Page 1
Novell®
www.novell.com
Novell Cluster ServicesTM Conversion Guide
Open Enterprise Server
2 SP3
December 22, 2010
AUTHORIZED DOCUMENTATION
Page 2

Legal Notices
Novell, Inc., makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents or use of this documentation, and
specifically disclaims any express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose.
Further, Novell, Inc., reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes to its content, at any time,
without obligation to notify any person or entity of such revisions or changes.
Further, Novell, Inc., makes no representations or warranties with respec t to any sof tware, a nd sp ecific ally disc laims
any express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Further, Novell, Inc.,
reserves the right to make changes to any and all parts of Novell software, at any time, without any obligation to
notify any person or entity of such changes.
Any products or technical information provided under this Agreement may be subject to U.S. export contr ols and the
trade laws of other countries. You agree to comply with all export control regulations and to obtain any required
licenses or classification to export, re-export or import deliverables. You agree not to export or re-export to entities on
the current U.S. export exclusion lists or to any embargoed or terrorist countries as specified in the U.S. export laws.
You agree to not use deliverables for prohibited nuclear, missile, or chemical biological weaponry end uses. See the
Novell International Trade Services Web page (http://www.novell.com/info/exports/) for more information on
exporting Novell software. Novell assumes no responsibility for your failure to obtain any necessary export
approvals.
Copyright © 2010 Novell, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, photocopied,
stored on a retrieval system, or transmitted without the express written consent of the publisher.
Novell, Inc.
404 Wyman Street, Suite 500
Waltham, MA 02451
U.S.A.
www.novell.com
Online Documentation: To access the latest online documentation for this and other Novell products, see
the Novell Documentation Web page (http://www.novell.com/documentation).
Novell Trademarks
For Novell trademarks, see the Novell Trademark and Service Mark list (http://www.novell.com/company/legal/
trademarks/tmlist.html).
Third-Party Materials
All third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Page 3

Contents
About This Guide 7
1 Planning the Cluster Conversion 9
1.1 Supported Conversion Paths. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.2 Supported Mixed-Node Clusters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.3 SBD Devices Must Be Marked as Shareable for Clustering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.4 Syntax Translation Issues for Load and Unload Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.5 Case Sensitivity Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.6 Adding a New NetWare Node to a Mixed-Node Cluster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.7 Converting Multiple NetWare Cluster Nodes to OES 2 Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.8 Converting Nodes that Contain the eDirectory Master Replica . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.9 Failing Over Service Cluster Resources on Mixed-Node Clusters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.10 Failing Over Data Cluster Resources on Mixed-Node Clusters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.11 Managing File Systems in Mixed-Node Clusters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.12 Using Novell iManager in Mixed-Node Clusters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
1.13 Using Novell Remote Manager Is Not Supported in Mixed-Node Clusters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
1.14 Using ConsoleOne Is Not Supported for Mixed-Node Clusters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
1.15 Using the Monitoring Function in Mixed-Node Clusters Is Not Supported. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2 Planning the Conversion of Cluster Resources 15
3 Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts 19
3.1 Translation of Cluster Resource Scripts for Mixed NetWare and Linux Clusters. . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.2 Comparing Script Length Limits for NetWare and Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.3 Comparing Script Commands for NetWare and Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.4 Comparing Master IP Address Scripts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.4.1 Master IP Address Resource Load Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.4.2 Master IP Address Resource Unload Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.5 Comparing NSS Pool Resource Scripts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.5.1 NSS Pool Resource Load Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.5.2 NSS Pool Resource Unload Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.6 Comparing File Access Protocol Resource Script Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.6.1 File Access Protocol Resource Load Scripts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.6.2 File Access Protocol Resource Unload Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.7 Customizing the Translation Syntax for Converting Load and Unload Scripts. . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.8 Adding Monitoring Scripts on Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
4 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux 27
4.1 Converting NetWare Cluster Nodes to OES 2 Linux (Rolling Cluster Conversion) . . . . . . . . . 27
4.2 Adding New OES 2 Linux Nodes to Your NetWare Cluster. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
4.3 Finalizing the Cluster Conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Contents 3
Page 4

5Novell AFP 35
6 Apache Web Server 37
6.1 Prerequisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
6.2 Converting the Apache Cluster Resource . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
6.3 Additional Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
6.3.1 Apache 2 Manual. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
6.3.2 Virtual Hosts Support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
7 Novell Archive and Version Services 41
7.1 Prerequisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
7.2 Copying Database Files from MySQL to PostgreSQL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
8 eDirectory Server Certificates 43
8.1 Server Certificate Changes in OES 2 Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
8.2 Using Internal Certificates in a Cluster. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
8.3 Using External Certificates i n a Cl u s ter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9Novell CIFS 45
10 Novell Distributed File Services VLDB 47
10.1 Cluster Migrating the Shared NSS Volume for the VLDB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
10.2 Adding a Linux Server as a Replica Site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
11 DHCP Server 51
11.1 Setting Up Novell DHCP on OES 2 Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
11.2 Prerequisites for Migration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
11.3 Migrating the DHCP Configuration from NetWare to Linux Clusters in the Same Tree. . . . . . 51
11.4 Post-Migration Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
12 DNS Server 53
12.1 Prerequisites for Migration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
12.2 Migrating the DNS Configuration from NetWare to Linux Clusters in the Same Tree . . . . . . . 53
12.3 Post-Migration Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
13 Novell iPrint 55
13.1 Installing iPrint on the OES 2 Linux Nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
13.2 Setting Up iPrint on the OES 2 Linux Nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
13.2.1 Preparing the OES 2 Linux Nodes for iPrint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
13.2.2 Setting Up iPrint on the OES 2 Linux iPrint Cluster Resource. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
13.2.3 Setting Up Preferred Nodes for the OES 2 Linux iPrint Cluster Resource . . . . . . . . 57
13.2.4 Editing the Load and Unload Scripts for the OES 2 Linux iPrint Cluster Resource . . 57
13.2.5 Verifying the Status of the iPrint Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
13.3 Migrating the iPrint Cluster Resource from NetWare to OES 2 Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
13.4 Finalizing the Cluster Conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
13.5 Additional Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
4 OES 2 SP3: Novell Cluster Services Conversion Guide
Page 5

14 MySQL 61
15 QuickFinder Server 63
15.1 Prerequisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
15.2 Setting Up QuickFinder Server on Linux Cluster Nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
15.3 Migrating QuickFinder Data from NetWare to Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
15.4 Post-Migration Considerations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
15.5 Searching the Cluster Volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
16 Novell St orage Services Pools 67
16.1 NSS Pool Cluster Migration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
16.2 NSS File System Migration to NCP Volumes or Linux POSIX File Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
16.3 Estimated Time Taken to Build the Trustee File on Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
A Documentation Updates 69
A.1 December 2010 (OES 2 SP3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
A.1.1 Apache Web Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
A.1.2 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
A.1.3 Novell Distributed File Services VLDB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
A.1.4 Planning the Cluster Conversion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
A.1.5 Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
A.2 May 31, 2010 (Maintenance Patch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
A.2.1 Novell AFP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
A.2.2 Novell CIFS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
A.3 January 29, 2010 (Maintenance Patch). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
A.3.1 Planning the Cluster Conversion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
A.3.2 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
A.4 January 20, 2010 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
A.4.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
A.5 January 4, 2010 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
A.5.1 eDirectory Server Certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
A.6 December 10, 2009 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
A.6.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
A.7 November 2009 (OES 2 SP2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
A.7.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
A.7.2 Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
A.8 July 30, 2009 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
A.8.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
A.8.2 Planning the Cluster Conversion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
A.9 June 22, 2009 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
A.9.1 Planning the Cluster Conversion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
A.10 June 5, 2009 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
A.10.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
A.10.2 Novell Storage Services Pools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
A.11 May 6, 2009 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
A.11.1 Planning the Cluster Conversion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
A.12 March 3, 2009 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
A.12.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
A.13 February 13, 2009 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
A.13.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
A.13.2 Novell Storage Services Pools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
A.13.3 Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Contents 5
Page 6

A.14 February 3, 2009 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
A.14.1 Novell AFP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
A.15 December 2008 (OES 2 SP1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
A.15.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Cluster to OES 2 Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
A.15.2 Planning the Cluster Conversion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
A.15.3 Planning the Conversion of Cluster Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
A.15.4 Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
6 OES 2 SP3: Novell Cluster Services Conversion Guide
Page 7

About This Guide
This guide describes how to convert Novell Cluster Services cluster nodes and resources from
NetWare 6.5 Support Pack (SP) 8 (with the latest patches) to Novell Open Enterprise Server (OES)
2 SP3.
This guide includes the following sections:
Chapter 1, “Planning the Cluster Conversion,” on page 9
Chapter 2, “Planning the Conversion of Cluster Resources,” on page 15
Chapter 3, “Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts,” on page 19
Chapter 4, “Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux,” on page 27
Chapter 5, “Novell AFP,” on page 35
Chapter 6, “Apache Web Server,” on page 37
Chapter 7, “Novell Archive and Version Services,” on page 41
Chapter 8, “eDirectory Server Certificates,” on page 43
Chapter 9, “Novell CIFS,” on page 45
Chapter 10, “Novell Distributed File Services VLDB,” on page 47
Chapter 11, “DHCP Server,” on page 51
Chapter 12, “DNS Server,” on page 53
Chapter 13, “Novell iPrint,” on page 55
Chapter 14, “MySQL,” on page 61
Chapter 15, “QuickFinder Server,” on page 63
Chapter 16, “Novell Storage Services Pools,” on page 67
Appendix A, “Documentation Updates,” on page 69
Audience
This guide is intended for Novell Cluster Services administrators and other administrators that are
responsible for clustered services and data. It is assumed that readers of this guide have a basic
understanding of Novell Cluster Services and of the services and file systems that are being
clustered.
Feedback
We want to hear your comments and suggestions about this manual and the other documentation
included with this product. Please use the User Comments feature at the bottom of each page of the
online documentation, or go to www.novell.com/documentation/feedback.html and enter your
comments there.
Documentation Updates
For the most recent version of the OES 2 SP3: Novell Cluster Services Conversion Guide, visit the
OES 2 SP3 documentation Web site (http://www.novell.com/documentation/oes2).
About This Guide 7
Page 8

Additional Documentation
For documentation on Novell Cluster Services and cluster resources management, see the OES 2
SP3 Clustering (High Availability) documentation Web site (http://www.novell.com/
documentation/oes2/cluster-services.html).
For information about managing a NetWare cluster, see the “Clustering NetWare Services” list on
the NetWare 6.5 SP8 Clustering (High Availability) documentation Web site (http://
www .novell.com/documentation/nw65/cluster-services.html#clust-config-resources).
8 OES 2 SP3: Novell Cluster Services Conversion Guide
Page 9

1
Planning the Cluster Conversion
Upgrading a NetWare 6.5 SP8 cluster to Novell Open Enterprise Server 2 SP3 Linux is a multiphase process referred to as a rolling cluster conversion. This approach lets you keep your cluster up
and running and lets your users continue to access cluster resources while the conversion is in
progress. During a rolling cluster conversion, one server is converted to OES 2 while the other
servers in the cluster continue running NetW are 6.5. Then another server can be converted to OES 2,
and then another , until a ll servers in the cluster have been converted. During the conversion, you can
also add OES 2 servers to the cluster, and remove NetWare 6.5 servers from the cluster.
Before you begin a conversion, make sure your system meets the requirements and caveats
described in this section. In addition, your OES 2 Linux nodes and network environment must meet
the cluster requirements as described in “Planning for Novell Cluster Services” in the OES 2 SP3 :
Novell Cluster Services 1.8.8 Administration Guide for Linux.
Section 1.1, “Supported Conversion Paths,” on page 9
Section 1.2, “Supported Mixed-Node Clusters,” on page 10
Section 1.3, “SBD Devices Must Be Marked as Shareable for Clustering ,” on pa ge 10
Section 1.4, “Syntax Translation Issues for Load and Unload Scripts,” on page 10
Section 1.5, “Case Sensitivity Issues,” on page 11
1
Section 1.6, “Adding a New NetWare Node to a Mixed-Node Cluster,” on page 11
Section 1.7, “Converting Multiple NetWare Cluster Nodes to OES 2 Linux,” on page 11
Section 1.8, “Converting Nodes that Contain the eDirectory Master Replica,” on page 12
Section 1.9, “Failing Over Service Cluster Resources on Mixed-Node Clusters,” on page 12
Section 1.10, “Failing Over Data Cluster Resources on Mixed-Node Clusters,” on page 12
Section 1.11, “Managing File Systems in Mixed-Node Clusters,” on page 12
Section 1.12, “Using Novell iManager in Mixed-Node Clusters,” on page 13
Section 1.13, “Using Novell Remote Manager Is Not Supported in Mixed-Node Clusters,” on
page 13
Section 1.14, “Using ConsoleOne Is Not Supported for Mixed-Node Clusters,” on page 13
Section 1.15, “Using the Monitoring Function in Mixed-Node Clusters Is Not Supported,” on
page 14
1.1 Supported Conversion Paths
The following conversion paths are supported from NetWare to OES 2 Linux:
From this NetWare platform
Interim platform upgrade for all
nodes
Before conversion to this platform
NetWare 6.5 SP8 Latest patches applied OES 2 SP3 Linux
NetWare 6.0 Latest support packs and patches
applied
OES 2 SP3 Linux
Planning the Cluster Conversion
9
Page 10

From this NetWare platform
Interim platform upgrade for all
nodes
Before conversion to this platform
NetWare 5.1 NetWare 6.5 SP8 with the latest
patches applied
Before converting NetWare 6.5 clusters or NetWare 6.0 clusters to OES 2 Linux, you must apply all
of the latest service packs and patches for that version. For information, see “Upgrading NetWare
Clusters” in the NW6.5 SP8: Novell Cluster Services 1.8.5 Administration Guide.
If you have a NetWare 5.1 cluster, you must upgrade all nodes to NetWare 6.5 (with the latest
service packs and patches) before you convert any nodes to OES 2 Linux or add OES 2 Linux nodes
to the cluster. For information, see “U pgrading NetWare Cluste rs” in the NW6.5 SP8: Novell Cluster
Services 1.8.5 Administration Guide.
OES 2 SP3 Linux
1.2 Supported Mixed-Node Clusters
During the conversion, the intermediate cluster is referred to as a mixed-node cluster because the
cluster contains both NetWare and Linux nodes. This is a temporary configuration that is supported
for the purpose of converting the cluster and is not supported as a long-term operational state of the
cluster.
A mixed cluster made up of NetWare 6.5 nodes and OES 2 Linux nodes is supported for the purpose
of converting the cluster from NetWare 6.5 (with the latest support packs and patches) to OES 2 SP3
Linux or later.
A mixed cluster made up of NetWare 6.0 nodes and OES 2 Linux nodes is supported for the purpose
of converting the cluster from NetWare 6.0 (with the latest support packs and patches) to OES 2 SP3
Linux or later.
A mixed cluster made up of NetWare 6.0 nodes, NetWare 6.5 nodes, and OES 2 Linux nodes is not
supported.
1.3 SBD Devices Must Be Marked as Shareable for Clustering
Novell Cluster Services for Linux requires that the devices used for the SBD partition be explicitly
marked as Shareable for Clustering. When converting a NetWare cluster, make sure that the SBD
device, or both devices for a mirrored SBD, are marked as Shareable for Clustering before you add
the first Linux node to the cluster.
1.4 Syntax Translation Issues for Load and Unload Scripts
Executing a script that is valid for the NetWa re p lat form is not ne cessarily reco gnize d on the O ES 2
Linux platform. When cluster migrating a reso urce from a NetWare node to a OES 2 Linux node, the
resource’s Load sc ri pt and Unload script need to be translat ed i n-memory while t he cluster cont ains
mixed nodes. It is also translated in-memory when the cluster is finally converted from NetWare to
Linux. This translation is done by the Cluster Translation Library script (
clstrlib.py
).
/opt/novell/ncs/bin/
10 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 11

IMPORTANT: If the commands in cluster resource’s load or unload scripts are not part of the
normal translation library, the cluster resource can end up in a comatose state.
Beginning in OES 2 SP2, Novell Cluster Services allows you to customize the translation syntax
that is used for load and unload scripts in mixed-node clusters by defining them in the
novell/ncs/customized_translation_syntax
reads the additional translation syntax from the syntax file. For information, see Section 3.7,
“Customizing the Translation Syntax for Converting Load and Unload Scripts,” on page 25.
file that you create. The
clstrlib.py
/var/opt/
script
1.5 Case Sensitivity Issues
When adding a Linux node to the existing NetWare cluster, there are two areas where case
sensitivity might be an issue:
Node name: After you install the Linux node into the NetWare cluster, the Linux node is
unable to join the cluster. T o resolve th is problem, edit the
file to modify the hostname of the node from lowercase (
characters (CLUSNODE1), reboot the server, then run the
This allows the cluster node to start and join the cluster.
NOTE: This case sensitivity issue has been resolved for OES 2 SP2 and later.
Cluster object name: The Cluster object name (such as
cn=Clustername,ou=context,o=org
Clustername.sbd
(
command displays the SBD name. If the case used when you enter the Cluster object name
-f
and SBD name during the Linux cluster install do not match the case used in eDirectory, the
cluster install fails to detect the SBD partition.
) matches the case of the object name in eDirectory. Running the
) is also present on the SBD partition. The SBD name
/etc/opt/novell/ncs/nodename
clusnode1
rcnovell-ncs start
) to all uppercase
command.
sbdutil
1.6 Adding a New NetWare Node to a MixedNode Cluster
You cannot add addi tional NetWare nodes to your cluster afte r adding a new Linux node o r changing
an existing NetW are cluster node to a Linux cluster node. If you want to add NetWare cluster nodes
after converting part of your cluster to Linux, you must first remove the Linux nodes from the
cluster.
1.7 Converting Multiple NetWare Cluster Nodes to OES 2 Linux
If you attempt to concurrently convert multiple NetWare cluster servers to OES 2 Linux, we strongly
recommend that you use the old NetWare node IP addresses for your Linux cluster servers. You
should record the NetWare node IP addresses before converting them to Linux.
If you must assign new node IP addresses, we recommend that you only convert one node at a time.
Planning the Cluster Conversion 11
Page 12

If new cluster node IP addresses are required and new server hardware is being used, another option
is to shut down the NetWare nodes that are to be removed and then add the new Linux cluster nodes.
After adding the new Linux cluster node s, you can remove th e NetWare clu ster node-re lated ob jects
as described in Step 5 of Section 4.1, “Converting NetWare Cluster N od es t o OES 2 Lin ux (Ro lli ng
Cluster Conversion),” on page 27.
IMPORTANT: Failure to follow these recommendations might result in NetWare server abends
and Linux server restarts.
1.8 Converting Nodes that Contain the eDirectory Master Replica
When converting NetWare cluster servers to Linux, do not convert the server that has the master
eDirectory replica first. If the server with the eDirect ory master replica is a cluster node, convert it at
the end of the rolling cluster conversion.
1.9 Failing Over Service Cluster Resources on Mixed-Node Clusters
For service cluster resources, the intention is to have a one-time cluster migration of the service
from NetWare to OES 2 Linux. After you cluster migrate the resource to an OES 2 Linux node, the
relocated resource should be cluster migrated only be tween nodes running the OES 2 Linux
platform.
1.10 Failing Over Data Cluster Resources on Mixed-Node Clusters
Pool cluster resources that were created on NetWare cluster nodes and migrated or failed over to
Linux cluster nodes can be migrated or failed back to NetWare cluster nodes.
Cluster resources that were created on Linux cluster nodes cannot be migrated or failed over to
NetWare cluster nodes.
If you cluster migrate an NSS pool from a NetWare cluster server to a Linux cluster server, it could
take several minutes for volume trustee assign ments to sync hronize after the mig ration. User s might
have limited access to the migrated volumes until after the synchronization process is complete.
1.11 Managing File Systems in Mixed-Node Clusters
In a mixed cluster of NetWare and OES 2 Linux nodes, Linux POSIX file systems as cluster
resources cannot be created until the entire c luster had been su ccessfully converted to OES 2 Linux.
Linux POSIX file systems as cluster resources cannot be migrated or fai led over to NetWare c luster
nodes.
Only NSS pool cluster resources that are created on a NetWare cluster node can be failed over
between Linux and NetWare nodes of a mixed-node cluster.
12 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 13

NetW are-to-Linux failover of NSS pool cluster resources requires that the Linux node be configured
for NSS and that the version of NSS supports the NSS media format and features that are currently
being used by the NSS pool cluster resource on NetWare.
No storage management functions should be executed in a mixed-node cluster unless you are
performing documented steps for the conversion. That is, do not create, delete, expand, o r modify
the properties for partitions, pools, or volumes for shared resources in the cluster unless the
conversion instructions specifically guide you to do so.
WARNING: Attempting to reconfigure shared storage in a mixed cluster can cause data loss.
If you need to configure (or reconfigure) existing shared NSS pools and volumes in a mixed-node
cluster, you must temporarily bring down all Linux cluster nodes prior to making changes, then
make the configuration changes on a NetWare node. Make sure the resources are working properly
on NetWare before having the Linux cluster nodes rejoin the cluster.
1.12 Using Novell iManager in Mixed-Node Clusters
Use Novell iManager 2.7.2 or later for all cluster administrati on in the mixed-node cluster. Using the
Clusters plug-in to iManager is required to manage the cluster after the first OES 2 Linux node is
added to the cluster.
The display of node IDs from the NetWare master node might be incomplete if you use other tools
like ConsoleOne and Novell Remote Manager in a mixe d-node cluster. However, you can use
admin/Novell/Cluster/NodeConfig.xml
on any cluster node to get the node IDs.
cat /
1.13 Using Novell Remote Manager Is Not Supported in Mixed-Node Clusters
Do not use Novell Remote Manager when managing mixe d-no de clu s ters. N ovell Remote Manager
is not supported for cluster management on OES 2 Linu x.
Because different time formats are used in the NCS Event log for NetWare and Linux, Novell
Remote Manager might have difficulty displaying the time of logged events. To avoid this problem
in a mixed-node cluster, use iManager to access the NCS Event log.
To reduce any confusion you might have when using Novell Remote Manager, you can unload
module
in Novell Remote Manager.
pcluster.nlm
and delete its references in
ldncs
and
uldncs
. This removes the Cluster tab
1.14 Using ConsoleOne Is Not Supported for Mixed-Node Clusters
Do not use ConsoleOne when managing mixed-node clusters. ConsoleOne is not supported for
cluster management on OES 2 Linux.
Planning the Cluster Conversion 13
Page 14

1.15 Using the Monitoring Function in MixedNode Clusters Is Not Supported
In mixed-node clusters, the Monitor function in Novell Cluster Services for Linux is not available.
You cannot enable the Monitor function or modify the Monitor script for cluster resources on the
Linux nodes until the conversion is finalized and all nodes in the cluster are running OES 2 Linux.
Then the monitor scripts are created automatically for each of the converted cluster resources.
14 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 15

2
Planning the Conversion of Cluster Resources
In addition to changing the operating system, the software and file systems for various clustered
services must also be considered in your conversion from NetWare 6.5 to Novell Open Enterprise
Server (OES) 2. This section provides an overview of the NetWare 6.5 services and their
counterparts in OES 2 SP3. Before you begin a conversion, make sure your system meets the
general requirements and caveats described in this section.
Converting cluster resources for OES 2 services from NetWare to Linux might require more than a
simple cluster migration from a NetWare node to a Linux node. For example, the service might
require that you use Migration Tool to convert the service to Linux. Some services require postconversion configuration to finalize the conversion. A few services on NetWare are not available on
OES 2 Linux, so you must use the standard Linux service instead.
See Table 2-1 for information about converting cluster resources for NetWare 6.5 SP8 services:
Table 2-1 Guidelines for Converting Service Cluster Resources from NetWare to Linux
Service on NetWare 6.5
SP8
Apache Web Server Yes See Chapter 6, “Apache Web Server,” on page 37.
Cluster Migrate the
Resource
Converting the Service to OES 2 Linux
2
Apple Filing Protocol
(AFP)
Archive and Version
Services
CIFS
(Windows File
Services)
DFS VLDB
(Distributed File
Services volume
location database)
DHCP Server Yes See Chapter 11, “DHCP Server,” on page 51.
DNS Server Yes See Chapter 12, “DNS Server,” on page 53 .
eDirectory Not clustered, but
Yes See Chapter 5, “Novell AFP,” on page 35.
No, but you can
migrate the database
Yes See Chapter 9, “Novell CIFS,” on page 45.
Yes See Chapter 10, “Novell Distributed File Services
requires special
handling
See Chapter 7, “Novell Archive and Version
Services,” on page 41.
VLDB,” on page 47.
See Section 1.8, “Converting Nodes that Contain the
eDirectory Master Replica,” on page 12.
Planning the Conversion of Cluster Resources
15
Page 16

Service on NetWare 6.5
SP8
Cluster Migrate the
Resource
Converting the Service to OES 2 Linux
eDirectory Certificate
Server
Not clustered, but
requires special
handling
The Certificate Authority (CA) service is not clusterenabled for NetWare or OES 2 Linux. There are no
cluster-specific tasks for the CA itself.
The Server Certificate service issues Server
Certificate objects that might need to reside on each
node in a cluster, depending on the service that is
clustered. NetWare and Linux generate certificates
differently, so the NetWare server’s certificate is not
reused for the OES 2 Linux server.
See Chapter 8, “eDirectory Server Certificates,” on
page 43.
exteNd Application
Server and MySQL
Not applicable The exteNd Application Server was discontinued as
an install option for NetWare 6.5 SP3. It is not
available for Linux.
See also MySQL in this table.
FTP No Use the Pure-FTPd service for Linux.
For information, see “Novell FTP (Pure-FTPd) and
OES 2” in the OES 2 SP3: Planning and
Implementation Guide.
iFolder No, but you can
migrate the settings
Novell iFolder 2.1x is not available on OES 2 Linux.
You must use Novell iFolder 3.x.
and data
After you add a Novell iFolder 3.x server to the
NetWare cluster and before you finalize the cluster
conversion, use iFolder migration procedures to
migrate the iFolder 2.1x server configuration and user
data from the source NetWare node to the target
Linux node. For information, see “Migrating iFolder
Services” in the Novell iFolder 3.8.4 Administration
Guide.
iPrint Yes See Chapter 13, “Novell iPrint,” on page 55.
MySQL No Use the MySQL 5.0.x software on OES2 Linux that is
NetStorage Not tested Clustering the NetStorage service is supported for
NFS No Use standard NFS service for Linux.
16 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
offered under the GPL.
See Chapter 14, “MySQL,” on page 61.
OES 2 SP1 Linux and later.
For information, see “Configuring NetStorage with
Novell Cluster Services” in the OES 2 SP3:
NetStorage Administration Guide.
Page 17

Service on NetWare 6.5
SP8
Cluster Migrate the
Resource
Converting the Service to OES 2 Linux
QuickFinder (Server
Synchronization
Feature)
No, but you can
migrate the settings
and data
You must create a new cluster resource. QuickFinder
5.0.x is supported only on OES 2 Linux. NetWare
uses QuickFinder 4.2.0. QuickFinder does not support
any automated procedure or scripts for a rolling
upgrade from Netware to Linux.
Instead of converting the resource, you can migrate
the settings from NetWare after you set up a
QuickFinder resource on Linux.
See Chapter 15, “QuickFinder Server,” on page 63.
NSS pools and
volumes
Yes See Chapter 16, “Novell Storage Services Pools,” on
page 67.
Tomcat No Use the standard Tomcat service for Linux.
Planning the Conversion of Cluster Resources 17
Page 18

18 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 19

3
Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts
You can use a rolling cluster conversion to convert a Nove ll Clu ster Service s cluste r fro m Ne tWare
6.5 SP8 to Novell Open Enterprise Server (OES) 2 SP3 Linux. This section describes how to prepare
for and perform the conversion, and how to manage the temporarily mixed cluster during the
conversion.
Section 3.1, “T ran s la tio n o f Clust er Reso urce Scrip ts for Mi xed Ne tWare an d Li nu x Cl ust ers,”
on page 19
Section 3.2, “Comparing Script Length Limits for NetWare and Linux,” on page 20
Section 3.3, “Comparing Script Commands for NetWare and Linux,” on page 20
Section 3.4, “Comparing Master IP Address Scripts,” on page 21
Section 3.5, “Comparing NSS Pool Resource Scripts,” on page 22
Section 3.6, “Comparing File Access Protocol Resource Script Commands,” on page 23
Section 3.7, “Customizing the Translation Syntax for Converting Load and Unload Scripts,” on
page 25
Section 3.8, “Adding Monitoring Scripts on Linux,” on page 26
3.1 Translation of Cluster Resource Scripts for
3
Mixed NetW are and Linux Clusters
Novell Cluster Services includes specialized script translation functionality, called the Cluster
Translation Library script (
servers coexist in the same cluster. It provides an automatic translation of the Master IP Address
resource and cluster-enabled NSS pool resource load and unload scripts from NetWare to Linux.
This functionality is also beneficial as you migrate NetWare cluster servers to Linux.
The Cluster Translation Library reads the NetWare load and unload scripts from eDirectory,
converts them, and writes them as Linux load and unload scri pt files. The Linux load and unload
script files are then searched for NetWare-specific command strings, and the command strings are
then either deleted or replaced with Linux-specific command strings. Separate Linux-specific
commands are also added, and the order of certain lines in the scripts is also changed to function
with Linux.
The Linux load and unload scripts are stored in files on Linux cluster servers, instead of being stored
in eDirectory like the NetWare scripts. The cluster resource name is used in the load and unload
script filenames. The path to the files is
IMPORTANT: Use the Properties > Scripts page in the Clusters plug-in in iManager whenever
you make manual changes to the load and unload scripts. The changes are automatically saved to the
files.
/opt/novell/ncs/bin/clstrlib.py
/var/opt/novell/ncs/
), to help NetWare and Linux
.
Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts
19
Page 20

The normal translations performed by the Cluster Translation Library are described in the following
sections:
Section 3.3, “Comparing Script Commands for NetWare and Linux,” on page 20
Section 3.4, “Comparing Master IP Address Scripts,” on page 21
Section 3.5, “Comparing NSS Pool Resource Scripts,” on page 22
Section 3.6, “Comparing File Access Protocol Resource Script Commands,” on page 23
IMPORTANT: If the commands in cluster resource’s load or unload scripts are not part of the
translation library, the cluster resource can end up in a comatose state.
Beginning in OES 2 SP2, Novell Cluster Services allows you to customize the translation syntax
that us used for load and unload scripts in mixed-platform situations by defining new syntax
translations to be used in addition to the normal translations. For information, see Section 3.7,
“Customizing the Translation Syntax for Converting Load and Unload Scripts,” on page 25.
3.2 Comparing Script Length Limits for NetWare and Linux
Scripts have different size limits on NetWare and OES 2 Linux. In a mixed-node cluster, the scripts
for NetWare resources that are cluster migrated to OES 2 Linux nodes are restricted to the NetWare
script-size limits until the final
cluster convert
command is issued.
The maximum supported lengths for cluster scripts’ content are as follows:
Script
Load script 924 bytes 924 bytes 3200 bytes
Unload script 924 bytes 924 bytes 3200 bytes
Monitor script Not supported Not supported 3200 bytes
NetWare 6.5 Resources
on NetWare Nodes
NetWare 6.5 Resources
on OES 2 Linux Nodes
OES 2 Linux Resources
and Converted NetWare
Resources After the Final
Conversion
In cases where a Linux converted script exceeds the imposed NetWare script size limit, it is best to
avoid bringing the resource online on OES 2 Linux nodes until the final cluster convert command
has been run.
IMPORTANT: Because the Linux script for GroupWise exceeds the NetWare script limit, we
recommend that you do not online GroupWise resources in while running in mixed-node clusters.
3.3 Comparing Script Commands for NetWare and Linux
Table 3-1 identifies some of the NetWare cluster load and unload script commands that the Cluster
Translation Library script searches for and the Linux commands that it replaces them with (unless
the commands are deleted).
20 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 21

Table 3-1 Cluster Script Command Comparison
Action NetWare Cluster Command Linux Cluster Command
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Delete
Delete
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
IGNORE_ERROR add secondary
ipaddress
IGNORE_ERROR del secondary
ipaddress
del secondary ipaddress ignore_error
add secondary ipaddress exit_on_error
IGNORE_ERROR NUDP
IGNORE_ERROR HTTP
nss /poolactivate= nss /poolact=
nss /pooldeactivate= nss /pooldeact=
mount volume_name VOLID=number exit_on_error ncpcon mount
NUDP ADD clusterservername
ipaddress
NUDP DEL clusterservername
ipaddress
ignore_error
add_secondary_ipaddress
ignore_error
del_secondary_ipaddress
del_secondary_ipaddress
add_secondary_ipaddress
(deletes the entire line)
(deletes the entire line)
volume_name=number
exit_on_error ncpcon bind
--ncpservername=ncpservername
--ipaddress=ipaddress
ignore_error ncpcon unbind
--ncpservername=ncpservername
--ipaddress=ipaddress
Delete
Delete
CLUSTER CVSBIND
CIFS
(deletes the entire line)
(deletes the entire line)
3.4 Comparing Master IP Address Scripts
Section 3.4.1, “Master IP Address Resource Load Script,” on page 21
Section 3.4.2, “Master IP Address Resource Unload Script,” on page 22
3.4.1 Master IP Address Resource Load Script
This section provides examples o f the master IP address resource load scripts on NetWare and
Linux.
“NetWare” on page 22
“Linux” on page 22
Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts 21
Page 22

NetWare
IGNORE_ERROR set allow ip address duplicates = on
IGNORE_ERROR CLUSTER CVSBIND ADD BCCP_Cluster 10.1.1.175
IGNORE_ERROR NUDP ADD BCCP_Cluster 10.1.1.175
IGNORE_ERROR add secondary ipaddress 10.1.1.175
IGNORE_ERROR HTTPBIND 10.1.1.175 /KEYFILE:"SSL CertificateIP"
IGNORE_ERROR set allow ip address duplicates = off
Linux
#!/bin/bash
. /opt/novell/ncs/lib/ncsfuncs
ignore_error add_secondary_ipaddress 10.1.1.175 -np
exit 0
3.4.2 Master IP Address Resource Unload Script
This section provides examples of the master IP address resource unload scripts on NetWare and
Linux.
“NetWare” on page 22
“Linux” on page 22
NetWare
IGNORE_ERROR HTTPUNBIND 10.1.1.175
IGNORE_ERROR del secondary ipaddress 10.1.1.175
IGNORE_ERROR NUDP DEL BCCP_Cluster 10.1.1.175
IGNORE_ERROR CLUSTER CVSBIND DEL BCCP_Cluster 10.1.1.175
Linux
#!/bin/bash
. /opt/novell/ncs/lib/ncsfuncs
ignore_error del_secondary_ipaddress 10.1.1.175
exit 0
3.5 Comparing NSS Pool Resource Scripts
Section 3.5.1, “NSS Pool Resource Load Script,” on page 22
Section 3.5.2, “NSS Pool Resource Unload Script,” on page 23
3.5.1 NSS Pool Resource Load Script
This section provides examples of the NSS pool resource load scripts on NetWare and Linux.
“NetWare” on page 23
“Linux” on page 23
22 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 23

NetWare
nss /poolactivate=HOMES_POOL
mount HOMES VOLID=254
CLUSTER CVSBIND ADD BCC_CLUSTER_HOMES_SERVER 10.1.1.180
NUDP ADD BCC_CLUSTER_HOMES_SERVER 10.1.1.180
add secondary ipaddress 10.1.1.180
CIFS ADD .CN=BCC_CLUSTER_HOMES_SERVER.OU=servers.O=lab.T=TEST_TREE.
Linux
#!/bin/bash
. /opt/novell/ncs/lib/ncsfuncs
exit_on_error nss /poolact=HOMES_POOL
exit_on_error ncpcon mount HOMES=254
exit_on_error add_secondary_ipaddress 10.1.1.180
exit_on_error ncpcon bind --ncpservername=BCC_CLUSTER_HOMES_SERVER
--ipaddress=10.1.1.180
exit 0
3.5.2 NSS Pool Resource Unload Script
This section provides examples of the NSS pool resource unload scripts on NetWare and Linux.
“NetWare” on page 23
“Linux” on page 23
NetWare
del secondary ipaddress 10.1.1.180
CLUSTER CVSBIND DEL BCC_CLUSTER_HOMES_SERVER 10.1.1.180
NUDP DEL BCC_CLUSTER_HOMES_SERVER 10.1.1.180
nss /pooldeactivate=HOMES_POOL /overridetype=question
CIFS DEL .CN=BCC_CLUSTER_HOMES_SERVER.OU=servers.O=lab.T=TEST_TREE.
Linux
#!/bin/bash
. /opt/novell/ncs/lib/ncsfuncs
ignore_error ncpcon unbind --ncpservername=BCC_CLUSTER_HOMES_SERVER
--ipaddress=10.1.1.180
ignore_error del_secondary_ipaddress 10.1.1.180
ignore_error nss /pooldeact=HOMES_POOL
exit 0
3.6 Comparing File Access Protocol Resource Script Commands
Section 3.6.1, “File Access Protocol Resource Load Scripts,” on page 24
Section 3.6.2, “File Access Protocol Resource Unload Scri pts,” on page 24
Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts 23
Page 24

3.6.1 File Access Protocol Resource Load Scripts
This section provides examples of the file access protocol commands for load scripts on NetWare
and Linux.
“NetWare” on page 24
“Linux” on page 24
NetWare
Protocol Script Command for Load Scripts
NCP
Novell AFP
Novell CIFS
NUDP ADD NCS1_P1_SERVER 10.10.10.194
AFPBIND ADD NCS1_P1_SERVER 10.10.10.204
CIFS ADD .CN=NCS1_P1_SERVER.O=novell.T=CLUSTER.
Linux
Protocol Script Command for Load Scripts
NCP
Novell AFP
Novell CIFS
# mount the NCP volume
exit_on_error ncpcon mount $NCP_VOLUME=VOL_ID,PATH=$MOUNT_POINT
exit_on_error ncpcon bind --ncpservername=NCS1_P1_SERVER
--ipaddress=10.10.10.194
exit_on_error cluster_afp.sh add NCS1_P1_SERVER 10.10.10.204
exit_on_error novcifs --add
--vserver=.CN=NCS1_P1_SERVER.O=novell.T=TREE-188. --ipaddr=<virtual_server_ip_address>
3.6.2 File Access Protocol Resource Unload Scripts
This section provides examples of the Novell AFP commands for unload scripts on NetWare and
Linux.
“NetWare” on page 24
“Linux” on page 25
NetWare
Protocol Script Command for Unload Scripts
NCP
Novell AFP
Novell CIFS
NUDP DEL NCS1_P1_SERVER 10.10.10.194
AFPBIND DEL NCS1_P1_SERVER 10.10.10.204
CIFS DEL .CN=NCS1_P1_SERVER.O=novell.T=TREE-188.
24 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 25

Linux
Protocol Script Command for Unload Scripts
NCP
Novell AFP
Novell CIFS
ignore_error ncpcon unbind --ncpservername=NCS1_P1_SERVER
--ipaddress=10.10.10.194
# dismount the NCP volume
ignore_error ncpcon dismount $NCP_VOLUME
ignore_error cluster_afp.sh del NCS1_P1_SERVER 10.10.10.204
ignore_error novcifs --remove
--vserver=.CN=NCS1_P1_SERVER.O=novell.T=TREE-188.
--ip-addr=<virtual_server_ip_address>
3.7 Customizing the Translation Syntax for Converting Load and Unload Scripts
The syntax for load and unload scripts differs for NetW are and Linux platforms. A script that is valid
for the NetWare platform is not necessarily recognized on the OES 2 Linux platform. In a mixedplatform cluster, a cluster resource’s load script and unload script must be translated to use the
proper syntax when running on the NetWare or Linux nodes. Translation occurs in-memory while
the cluster contains mixed-platform nodes, and during the final cluste r conversion of the cluster
from NetWare to Linux.
The translation between NetWare and Linu x ve rsion s of t he load and u nload scripts is perfo rmed by
the Cluster Translation Library script (
/opt/novell/ncs/bin/clstrlib.py
translations in the library are described in Section 3.1, “Translation of Cluster Resource Scripts for
Mixed NetWare and Linux Clusters,” on page 19. If the commands in a cluster resource’s load or
unload scripts are not part of the translation library, the cluster resource can end up in a comatose
state.
). The normal
Beginning in OES 2 SP2, Novell Cluster Services allows you to customize the translation syntax
that is used for load and unload scripts in mixed-platform situations by defining new syntax
translations in the
create. The
clstrlib.py
/var/opt/novell/ncs/customized_translation_syntax
script reads the additional translation syntax from the syntax file, and
file that you
processes them in addition to the normal translations in the Cluster Translation Library.
The customized translation supports using Python regular expressions to search for strings (
(\d+)
digits (
), and other data types. The search is case insensitive.
(\S+)
NOTE: Refer to information about Python regular expressions to learn how to create searches for
other data types.
In a text editor, create the
customized_translation_syntax
syntax that you need, then copy the file to the
/var/opt/novell/ncs/ folder
file with the additional translation
on each Linux
node in the mixed-platform cluster.
The syntax file should contain a four-line command for each type of translation you want to add:
Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts 25
),
Page 26

<R|D>
search_string
[replacement_data]
[preceding_data]
You can have any number of the four-line commands in the file. Use the following guidelines for
creating the syntax translation commands:
Line Description
<R|D>
search_string
[replacement_data]
[preceding_data]
Specify whether to replace (R) all matches or to delete (D) all matches of
the data type you are looking for in the load or unload script.
Specify the search string that is used to locate a line in the scripts.
Specify the replacement data used to replace a line matched by the
search performed.
Leave this line empty if there is no replacement.
Specify a line to be inserted before the first line that is matched by the
search performed.
Leave this line empty if there is no line to be inserted before the first
matching line.
The following four lines are sample code for a search command in the
customized_translation_syntax file. The fourth line is intentionally left empty.
R
^\s*bind\s+IP\s+(\S+)\s(\S+)\s+address=(\d+\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+)
ignore_error bind IP \1 \2 address=\3\n
exit_on_error ip addr add \3/32 dev \1
You can use the c
luster convert preview
command to verify that the
customized_translation_syntax file is working as intended for a particular resource.
root
1 On the master node, open a terminal console as the
user, then enter
cluster convert preview resource_name
3.8 Adding Monitoring Scripts on Linux
The monitoring script is available for cluster resources in Novell Cluster Services for OES 2 Linux.
However, in a mixed-node cluster, the cluster resources that you cluster migrate from NetWare to
Linux will not have a monitoring script du rin g t he conversion process. A monitoring script for each
of the former NetWare cluster resources is created automatically after you perform the final cluster
conversion step as described in Section 4.3, “Finalizing the Cluster Conversion,” on page 32.
Sample monitoring scripts are available in the cluste r reso urce temp lat es for t he vario us se rv ic es on
OES 2 Linux.
There might not be a monitoring script for iPrint. Print Manager has a built-in monitoring and restart
capability. Using the cluster resource monitoring script might cause a conflict.
26 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 27

4
Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux
You can use a rolling cluster conversion to convert a Nove ll Clu ster Service s cluste r fro m Ne tWare
6.5 SP8 to Novell Open Enterprise Server (OES) 2 SP3 Linux. This section describes how to prepare
for and perform the conversion, and how to manage the temporarily mixed cluster during the
conversion.
Section 4.1, “Converting NetWare Cluster Nodes to OES 2 Linux (Rolling Cluster
Conversion),” on page 27
Section 4.2, “Adding New OES 2 Linux Nodes to Your NetWare Cluster,” on page 30
Section 4.3, “Finalizing the Cluster Conversion,” on page 32
4.1 Converting NetWare Cluster Nodes to OES 2 Linux (Rolling Cluster Conversion)
Performing a rolling cluster conversion from NetWare 6.5 to OES 2 Linux lets you keep yo ur cluster
up and running and lets your users continue to access cluster resources while the conversion is being
performed.
During a rolling cluster conversion, one server is converted to Linux while the other servers in the
cluster continue running NetWare 6.5. Then, if desired, another server can be converted to OES 2
Linux, and then another, until all servers in the cluster have been converted to Linux. You can also
leave the cluster as a mixed NetWare and Linux cluster.
4
IMPORTANT: Before you begin, make sure you system meets the requirements and caveats in
“Planning for Novell Cluster Services” in the OES 2 SP3: Novell Cluster Services 1.8.8
Administration Guide for Linux. Also verify that your system meets the requirements in Chapter 1,
“Planning the Cluster Conversion,” on page 9.
If you are converting from NetWare on physical servers to OES 2 Linux on virtual servers (guest
operating systems running on Xen virtual machines), you can use the same method s and proc esses
as those used on a physical server. No additional changes or special configuration is required. For
information, see “Mixed Physical and Virtual Node Clusters” in the OES 2 SP3: Novell Cluster
Services 1.8.8 Administration Guide for Linux.
To perform a rolling cluster conversion from NetWare 6.5 to OES 2 Linux:
1 Before you add the first Linux node to the NetWare cluster , if the NetWare cluster uses an SB D,
make sure that the device (or devices) being used by the SBD are marked as Shareable for
Clustering.
You can use NSSMU or iManager to mark the SBD devices as shareable. It is not necessary to
bring the cluster down when changing the device attribute to Shareable for Clustering.
Using NSSMU:
1a Log in to the master node of the NetWare cluster as the administrator user.
nssmu
1b Enter
at the server console prompt.
Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux
27
Page 28

1c In the NSSMU main menu, select Devices.
1d In the Devices list, highlight the device that contains the SBD partition, then press F5 to
select it.
1e Press F6 to mark the device as Shareable for Clustering.
1f If the SBD partition is mirrored, repeat Step 1d and Step 1e to also mark the mirror device
as Shareable for Clustering.
1g Press Esc to exit NSSMU.
2 Make a note of the services that are installed on the server you are converting.
You might want to install the same component s on the Linux node if they are available.
3 On the NetWare server that you want to convert to Linux, remove eDirectory.
You can do this by running NWConfig, then selecting Product Options > Directory Options
<install NDS> > Remove Directory Services from this server.
4 Bring down the NetWare server you want to convert to Linux.
Any cluster resources that were running on the server should fail over to another server in the
cluster.
You can also manually cluster migrate the resources to another server in the cluster prior to
bringing down the server. This prevents the resources from failing back to the node after you
have completed the upgrade.
5 In eDirectory , remove (delete) the Cluster Node object, the Server object, and all corresponding
objects relating to the downed NetWare server.
Depending on your configuration, there could be 10 or more objects that relate to the downed
NetWare server.
6 Run DSRepair from another server in the eDirectory tree to fix any directory problems.
If DSRepair finds errors or problems, run it multiple times until no errors are returned.
7 Install OES 2 Linux on the server, but do not install the Novell Cluster Services option in OES
Services at this time.
You can use the same server name and IP address that we re used on the NetWare server. This is
suggested, but not required.
See the OES 2 SP3: Installation Guide for more information.
8 Set up and verify SAN connectivity for the Linux node.
Consult your SAN vendor documentation for SAN setup and connectivity instructions.
9 Install Novell Cluster Services and add the node to your existing NetWare 6.5 cluster.
root
9a Log in to the OES 2 Linux server as the
user.
9b In YaST, select Open Enterprise Server > OES Install and Configuration.
9c On the Software Selection page under OES Services, click Novell Cluster Services.
Services that you have already installed are indicated by a blue check mark in the status
check box next to the service.
For information about other install options, see “ Instal ling Nove ll Clu ster Service s du ring
a OES 2 Linux Installation” in the OES 2 SP3: Novell Cluster Services 1.8.8
Administration Guide for Linux.
9d Click Accept to begin the install, then click Continue to accept changed packages.
28 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 29

9e Continue through the installation process until you reach the Novell Open Enterprise
Server Configuration page.
9f Reconfigure LDAP Configuration of Open Enterprise Services to specify the credentials
for the container administrator user (or non-administrator user) who has the eDirectory
rights needed to install Novell Cluster Services.
For information about what rights are needed, see “Assigning Install Rights for Container
Administrators (or Non-Administrator Users)” in the OES 2 SP3: Novell Cluster Services
1.8.8 Administration Guide for Linux.
9f1 On the Novell Open Enterprise Server Configuration page under LDAP
Configuration of Open Enterprise Services, click the disabled link to enable re-
configuration.
The sentence changes to Reconfiguration is enabled.
9f2 Click the LDAP Configuration of Open Enterprise Services link to open the LDAP
Configuration page.
9f3 Specify the following values:
Admin name and context: The username and context (in LDAP form) of the
container administrator user (or non-administrator user) who has the eDirectory
rights needed to install Novell Cluster Services.
Admin password: The password of the container administrator (or non-
administrator user).
9f4 Click Next.
The install returns to the Novell Open Enterprise Server Configuration page.
9g On the Novell Open Enterprise Server Configuration page under No ve ll Clu s ter Serv ice s,
click the disabled link to enable configuration.
The sentence changes to Configuration is enabled.
9h Click the Novell Cluster Services link to open the Novell Cluster Services Configuration
page.
9i Click Existing Cluster, specify the fully distinguished name (FDN) of the cluster, then
click Next.
IMPORTANT: Use the comma format illustrated in the example. Do not use dots.
This is the name and eDirectory context of the cluster that you are adding this server to.
9j Select the IP address that Novell Cluster Services will use for this node.
Some servers have multiple IP addresses. This step lets you choose which IP address
Novell Cluster Services uses.
9k Deselect Start Services Now.
9l Click Next, then continue through the rest of the OES installation.
9m After the install is complete, use the Soft ware Upda ter (or other update metho ds) to install
any patches from the OES 2 Linux patch channel and any EVMS patches from the SUSE
Linux Enterprise Server 10 SP2 patch channel.
10 If you have a shared disk system on the cluster, enter
sbdutil -f
at the Linux terminal
console to verify that the node can see the cluster (SBD) partition on the SAN.
sbdutil -f
also tells you the device on the SAN where the SBD partition is located.
Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux 29
Page 30

11 Reboot the server.
12 (Optional) Manually migrate the resources that were on the old server nodes to thi s Linu x
server.
Some cluster resources for services on NetWare cannot b e u sed o n L inu x. For i nfo rma tio n, see
Chapter 1, “Planning the Cluster Conversion,” on page 9.
The resources can automatically fail back if all of the following apply:
The failback mode for the resources was set to Auto.
You used the same node number for this Linux server that was used for the former
NetWare server.
This only applies if this Linux server is the next server added to the cluste r.
This Linux server is the preferred node for the resources.
4.2 Adding New OES 2 Linux Nodes to Your NetW are Cluster
You can add new OES 2 Linux cluster nodes to your existing NetWare 6.5 cluster without bringing
down the cluster.
1 Before you add the first Linux node to the NetWare cluster , if the NetWare cluster uses an SB D,
make sure that the device (or devices) being used by the SBD are marked as Shareable for
Clustering.
You can use NSSMU or iManager to mark the SBD devices as shareable. It is not necessary to
bring the cluster down when changing the device attribute to Shareable for Clustering.
Using NSSMU:
1a Log in to the master node of the NetWare cluster as the administrator user.
1b Enter
1c In the NSSMU main menu, select Devices.
1d In the Devices list, highlight the device that contains the SBD partition, then press F5 to
1e Press F6 to mark the device as Shareable for Clustering.
1f If the SBD partition is mirrored, repeat Step 1d and Step 1e to also mark the mirror device
1g Press Esc to exit NSSMU.
2 Install OES 2 Linux on the new node, but do not install th e Novell Cluster Serv ices option from
OES Services at this time.
See the “OES 2 SP3: Installation Guide” for more information.
3 Set up and verify SAN connectivity for the new OES 2 Linux node.
Consult your SAN vendor documentation for SAN setup and connectivity instructions.
4 Install Novell Cluster Services on the OES 2 Linux node.
5 After the install, add the server to the NetWare cluster:
nssmu
at the server console prompt.
select it.
as Shareable for Clustering.
30 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 31

For detailed instructions, see “Adding a Node to an Existing Cluster” in the OES 2 SP3: Novell
Cluster Services 1.8.8 Administration Guide for Linux.
5a Log in to the OES 2 Linux server as the
root
user.
5b In YaST, select Open Enterprise Server > OES Install and Configuration.
5c On the Software Selection page unde r OES Services, verify that Novell Cluster Services is
selected, then click Accept to continue to the configuration.
Services that you have already installed are indicated by a blue check mark in the status
check box next to the service.
5d On the Software Configuration page, enable Novell Cluster Services configuration, then
click the Novell Cluster Services link.
5e When you are prompted, enter the credentials of the LDAP administrator that is
configured for the server.
5f On the Novell Cluster Services Configuration page, add the server to the existing NetWare
cluster, then click Next.
Parameter Action
New or Existing Cluster Select Existing Cluster.
Cluster FDN Browse to select the Cluster object for the
NetWare cluster, or type the cluster fully
distinguished name.
For example:
cn=nwcluster,ou=clusters,o=mycompany
5g On the Proxy User Configuration page, specify one of the following users as the NCS
Proxy user, then click Next.
OES Common Proxy User: If the OES Common Proxy User is enabled in
eDirectory, the Use OES Common Proxy User check box is automatically selected
and the NCS Proxy User Name and Specify NCS Proxy User Password fields are
populated with the credentials of the OES Common Proxy User.
LDAP Admin User: If the OES Common Proxy User is disabled in eDirectory, the
Use OES Common Proxy User check box is automatically deselected and the NCS
Proxy User Name and Specify NCS Proxy User Password fields are populated with
the credentials of the LDAP Admin user. The fields are also automatically populated
with the LDAP Admin credentials if you deselect the Use OES Common Proxy User
check box.
Another Administrator User: Deselect the Use OES Common Proxy User check
box, then specify the credentials of an administrator user.
You can reset the default settin gs by clickin g Back to return to th e Novell Cluster Servic es
Configuration page, then clicking Next to continue again to the Proxy User Configuration
page.
5h On the Configuration page, specify the following parameters, then click Finish.
Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux 31
Page 32

Parameter Action
IP address of this node If the server has multiple network adapters,
select the IP address that Novell Cluster
Services will use for this node.
Start Cluster Services now Deselect the check box. You will start Novell
Cluster Services software on this node
manually for the conversion process.
5i On the OES Server Configuration page, scroll down to the Novell Cluster Services entry
to review the summary of the Cluster Services configuration, then click Next.
Wait while Novell Cluster Services is configured.
5j After the configuration is completed, click Finish to exit the OES Configuration page,
then exit YaST.
6 If you have a shared disk system on the cluster, enter
sbdutil -f
at the Linux terminal
console to verify that the node can see the cluster (SBD) partition on the SAN.
sbdutil -f
7 Start cluster software by going to the
You must be logged in as root to run
will also tell you the device on the SAN where the SBD partition is located.
/etc/init.d
novell-ncs start
folder and running
.
novell-ncs start
8 Add and assign cluster resources to the new Linux cluster node.
For information, see “Configuring Preferred Nodes for a Resource” in the OES 2 SP3: Novell
Cluster Services 1.8.8 Administration Guide for Linux.
4.3 Finalizing the Cluster Conversion
If you have converted all nodes in a former NetWare cluster to OES 2 Linux, you must finalize the
conversion process by issuing the
cluster convert
command moves cluster resource load and unload scripts from the files where
cluster convert
they were stored on Linux cluster nodes into eDirectory. This enables a Linux cluster that has been
converted from NetWare to utilize eDirectory like the former NetWare cluster.
WARNING: After you finalize the cluster conversion, rollback to NetWare is not supported.
To finalize the cluster conversion:
1 Run
cluster convert preview resource_name
cluster node.
The
preview
switch lets you view the resource load and unload script changes that will be
made when the conversion is finalized. Replace resource_name with the name of a resource
that you want to preview.
Beginning in OES 2 SP3, you can preview the information for all cluster resources by issuing
the command without specifying a resource name.
2 Run
cluster convert commit
at the terminal console of one Linux cluster node to finaliz e
the conversion.
command on one Linux cluster node. The
at the terminal console of one Linux
.
32 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 33

The
cluster convert commit
command generates or regenerates the cluster resource
templates that are included with Novell Cluster Services for Linux. In addition to generating
Linux cluster resource templates, this command deletes all NetWare cluster resource templates
that have the same name as Linux cluster resource templates.
The cluster resource templates are automatically created when you create a new Linux cluster,
but are not created when you convert an existing NetWare cluster to Linux.
3 Update the cluster configuration on all nodes by run ning the cluster configuration daemon.
root
Enter the following command as the
/opt/novell/ncs/bin/ncs-configd.py -init
user on every node in the cluster:
This removes the NetWare nodes from the list of nodes in the cluster so they are not displayed
in iManager.
Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux 33
Page 34

34 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 35

5
Novell AFP
Novell Apple Filing Protocol (AFP) for Linux is available beginning in OES 2 SP1 Linux.
After you set up Novell AFP on the Linux node and before you finalize the NetWare-to-Linux
conversion, use the AFP function in the Migration Tool to convert the configuration. Fo r
information, see “Migrating AFP from NetWare to OES 2 SP3 Linux ” in the OES 2 SP3: Migration
Tool Administration Guide.
The commands in the scripts are also different. Af ter the migration, modify the load and unload
scripts on the Linux server. For information, see Section 3.6, “Comparing File Access Protocol
Resource Script Commands,” on page 23.
AFP on Linux supports NCP cross-protocol file locking, which allows NCP, AFP, and CIFS users to
access files on an NSS volume concurrently without data corruption by locking the files across
protocols. On Linux, the cross-protocol file locking parameter for NCP Server is disabled by default.
It must be enabled on each node in the cluster if you plan to give both NCP users and AFP users
access to NSS volume in the cluster. See “Configuring Cross-Protocol Fi le Locks for NCP Server”
in the OES 2 SP3: NCP Server for Linux Administration Guide.
5
Novell AFP
35
Page 36

36 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 37

6
Apache Web Server
This section describes how reuse the Apache Web Server cluster resource when you convert a
cluster from NetWare 6.5 SP8 to Novell Open Enterprise Server (OES) 2 for Linux.
For information about installing and configuring Apache on OES 2 Linux, see “Section 40, Apache
HTTP Server” (http://www.novell.com/documentation/sles10/book_sle_reference/data/
cha_apache2.html) in the SLES 10 SP3 Installation and Administration Guide (http://
www.novell.com/documentation/sles10/book_sle_reference/data/book_sle_reference.html).
Section 6.1, “Prerequisites,” on page 37
Section 6.2, “Converting the Apache Cluster Resource,” on page 37
Section 6.3, “Additional Information,” on page 40
6.1 Prerequisites
You must install Novell Storage Services on the OES 2 Linux servers in order to reuse the cluster
resource that contains the Web site files.
After you convert the cluster , you wil l install the Web and Lamp Server functional pattern and set up
Apache services.
6
6.2 Converting the Apache Cluster Resource
1 In iManager, offline the NSS pool cluster resource from a NetWare node, then modify its load
and unload scripts to remove the Apache start and stop commands.
2 In iManager, online the cluster resource on a NetWare node to activate the changes you made to
the scripts.
3 In iManager, cluster migrate the cluster resource to a Linux node, then offline the resource.
4 Complete the cluster conversion.
5 For each Linux node in the cluster, install the Web and LAMP Server option under the Linux
Primary Functions category.
The Web and LAMP Server pattern includes the Apache and MySQL packages, and scripting
languages such as PHP, Python, Ruby on Rails, and Perl.
5a Log in as the
5b In YaST, select Open Enterprise Server > OES Install and Configuration.
root
user, then open YaST.
Apache Web Server
37
Page 38
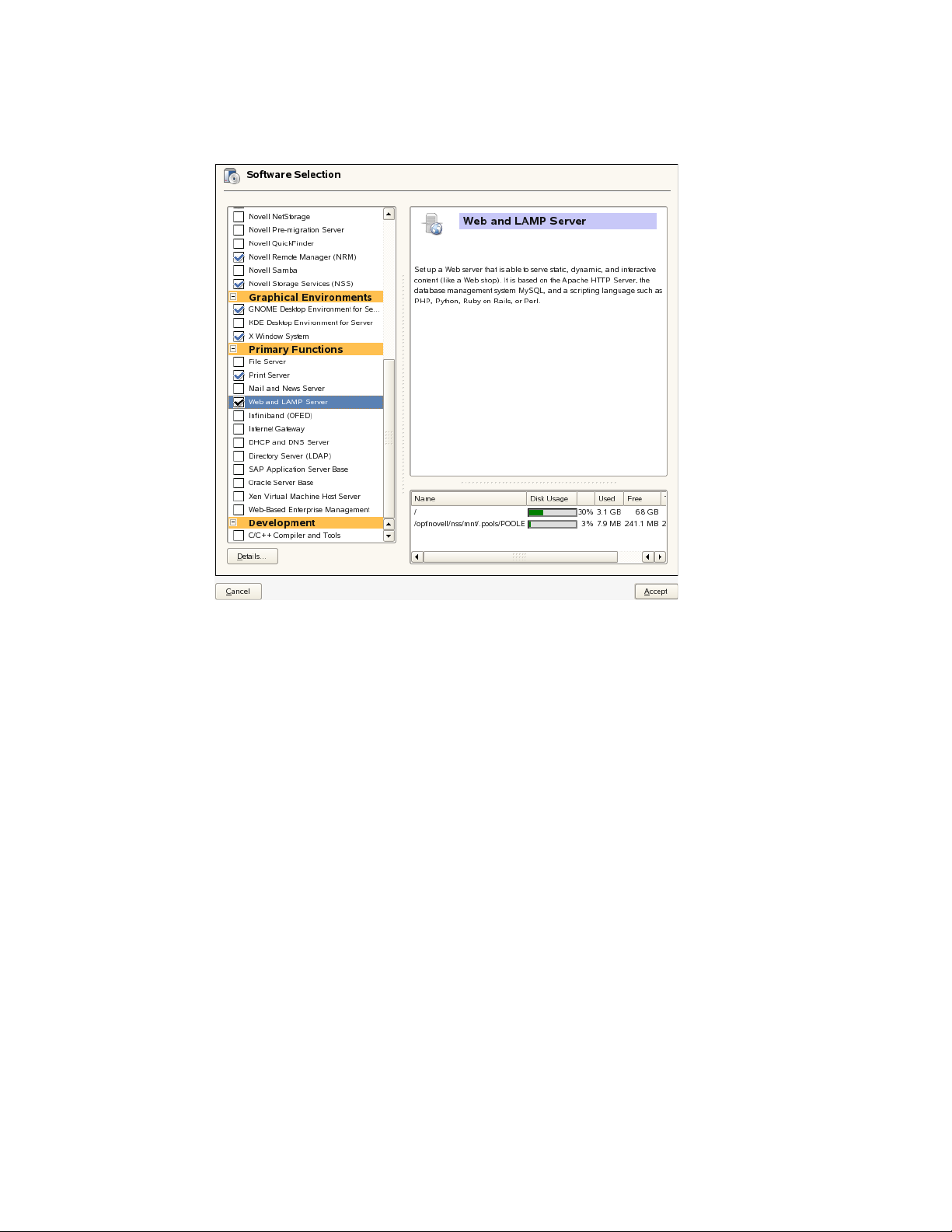
5c On the Software Selection page, under Primary Functions, select Web and LAMP Server,
then click Accept.
5d Continue with the installation.
6 (Optional) Install Tomcat.
root
6a Log in as the
user, then open YaST.
6b In Y aST, click Software in the left pane, then click Software Management in the right pane.
6c In the Search field, type
tomcat
, then click Search.
6d Select the Tomcat packages you want to install, then click Accept.
If you encounter a dependency conflict, select the package you want to install to resolve
the conflict, then click OK -- Try Again to continue with the installation.
root
7 After the Web services are installed on all nodes, log in as the
user on the master node,
then configure the Apache Web Server.
7a Log in as the
root
user, then open YaST.
In YaST, click Network Services in the left pane, then click HTTP Server in the rig ht pane .
Apache is referred to as the HTTP Server on Linux.
7b Configure the following HTTP Server settings by using the HTTP Server Wizard:
For wizard instructions, see “Section 40.2.2, Configuring Apache with YaST” (http://
www.novell.com/documentation/sles10/book_sle_reference/data/
sec_apache2_configuration.html#sec_apache2_configuration_yast) in the SLES 10 SP3
Installation and Administration Guide (h ttp://www.novell.com/documentation/sles10/
book_sle_reference/data/book_sle_reference.html).
Port (and open the firewall)
38 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 39

Network devices
Modules for scripting (PHPS, Perl, Python, Ruby)
Default host
Virtual host
The default host settings on Linux are:
Parameter Default Value
Port 80
Document Root
Alias
ScriptAlias
Include
Server Name /http://<fully_qualified_distinguished_name_or_ip_address>
Server Administrator E-
Mail
/srv/www/htdocs
Point the service to the virtual IP address of the NSS pool cluster
resource that contains the Web content.
/icons
/cgi-bin
/etc/apache2/conf.d
/etc/apache2/conf.d/apache2-manual.conf
<specify an e-mail address>
points to
points to
/usr/share/apache2/icons
/srv/www/cgi-bin
7c To verify that Apache has started successfully, open a Web browser and view the
following URL:
http://Web_server_address:port_number
where Web_server_address is the IP address or hostname of your Linux server and
port_number is the Apache listen port, which is 80 by default. For example:
http://192.168.1.18:80
http://localhost:80
If Apache is correctly set up, you should see a Web page that starts with the following
message:
If you can see this, it means that the installation of the Apache Web
Server software on this system was successful. You may now add content
to this directory and replace this page.
7d Replace the Apache test page (
/apache2/htdocs/index.html
) with your own home
page.
8 Copy the Apache configuration file (
/etc/apache2/httpd.conf
) to every Linux node in the
cluster.
9 (Optional) Set up an SSL certificate for the Apache server.
For information, see “Section 40.6, Setting Up a Secure Web Server with SSL” (http://
www .novell.com/documentation/sles10/book_sle_reference/data/cha_apache2.html) in the
SLES 10 SP3 Installation and Administra tion Guide (http://www.novell.com/documentation/
sles10/book_sle_reference/data/book_sle_reference.html).
10 In iManager, set up the preferred nodes for the Apache cluster resource.
Apache Web Server 39
Page 40

11 In iManager, modify the load and unload scripts for the cluster resource to add the Apache
service start and stop commands for Linux.
/usr/sbin/rcapache2 start
/usr/sbin/rcapache2 stop
12 Online the Apache cluster resource.
6.3 Additional Information
In addition to the SUSE documentation, the following Apache resources are available online.
Section 6.3.1, “Apache 2 Manual,” on page 40
Section 6.3.2, “Virtual Hosts Support,” on page 40
6.3.1 Apache 2 Manual
The Apache manual is available on the Apache HTTP Server Version 2.2 Documentation Web site
(http://httpd.apache.org/docs-2.2/). The package
manual. It is not installed by default.
root
1 Log in as the
2 At the terminal prompt, ente r
yast -i apache2-doc
user, then open a terminal console.
apache2-doc
also contains the complete Apache
Once installed, the Apache ma nual is available at
SUSE-specific configuration hints are available in the folder
apache2/README.*
.
http://localhost/manual/
/usr/share/doc/packages/
.
6.3.2 Virtual Hosts Support
On Linux, the Apache service allows you to set up virtual hosts that can be used with a single
instance of Apache instead of setting up different insta nces of Apache for each site. For information,
see the following resources:
“Virtual Host Configuration” (http://www.novell.com/documentation/sles10/
book_sle_reference/data/
sec_apache2_configuration.html#sec_apache2_configuration_manually_vhost) in the SLES 10
SP3 Installation and Administration Guide (http://www.novell.com/documentation/sles10/
book_sle_reference/data/book_sle_reference.html)
Apache Virtual Host documentation Web site (htt p://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/vhosts/)
40 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 41

7
Novell Archive and Version Services
On NetWare, Archive and Versioning Services uses a MySQL database. On Novell Open Enterprise
Server (OES) 2 Linux, it uses a PostgreSQL database. You can migrate the data from the MySQL
database to the PostgreSQL database on Linux. You must configure a new cluster resource on a
shared Linux POSIX file system for the PostgreSQL database.
The load script commands are al so different on OES 2 Linux. For information, see “Archive Load
and Unload Scripts” in the OES 2 SP3: Novell Archive and Version Services 2.1 Administrati on
Guide.
Section 7.1, “Prerequisites,” on page 41
Section 7.2, “Copying Database Files from MySQL to PostgreSQL,” on page 41
7.1 Prerequisites
Mixed-node operations are not supported by Novell A rchive and Version Services. Before you begin
the conversion, make sure that Archive and Version Services is not running on the NetWare servers
in the cluster.
7.2 Copying Database Files from MySQL to
7
PostgreSQL
1 Install Archive and Version Services on an OES 2 Linux node in the cluster.
2 Install Archive and Version Services on a a second OES 2 Linux node in the cluster.
3 Using database migration tools, migrate the data in the MySQL database on NetWare to the
PostgreSQL database on of the Linux nodes.
4 Cluster migrate the shared NSS pool resource that contains the volumes that were being
archived from the NetWare server to a Li nux node.
5 Remove the NetWare nodes from the cluster and finish the cluster conversion process.
6 On the OES 2 Linux cluster, set up Archive and Version Services as described in “Configuring
Archive and Version Service for Novell Cluster Services” in the OES 2 SP3: Novell Archive
and Version Services 2.1 Administration Guide.
7 On the Linux node where the primary NSS pool resources are active, use the Clusters plug-in
in iManager to create an Archive Versioning cluster resource.
8 Copy the database files from the single-server location (
) to the shared Linux POSIX volume that you created when you set up Archive and
data
Version Services for clustering in Step 7.
Use the
permissions.
9 Change the ownership of the new database location on the shared volume by entering the
following at a terminal console prompt:
cp -a
command at a terminal console prompt to copy all files and retain the
/var/opt/novell/arkmanager/
Novell Archive and Version Services
41
Page 42

chown -R arkuser:arkuser_prggrp /shared/datapath
10 Edit the
/etc/opt/novell/arkmanager/conf/arkdatadir.conf
file to change the
database location to new shared path.
11 Edit the
/opt/novell/arkmanger/bin/pg_restart.sh
file to change the line that starts the
PostgreSQL database to the following:
su arkuser -c "postmaster -D /shared/datapath -h 127.0.0.1 -p 5432 -i"
12 Start Archive and Version Services by entering
rcnovell-ark start
You should see Archive and Version Services and the PostgreSQL database starting.
42 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 43

8
eDirectory Server Certificates
Novell Certificate Server provides two categories of services: Certificate Au thority (CA) and Server
Certificates. The Certificate Authority services include the Enterprise CA and CRL (Certificate
Revocation List). Only one server can host the CA, and normally that same server hosts the CRLs if
they are enabled (although if you move the CA to a dif ferent server , the CRLs usually stay on the old
server). The CA and CRL services are not cluster-enabled in either NetWare or OES 2 Linux, and
therefore, there are no cluster-specific tasks for them.
Novell Certificate Server provides a Server Certificates service for NetWare and Linux. The service
is not clustered. However, clustered applications that use the server certificates must be able to use
the same server certificates on whichever cluster node they happen to be running. Use the
instructions in the following sections to set up Server Certificate objects in a clustered environment
to ensure that your cryptography-enabled appli cations that use Server Certificate objects always
have access to them.
The eDirectory Server Certificate objects are created differen tly in OES 2 Linux and cannot be
directly reused from the NetWare server. The differences and alternatives for setting up certificates
on Linux are described in the following sections:
Section 8.1, “Server Certificate Changes in OES 2 Linux,” on page 43
Section 8.2, “Using Internal Certificates in a Cluster,” on page 44
8
Section 8.3, “Using External Certificates in a Cluster,” on page 44
8.1 Server Certificate Changes in OES 2 Linux
When you install NetWare or OES 2 Linux in an eDirectory environment, the Server Certificate
service can create certificates for eDirectory services to use. In addition, custom certificates can be
created after the install by using iManager or command line commands.
For NetWare, all applications are integrated with eDirectory. This allows applications to
automatically use the server certificates created by Novell Certificate Server directly from
eDirectory . In a NetWare cluster, you might have copied the Server Certificate objec ts to all nodes in
the cluster using backup and restore functions as described in “Server Certificate Objects and
Clustering” (http://www.novell.com/documentation/crt33/crtadmin/data/a2ebopb.html#acebe5n) in
the Novell Certificate Server 3.3.2 Administration Guide (http://www.novell.com/documentation/
crt33/crtadmin/data/a2ebomw.html).
For OES 2 Linux, many applications (such as Apache and Tomcat) are not integrated with
eDirectory and therefore, cannot automatically use the certificates created by Novell Certificate
Server directly from eDirectory. By default, these services use self-signed certificates, which are not
in compliance with the X.509 requirements as specified in RFC 2459 and RFC 3280.
To address the difference, Novell Certificate Server offers an install option for OES 2 Linux called
Use eDirectory Certificates that automatically exports the default eDirectory certificate SSL
Certificate DNS and its key pair to the local file system in the following files:
/etc/ssl/servercerts/servercert.pem
/etc/ssl/servercerts/serverkey.pem
eDirectory Server Certificates
43
Page 44

8.2 Using Internal Certificates in a Cluster
Recent versions of Novell Certificate Server create default certificates that allow you to specify an
alternative IP address or DNS address by adding it in the Subject Alternative Name extension. This
requires that your DNS service be configured to reflect the cluster IP/DNS address as the default (o r
first) address. If the DNS service is set up correctly, the cluster applications can use the default
certificates without needing any administration.
IMPORTANT: If the DNS service is not set up correctly, then you must use the process described
for external certificates in “Using External Certificates in a Cluster” on page 44.
For OES 2 Linux clusters using the internal certificate method, make sure the DNS service is
configured to use the cluster IP/DNS address. During the OES 2 Linux install, select the Use
eDirectory Certificates option so that Novell Certificate Server automatically creates the SSL
Certificate DNS certificate with the correct IP/DNS address. By selecting the Use eDirectory
Certificates option during the install and using the cluster IP/DNS address, clustered applications
should be able to access the certificates without needing further configuration for the Server
Certificate object.
8.3 Using External Certificates in a Cluster
External (third-party) certificates create a Server Certificate object that includes the cluster's IP and/
or DNS address. Create a backup of this certificate. For each server in the cluster, create a Server
Certificate object with the same name by importing the previously created backup certificate and
key pair to a location on that server. This allows all of the servers in the cluster to use and share the
same certificate and key pair. After all cluster nodes have the certificate, configure the cluster
applications to use the server certificate.
IMPORTANT: This cluster task can also be used for sharing internal certificates on the cluster
nodes. In early versions of Novell Certificate Server, this was the only option available.
For information about exporting and using eDirectory Server Certificates for External Services, see
“Using eDirectory Certificates with External Applications” (http://www.novell.com/documentation/
crt33/crtadmin/data/bh9x78f.html) in th e Novell Certificate Server 3.3.2 Administration Guide
(http://www.novell.com/documentation/crt33/crtadmin/data/a2ebomw.html).
For OES 2 Linux clusters using the external certificate method, the solution is more complicated
than for internal certificates. You must create the certificate for each server in the cluster just as you
did for NetWare. You must also create a configuration on the SAS:Service object for each server so
that the common certificate is automatically exported to the file system where the non-eDirectory
enabled applications can use it.
44 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 45

9
Novell CIFS
Novell CIFS for Linux is available beginning in OES 2 SP1 Linux.
After you set up Novell CIFS on the Linux node and before you finalize the NetWare-to-Linux
conversion, use the CIFS function in the Migration Tool to convert the configuration. For
information, see “Migrating CIFS from NetW are to OES 2 SP3 Linux” in the OES 2 SP3: Migration
Tool Administration Guide.
The commands in the scripts are also different. Af ter the migration, modify the load and unload
scripts on the Linux server. For information, see Section 3.6, “Comparing File Access Protocol
Resource Script Commands,” on page 23.
CIFS on OES 2 SP1 Linux does not support NCP cross-protocol file locking.
Beginning in OES 2 SP2 Linux, CIFS supports NCP cross-protocol file locking, which allows NCP,
AFP, and CIFS users to access files on an NSS volume concurrently without data corruption by
locking the files across protocols. On Linux, the cross-protocol file locking parameter for NCP
Server is enabled by default. It must be enabled on each node in the cluster if you plan to give both
NCP users and CIFS users access to an NSS volume in the cluster. See “Configuring Cross-Protocol
File Locks for NCP Server” in the OES 2 SP3: NCP Server for Linux Administration Guide.
Beginning in OES 2 SP3 Linux, CIFS supports the merged view for Novell Dynamic Storage
Technology (DST) shadow volumes built with NSS volumes. Wait until the cluster conversion is
complete before attempting to set up DST shadow volumes in the OES 2 SP3 Linux cluster.
9
Novell CIFS
45
Page 46

46 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 47

10
Novell Distributed File Services VLDB
The Novell Distributed File Services vo lume location datab ase (VLDB)
on both NetWare and Linux. The shared NSS volume that contains the
migrated to the Linux server.
Use one of these two methods for migrating the VLDB from NetWare to Linux:
Section 10.1, “Cluster Migrating the Shared NSS Volume for the VLDB,” on page 47
Section 10.2, “Adding a Linux Server as a Replica Site,” on page 48
10.1 Cluster Migrating the Shared NSS Volume for the VLDB
Use this method if you want to use the same shared disk where the VLDB is currently stored.
1 For each Linux node where you expect to run the VLDB service, install Novell Storage
Services and any of its dependent services on the Linux node, then add it to the mixed cluster
that you are converting.
2 For each of the Linux nodes, assign the node’s nssadmin user as a trustee of the container that is
configured as the Management Context for the VLDB, and give the user at least the
Compare
rights to the
[All Attribute Rights]
property.
.dat
file format is the same
.dat
file can be cluster
Read
and
10
IMPORTANT: If the Management Context is configured to use the container that contains a
node’s Server object, the nssadmin User object for that server is a already a trustee of the
container and has the
nssadmin User object when you add rights for the
2a In iManager, select Rights > Modify Trustees .
2b Select the container that is configured as the Management Context, then click OK.
2c Click Add Trustee, select the nssadmin User object, then click OK.
The nssadmin User object is in the same container as its server. The username format is
servnameadmin.context. For example, if the server name is
then server1admin.ou1.mycompany is the nssadmin username.
2d Click Assigned Rights for the selected nssadmin User object.
2e Assign the Read and Compare rights to the [All Attribute Rights] property, then click
Done.
2f Click Apply to save and apply the changes.
2g Repeat Step 2c through Step 2f for each of the Linux nodes where you expect to run the
VLDB service.
3 Cluster migrate the DFS cluster resource from NetWare to Linux.
4 On the Linux node where the VLDB is active, offline the DFS cluster resource.
Supervisor
right. Do not modify the existing rights settings for this
[All Attribute Rights]
server1.ou1.mycompany
property.
,
Novell Distributed File Services VLDB
47
Page 48

5 Remove the NetWare clusters from the cluster by using the
cluster leave
command, then
finish the cluster conversion.
This automatically updates the basic cluster commands in the cluster resource scripts.
6 Using the Clusters plug-in in iManager, modify the load script of the DFS cluster resource to
change the
vldb /dir=vldbpath
vldb
command to the Linux format. For example, change it from
to
vldb -dir /vldbpath
7 Online the cluster resource.
8 Run a VLDB repair to ensure that the database is correct.
10.2 Adding a Linux Server as a Replica Site
Use this method if you want to use a different shared disk for the VLDB on Linux. You can do this
by adding a DFS replica site on Linux.
1 Install OES 2 Linux on the server that you want to add to the cluster. Make sure Novell Storage
Services and any of its dependent services are installed.
2 Assign the node’s nssadmin user as a trustee of the container that is configured as the
Read
and
Management Context for the VLDB, and give the user at least the
[All Attribute Rights]
the
property.
Compare
rights to
IMPORTANT: If the Management Context is configured to use the container that contains a
node’s Server object, the nssadmin User object for that server is a already a trustee of the
container and has the
Supervisor
nssadmin User object when you add rights for the
right. Do not modify the existing rights settings for this
[All Attribute Rights]
property.
2a In iManager, select Rights > Modify Trustees .
2b Select the container that is configured as the Management Context, then click OK.
2c Click Add Trustee, select the nssadmin User object, then click OK.
The nssadmin User object is in the same container as its server. The username format is
servnameadmin.context. For example, if the server name is
server1.ou1.mycompany
then server1admin.ou1.mycompany is the nssadmin username.
2d Click Assigned Rights for the selected nssadmin User object.
2e Assign the Read and Compare rights to the [All Attribute Rights] property, then click
Done.
2f Click Apply to save and apply the changes.
3 Create a shared NSS pool and volume on the OES 2 Linux server, or create a shared Linux
POSIX volume.
4 In iManager, add the Linux server as the second VLDB replica site for the DFS management
context, and point to the shared NSS volume as the VLDB location.
5 Allow the VLDB data to synchronize between the NetWare replica and the Linux replica.
6 In iManager, remove the NetWare instance of the replica site.
,
48 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 49

7 Add the Linux server to the mixed-node NetWare cluster.
8 Continue with the cluster conversion as described i n Section 4.1, “Converting NetWare Cluster
Nodes to OES 2 Linux (Rolling Cluster Conversion),” on page 27.
Novell Distributed File Services VLDB 49
Page 50

50 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 51

11
DHCP Server
The Novell DHCP Server for Linux is based on a standards-compliant implementation from ISC
that is distributed with SUSE Linux Enterprise Server. DHCP uses a different schema on Linux to
store the configuration in eDirectory.
After you set up Novell DHCP Server on the OES 2 Linux serv er and before you complete the
cluster conversion, you can use the DHCP option for the Migration T ool to convert the configuration
from NetW are to OES 2 Linux. You cannot directly reuse the data. Migrate your DHCP server data,
then perform the post-migration tasks to set up the configuration in the OES 2 Linux nodes of the
cluster.
Section 11.1, “Setting Up Novell DHCP on OES 2 Linux,” on page 51
Section 11.2, “Prerequisites for Migration,” on page 51
Section 11.3, “Migrating the DHCP Configuration from NetWare to Linux Clusters in the Same
Tree,” on page 51
Section 11.4, “Post-Migration Tasks,” on page 52
11.1 Setting Up Novell DHCP on OES 2 Linux
Novell DHCP Server for OES 2 Linux supports using a shared Linu x POSIX fi le system or a shared
NSS file system for the cluster resource. Set up DHCP on the OES 2 Linux servers by using one of
the following methods in the OES 2 SP3: Novell DNS/DHCP Administration Guide:
11
“Configuring DHCP with Novell Cluster Services for the NSS File System”
“Configuring DHCP with Novell Cluster Services for the Linux File System”
11 .2 Prerequisites for Migration
For more information about prerequisites, see “Migration Requirements” for DHCP in the OES 2
SP3: Migration Tool Administration Guide.
11.3 Migrating the DHCP Configuration from NetWare to Linux Clusters in the Same Tree
In this scenario, both the NetWare server and the OES 2 Linux server are in the same eDirectory
tree. The NetWare source server must be running NetWare 5.1 SP8 or later versions. The Linux
target server must be running OES 2 SP1 (or later) Linux on either 32-bit or 64-bit hardware.
Run the DHCP function in the Migration Tool from one of the OES 2 Linux nodes. Perform the Tree
Level Migration with the same Source server (tree to which NetWare clustered nodes are attached)
and T ar get server (tree to which the Linux clustered nodes are attached). This ensures that th e enti re
NetWare DHCP configuration data is available for OES 2 Linux DHCP.
For information, see “Migrating DHCP ” in the OES 2 SP3: Migration Tool Administration Guide,
and follow the instructions for NetWare and Linux in the same eDirectory tree.
DHCP Server
51
Page 52

IMPORTANT: Before starting the DHCP server on the Linux cluster, stop the DHCP server on the
NetWare cluster.
11.4 Post-Migration Tasks
1 Log in as the
root
user to the OES 2 Linux node where you ran the migration, then open a
terminal console
2 Online the DHCP service cluster resource by entering
cluster online resource_name
3 On the Linux node where you ran the migration:
3a Open the
/mount_path/etc/dhcpd.conf
file in a text editor.
Replace mount_path with the Linux path to the folder in the shared volume where DHCPspecific directories are created.
3b In the
3c Copy the
/mount_path/etc/dhcpd.conf
server-cn
parameter to the cn of the migrated DHCP server, then save your changes.
migrated_server.leases
folder or to the lease path specified in the Migration Tool to the
dhcp/db/
folder, then rename it to
file, change the value for the
file from
dhcpd.leases
/var/opt/novell/dhcp/leases/
.
ldap-dhcp-
/mount_path/var/lib/
4 Stop the DHCP server on the NetWare cluster by taking the NetWare DHCP cluster resource
offline.
5 Start the DHCP server on the Linux cluster.
rcnovell-dhcpd start
52 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 53

12
DNS Server
Y o u can migrate the data from the Novell DNS Server on NetWare to a Novell DNS Server on Linux
after you have installed and set up DNS services on an OES 2 SP1 Linux node in the cluster. You
cannot directly reuse the data.
Section 12.1, “Prerequisites for Migration,” on page 53
Section 12.2, “Migrating the DNS Configuration from NetWare to Linux Clusters in the Same
Tree,” on page 53
Section 12.3, “Post-Migration Tasks,” on page 53
12.1 Prerequisites for Migration
For information about prerequisites, see “Migrating DNS from NetWare to OES 2 SP3 Linux” in the
OES 2 SP3: Migration Tool Administration Guide.
12.2 Migrating the DNS Configuration from NetWare to Linux Clusters in the Same Tree
In this scenario, both the NetWare server and the OES 2 SP1 Linux server are in the same eDirectory
tree. The NetWare source server must be running NetWare 5.1 SP8 or later versions. The Linux
target server must be running OES 2 SP1 Linux on either 32-bit or 64-bit hardware.
12
Use iManager to move the DNS server from a NetWare NCP server to an OES 2 SP1 Linux NCP
server. For information see “Using iManager to Migrate Servers within the Same eDirectory Tree”
in the OES 2 SP3: Migration Tool Administration Guide.
12.3 Post-Migration Tasks
See “Post-Migration Procedure” in the OES 2 SP3: Migration Tool Administration Guide.
1 Use iManager or the Java Management Console to check for the existence of the following
objects:
DNS-DHCP
DNSDHCP-GROUP
RootServerInfo
DNS Server object
2 Use the Clusters plug-in for iManager to verify the Cluster load script and unload script of the
DNS cluster resources.
For information, see “DNS Load and Unload Scripts” in the OES 2 SP3: Novell DNS/DHCP
Administration Guide.
3 Start the DNS server on the OES 2 Linux cluster.
DNS Server
53
Page 54

54 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 55

13
Novell iPrint
This section describes how to convert the iPrint cluster resource from NetWare 6.5 SP8 to OES 2
Linux.
Section 13.1, “Installing iPrint on the OES 2 Linux Nodes,” on page 55
Section 13.2, “Setting Up iPrint on the OES 2 Linux Nodes,” on page 55
Section 13.3, “Migrating the iPrint Cluster Resource from NetWare to OES 2 Linux,” on
page 58
Section 13.4, “Finalizing the Cluster Conversion,” on page 59
Section 13.5, “Additional Information,” on page 59
13.1 Installing iPrint on the OES 2 Linux Nodes
Prepare the first OES 2 Linux server for use with iPrint in a cluster:
1 Install the following services on an OES 2 Linux server:
Novell iPrint
Novell Storage Services
Novell Cluster Services (but do not configure at install time)
Select at least these services and any dependent services that each one requires.
13
2 After the install, add the server to the NetWare cluster:
For instructions, see Section 4.2, “Adding New OES 2 Linux Nodes to Y our NetWare Cluster,”
on page 30.
13.2 Setting Up iPrint on the OES 2 Linux Nodes
Perform the steps in this section to set up iPrint and an iPrint cluster resource on the OES 2 Linux
nodes in the mixed-node cluster.
Section 13.2.1, “Preparing the OES 2 Linux Nodes for iPrint,” on page 55
Section 13.2.2, “Setting Up iPrint on the OES 2 Linux iPrint Cluster Resource,” on page 57
Section 13.2.3, “Setting Up Preferred Nodes for the OES 2 Linux iPrint Cluster Resource,” on
page 57
Section 13.2.4, “Editing the Load and Unload Scripts for the OES 2 Linux iPrint Cluster
Resource,” on page 57
Section 13.2.5, “Verifying the Status of the iPrint Setup,” on page 58
13.2.1 Preparing the OES 2 Linux Nodes for iPrint
Because iPrint on NetWare and iPrint on Linux are different, cluster migrating the iPrint cluster
resource from NetWare to Linux is not an option. You create a new pool cluster resource on an OES
2 Linux node that will be the iPrint cluster resource on Linux. To set up iPrint on each server, you
Novell iPrint
55
Page 56

move the iPrint configuration information from t he defaul t Linux installation path on each node to
the newly created shared NSS pool resource. Later, you will move the iPrint Driver Store and Print
Manager information from the NetWare resource to the OES 2 Linux resource.
1 In a Web browser, open iManager, then use the Storage role to create a new shared pool and
volume on one of the OES 2 Linux servers where iPrint is installed.
This is the iPrint cluster resource that will contain the iPrint data.
For information about creating a clustered NSS pool and volume, see “Creating Cluster-
Enabled Pools and Volum es ” in the OES 2 SP3: Novell Cluster Services 1.8.8 Administration
Guide for Linux.
2 On the first OES 2 Linux node, set up clustering for iPrint on the shared NSS volume that you
created in Step 1.
root
2a Log in as the
user to the OES 2 Linux node where the shared pool resource is active,
then open a terminal console.
2b Go to the
/opt/novell/iprint/bin
folder, then run the
iprint_nss_relocate
script
by entering
./iprint_nss_relocate -a admin_fdn -p admin_password -n
nss_volume_path -l cluster [-c <Specify Container FDN where iPrint LUM
object already
exists or should be created>] [-w <Specify Container FDN where Apache
LUM objects exist>]
Replace admin_fdn with the comma-delimited fully distinguished name of the iPrint
administrator user (such as
cn=admin,o=mycompany
). Replace admin_password with the
actual password of the specified iPrint administrator user. Replace nss_volume_path with
the Linux path (such as
/media/nss/NSSVOL1
) to the shared NSS volume where you
want to relocate the iPrint configuration data.
For information about the script options, see “Setting up iPrint on an NSS File System” in
the OES 2 SP3: iPrint for Linux Administration Guide.
For example, enter
./iprint_nss_relocate -a cn=admin,o=mycompany -p password -n /media/
nss/NSSVOL1 -l cluster -c o=mycompany,t=iPrint_Tree -w
o=mycompany,t=iPrint_Tree
2c Review the messages displayed on the screen to confirm the data mi gration from the loca l
Linux path to the shared NSS path is completed.
3 For each remaining Linux node in the cluster where iPrint is installed, set up clustering for
iPrint by doing the following:
3a Log in as the
root
user to the OES 2 Linux node where the shared pool resource is active,
then open a terminal console.
3b Cluster migrate the shared NSS pool resource from the active OES 2 Linux node to this
OES 2 Linux node by entering
cluster migrate resource_name node_name
3c Log in to the newly active OES 2 Linux node as the
console.
3d Run the
iprint_nss_relocate
script as described in Step 2b, using the same values.
3e Repeat Step 3a through Step 3d until all of the OES 2 Linux nodes are configur ed fo r
iPrint.
56 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
root
user, then open a terminal
Page 57

13.2.2 Setting Up iPrint on the OES 2 Linux iPrint Cluster Resource
1 In iManager, select iPrint > C r eate Driver Store, then create a Driver Store on the OES 2 Linux
node where the iPrint cluster resource is active.
For information, see “Creating a Driver Store” in the OES 2 SP3: iPrint for Linux
Administration Guide.
Use the IP or DNS name of the shared NSS pool resource that you created in Section 13.2.1,
“Preparing the OES 2 Linux Nodes for iPrint,” on page 55 as the Target Server. For the
eDirectory Server Name, choose an eDirectory server that holds a copy of the replica where the
Printer Agents will be created.
2 In iManager, select iPrint > Create Print Manager, then create a Print Manager on the OES 2
Linux node where the iPrint cluster resource is active.
For information, see “Creating a Print Manager” in the OES 2 SP3: iPrint for Linux
Administration Guide.
Use the IP or DNS name of the shared NSS pool resource that you created in Section 13.2.1,
“Preparing the OES 2 Linux Nodes for iPrint,” on page 55 as the iPrint Service. For the
eDirectory Server Name, choose same server that you specified for the Driver Store. Deselect
the Start print manager after creation option.
13.2.3 Setting Up Preferred Nodes for the OES 2 Linux iPrint Cluster Resource
Configure the Preferred Nodes list for the Linux shared NSS pool cluster resource to prevent an
inadvertent failback of the resource to a NetWare server.
1 In iManager, click Clusters > Cluster Manager, then select the cluster where the Linux shared
NSS pool resource is currently active.
2 Select the link for the OES 2 Linux shared NSS pool cluster resource to open its Properties
page.
3 Go to the Preferred Nodes tab.
4 Move all of the NetWare nodes from the Assigned Nodes list to Unassigned Nodes list .
5 Click OK to save your changes.
13.2.4 Editing the Load and Unload Scripts for the OES 2 Linux iPrint Cluster Resource
Edit the load and unload scripts for the OES 2 Linux iPrint cluster resource.
1 Edit the load script. Add the following lines to the existing load script before the
statement
ignore_error mv /media/nss/NSSVOL1/var/opt/novell/iprint/iprintgw.lpr /
media/nss/NSSVOL1/var/opt/novell/iprint/iprintgw.lpr.bak
NOTE: Replace
volume mount point.
/media/nss/NSSVOL1
in the above command with your actual cluster
exit 0
Novell iPrint 57
Page 58

exit_on_error rcnovell-idsd start
exit_on_error rcnovell-ipsmd start
2 Edit the unload script. Add the following lines to the existing unload script after the
novell/ncs/lib/ncsfuncs
ignore_error rcnovell-ipsmd stop
ignore_error rcnovell-idsd stop
3 Activate the load and unload scripts by taking the resource offline, then bringing the resource
online.
statement:
/opt/
13.2.5 Verifying the Status of the iPrint Setup
Verify that the iPrint cluster resource is working by cluster migrating the OES 2 Linux iPrint cluster
resource to each OES 2 Linux node in turn and performing the following checks:
root
1 Log in as the
then open a terminal console.
2 Check the status of the Print Manager and Driver Store.
rcnovell-ipsmd status
rcnovell-idsd status
3 Test the ability of
iprntman psm -l -u admin
4 Cluster migrate the iPrint cluster resource to another OES 2 Linux node by entering
cluster migrate resource_name node_name
5 Repeat this check for each OES 2 Linux node in the mixed-node cluster.
user on the OES 2 Linux node where the iPrint cluster resource is active,
iprntman
to authenticate the admin user (or other user given with
miggui
).
13.3 Migrating the iPrint Cluster Resource from NetW are to OES 2 Linux
After iPrint is configured for the OES 2 Linux nodes, you are ready to migrate the iPrint Driver
Store and Print Manager information from the NetWare iPrint cluster resource to the OES 2 Linux
iPrint cluster resource.
Perform the following steps in “Migrating an iPrint Cluster Resource” in the OES 2 SP3: Migration
Tool Administration Guide.
1 Perform the pre-migration checks as described in “Pre-Migration iPrint Configuration” in the
OES 2 SP3: Migration Tool Administration Guide.
2 Perform a consolidated migration of the iPrint service as described in “iPrint Consolidate
Migration” in the OES 2 SP3: Migration Tool Administration Guide.
Start the Migration Tool from the target server (the OES 2 Linux node where the iPrint cluster
resource is active).
For the source server, authenticate by using the IP address or DNS name of the NetWare iPrint
cluster resource.
For the target server, authenticate by using the IP address or DNS name of the Linux iPrint
cluster resource.
3 Verify that the migration was successful as described in “Verifying the Result of the iPrint
Migration” in the OES 2 SP3: Migration Tool Administration Guide.
58 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 59

4 Transition the Transition end-user printing from NetWare to Linux.
Offline the NetWare iPrint cluster resource.
View the NetWare iPrint cluster load script's /DNSNAME value.
Configure DNS to resolve the /DNSNA ME value to the IP address of the target Linux
cluster resource hosting the Print Manager.
NOTE: The propagation of the DNS change might take time, depending on your network.
DNSNAME is the address that the clients use to find the NetWare Print Manager. The
same DNSNAME is used to find the Linux Print Manager.
Update each of the Linux node
address.
Update the
the /DNSNAME.
Restart the Print Manager.
5 (Optional) Perform the post-migration steps as described in “Transfer ID” and “Post Transfer
ID Migration Steps ” in the OES 2 SP3: Migration Tool Administration Guide.
For detailed information about iPrint migration requ irements, pre-migration configuration,
migration procedures, post-migration tasks, and troubleshooting, see “Migrating iPrint from
NetWare or OES 2 Linux to OES 2 SP3 Linux” in the OES 2 SP3: Migration Tool Administration
Guide.
/etc/opt/novell/iprint/conf/ipsmd.conf
/etc/hosts
files to resolve to the Linux iPrint cluster IP
PSMHostAddress value to
13.4 Finalizing the Cluster Conversion
After your OES 2 Linux iPrint setup is working as expected, finalize the cluster conversion, as
described in Section 4.3, “Finalizing the Cluster Conversion,” on page 32.
13.5 Additional Information
See the following Novell Support Technical Information Documents (TIDs) for more information
about migrating iPrint from NetWare to OES 2 Linux:
TID 7005448: Migrating an iPrint Cluster from NetWare to OES 2 (http://www.novell.com/
support/viewContent.do?externalId=7005448)
TID 7004455: iPrint Migration Best Practices (http://www.novell.com/support/
viewContent.do?externalId=7004455)
Novell iPrint 59
Page 60

60 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 61

14
MySQL
On Linux, you can use the MySQL 5.0.x so ftwa re on No vell Op en Enterprise Server (OES) 2 Linux
that is offered under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
Configure the OES service to use MySQL 5.0.x on OES 2 Linux before setting up clustering for the
related MySQL database.
For the Linux version of MySQL, use a procedure similar to the one on NetWare to set up a new
cluster resource. Use the Linux commands for MySQL in the load and unload scripts. Use a Linux
path on a shared Linux POSIX file system for the MySQL database. As a general reference, see
“Configuring MySQL on Novell Clustering Services” in the.NW 6.5 SP8: Novell MySQL
Administration Guide
14
MySQL
61
Page 62

62 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 63

15
QuickFinder Server
In a Novell Cluster Services cluster, you must install QuickFinder on each node in the cluster. This
registers QuickFinder Server with each of the Web servers and application servers running on each
server. On OE S 2 Li nux, Qu ickF inder is i nstall ed by defau lt in the
recommend that you use the default path. After the installation, you must set up one or more virtual
search servers to enable QuickFinder Server to work in a cluster.
When the Linux setup is completed, you are ready to manually migrate settings from the NetWare
cluster to the Linux cluster. Set up QuickFinder on the OES 2 Linux cluster nodes, then manually
migrate QuickFinder data from a NetWare node to an OES 2 Linux node.
For information about using the QuickFinder Server Manager and other procedures for QuickFinder,
see the OES 2 SP3: Novell QuickFinder Server 5.0 Administration Guide.
Section 15.1, “Prerequisites,” on page 63
Section 15.2, “Setting Up QuickFinder Server on Linux Cluster Nodes,” on page 63
Section 15.3, “Migrating QuickFinder Data from NetWare to Linux,” on page 64
Section 15.4, “Post-Migration Consid erat ion s ,” on page 65
Section 15.5, “Searching the Cluster Volume,” on page 65
/var/lib/qfsearch
folder . We
15
15.1 Prerequisites
Before you begin:
1 On one Linux node, create a Linux POSIX cluster resource where all of the indexes and virtual
search server settings are to be stored.
For information, see “Configuring and Managing Cluster Resources for Shared Linux POSIX
Vol umes” in the OES 2 SP3: Novell Cluster Services 1.8.8 Administration Guide for Linux.
15.2 Setting Up QuickFinder Server on Linux Cluster Nodes
On each OES 2 Linux node, do the following to set up QuickFinder for Linux:
1 Cluster migrate the Linux POSIX cluster resource to the OES 2 Linux node where you want to
install QuickFinder
2 Install QuickFinder on the active cluster node.
3 Create a virtual search server to enable QuickFinder Server to work in a cluster.
Give each virtual search server the same name and location. After the first server is set up, any
settings that you create on the shared volume are automatically displayed.
3a On the active cluster node, open the QuickFinder Server Manager.
3b Click Global Settings, then click Add New Virtual Server.
3c In Name, specify the DNS name of the cluster.
QuickFinder Server
63
Page 64

3d In Location, specify the Linux path on the Linux POSIX cluster resource where all of the
indexes and virtual search server settings will be located.
3e Click Add.
4 Repeat Step 1 to Step 3 for each of the nodes in the cluster.
15.3 Migrating QuickFinder Data from NetWare to Linux
Use the following steps to migrate QuickFinder Server data from a NetWare server to a
corresponding Linux server. You must repeat the tasks for each NetWare server in the cluster. It
assumes a one-to-one server replacement in the cluster.
WARNING: Migrating indexes and virtual search server settings from a QuickFinder Server
running on NetWare to QuickFinder Server running on OES 2 Linux replaces the existing settings
on the Linux server. If you want to merge your NetWare settings with the existing Linux settings,
you must manually re-create the NetWare settings by using the QuickFinder Server Manager.
1 Open a Web browser, the access the QuickFinder Server Manager on the NetWare server.
http://servername/qfsearch/admin
2 Click Global Settings in the top toolbar.
3 Write down the paths for each virtual search server displayed in the Location column.
4 On the OES 2 Linux server where the shared volume is active, mount the NetWare server by
using the
ncpmount
5 Make a backup of the
command.
/var/lib/qfsearch/SiteList.properties
file.
Make sure that you don't have a file with this name as a backup on the NetWare server.
6 Copy all
NetWare server to
7 Copy
8 Copy
Templates
9 If any of the paths listed in Step 3 are not under
.properties
sys:/qfsearch/Sites
sys:/qfsearch/Templates
and
Cron.jobs
/var/lib/qfsearch
and all of its subdirectories to
.
files from the root folder
on the Linux server.
/var/lib/qfsearch/Sites
and all of its subdirectories to
sys:/qfsearch
sys:/qfsearch
/var/lib/qfsearch/
on the
(for example, if you installed
a virtual search server somewhere other than the default location), you must also copy those
paths to Linux.
For example, if you have the path
Linux server. You could copy it to
qfsearch/Sites/PartnerSite
10 Edit all NetWare paths in
sys:/SearchSites/PartnerSite,
/var/opt/SearchSites/PartnerSite
.
/var/lib/qfsearch/SiteList.properties
you must copy it to the
or
/var/lib/
to reflect the new
Linux paths.
For example, change
Or, as in the example in Step 9, change
SearchSites/PartnerSite
sys:/qfsearch
.
to
/var/lib/qfsearch.
sys:/SearchSites/PartnerSite
to
/var/opt/
.
Some paths might have one or two backslashes (\) that must be replaced with one forward slash
(/). For example,
.
docs
64 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
sys:\\qfsearch\\docs
needs to be changed to
/var/lib/qfsearch/
Page 65

11 Update all NetWare paths in the properties and configuration files copied in the steps above to
the Linux paths, and update any DNS names.
The following files must be updated:
AdminServlet.properties
Cron.jobs
Sites/Highlighter.properties
Sites/Print.properties
Sites/Search.properties
For each of the virtual search servers, modify the following:
qfind.cfg
Any of the above
IMPORTANT: Linux filenames are case sensitive.
The names of most properties files are mixed case, so make sure the files copied from NetWare
are the correct case. You can compare them to the
You might also need to update paths in templates. If you have problems such as a template not
being found or some properties not being set properly, check the case of the filename.
If you modified any “file” index paths to index d irectorie s on t he Linux server, that index must
be regenerated.
.properties
files, if they exist.
.properties.sample
files on Linux.
12 After all the files have been modified, run the following commands to set the access rights and
the owner and groups so that the QuickFinder engine has rights to access the files.
As the
chown -R root:www /var/lib/qfsearch
chmod -R 770 /var/lib/qfsearch
13 Repeat Step 1 to Step 12 for each NetWare and Linux pair of nodes.
root
user, enter
15.4 Post-Migration Considerations
QuickFinder Server 5.0 indexes are not compatible with previous versions of QuickFinder Server.
The indexes must be regenerated, and y ou c ann ot sy nch r on ize QuickFinder Server 5.0 indexes with
indexes from a previous version of QuickFinder Server (and vice-versa).
15.5 Searching the Cluster Volume
To perform a search on the shared volume after the NetWare migration is complete:
1 Open a Web browser, then enter
http://DNS_CLUSTER/qfsearch/search
QuickFinder Server sees the DNS and sends the request to the appropriate virtual search server.
QuickFinder Server 65
Page 66

66 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 67

16
Novell Storage Services Pools
Consider the guidelines in this section when converting Novell Storage Services (NSS) pool cluster
resources from NetWare to Novell Open Enterprise Server (OES) 2 Linux.
Section 16.1, “NSS Pool Cluster Migration,” on page 67
Section 16.2, “NSS File System Migration to NCP V olumes or Linux POSIX File Systems,” on
page 67
Section 16.3, “Estimated Time Taken to Build the Trustee File on Linux,” on page 67
16.1 NSS Pool Cluster Migration
In the mixed-node cluster, NSS pool cluster resources created on NetWare can be failed over or
cluster migrated to nodes that are running OES 2 Linux where NSS is installed and running. Some
NSS features are not available or work differently on Linux. For information, see “Cross-Platform
Issues for NSS” in the OES 2 SP3: NSS File System Administration Guide for Linux.
Pool snapshots use different technologies on NetWare and Linux. Make sure to delete pool
snapshots for all clustered pools before you begin the cluster conversion.
16.2 NSS File System Migration to NCP Volumes
16
or Linux POSIX File Systems
To move data from NSS file systems on NetWare to NCP volumes or to Linux POSIX file systems
on Linux, you must use the OES 2 SP1 Migrat ion too l. For information, se e “Migrating File System
from NetWare, OES 1 or OES 2 to OES 2 SP3 Linux” in the OES 2 SP3: Migration Tool
Administration Guide.
16.3 Estimated Time Taken to Build the Trustee File on Linux
On Linux, NCP Server stores file system trustees and rights information in the
.trustee_database.xml
system also stores this information in its file system metadata as it does on NetWare. This database
file is updated when you:
Add file system trustees and rights
Delete file system trustees and rights
Modify file system trustees and rights
When you migrate an NSS volume from NetWare to Linux, the tru stee database file does not exist.
NCP Server reads the trustee and rights information from the NSS file system metadata, validates
the User object, and stores the settings in a
the volume. The information collection process begins automatically when the NSS volume is
mounted on the OES 2 Linux server.
file at the root of each NSS volume or NCP volume. The NSS file
._NetWare/.trustee_database.xml
._NetWare/
file at the root of
Novell Storage Services Pools
67
Page 68

Testing found that building the intial datab ase on Linux for an existing volume takes about one
minute per 50,000 storage objects. Testing was done on the following configuration for the target
server:
HP DL380 G5
2 Quadcore Intel Xeon CPU E5345 @ 2.33 GHz
12 GB RAM
1 Gigabit NIC
2 HBAs with 4 paths to the EMC DMX Symmetrix Storage with 4 gigabits per second (Gbps)
bandwidth
68 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 69

A
Documentation Updates
This section contains information about documentation content changes made to information in the
Novell Cluster Services for Linux Conversion Guide since the initial Novell Clu s ter Service s 1.8.5
release for Novell Open Enterprise Server 2. If you are an existing user, review the change entries to
readily identify modified content. If you are a new user, simply read the guide in its current state.
This document was updated on the following dates:
Section A.1, “December 2010 (OES 2 SP3),” on page 69
Section A.2, “May 31, 2010 (Maintenance Patch),” on page 70
Section A.3, “January 29, 2010 (Maintenance Patch),” on page 71
Section A.4, “January 20, 2010,” on page 71
Section A.5, “January 4, 2010,” on page 72
Section A.6, “December 10, 2009,” on page 72
Section A.7, “November 2009 (OES 2 SP2),” on page 72
Section A.8, “July 30, 2009,” on page 73
Section A.9, “June 22, 2009,” on page 74
Section A.10, “June 5, 2009,” on page 74
Section A.11, “May 6, 2009,” on page 75
A
Section A.12, “March 3, 2009,” on page 75
Section A.13, “February 13, 2009,” on page 75
Section A.14, “February 3, 2009,” on page 76
Section A.15, “December 2008 (OES 2 SP1),” on page 76
A.1 December 2010 (OES 2 SP3)
This content in this guide previously appeared as the “Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2
Linux” chapter in the OES 2 SP2: Novell Cluster Services for Linux Administration Guide.
In addition, updates were made to the following section. The changes are explained below.
Section A.1.1, “Apache Web Server,” on page 69
Section A.1.2, “Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux,” on page 70
Section A.1.3, “Novell Distributed File Services VLDB,” on page 70
Section A.1.4, “Planning the Cluster Conversion,” on page 70
Section A.1.5, “Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts,” on page 70
A.1.1 Apache Web Server
This section was expanded to include installation and setup information that is specific to Linux.
Documentation Updates
69
Page 70

A.1.2 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux
Location Change
Step 1 in “Finalizing the
Cluster Conversion” on
page 32
Beginning in OES 2 SP3, you can use the
command to preview all resources.
all
A.1.3 Novell Distributed File Services VLDB
Location Change
Step 2 in “Cluster Migrating
the Shared NSS Volume for
the VLDB” on page 4 7
Step 2 in “Adding a Linux
Server as a Replica Site” on
page 48
For each of the Linux nodes, assign the node’s nssadmin user as a
trustee of the container that is configured as the Management Context for
the VLDB, and give the user at least the
[All Attribute Rights]
property.
Read
A.1.4 Planning the Cluster Conversion
Location Change
Section 1.11, “Managing File
Systems in Mixed-Node
Clusters,” on page 12
If you need to configure (or reconfigure) existing shared NSS pools and
volumes in a mixed-node cluster, you must temporarily bring down all
Linux cluster nodes prior to making changes, then make the configuration
changes on a NetWare node. Make sure the resources are working
properly on NetWare before having the Linux cluster nodes rejoin the
cluster.
cluster convert preview
and
Compare
rights to the
A.1.5 Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts
Location Change
Section 3.2, “Comparing
Script Length Limits for
NetWare and Linux,” on
page 20
This section is new.
A.2 May 31, 2010 (Maintenance Patch)
Updates were made to the following sections. The changes are explained below.
Section A.2.1, “Novell AFP,” on page 71
Section A.2.2, “Novell CIFS,” on page 71
70 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 71

A.2.1 Novell AFP
Location Change
Chapter 5, “Novell AFP,” on
page 35
Beginning in OES 2 SP2 Linux, the cross-protocol file locking parameter
for NCP Server is enabled by default.
A.2.2 Novell CIFS
Location Change
Chapter 9, “Novell CIFS,” on
page 45
Beginning in OES 2 SP2 Linux, the cross-protocol file locking parameter
for NCP Server is enabled by default.
A.3 January 29, 2010 (Maintenance Patch)
Updates were made to the following sections. The changes are explained below.
Section A.3.1, “Planning the Cluster Conversion,” on page 71
Section A.3.2, “Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux,” on page 71
A.3.1 Planning the Cluster Conversion
Location Change
“SBD Devices Must Be
Marked as Shareable for
Clustering” on page 10
This section is new.
A.3.2 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux
Location Change
“Converting NetWare Cluster
Nodes to OES 2 Linux
(Rolling Cluster Conversion)”
on page 27
“Adding New OES 2 Linux
Nodes to Your NetWare
Cluster” on page 30
Step1 on page 27 is new. Before you add the first Linux node to the
NetWare cluster , mark the NetW are cluster SBD devices as Shareable for
Clustering.
Step1 on page 30 is new. Before you add the first Linux node to the
NetWare cluster , mark the NetW are cluster SBD devices as Shareable for
Clustering
A.4 January 20, 2010
Updates were made to the following section. The changes are explained below.
Section A.4.1, “Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux,” on page 72
Documentation Updates 71
Page 72

A.4.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux
Location Change
“Converting NetWare Cluster
Nodes to OES 2 Linux
(Rolling Cluster Conversion)”
on page 27
“Finalizing the Cluster
Conversion” on page 32
.Step 11 was removed. A cluster restart is no longer required.
.Step 3 was revised. A cluster restart is no longer required.
A.5 January 4, 2010
Updates were made to the following section. The changes are explained below.
Section A.5.1, “eDirectory Server Certificates,” on page 72
A.5.1 eDirectory Server Certificates
Location Change
“Using Internal Certificates in
a Cluster” on page 44
.This section was modified for clarity.
.
A.6 December 10, 2009
Updates were made to the following section. The changes are explained below.
Section A.6.1, “Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux,” on page 72
A.6.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux
Location Change
Section 4.1, “Converting
NetWare Cluster Nodes to
OES 2 Linux (Rolling Cluster
Conversion),” on page27
Added the following instruction in Step 3 on page 28:
You can do this by running NWConf ig , then selecting Product Options >
Directory Options <install NDS> > Remove Directory Services from this
server.
A.7 November 2009 (OES 2 SP2)
Updates were made to the following sections. The changes are explained below.
Section A.7.1, “Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux,” on page 73
Section A.7.2, “Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts,” on page 73
72 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 73

A.7.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux
Location Change
Section 4.3, “Finalizing the
Cluster Conversion,” on
page 32
Modified Step 3 to state that you must run
ncs-configd.py -init
Cluster Services on each of the nodes in the cluster.
on each of the nodes in the cluster, or restart
/opt/novell/ncs/bin/
A.7.2 Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts
Location Change
Section 3.7, “Customizing
the Translation Syntax for
Converting Load and Unload
Scripts,” on page 25
This section is new.
A.8 July 30, 2009
Updates were made to the following section. The changes are explained below.
Section A.8.1, “Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux,” on page 73
Section A.8.2, “Planning the Cluster Conversion,” on page 73
A.8.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux
Location Change
Section 4.3, “Finalizing the
Cluster Conversion,” on
page 32
WARNING: After you finalize the cluster conversion, rollback to NetWare
is not supported.
A.8.2 Planning the Cluster Conversion
Location Change
Section 1.12, “Using Novell
iManager in Mixed-Node
Clusters,” on page 13
Section 1.13, “Using Novell
Remote Manager Is Not
Supported in Mixed-Node
Clusters,” on page 13
This section is new.
Use Novell iManager 2.7.2 or later for all cluster administration in the
mixed-node cluster.
Do not use Novell Remote Manager when managing mixed-node clusters.
Novell Remote Manager is not supported for cluster management on OES
2 Linux.
Documentation Updates 73
Page 74

Location Change
Section 1.14, “Using
ConsoleOne Is Not
Supported for Mixed-Node
Clusters,” on page 13
This section is new.
Do not use ConsoleOne when managing mixed-node clusters.
ConsoleOne is not supported for cluster management on OES 2 Linux.
A.9 June 22, 2009
Updates were made to the following section. The changes are explained below.
Section A.9.1, “Planning the Cluster Conversion,” on page 74
A.9.1 Planning the Cluster Conversion
Location Change
Section 1.13, “Using Novell
Remote Manager Is Not
Supported in Mixed-Node
Clusters,” on page 13
This section is new.
A.10 June 5, 2009
Updates were made to the following sections. The changes are explained below.
Section A.10.1, “Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux,” on page 74
Section A.10.2, “Novell Storage Services Pools,” on page 75
A.10.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux
Location Change
Section 4.1, “Converting
NetWare Cluster Nodes to
OES 2 Linux (Rolling Cluster
Conversion),” on page27
Section 4.2, “Adding New
OES 2 Linux Nodes to Your
NetWare Cluster,” on
page 30
In Step 10 on page 29, added clarification that checking for an SBD is
necessary only if the cluster has a shared disk system.
In Step 6 on page 32, added clarification that checking for an SBD is
necessary only if the cluster has a shared disk system.
74 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 75

A.10.2 Novell Storage Services Pools
Location Change
Chapter 16, “Novell Storage
Services Pools,” on page 67
Added information about how long it might take to build the trustee.xml file
during a migration from NetWare to Linux.
A.11 May 6, 2009
Updates were made to the following section. The changes are explained below.
Section A.11.1, “Planning the Cluster Conversion,” on page 75
A.11.1 Planning the Cluster Conversion
Location Change
Section 1.11, “Managing File
Systems in Mixed-Node
Clusters,” on page 12
If you need to configure (or reconfigure) existing shared NSS pools and
volumes or trustee assignments in a mixed-node cluster, you must
temporarily remove all Linux cluster nodes by issuing the
command prior to making any NSS changes.
leave
A.12 March 3, 2009
Updates were made to the following section. The changes are explained below.
cluster
Section A.12.1, “Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux,” on page 75
A.12.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux
Location Change
Step 3 in Section 4.3,
“Finalizing the Cluster
Conversion,” on page 32
You must restart the cluster so that clstrlib.ko is reloaded:
rcnovell-ncs restart
A.13 February 13, 2009
Errata were corrected. Updates were made to the following sections. The changes are explained
below.
Section A.13.1, “Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux,” on page 76
Section A.13.2, “Novell Storage Services Pools,” on page 76
Section A.13.3, “Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts,” on page 76
Documentation Updates 75
Page 76

A.13.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Clusters to OES 2 Linux
Location Change
Chapter 2, “Planning the
Conversion of Cluster
Resources,” on page 15
Added a link to the eDirectory caveat.
A.13.2 Novell Storage Services Pools
Location Change
Section 16.2, “NSS File
System Migration to NCP
Volumes or Linux POSIX File
Systems,” on page 67
This section is new.
A.13.3 Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts
Location Change
Section 3.1, “Translation of
Cluster Resource Scripts for
Mixed NetWare and Linux
Clusters,” on page 19
The path to the files is
/var/opt/novell/ncs/
.
A.14 February 3, 2009
Updates were made to the following section. The changes are explained below.
Section A.14.1, “Novell AFP,” on page 76
A.14.1 Novell AFP
Location Change
Chapter 5, “Novell AFP,” on
page 35
Added information about using the NCP cross-protocol file locking feature
on OES 2 SP1 Linux.
A.15 December 2008 (OES 2 SP1)
Updates were made to the following sections. The changes are explained below.
Section A.15.1, “Converting NetWare 6.5 Cluster to OES 2 Linux,” on page 77
Section A.15.2, “Planning the Cluster Conversion,” on page 77
76 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
Page 77

Section A.15.3, “Planning the Conversion of Cluster Resources,” on page 77
Section A.15.4, “Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts,” on page 77
A.15.1 Converting NetWare 6.5 Cluster to OES 2 Linux
Location Change
Section 4.1, “Converting
NetWare Cluster Nodes to
OES 2 Linux (Rolling Cluster
Conversion),” on page27
This procedure has been updated.
A.15.2 Planning the Cluster Conversion
Location Change
Section 1.15, “Using the
Monitoring Function in
Mixed-Node Clusters Is Not
Supported,” on page 14
This section is new.
A.15.3 Planning the Conversion of Cluster Resources
Location Change
Chapter 2, “Planning the
Conversion of Cluster
Resources,” on page 15
This section is new.
A.15.4 Planning the Conversion of Load and Unload Scripts
Location Change
Section 3.6, “Comparing File
Access Protocol Resource
Script Commands,” on
page 23
This section is new.
Documentation Updates 77
Page 78

78 OES 2 SP3: Novell Clu ster Services Conversion Guide
 Loading...
Loading...