Page 1

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management Appliance STM150, STM300, or STM600
Reference Manual
350 East Plumeria Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
USA
January 2011
202-10519-06
1.0
Page 2
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
© 2009–2011 NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated
into any language in any form or by any means without the written permission of NETGEAR, Inc.
Technical Support
Thank you for choosing NETGEAR. To register your product, get the latest product updates, or get support online,
visit us at http://support.netgear.com.
Phone (US & Canada only): 1-888-NETGEAR
Phone (Other Countries): See Support information card.
Product Updates
Product updates are available on the NETGEAR website at http://prosecure.netgear.com or
http://kb.netgear.com/app/home.
ProSecure Forum
Go to http://prosecure.netgear.com/community/forum.php for information about the ProSecure forum and to
become part of the ProSecure community.
Trademarks
NETGEAR, the NETGEAR logo, ReadyNAS, ProSafe, ProSecure, Smart Wizard, Auto Uplink, X-RAID2, and
NeoTV are trademarks or registered trademarks of NETGEAR, Inc. Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT, and Vista
are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Other brand and product names are registered trademarks or
trademarks of their respective holders.
Statement of Conditions
To improve internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, NETGEAR reserves the right to make changes
to the products described in this document without notice. NETGEAR does not assume any liability that may occur
due to the use, or application of, the product(s) or circuit layout(s) described herein.
Revision History
Manual Part
Number
202-10519-06 1.0 February 2011 Made the following changes:
Manual
Version
Number
Publication Date Description
• Upgraded the book to the new format.
• Entirely revised Chapter 6, Monitoring System Access and
Performance, to document the new Logs, Reports, and Alerts
configuration menus that replaced the old Logs & Report
configuration menu.
• Added Appendix A, Report Templates.
• Separated the traffic logs into email traffic logs and Web traffic
logs (see Configuring and Activating System, Email, and Syslog
Logs and Querying Logs).
• Under the Monitoring main navigation menu, replaced all
screen shots that showed the old Logs & Reports configuration
menu with screen shots that show the new Alerts, Logs, and
Reports configuration menus.
2 |
Page 3
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
202-10519-06
(continued)
202-10519-05 1.0 July 2010 Added the following major new features:
1.0 February 2011
(continued)
(continued)
• Revised the Setup Wizard update settings information (see
Setup Wizard Step 7 of 11: Update Settings), software update
information (see Updating the Software), and system status
information (see Viewing System Status).
• Network refresh and permanent MAC address bindings (see
Configuring the Network Refresh and Permanent MAC Address
Bindings)
• Setting exceptions for custom groups and custom categories,
and setting exceptions for file extensions and protocols (see
Setting Scanning Exclusions and Web Access Exceptions)
• Creating custom groups (see Creating Custom Groups for Web
Access Exceptions)
• Creating custom categories—see Creating Custom Categories
for Web Access Exceptions)
• Using the DC Agent (see Understanding the ProSecure DC
Agent, Requirements for the ProSecure DC Agent Software
and DC Agent Server, and Downloading ProSecure DC Agent
Software, and Creating and Deleting DC Agents)
Also added the following minor features:
• Requirement to accept terms of service agreement on the
Real-Time Blacklist screen
• Capability to set the public host, IP address, and port on the
Distributed Spam Analysis screen
• Capability to replace the content of a blocked page with custom
text
• Capability to enable and disable SSLv2
• Refinements in the active users search methods.
• Domain information in the output screens that are accessible
from the Monitoring menu
• Testing a URL as part of the diagnostics tools
202-10519-01 1.1 October 2009 Index update.
202-10519-01 1.0 September 2009 Initial publication of this reference manual.
| 3
Page 4

Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction
What Is the ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management Appliance
STM150, STM300, or STM600?. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
What Can You Do with an STM? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Key Features and Capabilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Stream Scanning for Content Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Easy Installation and Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Maintenance and Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
STM Model Comparison. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Service Registration Card with License Keys. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Package Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Hardware Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Front Panel Ports and LEDs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Rear Panel Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Bottom Panel with Product Label . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Choosing a Location for the STM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Using the Rack-Mounting Kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Chapter 2 Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your
Network
Choosing a Deployment Scenario . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Gateway Deployment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Server Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Segmented LAN Deployment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Understanding the Steps for Initial Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Qualified Web Browsers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Logging In to the STM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Understanding the Web Management Interface Menu Layout. . . . . . . .30
Using the Setup Wizard to Perform the Initial Configuration . . . . . . . . . . .32
Setup Wizard Step 1 of 10: Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Setup Wizard Step 2 of 11: Networking Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Setup Wizard Step 3 of 11: Time Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Setup Wizard Step 4 of 11: Email Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Setup Wizard Step 5 of 11: Web Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Setup Wizard Step 6 of 11: Email Notification Server Settings . . . . . . .42
Setup Wizard Step 7 of 11: Update Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Setup Wizard Step 8 of 11: HTTP Proxy Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Setup Wizard Step 9 of 11: Web Categories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Contents | 4
Page 5

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Setup Wizard Step 10 of 11: Configuration Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Setup Wizard Step 11 of 11: Restarting the System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Verifying Correct Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Testing Connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Testing HTTP Scanning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Registering the STM with NETGEAR. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
What to Do Next. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Chapter 3 Performing Network and System Management
Configuring Network Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Configuring Session Limits and Timeouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56
Configuring the Network Refresh and
Permanent MAC Address Bindings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Managing Permanent MAC Address Bindings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Configuring the HTTP Proxy Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
About Users with Administrative and Guest Privileges. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Changing Administrative Passwords and Timeouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Configuring Remote Management Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Using an SNMP Manager. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Supported MIB Browsers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Managing the Configuration File. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Backing Up Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Restoring Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
Reverting to Factory Default Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Updating the Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Scheduling Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Performing a Manual Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Critical Updates That Require a Restart. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Configuring Date and Time Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Managing Digital Certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
Managing the Certificate for HTTPS Scans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
Managing Trusted Certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Managing Untrusted Certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Managing the Quarantine Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
Managing the STM’s Performance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Chapter 4 Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans
About Content Filtering and Scans. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Default Email and Web Scan Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .85
Configuring Email Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Customizing Email Protocol Scan Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Customizing Email Anti-Virus Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
Email Content Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
Protecting Against Email Spam . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Configuring Web and Services Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Customizing Web Protocol Scan Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Configuring Web Malware Scans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
Contents | 5
Page 6

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Configuring Web Content Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .109
Configuring Web URL Filtering. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .116
HTTPS Scan Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .119
Specifying Trusted Hosts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .124
Configuring FTP Scans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .125
Configuring Application Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .127
Setting Scanning Exclusions and Web Access Exceptions . . . . . . . . . . .130
Setting Scanning Exclusions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .130
Setting Access Exception Rules for Web Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .132
Creating Custom Groups for Web Access Exceptions. . . . . . . . . . . . .139
Creating Custom Categories for Web Access Exceptions . . . . . . . . . .142
Chapter 5 Managing Users, Groups, and Authentication
About Users, Groups, and Domains. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .147
Configuring Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .148
Creating and Deleting Groups by Name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .149
Editing Groups by Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .150
Creating and Deleting Groups by IP Address and Subnet. . . . . . . . . .151
Configuring User Accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .152
Creating and Deleting User Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .153
Editing User Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .154
Configuring Authentication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .154
Understanding the STM’s Authentication Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .155
Understanding Active Directories and LDAP Configurations . . . . . . . .157
Creating and Deleting LDAP and Active Directory Domains . . . . . . . .161
Editing LDAP and Active Directory Domains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .164
Understanding the ProSecure DC Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .164
Requirements for the ProSecure DC Agent Software and
DC Agent Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .165
Downloading ProSecure DC Agent Software, and Creating
and Deleting DC Agents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .165
Creating and Deleting RADIUS Domains. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .167
Editing RADIUS Domains and Configuring VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .169
Global User Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .170
Viewing and Logging Out Active Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .172
6 | Contents
Chapter 6 Monitoring System Access and Performance
Configuring Logging, Alerts, and Event Notifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175
Configuring the Email Notification Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .176
Configuring and Activating System, Email, and Syslog Logs. . . . . . . .177
Configuring Alerts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .182
Monitoring Real-Time Traffic, Security, Statistics, and Web Usage. . . . .184
Understanding the Information on the Dashboard Screen. . . . . . . . . .184
Monitoring Web Usage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .190
Viewing System Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .192
Querying Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .194
Example: Using Logs to Identify Infected Clients. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .199
Page 7

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Log Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .199
Viewing, Scheduling, and Generating Reports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .200
Report Templates. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .200
Generating Reports for Downloading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .202
Scheduling Automatic Generation and Emailing of Reports. . . . . . . . .203
Advanced Report Filtering Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .204
Viewing and Managing the Quarantine Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .208
Using Diagnostics Utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .215
Using the Network Diagnostic Tools. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .216
Using the Realtime Traffic Diagnostics Tool. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .217
Gathering Important Log Information and
Generating a Network Statistics Report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .218
Restarting and Shutting Down the STM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .219
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting and Using Online Support
Basic Functioning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .223
Power LED Not On. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .223
Test LED or Status LED Never Turns Off. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .223
LAN or WAN Port LEDs Not On . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .224
Troubleshooting the Web Management Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .224
When You Enter a URL or IP Address a Time-Out Error Occurs. . . . . . .225
Troubleshooting a TCP/IP Network Using a Ping Utility. . . . . . . . . . . . . .225
Testing the LAN Path to Your STM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .226
Testing the Path from Your PC to a Remote Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . .226
Restoring the Default Configuration and Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .227
Problems with Date and Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .228
Using Online Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .228
Enabling Remote Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .228
Installing Hot Fixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .229
Sending Suspicious Files to NETGEAR for Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . .230
Accessing the Knowledge Base and Documentation. . . . . . . . . . . . . .231
Appendix A Report Templates
Appendix B Default Settings and Technical Specifications
Appendix C Related Documents
Appendix D Notification of Compliance
Index
Contents | 7
Page 8

1. Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the features and capabilities of the ProSecure
Web/Email Security Threat Management Appliance STM150, STM300, and STM600. It also
identifies the physical features of the appliances and the contents of the product packages.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• What Is the ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management Appliance STM150,
STM300, or STM600? on this page
• What Can You Do with an STM? on page 9
• Key Features and Capabilities on page 9
• Service Registration Card with License Keys on page 12
• Package Contents on page 13
• Hardware Features on page 14
• Choosing a Location for the STM on page 23
1
What Is the ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management Appliance STM150, STM300, or STM600?
The ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management Appliance STM150, STM300, or
STM600, hereafter referred to as the STM, is an appliance-based, Web and email security
solution that protects the network perimeter against Web-borne threats from spyware,
viruses, email, and blended threats. Ideally deployed at the gateway, it serves as the
network’s first line of defense against all types of threats, and complements firewalls,
intrusion detection systems (IDS)/intrusion prevention systems (IPS), dedicated Intranet
security products, and endpoint antivirus and antispyware software.
Powered by patent-pending Stream Scanning technology and backed by one of the most
comprehensive malware databases in the industry, the STM can detect and stop all known
spyware and viruses at the gateway, preventing them from reaching your desktops and
servers, where cleanup would be much more difficult.
In addition to scanning HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, POP3, and IMAP traffic, the STM protects
networks against spam phishing attacks and unwanted Web use. The STM is a
plug-and-play device that can be installed and configured within minutes.
Chapter 1. Introduction | 8
Page 9

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
What Can You Do with an STM?
The STM combines robust protection against malware threats with ease of use and
advanced reporting and notification features to help you deploy and manage the device with
minimal effort.
Here are some of the things that you can do with the STM:
• Protect the network instantly. The STM is a plug-and-play security solution that can be
instantly added to networks without the need for network reconfiguration.
• Scan network traffic for malware. Using the Stream Scanning technology, you can
configure the STM to scan HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, POP3, and IMAP protocols.
Unlike traditional batch-based scan engines that need to cache the entire file before they
can scan, this scan engine checks traffic as it enters the network, ensuring unimpeded
network performance.
• Set access policies for individual users or groups. You can configure Web and email
access policies for individual users and groups based on the STM’s local database, on a
group IP address, on a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) domain, group, or
user, or on a RADIUS VLAN.
• Receive real-time alerts and generate comprehensive reports. You can configure the
STM to send alerts when a malware attack or outbreak is detected on the network.
Real-time alerts can be sent by email, allowing you to monitor malware events wherever
you are.
By configuring the STM to send malware alerts, you can isolate and clean the infected
computer before the malware incident can develop into a full-blown outbreak. The STM
also provides comprehensive reports that you can use to analyze network and malware
trends.
• Manage through SNMP support. You can enable and configure the STM’s Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP) settings to receive SNMP traps through a
supported management information base (MIB) browser.
• Allow automated component updates. Downloading components regularly is the key to
ensuring updated protection against new threats. The STM makes this administrative
task easier by supporting automatic malware pattern, program, and engine updates.
Key Features and Capabilities
The STM provides the following key features and capabilities:
• Up to two pairs of 10/100/1000 Mbps Gigabit Ethernet WAN ports (see STM Model
Comparison on page 12).
• Scalable support (see STM Model Comparison on page 12) for:
- Up to 600 concurrent users
- Up to 6000 concurrently scanned HTTP sessions
Chapter 1. Introduction | 9
Page 10

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
- Up to 239 MB/s HTTP throughput
- Up to 960,000 emails per hour SMTP throughput
• Stream Scanning technology that enables scanning of real-time protocols such as HTTP.
• Comprehensive Web and email inbound and outbound security, covering six major
network protocols: HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, POP3, and IMAP.
• URL content filtering with 64 categories.
• Malware database containing hundreds of thousands of signatures of spyware, viruses,
and other malware threats.
• Very frequently updated malware signatures, hourly if required. The STM can
automatically check for new malware signatures as frequently as every 15 minutes.
• Multiple antispam technologies to provide extensive protection against unwanted emails.
• Spam and malware quarantine for easy analysis.
• Web application control, including access control for instant messaging, media
applications, peer-to-peer applications, and Web-based tools and toolbars.
• User management with LDAP, Active Directory, and RADIUS integration, allowing you to
configure access policies per user and per group.
• Easy, Web-based wizard setup for installation and management.
• SNMP-manageable.
• Dedicated management interface. (This feature is model dependent; see STM Model
Comparison on page 12.)
• Hardware bypass port to prevent network disruption in case of failure. (This feature is
model dependent; see STM Model Comparison on page 12.)
• Front panel LEDs for easy monitoring of status and activity.
• Internal universal switching power supply.
Stream Scanning for Content Filtering
Stream Scanning is based on the simple observation that network traffic travels in streams.
The STM scan engine starts receiving and analyzing traffic as the stream enters the network.
As soon as a number of bytes are available, scanning starts. The scan engine continues to
scan more bytes as they become available, while at the same time another thread starts to
deliver the bytes that have been scanned.
This multithreaded approach, in which the receiving, scanning, and delivering processes
occur concurrently, ensures that network performance remains unimpeded. The result is file
scanning that is up to five times faster than with traditional antivirus solutions—a performance
advantage that you will notice.
Stream Scanning also enables organizations to withstand massive spikes in traffic, as in the
event of a malware outbreak. The scan engine has the following capabilities:
• Real-time protection. The Stream Scanning technology enables scanning of previously
undefended real-time protocols, such as HTTP. Network activities susceptible to latency
(for example, Web browsing) are no longer brought to a standstill.
10 | Chapter 1. Introduction
Page 11

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
• Comprehensive protection. Provides both Web and email security, covering six major
network protocols: HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, POP3, and IMAP. The STM uses
enterprise-class scan engines employing both signature-based and distributed spam
analysis to stop both known and unknown threats. The malware database contains
hundreds of thousands of signatures of spyware, viruses, and other malware.
• Objectionable traffic protection. The STM prevents objectionable content from
reaching your computers. You can control access to the Internet content by screening for
Web categories, Web addresses, and Web services. You can log and report attempts to
access objectionable Internet sites.
• Automatic signature updates. Malware signatures are updated as frequently as every
hour, and the STM can check automatically for new signatures as frequently as every 15
minutes.
Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink
With its internal 10/100/1000 ports, the STM can connect to either a 10 Mbps standard
Ethernet network, a 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet network, or a 1000 Mbps Gigabit Ethernet
network. The interfaces are autosensing and capable of full-duplex or half-duplex operation.
The STM incorporates Auto Uplink
whether the Ethernet cable plugged into the port should have a “normal” connection such as
to a PC or an “uplink” connection such as to a switch or hub. That port then configures itself
correctly. This feature eliminates the need to think about crossover cables, as Auto Uplink
accommodates either type of cable to make the right connection.
TM
technology. Each Ethernet port automatically senses
Easy Installation and Management
You can install, configure, and operate the STM within minutes after connecting it to the
network. The following features simplify installation and management tasks:
• Browser-based management. Browser-based configuration allows you to easily
configure the STM from almost any type of operating system, such as Windows,
Macintosh, or Linux. A user-friendly Setup Wizard is provided, and online help
documentation is built into the browser-based Web Management Interface.
• SNMP. The STM supports SNMP to let you monitor and manage log resources from an
SNMP-compliant system manager. The SNMP system configuration lets you change the
system variables for MIB2.
• Diagnostic functions. The STM incorporates built-in diagnostic functions such as a ping
utility, traceroute utility, DNS lookup utility, and remote restart.
• Remote management. The STM allows you to log in to the Web Management Interface
from a remote location on the Internet. For security, you can limit remote management
access to a specified remote IP address or range of addresses.
• Visual monitoring. The STM’s front panel LEDs provide an easy way to monitor its
status and activity.
Chapter 1. Introduction | 11
Page 12
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Maintenance and Support
NETGEAR offers technical support seven days a week, 24 hours a day. Information about
support is available on the NETGEAR ProSecure website at
http://prosecure.netgear.com/support/index.php.
STM Model Comparison
The following table compares the three STM models to show the differences:
Table 1. Differences between the STM Models
Feature STM150 STM300 STM600
Performance and Sizing Guidelines
Concurrent users Up to 150 Up to 300 Up to 600
Web scan throughput 42 Mbps 136 Mbps 307 Mbps
Concurrent scanned HTTP connections 1500 3000 6000
SMTP throughput (emails per hour) 122,000 355,000 550,000
Hardware
Gigabit RJ-45 ports Total of 5 ports:
• 1 uplink
• 4 downlink
Gigabit RJ45 port pairs with failure bypass 0 1 pair of ports 2 pairs of ports
Dedicated management VLAN RJ45 ports 0 1 1
a. The STM600 provides two pairs of ports, allowing for support of two separate networks or subnets with
strict traffic separation.
Total of 3 ports:
• 1 pair of ports
(1 uplink and
1 downlink)
• 1 management
Total of 5 ports:
• 2 pairs of ports
(2 uplink and
2 downlink)
• 1 management
Service Registration Card with License Keys
Be sure to store the license key card that came with your STM in a secure location. You do
need these keys to activate your product during the initial setup.
a
12 | Chapter 1. Introduction
Page 13

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Figure 1.
Note: If you reset the STM to the original factory default settings after you
have entered the license keys to activate the STM (see Registering
the STM with NETGEAR on page 50), the license keys are erased.
The license keys and the different types of licenses that are
available for the STM are no longer displayed on the Registration
screen. However, after you have reconfigured the STM to connect to
the Internet and to the NETGEAR registration server, the STM
retrieves and restores all registration information based on its MAC
address and hardware serial number. You do not need to reenter the
license keys and reactivate the STM.
Package Contents
The STM product package contains the following items:
• ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management Appliance STM150, STM300, or
STM600
• One AC power cable
• Rubber feet (4) with adhesive backing
• One rack-mount kit
• Straight-through Category 5 Ethernet cable
Chapter 1. Introduction | 13
Page 14

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
• ProSecure™ Web/Email Security Threat Management Applliance STM150, STM300, or
STM600 Installation Guide
• Depending on the model purchased, service registration card with one or more license
keys
If any of the parts are incorrect, missing, or damaged, contact your NETGEAR dealer. Keep
the carton, including the original packing materials, in case you need to return the product for
repair.
Hardware Features
The front panel ports and LEDs, rear panel ports, and bottom label of the STM models are
described in this section.
Front Panel Ports and LEDs
The front panels of the three STM models provide different components.
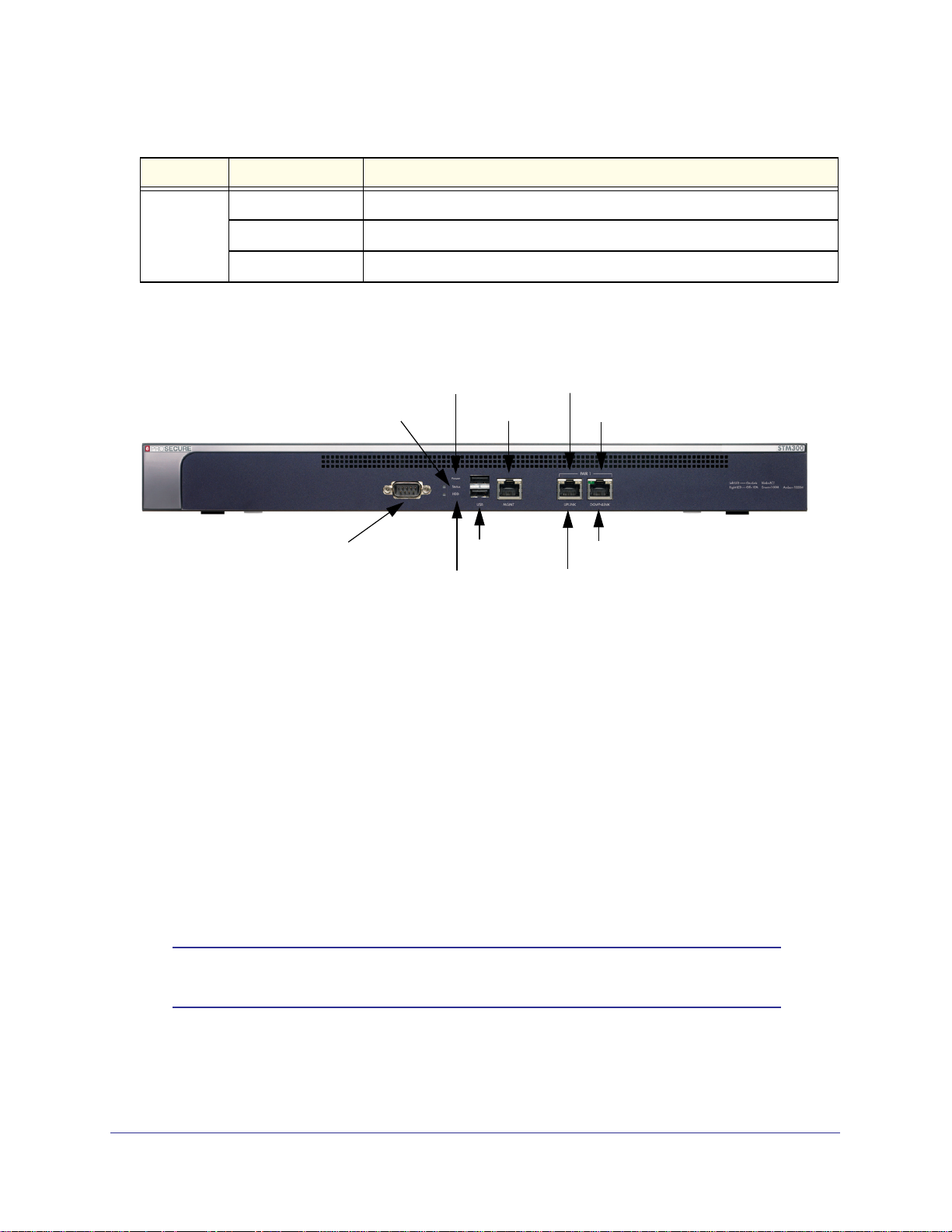
STM150 Front Panel
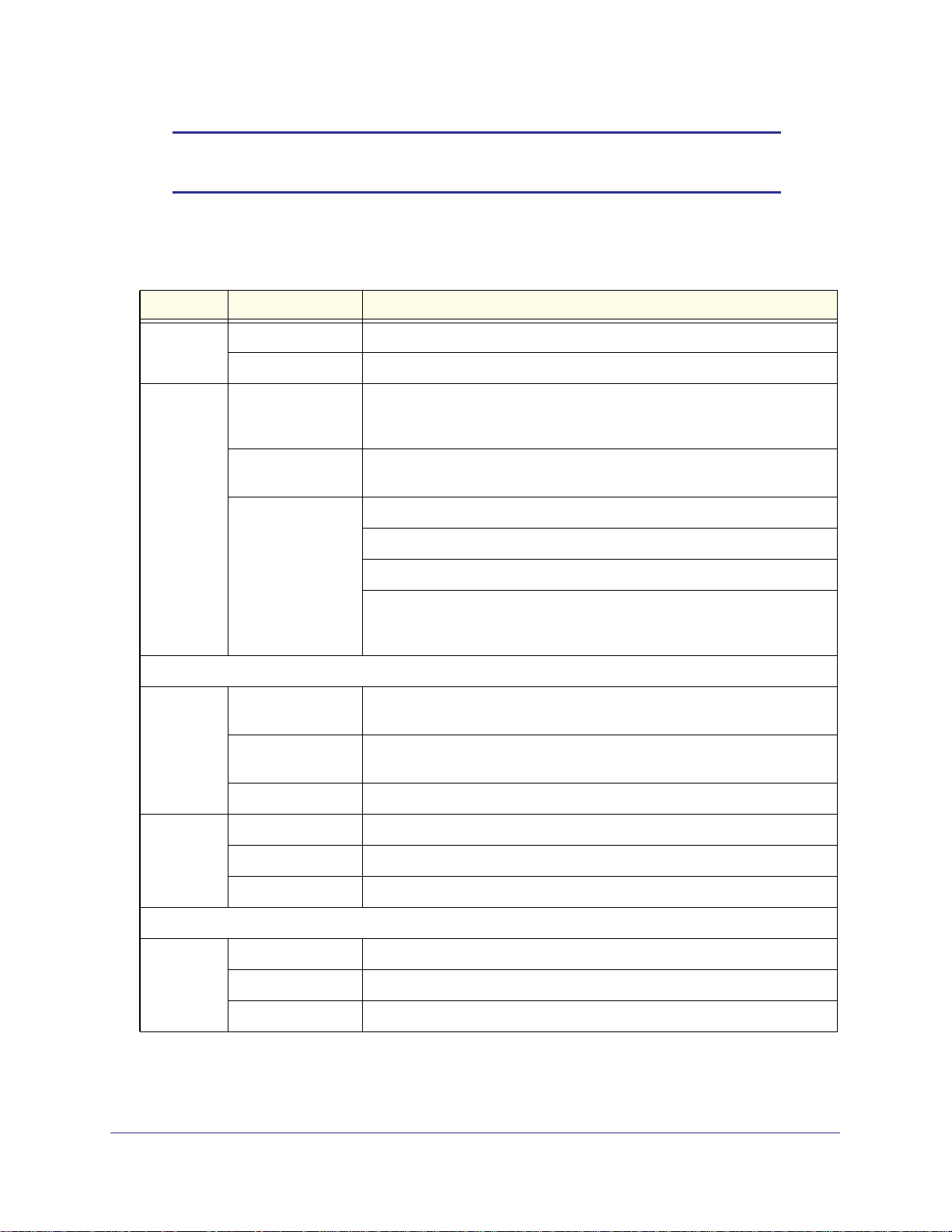
The following figure shows the front panel ports and status light-emitting diodes (LEDs) of the
STM150:
1) Power LED
4) Uplink LEDs
2) Test LED
Figure 2.
From left to right, the STM150’s front panel shows the following ports and LEDs:
1. Power LED.
2. Test LED.
3. One nonfunctioning USB port. This port is included for future management enhancements.
The port is currently not operable on any STM model.
3) USB port
4) Uplink port
5) Downlink LEDs
5) Downlink ports
4. One uplink (WAN) Gigabit Ethernet port with an RJ-45 connector, left LED, and right LED.
5. Four downlink (LAN) Gigabit Ethernet ports with RJ-45 connectors, left LEDs, and right
LEDs.
14 | Chapter 1. Introduction
Page 15
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Note: All Gigabit Ethernet ports provide switched N-way, automatic
speed-negotiating, auto MDI/MDIX technology.
The function of each STM150 LED is described in the following table:
Table 2. LED Descriptions for the STM150
Object Activity Description
Power On (green) Power is supplied to the STM.
Off Power is not supplied to the STM.
Test On (amber) during
startup
Off The system has completed its initialization successfully. The Test LED
Blinking (amber) The STM is shutting down.
Uplink (WAN) Port
Left LED Off The WAN port has no physical link, that is, no Ethernet cable is plugged into
On (green) The WAN port has a valid connection with a device that provides an Internet
Blink (green) Data is being transmitted or received by the WAN port.
Right LED Off The WAN port is operating at 10 Mbps.
The STM is initializing. After approximately 2 minutes, when the STM has
completed its initialization, the Test LED turns off. If the Test LED remains
on, the initialization has failed.
should be off during normal operation.
Software is being updated.
A hotfix is being installed.
One of the three licenses has expired. To stop the Test LED from blinking,
renew the license, or click the Stop LED Blinking button on the System
Status screen (see Viewing System Status on page 192).
the STM.
connection.
On (amber) The WAN port is operating at 100 Mbps.
On (green) The WAN port is operating at 1000 Mbps.
Downlink (LAN) Ports
Left LED Off The LAN port has no link.
On (green) The LAN port has detected a link with a connected Ethernet device.
Blink (green) Data is being transmitted or received by the LAN port.
Chapter 1. Introduction | 15
Page 16
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 2. LED Descriptions for the STM150 (Continued)
Object Activity Description
Right LED Off The LAN port is operating at 10 Mbps.
On (amber) The LAN port is operating at 100 Mbps.
On (green) The LAN port is operating at 1000 Mbps.
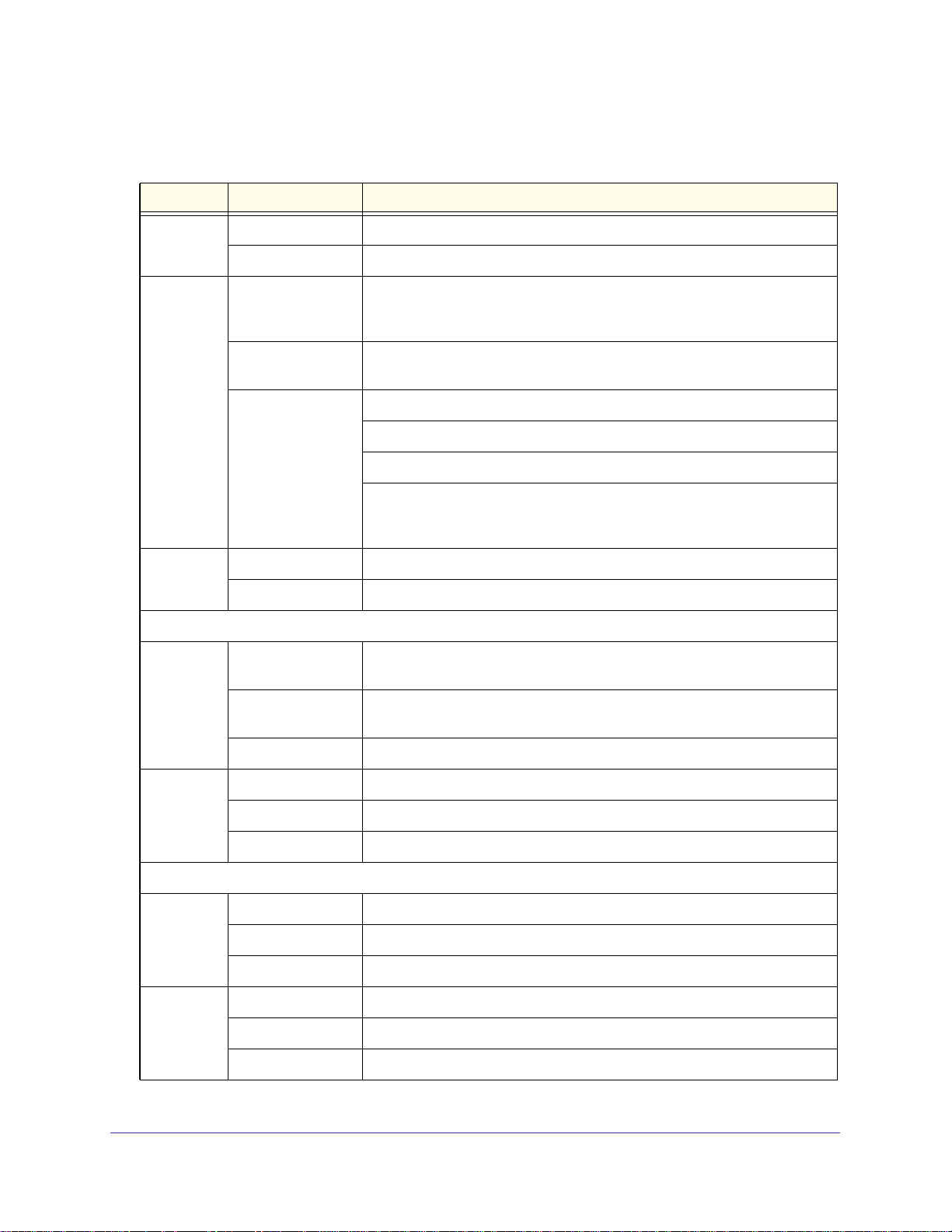
Front Panel STM300
The following figure shows the front panel ports and LEDs of the STM300:
7) Uplink LEDs
8) Downlink LEDs
8) Downlink port
7) Uplink port
Figure 3.
3) Status LED
1) Console port
2) Power LED
6) Mgmt port
5) USB port
4) HDD LED
From left to right, the STM300’s front panel shows the following ports and LEDs:
1. Console port. Port for connecting to an optional console terminal. The port has a DB9
male connector. The default baud rate is 9600 K. The pinouts are (2) Tx, (3) Rx, (5) and
(7) Gnd.
2. Power LED.
3. Status LED.
4. Hard drive (HDD) LED.
5. One nonfunctioning USB port. This port is included for future management enhancements.
The port is currently not operable on any STM model.
6. Dedicated management (Mgmt) Gigabit Ethernet port with an RJ-45 connector.
7. One uplink (WAN) Gigabit Ethernet port with an RJ-45 connector, left LED, and right LED.
8. One downlink (LAN) Gigabit Ethernet port with RJ-45 connectors, left LED, and right LED.
Note: All Gigabit Ethernet ports provide switched N-way, automatic
speed-negotiating, auto MDI/MDIX technology.
16 | Chapter 1. Introduction
Page 17
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
The function of each STM300 LED is described in the following table:
Table 3. LED Descriptions for the STM300
Object Activity Description
Power On (green) Power is supplied to the STM.
Off Power is not supplied to the STM.
Status On (amber) during
startup
Off The system has completed its initialization successfully. The Status LED
Blinking (amber) The STM is shutting down.
HDD On (Green) Information is being written to the hard drive.
Off No hard drive activity.
Uplink (WAN) Port
Left LED Off The WAN port has no physical link, that is, no Ethernet cable is plugged into
On (green) The WAN port has a valid connection with a device that provides an Internet
The STM is initializing. After approximately 2 minutes, when the STM has
completed its initialization, the Status LED turns off. If the Status LED
remains on, the initialization has failed.
should be off during normal operation.
Software is being updated.
A hotfix is being installed.
One of the three licenses has expired. To stop the Status LED from blinking,
renew the license, or click the Stop LED Blinking button on the System
Status screen (see Viewing System Status on page 192).
the STM.
connection.
Blink (green) Data is being transmitted or received by the WAN port.
Right LED Off The WAN port is operating at 10 Mbps.
On (green) The WAN port is operating at 100 Mbps.
On (amber) The WAN port is operating at 1000 Mbps.
Downlink (LAN) Ports
Left LED Off The LAN port has no link.
On (green) The LAN port has detected a link with a connected Ethernet device.
Blink (green) Data is being transmitted or received by the LAN port.
Right LED Off The LAN port is operating at 10 Mbps.
On (green) The LAN port is operating at 100 Mbps.
On (amber) The LAN port is operating at 1000 Mbps.
Chapter 1. Introduction | 17
Page 18
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
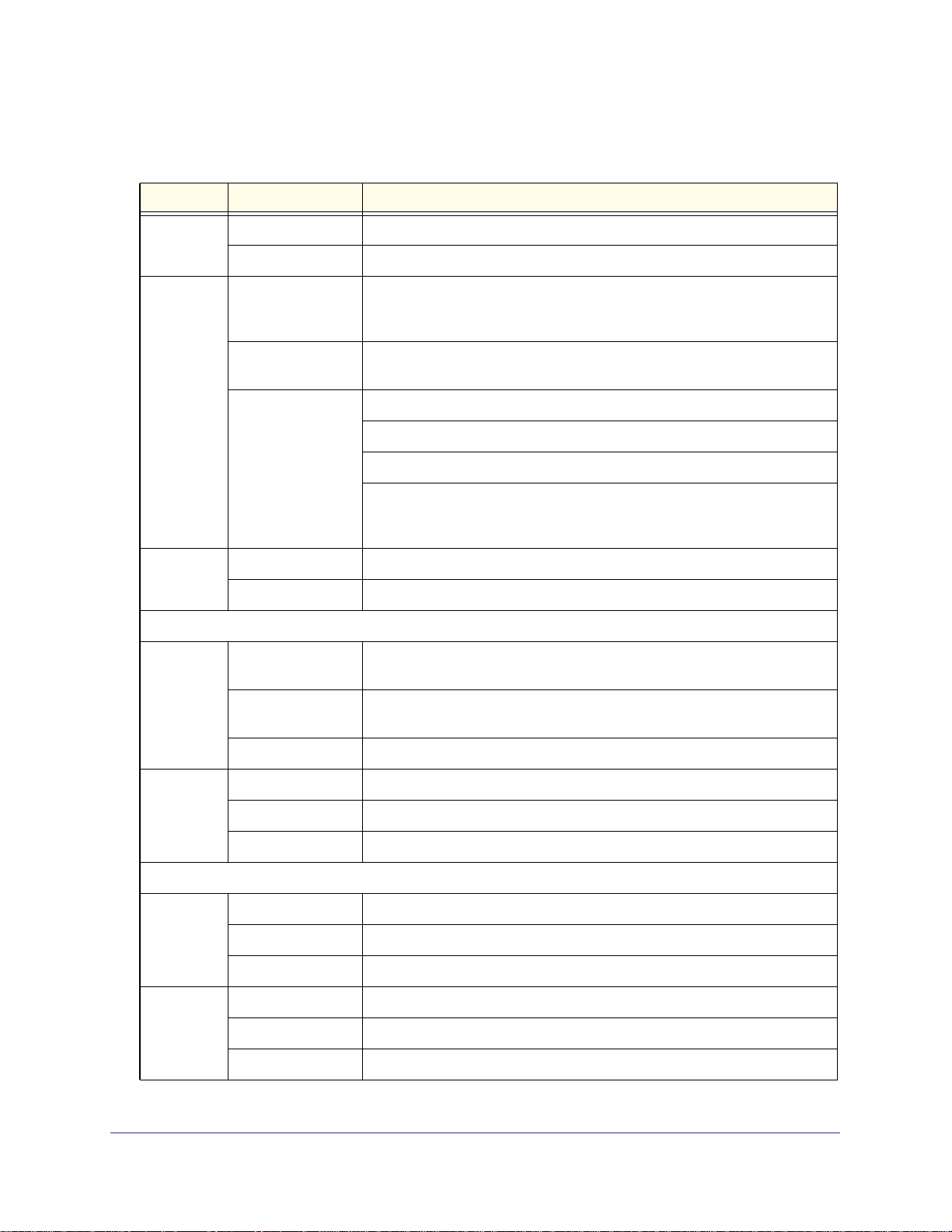
Front Panel STM600
The following figure shows the front panel ports and LEDs of the STM600:
7) Pair 1 LEDs
8) Pair 2 LEDs
8) Pair 2 ports
7) Pair 1 ports
Figure 4.
3) Status LED
1) Console port
2) Power LED
6) Mgmt port
5) USB port
4) HDD LED
From left to right, the STM600’s front panel shows the following ports and LEDs:
1. Console port. Port for connecting to an optional console terminal. The ports has a DB9
male connector. The default baud rate is 9600 K. The pinouts are (2) Tx, (3) Rx, (5) and
(7) Gnd.
2. Power LED.
3. Status LED.
4. Hard drive (HDD) LED.
5. One nonfunctioning USB port. This port is included for future management enhancements.
The port is currently not operable on any STM model.
6. Dedicated management (Mgmt) Gigabit Ethernet port with an RJ-45 connector.
7. Pair 1 uplink (WAN) and downlink (LAN) Gigabit Ethernet ports with RJ-45 connectors, left
LEDs, and right LEDs.
8. Pair 2 uplink (WAN) and downlink (LAN) Gigabit Ethernet ports with RJ-45 connectors, left
LEDs, and right LEDs.
Note: All Gigabit Ethernet ports provide switched N-way, automatic
speed-negotiating, auto MDI/MDIX technology.
18 | Chapter 1. Introduction
Page 19
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
The function of each STM600 LED is described in the following table:
Table 4. LED Descriptions for the STM600
Object Activity Description
Power On (green) Power is supplied to the STM.
Off Power is not supplied to the STM.
Status On (amber) during
startup
Off The system has completed its initialization successfully. The Status LED
Blinking (amber) The STM is shutting down.
HDD On (green) Information is being written to the hard drive.
Off No hard drive activity.
Uplink (WAN) Port
Left LED Off The WAN port has no physical link, that is, no Ethernet cable is plugged into
On (green) The WAN port has a valid connection with a device that provides an Internet
The STM is initializing. After approximately 2 minutes, when the STM has
completed its initialization, the Status LED turns off. If the Status LED
remains on, the initialization has failed.
should be off during normal operation.
Software is being updated.
A hotfix is being installed.
One of the three licenses has expired. To stop the Status LED from blinking,
renew the license, or click the Stop LED Blinking button on the System
Status screen (see Viewing System Status on page 192).
the STM.
connection.
Blink (green) Data is being transmitted or received by the WAN port.
Right LED Off The WAN port is operating at 10 Mbps.
On (green) The WAN port is operating at 100 Mbps.
On (amber) The WAN port is operating at 1000 Mbps.
Downlink (LAN) Ports
Left LED Off The LAN port has no link.
On (green) The LAN port has detected a link with a connected Ethernet device.
Blink (green) Data is being transmitted or received by the LAN port.
Right LED Off The LAN port is operating at 10 Mbps.
On (green) The LAN port is operating at 100 Mbps.
On (amber) The LAN port is operating at 1000 Mbps.
Chapter 1. Introduction | 19
Page 20
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Rear Panel Features
The rear panel of the STM150 differs from the rear panels of the STM300 and STM600.
Rear Panel STM150
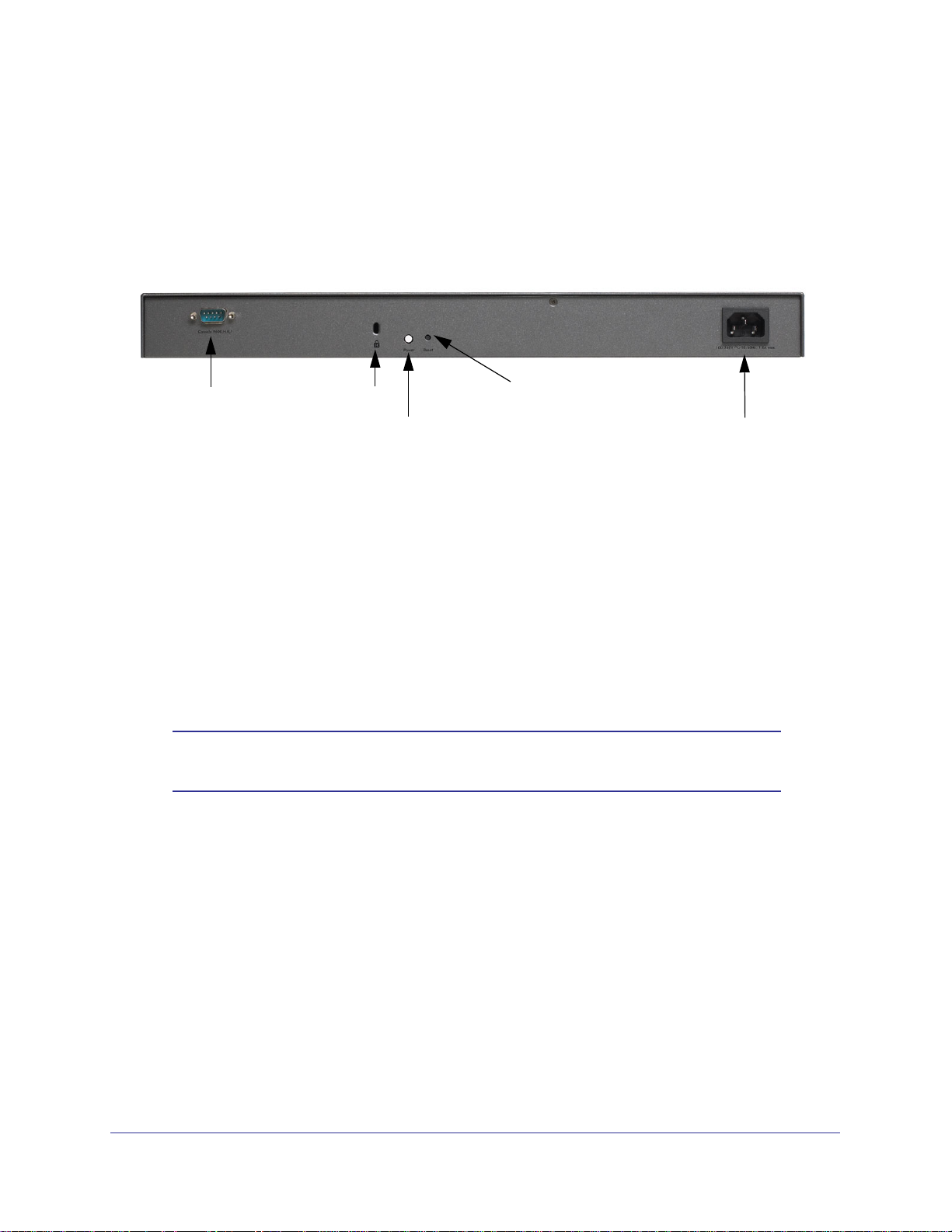
The following figure shows the rear panel components of the STM150:
1) Console port
Figure 5.
From left to right, the STM150’s rear panel components are:
1. Console port. Port for connecting to an optional console terminal. The port has a DB9
male connector. The default baud rate is 9600 K. The pinouts are (2) Tx, (3) Rx, (5) and
(7) Gnd.
2. Kensington lock. Attach an optional Kensington lock to prevent unauthorized removal of the
STM150.
3. Power button. Press to restart the STM150. Restarting does not reset the STM150 to its
factory defaults.
4. Reset button. Using a sharp object, press and hold this button for about 10 seconds until the
front panel Test LED flashes and the STM150 returns to factory default settings.
Note: If you reset the STM150, all configuration settings are lost and the
default passwords are restored.
5. AC power socket. Attach the power cord to this socket.
2) Lock
3) Power button
4) Reset button
5) AC power socket
20 | Chapter 1. Introduction
Page 21
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Rear Panel STM300 and STM600
The rear panels of the STM300 and STM600 are identical.
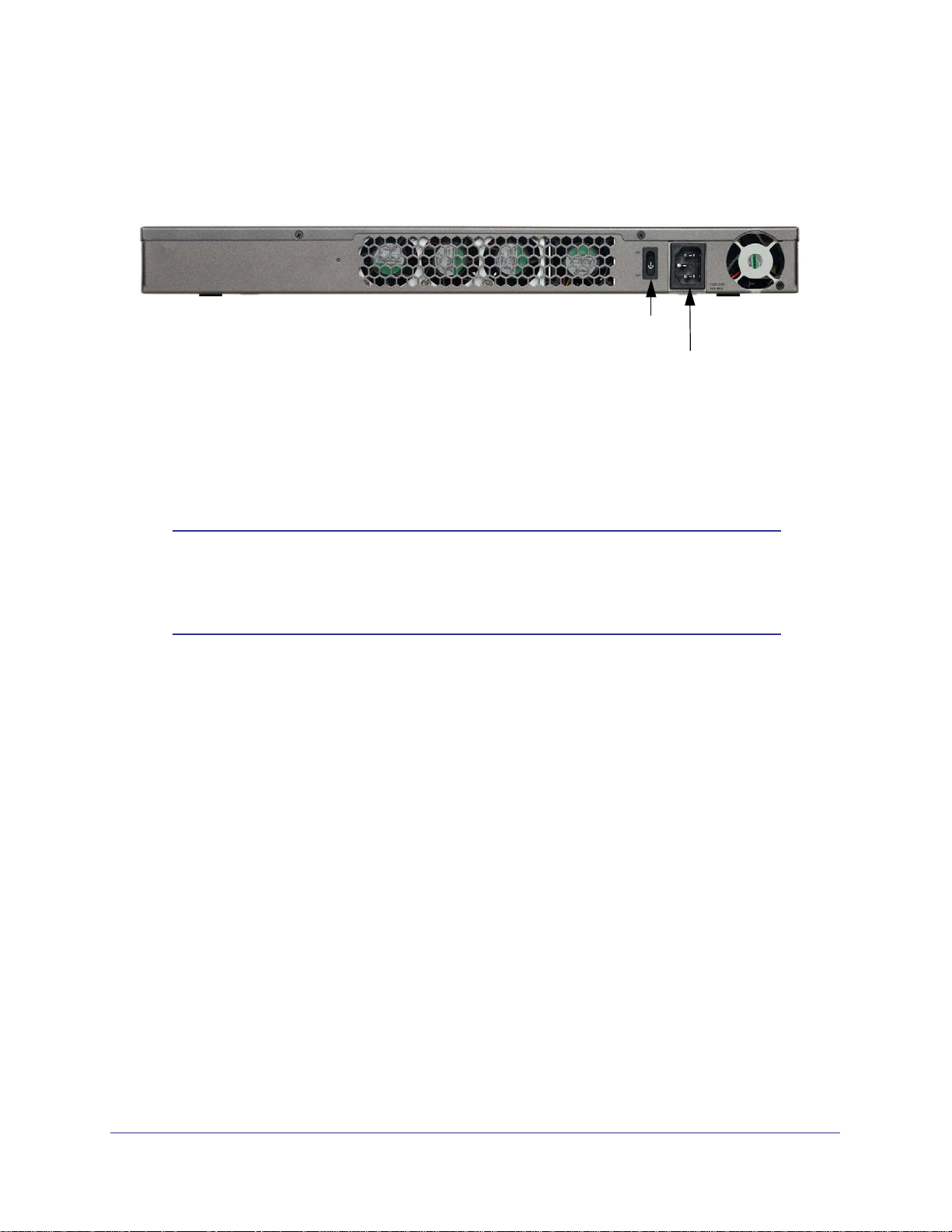
The following figure shows the rear panel components of the STM300 and STM600:
1) Power switch
2) AC power socket
Figure 6.
From left to right, the STM300’s and STM600’s rear panel components (excluding the four
fan air outlets) are:
1. Power switch. Switch to turn the STM300 or STM600 on or off. Restarting does not
reset the STM300 or STM600 to its factory defaults.
Note: The STM300 and STM600 do not provide a Reset button. For
information about how to reset the STM300 or STM600 to factory
default settings using the Web Management Interface, see
Reverting to Factory Default Settings on page 70.
2. AC power socket. Attach the power cord to this socket.
Chapter 1. Introduction | 21
Page 22
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Bottom Panel with Product Label
The product label on the bottom of the STM’s enclosure displays the STM’s default IP
address, default user name, and default password, as well as regulatory compliance, input
power, and other information.
STM150 Product Label
Figure 7.
STM300 Product Label
Figure 8.
22 | Chapter 1. Introduction
Page 23

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
STM600 Product Label
Figure 9.
Choosing a Location for the STM
The STM is suitable for use in an office environment where it can be freestanding (on its
runner feet) or mounted into a standard 19-inch equipment rack. Alternatively, you can
rack-mount the STM in a wiring closet or equipment room. A mounting kit, containing two
mounting brackets and four screws, is provided in the STM package.
Consider the following when deciding where to position the STM:
• The unit is accessible and cables can be connected easily.
• Cabling is away from sources of electrical noise. These include lift shafts, microwave
ovens, and air-conditioning units.
• Water or moisture cannot enter the case of the unit.
• Airflow around the unit and through the vents in the side of the case is not restricted.
Provide a minimum of 25 mm or 1 inch clearance.
• The air is as free of dust as possible.
• Temperature operating limits are not likely to be exceeded. Install the unit in a clean,
air-conditioned environment. For information about the recommended operating
temperatures for the STM, see Appendix B, Default Settings and Technical
Specifications.
Chapter 1. Introduction | 23
Page 24
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Using the Rack-Mounting Kit
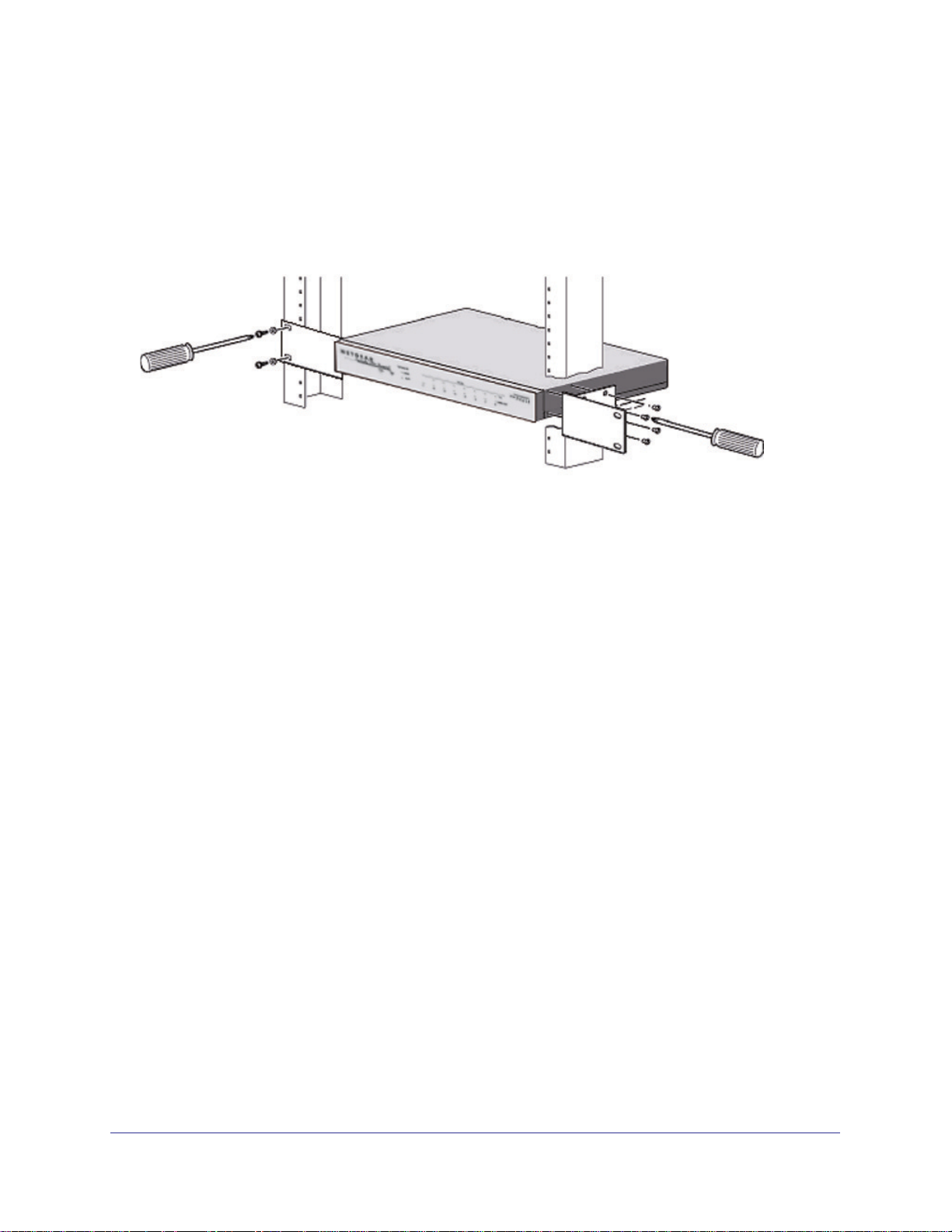
Use the mounting kit for the STM to install the appliance in a rack. (A mounting kit is provided
in the product package for the STM.) The mounting brackets that are supplied with the STM
are usually installed before the unit is shipped out. If the brackets are not yet installed, attach
them using the supplied hardware.
Figure 10.
Before mounting the STM in a rack, verify that:
• You have the correct screws (supplied with the installation kit).
• The rack onto which you will mount the STM is suitably located.
24 | Chapter 1. Introduction
Page 25

2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the
STM in Your Network
This chapter describes provisioning the STM in your network. This chapter contains the
following sections:
• Choosing a Deployment Scenario on this page
• Understanding the Steps for Initial Connection on page 27
• Logging In to the STM on page 28
• Using the Setup Wizard to Perform the Initial Configuration on page 32
• Verifying Correct Installation on page 49
• Registering the STM with NETGEAR on page 50
• What to Do Next on page 51
Choosing a Deployment Scenario
The STM is an inline transparent bridge appliance that can easily be deployed to any point
on the network without the need for network reconfiguration or additional hardware.
2
The following are the most common deployment scenarios for the STM. Depending on your
network environment and the areas that you want to protect, you can choose one or a
combination of the deployment scenarios that are described in the following sections:
• Gateway Deployment on this page
• Server Group on page 26
• Segmented LAN Deployment on page 27
Gateway Deployment
In a typical gateway deployment scenario, a single STM appliance is installed at the
gateway—between the firewall and the LAN core switch—to protect the network against all
malware threats entering and leaving the gateway. Installing the STM behind the firewall
protects it from denial of service (DoS) attacks.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 25
Page 26
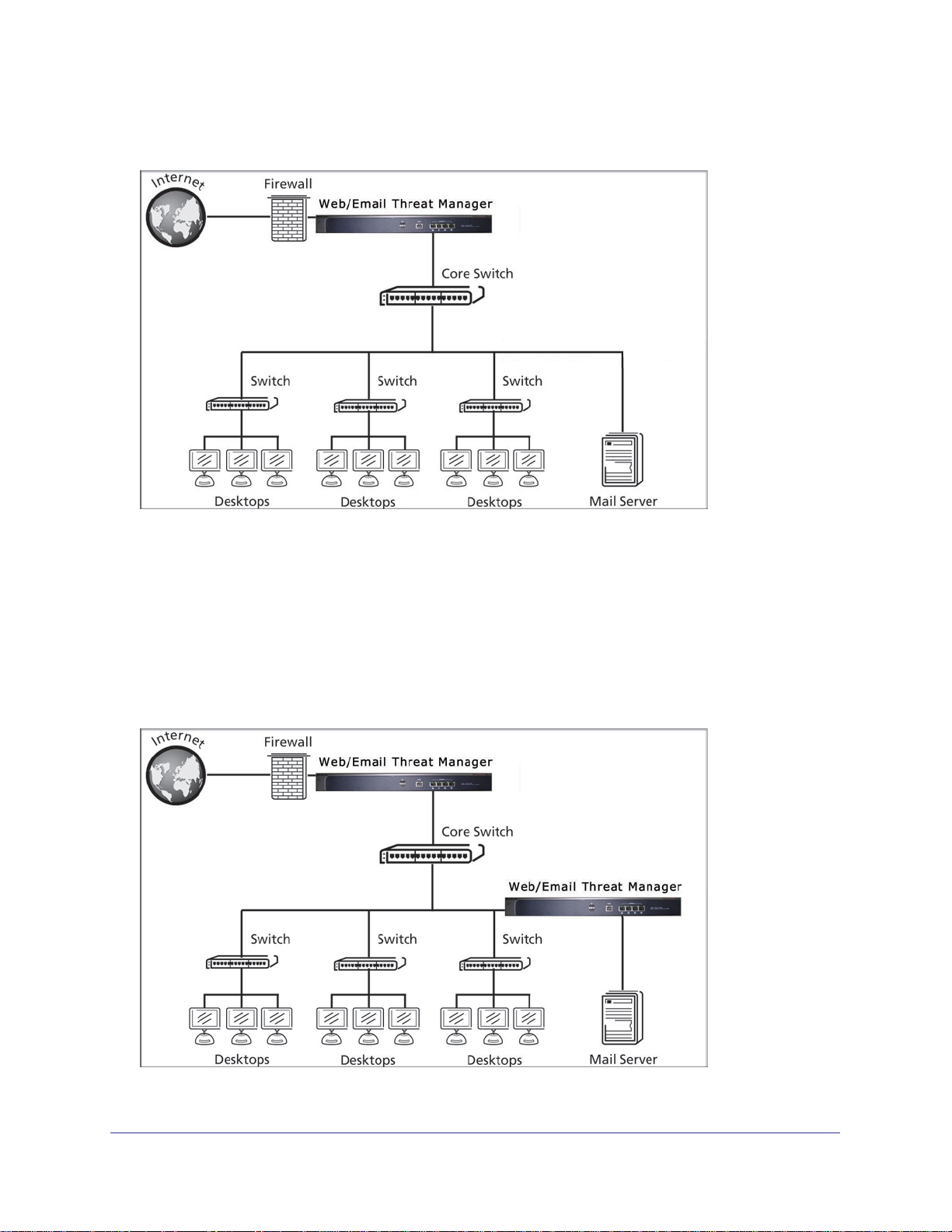
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
The following figure shows a typical gateway deployment scenario:
Figure 11.
Server Group
In a server group deployment, one STM appliance is installed at the gateway and another in
front of the server group to help protect the email server from threats from internal as well as
external clients. This type of deployment splits the network load and provides the email
server with dedicated protection against malware threats, including email-borne viruses and
spam. The following figure shows a typical server group deployment scenario:
Figure 12.
26 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 27
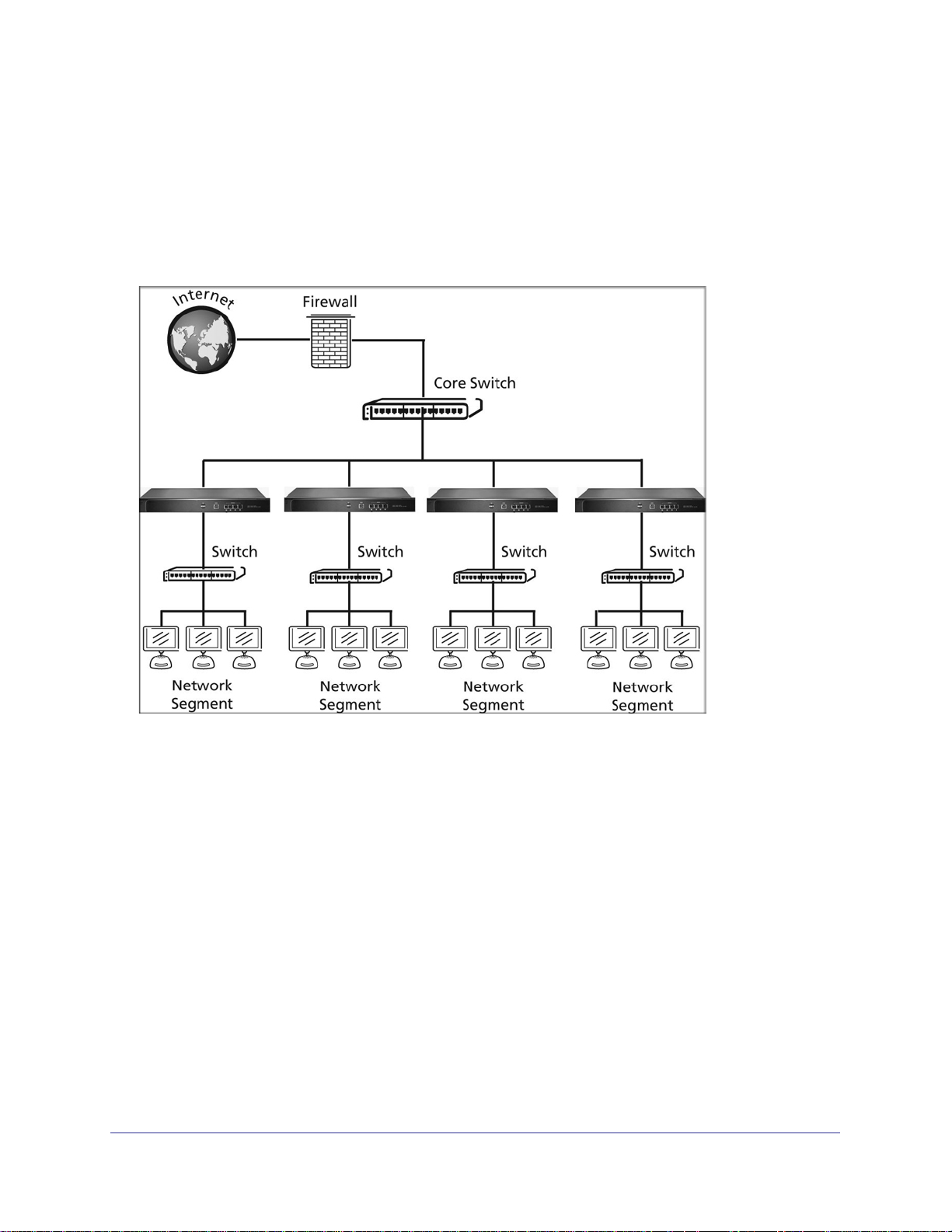
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Segmented LAN Deployment
In a segmented LAN deployment, one STM appliance is installed in front of each network
segment. VLAN traffic can pass through the STM and can be scanned by the STM. This type
of deployment splits the network load and protects network segments from malware threats
coming in through the gateway or originating from other segments. The following figure
shows a typical segmented LAN deployment scenario:
Figure 13.
Understanding the Steps for Initial Connection
Generally, five steps are required to complete the basic and security configuration of your
STM:
1. Connect the STM physically to your network. Connect the cables and restart your
network according to the instructions in the installation guide. See the ProSecure™
Web/Email Security Threat Management Appliance STM150, STM300, or STM600
Installation Guide for complete steps. A PDF of the Installation Guide is on the
NETGEAR ProSecure™ website at
http://prosecure.netgear.com/resources/document-library.php.
2. Log in to the STM. After logging in, you are ready to set up and configure your STM. See
Logging In to the STM on page 28.
3. Use the Setup Wizard to configure basic connections and security. During this phase,
you connect the STM to your network. See Using the Setup Wizard to Perform the Initial
Configuration on page 32.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 27
Page 28
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
4. Verify the installation. See Verifying Correct Installation on page 49.
5. Register the STM. See Registering the STM with NETGEAR on page 50.
Each of these tasks is described separately in this chapter.
Qualified Web Browsers
To configure the STM, you need to use a Web browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer
5.1 or later, Mozilla Firefox l.x or later, or Apple Safari 1.2 or later with JavaScript, cookies,
and SSL enabled.
Although these Web browsers are qualified for use with the STM’s Web Management
Interface, SSL VPN users should choose a browser that supports JavaScript, Java, cookies,
SSL, and ActiveX to take advantage of the full suite of applications. Note that Java is required
only for the SSL VPN portal, not for the Web Management Interface.
Logging In to the STM
To connect to the STM, your computer needs to be configured to obtain an IP address
automatically from the STM via DHCP. For instructions on how to configure your computer for
DHCP, see the document that you can access from Preparing Your Network in Appendix C.
To connect and log in to the STM:
1. Start any of the qualified browsers, as explained in Qualified Web Browsers on this
page.
2. Enter https://192.168.1.201 in the address field.
https://192.168.1.201
Figure 14.
Note: The STM factory default IP address is 192.168.1.201. If you change
the IP address, you need to use the IP address that you assigned to
the STM to log in to the STM.
The NETGEAR Configuration Manager Login screen displays in the browser (see the
following figure, which shows the STM300).
28 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 29
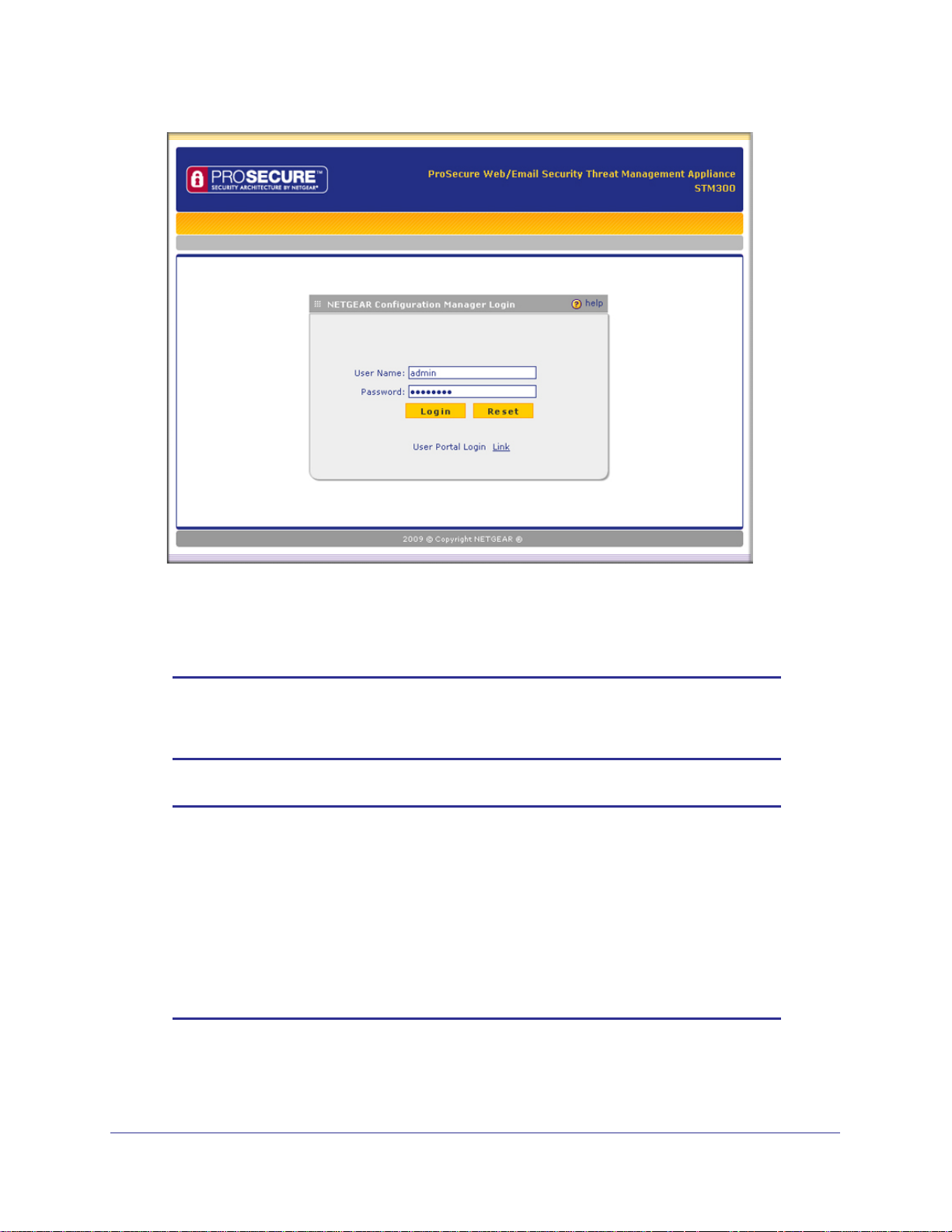
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Figure 15.
3. In the User Name field, type admin. Use lowercase letters.
4. In the Password field, type password. Here, too, use lowercase letters.
Note: The STM user name and password are not the same as any user
name or password you might use to log in to your Internet
connection.
Note: The first time that you remotely connect to the STM with a browser
via an SSL VPN connection, you might get a warning message
regarding the SSL certificate. If you are using a Windows computer
with Internet Explorer 5.5 or later, simply click Yes to accept the
certificate. Other browsers provide you with similar options to accept
and install the SSL certificate.
If you connect to the STM through the User Portal Login screen (see
Figure 88 on page 156), you can import the STM’s root certificate by
clicking the link at the bottom of the screen.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 29
Page 30

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
5. Click Login. The Web Management Interface displays, showing the Dashboard screen (see
the following figure, which shows only the top part of the screen). For information about this
screen, see Understanding the Information on the Dashboard Screen on page 184.
Note: During the initial setup, the Setup Wizard displays when you first log
in; afterward the login takes you to the Dashboard screen.
Figure 16.
Note: After 5 minutes of inactivity (the default login time-out), you are
automatically logged out.
Understanding the Web Management Interface Menu Layout
The following figure shows the menu at the top of the STM300’s Web Management Interface.
The Web Management Interface layouts of the STM150 and STM600 are identical to the
STM300.
30 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 31

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
3rd level: Submenu tab (blue)
2nd level: Configuration menu link (gray)
1st level: Main navigation menu link (orange)
Figure 17.
The Web Management Interface menu consists of the following components:
• 1st Level: Main navigation menu links. The main navigation menu in the orange bar
across the top of the Web Management Interface provides access to all the configuration
functions of the STM, and remains constant. When you select a main navigation menu
link, the letters are displayed in white against an orange background.
• 2nd Level: Configuration menu links. The configuration menu links in the gray bar
(immediately below the main navigation menu bar) change according to the main
navigation menu link that you select. When you select a configuration menu link, the
letters are displayed in white against a gray background.
• 3rd Level: Submenu tabs. Each configuration menu item has one or more submenu
tabs that are listed below the gray menu bar. When you select a submenu tab, the text is
displayed in white against a blue background.
The bottom of each screen provides action buttons. The nature of the screen determines
which action buttons are shown. The following figure shows an example:
Figure 18.
Any of the following action buttons might be displayed on screen (this list might not be
complete):
• Apply. Save and apply the configuration.
• Reset. Reset the configuration to default values.
• Test. Test the configuration before you decide whether or not to save and apply the
configuration.
• Auto Detect. Enable the STM to detect the configuration automatically and suggest
values for the configuration.
• Next. Go to the next screen (for wizards).
• Back. Go to the previous screen (for wizards).
• Search. Perform a search operation.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 31
Page 32

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
• Cancel. Cancel the operation.
• Send Now. Send a file or report.
When a screen includes a table, table buttons are displayed to let you configure the table
entries. The nature of the screen determines which table buttons are shown. The following
figure shows an example:
Figure 19.
Any of the following table buttons might be displayed on screen:
• Select All. Select all entries in the table.
• Delete. Delete the selected entry or entries from the table.
• Enable. Enable the selected entry or entries in the table.
• Disable. Disable the selected entry or entries in the table.
• Add. Add an entry to the table.
• Edit. Edit the selected entry.
• Up. Move the selected entry up in the table.
• Down. Move the selected entry down in the table.
Almost all screens and sections of screens have an accompanying help screen. To open the
help screen, click the question mark icon. ( ).
Using the Setup Wizard to Perform the Initial Configuration
The Setup Wizard facilitates the initial configuration of the STM by taking you through
11 screens, the last of which allows you to save the configuration.
To start the Setup Wizard:
1. Select Global Settings > Network Settings from the menu. The Network Settings
submenu tabs display with the Network Settings screen in view.
2. From the Network Settings configuration menu, select Setup Wizard.
The following sections explain the 11 configuration screens of the Setup Wizard. On the 10th
screen, you can save your configuration. The 11th screen is just an informational screen.
The tables in the following sections explain the buttons and fields of the Setup Wizard
screens. Additional information about the settings in the Setup Wizard screens is provided in
other chapters that explain manual configuration; each following section provides a specific
link to a section in another chapter.
32 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 33

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Setup Wizard Step 1 of 10: Introduction
Figure 20.
The first Setup Wizard screen is just an introductory screen. Click Next to go to the following
screen.
Setup Wizard Step 2 of 11: Networking Settings
Figure 21.
Enter the settings as explained in the following table, and then click Next to go the following
screen.
Note: After you have completed the steps in the Setup Wizard, you can
make changes to the network settings by selecting Global Settings
> Network Settings. For more information about these network
settings, see Configuring Network Settings on page 52.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 33
Page 34

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 5. Setup Wizard Step 2: Network Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Management Interface Settings
System Name The name for the STM for purposes of identification and management. The default
name is the name of your model (STM150, STM300, or STM600).
IP Address Enter the IP address of the STM through which you will access the Web
Management Interface. The factory default IP address is 192.168.1.201.
Note: If you change the IP address of the STM while being connected through the
browser, you will be disconnected. You then need to open a new connection to the
new IP address and log in again. For example, if you change the default IP address
from 192.168.1.201 to 10.0.0.1, you need to enter https://10.0.0.1 in your browser
to reconnect to the Web Management Interface.
Subnet Mask Enter the IP subnet mask. The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of
an IP address. Unless you are implementing subnetting, use 255.255.255.0 as the
subnet mask.
Gateway Address Enter the IP address of the gateway through which the STM is accessed.
Primary DNS Specify the IP address for the primary DNS server.
Secondary DNS As an option, specify the IP address for the secondary DNS server.
MTU Settings
Maximum Transmission
Unit
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the largest physical packet size that a
network can transmit. Packets that are larger than the MTU value are divided into
smaller packets before they are sent, an action that prolongs the transmission
process. For most Ethernet networks the MTU value is 1500 bytes, which is the
default setting.
Note: NETGEAR recommends synchronizing the STM’s MTU setting with that of
your network to prevent delays in transmission.
34 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 35

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Setup Wizard Step 3 of 11: Time Zone
Figure 22.
Enter the settings as explained in the following table, and then click Next to go the following
screen.
Note: After you have completed the steps in the Setup Wizard, you can
make changes to the date and time by selecting Administration >
System Date & Time. For more information about these settings,
see Configuring Date and Time Service on page 74.
Table 6. Setup Wizard Step 3: System Date and Time Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
System Date and Time
From the drop-down list, select an NTP server, or select to enter the time manually.
Use Default NTP Servers The STM regularly updates its real-time clock (RTC), which it uses for scheduling,
by contacting a default NETGEAR NTP server on the Internet. This is the default
setting.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 35
Page 36

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 6. Setup Wizard Step 3: System Date and Time Settings (Continued)
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Use Custom NTP Servers The STM regularly updates its RTC by contacting one of the two NTP servers
(primary and backup), both of which you need to specify in the fields that become
available when you select this option.
Note: If you select this option but leave either the Server 1 or Server 2 field blank,
both fields are automatically set to the default NETGEAR NTP servers.
Note: A list of public NTP servers is available at
http://support.ntp.org/bin/view/Servers/WebHome.
Server 1 Name /
IP Address
Server 2 Name /
IP Address
Manually Enter the Date
and Time
Time Zone
From the drop-down list, select the local time zone in which the STM operates. The correct time zone is required
in order for scheduling to work correctly. You do not need to configure daylight savings time, which is applied
automatically when applicable. Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the default setting.
Note: When you select a time zone that is not associated with a location, such as (GMT -08:00) GMT-8, daylight
savings time is automatically disabled. When you select a time zone that is associated with a location, such as
(GMT -08:00) Pacific Time ( US & Canada), daylight savings time is automatically enabled.
Date Enter the date in the yyyy-mm-dd (year-month-date) format.
Time Enter the time in the hh-mm-ss (hour-minutes-seconds) format.
Enter the IP address or host name of the primary NTP server.
Enter the IP address or host name of the secondary NTP
server.
36 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 37

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Setup Wizard Step 4 of 11: Email Security
Figure 23.
Enter the settings as explained in the following table, and then click Next to go the following
screen.
Note: After you have completed the steps in the Setup Wizard, you can
make changes to the email security settings by selecting Email
Security > Policy or Email Security > Anti-Virus. The Email
Anti-Virus screen also lets you specify notification settings and email
alert settings. For more information about these settings, see
Configuring Email Protection on page 87.
Tip: To enhance performance, you can disable scanning of any protocols that
are seldom or never used. Be mindful of the difference between userand server-generated traffic. For example, your mail server might not use
IMAP, but some users might configure IMAP clients.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 37
Page 38

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 7. Setup Wizard Step 4: Email Security Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Services to Scan
SMTP SMTP scanning is enabled by default on standard
service port 25.
POP3 POP3 scanning is enabled by default on standard
service port 110.
IMAP IMAP scanning is enabled by default on standard
service port 143.
Scan Action
SMTP From the SMTP drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken when an infected
email is detected:
• Quarantine attachment. The email is not blocked, but the attachment is removed and placed in
the malware quarantine for further research. In addition, a malware quarantine log entry is
created, and depending on the nature of the malware threat, also a virus log entry or a spyware
log entry.
• Delete attachment. The email is not blocked, but the attachment is deleted, and a virus log entry
or a spyware log entry is created.
• Block infected email. This is the default setting. The email is blocked, and a virus log entry or
a spyware log entry is created.
• Quarantine infected email. The email is placed in the malware quarantine for further research.
In addition, a malware quarantine log entry is created, and depending on the nature of the
malware threat, also a virus log entry or a spyware log entry.
• Log only. Only a virus log entry or a spyware log entry is created. The email is not blocked and
the attachment is not deleted.
To disable any of these services, clear the
corresponding check box. You can change
the standard service port or add another port
in the corresponding Ports to Scan field.
POP3 From the POP3 drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken when an infected
email is detected:
• Quarantine attachment. The email is not blocked, but the attachment is removed and placed in
the malware quarantine for further research. In addition, a malware quarantine log entry is
created, and depending on the nature of the malware threat, also a virus log entry or a spyware
log entry.
• Delete attachment. This is the default setting. The email is not blocked, but the attachment is
deleted, and a virus log entry or a spyware log entry is created.
• Log only. Only a virus log entry or a spyware log entry is created. The email is not blocked and
the attachment is not deleted.
IMAP From the IMAP drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken when an infected
email is detected:
• Quarantine attachment. The email is not blocked, but the attachment is removed and placed in
the malware quarantine for further research. In addition, a malware quarantine log entry is
created, and depending on the nature of the malware threat, also a virus log entry or a spyware
log entry.
• Delete attachment. This is the default setting. The email is not blocked, but the attachment is
deleted, and a virus log entry or a spyware log entry is created.
• Log only. Only a virus log entry or a spyware log entry is created. The email is not blocked and
the attachment is not deleted.
38 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 39

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 7. Setup Wizard Step 4: Email Security Settings (Continued)
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Scan Exceptions
From the drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken when an email attachment exceeds the
size that you specify in the file size field:
• Skip. The file is not scanned but skipped, leaving the end user vulnerable. This is the default setting.
• Block. The file is blocked and does not reach the end user.
The default and maximum file sizes are as follows:
• For the STM600, the default setting is to block any attachment larger than 10240 KB. The maximum file size
that you can specify is 51200 KB.
• For the STM300, the default setting is to block any attachment larger than 10240 KB. The maximum file size
that you can specify is 25600 KB.
• For the STM150, the default setting is to block any attachment larger than 8192 KB. The maximum file size
that you can specify is 25600 KB.
Note: Setting the maximum file size to a high value might affect the STM’s performance. NETGEAR
recommends the default value, which is sufficient to detect the vast majority of threats.
Setup Wizard Step 5 of 11: Web Security
Figure 24.
Enter the settings as explained in the following table, and then click Next to go the following
screen.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 39
Page 40

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Note: After you have completed the steps in the Setup Wizard, you can
make changes to the Web security settings by selecting Web
Security > Policy or Web Security > HTTP/HTTPS > Malware
Scan. The Malware Scan screen also lets you specify HTML
scanning and notification settings. For more information about these
settings, see Configuring Web and Services Protection on page 105.
Table 8. Setup Wizard Step 5: Web Security Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Services to Scan
HTTP HTTP scanning is enabled by
default on standard service port 80.
HTTPS HTTPS scanning is disabled by
default.
FTP FTP scanning is enabled by default
on standard service port 21.
Scan Action
HTTP From the HTTP drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken when an infected
Web file or object is detected:
• Quarantine file. The Web file or object is removed and placed in the malware quarantine for
further research. In addition, a malware quarantine log entry is created, and depending on the
nature of the malware threat, also a virus log entry or spyware log entry.
• Delete file. This is the default setting. The Web file or object is deleted, and a virus log entry or
spyware log entry is created.
• Log only. Only a virus log entry or spyware log entry is created. The Web file or object is not
deleted.
Select the Streaming check box to enable streaming of partially downloaded and scanned HTTP
file parts to the end user. This method allows the user to experience more transparent Web
downloading. Streaming is enabled by default.
To disable Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) scanning,
clear the corresponding check box. You can change the
standard service port or add another port in the
corresponding Ports to Scan field.
To enable Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket
Layer (HTTPS) scanning, select the corresponding check
box. You can change the standard service port (number 443)
or add another port in the corresponding Ports to Scan field.
To disable File Transfer Protocol (FTP) scanning, clear the
corresponding check box. You can change the standard
service port or add another port in the corresponding Ports to
Scan field.
40 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 41

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 8. Setup Wizard Step 5: Web Security Settings (Continued)
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
HTTPS From the HTTPS drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken when an infected
Web file or object is detected:
• Quarantine file. The Web file or object is removed and placed in the malware quarantine for
further research. In addition, a malware quarantine log entry is created, and depending on the
nature of the malware threat, also a virus log entry or spyware log entry.
• Delete file. This is the default setting. The Web file or object is deleted, and a virus log entry or
spyware log entry is created.
• Log only. Only a virus log entry or spyware log entry is created. The Web file or object is not
deleted.
Select the Streaming check box to enable streaming of partially downloaded and scanned HTTPS
file parts to the end user. This method allows the user to experience more transparent Web
downloading. Streaming is enabled by default.
FTP From the FTP drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken when an infected Web
file or object is detected:
• Quarantine file. The Web file or object is removed and placed in the malware quarantine for
further research. In addition, a malware quarantine log entry is created, and depending on the
nature of the malware threat, also a virus log entry or spyware log entry.
• Delete file. This is the default setting. The Web file or object is deleted, and a virus log entry or
spyware log entry is created.
• Log only. Only a virus log entry or spyware log entry is created. The Web file or object is not
deleted.
Scan Exceptions
From the drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken when a Web file or object exceeds the
size that you specify in the file size field:
• Skip. The file is not scanned but skipped, leaving the end user vulnerable. This is the default setting.
• Block. The file is blocked and does not reach the end user.
The default and maximum file sizes are as follows:
• For the STM600 and STM300, the default setting is to block any attachment larger than 10240 KB. The
maximum file size that you can specify is 51200 KB.
• For the STM150, the default setting is to block any attachment larger than 8192 KB. The maximum file size
that you can specify is 25600 KB.
Note: Setting the maximum file size to a high value might affect the STM’s performance. NETGEAR
recommends the default value, which is sufficient to detect the vast majority of threats.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 41
Page 42

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Setup Wizard Step 6 of 11: Email Notification Server Settings
Figure 25.
Enter the settings as explained in the following table, and then click Next to go the following
screen.
Note: After you have completed the steps in the Setup Wizard, you can
make changes to the administrator email notification settings by
selecting Global Settings > Email Notification Server. For more
information about these settings, see Configuring the Email
Notification Server on page 176.
Table 9. Setup Wizard Step 6: Email Notification Server Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Email Notification Server Settings
Show as Mail Sender A descriptive name of the sender for email identification purposes. For example,
enter stm600notification@netgear.com.
Send Notifications to The email address to which the notifications should be sent. Typically, this is the
email address of a user with administrative privileges.
SMTP Server The IP address and port number or Internet name and port number of your ISP’s
outgoing email SMTP server. The default port number is 25.
Note: If you leave this field blank, the STM cannot send email notifications.
Mail Server Requires
Authentication
If the SMTP server requires authentication, select the Mail Server Requires
Authentication check box and enter the following settings:
User Name The user name for SMTP server authentication.
Password The password for SMTP server authentication.
42 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 43

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Setup Wizard Step 7 of 11: Update Settings
Figure 26.
Enter the settings as explained in the following table, and then click Next to go the following
screen.
Note: After you have completed the steps in the Setup Wizard, you can
make changes to the security subscription update settings by
selecting Administration > Software Update. For more information
about these settings, see Updating the Software on page 71.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 43
Page 44

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 10. Setup Wizard Step 7: Update Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
System Information
You cannot configure this section; it is shown for information only. For the software, scan engine, (signature)
pattern file, and operating system (OS), the current version and the date of the last update are displayed.
Click + More to display the versions and most recent downloads for the antispam engine, applications engine,
applications pattern file, stream engine, stream pattern file, mini engine, mini pattern file, policyd, scand, urld,
update client, and rescue software.
Update Settings
Update From Select one of the following radio buttons:
• Default Update Server. The scan engine and signatures are updated from the
NETGEAR default update server.
• Another Update Server. The scan engine and signatures are updated from a server
that you specify by entering the server IP address or host name in the Server Address
field.
Server Address The update server IP address or host name.
Update Component Make one of the following selections from the drop-down list:
• Update Signature Patterns only. Only the (signature) pattern file is updated. The
software, scan engine, and OS are not updated.
• Update all Software and Signature Patterns. The software, scan engine,
(signature) pattern file, and OS are updated. This is the default setting.
Update Frequency
Make one of the following selections:
• Weekly. From the drop-down lists, specify the day, hour, and minutes that the update should occur.
• Daily. From the drop-down lists, specify the hour and minutes that the update should occur.
• Every. From the drop-down list, specify the frequency with which the update should occur.
44 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 45

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Setup Wizard Step 8 of 11: HTTP Proxy Settings
Figure 27.
Enter the settings as explained in the following table, and then click Next to go the following
screen.
Note: After you have completed the steps in the Setup Wizard, you can
make changes to the security subscription update settings by
selecting Global Settings> HTTP Proxy. For more information
about these settings, see Configuring the HTTP Proxy Settings on
page 60.
Table 11. Setup Wizard Step 8: HTTP Proxy Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
HTTPS Proxy Settings
Use a Proxy Server to
Connect to the Internet
If computers on the network connect to the Internet via a proxy server, select the
Use a Proxy Server to Connect to the Internet check box to specify and enable a
proxy server. Enter the following settings:
Proxy Server The IP address and port number of the proxy server.
User Name The user name for proxy server authentication.
Password The password for proxy server authentication.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 45
Page 46

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Setup Wizard Step 9 of 11: Web Categories
Figure 28.
Enter the settings as explained in the following table, and then click Next to go the following
screen.
46 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 47

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Note: After you have completed the steps in the Setup Wizard, you can
make changes to the content filtering settings by selecting Web
Security > HTTP/HTTPS > Content Filtering. The Content Filtering
screen lets you specify additional filtering tasks and notification
settings. For more information about these settings, see Configuring
Web Content Filtering on page 109.
Table 12. Setup Wizard Step 9: Web Categories Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Select the Web Categories You Wish to Block
Select the Enable Blocking check box to enable blocking of Web categories, which is the default setting.
Select the check boxes of any Web categories that you want to block. Use the action buttons in the following
way:
• Allow All. All Web categories are allowed.
• Block All. All Web categories are blocked.
• Set to Defaults. Blocking and allowing of Web categories are returned to their default settings. See Table 24
on page 85 for information about the Web categories that are blocked by default. Categories that are
preceded by a green rectangle are allowed by default; categories that are preceded by a pink rectangle are
blocked by default.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 47
Page 48

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Setup Wizard Step 10 of 11: Configuration Summary
Figure 29.
Click Apply to save your settings and automatically restart the system, or click Back to make
changes to the configuration.
48 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 49

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Setup Wizard Step 11 of 11: Restarting the System
Figure 30.
Wizard screen 11 is just an informational screen to let you know that the system restarts
automatically with the new configuration.
Verifying Correct Installation
Test the STM before deploying it in a live production environment. The following instructions
walk you through a couple of quick tests designed to ensure that your STM is functioning
correctly.
Testing Connectivity
Verify that network traffic can pass through the STM:
• Test an Internet URL (see Testing a URL on page 217).
• Ping the IP address of a device on either side of the STM.
Testing HTTP Scanning
If client computers have direct access to the Internet through your LAN, try to download the
eicar.com test file from http://www.eicar.org/download/eicar.com.
The eicar.com test file is a legitimate DoS program and is safe to use because it is not a
malware threat and does not include any fragments of malware code. The test file is provided
by EICAR, an organization that unites efforts against computer crime, fraud, and misuse of
computers or networks.
Verify that the STM correctly scans HTTP traffic:
1. Log in to the STM Web Management Interface, and then verify that HTTP scanning is
enabled. For information about how to enable HTTP scanning, see Customizing Web
Protocol Scan Settings on page 105.
2. Check the downloaded eicar.com test file, and note the attached malware information file.
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 49
Page 50

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Registering the STM with NETGEAR
To receive threat management component updates and technical support, you need to
register your STM with NETGEAR. The support registration keys are provided with the
product package (see Service Registration Card with License Keys on page 12).
The STM supports a bundle key, which is a single support registration key that provides all
three licenses: Web protection, Email protection, and Support & Maintenance.
Note: Activating the service licenses initiates their terms of use. Activate
the licenses only when you are ready to start using this unit. If your
unit has never been registered before, you can use the 30-day trial
period for all three types of licenses to perform the initial testing and
configuration. To use the trial period, do not click Register in step 5
of the following procedure but click Trial instead.
To activate the service licenses:
1. Ensure that your STM is connected to the Internet.
2. Select Support > Registration from the menu. The Registration screen displays:
Figure 31.
50 | Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
Page 51

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
3. In the Registration Key field, enter the license key.
4. Fill out the customer and VAR fields.
5. Click Register.
6. Repeat step 3 and step 5 for additional license keys.
The STM activates the licenses and registers the unit with the NETGEAR registration server.
Note: If you reset the STM to the original factory default settings after you
have entered the license keys to activate the STM (see Registering
the STM with NETGEAR on page 50), the license keys are erased.
The license keys and the different types of licenses that are
available for the STM are no longer displayed on the Registration
screen. However, after you have reconfigured the STM to connect to
the Internet and to the NETGEAR registration server, the STM
retrieves and restores all registration information based on its MAC
address and hardware serial number. You do not need to reenter the
license keys or reactivate the STM.
What to Do Next
You have completed setting up and deploying the STM to the network. The STM is now set
up to scan the protocols and services that you specified for malware threats and to perform
updates based on the configured update source and frequency.
If you need to change the settings, or to view reports or logs, log in to the STM Web
Management Interface, using the default IP address or the IP address that you assigned to
the STM in Setup Wizard Step 1 of 10: Introduction on page 33.
The STM is ready for use. However, the following sections describe some important tasks
that you might want to address before you deploy the STM in your network:
• Changing Administrative Passwords and Timeouts on page 62
• Managing Digital Certificates on page 76
• Configuring Groups on page 148
• Configuring User Accounts on page 152
• Configuring Authentication on page 154
• Setting Scanning Exclusions and Web Access Exceptions on page 130
Chapter 2. Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network | 51
Page 52

3. Performing Network and System
Management
This chapter describes the network settings, the system management features, and ways to
improve the performance of the STM. If you have used the Setup Wizard, you have already
configured some of these settings, but there are situations in which you might want to modify
them. This chapter contains the following sections:
• Configuring Network Settings on this page
• Configuring Session Limits and Timeouts on page 56
• Configuring the Network Refresh and Permanent MAC Address Bindings on page 57
• Configuring the HTTP Proxy Settings on page 60
• About Users with Administrative and Guest Privileges on page 61
• Configuring Remote Management Access on page 64
• Using an SNMP Manager on page 65
• Managing the Configuration File on page 67
• Updating the Software on page 71
• Configuring Date and Time Service on page 74
3
• Managing Digital Certificates on page 76
• Managing the Quarantine Settings on page 81
• Managing the STM’s Performance on page 82
Configuring Network Settings
If you have used the Setup Wizard, you might already have configured the Web
Management Interface and maximum transmission unit (MTU) settings; the Network Settings
screen allows you to modify these settings and to specify the interface speed and duplex
settings.
The STM requires a valid IP address to retrieve online updates and to enable access to its
Web Management Interface. If you have used the Setup Wizard to configure the STM, you
have already specified the management interface name and address settings and the size of
the MTU. In addition to modifying these settings, the Network Settings screen also allows
you to specify the interface speed and duplex settings for the management interface, for the
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 52
Page 53

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
STM600 or STM300 uplink and downlink interfaces, or for the STM150’s WAN and LAN
interfaces.
To configure the STM’s network settings:
1. Select Global Settings > Network Settings from the menu. The Network Settings
submenu tabs display with the Network Settings screen in view. (The following figure
shows the STM600.)
Figure 32. STM600
The following figure shows the Interface Speed & Duplex Settings section of the Network
Settings screen of the STM300:
Figure 33. STM300
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 53
Page 54

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
The following figure shows the Interface Speed & Duplex Settings section of the Network
Settings screen of the STM150:
Figure 34. STM150
2. Complete the fields and make your selections from the drop-down lists as explained in the
following table:
Table 13. Network Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Management Interface Settings
System Name The name for the STM for purposes of identification and management. The default
name is the name of your model (STM150, STM300, or STM600).
IP Address Enter the IP address of the STM through which you will access the Web Management
Interface. The factory default IP address is 192.168.1.201.
Note: If you change the IP address of the STM while being connected through the
browser, you will be disconnected. You then need to open a new connection to the new
IP address and log in again. For example, if you change the default IP address from
192.168.1.201 to 10.0.0.1, you need to enter https://10.0.0.1 in your browser to
reconnect to the Web Management Interface.
Subnet Mask Enter the IP subnet mask. The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an
IP address. Unless you are implementing subnetting, use 255.255.255.0 as the subnet
mask.
Gateway Address Enter the IP address of the gateway through which the STM is accessed.
Primary DNS Specify the IP address for the primary DNS server IP address.
Secondary DNS As an option, specify the IP address for the secondary DNS server IP address.
Interface Speed & Duplex Settings
These sections show the MAC address and assigned speed and duplex setting for each active interface.
The Set Speed/Duplex drop-down list allows you to select the speed and duplex setting for each active
interface. To set the speed to 1000baseT duplex (“full”), select auto to let the STM sense the speed
automatically.
Note: MGMT stands for management interface.
54 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 55

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 13. Network Settings (Continued)
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
STM600
(see Figure 32 on
page 53)
STM300
(see Figure 33 on
page 53)
STM150
(see Figure 34 on
page 54)
MGMT From the Set Speed/Duplex drop-down list, make one of the
PAIR1 UPLINK
PAIR1 DOWNLINK
PAIR2 UPLINK
PAIR2 DOWNLINK
MGMT From the Set Speed/Duplex drop-down list, make one of the
UPLINK
DOWNLINK
LAN1
LAN2
LAN3
LAN4
WAN
following selections:
• auto. Speed autosensing. This is the default setting.
• 10baseT/Half. Ethernet speed at half duplex.
• 10baseT/Full. Ethernet speed at full duplex.
• 100baseT/Half. Fast Ethernet speed at half duplex.
• 100baseT/Full. Fast Ethernet speed at full duplex.
following selections:
• auto. Speed autosensing. This is the default setting.
• 10baseT/Half. Ethernet speed at half duplex.
• 10baseT/Full. Ethernet speed at full duplex.
• 100baseT/Half. Fast Ethernet speed at half duplex.
• 100baseT/Full. Fast Ethernet speed at full duplex.
From the Set Speed/Duplex drop-down list, make one of the
following selections:
• auto. Speed autosensing. This is the default setting, which can
sense 1000BaseT speed at full duplex.
• 10baseT/Half. Ethernet speed at half duplex.
• 10baseT/Full. Ethernet speed at full duplex.
• 100baseT/Half. Fast Ethernet speed at half duplex.
• 100baseT/Full. Fast Ethernet speed at full duplex.
Note: All LAN interfaces share the same MAC address, speed,
and duplex mode.
Note: The STM150 does not provide a dedicated management
interface.
MTU Settings
Maximum
Transmission Unit
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the largest physical packet size that a
network can transmit. Packets that are larger than the MTU value are divided into
smaller packets before they are sent, an action that prolongs the transmission process.
For most Ethernet networks the MTU value is 1500 bytes, which is the default setting.
Note: NETGEAR recommends synchronizing the STM’s MTU setting with that of your
network to prevent delays in transmission.
3. Click Apply to save your settings. (If you click Reset, the STM restarts to restore the
default network settings.) Changing the network settings has the following consequences:
• Changing any of the settings in the Management Interface Settings section of the
screen causes the STM to restart.
• Changing any of the settings in the Interface Speed & Duplex Settings section of the
screen causes the network to restart.
• Changing the MTU setting causes services such as HTTP and SMTP to restart.
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 55
Page 56

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Configuring Session Limits and Timeouts
The Session Limits screen allows you to specify the total number of sessions per user (that
is, per IP address or single source machine) that are allowed on the STM. Session limiting is
disabled by default. When session limiting is enabled, you can specify the maximum number
of sessions per user either as an absolute number or as a percentage of the STM’s total
connection capacity per user, which is 10000 sessions. (You cannot change the total
connection capacity per user.) If a user exceeds the number of allocated sessions, packets
might be dropped.
Note: Some protocols such as FTP and RSTP create two sessions per
connection.
To configure session limits and timeouts:
1. Select Global Settings > Network Settings from the menu. The Network Settings
submenu tabs display with the Network Settings screen in view.
2. Click the Session Limits submenu tab. The Session Limits screen displays:
Figure 35.
56 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 57

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
3. Select the radio buttons, make your selections from the drop-down list, and complete the
fields as explained in the following table:
Table 14. Session Limits Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Session Limits
Do You Want to
Enable per-user
Session Limits?
Session Timeouts
If a session goes without data flow longer than the configured values, the session is terminated.
TCP Timeout The time in seconds after which a TCP session without data flow is terminated. The
UDP Timeout The time in seconds after which an UDP session without data flow is terminated. The
ICMP Timeout The time in seconds after which an ICMP session without data flow is terminated. The
Select the Yes radio button to enable session limits, and then fill in the Limit Type and
Limit Value fields. The No radio button is selected by default.
Limit Type From the Limit Type drop-down list, make one of the following selections:
• Percentage of Maximum Sessions. Session limits are set as a
percentage of the total connection capacity per user.
• Sessions per User. Session limits are set as an absolute number.
Limit Value Depending on the selection in the Limit Type field, this value is a
percentage or an absolute number.
The Total Number of Packets Dropped field, which you cannot configure, shows the total
number of packets that are dropped because the session limit has been exceeded.
default time is 1200 seconds.
default time is 180 seconds.
default time is 8 seconds.
4. Click Apply to save your settings. Changing any settings in the Session Timeouts section of
the screen requires the STM to restart. If you click Reset, the STM restarts to restore the
default network settings.
Configuring the Network Refresh and Permanent MAC Address Bindings
The STM integrates smart virtual MAC address detection to automatically detect virtual MAC
addresses and bind these to an interface. When the network topology changes, a virtual
MAC address might no longer be bound to the original interface. If this situation occurs, the
host to which the virtual MAC address is assigned is no longer able to communicate with
others through the STM. Therefore, the network need to be refreshed to enable the STM to
redetect the virtual MAC address on the correct interface.
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 57
Page 58

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
To refresh the network and view the MAC Address Bindings table:
1. Select Global Settings > Network Settings from the menu. The Network Settings
submenu tabs display with the Network Settings screen in view.
2. Click the Network Refresh submenu tab. The Network Refresh screen displays. (The
following figure shows the STM150.)
Figure 36.
58 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 59

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
3. Select the check boxes and radio buttons and make your selections from the drop-down list
as explained in the following table:
Table 15. Network Refresh Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Automatically Refresh the Network
Periodically
refresh the MAC
address
bindings
Click Apply to schedule the automatic refresh of the network, or click Reset to return to the default settings.
Manually Refresh the Network
Click Refresh to immediately refresh the network.
Note: When you click Refresh, the network restarts.
Note: The Advanced Settings button is described in the following section.
Select this check box to enable the periodic refresh of the dynamic MAC address
bindings. Specify if the refresh occurs either weekly or daily.
Weekly Select the Weekly radio button to enable a weekly refresh of the network,
and then specify when the refresh needs to occur by selecting the day,
hour, and minutes from the drop-down lists.
Daily Select the Daily radio button to enable a daily refresh of the network, and
then specify when the refresh needs to occur by selecting the hour and
minutes from the drop-down lists.
Managing Permanent MAC Address Bindings
You can permanently bind a MAC address to an interface. Such a binding does not change
when the network topology changes and does not need to be redetected by the STM.
To create a permanent MAC binding:
1. Select Global Settings > Network Settings from the menu. The Network Settings
submenu tabs display with the Network Settings screen in view.
2. Click the Network Refresh submenu tab. The Network Refresh screen displays (see the
previous figure, which shows the STM150). Locate the Manually Refresh the Network
section.
3. Click the Advanced Settings button. The screen expands to display the MAC Address
Bindings section.
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 59
Page 60

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
4. Complete the fields and make your selections from the drop-down lists as explained in the
following table:
Table 16. MAC Address Binding Settings
Setting Description
MAC Address Enter the MAC address that you want to bind permanently.
Port (STM150) or Interface
(STM300 and STM600)
Type This field is automatically determined: it displays Permanent or Dynamic.
From the drop-down list, select the interface to which the MAC address needs
to be bound.
5. To add the newly configured MAC address binding to the MAC Address Bindings table, click
the Add table button in the Action column.
The MAC Address Bindings table displays both the dynamic bindings that are automatically
detected by the STM and the permanent bindings that you have created.
Changing a Dynamic MAC Address Binding to a Permanent Binding
To change a dynamic binding to a permanent binding:
1. Locate the dynamic MAC address binding that you want bind permanently, and select an
interface from the Port drop-down list (STM150) or Interface drop-down list (STM300
and STM600).
2. Click the corresponding Add table button in the Action column.
Activating, Editing, or Deleting a Permanent MAC Address Binding
For each permanent binding in the MAC Address Bindings table, the Action column provides
two table buttons:
• Apply. Activates the permanent MAC address binding.
• Delete. Deletes the permanent MAC address binding from the table.
To assign another interface to a permanent MAC address binding:
1. Locate the dynamic MAC address binding that you want to edit, and select another
interface from the Port drop-down list (STM150) or Interface drop-down list (STM300
and STM600).
2. Click Apply to save your changes.
Configuring the HTTP Proxy Settings
If you have used the Setup Wizard, you might have already configured an HTTP proxy; the
HTTP Proxy screen allows you to modify these settings. If the STM is installed behind an
HTTP proxy, you might need to specify the HTTP proxy settings for the STM to connect to the
60 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 61

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Internet. The settings on the HTTP Proxy screen affect Web category filtering, distributed
spam analysis, and software updates.
To configure the HTTP proxy:
1. Select Global Settings > HTTP Proxy from the menu. The HTTP Proxy screen
displays:
Figure 37.
2. Select the check box and complete the fields as explained in the following table:
Table 17. HTTP Proxy Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
HTTPS Proxy Settings
Use a Proxy Server to
Connect to the Internet
If computers on the network connect to the Internet via a proxy server, select the
Use a Proxy Server to Connect to the Internet check box to specify and enable
a proxy server. Enter the following settings:
Proxy Server The IP address and port number of the proxy server.
User Name The user name for proxy server authentication.
Password The password for proxy server authentication.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
About Users with Administrative and Guest Privileges
There are two predefined user types that can access the STM’s Web Management Interface:
• Administrator. A user who has full access and the capacity to change the STM
configuration (that is, read/write access). The default user name for an administrator is
admin, and the default password for an administrator is password.
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 61
Page 62

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
• Guest user. A user who can only view the STM configuration (that is, read-only access).
The default user name for a guest is guest, and the default password for a guest is guest.
NETGEAR recommends that you change these passwords to more secure passwords.
The login window that is presented to the administrator and guest user is the NETGEAR
Configuration Manager Login screen (see Figure 87 on page 155).
Changing Administrative Passwords and Timeouts
In addition to changing the default password for the administrator and guest user, you can
use the Set Password screen to change the account names, and modify the Web
Management Interface timeout setting.
Note: The ideal password should contain no dictionary words from any
language, and should be a mixture of letters (both uppercase and
lowercase), numbers, and symbols. The password can be up to 64
characters.
To modify the administrator and guest accounts, and to modify the Web Management
Interface timeout setting:
1. Select Administration > Set Password from the menu. The Set Password screen
displays:
Figure 38.
62 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 63

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
2. To modify the administrator or guest settings, select the check box and complete the fields
as explained in the following table:
Table 18. Set Password Settings Screen: Administrator and Guest Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
User Selection
Select one of the following radio buttons:
• Edit Administrator Settings. Allows you to modify the administrator settings, while the guest settings
are masked out.
• Edit Guest Settings. Allows you to modify the guest settings, while the administrator settings are
masked out.
Administrator Settings/Guest Setting
New User Name The default user name. For the administrator account, the default name is admin;
for the guest account, the default name is guest.
Old Password The current (factory default) password.
New Password Enter the new password.
Retype New Password Confirm the new password.
3. Under the Administrator Settings and Guest Settings sections of the screen, click Apply to
save your settings.
4. If you modified the administrator settings and now want to modify the guest settings, or the
other way around, repeat step 2 and step 3 for the other settings.
5. To modify the Web Management Interface timeout settings, complete the field as explained
in the following table:
Table 19. Set Password Settings Screen: Web Interface Timeout Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Web Interface Timeout
Session Timeout Enter the period in seconds after which the Web Management Interface is
automatically logged off if no activity is detected. The default is 600 seconds. You
can configure a session timeout from 30 seconds to 9999 seconds.
6. Under the Web Interface Timeout section of the screen, click Apply to save your settings.
Note: After a factory default reset, the password and timeout values are
changed back to password and 600 seconds (5 minutes),
respectively.
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 63
Page 64

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Configuring Remote Management Access
An administrator can configure, upgrade, and check the status of the STM over the Internet
via a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPN connection.
You need to use an SSL VPN connection to access the STM from the Internet: type https://
(not http://) followed by the STM’s WAN IP address into your browser. For example, if the
STM’s WAN IP address is 172.16.0.123, type the following in your browser:
https://172.16.0.123.
The STM’s remote login URL is:
https://<IP_address> or https://<FullyQualifiedDomainName
Note: The STM is accessible to anyone who knows its IP address and
default password. Because a malicious WAN user can reconfigure
the STM and misuse it in many ways, NETGEAR highly
recommends that you change the admin and guest default
passwords before continuing (see Changing Administrative
Passwords and Timeouts on page 62).
To configure remote management:
1. Select Administration > Remote Management from the menu. The Remote
Management screen displays:
Figure 39.
64 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 65

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
2. In the Secure HTTPS Management section of the screen, enter number of the port that you
want to use to access Web Management Interface of the STM. The default setting is port
443, but you can enter a port ranging from 1024 to 65535. You cannot use some ports such
as 2080 and 8088 that might be used by the STM.
This section of the screen also displays the HTTPS hyperlink through which you can
access the Web Management Interface of the STM. The hyperlink consists of the IP
address or fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the STM and the port number that you
have assigned.
3. In the Access Control List section of the screen, you can specify IP addresses or IP address
ranges that you want to grant access to the Web Management Interface for increased
security. To specify a range, separate the beginning IP address and the ending IP address
by a hyphen (-).To allow access from all IP addresses and IP address ranges, leave this field
blank.
4. Click Apply to save your changes.
Note: To maintain security, the STM rejects a login that uses http://address
rather than the SSL https://address.
Note: The first time that you remotely connect to the STM with a browser
via an SSL VPN connection, you might get a warning message
regarding the SSL certificate. If you are using a Windows computer
with Internet Explorer 5.5 or later, simply click Yes to accept the
certificate.
Using an SNMP Manager
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) forms part of the Internet Protocol Suite as
defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). SNMP is used in network
management systems to monitor network-attached devices for conditions that warrant
administrative attention.
SNMP exposes management data in the form of variables on the managed systems, which
describe the system configuration. These variables can then be queried (and sometimes set)
by managing applications.
SNMP lets you monitor and manage your STM from an SNMP manager. It provides a remote
means to monitor and control network devices, and to manage configurations, statistics
collection, performance, and security. The STM provides support for report aggregation
through SNMP version 1 (SNMPv1) and version 2 (SNMPv2).
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 65
Page 66

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
To enable SNMP and to configure the SNMP settings:
1. Select Administration > SNMP from the menu. The SNMP screen displays:
Figure 40.
2. Select the radio buttons and complete the fields as explained in the following table:
Table 20. SNMP Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
SNMP Settings
Do You Want to
Enable SNMP?
Select one of the following radio buttons:
• Yes. Enable SNMP.
• No. Disable SNMP. This is the default setting.
Read Community The community string to allow an SNMP manager access to the
MIB objects of the STM for the purpose of reading only. The
default setting is public.
Set Community The community string to allow an SNMP manager access to the
MIB objects of the STM for the purpose of reading and writing.
The default setting is private.
66 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 67

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 20. SNMP Settings (Continued)
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Do You Want to
Enable SNMP?
(continued)
Trusted SNMP Hosts
Enter the IP addresses of the computers and devices to which you want to grant read-only (GET) or write
(SET) privileges on the STM. Separate IP addresses by a comma. To allow any trusted SNMP host access,
leave the field blank, which is the default setting.
SNMP Traps
Enter the IP addresses of the SNMP management stations that are allowed to receive the STM’s SNMP
traps. Separate IP addresses by a comma. If you leave the field blank, which is the default setting, no
SNMP management station can receive the STM’s SNMP traps.
Contact The SNMP system contact information that is available to the
SNMP manager. This setting is optional.
Location The physical location of the STM. This setting is optional.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
Supported MIB Browsers
After you have configured the SNMP settings, you need to enter the IP address of the STM in
the Management Information Base (MIB) browsers through which you want to query or
configure the STM. See the documentation of your MIB browser for instructions.
NETGEAR recommends the following MIB browsers for receiving the STM SNMP
notifications:
• MG-Soft
• SNMP
• Net-SNMP (Linux Text)
• SNMP Browser for KDE
The STM MIB structure is automatically downloaded by management stations. You should
start receiving notifications after you have enabled SNMP on the STM and added its IP
address into your MIB browsers.
Managing the Configuration File
The configuration settings of the STM are stored in a configuration file on the STM. This file
can be saved (backed up) to a PC, retrieved (restored) from the PC, or cleared to factory
default settings.
Once the STM is installed and works correctly, make a backup of the configuration file to a
computer. If necessary, you can later restore the STM settings from this file.
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 67
Page 68

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
The Backup and Restore Settings screen lets you:
• Back up and save a copy of the current settings
• Restore saved settings from the backed-up file
• Revert to the factory default settings.
To display the Backup and Restore Settings screen, select Administration > Backup and
Restore Settings from the menu:
Figure 41.
Backing Up Settings
The backup feature saves all STM settings to a file. These settings include:
• Network settings. IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and so on.
• Scan settings. Services to scan, primary and secondary actions, and so on.
• Update settings. Update source, update frequency, and so on.
• Antispam settings. Whitelist, blacklist, content filtering settings, and so on.
Back up your STM settings periodically, and store the backup file in a safe place.
Tip: You can use a backup file to export all settings to another STM that has
the same language and management software versions. Remember to
change the IP address of the second STM before deploying it to
eliminate IP address conflicts on the network.
68 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 69

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
To back up settings:
1. On the Backup and Restore Settings screen (see the previous figure), next to Save a
copy of current settings, click the Backup button to save a copy of your current settings.
A dialog box displays, showing the file name of the backup file.
Note: The backup file has the following format:
backup_$hostname_$productversion_$yyyymmdd.gpg.
$hostname: The host name of the STM that is configured on the
Network Settings screen, for example, STM600.
$productversion: The software version of the STM, for example,
2.0.0-39.
$yyyymmdd: The time when the backup is performed, for example,
20100617.
Using these examples, the backup file name would be
backup_STM600_2.0.0-39_20100617.gpg.
2. Select Save file, and then click OK.
3. Open the folder where you have saved the backup file, and then verify that it has been
saved successfully.
Note the following:
• If your browser is not configured to save downloaded files automatically, locate the folder
in which you want to save the file, specify the file name, and save the file.
• If you have your browser configured to save downloaded files automatically, the file is
saved to your browser’s download location on the hard disk.
Restoring Settings
WARNING!
Restore only settings that were backed up from the same software
version. Restoring settings from a different software version can
corrupt your backup file or the STM system software.
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 69
Page 70

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
To restore settings from a backup file:
1. On the Backup and Restore Settings screen (see Figure 41 on page 68), next to
Restore save settings from file, click Browse.
2. Locate and select the previously saved backup file.
3. When you have located the file, click the Restore button. A warning screen might appear,
and you might have to confirm that you want to restore the configuration.
The STM restarts. During the reboot process, the Backup and Restore Settings screen
remains visible. The reboot process is complete after several minutes when the Test LED on
the front panel goes off.
WARNING!
Once you start restoring settings, do not interrupt the process. Do
not try to go online, turn off the STM, shut down the computer, or
do anything else to the STM until the settings have been fully
restored.
Reverting to Factory Default Settings
To reset the STM to the original factory default settings, click the Default button next to
Revert to factory default settings on the Backup and Restore Settings screen (see Figure 41
on page 68).
The STM restarts. The Backup and Restore Settings screen remains visible during the reboot
process. The reboot process is complete after several minutes when the Test LED (STM150)
or Status LED (STM300 and STM600) on the front panel goes off.
WARNING!
When you restore the factory default settings, the STM settings
are erased. All content settings and scan settings are lost. Back
up your settings if you intend on using them.
Note: After rebooting with factory default settings, the STM administrator
account password is password, the guest account password is
guest, and the LAN IP address is 192.168.1.201.
70 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 71

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Note: For the STM150 only, there is an alternate way to return the settings
to factory defaults: Using a sharp object, press and hold the Reset
button on the rear panel of the STM150 (see Rear Panel STM150 on
page 20) for about 10 seconds until the front panel Test LED flashes
and the STM150 returns to factory default settings.
Updating the Software
If you have used the Setup Wizard, you might have already configured the software update
settings; the Software Update screen allows you to modify these settings.
The STM has four main software components:
• The application software that includes the network protocols, security services, Web
Management Interface, and other components.
• A scan engine that enables the STM to scan emails, attachments, Web files, and
applications, and that functions in conjunction with the pattern file.
• A pattern file that contains the virus signature files and virus database.
• An operating system (OS) that includes the kernel modules and hardware drives.
The STM provides two methods for updating components:
• Scheduled, automatic update
• Manual update
Because new virus threats can appear any hour of the day, it is very important to keep both
the pattern file and scan engine firmware as current as possible. The STM can automatically
check for updates, as often as every 15 minutes, to ensure that your network protection is
current.
Scheduling Updates
Enabling scheduled updates ensures that the STM automatically downloads the latest
components from the NETGEAR update server.
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 71
Page 72

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
To configure scheduled updates:
1. Select Administration > Software Update from the menu. The Software Update screen
displays:
Figure 42.
2. Select the radio buttons, complete the field, and make your selections from the drop-down
lists as explained in the following table:
Table 21. Software Update Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
System Information
You cannot configure this section; it is shown for information only. For the software, scan engine, (signature)
pattern file, and operating system (OS), the current version and the date of the last update are displayed.
Click + More to display the versions and most recent downloads for the antispam engine, applications
engine, applications pattern file, stream engine, stream pattern file, mini engine, mini pattern file, policyd,
scand, urld, update client, and rescue software.
72 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 73

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 21. Software Update Settings (Continued)
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Update Settings
Update From Select one of the following radio buttons:
• Default Update Server. The scan engine and signatures are updated from the
NETGEAR default update server.
• Another Update Server. The scan engine and signatures are updated from a
server that you specify by entering the server IP address or host name in the
Server Address field.
Server Address The update server IP address or host name.
Update Component Make one of the following selections from the drop-down list:
• Update Signature Patterns only. Only the (signature) pattern file is updated. The
software, scan engine, and OS are not updated.
• Update all Software and Signature Patterns. The software, scan engine,
(signature) pattern file, and OS are updated. This is the default setting.
Update Frequency
Make one of the following selections:
• Weekly. From the drop-down lists, specify the day, hour, and minutes that the update should occur.
• Daily. From the drop-down lists, specify the hour and minutes that the update should occur.
• Every. From the drop-down list, specify the frequency with which the update should occur.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
Performing a Manual Update
If you want to immediately check for and download available updates, perform a manual
update:
1. Select Administration > Software Update from the menu. The Software Update screen
displays (see the previous figure).
2. At the bottom of the screen, click Update Now. The STM contacts the update server and
checks for available updates. If updates are available, the Update Progress screen displays
to show the progress of the update:
Figure 43.
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 73
Page 74

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
3. After the update has finished, click Apply to activate the newly updated software.
Critical Updates That Require a Restart
If a downloaded update requires a restart, you are prompted to perform the update when you
log in to the STM. The following figure shows an example of a Critical Update screen, which
provides information about the update and allows you to install it immediately or at sa later
time. To install the update immediately, click Install Now. To install the update at a later time,
click Later.
Figure 44.
Configuring Date and Time Service
If you have used the Setup Wizard, you might have already configured the system date and
time settings; the System Date and Time screen allows you to modify these settings.
Configure date, time, and NTP server designations on the System Date and Time screen.
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a protocol that is used to synchronize computer clock times
in a network of computers. Setting the correct system time and time zone ensures that the
date and time recorded in the STM logs and reports are accurate. Changing the time zone
requires the STM to restart to apply the updated settings.
74 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 75

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
To set time, date, and NTP servers:
1. Select Administration > System Date and Time from the menu. The System Date and
Time screen displays:
Figure 45.
The top of the screen displays the current weekday, date, time, time zone, and year (in
the example in the previous figure: Current Time: 2009-08-02 00:19:30).
2. Select the radio buttons, complete the fields, and make your selections from the drop-down
list as explained in the following table:
Table 22. System Date and Time Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
System Date and Time
From the drop-down list, select an NTP server, or select to enter the time manually.
Use Default NTP
Servers
The STM regularly updates its real-time clock (RTC), which it uses for scheduling, by
contacting a default NETGEAR NTP server on the Internet. This is the default setting.
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 75
Page 76

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 22. System Date and Time Settings (Continued)
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Use Custom NTP
Servers
Manually Enter the
Date and Time
Time Zone
From the drop-down list, select the local time zone in which the STM operates. The correct time zone is
required in order for scheduling to work correctly. You do not need to configure daylight savings time, which
is applied automatically when applicable. GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) is the default setting.
Note: When you select a time zone that is not associated with a location such as (GMT -08:00) GMT-8,
daylight savings time is automatically disabled. When you select a time zone that is associated with a
location such as (GMT -08:00) Pacific Time ( US & Canada), daylight savings time is automatically enabled.
The STM regularly updates its RTC by contacting one of the two NTP servers (primary
and backup), both of which you need to specify in the fields that become available
when you select this option.
Note: If you select this option but leave either the Server 1 or Server 2 field blank,
both fields are automatically set to the default NETGEAR NTP servers.
Note: A list of public NTP servers is available at
http://support.ntp.org/bin/view/Servers/WebHome.
Server 1 Name /
IP Address
Server 2 Name /
IP Address
Date Enter the date in the yyyy-mm-dd (year-month-date) format.
Time Enter the time in the hh-mm-ss (hour-minutes-seconds) format.
Enter the IP address or host name the primary NTP server.
Enter the IP address or host name the secondary NTP server.
3. Click Apply to save your settings. Changing the time zone requires the STM to restart.
Note: If you select the default NTP servers or if you enter a custom server
FQDN, the STM determines the IP address of the NTP server by
performing a DNS lookup. You need to configure a DNS server
address on the Network Settings screen (see Configuring Network
Settings on page 52) before the STM can perform this lookup.
Managing Digital Certificates
The STM uses digital certificates (also known as X509 certificates) for secure Web access
connections over HTTPS (that is, SSL VPN connections).
Digital certificates can be either self-signed or can be issued by Certification Authorities
(CAs) such as an internal Windows server or an external organizations such as Verisign or
Thawte. On the STM, the uploaded digital certificate is checked for validity and purpose. The
digital certificate is accepted when it passes the validity test and the purpose matches its use.
76 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 77

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
The STM uses digital certificates to authenticate connecting HTTPS servers, and to allow
HTTPS clients to be authenticated by remote entities. A digital certificate that authenticates a
server, for example, is a file that contains the following elements:
• A public encryption key to be used by clients for encrypting messages to the server.
• Information identifying the operator of the server.
• A digital signature confirming the identity of the operator of the server. Ideally, the
signature is from a trusted third party whose identity can be verified.
When a security alert is generated, the user can decide whether or not to trust the host.
Figure 46.
You can obtain a digital certificate from a well-known commercial Certificate Authority (CA)
such as Verisign or Thawte. Because a commercial CA takes steps to verify the identity of an
applicant, a digital certificate from a commercial CA provides a strong assurance of the
server’s identity.
The STM contains a self-signed digital certificate from NETGEAR. This certificate can be
downloaded from the STM login screen or from the Certificate Management screen for
browser import. However, NETGEAR recommends that you replace this digital certificate
with a digital certificate from a well-known commercial CA prior to deploying the STM in your
network.
The STM’s Certificate Management screen lets you to view the currently loaded digital
certificate for HTTPS scans, upload a new digital certificate, manage the trusted CA
authorities list, and manage the untrusted certificates list.
To display the Certificate Management screen, select Web Security > Certificate
Management from the menu. Because of the size of this screen, and because of the way the
information is presented, the Certificate Management screen is divided and presented in this
manual in three figures (the following figure, Figure 48 on page 79, and Figure 49 on
page 80).
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 77
Page 78
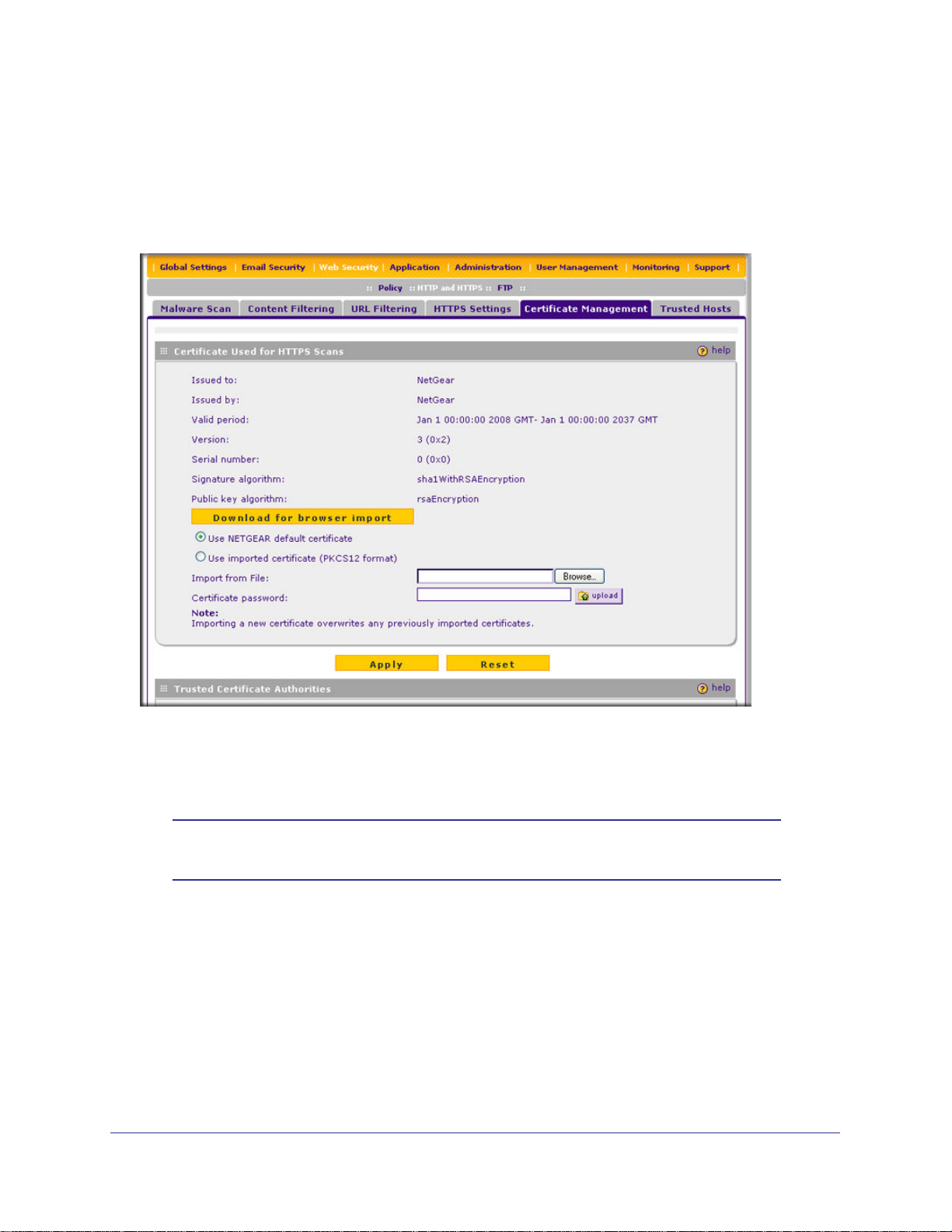
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Managing the Certificate for HTTPS Scans
To manage the STM’s active certificate that is used for HTTPS scans, select Web Security >
Certificate Management from the menu. The Certificate Management screen displays. The
following figure shows only the Certificate Used for HTTPS Scans section of the screen:
Figure 47. Certificate Management, screen 1 of 3
The top part of the Certificate Used for HTTPS Scans section displays information about the
current certificate that is used for HTTPS scans.
Note: For information about the HTTPS scanning process, HTTPS Scan
Settings on page 119.
To download the current certificate into your browser:
1. Click Download for browser import.
2. Follow the instructions of your browser to save the RootCA.crt file on your computer.
To reload the default NETGEAR certificate:
1. Select the Use NETGEAR default certificate radio button.
2. Click Apply to save your settings.
78 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 79

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
To import a new certificate:
1. Select the Use imported certificate (PKCS12 format) radio button.
2. Click Browse next to the Import from File field.
3. Navigate to a trusted certificate file on your computer. Follow the instructions of your browser
to place the certificate file in the Import from File field.
4. If required, enter the appropriate password in the Certificate password field.
5. Click the Upload button.
Note: If the certificate file is not in the pkcs12 format, the upload fails.
Importing a new certificate overwrites any previously imported
certificates.
6. Click Apply to save your settings.
Managing Trusted Certificates
To manage trusted certificates:
Select Web Security > Certificate Management from the menu. The Certificate
Management screen displays. The following figure shows only the Trusted Certificate
Authorities section of the screen:
Figure 48. Certificate Management, screen 2 of 3
The Trusted Certificate Authorities table contains the trusted certificates from third-party
websites that are signed by the Certificate Authorities.
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 79
Page 80

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
To view details of a trusted certificate:
1. From the Trusted Certificate Authorities table, select the certificate.
2. Click View Details. A new screen opens that displays the details of the certificate.
To delete a trusted certificate:
1. From the Trusted Certificate Authorities table, select the certificate.
2. Click Delete Selected.
To import a trusted certificate:
1. Click Browse next to the Import from File field.
2. Navigate to a trusted certificate file on your computer. Follow the instructions of your
browser to place the certificate file in the Import from File field.
3. Click the Upload button. The newly imported trusted certificate is added to the Trusted
Certificate Authorities table.
Managing Untrusted Certificates
To manage untrusted certificates:
Select Web Security > Certificate Management from the menu. The Certificate
Management screen displays. The following figure shows only the Untrusted Certificates
section of the screen:
Figure 49. Certificate Management, screen 3 of 3
When the STM detects an untrusted or invalid certificate, it automatically places the
certificate in the Untrusted Certificates table.
To view details of an untrusted certificate:
1. From the Untrusted Certificates table, select the certificate.
2. Click View Details. A new screen opens that displays the details of the certificate.
80 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 81

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
To delete an untrusted certificate:
1. From the Untrusted Certificates table, select the certificate.
2. Click Delete Selected.
To move an untrusted certificate to the Trusted Certificate Authorities table:
1. From the Untrusted Certificates table, select the certificate.
2. Click Add to Trusted List. The previously untrusted certificate is added to the Trusted
Certificate Authorities table.
Managing the Quarantine Settings
You can specify how much memory the STM reserves for quarantined items, and how long
these items remain in memory. In general, the default settings work well for most situations.
To change the quarantine settings:
1. Select Global Settings > Quarantine from the menu. The Quarantine screen displays:
Figure 50.
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 81
Page 82

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
2. Select the radio buttons, complete the field, and make your selections from the drop-down
lists as explained in the following table:
Table 23. Quarantine Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Malware Quarantine Area Size Specify the maximum amount of memory in MB that is allocated to
malware quarantine. This limit is cumulative for all users.
For the STM600, the default setting is 200 MB, and the maximum setting is
512 MB.
For the STM150 and STM300, the default setting is 100 MB, and the
maximum setting is 512 MB.
Note: After the limit has been exceeded, old items are automatically
purged from the malware quarantine to make space for new items.
Spam Quarantine Area Size Specify the maximum amount of memory in MB that is allocated to spam
quarantine. This limit is cumulative for all users.
For the STM600, the default setting is 1024 MB, and the maximum setting
is 2048 MB.
For the STM150 and STM300, the default setting is 512 MB, and the
maximum setting is 1024 MB.
Note: After the limit has been exceeded, old items are automatically
purged from the malware quarantine to make space for new items.
Quarantine Lifetime Specify how long items remain in quarantine before being automatically
purged. The default setting is 15 days. The maximum setting is 30 days.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
Note: For information about how to view and manage the quarantine files,
see Viewing and Managing the Quarantine Files on page 208.
Managing the STM’s Performance
Performance management consists of controlling the traffic through the STM so that the
necessary traffic gets through when there is a bottleneck and either reducing unnecessary
traffic or rescheduling some traffic to low-peak times to prevent bottlenecks from occurring in
the first place.
If you want to reduce traffic by preventing unwanted emails from reaching their destinations
or by preventing access to certain sites on the Internet, you can use the STM’s content
filtering feature. By default, this feature is disabled; all requested traffic from any website is
allowed with the exception of Web content categories that are mentioned in Default Email
and Web Scan Settings on page 85.
82 | Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management
Page 83

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
You can adjust the following features of the STM in such a way that the traffic load on the
WAN side decreases.
• Email content filtering. To reduce incoming email traffic, you can block emails with large
attachments, reject emails based on keywords, file extensions, or file names, and set
spam protection rules. There are several ways you can reduce unwanted email traffic:
- Setting the size of email files to be scanned. Scanning large email files requires
network resources and might slow down traffic. You can specify the maximum file or
message size that is scanned, and whether files that exceed the maximum size are
skipped (which might compromise security) or blocked. For more information, see
Exception Settings on page 90.
- Keyword, file extension, and file name blocking. You can reject emails based on
keywords in the subject line, file type of the attachment, and file name of the
attachment. For more information, see Email Content Filtering on page 94.
- Protecting against spam. Set up spam protection to prevent spam from using up
valuable bandwidth. For more information, see Protecting Against Email Spam on
page 97.
• Web content filtering. The STM provides extensive methods to filter Web content in
order to reduce traffic:
- Web category blocking. You can block entire Web categories because their content
is unwanted, offensive, or not relevant, or simply to reduce traffic. For more
information, see Configuring Web Content Filtering on page 109.
- File extension blocking. You can block files based on their extension. Such files can
include executable files, audio and video files, and compressed files. For more
information, see Configuring Web Content Filtering on page 109.
- URL blocking. You can specify URLs that are blocked by the STM. For more
information, see Configuring Web URL Filtering on page 116.
- Web services blocking. You can block Web applications such as instant messaging,
media, peer-to-peer, and tools. For more information, see Configuring Application
Control on page 127.
- Web object blocking. You can block the following Web component types: embedded
objects (ActiveX, Java, Flash), proxies, and cookies; and you can disable Java
scripts. For more information, see Configuring Web Content Filtering on page 109.
- Setting the size of Web files to be scanned. Scanning large Web files requires
network resources and might slow down traffic. You can specify the maximum file size
that is scanned, and whether files that exceed the maximum size are skipped (which
might compromise security) or blocked. For more information, see Configuring Web
Malware Scans on page 107.
For these features (with the exception of Web object blocking and setting the size of files
to be scanned), you can set schedules to specify when Web content is filtered (see
Configuring Web Content Filtering on page 109) and configure scanning exclusions and
access exceptions (see Setting Scanning Exclusions and Web Access Exceptions on
page 130). You can use the STM’s monitoring functions to assist you with performance
management (see Monitoring Real-Time Traffic, Security, Statistics, and Web Usage on
page 184).
Chapter 3. Performing Network and System Management | 83
Page 84

4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans
This chapter describes how to apply the content filtering features of the STM and how to
optimize scans to protect your network. This chapter contains the following sections:
• About Content Filtering and Scans on this page
• Configuring Email Protection on page 87
• Configuring Web and Services Protection on page 105
• Configuring Application Control on page 127
• Setting Scanning Exclusions and Web Access Exceptions on page 130
About Content Filtering and Scans
The STM provides very extensive Web content and email content filtering options, Web
browsing activity reporting, email antivirus and antispam options, and instant alerts via email.
You can establish restricted Web access policies that are based on the time of day, Web
addresses, and Web address keywords. You can also block Internet access by applications
and services, such as instant messaging and peer-to-peer file sharing clients.
4
Note: For information about how to monitor blocked content and malware
threats in realtime, see Monitoring Real-Time Traffic, Security,
Statistics, and Web Usage on page 184. For information about how
to view blocked content and malware threats in the logs, see
Querying Logs on page 194. For information about how to view
quarantined content, see Viewing and Managing the Quarantine
Files on page 208.
Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans | 84
Page 85

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Default Email and Web Scan Settings
For most network environments, the default scan settings and actions that are shown in the
following table work well, but you can adjust these to meet the needs of your specific
environment.
Table 24. Default Email and Web Scan Settings
Scan Type Default Scan Setting Default Action (if applicable)
Email Server Protocols
SMTP Enabled Block infected email
POP3 Enabled Delete attachment if infected
IMAP Enabled Delete attachment if infected
Web Server Protocols
HTTP Enabled Delete file if malware threat detected
HTTPS Disabled No action (scan disabled)
FTP Enabled Delete file if malware threat detected
Instant Messaging Services
Google Talk Allowed
ICQ Allowed
mIRC Allowed
MSN Messenger Allowed
QQ Allowed
Yahoo Messenger Allowed
Media Applications
iTunes (music store, update) Allowed
Quicktime (update) Allowed
Real Player (guide) Allowed
a
Rhapsody (guide, music store) Allowed
Winamp (Internet radio/TV) Allowed
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Services
BitTorrent Allowed
eDonkey Allowed
Gnutella Allowed
Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans | 85
Page 86

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 24. Default Email and Web Scan Settings (Continued)
Scan Type Default Scan Setting Default Action (if applicable)
Tools
Alexa Toolbar Allowed
GoToMyPC Allowed
Weatherbug Allowed
Yahoo Toolbar Allowed
Web Objects
Embedded Objects (ActiveX/Java/Flash) Allowed
Javascript Allowed
Proxy Allowed
Cookies Allowed
Web Content Categories
Commerce Allowed
Drugs and Violence Blocked
Education Allowed with the
exception of School
Cheating
Gaming Blocked
Inactive Sites Allowed
Internet Communication and Search Allowed with the
exception of Anonymizers
Leisure and News Allowed
Malicious Blocked
Politics and Religion Allowed
Sexual Content Blocked
Technology Allowed
Uncategorized Allowed
a. For the STM300 and STM600, files and messages that are larger than 10240 KB are skipped by default.
For the STM150, files and messages that are larger than 8192 KB are skipped by default.
86 | Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans
Page 87

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Configuring Email Protection
The STM lets you configure the following settings to protect the network’s email
communication:
• The email protocols that are scanned for malware threats
• Actions that are taken when infected emails are detected
• The maximum file sizes that are scanned
• Keywords, file types, and file names in emails that are filtered to block objectionable or
high-risk content
• Customer notifications and email alerts that are sent when events are detected
• Rules and policies for spam detection
Customizing Email Protocol Scan Settings
If you have used the Setup Wizard, you might have already configured the email policies; the
(email) Policy screen allows you to modify these settings.
To configure the email protocols and ports to scan:
1. Select Email Security > Policy from the menu. The (email) Policy screen displays:
Figure 51.
Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans | 87
Page 88

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
2. Select the check boxes and complete the fields and as explained in the following table:
Table 25. Email Policy Settings
Setting Description
Services to Scan
SMTP Select the SMTP check box to enable Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) scanning. This
service is enabled by default and uses default port 25.
POP3 Select the POP3 check box to enable Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3). This service is enabled
by default and uses default port 110.
IMAP Select the IMAP check box to enable Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP). This
service is enabled by default and uses default port 143.
Note: If a protocol uses a port other than the standard service port (for
example, port 25 for SMTP), enter this nonstandard port in the Ports
to Scan field. For example, if the SMTP service on your network
uses both port 25 and port 2525, enter both port numbers in the
Ports to Scan field and separate them by a comma.
Note: The following protocols are not supported by the STM: SMTP over
SSL using port number 465, POP3 over SSL using port number 995,
and IMAP over SSL using port number 993.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
Customizing Email Anti-Virus Settings
If you have used the Setup Wizard, you might have already configured the email antivirus
action and exception settings; the Action and Exception screens allows you to modify these
settings. The Notification screen allows you to specify the email antivirus notification settings.
Whether or not the STM detects an email virus, you can configure it to take a variety of
actions (some of the default actions are listed in Table 24 on page 85), set exceptions for file
sizes, and specify which notifications, emails, or both need to be sent to the end users.
88 | Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans
Page 89

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Action Settings
To configure the email antivirus action settings:
1. Select Email Security > Anti-Virus from the menu. The Anti-Virus submenu tabs
display with the Action screen in view:
Figure 52.
2. Make your selections from the drop-down lists as explained in the following table:
Table 26. Email Anti-Virus Action Settings
Setting Description
Action
SMTP From the SMTP drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken when an
infected email is detected:
• Quarantine attachment. The email is not blocked, but the attachment is removed and
placed in the malware quarantine for further research. In addition, a malware quarantine
log entry is created, and depending on the nature of the malware threat, also a virus log
entry or a spyware log entry.
• Delete attachment. The email is not blocked, but the attachment is deleted, and a virus
log entry or a spyware log entry is created.
• Block infected email. This is the default setting. The email is blocked, and a virus log
entry or a spyware log entry is created.
• Quarantine infected email. The email is placed in the malware quarantine for further
research. In addition, a malware quarantine log entry is created, and depending on the
nature of the malware threat, also a virus log entry or a spyware log entry.
• Log only. Only a virus log entry or a spyware log entry is created. The email is not
blocked and the attachment is not deleted.
Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans | 89
Page 90

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 26. Email Anti-Virus Action Settings (Continued)
Setting Description
POP3 From the POP3 drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken when an
infected email is detected:
• Quarantine attachment. The email is not blocked, but the attachment is removed and
placed in the malware quarantine for further research. In addition, a malware quarantine
log entry is created, and depending on the nature of the malware threat, also a virus log
entry or a spyware log entry.
• Delete attachment. This is the default setting. The email is not blocked, but the
attachment is deleted, and a virus log entry or a spyware log entry is created.
• Log only. Only a virus log entry or a spyware log entry is created. The email is not
blocked and the attachment is not deleted.
IMAP From the IMAP drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken when an
infected email is detected:
• Quarantine attachment. The email is not blocked, but the attachment is removed and
placed in the malware quarantine for further research. In addition, a malware quarantine
log entry is created, and depending on the nature of the malware threat, also a virus log
entry or a spyware log entry.
• Delete attachment. This is the default setting. The email is not blocked, but the
attachment is deleted, and a virus log entry or a spyware log entry is created.
• Log only. Only a virus log entry or a spyware log entry is created. The email is not
blocked and the attachment is not deleted.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
Exception Settings
To configure the email antivirus exception settings:
1. Select Email Security > Anti-Virus from the menu. The Anti-Virus submenu tabs
display with the Action screen in view.
2. Click the Exceptions submenu tab. The Exceptions screen displays:
Figure 53.
90 | Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans
Page 91
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
3. Make your selection from the drop-down list and complete the field as explained in the
following table:
Table 27. Email Anti-Virus Exception Settings
Setting Description
Scan Exceptions
From the drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken when an email attachment exceeds
the size that you specify in the file size field:
• Skip. The file is not scanned but skipped, leaving the end user vulnerable. This is the default setting.
• Block. The file is blocked and does not reach the end user.
The default and maximum file sizes are:
• For the STM600 and STM300, the default setting is to block any attachment larger than 10240 KB. The
maximum file size that you can specify is 51200 KB.
• For the STM150, the default setting is to block any attachment larger than 8192 KB. The maximum file
size that you can specify is 25600 KB.
Note: Setting the maximum file size to a high value might affect the STM’s
performance. NETGEAR recommends the default value, which is
sufficient to detect the vast majority of threats.
4. Click Apply to save your settings.
Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans | 91
Page 92

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Notification Settings
To configure the email antivirus notification settings:
1. Select Email Security > Anti-Virus from the menu. The Anti-Virus submenu tabs
display with the Action screen in view.
2. Click the Notifications submenu tab. The Notifications screen displays:
Figure 54.
92 | Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans
Page 93

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
3. Complete the fields, select the check boxes, and make your selections from the drop-down
lists as explained in the following table:
Table 28. Email Anti-Virus Notification Settings
Setting Description
Notification Settings
Insert Warning into
Email Subject (SMTP)
Append Safe Stamp
(SMTP and POP3)
Append Warning if
Attachment Exceeds
Scan Size Limit (SMTP
and POP3)
Replace Infected
Attachments with the
Following Warning
Message
For SMTP email messages, select this check box to insert a warning into the email
subject line:
• Malware Found. If a malware threat is found, a [MALWARE INFECTED]
message is inserted. You can change this default message.
• No Malware Found. If no malware threat is found, a [MALWARE FREE]
message is inserted. You can change this default message.
By default, this check box is cleared and no warnings are inserted.
For SMTP and POP3 email messages, select this check box to insert a default
safe stamp message at the end of an email. The safe stamp insertion serves as a
security confirmation to the end user. You can change the default message. By
default, this check box is cleared and no safe stamp is inserted.
For SMTP and POP3 email messages, select this check box to append a default
warning message to an email if the message or an attachment to the message
exceeds the scan size limit. The warning message informs the end user that the
attachment was skipped and might not be safe to open. You can change the
default message. By default, this check box is selected and a warning message is
appended to the email.
Select this check box to replace an email that is infected with a default warning
message. The warning message informs the end user about the name of the
malware threat. You can change the default message to include the action that the
STM has taken (see the following example). By default, this check box is selected,
and a warning message replaces an infected email.
The following is a sample message where the %VIRUSINFO% metaword is
replaced with the EICAR test virus:
This attachment contains malware: File 1.exe contains malware EICAR.
Action: Delete.
Note: Make sure that you keep the %VIRUSINFO% metaword in a message to
enable the STM to insert the correct malware threat information.
Email Alert Settings
Note: Ensure that the email notification server (see Configuring the Email Notification Server on page 176)
is configured before you specify the email alert settings.
Send alert to In addition to inserting a warning message to replace an infected email, you can
configure the STM to send a notification email to the sender, the recipient, or both
by selecting the corresponding check box or check boxes. By default, both check
boxes are cleared and no notification email is sent.
Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans | 93
Page 94

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 28. Email Anti-Virus Notification Settings (Continued)
Setting Description
Subject The default subject line for the notification email is “Malware detected!” You can
change this subject line.
Message The warning message informs the sender, the recipient, or both about the name of
the malware threat. You can change the default message to include more
information.
Make sure that you keep the %VIRUSINFO% metaword in a message to enable
the STM to insert the correct malware threat information. In addition to the
%VIRUSINFO% metaword, you can insert the following metawords in your
customized message: %TIME%, %PROTOCOL%, %FROM%, %TO%,
%SUBJECT%, %FILENAME%, %ACTION%, %VIRUSNAME%.
4. Click Apply to save your settings.
Email Content Filtering
The STM provides several options to filter unwanted content from emails. You can filter
content from emails based on keywords in the subject line, file type of the attachment, and file
name of the attachment. You can also set an action to perform on emails with
password-protected attachments.
Several types of email blocking are available:
• Keyword blocking. You can specify words that, should they appear in the email subject
line, cause that email to be blocked by the STM.
• Password-protected attachments. You can block emails based on password-protected
attachments such as .zip or .rar attachments.
• File extension blocking. You can block emails based on the extensions of attached files.
Such files can include executable files, audio and video files, and compressed files.
• File name blocking. You can block emails based on the names of attached files. Such
names can include, for example, names of known malware threats such as the Netsky
worm (which normally arrives as netsky.exe).
94 | Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans
Page 95

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
To configure email content filtering:
1. Select Email Security > Filters from the menu. The Filters screen displays:
Figure 55.
Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans | 95
Page 96

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
2. Complete the fields and make your selections from the drop-down lists as explained in the
following table:
Table 29. Email Filter Settings
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Filter by Subject Keywords
Keywords Enter keywords that are detected in the email subject line. Use commas to separate
different keywords. The total maximum length of this field is 2048 characters, excluding
duplicate words and delimiter commas.
Action SMTP From the SMTP drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken
when a keyword that is defined in the Keywords field is detected:
• Block email & Log. The email is blocked, and a log entry is created.
• Log. This is the default setting. Only a log entry is created. The email is not
blocked.
POP3 From the POP3 drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken
when a keyword that is defined in the Keywords field is detected:
• Block email & Log. The email is blocked, and a log entry is created.
• Log. This is the default setting. Only a log entry is created. The email is not
blocked.
Filter by Password-Protected Attachments (ZIP, RAR, etc.)
Action SMTP From the SMTP drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken
when a password-protected attachment to an email is detected:
• Block attachment & Log. The email is not blocked, the attachment is blocked,
and a log entry is created.
• Block email & Log. The email is blocked, and a log entry is created.
• Log. This is the default setting. Only a log entry is created. The email and
attachment are not blocked.
POP3 From the POP3 drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken
when a password-protected attachment to an email is detected:
• Block attachment & Log. The email is not blocked, the attachment is blocked,
and a log entry is created.
• Log. This is the default setting. Only a log entry is created. The email and
attachment are not blocked.
IMAP From the IMAP drop-down list, specify one of the following actions to be taken
when a password-protected attachment to an email is detected:
• Block attachment & Log. The email is not blocked, the attachment is blocked,
and a log entry is created.
• Log. This is the default setting. Only a log entry is created. The email and
attachment are not blocked.
96 | Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans
Page 97

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
Table 29. Email Filter Settings (Continued)
Setting Description (or Subfield and Description)
Filter by File Type
File Extension By default, the File Extension field lists the most common file extensions that are detected.
You can manually add or delete extensions. Use commas to separate different extensions.
You can enter a maximum of 40 file extensions; the maximum total length of this field,
excluding the delimiter commas, is 160 characters.
You can also use the drop-down list to add predefined file extensions from a specific
category to the File Extension field:
• None. No file extensions are added to the File Extension field. This is the default setting.
• Executables. Executable file extensions (exe, com, dll, so, lib, scr, bat, and cmd) are
added to the File Extension field.
• Audio/Video. Audio and video file extensions (wav, mp3, avi, rm, rmvb, wma, wmv, mpg,
mp4, and aac) are added to the File Extension field.
• Compressed Files. Compressed file extensions (zip, rar, gz, tar, and bz2) added to the
File Extension field.
Action SMTP From the drop-down list, specify an action when an email attachment with a file
POP3
IMAP
extension that is defined in the File Extension field is detected. The drop-down list
selections and defaults are the same as the ones for the Filter by
Password-Protected Attachments (ZIP, RAR, etc.) section earlier in this table.
Filter by File Name
File Name Enter the file names that are detected. For example, to block the Netsky worm (which
normally arrives as netsky.exe), enter netsky.exe. You can enter a maximum of 20 file
names. Use commas to separate multiple file names. The maximum total length of this field
is 400 characters, excluding the delimiter commas.
Action SMTP From the drop-down list, specify an action when an email attachment with a name
POP3
IMAP
that is defined in the File Name field is detected. The drop-down list selections
and defaults are the same as the ones for the Filter by Password-Protected
Attachments (ZIP, RAR, etc.) section earlier in this table.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
Protecting Against Email Spam
The STM integrates multiple antispam technologies to provide comprehensive protection
against unwanted email. You can enable all or a combination of these antispam technologies.
The STM implements these spam prevention technologies in the following order:
1. Whitelist. Emails from the specified sources or to the specified recipients are not
considered spam and are accepted.
2. Blacklist. Emails from the specified sources are considered spam and are blocked.
3. Real-time blacklist. Emails from known spam sources that are collected by blacklist
providers are blocked.
4. Distributed spam analysis. Emails that are detected as spam by the NETGEAR Spam
Classification Center are either tagged, blocked, or quarantined.
Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans | 97
Page 98

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
This order of implementation ensures the optimum balance between spam prevention and
system performance. For example, if an email originates from a whitelisted source, the STM
delivers the email immediately to its destination inbox without implementing the other spam
prevention technologies, thereby speeding up mail delivery and conserving the STM system
resources. However, regardless of whether or not an email is whitelisted, it is still scanned by
the STM’s antimalware engines.
You can configure these antispam options in conjunction with content filtering to optimize
blocking of unwanted mails.
Note: Emails that are sent through the STM over an authenticated
connection between a client and an SMTP mail server are not
checked for spam.
Note: An email that has been checked for spam by the STM contains an
“X-STM-SMTP” (for SMTP emails) or “X-STM-POP3” (for POP-3
emails) tag in its header.
Setting Up the Whitelist and Blacklist
You can specify emails that are accepted or blocked based on the originating IP address,
domain, and email address by setting up the whitelist and blacklist. You can also specify
emails that are accepted based on the destination domain and email address.
The whitelist ensures that email from listed (that is, trusted) sources and recipients is not
mistakenly tagged as spam. Emails going to and from these sources and recipients are
delivered to their destinations immediately, without being scanned by the antispam engines.
This can help to speed up the system and network performance. The blacklist, on the other
hand, lists sources from which all email messages are blocked. You can enter up to 200
entries per list, separated by commas.
Note: The whitelist takes precedence over the blacklist, which means that
if an email source is on both the blacklist and the whitelist, the email
is not scanned by the antispam engines.
98 | Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans
Page 99

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
To configure the whitelist and blacklist:
1. Select Email Security > Anti-Spam from the menu. The Anti-Spam submenu tabs
display, with the Whitelist/Blacklist screen in view:
Figure 56.
Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans | 99
Page 100

ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance
2. Complete the fields as explained in the following table:
Table 30. Whitelist/Blacklist Settings
Setting Description
Sender IP Address (SMTP)
Whitelist Enter the source IP addresses from which emails can be trusted.
Blacklist Enter the source IP addresses from which emails are blocked.
Click Apply to save your settings, or click Reset to clear all entries from these fields.
Sender Domain (SMTP and POP3)
Whitelist Enter the sender email domains from which emails can be trusted.
Blacklist Enter the sender email domains from which emails are blocked.
Click Apply to save your settings, or click Reset to clear all entries from these fields.
Sender Email Address (SMTP and POP3)
Whitelist Enter the email addresses from which emails can be trusted.
Blacklist Enter the email addresses from which emails are blocked.
Click Apply to save your settings, or click Reset to clear all entries from these fields.
Recipients Domain (SMTP and POP3)
Whitelist Enter the email domains of the recipients to which emails can be safely delivered.
Click Apply to save your settings, or click Reset to clear all entries from this field.
Recipients Email Address (SMTP and POP3)
Whitelist Enter the email addresses of the recipients to which emails can be safely delivered.
Click Apply to save your settings, or click Reset to clear all entries from this field.
Note: In the fields of the Whitelist/Blacklist screen, use commas to
separate multiple entries. For IP addresses, use a hyphen to
indicate a range (for example, 192.168.32.2-192.168.32.8.)
Configuring the Real-Time Blacklist
Blacklist providers are organizations that collect IP addresses of verified open SMTP relays
that might be used by spammers as media for sending spam. These known spam relays are
compiled by blacklist providers and are made available to the public in the form of real-time
blacklists (RBLs). By accessing these RBLs, the STM can block spam originating from known
spam sources.
100 | Chapter 4. Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans
 Loading...
Loading...