
After Sales Technical Documentation
Appendix 2 – Transceiver THF–9P
Chapter 1
TRANSCEIVER
Original, 01/97

THF–9P
After Sales
Transceiver
CONTENTS
Introduction 2 – 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functional Description 2 – 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Block Diagram 2 – 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modules 2 – 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electrical Specifications 2 – 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transceiver General Specifications 2 – 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter Branch 2 – 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver Branch 2 – 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RX Synthesizer 2 – 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TX Synthesizer 2 – 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Exploded View of THF–9 2 – 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Assembly Parts of THF–9 2 – 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parts List of GP3P EDMS issue 1.3 2 – 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Technical Documentation
Page 1 – 2
Original, 01/97
After Sales
THF–9P
Technical Documentation
Introduction
Functional Description
The transceiver electronics consist of UI module PCB and RF/system PCB.
UI module is connected to system module with a connector. System and rf
submodules are interconnected with PCB wiring. Unit can be connected to
accessories with a bottom system connector, which includes charging and
accessory control.
RF block is designed for a hand portable phone, which operates in NMT450
systems. Purpose of the RF module is to receive and demodulate radio frequency signal from the base station and to transmit a modulated RF signal
to the base station.
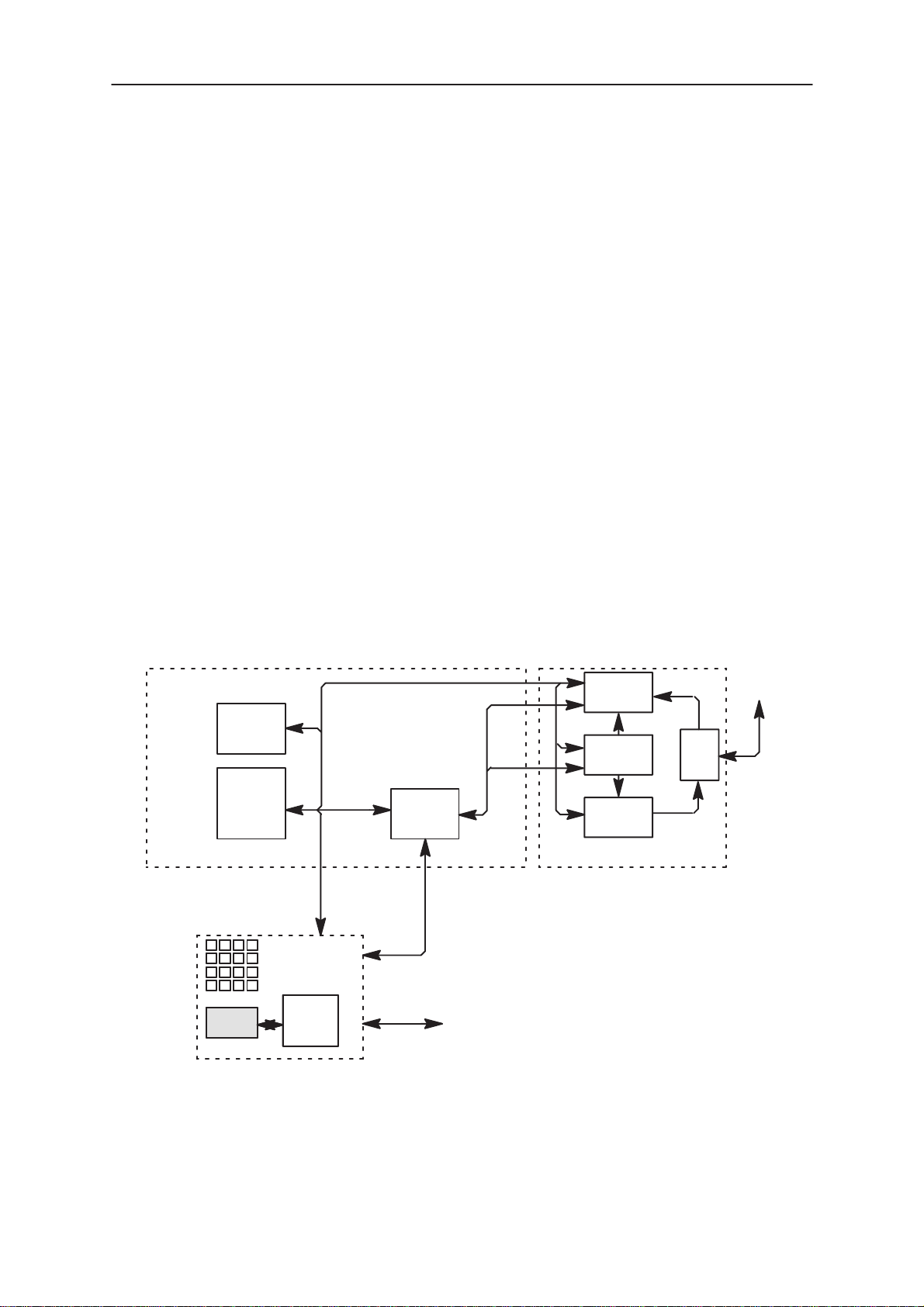
Block Diagram
THF–9 consist of 2 pcbs, GP3 and GU3F. GP3 consist of 2 submodules,
BASEBAND and RF. The BASEBAND module consists of 3 functional
blocks: PWRU, CTRLU and AUDIO; and the RF module consists of 3 functional blocks: RX, SYNT , and TX. The pcb GU3E is the User Interface module
(UIF–module).
Transceiver
PWRU
CTRLU
BASEBAND–submodule
UIF–module
LCDLCD
LCD Driver
AUDIO
MIC/EAR
BUZZER
RX
SYNT
TX
RF–submodule
ANT
DUP
Original, 01/97
Page 1 – 3

THF–9P
After Sales
Transceiver
Modules
Transceiver THF–9P 0501118
• system module GP3P 0200977
• display module GU3F 0200779
• mechanics MTHF9P 0261349
Note: When ordering the system module as a spare part use code
0200998
Electrical Specifications
Transceiver General Specifications
Number of channel
Duplex spacing
Channel spacing
Technical Documentation
200
10 MHz
25 kHz
Frequency stability
Antenna impedance
Audio output
Short–code memory locations
Identification number of the dealer,
the date when the telephone will be
delivered to the customer,
subscriber number and locking code
Signalling
Transmitter Branch
Frequency band
Output RF power levels
Spurious signals
Modulation
better than ±1.0 kHz
50
Ω
1.5 mW into 750 ohms
0, 00, 1...99
are programmed in EEPROM
1200–baud FFSK
452.500...457.475 MHz
0.15 W, 1.0 W
< 0.25 µW f=100 kHz...1 GHz
<
1.0 µW f= 1 GHz...4 GHz
FM, pre–emphasis of 6 dB/octave
Page 1 – 4
Deviation ±
• with 4000 Hz supervisory signal ±
FFSK deviation
• 1200 Hz (”1” frequency) ±
• 1800 Hz (”0” frequency) ±
Harmonic distortion
4.7 kHz max.
5.0 kHz max.
2800 Hz ±400 Hz
4200 Hz ±600 Hz
< 5 %
Original, 01/97

After Sales
THF–9P
Technical Documentation
Audio frequency response
Adjacent channel power
Audio inter–odulation products
Residual modulation
• linear
• psophometric
Audio muting
Compander (SW enabled)
• expansion ratio
• dynamic range
Transceiver
300...500 Hz (+1...–3 dB),
500...2000 Hz (± 1 dB),
2...3 kHz (+1...–3 dB),
pre–emphasis 6 dB / octave
< –70 dB
< –20 dB
< –20 dB (peak)
< –40 dB (RMS)
> 40 dB
1:2
0...–50 dB ±1 dB
Receiver Branch
Frequency band
Sensitivity
Adjacent channel selectivity
Spurious response rejection
Inter–modulation rejection
Blocking
Spurious emission
Audio inter–modulation products
AM suppression
Noise
• without psophometric filter
• with psophometric filter
Harmonic distortion
Audio frequency response
462.500...467.475 MHz
<–113 dBm (20 dB SINAD psoph.)
> 67 dB
> 67 dB
> 67 dB
> 87 dB
< 2.0 nW f=100 kHz...1 GHz
< 20 nW f=1 GHz...4 GHz
< –20 dB (1600 Hz)
> 30 dB
< –20 dB
< –40 dB
< 5 %
300...500 Hz (+1...–3 dB),
500...2000 Hz (± 1 dB),
2...3 kHz (+1...–3 dB),
de–emphasis of 6 dB / octave
Expander (SW enabled)
• expansion ratio
• dynamic range
Original, 01/97
1:2
0...–50 dB ±1 dB
Page 1 – 5

THF–9P
After Sales
Transceiver
RX Synthesizer
Frequency tolerance at startup ±
Frequency range
Output level
Phase noise
Residual deviation
Settling time
CHN–>CHN+1
CHN–>CHN+?
TX Synthesizer
Transmitted frequency difference from
Technical Documentation
2.5 ppm
417.500...422.475 MHz
1 dBm ±2 dB
< –118 dBc/Hz (@25 kHz)
< 50 Hz
< 5 ms
< 25 ms
BS in conversation mode ±
Frequency range
Output level
Phase noise
Residual deviation
Settling time
CHN–>CHN+1
CHN–>CHN+?
Modulation linearity
250 Hz
452.500...457.475 MHz
1 dBm ±2 dB
< –116 dBc/Hz (@25 kHz)
< 50 Hz
< 15 ms
< 35 ms
< 1.5 dB
Page 1 – 6
Original, 01/97
 Loading...
Loading...