Page 1

N0087114 1.0
December 15, 2005
Norstar
R2MFC Card Installation and
Configuration Guide
Page 2
2
Copyright © Nortel Networks Limited 2005. All rights reserved.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and
recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied
warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The
information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks NA Inc.
Trademarks
NORTEL NETWORKS is a trademark of Nortel Networks.
Microsoft, MS, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
International Regulatory Information
The CE Marking on this equipment indicates compliance with
the following:
This device conforms to Directive 1999/5/EC on Radio
Equipment and Telecommunications Terminal Equipment as
adopted by the European Parliament And Of The Council.
This is a class A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in
which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Hereby, Nortel Networks declares that this equipment is in compliance with the essential
requirements and other relevant provisions of Directive 1999/5/EC.
Information is subject to change without notice. Nortel Networks reserves the right to make
changes in design or components as progress in engineering and manufacturing may warrant. This
equipment has been tested and found to comply with the European Safety requirements EN 60950
and EMC requirements EN 55022 (Class A) and EN 55024. These EMC limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial and light industrial environment.
Warning: This is a class A product. In a domestic environment this product
may cause radio interference in which case the user may be required to take
adequate measures. The above warning is inserted for regulatory reasons. If
any customer believes that they have an interference problem, either because
their Nortel Networks product seems to cause interference or suffers from
interference, they should contact their distributor immediately. The distributor
will assist with a remedy for any problems and, if necessary, will have full
support from Nortel Networks.
N0087114 1.0
Page 3
Safety
This equipment meets all applicable requirements of both the CSA C22.2 No.60950 and UL
60950.
3
The shock hazard symbol within an equilateral triangle is intended to alert personnel
to electrical shock hazard or equipment damage. The following precautions should
also be observed when installing telephone equipment.
• Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
• Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed
for wet locations.
• Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has
been disconnected at the network interface.
• Use caution when working with telephone lines.
Danger: Risk of shock.
Read and follow installation instructions carefully.
Ensure the system and system expansion units are unplugged from the power socket and
that any telephone or network cables are unplugged before opening the system or system
expansion unit.
If installation of additional hardware and /or servicing is required, disconnect all telephone
cable connections prior to unplugging the system equipment.
Ensure the system and system expansion units are plugged into the wall socket using a
three-prong power cable before any telephone cables are connected.
Caution: Only qualified persons should service the system.
The installation and service of this hardware is to be performed only by service personnel
having appropriate training and experience necessary to be aware of hazards to which they
are exposed in performing a task and of measures to minimize the danger to themselves or
other persons.
Electrical shock hazards from the telecommunication network and AC mains are possible
with this equipment. To minimize risk to service personnel and users, the system must be
connected to an outlet with a third-wire ground. Service personnel must be alert to the
possibility of high leakage currents becoming available on metal system surfaces during
power line fault events near network lines. These leakage currents normally safely flow to
Protective Earth ground via the power cord. Therefore, it is mandatory that connection to
an earthed outlet is performed first and removed last when cabling to the unit. Specifically,
operations requiring the unit to be powered down must have the network connections
(central office lines) removed first.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 4

4
Important Safety Instructions
The following safety instructions cover the installation and use of the Product. Read carefully and
retain for future reference.
Installation
WARNING: To avoid electrical shock hazard to personnel or equipment damage observe the
following precautions when installing telephone equipment:
1. Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
2. Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed for wet
locations.
3. Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has been
disconnected at the network interface.
4. Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines. The exclamation point within an
equilateral triangle is intended to alert the user to the presence of important operating and
maintenance (servicing) instructions in the literature accompanying the product.
Use
When using your telephone equipment, basic safety precautions should always be followed to
reduce risk of fire, electric shock and injury to persons, including the following:
1. Read and understand all instructions.
2. Follow the instructions marked on the product.
3. Unplug this product (or host equipment) from the wall outlet before cleaning. Do not use liquid
cleaners or aerosol cleaners. Use a damp cloth for cleaning.
4. Do not use this product near water, for example, near a bath tub, wash bowl, kitchen sink, or
laundry tub, in a wet basement, or near a swimming pool.
5. Do not place this product on an unstable cart, stand or table. The product may fall, causing
serious damage to the product.
6. This product should never be placed near or over a radiator or heat register. This product should
not be placed in a built-in installation unless proper ventilation is provided.
7. Do not allow anything to rest on the power cord. Do not locate this product where the cord will
be abused by persons walking on it.
N0087114 1.0
Page 5

8. Do not overload wall outlets and extension cords as this can result in the risk of fire or electric
shock.
9. Never spill liquid of any kind on the product.
10. To reduce the risk of electric shock do not disassemble this product, but have it sent to a
qualified service person when some service or repair work is required.
11. Unplug this product (or host equipment) from the wall outlet and refer servicing to qualified
service personnel under the following conditions:
a) When the power supply cord or plug is damaged or frayed.
b) If the product has been exposed to rain, water or liquid has been spilled on the product,
disconnect and allow the product to dry out to see if it still operates; but do not open up the
product.
c) If the product housing has been damaged.
d) If the product exhibits a distinct change in performance.
5
12. CAUTION: To eliminate the possibility of accidental damage to cords, plugs, jacks, and the
telephone, do not use sharp instruments during the assembly procedures
13. WARNING: Do not insert the plug at the free end of the handset cord directly into a wall or
baseboard jack. Such misuse can result in unsafe sound levels or possible damage to the handset.
14. Save these instructions.
Emergency Calling
Caution: Warn ing
Local, state and federal requirements for Emergency services support by Customer
Premises Equipment vary. Consult your telecommunication service provider regarding
compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Hearing Aid Compatibility
System telephones are hearing-aid compatible, as defined in Section 68.316 of Part 68 FCC Rules.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 6

6
Limited Warranty
Nortel Networks warrants this product against defects and malfunctions during a one (1) year
period from the date of original purchase. If there is a defect or malfunction, Nortel Networks
shall, at its option, and as the exclusive remedy, either repair or replace the telephone set at no
charge, if returned within the warranty period.
If replacement parts are used in making repairs, these parts may be refurbished, or may contain
refurbished materials. If it is necessary to replace the telephone set, it may be replaced with a
refurbished telephone of the same design and color. If it should become necessary to repair or
replace a defective or malfunctioning telephone set under this warranty, the provisions of this
warranty shall apply to the repaired or replaced telephone set until the expiration of ninety (90)
days from the date of pick up, or the date of shipment to you, of the repaired or replacement set, or
until the end of the original warranty period, whichever is later. Proof of the original purchase date
is to be provided with all telephone sets returned for warranty repairs.
Exclusions
Nortel Networks does not warrant its telephone equipment to be compatible with the equipment of
any particular telephone company. This warranty does not extend to damage to products resulting
from improper installation or operation, alteration, accident, neglect, abuse, misuse, fire or natural
causes such as storms or floods, after the telephone is in your possession.
Nortel Networks shall not be liable for any incidental or consequential damages, including, but not
limited to, loss, damage or expense directly or indirectly arising from the customers use of or
inability to use this telephone, either separately or in combination with other equipment. This
paragraph, however, shall not apply to consequential damages for injury to the person in the case
of telephones used or bought for use primarily for personal, family or household purposes.
This warranty sets forth the entire liability and obligations of Nortel Networks with respect to breach of
warranty, and the warranties set forth or limited herein are the sole warranties and are in lieu of all other
warranties, expressed or implied, including warranties or fitness for particular purpose and merchantability.
Warranty Repair Services
Should the set fail during the warranty period:
In North America, call 1-800-574-1611 for further information.
Outside North America, contact your sales representative for return instructions. You will be
responsible for shipping charges, if any. When you return this telephone for warranty service, you
must present proof of purchase.
N0087114 1.0
Page 7

After Warranty Service
Nortel Networks offers ongoing repair and support for this product. This service provides repair or
replacement of your Nortel Networks product, at Nortel Networks’s option, for a fixed charge.
You are responsible for all shipping charges. For further information and shipping instructions:
In North America, contact our service information number: 1-800-574-1611.
Outside North America, contact your sales representative.
Repairs to this product may be made only by the manufacturer and its authorized agents, or by others who
are legally authorized. This restriction applies during and after the warranty period. Unauthorized repair
will void the warranty.
7
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 8

8
N0087114 1.0
Page 9
Contents
International Regulatory Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Important Safety Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Emergency Calling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Hearing Aid Compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Limited Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Exclusions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Warranty Repair Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
After Warranty Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Before you begin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
How to get Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Acronyms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
9
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Getting Help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Getting Help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code . . . . . . . . 16
Getting Help through a Nortel distributor or reseller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Chapter 1
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Administration and maintenance tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
R2MFC card faceplate elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
System Status LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Config DIP switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
RS232 port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
E1 Status LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Bantam jacks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
BNC and RJ-48 connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Chapter 2
Preparing to install the R2MFC card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Installation process map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Host system setup requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
R2MFC card setup requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Config DIP switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Environment checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Electrical requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Software requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 10

10
Customer-supplied hardware requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Chapter 3
Installing the R2MFC card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Shutting down the system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Installing an R2MFC card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Installing an R2MFC card in the Norstar system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Reconnecting the equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Removing an R2MFC card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Removing an R2MFC card from the Norstar System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Wiring an R2MFC card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Connecting an R2MFC card to a service provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Chapter 4
Configuring the R2MFC card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
R2MFC side (External Link) configurable parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Physical line characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
E1 framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Line signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
End of dialing (incoming) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
End of dialing (outgoing) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Disable ANI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Default category . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Default subscriber status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Configuring the R2MFC (external) link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Setting Config DIP switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Creating a customized country code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
PRI side (Internal Link) configurable parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
E1 Framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Configuring the PRI (internal) link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Turning on second dial tone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Chapter 5
R2MFC card maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Inter-working functionality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Clock synchronization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Diagnostic tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Setting the R2MFC card to diagnostic or loopback mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Alarms Measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
N0087114 1.0
Group I errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Page 11

Group II errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Alarms propagation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Faceplate LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Logs and traces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Error messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Replacing an R2MFC card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Upgrading firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Chapter 6
Command Line Interface (CLI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Users and passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Accessing the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
LOad directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
INfo directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
VIew directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
CNtrl directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
COnfig directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
ALarm directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
SWerr directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
MFC directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
R2 directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
PRI directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
11
Appendix A
Config DIP switch settings and definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Country code defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Mexico Config 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
E1 physical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
E1 framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
R2 line signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
MFC register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Mexico Config 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
E1 physical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
E1 framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
R2 line signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
MFC register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Brazil Config 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
E1 physical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
E1 framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 12

12
R2 line signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
MFC Register Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Brazil Config 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
E1 physical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
E1 framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
R2 line signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
MFC Register Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Argentina Config 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
E1 Physical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
E1 Framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Frame mode: Alternate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
R2 Line Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
MFC Register Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Columbia Config 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
E1 Physical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
E1 Framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Frame mode: Alternate (card default, not affected by DIP switch) . . . . . . . . . 91
Register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
R2 Line Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
MFC Register Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Malaysia and Singapore Config 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
E1 Physical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
E1 Framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Frame mode: Alternate (card default, not affected by DIP switch) . . . . . . . . . 94
Register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
R2 Line Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
MFC Register Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Korea Config 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
E1 Physical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
E1 Framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Frame mode: Alternate (card default, not affected by DIP switch) . . . . . . . . . 96
Register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
R2 Line Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
MFC Register Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
India Config 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
E1 Physical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
E1 Framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Frame mode: Alternate (card default, not affected by DIP switch) . . . . . . . . . 99
Register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
R2 Line Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
MFC Register Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
N0087114 1.0
Page 13

China and Thailand Config 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
E1 Physical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
E1 Framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Frame mode: CRC4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
R2 Line Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
MFC Register Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Indonesia Config 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
E1 Physical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
E1 Framing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Frame mode: Alternate (card default, not affected by DIP switch) . . . . . . . . 104
Register signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
R2 Line Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
MFC Register Signaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Appendix B
Diagnostic and loopback DIP switch settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
13
Appendix C
MFC Signal Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Appendix D
CLI Cable Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 14

14
N0087114 1.0
Page 15
Preface
This guide explains how to install, configure, and maintain the Nortel R2MFC card.
The guide also provides information about the Command Line Interface (CLI) tool used to
configure, operate, administer and maintain the R2MFC card from a computer.
The document contains the following chapters:
Chapter 1, “Overview” — introduces the elements of the R2MFC card.
Chapter 2, “Preparing to install the R2MFC card” — describes the process of preparing for
R2MFC card installation.
Chapter 3, “Installing the R2MFC card” — describes the process of installing the R2MFC card
and connecting the R2MFC card to the host system.
15
Note: The CLI is separate from the Norstar Remote Utilities (NRU) tool.
Chapter 4, “Configuring the R2MFC card” — describes the configuration tools and the process of
configuring the R2MFC card.
Chapter 5, “R2MFC card maintenance” — describes the maintenance tools and the process of
maintaining the R2MFC card.
Chapter 6, “Command Line Interface (CLI)” — describes the Command Line Interface and the
commands used to configure, operate, administer, and maintain the R2MFC card.
Before you begin
This guide assumes the following:
• The host system is installed and initialized and is working correctly.
• The host system is running Norstar MICS 4.0, or greater. The R2MFC card is not compatible
with Norstar CICS systems. Second dial tone is available only on Norstar 6.0 or higher.
• The R2MFC card must be installed in the Norstar main chassis, the R2MFC card is not
compatible with the Norstar trunk module.
• Users have a working knowledge of the host system operations.
• All configuration installers have a working knowledge of the Windows operating system and
graphical user interfaces.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 16

16 Preface
How to get Help
This section explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site
The best way to get technical support for Nortel products is from the Nortel Technical Support
Web site:
http://www.nortel.com/support
This site provides quick access to software, documentation, bulletins, and tools to address issues
with Nortel products. More specifically, the site enables you to:
• download software, documentation, and product bulletins
• search the Technical Support Web site and the Nortel Knowledge Base for answers to
technical issues
• sign up for automatic notification of new software and documentation for Nortel equipment
• open and manage technical support cases
Getting Help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center
If you don’t find the information you require on the Nortel Technical Support Web site, and have a
Nortel support contract, you can also get help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835).
Outside North America, go to the following Web site to obtain the phone number for your region:
http://www.nortel.com/callus
Getting Help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code
To access some Nortel Technical Solutions Centers, you can use an Express Routing Code (ERC)
to quickly route your call to a specialist in your Nortel product or service. To locate the ERC for
your product or service, go to:
http://www.nortel.com/erc
Getting Help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor or authorized
reseller, contact the technical support staff for that distributor or reseller.
N0087114 1.0
Page 17

Acronyms
This guide uses the following acronyms (listed in alphabetical order):
AIS Alarm Indication Signal
ANI Automatic Number Identification
BPV Bipolar Violations
CLI Command Line Interface
CLID Calling Line Identification
CO Central Office
CRC4 Cyclic Redundancy Check 4
CSU Channel Service Unit
DCH D-Channel Handler
DTI Card Digital Interface Card
DTMF Dual Tone Multi-Frequency
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Prorammable Read Only Memory
ETSI European Telecommunications Standards Institute
FBER Frame Bit Error
Preface 17
FEBE Far End Block Error
ICS Integrated Communication System
ISDN Integrated Services Digital Network
KSU Key Service Unit
LFA Loss of Frame Alignment
LMA Loss of Multiframe Alignment
LOS Loss of Signal
MFC Multi-Frequency Compelled
MSC Media Services Card
OOF Out-of-Frame
OOM Out of CRC-4 Multiframe Alignment
OOS Out Of Service
PCM Pulse Code Modulation
PRI Primary Rate Interface
RAI Remote Alarm Indication
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 18

18 Preface
N0087114 1.0
Page 19
Chapter 1
Overview
This chapter provides an overview of the R2MFC card.
This chapter includes the following information:
• “General information”
• “Administration and maintenance tools” on page 20
• “R2MFC card faceplate elements” on page 20
General information
The R2MFC card is a digit trunk interface card (DTI card) that provides MFC-R2 connectivity
over an E1 trunk. The card works as a converter between Euro-ISDN and MFC-R2 protocols,
allowing the MFC-R2 protocol E1 to work directly with the Norstar system without the use of an
external converter. The Norstar system recognizes the converter as a Euro-ISDN trunk DTI card
and, therefore, provides all of the functionality on the MFC-R2 E1 that is available on a
Euro-ISDN E1. The MFC-R2 trunk is controlled by DIP switches and the Command Line
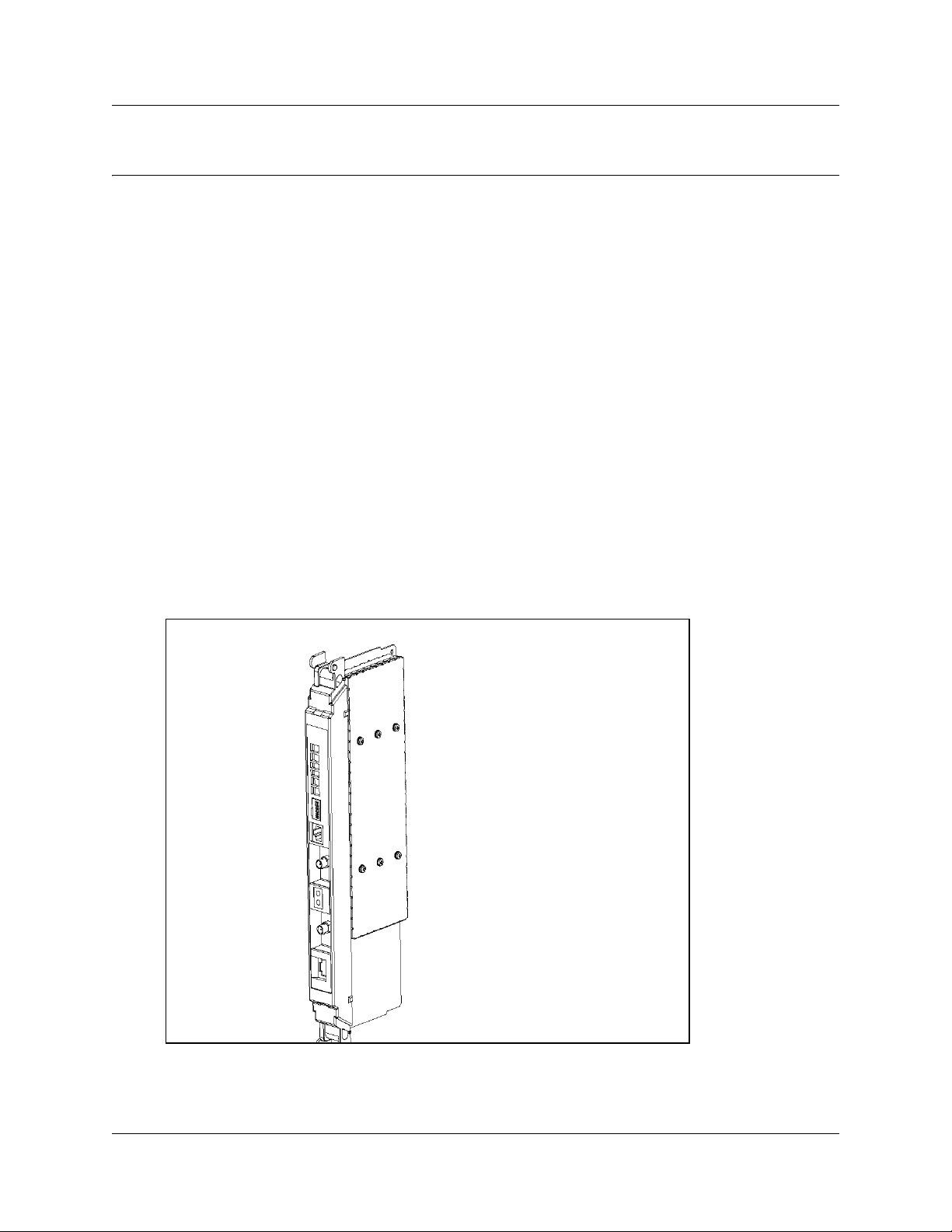
Interface (CLI) on the R2MFC card. Figure 1 provides an illustration of the R2MFC card.
19
Figure 1 R2MFC card
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 20
20 Chapter 1 Overview
Administration and maintenance tools
R2MFC card configuration involves the following:
• Internal link configuration for the PRI internal link to the Norstar system. The internal link
uses preset characteristics and, therefore, does not require localization.
• External link configuration of the MFC-R2 E1 the external interface to public network. The
external link allows for localization in different countries.
External link configuration is performed using the DIP switches on the front of the R2MFC card or
by using the CLI, which is accessed through a serial port on the faceplate of the R2MFC card.
Internal link configuration is performed using a Norstar digital telephone set. Refer to
“Configuring the R2MFC card” on page 35 for information on how to use the configuration
tools.
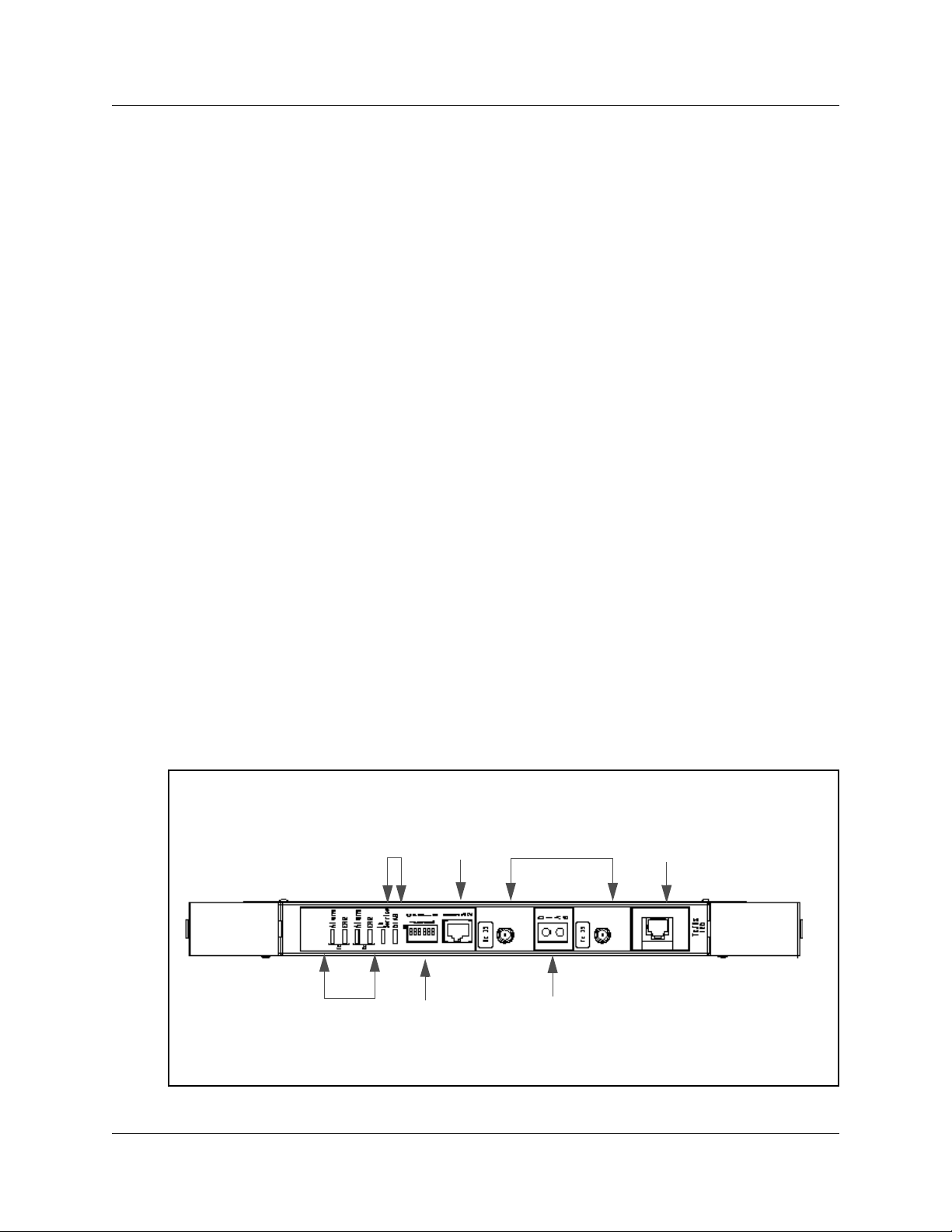
R2MFC card faceplate elements
The faceplate of the R2MFC card consists of the following elements:
• “System Status LEDs” on page 21
• “Config DIP switches” on page 21
• “RS232 port” on page 21
• “E1 Status LEDs” on page 22
• “Bantam jacks” on page 22
• “BNC and RJ-48 connectors” on page 22
Figure 2 illustrates the placement of these elements.
Figure 2 R2MFC card faceplate
Card laying horizontally
Card status
2 LEDS
RJ-45
75
Ω
E1 BNC
120 Ω E1
RJ-48
N0087114 1.0
E1 status
4 LEDS
DIP
switches
Bantam
jacks
Page 21
Chapter 1 Overview 21
n
System Status LEDs
The R2MFC card has two visual status monitor indicators near the top of the faceplate. They are:
• In Service LED — This green LED indicates the status of the E1 signal coming to the
R2MFC card from the Norstar System.
• Diag LED — This red LED indicates if the R2MFC card is in a diagnostic or loopback
mode.
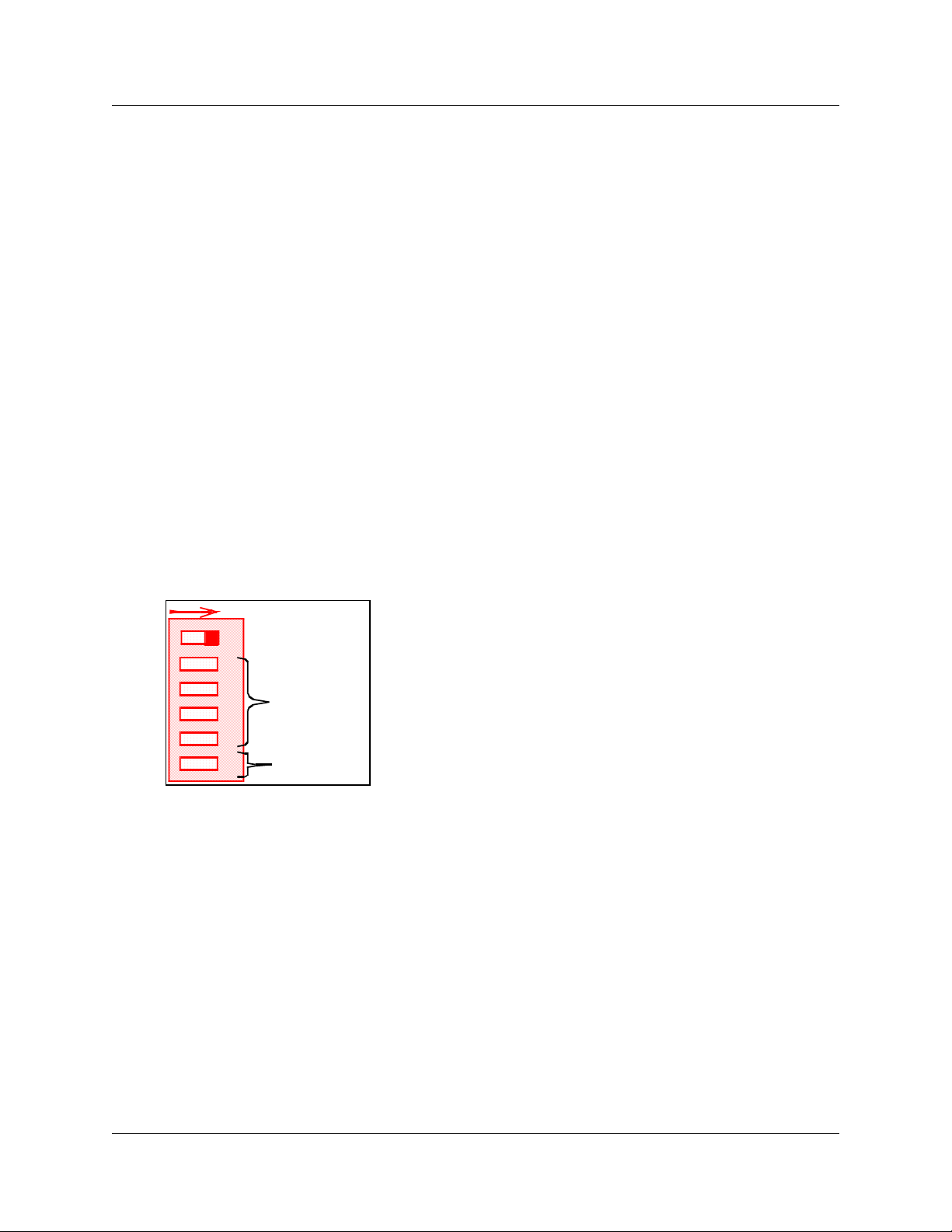
Config DIP switches
The R2MFC card has six config DIP switches on its faceplate. Use these DIP switches to set the
following configurations for the R2MFC card:
• country
• problem diagnosis
• second dial tone
You must set these DIP switches before power is connected to the R2MFC card. Figure 3 shows
the Config DIP switches.
Figure 3 Config DIP Switches
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
For DIP switch values and configuration information, see “Configuring the R2MFC (external)
link” on page 39.
These DIP switches are also used for problem diagnostics. For specific settings and uses, see
“Diagnostic tools” on page 49.
configuratio
dial tone
RS232 port
An RJ-45 serial port connector named RS232 is located on the faceplate of the R2MFC card. Use
the N0026100 cable, shipped with the R2MFC card, to connect a computer to the RS232 port for
advanced configuration or for CLI-based diagnostics of the R2MFC card. Appendix D, “CLI
Cable Pinout,” on page 111 shows the pinout information to make a new N0026100 cable.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 22

22 Chapter 1 Overview
E1 Status LEDs
The R2MFC card has four visual status monitor indicators at the top of the faceplate. They are:
• ERR Tx — indicates a Transmit error on the external E1 link
• ERR Rx — indicates a Receive error on the external E1link
• ALM Tx — indicates a Transmit alarm on the external E1 link
• ALM Rx — indicates a Receive alarm on the external E1 link
Bantam jacks
The R2MFC card contains Bantam jacks in the middle of the faceplate, to be used for connecting
diagnostic equipment. The jacks are labeled DIAG.
BNC and RJ-48 connectors
The R2MFC card has both BNC and RJ-48 external E1 connectors located in the middle and
bottom portion of the faceplate. Use these connectors to connect the R2MFC card to the Central
Office (CO).
The default interface is based on the country code selected. Mexico variant 1 is the factory default.
See Appendix A, “Config DIP switch settings and definitions,” on page 77 for the country code
default settings.
N0087114 1.0
Page 23
Chapter 2
Preparing to install the R2MFC card
This chapter provides an overview of the preparation required to install the R2MFC card in a host
system. (The host system is the Norstar system to which the R2MFC card connects.)
The information in this chapter is based on the following assumptions:
• The host system is installed, initialized, and tested.
• The installer has a working knowledge of the host system and an understanding of
telecommunications.
This chapter contains the following information:
• “Installation process map”
• “Host system setup requirements” on page 24
• “R2MFC card setup requirements” on page 24
• “Customer-supplied hardware requirements” on page 25
23
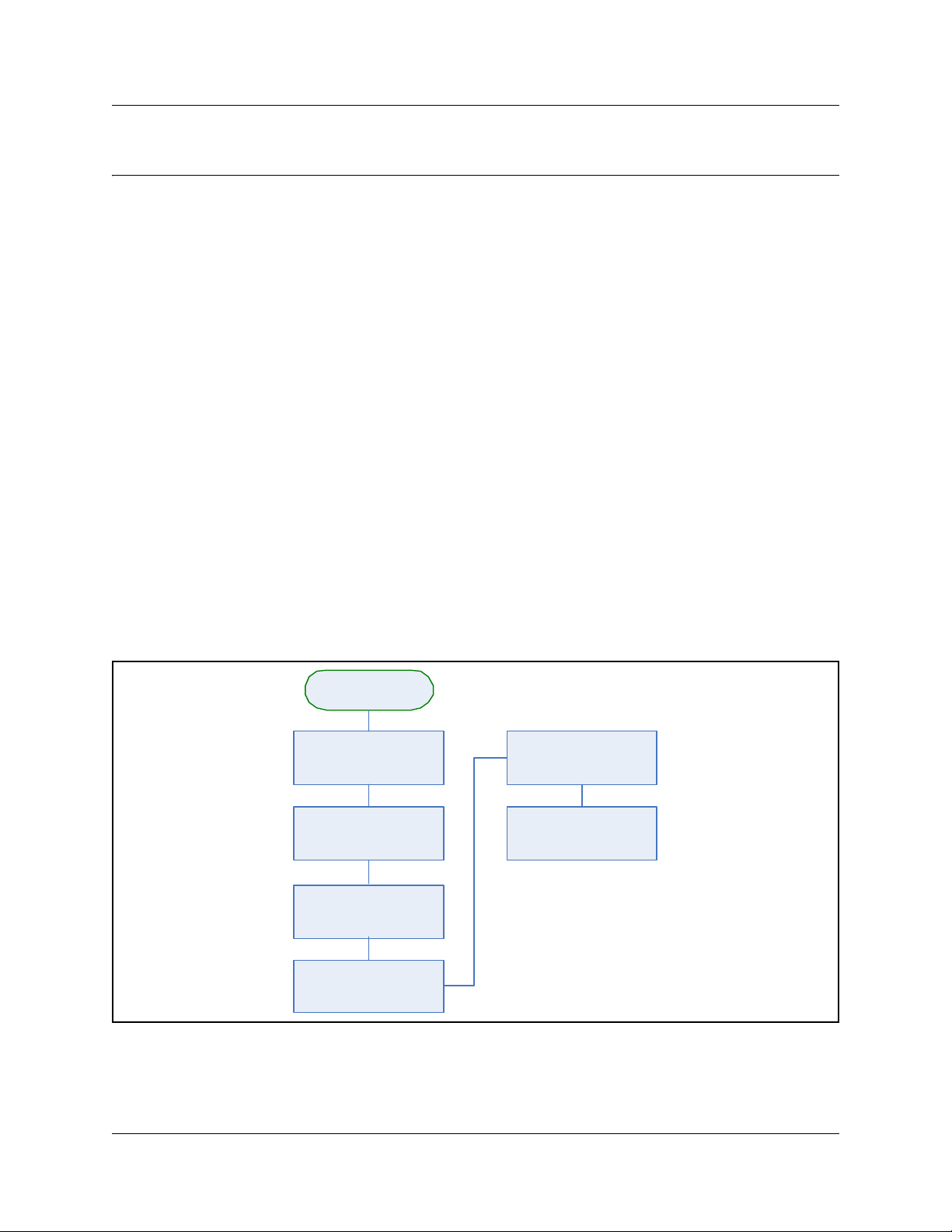
Installation process map
Figure 4 provides an overview of the R2MFC card installation preparation.
Figure 4 Overview of the R2MFC card installation preparation
Installation
preparation
Ensure that Norstar is
installed and configured
properly
Determine the correct
country and variant
Ensure environmental
requirements are met
Ensure that all of the
customer supplied
hardware is present
requirements are met
requirements are met
Ensure electrical
Ensure software
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 24

24 Chapter 2 Preparing to install the R2MFC card
Host system setup requirements
Table 1 describes the tasks that you must complete on the host system before proceeding with the
installation of the R2MFC card.
Table 1 Host system setup requirements
Task Location of task information
Install host system Norstar: Modular ICS Installer Guide
Determine if host system has
enough system capacity
Configure E1 Settings Norstar: Programming Record
Norstar: Modular ICS Installer Guide
R2MFC card setup requirements
This section provides the following information about the setup requirements for the R2MFC card:
• “Config DIP switches”
• “Environment checklist”
• “Electrical requirements” on page 25
• “Software requirements” on page 25
Config DIP switches
Determine and set the Config DIP switches to the correct country code, and second dial tone
setting for the R2MFC card. Predefined country codes are set by the Config DIP switches. Special
configurations are set through the CLI. See “Configuring the R2MFC (external) link” on page 39
for a procedure on how to set the DIP switches for a predefined country code or how to create a
special configuration to meet the installation needs.
The default country code setting is Mexico config 1. See Appendix A, “Config DIP switch settings
and definitions,” on page 77 for a list of the available country codes, the country default settings,
and the second dial tone settings.
Second dial tone, when turned on, generates and supplies a second dial tone to the end user, after
the end user dials the trunk access code. The end user hears a dial tone between the last digit of the
access code, indicating that a line was accessed. See “Turning on second dial tone” on page 45 for
a procedure on how to set the DIP switches, and configure the Norstar system for second dial tone
to work properly.
N0087114 1.0
Page 25

Chapter 2 Preparing to install the R2MFC card 25
Environment checklist
The R2MFC card environmental requirements are covered by the host system environment setup.
See the Norstar Installer Guide supplied with the host system for details of environmental
requirements.
Electrical requirements
The R2MFC card power is supplied through the chassis on the host sytem. See the Norstar
Installer Guide supplied with the host system for details of the electrical requirements.
Software requirements
R2MFC card firmware upgrades are posted at www.nortel.com under Support & Training >
Technical Support > Software Downloads. Access this web site to see if there is a newer version
of firmware available than the firmware shipped on the R2MFC card. See “Upgrading firmware”
on page 55 for information on how to upgrade to the latest release of firmware.
Customer-supplied hardware requirements
The following equipment is required to install of the R2MFC card:
• A Norstar digital telephone set for programming of the Norstar system.
• An E1 connection from local telephony service provider. A full description of the signaling
provided over the E1 by the CO.
• Computer with monitor and serial port for access to the CLI. Required only if system is not
using a country code defined by the Config DIP switches.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 26

26 Chapter 2 Preparing to install the R2MFC card
N0087114 1.0
Page 27
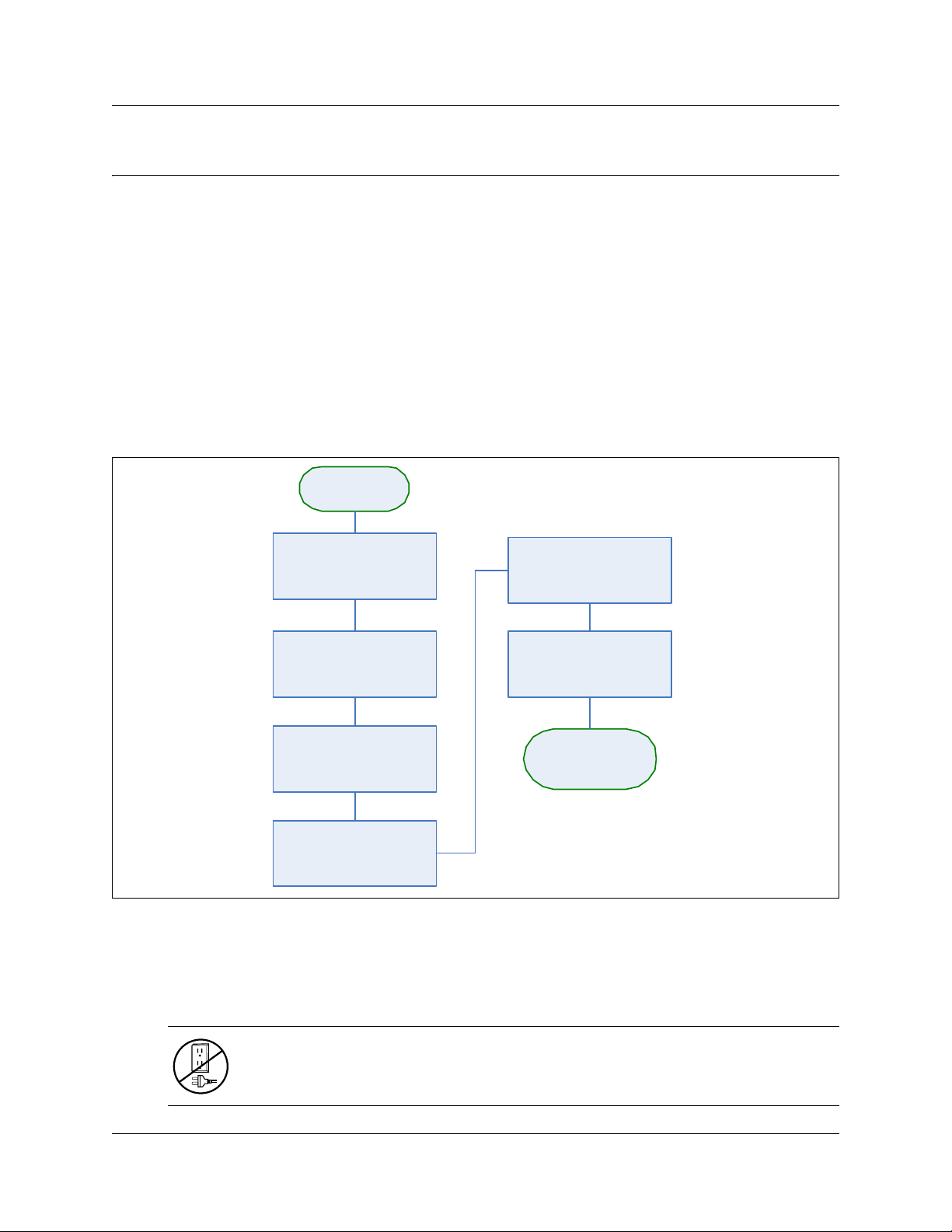
Chapter 3
Installing the R2MFC card
This chapters describes how to install and remove an R2MFC card in a host Norstar system.
This chapter provides the following installation and removal procedures:
• “Shutting down the system”
• “Installing an R2MFC card” on page 28
• “Removing an R2MFC card” on page 30
• “Wiring an R2MFC card” on page 31
Figure 5 provides an overview of the steps for installing the R2MFC card.
Figure 5 Overview of the R2MFC card installation
Set card DIP
switches
27
Disconnect cables from
the KSU
Disconnect power from
unit
Install new R2MFC
Card
Restore power to
Norstar
Shutting down the system
Before you shut down the system or perform any maintenance procedures, read the following
warnings to ensure you and your system are properly protected.
Reconnect all cables
Monitor LEDs for power
and status
Continue with
system
initialization
Warning: If you are installing a new Norstar, refer to the Installer guide for the host
system for instructions about installing a new system before you connect the system to
the AC power outlet.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 28
28 Chapter 3 Installing the R2MFC card
Warning: Failure to follow procedures to properly disconnect the Norstar and
expansion unit can result in module or system damage.
Warning: Ensure you are properly grounded before handling modules or any
components that are part of the Norstar hardware.
1 Attach one end of the grounding strap to your wrist and the other end to a grounded metal
surface.
2 Ensure the cables connected to the front of the Norstar and the expansion module are clearly
marked as to how they are connected.
3 Remove the cables from all the R2MFC cards on the Norstar base module and the expansion
module (if attached).
4 Disconnect the Norstar and expansion module power cords from the AC outlet.
Installing an R2MFC card
Follow the procedures in this section to install an R2MFC card in a Norstar platform base module.
Refer to the Installer Guide for the host Norstar system for detailed information on placement of
cards.
Installing an R2MFC card in the Norstar system
Perform the following steps to install an R2MFC card in the Norstar system:
Caution: Only install the R2MFC card when the system is powered down. See
“Shutting down the system” on page 27.
1 Ensure that the faceplate Config DIP switches on the R2MFC card are set correctly. For
information on how to set the faceplate switches, refer to “Setting Config DIP switches” on
page 39.
2 Select an open card slot.
3 With the face of the R2MFC card facing toward you, insert the R2MFC card into the open slot.
Install trunk cartridges in the ICS (Integrated Communication System) beginning with Slot 4,
then Slot 3.
4 Push the R2MFC card completely into the unit.
Figure 6 on page 29 shows an R2MFC card being installed.
N0087114 1.0
Page 29
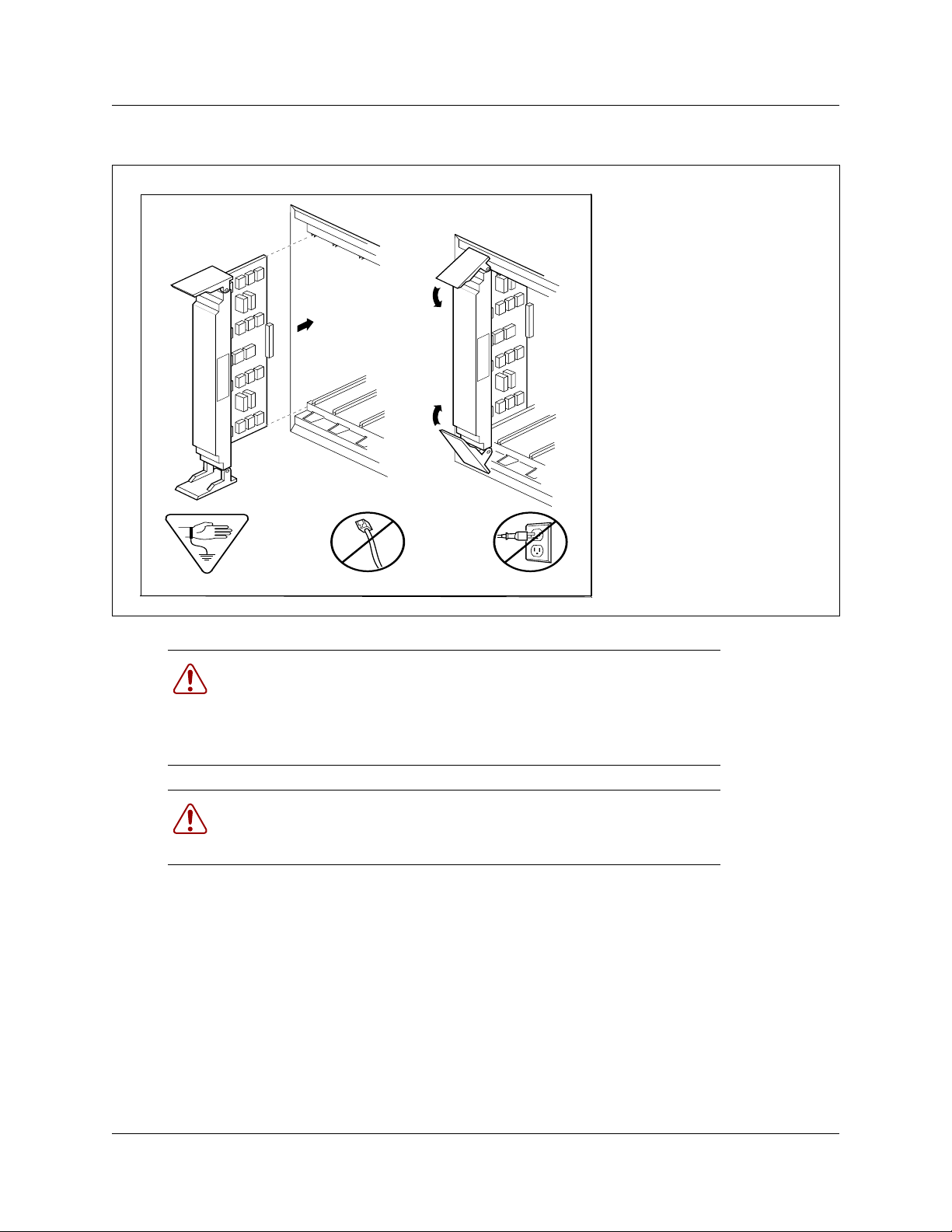
Figure 6 Installing a R2MFC card
Chapter 3 Installing the R2MFC card 29
Insert card and close clips
simultaneously.
Warning: Close clips simultaneously.
It is important to center and close the two clips on the cartridge
simultaneously, otherwise the cartridge may become misaligned in its
slot or with its connector. If improperly inserted, the connector will be
damaged.
Warning: PCB is electrostatic-sensitive.
Do not touch the printed circuit board on a cartridge. This is an
electrostatic-sensitive device.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 30
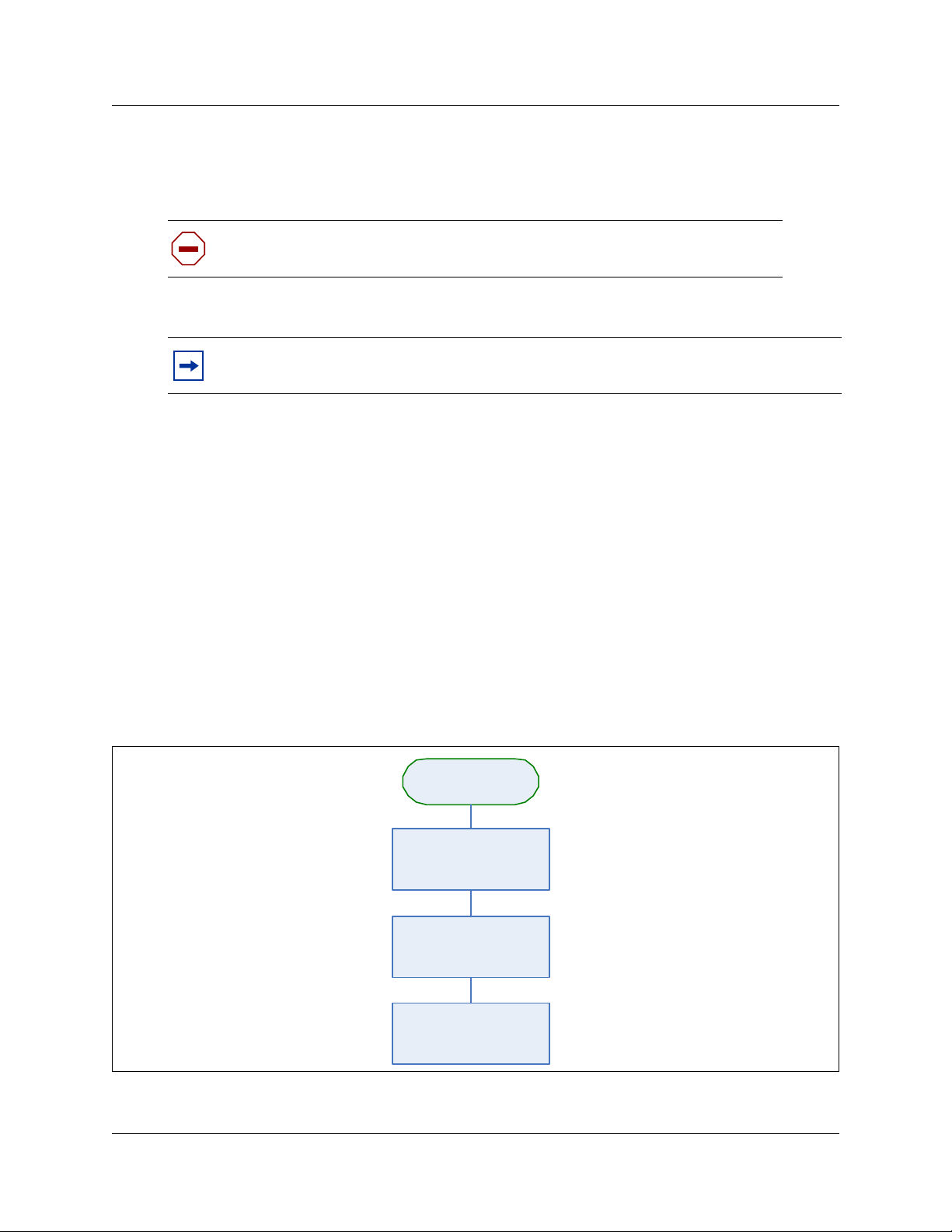
30 Chapter 3 Installing the R2MFC card
Reconnecting the equipment
After you install the card correctly into the bay, you must return the equipment to operation.
Caution: Complete the following steps carefully to ensure you return your
system to operation without endangering the equipment or yourself.
1 Plug the power cords for the Norstar and any expansion modules back into the AC outlets.
Note: The Norstar system starts up when you connect the AC power cord. System
startup takes several minutes to complete.
2 Connect the cables to the proper outlets on the R2MFC card on the Norstar.
3 Check that the LEDs on the newly installed R2MFC card are on and indicating the correct
state. Refer to “Faceplate LEDs” on page 53 for a detailed description of the LED states.
4 Confirm that the Norstar is functioning properly by testing to make sure it works the same as it
did before installing the R2MFC card.
5 Configure the card. Refer to Chapter 4, “Configuring the R2MFC card,” on page 35 for
details.
Removing an R2MFC card
Follow the procedures in this section to remove an R2MFC card from a Norstar system.
Figure 7 provides an overview of the process for removing an R2MFC card.
Figure 7 Overview of removing an R2MFC card
Shut down Norstar
Remove cables
Disconnect power from
Norstar System
System
N0087114 1.0
Remove R2MFC
Card
Page 31

Chapter 3 Installing the R2MFC card 31
Removing an R2MFC card from the Norstar System
Perform the following steps to remove an R2MFC card from the Norstar platform base chassis.
Remove the R2MFC cards after the system is powered down.
1 Remove any cabling from the R2MFC card faceplate.
2 Power-down the Norstar system (see “Shutting down the system” on page 27).
3 Lift the clip located at the top of the R2MFC card and push down the clip located at the bottom
of the R2MFC card. Pull outward to eject the R2MFC card from the Norstar system.
4 Grasp the top and bottom edges of the R2MFC card. Remove the R2MFC card from the
Norstar system. Place the R2MFC card in a clean, safe, and static-free area.
Wiring an R2MFC card
This section describes how to wire the cables that connect to the R2MFC card. The R2MFC card is
connected to the CO by either RJ48C or BNC connectors. The BNC connector is the default
interface. You can change the default connector either by setting the country - selection DIP
switches or by creating a custom country code profile through the CLI. See “Configuring the
R2MFC (external) link” on page 39 for information on how to change the active interface. Refer
to the Installer Guide for the Norstar host system for wiring not related to the R2MFC card.
If the 75 Ω BNC connector pair is used, you require two coax cables for transmit and receive.
If the 120 Ω RJ-48 connector is used, set up the cable pinout as shown in Figure 8 on page 32:
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 32

32 Chapter 3 Installing the R2MFC card
Figure 8 R2MFC card RJ48 wiring array
R2MFC card connector
To network To plug
Receive from
network
1- RX_tip
2 - RX_ring
3 - RX_shield
Transmit to network
4-TX_tip
5-TX_ring
6-TX_shield
RJ48 jack
Warning: Allow only qualified persons to service the Norstar system.
Service personnel with the appropriate training and experience, must perform the
installation and service of this unit. Service personnel must be aware of the hazards of
working with telephony equipment and wiring. They must have experience in techniques
that minimize any danger of shock or equipment damage.
Warning: Leakage currents
Service personnel must be alert to the possibility of high-leakage currents becoming
available on metal system surfaces during power line fault events on network lines. These
leakage currents normally safely flow to Protective Earth ground through the power cord.
However, if the AC power is unplugged prior to disconnecting the cables from the front of
the base function tray, high-leakage currents available on metal system surfaces can occur.
System shutdown: You must disconnect the R2MFC cardcables from the system before
disconnecting the power cord from a grounded outlet.
System startup: You must reconnect the power cords to a grounded outlet before
reconnecting the cables to an R2MFC card.
N0087114 1.0
Page 33

Danger: Electrical shock hazards
Electrical shock hazards from the telecommunications network and AC mains are possible
with this equipment. To minimize risk to service personnel and users, you must connect
the Norstar system to an outlet with a third-wire ground. In addition, all unused slots must
have blank faceplates installed. The covers on all units must be in place at the completion
of any servicing.
Figure 9 on page 33 provides an overview of the process for connecting trunk wiring to the Norstar
R2MFC cards.
Figure 9 Trunk wiring overview
Install R2MFC
Chapter 3 Installing the R2MFC card 33
Card
Read warnings
Determine the correct
connector to use
Connect cables to
appropriate
modules
Continue with setup
procedures
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 34

34 Chapter 3 Installing the R2MFC card
Connecting an R2MFC card to a service provider
Warning: Electrical shock warning.
The Norstar R2MFC cards are safety-approved for installation into Norstar base units and
expansion units. Both the installer and user are responsible to ensure that installation of
the Norstar hardware does not compromise existing Safety approvals.
BEFORE YOU OPEN the Norstar base unit or Norstar expansion unit, ensure that the
network telecom cables are unplugged, and that the unit is then disconnected from the AC
power source.
Do not connect any telephones to wiring that runs outside the building.
Read and follow the installation instructions carefully.
Perform the following steps to connect an R2MFC card to the network:
1 Determine the connector type to be used, either RJ48C or BNC connectors.
2 Locate the appropriate connector on the front of the R2MFC card.
3 Attach the transmit BNC cable to the connector labeled Tx and the receive BNC cable to the
connector labeled Rx, for countries using BNC connections. Insert the connector into the RJ48
jack on the card, for countries using the RJ48 connections. Figure 8 on page 32 shows the
wiring pinouts for an R2MFC card to connect to a service provider using RJ48 connectors.
4 Use a Norstar telset to configure the lines or sets associated with the R2MFC card. Refer to the
Norstar Installer guide for the host system for more information.
Refer to the Norstar Installer guide for the host system for information on changing the default
settings for each line/loop.
N0087114 1.0
Page 35

Chapter 4
Configuring the R2MFC card
Trunk protocol conversion provides interworking between two different trunk protocols, and
requires configuration for the following:
• E1- MFCR2
• E1- ETSI Euro-PRI
The R2MFC is the external interface. The external interface connects to a public network. The
R2MFC card contains preprogrammed country-specific R2MFC settings that you can select using
the DIP switches on the faceplate of the R2MFC card. The R2MFC settings can also be
customized. The PRI is an internal link to the Norstar System. The PRI settings are configured to a
predefined setting when the region is selected during Norstar System initialization. The PRI does
not require customization, but it must be configured as detailed in “Configuring the PRI (internal)
link” on page 43.
This chapter lists the configurable parameters of both the R2MFC side and the PRI side of the
R2MFC card, and explains how to configure them. Figure 10 provides an overview of the
configuration process.
35
Figure 10 Configuring the R2MFC card
Install the
R2MFC Card
Determine the correct
configuration
parameters for the
external link
Does the
setup require custom
settings?
NO
Set Config DIP switches
YES
Create a new
customized country
code
Determine the correct
configuration
parameters for the
internal link
Configure the internal
PRI link through a
Norstar telephone set
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 36

36 Chapter 4 Configuring the R2MFC card
R2MFC side (External Link) configurable parameters
Physical line characteristics
The R2MFC card has two options for physical connections on the faceplate:
1 RJ-48 connector for twisted pair cable (line impedance of 120 Ohms)
2 a pair of mini BNC connectors for coax cables (line impedance of 75 Ohms)
The BNC connectors can have one of the following:
• TX shielding connected to ground (default)
• RX and TX shielding not connected to ground
Only one of the two connector types can be active. The default active interface is the BNC
connector. The BCN connector is part of the country-specific defaults for Mexico variant 1. Each
of the country codes activates the appropriate connector, based on the country standard for
connectors.
The active interface can be customized in the firmware through the CLI by using commands in the
COnfig directory.
E1 framing
The external link uses Channel Associated Signaling on timeslot 16, therefore; TS16 multiframe
format is always used. In addition, optional CRC4 multiframe can be used (for monitoring digital
transmission quality), instead of basic “alternate frame” format.
The CRC4 multiframe option is activated by the firmware as part of the country-specific defaults.
PCM coding is A-law.
These settings can be customized in the firmware through the CLI by using commands in the
ALarm directory.
Note: Configure changes made to the framing parameters in both the R2MFC card and the
Norstar System.
Line signaling
Line signaling (for example, seize, answer, and disconnect) are implemented by R2 Channel
Associated Signaling known as ABCD bits. Only the two bits AB are used for line signaling. The
state (value) of the bits indicate the signal.
N0087114 1.0
Page 37

Chapter 4 Configuring the R2MFC card 37
The channels are always bidirectional, (that is, they accept incoming calls or originate outgoing
calls). The channel behavior also supports one-way trunks. The direction of the signal does not
need to be configured. Because the R2MFC card is passive, the R2MFC card does not initiate
calls; it only passes call origination attempts from one side to the other. The R2MFC card assumes
that the two sides (Norstar System and CO) respect the direction of the trunk as agreed between
them.
The meaning of the bit states are part of the country-specific parameters; however, they can be
customized through the CLI by using commands in the R2 directory.
The following are additional options included in country-specific parameters:
• use backward force-release signal to clear back (yes/no)
• release-guard state (timer) when clearing back (timer value)
• optional CD bits value (usually ignored)
Register signaling
Register signaling (digits transmission) is implemented by in-band dual-tone signals known as
MFC-R2. Physically, there are 15 forward signals and 15 backward signals. The standard defines
two stages of the signaling. The meaning of the signal depends on the stage and the direction of the
call. In total, there are four tables of 15 signals each. See Appendix A, “Config DIP switch settings
and definitions,” on page 77 for MFC country-specific signal tables.
The meaning of MFC signals can be different when transmitted or received. MFC signal tables are
part of the country-specific parameters. The meaning of the MFC signals in the R2MFC card are
configurable through the CLI by using commands in the MFC directory.
The following are other options included in country-specific parameters:
End of dialing (incoming)
End of dialing for an incoming call can be configured by using the CLI. See Table 2, for the end of
dialing options.
Table 2 Minimum (or fixed) number length + timer parameters (Sheet 1 of 2)
Option Parameters Meaning Default
Explicit ‘End of dial’ signal
(I-15)
None The preset option for all
countries. However, signal
has low significance, because
the end of dialing is
determined by the Norstar
System (PRI side) when it
receives the last digit of the
number.
Yes
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 38

38 Chapter 4 Configuring the R2MFC card
Table 2 Minimum (or fixed) number length + timer parameters (Sheet 2 of 2)
Option Parameters Meaning Default
Minimum (or fixed) number
length and timer
Minimum (or fixed) number
length and timer
Minimum (or fixed) number
length and timer
Minimum (or fixed) number
length and timer
Minimal number of digits Receiving minimum number of
digits + optional number of
Optional number of additional
digits
Interdigit timer in the minimal
interval (long timer)
Interdigit timer in the optional
interval (short timer)
digits means end of dial
(maximum length reached)
When a fixed length number is
always expected, set the
optional number of digits to 0.
Expiry of the long timer means
MFC error - number
incomplete.
Expiry of the short timer
means end of dial.
No
No
No
No
End of dialing (outgoing)
End of dialing in outgoing calls is indicated by MFC signal “I15” (or equivalent country-specific
signal). This signal is sent if the far-end requests next digit beyond the last digit of the dialed
number.
When R2MFC card originates a call to the CO, the R2MFC card has already received the whole
dialed number from the Norstar System. This is because the digits are passed from Norstar System
to the R2MFC card by PRI “en-bloc.” This operation mode means that Norstar System determines
user end-of-dialing either by number of digits, explicit input from user (for example, the “#” digit),
or timeout.
Disable ANI
The ANI request option can be disabled. When disabled:
• Incoming call — R2MFC card does not request ANI.
• Outgoing call — When far end requests ANI, R2MFC card answers “ANI not available.”
Default category
The MFC subscriber category, sent by R2MFC card in outgoing calls, is fixed. The default
category for all countries is II1 (subscriber without priority). If needed, the default can be changed
by CLI.
Default subscriber status
The user can set default subscriber status (for example, free, busy, and vacant number) for
incoming calls. When this feature is enabled, the R2MFC card in an incoming call sends the preset
default subscriber status, instead of the status received from the PRI status.
N0087114 1.0
Page 39

Chapter 4 Configuring the R2MFC card 39
The subscriber status option is not enabled in R2MFC card; therefore, the subscriber status is
translated from ISDN message to MFC, and vice versa.
Configuring the R2MFC (external) link
The R2MFC (external) link is configured directly on the R2MFC card by setting DIP switches,
and using a CLI on the R2MFC card. Standard predefined configurations already exist, and must
be used, whenever possible. Country code configurations set by DIP switches, are hard-coded, and
can be changed only by using the CLI. See “Setting Config DIP switches” for a description of how
to set the predefined country code and second dial tone settings. The CLI can be used to create a
customized country codes. See “Creating a customized country code” on page 40 for a procedure
on how to create the customized country code.
Setting Config DIP switches
The Config DIP switch settings include diagnostic mode, country codes, and second dial tone.
Country codes include the default settings for the connection (link) for the country selected. See
Appendix A, “Config DIP switch settings and definitions,” on page 77 for the country code DIP
switch settings and their specifications.
Perform the following steps to set the Config DIP switches:
1 Set the Config DIP switches to the appropriate country code and second dial tone setting that
coincides with your location.
Caution: Country configuration is read by the firmware upon power up or
insertion into the ICS. Changing the country, while the R2MFC card is operating,
causes the firmware to restart automatically after a delay of five seconds from the
last DIP switch change. All active calls during the restart are dropped.
See Appendix A, “Config DIP switch settings and definitions,” on page 77 for predefined
country code DIP switch settings and their specifications.
See “Turning on second dial tone” on page 45 for the procedure to turn on second dial tone.
The Config DIP switch settings are divided into the following parts:
• country or diagnostics - DIP switch 1
• country code - DIP switches 2 through 5
• second dial tone (on/off) - DIP switch 6
Figure 11 on page 40 shows the Config DIP switch layout.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 40

40 Chapter 4 Configuring the R2MFC card
n
Figure 11 Config DIP switch layout
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
configuratio
dial tone
Note: Mexico Config 1 country code is the factory default setting. It is
the setting used if an invalid country value is set, or if a custom profile is
selected that does not exist.
2 Insert the R2MFC card into the Norstar ICS.
Creating a customized country code
If the R2MFC card required settings are not identical to any country code, customization can be
performed using the CLI through the serial port. Perform the following steps for configuring the
customized country codes:
1 Set the Config DIP switches to match the country code closest to customer requirements. See
Appendix A, “Config DIP switch settings and definitions,” on page 77.
Caution: Country configuration is read by the firmware upon power up or
insertion into the ICS. Changing the country, while the R2MFC card is operating,
causes the firmware to restart automatically after a delay of five seconds from the
last DIP switch change. All active calls during the restart are dropped.
2 Make the required modifications by CLI. See Chapter 6, “Command Line Interface (CLI),” on
page 59 for an explanation of how to access and navigate the CLI.
• Configuration changes made through the CLI immediately affect the operating parameters
in RAM.
• Use the SaveCfg - (save configuration permanently on flash) command to save the new
settings on non-volatile Flash memory.
N0087114 1.0
Page 41

Chapter 4 Configuring the R2MFC card 41
The custom profile remains in EEPROM, even if different country codes are selected with
the DIP switches, and is available again when the “custom profile” DIP switch setting is
selected. The first configuration change by the CLI overwrites the existing custom profile
as described above.
Note: Only one custom profile exists in EEPROM, so the SaveCfg
command overwrites the previous custom profile saved to the EEPROM.
3 Set the Config DIP switches to custom profile. The new custom profile is used upon restart.
See Figure 12 for the custom profile DIP switch setting.
Figure 12 Custom profile DIP switch setting
Custom
Profile
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
PRI side (Internal Link) configurable parameters
The R2MFC card is recognized by the Norstar System as a Euro-ISDN PRI line. The configuration
for the PRI side (internal link) of the link is performed on the Norstar System through a Norstar
digital telephone set. Refer to the Installer guide for the host system for complete information on
the parameters that can be configured through the Norstar System. PRI side, internal link, and
operational parameters for E1framing and signaling are listed below:
E1 Framing
The list of E1 framing parameters are listed in Table 3.
Table 3 E1 framing default parameters
Parameter Operational Value
Frame format alternate frame
PCM coding A-law
Common Channel Signaling TS16
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 42

42 Chapter 4 Configuring the R2MFC card
Signaling
The list of layer 2 signaling parameters are listed in Table 4.
Table 4 Layer 2 signaling parameters
Parameter Operational Value
D-channel LAP D
Window size 7
Modulo 128
Layer 3 signaling parameters are listed in Table 5.
Table 5 Layer 3 signaling parameters
Parameter Operational Value
Protocol ETSI Euro-ISDN (ETS 300 102). The R2MFC
Incoming calls from CO to Norstar System - Digit
dialing mode
Outgoing calls from Norstar System to CO - Digit
dialing mode
Bearer capability for calls initiated by Norstar
System
Bearer capability for calls initiated from the
R2MFC card to the Norstar System
card upper board is the NETWORK side, so the
Norstar System must be configured as USER
side.
Overlap. Every digit is passed to the Norstar
System; the Norstar System determines when
the number is complete. The call can be set up
immediately after the last digit is dialed.
Overlap - for systems requiring second dial tone
from the R2MFC card.
R2MFC accepts bearer capability requests of
services: voice, audio, fax, modem.
Bearer capability indicates a normal voice
service.
N0087114 1.0
Page 43

Configuring the PRI (internal) link
The Norstar System installs default settings for DTI cards that vary depending on the region
chosen during startup. Your Norstar System must be in Profile 2
systems that use ETSI ISDN lines with A-law). These settings for the R2MFC card can be
verified and customized using a Norstar digital telephone set.
Perform the following steps to set your Norstar profile to Profile 2:
Note: You must perform this procedure BEFORE you run Startup,
within the first 15 minutes after you plug in your KSU (Key Service
Unit).
1 Retrieve the programming overlay from the Norstar Installer Guide provided with the host
system.
Telephone set overlays, showing the location of buttons, are found in the Installer Guide
provided with the Norstar host system.
2 Place the programming overlay over the buttons on the Norstar phone set used to program the
Norstar settings.
Chapter 4 Configuring the R2MFC card 43
(this profile is for international
3 Enter the Profile access code from a programming set by pressing
≤••∏ВШПИТ‰ (**7763453).
4 Enter the password, when prompted:
Ç؈ÏÈÌ (266344).
Region: PROF1 is displayed.
5 Press the key below CHANGE to scroll to profile number 2.
6 Click the display key for OK when you reach the profile 2.
The display shows Reset System?.
7 Press OK.
8 Press
Perform the following steps to verify and customize the PRI (internal) link:
1 Enter the Profile access code from a programming set by pressing
2 Enter the password, when prompted:
® to exit.
≤••Ç؈ÏÈÌ
Ç؈ÏÈÌ (266344)
(**266344).
3 Select the hardware item, press ‘until the display shows Hardware.
4 Press ≠.
The display shows Show module.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 44

44 Chapter 4 Configuring the R2MFC card
5 Press ‘.
The display shows Card on KSU.
6 Press ≠.
The display shows Cd1-KSU.
7 Press ‘ until the display shows the card you want to view (CD1 — the right most
DTI card).
8 Press CHANGE to view the different cards: Loop, T1, PRI, BRI-U4, BRI-U2 or
BRI-ST.
9 Select PRI and press ≠.
The display shows Clear line data.
10 Select Y (yes) to confirm your selection.
Note: You cannot change this setting unless you first disable the Trunk
Cartridge using Module Status in Maintenance. Remember to enable the
Trunk Cartridge once you complete the programing.
11 Press ‘.
The display shows Lines 001-030.
12 Press ‘.
The display shows BchanSeq.
You must choose the opposite setting of your service provider. However, if all lines for two
DTI cards (configured as PRI) are in the same PRI pool, then you must set both cards to use
the descending B-channel sequence mode. As a result, the service provider must use ascending
mode.
13 Press CHANGE to select either ascending or descending.
14 Press ‘.
The display shows CRC4.
15 Press CHANGE to select OFF.
16 Press ‘.
The display shows ClockSrc.
17 Press CHANGE to toggle the setting (Primary).
18 Press ‘.
The display shows Ovlap recving.
19 Press CHANGE to select Y.
20 Press
The display shows Lol num len.
N0087114 1.0
‘.
Page 45

21 Press CHANGE and enter the appropriate number.
Press to exit.
Turning on second dial tone
Note: In most E1 network configurations, you need one DTI or
DTI card configured as PRI in your ICS to act as a primary
reference. The only application where you might not have a DTI or
a DTI card configured as PRI designated as primary reference is in
a network where your Norstar system is connected back-to-back
with another switch using a E1 link. If the other switch is
loop-timed to your Norstar system, your DTI or DTI card
configured as PRI can be designated as a timing master.
If your Norstar system has two or more DTIs, you cannot assign
more than one DTI as primary reference, or all of the DTIs as
secondary reference. You can only have one primary reference and
one secondary reference per system. See E1 or ISDN-PRI
configuration for more information
Chapter 4 Configuring the R2MFC card 45
Second dial tone is only available on Norstar MICS 6.0 or higher. Second dial tone, when turned
on, generates and supplies, a second dial tone to the end user, after the end user dials the trunk
access code. Second dial tone can be used with any country code, including customized country
codes. DIP switch 6 is designated for turning on or off second dial tone. Changes to the dial tone
DIP switch become effective as soon as the DIP switch changes position, and does not require a
restart to take effect. The Norstar outgoing dialing must be set to Overlap in order for second dial
tone to work properly.
Perform the following steps to turn on second dial tone:
1 Enter the Profile access code from a programming set by pressing
≤••Ç؈ÏÈÌ
2 Enter the password, when prompted:
Ç؈ÏÈÌ (266344)
3 Select the Services item (press ‘ until the display shows Services).
4 Press ≠.
The display shows Ringing Service.
5 Press ‘ until the display shows Routing Service.
The display shows Routing Service.
(**266344).
6 Press ≠.
The display shows Show Route:_ _ _.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 46

46 Chapter 4 Configuring the R2MFC card
7 Type in the router number.
Rt3 nnn appears.
8 Press ≠.
9 Press ‘ until the display shows SrvcType.
10 Press ≠.
The display shows Dial out:no number.
11 Press ‘ until the display shows Overlap.
12 Press CHANGE to select Y.
13 Press to exit.
14 Set Config DIP switch number 6 to the ON position. See Figure 12 on page 41 for the Config
DIP switch layout.
N0087114 1.0
Page 47

Chapter 5
R2MFC card maintenance
This chapter describes the general maintenance of the R2MFC card after it is installed and is
running properly. It includes the following sections:
• Inter-working functionality
• “Clock synchronization” on page 48
• “Diagnostic tools” on page 49
• “Alarms” on page 50
• “Faceplate LEDs” on page 53
• “Logs and traces” on page 54
• “Error messages” on page 54
• “Replacing an R2MFC card” on page 54
• “Upgrading firmware” on page 55
Inter-working functionality
47
All channels on both sides of the R2MFC card are bidirectional: they accept both incoming and
outgoing calls. If unidirectional trunks are used, the direction is handled by the far ends (Norstar
and CO); the direction need not be configured in the R2MFC card.
In order to handle bidirectional calls, and eliminate internal collisions (when both sides originate a
call on the same channel simultaneously), the R2MFC card allows flexible channel inter working;
calls originating on a channel can use any free channel on the opposite side.
On incoming calls to the Norstar, the far-end (for example, CO switch) selects the MFC channel.
The R2MFC card presents the call to the Norstar by PRI and allows the Norstar to determine
which channel to use.
On outgoing calls, the Norstar selects on which PRI channel the call starts. The R2MFC card
selects a free MFC channel, and originates the outgoing call on it. For this purpose, the R2MFC
card supports 3 search methods to select a free MFC channel:
• Round robin (default)
• Linear ascending
• Linear descending
The MFC channel selection method can be modified through the CLI. See Chapter 6, “Command
Line Interface (CLI),” on page 59 for commands available through the CLI.
Digital
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 48

48 Chapter 5 R2MFC card maintenance
During call setup, the following information is passed between the Norstar and the CO:
1 Dialed digits — Dialed digits are passed without any change. Up to 24 digits can be dialed.
The MFC trunk is capable of repeating dialed digits on outgoing calls to the CO, when
requested according to protocol.
Digits are passed immediately to Norstar as they are received (PRI overlap mode) on incoming
calls from CO to Norstar. This causes the Norstar to determine end of dialing, and to
immediately signal call completion.
2 Calling number — (in PRI: CLID; in MFC: ANI) This number is passed without any change,
and can be up to 16 digits long.
3 Termination status — Termination status is translated as presented in the Table 6. The table
shows both directions. When translating a signal, only the bold value is used.
Table 6 Translation of Subscriber Status
Subscriber State PRI Signal MFC Signal
Free (ringing) ALERTING BW_FreeCharge (B6)
BW_FreeNoChrg (B7)
Busy Cause 17 BW_Busy (B3)
Unallocated number Cause 1 BW_Unlocated (B5)
Network congestion
or general failure
Line out of order Cause 27 BW_OutOfOrder (B8)
Number changed Cause 22 BW_ChangOrder (B2)
1 MFC signal is indicated by meaning. Actual signal depends on country; ITU/T standard is indicated in parentheses.
Cause 42
All other values
BW_B_Congest (B4)
Unknown signal
1
Other protocol-specific fields are not translated from side to side. They are handled as described
Table 6 in the protocols implementation.
Clock synchronization
By default, the R2MFC card synchronizes on the external E1 line, and transmits this clock on the
internal link to the Norstar. By doing so, the Norstar can synchronize on the external link.
Slips can occur between the Norstar and the R2MFC card, if the Norstar must synchronize on
another DTI card. To avoid slips, the R2MFC card must synchronize on the internal link to the
Norstar, instead of the external E1 line. Synchronization settings can be set up by using the CLI.
See Chapter 6, “Command Line Interface (CLI),” on page 59 for commands available through the
CLI.
N0087114 1.0
Page 49

Diagnostic tools
The R2MFC card has three diagnostic settings and two loopback settings available to help with the
troubleshooting process. When the R2MFC card is running in diagnostic or loopback mode, the
signals from the Norstar to the CO, or from the CO to the Norstar, can be intercepted by placing
diagnostic equipment in the bantam jacks on the front of the R2MFC card. This allows the external
R2MFC link, or the internal E1, to be checked for communication errors. The signal can be traced
from start to finish, helping to determine the source of the errors.
Chapter 5 R2MFC card maintenance 49
See Table 7 for a description of the diagnostic and loopback modes.
Figure 13 shows a diagram
of the signal flows for both the diagnostic and loopback settings.
Table 7 Diagnostic and loopback modes
Mode Description Call
Availability
Diagnostic Mode 1 Routes the E1 transmit signal from the Norstar through the
R2MFC card out to the bantam jack.
Diagnostic Mode 2 Routes the E1 transmit signal from the CO through the
Diagnostic Mode 3 Routes the E1 received signal from the Norstar out to the
Loopback mode 1
(continuity mode)
Loopback mode 2
(card edge loopback)
Figure 13 Diagnostic and loopback settings
R2MFC card out to the bantam jack.
bantam jack without any interaction with the R2MFC card.
Routes the E1 signal received from the CO back out to the CO
without any interaction with the R2MFC card.
Routes the E1 tranmitted signal from the Norstar through the
R2MFC card and back to the Norstar.
Available to
process calls
Available to
process calls
Available to
process calls
Not available to
process calls
Not available to
process calls
bantam jack
N
o
r
s
t
a
r
DTI
firmware
D3
Digital
D2
P
R
M
F
I
C
D1
L2
L1
CO
MFCR2 Convertor
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 50

50 Chapter 5 R2MFC card maintenance
Setting the R2MFC card to diagnostic or loopback mode
The R2MFC card is placed in diagnostic or loopback mode by setting the Config DIP switches in
either the diagnostic or loopback position. Perform the following steps to set the R2MFC card into
either diagnostic or loopback mode:
1 Set the Config DIP switches to the desired diagnostic or loopback mode while the R2MFC
card is still powered up. See See Appendix B, “Diagnostic and loopback DIP switch settings,”
on page 107.
The selected diagnostic or loopback mode becomes active five seconds after the last DIP
switch change. The last country configuration stays in effect until a restart occurs.
2 Perform desired testing.
3 Reset the DIP switches back to the appropriate country code after testing has been completed
so that the correct country code is read upon a restart.
Warning: Restarting the R2MFC card, while the Config DIP switches
are in a diagnostic or loopback mode, causes the R2MFC card to start up
in the diagnostic or loopback mode with the default country setting of
Mexico config 1.
Alarms
Performance is monitored on both the internal (PRI) and external (MFC) links, but the actions
when errors occur are different. Alarms and events handling include three types of actions:
1 Propagating Alarms:
a Alerts the far-end by transmitting remote alarm indication (RAI).
b Passes alarm conditions from link to link.
2 Reflecting alarm conditions on faceplate LEDs
3 Printing to error logs
Alarms Measurements
This section describes the mechanism and terminology of alarms measurements, and the actions
taken when alarms occur or stop. Several performance indicators are monitored in order to detect
E1 signal degradation; these indicators are categorized into two groups:
• Group I errors: These are events that can be counted, and are not continuous conditions. The
number of events is counted, and is compared with thresholds (number of events in a specific
time interval) used to evaluate the severity of the alarm condition.
• Group II errors: These are continuous conditions. These indicators can turn on and off
rapidly, or they can remain on or off.
N0087114 1.0
Page 51

Chapter 5 R2MFC card maintenance 51
Each group of performance indicators are handled differently.
Group I errors
Each error has two thresholds of error rate, which defines two levels of error severity:
• Maintenance — error exists but acceptable (service available)
• Out Of Service (OOS) — severe error (service not available)
Group I errors are the following:
1 Bipolar Violations (BPV) — Errors in the bits coding.
2 Frame Bit Error (FBER) — Errors in the frame alignment word.
3 SLIPs — The replication or deletion of the 256 payload bits of an E1 frame. This error
indicates that the local E1 clock is not synchronized with the far end.
4 CRC-4 errors — Received CRC code is not identical to a locally calculated code. This alarm
is only relevant when in CRC-4.
5 Far-end block error (FEBE) — Far end has detected a CRC-4 error. This alarm is only
relevant when in CRC-4.
Group II errors
Group II alarms occur when an alarm persists for a predefined period. The alarm is considered
cleared when it does not occurred for a predefined period.
See Table 8 for incoming-signal Group II errors listed from highest to lowest priority. Group II
errors are ordered by priority; when a high priority error exists, any errors of lower priority are
irrelevant.
Table 8 Incoming signal errors (Sheet 1 of 2)
Alarm Cause
Loss of Signal (LOS) No reception of incoming electrical signal on the line (cable cut or
removed).
Alarm Indication Signal (AIS) Reception of incoming signal is all ones. Usually indicates that the
far-end is out-of-service
Out-of-Frame (OOF) No detection of Frame Alignment Signal. The incoming signal is
Out Of Multiframe TS16 (OOM
Alarm Indication Signal in TS16
(AIS
TS16
TS16
)
)
corrupted. This alarm is also known as Loss of Frame (LFA).
No detection of Multiframe Alignment Signal. When this alarm is active,
Channel Associated Signaling (R2) is impossible. This alarm is not
applicable to the PRI (internal link). This alarm is also known as Loss of
Multiframe Alignment - (LMA).
Reception of AIS is all ones in TS16. This is an optional alarm. It can be
enabled or disabled in configuration. By default, this option is off. When
this alarm is active, any signaling on TS16 is impossible.
Digital
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 52

52 Chapter 5 R2MFC card maintenance
Table 8 Incoming signal errors (Sheet 2 of 2)
Alarm Cause
Loss of CRC-4 Multiframe
Alignment (OOM)
Remote Alarm Indication (RAI) Indication that the far-end has trouble with its incoming signal. This
Remote Alarm Indication TS16
(RAI
TS16
)
CRC-4 multiframe cannot be recognized. When this alarm is active,
CRC-4 errors (of group I) cannot be measured. This alarm is relevant
only when CRC-4 multiframe mode is used.
alarm is also known as yellow alarm.
Indication that the far-nd has lost TS16 multiframe alignment on its
incoming signal.
This alarm is not applicable to PRI (internal link).
Alarms propagation
This section describes the actions taken when alarms occur or stop. When alarms occur, the
far-end is alerted by a remote alarm indication, and an alarm is transmitted on the opposite link.
Table 9 table shows the reactions for Group I alarms when they enter the Out-Of-Service (OOS)
state.
Table 9 Group I Alarms propagation
Error Condition Alarm Transmitted to far end Alarm sent on opposite link
BPV RAI AIS
FBER RAI AIS
Slips RAI AIS
CRC-4 errors RAI AIS
FEBE none none
Table 10 shows the reactions for Group II alarms when they persist.
Table 10 Group II alarms propagation
Error Condition Alarm Transmitted to far-end Alarm sent on opposite link
LOS RAI AIS
AIS RAI AIS
OOF RAI AIS
OOM
AIS
TS16
RAI None RAI
RAI
TS16
DCH down None AIS
N0087114 1.0
TS16
RAI
RAI
None RAI
AIS
TS16
AIS
TS16
TS16
Page 53

Chapter 5 R2MFC card maintenance 53
Faceplate LEDs
There are two sets of LEDs on the faceplate of the R2MFC card. The system status LEDs are made
up of the In Service LED and the Diag LED. Table 11 shows the LEDs and their states.
Table 11 System status monitor LEDs
LED Status
LED Name Green Solid Green Flashing Red Solid Red Flashing OFF
In-Service
Diag
• As the Norstar starts, the In Service LED is Green Flashing.
• When the R2MFC card operates properly, the In Service LED is Green Solid.
• During an alarm on the internal PRI link, the In Service LED is off.
• During test mode, the Diag LED is red.
The second set of LEDs on the faceplate indicate the operation status for the E1. Table 12
describes the LEDs and what status they indicate.
Table 12 System status monitor LEDs
Normal Operation Start Up N/A N/A Out-of-Service
N/A N/A Test Mode N/A Normal Operation
LED Name Yellow LED OFF Red LED
ALM Rx Problem with digital input on external
R2 link; link unusable.
ERR Tx Remote Alarm Indication (RIA)
transmitted on external R2 link.
ALM Tx N/A Normal
ERR Rx Degradation of digital input on external
R2 link; link is still usable.
Normal
Operation
Normal
Operation
Operation
Normal
Operation
N/A
N/A
Inability to transmit: Alarm
Indication Signal (AIS) sent on
external R2 link
N/A
• On power up, all four LEDs are set to off.
• The ERR Tx is only relevant when the ALM Tx and ALM Rx LEDs are off.
• ERR Rx is triggered when the Tx ALM exceeds maintenance thresholds: BPV, CRC4, and
slip.
• ALM Tx is triggered by loss of communication with lower board (PRI board), or other internal
error.
• ALM Rx is triggered by LOS, AIS, OOF, OOM, and when the ERR Rx alarm exceeds OOS
threshold: BPV, CRC4, and slip.
• RAI transmission indicates a receive fault.
Digital
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 54

54 Chapter 5 R2MFC card maintenance
Logs and traces
Logs are available through the Logger directory in the CLI. This directory contains commands that
allow filters to be placed on the E1, for different types of errors, down to the channel level. Errors
can be stored in buffer, and then viewed or printed.
Error messages
Software error messages are available through the SWerr directory in the CLI. The errors are
stored in a cyclic buffer that can be accessed to help in troubleshooting. See “SWerr directory” on
page 69 for specific commands and details.
Replacing an R2MFC card
When an R2MFC card requires replacement, follow the steps in this section.
Warning: This section describes replacing a card with the same type of card. If you want
to replace a card with a different type of card, you must treat it as a new installation. Refer
to the Installation and Maintenance guide to ensure the new module does not overrun any
lines already assigned to other card.
Figure 14 on page 54 provides an overview of the process for replacing R2MFC cards.
Figure 14 Overview of card replacement process
Firmware upgrade
required
Disconnect cables from
the R2MFC card
Remove power from
Norstar system
Remove failed R2MFC
Card
Set DIP switches on
new R2MFC Card to
match old R2MFC
Card
Install new R2MFC
Card in Norstar System
Restore power to
Norstar System
Reconnect all cables
Monitor LEDs for power
and status
Check the Norstar Sytem
for proper operation
N0087114 1.0
Page 55

If replacement of the R2MFC card is required, perform the follow steps to properly replace the
card:
1 Record any customized R2MFC card country code settings.
2 Remove all cables and disconnect the Norstar from the AC power outlet.
3 Follow the steps in “Shutting down the system” on page 27 to ensure the system shuts down
correctly.
4 Use a flathead screw driver to release the top and bottom clips on the R2MFC card. Refer to
Figure 6 on page 29 for the location of the clips.
5 Slide the R2MFC card out of the module in which it is installed.
6 Record the switch settings from the old R2MFC card.
7 Set the DIP switches on the new card to match the settings you recorded in the previous step.
8 Refer to “Installing an R2MFC card” on page 28 to install the R2MFC card in the module.
9 Refer to “Reconnecting the equipment” on page 30 to restore the system to operation.
Upgrading firmware
Chapter 5 R2MFC card maintenance 55
Normal installation does not require firmware download. A firmware upgrade can be required at
some point to incorporate bug fixes or new features.
The following items are required for a firmware download:
• firmware load file
• PC connected to the RS232 serial port of the R2MFC card through COM1
• PC program delivered by the supplier: Bload1.exe for COM1
Note: The version of the firmware, running on an installed R2MFC card, is found by
using the
“Command Line Interface (CLI)” for details on the CLI.
Figure 15 on page 56 provides an overview of the process for upgrading R2MFC card firmware.
Fwversion command in the INfo directory of the CLI. See Chapter 6,
Digital
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 56

56 Chapter 5 R2MFC card maintenance
Figure 15 Upgrading firmware overview
Firmware Upgrade
Required
Copy the firmware load
and PC program files to
PC
Connect PC to the
R2MFC Card
Open a Hyper-terminal
session to connect to
R2MFC Card
Is firmware
corrupted?
No
Disable links
Yes
Prepare R2MFC Card
for upload
Upload new firmware
file
Verify the version of
new firmware
Disconnect PC from
R2MFC Card
Check the Norstar
System to see if it is
working properly
Perform the following steps to download the firmware the R2MFC card:
1 Copy the firmware load file and the PC program files, bload1.exe, to the same directory on the
PC.
2 Use the shipped cable, part number N0026100, to connect a PC to the RS-232 port on the
faceplate of the R2MFC card through COM1.
3 Open a new Hyper-terminal session on the PC using the parameters listed in Table 13.:
Table 13 Hyper-terminal setup parameters
Parameter Setting
Connect using COM 1
Bits per second 19 200
Data bits 8
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Flow Control None
4 Go to step 11 if the existing firmware is corrupted. Corrupted firmware is indicated if the
BOOT program displays:
load, switch, fload, fswitch, checksum, DisMem, DisWord, *=quit
----> user monitor:
5 Wait for the monitor line (flashing cursor) to appear on the terminal session.
N0087114 1.0
Page 57

Chapter 5 R2MFC card maintenance 57
6 Go to step 8 if the Norstar is not active and no calls are running. If calls are running, access the
Control directory.
7 Execute the soft disable (LSD), or immediate disable (LID), to disable the links.
8 Enter the load subdirectory.
9 Execute load y command.
10 Wait for the output of the boot monitor.
11 Enter fload to prepare the R2MFC card for the uploading of firmware.
The R2MFC card will not respond while it is waiting for a download.
12 Release the COM port by closing the Hyper-terminal session.
13 Run the download programs on the PC through the Start > run menu:
•//file path/Bload1 <load_file>
The program responds: starting rec 0. Hit any key to continue...
14 Press <Enter>. The program starts the download, and shows its progress by displaying the
number of processed records.
When finished, the program prints: Download ended successfully!
15 Verify the version of firmware uploaded by using the
Fwversion command in the INfo
directory of the CLI. See Chapter 6, “Command Line Interface (CLI)” for details on the CLI.
16 Close the program window.
17 Remove the cable (part number
N0026100) connecting the RS232 port and the COM port
from the R2MFC card.
Tips: Upgrading the firmware does not erase the custom profile, if the custom profile is
saved in EEPROM.
Digital
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 58

58 Chapter 5 R2MFC card maintenance
N0087114 1.0
Page 59

Chapter 6
Command Line Interface (CLI)
Overview
This chapter describes the Command Line Interface (CLI) available through the serial port.
Command Line Interface (CLI) commands are organized as a tree of directories. Each directory
contains a set of commands related to a specific purpose or subject. The available directories for
R2MFC card are:
•LOad
•INfo
•VIew
•CNtrl
•COnfig
•ALarm
59
•SWerr
•MFC
•R2
•PRI
Note: Most directories and commands have a short form indicated by uppercase letters.
To access a directory, type the directory name or the short form. A list (or menu) of available
commands or subdirectories displays. The commands are not case-sensitive.The list displays again
if you type an incorrect command or an empty command.
To go to the previous menu level in the tree, type an asterisk (*).
Users and passwords
The CLI contains the following two hard-coded user names with passwords:
• RS232 — This is the default user, which does not require a password. This user accesses
configuration and maintenance commands.
• admin — Password: admin. This user has access to the same set of commands as RS232.
Note: Users and passwords are case-sensitive.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 60

60 Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI)
Accessing the CLI
The CLI is accessed through the RS-232 port on the faceplate of the R2MFC card. The cable that
was shipped with the R2MFC card, part number N0026100, is used to connect a computer to the
R2MFC card.
Perform the following steps to access the CLI:
1 Use the shipped cable to connect a PC to the RS-232 port on the faceplate of the R2MFC card
through COM1.
2 Open a Hyper-terminal session on the PC using the following parameters:
Table 14 Hyper-terminal setup parameters
Parameter Setting
Connect using COM 1 or COM 2
Bits per second 19 200
Data bits 8
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Flow Control None
3 Wait for monitor line (flashing cursor) to appear on the terminal session.
4 Switch to appropriate user by using the
su command and entering the appropriate username
and password.
5 Access the desired directory using the directory commands listed in this chapter.
6 Execute any desired commands.
7 Release the COM port by closing the Hyper-terminal session.
8 Remove the cable connecting the PC to the R2MFC card.
N0087114 1.0
Page 61

Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI) 61
Commands
The following section lists and describes the CLI commands for the available directories.
LOad directory
Table 15 includes the CLI commands for firmware download and card restart. The commands are
accessed from the LOad directory.
Table 15 LOad directory CLI commands
CLI command Description
RST Restarts card firmware regardless of current state.
There is no prompt to confirm the restart.
load y Configures the hardware to accept downloads
fload Downloads the firmware.
INfo directory
Table 16 includes the CLI command to display and print information for troubleshooting problems
in the field. The command is accessed from the INfo directory.
Table 16 INfo directory CLI commands
CLI command Description
Fwversion Displays the firmware versions and the state of the DIP switches.
SystTime Prints the current time and how long the load has been in-service.
ALarm Prints the status of the E1 alarms on both links.
ChannelSummary Prints a summary of all PRI and MFC channels currently in use; for example,
not in idle state
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 62

62 Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI)
VIew directory
Table 17 includes the CLI commands to display the setup parameters. The commands are accessed
from the VIew directory.
Table 17 VIew directory CLI commands
CLI command Description
LNst Displays the status of both links.
ChSt <chan1> <chan2> Displays the status of the channels in the given range.
Where:
chan1 is the lower limit of the range.
chan2 is the upper limit of the range.
The values for chan1 and chan2 are 1...15, 17...31.
ChDt <chan> Prints the channel data.
Where:
chan is the channel number in the range of 1...15, 17...31.
ChDtGrp Prints data for a range of channels.
TT <num> Prints the timer table that contains the timer values in milliseconds.
Where:
num is either 1 (Outgoing timers) or 2 (Incoming timers).
If you do not enter a value for num, all timers are printed.
MR <mfc_link_no> <num> Displays the MFC/R2 generic parameters for each link.
Where:
mfc_link_no is the value of the MFC link number, either 0 or 1.
num is 0 (R2 signals), 1 (MFC Tx signals), or 2 (MFC Rx signals).
If you do not enter a value for num, all MFC/R2 signals are printed.
N0087114 1.0
Page 63

Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI) 63
CNtrl directory
Table 18 includes the CLI commands for maintenance functions. The commands are accessed
from the CNtrl directory. All enable and disable commands are to be used for troubleshooting
purposes only. For normal operation, both links and all channels must be enabled (default state).
This includes links and channels in an environment with a partial E1 arrangement.
Warning: Channels are not available to process calls when a link is disabled. If a
link is disabled the R2MFC card is out-of-service.
Table 18 CNtrl directory CLI commands (Sheet 1 of 3)
CLI command Description
CSd <chan> Performs channel soft-disabling.
Where:
chan is the channel number in the range of 1...15, 17...31.
If there is a call on the channel, the system disables the channel after the
current call process is complete. This command sends messages to both
links.
CSdGrp <start_chan> <end_chan> Performs soft-disabling on a group of channels.
Where:
start_chan is the first channel in the group.
end_chan is the last channel in the group.
The values for start_chan and end_chan are 1...15, 17...31.
If there is a call on the channel, the system disables the channel after the
current call process is complete. This command sends messages to both
links.
CId <chan> Performs immediate disabling on a channel.
Where:
chan is the channel number in the range of 1...15, 17...31.
If there is a call on the channel, the system ends the call and disables the
channel. This command sends messages to both links.
CIdGrp <start_chan> <end_chan> Performs immediate disabling on a group of channels.
Where:
start_chan is the first channel in the group.
end_chan is the last channel in the group.
The values for start_chan and end_chan are 1...15, 17...31.
If there is a call on a channel, the system ends the call and disables the
channel. This command sends messages to both links.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 64

64 Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI)
Table 18 CNtrl directory CLI commands (Sheet 2 of 3)
CLI command Description
CEnbl <chan> Performs channel enabling.
Where:
chan is the channel number in the range of 1...15, 17...31.
This command sends a message to both protocol handlers.
CEnblGrp <start_chan>
<end_chan>
LSd Performs link soft-disabling, which disables IDLE channels immediately.
LId Performs immediate link disabling.
LEnbl Performs link enabling.
CoFlm <chan> Transfers a disabled channel to an offline state.
Performs channel enabling on a group of channels.
Where:
start_chan is the first channel in the group.
end_chan is the last channel in the group.
The values for start_chan and end_chan are 1...15, 17...31.
If there is a call in progress, the system disables the channel after the
current call is complete. This command sends a message to both protocol
handlers.
If there is a call in progress, the system ends the call and disables the
channel. This command sends a message to both protocol handlers.
The command sends a message to both protocol handlers.
Where:
chan is the channel number in the range of 1...15, 17...31.
CoFlmGrp <start_chan>
<end_chan>
N0087114 1.0
The command sends a message to both protocol handlers.
Transfers disabled channels to an offline state.
Where:
start_chan is the first channel in the group.
end_chan is the last channel in the group.
The values for start_chan and end_chan are 1...15, 17...31.
The command sends messages to both protocol handlers.
Page 65

Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI) 65
Table 18 CNtrl directory CLI commands (Sheet 3 of 3)
CLI command Description
CoNlm <chan> Transfers the channel to an online state.
Where:
chan is the channel number in the range of 1...15, 17...31.
If the system accepts the message, the channel becomes disabled. This
command sends a message to both protocol handlers.
CoNlmGrp <start_chan>
<end_chan>
MC <link_num> Sets the side that is used as clock source.
Transfers a group of channels to an online state.
Where:
start_chan is the first channel in the group.
end_chan is the last channel in the group.
The values for start_chan and end_chan are 1...15, 17...31.
If the system accepts the messages, the channels become disabled.
Where:
link_num is either 0 (link 0) or 1 (link 1).
If this command is entered without a parameter, the current clock master is
printed.
COnfig directory
Table 19 includes the CLI commands for general card configuration. The commands are accessed
from the COnfig directory.
Table 19 COnfig directory CLI commands (Sheet 1 of 2)
CLI command Description
LinePhy <phy_mode> Sets the physical interface type of the external E1 line.
Where phy_mode can be:
0 indicating 120 Ohm (RJ48 connector).
1 indicating 75 Ohm (RX and TX, BNC connector), grounded shield.
2 indicating 75 Ohm (TX BNC connectors), not-grounded shield.
SaveCfg Stores the current configuration on non-volatile Flash memory.
All parameters are stored-country-specific and non-country-specific. The
stored configuration is used when the config DIP switches on the faceplate
are set to custom profile. Only one configuration (custom profile) is stored.
This command deletes the previous configuration contents.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 66

66 Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI)
Table 19 COnfig directory CLI commands (Sheet 2 of 2)
CLI command Description
EraseCfg Erases the configuration from non-volatile Flash memory.
As a result, the custom profile does not exist, and other parameters are not
included in custom profile use factory default settings. A live system is not
affected, because current configuration is stored in RAM. The R2MFC card
tries to read configuration from Flash memory on restart.
DEbnc <link> <msec> Updates the line signal debounce time.
Where:
link is the link number, either 0 or 1.
msec is the time, in milliseconds, ranging from 10 to 200.
The value for msec should be in multiples of 5. If not, then the system
rounds it off to the nearest multiple of 5.
ST <year> <month> <day> <hour>
<min> <sec>
Sets the current system time.
Where:
year = yyyy
month = 1...12
day = 1...31
hour = 0...23
min = 0...59
sec = 0...59
If you enter the ST command without parameters, the system displays the
current system time.
N0087114 1.0
Page 67

ALarm directory
Table 20 includes the CLI commands for alarm configuration and status. The commands are
accessed from the ALarm directory.
Table 20 ALarm directory CLI commands (Sheet 1 of 2)
CLI command Description
G1Res <link_no> <group I alarms> Resets Group 1 alarm counters.
Where:
link_no is the link number, either 0 or 1.
Group I alarms defines the group and can have values of:
• 0 – BPV
• 1 – FBER
• 2 – SLIP
• 3 – CRC4
•4 – ALL
Bit3 <link_no> <bit3> Used for bit 3 option handling.
Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI) 67
Where:
link_no is the link number, 0 or 1.
bit3 is the option flag, 0 (off) or 1 (on).
OP16 <link_no> <AIS
FR <link_no> <fr_mode> Changes the frame mode.
G1th <link_no> <pra> <limcount> Sets the group I alarm thresholds.
> Used for AIS
TS16
Where:
link_no is the link number, 0 or 1.
AIS
Where:
link_no is the PCM link number, 0 or 1.
fr_mode is 0 (ALTRNT2_FRM) or 1 (MULTIFRM_CRC4)
Default for link 0 (external) depends on country selection. Default for link 1
(internal) is set to alternate and should not be changed to multframe.
Where:
link_no is the PCM link number, 0 or 1.
pra is the problem group I errors and can have values of:
• 0 – BPV
• 1 – FBER
• 2 – SLIP
• 3 – CRC4
limcount is the threshold error count in the range of 1...1000.
is the option flag, 0 (off) or 1 (on).
TS16
option handling.
TS16
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 68

68 Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI)
Table 20 ALarm directory CLI commands (Sheet 2 of 2)
CLI command Description
GRDtime <link_no> <grs_state>
<grd_time>
G2Gtime <link_no> <grd_time> Changes the group 2 alarm guard time for the required grade of service
G2Ptime <link_no> <perstime> Changes persistence time for group 2 alarm handling.
DB <link_no> Displays the R2MFC card alarm task database content.
Changes group 1 alarm guard time for the required grade of service state.
Where:
link_no is the PCM link number, 0 or 1.
grs_state is the grade of service state, 1 (mnt state) or 2 (oos state).
grd_time is the guard time in the range of 20...50000.
state.
Where:
link_no is the PCM link number, 0 or 1.
grd_time is the group guard time in the range of 0...50000.
Where:
link_no is the PCM link number, 0 or 1.
perstime is the persistence time for group 2 alarm handling in the range of
0...50000.
Where:
link_no is the PCM link number, 0 or 1.
N0087114 1.0
Page 69

Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI) 69
SWerr directory
Table 21 includes the CLI commands for the Software Error (SWerr) utility. The firmware stores
the Swerr messages into a cyclic buffer. The contents of the buffer are printed upon request.The
commands are accessed from the SWerr directory.
Table 21 SWerr directory CLI commands
CLI command Description
PS <num> Prints the Swerr buffer constants. All the accumulated swerr messages are
printed.
Where:
num is the number of error messages to print (optional).
The buffer stores the 20 most recent messages.
GF Displays the swerr error levels and control flags.
There are three error levels: inform, serious, and fatal. Each level has two
flags: Insert_flag, which stores error information in the buffer, and Print_flag,
which prints to the serial port when an error occurs.
CF <level> <insert_flag>
<Fast_print_flag>
<user_func_addr>
DEL < number> Deletes swerr messages from the buffer.
DWN Prints detailed debug information for one swerr message, stepping down
UP Prints detailed debug information for one swerr message, stepping up
PP Prints detailed debug information for the current swerr message.
HeLP Prints the descriptions of all the commands in the swerr directory.
Changes swerr control flags.
Where:
level is in the range of 0...2.
insert_flag is true or false
Fast_print_flag is in the range of 0...2 (0 = print, 1 = print, 2 = fast print).
user_func_addr is the user function address (for firmware engineers only).
Where:
number is the number of swerr messages to delete (oldest messages are
deleted). Enter 0 to delete all swerr messages.
(back in time).
(forward in time).
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 70

70 Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI)
MFC directory
Table 22 includes the CLI commands for the configuration and control of MFC-R2 protocols. The
commands are accessed from the MFC directory.
Table 22 MFC directory CLI commands (Sheet 1 of 3)
CLI command Description
ICm <mfc_link>
<incoming_timer_type> <msec>
OGm <mfc_link>
<outgoing_timer_type> <msec>
REgSign <mfc_link><rs_name> Sets the register signaling
AniOption <mfc_link><flag> Enables or disables the ANI option.
Sets and displays incoming call timers.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of required mfc/r2 links.
incoming_timer_type is one of the timers defined for incoming mfc call
processing.
msec is the time interval in msec.
Sets and displays outgoing call timers.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of required mfc/r2 links.
outgoing_timer_type is one of the timers defined for outgoing mfc call
processing.
msec is the time interval in msec.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
rs_name is the signaling type, 0 (MFC) or 1 (SMFC).
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
flag defines the ANI option as enabled (0) or disabled (1).
When disabled, ANI is not requested in incoming calls and not transmitted in
outgoing calls.
mfcINDia<flag> Enables or disables the processing of the special MFC option for India.
Where:
flag defines the Special ANI digit option as enabled (0) or disabled (1).
When enabled, the prefix of one is expected on incoming calls and is
transmitted on outgoing calls.
N0087114 1.0
Page 71

Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI) 71
Table 22 MFC directory CLI commands (Sheet 2 of 3)
CLI command Description
CatgOpt <mfc_link> <flag> Defines which MFC category to transmit in outgoing calls.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
flag defines the MFC category (default is 0).
DefltCatgVal <mfc_link><category> Defines the MFC category value when CatgOpt is set to the default value.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
category is the MFC category in the range of 1...15.
SubsIndOpt <mfc_link> <flag> Defines which subscriber status to send when an incoming MFC call
DefltSubsVal
<mfc_link><subscriber>
EndDialType
<mfc_link><direction><type>
terminates successfully.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
flag is the subscriber status, 0 (subscriber option is default value) or 1
(subscriber option is received value).
Defines the subscriber status value when the SubsIndOpt commands is set
to the default value.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
subscriber can have the values of:
• 0 = speech_charge (A group)
• 1 = free_charge
• 2 = free_no_charge
• 3 = control_charge
Defines how to handle MFC end of dial.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
direction is 0 (IC), 1 (OG), or 2 (both).
type is either 0 (Ix signal) or 1 (fix number of digits).
SetDigitCount <mfc_link>
<count_type> <value>
Sets the number of expected digits when the EndDialType is set to a fixed
number of digits.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
count_type is either 0 (minimal range) or 1 (optional range).
value has values of 3...12 for minimal range or 0...15 for optional range.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 72

72 Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI)
Table 22 MFC directory CLI commands (Sheet 3 of 3)
CLI command Description
EndAniType
<mfc_link><direction><type>
SetAniCount <mfc_link> <value> Defines the number of expected ANI digits when EndAniType is set to a
ARP <mfc_link> <Dig_num> Sets the number of received DID digits, after which the R2MFC card sends
BCatOpt <mfc_link><pls/cmpl> Defines BW_BCateg signal as pulse or compelled signal.
Defines how to determine end of ANI digits.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
direction is 0 (IC), 1 (OG), or 2 (both).
type is either 0 (Ix signal) or 1 (fixed number of digits).
fixed number of digits.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
value is the expected number of ANI digits in the range of 1...16.
ANI requests to the CO.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
Dig_num is the number of digit after which ANI is requested in the range of
1...20, or 0 (after the last digit).
This command is for incoming calls only.
MTS <mfc_link>
<MFC_signal_meaning>
<MFC_signal>
MRS <mfc_link> <MFC_signal>
<MFC_signal_meaning>
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
pls/cmpl is either 0 (BCategory is compelled signal) or 1 (BCategory is
pulsed signal).
Sets the MFC transmit signals value. For each logical meaning, sets which
MFC physical signal is actually sent.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
MFC_signal_meaning is one of the MFC signals meaning in the range of
0...49. See Chapter , “MFC Signal Definitions,” on page 109 MFC definition
tables.
MFC_signal is either Forward (I,II) or Backward (A,B) signals.
Defines how to interpret received MFC signals. For each MFC physical
signal sets its logical meaning.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
MFC_signal is either Forward (I,II) or Backward (A,B) signals.
MFC_signal_meaning is one of the MFC signals meaning in the range of
0...49. See Chapter , “MFC Signal Definitions,” on page 109 for MFC
definition tables.
N0087114 1.0
Page 73

R2 directory
Table 23 includes the CLI commands for R2 line signaling. The commands are accessed from the
R2 directory.
Table 23 R2 directory CLI commands (Sheet 1 of 2)
CLI command Description
Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI) 73
RS <link> <line_signal_meaning>
<R2_signal>
CD <link> <CD_bits_value> Sets a fixed value to be transmitted on CD bits.
Sets the R2 signaling values.
Where:
link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
line_signal_meaning is one of the line signal meaning codes.
R2_signal is the ABCD bits value of 0, 1, 2, or 3.
Use this command after clearing the R2 signaling value.
The R2 signaling values must follow these rules:
FW_IDLE = BW_IDLE = FW_CLEAR_FORWARD
FW_SEIZE != FW_IDLE
FW_SEIZE != BW_BLOCK
BW_SEIZE_ACK = BW_CLEAR_BACK = BW_BLOCK
BW_SEIZE_ACK != BW_IDLE
BW_SEIZE_ACK != FW_SEIZE
BW_ANSWER: this signal must be different than all other BW signals.
BW_FORCE_RELEASE: (if used) this signal must be different than all other
BW signals.
Where:
link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
CD_bit_values is 0, 1, 2, or 3.
ER <mfc_link> Erases the R2 signaling table values.
Where:
mfc_link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
RingOpt <link><flag> Sets the ringing signal.
Where:
link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
flag is either 0 (ringing signal is not used) or 1 (ringing signal is used).
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 74

74 Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI)
Table 23 R2 directory CLI commands (Sheet 2 of 2)
CLI command Description
SeizeOption <link><flag> Sets seize interworking with opposite link upon detecting seize from far end.
Where:
link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
flag is either 0 (seize process is autonomic) or 1 (seize process is
dependant).
Autonomic - link responds to seize without waiting for opposite link ack.
Dependant - link waits for opposite link ack before sending its ack.
SzAckOpt <link><flag> Work with seize ack or not.
Where:
link is the number of the link, 0 or 1.
flag is either 0 (seize ack is not used) or 1 (seize ack is used).
SearchMode <link><mode> Sets MFC channel allocation mode.
Where:
link is the number of the link, 0 or 1 (applicable to link 0 only).
mode is either 0(round robin), 1 (linear ascending), or 2 (linear descending)
Round robin (default) - start search for next available channel after last
channel used.
linear ascending - search for next available channel from channel 1 up.
linear descending - search for next available channel from 30 down.
New defined mode is effective immediately after it is defined. It must be
saved, by using the SaveCfg command, to remain in effect after a restart.
The new mode is saved on the EEPROM, and is always in effect, regardless
of the Config DIP switch settings (mode is not part of the country code
configuration).
N0087114 1.0
Page 75

Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI) 75
PRI directory
Table 24 includes the CLI commands for the PRI directory. The commands are accessed from the
PRI directory.
Table 24 PRI directory CLI commands
CLI command Description
UNS Displays the user and network side information.
For R2MFC card the value is hard-coded as network side.
SDT <dial_type> Sets the dial type to overlap or non-overlap.
Where:
dial_type is either 0 (enblock/non-overlap) or 1 (overlap).
The default is non-overlap.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 76

76 Chapter 6 Command Line Interface (CLI)
N0087114 1.0
Page 77

Appendix A
n
Config DIP switch settings and definitions
This appendix shows the faceplate DIP switch settings for the country codes and for second dial
tone. It also contains the definitions of the settings for the different countries codes.
See Figure 17 on page 78 for country code and second dial tone DIP switch settings.
Figure 16 shows the Config DIP switch layout.
Figure 16 Config DIP Switches
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
configuratio
dial tone
77
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 78

78 Config DIP switch settings and definitions
Figure 17 DIP switch settings for country selection
Mexico 1
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
Columbia 1
ON
1
2
3
4
5
Mexico 2
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
Columbia 2
ON
1
2
3
4
5
Argentina
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
Malaysia
Singapore
ON
1
2
3
4
5
Peru
ON
Korea
ON
Brazil 1
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
2
3
4
5
6
India
ON
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
Brazil 2
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
China
Thailand
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
Indonesia
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
6
Unassigned
ON
Unassigned
1
2
3
4
5
6
Note: Second dial tone is controlled using switch 6. Changes to this switch are
effective immediately, and do not cause the R2MFC card to restart. Also, the
Norstar must be set to outgoing dialing mode overlap for the dial tone to be heard.
6
Custom
Profile
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
6
Dial Tone
Disabled
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
6
Dial Tone
Enabled
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
6
ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
N0087114 1.0
Page 79

Country code defaults
This section contains the default configuration associated to the country code set by the DIP
switches on the faceplate of the R2MFC card.
Mexico Config 1
E1 physical characteristics
• Connector type: BNC 75 Ω
• Line coding: HDB3
E1 framing
Frame mode: Alternate (card default, not affected by DIP switch)
Register signaling
• Regret option: OFF
• End of dialing (Incoming): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
• End of dialing (Outgoing): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
Config DIP switch settings and definitions 79
R2 line signaling
Mexico Config 1 R2 signals are according to CCITT standard. See Table 25 for the Mexico Config
1 R2 signal definitions.
Table 25 Mexico Config 1 R2 A/B signals
Forward Backward
SignalABSignalAB
Idle 1 0 Idle 1 0
Seize 0 0 Seize acknowledge 1 1
Clear forward 1 0 Answer 0 1
Clear back 1 1
Block 1 1
Note: CD bits are not used. They are set to 01 in transmit direction, and are ignored in receive direction.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 80

80 Config DIP switch settings and definitions
MFC register signaling
MFC signal definitions depends on the stage and the direction of the call; there are four tables of
15 signals each: the first stage uses I signals forward and A signals backward, and the second stage
uses II signals forward and B signals backward. The meaning of the signals can also be different
when being transmitted or received. Meanings of the MFC signals are configurable. MFC signal
tables are part of the country-specific parameters.
Table 26 shows the MFC signal configuration in the R2MFC card accessed through the CLI for
Mexico Config 1. Table 27 shows the MFC transmitted signal configuration in the R2MFC card
accessed through the CLI for Mexico Config 1. These values are preconfigured by the faceplate
DIP switches as shown in Figure 17 on page 78. See Chapter 6, “Command Line Interface (CLI),”
on page 59 for information on the CLI.
Table 26 Interpretation of received MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_1 I_1 FW_Categ_1 II_1 BW_DigitOrAni A_1 BW_FreeCharge B_1
FW_Digit_2 I_2 FW_Categ_2 II_2 BW_ReSend A_2 BW_Busy B_2
FW_Digit_3 I_3 FW_Categ_3 II_3 BW_BCateg A_3 BW_B_Congest B_3
FW_Digit_4 I_4 FW_Categ_4 II_4 BW_A_Congest A_4 BW_B_Congest B_4
FW_Digit_5 I_5 FW_Categ_5 II_5 BW_RtrnToA A_5 BW_FreeNoChrg B_5
FW_Digit_6 I_6 FW_Categ_6 II_6 BW_CatgSamDig A_6 BW_B_Congest B_6
FW_Digit_7 I_7 FW_Categ_7 II_7 BW_Illegal A_7 BW_B_Congest B_7
FW_Digit_8 I_8 FW_Categ_8 II_8 BW_Illegal A_8 BW_B_Congest B_8
FW_Digit_9 I_9 FW_Categ_9 II_9 BW_Illegal A_9 BW_B_Congest B_9
FW_Digit_0 I_10 FW_Categ_10 II_10 BW_Illegal A_10 BW_B_Congest B_10
FW_Digit_11 I_11 FW_Categ_11 II_11 BW_Illegal A_11 BW_B_Congest B_11
FW_ReqFault I_12 FW_Categ_12 II_12 BW_Illegal A_12 BW_B_Congest B_12
FW_Digit_13 I_13 FW_Categ_13 II_13 BW_Illegal A_13 BW_B_Congest B_13
FW_Digit_14 I_14 FW_Categ_14 II_14 BW_Illegal A_14 BW_B_Congest B_14
FW_EndANIdgts I_15 FW_Categ_15 II_15 BW_Illegal A_15 BW_B_Congest B_15
Table 27 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals (Sheet 1 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_NextDig A_1 FW_ReqFault I 15 FW_Categ_1 II 1
BW_BCateg A_3 FW_EndDigits I 15 FW_Categ_2 II 2
BW_RtrnToA A_5 FW_EndANIdgts I 15 FW_Categ_3 II 3
BW_A_Congest A_4 FW_Digit_1 I 1 FW_Categ_4 II 4
BW_B_Congest B_4 FW_Digit_2 I 2 FW_Categ_5 II 5
BW_Category A_6 FW_Digit_3 I 3 FW_Categ_6 II 6
BW_SpeechChrg NO_SG FW_Digit_4 I 4 FW_Categ_7 II 7
N0087114 1.0
Page 81

Config DIP switch settings and definitions 81
Table 27 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals (Sheet 2 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_OrigDn A_1 FW_Digit_5 I 5 FW_Categ_8 II 8
BW_FreeCharge B_1 FW_Digit_6 I 6 FW_Categ_9 II 9
BW_FreeNoChrg B_5 FW_Digit_7 I 7 FW_Categ_10 II 10
BW_CntrCharge B_1 FW_Digit_8 I 8 FW_Categ_11 II 11
BW_Busy B_2 FW_Digit_9 I 9 FW_Categ_12 II 12
BW_Unlocated B_4 FW_Digit_10 I 10 FW_Categ_13 II 13
BW_OutOfOrder B_4 FW_Digit_11 I 11 FW_Categ_14 II 14
BW_ChangOrder B_4 FW_Digit_12 I 12 FW_Categ_15 II 15
FW_Digit_13 I 13 FW_KD_Local II 3
FW_Digit_14 I 14 FW_KD_LnDst II 2
FW_Digit_15 I 15
Mexico Config 2
E1 physical characteristics
• Connector type: BNC 75 Ω
• Line coding: HDB3
E1 framing
Frame mode: Alternate (card default, not affected by DIP switch)
Register signaling
• Regret option: OFF
• End of dialing (Incoming): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
• End of dialing (Outgoing): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 82

82 Config DIP switch settings and definitions
R2 line signaling
Mexico Config 2 R2 signals are according to CCITT standard. See Table 28 for the Mexico Config
2 R2 signal definitions.
Table 28 Mexico Config 2 R2 A/B signals
Forward Backward
SignalABSignalAB
Idle 1 0 Idle 1 0
Seize 0 0 Seize acknowledge 1 1
Clear forward 1 0 Answer 0 1
Clear back 1 1
Block 1 1
Note: CD bits are not used. They are set to 01 in transmit direction, and are ignored in receive direction.
MFC register signaling
MFC signal definitions depends on the stage and the direction of the call; there are four tables of
15 signals each: the first stage uses I signals forward and A signals backward, and the second stage
uses II signals forward and B signals backward. The meaning of the signals can also be different
when being transmitted or received. Meanings of the MFC signals are configurable. MFC signal
tables are part of the country-specific parameters.
Table 29 shows the MFC signal configuration in the R2MFC card accessed through the CLI for
Mexico Config 2. Table 30 on page 83 shows the MFC transmitted signal configuration in the
R2MFC card accessed through the CLI for Mexico Config 2. These values are preconfigured by
the faceplate DIP switches as shown in Figure 17 on page 78. See Chapter 6, “Command Line
Interface (CLI),” on page 59 for information on the CLI.
Table 29 Interpretation of received MFC signals (Sheet 1 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_1 I_1 FW_Categ_1 II_1 BW_NextDig A_1 BW_FreeCharge B_1
FW_Digit_2 I_2 FW_Categ_2 II_2 BW_PrevDigit A_2 BW_Busy B_2
FW_Digit_3 I_3 FW_Categ_3 II_3 BW_BCateg A_3 BW_B_Congest B_3
FW_Digit_4 I_4 FW_Categ_4 II_4 BW_A_Congest A_4 BW_B_Congest B_4
FW_Digit_5 I_5 FW_Categ_5 II_5 BW_Category A_5 BW_Unlocated B_5
FW_Digit_6 I_6 FW_Categ_6 II_6 BW_SpeechChrg A_6 BW_B_Congest B_6
FW_Digit_7 I_7 FW_Categ_7 II_7 BW_Prev2Digit A_7 BW_B_Congest B_7
N0087114 1.0
Page 83

Config DIP switch settings and definitions 83
Table 29 Interpretation of received MFC signals (Sheet 2 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_8 I_8 FW_Categ_8 II_8 BW_Prev3Digit A_8 BW_OutOfOrder B_8
FW_Digit_9 I_9 FW_Categ_9 II_9 BW_OrigDn A_9 BW_B_Congest B_9
FW_Digit_0 I_10 FW_Categ_10 II_10 BW_ReSend A_10 BW_B_Congest B_10
FW_Digit_11 I_11 FW_Categ_11 II_11 BW_NextDig A_11 BW_B_Congest B_11
FW_ReqFault I_12 FW_Categ_12 II_12 BW_Illegal A_12 BW_B_Congest B_12
FW_Digit_13 I_13 FW_Categ_13 II_13 BW_Illegal A_13 BW_B_Congest B_13
FW_Digit_14 I_14 FW_Categ_14 II_14 BW_Illegal A_14 BW_B_Congest B_14
FW_Enddigits I_15 FW_Categ_15 II_15 BW_Illegal A_15 BW_B_Congest B_15
Table 30 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_NextDig A 1 FW_ReqFault I 12 FW_Categ_1 II 1
BW_BCateg A 3 FW_EndDigits I 15 FW_Categ_2 II 2
BW_RtrnToA A 1 FW_EndANIdgts I 15 FW_Categ_3 II 3
BW_A_Congest A 4 FW_Digit_1 I 1 FW_Categ_4 II 4
BW_B_Congest B 4 FW_Digit_2 I 2 FW_Categ_5 II 5
BW_Category A 6 FW_Digit_3 I 3 FW_Categ_6 II 6
BW_SpeechChrg NO SIG FW_Digit_4 I 4 FW_Categ_7 II 7
BW_OrigDn A 1 FW_Digit_5 I 5 FW_Categ_8 II 8
BW_FreeCharge B 1 FW_Digit_6 I 6 FW_Categ_9 II 9
BW_FreeNoChrg B 1 FW_Digit_7 I 7 FW_Categ_10 II 10
BW_CntrCharge B 1 FW_Digit_8 I 8 FW_Categ_11 II 11
BW_Busy B 2 FW_Digit_9 I 9 FW_Categ_12 II 12
BW_Unlocated B 5 FW_Digit_10 I 10 FW_Categ_13 II 13
BW_OutOfOrder B 8 FW_Digit_11 I 11 FW_Categ_14 II 14
BW_ChangOrder B 4 FW_Digit_12 I 12 FW_Categ_15 II 15
FW_Digit_13 I 13 FW_KD_Local II 3
FW_Digit_14 I 14 FW_KD_LnDst II 2
FW_Digit_15 I 15
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 84

84 Config DIP switch settings and definitions
Brazil Config 1
E1 physical characteristics
• Connector type: BNC 75 Ω
• Line coding: HDB3
E1 framing
Frame mode: Alternate
Register signaling
• Regret option: ON
• End of dialing (Incoming): 4
• End of dialing (Outgoing): 4
R2 line signaling
Brazil Config 1 R2 signals are according to CCITT standard. See Table 31 for the Brazil Config 1
R2 signal definitions.
Table 31 Brazil Config 1 R2 A/B signals
Forward Backward
SignalABSignalAB
Idle 1 0 Idle 1 0
Seize 0 0 Seize acknowledge 1 1
Clear forward 1 0 Answer 0 1
Clear back 1 1
Block 1 1
Note: CD bits are not used. They are set to 01 in transmit direction, and are ignored in receive direction.
MFC Register Signaling
MFC signal definitions depends on the stage and the direction of the call; there are four tables of
15 signals each: the first stage uses I signals forward and A signals backward, and the second stage
uses II signals forward and B signals backward. The meaning of the signals can also be different
when being transmitted or received. Meanings of the MFC signals are configurable. MFC signal
tables are part of the country-specific parameters.
N0087114 1.0
Page 85

Config DIP switch settings and definitions 85
Table 32 shows the MFC signal configuration in the R2MFC card accessed through the CLI for
Brazil Config 1. Table 33 shows the MFC transmitted signal configuration in the R2MFC card
accessed through the CLI for Brazil Config 1. These values are pre-configured by the faceplate
DIP switches as shown in Figure 17 on page 78. See Chapter 6, “Command Line Interface (CLI),”
on page 59 for information on the CLI.
Table 32 Interpretation of received MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_1 I_1 FW_Categ_1 II_1 BW_NextDig A_1 BW_FreeCharge B_1
FW_Digit_2 I_2 FW_Categ_2 II_2 BW_ReSend A_2 BW_Busy B_2
FW_Digit_3 I_3 FW_Categ_3 II_3 BW_BCateg A_3 BW_BW_OutOfOrder B_3
FW_Digit_4 I_4 FW_Categ_4 II_4 BW_A_Congest A_4 BW_B_Congest B_4
FW_Digit_5 I_5 FW_Categ_5 II_5 BW_CategOrAni A_5 BW_FreeNoChrg B_5
FW_Digit_6 I_6 FW_Categ_6 II_6 BW_Illegal A_6 BW_FreeCharge B_6
FW_Digit_7 I_7 FW_Categ_7 II_7 BW_Prev2Digit A_7 BW_Unlocated B_7
FW_Digit_8 I_8 FW_Categ_8 II_8 BW_Prev3Digit A_8 BW_B_Congest B_8
FW_Digit_9 I_9 FW_Categ_9 II_9 BW_PrevDigit A_9 BW_B_Congest B_9
FW_Digit_0 I_10 FW_Categ_10 II_10 BW_Illegal A_10 BW_B_Congest B_10
FW_Digit_11 I_11 FW_Categ_11 II_11 BW_Illegal A_11 BW_B_Congest B_11
FW_ReqFault I_12 FW_Categ_12 II_12 BW_Illegal A_12 BW_B_Congest B_12
FW_Digit_13 I_13 FW_Categ_13 II_13 BW_Illegal A_13 BW_B_Congest B_13
FW_Digit_14 I_14 FW_Categ_14 II_14 BW_Illegal A_14 BW_B_Congest B_14
FW_EndDigits I_15 FW_Categ_15 II_15 BW_Illegal A_15 BW_B_Congest B_15
Table 33 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals (Sheet 1 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_NextDig A 1 FW_ReqFault I 12 FW_Categ_1 II 1
BW_BCateg A 3 FW_EndDigits I 15 FW_Categ_2 II 2
BW_RtrnToA A 1 FW_EndANIdgts I 15 FW_Categ_3 II 3
BW_A_Congest A 4 FW_Digit_1 I 1 FW_Categ_4 II 4
BW_B_Congest B 4 FW_Digit_2 I 2 FW_Categ_5 II 5
BW_Category A 5 FW_Digit_3 I 3 FW_Categ_6 II 6
BW_SpeechChrg NO SIG FW_Digit_4 I 4 FW_Categ_7 II 7
BW_OrigDn A 5 FW_Digit_5 I 5 FW_Categ_8 II 8
BW_FreeCharge B 1 FW_Digit_6 I 6 FW_Categ_9 II 9
BW_FreeNoChrg B 5 FW_Digit_7 I 7 FW_Categ_10 II 10
BW_CntrCharge B 1 FW_Digit_8 I 8 FW_Categ_11 II 11
BW_Busy B 2 FW_Digit_9 I 9 FW_Categ_12 II 12
BW_Unlocated B 7 FW_Digit_10 I 10 FW_Categ_13 II 13
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 86

86 Config DIP switch settings and definitions
Table 33 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals (Sheet 2 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_OutOfOrder B 4 FW_Digit_11 I 11 FW_Categ_14 II 14
BW_ChangOrder B 4 FW_Digit_12 I 12 FW_Categ_15 II 15
FW_Digit_13 I 13 FW_KD_Local II 3
FW_Digit_14 I 14 FW_KD_LnDst II 2
FW_Digit_15 I 15
Brazil Config 2
E1 physical characteristics
• Connector type: BNC 75 Ω
• Line coding: HDB3
E1 framing
Frame mode: Alternate
Register signaling
• Regret option: OFF
• End of dialing (Incoming): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
• End of dialing (Outgoing): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
N0087114 1.0
Page 87

Config DIP switch settings and definitions 87
R2 line signaling
Brazil Config 2 R2 signals are according to CCITT standard. See Table 34 for the Brazil Config 2
R2 signal definitions.
Table 34 Brazil Config 2 R2 A/B signals
Forward Backward
SignalABSignalAB
Idle 1 0 Idle 1 0
Seize 0 0 Seize acknowledge 1 1
Clear forward 1 0 Answer 0 1
Clear back 1 1
Block 1 1
Note: CD bits are not used. They are set to 01 in transmit direction, and are ignored in receive direction.
MFC Register Signaling
MFC signal definitions depends on the stage and the direction of the call, there are four tables of
15 signals each: the first stage uses I signals forward and A signals backward, and the second stage
uses II signals forward and B signals backward. The meaning of the signals can also be different
when being transmitted or received. Meanings of the MFC signals are configurable. MFC signal
tables are part of the country-specific parameters.
Table 35 shows the MFC signal configuration in the R2MFC card accessed through the CLI for
Brazil Config 2. Table 36 on page 88 shows the MFC transmitted signal configuration in the
R2MFC card accessed through the CLI for Brazil Config 2. These values are preconfigured by the
faceplate DIP switches as shown in Figure 17 on page 78. See Chapter 6, “Command Line
Interface (CLI),” on page 59 for information on the CLI.
Table 35 Interpretation of received MFC signals (Sheet 1 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_1 I_1 FW_Categ_1 II_1 BW_NextDig A_1 BW_FreeCharge B_1
FW_Digit_2 I_2 FW_Categ_2 II_2 BW_ReSend A_2 BW_Busy B_2
FW_Digit_3 I_3 FW_Categ_3 II_3 BW_BCateg A_3 BW_B_Congest B_3
FW_Digit_4 I_4 FW_Categ_4 II_4 BW_A_Congest A_4 BW_B_Congest B_4
FW_Digit_5 I_5 FW_Categ_5 II_5 BW_CategOrAni A_5 BW_FreeNoChrg B_5
FW_Digit_6 I_6 FW_Categ_6 II_6 BW_Illegal A_6 BW_B_Congest B_6
FW_Digit_7 I_7 FW_Categ_7 II_7 BW_Prev2Digit A_7 BW_Unlocated B_7
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 88

88 Config DIP switch settings and definitions
Table 35 Interpretation of received MFC signals (Sheet 2 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_8 I_8 FW_Categ_8 II_8 BW_Prev3Digit A_8 BW_B_Congest B_8
FW_Digit_9 I_9 FW_Categ_9 II_9 BW_PrevDigit A_9 BW_B_Congest B_9
FW_Digit_0 I_10 FW_Categ_10 II_10 BW_Illegal A_10 BW_B_Congest B_10
FW_Digit_11 I_11 FW_Categ_11 II_11 BW_Illegal A_11 BW_B_Congest B_11
FW_ReqFault I_12 FW_Categ_12 II_12 BW_Illegal A_12 BW_B_Congest B_12
FW_Digit_13 I_13 FW_Categ_13 II_13 BW_Illegal A_13 BW_B_Congest B_13
FW_Digit_14 I_14 FW_Categ_14 II_14 BW_Illegal A_14 BW_B_Congest B_14
FW_EndDigits I_15 FW_Categ_15 II_15 BW_Illegal A_15 BW_B_Congest B_15
Table 36 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_NextDig A 1 FW_ReqFault I 12 FW_Categ_1 II 1
BW_BCateg A 3 FW_EndDigits I 15 FW_Categ_2 II 2
BW_RtrnToA A 1 FW_EndANIdgts I 15 FW_Categ_3 II 3
BW_A_Congest A 4 FW_Digit_1 I 1 FW_Categ_4 II 4
BW_B_Congest B 4 FW_Digit_2 I 2 FW_Categ_5 II 5
BW_Category A 5 FW_Digit_3 I 3 FW_Categ_6 II 6
BW_SpeechChrg NO SIG FW_Digit_4 I 4 FW_Categ_7 II 7
BW_OrigDn A 5 FW_Digit_5 I 5 FW_Categ_8 II 8
BW_FreeCharge B 1 FW_Digit_6 I 6 FW_Categ_9 II 9
BW_FreeNoChrg B 5 FW_Digit_7 I 7 FW_Categ_10 II 10
BW_CntrCharge B 1 FW_Digit_8 I 8 FW_Categ_11 II 11
BW_Busy B 2 FW_Digit_9 I 9 FW_Categ_12 II 12
BW_Unlocated B 7 FW_Digit_10 I 10 FW_Categ_13 II 13
BW_OutOfOrder B 4 FW_Digit_11 I 11 FW_Categ_14 II 14
BW_ChangOrder B 4 FW_Digit_12 I 12 FW_Categ_15 II 15
FW_Digit_13 I 13 FW_KD_Local II 3
FW_Digit_14 I 14 FW_KD_LnDst II 2
FW_Digit_15 I 15
Argentina Config 1
E1 Physical Characteristics
• Connector type: BNC 75 Ω
• Line coding: HDB3
N0087114 1.0
Page 89

E1 Framing
Frame mode: Alternate
Register signaling
• Regret option: OFF
• End of dialing (Incoming): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
• End of dialing (Outgoing): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
R2 Line Signaling
Argentina Config 1 R2 signals are according to CCITT standard.See Table 37 for the Argentina
Config 1 R2 signal definitions.
Table 37 Argentina Config 1 R2 A/B Signals
Config DIP switch settings and definitions 89
Forward Backward
SignalABSignalAB
Idle 1 0 Idle 1 0
Seize 0 0 Seize acknowledge 1 1
Clear forward 1 0 Answer 0 1
Clear back 1 1
Block 1 1
CD bits are not used. They are set to 01 in transmit direction, and are ignored in receive direction.
MFC Register Signaling
MFC signal definitions depends on the stage and the direction of the call, there are four tables of
15 signals each: the first stage uses I signals forward and A signals backward, and the second stage
uses II signals forward and B signals backward. The meaning of the signals can also be different
when being transmitted or received. Meanings of the MFC signals are configurable. MFC signal
tables are part of the country-specific parameters.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 90

90 Config DIP switch settings and definitions
Table 38 shows the MFC received signal configuration in the R2MFC card accessed through the
CLI for Argentina Config 1. Tabl e 39 shows the MFC transmitted signal configuration in the
R2MFC card accessed through the CLI for Argentina Config 1. These values are pre-configured
by the faceplate DIP switches as shown in Figure 17 on page 78. See Chapter 6, “Command Line
Interface (CLI),” on page 59 for information on the CLI.
Table 38 Interpretation of received MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_1 I_1 FW_Categ_1 II_1 BW_NextDig A_1 BW_B_Congest B_1
FW_Digit_2 I_2 FW_Categ_2 II_2 BW_PrevDigit A_2 BW_FreeCharge B_2
FW_Digit_3 I_3 FW_Categ_3 II_3 BW_BCateg A_3 BW_Busy B_3
FW_Digit_4 I_4 FW_Categ_4 II_4 BW_A_Congest A_4 BW_B_Congest B_4
FW_Digit_5 I_5 FW_Categ_5 II_5 BW_CategOrAni A_5 BW_Unlocated B_5
FW_Digit_6 I_6 FW_Categ_6 II_6 BW_SpeechChrg A_6 BW_FreeCharge B_6
FW_Digit_7 I_7 FW_Categ_7 II_7 BW_Prev2Digit A_7 BW_FreeNoChrg B_7
FW_Digit_8 I_8 FW_Categ_8 II_8 BW_Prev3Digit A_8 BW_OutOfOrder B_8
FW_Digit_9 I_9 FW_Categ_9 II_9 BW_SameDigit A_9 BW_B_Congest B_9
FW_Digit_0 I_10 FW_Categ_10 II_10 BW_ReSend A_10 BW_B_Congest B_10
FW_Digit_11 I_11 FW_Categ_11 II_11 BW_Illegal A_11 BW_B_Congest B_11
FW_ReqFault I_12 FW_Categ_12 II_12 BW_Illegal A_12 BW_B_Congest B_12
FW_Digit_13 I_13 FW_Categ_13 II_13 BW_Illegal A_13 BW_B_Congest B_13
FW_Digit_14 I_14 FW_Categ_14 II_14 BW_Illegal A_14 BW_B_Congest B_14
FW_EndDigits I_15 FW_Categ_15 II_15 BW_Illegal A_15 BW_B_Congest B_15
Table 39 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals (Sheet 1 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_NextDig A 1 FW_ReqFault I 12 FW_Categ_1 II 1
BW_BCateg A 3 FW_EndDigits I 15 FW_Categ_2 II 2
BW_RtrnToA A 1 FW_EndANIdgts I 15 FW_Categ_3 II 3
BW_A_Congest A 4 FW_Digit_1 I 1 FW_Categ_4 II 4
BW_B_Congest B 4 FW_Digit_2 I 2 FW_Categ_5 II 5
BW_Category A 5 FW_Digit_3 I 3 FW_Categ_6 II 6
BW_SpeechChrg A 6 FW_Digit_4 I 4 FW_Categ_7 II 7
BW_OrigDn A 5 FW_Digit_5 I 5 FW_Categ_8 II 8
BW_FreeCharge B 6 FW_Digit_6 I 6 FW_Categ_9 II 9
BW_FreeNoChrg B 7 FW_Digit_7 I 7 FW_Categ_10 II 10
BW_CntrCharge NO SIG FW_Digit_8 I 8 FW_Categ_11 II 11
BW_Busy B 3 FW_Digit_9 I 9 FW_Categ_12 II 12
BW_Unlocated B 5 FW_Digit_10 I 10 FW_Categ_13 II 13
N0087114 1.0
Page 91

Config DIP switch settings and definitions 91
Table 39 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals (Sheet 2 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_OutOfOrder B 8 FW_Digit_11 I 11 FW_Categ_14 II 14
BW_ChangOrder B 4 FW_Digit_12 I 12 FW_Categ_15 II 15
FW_Digit_13 I 13 FW_KD_Local II 3
FW_Digit_14 I 14 FW_KD_LnDst II 2
FW_Digit_15 I 15
Columbia Config 1
E1 Physical Characteristics
• Connector type: BNC 75 Ω
• Line coding: HDB3
E1 Framing
Frame mode: Alternate (card default, not affected by DIP switch)
Register signaling
• Regret option: OFF
• End of dialing (Incoming): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
• End of dialing (Outgoing): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 92

92 Config DIP switch settings and definitions
R2 Line Signaling
Columbia Config 1 R2 signals are according to CCITT standard.See Table 37 for the Columbia
Config 1 R2 signal definitions.
Table 40 Argentina Config 1 R2 A/B Signals
Forward Backward
SignalABSignalAB
Idle 1 0 Idle 1 0
Seize 0 0 Seize acknowledge 1 1
Clear forward 1 0 Answer 0 1
Clear back 1 1
Block 1 1
CD bits are not used. They are set to 01 in transmit direction, and are ignored in receive direction.
MFC Register Signaling
MFC signal definitions depends on the stage and the direction of the call, there are four tables of
15 signals each: the first stage uses I signals forward and A signals backward, and the second stage
uses II signals forward and B signals backward. The meaning of the signals can also be different
when being transmitted or received. Meanings of the MFC signals are configurable. MFC signal
tables are part of the country-specific parameters.
Table 38 shows the MFC received signal configuration in the R2MFC card accessed through the
CLI for Argentina Config 1. Tabl e 39 shows the MFC transmitted signal configuration in the
R2MFC card accessed through the CLI for Argentina Config 1. These values are pre-configured
by the faceplate DIP switches as shown in Figure 17 on page 78. See Chapter 6, “Command Line
Interface (CLI),” on page 59 for information on the CLI.
Table 41 Interpretation of received MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_1 I_1 FW_Categ_1 II_1 BW_DigitOrAni A_1 BW_FreeCharge B_1
FW_Digit_2 I_2 FW_Categ_2 II_2 BW_Resend A_2 BW_Busy B_2
FW_Digit_3 I_3 FW_Categ_3 II_3 BW_BCateg A_3 BW_ChngOrder B_3
FW_Digit_4 I_4 FW_Categ_4 II_4 BW_A_Congest A_4 BW_B_Congest B_4
FW_Digit_5 I_5 FW_Categ_5 II_5 BW_Illegal A_5 BW_FreeNoChrg B_5
FW_Digit_6 I_6 FW_Categ_6 II_6 BW_A_Congest A_6 BW_FreeCharge B_6
FW_Digit_7 I_7 FW_Categ_7 II_7 BW_A_Congest A_7 BW_B_Congest B_7
N0087114 1.0
Page 93

Config DIP switch settings and definitions 93
Table 41 Interpretation of received MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_8 I_8 FW_Categ_8 II_8 BW_Illegal A_8 BW_B_Congest B_8
FW_Digit_9 I_9 FW_Categ_9 II_9 BW_Illegal A_9 BW_B_Congest B_9
FW_Digit_0 I_10 FW_Categ_10 II_10 BW_Illegal A_10 BW_B_Congest B_10
FW_Digit_11 I_11 FW_Categ_11 II_11 BW_Illegal A_11 BW_B_Congest B_11
FW_ReqFault I_12 FW_Categ_12 II_12 BW_Illegal A_12 BW_B_Congest B_12
FW_Digit_13 I_13 FW_Categ_13 II_13 BW_Illegal A_13 BW_B_Congest B_13
FW_Digit_14 I_14 FW_Categ_14 II_14 BW_Illegal A_14 BW_B_Congest B_14
FW_EndDigits I_15 FW_Categ_15 II_15 BW_Illegal A_15 BW_B_Congest B_15
Table 42 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_NextDig A 1 FW_ReqFault I 15 FW_Categ_1 II 1
BW_BCateg A 3 FW_EndDigits I 15 FW_Categ_2 II 2
BW_RtrnToA A 1 FW_EndANIdgts I 15 FW_Categ_3 II 3
BW_A_Congest A 4 FW_Digit_1 I 1 FW_Categ_4 II 4
BW_B_Congest B 4 FW_Digit_2 I 2 FW_Categ_5 II 5
BW_Category A 6 FW_Digit_3 I 3 FW_Categ_6 II 6
BW_SpeechChrg NO SIG FW_Digit_4 I 4 FW_Categ_7 II 7
BW_OrigDn A 1 FW_Digit_5 I 5 FW_Categ_8 II 8
BW_FreeCharge B 1 FW_Digit_6 I 6 FW_Categ_9 II 9
BW_FreeNoChrg B 5 FW_Digit_7 I 7 FW_Categ_10 II 10
BW_CntrCharge B 1 FW_Digit_8 I 8 FW_Categ_11 II 11
BW_Busy B 2 FW_Digit_9 I 9 FW_Categ_12 II 12
BW_Unlocated B 3 FW_Digit_10 I 10 FW_Categ_13 II 13
BW_OutOfOrder B 4 FW_Digit_11 I 11 FW_Categ_14 II 14
BW_ChangOrder B 3 FW_Digit_12 I 12 FW_Categ_15 II 15
FW_Digit_13 I 13 FW_KD_Local II 3
FW_Digit_14 I 14 FW_KD_LnDst II 2
FW_Digit_15 I 15
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 94

94 Config DIP switch settings and definitions
Malaysia and Singapore Config 1
E1 Physical Characteristics
• Connector type: BNC 75 Ω
• Line coding: HDB3
E1 Framing
Frame mode: Alternate (card default, not affected by DIP switch)
Register signaling
• Regret option: OFF
• End of dialing (Incoming): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
• End of dialing (Outgoing): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
R2 Line Signaling
Malaysia and Singapore Config 1 R2 signals are according to CCITT standard.See Table 37 for
the Malaysia and Singapore Config 1 R2 signal definitions.
Table 43 Argentina Config 1 R2 A/B Signals
Forward Backward
SignalABSignalAB
Idle 1 0 Idle 1 0
Seize 0 0 Seize acknowledge 1 1
Clear forward 1 0 Answer 0 1
Clear back 1 1
Block 1 1
CD bits are not used. They are set to 01 in transmit direction, and are ignored in receive direction.
N0087114 1.0
Page 95

Config DIP switch settings and definitions 95
MFC Register Signaling
MFC signal definitions depends on the stage and the direction of the call, there are four tables of
15 signals each: the first stage uses I signals forward and A signals backward, and the second stage
uses II signals forward and B signals backward. The meaning of the signals can also be different
when being transmitted or received. Meanings of the MFC signals are configurable. MFC signal
tables are part of the country-specific parameters.
Table 38 shows the MFC received signal configuration in the R2MFC card accessed through the
CLI for Argentina Config 1. Tabl e 39 shows the MFC transmitted signal configuration in the
R2MFC card accessed through the CLI for Argentina Config 1. These values are pre-configured
by the faceplate DIP switches as shown in Figure 17 on page 78. See Chapter 6, “Command Line
Interface (CLI),” on page 59 for information on the CLI.
Table 44 Interpretation of received MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_1 I_1 FW_Categ_1 II_1 BW_NextDigit A_1 BW_FreeCharge B_1
FW_Digit_2 I_2 FW_Categ_2 II_2 BW_Resend A_2 BW_Busy B_2
FW_Digit_3 I_3 FW_Categ_3 II_3 BW_BCateg A_3 BW_Unlocated B_3
FW_Digit_4 I_4 FW_Categ_4 II_4 BW_A_Congest A_4 BW_B_Congest B_4
FW_Digit_5 I_5 FW_Categ_5 II_5 BW_Illegal A_5 BW_FreeNoChrg B_5
FW_Digit_6 I_6 FW_Categ_6 II_6 BW_CategOrAni A_6 BW_B_Congest B_6
FW_Digit_7 I_7 FW_Categ_7 II_7 BW_Illegal A_7 BW_B_Congest B_7
FW_Digit_8 I_8 FW_Categ_8 II_8 BW_PrevDigit A_8 BW_B_Congest B_8
FW_Digit_9 I_9 FW_Categ_9 II_9 BW_Prev2Digit A_9 BW_B_Congest B_9
FW_Digit_0 I_10 FW_Categ_10 II_10 BW_Illegal A_10 BW_B_Congest B_10
FW_Digit_11 I_11 FW_Categ_11 II_11 BW_Illegal A_11 BW_B_Congest B_11
FW_ReqFault I_12 FW_Categ_12 II_12 BW_Illegal A_12 BW_B_Congest B_12
FW_Digit_13 I_13 FW_Categ_13 II_13 BW_Category A_13 BW_B_Congest B_13
FW_Digit_14 I_14 FW_Categ_14 II_14 BW_Illegal A_14 BW_B_Congest B_14
FW_EndDigits I_15 FW_Categ_15 II_15 BW_Illegal A_15 BW_B_Congest B_15
Table 45 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals (Sheet 1 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_NextDig A 1 FW_ReqFault I 12 FW_Categ_1 II 1
BW_BCateg A 3 FW_EndDigits I 15 FW_Categ_2 II 2
BW_RtrnToA A 1 FW_EndANIdgts I 15 FW_Categ_3 II 3
BW_A_Congest A 4 FW_Digit_1 I 1 FW_Categ_4 II 4
BW_B_Congest B 4 FW_Digit_2 I 2 FW_Categ_5 II 5
BW_Category A 6 FW_Digit_3 I 3 FW_Categ_6 II 6
BW_SpeechChrg NO SIG FW_Digit_4 I 4 FW_Categ_7 II 7
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 96

96 Config DIP switch settings and definitions
Table 45 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals (Sheet 2 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_OrigDn A 6 FW_Digit_5 I 5 FW_Categ_8 II 8
BW_FreeCharge B 1 FW_Digit_6 I 6 FW_Categ_9 II 9
BW_FreeNoChrg B 5 FW_Digit_7 I 7 FW_Categ_10 II 10
BW_CntrCharge NO SIG FW_Digit_8 I 8 FW_Categ_11 II 11
BW_Busy B 2 FW_Digit_9 I 9 FW_Categ_12 II 12
BW_Unlocated B 3 FW_Digit_10 I 10 FW_Categ_13 II 13
BW_OutOfOrder B 4 FW_Digit_11 I 11 FW_Categ_14 II 14
BW_ChangOrder B 4 FW_Digit_12 I 12 FW_Categ_15 II 15
FW_Digit_13 I 13 FW_KD_Local II 3
FW_Digit_14 I 14 FW_KD_LnDst II 2
FW_Digit_15 I 15
Korea Config 1
E1 Physical Characteristics
• Connector type: BNC 75 Ω
• Line coding: HDB3
E1 Framing
Frame mode: Alternate (card default, not affected by DIP switch)
Register signaling
• Regret option: OFF
• End of dialing (Incoming): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
• End of dialing (Outgoing): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
N0087114 1.0
Page 97

Config DIP switch settings and definitions 97
R2 Line Signaling
Korea Config 1 R2 signals are according to CCITT standard.See Table 37 for the Korea Config 1
R2 signal definitions.
Table 46 Argentina Config 1 R2 A/B Signals
Forward Backward
SignalABSignalAB
Idle 1 0 Idle 1 0
Seize 0 0 Seize acknowledge 1 1
Clear forward 1 0 Answer 0 1
Clear back 1 1
Block 1 1
CD bits are not used. They are set to 01 in transmit direction, and are ignored in receive direction.
MFC Register Signaling
MFC signal definitions depends on the stage and the direction of the call, there are four tables of
15 signals each: the first stage uses I signals forward and A signals backward, and the second stage
uses II signals forward and B signals backward. The meaning of the signals can also be different
when being transmitted or received. Meanings of the MFC signals are configurable. MFC signal
tables are part of the country-specific parameters.
Table 38 shows the MFC received signal configuration in the R2MFC card accessed through the
CLI for Argentina Config 1. Tabl e 39 shows the MFC transmitted signal configuration in the
R2MFC card accessed through the CLI for Argentina Config 1. These values are pre-configured
by the faceplate DIP switches as shown in Figure 17 on page 78. See Chapter 6, “Command Line
Interface (CLI),” on page 59 for information on the CLI.
Table 47 Interpretation of received MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_1 I_1 FW_Categ_1 II_1 BW_NextDigit A_1 BW_B_Congest B_1
FW_Digit_2 I_2 FW_Categ_2 II_2 BW_PrevDigit A_2 BW_ChngOrder B_2
FW_Digit_3 I_3 FW_Categ_3 II_3 BW_BCateg A_3 BW_Busy B_3
FW_Digit_4 I_4 FW_Categ_4 II_4 BW_A_Congest A_4 BW_B_Congest B_4
FW_Digit_5 I_5 FW_Categ_5 II_5 BW_CategOrAni A_5 BW_Unlocated B_5
FW_Digit_6 I_6 FW_Categ_6 II_6 BW_SpeechChrg A_6 BW_FreeChrg B_6
FW_Digit_7 I_7 FW_Categ_7 II_7 BW_Prev2Digit A_7 BW_FreeNoChrg B_7
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 98

98 Config DIP switch settings and definitions
Table 47 Interpretation of received MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_8 I_8 FW_Categ_8 II_8 BW_Prev3Digit A_8 BW_OutOfOrder B_8
FW_Digit_9 I_9 FW_Categ_9 II_9 BW_ReSend A_9 BW_B_Congest B_9
FW_Digit_0 I_10 FW_Categ_10 II_10 BW_Illegal A_10 BW_B_Congest B_10
FW_Digit_11 I_11 FW_Categ_11 II_11 BW_Illegal A_11 BW_B_Congest B_11
FW_ReqFault I_12 FW_Categ_12 II_12 BW_Illegal A_12 BW_B_Congest B_12
FW_Digit_13 I_13 FW_Categ_13 II_13 BW_Illegal A_13 BW_B_Congest B_13
FW_Digit_14 I_14 FW_Categ_14 II_14 BW_Illegal A_14 BW_B_Congest B_14
FW_EndDigits I_15 FW_Categ_15 II_15 BW_Illegal A_15 BW_B_Congest B_15
Table 48 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_NextDig A 1 FW_ReqFault I 12 FW_Categ_1 II 1
BW_BCateg A 3 FW_EndDigits I 15 FW_Categ_2 II 2
BW_RtrnToA A 1 FW_EndANIdgts I 15 FW_Categ_3 II 3
BW_A_Congest A 4 FW_Digit_1 I 1 FW_Categ_4 II 4
BW_B_Congest B 4 FW_Digit_2 I 2 FW_Categ_5 II 5
BW_Category A 5 FW_Digit_3 I 3 FW_Categ_6 II 6
BW_SpeechChrg A 6 FW_Digit_4 I 4 FW_Categ_7 II 7
BW_OrigDn A 5 FW_Digit_5 I 5 FW_Categ_8 II 8
BW_FreeCharge B 6 FW_Digit_6 I 6 FW_Categ_9 II 9
BW_FreeNoChrg B 7 FW_Digit_7 I 7 FW_Categ_10 II 10
BW_CntrCharge NO SIG FW_Digit_8 I 8 FW_Categ_11 II 11
BW_Busy B 3 FW_Digit_9 I 9 FW_Categ_12 II 12
BW_Unlocated B 5 FW_Digit_10 I 10 FW_Categ_13 II 13
BW_OutOfOrder B 8 FW_Digit_11 I 11 FW_Categ_14 II 14
BW_ChangOrder B 2 FW_Digit_12 I 12 FW_Categ_15 II 15
FW_Digit_13 I 13 FW_KD_Local II 3
FW_Digit_14 I 14 FW_KD_LnDst II 2
FW_Digit_15 I 15
N0087114 1.0
Page 99

Config DIP switch settings and definitions 99
India Config 1
E1 Physical Characteristics
• Connector type: BNC 75 Ω
• Line coding: HDB3
E1 Framing
Frame mode: Alternate (card default, not affected by DIP switch)
Register signaling
• Regret option: OFF
• End of dialing (Incoming): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
• End of dialing (Outgoing): terminated by indication from destination switch, or by MFC
forward signal FW_EndDigits
R2 Line Signaling
India Config 1 R2 signals are according to CCITT standard.See Table 37 for the India Config 1 R2
signal definitions.
Table 49 Argentina Config 1 R2 A/B Signals
Forward Backward
SignalABSignalAB
Idle 1 0 Idle 1 0
Seize 0 0 Seize acknowledge 1 1
Clear forward 1 0 Answer 0 1
Clear back 1 1
Block 1 1
CD bits are not used. They are set to 01 in transmit direction, and are ignored in receive direction.
R2MFC Card Installation and Configuration Guide
Page 100

100 Config DIP switch settings and definitions
MFC Register Signaling
MFC signal definitions depends on the stage and the direction of the call, there are four tables of
15 signals each: the first stage uses I signals forward and A signals backward, and the second stage
uses II signals forward and B signals backward. The meaning of the signals can also be different
when being transmitted or received. Meanings of the MFC signals are configurable. MFC signal
tables are part of the country-specific parameters.
Table 38 shows the MFC received signal configuration in the R2MFC card accessed through the
CLI for Argentina Config 1. Tabl e 39 shows the MFC transmitted signal configuration in the
R2MFC card accessed through the CLI for Argentina Config 1. These values are pre-configured
by the faceplate DIP switches as shown in Figure 17 on page 78. See Chapter 6, “Command Line
Interface (CLI),” on page 59 for information on the CLI.
Table 50 Interpretation of received MFC signals
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
FW_Digit_1 I_1 FW_Categ_1 II_1 BW_NextDigit A_1 BW_Illegal B_1
FW_Digit_2 I_2 FW_Categ_2 II_2 BW_ReSend A_2 BW_Busy B_2
FW_Digit_3 I_3 FW_Categ_3 II_3 BW_BCateg A_3 BW_Busy B_3
FW_Digit_4 I_4 FW_Categ_4 II_4 BW_OrigDn A_4 BW_B_Congest B_4
FW_Digit_5 I_5 FW_Categ_5 II_5 BW_CategOrAni A_5 BW_Unlocated B_5
FW_Digit_6 I_6 FW_Categ_6 II_6 BW_Illegal A_6 BW_FreeChrg B_6
FW_Digit_7 I_7 FW_Categ_7 II_7 BW_Prev2Digit A_7 BW_Unlocated B_7
FW_Digit_8 I_8 FW_Categ_8 II_8 BW_Prev3Digit A_8 BW_B_Congest B_8
FW_Digit_9 I_9 FW_Categ_9 II_9 BW_PrevDigit A_9 BW_B_Congest B_9
FW_Digit_0 I_10 FW_Categ_10 II_10 BW_Illegal A_10 BW_B_Congest B_10
FW_Digit_11 I_11 FW_Categ_11 II_11 BW_Illegal A_11 BW_B_Congest B_11
FW_ReqFault I_12 FW_Categ_12 II_12 BW_Illegal A_12 BW_B_Congest B_12
FW_Digit_13 I_13 FW_Categ_13 II_13 BW_Illegal A_13 BW_B_Congest B_13
FW_Digit_14 I_14 FW_Categ_14 II_14 BW_Illegal A_14 BW_B_Congest B_14
FW_EndDigits I_15 FW_Categ_15 II_15 BW_Illegal A_15 BW_B_Congest B_15
Table 51 Interpretation of transmitted MFC signals (Sheet 1 of 2)
Meaning Signal Meaning Signal Meaning Signal
BW_NextDig A 1 FW_ReqFault I 12 FW_Categ_1 II 1
BW_BCateg A 3 FW_EndDigits I 15 FW_Categ_2 II 2
BW_RtrnToA A 1 FW_EndANIdgts I 15 FW_Categ_3 II 3
BW_A_Congest NO SIG FW_Digit_1 I 1 FW_Categ_4 II 4
BW_B_Congest B 4 FW_Digit_2 I 2 FW_Categ_5 II 5
BW_Category A 5 FW_Digit_3 I 3 FW_Categ_6 II 6
BW_SpeechChrg NO SIG FW_Digit_4 I 4 FW_Categ_7 II 7
N0087114 1.0
 Loading...
Loading...