Nissan 300zx Engine Fuel Emission Control System EF EC 1984 Owner's Manual

ENGINE
FUEL
&
-
SECTION
EMISSION
-
EFaEC
CONTENTS
PRECAUTIONS
COMPONENT PARTS LOCATION
ECCS DIAGRAM
ECCS CHART ..
ECC.S WIRING DIAGRAM
FUEL FLOW SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
AIR FLOW SYSTEM DESCRIPTION ....
E C C
S.
DESCRIPTION
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
SE LF-D I AGNOSIS
ELECTRONfC CONTROL SYSTEM INSPECTION
MIXTURE RATIO FEEDBACK SYSTEM INSPECTION
FUEL SYSTEM INSPECTION
TURBOCHARGER
INJECTOR COOLING FAN (VG30ET)
PRESSURE REGULATOR CONTROL
CRANKCASE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
EXHAUST EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
SERVICE DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS
. ...
..
. . .
. .
..
.
. . . . ...
.
..
..
..
.
.
(S
DS).
..
. . . .
.
..
..
...
. . .
. . . .
CONTROL
..
..
..
...
.
,
.
..
.
SYSTEM
.
.
EF&EC-
.
EF&EC-
EF & ECEF&ECEF&ECEF & EC-10
&
EC-11
EF
,
EF&EC-13
EF
&
EC-28
&
EC-35
EF
EF
&
EC43
EF & EC-60
&
EC-63
EF
EF
&
EC-66
EF
&
EC-69
EF
&
EC-72
. .
EF & EC-74
&
EC-75
EF
,
EF&EC-76
EF
&
EC-79
2
3
4
6
8
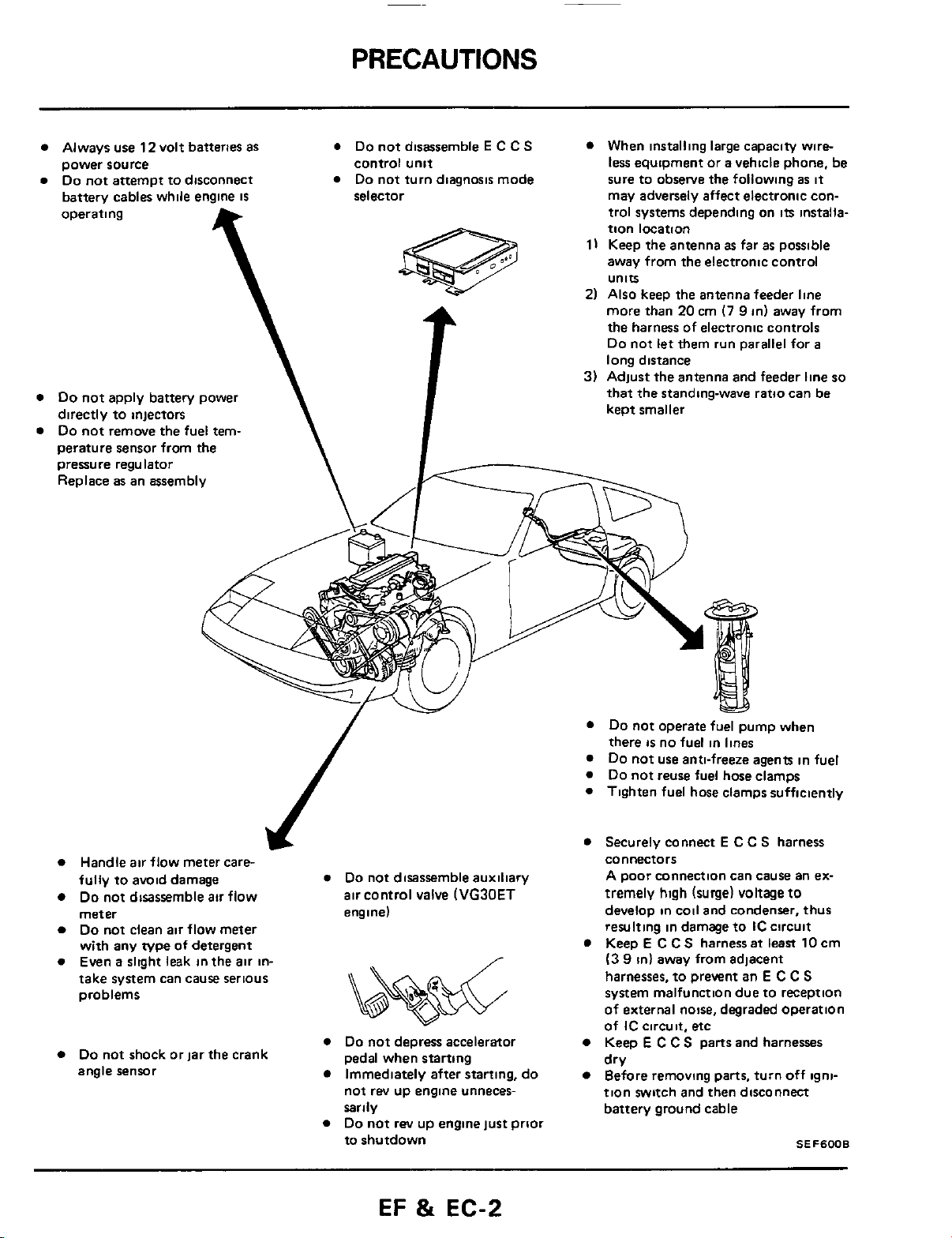
PRECAUTIONS
Always use
power source
Do
not
battery cables while engine
operating
Do
not apply battery power
directly to injectors
Do
not remove the fuel tem-
perature sensor from
pressure regulator
Replace as an assembly
12
volt batteries as
attempt to disconnect
\
the
*
Do
not disassemble E C
control unit
Do
not turn diagnosis mode
\
selector
T
IS
C
S
When installing large capacity wire-
less equipment or a vehicle phone, be
sure to obsetve the following
may adversely affect electronic control systems depending on its
tion location
1)
Keep the antenna as far as possible
away from the electronic control
units
2)
Also keep the antenna feeder line
20
cm
(7
9
more than
the harness of electronic controls
Do
not let them run parallel for
long distance
3)
Adjust the antenna and feeder line
that the standing-wave
keot smaller
in) away from
ratio
can be
as
it
installa-
a
so
\
J
Handle air flow meter care-
fully to avoid damage
Do
not disassemble
meter engine)
Do
not clean
with any type of detergent
0
Even a slight leak in the air
take system can cause serious
problems
Do
not shock or
angle sensor
air
air
flow meter
jar
the crank
flow
in-
*
Do
not disassemble auxiliary
air
control valve
(VG30ET
/
&&%$$?&
Do
not
depress accelerator
pedal when starting
Immediately after starting, do
up
not rev
sarily
Do
to shutdown
engine unneces-
not rev up engine just prioi
Do
not operate fuel pump when
there
is
Do
0
Do
0
Tighten fuel hose clamps sufficiently
Securely connect
connectors
A
tremely
develop in coil and condenser,
resulting in damage to
Keep
(3
harnesses, to prevent an
system malfunction due to reception
of external noise, degraded operation
of
Keep
dry
Before removing parts, turn off ignition switch and then disconnect
battery ground cable
no fuel
not use anti-freeze agents in fuel
not reuse fuel hose clamps
poor connection can cause an ex-
high
E
C C
9
in) away from adjacent
IC
circuit. etc
E
C
in
lines
E
C C
(surge) voltage
S
harness at least
C
S
parts and harnesses
S
IC
E
harness
to
circuit
C C
thus
10
cm
S
SEF6008
EF
&
EC-2
E
C
C
S
conlr01
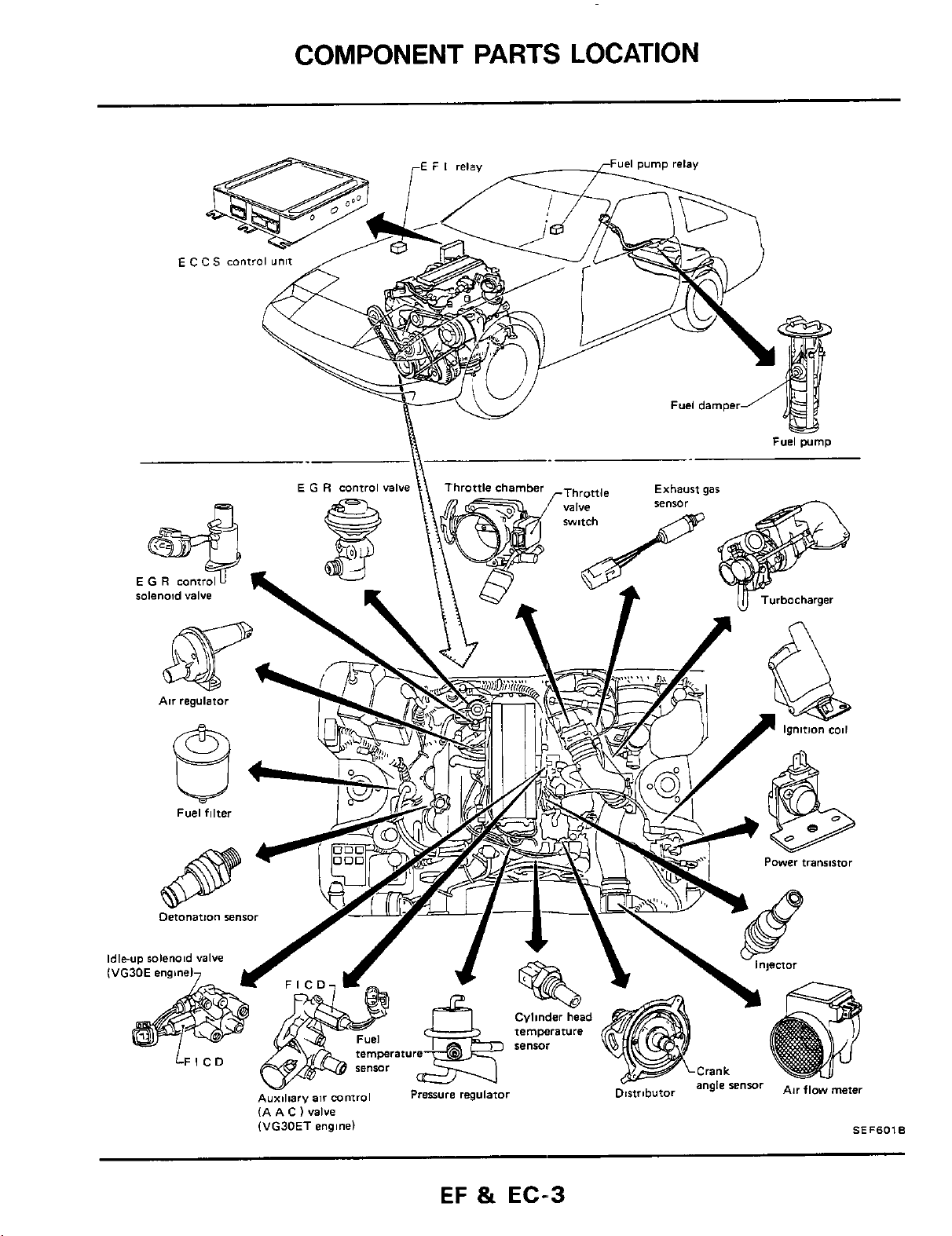
COMPONENT PARTS LOCATION
unit
IA A C
(valve
(VG30ET
engine)
EF
&
SEFBOlB
EC-3
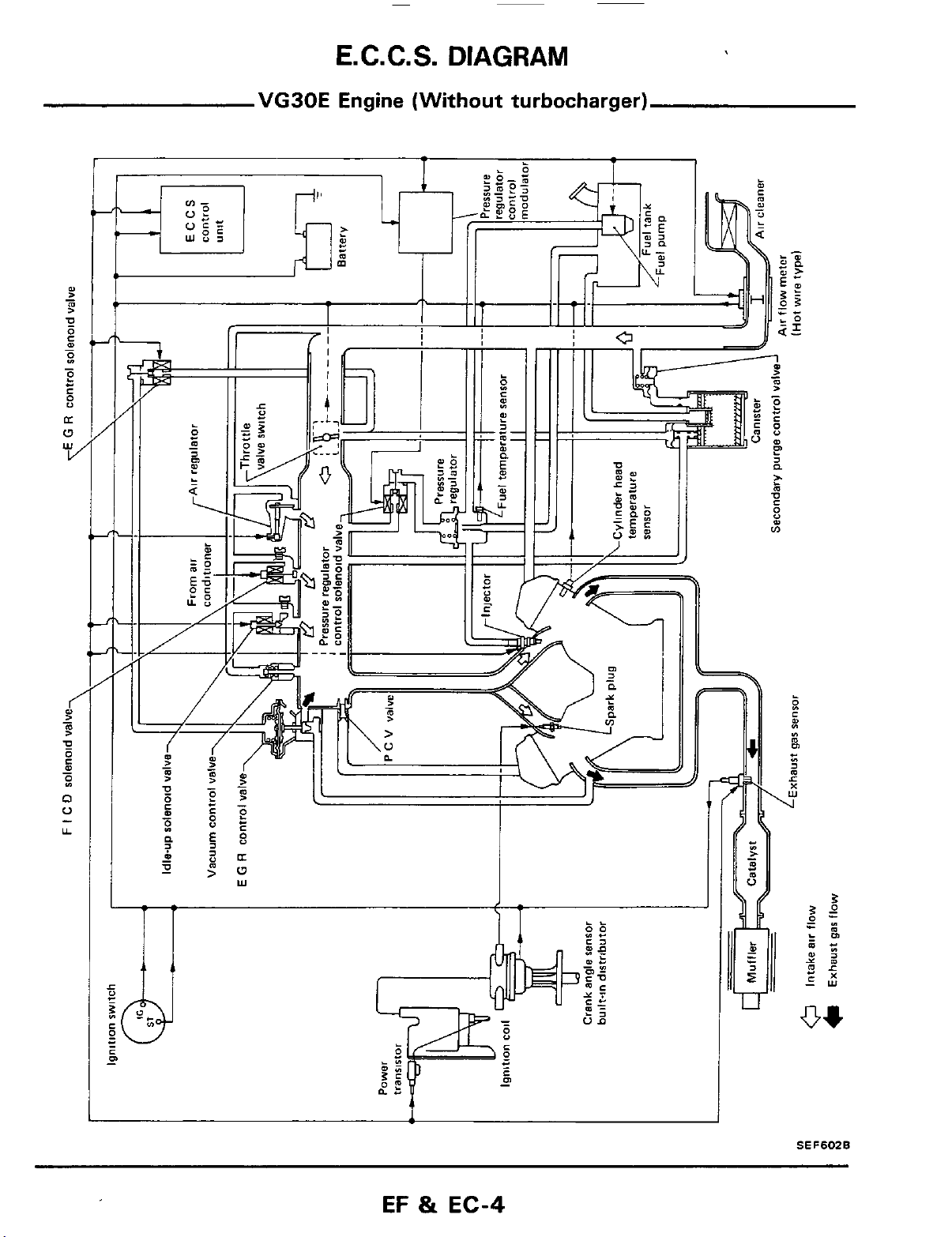
E.
C.C.
S.
DIAGRAM
VG30E
Engine (Without turbocharger)
EF
&
SEF602B
EC-4
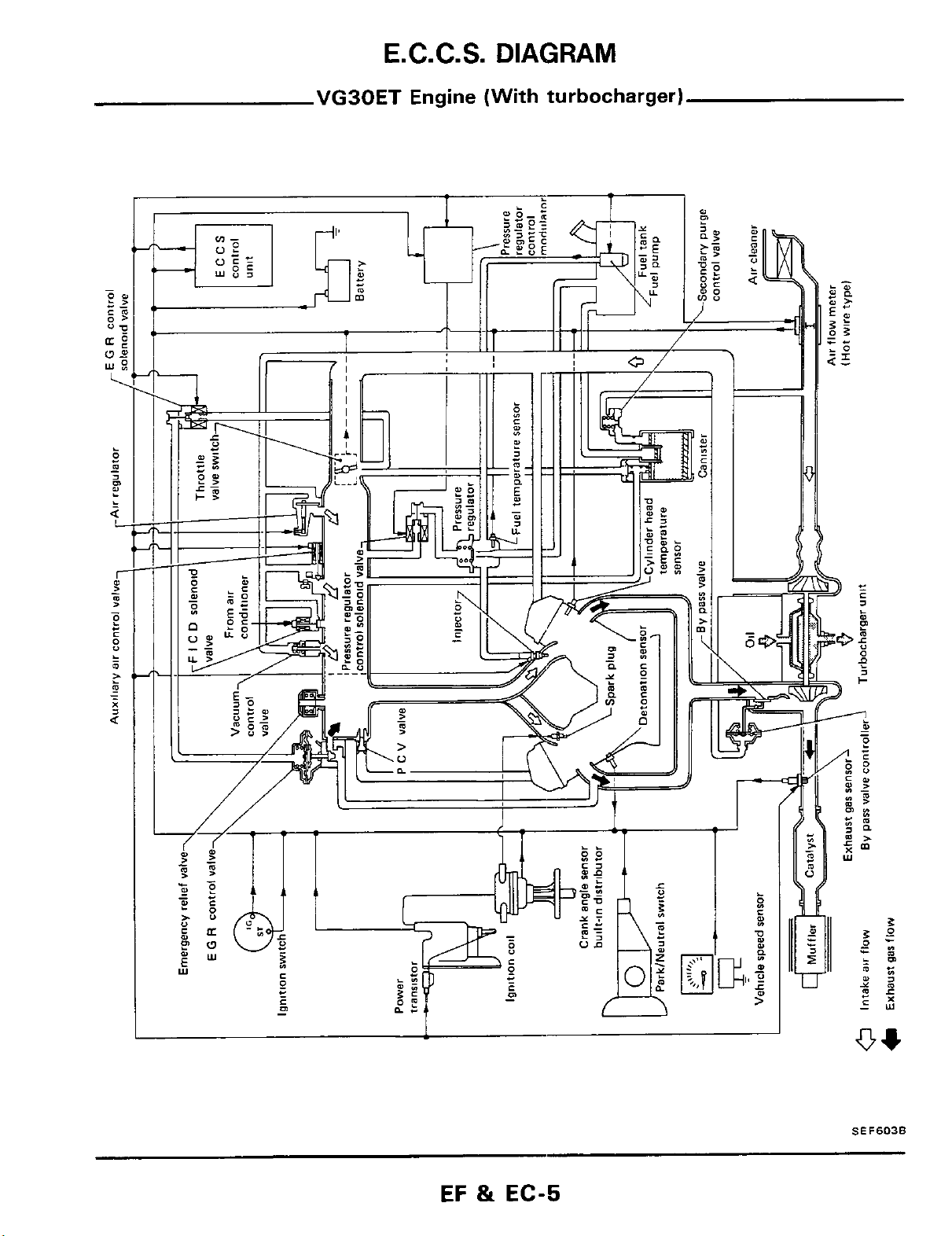
E.C.C.S.
DIAGRAM
VG30ET
Engine
(With turbocharger)
EF
&
L
SEF603B
EC-5
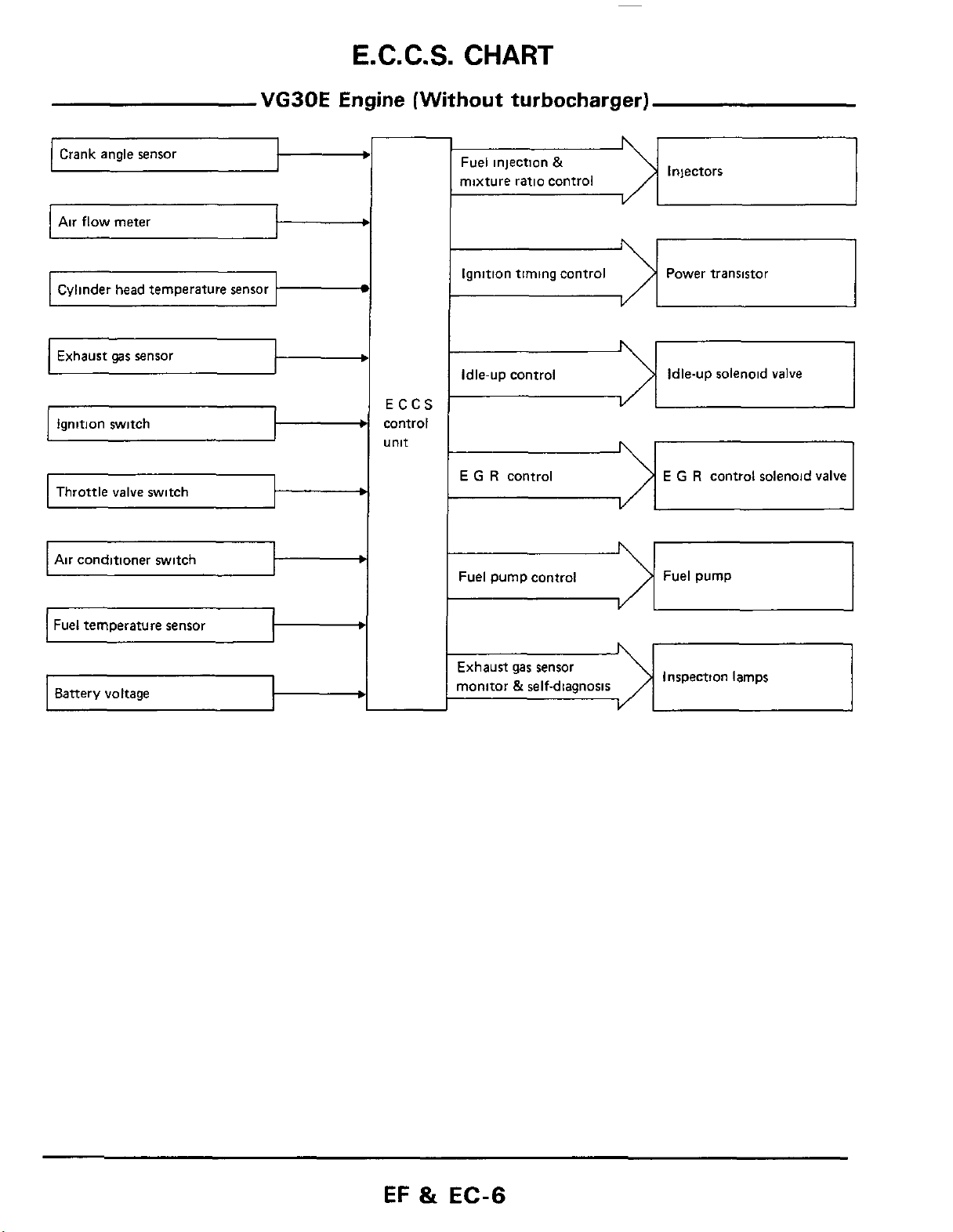
E.C.C.S.
CHART
Crank angle sensor
Exhaust
Throttle valve switch
gas
sensor
VG30E
Engine (Without turbocharger)
-\
t
ECCS
b
control
unit
-b
Fuel injection
mixture ratio control
Ignition timing control Power transistor
Idle-up control Idle-up solenoid valve
E
G
R
&
VI
control
I
Injectors
E G R
1
1
control solenoid valve
Air conditioner switch
Battery voltage
1
t
%el pump control
-1
ixhaust gas sensor
&
nonitor
self-diamosis
Fuel pump
I
Inspection lamps
EF
&
EC-6
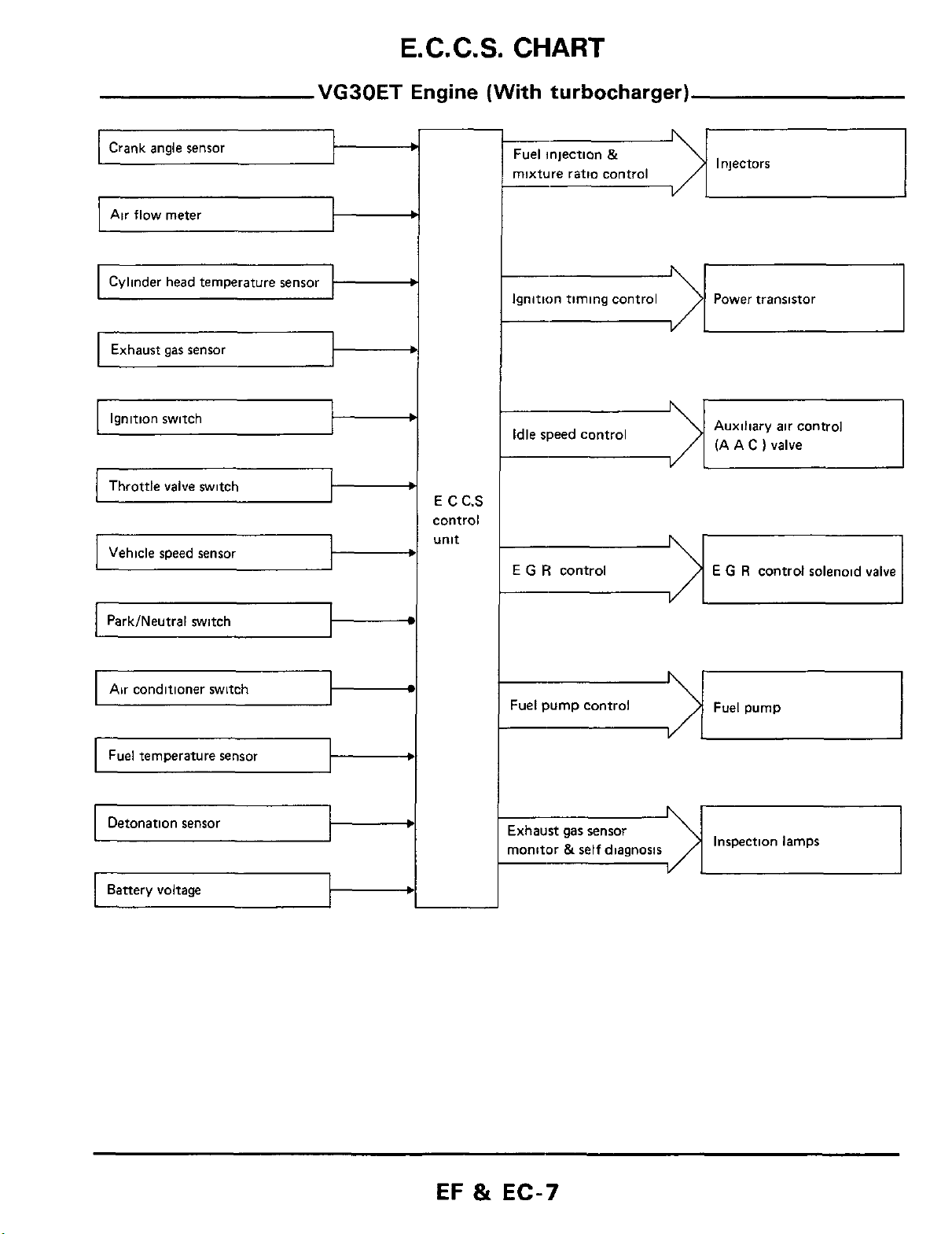
E.
C.
C.S.
CHART
Air flow meter
Cylinder head temperature sensor
Ignition switch
Throttle
valve
switch
VG30ET
I
Engine (With turbocharger)
Fuel injection
mixture ratio control
&
--I
c
b
Ignition timing control Power transistor
b
b
b
b
E
C
C.S
control
unit
-dI
Idle speed control
E
G
R
control
YL
Injectors
Auxiliary air control
C
)
(A A
E G R
valve
control solenoid
I
valve
Park/Neutral switch
Air conditioner switch
I
Fuel pump control Fuel pump
b
b
ixhaust
nonitor
gas
&
sensor
self
diagnosis
Inspection lamps
I
EF
&
EC-7
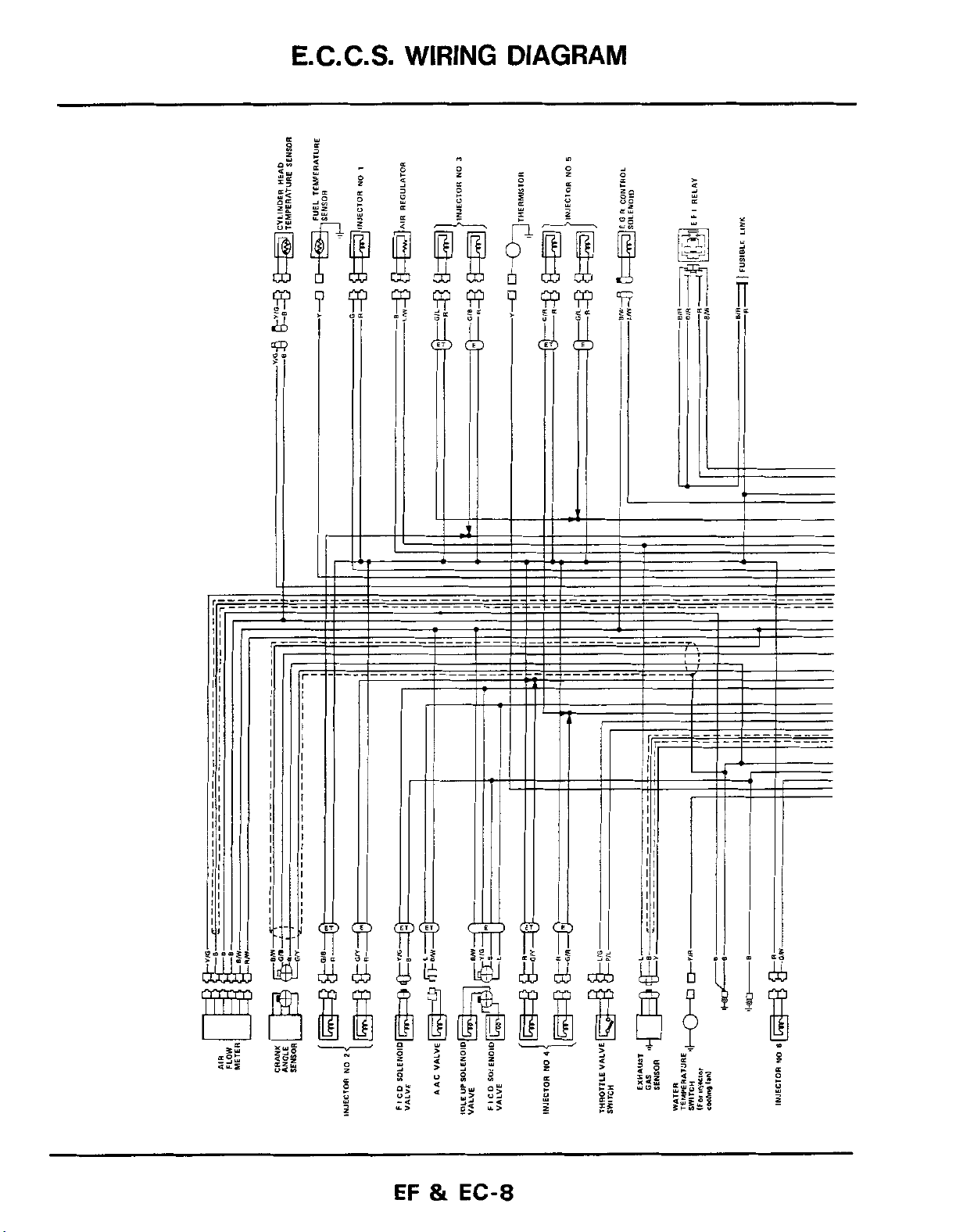
E.C.C.S.
WIRING DIAGRAM
i-
1
EF & EC-8
=
e
Y
2
UI
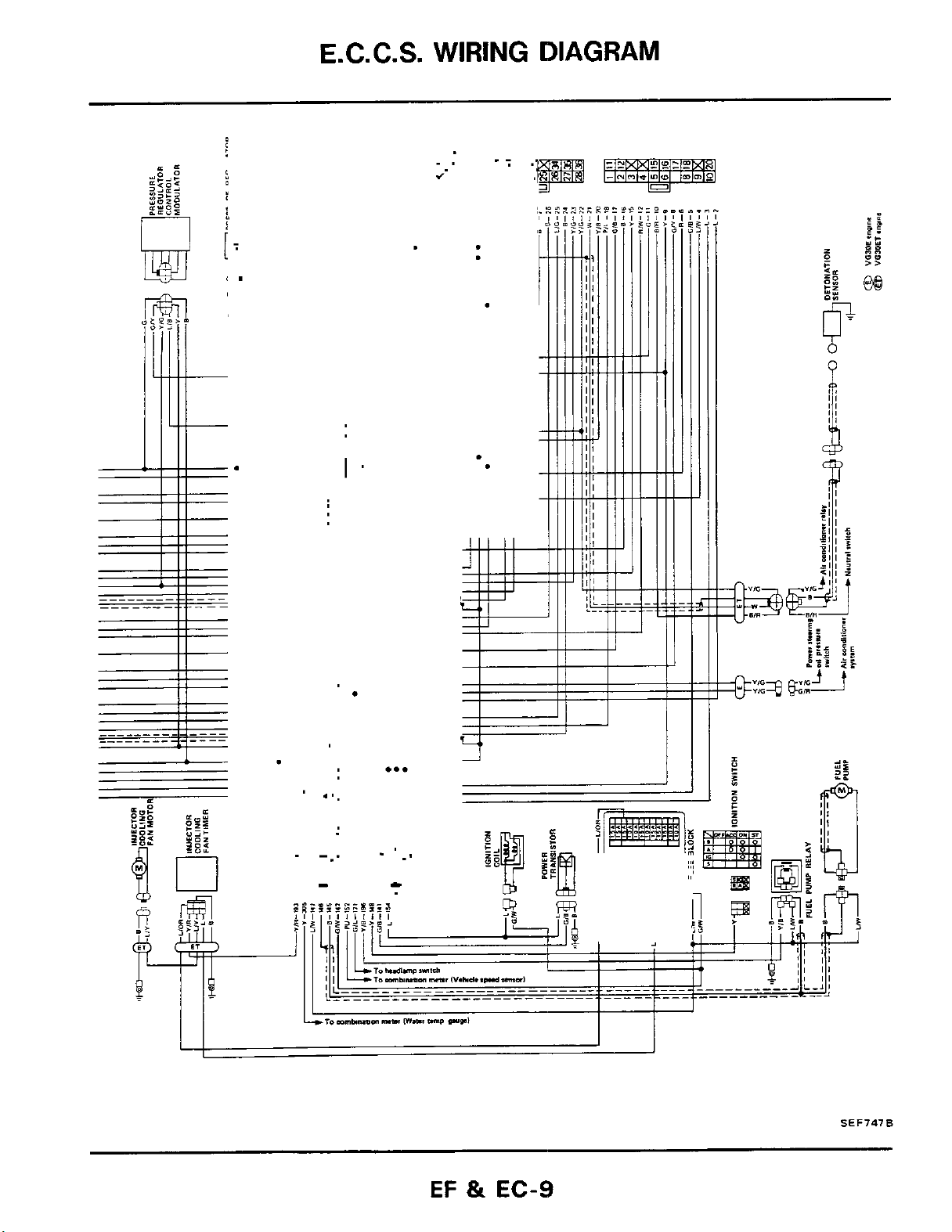
E.C.C.S.
I'
WIRING
.
DIAGRAM
.
...
SEF747B
EF
&
EC-9
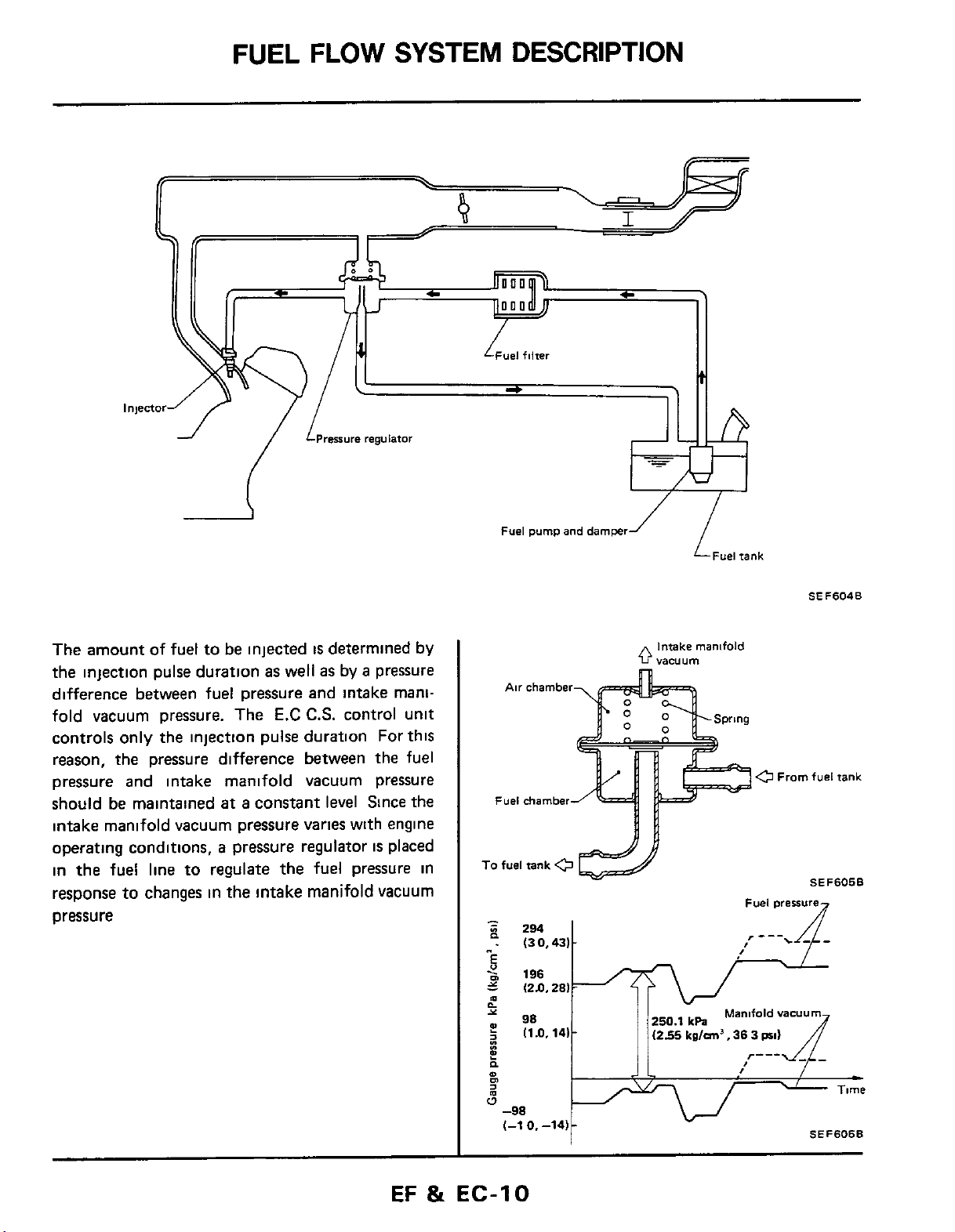
FUEL
FLOW
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The amount of fuel to
the injection pulse duration
difference between fuel pressure and intake manifold vacuum pressure. The
controls only the injection pulse duration For this
reason,
pressure and intake manifold vacuum pressure
should be maintained
intake
operating conditions,
in
response to changes
pressure
the
pressure difference between the fuel
manifold vacuum pressure varies with engine
the fuel line
be
injected
as
at a constant level Since the
a
pressure regulator
to
regulate
in
the intake manifold vacuum
well
E.C
the
is
determined by
as
by a pressure
C.S.
control unit
fuel
pressure in
IS
placed
Fuel
Fuel
pump
chamber
and
damper
’
0
intake
vacuum
iFueirank
manifold
a
Fuel
SEF604B
From
SEF605B
presswe
fuel
tank
EF
&
EC-10
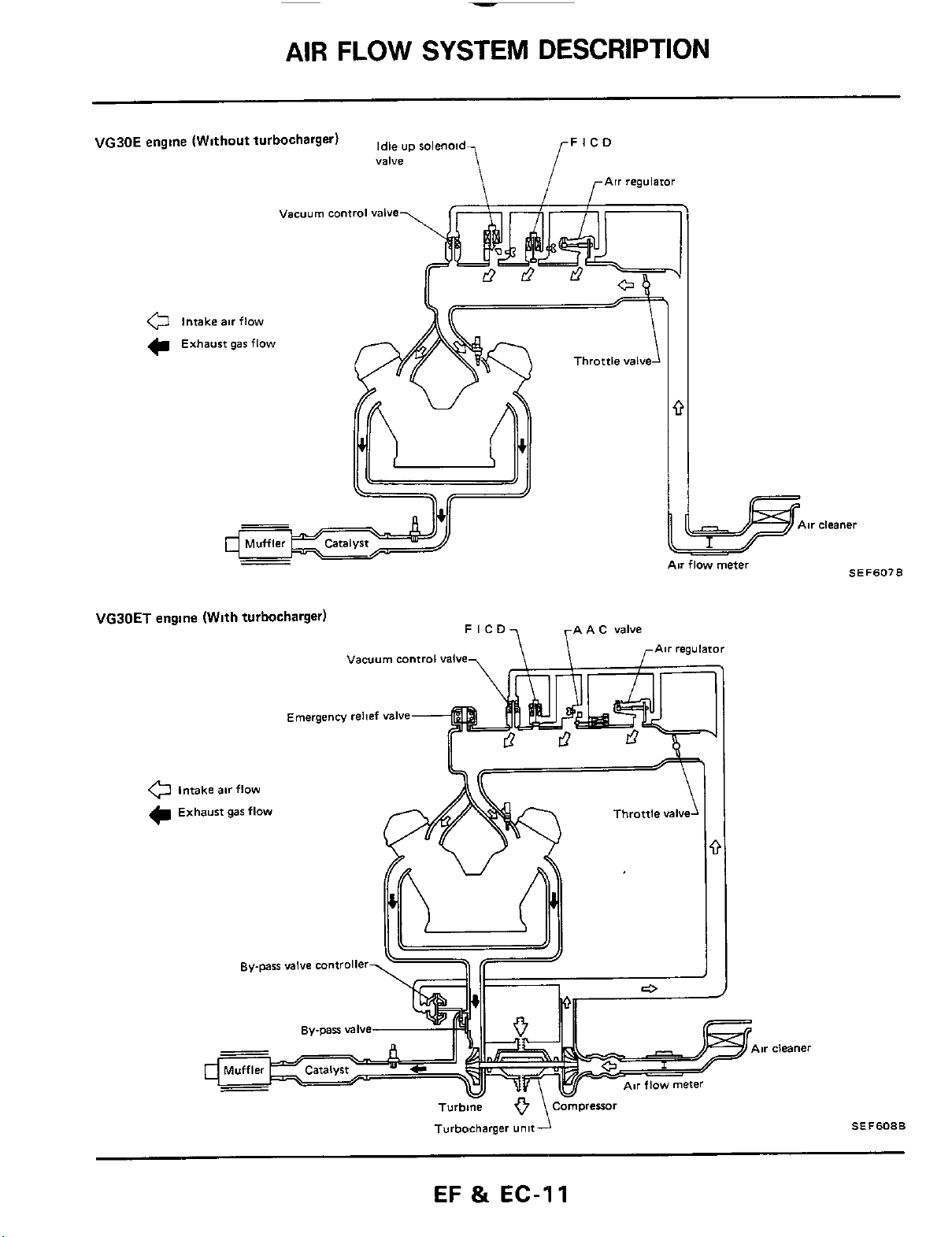
AIR
FLOW
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
VG30E
engine (Without turbocharger)
0
Intake
air
flow
C
Exhaust
gar flow
Valve
up
roleno,,,
FlCD
r
Air
cleaner
VGJOET
engine (With turbocharger)
Emergency relief
0
Intake
air
flow
Exhaust
gar
flow
Vacuum
valve
control
valve
cleaner
Turbbne
Turbocharger
-
unit-
\Compresor
EF & EC-11
SE
F
608
B
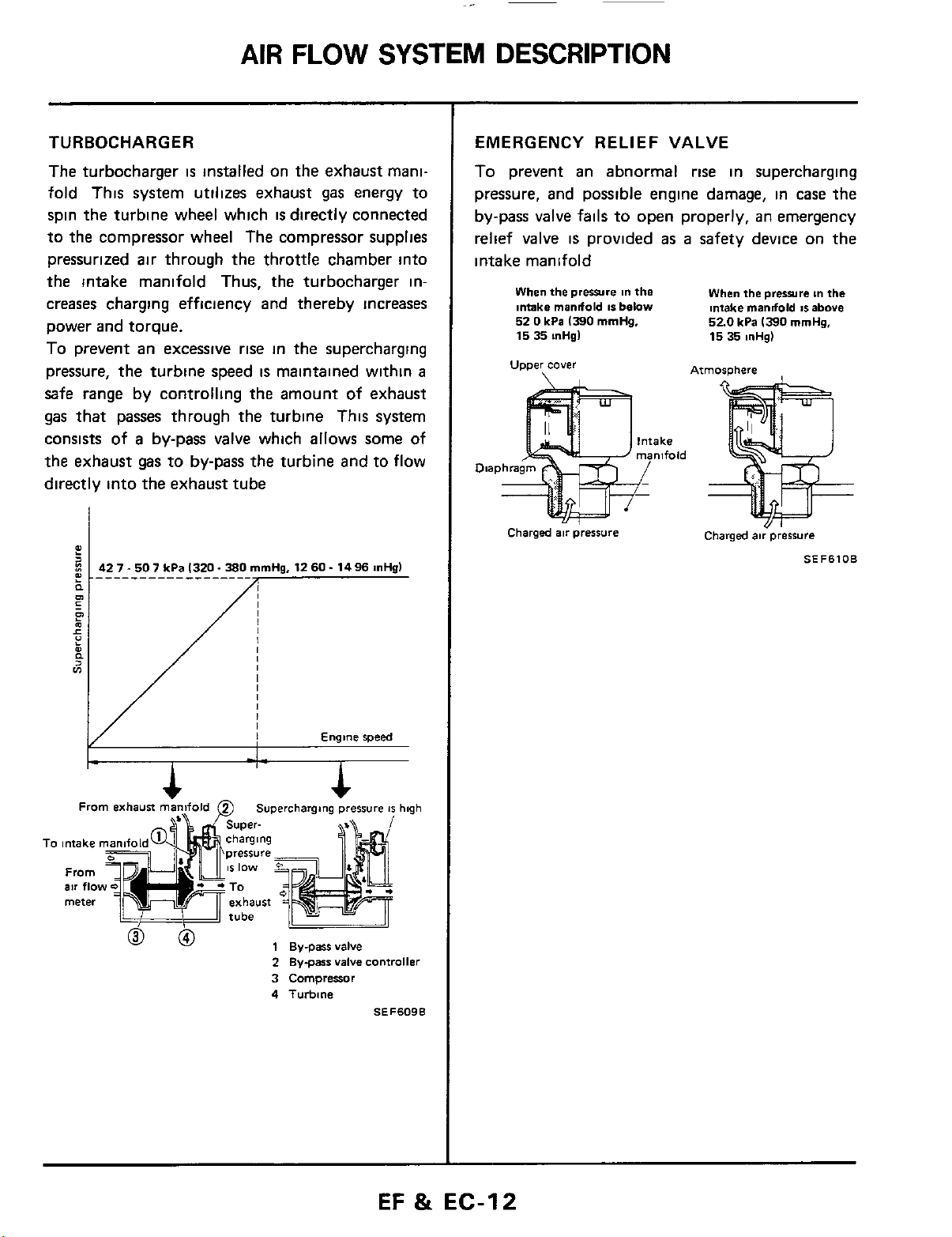
AIR
FLOW
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
TURBOCHARGER
The turbocharger
is
installed on the exhaust manifold This system utilizes exhaust gas energy to
spin the turbine wheel which
is
directly connected
to the compressor wheel The compressor supplies
pressurized air through the throttle chamber into
the intake manifold Thus, the turbocharger increases charging efficiency and thereby increases
power and torque.
To prevent an excessive rise in the supercharging
pressure, the turbine speed
is
maintained within
a
safe range by controlling the amount of exhaust
gas
that passes through the turbine This system
consists of
the
exhaust gas to by-pass
a
by-pass valve which allows some of
the
turbine and to flow
directly into the exhaust tube
EMERGENCY RELIEF VALVE
To
prevent an abnormal
rise
in supercharging
pressure, and possible engine damage, in case
by-pass valve
relief valve
fails
to open properly, an emergency
is
provided
as
a
safety device on the
intake manifold
When
the
Intake
52
0
15
35
Upper
Charged
prwre
mandold
kPa
1390
inHgl
cover
air
pressure
in
IS
below
mmHg.
the
When
the
intake
520
kPa
15
35
Atmosphere
Charged
prerrura
mandold
1390
mrnHg,
mHg)
air pressure
tn
IS
above
SEF6lOB
the
the
From
b==iF
exhausi
To
intake
To
intake
From
From
air
flo
air
flo
meter
meter
h
man2fold
0
Engine
Superchargang
2
Bygars
3
Compressor
4
Turbine
speed
pressure
valve
controller
41
hqh
SEF609B
EF
&
EC-12
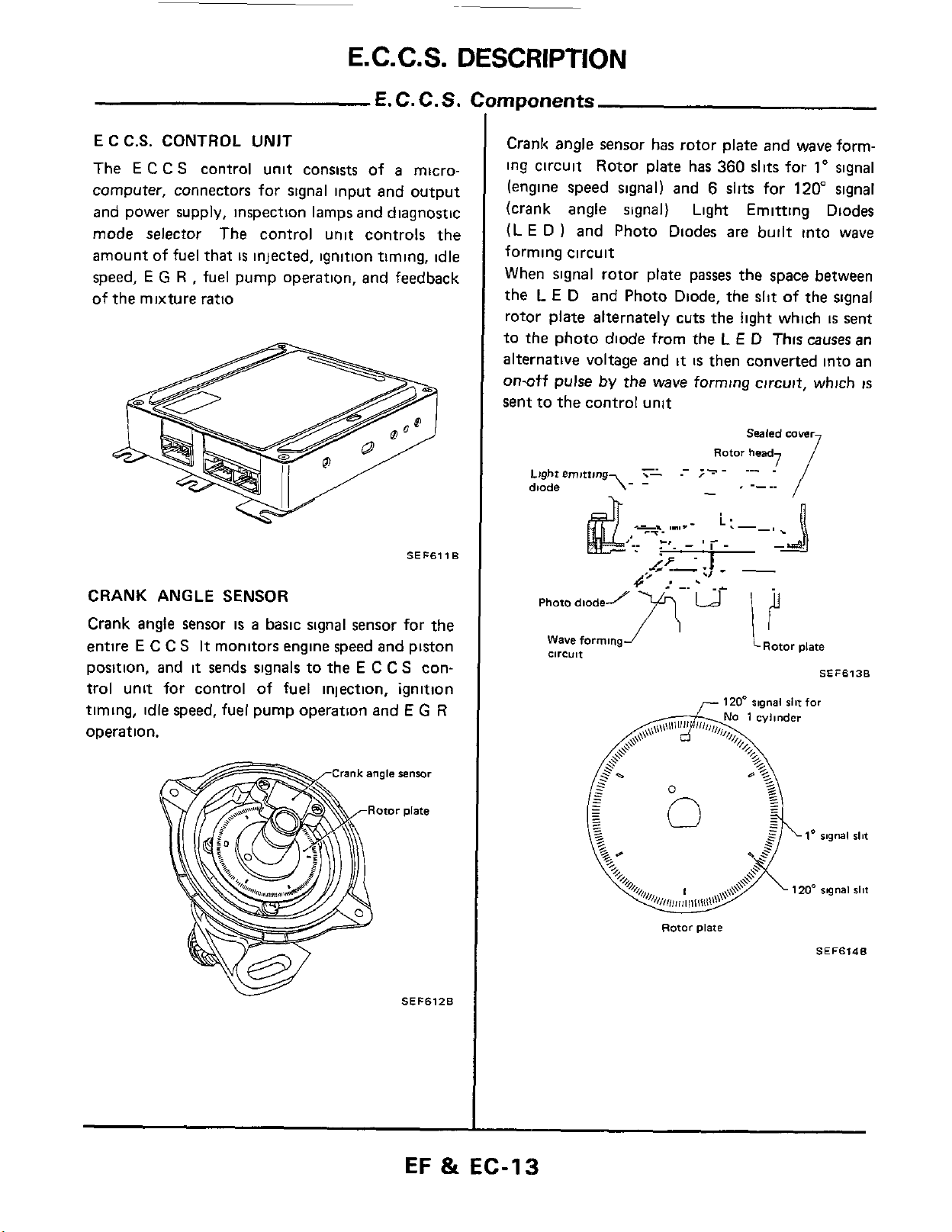
E.C.C.S.
DESCRIPTION
E.C.C.S.
E
C
C.S.
CONTROL UNIT
The
E
C
C
S
control unit consists of a microcomputer, connectors for signal input and output
and power supply, inspection lamps and diagnostic
mode selector The control unit controls the
amount
speed,
of
CRANK ANGLE SENSOR
Crank angle sensor
entire
position, and
trol unit for control of
timing, idle speed, fuel pump operation and
operation.
of
fuel that
E G R
the mixture ratio
E
C
,
fuel pump operation, and feedback
It monitors engine speed
C
S
it
sends signals to the E C C S con-
is
injected, ignition timing, idle
SEF611
is
a
basic signal sensor for the
and
piston
fuel
injection, ignition
E
G
R
B
rnponents
Crank angle
ing circuit Rotor plate has
(engine speed signal) and
(crank angle signal) Light Emitting Diodes
(L
E
D ) and Photo Diodes are built into wave
forming circuit
When
the
rotor plate alternately cuts the light which
to
alternative voltage and
on-otf
sent to the control unit
signal
L
E
the
Lighremitring
diode
Phatodlodel
Wave
circurt
sensor
rotor plate passes
D and Photo Diode, the
photo diode from the
pulse by the wave forming circuit, which
has
-.
'I-
1-
.
A.
-7.
l.lll-
I
-,
..
.
ir-
rotor plate and wave form-
360
slits
for
1"
signal
6
slits
for
120"
signal
the
space between
slit
of
the signal
is
sent
L E D
it
is
then converted into an
Rotor
-
.
;--
-
i:--,
_,-
I-
.I
Sealed
head
.--
,
This
mwr
?
.J
-
causes
4,,
fi-.
forming-'
h-
1
,h
'-Rotor
piate
SEFBlJB
an
IS
EF
&
EC-13
Rotor
plate
SEF614B
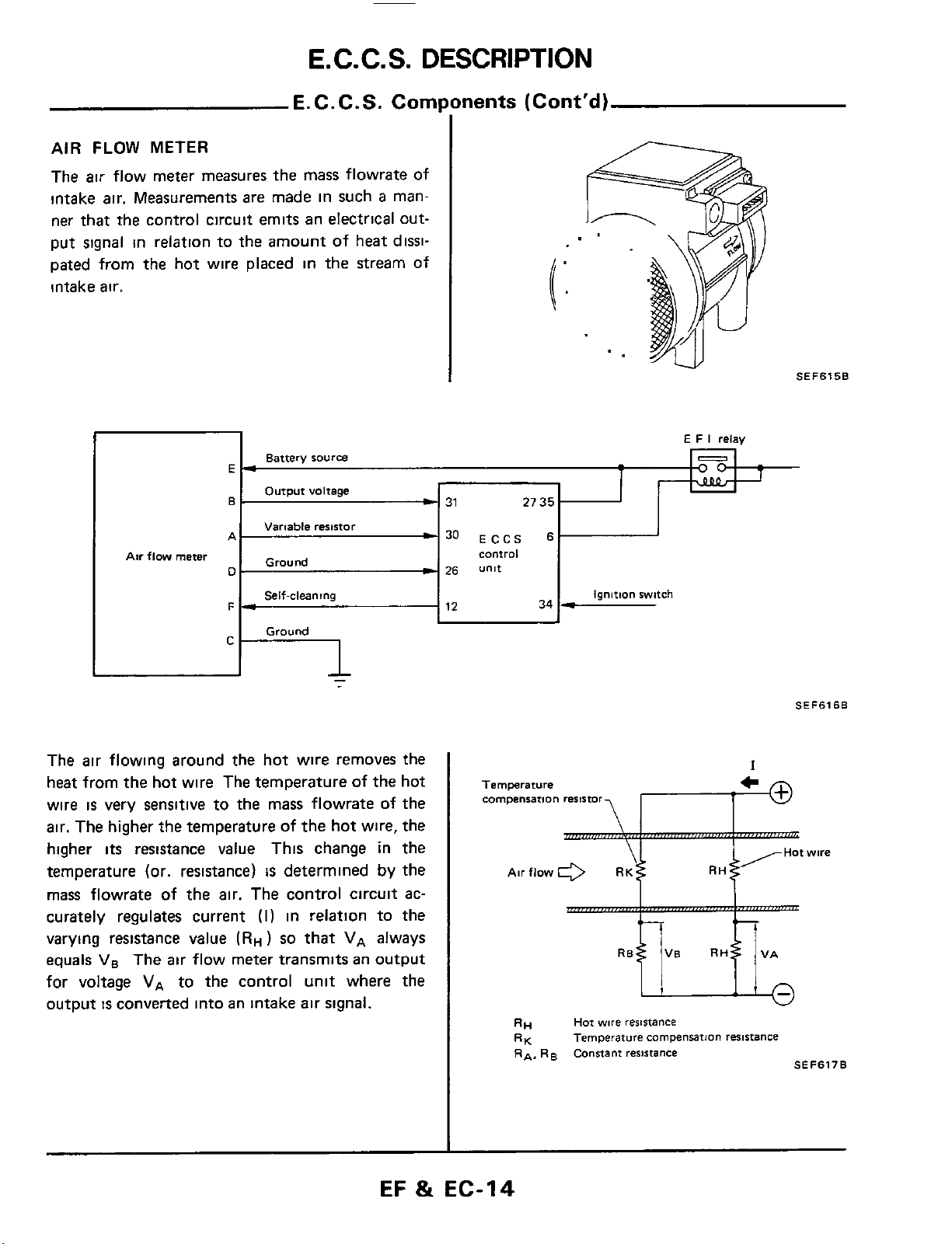
E.C.C.S.
E.C.C.S. Components (Cont'd)
AIR
FLOW
The
air
intake air. Measurements are made in such
ner
that
put signal
pated from the hot wire placed
intake
air.
METER
flow meter measures the mass flowrate of
the control circuit emits an electrical out-
in
relation to the amount of heat dissi-
in
the stream of
DESCRIPTION
a
man-
Battery
Output
Ground
Ground
source
voltage
resistor
Air
flow
meter
El
6-
Variable
A
0.
Self-cleaning
F-
C
-
The air flowing around the hot wire removes the
heat from
wire
air.
The
higher
temperature (or. resistance)
mass flowrate of the air. The control circuit
curately regulates current
varying resistance value
equals
for voltage
output
the
hot wire The temperature of the hot
is
very sensitive to the mass flowrate of the
higher the temperature
its
resistance value This change in the
VB
The air flow meter transmits
VA
to
the control unit where the
is
convened into
an
of
the hot wire, the
IS
determined
(I)
in relation to the
(RH)
so
that
intake air signal.
VA
an
by
always
output
the
ac-
I
31
w30
25
12
-
27
ECCS
comroi
unit
34
Temperature
compensation
RH
RK
RA.
35
6
-
resistor
RB
-
1
ignition
Hot
wore
reststance
Temperature
Constant
reSiiIanCe
E F I
switch
campenration
SEF615B
relay
SEFSlSB
I
twire
resistance
SEFS17B
I
EF & EC-14
E. C. C.
S.
DESCRIPTION
E.C.C.S.
Self-cleaning
After engine
heats up the hot wire to approximately
(1,832"F)
hot wire
Self-cleaning operation
_____~
After running engine
After driving vehicle at above
(12
MPH)
Cylinder head temperature
(239°F)
115OC
is
stopped, the E C.C S control unit
to burn out dust which adhered to the
-
kmlh
-
1
rec
Operation
Condition
~
at
above 1,500 rpm
5
rec
20
is
more than
Corn1
1,OOO"C
SEF618B
Operates
nents (Cont'd)
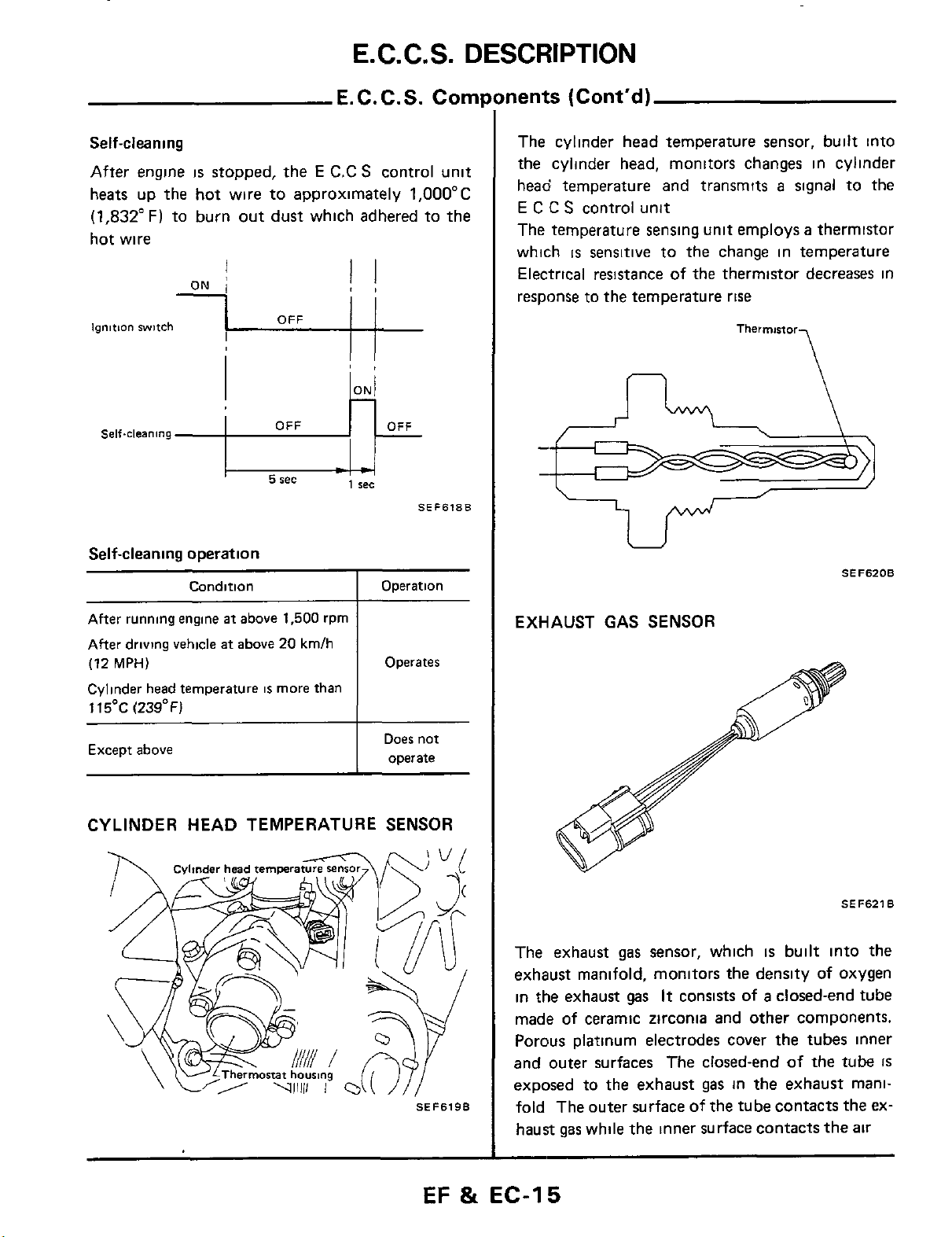
The cylinder head temperature sensor, built into
the cylinder head, monitors changes in cylinder
a
head temperature and transmits
E
C C S control unit
The temperature sensing unit employs
which
Electrical resistance
response to the temperature
is
sensitive to the change in temperature
of
the thermistor decreases in
rise
Thermmor
signal to the
a
thermistor
U
SEF6208
EXHAUST GAS SENSOR
Except above
Does not
operate
CYLINDER HEAD TEMPERATURE SENSOR
SEF6198
SEF621
The exhaust
exhaust manifold, monitors the density
in
the exhaust
made
of ceramic zirconia and other components.
gas
sensor, which
gas
It
consists
is
built into the
of
a
closed-end tube
of
oxygen
Porous platinum electrodes cover the tubes inner
and outer surfaces The closed-end
exposed to the exhaust
fold The outer surface
haust
gas
while the inner surface contacts the
gas
in the exhaust mani-
of
the tube contacts the ex-
of
the
tube
air
IS
EF
&
EC-15
E.C.C.S.
DESCRIPTION
E.
C. C.
S.
Corn1
In
order to ensure the stable performance
exhaust
inside the zirconia tube
gas
sensor, a ceramic heater
,-Ceramic
.-
. ..
.
zirmnia tube
.
...
..
. . ..
..
.
.
of
is
employed
the
--_
SEF622B
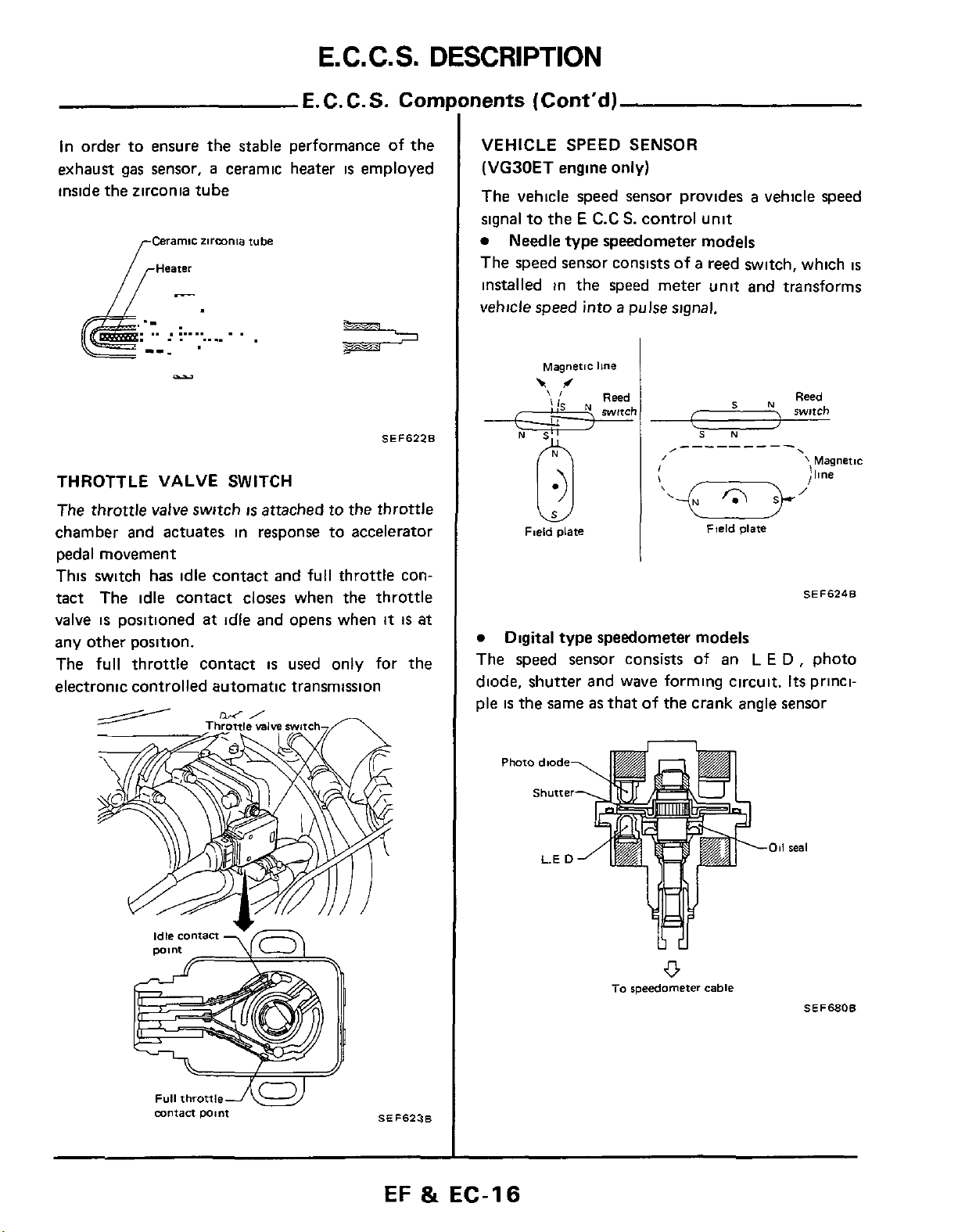
THROTTLE VALVE SWlTCl
The throttle valve switch
chamber and actuates in
pedal movement
This switch has idle contact and full throttle contact The idle contact closes when the throttle
valve
is
positioned
any other position.
The full throttle contact
electronic controlled automatic transmission
at
is
attached to the throttle
response to accelerator
idle
and opens when
is
used
only for the
it
is
at
nents
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
(VG30ET
The vehicle speed sensor provides a vehicle speed
signal
The speed sensor consists of
installed
vehicle
The speed sensor consists of
diode, shutter and wave forming circuit.
ple
(Cont'd)
engine
to
the
Needle
in
speed
Magnetic
\#
\I
i
:
!'
N
S"
Field
0
plate
Digital type speedometer models
is
the same
only)
E
C.C
S.
control unit
type speedometer models
a
reed switch, which
the speed meter unit and transforms
into
a
pulse signal.
line
Reed
sw17CI
i
Field
plate
an
as
that
of
the crank angle sensor
L E D
SEF624B
,
photo
Its
princi-
IS
Full
throttle
contact
p0,nt
SEF623B
EF
&
EC-16
To
speedometer
0
cable
011
seal
SEFS80B
E.
C.
C.
S.
DESCRIPTION
E.C.C.S. Corn
FUEL TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The fuel temperature sensor
sure regulator, and senses fuel temperature When
the fuel temperature
level, the
ed
Fuel
Do not remove fuel temperature sensor from pressure regulator. Always replace as
E
C C
temprature
S
$ens
IS
control unit enriches fuel inject-
is
built into the pres-
higher than the specified
Pressure
an
assembly.
regulator
SEF625B
lnents (Cont’d)
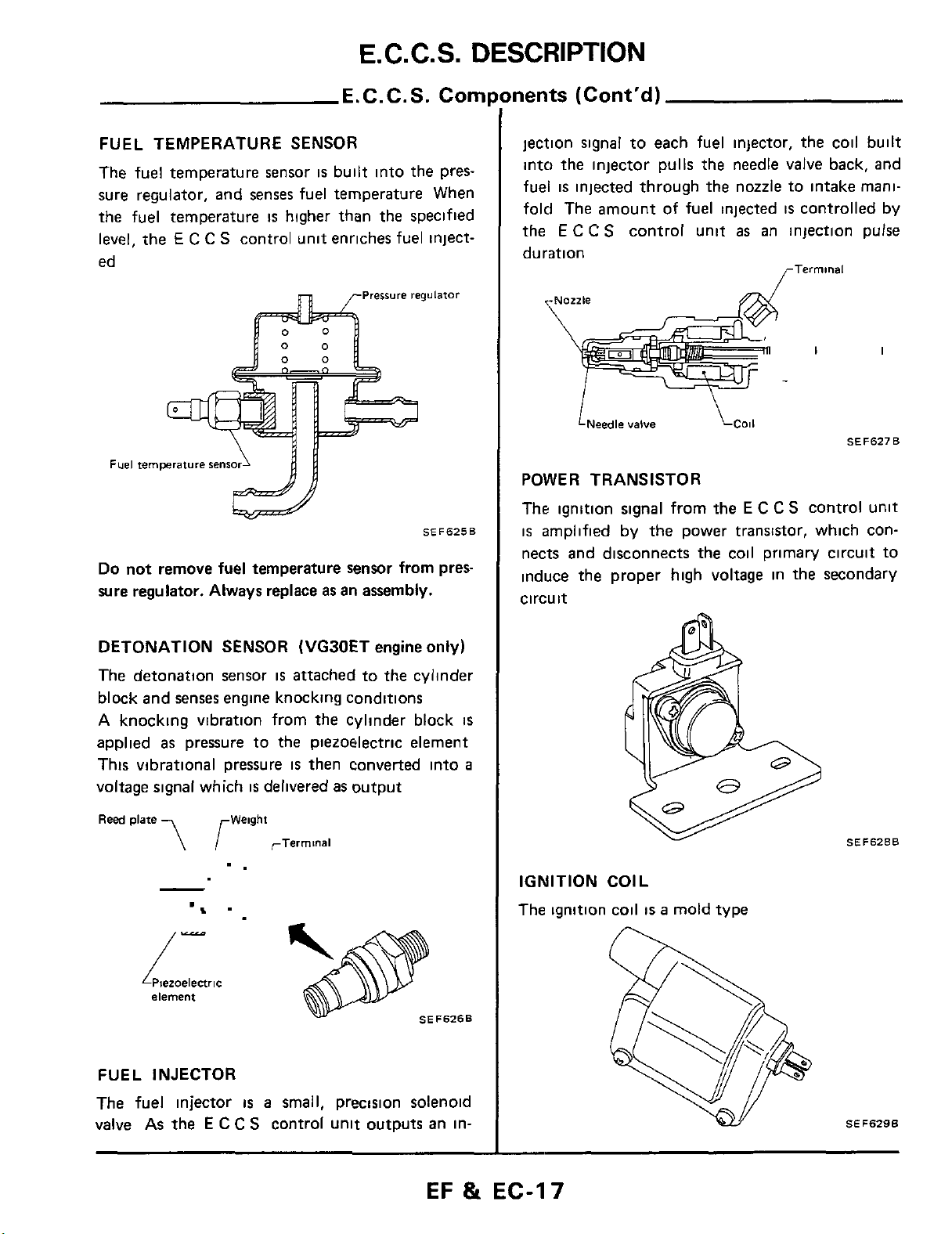
jection signal to each fuel injector, the coil built
into the injector pulls the needle valve back, and
fuel
is
injected through the nozzle to intake mani-
fold The amount of fuel injected
the
E
C C
S
control unit
duration
<-Nozzle
as
is
controlled by
an injection pulse
\
LNeedle
POWER TRANSISTOR
The ignition signal from the
is
amplified by the power transistor, which connects and disconnects the coil primary circuit to
induce the proper high voltage in the secondary
circuit
valve
E
C C
SEF627B
S
control unit
DETONATION SENSOR
The detonation sensor
block and senses engine knocking conditions
A
knocking vibration from the cylinder block
applied
This vibrational pressure
voltage signal which
Reed
plate
as
pressure to the piezoelectric element
is
,,
,-Weight
(VG30ET
is
attached to
IS
then converted into
delivered
rTerminal
as
output
engine only)
the
-.
/-
Piezoelectric
element
FUEL INJECTOR
cylinder
is
a
SEFSZSB
IGNITION COIL
The ignition coil
IS
a
mold type
SEFSZBB
The
fuel
injector
valve As the
E
C C
is
a
small, precision solenoid
S
control unit outputs an in-
EF
&
EC-17
E. C. C.
S.
DESCRIPTION
E.C.C.S. Corn1
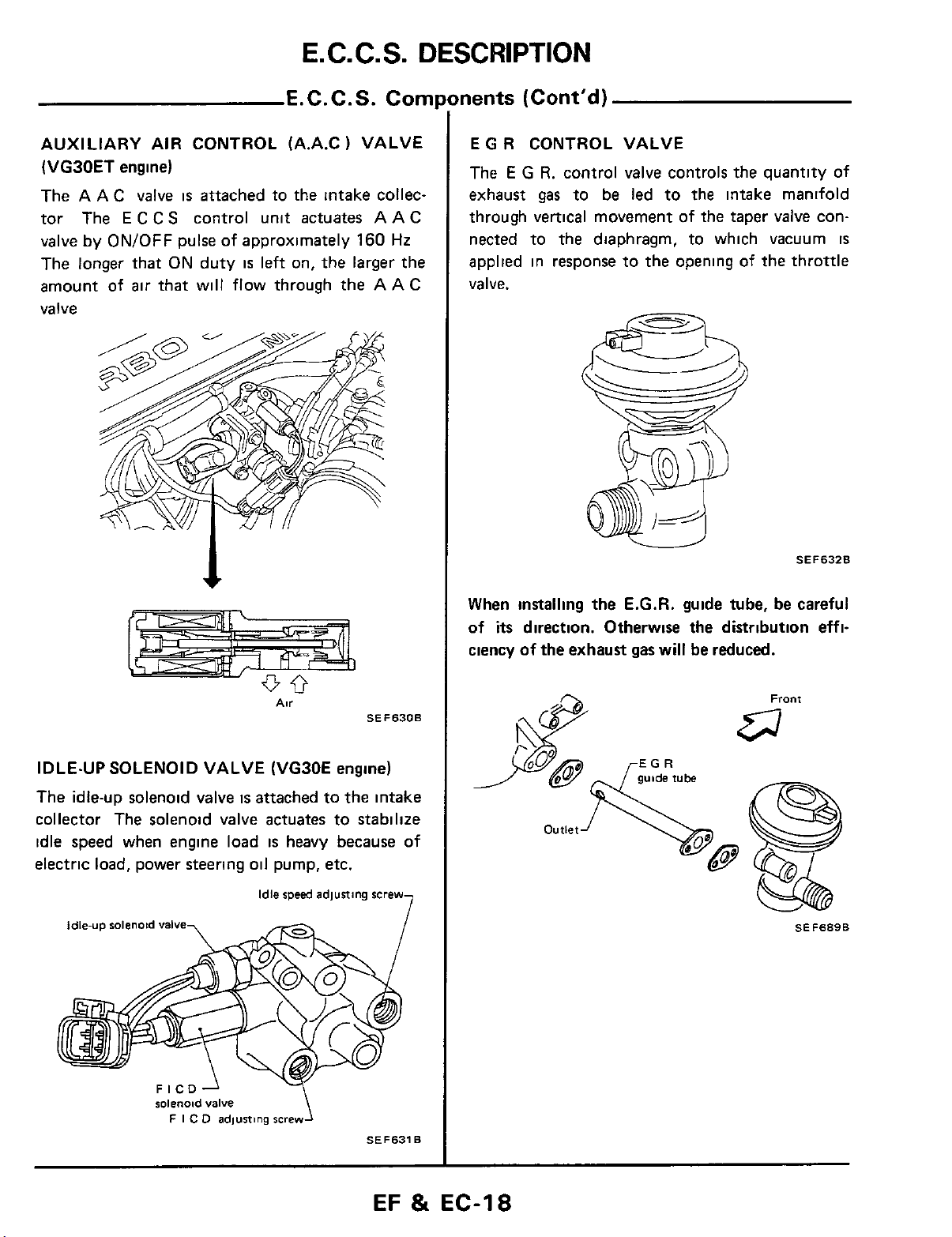
AUXILIARY AIR CONTROL (A.A.C 1 VALVE
A
A C
engine)
valve
is
attached to the intake collec-
E
C
CS
control unit actuates
is
left
air
that will flow through the
on, the
AAC
160
Hz
larger
A A C
the
(VG30ET
The
tor The
valve by ON/OFF pulse of approximately
The longer that ON duty
amount of
valve
nents (Cont'd)
E
G R CONTROL VALVE
The
E G R.
exhaust
through vertical movement of the taper valve connected to the diaphragm, to which vacuum
applied in response to the opening
valve.
control valve controls the quantity of
gas
to be led to the intake manifold
of
the throttle
IS
1
AV
IDLE-UP SOLENOID VALVE (VG30E
The idle-up solenoid
collector The solenoid valve actuates to stabilize
idle speed when engine load
electric load, power steering oil pump, etc.
ldleup
solenoid
valve
valve
is
attached to
is
heavy because of
idle
speed
adiuning
SEF630B
engine)
the
intake
screw
7
When
of
ciency of the exhaust gas will be reduced.
installing
its
direction. Otherwise the distribution
the
E.G.R.
guide tube, be careful
SEF632B
effi-
SEF689B
FICDJ
solenoid
F
I
C
valve
D
adjusling
screw
SEF631
EF
B
8i
EC-18
E.
C.
C.
S.
DESCRIPTION
E.C.C.S. Components (Cont’d)
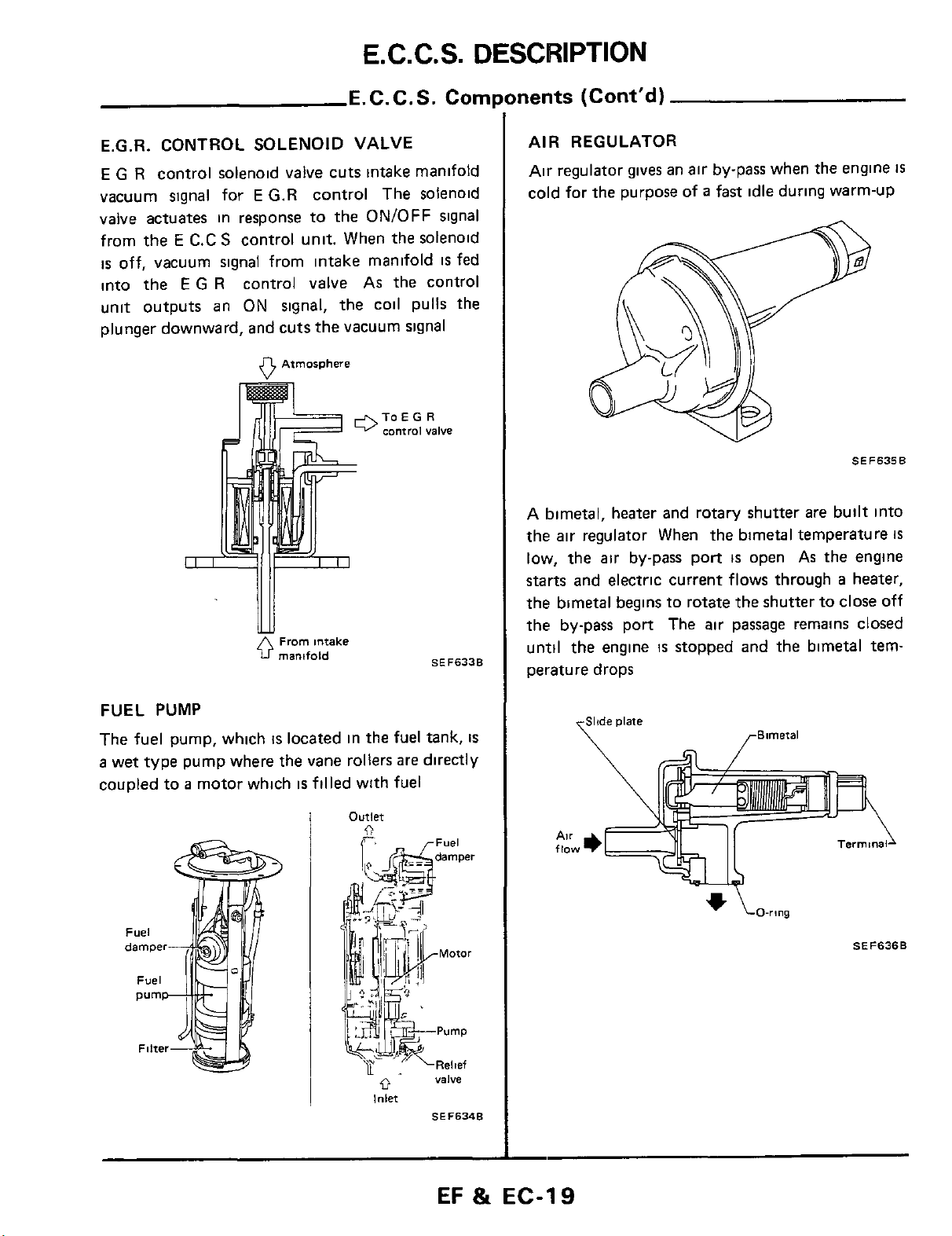
E.G.R. CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE
E
G
R
control solenoid valve cuts intake manifold
vacuum signal for
valve actuates in response to the ON/OFF signal
from
the
E
C.C
is
off, vacuum signal from intake manifold
into the
unit outputs an ON signal, the coil pulls the
plunger downward, and cuts the vacuum signal
E
G
E
G.R
control The solenoid
S
control unit. When the solenoid
R
control valve
9
Atmosphere
From
0
intake
manifold
As
the control
ToEGR
control
is
fed
valve
SEF6336
AIR REGULATOR
Air regulator gives an
cold for the purpose of a fast idle during warm-up
A bimetal, heater and rotary shutter
the air regulator When the bimetal temperature
low,
the air by-pass port
starts
the bimetal begins to rotate the shutter
the by-pass port The air passage remalns closed
until the engine
perature drops
and electric current flows through a heater,
air
by-pass when the engine
SE
are
built into
is
open As the engine
to
close off
is
stopped and the bimetal tem-
F635
IS
is
B
FUEL PUMP
The fuel pump, which
a
wet type pump where the vane rollers are directly
coupled to
a
motor which
is
located in the
is
filled with fuel
1
Outlet
fuel
tank,
A
IS
SEF636B
EF
&
EC-19
E.C.C.S.
DESCRIPTION
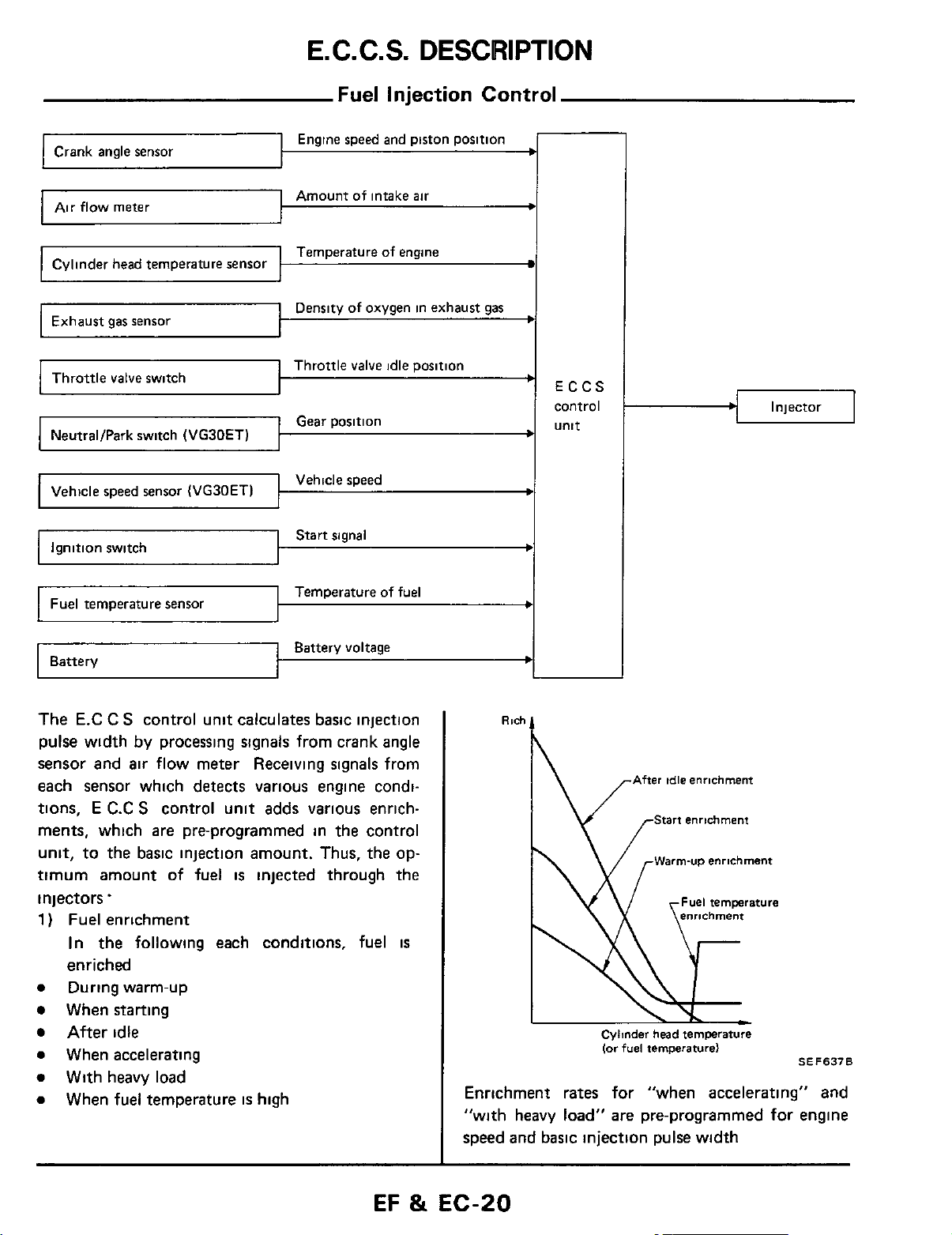
Fuel Injection Control
Engine
speed
and piston
position
Air
flow
I I
Cylinder
Exhaust
Throttle
NeutraVPark
I
Battery
meter
head
temperature
gas
sensor
valve
switch
switch (VG30ET)
sensor
Amount
Temperature
Density
Throttle
Gear
position
I
Vehicle
Start
signal
Temperature
Battery
of
intake
of
of
oxygen
valve
speed
of
voltage
engine
idle
fuel
air
in
exhaust
position
gas
I
'
ECCS
control
unit
.I
Injector
The
E.C
C
S
control unit calculates basic injection
pulse
width
by
processing signals from crank angle
sensor and air flow meter Receiving signals from
each sensor which detects various engine conditions,
ments, which are pre-programmed
unit,
timum
E
C.C
S
control
to
the basic injection amount. Thus,
amount
of
fuel
unit
adds various enrich-
is
injected through the
in
the control
the
op-
injectors.
1
)
Fuel
enrichment
In
the following each conditions,
fuel
is
enriched
e
During warm-up
When starting
After idle
e
When accelerating
e
With heavy load
e
When fuel temperature
is
high
Rlch
'
Enrichment rates
"with
heavy load" are pre-programmed
\/
Cylmder
(or
fuel
for
.-Warm-u~
head
temperature
temperature1
"when accelerating" and
speed and basic injection pulse
enrichment
width
for
SE
F637
engine
0
EF
&
EC-20
E.
C.
C.
S.
DESCRIPTION
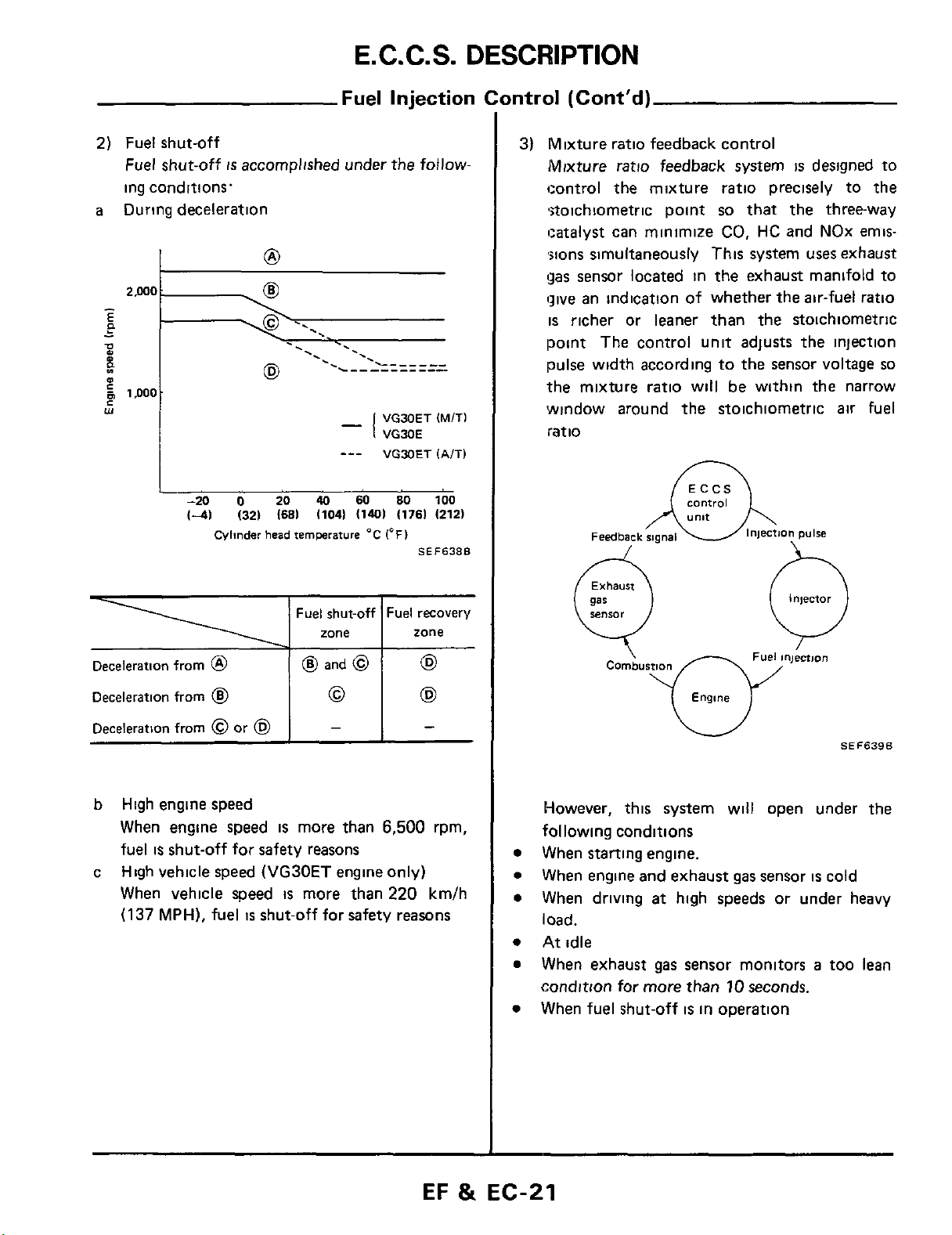
2)
Fuel
shut-off
Fuel
shut-off
ing conditions.
a
During deceleration
-
-20
(-41
Fuel
is
accomplished under the follow-
-..
.
.
._
.
.
_--
0
1321
Cvlinder
head
40 60
20
(681
11041
IemPerature "C
Injection
'.
VG30ET (MITI
VG30E
VGXIET
SO
(1401
(1761
1°F)
IA/Tl
100
12121
SEF638B
mtrol (Cont'd)
3)
Mixture ratio feedback control
Mixture
control the mixture ratio precisely to the
*stoichiometric point
!catalyst can minimize
';ions simultaneously This system
gas
give an indication of whether the air-fuel ratio
is
point The control unit adjusts the injection
pulse
the mixture ratio will be within the narrow
window around the stoichiometric
ratio
ratio
feedback system
so that the three-way
CO,
senwr located in the exhaust manifold to
richer or leaner
width according
than
eontroi
to
the sensor voltage so
is
HC
and NOx emis-
uses
the stoichiometric
designed to
exhaust
air
fuel
Deceleration from
Deceleration from
Deceleration from 0 or
b
High engine speed
When engine speed
fuel
is
High vehicle speed
c
When vehicle speed
(137
MPH), fuel
@
@
shut-off for safety reasons
@
and
0
@
is
(VG30ET
is
is
shut-off for safety
-
more than 6,500 rpm,
engine
more than
@
62
(E9
-
only)
220
reasons
km/h
Injector
0
Combustm
Engme
However, this system will open under the
following conditions
When starting engine.
When engine and exhaust
When driving
load.
At idle
When exhaust
condition for more than
When fuel shut-off
at
high speeds or under heavy
gas
sensor monitors a too lean
is
gas
sensor
10
seconds.
in omration
is
cold
EF
&
EC-21

E.C.C.S.
DESCRIPTION
-Fuel
4)
Simultaneous injection and group injection
On
injection systems
injection and group injection. In the former,
fuel
neously twice each engine cycle
In other words, pulse signals
are simultaneously transmitted from the
E
times for each engine cycle
In the group injection system, six injectors are
divided into
and
into each group separately once each engine
cycle
Group
NO
1
NO
2
No
3
No
4
No 5 cylinder
No
6cylinder
injection Control (Cont'd)-
the
VG30ET
is
injected into
C.C.S. control unit to the six injectors
two
No
4,
No
injection
cylmder
cylindercylinder
cylmdern
u
-
engines,
are
groups
5,
No
two
types
used
-
simultaneous
all
six cylinders simulta-
of
the same width
-
No
1,
No.
2,
6 And
fuel
is
n
_n
L-
1
engine
cvcle4
of
fuel
two
No.
3
injected
.
Slrnultaneous
No
1
NO 2 cylinder
No
3
No
4
No
5
No
6
When any
injection shifts to simultaneous injection from
group injection.
Engine speed
Injection
Cylinder head temperature
(1
cylinder
cylinder
cylinder
cylinder
cylinder
40"
F)
ln,ect,On
u
-
u
u
u
u
I
of
the following conditions are met, fuel
is
pulse
duration
1
engm
more than
is
cycle
I
SEF640B
3,000
more than 6.5ms
rpm
IS
below 60°C
EF
&
EC-22
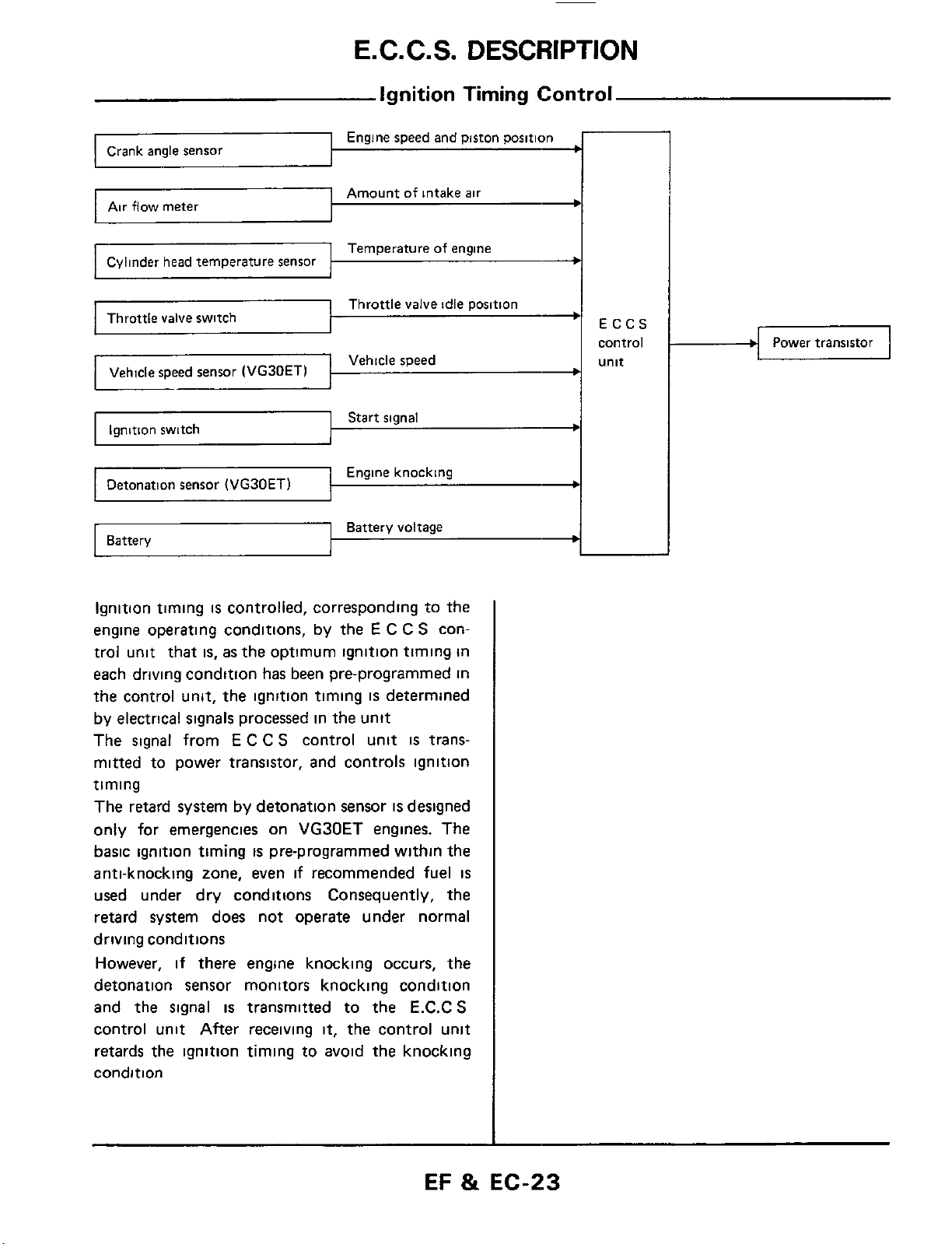
E.
C.
C.
S.
DESCRIPTION
Ignition Timing Control
Crank angle sensor
Air flow meter
Cylinder head temperature sensor
Vehicle speed sensor
I
Ignition switch
Detonation sensor
Battery
~
(VG30ETl
Engine speed and piston position
Amount of intake
Temperature of engine
Throttle valve idle position
Vehicle
1
Start signal
Engine knocking
Battery voltage
speed
air
Power transistor
I
Ignition timing
engine operating conditions, by the
trol unit that
each driving condition has been pre-programmed in
the control unit, the ignition timing
by electrical signals processed in the unit
The signal from
mitted to power transistor, and controls ignition
timing
The retard system by detonation sensor
only for emergencies on VG30ET engines. The
basic ignition timing
anti-knocking zone, even
used under dry conditions Consequently, the
retard system does not operate under normal
driving conditions
However,
detonation sensor monitors knocking condition
and
the signal
control unit After receiving
retards the ignition timing to avoid the knocking
condition
is
controlled, corresponding to the
E
C C S con-
is,
as
the optimum ignition timing in
IS
determined
E
C C S control unit
is
pre-programmed within the
if
recommended fuel
if
there engine knocking occurs, the
is
transmitted to the E.C.C
it,
the control unit
is
is
designed
trans-
is
S
EF
&
EC-23
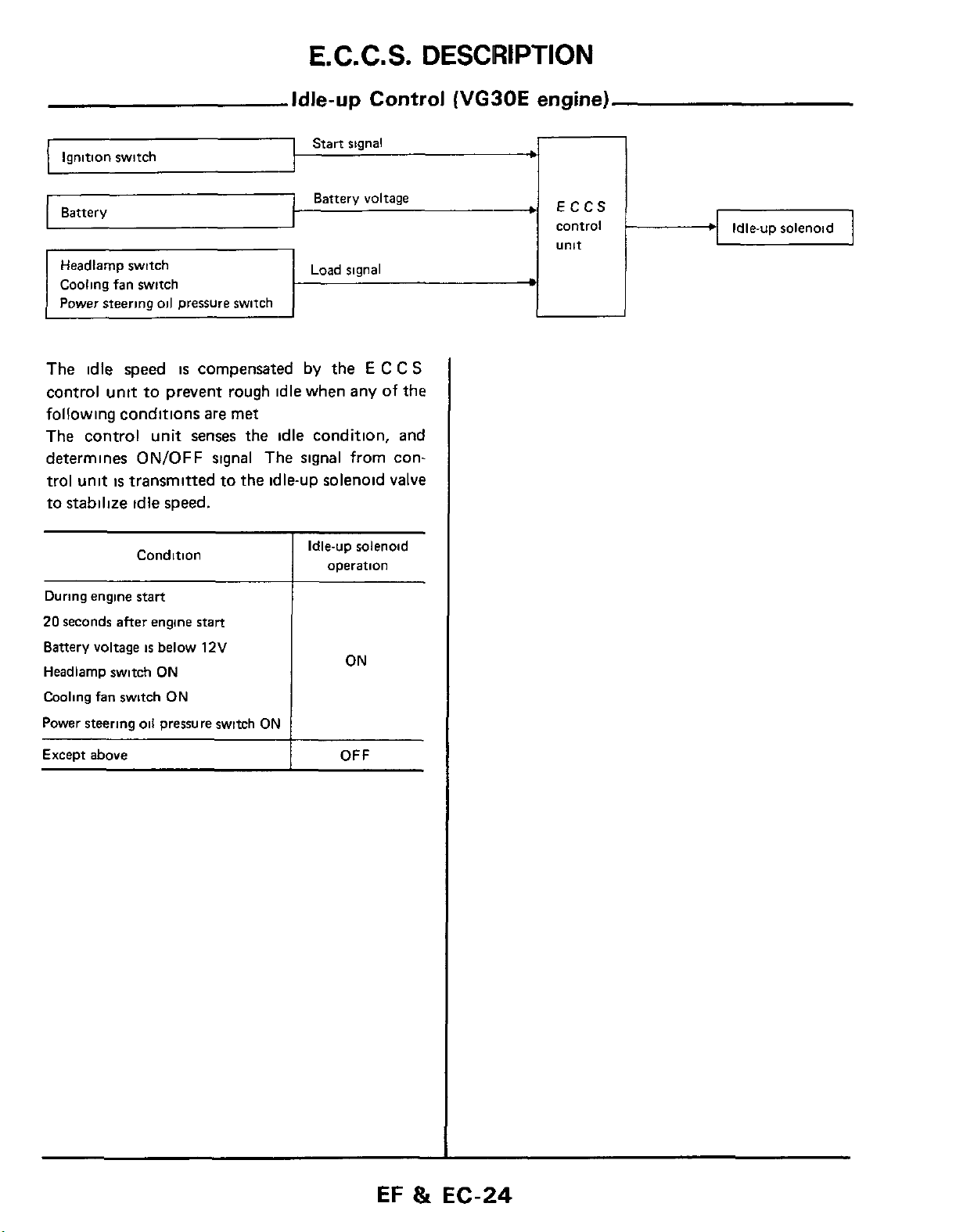
E.C.C.S.
DESCRIPTION
Idle-up Control
Ignition switch
Battery
~-
Headlarnp switch Load signal
Cooling fan switch
Power steering
The idle
oil
speed
pressure switch
is
compensated
control unit to prevent rough idle when any of the
are
following conditions
met
The control unit senses the idle condition, and
determines
trol unit
is
ON/OFF
transmitted to the idle-uD solenoid valve
signal The signal from con-
to stabilize idle speed.
Condition
Start signal
Battery voltage
by
the
E
C
Idle-up solenoid
operation
C
S
(VG30E
engine)
ECCS
control
unit
During engine start
20
seconds after engine
Battery voltage
Headlarnp switch
Cooling fan switch
Power steering oil pressure switch
Except above
is
below
ON
ON
start
12V
ON
ON
OFF
EF
8t
EC-24
 Loading...
Loading...