Netgear WNDAP660 Installation Manual [zh]

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Reference Manual
350 East Plumeria Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
USA
November, 2015
202-10984-03
ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Support
Thank you for purchasing this NETGEAR product. You can visit www.netgear.com/support to register your product, get
help, access the latest downloads and user manuals, and join our community. We recommend that you use only official
NETGEAR support resources.
Conformity
For the current EU Declaration of Conformity, visit http://kb.netgear.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/11621.
Compliance
For regulatory compliance information, visit http://www.netgear.com/about/regulatory.
For the Notification of Compliance statement, visit
http://www.netgear.com/images/pdf/Notification_of_Compliance.pdf.
See the regulatory compliance document before connecting the power supply.
Trademarks
© NETGEAR, Inc., NETGEAR and the NETGEAR Logo are trademarks of NETGEAR, Inc. Any non-NETGEAR trademarks
are used for reference purposes only.
Revision History
Publication Part Number Publish Date Comments
202-10984-03 November 2015 Revised the Support section on this page.
202-10984-02 October 2015 Removed the Notification of Compliance appendix and
provided a Notification of Compliance link on this page.
202-10984-01 (v2.0) October 2012 Minor nontechnical revisions.
202-10984-01 (v1.0) September 2012 First publication.
2

Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction
Chapter 2 Installation and Basic Configuration
About the ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point
WNDAP660 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
What Is in the Box? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Key Features and Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Supported Standards and Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Key Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
802.11b/g/n and 802.11a/n Standards–Based Wireless Networking. . .11
Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Hardware Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Top Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Bottom Panel with Product Label . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Register the Wireless Access Point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
What You Need Before You Begin. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Wireless Equipment Placement and Range Guidelines. . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Ethernet Cabling Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
LAN Configuration Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Hardware Requirements for Computers on Your LAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Operating Frequency (Channel) Guidelines. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Requirements for Entering IP Addresses. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Install and Configure the Wireless Access Point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Connect the Wireless Access Point to a Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Log In to the Wireless Access Point. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Configure Basic General System Settings and Time Settings . . . . . . . .23
Configure the IPv4 Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Configure the Optional DHCPv4 Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Configure the Basic Wireless Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Test Basic Wireless Connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Mount the Wireless Access Point. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Ceiling Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Wall Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Desk Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Chapter 3 Wireless Configuration and Security
Wireless Data Security Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
3

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Security Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Before You Change the SSID, WEP, and WPA Settings. . . . . . . . . . . .46
Configure and Enable Security Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Configure RADIUS Server Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Restrict Wireless Access by MAC Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Schedule the Wireless Radios to Be Turned Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Configure Basic Wireless Quality of Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Chapter 4 Management and Monitoring
Enable Remote Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
SNMP Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Secure Shell and Telnet Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Upgrade the Wireless Access Point Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Web Browser Upgrade Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
TFTP Server Upgrade Procedure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
Manage the Configuration File or Reset to Factory Defaults . . . . . . . . . . .70
Save the Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Restore the Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Restore the Wireless Access Point to the Factory Default Settings. . . .71
Reboot the Wireless Access Point without Restoring the
Default Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Change the Administrator Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Manage User Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Enable the Syslog Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
Monitor the Wireless Access Point. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
View System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Monitor Wireless Stations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
View the Activity Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Traffic Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
Enable Rogue AP Detection and Monitor Access Points. . . . . . . . . . . . . .85
Enable and Configure Rogue AP Detection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .85
View and Save Access Point Lists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Configure Wireless Intrusion Detection and Prevention. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .89
Configure Wireless Intrusion Detection and Prevention Policy Settings 89
Configure Wireless Intrusion Detection and Prevention Mail Settings . .95
Monitor Traps, Counters, and Ad Hoc Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .96
Chapter 5 Advanced Configuration
Configure IPv6 Settings and Optional DHCPv6 Server Settings . . . . . . . .99
Configure the IPv6 Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
Configure the Optional DHCPv6 Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .101
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol, 802.1Q VLAN, and
Link Layer Discovery Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Configure STP and VLANs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Configure Ethernet LLDP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Configure Hotspot Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .106
Configure Advanced Wireless Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
4

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Configure Advanced Quality of Service Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
Configure Quality of Service Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .113
Configure Wireless Bridging. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .119
Configure a Point-to-Point Wireless Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .119
Configure a Point-to-Multipoint Wireless Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .123
Configure the Wireless Access Point to Repeat the Wireless
Signal Using Point-to-Multipoint Bridge Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .127
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
Basic Functioning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .133
Verify the Correct Sequence of Events at Startup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .133
No LEDs Are Lit on the Wireless Access Point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .133
The Active LED or the LAN LED Is Not Lit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .134
The WLAN LED Does Not Light Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .134
You Cannot Access the Internet or the LAN from a
Wireless-Capable Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .135
You Cannot Configure the Wireless Access Point from a Browser . . . . .135
When You Enter a URL or IP Address a Time-Out Error Occurs. . . . . . .136
Troubleshoot a TCP/IP Network Using the Ping Utility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .136
Test the LAN Path to Your Wireless Access Point. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .137
Test the Path from Your Computer to a Remote Device . . . . . . . . . . .138
Problems with Date and Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .138
Use the Packet Capture Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .139
Appendix A Supplemental Information
Technical Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .140
Factory Default Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .143
Appendix B Command-Line Reference
Index
5
1. Introduction
This chapter introduces the NETGEAR® ProSAFE® Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N
Access Point WNDAP660 and describes some of the key features. The chapter includes the
following sections:
• About the ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
• What Is in the Box?
• System Requirements
• Key Features and Standards
• Hardware Description
• Register the Wireless Access Point
Note: For more information about the topics covered in this manual, visit
the Support website at http://support.netgear.com.
1
Note: Firmware updates with new features and bug fixes are made
available from time to time at downloadcenter.netgear.com. Some
products can regularly check the site and download new firmware,
or you can check for and download new firmware manually. If the
features or behavior of your product do not match what is described
in this guide, you might need to update your firmware.
About the ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
The ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660, going
forward in this manual referred to as the wireless access point, is a powerful building block of
a wireless LAN infrastructure. It provides concurrent 2.4 GHz 802.11b/g/n and
5 GHz 802.11a/n connectivity between wired Ethernet networks and radio-equipped wireless
notebook systems, desktop systems, print servers, and other devices. Support for three
6

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
transmit radio chains and three receive radio chains, also referred to as 3x3 multiple input,
multiple output (MIMO), can increase wireless throughput considerably.
The wireless access point provides wireless connectivity to multiple wireless network devices
within a fixed range or area of coverage—interacting with a wireless network interface card
(NIC) through an antenna. T ypically , an individual in-building wireless access point provides a
maximum connectivity area with about a 500-foot radius. The wireless access point can
support a maximum of 128 clients in a range of several hundred feet. The throughput is
shared between all clients. Make sure that you install a sufficient number of wireless access
points to meet the required coverage, throughput, and quality of your wireless network.
The wireless access point acts as a bridge between the wired LAN and wireless clients.
Connecting multiple wireless access points through a wired Ethernet backbone can further
increase the wireless network coverage. As a mobile computing device moves out of the
range of one wireless access point, it moves into the range of another. As a result, wireless
clients can freely roam from one wireless access point to another and still maintain a
seamless connection to the network.
The autosensing capability of the wireless access point allows packet transmission at up to
450 Mbps, or at reduced speeds to compensate for distance or electromagnetic interference.
Advanced wireless features that are supported on the wireless access point include a
wireless intrusion detection system (IDS), wireless intrusion prevention system (IPS),
configurable wireless QoS policies, and band steering.
You can manage the wireless access point from either an IPv4 or IPv6 address, and the
wireless access point can allocate either IPv4 or IPv6 DHCP addresses to its wireless clients.
What Is in the Box?
The product package contains the following items:
• ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
• Power adapter and cord (12 VCD, 1.5A)
• Straight-through Category 5 Ethernet cable
• Installation guide
• Resource CD, which includes this manual
• Wall-mount kit made up of brackets and hardware
Contact your reseller or customer support in your area if there are any missing or damaged
parts.
See the NETGEAR website at http://support.netgear.com/general/contact/default.aspx for
the telephone number of customer support in your area. Keep the installation guide, along
with the original packing materials. If you need to return the wireless access point for repair,
use the packing materials to repack the wireless access point.
Introduction
7

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
System Requirements
Before installing the wireless access point, make sure that your system meets these
requirements:
• A 10/100/1000 Mbps local area network device such as a hub or switch
• The Category 5 UTP straight-through Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connector included in the
package, or one like it
• A 100–120V, 50–60 Hz AC power source
• A computer with the TCP/IP protocol installed and a web browser for configuration, such
as Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 or later, or Mozilla 1.5 or later
• An 802.11a/n- or 802.11b/g/n-compliant device, such as the NETGEAR N600 Wireless-N
Dual Band USB Adapter (WNDA3100)
Key Features and Standards
• Supported Standards and Conventions
• Key Features
• 802.11b/g/n and 802.11a/n Standards–Based Wireless Networking
• Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink
The wireless access point is easy to use and provides solid wireless and networking support.
It also offers a wide range of security options.
Supported Standards and Conventions
The wireless access point supports the following standards and conventions:
• Standards compliance. The wireless access point complies with the IEEE 802.11a/b/g
standards for wireless LANs and is Wi-Fi certified for 802.11n standard.
• WPA and WPA2. The wireless access point provides WPA and WPA2 enterprise-class
strong security with RADIUS and certificate authentication as well as dynamic encryption
key generation. The WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK pre-shared key authentication does not
have the overhead of RADIUS servers but provides the strong security of WPA.
• Multiple BSSIDs. The wireless access point supports multiple BSSIDs. When a wireless
access point is connected to a wired network and a set of wireless stations, it is called a
basic service set (BSS). The basic service set identifier (BSSID) is a unique identifier
attached to the header of packets sent over a WLAN that differentiates one WLAN from
another when a mobile device tries to connect to the network.
The multiple BSSID feature allows you to configure up to 16 SSIDs (8 per radio) on your
wireless access point and assign different configuration settings to each SSID. All the
configured SSIDs are active, and the network devices can connect to the wireless access
point by using any of these SSIDs.
Introduction
8

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
• DHCP server and client. The DHCP server of the wireless access point can provide a
dynamic IPv4 or IPv6 address to wireless clients. The wireless access point can also act
as a client and obtain an IPv4 or IPv6 address from a DHCP server on the LAN.
• SNMP. The wireless access point supports Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP) for Management Information Base (MIB) management.
• STP and LLDP. The wireless access point supports Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and
Ethernet Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP). LLDP is enabled by default.
• 802.1Q VLAN. A network of computers can behave as if they are connected to the same
network even though they might actually be physically on different segments of a LAN.
Virtual LANs (VLANs) are configured through software rather than hardware, which
makes them very flexible. VLANs are very useful for user and host management,
bandwidth allocation, and resource optimization.
Key Features
The wireless access point provides solid functionality, including the following features:
• Dual band. The wireless access point can operate concurrently in the 2.4 GHz and
5 GHz bands.
• Band steering. Band steering can ensure that a dual-band wireless station operates in
the 5 GHz band rather than in the 2.4 GHz band, which is often highly congested. Band
steering can also move a wireless station that already operates in the 2.4 GHz band to
the 5 GHz band. Band steering is an advanced wireless feature that reduces the client
density in the 2.4 GHz band and increases the wireless network capacity.
• IPv4 and IPv6. The wireless access point is manageable from either an IPv4 or IPv6
address, it can function as an IPv4 or IPv6 DHCP client, and its DHCP server can
allocate either IPv4 or IPv6 addresses.
• Multiple operating modes:
- Wireless access point. Operates as a standard 802.1 1b/g/n and 802.11a/n wireless
access point.
- Point-to-point bridge. In this mode, the wireless access point communicates only
with another bridge-mode wireless station or wireless access point. Network
authentication should be used to protect this communication.
- Point-to-multipoint bridge. Select this option only if this wireless access point is the
master for a group of bridge-mode wireless stations. The other bridge-mode wireless
stations send all traffic to this master and do not communicate directly with each
other. Network authentication should be used to protect this traffic.
- Repeater. In this mode, the wireless access point does not function as an access
point for clients but functions only in point-to-multipoint bridge mode to repeat the
wireless signal and send all traffic to a remote access point. Network authentication
should be used to protect this communication.
• WMM. Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) is a subset of the 802.11e standard. WMM allows
wireless traffic to have a range of priorities, depending on the kind of data.
Time-dependent information, like video or audio, has a higher priority than normal traffic.
For WMM to function correctly, wireless clients also need to support WMM.
Introduction
9

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
• QoS. Quality of Service (QoS) support lets you configure parameters that affect traffic
flowing from the wireless access point to the client station and traffic flowing from the
client station to the wireless access point:
- The QoS settings let you prioritize traffic, such as voice and video traffic, so that
packets do not get dropped.
- The QoS policies let you configure classifications (match clauses) and apply traffic to
eight priority queues based on IP precedence, DSCP, MAC address, IP address, and
other information that might be present in Layer 2 and Layer 3 packet headers.
• Wireless IDS/IPS. The wireless intrusion detection system (IDS) and intrusion prevention
system (IPS) can detect and prevent a variety of wireless attacks. Attacks are covered by
preconfigured policy rules. When an attack occurs, the wireless access point can notify a
network administrator though an email.
• Hotspot support. You can allow all HTTP (TCP, port 80) requests to be captured and
redirected to the URL you specify.
• Rogue AP and ad hoc network detection. Rogue AP filtering and ad hoc network
detection ensure that unknown APs and networks are not given access to any part of the
secured wireless and wired LAN.
• Access control. MAC address filtering can ensure that only trusted wireless stations can
use the wireless access point to gain access to the wireless and wired LAN.
• Security profiles. When using multiple BSSIDs, you can configure unique security
settings (encryption, SSID, and so on) for each BSSID.
• Hidden mode. The SSID is not broadcast, assuring that only clients configured with the
correct SSID can connect.
• Secure Telnet command-line interface. The secure Telnet command-line interface
(CLI) enables direct secure access over the serial port and easy scripting of configuration
of multiple wireless access points across an extensive network through the Ethernet
interface. A Secure Shell (SSH) client is required.
• Upgradeable firmware. Firmware is stored in a flash memory . You can upgrade it easily,
using only your web browser, and you can upgrade it remotely. You can also use the
command-line interface.
• Configuration backup. Configuration settings can be backed up to a file and restored.
• Secure and economical operation. Adjustable power output allows more secure or
economical operation.
• PoE support. Using Power over Ethernet (PoE), any 802.3af-compliant midspan or
end-span sources can supply power to the wireless access point over one or two
Ethernet ports. The wireless access point can receive all required power on one Ethernet
port from a single PoE source. However, with two Ethernet ports and two PoE sources,
power redundancy ensures that if one Ethernet port is down, the other Ethernet port can
still supply all power to the wireless access point for continued operation.
• Autosensing Ethernet connection with
Auto Uplink™ interface. Connects to
10/100/1000 Mbps IEEE 802.3 Ethernet networks.
• LED indicators. Power/Test, Active, LAN, and WLAN for each radio mode are easily
identified.
Introduction
10

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
• VLAN security profiles. Each security profile is automatically allocated a VLAN ID when
the security profile is modified.
802.11b/g/n and 802.11a/n Standards–Based Wireless Networking
The wireless access point provides a bridge between wired Ethernet LANs and 802.11b/g/nand 802.11a/n-compatible wireless LAN networks. It provides connectivity between wired
Ethernet networks and radio-equipped wireless notebook systems, desktop systems, print
servers, and other devices.
In addition, the wireless access point supports the following wireless features:
• Aggregation support
• Reduced InterFrame spacing support
• 3 x 3 multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) support
• Distributed coordinated function (CSMA/CA, back-off procedure, ACK procedure,
retransmission of unacknowledged frames)
• RTS/CTS handshake
• Beacon generation
• Packet fragmentation and reassembly
• Auto or long preamble
• Roaming among wireless access points on the same subnet
Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink
The wireless access point can connect to a standard Ethernet network. The LAN interface is
autosensing and capable of full-duplex or half-duplex operation.
The wireless access point incorporates Auto Uplink technology. The Ethernet port
automatically senses whether the Ethernet cable plugged into the port should have a
“normal” connection such as to a computer or an “uplink” connection such as to a switch or
hub. That port then configures itself correctly. This feature also eliminates any concerns
about crossover cables, as Auto Uplink accommodates either type of cable to make the right
connection.
Hardware Description
This section describes the top and rear hardware functions of the wireless access point.
• Top Panel
• Rear Panel
• Bottom Panel with Product Label
Introduction
11

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Top Panel
The LEDs of the wireless access point are described in the following figure and table:
1
23
4
5
6
Figure 1.
Table 1. Top panel LEDs
Item LED Description
1 Power/Test Off Power is off.
On (green) Power is on.
Amber, then blinking
green
2 Active Off No Ethernet traffic is detected, or no link is detected.
On or blinking (green) Ethernet traffic is detected.
3 LAN 1 Off 10 Mbps or no link is detected on LAN port 1.
Amber 10/100 Mbps link is detected on LAN port 1.
Green 1000 Mbps link is detected on LAN port 1.
A self-test is running or software is being loaded.
During startup, the LED is first steady amber, then
goes off, and then blinks green before turning steady
green after about 45 seconds. If after 1 minute the
LED remains amber or continues to blink green, it
indicates a system fault.
4 LAN 2 Off 10 Mbps or no link is detected on LAN port 2.
Amber 10/100 Mbps link is detected on LAN port 2.
Green 1000 Mbps link is detected on LAN port 2.
Introduction
12

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Table 1. Top panel LEDs (continued)
Item LED Description
5
2.4
Ghz
6
5
Ghz
Rear Panel
WLAN Off Wireless 802.11b/g/n (2.4 GHz) LAN is not ready, or
no wireless activity is detected.
On or blinking (green) Wireless 802.11b/g/n (2.4 GHz) LAN is ready, or
wireless activity is detected.
WLAN Off Wireless 802.11n/a (5 GHz) LAN is not ready, or no
wireless activity is detected.
On or blinking (green) Wireless 802.11n/a (5 GHz) LAN is ready, or wireless
activity is detected.
1
Figure 2.
2
3
4
5
6
8
7
9
The rear panel components of the wireless access point, from left to right, are described in
the following list:
1. First reverse SMA connector for an optional 2.4 GHz antenna.
2. Factory default Reset button. Using a sharp object, press and hold this button for about
5 seconds to reset the wireless access point to factory defaults settings. All configuration
settings are lost, and the default password is restored. For more information, see Restore
the Wireless Access Point to the Factory Default Settings on page 71.
3. First 10/100/1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet (RJ-45) port with Auto Uplink (Auto MDI-X) with
IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet (PoE) support for connection to a switch or router.
4. Second 10/100/1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet (RJ-45) port with Auto Uplink (Auto MDI-X)
with IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet (PoE) support for connection to a switch or router.
5. Second reverse SMA connector for an optional 2.4 GHz antenna.
6. Console port for connecting to an optional console terminal. The port has an RJ-45
connector and supports the following settings: 9600 K default baud rate, 8 data bits, no (N)
parity bit, and one (1) stop bit.
7. Cable security lock receptacle for an optional lock.
Introduction
13

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
8. Power socket for a 12 VDC, 1.5A power adapter.
9. Third reverse SMA connector for an optional 2.4 GHz antenna.
Note: The wireless access point can support up to three optional 2.4 GHz
antennas.
Bottom Panel with Product Label
The product label on the bottom of the wireless access point’s enclosure displays factory
default settings, regulatory compliance, and other information:
Figure 3.
Register the Wireless Access Point
To qualify for product updates and product warranty, NETGEAR encourages you to register
your product. The first time that you connect to the wireless access point while it is connected
to the Internet, you have the option to register your product. At any time, you can register
your product from the web management interface, or you can go to the NETGEAR website
for registration at https://my.netgear.com/registration/login.aspx.
To register the wireless access point with NETGEAR:
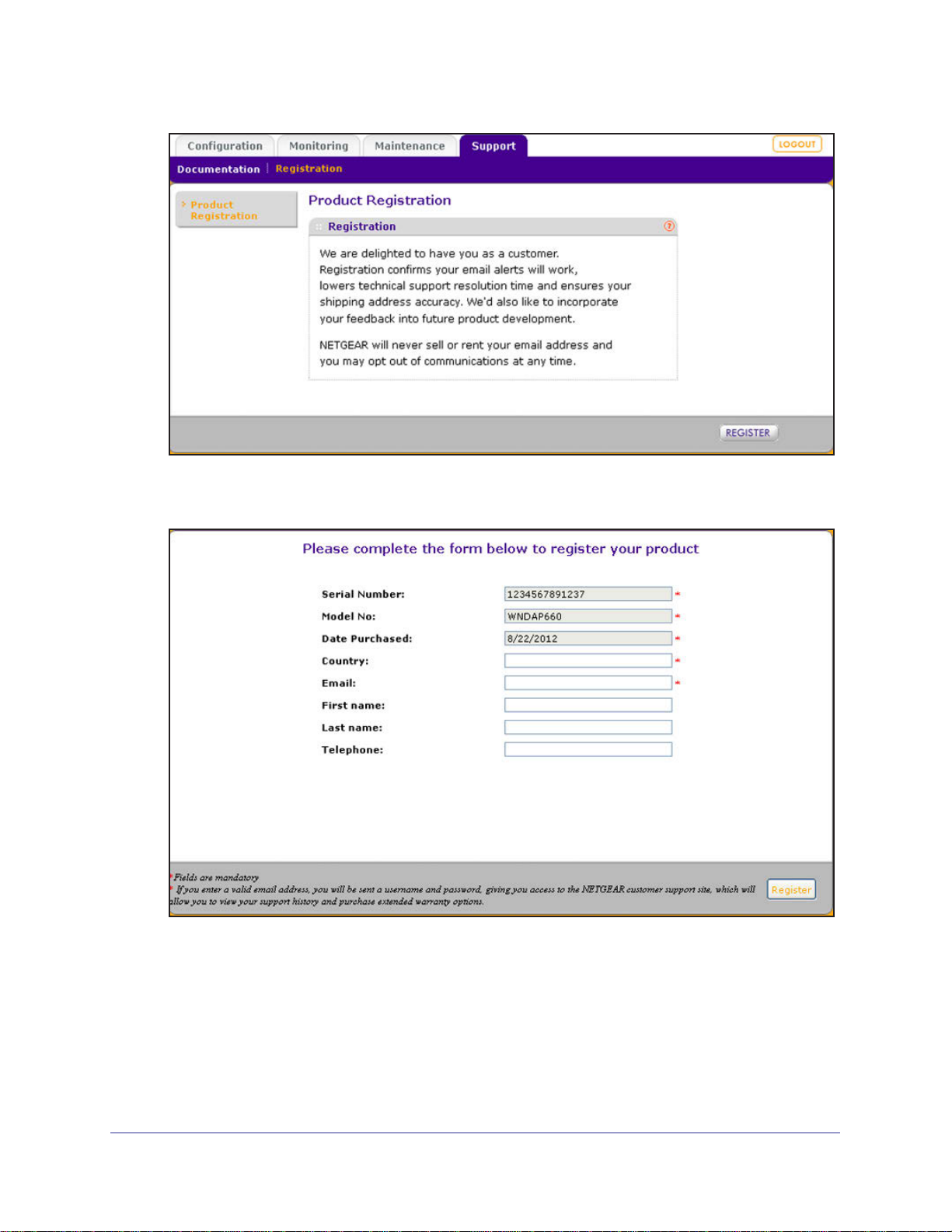
1. Select Support > Registration. The Product Registration screen displays:
Introduction
14
ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Figure 4.
2. Click Register. A new screen displays in your browser:
Figure 5.
3. Enter the information in the blank fields. The serial number, model number, and date of
purchase are entered automatically.
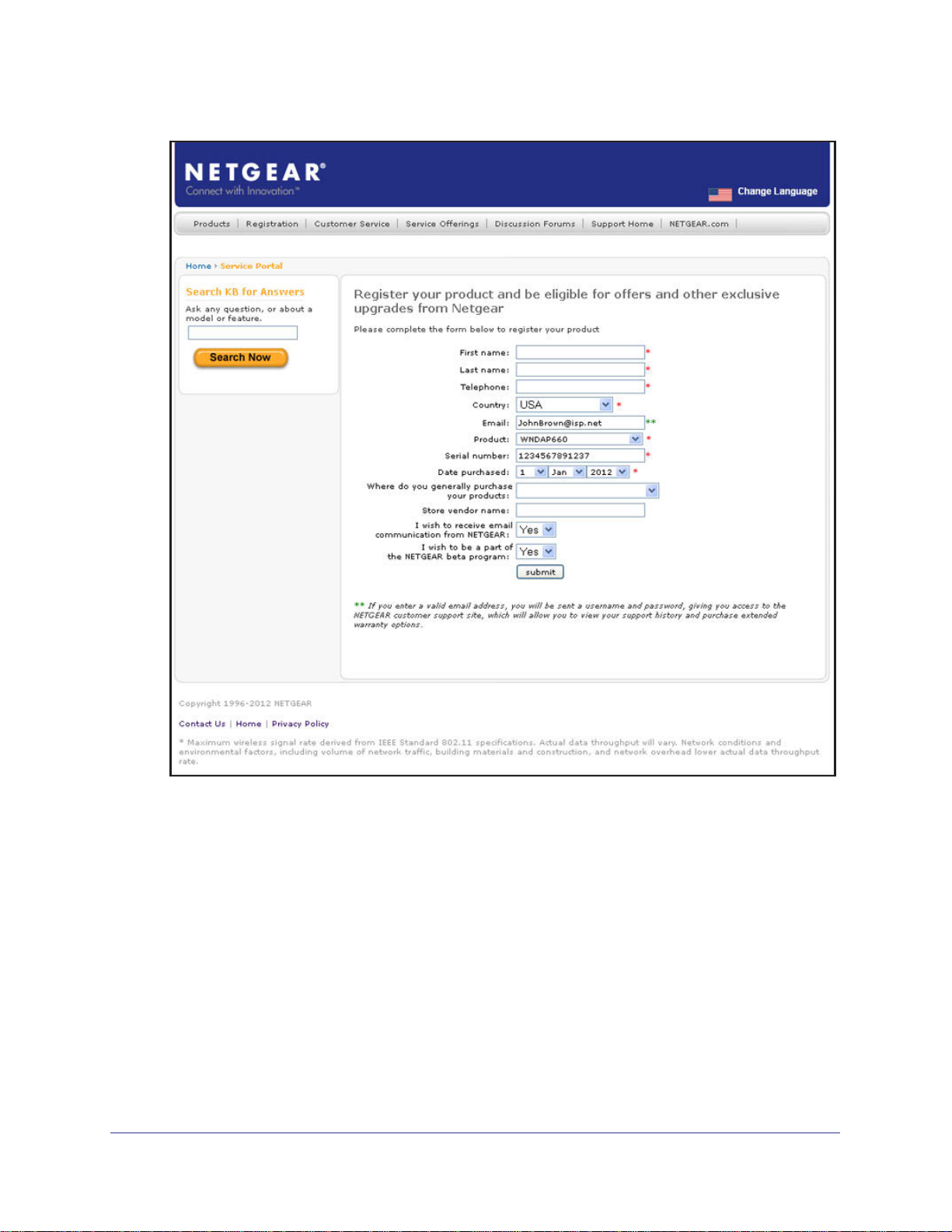
4. Click Register. The registration web page displays:
Introduction
15
ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Figure 6.
5. Complete the registration form.
6. Click submit.
Introduction
16

2. Installation and Basic Configuration
This chapter describes how to install and configure the wireless access point for wireless
connectivity to your LAN. This basic configuration enables computers with 2.4 GHz 802.11b/g/n
and 5 GHz 802.1 1a/n wireless adapters to connect to the Internet or access printers and files on
your LAN. In planning your wireless network, consider the level of security required. Chapter 3,
Wireless Configuration and Security, describes how to set up wireless security for your network.
This chapter includes the following sections:
• What You Need Before You Begin
• Install and Configure the Wireless Access Point
• Test Basic Wireless Connectivity
• Mount the Wireless Access Point
What You Need Before You Begin
2
• Wireless Equipment Placement and Range Guidelines
• Ethernet Cabling Requirements
• LAN Configuration Requirements
• Hardware Requirements for Computers on Your LAN
• Operating Frequency (Channel) Guidelines
• Requirements for Entering IP Addresses
You need to consider the following guidelines and requirements before you can set up your
wireless access point. See also System Requirements on page 8.
Wireless Equipment Placement and Range Guidelines
The range of your wireless connection can vary significantly based on the location of the
wireless access point. The latency, data throughput performance, and power consumption of
wireless adapters also vary depending on your configuration choices.
17

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Note: Failure to follow these guidelines can result in significant
performance degradation or inability to connect wirelessly to the
wireless access point. For complete performance specifications, see
Appendix A, Supplemental Information.
Note: Before you position and mount the wireless access point at its
permanent position, first configure the wireless access point and test
the computers on your LAN for wireless connectivity as explained in
this chapter.
For best results, place your wireless access point according to the following general
guidelines:
• Near the center of the area in which the wireless devices will operate.
• In an elevated location such as a high shelf where the wirelessly connected devices have
line-of-sight access (even if through walls).
• Away from sources of interference, such as computers, microwaves ovens, and 2.4 GHz
cordless phones.
• Away from large metal surfaces or water.
• Placing an external antenna in a vertical position provides best side-to-side coverage.
Placing an external antenna in a horizontal position provides best up-and-down coverage.
(An external antenna does not come standard with the wireless access point.)
• If you are using multiple wireless access points, it is better if adjacent wireless access
points use different radio frequency channels to reduce interference. The recommended
channel spacing between adjacent wireless access points is five channels (for example,
use Channels 1 and 6, or 6 and 11, or 1 and 11).
The time it takes to establish a wireless connection can vary depending on both your security
settings and placement. WEP connections can take slightly longer to establish. Also, WEP
encryption can consume more battery power on a notebook computer.
Ethernet Cabling Requirements
The wireless access point connects to your LAN using twisted-pair Category 5 Ethernet cable
with RJ-45 connectors.
LAN Configuration Requirements
For the initial configuration of your wireless access point, you need to connect a computer to
the wireless access point.
Installation and Basic Configuration
18

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Hardware Requirements for Computers on Your LAN
To connect to the wireless access point on your network, each computer needs to have an
802.11b/g/n or 802.11a/n wireless adapter installed. NETGEAR recommends using the
wireless access point with computers that have the NETGEAR N600 Wireless Dual Band
USB Adapter (WNDA3100) installed.
Operating Frequency (Channel) Guidelines
You do not need to change the operating frequency (channel) unless you notice interference
problems or you place the wireless access point near another wireless access point. If you do
change the operating frequency, observe the following guidelines:
• Wireless access points use a fixed channel. You can select a channel that provides the
least interference and best performance. In the United States and Canada, 11 channels
are available.
• If you use multiple wireless access points, it is better if adjacent wireless access points
use different channels to reduce interference. The recommended channel spacing
between adjacent wireless access points is 5 channels (for example, use channels 1 and
6, or 6 and 11).
• In infrastructure mode (which is the default mode for the wireless access point), wireless
stations normally scan all channels, looking for a wireless access point. If more than one
wireless access point can be used, the one with the strongest signal is used. This is
possible only if the wireless access points use the same SSID.
Requirements for Entering IP Addresses
IPv4
The fourth octet of an IP address needs to be between 0 and 255 (both inclusive). This
requirement applies to any IP address that you enter on a screen of the web management
interface.
IPv6
IPv6 addresses are denoted by eight groups of hexadecimal quartets that are separated by
colons. Any four-digit group of zeroes within an IPv6 address can be reduced to a single zero
or altogether omitted.
The following errors invalidate an IPv6 address:
• More than eight groups of hexadecimal quartets
• More than four hexadecimal characters in a quartet
• More than two colons in a row
Installation and Basic Configuration
19

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Install and Configure the Wireless Access Point
Install and configure your wireless access point in the order of the following sections:
1. Connect the Wireless Access Point to a Computer
2. Log In to the Wireless Access Point
3. Configure Basic General System Settings and Time Settings
4. Configure the IPv4 Settings
5. Configure the Optional DHCPv4 Server
6. Configure the Basic Wireless Settings
Before installing the wireless access point, make sure that your Ethernet network functions.
After you have connected the wireless access point to the Ethernet network, computers with
802.11b/g/n and 802.11a/n wireless adapters are able to communicate with the Ethernet
network.
For this to work correctly, verify that you have met all the system requirements, shown in
System Requirements on page 8.
Connect the Wireless Access Point to a Computer
Tip: Before you place the wireless access point in an elevated position that is
difficult to reach, first set up and test the wireless access point to verify
wireless network connectivity.
To set up the wireless access point:
1. Unpack the box and verify the contents.
2. Prepare a computer with an Ethernet adapter. If this computer is already part of your
network, record its TCP/IP configuration settings. Configure the computer with a static IP
address of 192.168.0.210 and 255.255.255.0 as the subnet mask.
3. Connect an Ethernet cable from the wireless access point to the computer (point A in the
following figure).
4. Securely insert the other end of the cable into the wireless access point’s Ethernet port
.
(point B in the following figure).
Installation and Basic Configuration
20

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
A
Ethernet cable
B
Figure 7.
5. Turn on your computer.
6. Connect the power adapter to the wireless access point.
Tip: The wireless access point supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) with
power redundancy. Both Ethernet ports can provide power. If you have a
switch that provides PoE, you do not need to use the power adapter to
power the wireless access point. Using PoE can be especially
convenient when the wireless access point is installed in a high location
far away from a power outlet.
Ethernet port
7. Verify the following:
Power/T est LED. The Power/Test LED blinks when the wireless access point is
first turned on. (To be exact, during startup, the LED is first steady amber, then
goes off, and then blinks green.) After about 45 seconds, the LED should stay lit
(steady green). If after 1 minute the Power/Test LED is not lit or is still blinking,
check the connections and see if the power outlet is controlled by a wall switch
that is turned off.
Active LED. The Active LED is lit or blinks green when there is Ethernet traffic.
LAN 1 LED. The LAN LED indicates the LAN speed for LAN port 1: green for
1000 Mbps, amber for 100 Mbps, and no light for 10 Mbps. If the LAN LED is not
lit, make sure that the Ethernet cable is securely attached at both ends.
LAN 2 LED. The LAN LED indicates the LAN speed for LAN port 2: green for
1000 Mbps, amber for 100 Mbps, and no light for 10 Mbps. If the LAN LED is not
lit, make sure that the Ethernet cable is securely attached at both ends.
Installation and Basic Configuration
21
ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
2.4
Ghz
5
Ghz
WLAN LED. The 2.4 GHz WLAN LED is lit or blinks green when the wireless LAN
(WLAN) is ready.
WLAN LED. The 5 GHz WLAN LED is lit or blinks green when the wireless LAN
(WLAN) is ready.
Log In to the Wireless Access Point
The default IP address of your wireless access point is 192.168.0.100. By default, the DHCP
client on the wireless access point is disabled so you can log in using the default IP address.
To log in to the wireless access point:
1. Open a web browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 or later, or Mozilla Firefox
1.5 or later.
2. Connect to the wireless access point by entering its default address of 192.168.0.100 into
your browser (use http and not https). The Login screen displays:
Figure 8.
3. Enter the default user name of admin and the default password of password.
4. Click Login. The web browser displays the basic General system settings screen under the
Configuration tab of the main menu as shown in Figure 1 1 on page 23.
Web Management Interface
The navigation tabs across the top of the web management interface provide access to all
the configuration functions of the wireless access point and remain constant. The menu items
in the blue bar change according to the navigation tab that is selected.
Installation and Basic Configuration
22
ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Figure 9.
The bottom right corner of all screens that allow you to make configuration changes show the
Apply and Cancel buttons, and on several screens the Edit button.
Figure 10.
These buttons have the following functions:
• Edit. Allows you to edit the existing configuration.
• Cancel. Cancels all configuration changes that you made on the screen.
• Apply. Saves and applies all configuration changes that you made on the screen.
Configure Basic General System Settings and Time Settings
Note: After you have successfully logged in to the wireless access point,
the basic General system settings screen displays.
To configure basic system settings:
1. Select Configuration > System > Basic > General. The basic General system settings
screen displays:
Figure 11.
Installation and Basic Configuration
23
ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
2. Configure the settings as explained in the following table:
Table 2. Basic general system settings
Setting Description
Access Point Name This unique name is the wireless access point NetBIOS name. The name is printed
on the rear label of the wireless access point. The default is netgearxxxxxx, in which
xxxxxx represents the last 6 digits of the wireless access point MAC address. You
can replace the default name with a unique name up to 15 characters long. The
access point name can be retrieved through SNMP.
Country / Region From the Country / Region drop-down list, select the country where the wireless
access point is installed.
Note: It might not be legal to operate this wireless access point in a region other than
one of those identified in this field.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
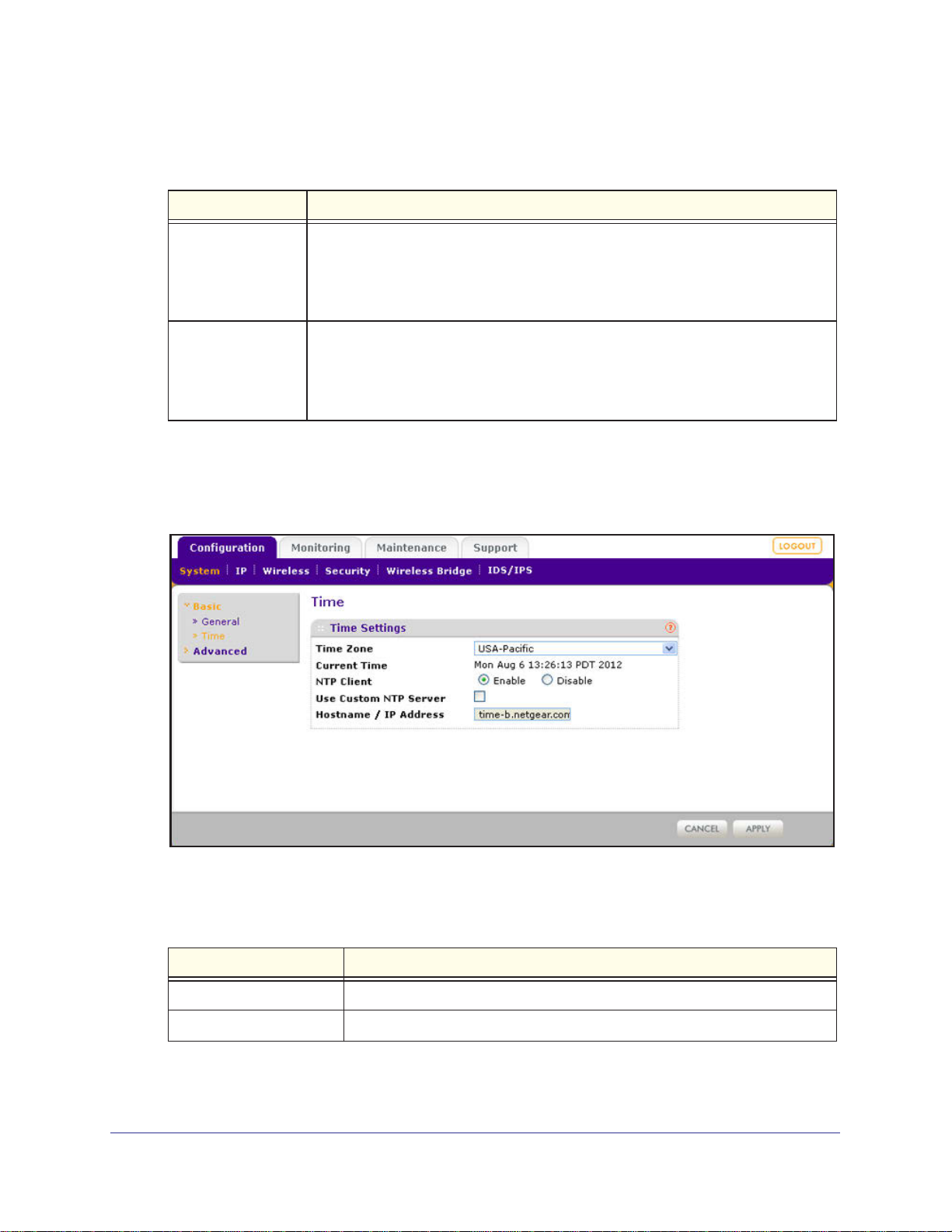
To configure time settings:
1. Select Configuration > System > Basic > Time . The Time screen displays:
Figure 12.
2. Configure the settings as explained in the following table:
Table 3. Time system settings
Setting Description
Time Zone Select the time zone to match your location.
Current Time This is a nonconfigurable field that displays the current date and time.
Installation and Basic Configuration
24

ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Table 3. Time system settings (continued)
Setting Description
NTP Client Enable the Network Time Protocol (NTP) client to synchronize the time of the
wireless access point with an NTP server. By default the Enable radio button is
selected.
Use Custom NTP Server Select this check box if you want to use a custom NTP server.
Note: You need to have an Internet connection to use an NTP server that is
not on your local network.
Hostname /
IP Address
Enter the host name or IP address of the custom NTP server.
The default is time-b.netgear.com.
Note: If you use a host name, make sure that you have
configured a DNS server. For more information, see the next
section.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
Configure the IPv4 Settings
Note: For information about how to configure the IPv6 settings, see
Configure the IPv6 Settings on page 99.
WARNING:
If you enable the DHCP client, the IP address of the wireless
access point changes when you click Apply, causing you to lose
your connection to the wireless access point. You then need to
use the new IP address to reconnect to the wireless access point.
Tip: If you enable the DHCP client on the wireless access point, you can
discover the new IP address of the wireless access point by accessing
the DHCP server on your LAN, or by using a network IP address scanner
application.
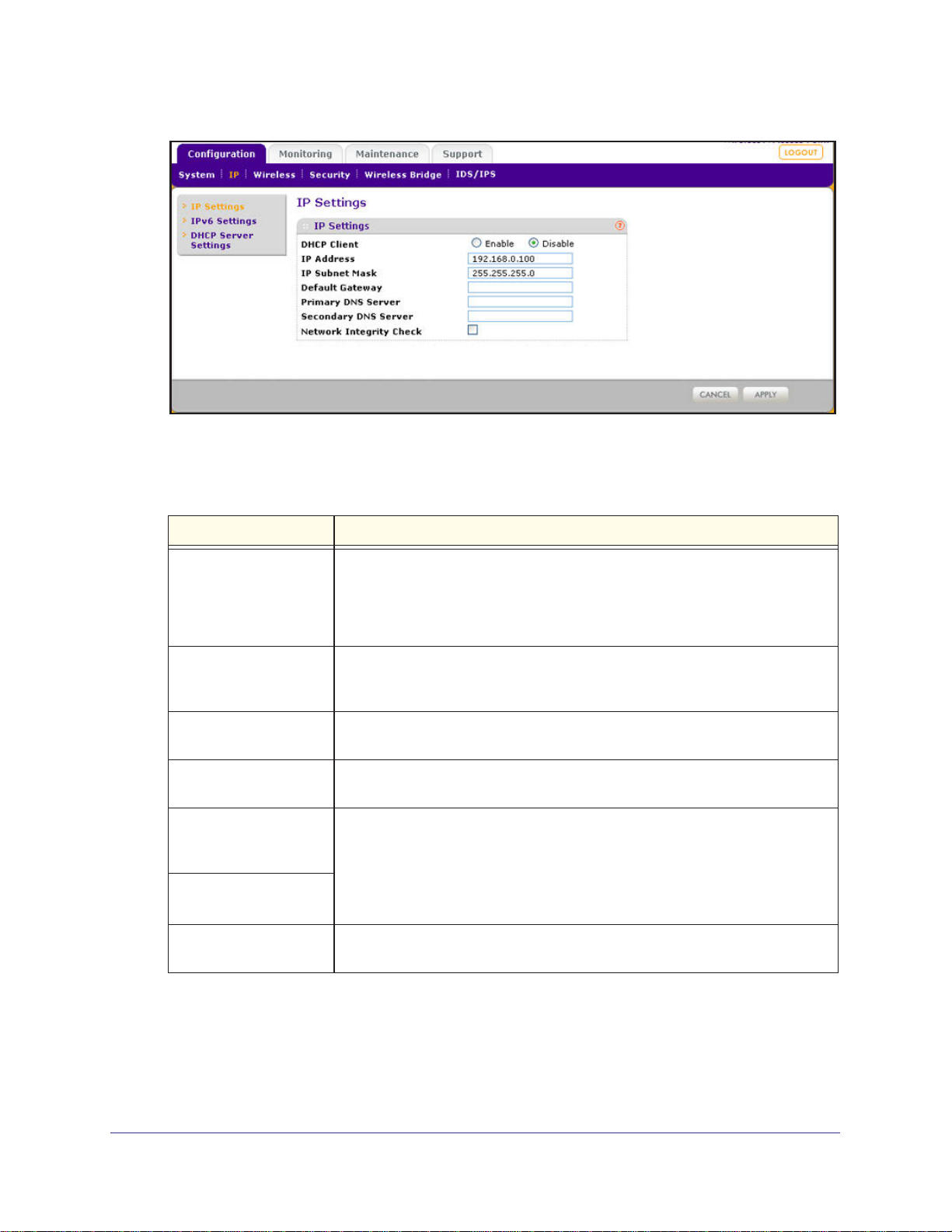
To configure the IPv4 settings:
1. Select Configuration > IP > IP Settings. The IP Settings screen displays:
Installation and Basic Configuration
25
ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Figure 13.
2. Configure the IPv4 settings as explained in the following table:
Table 4. IPv4 settings
Setting Description
DHCP Client By default, the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client is disabled. If
you have a DHCP server on your LAN and you select the Enable check box, the
wireless access point receives its IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
settings automatically from the DHCP server on your network when you connect
the wireless access point to your LAN.
IP Address Enter the IP address of your wireless access point. The default IP address is
192.168.0.100. To change the address, enter an unused IP address from the
address range used on your LAN, or enable DHCP the server.
IP Subnet Mask Enter the network number portion of an IP address. Unless you are
implementing subnetting, enter 255.255.0.0 as the subnet mask.
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the ISP gateway to which the wireless access point
connects.
Primary DNS Server Enter the IP address of the primary and secondary DNS servers.
A DNS server is a host on the Internet that translates Internet names (such as
www.netgear.com) to numeric IP addresses. Typically your ISP transfers the IP
Secondary DNS Server
Network Integrity Check Select this check box to validate that the upstream link is active before allowing
address of one or two DNS servers to your wireless access point during login. If
the ISP does not transfer an address, you need to obtain it from the ISP and
enter it manually in this field.
wireless associations. Ensure that the default gateway is configured.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
Installation and Basic Configuration
26
ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Configure the Optional DHCPv4 Server
The wireless access point provides a built-in DHCPv4 server for wireless clients only, which
can be especially useful in small networks. When the DHCP server is enabled, the wireless
access point provides preconfigured TCP/IP configurations to all connected wireless
stations.
Note: For information about how to configure the DHCPv6 server, see
Configure the Optional DHCPv6 Server on page 101.
To configure DHCPv4 server settings:
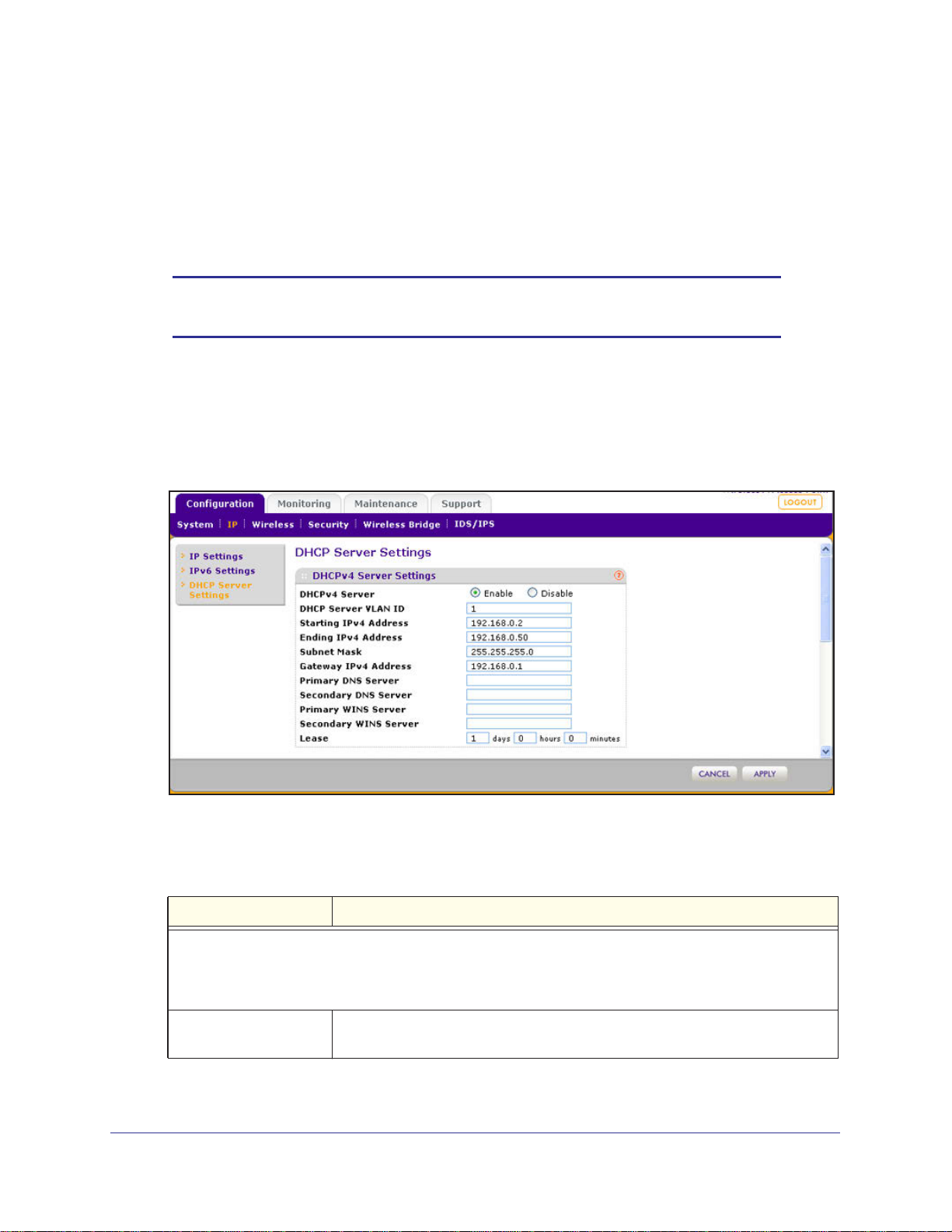
1. Select Configuration > IP > DHCP Server Settings. The DHCP Server Settings screen
displays. The following figure displays the DHCPv4 server settings only. For information
about the DHCPv6 server settings, see Configure the Optional DHCPv6 Server on
page 101.
Figure 14.
2. Configure the settings as explained in the following table:
Table 5. DHCP server settings for IPv4
Setting Description
Select the DHCPv4 Server check box to enable the DHCP server. Use the default settings or specify the
pool of IPv4 addresses to be assigned by setting the starting IPv4 address and ending IPv4 address. These
addresses should be part of the same IPv4 address subnet as the wireless access point’s LAN IPv4
address.
DHCP Server VLAN ID Enter the VLAN ID for the DHCP server. The VLAN ID range is from 1 to 4094.
The default VLAN is 1.
Installation and Basic Configuration
27
ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Table 5. DHCP server settings for IPv4 (continued)
Setting Description
Starting IPv4 Address Enter the first address in the range of IPv4 addresses to be assigned to DHCP
clients. The default address is 192.168.1.02.
Ending IPv4 Address Enter the last address in the range of IPv4 addresses to be assigned to DHCP
clients. The default address is 192.168.1.50.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask to be used by DHCP clients. The default mask is
255.255.255.0.
Gateway IPv4 Address Enter the IPv4 address of the default routing gateway to be used by DHCP
clients. The default address is 192.168.0.1.
Primary DNS Address Enter the IP address of the primary Domain Name System (DNS) server
available to DHCP clients.
Secondary DNS Address Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server available to DHCP clients.
Primary WINS Server Enter the IP address of the primary WINS server for the network, if there is any.
Secondary WINS Server Enter the IP address of the secondary WINS server for the network, if there is
any.
Lease Enter the period that the DHCP server grants to DHCP clients to use the
assigned IP addresses. The default time is one day.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
Configure the Basic Wireless Settings
For proper compliance and compatibility between similar products in your coverage area, you
need to configure the 802.1 1b/g/n and 802.1 1a/n wireless adapter settings correctly, including
the operating channel and country. You also need to configure the basic wireless network
settings for wireless devices to connect to your network. For other wireless features,
including wireless security, see Chapter 3, Wireless Configuration and Security.
WARNING:
If you configure the wireless access point from a wireless
computer and you change the wireless access point’s SSID,
channel, or wireless security settings, you lose your wireless
connection when you click Apply. You then need to change the
wireless settings of your computer to match the wireless access
point’s new settings.
Installation and Basic Configuration
28
ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Configure 802.11b/bg/ng Wireless Settings
To configure the 802.11b/g/n wireless settings:
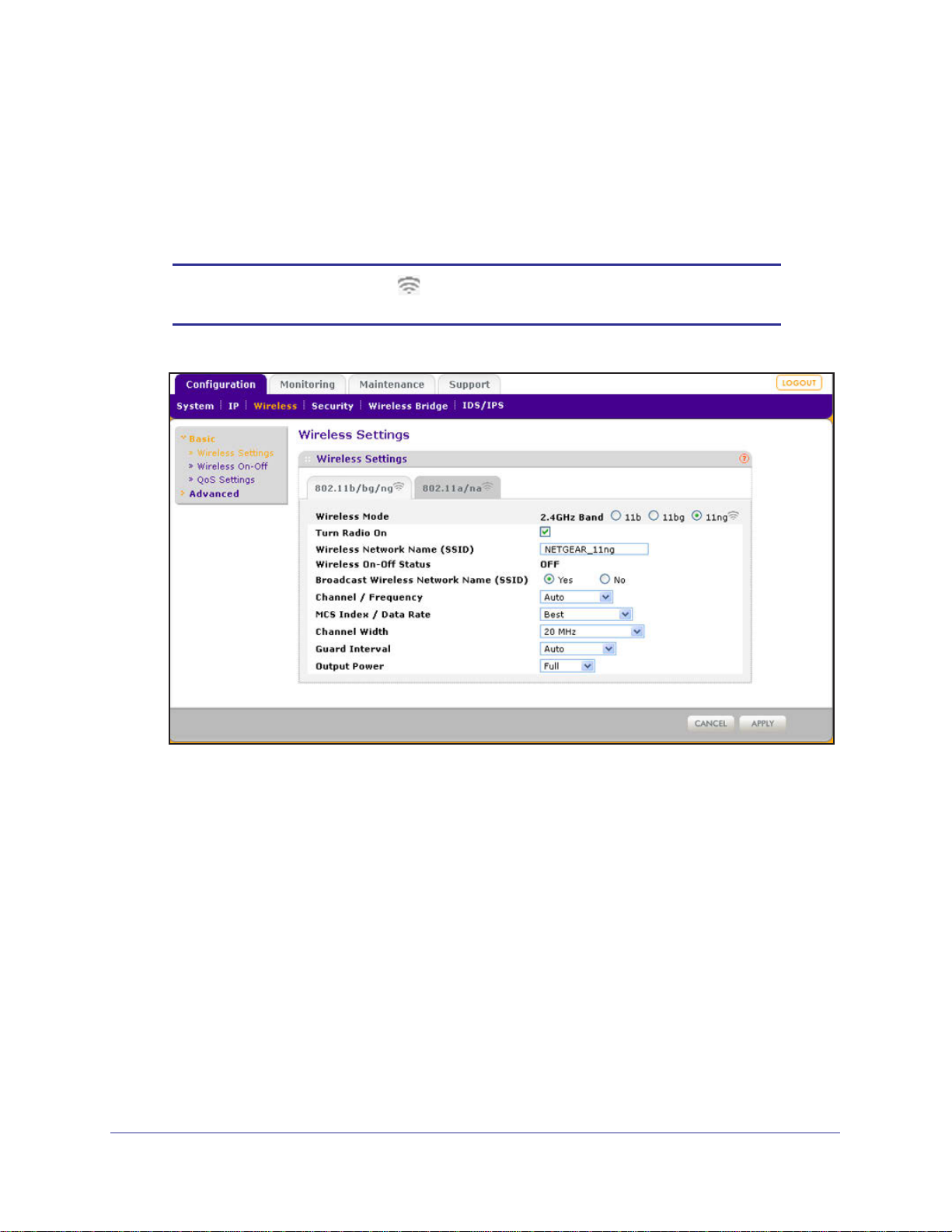
1. Select Configuration > Wireless > Basic > Wireless Settings. The basic Wireless
Settings screen displays. (The following figure shows the 11ng settings.)
Note: The radio wave icon ( ) displays next to the enabled wireless mode
(b, bg, or ng).
Figure 15.
2. Specify the wireless mode in the 2.4 GHz band by selecting one of the following radio
buttons:
• 11b. Both 802.11n- and 802.11g-compliant devices can connect to the access point
because they are backward compatible.
11bg. 802.11n-compliant devices can connect to the access point because they are
•
backward compatible.
• 11ng. This is the default setting. 802.11b-compliant devices cannot connect to the
access point. If you keep the default setting, go to Step 5.
When you change the wireless mode, the Turn Radio On check box is automatically
cleared, and all fields, buttons, and drop-down lists onscreen are masked out.
3. Turn on the radio by selecting the Turn Radio On check box. A pop-up screen displays.
Installation and Basic Configuration
29
ProSAFE Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660
Note: Under normal conditions, you want the radio to be turned on. Turning off
the radio disables access through the wireless access point, which can be
helpful for configuration, network tuning, or troubleshooting activities.
4. Click OK to confirm the change of wireless mode. The change does not take effect until you
click the Apply button after you have completed the wireless configuration.
5. Specify the remaining wireless settings as explained the following table:
Table 6. Basic 2.4 GHz band wireless settings
Setting Descriptions
Wireless Network Name
(SSID)
Wireless On-Off Status This field is not configurable. It shows the status of the wireless scheduler. For
Broadcast Wireless
Network Name (SSID)
Channel / Frequency From the drop-down list, select the channel you wish to use for your wireless
Enter a 32-character (maximum) service set identifier (SSID); the characters are
case-sensitive. The default is NETGEAR_1 1ng. The SSID assigned to a wireless
device needs to match the wireless access point’s SSID for the wireless device
to communicate with the wireless access point. If the SSIDs do not match, you
do not get a wireless connection to the wireless access point.
more information, see Schedule the Wireless Radios to Be Turned Off on
page 61.
Select the Yes radio button to enable the wireless access point to broadcast its
SSID, allowing wireless stations that have a null (blank) SSID to adopt the
wireless access point’s SSID. Yes is the default setting. To prevent the SSID
from being broadcast, select the No radio button.
LAN. The wireless channels and frequencies depend on the country and
wireless mode. The default setting is Auto.
Note: It should not be necessary to change the wireless channel unless you
experience interference (indicated by lost connections or slow data transfers). If
this happens, you might want to experiment with different channels to see which
is the best. For more information, see Operating Frequency (Channel)
Guidelines on page 19.
Note: For more information about available channels and frequencies, see
Technical Specifications on page 140.
11ng mode only
Note: For most
networks, the default
settings work fine.
MCS Index / Data
Rate
Channel Width From the drop-down list, select a channel width. The options
Guard Interval From the drop-down list, select the guard interval to protect
From the drop-down list, select a Modulation and Coding
Scheme (MCS) index and transmit data rate for the wireless
network. The default setting is Best. For a list of all options
that you can select from in 11ng mode, see Factory Default
Settings on page 143.
are Dynamic 20/40 MHz, 20 MHz, and 40 MHz. The default is
20 MHz. A wider channel improves the performance, but
some legacy devices can operate only in either 20 MHz or
40 MHz.
transmissions from interference. The default is Auto, or you
can select Long - 800 ns. Some legacy devices can operate
only with a long guard interval.
Installation and Basic Configuration
30
 Loading...
Loading...