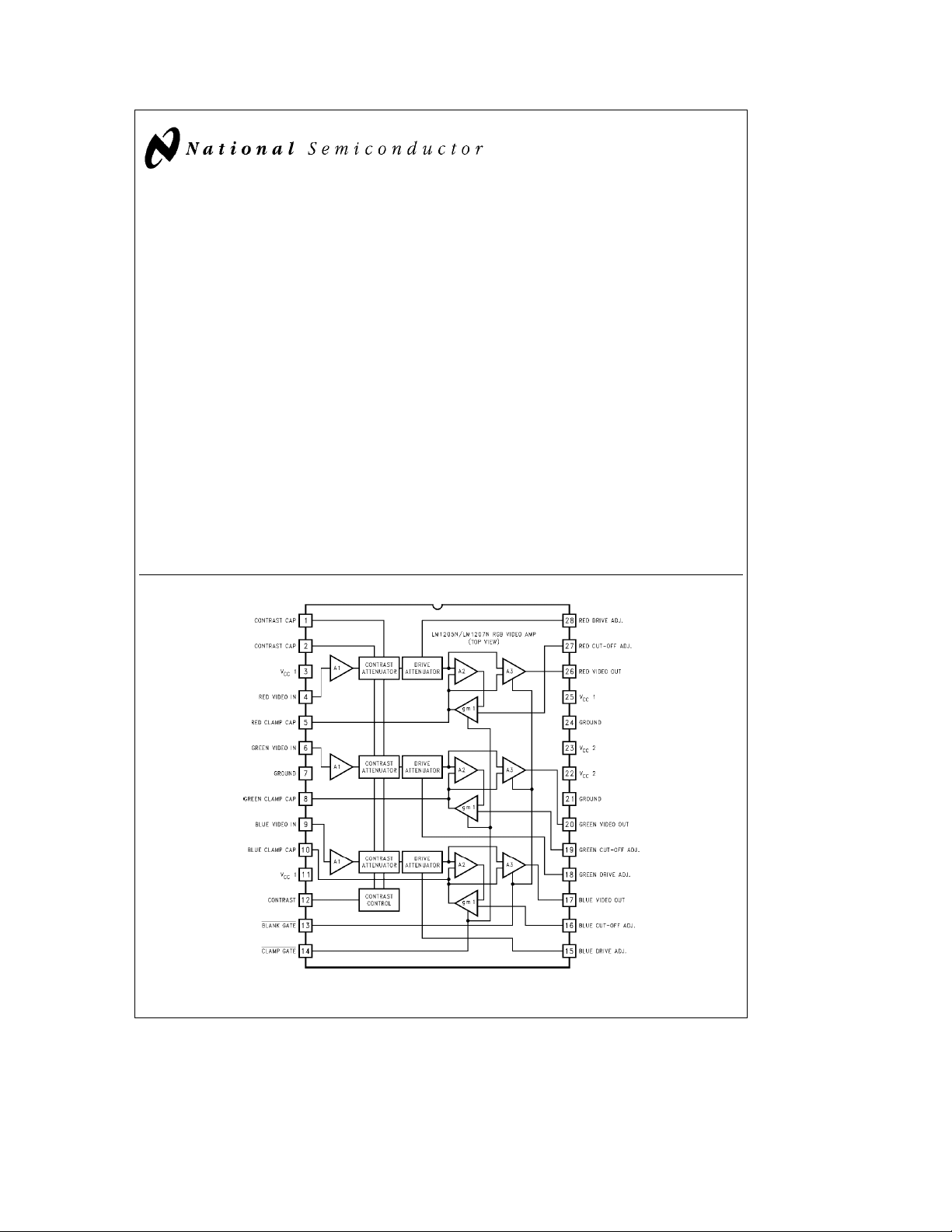
LM1205/LM1207
130 MHz/85 MHz RGB Video Amplifier System with
Blanking
Y
General Description
The LM1205/LM1207 is a very high frequency video amplifier system intended for use in high resolution RGB monitor
applications. In addition to the three matched video amplifiers, the LM1205/LM1207 contains three gated single ended input black level clamp comparators for brightness control, three matched DC controlled attenuators for contrast
control, and three DC controlled sub-contrast attenuators
providing gain trim capability for white balance. All DC control inputs offer high input impedance and an operation
range from 0V to 4V for easy interface to bus controlled
alignment systems. The LM1205/LM1207 also contains a
blanking circuit which clamps the video output voltage during blanking to within 0.1V above ground. This feature provides blanking capability at the cathodes of the CRT. A spot
killer is provided for CRT phosphor protection during powerdown.
Features
Y
Three wideband video amplifiers 130 MHz (LM1205)
b
3dB(4VPPoutput)
Y
Matched (g0.1 dB or 1.2%) attenuators for contrast
control
Three externally gated single ended input comparators
for cutoff and brightness control
Y
0V to 4V, high input impedance DC contrast control
l
(
40 dB range)
Y
0V to 4V, high input impedance DC drive control for
each video amplifier (
Y
Spot killer, blanks output when V
Y
Capable of 7 VPPoutput swing (slight reduction in
b
6 dB to 0 dB range)
CC
k
bandwidth)
Y
Output stage blanking
Y
Output stage directly drives most hybrid or discrete
CRT drivers
Applications
Y
High resolution RGB CRT monitors
Y
Video AGC amplifiers
Y
Wideband amplifiers with gain and DC offset controls
Y
Interface amplifiers for LCD or CCD systems
@
LM1205/LM1207 130 MHz/85 MHz RGB Video Amplifier System with Blanking
January 1996
10.6V
Block and Connection Diagram
FIGURE 1
Order Number LM1205N or LM1207N
See NS Package Number N28B
C
1996 National Semiconductor Corporation RRD-B30M66/Printed in U. S. A.
TL/H/11881
TL/H/11881– 1
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales
Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (V
Pins 3, 11, 22, 23, 25 (Note 3) 15V
CC
)
Operating Ratings (Note 2)
Temperature Range
Supply Voltage (VCC) 10.8VsV
Peak Video Output Source Current
(Any One Amp) Pins 17, 20 or 26 28 mA
t
Voltage at Any Input Pin (V
)V
IN
CC
t
V
GND
IN
Power Dissipation (PD)
(Above 25
Thermal Resistance (iJA)50
Junction Temperature (T
C Derate Based on iJAand TJ) 2.5W
§
) 150§C
J
C/W
§
ESD Susceptibility (Note 4) 2 kV
Pins 12, 13 and 14 1.9 kV
4V; V
b
65§Cto150§C
C
§
e
4V unless otherwise stated.
drive
(Figure 2 ),
Storage Temperature
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec.) 265
DC Electrical Characteristics See DC Test Circuit
e
V
0V; V
14
cut-off
e
1.0V; V
e
13
Symbol Parameter Conditions
I
S
V
4, 6, 9
R
IN
V
14l
V
14h
I
14l
I
14h
I
clamp
I
bias
V
13l
V
13h
I
13l
I
13h
V
OL
V
OH
V
O(1V)
DV
O(1V)
Supply Current V
Video Amplifier Input Bias Voltage 2.8 V
Video Input Resistance Any One Amplifier 20 kX
Clamp Gate Low Input Voltage Clamp Comparators On 1.2 0.8 V (max)
Clamp Gate High Input Voltage Clamp Comparators Off 1.6 2.0 V (min)
Clamp Gate Low Input Current V
Clamp Gate High Input Current V
Clamp Cap Charge Current Clamp Comparators On
Clamp Cap Bias Discharge Current Clamp Comparators Off 500 nA
Blank Gate Low Input Voltage Blank Gate On 1.2 0.8 V (max)
Blank Gate High Input Voltage Blank Gate Off 1.6 2.0 V (min)
Blank Gate Low Input Current V
Blank Gate High Input Current V
Video Output Low Voltage V
Video Output High Voltage V
Video Black Level Output Voltage V
Video D Black Level Output Voltage Between Any Two Amplifiers,
VOL(blanked) Video Output Blanked Voltage V
I
12, 15, 18 or 28
I
16, 19 and 27
V
spot
Contrast/Drive Control Input Current V
Cut-Off Control Input Current (All Inputs) V
Spot Killer Voltage VCCAdjusted to Activate 10.4 10.8 V (max)
a
V
CC1
CC2,RL
e
0V
14
e
12V 0.01 1.0 mA (max)
14
e
0V
13
e
12V 0.01 1.0 mA (max)
13
e
0V 0.15 0.5 V (max)
cut-off
e
9V 7.5 7 V (min)
cut-off
e
1V 1.0 V (Note 8)
cut-off
e
V
1V
cut-off
e
0V 35 70 mV (max)
13
e
e
0V to 4V
V
drive
contrast
cut-off
b
e
T
25§C; V
A
CC1
e
e
V
12V. V
CC2
Typical Limit
(Note 5) (Note 6)
e %
(Note 7) 90 105 mA (max)
e
0V to 4V
b
g
750
b
8.5
g
100 mV (max)
b
250 nA
b
500 nA
b
1
5 mA (max)
g
500 mA (min)
b
11.0 mA (max)
20§Cto80§C
s
13.2V
CC
e
4V;
12
Units
http://www.national.com 2
AC Electrical Characteristics See AC Test Circuit
(Figure 3)
adjust Video Output pins 17, 20, and 26 to 4V DC for the AC test unless otherwise stated. (Note 14)
,T
e
25§C; V
A
Symbol Parameter Conditions
A
V max
DA
V2V
DA
V 0.25V
DDrive Drive Control Range V
A
V match
A
V track1
THD Video Amplifier Distortion V
Video Amplifier Gain V12e4V, V
V
drive
Attenuation@2V Ref: AVmax, V12e2V
Attenuation@0.25V Ref: AVmax, V12e0.25V
drive
Absolute Gain Match@AVmax V12e4V, V
Gain Change Between Amplifiers V12e4V to 2V (Notes 9, 10)
e
O
f(b3 dB) Video Amplifier Bandwidth V12e4V, V
(Notes 11, 12)
tr(Video) Video Output Rise Time (Note 11) V
e
V
O
e
O
e
635 mV
IN
e
4V
e
0V to 4V, V12e4V 6 dB
drive
e
4V (Note 9)
PP
1VPP,fe10 kHz 1 %
e
4V, LM1205 130
drive
4V
4V
PP
PP
LM1207 85
LM1205 2.6
e
e
V
CC2
12V. Manually
Units
CC1
Typical Limit
(Note 5) (Note 6)
7.0 6.0 V/V (min)
16.9 15.6 dB (min)
b
6dB
b
40 dB
g
0.3 dB
g
0.1 dB
MHz
LM1207 4.3
tf(Video) Video Output Fall Time (Note 11) V
e
4V
O
PP
LM1205 3.6
LM1207 4.3
V
10 kHz Video Amplifier 10 kHz Isolation V12e4V (Note 13)
sep
V
10 MHz Video Amplifier 10 MHz Isolation V12e4V (Notes 11, 13)
sep
tr(Blank) Blank Output Rise Time (Note 11) Blank Outpute1V
t
(Blank) Blank Output Fall Time (Note 11) Blank Outpute1V
f
t
(Clamp) Min. Back Porch Clamp Pulse Width 200 ns
pw
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur.
Note 2: Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. For guaranteed specifications
and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. The guaranteed specifications apply only for the test conditions listed. Some performance characteristics
may degrade when the device is not operated under the listed test conditions.
Note 3: V
Note 4: Human body model, 100 pF discharged through a 1.5 kX resistor.
Note 5: Typical specifications are specified at
Note 6: Tested limits are guaranteed to National’s AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level).
Note 7: The supply current specified is the quiescent current for V
depends on the output load. With video output at 1V DC, the additional current through V
Note 8: Output voltage is dependent on load resistor. Test circuit uses R
Note 9: Measure gain difference between any two amplifiers. V
Note 10: D A
gain change between any two amplifiers with the contrast voltage (V12) at either 4V or 2V measured relative to an A
max the three amplifiers’ gains might be 17.1 dB, 16.9 dB and 16.8 dB and change to 11.2 dB, 10.9 dB, and 10.7 dB respectively for V12e2V. This yields the
measured typical
Note 11: When measuring video amplifier bandwidth or pulse rise and fall times, a double sided full ground plane printed circuit board without socket is
recommended. Video amplifier 10 MHz isolation test also requires this printed circuit board. The reason for a double sided full ground plane PCB is that large
measurement variations occur in single sided PCBs.
Note 12: Adjust input frequency from 10 MHz (A
Note 13: Measure output levels of the other two undriven amplifiers relative to the driven amplifier to determine channel separation. Terminate the undriven
amplifier inputs to simulate generator loading. Repeat test at f
Note 14: During the AC tests the 4V DC level is the center voltage of the AC output signal. For example, if the output is 4 V
and 6V DC.
supply pins 3, 11, 22, 23, 25 must be externally wired together to prevent internal damage during VCCpower on/off cycles.
CC
a
25§C and represent the most likely parametric norm.
and V
CC2
e
L
635 mVPP.
10 MHz for V
with R
390X.
sep 10 MHz
CC1
e
track is a measure of the ability of any two amplifiers to track each other and quantifies the matching of the three attenuators. It is the difference in
V
g
0.1 dB channel tracking.
max reference level) to theb3 dB corner frequency (f
V
IN
e
IN
L
e %
CC2
PP
PP
, see
Figure 2’s
is8mAfor
.
test circuit. The supply current for V
Figure 2’s
b
3dB
b
70 dB
b
50 dB
7ns
7ns
(pin 23) also
test circuit.
max condition, V12e4V. For example, at A
V
).
the signal will swing between 2V DC
PP
CC2
ns
ns
V
http://www.national.com3
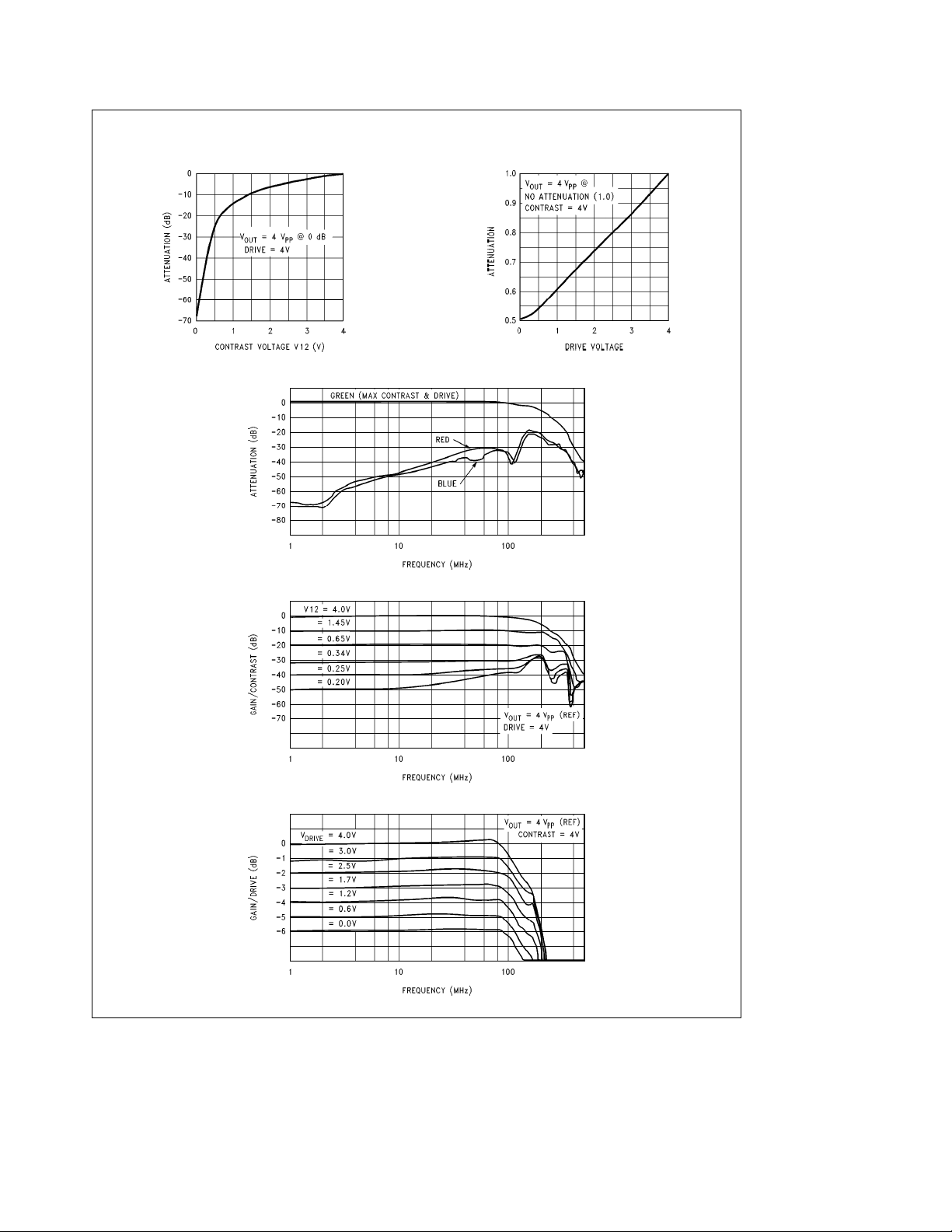
Typical Performance Characteristics V
Attenuation vs Contrast Voltage
CC
e
12V, T
e
25§C unless otherwise specified
A
Attenuation vs Drive Voltage
TL/H/11881– 2
LM1205 Crosstalk vs Frequency
LM1205 Contrast vs Frequency
LM1205 Drive vs Frequency
TL/H/11881– 3
TL/H/11881– 4
TL/H/11881– 5
http://www.national.com 4
TL/H/11881– 6
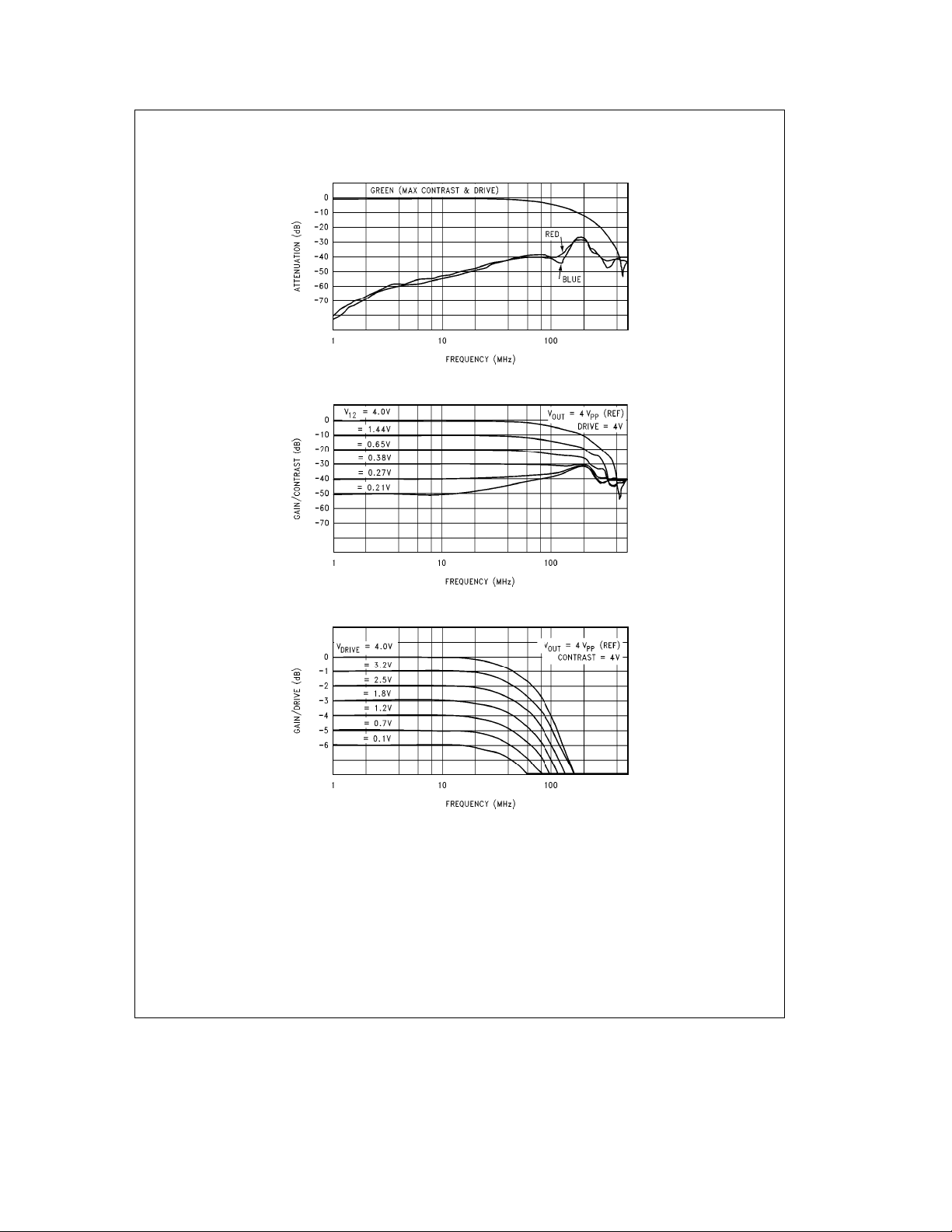
Typical Performance Characteristics V
LM1207 Crosstalk vs Frequency
LM1207 Contrast vs Frequency
CC
e
12V, T
e
25§C unless otherwise specified (Continued)
A
TL/H/11881– 7
LM1207 Drive vs Frequency
TL/H/11881– 8
TL/H/11881– 9
http://www.national.com5
Applications Information
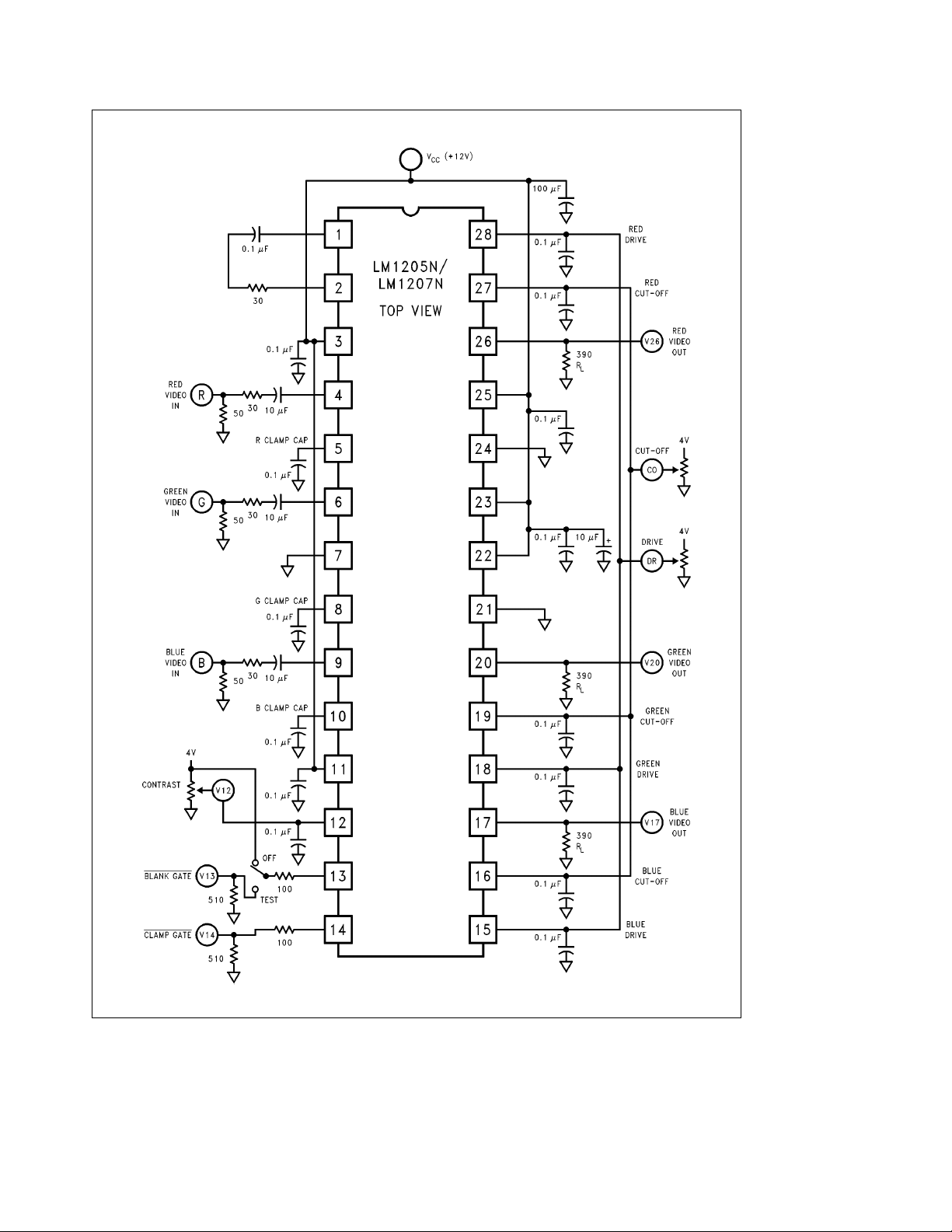
FIGURE 2. LM1205N/LM1207N DC Test Circuit
http://www.national.com 6
TL/H/11881– 10
Applications Information (Continued)
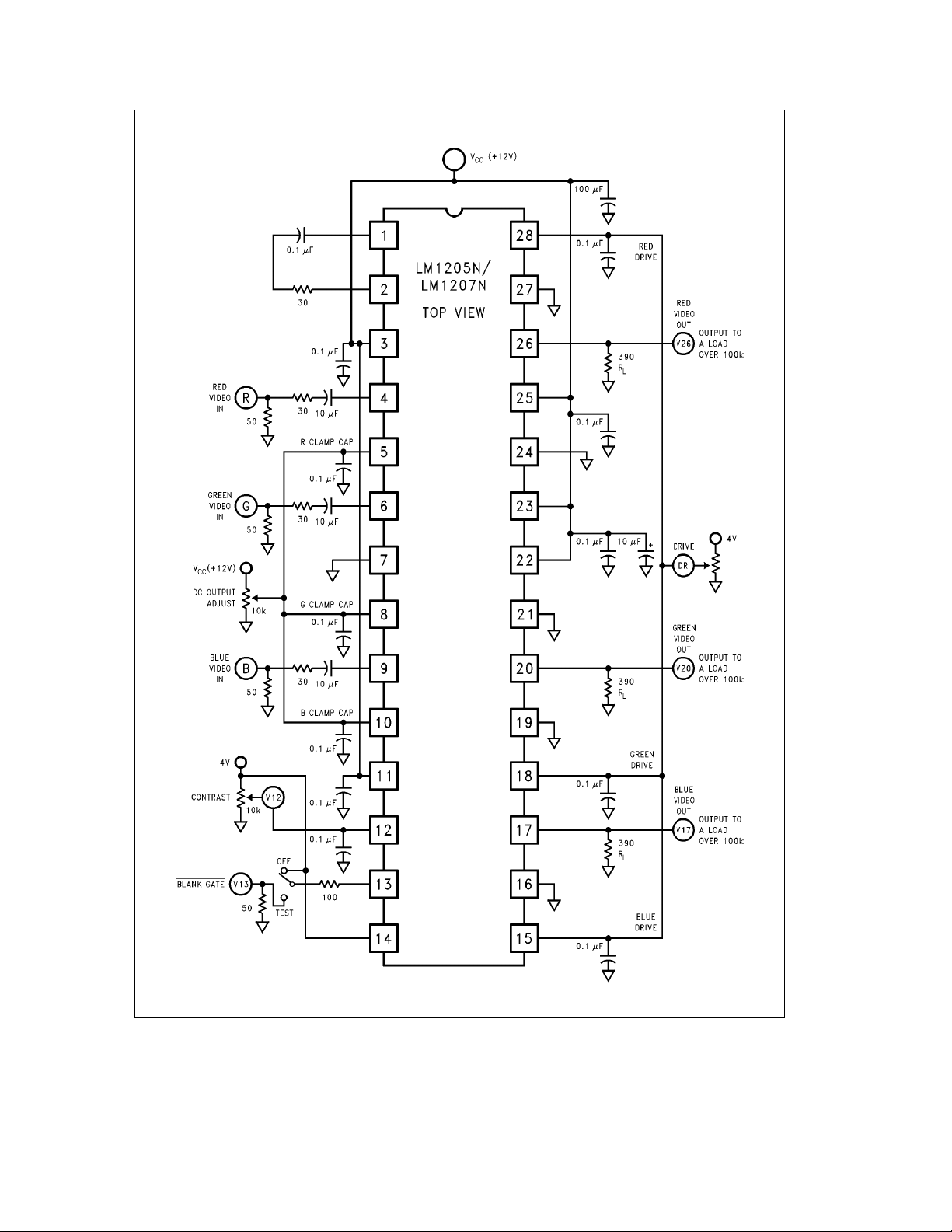
FIGURE 3. LM1205N/LM1207N AC Test Circuit
TL/H/11881– 11
http://www.national.com7
Applications Information (Continued)
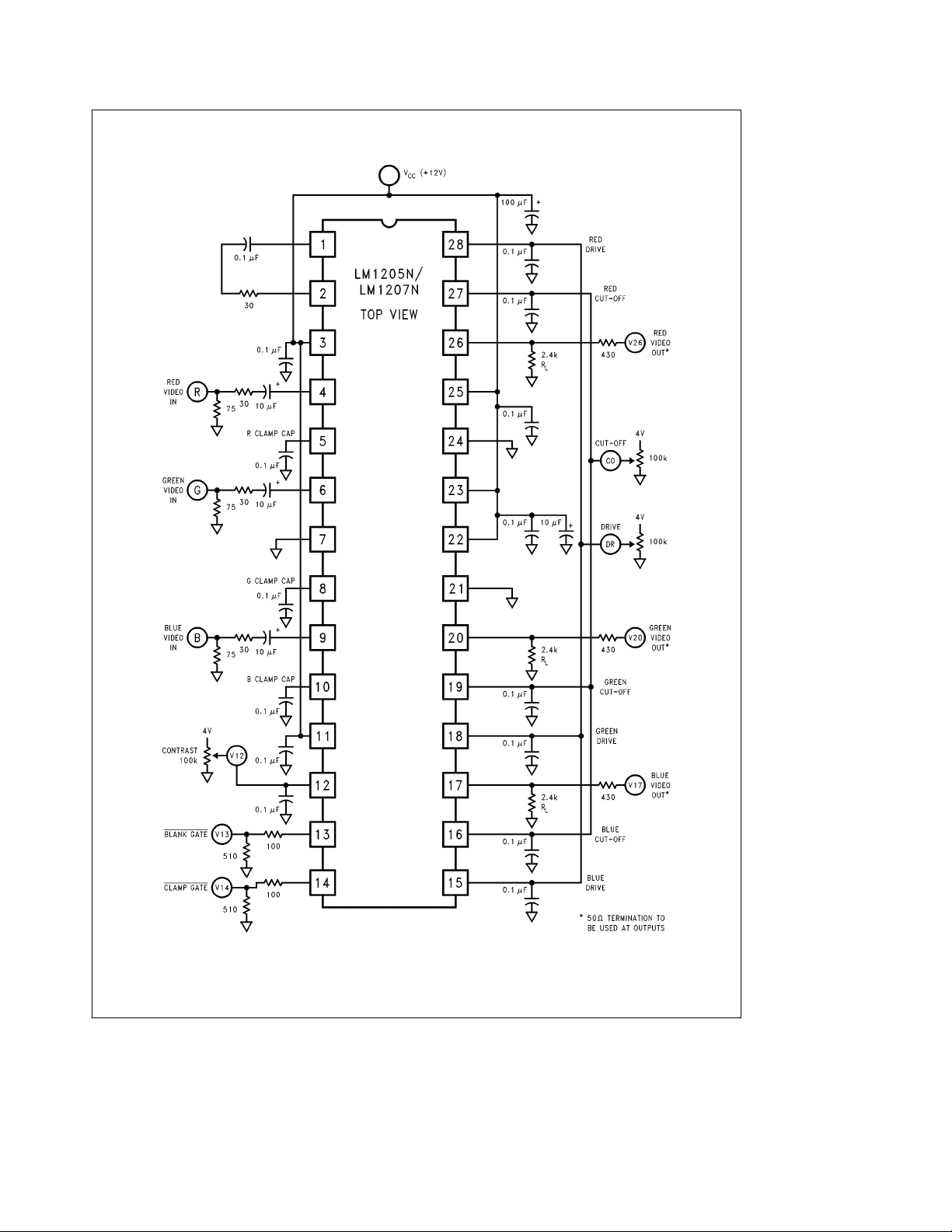
FIGURE 4. LM1205N/LM1207N PCB Test Circuit
http://www.national.com 8
TL/H/11881– 12

Applications Information (Continued)
Figure 5
shows the block diagram of a typical analog RGB
color monitor. The RGB monitor is used with CAD/CAM
work stations, PC’s, arcade games and in a wide range of
other applications that benefit from the use of color display
terminals. The RGB color monitor characteristics may differ
in such ways as sweep rates, screen size, CRT color trio
spacing (dot pitch), or in video amplifier bandwidths but will
still be generally configured as shown in
horizontal and vertical sync signals may be required or they
may be contained in the green video input signal. The video
input signals are usually supplied by coax cable which is
terminated into 75X at the monitor input and internally AC
coupled to the video amplifiers. These input signals are approximately 1V peak to peak in amplitude and at the input of
the high voltage video section, approximately 5V peak to
peak. At the cathode of the CRT the video signals can be as
high as 60V peak to peak. One important requirement of the
three video amplifiers is that they match and track each
other over the contrast and brightness control range. The
Figure 5
GAIN AND DC CONTROL’’ describes the function of the
LM1205/LM1207 which contains the three matched video
amplifiers, contrast control and brightness control. The
LM1205/LM1207 also provides the capability to blank at the
cathode of the CRT.
block labeled ‘‘VIDEO AMPLIFICATION WITH
Figure 5
. Separate
Functional Description
Figure 6
is a detailed block diagram of the green channel of
the LM1205/LM1207 along with the recommended external
components. The IC pin numbers are circled and all external
components are shown outside the dashed line. The other
two video channels are identical to the green channel, only
the numbers to the pins unique to each channel are different. The input video is normally terminated into 75X. The
termination resistor depends on the impedance of the coax
cable being used, 75X being the most common impedance
used in video applications. The video signal is AC coupled
through a 10 mF capacitor to the input, pin 6. There is no
standard for the DC level of a video signal, therefore the
signal must be AC coupled to the LM1205/LM1207. Internal
to the LM1205/LM1207 is a 2.8V reference, giving the input
video an offset voltage of 2.8V. This voltage was selected to
give the input video enough DC offset to guarantee that the
lowest voltage of the video signal at pin 6 is far enough
above ground to keep the LM1205/LM1207 in the active
region. The 200X resistor at the input is for ESD protection
and for current limiting during any voltage surge that may
occur at the input, driving pin 6 above V
signal is buffered by
verting amplifier is shown with a ‘‘
the amplifier designation. The output of
contrast and drive attenuator sections.
The contrast and drive control sections are virtually identical. Both sections take a 0V to 4V input voltage, 4V giving
the maximum gain for either the contrast or the drive. This is
a high impedance input, allowing for an easy interface to 5V
DACs. One may also use 100k potentiometers with no degradation in performance. The contrast control section is
common to all three channels. It converts the input voltage
at pin 12 to a couple of internal DC voltages that control the
gain of the contrast attenuator. Referring to the Attenuation
vs Contrast Voltage under typical performance characteristics note that a 4V control voltage results in no attenuation
of the video signal. A 0.25V control voltage results in an
attenuation of 40 dB. Again note that these internal control
voltages are common to all three channels. To minimize
crosstalk, these voltages go to pins 1 and 2. Minimizing
crosstalk is done by adding the RC network shown in the
block diagram
b
A1. In this circuit description an in-
(Figure 6)
.
. The input video
CC
b
’’ (minus sign) in front of
b
A1 goes to the
FIGURE 5. Typical RGB Color Monitor Block Diagram
TL/H/11881– 13
http://www.national.com9

Functional Description (Continued)
The 0V to 4V drive control signal comes in on pin 18. Each
channel has its own drive section, therefore the crosstalk
compensation needed for the contrast control voltages is
not required for the drive control, thus no external pins for
the drive control. The drive attenuator gives an attenuation
range from 0 dB to
for the drive attenuator is desirable and intentionally designed because the drive is used only to balance the overall
gain of each color channel, giving the correct color temperature on the CRT.
The output of the drive attenuator stage goes to A2, the
amplifier in the DC restoration section. The video signal
goes to the non-inverting input of A2. The inverting side of
A2 goes to the output of gm1, the clamp comparator, and
the clamp capacitor at pin 8.
During the back porch period of the video signal a negative
going clamp pulse from pin 14 is applied to the clamp comparator, turning on the comparator. This period is where the
black level of the video signal at the output of the LM1205/
LM1207 is compared to the desired black level which is set
at pin 19.
relative to the video signal. The clamp capacitor is charged
or discharged by gm1, generating the correction voltage
needed at the inverting input of A2 to set the video output to
the correct DC level. Removing the clamp pulse turns off
gm1 with the correction voltage being maintained by the
clamp capacitor during active video. Both the clamp pulse
and the blank pulse at pin 13 are TTL voltage levels.
There are actually two output sections,
sections have been designed to be identical, except
has more current drive capability. The output transistor
shown is part of
the user knows the configuration of the output stage.
does not go to the outside world, it is used for feeding back
the video signal for DC restoration. Its output goes directly
b
6 dB. A small gain adjustment range
Figure 7
shows the timing of the clamp pulse
b
b
A4, but has been shown separately so
A3 andbA4. Both
b
A4
b
A3
to the inverting input of the clamp comparator via the voltage divider formed by the 500X and 4k resistors.
be close to the same output as
track due to the similar design of the two output stages.
However, the current at the output of
the current at the output of
b
A3 and will temperature
b
b
A3. To balance both outputs, a
A4 will be ten times
load resistance of 390X needs to be connected from pin 20,
the green video output pin, to ground. Another input to
b
A4 will
b
A4
is the blank pulse. When a negative going blank pulse is
applied to pin 13, the output of the LM1205/LM1207 is driven to less than 0.1V above ground. Using the timing shown
in
Figure 7
for the blank pulse, the output of the LM1205/
LM1207 will be less than 0.1V during the inactive portion of
the video signal. This is a ‘‘blacker than black’’ condition,
blanking the CRT at the cathodes. By using the blank function of the LM1205/LM1207 no grid blanking is necessary.
Note that the DC restoration is done by feeding back the
video signal from
b
A3, but blanking is done atbA4. By
using the two output stages, blanking can be done at the
CRT cathodes, and at the same time activate the DC restoration loop.
V
goes to pins 3, 11, and 25 (see
CC1
pins are all internally connected. For proper operation of the
LM1205/LM1207 it is necessary to connect all the V
pins to the input power to the PCB and bypass each pin with
a 0.1 mF capacitor. V
23 for the three output stages. This is a separate power
input from V
the two different power inputs. There must be a connection
, there are no internal connections between
CC1
on the PCB between V
be bypassed by a parallel connection of a 10 mF and 0.1 mF
is the input power at pins 22 and
CC2
CC1
and V
Figure 1
). These three
. Pins 22 and 23 must
CC2
CC1
capacitors. The ground connections for the LM1205/
LM1207 are at pins 7, 21, and 24. All three ground pins are
internally connected, and these pins must also be connected externally to a good ground plane for proper operation of
the LM1205/LM1207.
http://www.national.com 10

Functional Description (Continued)
FIGURE 6. Block Diagram of LM1205/LM1207 Video Amplifier
FIGURE 7. Timing Diagram
TL/H/11881– 15
Circuit Description
VIDEO AMPLIFIER INPUT STAGE
Figure 8
is a simplified schematic of one of the three video
amplifiers input stage along with the recommended external
components. The IC pin numbers are circled and all external
components are shown outside the dashed line. The video
TL/H/11881– 14
input is applied to pin 6 via a 10 mF coupling capacitor and a
30X resistor. The resistor is added to limit the current
through the input pin should an applied voltage surge rise
above V
LM1205/LM1207 is not degraded by the 30X resistor. However, if EMI is a concern this resistor can be increased to
well over 100X where the rise and fall times will start to
become longer. DC bias to the input pin is provided by Q5
and its associated input circuitry. Z1 is a 5.6V zener that
generates the input bias voltage. Q1 is a buffer to the zener
reference voltage with 5.0V generated at its emitter. Q3 and
Q4 are connected as diodes. Q2 is close to being a diode in
this circuit. This configuration will give about 2.0V at the
collector of Q2. R2 and R3 are a voltage divider, setting the
base of Q5 to about 3.5V. This sets the emitter of Q5 to
about 2.8V, the bias voltage of the video input. This bias
voltage is necessary to assure that the entire video signal
stays within the active operating region of the LM1205/
LM1207. The bias voltage goes through R6, a 20k resistor,
to the video input at pin 6. R4 and R6 are of the same value
or drop below ground. The performance of the
CC
http://www.national.com11

Circuit Description (Continued)
and R4 is used to compensate for beta variations of the
transistors. Note that the bias voltage passes through three
diode drops (Q5, Q6, and Q7) before setting the voltage
across R9. Q2, Q3, and Q4 also provide three diode drops
to the bias voltage at the base of Q5, temperature compensating for the diode drops of Q5, Q6, and Q7. This insures
that the bias voltage across R9 remains very constant over
temperature, providing an accurate bias current for the differential transistor pair Q8 and Q9, thus assuring proper operation of the contrast control.
Q6 serves as a buffer to the input video signal. Its emitter
drives the base of Q7. Thus the video signal modulates the
current flowing through R9, which in turn modulates the currents through the differential pair formed by Q8 and Q9. The
current flow through Q8 and Q9 is controlled by a DC voltage from the Contrast Control circuit. This DC voltage is
common to all three channels. Increasing the voltage to the
base of Q9 with respect to the base of Q8 increases the
current flow through Q9. A higher current flow through Q9
increases the video gain (contrast) of the LM1205/LM1207.
Q10 and Q11 also form a differential pair at the collector of
Q9. The operation of this differential pair is similar to Q8 and
Q9. The DC control voltage is from the Drive Control cir-
cuits. Each channel has its own drive control circuit. Increasing the voltage to the base of Q11 increases the video
gain (drive) of the LM1205/LM1207. R10 and R11 are of
the same value, but R10 is common to both Q10 and Q11. If
all the current is flowing through Q10, the video amplitude
would only be half of the maximum gain (all current flowing
through Q11). This gives the drive control a total gain adjustment range of 6 dB. Since the drive control is only used
to balance the color of each channel a small adjustment
range is desirable. Q12 through Q17 are part of the final
section shown in
stage. The clamp comparator
cap at pin 8 to a voltage that sets the correct black level of
the video signal. This cap is also connected to the base of
Q17. Q17 and Q16 are one half of the darlington differential
pair. The clamp cap voltage establishes the current flow
through R16, Q15, and R15. With the bases of Q14 and
Q15 held to the same voltage the current through Q15 is
mirrored into Q14 and the other half of the differential pair,
Q12 and Q13. By this current mirror the voltage at the collector of Q14 is set to the correct DC value for the video
signal by controlling the voltage drop across R13, completing the DC restoration.
Figure 8
. DC restoration is done at this
(Figure 11)
drives the clamp
FIGURE 8. Simplified Schematic of LM1205/LM1207 Video Amplifier Input Stage
http://www.national.com 12
TL/H/11881– 16

Circuit Description (Continued)
CONTRAST CONTROL
Figure 9
ure 8
is a simplified schematic of the Contrast Control
circuit. The output of this circuit is common to all three channels. A reference voltage is generated by Z2, Q34, Q35,
R30, and R31. Q36, Q39, and Q41 are all current sources
that are controlled by the reference voltage. The contrast
signal has a 0V to 4V range with its input at pin 12. R32 is
used for current limiting any voltage surge that may occur at
pin 12. Note that the input stage (Q37, Q38, and Q42) are
all PNP transistors. This configuration is necessary for operation down to near ground. At Q44 the input voltage is converted to a current by R33. The input stage will apply the
same voltage across R33 as is applied at the input and with
no temperature variations from the transistors. Q37 is connected to a current source (Q36) to keep a constant current
flow through Q37 and a predictable diode voltage for the
base-emitter of Q37. Q40 is connected as a diode and is
biased by the current source Q39. The current through Q40
is mirrored into Q43, giving a current bias for Q42. Again this
is done to give a predictable diode voltage for Q42. Q41 is a
current source for both Q38 and Q42. With the current
through Q42 already established, the rest of the current
from Q41 flows through Q38. As one can see the input voltage is accurately reflected across R33 with no temperature
coefficients from the input stage of the contrast control circuit.
Pin 1 of the contrast control output is held at a constant
voltage two diode drops below (/2V
erence the base of Q51 is held at exactly (/2V
R45 form a voltage divider. With both Q53 and Q54 con-
. To generate this ref-
CC
. R44 and
CC
nected as diodes the voltage at the junction of R44 and R45
is (/2V
plus one diode drop. Q52 is a buffer to this refer-
CC
ence voltage, generating exactly (/2V
used to drive the bases of Q49 and Q50 to one diode drop
at its emitter. Q51 is
CC
below the reference voltage. Q50 is used to further buffer
the reference voltage to the base of Q9 (see
Figure 8
) and
the corresponding transistors in the other channels. Q48 is
used to bias the collector of Q49 to (/2V
age as the collector of Q47 when the differential pair is bal-
, the same volt-
CC
anced. This keeps the characteristics of Q47 and Q49 well
matched. Going back to Q44 and R33; these parts set up a
current source that varies the current through R36. With a
2V contrast voltage the differential pair is balanced, meaning that the voltage drop across R36 is (/2V
the voltage at R36, driving the bases of Q46 and Q47. Q46
further buffers the voltage, driving the base of Q8 (see
. Q45 buffers
CC
Fig-
) and the corresponding transistors in the other two
channels. In the balanced condition the voltage at pin 2 will
also be two diode drops below (/2V
anced drive to the differential pair consisting of Q8 and Q9
, giving a well bal-
CC
in the video amplifier input stage. With the contrast voltage
set to 0V, the voltage at pin 2 will increase by about 400 mV
to 500 mV. A 4V contrast voltage decreases the voltage at
pin 2 by about 400 mV to 500 mV from the balanced condition. Reviewing
Figure 8
note that decreasing the voltage at
pin 2 will decrease the current flow through Q8. Thus the
current flow through Q9 increases, increasing the gain of
the LM1205/LM1207. So increasing the contrast control
voltage at pin 12 increases the gain of the LM1205/
LM1207. The contrast control voltage from Q46 and Q50 is
common to all three channels. To minimize crosstalk it is
necessary to add a decoupling capacitor of 0.1 mF across
R37 and R40. Since this can only be done externally, these
two nodes are brought out to pins 1 and 2. The 30X resistor
is added in series with the capacitor for improving stability.
To prevent a destructive current surge due to shorting either
pins 1 or 2 to ground R38 was added for current limiting.
DRIVE CONTROL
Figure 10
is a simplified schematic of the Drive Control circuit. Each channel has its own drive control circuit. This
circuit is almost identical to
Figure 9
, the contrast control
circuit. It will be easier to cover the differences between the
two circuits instead of going through virtually the same circuit description. Note that the input stage is exactly the
same. The generation of the reference voltage at the right
hand side of
Figure 9
the base of Q72 is to be )/3V
circuit the reference voltage at the base of Q51 was to be
(/2V
voltage divider. With the two to one ratio it is now necessary
Figure 10
is slightly different than the circuit in
. ln the drive control circuit the reference voltage at
. In the contrast control
CC
. To generate the )/3VCCR57andR58forma2to1
CC
to have three transistors connected as diodes, which are
Q74, Q75, and Q76. Q73 is the buffer for this voltage divider
and its emitter is exactly )/3V
sation. R52 and R53 also differ from their corresponding
resistors in
Figure 9
, R36 and R39. The value difference is
so the base of Q66 is also at )/3V
voltage is at 2V. R38 in
with temperature compen-
CC
when the input drive
CC
Figure 9
was needed for current
limiting at the output pins. Since each channel has its own
drive control circuit no filtering is required, eliminating the
need for external pins. With no external pins no current limiting is necessary, thus the 1k resistor is not used in the drive
control circuit.
http://www.national.com13

Circuit Description (Continued)
FIGURE 9. Simplified Schematic of LM1205/LM1207 Contrast Control
FIGURE 10. Simplified Schematic of LM1205/LM1207 Drive Control
TL/H/11881– 17
TL/H/11881– 18
http://www.national.com 14

Circuit Description (Continued)
CLAMP COMPARATOR CIRCUIT
Figure 11
circuit. Q85 and its input transistors, Q81 and Q82 are one
half of the differential pair. The base of Q81 is connected to
pin 19 via R62. This is the positive input to the comparator.
Q88 and its input transistors, Q90 and Q91 are the other
half of the differential pair. The base of Q92 is connected to
the junction of R19 and R20 in
negative input to the comparator. R73 is included only to
match the input characteristics of the positive input, which
requires the 100X resistor. The negative comparator input is
the feedback from the output stage as briefly described in
the block diagram and covered in more detail in the output
stage circuit description. Q86 is the current source for the
differential pair. It is turned on and off by the output of the
clamp gate circuit
cuit has a current flow of about 225 mA when it is turned on.
This current is mirrored into Q86. Assume that the inputs to
the comparator are equal, making the differential pair balanced. ln this condition Q85 and Q88 each have a current
flow of 113 mA. Looking at the Q85 side of the circuit, Q84
will also have 113 mA of current flow. Q80 is set up as a
current mirror to Q84, but its emitter resistor is one fourth
the emitter resistance of Q84. Thus the current flow for Q80
is four times the current flow thru Q84, or 450 mA. Q83 has
been added to help drive the base of Q80, increasing the
accuracy of the current mirror. The collector of Q80 directly
charges the capacitor as a current source of 450 mA. R65 is
added to discharge the charge stored in the bases of Q80
and Q84. This is necessary to quickly turn off the current
charge of the clamp capacitor as the comparator section is
turned off. Q87, Q89, and Q90 work in exactly the same
way. However, the collector of Q91 drives another current
mirror with the 450 mA. This current flows thru Q78. Q77 is a
current mirror with Q78, thus 450 mA also flows thru Q77.
Q79 has been added to help drive the base of Q77, again
adding to the accuracy of the current mirror. Since Q77 is on
the ground side of the circuit it discharges the clamp
is a simplified schematic of the clamp comparator
(Figure 12)
Figure 14
. Q102 of the clamp gate cir-
via R73. This is the
capacitor with 450 mA. ln this balanced condition the charge
and discharge current are equal, thus the voltage across the
clamp capacitor remains unchanged.
Going back to the input stages, note that both inputs, Q81
and Q92, are driven by a 50 mA current source. This keeps
both transistors turned on even when the differential pair,
Q85 and Q88, is turned off. Q82 and Q90 are added to help
drive the bases of Q85 and Q88 respectively. R64 and R72
are added to help discharge the charge stored in the bases
of Q85 and Q88 as these two transistors are turned off.
Since the input stage remains active the differential pair is
quickly turned off. The comparator can also be more quickly
turned on with the input stages remaining active. R67 is
used to assure that the potential difference across the differential pair is minimal during turnoff. Without R67 there
could be a little extra charge or discharge of the clamp capacitor during turnoff, creating an error in the black level of
the video signal. Now assume that the input to pin 19 is
slightly higher than the reference voltage to the negative
input of the comparator. The voltage at the base of Q85 is
now higher than the base of Q88. This creates an increased
current flow thru Q85 and an equal decrease of current flow
thru Q88. This current change is multiplied by four in the
increase of current flow thru Q80. Likewise the current flow
thru Q77 and Q91 is decreased by four times the current
change in Q88. ln the extreme case the current flow thru
Q80 can increase to 900 mA and there would be no current
flow thru Q77. Q80 does charge the clamp capacitor, thus
the voltage across the capacitor will increase. The above is
all reversed when the input to Q92 rises above the input
level of Q81. If the base of Q86, the current source to the
differential pair, is forced close to ground, then there is no
current flow thru Q86 and the differential pair, Q85 and Q88.
With the current flow thru the differential pair set the zero,
all the current mirrors would also have no current flow. Thus
the voltage on the camp capacitor would remain constant,
the desired result during active video.
http://www.national.com15

Circuit Description (Continued)
FIGURE 11. Simplified Schematic of LM1205/LM1207 Clamp Comparator Circuit
CLAMP GATE CIRCUIT
Figure 12
cuit. A voltage reference is setup by Z3 and by Q104 and
Q105 connected as diodes, generating a 7V base drive to
Q94, Q99 and Q101. Q94 is used to bias the input stage.
This stage is designed to accept TTL levels at pin 14. Q95
and Q97 form a differential pair. The base of Q97 is set to
2.1V by Q99 driving the voltage divider formed by R77 and
R78. In a balanced condition the base of Q95 is also at
2.1V. Q96 is connected as a diode and the current flow thru
it is mirrored into Q98. Also the input to pin 14 would be one
diode drop below 2.1V, or around 1.4V. R74 is added to the
http://www.national.com 16
is a simplified schematic of the Clamp Gate cir-
TL/H/11881– 19
input for current limiting during any possible voltage surge at
pin 14. With no resistors at the emitters of Q96 and Q98 this
circuit will quickly switch. Below 1.4V (1.2V typical) Q95 is
turned on and Q97 is turned off. Above 1.4V (1.6V typical)
Q97 is turned on and Q95 is turned off. With Q97 turned on
Q100 is also turned on. This pulls the current thru R79 to
ground, turning off Q102 and Q103. Remember Q102 is a
current mirror to Q86 in the clamp comparator. With Q102
turned off, the clamp comparator is also turned off. When
the input signal goes below 1.2V, Q97 and Q100 will be
turned off. This allows Q102 to turn on, turning on the clamp

Circuit Description (Continued)
comparators of the three video channels. Q103 is added to
help drive the base of Q86 in the clamp comparator, increasing the accuracy of the current mirror. Q101 drives
R79 and R80. This sets the current thru Q102, thus setting
the current thru Q86 of the clamp comparator.
BLANK GATE CIRCUIT
Figure 13
With the exception of the simple output stage and the spot
killer circuit, this circuit is almost identical to the clamp gate
circuit. The only difference is that the output stage is driven
from the opposite side of the differential pair. Thus Q111 is
connected as a diode instead of Q109. With the input at pin
13 at a low level Q108 is turned on, also turning on Q29, the
output transistor. Q29 is part of the blanking circuit in the
output stage shown in
output is clamped to a blanking level that is ‘‘blacker than
black’’, allowing blanking to be done on the cathodes of the
CRT.
The spot killer circuit is used to force the outputs of the
LM1205/LM1207 into blanking when the V
10.6V. Forcing the outputs to a blacker-than-black level will
is a simplified schematic of the Blank Gate circuit.
Figure 14
. When Q29 is turned on the
drops below
CC
drive the cathode driver stage well above the black level,
cutting off the beam current in the CRT. This prevents the
bright spot from occurring when the monitor is turned off,
preserving the phosphor of the CRT. The CRT will also have
its beam current cut off during the time the monitor is first
turned on. This is not a critical period for the CRT since the
filaments have not warmed up to generate a current flow.
The comparator along with R89, R90, and Q115 all form the
spot killer circuit. Q115 acts the same as Q106. When Q115
has a high signal at its base it is turned off and the outputs
of the LM1205/LM1207 are in the normal operating mode.
A low signal at the base of Q115 turns on this transistor,
blanking the outputs of the LM1205/LM1207. Q115 is driven by the output of the comparator. The inverting input of
the comparator is connected to an internal 1.2V reference.
The non-inverting side is connected to a resistor divider network, R89 and R90. When V
verting input is above the 1.2V reference, therefore the out-
is above 10.6V the non-in-
CC
put of the comparator is high. This high output turns off
Q115. Once the V
output goes low, turning on Q115 which forces the outputs
drops below 10.6V the comparator’s
CC
into the blanking mode.
FIGURE 12. Simplified Schematic of LM1205/LM1207 Clamp Gate Circuit
TL/H/11881– 20
http://www.national.com17

Circuit Description (Continued)
FIGURE 13. Simplified Schematic of LM1205/LM1207 Blank Gate Circuit
VIDEO AMPLIFIER OUTPUT STAGE WITH BLANK
CIRCUIT
Figure 14
Output Stage including the blanking circuit. Q18 serves as a
buffer between the DC restoration stage shown in
and the output stage. A current source is used to fix the
current flow thru Q18 keeping it well within its operating
range. The emitter of Q18 drives the bases of Q19 and Q24
with the current thru Q24 being twice that of Q19. Q19,
along with Q20 thru Q23 duplicate the actual output stage
going to pin 20. Q19 inverts the video signal (note that the
video signal was inverted at Q7 in
nal inversions of the video signal in the LM1205/LM1207,
the output is non-inverted. The collector of Q19 gives a gain
of
through Q23 are all connected as diodes with the emitter of
Q23 driving R19 and R20. The junction of R19 and R20 is
connected to the base of Q92 via R73 (shown in
this being the feedback to the negative input of the clamp
comparator. This stage is independent of the actual output
stage at pin 20, but is where the feedback is done for DC
restoration. Therefore it is possible to blank the actual output stage below the black level without affecting the DC
restoration feedback loop. Q24 is the equivalent part of Q19
in the actual output stage. It also inverts the video signal
with a gain of
Q32 each give a diode drop to the level of the video signal,
similar to being connected as diodes. Being connected as
is a simplified schematic of the Video Amplifier
Figure 8
Figure 8
). With two inter-
b
10 to the video signal and drives the base of Q20. Q21
Figure 11
b
10 and drives the base of Q30. Q30 thru
emitter-followers these transistors also give current gain to
the signal. Q33 comes close to also giving a diode drop to
the signal, the voltage drop across R27 being insignificant.
R27 has been added to give some isolation between Q33
and the internal circuits of the LM1205/LM1207, adding to
the stability of the device. Q33 also has R29 in its emitter for
isolation from capacitive loads and current limiting from any
possible voltage surges. R28 is at the collector of Q33 is
also for current limiting from voltage surges and minimizing
crosstalk between the three channels through the V
To match the loading of the feedback section the output at
pin 20 should have a load of 390X. To minimize power consumption the feedback section uses resistor values 10
times larger than those at pin 20. The current source at the
emitter of Q33 provides for the capability to set the black
level as low as 0.5V.
The video signal does go thru a number of diode drops at
the output stage. One may be concerned that the tracking
),
over temperature could be a problem. The feedback section
has been designed to temperature track the output stage.
The feedback for DC restoration eliminates the temperature
coefficients of the diode junctions. The remaining section to
be covered is the blanking section. This section comprises
of Q25 thru Q29. Q26 thru Q28 are connected as diodes.
Q25 provides current gain to this stage to adequately pull
down the base of Q30 during blanking and also adding another diode potential. During blanking the base of Q30 will
be four diode drops above ground, plus the saturation volt-
TL/H/11881– 21
line.
CC
http://www.national.com 18

Circuit Description (Continued)
age of Q29. There are also four diode drops from the base
of Q30 to the output, pin 20. Therefore during blanking pin
20 will be less than 100 mV above ground, enabling the
designer to blank at the cathode of the CRT. R23 is added
to quickly turn off Q25 by discharging its base when the
blanking signal is removed.
Figure 14
LM1205/LM1207. All the V
internally connected together. A 0.1 mF bypass capacitor
must be located close to each pin and connected to ground.
Further bypassing is done by a 100 mF capacitor. This capacitor needs to be located on the board close to the
LM1205/LM1207. Pins 22 and 23 are the V
10 mF and a 0.1 mF bypass capacitors must be located
close to pins 22 and 23. Correct bypassing of pins 22 and
23 is very important. If the bypassing is not adequate then
the outputs of the LM1205/LM1207 will have ringing, or
even worse they may oscillate. The ground side of the bypass capacitors at pins 22 and 23 must be returned to a
ground plane with no interruptions from other traces between these capacitors and the ground pins 21 and 24 of
the LM1205/LM1207.
also shows the power and ground pins to the
pins (pins 3, 11, 25) are all
CC1
CC2
pins. A
Applications of the LM1205/
LM1207
Figure
15 is the schematic of the demonstration board designed at National.
onstration board. Note that the schematic shown in
Figure 16
is the actual layout of the dem-
Figure 15
ure 4
that in
for both drive and cutoff, making this circuit a good design
for monitor applications. Each CRT will have a slightly different cutoff voltage for each color, making it necessary to
provide separate adjustments in order to accurately set the
cutoff for each color. The gain of each color of the CRT is
also slightly different; if the color temperature of the display
is to be accurately set then each channel of the LM1205/
LM1207 must have individual gain adjustments. Thus each
channel has its own drive control. Once the drive control is
set, the gain between the three color channels will closely
track as the contrast is adjusted. All the jumpers needed to
design a single sided PC board are shown in the schematic.
The resistors and jumpers with no reference designation are
the connections between the PC board and the connectors
mounted on the PC board. CN1 thru CN8 are BNC connectors.
A30Xresistor is in series with each of the video inputs. A
voltage surge may occur at these inputs when either the
inputs are first connected to another system, or when the
system is powered up before the monitor is turned on. If this
voltage surge exceeds the supply voltage (at ground potential if the monitor is not powered up) of the LM1205/
LM1207, or goes below ground, current will flow through the
parasitic devices of the LM1205/LM1207. This current is
limited by the 30X resistors, preventing a potential catastrophic failure. A 100X resistor is added to the Blank Gate
is almost identical to the schematic shown in
. The only difference between the two schematics is
Figure 15
each channel has individual adjustments
Fig-
FIGURE 14. Simplified Schematic of LM1205/LM1207 Video Amplifier Output Stage with Blank Circuit
http://www.national.com19
TL/H/11881– 22

Applications of the LM1205/LM1207 (Continued)
and Clamp Gate inputs. These two resistors also limit the
current during a voltage surge. A larger resistor is required
because these inputs are DC coupled, allowing the current
to continuously flow into these inputs before the monitor is
turned on. 100X resistors are not recommended at the video inputs because this resistance value will start to roll off
the frequency response of the LM1205/LM1207.
Note that the layout shown in
extensive ground plane. One must remember that the
LM1205/LM1207 is a 130 MHz/85 MHz part and a single
sided board is difficult to successfully design. A ground
plane similar to the layout shown in
vided for good performance of the LM1205/LM1207 when
using either a single sided or double sided board. The layout
of this board demonstrates the importance of grounding.
The results of this layout are shown in
17d
. In these photographs the LM1205 rise time was 2.25
ns and its fall time was 3.00 ns. For the LM1207, the rise
time was 4.10 ns and the fall time 3.85 ns. The output was a
4V
signal and the cutoff voltage was set to 2V. The
PP
Figure 16
Figure 16
does have a very
must be pro-
Figures 17a
through
overshoot will subsequently be filtered out by the loading
effects of the CRT driver stage and the CRT itself. When the
LM1205/LM1207 is designed into a video board one must
keep the ground to the CRT driver stage separate from the
ground of the LM1205/LM1207, connecting the two
grounds together only at one point. National Semiconductor
also manufactures a line of CRT drivers. Please contact National for additional information. These drivers greatly simplify the driver design allowing for shorter design cycles. Of
course the LM1205/LM1207 can also be designed with a
discrete driver stage.
ple cascode CRT driver. The LM1205/LM1207 block would
be the same schematic as shown in
REFERENCES
Zahid Rahim, ‘‘Guide to CRT Video Design,’’ Application
Note 861, National Semiconductor Corp., Jan. 1993
Ott, Henry W.
Systems,
Figure 18
shows a design using a sim-
Figure 15
Noise Reduction Techniques in Electronic
John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1976
.
FIGURE 15. Demonstration Board Schematic
http://www.national.com 20
TL/H/11881– 23

Applications of the LM1205/LM1207 (Continued)
FIGURE 16. Demonstration Board Layout
TL/H/11881– 24
http://www.national.com21

Applications of the LM1205/LM1207 (Continued)
FIGURE 17a. LM1205 Rise Time
FIGURE 17c. LM1207 Rise Time
TL/H/11881– 25
TL/H/11881– 27
FIGURE 17b. LM1205 Fall Time
TL/H/11881– 26
TL/H/11881– 28
FIGURE 17d. LM1207 Fall Time
FIGURE 18. LM1205/LM1207 Typical Application
http://www.national.com 22
TL/H/11881– 29

http://www.national.com23

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
Order Number LM1205N or LM1207N
NS Package Number N28B
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT OF NATIONAL
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or 2. A critical component is any component of a life
LM1205/LM1207 130 MHz/85 MHz RGB Video Amplifier System with Blanking
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant support device or system whose failure to perform can
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and whose be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life
failure to perform, when properly used in accordance support device or system, or to affect its safety or
with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can effectiveness.
be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury
to the user.
National Semiconductor National Semiconductor National Semiconductor National Semiconductor
Corporation Europe Hong Kong Ltd. Japan Ltd.
1111 West Bardin Road Fax:
Arlington, TX 76017 Email: europe.support@nsc.com Ocean Centre, 5 Canton Rd. Fax: 81-043-299-2408
Tel: 1(800) 272-9959 Deutsch Tel:
Fax: 1(800) 737-7018 English Tel:
http://www.national.com
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
Fran3ais Tel:
Italiano Tel:a49 (0) 180-534 16 80 Fax: (852) 2736-9960
a
49 (0) 180-530 85 86 13th Floor, Straight Block, Tel: 81-043-299-2308
a
49 (0) 180-530 85 85 Tsimshatsui, Kowloon
a
49 (0) 180-532 78 32 Hong Kong
a
49 (0) 180-532 93 58 Tel: (852) 2737-1600
 Loading...
Loading...