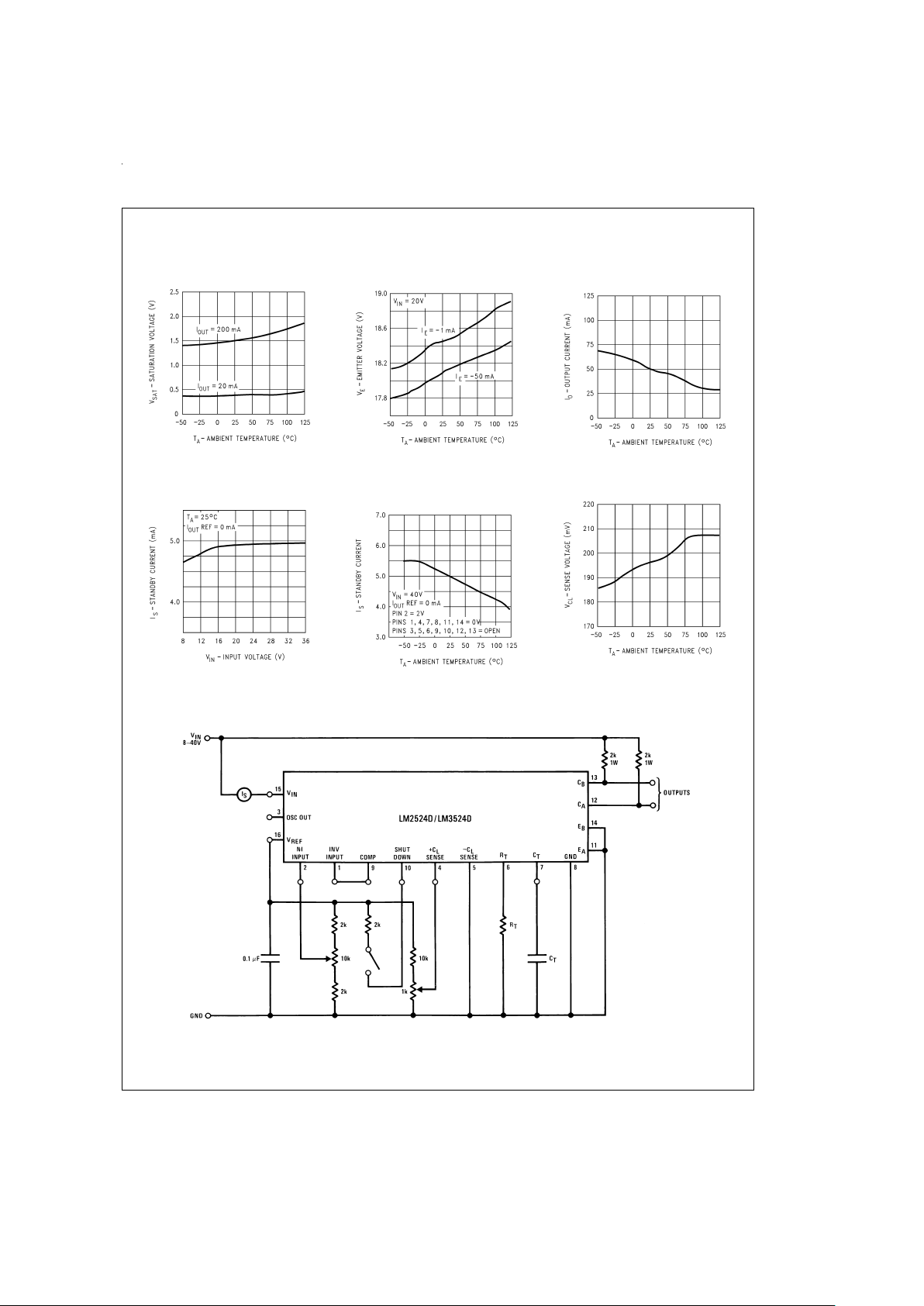
Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Test Circuit
Output Transistor
Saturation Voltage
DS008650-31
Output Transistor Emitter
Voltage
DS008650-32
Reference Transistor
Peak Output Current
DS008650-33
Standby Current
vs Voltage
DS008650-34
Standby Current
vs Temperature
DS008650-35
Current Limit Sense Voltage
DS008650-36
DS008650-4
www.national.com5
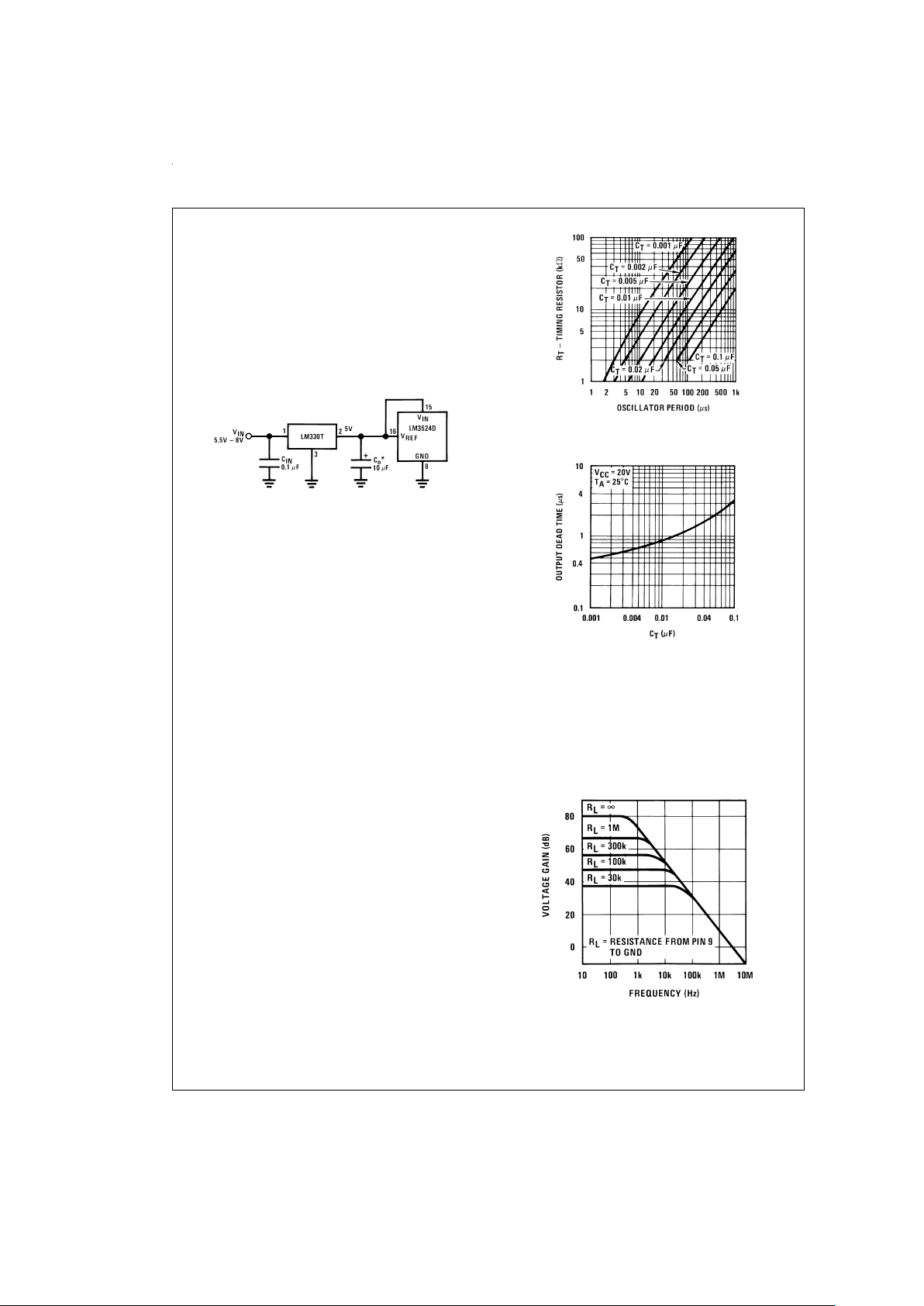
Functional Description
INTERNAL VOLTAGE REGULATOR
The LM3524D has an on-chip 5V, 50 mA, short circuit protected voltage regulator. This voltage regulator provides a
supply for all internal circuitry ofthe device and can be used
as an external reference.
For input voltages of less than 8V the 5V output should be
shorted to pin 15, V
IN
, which disables the 5V regulator. With
these pins shorted the input voltage must be limited to a
maximum of6V. If input voltages of 6V–8V are to be used, a
pre-regulator, as shown in
Figure 1
, must be added.
OSCILLATOR
The LM3524D provides a stable on-board oscillator. Its frequency isset by an external resistor, R
T
and capacitor, CT.A
graph of R
T,CT
vs oscillator frequency is shown is
Figure 2
.
The oscillator’s output provides the signals for triggering an
internal flip-flop, which directs the PWM information to the
outputs, and a blanking pulse to turn off both outputs during
transitions to ensure that cross conduction does not occur.
The width of the blanking pulse, or dead time, is controlled
by thevalue of C
T
, asshown in
Figure 3
. The recommended
values of R
T
are 1.8 kΩ to 100 kΩ, and for CT, 0.001 µF to
0.1 µF.
If two or more LM3524D’s must be synchronized together,
the easiest method is to interconnect all pin 3 terminals, tie
all pin 7’s (together)to asingle C
T
, and leave allpin 6’sopen
except one which is connected to a single R
T
. This method
works well unless the LM3524D’s are more than 6" apart.
A second synchronization method is appropriate for any cir-
cuit layout. One LM3524D,designated asmaster, must have
its R
TCT
set for the correct period. The other slave
LM3524D(s) should each have an R
TCT
set for a 10%longer
period. All pin 3’s must then be interconnected to allow the
master to properly reset the slave units.
The oscillator may be synchronized to an external clock
source by setting the internal free-running oscillator frequency 10%slower than the external clock and driving pin 3
with a pulse train (approx. 3V) from the clock. Pulse width
should be greater than 50 ns to insure full synchronization.
ERROR AMPLIFIER
The error amplifier is a differential input, transconductance
amplifier. Its gain, nominally 86dB, is set by either feedback
or output loading. This output loading can be done with either purely resistive or a combination of resistive and reactive components. A graph of the amplifier’s gain vs output
load resistance is shown in
Figure 4
.
The output of the amplifier, or input to the pulse width modulator, can be overridden easily as its output impedance is
very high (Z
O
≅
5MΩ). For this reason a DC voltage can be
DS008650-10
*Minimum COof 10 µF required for stability.
FIGURE 1.
DS008650-5
FIGURE 2.
DS008650-6
FIGURE 3.
DS008650-7
FIGURE 4.
www.national.com 6
 Loading...
Loading...