Page 1

Nortel AS 5300
Nortel Application Server 5300
Application Programming
Interfaces Reference
Release: 1.0
Document Revision: 01.01
www.nortel.com
NN42040-110
.
Page 2

Nortel AS 5300
Release: 1.0
Publication: NN42040-110
Document status: Standard
Document release date: 11 June 2008
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
All Rights Reserved.
Sourced in Canada
LEGAL NOTICE
While the information in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable, except as otherwise expressly
agreed to in writing NORTEL PROVIDES THIS DOCUMENT "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OR CONDITION OF
ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. The information and/or products described in this document are
subject to change without notice.
Nortel, the Nortel logo, and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
.
Page 3

.
Contents
New in this release 5
Other changes 5
Introduction 7
Audience 7
Related documents 7
Application Programming Interface fundamentals 9
Open Provisioning Interface fundamentals 9
Bulk Provisioning Tool fundamentals 10
Using the Bulk Provisioning Tool 13
Install and launch the BPT 13
BPT main menu 13
BPT provisioning methods 16
BPT files and scripts 16
BPT conventions and examples 17
BPT Help option 24
BPT limitations 25
3
Why use the Bulk Provisioning Tool 10
Bulk Provisioning Tool requirements 11
Files 16
Scripts 17
Method and file syntax conventions 17
Create and manage provisioning roles using the BPT 21
BPT mapping to the Provisioning Client 25
Batch processing 26
Resource use 26
Provisioning data visibility 27
Using the Open Provisioning Interface 29
Security, authentication, and authorization 29
Security 29
Authentication 30
Authorization 32
Third-party client development 33
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 4

4
Get the WSDL 33
Generate stubs 33
Implement interface accessing stubs 34
Access stubs from the third-party application 34
Starting the Bulk Provisioning Tool 35
Downloading the Bulk Provisioning Tool to a workstation 36
Launching the BPT on a workstation 36
Creating Open Provisioning Interface clients 39
Downloading the Axis toolkit 41
Retrieving the error codes 41
Configuring the class path 41
Downloading the WSDL file 42
Compiling the client stubs 42
Writing a client to perform some specific OPI operations 43
Accessing the OPI Java docs 47
Importing a CA Certificate into the BPT 51
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 5

.
New in this release
This chapter details what’s new in Nortel AS 5300 Application
Programming Interface Reference, NN42040-110 for Nortel Application
Server (AS) 5300 Release 1.0.
This document is new for Nortel AS 5300 Release 1.0.
Other changes
Table 1
Revision history
June 11, 2008 Standard 01.01. This document is new for Nortel AS 5300 Release 1.0.
5
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 6

6 New in this release
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 7

.
Introduction
This document discusses the Nortel Application Server (AS) 5300
Application Programming Interface (API) available to third party clients
for provisioning and administering the AS 5300 system from a remote
workstation.
Attention: Some services/features referred to in this document are not
supported in AS 5300 Release 1.0. For more information about what
services/features are supported in AS 5300 Release 1.0, see Nortel
Application Server 5300 Overview, (NN42040-100).
Navigation
•
"Application Programming Interface fundamentals" (page 9)
•
"Using the Bulk Provisioning Tool" (page 13)
7
•
"Using the Open Provisioning Interface" (page 29)
•
"Starting the Bulk Provisioning Tool" (page 35)
•
"Creating Open Provisioning Interface clients" (page 39)
•
"Accessing the OPI Java docs" (page 47)
•
"Importing a CA Certificate into the BPT" (page 51)
Audience
This document is for programmers and administrators, and assumes that
the reader is familiar with object-oriented programming.
Related documents
The following AS 5300 documents contain related material:
• Personal Agent User Guide, NN42040-105
• Alarm and Log Reference, NN42040-701
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
.
Page 8

8 Introduction
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 9

.
Application Programming Interface
fundamentals
The Application Server (AS) 5300 provides Application Programming
Interface (API) support for third-party client applications. This support
consists of one main API and one tool:
•
Open Provisioning Interface (OPI)
• Bulk Provisioning Tool (BPT)
Open Provisioning Interface (OPI) is an API for third-party client
applications, and is the foundation for the Bulk Provisioning Tool (BPT).
The BPT facilitates the provisioning of the AS 5300 system with large
(bulk) amounts of data. It also retrieves large (bulk) amounts of data from
the AS 5300 system.
Navigation
•
"Open Provisioning Interface fundamentals" (page 9)
9
•
"Bulk Provisioning Tool fundamentals" (page 10)
Open Provisioning Interface fundamentals
The OPI is used to remotely provision the AS 5300 system. OPI is
based on version 1.1 of the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP)
and the emerging Web services standard. SOAP is a cross-platform,
cross-language, text-based protocol, utilizing the benefits of Extensible
Markup Language (XML). SOAP is commonly used as a tool in distributed
applications named Web services. SOAP is not transport dependent,
therefore OPI uses Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) as a transport
protocol.
OPI supports version 1.1 of the industry-standard Web Services
Description Language (WSDL). WSDL is an XML language that contains
information about the interface, semantics, and administration of a call to a
Web service. WSDL enables service providers to provision their AS 5300
system with existing and custom applications. By supporting the WSDL
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
Nortel AS 5300
11 June 2008
.
Page 10

10 Application Programming Interface fundamentals
standard, service providers rapidly develop client-side code with standard
toolsets. A detailed description of the WSDL standard is available online at
the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) web site at w
The goal of OPI is to allow customer-specific applications to interface with
the AS provisioning system. Once developed, the application passes an
object to a generated stub. The stub translates the object into a SOAP
message and passes it along to the skeleton in the Provisioning Manager.
The skeleton translates the SOAP message back to an object, and sends
it to the Provisioning Manager data access processes. The data access
processes the interface with the Oracle Database. The translations happen
in reverse from the database to the customer application.
Bulk Provisioning Tool fundamentals
The Bulk Provisioning Tool (BPT) enables administrators to provision
Application Server (AS) 5300 services from outside the Provisioning Client.
It enables both bulk transactions and individual requests. The BPT is built
on the Open Provisioning Interface (OPI), and accesses all the commands
available through the OPI.
ww.w3.org/TR/wsdl.
Communications between the BPT and the Provisioning server use the
OPI. OPI itself is the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) over HTTP.
Attention: Do not use the BPT for large transactions during regular
business hours. In deployments where the BPT uses the same network
(LAN) as the LAN processing sessions, large BPT transactions may impact
network performance.
Why use the Bulk Provisioning Tool
The BPT is extremely useful for provisioning systems with numerous
subscribers. Some of the scenarios where administrators benefit from
using the BPT are:
• adding a large number of subscribersThe BPT provides bulk imports of
provisioning data from text files. The files can be generated from other
applications.
• exporting provisioning dataThe BPT provides bulk exports of
provisioning data, writing it to files. The files can then be used with
other applications.
• modifying a large number of subscribersThe BPT enables bulk
modifications, such as modifying subscriber service packages when
new features are added.
• extracting information from the database for reporting purposesFor
example, a list of provisioned subscribers can be extracted from the
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 11
database with the BPT and compared against active subscribers listed
in the Internet Protocol Detail Record (IPDR) accounting records. As
another example, a list of gateways can be extracted and imported into
a downstream billing application.
Bulk Provisioning Tool requirements
The following table lists the requirements to run the BPT.
Table 2
Bulk Provisioning Tool requirements
Bulk Provisioning Tool fundamentals 11
Minimum PC or terminal
requirements
For telnet remote access Compatible (tested) telnet terminals:
Java 1.6 + JRE in the system classpath
•
Windows Telnet client
• Putty
•
Hummingbird Telnet
•
KevTerm
Noncompatible telnet terminals:
• CRT
Log on requirement To begin a BPT session, the administrator needs to be, at minimum,
a provisioned general administrator.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 12

12 Application Programming Interface fundamentals
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 13

.
Using the Bulk Provisioning Tool
This chapter contains all of the information you need to use the AS 5300
Bulk Provisioning Tool (BPT).
Navigation
•
"Install and launch the BPT" (page 13)
• "BPT main menu" (page 13)
• "BPT provisioning methods" (page 16)
• "BPT files and scripts" (page 16)
• "BPT conventions and examples" (page 17)
•
"BPT Help option" (page 24)
•
"BPT limitations" (page 25)
Install and launch the BPT
For procedures on downloading, installing, and launching the BPT, see
"Starting the Bulk Provisioning Tool" (page 35).
13
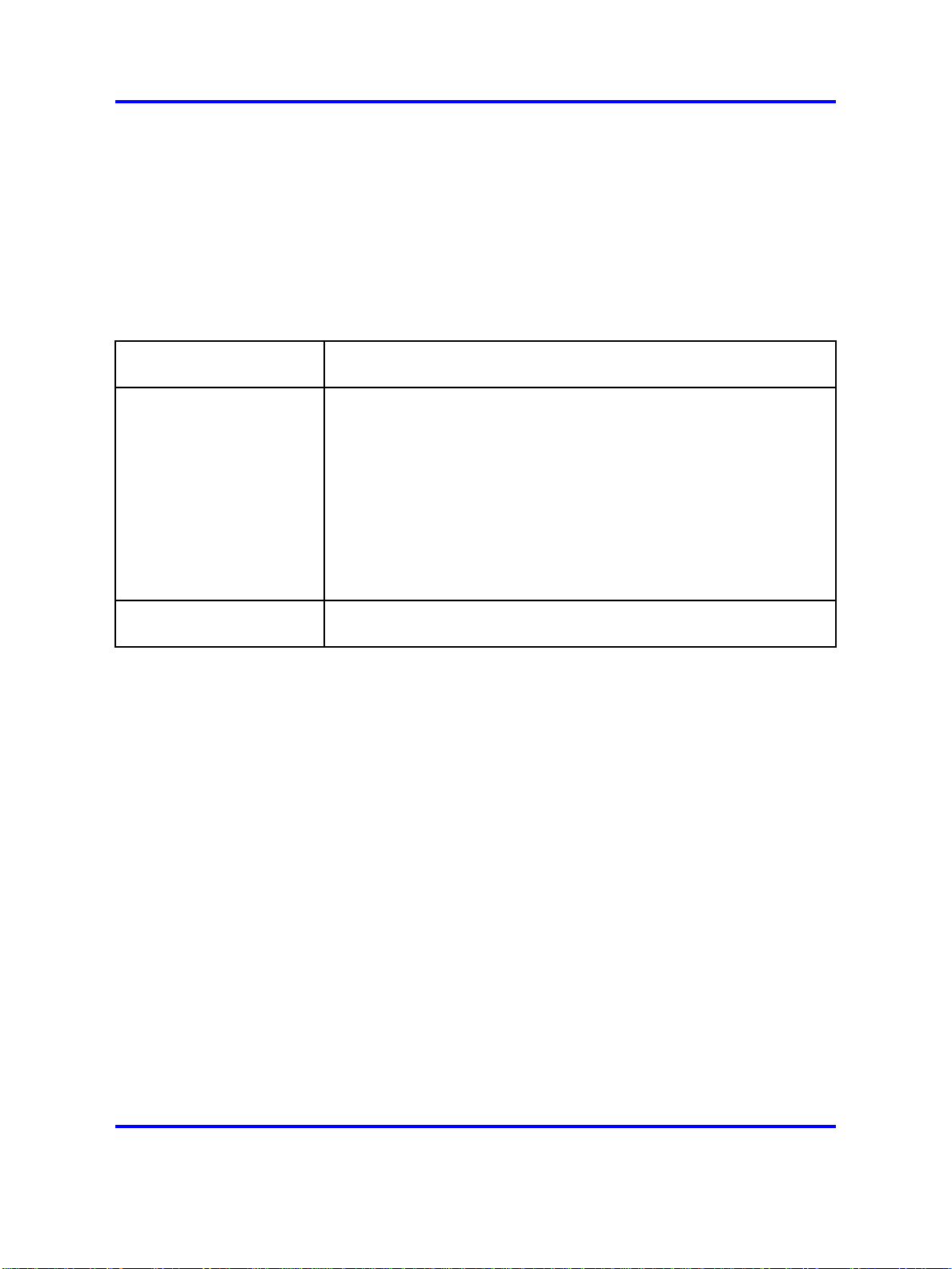
BPT main menu
The BPT main menu lists the various categories of available BPT
provisioning methods.
After successfully logging on to the workstation, the BPT main menu
appears.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
.
Page 14
14 Using the Bulk Provisioning Tool
Figure 1
BPT main menu
An arrow following a menu item indicates a submenu. Choose the
submenu by entering the menu item number at the prompt.
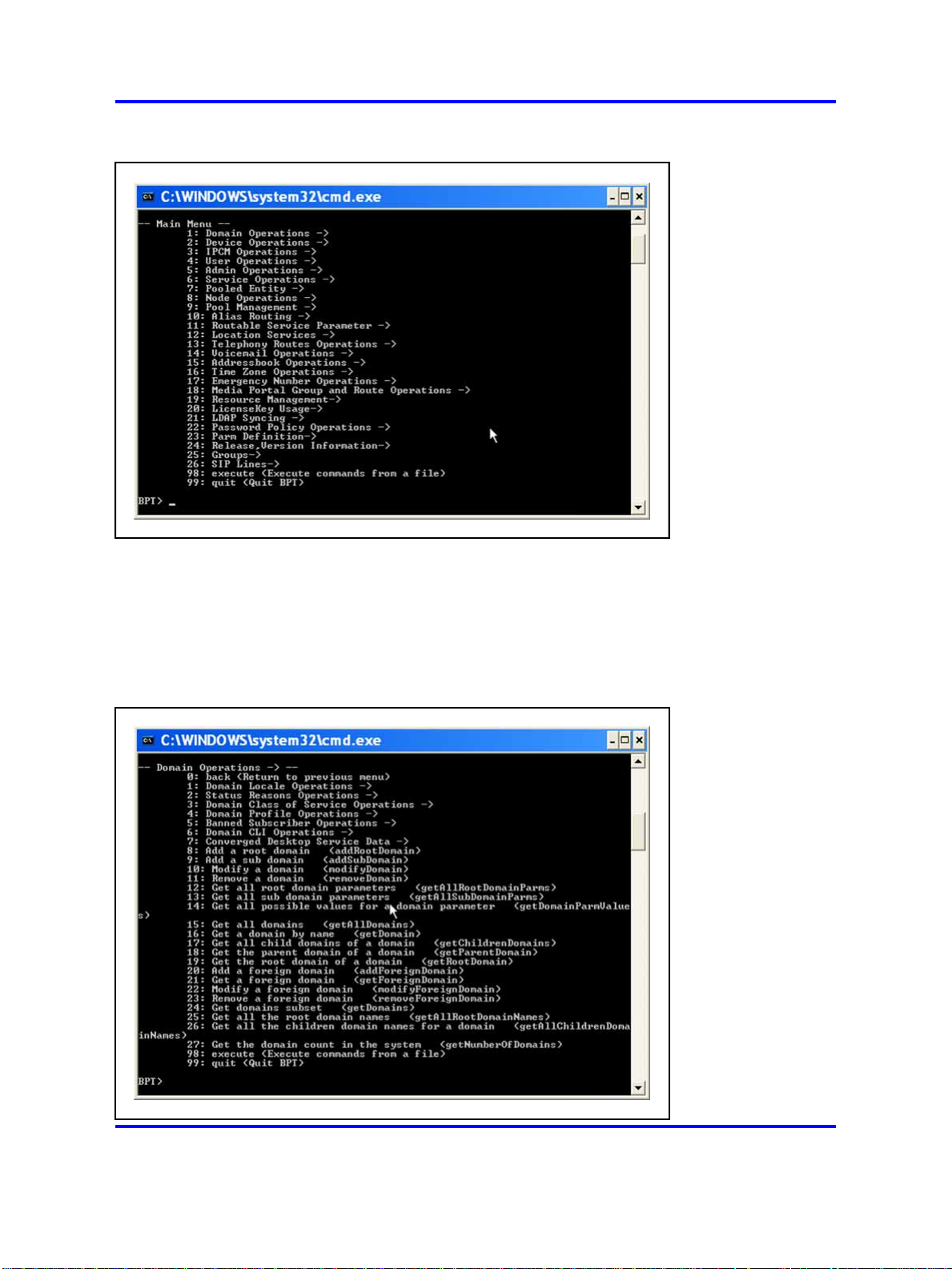
For example, to access the Domain Operations submenu, type 1 and
press Enter. The BPT displays the Domain Operations submenu.
Figure 2
Accessing the Domain Operations submenu
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 15
Entering 0 (zero) returns you to the parent of a submenu.
The provisioning method name appears inside the parentheses that follow
the provisioning method description in the menu. The menu structure is
only for usability. Any provisioning method can be entered at the prompt,
regardless of the menu opened.
For example, if you want to execute the getRootDomain provisioning
method, you do not need to be in the Domain Operations menu.
The following table lists the available BPT main menu commands.
Table 3
BPT main menu commands
BPT main menu 15
Command
0
1-97
98 <file name>
99
quit
help
help <method name>
<method name> using (<parm a>,
<parm b>)
<method name> using file <file
name>
<method name> using * into
<file name>
Description
Return to the previous menu.
Execute the given method or continue to a submenu.
Execute all methods inside the specified file. Each line in
the file must be a method in a valid format.
Exit the BPT.
Exit the BPT.
Display this list of commands.
Display the usage for a given method.
Execute the given method with the required parameters.
The parameter list must be separated by commas
and must adhere to the order presented in the syntax
description. If no parameters are required, this can be left
blank.
Execute the given method with the parameters contained
in the specified file. This command is useful for bulk
additions (for example, users, telephones), allowing the
separation of the definition and execution of the method.
Execute the given method (using either command line
options or parameters from a file) and insert the returned
value into the specified file. This is useful when exporting
bulk data, such as 1000 users, and you want to save the
output.
For information about BPT command syntax conventions and examples, see "BPT
conventions and examples" (page 17).
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
Nortel AS 5300
11 June 2008
.
Page 16
16 Using the Bulk Provisioning Tool
Table 3
BPT main menu commands (cont’d.)
Command
execute <file name>
execute <file name> into <file
name>
For information about BPT command syntax conventions and examples, see "BPT
conventions and examples" (page 17).
Description
Execute all the methods contained in the specified file.
Each line in the file must be a method in the valid format.
Execute all the methods contained in the specified file and
writes the output to a second file instead of writing the
output to the screen. Each line in the input file must be a
method in the valid format.
BPT provisioning methods
The BPT provisioning methods are the same as the Open Provisioning
Interface (OPI) provisioning methods. OPI provisioning methods are a
collection of Web services that you use to provision subscribers, and
service data for the subscribers. The detailed documentation for each
of the OPI Web services is available in a zip file (OPIJavaDocs.zip)
included on the AS 5300 Documentation CD.
To access the OPI Web services documentation, see "Accessing the OPI
Java docs" (page 47).
BPT files and scripts
Files and scripts are important when performing bulk provisioning
transactions. Files enable the import and export of many database entries.
Scripts enable administrators to execute multiple BPT provisioning
methods in one step.
This section describes the role of files and scripts in the Bulk Provisioning
Tool.
Navigation
• "Files" (page 16)
• "Scripts" (page 17)
Files
Most of the BPT provisioning methods have the option of using text files.
Provisioning data can be imported from a file and put into the database, or
exported from the database and written to text files.
Text file (*.txt) contents use the comma separated value (CSV) format. By
using this format, files can be generated by, or imported into, third-party
applications that recognize the CSV file content.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 17

Files must use a specific syntax for a BPT provisioning method to be
invoked successfully on the Provisioning Server. You can view the
required file syntax by using the BPT Help option ("BPT Help option" (page
24)).
Scripts
A script is basically a text file, where each line of the file consists of a
single provisioning method. When executed, each provisioning method
in the script is invoked sequentially and can reference a separate file for
importing or exporting data. Each provisioning method and its referenced
file must use the correct syntax for the script to be executed successfully.
An exclamation mark (!) is used at the start of a line to add a comment line
in the script file (for example: ! - script updated 2008.04.01)
BPT conventions and examples
This section describes the command syntax and usage conventions for
Bulk Provisioning Tool (BPT) provisioning methods and an example of a
provisioning method.
BPT conventions and examples 17
Navigation
• "Method and file syntax conventions" (page 17)
•
"Create and manage provisioning roles using the BPT" (page 21)
Method and file syntax conventions
This section describes the command syntax that must be used for
executing BPT provisioning methods from the BPT command line and
BPT input files.
Navigation
• "Optional syntax" (page 18)
•
"Brackets" (page 18)
•
"Angle brackets" (page 18)
• "Square brackets" (page 19)
• "Bar" (page 19)
• "Comma separated strings" (page 20)
• "Fully qualified user name" (page 20)
• "Success indication on remove methods" (page 20)
• "Unknown error messages" (page 21)
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 18

18 Using the Bulk Provisioning Tool
Optional syntax
In BPT provisioning method syntax, the word [optional] indicates that what
follows is optional and is not needed to invoke the method. Typically,
the option is the writing of the returned values to a text file. You do not
include [optional] when entering the syntax. For example, the following is
the complete syntax for the getSysRoles method:
getSysRoles [optional] into <file name>
To write the returned information to the screen, you use the syntax:
getSysRoles. To write the returned information to a file named
roles.txt, you use the syntax: getSysRoles into roles.txt. The
system creates the file with the name entered in the BPT command line.
When a get* command is not limited to a specific instance (for example,
getSysRoles or getAllRights), you cannot use the shortcut number
(BPT main menu option) when writing to a file. You must enter the BPT
provisioning method syntax on the BPT command line. If you use the
shortcut number, the returned information is written to the screen by
default.
Brackets
Brackets () are required around the parameters when shown in the BPT
provisioning method syntax. For example, the following is the syntax for
the getRole provisioning method:
getRole using (Role name) | file <file name> [optional] into
<file name>
With this provisioning method, brackets are required around the
provisioning Role name. For example, to retrieve the definition for the
configured SuperUser role, you use the following syntax: getRole
using (SuperUser).
Angle brackets
Angle brackets (<>) in the syntax indicate a variable. You replace the
variable name and angle brackets with the specific variable when you
invoke the provisioning method. For example, the following is the syntax
for the getSysRoles provisioning method:
getSysRoles [optional] into <file name>
With this provisioning method, the angle brackets indicate that file name
is a variable, replaced when using the provisioning method. For example,
if you want to write the returned values to a file name called roles.txt,
you use the syntax: getSysRoles into roles.txt.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 19

BPT conventions and examples 19
Square brackets
Square brackets ([ ]) in the syntax indicate a string of variables, separated
by commas. The square brackets must be included when shown in the
BPT provisioning method syntax. For example, the following is the syntax
for the addRole provisioning method:
addRole using ([Name of the Provisioning Role,Description
of the Role,[[The Provisioning Right Type,The Read
privilege,The write privilege,The delete privilege], ..
,[The Provisioning Right Type,The Read privilege,The write
privilege,The delete privilege]]]) | file <file name>
[optional] into <file name>
With this provisioning method, the square brackets separate fields
of the role description being added. For example, if you are adding
a role called AddExample, the syntax looks like: addRole using
([AddExample,BPT add example,[[Domain Management,
true,true,false],[Device Management,true,false,
false],[Admin,true,true,true]]]).
Bar
A bar (|) in the syntax means that there are two ways of entering the
required provisioning method information. Typically, the bar is used for the
data entry option—entering the data in the command line or using data in a
file. For example, the following is the syntax for the getRole provisioning
method:
getRole using (Role name) | file <file name> [optional] into
<file name>
With this provisioning method, you can enter the Role name in the BPT
command line, or enter it using a file. For example, the following is the
syntax for invoking the provisioning method on the BPT command line for
the Superuser role: getRole using (SuperUser).
Optionally, you can invoke the provisioning method using the Role name
listed in a file. For example, the following is the syntax to invoke the
provisioning method using a file (containing the Superuser role) called
SuperUser_role.txt: getRole using file SuperUser_role.txt.
The contents of the file must be in the correct format. Use the help
command to display the BPT required file format. Note in the above
example, that the role name in the file is not enclosed in brackets as it is if
this method is invoked from the BPT command line.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 20

20 Using the Bulk Provisioning Tool
Comma separated strings
Provisioning method syntax can include a string of comma-separated
variables. For example, the following is the syntax for the addAdmin
provisioning method:
addAdmin using ([The Admin user name,Password,Admin
First Name,Admin Last Name,Admin Status,Admin Email
Address,Office Phone Number,Home Phone Number,Cell Phone
Number,Pager Number,Fax Number,Voicemail Number,VPN
Number,System defined role,Time Zone,Locale,Provisioning
Role,[The list of Domains that he is assigned to, .. ,The
list of Domains that he is assigned to]]) | file <file name>
[optional] into <file name>
Follow the required format when invoking the provisioning method
from the BPT command line or using a file. If nothing appears
between two commas, the associated field in the database is
not updated. For example, the following addAdmin provisioning
method contains minimal administrator information, but still
requires the commas to denote the blank fields: addAdmin using
([newguy,mysecret,John,Edwards,Active,,,, ,,,,,Default
Admin,,English,Devices only,[yourcompany.com]]).
Fully qualified user name
Some methods require a fully qualified user name—a user name that is
complete with the domain name (for example, joe@mydomain.com). This
information is available in the Provisioning Client field descriptions.
Success indication on remove methods
Some BPT provisioning methods can remove data, and return an
indication of success even if the data did not preexist in the database. This
mirrors the functionality of the database. A success indication for a remove
provisioning method, indicates that the associated data no longer exists
in the database.
When possible, BPT provisioning methods provide additional indication (in
the form of an error message) regarding specific data elements (domain
and devices) that are not preexisting in the database when the remove
method is invoked. These messages appear on the BPT screen.
For example, if the domain nn.com does not exist, an invocation of
removeUser using (jimbob@nn.com) returns an error indication of
Invalid Data: Domain Not found ’nn.com’, because the domain
is not valid.
If the domain is valid and the user is not preexisting, then a success
indication is returned, because the user is not configured on the system.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 21

BPT conventions and examples 21
Unknown error messages
If an unknown error occurs when invoking a method, the BPT prompts
the administrator to check the logs for more information. The logs are not
accessible to the BPT user. If you see this error message and cannot
proceed with the BPT provisioning task, contact your next level of support.
Create and manage provisioning roles using the BPT
This section describes how to create and manage a provisioning role using
the Bulk Provisioning Tool (BPT).
Navigation
•
"Define the new provisioning role" (page 21)
• "Add the new provisioning role" (page 22)
• "View the new provisioning role" (page 22)
• "Delete the new provisioning role" (page 23)
Define the new provisioning role
Use the following provisioning method to add a new provisioning role using
the BPT file method:
addRole using ([Name of the Provisioning Role,Description
of the Role,[[The Provisioning Right Type,The Read
privilege,The write privilege,The delete privilege], ..
,[The Provisioning Right Type,The Read privilege,The write
privilege,The delete privilege]]]) | file <file name>
[optional] into <file name>
Assume that you are adding a new role with the following properties:
Table 4
Role properties
Role name: ExampleRole
Role Description: BPT Add example
Domain Management privileges: R, W
Device Management privileges: R
Admin privileges: R,W,D
Enter the provisioning role properties outlined in the previous
table into a file named addexample.txt located in a local
directory (D:\prov) of your work station. The contents of the file
(on one line in the file) are as follows: [AddExample,BPT add
example,[[Domain Management,true,true,false],[Device
Management,true,false,false],[Admin,true,true,true]]].
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 22

22 Using the Bulk Provisioning Tool
Add the new provisioning role
To add the new role, enter the following in the BPT command line:
addRole using file D:\prov\addexample.txt
The BPT indicates whether the provisioning method succeeded or failed,
as shown in the following figure.
Figure 3
BPT showing a successful add
View the new provisioning role
To view the new provisioning role in the BPT, use the getRole
provisioning method with the following syntax:
getRole using (AddExample)
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 23

Figure 4
getRole method invoked in the BPT
The BPT returns the following information:
BPT conventions and examples 23
[AddExample,BPT add example,[[Domain Management,true,true
,false],[Device Management,true,false,false],[Admin,tr
ue,true,true]]]
The information is identical to the file contents used to create the new role
(see "Define the new provisioning role" (page 21)).
Delete the new provisioning role
To delete the new role, use the provisioning method removeRole with
the following syntax:
removeRole using (AddExample)
The BPT indicates whether the provisioning method succeeded or failed,
as shown in the following figure.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 24

24 Using the Bulk Provisioning Tool
Figure 5
removeRole method invoked on the BPT
BPT Help option
BPT provisioning methods are identical to OPI provisioning methods. The
BPT Help option enables you to view the required syntax for a BPT (OPI)
provisioning method and its associated text file.
For example, to view the help on the addRole provisioning method, enter:
help addRole
or, if using the BPT Main menu number shortcut, enter: help 1
The BPT displays the BPT (OPI) provisioning method syntax, followed by
the required file syntax, as shown in the following figure.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 25

Figure 6
Invoking a help command in the BPT
BPT limitations 25
Attention: The BPT Help function only contains the syntax of the BPT
(OPI) provisioning methods and associated file contents. For more
information about the parameters available for each OPI provisioning
method, see AS 5300 Provisioning Client Help, NN42040-502.
BPT limitations
The following sections describe certain limitations that you must be aware
of when using the Bulk Provisioning Tool.
Navigation
• "BPT mapping to the Provisioning Client" (page 25)
• "Batch processing" (page 26)
•
• "Provisioning data visibility" (page 27)
BPT mapping to the Provisioning Client
There is not a one-to-one mapping between BPT provisioning methods
and Provisioning Client screens. Most, but not all, individual BPT
provisioning methods map to a provisioning screen in the Provisioning
Client.
"Resource use" (page 26)
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 26

26 Using the Bulk Provisioning Tool
In most cases, variables and properties used by the BPT provisioning
methods map to fields in the Provisioning Client. For Provisioning Client
field descriptions, see AS 5300 Provisioning Client Help, NN42040-502.
For example, the addRole provisioning method maps to the Add a New
Role window of the Provisioning Client (Admins > Add Roles).
Batch processing
A maximum of 1000 entries are processed together at a time. All bulk
processing is on an all-or-none basis.
For example, you can do a bulk add of 3000 subscribers to the system
from a file. Each subscriber is one line in the file. The BPT processes the
information in three blocks of 1000 lines each. If an error occurs during
processing of a block, such as a user name already in use, the BPT will
not process any lines in that block.
Resource use
The BPT processes the provisioning information before uploading it
to the database. During the processing, the BPT uses all available
CPU resources, whether the processing is performed on a server or a
workstation. CPU usage declines as the provisioning data is uploaded to
the database.
When performing bulk provisioning using files with a large number of
entries, use a BPT residing on a workstation. Performing the task on
a server can affect the performance of in-progress sessions using the
component services running on the server.
Nortel recommends using the BPT during off-peak times or maintenance
windows when large amounts of information are being added.
Bulk provisioning of users
Bulk provisioning of users (through BPT or an OPI client) puts a large
load on the database in the AS 5300 system. Therefore, bulk provisioning
must be throttled to prevent the database from becoming overloaded
while handling the BPT "add user" requests. The BPT or OPI client must
implement the following required sleep/wait times between "add user"
requests when adding users in bulk:
• For a system running at 80 percent call capacity, add 500 users at
a time. Sleep/wait at least 300 seconds before adding the next 500
users. This rate is approximately 6000 users added an hour.
• For a system running at 20 percent call capacity, add 500 users at
a time. Sleep/wait at least 225 seconds before adding the next 500
users. This rate is approximately 8000 users added an hour.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 27

Provisioning data visibility
Provisioning data added using the BPT is immediately available to other
provisioning clients connected to the same instance of the Provisioning
Manager. However, it can take up to five minutes before the same data
is visible to clients connected to a second instance of a Provisioning
Manager running in the system.
BPT limitations 27
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 28

28 Using the Bulk Provisioning Tool
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 29

.
Using the Open Provisioning Interface
This chapter contains all of the information you need to use the Open
Provisioning Interface.
Navigation
•
"Security, authentication, and authorization" (page 29)
•
"Third-party client development" (page 33)
Security, authentication, and authorization
The following sections describe the security, authentication, and
authorization considerations for using the Open Provisioning Interface.
Navigation
•
"Security" (page 29)
•
"Authentication" (page 30)
29
•
"Authorization" (page 32)
Security
OPI supports security through the use of:
opicert.cer—Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificate file
•
• opitruststore—key store file
These files are required when you connect to the Provisioning Server
through HTTP Secure (HTTPS). You use the following command line
parameters:
Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=opitruststore
-Djavx.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=opitruststore
When you have a Certificate Authority (CA) Certificate, you must import it
into the key store file (opitruststore). For instructions, see "Importing a
CA Certificate into the BPT" (page 51).
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
.
Page 30

30 Using the Open Provisioning Interface
Authentication
The Provisioning Server authenticates each request to ensure that the
request is received from a valid client application. The client application
needs to provide a user identity (user name) and authentication
information (password) in the HTTP/SOAP request.
The supported authentication mechanisms are HTTP Basic Authentication
– Onboard Authentication and WS-Security UsernameToken.
Navigation
•
"HTTP Basic Authentication – Onboard Authentication" (page 30)
• "WS-Security UsernameToken" (page 30)
HTTP Basic Authentication – Onboard Authentication
The username and password of the user are configured in the HTTP
Headers. The following figure shows a sample HTTP header/SOAP
message with the required information.
Figure 7
Sample HTTP header/SOAP message
WS-Security UsernameToken
The user’s username and password are configured in the WS Security
Headers. A sample WS-Security header/SOAP message with the required
information is shown in the following figure.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 31

Figure 8
Sample WS-Security header/SOAP message
A special note for .NET authentication headers
Security, authentication, and authorization 31
The authentication headers for AXIS toolkit-generated stubs are set on the
client stub as described in the preceding example. In that scenario, the
client stub is cast down to a org.apache.axis.client.Stub object. In the case
of a .NET client, this must be done differently. The AS 5300 OPI currently
supports HTTP and HTTPS authentication and the authentication headers
must be set to Base64 encoded authentication on the client side.
The sample code in the following figure shows how to set the
authentication headers for a .NET client. The code must be added in the
stub class so that it may hijack the request and add the headers to it.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 32

32 Using the Open Provisioning Interface
Figure 9
Setting authentication headers
Authorization
After the OPI request is authenticated, you must be authorized before
performing the action. The authorization includes both domain-level
authorization and provisioning-level authorization. If either authorization
fails, a SOAP fault is sent back, indicating the reason for failure, and the
action is not performed.
Navigation
• "Domain-level authorization" (page 32)
• "Provisioning-level authorization" (page 32)
Domain-level authorization
Each administrator is assigned one or more domains for access and
control, which can be overridden by the All domain access in role
creation. For instance, the AS 5300 system might consist of three
separate domains, Widget.com, Gadget.com, and Sprocket.com. An
administrator, WidgetAdmin, can be created with only Widget.com in the
list of provisionable domains. This limits WidgetAdmin to provisioning
activities inside the Widget.com domain only, and does not permit access
to the other domains. Therefore, if a request from WidgetAdmin comes in
to modify a user outside of the Widget.com domain, it is rejected because
it failed authorization. In addition, attempts to list domain information can
only return Widget.com information.
Provisioning-level authorization
The Provisioning Manager of the AS 5300 system is broken into various
major categories (Domains, Users, Telephony Routes, and so on). The
provisioning system enables the creation of various administrator roles
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 33

across these categories. Upon creation, the administrator is assigned
to a particular role. This enables the service provider to create various
administrator roles to suit specific needs. In each category, the role can
have any combination of the following rights: Read, Write, and Delete. For
example, a user admin role can be created which gives the ability to read
domain information, and to read, modify, and delete user information. The
administrators given this role cannot manipulate the telephony routes, or
other areas of the AS 5300 system. OPI authorizes each request to verify
that the incoming credentials have the appropriate role to perform the
given action.
Third-party client development
This section describes the steps necessary to develop third-party
Provisioning clients.
OPI provides customer-specific applications with an interface into the
AS 5300 provisioning system. The customer application passes an object
to a generated stub. The stub translates the object into a SOAP message
and passes it to the skeleton in the Provisioning Manager. The skeleton
translates the SOAP message back to an object, and sends it to the
Provisioning Manager data access processes. The data access processes
communicate with the Oracle Database. The translations happen in
reverse from the Provisioning Manager to the customer application.
Third-party client development 33
Navigation
• "Get the WSDL" (page 33)
•
"Generate stubs" (page 33)
•
"Implement interface accessing stubs" (page 34)
•
"Access stubs from the third-party application" (page 34)
Get the WSDL
The WSDL file for AS 5300 is stored on the System Manager server.
Retrieve the file from the loads directory on the System Manager server,
located at /var/mcp/loads/<loadname>/clientAPI/wsdl/opi/*
.wsdl.
Generate stubs
The stub is a translator. It takes the OPI object, converts it to a SOAP
message and sends it to the Provisioning Manager. Likewise, a SOAP
message from the Provisioning Manager is translated back to an OPI
object. HTTP and HTTPS are used as the transport for OPI. The
Provisioning Module listens on port 8080 for the SOAP over HTTP
messages, and port 8443 for the SOAP over HTTPS messages.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 34

34 Using the Open Provisioning Interface
Figure 10
Interactions of the stub
You generate stubs using a supported toolset. Currently, only the
1.3 Final version of the Apache Axis (Apache Extensible Interaction
System w
s.apache.org/axis) toolsets are tested and approved. Axis is
Java-specific and creates a Java stub. The OPI WSDL may work with
other toolsets, but thorough testing has not been completed.
For instructions to download the Axis toolset, see "Downloading the Axis
toolkit" (page 41).
Implement interface accessing stubs
An interface must be developed to access the stubs. The interface must
support authentication on each OPI request.
If the credentials are not present or validation fails, a SOAP fault is sent
back to indicate the failure and the action is not performed.
Access stubs from the third-party application
When the interface accesses or invokes the stubs, the stub generates a
SOAP message that is sent to the Provisioning Manager on port 8443
or 8080. The stub is basically a translator. It takes the "user" object
(whatever type of object) from the interface, converts it to a SOAP
message, and sends it to the Provisioning Manager. The skeleton on the
server with the Provisioning Manager does the reverse, takes the SOAP
message, translates it back to a user object (whatever type of object), and
sends it to the Provisioning Manager data store, which stores it in the
database.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 35

.
Starting the Bulk Provisioning Tool
This chapter contains the procedures necessary to start the Bulk
Provisioning Tool (BPT) on a remote workstation. This facilitates the use
of files and scripts without affecting the performance of the server hosting
the Provisioning Manager.
Starting the Bulk Provisioning Tool
35
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 36

36 Starting the Bulk Provisioning Tool
Navigation
•
"Downloading the Bulk Provisioning Tool to a workstation" (page 36)
• "Launching the BPT on a workstation" (page 36)
Downloading the Bulk Provisioning Tool to a workstation
Use this procedure to download the BPT to a workstation.
Procedure Steps
Step Action
1
2 Open the System folder.
3 Click Tools.
Figure 11
BPT download window
4 Follow the instructions in the BPT download window to install the
Log on to the Provisioning Client.
The BPT download window appears.
required files onto the local workstation.
Launching the BPT on a workstation
Use this procedure to launch the BPT on a remote workstation.
Procedure Steps
Step Action
1 Execute the bpt.bat (Windows) or bpt.sh (Solaris) script.
Nortel AS 5300
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
--End--
Page 37

Launching the BPT on a workstation 37
The BPT application launches.
2
Enter your administrator username and password.
The Bulk Provisioning Tool main menu appears. See Figure 1
"BPT main menu" (page 14) .
--End--
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 38

38 Starting the Bulk Provisioning Tool
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 39

.
Creating Open Provisioning Interface
clients
This chapter describes the steps necessary to create Open Provisioning
Interface (OPI) clients and provides an example of how to write a client to
perform specific OPI provisioning methods.
Prerequisites for creating OPI clients
You must:
• have a working knowledge of Java application development.
•
be comfortable using DOS commands.
• have the Java Developer Kit (JDK) 1.6.
•
have the Java executable available in the system path.
•
have the AXIS toolkit version 1.3 Final.
39
Attention: Toolkits other than the Axis toolkit can be used to develop
OPI clients using the WSDL file.
Creating OPI clients
The following task flow shows the processes involved in creating OPI
clients.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
.
Page 40

40 Creating Open Provisioning Interface clients
Figure 12
Task flow for creating OPI clients
Navigation
•
"Downloading the Axis toolkit" (page 41)
• "Retrieving the error codes" (page 41)
• "Configuring the class path" (page 41)
• "Downloading the WSDL file" (page 42)
• "Compiling the client stubs" (page 42)
• "Writing a client to perform some specific OPI operations" (page 43)
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 41

Downloading the Axis toolkit
Use this procedure to download the AXIS toolkit version 1.3 Final. The
Axis 1.3 Final toolkit is a free download from the Apache Web site.
Procedure Steps
Step Action
1 Navigate to the AXIS toolkit page on the Apache web site.
h
ttp://ws.apache.org/axis
Nortel recommends version 1.4 Final (Latest).
Configuring the class path 41
2
Download the 1.3 Final version zip file (axis-bin-1_4.zip)to
a drive on your PC.
3 Unzip the axis-bin-1_4.zip zip file to a folder on your PC..
For example, use D:\axis-1_4
Retrieving the error codes
Use this procedure to retrieve error codes.
Procedure Steps
Step Action
1
2
3
Open Axis Fault file.
Get FaultDetails from the AxisFault.
Get the value for the child element with the name
mcperrorcode.
--End--
--End--
Configuring the class path
Use this procedure to set up the classpath for jar files. The classpath
needs to be set for specific jar files that are part of the Axis toolkit.
Procedure Steps
Step Action
1 In the DOS window, open a command prompt.
2 Set the classpath for all the jar files found in the directory
D:\axis-1_4\webapps\axis\WEB-INF\lib.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
11 June 2008
Page 42

42 Creating Open Provisioning Interface clients
set CLASSPATH= D:\axis-1_4\webapps\axis\WEB-INF\
lib\axis.jar;D:\axis-1_4\webapps\axis\WEB-INF\l
ib\axis-ant.jar;D:\axis-1_4\webapps\axis\WEB-IN
F\lib\commons-discovery-0.2.jar;D:\axis-1_4\web
apps\axis\WEB-INF\lib\commons-logging-1.0.4.jar
;D:\axis-1_4\webapps\axis\WEB-INF\lib\jaxrpc.ja
r;D:\axis-1_4\webapps\axis\WEB-INF\lib\log4j-1.
2.8.jar;D:\axis-1_4\webapps\axis\WEB-INF\lib\sa
aj.jar;D:\axis-1_4\webapps\axis\WEB-INF\lib\wsd
l4j-1.5.1.jar
3
Create a folder for the generated client stubs (for example,
D:\opiclient).
Downloading the WSDL file
Use the following procedure to download the WSDL file. The WSDL file for
the AS 5300 is stored on the System Manager server.
Procedure Steps
Step Action
1
Retrieve the WSDL file from the loads directory on the System
Manager server.
<loadname>/wsdl/opi
Compiling the client stubs
Use the following procedure to compile the client stubs.
--End--
--End--
Procedure Steps
Step Action
1 Open a command prompt and navigate to the directory
2
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
containing the downloaded WSDL file.
For example: D:\opiclient.
Run the WSDL2JAVA tool on the WSDL file.
For example:
java org.apache.axis.wsdl.WSDL2Java -O -1 -d Session
-Nurn:OPI com.client.opi.service opi.wsdl
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 43

Writing a client to perform some specific OPI operations 43
This creates the client stubs under D:\opiclient\com\clien
t\opi\service
The stubs contain all the provisioning methods that are exposed
by the OPI web service, and the same methods that can be seen
in the WSDL.
The arguments provided to these provisioning methods are
generated in the directory D:\opiclient\com\nortelnet
works\ims\opi.
All the OPI provisioning methods are Java Bean objects and are
used to configure and retrieve data for different functionality.
Each element in the data object is of a type specified in the OPI.
The name space mapping from OPI to com.client.opi.serv
ice can be changed to another mapping.
Attention: The OPISoapBindingStub.java file, generated
under com\client\opi\service, has a large static block
that will not compile. You must edit this file by hand to split
the large static block into two or three smaller ones so that it
compiles. This is a known issue due to the fact that the code is
automatically generated.
3
Compile the files that are generated in the previous step using
either the command line command javac or an Interactive
Development Environment (IDE) such as netbeans or
eclipse, and save them in a separate folder.
The Client classes are now ready to be used.
--End--
Writing a client to perform some specific OPI operations
Use this procedure to write a client to perform some specific OPI
operations.
Once the OPI stubs have been generated and compiled, the real OPI
client can be constructed and OPI provisioning method calls can be made
using the following procedure.
Procedure Steps
Step Action
1 Instantiate the OPIServiceLocator.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 44

44 Creating Open Provisioning Interface clients
2
Instantiate a URL object that will point to the Provisioning Server
location and the OPI web service running on it.
3
Invoke the getOPI call on the OPIServiceLocator instance
with the URL.
This action will result in an instance of the OPI object, which can
be used to make OPI provisioning method calls.
4
Set the authentication information on the OPI object.
Perform this action by downcasting the OPI object as a
org.apache.axis.client.Stub object.
5
Set the OPI Client Version number in a SOAP Header.
This is used by the Provisioning Server to determine the version
of the provisioning client and return data that the Provisioning
Client can understand.
6 Make the OPI provisioning method call (for example, getUser)
by invoking the same on the OPI instance.
The arguments to this provisioning method are the data objects
generated during the stub generation process. For example, for
the addUser method, pass in the domainName and the User
object, which is populated with the user data.
--End--
Example - Writing a client
The following figure shows an example of writing a client. In the example,
the class is placed under D:\opiclient.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 45

Writing a client to perform some specific OPI operations 45
The client class can be compiled similarly to the compilation of the OPI
Stubs, and executed. The OPI Stub classes and AXIS toolkit jars must be
present in the classpath during execution, as demonstrated in the following
figure.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 46

46 Creating Open Provisioning Interface clients
Figure 13
Compiling the client class
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 47

.
Accessing the OPI Java docs
This procedure describes how to access the Open Provisioning Interface
(OPI) Java docs. These Java docs represent the various categories of
OPI web services available. Each OPI web service category contains a
description of the OPI web service in general, and descriptions of each
associated provisioning operation (OPI provisioning method) and bean
objects.
WSVersionOPI is a special OPI web service that provides the current
Web Services Description Language (WSDL) version. Each OPI web
service has an associated WSDL version. You must configure the
appropriate WSDL version in the SOAP header for every OPI web service
you request.
Procedure Steps
Step Action
47
1
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
Unzip the OPIJavaDocs.zip file on your AS 5300
Documentation CD to your local drive.
The unzip operation creates a folder named OPI Java Docs
containing a sub-folder for every category of OPI web service
available. Each sub-folder is named the same as the OPI web
service category it represents.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
.
Page 48

48 Accessing the OPI Java docs
Figure 14
OPIJavadocs file unzipped
2 Click on the subfolder for the OPI web service category you wish
to query or use.
For example, if you wish to query or use the AdminAuthe
ntication OPI web service, navigate to and click on the
AdminAuthentication subfolder in the OPI Java Docs
folder.
A list of sub-folders and files related to the AdminAuthentica
tion OPI web service opens.
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 49

Writing a client to perform some specific OPI operations 49
Figure 15
Accessing the javadocs for the AdminAuthentication OPI web
service
3 Double-click on the index.html file in the AdminAuthentica
tion OPI Web service folder.
The javadoc for the AdminAuthentication OPI Web service
opens in the browser.
You can go through the various links available in the javadoc to
get a description of the AdminAuthentication Web service,
the associated OPI provisioning methods, and the bean objects.
--End--
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 50

50 Accessing the OPI Java docs
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 51

.
Importing a CA Certificate into the BPT
Use this procedure to import a Certificate Authority (CA) certificate into
the opitruststore.
Procedure Steps
Step Action
1 Copy the NorlockPKI.cer certificate file to the D:\temp
folder.
51
2
3 Enter the following command (on one line):
Open a command prompt in the DOS window.
keytool -import -alias NorlockPKI -file
D:\temp\NorlockPKI.cer -keystore opitruststore
The tool presents details about the certificate and gives the
fingerprint of the certificate for validation.
The tool prompts: Trust this certificate? [no]:
4 If the certificate is correct, enter: yes
OR
If the certificate is not correct, enter:
nO
5 To verify that the certificate is now in the BPT trust store, enter
the following command (on one line):
keytool -list -v -keystore opitruststore
The tool displays the contents of the BPT trust store.
--End--
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 52

52 Importing a CA Certificate into the BPT
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
.
Nortel AS 5300
NN42040-110 01.01 Standard
11 June 2008
Page 53

Page 54

Nortel AS 5300
Nortel Application Server 5300 Application Programming
Interfaces Reference
Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks
All Rights Reserved.
Release: 1.0
Publication: NN42040-110
Document status: Standard
Document revision: 01.01
Document release date: 11 June 2008
To provide feedback or to report a problem in this document, go to www.nortel.com/documentfeedback.
www.nortel.com
Sourced in Canada
LEGAL NOTICE
While the information in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable, except as otherwise expressly agreed to in writing
NORTEL PROVIDES THIS DOCUMENT "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OR CONDITION OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS
OR IMPLIED. The information and/or products described in this document are subject to change without notice.
Nortel, the Nortel logo, and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
.
 Loading...
Loading...