NSC JM38510R76506SR, JM38510R76506S2, JM38510R76506BS Datasheet
54AC299•54ACT299
8-Input Universal Shift/Storage Register with Common
Parallel I/O Pins
General Description
The ’AC/’ACT299 is an 8-bit universal shift/storage register
with TRI-STATE
®
outputs. Four modes of operation are possible: hold (store), shiftleft,shiftrightand load data. The parallel load inputs and flip-flop outputs are multiplexed to reduce the total number of package pins. Additional outputs
are provided for flip-flops Q
0,Q7
to allow easy serial cascading.A separate active LOW Master Reset is used to reset the
register.
Features
n ICCand IOZreduced by 50
%
n Common parallel I/O for reduced pin count
n Additional serial inputs and outputs for expansion
n Four operating modes: shift left, shift right, load and
store
n TRI-STATE outputs for bus-oriented applications
n Outputs source/sink 24 mA
n ’ACT299 has TTL-compatible inputs
n Standard Microcircuit Drawing (SMD)
’AC299: 5962-88754
’ACT299: 5962-88771
Ordering Code:
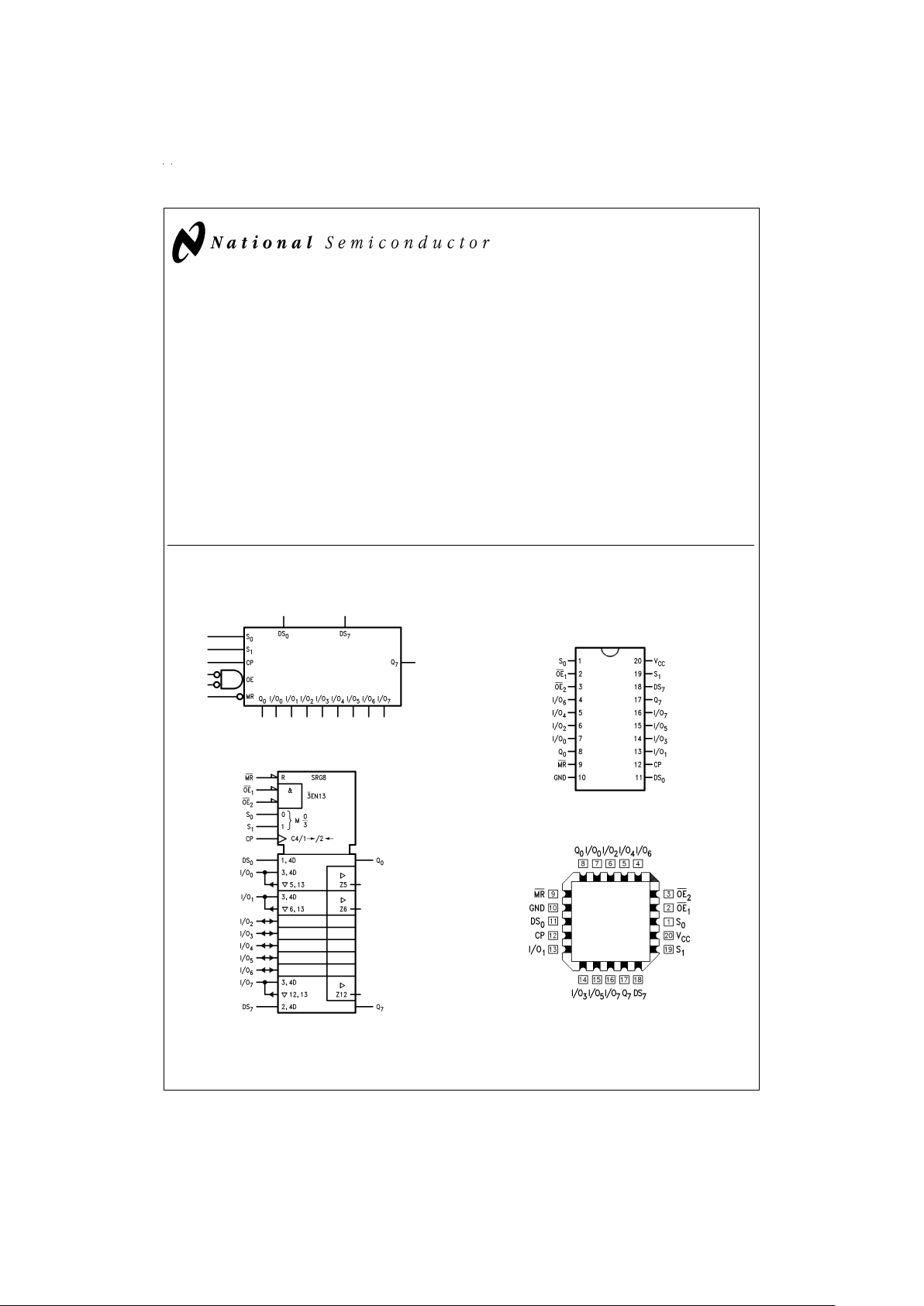
Logic Symbols Connection Diagrams
TRI-STATE®is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
FACT
®
is a registered trademark of Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation.
DS100252-1
IEEE/IEC
DS100252-4
Pin Assignment
for DIP and Flatpak
DS100252-2
Pin Assignment for LCC
DS100252-3
September 1998
54ACC299
•
54ACT299 8-Input Universal Shift/Storage Register with Common Parallel I/O Pins
© 1998 National Semiconductor Corporation DS100252 www.national.com
Connection Diagrams (Continued)
Pin Names Description
CP Clock Pulse Input
DS
0
Serial Data Input for Right Shift
DS
7
Serial Data Input for Left Shift
S
0,S1
Mode Select Inputs
MR
Asynchronous Master Reset
OE
1
,OE
2
TRI-STATE Output Enable Inputs
I/O
0
–I/O
7
Parallel Data Inputs or
TRI-STATE Parallel Outputs
Q
0,Q7
Serial Outputs
Functional Description
The ’AC/’ACT299 contains eight edge-triggered D-type
flip-flops and the interstage logic necessary to perform synchronous shift left, shift right, parallel load and hold operations. The type of operation is determined by S
0
and S1,as
shown in the Truth Table. All flip-flop outputs are brought out
through TRI-STATE buffers to separate I/O pins that also
serve as data inputs in the parallel load mode. Q
0
and Q7are
also brought out on other pins for expansion in serial shifting
of longer words.
ALOW signal on MR overrides the Select and CP inputs and
resets the flip-flops. All other state changes are initiated by
the rising edge of the clock. Inputs can change when the
clock is in either state provided only that the recommended
setup and hold times, relative to the rising edge of CP, are
observed.
AHIGH signal on either OE
1
or OE2disables the TRI-STATE
buffers and puts the I/O pins in the high impedance state. In
this condition the shift, hold, load and reset operations can
still occur. The TRI-STATEbuffers are also disabled by HIGH
signals on both S
0
and S1in preparation for a parallel load
operation.
Truth Table
Inputs Response
MR
S1S0CP
L X X X Asynchronous Reset;
Q
0–Q7
=
LOW
HHH
N
Parallel Load; I/O
n
→
Q
n
HLH
N
Shift Right; DS
0
→
Q
0
,
Q
0
→
Q
1
, etc.
HHL
N
Shift Left, DS
7
→
Q
7
,
Q
7
→
Q
6
, etc.
H L L X Hold
H=HIGH Voltage Level
L=LOW Voltage Level
X=Immaterial
N
=
LOW-to-HIGH Transition
www.national.com 2
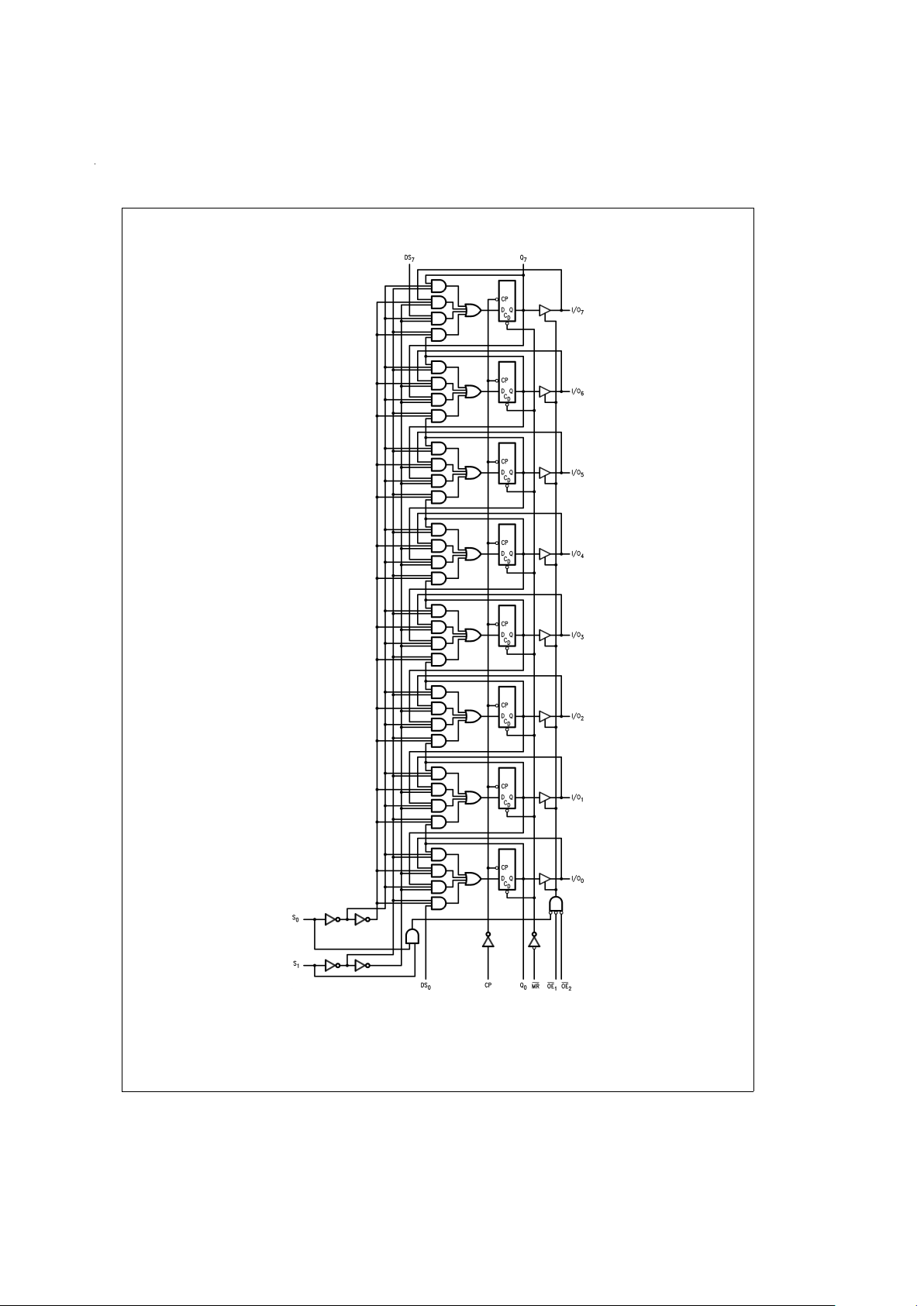
Logic Diagram
DS100252-5
Please note that this diagram is provided only for the understanding of logic operations and should not be used to estimate propagation delays.
www.national.com3
 Loading...
Loading...