Page 1
Part No. 209195-A
March 2001
4401 Great America Parkway
Santa Clara, CA 95054
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 2

2
Copyright © 2001 Nortel Networks
All rights reserved. March 2001.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and
recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied
warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The
information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks NA Inc.
Trademarks
NORTEL NETWORKS is a trademark of Nortel Networks.
Passport is a registered trademark of Nortel Networks.
Microsoft, MS, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Statement of conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, Nortel Networks NA Inc. reserves
the right to make changes to the products described in this document without notice.
Nortel Networks NA Inc. does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of the product(s) or
circuit layout(s) described herein.
USA requirements only
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Compliance Notice: Radio Frequency Notice
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to
Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when
the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy. If it is not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, it may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which
case users will be required to take whatever measures may be necessary to correct the interference at their own expense.
European requirements only
EN 55 022 statement
This is to certify that the Nortel Networks Passport is shielded against the generation of radio interference in accordance
with the application of Council Directive 89/336/EEC, Article 4a. Conformity is declared by the application of EN 55
022 Class A (CISPR 22).
Warning: This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which
case, the user may be required to take appropriate measures.
Achtung: Dieses ist ein Gerät der Funkstörgrenzwertklasse A. In Wohnbereichen können bei Betrieb dieses Gerätes
Rundfunkstörungen auftreten, in welchen Fällen der Benutzer für entsprechende Gegenmaßnahmen verantwortlich ist.
Attention: Ceci est un produit de Classe A. Dans un environnement domestique, ce produit risque de créer des
interférences radioélectriques, il appartiendra alors à l’utilisateur de prendre les mesures spécifiques appropriées.
209195-A
Page 3

EC Declaration of Conformity
This product conforms (or these products conform) to the provisions of the R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC.
Japan/Nippon requirements only
Voluntary Control Council for Interference (VCCI) statement
Taiwan requirements
Bureau of Standards, Metrology and Inspection (BSMI) Statement
3
Canada requirements only
Canadian Department of Communications Radio Interference Regulations
This digital apparatus Passport does not exceed the Class A limits for radio-noise emissions from digital apparatus as set
out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique du ministère des Communications
Cet appareil numérique Passport respecte les limites de bruits radioélectriques visant les appareils numériques de classe
A prescrites dans le Règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique du ministère des Communications du Canada.
Nortel Networks NA Inc. software license agreement
NOTICE: Please carefully read this license agreement before copying or using the accompanying software or installing
the hardware unit with pre-enabled software (each of which is referred to as “Software” in this Agreement). BY
COPYING OR USING THE SOFTWARE, YOU ACCEPT ALL OF THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF THIS
LICENSE AGREEMENT. THE TERMS EXPRESSED IN THIS AGREEMENT ARE THE ONLY TERMS UNDER
WHICH NORTEL NETWORKS WILL PERMIT YOU TO USE THE SOFTWARE. If you do not accept these terms
and conditions, return the product, unused and in the original shipping container, within 30 days of purchase to obtain a
credit for the full purchase price.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 4

4
1. License grant. Nortel Networks NA Inc. (“Nortel Networks”) grants the end user of the Software (“Licensee”) a
personal, nonexclusive, nontransferable license: a) to use the Software either on a single computer or, if applicable, on a
single authorized device identified by host ID, for which it was originally acquired; b) to copy the Software solely for
backup purposes in support of authorized use of the Software; and c) to use and copy the associated user manual solely
in support of authorized use of the Software by Licensee. This license applies to the Software only and does not extend
to Nortel Networks Agent software or other Nortel Networks software products. Nortel Networks Agent software or
other Nortel Networks software products are licensed for use under the terms of the applicable Nortel Networks NA Inc.
Software License Agreement that accompanies such software and upon payment by the end user of the applicable
license fees for such software.
2. Restrictions on use; reservation of rights. The Software and user manuals are protected under copyright laws.
Nortel Networks and/or its licensors retain all title and ownership in both the Software and user manuals, including any
revisions made by Nortel Networks or its licensors. The copyright notice must be reproduced and included with any
copy of any portion of the Software or user manuals. Licensee may not modify, translate, decompile, disassemble, use
for any competitive analysis, reverse engineer, distribute, or create derivative works from the Software or user manuals
or any copy, in whole or in part. Except as expressly provided in this Agreement, Licensee may not copy or transfer the
Software or user manuals, in whole or in part. The Software and user manuals embody Nortel Networks’ and its
licensors’ confidential and proprietary intellectual property. Licensee shall not sublicense, assign, or otherwise disclose
to any third party the Software, or any information about the operation, design, performance, or implementation of the
Software and user manuals that is confidential to Nortel Networks and its licensors; however, Licensee may grant
permission to its consultants, subcontractors, and agents to use the Software at Licensee’s facility, provided they have
agreed to use the Software only in accordance with the terms of this license.
3. Limited warranty. Nortel Networks warrants each item of Software, as delivered by Nortel Networks and properly
installed and operated on Nortel Networks hardware or other equipment it is originally licensed for, to function
substantially as described in its accompanying user manual during its warranty period, which begins on the date
Software is first shipped to Licensee. If any item of Software fails to so function during its warranty period, as the sole
remedy Nortel Networks will at its discretion provide a suitable fix, patch, or workaround for the problem that may be
included in a future Software release. Nortel Networks further warrants to Licensee that the media on which the
Software is provided will be free from defects in materials and workmanship under normal use for a period of 90 days
from the date Software is first shipped to Licensee. Nortel Networks will replace defective media at no charge if it is
returned to Nortel Networks during the warranty period along with proof of the date of shipment. This warranty does not
apply if the media has been damaged as a result of accident, misuse, or abuse. The Licensee assumes all responsibility
for selection of the Software to achieve Licensee’s intended results and for the installation, use, and results obtained
from the Software. Nortel Networks does not warrant a) that the functions contained in the software will meet the
Licensee’s requirements, b) that the Software will operate in the hardware or software combinations that the Licensee
may select, c) that the operation of the Software will be uninterrupted or error free, or d) that all defects in the operation
of the Software will be corrected. Nortel Networks is not obligated to remedy any Software defect that cannot be
reproduced with the latest Software release. These warranties do not apply to the Software if it has been (i) altered,
except by Nortel Networks or in accordance with its instructions; (ii) used in conjunction with another vendor’s product,
resulting in the defect; or (iii) damaged by improper environment, abuse, misuse, accident, or negligence. THE
FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND LIMITATIONS ARE EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES AND ARE IN LIEU OF ALL
OTHER WARRANTIES EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Licensee is responsible for the security of its
own data and information and for maintaining adequate procedures apart from the Software to reconstruct lost or altered
files, data, or programs.
4. Limitation of liability. IN NO EVENT WILL NORTEL NETWORKS OR ITS LICENSORS BE LIABLE FOR
ANY COST OF SUBSTITUTE PROCUREMENT; SPECIAL, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES; OR ANY DAMAGES RESULTING FROM INACCURATE OR LOST DATA OR LOSS OF USE OR
PROFITS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE PERFORMANCE OF THE SOFTWARE, EVEN IF
NORTEL NETWORKS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT
SHALL THE LIABILITY OF NORTEL NETWORKS RELATING TO THE SOFTWARE OR THIS AGREEMENT
EXCEED THE PRICE PAID TO NORTEL NETWORKS FOR THE SOFTWARE LICENSE.
209195-A
Page 5

5. Government licensees. This provision applies to all Software and documentation acquired directly or indirectly by or
on behalf of the United States Government. The Software and documentation are commercial products, licensed on the
open market at market prices, and were developed entirely at private expense and without the use of any U.S.
Government funds. The license to the U.S. Government is granted only with restricted rights, and use, duplication, or
disclosure by the U.S. Government is subject to the restrictions set forth in subparagraph (c)(1) of the Commercial
Computer Software––Restricted Rights clause of FAR 52.227-19 and the limitations set out in this license for civilian
agencies, and subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause of DFARS
252.227-7013, for agencies of the Department of Defense or their successors, whichever is applicable.
6. Use of software in the European Community. This provision applies to all Software acquired for use within the
European Community. If Licensee uses the Software within a country in the European Community, the Software
Directive enacted by the Council of European Communities Directive dated 14 May, 1991, will apply to the examination
of the Software to facilitate interoperability. Licensee agrees to notify Nortel Networks of any such intended
examination of the Software and may procure support and assistance from Nortel Networks.
7. Term and termination. This license is effective until terminated; however, all of the restrictions with respect to
Nortel Networks’ copyright in the Software and user manuals will cease being effective at the date of expiration of the
Nortel Networks copyright; those restrictions relating to use and disclosure of Nortel Networks’ confidential information
shall continue in effect. Licensee may terminate this license at any time. The license will automatically terminate if
Licensee fails to comply with any of the terms and conditions of the license. Upon termination for any reason, Licensee
will immediately destroy or return to Nortel Networks the Software, user manuals, and all copies. Nortel Networks is not
liable to Licensee for damages in any form solely by reason of the termination of this license.
8. Export and re-export. Licensee agrees not to export, directly or indirectly, the Software or related technical data or
information without first obtaining any required export licenses or other governmental approvals. Without limiting the
foregoing, Licensee, on behalf of itself and its subsidiaries and affiliates, agrees that it will not, without first obtaining all
export licenses and approvals required by the U.S. Government: (i) export, re-export, transfer, or divert any such
Software or technical data, or any direct product thereof, to any country to which such exports or re-exports are restricted
or embargoed under United States export control laws and regulations, or to any national or resident of such restricted or
embargoed countries; or (ii) provide the Software or related technical data or information to any military end user or for
any military end use, including the design, development, or production of any chemical, nuclear, or biological weapons.
9. General. If any provision of this Agreement is held to be invalid or unenforceable by a court of competent
jurisdiction, the remainder of the provisions of this Agreement shall remain in full force and effect. This Agreement will
be governed by the laws of the state of California.
Should you have any questions concerning this Agreement, contact Nortel Networks, 4401 Great America Parkway, P.O.
Box 58185, Santa Clara, California 95054-8185.
LICENSEE ACKNOWLEDGES THAT LICENSEE HAS READ THIS AGREEMENT, UNDERSTANDS IT, AND
AGREES TO BE BOUND BY ITS TERMS AND CONDITIONS. LICENSEE FURTHER AGREES THAT THIS
AGREEMENT IS THE ENTIRE AND EXCLUSIVE AGREEMENT BETWEEN NORTEL NETWORKS AND
LICENSEE, WHICH SUPERSEDES ALL PRIOR ORAL AND WRITTEN AGREEMENTS AND
COMMUNICATIONS BETWEEN THE PARTIES PERTAINING TO THE SUBJECT MATTER OF THIS
AGREEMENT. NO DIFFERENT OR ADDITIONAL TERMS WILL BE ENFORCEABLE AGAINST NORTEL
NETWORKS UNLESS NORTEL NETWORKS GIVES ITS EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT, INCLUDING AN
EXPRESS WAIVER OF THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT.
5
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 6

6
209195-A
Page 7

Contents
Preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Before you begin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Text conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Related publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
How to get help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Chapter 1
About the Passport 8672ATM Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
ATM ELANs, and Ethernet VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Virtual network router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Traffic shaping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
RFC 1483 Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Physical description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Media dependent adapters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Online LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
MDA LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Console and Diag ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
7
Chapter 2
Passport 8672ATM Module technology overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
ATM terms and acronyms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
SONET terms and acronyms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
SONET transmission rates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 8

8 Contents
Chapter 3
Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Safety and environmental precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Verifying installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
MDA insertion and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Replacing a module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Chapter 4
Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager. . . . . . . . 47
Port numbering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Starting the system after a module replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Starting the system with an empty slot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Device Manager access and passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Installing Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Configuring ATM using Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Resetting the module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Viewing MDA information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Enabling or disabling a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Editing port parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Editing ATM and framing parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Editing circuit parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Deleting a PVC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Configuring ATM 1483 ELAN parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Deleting an ATM 1483 ELAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Displaying statistics using Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Testing using Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
209195-A
Chapter 5
Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Command line interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Configuration commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Module commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Page 9

Contents 9
1483 ELAN statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
config atmcard elan-stats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
clear atm elan-stats <vlan id> . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
show atm elan-stats <vlan id> . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
clear atm elan-stats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Port commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
config atm command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
config atm pvc command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
config atm pvc 1483 command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
config atm info command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Show commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
show ports info atm all command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
show ports info atm ports command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
show ports info atm pvc command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
show ports info atm 1483 command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
show ports stats atmport command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
show ports stats atm felinecurrent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
show ports stats atm felineinterval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
show ports stats atm fepathcurrent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
show ports stats atm fepathinterval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
show ports stats atm linecurrent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
show ports stats atm lineinterval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
show ports stats atm pathcurrent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
show ports stats atm pathinterval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
show ports stats atm sectioncurrent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
show ports stats atm sectioninterval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
show ports stats atm sonetmediumtbl . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Web management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
ATM folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Chapter 6
Configuring the Passport 8672ATM Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Initial configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Changing the clock setting using Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Changing the clock setting using the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 10

10 Contents
Basic configuration procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Bridging point-to-point traffic using an ATM 1483 PVC using Device Manager . . 118
Configuring an ATM 1483 PVC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Associating the PVC with the VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Bridging point-to-point traffic using an ATM 1483 PVC using the CLI . . . . . . . . . 125
Bridging point-to-multipoint traffic using an ATM 1483 PVC using
Bridging point-to-multipoint traffic using an ATM 1483 PVC using the CLI . . . . . 127
Configuring an IP routing 1483 PVC using Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Configuring an IP routing 1483 PVC using the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Configuring an IPX routing 1483 PVC using Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Configuring an IPX routing 1483 PVC using the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Creating a VLAN “byPort” and adding ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Configuring two ATM 1483 PVCs on the same ATM port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Associating the PVCs with the same VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Creating two VLANs “byPort” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Assigning IP addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Enabling RIP routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Enabling OSPF routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Configuring a null-encapsulation PVC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Associating the PVC with the VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Creating two VLANs “byPort” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Configuring IPX network numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Enabling IPX forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Enabling IPX network number forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Configuring a null-encapsulation PVC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Associating the PVC with the VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
209195-A
Appendix A
Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Appendix B
Factory defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Page 11

Figures
Figure 1 Passport 8672ATM module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 2 1-port OC-12c/STM-4 MDA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 3 4-port OC-3c/STM-1 MDA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 4 Passport 8672 ATM module with OC-12c/STM-4 MDA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 5 Removing the filler panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 6 Extending the inserter/extractor levers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 7 Inserting the Passport 8672ATM Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 8 Closing the inserter/extractor levers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 9 Tightening the retainer screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 10 Unsuccessful download screen output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 11 Passport 8000 series chassis with Passport 8672ATM Module . . . . . . . . 50
Figure 12 Interface tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Figure 13 Card tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Figure 14 ATM tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Figure 15 MDA dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Figure 16 ATM tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Figure 17 ATM PVC tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Figure 18 Insert ATM PVC dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Figure 19 ATM PVC tab with PVC selected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Figure 20 ATM 1483 ELAN tab (left section) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Figure 21 ATM 1483 ELAN tab (right section) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Figure 22 Insert ATM 1483 ELAN dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Figure 23 Insert ATM 1483 ELAN dialog box for IP routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Figure 24 Insert ATM 1483 ELAN dialog box for IPX routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Figure 25 ATM 1483 ELAN tab with ElanId selected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Figure 26 show atm elan-stats command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Figure 27 Sample output for the config atm info command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
11
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 12

12 Figures
Figure 28 show ports info atm all command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Figure 29 show ports info atm ports command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Figure 30 show ports info atm pvc command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Figure 31 show ports info atm 1483 command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Figure 32 show ports stats atmport [<port num>] command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Figure 33 show ports stats atm felinecurrent command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Figure 34 show ports stats atm felineinterval command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Figure 35 show ports stats atm fepathcurrent command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Figure 36 show ports stats atm fepathinterval command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Figure 37 show ports stats atm linecurrent command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Figure 38 show ports stats atm lineinterval command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Figure 39 show ports stats atm pathcurrent command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Figure 40 show ports stats atm pathinterval command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Figure 41 show ports stats atm sectioncurrent command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Figure 42 show ports stats atm sectioninterval command output . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Figure 43 show ports stats atm sonetmediumtbl command output . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Figure 44 System page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Figure 45 ATM menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Figure 46 PVC page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Figure 47 1483 ELAN page, (left section) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Figure 48 1483 ELAN page, (right section) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Figure 49 Port page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Figure 50 ATM tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Figure 51 Point-to-point bridging using 1483 PVCs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Figure 52 Basic tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Figure 53 VLAN, Insert Basic dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Figure 54 VlanPortMembers dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Figure 55 Point-to-multipoint bridging using ATM 1483 PVCs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Figure 56 IP routing with ATM 1483 PVCs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Figure 57 IP Address tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Figure 58 IP, VLAN, Insert IP Address dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Figure 59 RIP tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Figure 60 OSPF tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
209195-A
Page 13

Figures 13
Figure 61 IPX routing with ATM 1483 PVCs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Figure 62 IPX VLAN dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Figure 63 IPX VLAN, Insert dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Figure 64 Globals tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Figure 65 Circuits tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 14

14 Figures
209195-A
Page 15

Tables
Table 1 Passport 8672ATM Module online LED indications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 2 MDA LED indications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Table 3 Device Manager port color codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 4 Device Manager buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 5 Interface tab items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Table 6 Card tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Table 7 ATM tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Table 8 MDA dialog box fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Table 9 ATM tab items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Table 10 ATM PVC tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 11 Insert ATM PVC dialog box fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Table 12 ATM 1483 ELAN tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Table 13 Insert ATM 1483 ELAN dialog box items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Table 14 config atmcard command parameters and variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Table 15 Information fields for the show atm elan-stats command . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Table 16 config atm command parameters and variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Table 17 config atm pvc command parameters and variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Table 18 config atm pvc 1483 bridged command parameters and variables . . . . . 80
Table 19 config atm pvc 1483 ip command parameters and variables . . . . . . . . . . 81
Table 20 config atm pvc 1483 ipx command parameters and variables . . . . . . . . . 81
Table 21 Information fields for the show ports info atm all command . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Table 22 Information fields for the show ports info atm ports command . . . . . . . . . 86
Table 23 Information fields for the show ports info atm pvc command . . . . . . . . . . 87
Table 24 Information fields for the show ports info atm 1483 command . . . . . . . . 88
Table 25 Information fields for the show ports stats atmport command . . . . . . . . . 90
Table 26 Information fields for the show ports stats atm felinecurrent command . . 92
Table 27 Information fields for the show ports stats atm felineinterval command . 93
Table 28 Information fields for the show ports stats atm fepathcurrent command . 95
Table 29 Information fields for the show ports stats atm fepathinterval command . 96
15
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 16

16 Tables
Table 30 Information fields for the show ports stats atm linecurrent command . . 97
Table 31 Information fields for The show ports stats atm lineinterval command . . 99
Table 32 Information fields for the show ports stats atm pathcurrent command . 100
Table 33 Information fields for the show ports stats atm pathinterval command 101
Table 34 Information fields for the show ports stats atm sectioncurrent command 103
Table 35 Information fields for the show ports stats atm sectioninterval
Table 36 Information fields for output of the show ports stats atm
Table 37 System page fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Table 38 PVC page items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Table 39 1483 ELAN page items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Table 40 Port page items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Table 41 Basic tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Table 42 VLAN, Insert Basic dialog box fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Table 43 VlanPortMembers dialog box fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Table 44 IP Address tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Table 45 IP, VLAN, Insert IP Address dialog box fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Table 46 RIP tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Table 47 OSPF tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Table 48 IPX VLAN dialog box fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Table 49 IPX VLAN, Insert dialog box fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Table 50 Globals tab item . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Table 51 Circuits tab fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Table 52 Factory default settings for the Passport 8672ATM Module . . . . . . . . . . 145
command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
sonetmediumtbl command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
209195-A
Page 17

Preface
The Passport® 8672ATM Module is part of the Nortel Networks Passport 8600
Series line of communications products. This module is the Passport
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) module for the Passport 8600 chassis. This
guide describes the features and operations of the module and provides
instructions for installing and managing the module.
Before you begin
This guide is intended for network installers and system administrators who are
responsible for installing, configuring, or maintaining networks. This guide
assumes that you have the following background:
• Understanding of the transmission and management protocols used on your
network
• Experience with windowing systems or graphical user interfaces (GUIs)
17
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 18

18 Preface
Text conventions
This guide uses the following text conventions:
angle brackets (< >) Indicate that you choose the text to enter based on the
description inside the brackets. Do not type the
brackets when entering the command.
Example: If the command syntax is
ping <ip_address>, you enter
ping 192.32.10.12
bold Courier text
Indicates command names and options and text that
you need to enter.
Example: Use the
Example: Enter
dinfo command.
show ip {alerts|routes}.
braces ({}) Indicate required elements in syntax descriptions where
there is more than one option. You must choose only
one of the options. Do not type the braces when
entering the command.
Example: If the command syntax is
show ip {alerts|routes}, you must enter either
show ip alerts or show ip routes, but not
both.
brackets ([ ]) Indicate optional elements in syntax descriptions. Do
not type the brackets when entering the command.
Example: If the command syntax is
show ip interfaces [-alerts], you can enter
either
show ip interfaces or
show ip interfaces -alerts.
ellipsis points (. . . ) Indicate that you repeat the last element of the
command as needed.
Example: If the command syntax is
ethernet/2/1 [<parameter> <value>]... ,
you enter
ethernet/2/1 and as many
parameter-value pairs as needed.
209195-A
Page 19

Preface 19
italic text Indicates new terms, book titles, and variables in
command syntax descriptions. Where a variable is two
or more words, the words are connected by an
underscore.
Example: If the command syntax is
show at <valid_route>, valid_route is one
variable and you substitute one value for it.
plain Courier
text
Indicates command syntax and system output, for
example, prompts and system messages.
Example:
Set Trap Monitor Filters
separator ( > ) Shows menu paths.
Example: Protocols > IP identifies the IP command on
the Protocols menu.
vertical line (
| ) Separates choices for command keywords and
arguments. Enter only one of the choices. Do not type
the vertical line when entering the command.
Example: If the command syntax is
show ip {alerts|routes}, you enter either
show ip alerts or show ip routes, but not
both.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 20

20 Preface
Related publications
For more information about the Passport 8600 Series products and management
software, refer to the following publications:
• Getting Started with the Passport 8000 Series Management Software
(part number 209663-C)
Outlines the procedures for installing and booting your Passport 8600 Series
8000 series switch, as well as instructions for installing the Passport
8672ATM Module.
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Management Software Switching
Operations Release 3.1 (part number 207414-D)
Describes how to use Device Manager to configure and manage switching
functions with the Passport 8600 Series switch, including procedures and
illustrations of pertinent screens.
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Management Software Routing
Operations Release 3.1 (part number 207415-C)
209195-A
Describes how to use Device Manager to configure and manage routing
functions with the Passport 8600 Series switch, including procedures and
illustrations of pertinent screens.
• Networking Concepts for the Passport 8000 Series Switch
(part number 207307-C)
General information and description of how the Passport 8000 Series switch
handles various networking features such as VLANs, MultiLinkTrunking,
OSPF, RIP, IPX, ATM, and SONET.
• Passport 8000 Series Network Design Guidelines Release 3.0 Implementation
Notes (part number 210128-A)
Provides guidelines for using the switching and routing features of the
Passport 8000 Series switches and software to design effective networks.
• Using the Passport 8100 Modules (part number 204515-D)
Provides information about the Passport 8100 module, including descriptions
of operational features, installation instructions, basic setup procedures, and
technical specifications.
Page 21

Preface 21
• Using the Passport 8600 Modules (part number 207306-C)
Provides information about the Passport 8600 module, including descriptions
of operational features, installation instructions, basic setup procedures, and
technical specifications.
• Using the Passport 8672ATM Module (part number 209195-A)
Describes hardware features, installation instructions, and specific
management procedures for the Passport [Model #].
• Using the Passport 8683POS Module (part number 209564-A)
Describes hardware features, installation instructions, and specific
management procedures for the Passport 8600 Series 8683POS Module.
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Command Line Interface Switching
Operations Release 3.1 (part number 207308-D)
Describes how to use the CLI to configure and manage switching functions
with the Passport 8000 Series switch, including procedures and illustrations of
pertinent commands.
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Command Line Interface Routing
Operations (part number 208967-C)
Describes how to use the CLI to configure and manage routing functions with
the Passport 8000 Series switch, including procedures and illustrations of
pertinent commands.
You can print selected technical manuals and release notes free, directly from the
Internet. Go to the www25.nortelnetworks.com/library/tpubs/ URL. Find the
product for which you need documentation. Then locate the specific category and
model or version for your hardware or software product. Use Adobe Acrobat
Reader to open the manuals and release notes, search for the sections you need,
and print them on most standard printers. Go to Adobe Systems at the
www.adobe.com URL to download a free copy of the Adobe Acrobat Reader.
You can purchase selected documentation sets, CDs, and technical publications
through the Internet at the www1.fatbrain.com/documentation/nortel/ URL.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 22

22 Preface
How to get help
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel Networks product from a
distributor or authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff for that
distributor or reseller for assistance.
If you purchased a Nortel Networks service program, contact one of the following
Nortel Networks Technical Solutions Centers:
Technical Solutions Center Telephone
EMEA (33) (4) 92-966-968
North America (800) 2LANWAN or (800) 252-6926
Asia Pacific (61) (2) 9927-8800
China (800) 810-5000
An Express Routing Code (ERC) is available for many Nortel Networks products
and services. When you use an ERC, your call is routed to a technical support
person who specializes in supporting that product or service. To locate an ERC for
your product or service, go to the www12.nortelnetworks.com/ URL and click
ERC at the bottom of the page.
209195-A
Page 23

Chapter 1 About the Passport 8672ATM Module
The Passport 8672ATM Module provides network transmission using ATM
technology. The Passport 8672ATM Module enables MAN/WAN/campus
connectivity for the Passport 8600 Routing Switch with the capability to
interconnect frame-switched networks using a backbone ATM network. The
module also provides existing ATM customers with the capability for connectivity
to the Passport 8600 Routing Switch. (For more information on ATM, refer to the
ATM Forum Web site at the http://www.atmforum.com URL.)
The Passport 8672ATM Module occupies a single slot in a Passport 8600 series
chassis. The module is a baseboard with room for two of the following optional
Media dependent adapters (MDAs):
• 1-port OC-12c/STM-4: single-mode fiber (SMF) or multimode fiber (MMF)
using the Synchronous Optical Network (SONET/SDH) media
• 4-port OC-3c/STM-1: SMF or MMF using SONET media
23
The Passport 8672ATM Module for the Passport 8000 series chassis can be used
as an edge device for WAN connectivity in the data center; it is used to connect
Passport 8600 to public or private ATM networks. You can also use the Passport
8672ATM Module in the wiring closet in inter-building connection technology in
campus networks where each building is supported by frame-switched networks.
Another network application of the Passport 8672ATM Module is a direct
connection between one Passport 8600 series switch with a Passport 8672ATM
Module in one building to an identical module in another Passport 8600 Series
switch at another building. You connect the switches with a dedicated fiber link or
with a SONET multiplex network. Each building may be individually supported
by either frame-switched or ATM technology.
You can use up to two Passport 8672ATM Modules in one Passport 8600 series
chassis.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 24

24 Chapter 1 About the Passport 8672ATM Module
Refer to Networking Concepts for the Passport 8000 Series Switch for a thorough
discussion of the complete functionality of the Passport 8000 series product line,
including the Passport 8672ATM Module. Note that Spanning Tree Groups
(STGs), VRRP, DiffServ, and ATM QoS are not supported on this module.
This chapter provides the following information about the Passport 8672ATM
Module:
•“Features,” next
• “Physical description” on page 26
Features
The Passport 8672ATM Module has the following features:
• RFC 1483 ATM PVC support
— Bridged PVC
— IP routed PVC
— IPX routed PVC
• Both RFC 1483 LLC/SNAP encapsulation and Null encapsulation
• RFC 1483 point-to-point bridging—up to 64 PVCs per ELAN
• MLT using bridged RFC 1483 PVCs
• VBR traffic shaping per port
• Front-panel Online LED to monitor module operation
• Ability to remove and install a module (hot-swap) without resetting the switch
(MDAs are not hot-swappable)
• AAL 5
• Hardware diagnostics
• Proprietary MIB support for configuration of RFC 1483 and ATM port
specific setup
• Manageable through the Passport CLI or Device Manager, the SNMP-based
graphical interface
• Monitored through a World Wide Web browser from anywhere on the
network.
209195-A
Page 25

Chapter 1 About the Passport 8672ATM Module 25
ATM ELANs, and Ethernet VLANs
The Passport 8672ATM Module supports ATM Forum Emulated LANs (ELANs).
An ELAN extends an Ethernet VLAN, which is a broadcast domain, over an ATM
network.
In general, there is a one-to-one mapping between an ATM ELAN and an Ethernet
VLAN. An ATM ELAN never spans more than one ATM port because the
software considers each ATM port completely separate.
The Passport 8672ATM Module participates in ELANs as RFC 1483 PVCs. Only
Ethernet ELANs are supported on this module.
If you delete a VLAN, you delete 1483 ELANs associated with the VLAN.
Virtual network router
Virtual network router (VNR) refers to the routing functions between two ATM
virtual/emulated networks. You can use the Passport 8672ATM Module as an IPand IPX-optimized VNR.
Traffic shaping
The Passport 8672ATM Module supports traffic shaping, which is enabled or
disabled on a port-by-port basis. Where it is enabled, a single traffic rate is
enforced for those ports. The maximum available rate for traffic shaping does not
exceed the maximum rate for the slowest interface on the module. Traffic shaping
is disabled by default. Traffic shaping is performed at the port level and not at the
PVC level.
The module provides support for unspecified bit rate (UBR) and variable bit rate
(VBR), both real-time and non-real-time; it does not support available bit rate
(ABR) or constant bit rate (CBR). Traffic shaping per port is supported on all
permanent virtual circuits (PVCs).
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 26
26 Chapter 1 About the Passport 8672ATM Module
RFC 1483 Support
The system software on the Passport 8672ATM Module supports the
configuration of RFC 1483 LAN clients with multiprotocol encapsulation. RFC
1483 supports standards-based methods of encapsulation that enable connectivity
with third-party ATM devices. Multiprotocol encapsulation provides the
capability to set up PVCs between Centillion ATM virtual ports (VPorts) and
other clients based on LLC encapsulation. The current Centillion platform only
supports bridged variations of RFC 1483.
The Passport 8672ATM Module supports the following types of RFC 1483
ELANs:
• RFC 1483 bridged 802.3. The links can be set up within a single device or
with another switch. Multiple RFC 1483 links can be set up within one
ELAN. In all cases, the PVCs must be set up without loops; STP must be
disabled. Both LLC and NULL encapsulation are supported.
• RFC 1483 routed IP and IPX. An RFC 1483 routed VLAN always contains
only one PVC, corresponding to a point-to-point link between routers. The
ATM ELAN is bridged to a single Ethernet VLAN. The software adds and
removes the MAC header, as appropriate. When configuring an IP and IPX
routed circuit, the ATM port must be the only port assigned to the VLAN.
ATM ports do not support bridge/router (BROUTER) configurations.
Physical description
The Passport 8672ATM Module (Figure 1) is a single-slot module for the Passport
8600 Series chassis. Online LEDs indicate module operation.
Figure 1 Passport 8672ATM module
209195-A
8672 ATM
OnlineMDA 2MDA 1
9901EA
Page 27
9725EA
9726EA
Chapter 1 About the Passport 8672ATM Module 27
To configure and manage the Passport 8672ATM Module, connect to the Passport
8690SF Module. For information on connecting to the Passport 8690SF console
port, refer to Using the Passport 8600 Modules.
Media dependent adapters
The Passport 8672ATM Module has space for two media dependent adapters
MDAs) that have their own LEDs. You can use up to two of the following MDAs
with the Passport 8672ATM Module:
• 1-port OC-12c/STM-4: SMF or MMF using SONET media
• 4-port OC-3c/STM-1: SMF or MF using SONET media
You can mix these MDAs on the Passport 8672ATM Module. Contact your Nortel
Networks representative for other MDAs that are available for this product.
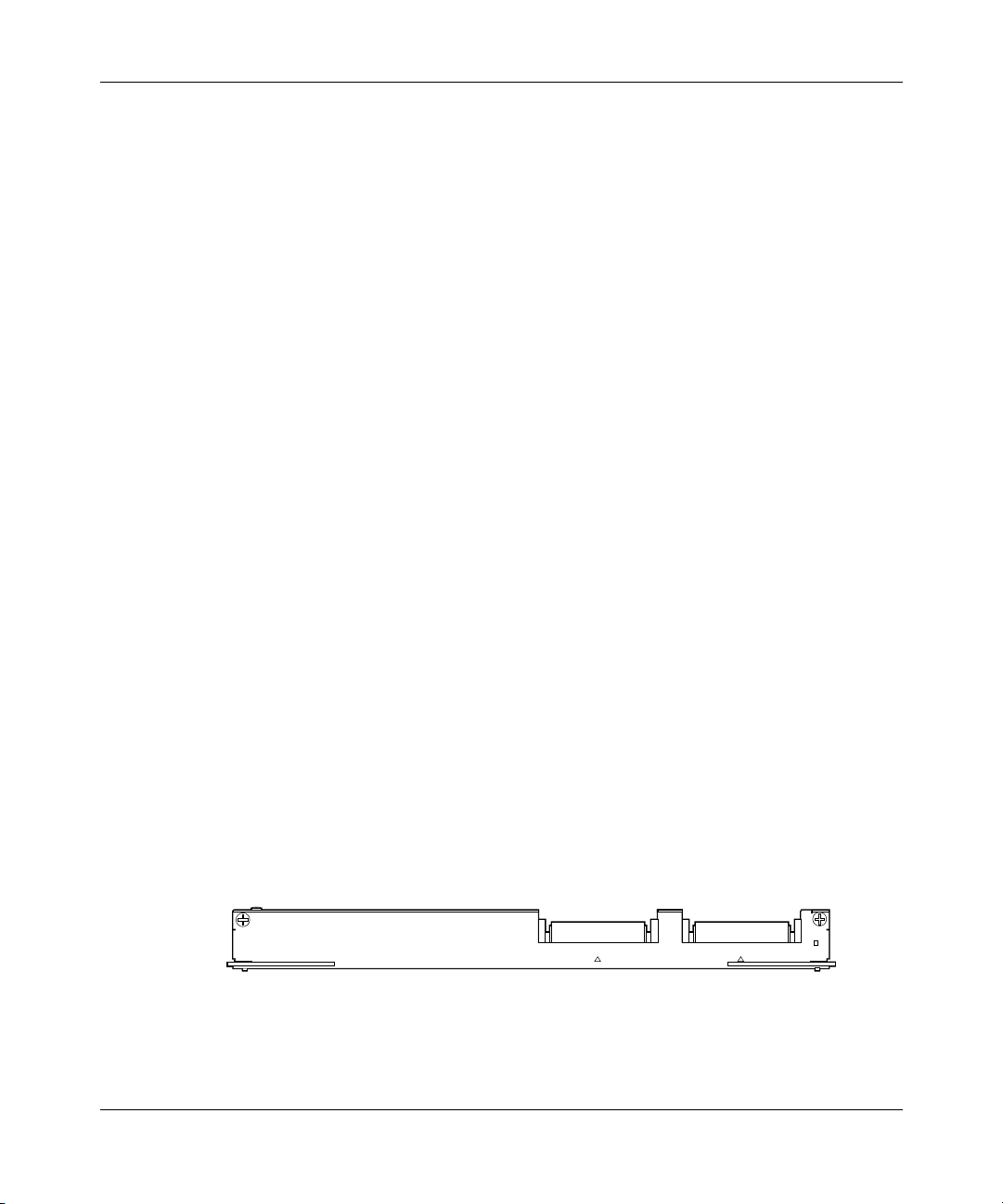
Figure 2 shows the OC-12c/STM-4 MDA, and Figure 3 shows the OC-3c/STM-1
MDA.
Figure 2 1-port OC-12c/STM-4 MDA
Figure 3 4-port OC-3c/STM-1 MDA
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 28
28 Chapter 1 About the Passport 8672ATM Module
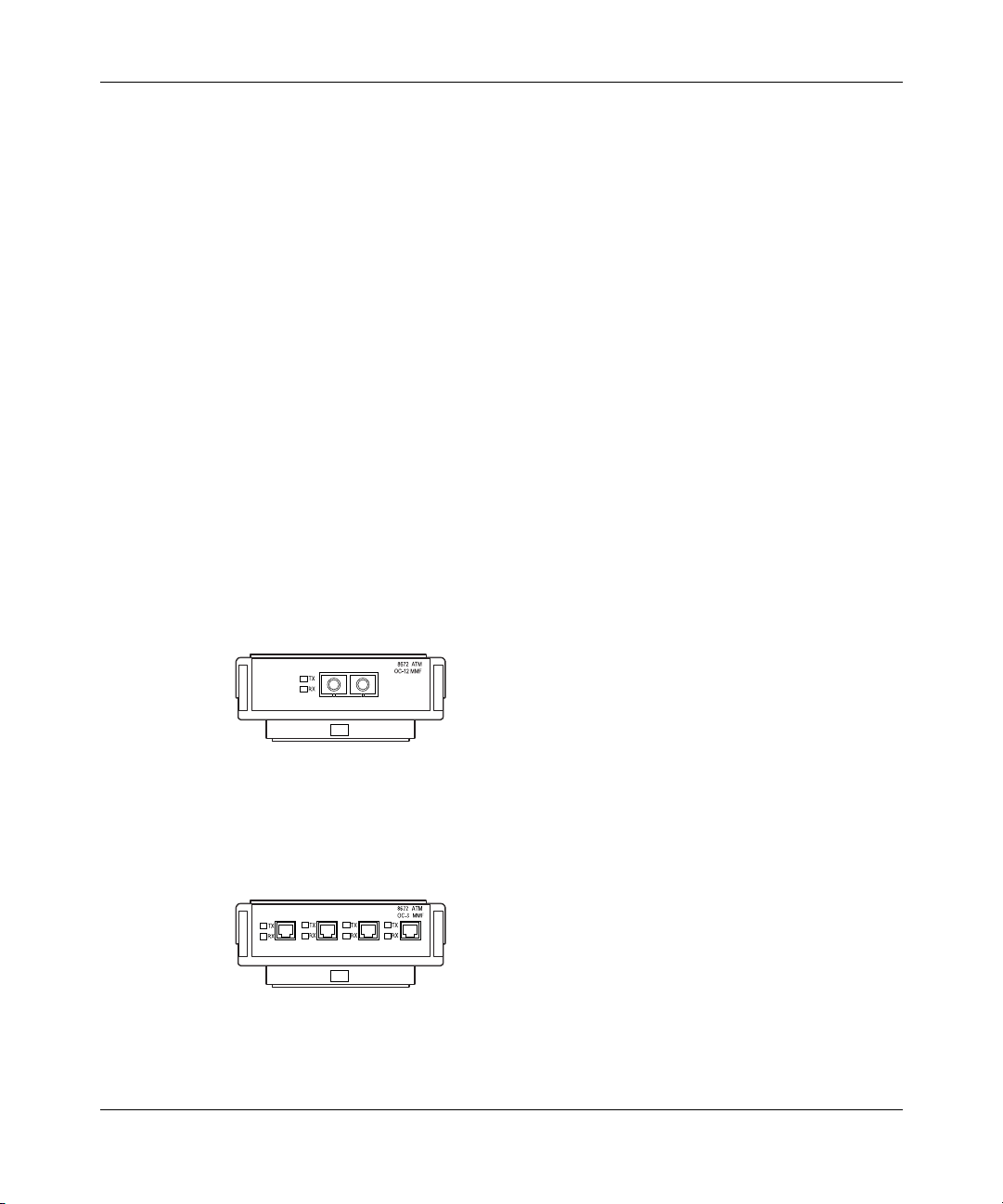
Figure 4 shows the Passport 8672ATM Module with one OC-12c/STM-4 MDA
installed. For information on installing the MDAs, refer to Installing the Passport
8672ATM Module MDAs.
Figure 4 Passport 8672 ATM module with OC-12c/STM-4 MDA
Online LED
The front panel of the Passport 8672ATM Module has an Online LED that
indicates whether or not the module has power applied and is initialized correctly.
When the Passport 8672ATM Module is first inserted into the chassis, the Online
LED turns amber until the board is recognized by the system and passes a
power-on self-test. If the module fails the self-test, the light is off. When the board
passes the self-test and goes online, the LED illuminates a solid green.
8672 ATM
OnlineMDA 2MDA 1
9724EA
209195-A
Note: You cannot configure the Passport 8672ATM Module until the
online LED on the module is steadily lit green and you have inserted at
least one MDA.
Table 1 lists the Passport 8672ATM Module online LED indications.
Table 1 Passport 8672ATM Module online LED indications
Online LED State
Off Card is not receiving power.
Amber Card is initializing or downloading.
Amber Card is offline.
Green Card is online.
Page 29

Chapter 1 About the Passport 8672ATM Module 29
MDA LEDs
Table 2 lists the MDA LED indications.
Table 2 MDA LED indications
LED Color Port State
Tx Amber Alarm (RDI) condition, admin state down
Tx Green Transmitting data
Tx Off No traffic, no alarm
Rx Amber Alarm (OOF/LOF/LOS) condition, admin
Rx Solid green Admin stateup
Rx Flashing green Receiving data
Tx and Rx Flashing amber Admin state down, out of order
state down
Note: When there is continuous traffic, the Tx LED is solid green. If
traffic is slow, the Tx LED may be flashing green.
Console and Diag ports
Use the Console port on the Passport 8690 SF module to access management
functions for the Passport 8672ATM Module. For information on connecting to
the Console port on the Passport 8690 SF module, refer to Getting Started with the
Passport 8000 Series Management Software.
The Diag port on the Passport 8672ATM Module is used only by Nortel Networks
personnel for debugging purposes. You can see diagnostic messages but you
cannot input any text.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 30

30 Chapter 1 About the Passport 8672ATM Module
209195-A
Page 31

Chapter 2 Passport 8672ATM Module technology overview
This chapter contains the following information:
• “ATM terms and acronyms,” next
• “SONET terms and acronyms” on page 33
ATM terms and acronyms
Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) is a connection-oriented, cell-based
technology that relays traffic across a network. ATM provides a cost-effective
way of transmitting voice, video, and data across a network at high speeds. It
offers topology-independent, resilient networking technology.
31
An ATM cell is a fixed-length packet of 53 bytes. It consists of a 5-byte header
containing address information and a fixed 48-byte information field. The
fixed-length cell size allows you to predict network delays.
The following terms and acronyms are frequently used with ATM information:
• ATM: Asynchronous transfer mode. ATM is a switched, connection-oriented,
fixed-length, cell-based transmission method specifically designed to run at
high data rates and to carry a complete range of user traffic, including voice,
data, and video. ATM uses dedicated media connections running in parallel,
allowing simultaneous multiple connections through a single switch device at
very high speeds.
• PVC: Permanent virtual circuit. Dedicated connection between devices that is
manually set up.
• SVC: Switched virtual circuit. On-demand connection between an ATM or
frame relay source and destination that lasts for the duration of the
transmission.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 32

32 Chapter 2 Passport 8672ATM Module technology overview
• VC: Virtual circuit. This is a network service that provides
connection-oriented service regardless of the underlying network structure.
• VP: Virtual path. A virtual path is a set of virtual channels between a common
source and destination. The virtual channels in a virtual path are logically
associated with a common identifier, the virtual path identifier.
• VPI: Virtual path identifier. Identifier contained in the ATM cell header to
designate the virtual path on the physical ATM link.
• VCI: Virtual circuit identifier. Address or label contained in the ATM cell
header to designate the virtual circuit within the virtual path on the physical
ATM l i n k
• ELAN: Emulated LAN. Following the ATM Forum specification, ELANs
make connection-oriented ATM networks look like connectionless LANs.
• UBR: Unspecified bit rate. UBR is an ATM service category that does not
specify traffic-related service guarantees. No numerical commitments are
made with respect to the cell loss ratio or to the cell transfer delay.
• VBR: Variable bit rate. VBR is an ATM Forum-defined service category that
supports variable bit rate data traffic with average and peak traffic parameters.
• PCR: Peak cell rate. The PCR, in cells/second, is the maximum cell rate.
• SCR: Sustainable cell rate. The SCR is an upper bound on the cell rate that is
long relative to that of the PCR. Enforcement of this bound by the Usage
Parameter Control allows the network to allocate sufficient resources, but less
than those for the PCR, to ensure that the specified cell loss ratio can be
achieved.
• MBS: Maximum burst size. The signaling method determines the MBS,
which is coded as a number of cells, that can be transmitted at peak rate and
still conform to the overall algorithm.
209195-A
Data transmission (also called cell switching) through the ATM network relies on
establishing logical connections between ATM devices. ATM is a
connection-oriented service, which means that an ATM device cannot transmit
information until it establishes a connection with a receiving device.
Page 33

Chapter 2 Passport 8672ATM Module technology overview 33
SONET terms and acronyms
This section provides a brief listing of common Synchronous Optical Network
(SONET) terms. SONET is a medium for transmitting data that uses fiber optic
cables.
The following terms and acronyms are frequently used with SONET information:
• SONET: Synchronous Optical Network. SONET is a family of fiber optic
transmission rates that provides the flexibility to transport many digital
signals with different capacities. This ANSI standard provides for
transmission from OC-1 to OC-48 and greater.
• SDH: Synchronous Digital Hierarchy. SDH is a standard technology for
optical fiber-based synchronous data transmission. SDH is the international
equivalent of SONET.
• OC-3: Optical Carrier-level 3. OC-3 is an optical fiber transmission system at
155 Mb/s.
• OC-3c/STM-1: Optical Carrier-level 3 concatenation. OC-3c/STM-1 is an
optical fiber transmission system that carries STS-3c/STM-1 frame structures
at 155 Mb/s. Concatenation refers to the fact that there is only one logical data
stream (rather than supporting a channelized structure).
• OC-12: Optical Carrier-level 12. OC-12 is an optical fiber transmission
system at 622 Mb/s.
• OC-12c/STM-4: Optical Carrier-level 12 concatenation. OC-12c/STM-4 is an
optical fiber transmission system that carries STS-12c/STM-4 frame
structures at 622 Mb/s. Concatenation refers to the fact that there is only one
logical data stream (rather than supporting a channelized structure).
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 34

34 Chapter 2 Passport 8672ATM Module technology overview
SONET transmission rates
The following transmission rates are commonly used with SONET:
• OC-3c/STM-1: 155.52 Mb/s (and SDH/STM-1)
• OC-12c/STM-4: 622.08 Mb/s (and SDH/STM-4)
The SONET specification defines optical both as:
• Single-mode fiber (SMF)
• Multimode fiber (MMF)
Note: The estimated maximum transmission distance for OC-3c SMF is
20 kilometers (km); for OC-3c MMF is 2 km; for OC-12c SMF is 15 km;
for OC-12c MMF is 500 m.
209195-A
Page 35

Chapter 3 Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module
This chapter describes the procedure for installing the Passport 8672ATM
Module. It covers the following topics:
• “Safety and environmental precautions,” next
• “Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module” on page 37
• “Verifying installation” on page 40
• “Initialization” on page 40
• “MDA insertion and configuration” on page 43
• “Replacing a module” on page 44
For more information about the Passport 8600 chassis, refer to the following
documents:
35
• Getting Started with Passport 8000 Series Management Software
• Using the Passport 8600 Modules
• Installing the Passport 8600 Modules
Safety and environmental precautions
Before you begin performing any installation or replacement procedure on the
Passport switch, please note the following safe handling guidelines:
• To prevent damage caused by electrostatic discharge (ESD), handle the switch
chassis and modules only when you, the chassis, and the chassis modules are
properly grounded. Nortel Networks recommends the use of a grounding
wrist strap.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 36

36 Chapter 3 Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module
• When handling modules, do not touch components on the modules; always
handle modules by their edges. Store unused modules in their protective
packaging.
Warning: Fiber optic equipment can emit laser or infrared light that can
injure your eyes. Never look into an optical fiber or connector port.
Always assume that fiber optic cables are connected to a light source.
Warning: Vorsicht: Glasfaserkomponenten können Laserlicht bzw.
Infrarotlicht abstrahlen, wodurch Ihre Augen geschädigt werden
können. Schauen Sie niemals in einen Glasfaser-LWL oder ein
Anschlußteil. Gehen Sie stets davon aus, daß das Glasfaserkabel an eine
Lichtquelle angeschlossen ist.
Warning: Avertissement: L’équipement à fibre optique peut émettre
des rayons laser ou infrarouges qui risquent d’entraîner des lésions
oculaires. Ne jamais regarder dans le port d’un connecteur ou d’un câble
à fibre optique. Toujours supposer que les câbles à fibre optique sont
raccordés à une source lumineuse.
Warning: Advertencia: Los equipos de fibra óptica pueden emitir
radiaciones de láser o infrarrojas que pueden dañar los ojos. No mire
nunca en el interior de una fibra óptica ni de un puerto de conexión.
Suponga siempre que los cables de fibra óptica están conectados a una
fuente luminosa.
Warning: Avvertenza: Le apparecchiature a fibre ottiche emettono
raggi laser o infrarossi che possono risultare dannosi per gli occhi. Non
guardare mai direttamente le fibre ottiche o le porte di collegamento.
Tenere in considerazione il fatto che i cavi a fibre ottiche sono collegati
a una sorgente luminosa.
8769EB
209195-A
Page 37

Chapter 3 Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module 37
Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module
To install the Passport 8672ATM Module:
1 Remove the filler panel from the module slot in the Passport 8600 series
chassis (Figure 5).
Figure 5 Removing the filler panel
9058FB
2 Make sure the inserter/extractor levers are extended away from the Passport
8672ATM Module front panel (Figure 6).
Figure 6 Extending the inserter/extractor levers
9059FA
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 38

38 Chapter 3 Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module
.
Note: Always handle an I/O module by the sides and carefully slide it
out of the chassis. Place the module on a grounded work surface and in
an antistatic bag for storage.
3 Handling the Passport 8672ATM Module by the sides only, carefully align it
with the card guides in the chassis. Slide the module into the slot until the
module connectors touch the chassis backplane (Figure 7).
Figure 7 Inserting the Passport 8672ATM Module
MDA1
8672ATM
MDA2
Online
10036FA
4 Rotate the inserter/extractor levers to seat the backplane connectors
(Figure 8).
209195-A
Page 39

Chapter 3 Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module 39
Figure 8 Closing the inserter/extractor levers
MDA1
8672ATM
MDA2
Online
5 Tighten the retaining screws (Figure 9).
Figure 9 Tightening the retainer screws
MDA1
8672ATM
MDA2
Online
10037FA
10038FA
You must install at least one MDA on the Passport 8672ATM Module in order to
pass traffic. For instructions on installing MDAs, refer to Installing the Passport
8672ATM Module MDAs.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 40

40 Chapter 3 Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module
For information on configuring and managing the Passport 8672ATM Module,
refer to Chapter 4, “Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device
Manager,” on page 47, to Chapter 5, “Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module
with the CLI,” on page 73, and to Chapter 6, “Configuring the Passport 8672ATM
Module,” on page 115.
Verifying installation
The Passport 8672ATM Module front panel has an Online LED that indicates
whether or not the module has power applied and is initialized correctly. For
information on online LEDs, see “Online LED” on page 28.
Note: You cannot configure the Passport 8672ATM Module until the
online LED on the module is steadily lit green and you have inserted at
least one MDA.
Initialization
When the Passport 8672ATM Module is installed into a Passport 8600 series
chassis, ensure that the Passport 8690SF module in the same chassis has a
PCMCIA card inserted and that the PCMCIA card contains the p80t3100.dld
image, which supports the Passport 8672ATM Module. For more information
about the PCMCIA slot and the Passport 8690SF module, refer to Using the
Passport 8600 Modules.
The Passport 8690SF module retrieves the image file p80t3100.dld to download
to the Passport 8672ATM Module. First, the Passport 8690SF module searches the
host flash memory for the file, then the PCMCIA card. The Passport 8690SF
module downloads the image file to the Passport 8672ATM Module and identifies
which MDAs are installed. The screen displays following message:
Using image = /slot/p80t3100.dld for ATM card download.
ATM card: Slot 4 MDA [OC-12c MM] [Quad OC-3c MM] Ver=2.2
If the image file is not found in either the flash memory or the PCMCIA, the
system stops and the screen displays an error message such as:
209195-A
Page 41

Chapter 3 Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module 41
ERROR Task=rcStart Couldn’t find an ATM download image!
Aborting card initialization in Slot=4
or:
ERROR Task=rcStart portPresent:port=X/X, invalid port Type
The Passport 8672ATM Module requests a redownload from the Passport 8690SF
module, and the screen displays the following message:
Redownload requested by ATM card in slot <number>.
If the image download is unsuccessful, the screen displays the following message:
ATM card in slot <number> not ready.
If there are three unsuccessful attempts to download, the screen displays the
message shown in Figure 10.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 42

42 Chapter 3 Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module
Figure 10 Unsuccessful download screen output
Copyright (c) 1998-2001 Nortel Networks, Inc.
CPU Slot 6: PPC 740 Map B
Version: 1.0.0.2/3
Creation Time: Jun 29 2000, 23:24:35
Hardware Time: AUG 09 2000, 14:02:57 UTC
Memory Size: 0x04000000
Start Type: cold
CENTENNIAL ATA
/flash/ - Volume is OK
Loaded boot configuration from file /flash/boot.cfg
Press <Return> to stop auto-boot...
/pcmcia/ - Volume is OK
2744752 to 12936388 (12936388)
Starting at 0x10000...
CENTENNIAL ATA
Passport 8600 System Software Release REL3.1.0.0_B022
Copyright (c) 1996-2000 Nortel Networks, Inc.
Waiting for cpu in slot 5 ... 2 seconds
[08/09/00 14:03:13] System boot
/pcmcia/ - Volume is OK
[08/09/00 14:03:13] Passport System Software Release REL3.1.0.0_B022
[08/09/00 14:03:15] Card inserted: Slot=1 Type=8624FX
[08/09/00 14:03:15] Card inserted: Slot=2 Type=8648TX
[08/09/00 14:03:15] Card inserted: Slot=3 Type=8608SX
[08/09/00 14:03:15] Card inserted: Slot=4 Type=8608AT
[08/09/00 14:03:18] Initializing 8624FX in slot #1 ...
[08/09/00 14:03:19] Initializing 8648TX in slot #2 ...
[08/09/00 14:03:21] Initializing 8608SX in slot #3 ...
[08/09/00 14:03:24] Initializing 8608AT in slot #4 ...
/flash/ - Volume is OK
[08/09/00 14:03:30] ERROR Task=rcStart Couldn’t find an ATM download
image! Aborting card initialization in Slot=4!
[08/09/00 14:03:30] Initialization of card failed for Slot 4 !
[08/09/00 14:03:30] Loading configuration from /flash/config.cfg
[08/09/00 14:03:30] The system is ready
[08/09/00 14:03:30] ERROR Task=rcStart smMsgSend: failed, DataLength
(0)too large
********************************
* Nortel Networks, Inc. *
* Copyright (c) 1996-2000 *
* All Rights Reserved *
* Passport 8006 *
* Software Release REL3.1.0.0_B02
********************************
Login: [08/09/00 14:04:15] Sending Cold-Start Trap
209195-A
Page 43

Chapter 3 Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module 43
After the image loads onto the Passport 8672ATM Module, it performs a series of
self-diagnostic tests. If the module fails the diagnostics, the screen displays the
following message:
Fatal bring up error on ATM card in slot <number>.
If you see this message, contact a service representative. For information on
contacting service representatives, refer to “How to get help” on page 22.
When the image successfully loads onto the Passport 8672ATM Module, the
screen displays the following message:
ATM card in slot <number> is online.
The Passport 8690SF module can download the image to two Passport 8672ATM
Modules in the same Passport 8600 series chassis simultaneously.
Note: If you accidentally delete the image file, reset the card and
redownload the file. For information on how to reset the card, see
“Resetting the module” on page 54.
If you have one MDA installed, you can proceed to configure the Passport
8672ATM Module.
Note: You must save your configuration (using either the CLI or Device
Manager) to preserve the configuration changes you made to the
Passport 8672ATM Module across reboots.
MDA insertion and configuration
Once you insert an MDA, you must complete some basic configuration tasks for
the Passport 8672ATM Module to begin switching operations as soon as it
completes initialization. For information on installing MDAs, refer to Installing
the Passport 8672ATM Module MDAs.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 44

44 Chapter 3 Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module
To verify that the Passport 8672ATM Module is ready to receive and transmit
traffic, check the LEDs on the module and the MDA. Once you enable the ports
using the CLI or Device Manager, the online LED on the module lights steady
green, and the module is ready. See “Online LED” on page 28 and “MDA LEDs”
on page 29.
For information on enabling ports, refer to “Enabling or disabling a port” on
page 58.
You configure and manage the Passport 8600 series switch operation for your
network using the command line interface (CLI) or SNMP-based network
management software, such as Device Manager. For information on configuring
and managing the Passport 8672ATM Module, refer to Chapter 4, “Managing the
Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager,” on page 47, to Chapter 5,
“Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI,” on page 73, and to
Chapter 6, “Configuring the Passport 8672ATM Module,” on page 115.
Factory default settings for the Passport 8672ATM Module are shown in
Appendix B, “Factory defaults,” on page 145.
Replacing a module
You can hot-swap Passport 8672ATM Modules as long as the module you are
inserting has the same MDAs installed as the module you are replacing. In this
case, the system saves the previous configurations. If you hot-swap the module
with a module that has different MDAs installed, you must reconfigure the
module.
If you are hot-swapping modules, read the following section for information about
how the routing switch recognizes replacement modules and how to avoid
potential problems.
Warning: The Passport 8672ATM Module itself is hot-swappable; the
MDAs necessary to pass traffic on the module are not hot-swappable.
209195-A
Page 45

Chapter 3 Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module 45
Starting the system after a module replacement
After you a replace a module on the chassis, you can expect the following results:
• In a running system, when you replace an I/O module with a module of the
same type, the system restores the configuration of all the ports.
• When you replace a module with one of a different type, the system discards
the configuration of the old ports, and the new ports are added to either the
default VLAN or a null VLAN, depending on the operating mode of the
switch.
• When you save the configuration in nonvolatile random access memory
(NVRAM), turn off the switch, replace a module with a different module
type, and turn the system on again, the system discards the configuration of
the old ports, and adds new ports to either the default VLAN or an unassigned
VLAN, depending on the operating mode of the switch.
Starting the system with an empty slot
When you save the configuration in NVRAM, shut down the system, remove a
module, turn on the chassis with that slot empty, and then populate the slot with a
module of the same type as the one previously there, the system is not able to
restore the original configuration.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 46

46 Chapter 3 Installing the Passport 8672ATM Module
209195-A
Page 47

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
Two management tools enable you to manage your Passport 8672ATM Module:
Device Manager and the command line interface (CLI). You can also use the
embedded Web-based management feature to monitor the 8672ATM Module.
This chapter contains information on these topics:
• “Port numbering,” next
• “Device Manager” on page 48
Refer to Chapter 5, “Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI” for
information about managing your Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI and
monitoring the module with the Web-based management features.
47
Port numbering
You must install an MDA into the Passport 8672ATM Module in order to have
connectivity. The module contains two slots for MDAs, and you can mix and
match among the following MDAs, which are available in both SMF and MMF:
• 1-port OC-12c/STM-4
• 4-port OC-3c/STM-1
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 48

48 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
The management systems identify an interface by its slot number (in the Passport
8600 series chassis) and its port number, using the syntax slot number/port
number (s/p). The Passport 8672ATM Module can contain up to eight ports when
two 4-port MDAs are inserted. Port numbers 1 to 4 are reserved for the MDA in
the left slot regardless of the actual physical number of ports. Port numbers 5 to 8
apply to the MDA in the right slot regardless of the actual physical number of
ports.
For example, a Passport 8672ATM Module in the third slot of the Passport 8600
series chassis with an OC-12c/STM-4 MDA in the left slot and an OC-3c/STM-1
MDA in the right slot has the following port numbers for management and
configuration:
• 3/1: OC-12c
• 3/5: OC-3c/STM-1, left port
• 3/6: OC-3c/STM-1, port second from left
• 3/7: OC-3c/STM-1, port second from right
• 3/8: OC-3c/STM-1, right port
As another example of port numbering, a Passport 8672ATM Module in the
second slot of the chassis with two OC-12c/STM-4 MDAs installed has the
following port numbers:
• 2/1: OC-12c/STM-4, left
• 2/5: OC-12c/STM-4, right
A Passport 8672ATM Module with two OC-3c/STM-1 MDAs installed has ports
numbered consecutively 1 through 8, from left to right.
Device Manager
Passport Device Manager is an SNMP-based graphical user interface tool
designed to manage single devices. In order to use Device Manager, you must
have network connectivity to a management station running Device Manager on
one of the supported platforms.
For detailed information on all aspects of installing and running Device Manager,
refer to:
209195-A
Page 49

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager 49
• Getting Started with the Passport 8000 Series Management Software
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Management Software Routing
Operations
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Management Software Switching
Operations
The following sections describe the Device Manager features that are specific to
the Passport 8672ATM Module:
• “Installing Device Manager,” next
• “Configuring ATM using Device Manager” on page 51
• “Displaying statistics using Device Manager” on page 71
• “Testing using Device Manager” on page 71
Device Manager access and passwords
For a complete discussion of Passport access levels and passwords, refer to
Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Management Software Switching
Operations.
Installing Device Manager
To install Device Manager:
1 Download the Device Manager software from the CD.
2 Double-click the icon and follow the instructions on the screen.
When you launch Device Manager, a graphical image of the Passport 8600
chassis with the Passport 8672ATM Module installed is displayed (Figure 11).
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 50

50 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
Figure 11 Passport 8000 series chassis with Passport 8672ATM Module
209195-A
The ports on the graphical image are color-coded to provide at-a-glance port
status. Table 3 shows the status assigned to each color.
Table 3 Device Manager port color codes
Field Description
Green Port is operating.
Red Port has been manually disabled.
Orange Port has no link.
Light blue Port is in standby mode.
Dark blue Port is being tested.
Gray Port is unmanageable.
Page 51

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager 51
Additionally, many Device Manager windows and dialog boxes contain buttons.
Table 4 describes the function of these buttons.
Table 4 Device Manager buttons
Field Description
Apply Applies the changes you entered to fields in a window or dialog box.
Refresh Refreshes the information in the window. Each time you click Refresh,
new information is polled form the switch and displays.
Close Closes the window or dialog box and disregards any changes you
Help Does not function with the Passport 8672ATM Module.
Insert Inserts or creates a new group, such as traps.
Resize Columns Resizes column on the screen.
made to fields.
Note: You must always click Apply at the bottom of the tab to
implement any changes you make.
Configuring ATM using Device Manager
Use Device Manager tabs and dialog boxes described in the following sections to
configure and manage the Passport 8672ATM Module.
To change the default settings on the Passport 8672ATM Module or to perform
any configuration tasks in Device Manager, select the port you want to configure
and open the Interface tab.
To open the Interface tab, do one of the following:
• Right-click on the port. A shortcut menu opens. Choose Edit.
• Double-click on the port.
The Port dialog box opens with the Interface tab displayed (Figure 12).
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 52

52 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
Figure 12 Interface tab
209195-A
Table 5 describes the items in the Interface tab.
Page 53

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager 53
Table 5 Interface tab items
Item Description
Index Unique value assigned to each interface. The value ranges between
Name Displays the name of this port. To assign or change a name to the port,
Descr Displays the port type of this interface, which may be:
Type Displays the media type of this interface, which may be:
PhysAddress MAC address assigned to a particular interface.
VendorDescr Vendor description.
AdminStatus Sets the port to either of the following states:
OperStatus Displays the current operational state of the interface, either:
LastChange Displays the value of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its
OperSpeed Displays the current operating speed of the ATM port. For OC-3c, the
16 and 255.
highlight the field and enter alphanumeric characters.
• OC-3c MMF or SMF
• OC-12c MMF or SMF
The card and port numbers are also shown.
• rcOc3cAtmSM
• rcOc3cAtmMM
• rcOc12cAtmSM
• rcOc12cAtmMM
• up
• down
When a managed system initializes, all interfaces start with
AdminStatus in the down state. As a result of either management or
configuration action, the AdminStatus is changed to the up state (or
remains in the down state).
• up
• down
If AdminStatus is down, then OperStatus should be down.
If AdminStatus is changed to up, then OperStatus should change to
up if the interface is ready to transmit and receive network traffic.
It should remain in the down state if and only if there is a fault that
prevents it from going to the up state.
current operational state. If the current state was entered prior to the
last reinitialization of the local network management subsystem, the
value is zero.
operating speed is 155.52 Mb/s; for OC-12c, it is 622.08 Mb/s.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 54

54 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
Table 5 Interface tab items (continued)
Item Description
Action Sets one of the following port-related actions:
• none
• flushMacFdb—flush MAC forwarding table for port
• flushArp—flush ARP table for port
• flushIp—flush IP route table for port
• flushAll—flush all tables for port
• triggerRipUpdate—manually update the RIP table
Result Displays result from the last system action.
From the Interface tab, select other ATM-specific tabs to configure the port or
change current or default configurations.
Resetting the module
To reset the module:
209195-A
1 Highlight the module.
2 Choose Edit > Card.
The Card dialog box opens with the Card tab displayed (Figure 13).
Page 55

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager 55
Figure 13 Card tab
Table 6 describes the fields in the Card tab.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 56

56 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
Table 6 Card tab fields
Field Description
FrontType Card type.
FrontDescription ATM.
FrontAdminStatus Administrative status of the card.
FrontOperStatus Operational status of the card.
FrontSerialNum Serial number of card.
FrontHWVersion Hardware version.
FrontPartNumer Part number.
FrontDateCode Date code.
FrontDeviations Deviations.
BackType Card back type.
BackDescription Description.
BackSerialNum Serial Number.
BackHWVersion Hardware version.
BackPartNumer Part number.
BackDateCode Date code.
BackDeviations Deviations.
209195-A
3 Click the ATM tab.
The ATM tab opens (Figure 14).
Page 57

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager 57
Figure 14 ATM tab
Table 7 describes the fields in the ATM tab.
Table 7 ATM tab fields
Field Description
Action: reset Resets the card.
ImageFileName Name of the image file which downloads at initialization.
4 Click reset.
5 Click Apply.
Viewing MDA information
To view information on the MDA you are using,
1 Highlight the MDA.
2 Choose Edit > Mda.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 58

58 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
The MDA dialog box opens (Figure 15).
Figure 15 MDA dialog box
Table 8 describes the fields in the MDA dialog box.
Table 8 MDA dialog box fields
Field Description
Type Media type:
• rc<XXXX>Oc3BaseSM.
• rc<XXXX>Oc3BaseMM.
• rc<XXXX>Oc12BaseSM.
• rc<XXXX>Oc12BaseMM.
Description MDA type:
• Quad OC-3c SM — quad port OC-3c single-mode fiber.
• Quad OC-3c MM — quad port OC-3c multimode fiber.
• OC-12c SM — single port OC-12c single-mode fiber.
• OC-12c MM — single port OC-12c multimode fiber.
209195-A
Enabling or disabling a port
You can enable or disable a port by two methods. To enable or disable a port
through the Device Manager menu bar:
1 On the device view, highlight a port.
2 From the Device Manager menu bar, choose Edit > Port.
The Port dialog box opens with the Interface tab displayed (Figure 12 on
page 52).
3 In the AdminStatus area, click up to enable the port, or click down to disable
the port.
Page 59

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager 59
4 Click Apply.
To enable or disable a port using a shortcut menu:
1 Right-click on the port.
A shortcut menu opens.
2 Choose Enable or Disable.
Editing port parameters
To view or change the general parameters of the port:
1 On the device view, highlight a port.
2 Choose Edit > Port.
The Port dialog box opens with the Interface tab displayed (Figure 12 on
page 52).
Editing ATM and framing parameters
To view or change the ATM and framing parameters of the port:
1 On the device view, highlight a port.
2 Choose Edit > Port.
The Port dialog box opens with the Interface tab displayed (Figure 12 on
page 52).
3 Click the ATM tab.
The ATM tab opens (Figure 16).
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 60

60 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
Figure 16 ATM tab
209195-A
Table 9 describes the items in the ATM tab.
Table 9 ATM t ab items
Item Description
ifIndex Interface Index.
MediaType mmf (multimode fiber) or smf (single-mode fiber)
LineSpeed For OC-3c, the operating speed is 155.52 Mb/s; for OC-12c, it is
622.08 Mb/s.
NumVpiBits For OC-3c, 11 bits split between NumVpiBits and NumVciBits.
NumVpiBits cannot exceed 6 bits for OC-3c.
For OC-12c, 13 bits split between NumVpiBits and NumVciBits.
NumVpiBits cannot exceed 8 bits for OC-12c.
NumVciBits This field is read only. It takes remaining bits from NumVpiBits. For
example, if NumVpiBits is 3 for OC-3c, then NumVciBits is 8.
Page 61

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager 61
Table 9 ATM tab items (continued)
Item Description
ScrambleEnable Sets the port to scramble the data by clicking the box.
FramingMode Sets the framing for the port to:
• sonet, which means the Synchronous Optical Network format, the
standard format in North America.
• sdh, which means the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy clock format,
the standard format in Europe.
ClockSource Sets the clock source for the port to:
• loopTimed, which means clocking is derived from the SONET line.
• freeRunning, which means clocking is derived from the on-board
clock.
Note: If you have two connected Passport 8672ATM Modules, you
must set both to freeRunning or one to freeRunning and one to
loopTimed; do not set both to loopTimed.
LoopBackMode Sets the loopback mode to:
• off
• internal
• external
MacAddress MAC address assigned to a particular interface.
Editing circuit parameters
To view and configure ATM PVC parameters:
1 On the device view, highlight a port.
2 Choose Edit > Port.
The Port dialog box opens with the Interface tab displayed (Figure 12 on
page 52).
3 Click the ATM PVC tab.
The ATM PVC tab opens (Figure 17).
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 62

62 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
Figure 17 ATM PVC t a b
Table 10 describes the fields in the ATM PVC tab.
Table 1 0 ATM PVC tab fields
Item Description
Vpi Virtual path identifier.
Vci Virtual circuit identifier.
PvcId Internal index ID of the PVC.
Name Emulated LAN name.
Encapsulation Encapsulation type: null or llcSnap.
ServiceType Unspecified bit rate (ubr) or variable bit rate (vbr).
PeakCellRate Peak cell rate, in cells/second, is the maximum cell rate.
Note: IP multicast traffic between a Passport module and other
devices may not perform as well as expected unless the peak cell
rate and the sustained cell rate values are updated to their
maximum values; only applicable if the Service Type is vbr.
SustainedCellRate Sustainable cell rate is an upper bound on the cell rate that is long
relative to that of the PCR; only applicable if the Service Type is vbr.
MaxBurstSize Maximum burst size determined by the signaling method; It is coded
as a number of cells that can be transmitted at peak rate and still
conform to the overall algorithm; only applicable if the Service Type
is vbr.
209195-A
4 Click Insert.
The Insert ATM PVC dialog box opens (Figure 18).
Page 63

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager 63
Figure 18 Insert ATM PVC dialog box
Table 11 describes the fields in the Insert ATM PVC dialog box.
Table 11 Insert ATM PVC dialog box fields
Item Description
Vpi Numeric value, within the range 0...255.
Vci Numeric value, within the range 0...65535
Note: For <vpi.vci>, 0.0 is not supported.
Name Alphanumeric characters to assign a name to the PVC.
Encapsulation Encapsulation type: null or llcSnap.
ServiceType Unspecified bit rate (ubr) or variable bit rate (vbr).
PeakCellRate Numeric value, within the range 86...733490; only applicable if
the Service Type is vbr.
SustainedCellRate Numeric value, within the range 86...733490; only applicable if
MaxBurstSize Numeric value, within the range 2...255; only applicable if the
the Service Type is vbr.
Service Type is vbr.
5 In the Vpi field, type the VPI-bit size (an integer between 0 and 255).
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 64

64 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
6 In the Vci field, type the VCI-bit size (an integer between 0 and 65, 535).
Note: For <vpi.vci>, 0.0 is not supported.
7 In the Name field, type the name of the ATM PVC.
8 In the Encapsulation field, select the encapsulation method (null or IIcSnap).
9 In the Service Type field, select the service type (ubr or vbr).
10 If you select vbr in the Service Type field:
a In the PeakCellRate field, enter the PCR (an integer between 86 and
733490).
b In the SustainedCellRate field, enter the SCR (an integer between 86 and
733490).
c In the MaxBurstSize, type the maximum burst size (an integer between 2
and 255).
11 Click Insert.
The Insert ATM PVC dialog box closes.
12 Click Close.
Deleting a PVC
To dele te a PVC :
1 On the device view, highlight a port.
2 Choose Edit > Port.
The Port dialog box opens with the Interface tab displayed (Figure 12 on
page 52).
3 Click the ATM PVC tab.
4 The ATM PVC tab opens.
5 Click a PvcId entry in the table for the PVC you want to delete.
Figure 19 shows a highlighted PvcId entry.
209195-A
Page 65

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager 65
Figure 19 ATM PVC tab with PVC selected
6 Click Delete.
The PVC is deleted.
Configuring ATM 1483 ELAN parameters
To view and configure ATM 1483 ELAN parameters for the port:
1 On the device view, highlight a port.
2 Choose Edit > Port.
The Port dialog box opens with the Interface tab displayed (Figure 12 on
page 52).
3 Click the ATM 1483 ELAN tab.
The ATM 1483 ELAN tab opens (Figure 20 and Figure 21).
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 66

66 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
Figure 20 ATM 1483 ELAN tab (left section)
Figure 21 ATM 1483 ELAN tab (right section)
209195-A
Table 12 describes the fields in the ATM 1483 ELAN tab.
Table 1 2 ATM 1483 ELAN tab fields
Field Description
VlanId VLAN to which the ELAN belongs.
ElanId Internal ID of the ELAN.
NumPvcIds Number of PVCs pairs used in the ELAN.
PvcIds List of PVC IDs, minimum of 1 required.
ConnectType Type of connection: bridged, IP or IPX.
VlanMacAddress MAC address assigned to this VLAN: used in IP and IPX
routed circuits when there is no appropriate destination
MAC to use.
Page 67

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager 67
Table 1 2 ATM 1483 ELAN tab fields (continued)
Field Description
DummyMacAddress Dummy MAC address assigned to this VLAN: used in IP
LocalIpAddress Local IP address for connection type IP.
RemoteIpAddress Remote IP address for connection type IP.
InArpSendEnable Enables ARP sending on the ELAN for connection type IP.
InArpSendInterval Interval of ARP sending for connection type IP.
IpxVlanEncapMethod One of the following:
IpxNetworkNum Network number; IPX only.
StgId Spanning tree group ID. Only for bridge connection type.
rcStgTaggedBpduVlanId VLAN ID used for tagging BPDUs.
and IPX routed circuits when there is no appropriate source
MAC to use.
• llc
•snap
• ether-ii
•raw
4 Click Insert.
The Insert ATM 1483 ELAN dialog box opens (Figure 22).
Figure 22 Insert ATM 1483 ELAN dialog box
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 68

68 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
Table 13 describes the items in the Insert ATM 1483 ELAN dialog box.
Table 1 3 Insert ATM 1483 ELAN dialog box items
Item Description
VlanId VLAN ID.
PvcIds Value for Pvc IDs.
ConnectType Types of connection: bridged, IP or IPX.
LocalIpAddress IP address of the device.
RemoteIpAddress IP address of the device to which you are connecting.
InArpSendEnable Enables ARP sending on the ELAN for connection type IP.
InArpSendInterval Interval of ARP sending for connection type IP.
IpxVlanEncapMethod IPX encapsulation protocol: llc, snap, ether-ii, or raw.
IpxNetworkNum Network number; numeric value, within the range
0...2147483647.
5 In the VlanId field, type the VLAN ID.
209195-A
6 In the PvcIds field, type the PVC ID.
Note: For <vpi.vci>, 0.0 is not supported.
7 In the ConnectType field, select the type of routing protocol: bridged, ip, or
ipx.
8 If bridged is selected in the ConnectType field, click Insert.
9 If Ip is selected in the ConnectType field, complete the following fields:
a In the LocalIpAddress field, type the IP address of the device.
b In the RemoteIpAddress field, type the IP address of the device that you
are connecting to in the 1483 ELAN.
c Select the InArpSendEnable option to enable Arp packets.
d In the InArpSendInterval field, type the time interval between 0 and 60
seconds.
e Click Insert.
Page 69

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager 69
Figure 23 shows the relevant fields for IP routing.
Figure 23 Insert ATM 1483 ELAN dialog box for IP routing
10 If Ipx is selected in the ConnectType field, complete the following fields:
a In the IpxVlanEncapMethod, select the encapsulation method (llc, snap,
ether-ii, or raw).
b In the IpxNetworkNum field, enter the network number (an integer
between 0 and 2147483647.
c Click Insert.
Figure 24 shows the relevant fields for IPX routing.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 70

70 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
Figure 24 Insert ATM 1483 ELAN dialog box for IPX routing
Deleting an ATM 1483 ELAN
To delete an ATM 1483 ELAN:
1 On the device view, highlight a port.
2 Choose Edit > Port.
The Port dialog box opens with the Interface tab displayed (Figure 12 on
page 52).
3 Click the ATM 1483 ELAN tab.
4 The ATM 1483 ELAN tab opens.
5 Select the ATM 1483 ELAN to be deleted by clicking the ElanId entry in the
table.
Figure 25 shows a highlighted ElanId entry.
209195-A
Page 71

Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager 71
Figure 25 ATM 1483 ELAN tab with ElanId selected
6 Click Delete.
The ATM 1483 ELAN is deleted.
Displaying statistics using Device Manager
Statistics are not supported in Device Manager in this release. See the “show ports
stats atmport command” on page 89 for information on statistics in the CLI.
Testing using Device Manager
Testing is not supported in this release.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 72

72 Chapter 4 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device Manager
209195-A
Page 73

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
You can manage your Passport 8672ATM Module through the command line
interface (CLI). You can also use the embedded Web-based management feature
to monitor the 8672ATM Module.
This chapter contains information on these topics:
• “Command line interface,” next
• “show ports stats atm felinecurrent” on page 91
• “Web management” on page 106
Refer to Chapter 4, “Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with Device
Manager” for information about port numbering and managing your Passport
8672ATM Module through Device Manager.
73
Command line interface
You can use the command line interface (CLI) to perform most module
management tasks. For more information about the CLI, refer to:
• Getting Started with the Passport 8000 Series Management Software
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Command Line Interface Switching
Operations
• Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Command Line Interface Routing
Operations
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 74

74 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
This section contains the following information:
• “Configuration commands,” next
• “Show commands” on page 82
Configuration commands
This section describes the CLI configuration commands available with the
Passport 8672ATM Module. There are three types of configuration commands:
• “Module commands,” next
• “1483 ELAN statistics” on page 75
• “Port commands” on page 77
Note: If you replace one card with another type of card, Nortel
Networks recommends that you go to the root level of the CLI directory
before using any CLI commands.
209195-A
Module commands
The module commands allow you to:
• Reset the module
• View ELAN statistics
• Display the image filename for the Passport 8672ATM Module.
The syntax is:
config atmcard
The required variable <atmslot number> is the slot number of the module in
the Passport 8600 chassis. Table 14 describes the parameters and variables for the
config atmcard command.
<atmslot number>
Page 75

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 75
Table 1 4 config atmcard command parameters and variables
Parameters and variables Description
card-reset Resets the card.
elan-stats
<enable|disable>
info
Enables collection of ELAN statistics.
Displays the image filename for the module.
1483 ELAN statistics
The 1483 ELAN statistics commands allow you to collect ELAN statistics for an
ATM port. The commands are:
• config atmcard <slot_number> elan-stats <enable|disable>
• clear atm elan-stats <vlan_id>
• show atm elan-stats <vlan_id>
config atmcard elan-stats
The collection of ELAN statistics is disabled by default to avoid slowing data
forwarding performance. ELAN statistics should be disabled after collection.
Enabling or disabling the collection of ELAN statistics does not clear the ELAN
statistics counters. This allows the ELAN statistics to be reviewed after the feature
is disabled.
clear atm elan-stats <vlan id>
This command allows you to clear statistics for a particular VLAN ID.
The syntax is:
clear atm elan-stats <vlan_id>
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 76

76 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
show atm elan-stats <vlan id>
Use this command to display the ELAN statistics for a particular VLAN ID. If the
collection of ELAN statistics is disabled, a message is printed before the ELAN
statistics.
Figure 27 shows sample output from the
show atm elan-stats <vlan_id>
command.
Figure 26 show atm elan-stats command output
Passport-8610:5# show atm elan-stats 7
=====================================================================
ATM ELAN STATISTICS
=====================================================================
InOctets: 3208404820 InErrors: 0 InDiscards: 0
OutOctets: 3208281916 OutErrors: 0 OutDiscards: 0
InUcastPkts: 130202 InMcastPkts: 395 InBCastPkts: 59134772
OutUcastPkts: 129406 OutMcastPkts: 391 OutBCastPkts: 59133296
Table 15 describes the information fields for the show atm elan-stats
command.
Table 1 5 Information fields for the show atm elan-stats command
Field Description
InOctets Octets received from the ATM interface. This includes the
OutOctets Octets transmitted out of the ATM interface.
InErrors AAL5 CPCS PDUs received with errors from the ATM
OutErrors Number of AAL5 CPCS PDUs that could not be transmitted
“InDiscards" PDUs.
NOTE: For a Bridge ELAN Type with multiple PVCs, there
will be multiple packets transmitted for a multicast packet,
or for a unicast packet that is not in the CAM. Thus, the
OutOctets may not correlate to the OutUcastPkts +
OutMcastPkts + OutBcastPkts.
interface. These errors include CRC-32 errors, SAR
time-out errors, and oversized SDU errors.
due to error.
209195-A
Page 77

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 77
Table 1 5 Information fields for the show atm elan-stats command (continued)
Field Description
InDiscards Number of received AAL5 CPCS PDUs discarded.
OutDiscards Ethernet packets discarded.
InUcastPkts Number of unicast packets received on the ELAN.
OutUcastPkts Number of unicast packets transmitted on the ELAN.
InMcastPkts Number of Multicast packets received on the ELAN.
OutMcastPkts Number of Multicast packets transmitted on the ELAN.
InBcastPkts Number of broadcast packets received on the ELAN.
OutBcastPkts Number of broadcast packets transmitted on the ELAN.
clear atm elan-stats
Use this command to clear the ELAN statistics for a particular VLAN ID. The
syntax is:
clear atm elan-stats <vlan_id>
Port commands
The port commands allow you to perform general configuration on the Passport
8672ATM Module. The port config commands are:
• config atm <ports>
• config atm <ports> pvc
• config atm <ports> pvc 1483 {bridged|ip|ipx}
• config atm <ports> info
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 78

78 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
config atm command
Table 16 describes the parameters and variables for the config atm <ports>
command.
Table 1 6 config atm command parameters and variables
Parameters and variables Description
action <action choice> Flushes a MAC, ARP, or IP table or triggers a RIP update. Choices
number-vpi-bits <number-vpi-bits> • Sets the number of bits used to represent VPI. Enter integer from
scrambling <enable | disable> Enables or disables scrambling.
framing-mode <sonet | sdh> Sets the framing to:
clock-source <loop-timed |
free-running>
loop-back-mode <off | internal |
remote>
state <enable | disable> Sets the state of the port to enabled or disabled.
are:
• none
• flushMacFdb
•flushArp
•flushIp
•flushAll
• triggerRipUpdate
0 to 8.
• For OC-3c, 11 bits split between NumVpiBits and NumVciBits.
NumVpiBits cannot exceed 6 bits for OC-3c.
• For OC-12c, 13 bits split between NumVpiBits and NumVciBits.
NumVpiBits cannot exceed 8 bits for OC-12c.
• sonet, which
standard format used in North America.
• sdh, which
standard format used in Europe.
Sets the transmit clock source to:
• loop-timed, which means clocking is derived from line.
• free-running, which means clocking is derived from on-board
clock.
Note that if you have two connected Passport 8672ATM Modules, you
must set both to free-running or one to loop-timed and one to
free-running; do not set both to loop-timed.
Sets the loopback mode to:
•off
• internal
• external
means the Synchronous Optical Network format;
means the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy clock format;
209195-A
Page 79

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 79
Table 1 6 config atm command parameters and variables (continued)
Parameters and variables Description
info Shows the last saved port settings and the next-level CLI commands.
perform-tagging <enable |
disable>
Note that this does not show the current settings, but the last saved
settings.
Enables or disables tagging.
config atm pvc command
Table 17 describes the parameters and variables for the config atm pvc
command.
Table 1 7 config atm pvc command parameters and variables
Parameters and variables Description
create < vpi.vci> [name <value>]
[enc <value>] [serv <value>] [pcr
<value>] [scr <value>] [mbs
<value>]
delete <vpi.vci> Deletes the specified PVC. Note that this command will fail if the PVC
info [<ports>] Displays PVC information.
Creates a PVC. The required parameters are:
• vpi is the circuit VPI. Enter a numeric value, within the range
0...255.
• vci is the circuit VCI. Enter a numeric value, within the range
0...65535.
Note: For <vpi.vci>, 0.0 is not supported.
The optional parameters are:
• name is the display string. Enter up to 256 alphanumeric
characters to name PVC.
• enc is the 1483 encapsulation method, either null or llc-snap.
• serv is the bit rate, either ubr or vbr.
• pcr, with VBR only, is the peak cell rate. Enter an integer from 86 to
733490.
• scr, with VBR only, is the sustained cell rate. Enter an integer from
86 to 733490.
• mbs, with VBR only, is the maximum burst size. Enter an integer
from 2 to 255.
Note that no VLANs or ELANs are bound to this PVC until you add
VLAN membership using the config atm <ports> pvc 1483 commands.
is still being used by RFC 1483 traffic.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 80

80 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
config atm pvc 1483 command
Use the config atm pvc 1483 commands to configure 1483 parameters on
the Passport 8672ATM Module. The syntax is:
config atm <ports> pvc 1483 bridged
•
• config atm <ports> pvc 1483 ip
• config atm <ports> pvc 1483 ipx
Table 18 describes the parameters and variables for the config atm <ports>
pvc 1483 command.
Table 1 8 config atm pvc 1483 bridged command parameters and variables
Parameters and variables Description
add <vid> <vpi.vci> [,<vpi.vci>]... Adds a number of PVCs to the specified 1483 ELAN. The required
parameters are:
• vid means VLAN ID number.
• vpi.vci means circuit VPI number and the circuit VCI numbers,
respectively; they are separated by a period.
Note: This command fails if the specified VIDs or VPI/VCI pairs belong
to another ELAN or already exist on this ELAN.
create <vid> <vpi.vci>
[,<vpi.vci>]...
delete <vid> Deletes the specified ELAN.
remove <vid> <vpi.vci>
[,<vpi.vci>]...
info Displays information on 1483 ELANs.
Creates a 1483 ELAN consisting of the specified PVCs. The required
parameters are:
• vid means VLAN ID number.
• vpi.vci means circuit VPI number and the circuit VCI numbers,
respectively; they are separated by a period.
Note: This command fails if the specified VIDs or VPI/VCI pairs belong
to another ELAN or already exist on this ELAN.
Removes a number of PVCs from the specified 1483 ELAN. The
required parameters are:
• vid means VLAN ID number.
• vpi.vci means circuit VPI number and the circuit VCI numbers,
respectively; they are separated by a period.
Note that this command fails if the PVCs are not present.
209195-A
Table 19 describes the parameters and variables for the config atm pvc
1483 ip command.
Page 81

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 81
Table 1 9 config atm pvc 1483 ip command parameters and variables
Parameters and variables Description
create <vid> <vpi.vci> <remoteip> Creates a routed 1483 IP circuit on the specified VLAN to the
delete <vid> Deletes the routed 1483 IP circuit on the specified VLAN.
info Displays information on routed 1483 IP circuits.
specified remote router interface. The optional parameters are:
• vid means VLAN ID number.
• vpi.vci means circuit VPI number and the circuit VCI numbers,
respectively; they are separated by a period.
• remoteip is the IP address of the remote router interface.
Note that the VLAN ID can exist only on this port.
Table 20 describes the parameters and variables for the config atm pvc
1483 ipx command.
Table 2 0 config atm pvc 1483 ipx command parameters and variables
Parameters and variables Description
create <vid> <vpi.vci> <ipx> Creates a routed 1483 IPX circuit on the specified VLAN to the
delete <vid> Deletes the routed 1483 IPX circuit on the specified VLAN.
info Displays information on routed 1483 IPX circuits.
specified remote router interface. The optional parameters are:
• vid means VLAN ID number.
• vpi.vci means circuit VPI number and the circuit VCI numbers,
respectively; they are separated by a period.
• ipx is the IPX Network number of the remote router interface. If this
number is not given, the first IPX Network number configured for
the specified VLAN is used.
Note that the VLAN ID must be previously configured for IPX on this
port.
No ARP functionality is available on this IPX segment.
config atm info command
Figure 27 shows a sample of the output resulting from executing the config atm
command.
info
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 82

82 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
Figure 27 Sample output for the config atm info command
number-vpi-bits : 4
scrambling : Enable
framing-mode : SONET
clock-source : Free Running
loop-back-mode : off
state : up
Show commands
This section discusses the CLI show commands available with the Passport
8672ATM Module. These commands allow you to view information about the
module:
show ports info atm all [<ports>]
show ports info atm ports [<ports>]
show ports info atm pvc [<ports>]
show ports info atm 1483 [<ports>]
show ports stats atmport [<ports>]
show ports stats atm felinecurrent [<ports>]
show ports stats atm felineinterval <intervalid> [<ports>]
show ports stats atm fepathcurrent [<ports>]
show ports stats atm fepathinterval <intervalid> [<ports>]
show ports stats atm linecurrent [<ports>]
show ports stats atm lineinterval <intervalid> [<ports>]
show ports stats atm pathcurrent [<ports>]
show ports stats atm pathinterval <intervalid> [<ports>]
show ports stats atm sectioncurrent [<ports>]
show ports stats atm sectioninterval <intervalid> [<ports>]
show ports stats atm sonetmediumtbl [<ports>]
209195-A
Refer to Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Command Line Interface
Switching Operations, and Reference for the Passport 8000 Series Command Line
Interface Routing Operations for a complete list of CLI show commands.
show ports info atm all command
This command displays information (Figure 28) about the configuration for the
specified port or for all ports. The command uses the syntax:
show ports info atm all [<ports>]
Page 83

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 83
Figure 28
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/info/atm# all
=======================================================
======================================================
PORT MDA SCRAMBLE FRAMING MAX-BITS CLOCK LOOPBACK ADMIN
NUM DESCRIPION ENABLE MODE VPI VCI SOURCE MODE STATE STATUS
--------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 OC-12c MM enable SONET 4 9 free off up up
3/5 Quad OC-3c MM enable SONET 2 9 free off up up
3/6 Quad OC-3c MM enable SONET 2 9 free off up down
3/7 Quad OC-3c MM enable SONET 4 7 free off up down
=====================================================================
=====================================================================
PORT PVC SERVICE
NUM VPI.VCI ENCAPS TYPE
--------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 0.100 llc-snap UBR
3/1 3.200 llc-snap UBR
3/6 0.33 llc-snap UBR
3/6 3.90 llc-snap UBR
=====================================================================
=====================================================================
PORT VLAN PVC
NUM ID LIST
-------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 6 0.100
3/8 4 3.40,4.50
=====================================================================
=====================================================================
PORT VLAN PVC VLAN LOCAL REMOTE
NUM ID VPI.VCI MAC ADDRESS IP ADDRESS IP ADDRESS
--------------------------------------------------------------------3/6 7 0.100 00:e0:7b:7b:52:01 10.10.80.239 10.10.80.230
====================================================================
=====================================================================
PORT VLAN PVC VLAN IPX NETWORK IPX
NUM ID VPI.VCI MAC ADDRESS NUMBER ENCAP
--------------------------------------------------------------------3/5 17 0.100 00:e0:7b:7b:52:03 10-11Xethernet-ii
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/info/atm# all
show ports info atm all command output
ATM Port Configuration
ATM PVC
1483 Bridged
1483 IP
1483 IPX
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 84

84 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
Table 21 describes the information fields for the show ports info atm
all command.
Table 2 1 Information fields for the show ports info atm all command
Field Description
PORT NUM Port number.
MDA DESCRIPTION This field describes the MDA:
• Quad OC-3c SM — quad port OC-3c single-mode fiber
• Quad OC-3c MM — quad port OC-3c multimode fiber
• OC-12c SM — single port OC-12c single-mode fiber
• OC-12c MM — single port OC-12c multimode fiber
SCRAMBLE ENABLE Parameter that enables/disables the scrambling option.
FRAMING MODE Indicates the framing for the port, either:
• sonet, which means the Synchronous Optical Network
format, the standard format in North America.
• sdh, which means the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
clock format, the standard format in Europe.
MAX-BITS VPI For OC-3c, 11 bits split between NumVpiBits and
MAX-BITS VCI This field is read only. It takes remaining bits from
CLOCK SOURCE Indicates whether the Clock Source is either:
LOOPBACK MODE Indicates the loopback mode::
ADMIN STATE Indicates the Admin State of the port, either:
STATUS Indicates the status of the port, either:
PVC VPI.VCI Permanent virtual circuit and the associated vpi and vci
NumVciBits. NumVpiBits cannot exceed 6 bits for OC-3c.
For OC-12c, 13 bits split between NumVpiBits and
NumVciBits. NumVpiBits cannot exceed 8 bits for OC-12c.
NumVpiBits. For example, if NumVpiBits is 3 for OC-3c,
then NumVciBits is 8.
• line
• internal
• off
• internal
• external
• up
• down
• up
• down
numeric identifiers.
209195-A
Page 85

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 85
Table 2 1 Information fields for the show ports info atm all command (continued)
Field Description
ENCAPS Encapsulation methods: either null, or llc-snap.
SERVICE TYPE Unspecified bit rate (ubr) or variable bit rate (vbr).
VLAN ID VLAN name to which the ELAN belongs.
PVC LIST List of permanent virtual circuits.
VLAN MAC ADDRESS The MAC address assigned to this VLAN (used in IP and
IPX routed circuits when there is no appropriate destination
MAC to use).
LOCAL IP ADDRESS The local Ip address for connection type IP.
REMOTE IP ADDRESS The remote Ip address for connection type IP.
IPX NETWORK NUMBER Network number.
IPX ENCAP Encapsulation method: llc, snap, ether-ii or raw.
show ports info atm ports command
This command displays information (Figure 29) about the configuration of ATM
ports. The command uses the syntax:
show ports info atm ports
Figure 29 show ports info atm ports command output
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/info/atm# ports
=======================================================================
=======================================================================
PORT MDA SCRAMBLE FRAMING MAX-BITS CLOCK LOOPBACKADMIN STATUS
NUM DESCRIPION ENABLE MODE VPI VCI SOURCE MODE STATE
----------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 OC-12c MM enable SONET 4 9 free off up up
3/5 Quad OC-3c MM enable SONET 2 9 free off up up
3/6 Quad OC-3c MM enable SONET 2 9 free off up down
3/7 Quad OC-3c MM enable SONET 4 7 free off up up
3/8 Quad OC-3c MM enable SONET 4 7 free off up up
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/info/atm#
ATM Port Configuration
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 86

86 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
Table 22 describes the information fields for the show ports info atm
ports command.
Table 2 2 Information fields for the show ports info atm ports command
Field Description
PORT NUM Port number.
MDA DESCRIPTION This field describes the MDA:
• Quad OC-3c SM — dual port OC-3c single-mode fiber
• Quad OC-3c MM — dual port OC-3c multimode fiber
• OC-12c SM — single port OC-12c single-mode fiber
• OC-12c MM — single port OC-12c multimode fiber
SCRAMBLE ENABLE Parameter that enables/disables the scrambling option.
FRAMING MODE Indicates the framing for the port, either:
• sonet, which means the Synchronous Optical Network
format, the standard format in North America.
• sdh, which means the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
clock format, the standard format in Europe.
MAX-BITS VPI For OC-3c, 11 bits split between NumVpiBits and
MAX-BITS VCI This field is read only. It takes remaining bits from
CLOCK SOURCE Indicates whether the Clock Source is either:
LOOPBACK MODE Indicates the loopback mode:
ADMIN STATE Indicates the Admin State of the port, either:
STATUS Indicates the status of the port, either:
NumVciBits. NumVpiBits cannot exceed 6 bits for OC-3c.
For OC-12c, 13 bits split between NumVpiBits and
NumVciBits. NumVpiBits cannot exceed 8 bits for OC-12c.
NumVpiBits. For example, if NumVpiBits is 3 for OC-3c,
then NumVciBits is 8.
• line
• internal
• off
• internal
• external
• up
• down
• up
• down
209195-A
Page 87

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 87
show ports info atm pvc command
This command displays information (Figure 30) about the permanent virtual
circuits (PVCs) for the specified port or for all ports. The command uses the
syntax:
show ports info atm pvc [<ports>]
Figure 30 show ports info atm pvc command output
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/info/atm# pvc
=======================================================
ATM PVC
=======================================================
PORT PVC SERVICE
NUM VPI.VCI ENCAPS TYPE
------------------------------------------------------3/1 0.100 llc-snap UBR
3/1 3.200 llc-snap UBR
3/6 0.33 llc-snap UBR
3/6 3.90 llc-snap UBR
3/8 3.40 llc-snap UBR
3/8 4.50 llc-snap UBR
3/8 7.100 llc-snap UBR
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/info/atm#
Table 23 describes the information fields for the show ports info atm
pvc command.
Table 2 3 Information fields for the show ports info atm pvc command
Field Description
PORT NUM Port number.
PVC VPI.VCI Permanent virtual circuit and the associated vpi and vci
ENCAPS Encapsulation method: null or llc-snap.
SERVICE TYPE Unspecified bit rate (ubr) or variable bit rate (vbr).
numeric identifiers.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 88

88 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
show ports info atm 1483 command
This command displays information (Figure 31) about 1483 circuits for the
specified port or for all ports. The command uses the syntax:
show ports info atm 1483 [<ports>]
Figure 31 show ports info atm 1483 command output
Passport-8610:5# show ports info atm 1483 3/8
================================================================
1483 Bridged
================================================================
PORT VLAN PVC
NUM ID LIST
----------------------------------------------------------------
================================================================
1483 IP
================================================================
PORT VLAN PVC VLAN LOCAL REMOTE
NUM ID VPI.VCI MAC ADDRESS IP ADDRESS IP ADDRESS
--------------------------------------------------------------3/8 7 0.100 00:e0:7b:7b:52:01 10.10.80.239 10.10.80.2
================================================================
1483 IPX
================================================================
PORT VLAN PVC VLAN IPX NETWORK IPX
NUM ID VPI.VCI MAC ADDRESS NUMBER ENCAP
---------------------------------------------------------------Passport-8610:5#
209195-A
Table 24 describes the information fields for the show ports info atm
1483 command.
Table 2 4 Information fields for the show ports info atm 1483
command
Field Description
PORT NUM Port number.
VLAN ID VLAN name to which the ELAN belongs.
PVC LIST List of permanent virtual circuits.
Page 89

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 89
Table 2 4 Information fields for the show ports info atm 1483
command (continued)
Field Description
VLAN MAC ADDRESS MAC address assigned to this VLAN: used in IP and IPX
LOCAL IP ADDRESS Local IP address for connection type IP.
REMOTE IP ADDRESS Remote IP address for connection type IP.
IPX NETWORK NUMBER Network number.
IPX ENCAP Encapsulation method: llc, snap, ether-ii, or raw.
routed circuits when there is no appropriate destination
MAC to use.
show ports stats atmport command
This command displays statistics for atm ports (Figure 32). The command uses
the syntax:
show ports stats atmport [<port num>]
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 90

90 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
Figure 32 show ports stats atmport [<port num>] command output
Passport-8606:6/show/ports/stats# atmport
===========================================================================
ATM Port Statistics I
===========================================================================
PORT IN OUT IN CORR IN UNCORR
NUM CELLS CELLS HCS ERR HCS ERR
--------------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 0 6744908 0 0
3/2 0 6744901 0 0
3/3 0 6744893 0 0
3/4 0 6744888 0 0
3/5 0 35314189 0 0
===========================================================================
ATM Port Statistics II
===========================================================================
PORT IN OUT IN DROP OUT DROP UNKNOWN VPI/VCI IDLE
NUM PKTS PKTS PKTS PKTS CELLS CELLS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 0 0 0 0 0 6746913
3/2 0 0 0 0 0 6746912
3/3 0 0 0 0 0 6746913
3/4 0 0 0 0 0 8096349
3/5 0 0 0 0 0 42386582
Passport-8606:6/show/ports/stats#
Table 25 describes the information fields for the show ports stats
atmport command.
Table 2 5 Information fields for the show ports stats atmport
command
Field Description
PORT NUM Port number.
IN CELLS Received cells.
OUT CELLS Transmitted cells.
IN CORR HCS ERR Number of inbound packets that contained errors
209195-A
preventing them from being deliverable to a higher-layer
protocol.
Page 91

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 91
Table 2 5 Information fields for the show ports stats atmport
command (continued)
Field Description
IN UNCORR HCS ERR Number of packets received using the interface which were
IN PKTS Number of packets received.
OUT PKTS Number of packets transmitted.
IN DROP PKTS Number of in-bound packets dropped.
OUT DROP PKTS Number of out-bound packets dropped.
UNKNOWN VPI/VCI CELLS Number of packets for which the vpi/vci values are
IDLE CELLS Cells that are inactive.
discarded because of an unknown or unsupported
protocol.
unknown.
show ports stats atm felinecurrent
This command displays current statistics on the far end line, which is at the
receiving end. The command uses the syntax:
show ports stats atm felinecurrent [<ports>]
Figure 33 shows sample output for the show ports stats atm
felinecurrent
command.
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 92

92 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
Figure 33 show ports stats atm felinecurrent command output
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/stats/atm# felinecurrent
======================================================================
ATM Far End Line Current Stats
======================================================================
PORT ERRORED SECONDS SEVERELY ERRORED CODE VIOLATION UNAVAILABLE
NUM COUNT (ES) COUNT (SES) COUNT (CV-L) SECONDS(UAS)
---------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 0 0 0 0
3/5 0 0 0 0
9/1 0 0 0 0
9/2 0 0 0 0
9/3 0 0 0 0
9/4 0 0 0 0
9/5 0 0 0 0
9/6 0 0 0 0
9/7 0 0 0 0
9/8 0 0 0 0
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/stats/atm# felinecurrent
209195-A
Table 26 describes the information fields for the show ports stats atm
felinecurrent
Table 2 6 Information fields for the show ports stats atm felinecurrent command
Field Description
PORT NUM Port number.
ERRORED SECONDS
COUNT (ES)
SEVERELY ERRORED
COUNT (SES)
CODE VIOLATION COUNT
(CV-L)
UNAVAILABLE SECONDS Number of seconds that the interface is unavailable.
command.
Errored Second (ES) is a second with one or more Coding
Violations (CV) or one or more incoming defects (for
example, SEF, LOS, AIS, LOP).
Severely Errored Second (SES) is a second with x or more
CVs, or one or more incoming defects.
Coding Violations (CV) are Bit Interleaved Parity (BIP)
errors that are detected in the incoming signal. CV
counters are incremented for each BIP error detected.
Page 93

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 93
show ports stats atm felineinterval
This command displays statistics (Figure 34) on the far end line over a 15-minute
interval. You specify which interval, or span of intervals, to display for the
command. The command uses the syntax:
show ports stats atm felineinterval <intervalid> [<ports>]
Figure 34 show ports stats atm felineinterval command output
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/stats/atm# felineinterval 96
======================================================================
ATM Far End Line Interval Stats
======================================================================
PORT ERRORED SECONDS SEVERELY ERRORED CODE VIOLATION UNAVAILABLE
NUM COUNT (ES) COUNT (SES) COUNT (CV-L) SECONDS(UAS)
---------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 0 0 0 0
3/5 0 0 0 0
9/1 0 0 0 0
9/2 0 0 0 0
9/3 0 0 0 0
9/4 0 0 0 0
9/5 0 0 0 0
9/6 0 0 0 0
9/7 0 0 0 0
9/8 0 0 0 0
INTERVAL ID = 96
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/stats/atm#
Table 27 describes the information fields for the show ports stats atm
felineinterval
Table 2 7 Information fields for the show ports stats atm felineinterval
command
Field Description
PORT NUM Port number.
ERRORED SECONDS
COUNT (ES)
command.
Errored Second (ES) is a second with one or more Coding
Violations (CV) or one or more incoming defects (for
example, SEF, LOS, AIS, LOP).
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 94

94 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
Table 2 7 Information fields for the show ports stats atm felineinterval
command (continued)
Field Description
SEVERELY ERRORED
COUNT (SES)
CODE VIOLATION COUNT
(CV-L)
UNAVAILABLE SECONDS
(UAS)
INTERVAL ID Specified interval.
Severely Errored Second (SES) is a second with x or more
CVs, or one or more incoming defects.
Coding Violations (CV) are Bit Interleaved Parity (BIP)
errors that are detected in the incoming signal. CV
counters are incremented for each BIP error detected.
The number of seconds that the interface is unavailable.
show ports stats atm fepathcurrent
This command displays current statistics (Figure 35) for the far end path, which is
at the receiving end. The command uses the syntax:
show ports stats atm fepathcurrent [<ports>]
Figure 35 show ports stats atm fepathcurrent command output
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/stats/atm# fepathcurrent
=========================================================================
ATM Far End Path Current Stats
=========================================================================
PORT ERRORED SECONDS SEVERELY ERRORED CODE VIOLATION UNAVAILABLE
NUM COUNT (ES) COUNT (SES) COUNT (CV-P) SECONDS(UAS)
------------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 0 0 0 264
3/5 0 0 0 264
9/1 0 0 0 0
9/2 0 0 0 0
9/3 0 0 0 0
9/4 0 0 0 0
9/5 0 0 0 0
9/6 0 0 0 0
9/7 0 0 0 0
9/8 0 0 0 0
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/stats/atm# fepathcurrent
209195-A
Page 95

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 95
Table 28 describes the information fields for the show ports stats atm
fepathcurrent
Table 2 8 Information fields for the show ports stats atm fepathcurrent command
Field Description
PORT NUM Port number.
ERRORED SECONDS
COUNT (ES)
SEVERELY ERRORED
COUNT (SES)
CODE VIOLATION COUNT
(CV-P)
UNAVAILABLE SECONDS
(UAS)
command.
Errored Second (ES) is a second with one or more Coding
Violations (CV) or one or more incoming defects (for
example, SEF, LOS, AIS, LOP).
Severely Errored Second (SES) is a second with x or more
CVs, or one or more incoming defects.
Coding Violations (CV) are Bit Interleaved Parity (BIP)
errors that are detected in the incoming signal. CV
counters are incremented for each BIP error detected.
The number of seconds that the interface is unavailable.
show ports stats atm fepathinterval
This command displays statistics (Figure 36) on the far end path over a 15-minute
interval. You specify the interval or span of intervals to display. The command
uses the syntax:
show ports stats atm fepathinterval <intervalid> [<ports>]
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 96

96 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
Figure 36 show ports stats atm fepathinterval command output
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/stats/atm# fepathinterval 96
=========================================================================
ATM Far End Path Interval Stats
=========================================================================
PORT ERRORED SECONDS SEVERELY ERRORED CODE VIOLATION UNAVAILABLE
NUM COUNT (ES) COUNT (SES) COUNT (CV-P) SECONDS(UAS)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 0 0 0 900
3/5 0 0 0 900
9/1 0 0 0 0
9/2 0 0 0 0
9/3 0 0 0 0
9/4 0 0 0 0
9/5 0 0 0 0
9/6 0 0 0 0
9/7 0 0 0 0
9/8 0 0 0 0
INTERVAL ID = 96
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/stats/atm# fepathinterval 96
209195-A
Table 29 describes the information fields for the show ports stats atm
fepathinterval
Table 2 9 Information fields for the show ports stats atm fepathinterval command
Field Description
PORT NUM Port number.
ERRORED SECONDS
COUNT (ES)
SEVERELY ERRORED
COUNT (SES)
CODE VIOLATION COUNT
(CV-P)
UNAVAILABLE SECONDS
(UAS)
INTERVAL ID Specified interval.
command.
Errored Second (ES) is a second with one or more Coding
Violations (CV) or one or more incoming defects (for
example, SEF, LOS, AIS, LOP).
Severely Errored Second (SES) is a second with x or more
CVs, or one or more incoming defects.
Coding Violations (CV) are Bit Interleaved Parity (BIP)
errors that are detected in the incoming signal. CV
counters are incremented for each BIP error detected.
Number of seconds that the interface is unavailable.
Page 97

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 97
show ports stats atm linecurrent
This command displays current statistics (Figure 37) for the line. The command
uses the syntax:
show ports stats atm linecurrent [<ports>]
Figure 37 show ports stats atm linecurrent command output
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/stats/atm# linecurrent
=========================================================================
ATM Line Current Stats
========================================================================
PORT ERRORED SECONDS SEVERELY ERRORED CODE VIOLATION UNAVAILABLE
NUM COUNT (ES) COUNT (SES) COUNT (CV-L) SECONDS (UAS) STATUS
------------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 0 0 0 110 LineAIS
3/5 0 0 0 110 Line AIS
9/1 0 0 0 0 No Defect
9/2 0 0 0 0 No Defect
9/3 0 0 0 0 No Defect
9/4 0 0 0 0 No Defect
9/5 0 0 0 0 No Defect
9/6 0 0 0 0 No Defect
9/7 0 0 0 0 No Defect
9/8 0 0 0 0 No Defect
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/stats/atm# linecurrent
Table 30 describes the information fields for the show ports stats atm
linecurrent
Table 3 0 Information fields for the show ports stats atm linecurrent
command
Field Description
PORT NUM Port number.
ERRORED SECONDS
COUNT (ES)
command.
Errored Second (ES) is a second with one or more Coding
Violations (CV) or one or more incoming defects (for
example, SEF, LOS, AIS, LOP).
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 98

98 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
Table 3 0 Information fields for the show ports stats atm linecurrent
command (continued)
Field Description
SEVERELY ERRORED
COUNT (SES)
CODE VIOLATION COUNT
(CV-P)
UNAVAILABLE SECONDS
(UAS)
STATUS Status of defects.
Severely Errored Second (SES) is a second with x or more
CVs, or one or more incoming defects.
Coding Violations (CV) are Bit Interleaved Parity (BIP)
errors that are detected in the incoming signal. CV
counters are incremented for each BIP error detected.
Number of seconds that the interface is unavailable.
show ports stats atm lineinterval
This command displays statistics (Figure 38) for the line over a 15-minute
interval. You can specify any interval or span of intervals. The command uses the
syntax:
show ports stats atm lineinterval <intervalid> [<ports>]
Figure 38 show ports stats atm lineinterval command output
Passport-8610:5/show/ports# stats atm lineinterval 96
===========================================================================
ATM Line Interval Stats
===========================================================================
PORT ERRORED SECONDS SEVERELY ERRORED CODE VIOLATION UNAVAILABLE
NUM COUNT (ES) COUNT (SES) COUNT (CV-L) SECONDS (UAS)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 0 0 0 990
3/5 0 0 0 990
9/1 0 0 0 0
9/2 0 0 0 0
9/3 0 0 0 0
9/4 0 0 0 0
9/5 0 0 0 0
9/6 0 0 0 0
9/7 0 0 0 0
9/8 0 0 0 0
INTERVAL ID = 96
Passport-8610:5/show/ports#
209195-A
Page 99

Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI 99
Table 31 describes the information fields for the show ports stats atm
lineinterval
Table 3 1 Information fields for The show ports stats atm lineinterval command
Field Description
PORT NUM Port number.
ERRORED SECONDS
COUNT (ES)
SEVERELY ERRORED
COUNT (SES)
CODE VIOLATION COUNT
(CV-P)
UNAVAILABLE SECONDS
(UAS)
command.
Errored Second (ES) is a second with one or more Coding
Violations (CV) or one or more incoming defects (for
example, SEF, LOS, AIS, LOP).
Severely Errored Second (SES) is a second with x or more
CVs, or one or more incoming defects.
Coding Violations (CV) are Bit Interleaved Parity (BIP)
errors that are detected in the incoming signal. CV
counters are incremented for each BIP error detected.
Number of seconds that the interface is unavailable.
show ports stats atm pathcurrent
This command displays current statistics (Figure 39) on the path, on the
transmitting end. The command uses the syntax:
show ports stats atm pathcurrent [<ports>]
Using the Passport 8672ATM Module
Page 100

100 Chapter 5 Managing the Passport 8672ATM Module with the CLI
Figure 39 show ports stats atm pathcurrent command output
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/stats/atm# pathcurrent
=========================================================================
ATM Path Current Stats
=========================================================================
PORT ERRED SECS SEVERELY ERRED CODE VIOLATION UNAVAILABLE
NUM COUNT (ES) COUNT (SES) COUNT (CV-P) SECONDS (UAS) STATUS WIDTH
------------------------------------------------------------------------3/1 0 0 0 160 Path AIS 3
3/5 0 0 0 160 Path AIS 3
9/1 0 0 0 0 No Defect 2
9/2 0 0 0 0 No Defect 2
9/3 0 0 0 0 No Defect 2
9/4 0 0 0 0 No Defect 2
9/5 0 0 0 0 No Defect 2
9/6 0 0 0 0 No Defect 2
9/7 0 0 0 0 No Defect 2
9/8 0 0 0 0 No Defect 2
Passport-8610:5/show/ports/stats/atm#
209195-A
Table 32 describes the information fields for the show ports stats atm
pathcurrent
Table 3 2 Information fields for the show ports stats atm pathcurrent command
Field Description
PORT NUM Port number.
ERRED SECS COUNT (ES) Errored Second (ES) is a second with one or more Coding
SEVERELY ERRED
COUNT (SES)
CODE VIOLATION COUNT
(CV-P)
UNAVAILABLE SECONDS
(UAS)
STATUSWIDTH Status and number of defects.
command.
Violations (CV) or one or more incoming defects (for
example, SEF, LOS, AIS, LOP).
Severely Errored Second (SES) is a second with x or more
CVs, or one or more incoming defects.
Coding Violations (CV) are Bit Interleaved Parity (BIP)
errors that are detected in the incoming signal. CV
counters are incremented for each BIP error detected.
Number of seconds that the interface is unavailable.
 Loading...
Loading...