Page 1

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Soft ware v2.0
September 5, 2003
NETGEAR, Inc.
4500 Great America
Parkway
Santa Clara, CA
Page 2

© 2003 by NETGEAR, Inc. , September 5, 2003. FullManual All rights reserved.
Technical Support
Please register to obtain technical support. Please retain your proof of purchase and warranty
information.
To register your product, get product support or obtain product information and product
documentation, go to http://www.NETGEAR.com
Web, you may register your product by filling out the registration card and mailing it to
NETGEAR customer service.
. If you do not have access to the World Wide
You will find technical support information at: http://www.NETGEAR.com/
through the customer
service area. If you want to contact technical support by telephone, see the support information
card for the correct telephone number for your country.
Trademarks
NETGEAR is a registered trademark of NETGEAR, INC. Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Other brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. Information is
subject to change without notice. All rights reserved.
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, NETGEAR reserves the right to
make changes to the products described in this document without notice. NETGEAR does not assume any liability that
may occur due to the use or application of the product(s) or circuit layout(s) described herein.
Regulatory Compliance Information
This device is restricted to indoor use due to reduce the potential for harmful interference to co-channel Mobile Satellite
and Radar Systems.
ii
Page 3

Canadian Department of Communications Compliance Statement
This Class B Digital apparatus (GSM73xx Level 3 Managed Switch Software v2) meets all the
requirements of the Canadian Interference Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numerique del la classe B respect les exigences du Regalement sur le material broilleur du Canada.
This device comples with Class B limits of Industry of Canada. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
EN 55 022 Declaration of Conformance
This is to certify that the GSM73xx Level 3 Managed Switch Software v2 is shielded against the generation of radio
interference in accordance with the application of Council Directive 89/336/EEC, Article 4a. Conformity is declared by
the application of EN 55 022 Class B (CISPR 22).
iii
Page 4

iv
Page 5

Contents
Chapter 1
About This Guide
About this Manual ...........................................................................................................1-1
Organization of This Manual ........................................ ... .... ... ..................................1-1
Typographical Conventions ......................................................................................1-2
Special Message Formats ........................................................................................1-2
How to Navigate this Manual ..........................................................................................1-3
How to Print this Manual .................................................................................................1-4
Chapter 2
Switch Management Overview
Switch Management Overview .................................................. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ...............2-1
Chapter 3
Administration Console Telnet Interface
Setting Up Your Switch Using Direct Console Access .................................. .......... ........3-1
Introduction to the Command Menu Interface ................................................................3-3
Chapter 4
Web-Based Management Interface
How to Log In to the GSM73xx .......................................................................................4-2
Web-Based Management Utility Introduction .................................................................4-3
Interactive Switch Image . ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ..................................................................4-4
Menus ......................................................................................................................4-5
System-Wide Popup Menus .....................................................................................4-6
Port-Specific Popup Menus ......................................................................................4-7
Chapter 5
Command Line Interface Syntax
CLI Command Format ....................................................................................................5-1
CLI Command Values .....................................................................................................5-2
CLI Command Conventions ...........................................................................................5-2
CLI Annotations ..............................................................................................................5-3
Contents v
Page 6

Chapter 6
Quick Startup
Quick Starting the Switch ................................................................................................6-1
Software Version Information ...................................................................................6-1
Physical Port Data ....................................................................................................6-2
User Account Management .................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ............6-2
IP Address .................................... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ........................6-3
Uploading from Switch to Out-of-Band PC (Only XMODEM) ...................................6-4
Downloading from Out-of-Band PC to Switch (Only XMODEM) ..............................6-5
Downloading from TFTP Server ...............................................................................6-6
Factory Defaults .... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ........................6-6
Basic Configuration Examples ........................................................................................6-7
Port Routing, RIP, and OSPF Configuration ............................................................6-7
RIP and OSPF VLAN Routing ..................................................................................6-8
VLAN Example .............................................................................................................6-11
SOLUTION 1 ...................................... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... ... ..........6-12
SOLUTION 2 ...................................... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... ... ..........6-12
Chapter 7
Switching Commands
System Information and Statistics Commands ...............................................................7-1
show inventory .........................................................................................................7-1
show sysinfo .............................................................................................................7-2
config sysname ............................... ... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..7-2
config syslocation .. ....................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ..7-2
config syscontact .......................... ... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ..................7-3
show arp switch ........................................................................................................7-3
show forwardingdb table ..........................................................................................7-3
show stats port detailed ...........................................................................................7-4
show stats port summary .......................................................................................7-10
show stats switch detailed ......................................................................................7-11
show stats switch summary ...................................................................................7-13
show eventlog ........................................................................................................7-13
show msglog ..........................................................................................................7-14
show traplog ...........................................................................................................7-14
Management Commands .............................................................................................7-15
vi Contents
Page 7

show network .........................................................................................................7-15
config network parms ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .............7-15
config network protocol ................................ ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ..........................7-15
config network webmode ............................................................. ..........................7-16
config network javamode .......................................................................................7-16
config prompt .. ....................................... ... ... ....................................... ... ... ... ..........7-16
show serial .............................................................................................................7-16
config serial baudrate ... ... ... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... .... ... ...................7-17
config serial timeout ...............................................................................................7-17
config snmpcommunity accessmode ........................... ... .......................................7-17
config snmpcommunity create ......................................................... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-18
config snmpcommunity delete ................................................................................7-18
config snmpcommunity ipaddr ............................................................ ... ... ... .... ... ...7-18
config snmpcommunity ipmask .... ...... .... ................................................................7-18
config snmpcommunity mode ... ... ... ... .... ... .............................................................7-19
show snmptrap .......................................................................................................7-19
config snmptrap create .................................... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ...... .... ......7-19
config snmptrap delete ...........................................................................................7-20
config snmptrap ipaddr ...........................................................................................7-20
config snmptrap mode ............................... ... ... ... ....................................... ... ..........7-20
show trapflags ........................................................................................................7-20
config trapflags authentication .. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .......................................7-21
config trapflags bcaststorm ............................. ... .... ... .............................................7-21
config trapflags linkmode .......................................................................................7-21
config trapflags multiusers .....................................................................................7-22
config trapflags stpmode .... ... .... ... ... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-22
show telnet .............................................................................................................7-22
config telnet maxsessions ............... ... .... ................................................................7-22
config telnet mode ........ ... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... .............................7-23
config telnet timeout ........ ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ......................7-23
show forwardingdb agetime ...................................................................................7-23
config forwardingdb agetime ........ ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... .......................................... ......7-24
Device Configuration Commands .................................................................................7-24
show switchconfig ..................................................................................................7-24
config switchconfig broadcast ............................ .... ... ... ... .......................................7-24
Contents vii
Page 8

config switchconfig flowcontrol .................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-25
show port ................................................................................................................7-26
config port adminmode .............................. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ................................7-26
config port linktrap . ....................................... ... ... .... ... ... ....................................... ...7-27
config port physicalmode ....................................................... ... ... .... ... ... ................7-27
config port lacpmode .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .......................................................................7-27
config port autoneg .. .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... .... ... ................................7-27
show lag .................................................................................................................7-28
config lag create ....... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................................7-28
config lag addport ...................................................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... ..........7-28
config lag deleteport ........ ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................................7-29
config lag adminmode ........... .... ... ... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-29
config lag linktrap ................................... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ...................................7-29
config lag name ........ .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... .... ...................................7-29
config lag deletelag ................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ................................7-30
config lag stpmode .......... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-30
show vlan summary ...............................................................................................7-30
show vlan detailed ..................................................................................................7-31
config vlan create ..... .... ... ... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... .............................7-32
config vlan delete ............................... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... .............7-32
config vlan name ............. ... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ................7-32
config vlan makestatic ..... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................................7-32
config vlan participation ............................. ... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-33
config vlan port tagging ................ ... ... .... ................................................................7-33
show vlan port ........................................................................................................7-33
config vlan port pvid ............................... ...................................... .... ... ... ................7-34
config vlan port acceptframe ........ ...... .... ................................................................7-34
config vlan port ingressfilter ............................................................. ......................7-35
show protocol .........................................................................................................7-35
config protocol create ................................ ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .......................................7-35
config protocol delete ...... ... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ................7-35
config protocol protocol add ...................................................................................7-36
config protocol protocol remove .............................................................................7-36
config protocol vlan add .........................................................................................7-36
config protocol vlan remove ................................................................................... 7-36
viii Contents
Page 9

config protocol interface add .................. ................................................................ 7-37
config protocol interface remove ..................... ....................................................... 7-37
show garp info ........................................................................................................7-37
show garp interface ................................................................................................7-37
config garp gmrp adminmode ................................................................................7-39
config garp gmrp interfacemode ............................................................................7-39
config garp gvrp adminmode ..................................................................................7-39
config garp gvrp interfacemode .......................... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ......7-39
config garp jointimer ..... ... .......................................................................................7-40
config garp leavetimer ............................................................................................7-40
config garp leavealltimer ........................................................................................ 7-40
show igmpsnooping ...............................................................................................7-41
config igmpsnooping adminmode ............................................................. ... .... ... ...7-41
config igmpsnooping groupmembershipinterval .....................................................7-42
config igmpsnooping maxresponse ........................................................................7-42
config igmpsnooping mcrtrexpiretime .............................................. ... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-42
config igmpsnooping interface mode ..................................................... ... ... .... ... ...7-42
show mfdb table .....................................................................................................7-43
show mfdb gmrp ..................................... ... ... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-43
show mfdb igmpsnooping ......................................................................................7-44
show mfdb staticfiltering .........................................................................................7-44
show mfdb stats .....................................................................................................7-45
show mirroring ........................................................................................................7-45
config mirroring create . ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................................7-45
config mirroring delete ............................................................................................7-46
config mirroring mode .. ... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .............7-46
show macfilter ........................................................................................................7-46
config macfilter create .. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... ..........7-47
config macfilter remove ...... ....................................................................................7-47
config macfilter addsrc ........................... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .......................................7-47
config macfilter delsrc ..................................................... .... ... ... ... .... ......................7-48
config macfilter adddest ............................ ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ...7-48
config macfilter deldest ............................................................. ... ..........................7-48
Spanning Tree Commands ....... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .......................................... .............7-49
show spanningtree summary .................................................................................7-49
Contents ix
Page 10

config spanningtree adminmode ........ .... ... ... ... .......................................... ... .... ... ...7-50
config spanningtree forceversion ........................... .......................................... ......7-50
config spanningtree configuration name ............................. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-50
config spanningtree configuration revision ... ... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ...7-51
show spanningtree port ..........................................................................................7-51
config spanningtree port bpdumigrationcheck .......................................................7-51
config spanningtree port mode .................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ................7-52
show spanningtree bridge ......................................................................................7-52
config spanningtree bridge maxage .......................................................................7-52
config spanningtree bridge hellotime .....................................................................7-52
config spanningtree bridge forwarddelay ...............................................................7-53
config spanningtree bridge priority ..... ....................................................................7-53
show spanningtree cst detailed ..............................................................................7-53
show spanningtree cst port summary ....................................................................7-54
show spanningtree cst port detailed .......................................................................7-54
config spanningtree cst port pathcost ....................................................................7-55
config spanningtree cst port priority .......................................................................7-55
config spanningtree cst port edgeport .................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-56
config spanningtree mst create ................................................. ... .... ... ... ... .............7-56
config spanningtree mst delete .......................... ....................................... ... .... ... ...7-56
config spanningtree mst vlan add ................................................................ .... ... ...7-56
config spanningtree mst vlan remove .............................................................. ... ...7-57
config spanningtree mst priority ............................................................. ... ... .... ... ...7-57
config spanningtree mst port pathcost ................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ..........7-57
config spanningtree mst port priority .. .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .............................7-57
show spanningtree mst summary ..........................................................................7-58
show spanningtree mst detailed .............................................................................7-58
show spanningtree mst port summary ...................................................................7-59
show spanningtree mst port detailed .....................................................................7-59
show spanningtree vlan .........................................................................................7-60
User Account Management Commands .......................................................................7-60
show users .............................................................................................................7-60
config users add ....... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... .... ... ................................7-61
config users passwd ............................... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ...................................7-61
config users delete ............. ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................................7-61
x Contents
Page 11

config users snmpv3 authentication ............................. .................................... ...... 7-61
config users snmpv3 encryption ................................... ....... ...... ... ....... ...... ....... ......7-62
config users snmpv3 accessmode .. ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ................................................7-62
show loginsession ..................................................................................................7-62
config loginsession close ............................................. ... .... ... ... ... ..........................7-63
Security Commands .................... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................................7-63
config radius maxretransmit ...................................................................................7-63
config radius timeout .............................................................................................7-63
config radius accounting mode .............................................................................7-64
config radius accounting server add .....................................................................7-64
config radius accounting server port .....................................................................7-64
config radius accounting server remove ...............................................................7-65
config radius accounting server secret ..................................................................7-65
config radius server add .. ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................................................7-65
config radius server port ........................................................................................7-65
config radius server remove ..... ... ...... ....................................................................7-66
config radius server secret .... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ...7-66
config radius server primary . .... ... ... ... .... ................................................................7-66
config radius server msgauth ... ... ... ... ....................................................................7-66
show radius summary ...........................................................................................7-67
show radius server summary ................................................................................7-67
show radius server stats ......................................................................................7-67
show radius accounting summary ........................................................................7-68
show radius accounting stats ................................................................................7-69
show radius stats ...................................................................................................7-70
clear radius stats ....................................................................................................7-70
config dot1x adminmode ................. ... .... ... .............................................................7-70
config dot1x port initialize ..... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-70
config dot1x port reauthenticate ..... ... ....................................................................7-70
config dot1x port controldir .............................. ................................. ...................... 7-71
config dot1x port controlmode ... ... ... ... .... ................................................................7-71
config dot1x port quietperiod ....................................... .................................... ...... 7-71
config dot1x port transmitperiod ........ ....................................................................7-72
config dot1x port supptimeout ................ ................................................................7-72
config dot1x port servertimeout . ... ... ... .... ................................................................7-72
Contents xi
Page 12

config dot1x port maxrequests .......... .... ................................................................7-72
config dot1x port reauthperiod ..............................................................................7-72
config dot1x port reauthenabled ............................................................................7-73
show dot1x summary .............................................................................................7-73
show dot1x port summary ......................................................................................7-73
show dot1x port detailed ........................................................................................7-73
show dot1x port stats ............................................................................................7-75
clear dot1x port stats ..............................................................................................7-76
config authentication login create ..........................................................................7-76
config authentication login delete ..........................................................................7-76
config authentication login set .. ... ....................................... ... ................................7-77
config dot1x defaultlogin .... ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................................7-77
config dot1x login ..................................................................................................7-77
config dot1x port users add ...................................................................................7-77
config dot1x port users remove .............................................................................7-78
config users defaultlogin . ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................................7-78
config users login ..................................................................................................7-78
show authentication login info ...............................................................................7-78
show authentication login users ............................................................................7-79
show dot1x port users ...........................................................................................7-79
show users authentication ......................................................................................7-79
System Utilities .............................................................................................................7-79
save config .............................................................................................................7-80
logout .....................................................................................................................7-80
transfer upload mode ............................................................................................. 7-80
transfer upload serverip .........................................................................................7-80
transfer upload path ...............................................................................................7-80
transfer upload filename ...................................................................... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-81
transfer upload datatype ........................................................................................7-81
transfer upload start ...............................................................................................7-82
transfer download mode .........................................................................................7-82
transfer download serverip ........................... .................................... ...................... 7-82
transfer download path ....................................... ............. ............. ............. .............7-82
transfer download filename .................................... ................................................ 7-83
transfer download datatype ....................................... .......................................... ...7-83
xii Contents
Page 13

transfer download start .................................... ............. ............. ............. ............. ...7-83
clear transfer ..........................................................................................................7-83
clear config .............................................................................................................7-84
clear pass ...............................................................................................................7-84
clear traplog ...........................................................................................................7-84
clear vlan ................................................................................................................7-84
clear lag ..................................................................................................................7-84
clear stats port ........................................................................................................7-84
clear stats switch ....................................................................................................7-85
clear igmpsnooping ................................................................................................7-85
reset system ...........................................................................................................7-85
ping ........................................................................................................................7-85
Chapter 8
Routing Commands
Routing Commands ........................................................................................................8-1
show arp table ..........................................................................................................8-1
config arp agetime .............................. .... ... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ..8-2
config arp cachesize .................................................... ... .... ... ..................................8-2
config arp create ... ....................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ..8-2
config arp delete .............................. ... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... ... ............8-2
config arp resptime ................................. ... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ..8-2
config arp retries .......................................................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..................8-3
show ip interface ......................................................................................................8-3
config interface encaps .......................... ... ... ... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ..8-4
config interface routing .............................. ... ... ... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ..8-4
config ip interface mtu .. ... ....................................... ... ... ... ....................................... ..8-4
config ip interface netdirbcast ..................................................................................8-5
config ip interface create ....... .... ... ... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..8-5
config ip interface delete ........................ ... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ........8-5
show ip summary .....................................................................................................8-5
config ip forwarding ......... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... ............8-6
show ip stats ............................................................................................................8-6
config routing ................................ ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... .....................8-6
show ip vlan .............................................................................................................8-6
config ip vlan routing create .....................................................................................8-7
Contents xiii
Page 14

config ip vlan routing delete .....................................................................................8-7
show router ip interface summary ............................................................................8-7
show router ospf info ................................................................................................8-8
config router id ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ..8-8
config trapflags ospf ..... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... ............8-9
config router ospf adminmode ............................................. ............. ............ ............8-9
config router ospf asbr .................................................... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ........ 8-9
config router ospf preference ...................................................................................8-9
show router ospf interface info .................................................................................8-9
show router ospf interface stats .............................................................................8-10
show router ospf interface summary ......................................................................8-11
config router ospf interface areaid ..........................................................................8-12
config router ospf interface authtypekey ................................................................8-12
config router ospf interface interval dead ...............................................................8-12
config router ospf interface interval hello ...............................................................8-13
config router ospf interface interval retransmit ....................................................... 8-13
config router ospf interface iftransitdelay ...............................................................8-13
config router ospf interface mode ........................................ ... ................................8-13
config router ospf interface priority .........................................................................8-14
config router ospf interface cost .............................................................................8-14
show router ospf area info ......................................................................................8-14
show router ospf area range ..................................................................................8-15
config router ospf area range create ............ ....................................... ... ... ... .... ... ...8-15
config router ospf area range delete ............................ ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ................8-16
config router ospf area stub metric value ........ ... .... ... ... ... .......................................8-16
config router ospf area stub metric type . ...................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ...... 8-16
config router ospf area stub summarylsa .. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .......................................8-16
config router ospf area stub create .... ....................................................................8-17
config router ospf area stub delete .........................................................................8-17
config router ospf area delete ................................................................................8-17
show router ospf neighbor detailed ........................................................................8-17
show router ospf neighbor table .............................................................................8-18
show router ospf stub table ....................................................................................8-19
show router ospf lsdb summary .............................................................................8-19
show router rip info .................................................................................................8-20
xiv Contents
Page 15

show router rip interface detailed ...........................................................................8-20
show router rip interface summary .........................................................................8-21
config router rip adminmode ..................................................................................8-21
config router rip preference ....................................................................................8-22
config router rip interface authtypekey ......................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...8-22
config router rip interface defaultmetric .................. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ...................8-22
config router rip interface mode .......................................... ... ... ... .... ......................8-23
config router rip interface version receive .............. ... ... ... .... ... ... .............................8-23
config router rip interface version send ............................................ ... ... ... .............8-23
show router ospf virtif detailed ...............................................................................8-24
show router ospf virtif summary .............................................................................8-24
config router ospf virtif create .................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ......8-24
config router ospf virtif delete .......... ... ....................................................................8-25
config router ospf virtif authtypekey .......................................................................8-25
config router ospf virtif transdelay ..........................................................................8-25
config router ospf virtif interval dead ......................................................................8-25
config router ospf virtif interval hello .......................... ... ... .... ... ................................8-26
config router ospf virtif interval retransmit ..............................................................8-26
config router ospf exoverflowinterval ............................ ............. ............. ............. ...8-26
config router ospf extlsdblimit .................................................................................8-26
show router route table ..........................................................................................8-27
show router route bestroutes .................................................................................8-27
show router route entry ..........................................................................................8-27
show router route preferences ...............................................................................8-28
config router route create .......................................................................................8-28
config router route delete .......................................................................................8-29
config router route preference ................................................................................8-29
config router route default create ...........................................................................8-29
config router route default delete ...........................................................................8-29
show router vrrp info ..............................................................................................8-29
config router vrrp adminmode ................................................................................8-30
show router vrrp interface detailed .........................................................................8-30
show router vrrp interface summary .......................................................................8-30
show router vrrp interface stats ..............................................................................8-31
config router vrrp interface adminmode .................................................................8-32
Contents xv
Page 16

config router vrrp interface routerID .......................................................................8-32
config router vrrp interface priority .........................................................................8-32
config router vrrp interface ipaddress .....................................................................8-33
config router vrrp interface preemptmode ..............................................................8-33
config router vrrp interface advinterval ...................................................................8-33
config router vrrp interface authdetails ...................................................................8-33
config router vrrp removedetails .......................................... ............. ............ ..........8-34
config router rtrdiscovery adminmode ....................................................................8-34
config router rtrdiscovery maxinterval ....................................................................8-34
config router rtrdiscovery mininterval .....................................................................8-34
config router rtrdiscovery lifetime ...........................................................................8-35
config router rtrdiscovery address ..........................................................................8-35
config router rtrdiscovery preference .....................................................................8-35
show router rtrdiscovery .........................................................................................8-35
show router bootpdhcprelay ...................................................................................8-36
config router bootpdhcprelay circuitidoptionmode ..................................................8-36
config router bootpdhcprelay adminmode ..............................................................8-36
config router bootpdhcprelay maxhopcount ...........................................................8-37
config router bootpdhcprelay minwaittime ..............................................................8-37
config router bootpdhcprelay serverip ....................................................................8-37
Chapter 9
CLI Commands: Differentiated Services
General Commands ................................................. .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ...............9-2
config diffserv adminmode .......................................................................................9-2
Class Commands ..................... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..9-3
config diffserv class create acl ........................ ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ...............................9-3
config diffserv class create all ......................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ...............................9-4
config diffserv class create any . ... ... ... .... ... ...............................................................9-4
config diffserv class delete .......................................................................................9-4
config diffserv class rename ............................................ ................. ................ ........9-5
config diffserv class match cos ................................................................................9-5
config diffserv class match dstip ..............................................................................9-5
config diffserv class match dstl4port keyword ..................................... ..................... 9-6
config diffserv class match dstl4port number ........................................................... 9-6
config diffserv class match dstl4port range ..............................................................9-7
xvi Contents
Page 17

config diffserv class match dstmac ..........................................................................9-7
config diffserv class match every .............................................................................9-7
config diffserv class match ipdscp .......................................... ................ ................ ..9-8
config diffserv class match ipprecedence ................................................................9-8
config diffserv class match iptos ..............................................................................9-9
config diffserv class match protocol keyword ................................... ...................... 9-10
config diffserv class match protocol number .......................................................... 9-10
config diffserv class match refclass ........................................ ................ ................9-11
config diffserv class match srcip ............................................................................9-11
config diffserv class match srcl4port keyword .................................. ...................... 9-12
config diffserv class match srcl4port number ......................................................... 9-12
config diffserv class match srcl4port range ............................................................ 9-13
config diffserv class match srcmac ........................................................................9-13
config diffserv class match vlan .............................................................................9-13
Policy Commands .........................................................................................................9-14
config diffserv policy create ....................................... ............................................. 9-14
config diffserv policy delete .................................................................................... 9-15
config diffserv policy rename ..................................................................................9-15
config diffserv policy class add ...............................................................................9-15
config diffserv policy class remove ......................................... ................ ................9-15
config diffserv policy bandwidth kbps . ....................................................................9-16
config diffserv policy bandwidth percent ...................................................... .... ... ...9-16
config diffserv policy expedite kbps ........................................................................9-17
config diffserv policy expedite percent ...................................................................9-18
config diffserv policy mark cos ...............................................................................9-18
config diffserv policy mark ipdscp ..........................................................................9-19
config diffserv policy mark ipprecedence ............................ ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .............9-19
config diffserv policy police action conform drop ....................................... .............9-19
config diffserv policy police action conform markdscp ...........................................9-20
config diffserv policy police action conform markprec ............................................9-20
config diffserv policy police action conform send ................................................... 9-20
config diffserv policy police action exceed drop .....................................................9-21
config diffserv policy police action exceed markdscp .............................................9-21
config diffserv policy police action exceed markprec .............................................9-22
config diffserv policy police action exceed send ....................................................9-22
Contents xvii
Page 18

config diffserv policy police action nonconform drop ..............................................9-22
config diffserv policy police action nonconform markdscp .....................................9-23
config diffserv policy police action nonconform markprec ......................................9-23
config diffserv policy police action nonconform send .............................................9-23
config diffserv policy police style simple .................................................................9-24
config diffserv policy police style singlerate ...........................................................9-24
config diffserv policy police style tworate ...............................................................9-25
config diffserv policy randomdrop ..........................................................................9-26
config diffserv policy shape average ......................................................................9-26
config diffserv policy shape peak ...........................................................................9-27
Service Commands ......................................................................................................9-27
config diffserv service add ...................... ................................................................9-28
config diffserv service remove ................................... ................ ................ .............9-28
Show Commands ..................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .............................................................9-29
show diffserv class detailed ...................................................................................9-29
show diffserv class summary .................................................................................9-30
show diffserv info ...................................................................................................9-30
show diffserv policy detailed ..................................................................................9-31
show diffserv policy summary ................................................................................9-33
show diffserv service info detailed .........................................................................9-34
show diffserv service info summary .......................................................................9-34
show diffserv service stats detailed ........................................................................9-35
show diffserv service stats summary ......................................................................9-37
Chapter 10
ACL Commands
Show Commands ..................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .............................................................10-1
show acl summary .................................................................................................10-1
show acl detailed ....................................................................................................10-1
Config Commands ........................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ... ...10-2
config acl create ........... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................................10-2
config acl delete ................................. ....................................................................10-2
config acl rule create ..............................................................................................10-2
config acl rule delete ..............................................................................................10-3
config acl rule action ....................................................... .... ... ................................10-3
config acl rule match dstip ............................................................ .... ... ... ................10-3
xviii Contents
Page 19

config acl rule match dstl4port keyword .................................................... ... .... ... ...10-3
config acl rule match dstl4port range ........................ ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ...................10-4
config acl rule match every .................................................... ... .............................10-4
config acl rule match ipdscp .. .................................................................................10-4
config acl rule match ipprecedence .............................. ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...10-5
config acl rule match iptos ......................... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ...10-5
config acl rule match protocol keyword ..................................................................10-6
config acl rule match protocol number ...................................................................10-6
config acl rule match srcip ...................... ... ... ... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ...10-6
config acl rule match srcl4port keyword .................................................... .............10-7
config acl rule match srcl4port range ........................ ... ... .... ...................................10-7
config acl interface add ................................... ... .... ... .............................................10-7
config acl interface remove ............................. ....................................... ... ... .... ... ...10-8
Appendix A
Cabling Guidelines
Fast Ethernet Cable Guidelines .................... ................... ................... .................... ......11-1
Category 5 Cable ..........................................................................................................11-2
Category 5 Cable Specifications ............................................................................11-2
Twisted Pair Cables ...............................................................................................11-3
Patch Panels and Cables .......... ... ... ... .... ... .............................................................11-4
Using 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet over Category 5 Cable ......................................11-5
Cabling ...................................... ................................................................ ............. 11-5
Near End Cross Talk (NEXT) .................................................................................11-6
Patch Cables ..........................................................................................................11-6
RJ-45 Plug and RJ-45 Connectors ........................................................................11-6
Conclusion .............................................................................................................11-8
Appendix B
802.1x Port-Based Authentication Overview
Appendix C
Glossary
Numeric ........................................................................................................................13-1
A ...................................................................................................................................13-2
B ...................................................................................................................................13-4
C ..................................... ........................................................................... ...................13-5
D ..................................... ........................................................................... ...................13-7
Contents xix
Page 20

E ...................................................................................................................................13-8
F ...................................................................................................................................13-9
G ..................................... .............................................. ..............................................13-10
H ..................................... ........................................................................... .................13-11
I .................................... ............. .......... ............. ............. ............. ............. ............ ........13-11
J ...................................... .............................................. ..............................................13-13
L ...................................... ................. ............. ................ ................ ................ ..............13-13
M ..................................... ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ..............13-14
N ..................................... ........................................................................... .................13-17
O ..................................... .............................................. ..............................................13-18
P .................................................................................................................................13-18
Q ..................................... .............................................. ..............................................13-20
R ..................................... ........................................................................... .................13-20
S .................................................................................................................................13-21
T .................................................................................................................................13-23
U ..................................... ........................................................................... .................13-24
V .................................................................................................................................13-25
W ................................................................................................................................13-25
X .................................................................................................................................13-26
Index
xx Contents
Page 21

Chapter 1
About This Guide
Thank you for purchasing the NETGEAR™ GSM73xx L3 Switch.
About this Manual
This reference manual assumes that the reader has basic-to-intermediate computer and Internet
skills. However, basic computer network, Internet, and wireless technology tutorial information is
provided in the Appendices.
This document describes configuration commands for the 7000 Series L3 Managed Switch
software. The commands can be accessed from the CLI, telnet, and Web interfaces.
This document was created primarily for system administrators configuring and operating a
system using 7000 Series L3 Managed Switch software. It is intended to provide an understanding
of the configuration options of 7000 Series L3 Managed Switch software.
It is assumed that the reader has an understanding of the relevant switch platforms. It is also
assumed that the reader has a basic knowledge of Ethernet and networking concepts.
Organization of This Manual
This document describes configuration commands for the 7000 Series L3 Managed Switch
software. The commands can be accessed from the CLI, telnet, and Web interfaces.
• Chapter 6, “Quick Startup” details the procedure to quickly become acquainted with the 7000
Series L3 Managed Switch Software.
• Chapter 7, “Switching Commands” describes the Switching commands.
• Chapter 8, “Routing Commands” describes the Routing commands.
Note: Refer to the release notes for the 7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Software application
level code. The release notes detail the platform specific functionality of the Switching, Routing,
SNMP, Config, Management, and Bandwidth Provisioning packages.
About This Guide 1-1
Page 22
7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Typographical Conventions
This guide uses the following typographical conventions:
Table 1. Typographical conventions
italics Emphasis.
bold times roman User input.
[Enter] Named keys in text are shown enclosed in square brackets. The notation [Enter]
is used for the Enter key and the Return key.
[Ctrl]+C Two or more keys that must be pressed simultaneously are shown in text linked
with a plus (+) sign.
SMALL CAPS
DOS file and directory names.
Special Message Formats
This guide uses the following formats to highlight special messages:
Note: This format is used to highlight information of importance or special interest.
This manual is written according to these specifications:
Table 1-1. Manual Specifications
Product Version GSM73xx Level 3 Managed Switch Software v2
Manual Publication Date September 5, 2003
1-2 About This Guide
Page 23
7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
How to Navigate this Manual
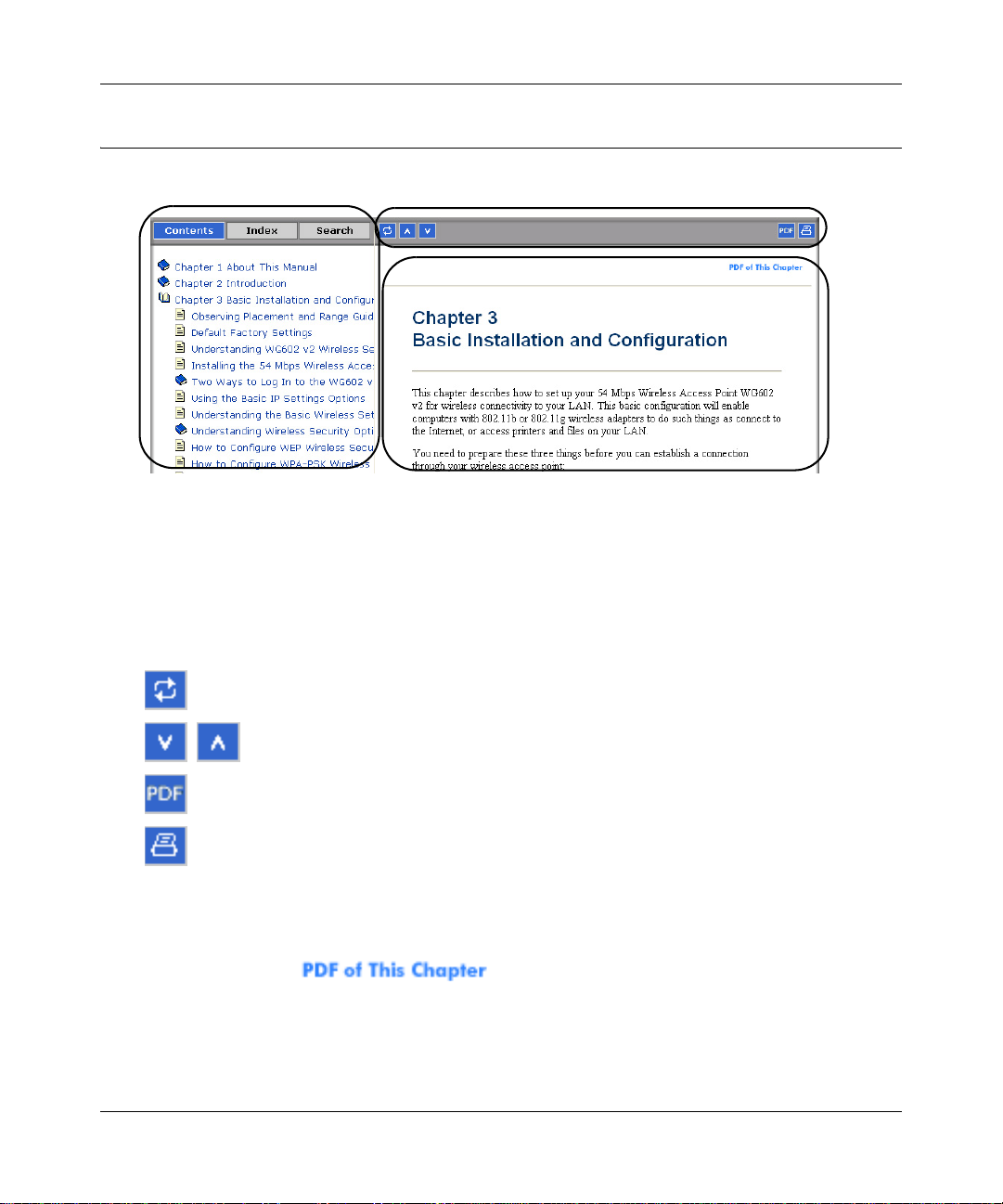
The HTML version of this manual includes these features.
1
2
3
Figure 1-1: HTML version of this manual
1. Left pane. Use the left pane to view the Contents, Index, and Search tabs.
To view the HTML version of the manual, you must have a version 4 or later browser with
JavaScript enabled.
2. Toolbar buttons. Use the toolbar buttons across the top to navigate, print pages, and more.
The Show in Contents button locates the current topic in the Contents tab.
Previous/Next buttons display the previous or next topic.
The PDF button links to a PDF version of the full manual.
The Print button prints the current topic. Using this button when a
step-by-step procedure is displayed will send the entire procedure to your
printer--you do not have to worry about specifying the correct range of pages.
3. Right pane. Use the right pane to view the contents of the manual. Also, each page of the
manual includes a link at the top right which links to a PDF file
containing just the currently selected chapter of the manual.
About This Guide 1-3
Page 24

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
How to Print this Manual
To print this manual you man choose one of the following several options, according to your
needs.
• Printing a “How To” Sequence of Steps in the HTML View. Use the Print button on the
upper right of the toolbar to print the currently displayed topic. Using this button when a
step-by-step procedure is displayed will send the entire procedure to your printer--you do not
have to worry about specifying the correct range of pages.
• Printing a Chapter. Use the link at the top right of any page.
– Click “PDF of This Chapter” link at the top right of any page in the chapter you want to
print. A new browser window opens showing the PDF version of the chapter you were
viewing.
– Click the print icon in the upper left of the window.
– Tip: If your printer supports printing two pages on a single sheet of paper, you can save
paper an printer ink by selecting this feature.
• Printing the Full Manual. Use the PDF button in the toolbar at the top right of the browser
window.
– Click PDF button. A new browser window opens showing the PDF version of the chapter
you were viewing.
– Click the print icon in the upper left of the window.
– Tip: If your printer supports printing two pages on a single sheet of paper, you can save
paper an printer ink by selecting this feature.
1-4 About This Guide
Page 25

Chapter 2
Switch Management Overview
This chapter gives an overview of switch management, including the methods you can use to
manage your NETGEAR GSM73xx Level 3 Managed Switch Software v2.
• Management Access Overview
• SNMP Access
• Protocols
The 7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Software
• Assist attached hardware in switching frames, based on Layer 2 or 3 information contained in
the frames.
• Provide a complete switch management portfolio for the network administrator.
software has two purposes:
Switch Management Overview
Fast Ethernet (FEN) and Gigabit Ethernet (GEN) switching continues to evolve from high-end
backbone applications to desktop switching applications. The price of the technology continues to
decline, while performance and feature sets continue to improve. Devices that are capable of
switching Layers 2, 3, and 4 are increasingly in demand. The GSM73xx Level 3 Managed Switch
Software v2 provides a flexible solution to these ever-increasing needs.
The GSM73xx Level 3 Managed Switch Software v2 provides the network administrator with a
set of comprehensive management functions for managing both the GSM73xx and the network.
The network administrator has a choice of three easy-to-use management methods:
• Web-based
• VT100 interface
Note: When configuring a device by use of a configuration file, the maximum number of
configuration file command lines is 2000.
• Simple Network Protocol Management (SNMP)
Switch Management Overview 2-1
Page 26

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Each management method enables the network administrator to configure, manage, and control
the GSM73xx locally or remotely using in-band or out-of-band mechanisms. Management is
standards-based, with configuration parameters and a private MIB providing control for functions
not completely specified in the MIBs.
Table 2-1. Comparing Switch Management Methods
Management Method Advantages Disadvantages
Administration
console
Web browser
or Telnet
SNMP Agent • Communicates with switch functions at the
• Out-of-band access via direct cable
connection means network bottlenecks,
crashes, and downtime do not slow or
prevent access
• No IP address or subnet needed
• Menu or CLI based
• Hyper Terminal access to full functionality
(Hyper Terminal are built into Microsoft
Windows 95/98/NT/2000 operating
systems)
• Secure – make sure the switch is installed in a
secure area.
• Can be accessed from any location via the
switch’s IP address
• Ideal for configuring the switch remotely
• Compatible with Internet Explorer and
Netscape Navigator Web browsers
• Familiar browser interface
• Graphical data available
• Most visually appealing
• Menu or CLI interfaces available
Management Information Base (MIB) level
• Based on open standards
• Must be near switch or use dial-up
connection
• Not convenient for remote users
• Not graphical
• Security can be compromised (hackers
can attack if they know IP address)
• May encounter lag times on poor
connections
• Displaying graphical objects over a
browser interface may slow navigation
• Requires SNMP manager software
• Least visually appealing of all three
methods
• Limited amount of information
available
• Some settings require calculations
• Security can be compromised (hackers
need only know the community name)
2-2 Switch Management Overview
Page 27
Chapter 3
Administration Console Telnet Interface
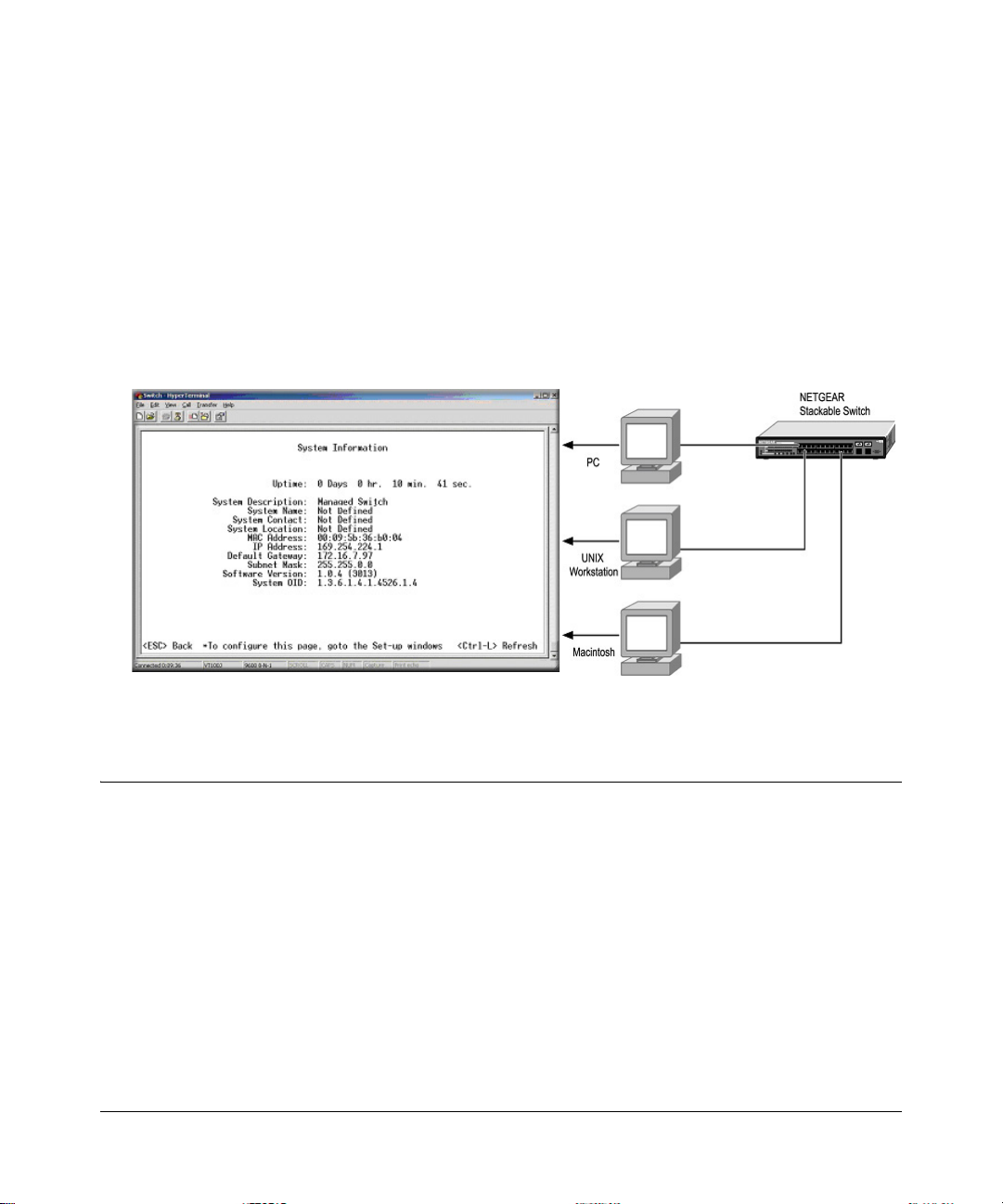
The administration console is an internal, character-oriented, VT-100/ANSI menu-driven user
interface for performing management activities. Using this method, you can view the
administration console from a terminal, PC, Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation connected to
the switch’s console port. Figure 3-1 shows an example of this management method.
Figure 3-1: Administration Console Management Method
Setting Up Your Switch Using Direct Console Access
The direct access management method is required when you initially set up your switch.
Thereafter, the convenience and additional features of the Web management access method
(described in chapter 4) make it the best method to manage the switch.
Direct access to the switch console is achiev ed by connecting the switch’s console port to a
VT-100 or compatible terminal or to a PC, Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation equipped with
a terminal-emulation program. This connection is made using the null-modem cable supplied with
the switch.
Administration Console Telnet Interface 3-1
Page 28
7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Examples of terminal-emulation programs include:
• Hyper Terminal, which is included with Microsoft Windows operating systems
• ZTerm for the Apple Macintosh
• TIP for UNIX workstations
This example describes how to set up the connection using a Hyper Terminal on a PC, but other
systems follow similar steps.
1. Click the Windows Start button. Select Accessories and then Communications. Hyper
Terminal should be one of the options listed in this menu. Select Hyper Terminal
2. The following screen will appear. Enter a name for this connection. In the example below, the
name of the connection is GSM73xx. Click OK.
Figure 3-2: Connection Description
3.
The following screen will appear. In the bot tom, drop down box labeled Connect Using:, click
the arrow and choose the COM port to which the switch will connect. In the example below,
COM1 is the port selected. Click OK.
Figure 3-3: COM Port Selection
3-2 Administration Console Telnet Interface
Page 29
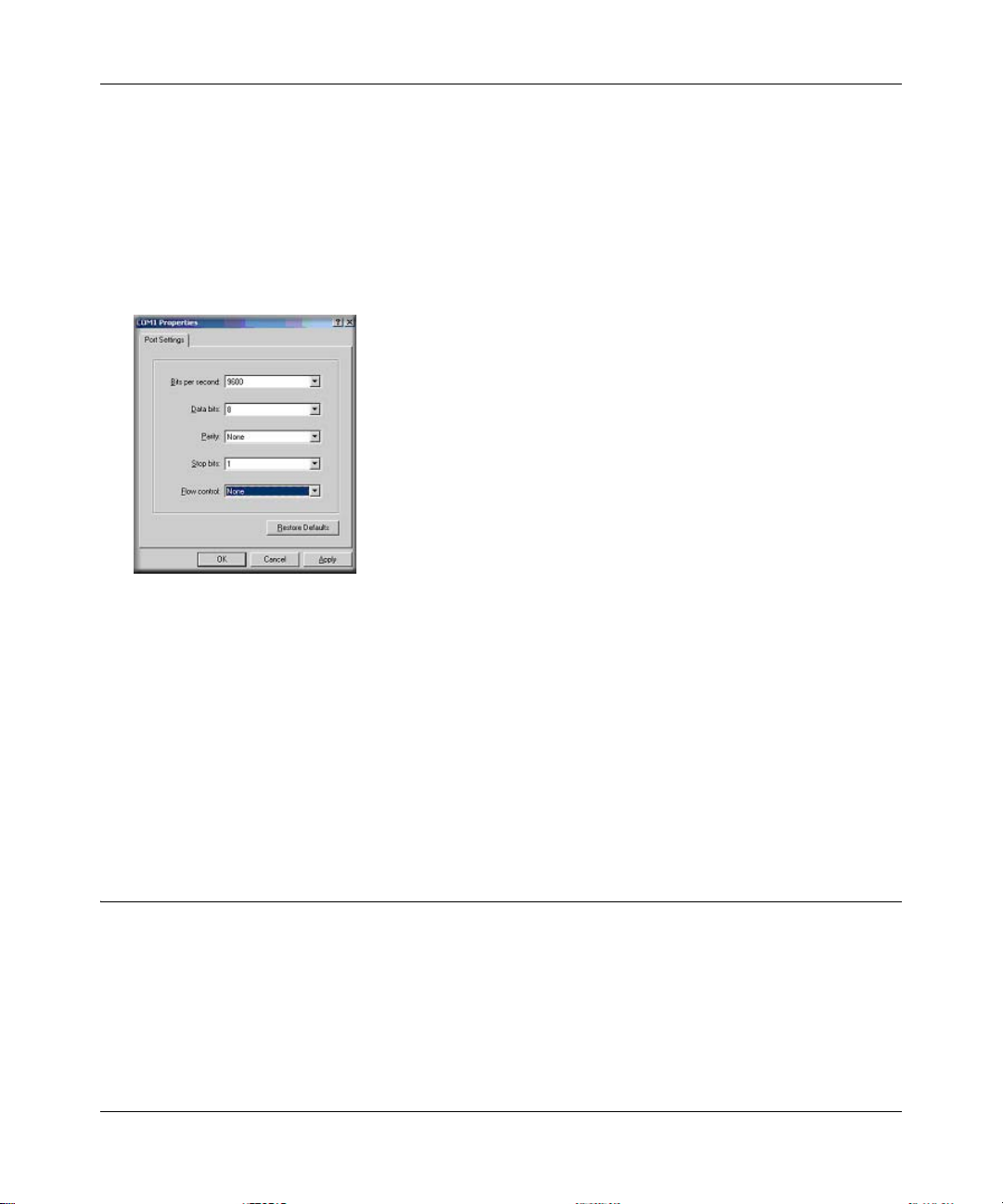
7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
When the following screen appears, make sure that the port setting are as follows:
4.
Baud Rate: 9600
Data Bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop Bits: 1
Flow Control: None
Figure 3-4: Connection Settings
5.
Click OK.
The Hyper Terminal window will open and you should be connected to the switch. If you do not
get a welcome screen or a system menu, hit the return key.
When attached to the User Interface via a Telnet Session, the following must be set in order to use
the arrow keys: Under the terminal pull down menu choose Properties and make sure the VT100
Arrows option is turned on.
Introduction to the Command Menu Interface
The switch offers a Command Menu Interface (CMI), which is a menu-driven method for
managing the switch, as well as a Command Line Interface (CLI), which uses text inputs to
manage the switch. The CLI is accessed through the CMI, but is not addressed in this chapter.
Chapter 5 discusses the CLI in detail.
Administration Console Telnet Interface 3-3
Page 30

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
There are several characteristics to the CMI pages that are necessary to know before proceeding to
use it. The T AB key or the arrow keys may be used to move within menus and sub-screens. At the
bottom of every screen are some key commands available to the user for that particular screen, as
well as some helpful information.
The common keystrokes and their definitions and intricacies are listed below:
• ESC Return to the previous menu or screen, or abort editing
• Tab Select field
• Ctrl-L Refresh the screen
• Ctrl-D Log off (password enabled)
• Ctrl-M Move to field (Switch Statistics and Port Configuration menus only)
• Ctrl-W Saves current configuration to Non-Volatile RAM (NVRAM)
• Spacebar Toggles between possible settings for a field
• Enter Select a menu item, edit a field, or accept a value after editing a field
• Ctrl-X Delete a table entry
The main menu displays all the sub-menus that are available. Striking ‘Enter’ when an option is
highlighted will confirm the choice of the specified sub-menu. The ‘hotkey’ or letter in front of
each menu option can also be typed to directly choose that option.
To logout of the user interface, hit Ctrl-D at any time during your telnet session. You will be
brought back to the login screen (password enabled) or Main Menu (password disabled).
3-4 Administration Console Telnet Interface
Page 31

Chapter 4
Web-Based Management Interface
Your NETGEAR GSM73xx Level 3 Managed Switch Software v2 provides a built-in browser
interface that lets you configure and manage it remotely using a standard Web browser such as
Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or later or Netscape Navigator 6.0 or later.
This interface also allows for system monitoring and management of the switch. The ‘help’ page
will cover many of the basic functions and features of the switch and it’s web interface.
When you configure the switch for the first time from the console, you can assign an IP address
and subnet mask to the switch. Thereafter, you can access the switch’ s Web interface directly using
your W eb browser by entering the switch’s IP address into the address bar. In this way, you can use
your Web browser to manage the switch from a central location, just as if you were directly
connected to the switch’s console port. Figure 4-1 shows this management method.
Figure 4-1: Web Management Method
The 6 menu options available are: System, Status, Set-up, Tools, Security, and Advanced. There is
a help menu in the top of right side of screen; you can click the ‘help’ or the question mark to read
the help menu.
The help menu contains:
• Web-Based Management Introduction to the Web management features.
• Device Management Introduction of the basic icons and management of the device
• Interface Operations Describes Web browser requirements, and common commands
Web-Based Management Interface 4-1
Page 32

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
• Product Overview Describes supported SNMP and Web management features
• Summary of Features Feature List
How to Log In to the GSM73xx
The GSM73xx Level 3 Managed Switch Software v2 can be configured remotely from Microsoft
Internet Explorer browser version 5.0 or above, or Netscape Navigator web browser version 4.78
or above.
1. Determine the IP address of your GSM73xx.
2. Open a Web browser such as Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator.
3. Log in to the GSM73xx using the IP address of http://192.168.0.1 or at whatever IP address
the unit is currently configured with. Use the default user name of admin and default of no
password, or whatever LAN address and password you have set up.
.
Figure 4-2: GSM73xx IP address in browser address bar
A login window like the one shown below opens:
Figure 4-3: Login splash screen
Click the Login link.
4-2 Web-Based Management Interface
Page 33

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
A user name and password dialog box opens like this one.
Figure 4-4: User name/password dialog box
4.
Type the default user name of admin and default of no password, or whatever password you
have set up.
Once you have entered your access point name, your Web browser should automatically find
the GSM73xx L3 Switch and display the home page, as shown below.
Web-Based Management Utility Introduction
Figure 4-5: GSM7324 System description page
Web-Based Management Interface 4-3
Page 34

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
This welcome page displays system information, such as:
• System Description
•System Name
• System Contact
• System Uptime
• IP Address
• System OID (used for production testing)
Figure 4-6: GSM7312 System information page
Interactive Switch Image
Figure 4-7: GSM7312 Interactive switch image
This dynamic image shows various real time conditions about the switch, including the status, fan
operation, power, and the connectivity and traffic indication for each port. In addition, using the
popup menus described below, you can directly access a wealth of information by right-clicking
on a port and selecting a menu item from the popup-menu that displays.
4-4 Web-Based Management Interface
Page 35

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Figure 4-8: GSM7324 Interactive switch image
Menus
The Web-based interface enables navigation through several menus. The main navigation menu is
on the left of every page and contains the screens that let you access all the commands and
statistics the switch provides.
The main menus are:
•System
• Switching
• Routing
•QoS
Web-Based Management Interface 4-5
Page 36

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
System-Wide Popup Menus
The GSM73xx L3 Switch also provides several popup menus.
Figure 4-9: Switch popup menus
You can also access the main navigation menu by right clicking on the image of the switch and
browsing to the menu you want to use.
4-6 Web-Based Management Interface
Page 37

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Port-Specific Popup Menus
The GSM73xx L3 Switch also provides several popup menus for each port.
Figure 4-10: Switch popup menus
You can access a port-specific popup menu by right clicking on the port in the image of the switch
and browsing to the menu you want to use.
Web-Based Management Interface 4-7
Page 38

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
4-8 Web-Based Management Interface
Page 39

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Chapter 5
Command Line Interface Syntax
The Command Line Interface (CLI) syntax, conventions and terminology are described in this
section. Each CLI command is illustrated using the structure outlined below.
CLI Command Format
Commands are followed by values, parameters or both.
Example 1: config network parms <ipAddr> <netmask> [gateway]
– config network parms is the command name.
– <ipAddr> <netmask> are the required values for the command.
– [gateway] is the optional value for the command.
Example 2: config syslocation <location>
– config syslocation is the command name.
– <location> is the required parameter for the command.
Example 3: config lag deleteport <logical slot.port> < slot.port|all>
– config lag deleteport is the command name.
– <logical slot.port> <slot.port|all> are the required values for the
command.
• Command: The text in bold, non-italic font must be typed exactly as shown.
• Parameters: Parameters are order dependent.
The text in bold italics should be replaced with a name or number. To use spaces as part of a
name parameter, enclose it in double quotes like this: "System Name with Spaces".
Parameters may be mandatory values, optional values, choices or a combination.
– <parameter>. The <> angle brackets indicate that a mandatory parameter must be entered
in place of the brackets and text inside them.
Command Line Interface Syntax 5-1
Page 40

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
– [parameter]. The [] square brackets indicate that an optional parameter must be entered in
place of the brackets and text inside them.
– choice1|choice2. The | indicates that only one of the parameters should be entered.
CLI Command Values
ipAddr This parameter is a valid IP address, made up of four decimal
bytes ranging from 0 to 255. The default for all IP parameters
consists of zeros (that is, 0.0.0.1). The interface IP address of
0.0.0.0 is invalid. In some cases, the IP address can also be
entered as a 32-bit number.
macAddr The MAC address format is six hexadecimal numbers separated
by colons, for example 0:6:29:32:81:40.
areaid Area IDs may be entered in dotted-decimal notation (for example,
0.0.0.1). An area ID of 0.0.0.0 is reserved for the backbone. Area
IDs have the same form as IP addresses, but are distinct from IP
addresses. The IP network number of the sub-netted network may
be used for the area ID.
routerid The value of <router id> must be entered in 4-digit dotted-deci-
mal notation (for example, 0.0.0.1). A router ID of 0.0.0.0 is
invalid.
slot.port This parameter denotes a valid slot number and a valid port num-
ber. For example, 0.1 represents slot number 0 and port number 1.
The <slot.port> field is composed of a valid slot number and a
valid port number separated by a period (.).
logical slot.port This parameter denotes a logical slot number and logical port
number assigned. This is applicable in the case of a LAG. The
operator can use the logical slot number and the logical port number to configure the LAG.
CLI Command Conventions
Network address are used to define a link to a remote host, workstation or network. Network
addresses are shown using the following syntax:
5-2 Command Line Interface Syntax
Page 41

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Table 1. Network Address Syntax
Address Type Format Range
ipAddr
macAddr
A.B.C.D 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
(decimal)
YY:YY:YY:YY:YY:YY hexidecimal digit pairs
Double quotation marks such as "System Name with Spaces" set off user defined strings. If the
operator wishes to use spaces as part of a name parameter then it must be enclosed in double
quotation marks.
Entering '@' in front of any command will allow the user to reference any root command from
anywhere in the tree. For example, '>config router>@show arp table' will display the ARP table
even though the command was not executed from the root level.
Command completion finishes spelling the command when enough letters of a command are typed
to uniquely identify the command word. The command may be executed by typing <enter>
(command abbreviation) or the command word may be completed by typing the <tab> or <space
bar> (command completion).
The value 'Err' designates that the requested value was not internally accessible. This should never
happen and indicates that there is a case in the software that is not handled correctly.
The value of '-----' designates that the value is unknown.
CLI Annotations
The CLI allows the user to type single-line annotations at the command prompt for use when
writing test or configuration scripts and for better readability . The exclamation point (‘!’) character
flags the beginning of a comment. The comment flag character can begin a word anywhere on the
command line and all input following this character is ignored. Any command line that begins
with the character ‘!’ is recognized as a comment line and ignored by the parser.
Some examples are provided below:
! Script file for displaying the ip interface
! Display information about interfaces
show ip interface 0.1 !Displays the information about the first interface
! Display information about the next interface
show ip interface 0.2
! End of the script file
Command Line Interface Syntax 5-3
Page 42

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
5-4 Command Line Interface Syntax
Page 43

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Chapter 6
Quick Startup
The CLI Quick Start up details procedures to quickly become acquainted with the 7000 Series L3
Managed Switch Software.
Quick Starting the Switch
1. Read the device Installation Guide for the connectivity procedure. In-band connectivity allows
access to the 7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Software locally or from a remote workstation.
The device must be configured with IP information (IP address, subnet mask, and default
gateway).
2. Turn the Power ON.
3. Allow the device to load the software until the login prompt appears. The device initial state is
called the default mode.
4. When the prompt asks for operator login, execute the following steps:
• Type the word admin in the login area. Since a number of the Quick Setup commands
require administrator account rights, log in using an administrator account.
• Do not enter a password because there is no password in the default mode.
• Press the enter key two times.
Software Version Information
Table 6-1. Quick Start Up Software Version Information
Command Details
show inventory Allows the user to see the software version the device contains
Machine Model (The type and number of ports the device provides.)
For example:
System Description ................................ netgear
Machine Type ......………......................... 2402
Burned In MAC Address ........................ 00:06:29:32:81:40
Software Version ..................................... 2.0.0.0
Quick Startup 6-1
Page 44

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Physical Port Data
Table 6-2. Quick Start Up Physical Port Data
Command Details
show port all Displays the Ports
Slot.Port
Slot Options
0 - The slots on the front of the switch (10/100 ports)
Port Options
Type - Indicates if the port is a special type of port
STP State - Displays the Spanning Tree status
Admin Mode - Selects the Port Control Administration State
Physical Mode - Selects the desired port speed and duplex mode
Physical Status - Indicates the port speed and duplex mode
Link Status - Indicates whether the link is up or down
Link Trap - Determines whether or not to send a trap when link status changes
LACP Mode - Displays whether LACP is enabled or disabled on this port.
User Account Management
Table 6-3. Quick Start Up User Account Management
Command Details
show users Displays all of the users that are allowed to access the switch
Access Mode - Shows whether the user is able to change
parameters on the switch (Read/Write) or is only able to view then
(Read Only).
As a factory default, admin has Read/Write access and guest has
Read Only access. There can only be one Read/Write user and up
to 5 Read Only users.
show loginsession Displays all of the login session information
6-2 Quick Startup
Page 45

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Table 6-3. Quick Start Up User Account Management
Command Details
config users passwd <user> Allows the user to set passwords or change passwords needed to
log in.
A prompt will appear after the command is entered requesting the
users old password. In the absence of an old password leave the
area blank. The operator must press enter to execute the
command.
The system then prompts the user for a new password then a
prompt to confirm the new password. If the new password and the
confirmed password match a message will be displayed
save config This will save passwords and all other changes to the device.
If you do not save config, all configurations will be lost when a
power cycle is performed on the switch or when the switch is reset
logout Logs the user out of the switch
IP Address
To view the network parameters the operator can access the device by the following three
methods.
• Simple Network Management Protocol - SNMP
•Telnet
• Web Browser
Note: Helpful Hint: The user should do a save config after configuring the network parameters so
that the configurations are not lost
Table 6-4. Quick Start Up IP Address
Command Details
show network Displays the Network Configurations
IP Address - IP Address of the interface
Default IP is 0.0.0.0
Subnet Mask - IP Subnet Mask for the interface
Default is 0.0.0.0
Default Gateway - The default Gateway for this interface
Default value is 0.0.0.0
Quick Startup 6-3
Page 46

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Table 6-4. Quick Start Up IP Address
Command Details
Burned in MAC Address - The Burned in MAC Address used for
in-band connectivity
Locally Administered MAC Address - Can be configured to allow
a locally administered MAC address
MAC Address Type - Specifies which MAC address should be
used for in-band connectivity
Network Configurations Protocol Current - Indicates which
network protocol is being used
Default is DHCP
Java Mode - Specifies whether the switch should allow the Java
applet to show the interactive switch graphic (see “Interactive
Switch Image” on page 4-4)
Default is enable
config network parms config network parms <ipAddr> <Mask> <gateway>
IP Address range from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Subnet Mask range from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Gateway Address range from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Uploading from Switch to Out-of-Band PC (Only XMODEM)
Table 6-5. Quick Start Up Uploading from Switch to Out-of-Band PC (Only XMODEM)
Command Details
transfer upload mode xmodem Changes mode to xmodem which is initiated by the
serial EIA 232 port
6-4 Quick Startup
Page 47

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Table 6-5. Quick Start Up Uploading from Switch to Out-of-Band PC (Only XMODEM)
Command Details
transfer upload datatype
<config|errorlog|systemtrace|traplog>
The types are:
config - configuration file
errorlog - error log
system trace - system trace
traplog - trap log
transfer upload start This starts the upload and also displays the mode of
uploading and the type of upload it is and confirms
the upload is taking place.
For example:
If the user is using HyperTerminal, the user must
specify where the file is going to be received by the
PC.
Downloading from Out-of-Band PC to Switch (Only XMODEM)
T able 6-6. Quick Start up Downloading from Out-of-Band PC to Switch (Only XMODEM)
Command Details
transfer download mode xmodem Makes the download mode to be xmodem
transfer download datatype <config/code> Sets the download datatype to be an image or
config file.
The default is a code file.
transfer download start For example:
If the user is using HyperT erminal, the user must
specify which file is to be sent to the switch.
The Switch will restart automatically once the
code has been downloaded.
Quick Startup 6-5
Page 48

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Downloading from TFTP Server
Before starting a TFTP server download, the operator must complete the Quick Start up for the IP
Address.
Table 6-7. Quick Start Up Downloading from TFTP Server
Command Details
transfer download mode TFTP Makes the download mode to be TFTP
transfer download datatype <config/code> Sets the download datatype to be an image or
config file.
The default is a code file.
transfer download filename <name> The name can ONLY be an image file or a
configuration file of the switch.
transfer download serverip <ipAddr> The IP Address is the source IP Address.
transfer download start Starts the TFTP download
Factory Defaults
Table 6-8. Quick Start Up Factory Defaults
Command Details
clear config Enter yes when the prompt pops up to clear all the configurations
made to the switch.
save config Enter yes when the prompt pops up that asks if you want to save the
configurations made to the switch.
reset system OR Cold Boot the
Switch
Enter yes when the prompt pops up that asks if you want to reset the
system.
This is the users choice either reset the switch or cold boot the
switch, both work effectively.
6-6 Quick Startup
Page 49

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Basic Configuration Examples
This section provides configuratoin examples for port and VLAN routing, and VLAN
configurations.
Port Routing, RIP, and OSPF Configuration
This section presents routing configuration examples for routing, RIP, and OSPF.
The configuration commands used in the following example enable routing on ports 0.2, 0.3, and
0.5.
.
Table 6-9. Routing Configuration Example
Routing
config routing enable
config interface routing 0.2 enable
config interface routing 0.3 enable
config interface routing 0.5 enable
config ip interface create 0.5 192.150.5.1 255.255.255.0
config ip interface create 0.2 192.150.2.1 255.255.255.0
config ip interface create 0.3 192.150.3.1 255.255.255.0
The config commands used in the following example enable RIP on ports 0.12 and 0.13
Table 6-10. RIP Configuration Example
RIP
config routing enable
config ip interface create 0.12 192.150.12.1 255.255.255.0
config ip interface create 0.13 192.150.13.1 255.255.255.0
config interface routing 0.12 enable
config interface routing 0.13 enable
config router id 192.150.1.1
config router rip adminmode enable
config router rip interface mode 0.12 enable
config router rip interface mode 0.13 enable
Quick Startup 6-7
Page 50

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
The config commands used in the following example enable OSPF on ports 0.1 and 0.2
Table 6-11. OSPF Configuration Example
OSPF
config routing enable
config interface routing 0.1 enable
config interface routing 0.2 enable
config router id 192.150.2.1
config router ospf interface areaid 0.1 0.0.0.0
config router ospf interface areaid 0.2 0.0.0.0
config ip interface create 0.1 192.150.2.1 255.255.255.0
config ip interface create 0.2 192.150.3.1 255.255.255.0
config router ospf adminmode enable
config router ospf interface mode 0.1 enable
config router ospf interface mode 0.2 enable
RIP and OSPF VLAN Routing
This section provides examples of VLAN Routing for RIP and OSPF.
This example creates two router ports to run RIP 2.
6-8 Quick Startup
Page 51

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Table 6-12. VLAN Routing RIP Configuration
Step Example CLI Command
1. Create VLAN Disable console timeout.
config serial timeout 0
Create VLAN. SC box only supports VLAN routing,
router port has to join VLAN.
config vlan create 10
config vlan create 20
Physical Port IDs are 0.1 and 0.2.
config vlan participation include 10 0.1
config vlan participation include 20 0.2
Create PVID for ports.
config vlan port pvid 10 0.1
config vlan port pvid 20 0.2
2. Create IP VLAN routing config ip vlan routing create 10
config ip vlan routing create 20
3. Enable the routing
function for the virtual router
4. Config Router ID (virtual) config router id 192.168.111.50
5. Config IP interface
(virtual)
6. Enable RIP protocol config router rip adminmode enable
config routing enable
Assign IP to router port 5.1 and 5.2.
config ip interface create 5.1 9.1.1.1 255.0.0.0
config ip interface create 5.2 192.168.111.1
255.255.255.0
config router rip interface mode 5.1 enable
config router rip interface mode 5.2 enable
Quick Startup 6-9
Page 52

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
This example creates two router ports to run OSPF.
Table 6-13. VLAN Routing OSPF Configuration
Step Example CLI Command
1. Create VLAN Disable console timeout.
config serial timeout 0
Create VLAN. SC box only supports VLAN routing,
router port has to join VLAN.
config vlan create 10
config vlan create 20
Physical Port IDs are 0.1 and 0.2.
config vlan participation include 10 0.1
config vlan participation include 20 0.2
Create PVID for ports.
config vlan port pvid 10 0.1
config vlan port pvid 20 0.2
2. Create IP VLAN routing config ip vlan routing create 10
config ip vlan routing create 20
3. Enable the routing
function for the virtual router
4. Config Router ID (virtual) config router id 192.168.111.50
5. Config IP interface
(virtual)
6. Enable OSPF protocol config router ospf adminmode enable
config routing enable
Assign IP to router port 5.1 and 5.2.
config ip interface create 5.1 9.1.1.1 255.0.0.0
config ip interface create 5.2 192.168.111.1
255.255.255.0
config router ospf interface mode 5.1 enable
config router ospf interface mode 5.2 enable
6-10 Quick Startup
Page 53

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
VLAN Example
LAN switches can segment networks into logically defined virtual workgroups.This logical
segmentation is commonly referred as a virtual LAN (VLAN). This logical segmentation of
devices provides better LAN administration, security, and management of broadcast activity over
the network. V irtual LANs have become an integral feature of switched LAN solutions.
The VLAN example below demonstrates a simple VLAN configuration with a 7000 Series L3
Managed Switch.
If a single port is a member of VLANs 2, 3 and 4, the port expects to see traffic tagged with either
VLAN 2,3 or 4.
The PVID (Port Vi rtual Identificat ion) could be something entirely different, for example '12' and
things would still work fine, just so incoming traffic was tagged.
Example:
• Project A = (VLAN2, ports 1,2)
• Project B = (VLAN3, ports 3,4)
• Project C = (VLAN4, ports 5,6)
• Project P = (VLAN 9, port 7)
Table 6-14. Creating the VLANs
VLAN Command
create VLAN 2 config vlan create 2
config vlan participation include 2 0.1
config vlan participation include 2 0.2
create VLAN 3 config vlan create 3
create VLAN 4 config vlan create 4
create VLAN 9 config vlan create 9
Quick Startup 6-11
config vlan participation include 3 0.3
config vlan participation include 3 0.4
config vlan participation include 4 0.5
config vlan participation include 4 0.6
config vlan participation include 9 0.1
config vlan participation include 9 0.2
config vlan participation include 9 0.3
config vlan participation include 9 0.4
config vlan participation include 9 0.5
config vlan participation include 9 0.6
config vlan participation include 9 0.7
Page 54

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
SOLUTION 1
All traffic entering the ports is tagged traffic. Since the traffic is tagged, the PVID configuration
for each port is not a concern.
• The network card configuration for devices on Project A must be set to tag all traffic with
'VLAN 2'
• The network card configuration for devices on Project B must be set to tag all traffic with
'VLAN 3'
• The network card configuration for devices on Project C must be set to tag all traffic with
'VLAN 4'
• The network card configuration for devices on Project P must be set to tag all traffic with
'VLAN 9'
SOLUTION 2
The network card configuration for devices on Project A, B and C should be set to NOT tag traffic.
To take care of these untagged frames configure the following:
• config vlan ports pvid 2 0.1
• config vlan ports pvid 2 0.2
• config vlan ports pvid 3 0.3
• config vlan ports pvid 3 0.4
• config vlan ports pvid 4 0.5
• config vlan ports pvid 4 0.6
6-12 Quick Startup
Page 55

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Chapter 7
Switching Commands
This chapter provides detailed explanation of the Switching commands. The commands are
divided into five functional groups:
• Show commands display switch settings, statistics, and other information.
• Config commands configure features and options of the switch. For every config command
there is a show command that displays the config setting.
• Transfer commands transfer configuration and informational files to and from the switch.
• Save commands save the switch configuration.
• Clear commands clear some or all of the settings to factory defaults.
This chapter is organized by configuration type:
• System information and statistics commands
• Management commands
• Device configuration commands
• User account management commands
• System utilities
System Information and Statistics Commands
These commands display and configure system information and statistics.
show inventory
This command displays inventory information for the switch.
Format show inventory
Switch Description Text used to identify the product name of this switch.
Switching Commands 7-1
Page 56

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Machine Type Specifies the machine model as defined by the Vital Product
Data.
Burnedin MAC Address Universally assigned network address.
Software Version The release.version.revision number of the code currently run-
ning on the switch.
show sysinfo
This command displays switch information.
Format show sysinfo
Switch Description Text used to identify this switch.
System Name Name used to identify the switch.
System Location Text used to identify the location of the switch. May be up to 31
alpha-numeric characters. The factory default is blank.
System Contact Text used to identify a contact person for this switch. May be up
to 31 alpha-numeric characters. The factory default is blank.
System ObjectID The base object ID for the switch’s enterprise MIB.
IP Address The IP address currently assigned to the switch.
System Up Time The time in days, hours and minutes since the last switch reboot.
MIBs Supported A list of MIBs supported by this agent.
config sysname
This command sets the name assigned to the switch.The range for name is from 1 to 31
alphanumeric characters.
Default Blank
Format config sysname <name>
config syslocation
This command sets the physical location of the switch. The range for name is from 1 to 31
alphanumeric characters.
Default Blank
Format config syslocation <location>
7-2 Switching Commands
Page 57

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config syscontact
This command sets the organization responsible for the network. The range for name is from 1 to
31 alphanumeric characters.
Default Blank
Format config syscontact <contact>
show arp switch
This command displays connectivity between the switch and other devices. The Address
Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache identifies the MAC addresses of the IP stations communicating
with the switch.
Format show arp switch
MAC Address A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and/
or filtering information. The format is 6 two-digit hexadecimal
numbers that are separated by colons, for example
01:23:45:67:89:AB
IP Address The IP address assigned to each interface.
Slot.Port This parameter denotes a valid slot number and a valid port num-
ber.
show forwardingdb table
This command displays the forwarding database entries. If the command is entered with no
parameter, the entire table is displayed. This is the same as entering the optional
Alternatively, the administrator can enter a MAC Address to display the table entry for the
requested MAC address and all entries following the requested MAC address.
Format show forwardingdb table [macaddr/all]
Mac Address A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and
or filtering information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for example
01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will be
displayed as 8 bytes. In an SVL system, the MAC address will be
displayed as 6 bytes.
Slot.Port The port which this address was learned.
if Index This object indicates the ifIndex of the interface table entry as s o-
ciated with this port.
Switching Commands 7-3
all parameter.
Page 58

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Status The status of this entry. The meanings of the values are:
Static The value of the corresponding instance was added by the
system or a user and cannot be relearned.
Learned The value of the corresponding instance was learned,
and is being used.
Management The value of the corresponding instance is also the
value of an existing instance of dot1d Static Address. Currently
this is used when enabling VLANs for routing.
Self The value of the corresponding instance is the system’s own
MAC address.
GMRP Learned The value of the corresponding instance was
learned via GMRP.
Other The value of the corresponding instance does not fall into
one of the other categories.
show stats port detailed
This command displays detailed statistics for a specific port.
Format show stats port detailed <slot.port>
Packets Received Octets Received - The total number of octets of data (including
those in bad packets) received on the network (excluding framing
bits but including FCS octets). This object can be used as a reasonable estimate of ethernet utilization. If greater precision is
desired, the etherStatsPkts and etherStatsOctets objects should be
sampled before and after a common interval. The result of this
equation is the value Utilization which is the percent utilization of
the ethernet segment on a scale of 0 to 100 percent.
Packets Received < 64 Octets - The total number of packets
(including bad packets) received that were < 64 octets in length
(excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Packets Received 64 Octets - The total number of packets
(including bad packets) received that were 64 octets in length
(excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Packets Received 65-127 Octets - The total number of packets
(including bad packets) received that were between 65 and 127
octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including
FCS octets).
7-4 Switching Commands
Page 59

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Packets Received 128-255 Octets - The total number of packets
(including bad packets) received that were between 128 and 255
octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including
FCS octets).
Packets Received 256-511 Octets - The total number of packets
(including bad packets) received that were between 256 and 511
octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including
FCS octets).
Packets Received 512-1023 Octets - The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between 512 and
1023 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets Received 1024-1518 Octets - The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between 1024 and
1518 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets Received 1519-1522 Octets - The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between 1519 and
1522 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets Received > 1522 Octets - The total number of packets
received that were longer than 1522 octets (excluding framing
bits, but including FCS octets) and were otherwise well formed.
Packets Received
Successfully Total - The total number of packets received that were without
errors.
Unicast Packets Received - The number of subnetwork-unicast
packets delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
Multicast Packets Received - The total number of good packets
received that were directed to a multicast address. Note that this
number does not include packets directed to the broadcast
address.
Broadcast Packets Received - The total number of good packets
received that were directed to the broadcast address. Note that
this does not include multicast packets.
Switching Commands 7-5
Page 60

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Packets Received with
MAC Errors
Total - The total number of inbound packets that contained errors
preventing them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
Jabbers Received - The total number of packets received that
were longer than 1518 octets (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets), and had either a bad Frame Check Sequence
(FCS) with an integral number of octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS
with a non-integral number of octets (Alignment Error). Note that
this definition of jabber is different than the definition in IEEE-
802.3 section 8.2.1.5 (10BASE5) and section 10.3.1.4
(10BASE2). These documents define jabber as the condition
where any packet exceeds 20 ms. The allowed range to detect
jabber is between 20 ms and 150 ms.
Fragments/Undersize Received - The total number of packets
received that were less than 64 octets in length (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Alignment Errors - The total number of packets received that
had a length (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) of
between 64 and 1518 octets, inclusive, but had a bad Frame
Check Sequence (FCS) with a non-integral number of octets.
FCS Errors - The total number of packets received that had a
length (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) of
between 64 and 1518 octets, inclusive, but had a bad Frame
Check Sequence (FCS) with an integral number of octets
Overruns - The total number of frames discarded as this port was
overloaded with incoming packets, and could not keep up with
the inflow .
Received Packets
not forwarded
Total - A count of valid frames received which were discarded
(i.e. filtered) by the forwarding process.
Local Traffic Frames - The total number of frames dropped in
the forwarding process because the destination address was
located off of this port.
802.3x Pause Frames Received - A count of MAC Control
frames received on this interface with an opcode indicating the
PAUSE operation. This counter does not increment when the
interface is operating in half-duplex mode.
7-6 Switching Commands
Page 61

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Unacceptable Frame Type - The number of frames discarded
from this port due to being an unacceptable frame type.
VLAN Membership Mismatch - The number of frames discarded on this port due to ingress filtering.
VLAN Viable Discards - The number of frames discarded on
this port when a lookup on a particular VLAN occurs while that
entry in the VLAN table is being modified, or if the VLAN has
not been configured.
Multicast Tree Viable Discards - The number of frames discarded when a lookup in the multicast tree for a VLAN occurs
while that tree is being modified.
Reserved Address Discards - The number of frames discarded
that are destined to an IEEE 802.1 reserved address and are not
supported by the system.
Broadcast Storm Recovery - The number of frames discarded
that are destined for FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF when Broadcast Storm
Recovery is enabled.
CFI Discards - The number of frames discarded that have CFI
bit set and the addresses in RIF are in non-canonical format.
Upstream Threshold - The number of frames discarded due to
lack of cell descriptors available for that packet's priority level.
Packets Transmitted Octets Total Bytes - The total number of octets of data (including those
in bad packets) received on the network (excluding framing bits
but including FCS octets). This object can be used as a reasonable
estimate of ethernet utilization. If greater precision is desired, the
etherStatsPkts and etherStatsOctets objects should be sampled
before and after a common interval.
Packets Transmitted 64 Octets - The total number of packets
(including bad packets) received that were 64 octets in length
(excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Packets Transmitted 65-127 Octets - The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between 65 and
127 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Packets Transmitted 128-255 Octets - The total number of
packets (including bad packets) received that were between 128
Switching Commands 7-7
Page 62

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
and 255 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets Transmitted 256-511 Octets - The total number of
packets (including bad packets) received that were between 256
and 511 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets Transmitted 512-1023 Octets - The total number of
packets (including bad packets) received that were between 512
and 1023 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets Transmitted 1024-1518 Octets - The total number of
packets (including bad packets) received that were between 1024
and 1518 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets Transmitted 1519-1522 Octets - The total number of
packets (including bad packets) received that were between 1519
and 1522 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Max Info - The maximum size of the Info (non-MAC) field that
this port will receive or transmit.
Packets Transmitted
Successfully
Total - The number of frames that have been transmitted by this
port to its segment.
Unicast Packets Transmitted - The total number of packets that
higher-level protocols requested be transmitted to a subnetworkunicast address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Multicast Packets Transmitted - The total number of packets
that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted to a Multicast
address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Broadcast Packets Transmitted - The total number of packets
that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted to the Broadcast address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Transmit Errors Total Errors - The sum of Single, Multiple, and Excessive Colli-
sions.
FCS Errors - The total number of packets transmitted that had a
length (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) of
7-8 Switching Commands
Page 63

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
between 64 and 1518 octets, inclusive, but had a bad Frame
Check Sequence (FCS) with an integral number of octets
Oversized - The total number of frames that exceeded the max
permitted frame size. This counter has a max increment rate of
815 counts per sec. at 10 Mb/s.
Underrun Errors - The total number of frames discarded
because the transmit FIFO buffer became empty during frame
transmission.
Transmit Discards Total Discards - The sum of single collision frames discarded,
multiple collision frames discarded, and excessive frames discarded.
Single Collision Frames - A count of the number of successfully
transmitted frames on a particular interface for which transmission is inhibited by exactly one collision.
Multiple Collision Frames - A count of the number of successfully transmitted frames on a particular interface for which transmission is inhibited by more than one collision.
Excessive Collisions - A count of frames for which transmission
on a particular interface fails due to excessive collisions.
Port Membership - The number of frames discarded on egress
for this port due to egress filtering being enabled.
VLAN Viable Discards - The number of frames discarded on
this port when a lookup on a particular VLAN occurs while that
entry in the VLAN table is being modified, or if the VLAN has
not been configured.
Protocol Statistics BPDU's received - The count of BPDU's (Bridge Protocol Data
Units) received in the spanning tree layer.
BPDU's Transmitted - The count of BPDU's (Bridge Protocol
Data Units) transmitted from the spanning tree layer.
802.3x Pause Frames Received - A count of MAC Control
frames received on this interface with an opcode indicating the
PAUSE operation. This counter does not increment when the
interface is operating in half-duplex mode.
GVRP PDU's Received - The count of GVRP PDU's received in
the GARP layer.
Switching Commands 7-9
Page 64

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
GVRP PDU's T ransmitted - The count of GVRP PDU's transmitted from the GARP layer.
GVRP Failed Registrations - The number of times attempted
GVRP registrations could not be completed.
GMRP PDU's received - The count of GMRP PDU's received in
the GARP layer.
GMRP PDU's Transmitted - The count of GMRP PDU's transmitted from the GARP layer.
GMRP Failed Registrations - The number of times attempted
GMRP registrations could not be completed.
STP BPDUs Transmitted - Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units sent
STP BPDUs Received - Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol
Data Units received
RST BPDUs Transmitted - Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
Bridge Protocol Data Units sent
RSTP BPDUs Received - Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge
Protocol Data Units received
MSTP BPDUs Transmitted - Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Bridge Protocol Data Units sent
MSTP BPDUs Received - Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Bridge Protocol Data Units received
Time Since Counters
Last Cleared The elapsed time, in days, hours, minutes, and seconds since the
statistics for this port were last cleared.
show stats port summary
This command displays a summary of statistics for a specific port.
Format show stats port summary <slot.port>
Packets Received
Without Error
Packets Received
With Error
7-10 Switching Commands
The total number of packets (including broadcast packets and
multicast packets) received by the processor.
The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing
them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
Page 65

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Broadcast Packets Received The total number of packets received that were directed to the
broadcast address. Note that this does not include multicast packets.
Packets Transmitted
Without Error The total number of packets transmitted out of the interface.
Transmit Packets Errors The number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted
because of errors.
Collisions Frames The best estimate of the total number of collisions on this Ether-
net segment.
Time Since Counters
Last Cleared The elapsed time, in days, hours, minutes, and seconds since the
statistics for this port were last cleared.
show stats switch detailed
This command displays detailed statistics for all CPU traffic.
Format show stats switch detailed
Total Packets Received (Octets)- The total number of octets of
data received by the processor (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Packets Received Without Error- The total number of packets
(including broadcast packets and multicast packets) received by
the processor.
Unicast Packets Received - The number of subnetwork-unicast
packets delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
Multicast Packets Received - The total number of packets
received that were directed to a multicast address. Note that this
number does not include packets directed to the broadcast
address.
Broadcast Packets Received - The total number of packets
received that were directed to the broadcast address. Note that
this does not include multicast packets.
Receive Packets Discarded - The number of inbound packets
which were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had
been detected to prevent their being deliverable to a higher-layer
protocol. A possible reason for discarding a packet could be to
free up buffer space.
Switching Commands 7-11
Page 66

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Octets Transmitted - The total number of octets transmitted out
of the interface, including framing characters.
Packets Transmitted without Errors - The total number of
packets transmitted out of the interface.
Unicast Packets Transmitted - The total number of packets that
higher-level protocols requested be transmitted to a subnetworkunicast address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Multicast Packets Transmitted - The total number of packets
that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted to a Multicast
address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Broadcast Packets Transmitted - The total number of packets
that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted to the Broadcast address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Transmit Packets Discarded - The number of outbound packets
which were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had
been detected to prevent their being deliverable to a higher-layer
protocol. A possible reason for discarding a packet could be to
free up buffer space.
Most Address Entries Ever Used - The highest number of Forwarding Database Address Table entries that have been learned
by this switch since the most recent reboot.
Address Entries in Use - The number of Learned and static
entries in the Forwarding Database Address Table for this switch.
Maximum VLAN Entries - The maximum number of Virtual
LANs (VLANs) allowed on this switch.
Most VLAN Entries Ever Used - The largest number of VLANs
that have been active on this switch since the last reboot.
Static VLAN Entries - The number of presently active VLAN
entries on this switch that have been created statically.
Dynamic VLAN Entries - The number of presently active
VLAN entries on this switch that have been created by GVRP
registration.
VLAN Deletes - The number of VLANs on this switch that have
been created and then deleted since the last reboot.
Time Since Counters
Last Cleared
The elapsed time, in days, hours, minutes, and seconds, since the
statistics for this switch were last cleared.
7-12 Switching Commands
Page 67

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
show stats switch summary
This command displays a count of all CPU traffic.
Format show stats switch summary
Packets Received
Without Error
Broadcast Packets
Received
Packets Received
With Error The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing
Packets Transmitted
Without Error
Broadcast Packets
Transmitted
Transmit Packet Errors The number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted
Address Entries
Currently In Use
VLAN Entries
Currently In Use The number of VLAN entries presently occupying the VLAN
Time Since Counters
Last Cleared
The total number of packets (including broadcast packets and
multicast packets) received by the processor.
The total number of packets received that were directed to the
broadcast address. Note that this does not include multicast packets.
them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
The total number of packets transmitted out of the interface.
The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requ ested
to be transmitted to the Broadcast address, including those that
were discarded or not sent.
because of errors.
The total number of Forwarding Database Address Table entries
now active on the switch, including learned and static entries.
table.
The elapsed time, in days, hours, minutes, and seconds since the
statistics for this switch were last cleared.
show eventlog
This command displays the event log, which contains error messages from the system. The event
log is not cleared on a system reset.
Format show eventlog
File The file in which the even t or igin ated.
Line The line number of the event
Switching Commands 7-13
Page 68

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Task Id The task ID of the event.
Code The even t cod e.
Time The time this event occurred.
Note: Event log information is retained across a switch reset.
show msglog
This command displays the message log maintained by the switch. The message log contains
system trace information.
The trap log contains a maximum of 256 entries that wrap.
Format show msglog
Message The message that has been logged.
Note: Message log information is not retained across a switch reset.
show traplog
This command displays the trap log maintained by the switch.
The trap log contains a maximum of 256 entries that wrap.
Format show traplog
Number of Traps since
last reset
The number of traps that have occurred since the last reset of this
device.
Number of Traps since log
last displayed
The number of traps that have occurred since the traps were last
displayed. Getting the traps by any method (terminal interface
display, Web display, upload file from switch etc.) will result in
this counter being cleared to 0.
Log The sequence number of this trap.
System Up Time The relative time since the last reboot of the switch at which this
trap occurred.
Trap The relevant information of this trap.
Note: Trap log information is not retained across a switch reset.
7-14 Switching Commands
Page 69

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Management Commands
These commands manage the switch and show current management settings.
show network
This command displays network configuration settings that are vital for switch operation.
Format show network
IP Address The IP address of the interface. The factory default value is
0.0.0.0
Subnet Mask The IP subnet mask for this interface. The factory default value is
0.0.0.0
Default Gateway The default gateway for this IP interface. The factory default
value is 0.0.0.0
BurnedIn MAC Address The burnedin MAC address used for in-band connectivity.
Network Configuration
Protocol Current Indicates which network protocol is being used. The options are
bootp|dhcp|none.
Web Mode Specifies if the switch should allow access from a web browser.
Enabled means the switch can be managed from a web browser.
The factory default is enabled.
Java Mode Specifies if the switch should allow access to the Java applet in
the header frame. Enabled means the applet can be viewed. The
factory default is enabled.
config network parms
This command sets the IP Address, subnet mask and gateway of the router. The IP Address and the
gateway must be on the same subnet.
Format config network parms <ipAddr> <netmask>
[gateway]
config network protocol
This command specifies the network configuration protocol to be used. If you modify this value
change is effective immediately.(See “save config” on page 80.)
Switching Commands 7-15
Page 70

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Default none
Format config network protocol <none|bootp|dhcp>,
where bootp indicates that the switch periodically sends
requests to a Bootstrap Protocol (BootP) server or a dhcp server
until a response is received. none indicates that the switch
should be manually configured with IP information.
config network webmode
This command enables or disables access to the switch through the Web interface. When access is
enabled, the user can login to the switch from the Web interface. When access is disabled, the user
cannot login to the switch's Web server.
Disabling the Web interface takes effect immediately. All interfaces are effected.
Default enable
Format config network webmode <enable|disable>
config network javamode
This command specifies whether or not the switch should allow access to the Java applet in the
header frame of the W eb interface. When access is enabled, the Java applet can be viewed from the
Web interface. When access is disabled, the user cannot view the Java applet.
Default enable
Format config network javamode <enable|disable>
config prompt
This command changes the name of the prompt. The length of name may be up to 64 alphanumeric
characters.
Default <model #>
Format config prompt <system prompt>
show serial
This command displays serial communication settings for the switch.
Format show serial
7-16 Switching Commands
Page 71

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Serial Port Login
Timeout (minutes)
Specifies the time, in minutes, of inactivity on a Serial port connection, after which the Switch will close the connection. Any
numeric value between 0 and 160 is allowed, the factory default
is 5. A value of 0 disables the timeout.
Baud Rate The default baud rate at which the serial port will try to connect.
This is selected from a pull-down menu. The available values are
1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400,57600, and 115200 baud.
The factory Default is 9600 baud.
Character Size The number of bits in a character . The number of bits is always 8.
Flow Control Whether Hardware Flow-Control is enabled or disabled. Hard-
ware Flow Control is always disabled.
Stop Bits The number of Stop bits per character . The nu mber of S top bits is
always 1.
Parity Type The Parity Method used on the Serial Port. The Parity Method is
always None.
config serial baudrate
This command specifies the communication rate of the terminal interface. The supported rates are
1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200.
Default 9600
Format config serial baudrate <speed>
config serial timeout
This command specifies the maximum connect time (in minutes) without console activity . A value
of 0 indicates that a console can be connected indefinitely. The time range is 0 to 160.
Default 5
Format config serial timeout <0 - 160>
config snmpcommunity accessmode
This command restricts access to switch information. The access mode can be read-only (also
called public) or read/write (also called private).
Format config snmpcommunity accessmode <ro|rw>
<name>
Switching Commands 7-17
Page 72

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config snmpcommunity create
This command adds (and names) a new SNMP community. A community name is a name
associated with the switch and with a set of SNMP managers that manage it with a specified
privileged level. The length of name can be up to 16 case-sensitive characters.
Note: Community names in the SNMP community table must be unique. If you make multiple
entries using the same community name, the first entry is kept and processed and all duplicate
entries are ignored.
Default Two default community names: Public and Private. You can
replace these default community names with unique identifiers
for each community. The default values for the remaining four
community names are blank.
Format config snmpcommunity create <name>
config snmpcommunity delete
This command removes this community name from the table. The name is the community name to
be deleted.
Format config snmpcommunity delete <name>
config snmpcommunity ipaddr
This command sets an IP address for an SNMP community. The address is the associated
community SNMP packet sending address. The name is the applicable community name. The
community name may be up to 16 alphanumeric characters.
Default 0.0.0.0
Format config snmpcommunity ipaddr <ipAddr> <name>
config snmpcommunity ipmask
This command sets a client IP mask for an SNMP community. The address is the associated
community SNMP packet sending address. The name is the applicable community name. The
community name may be up to 16 alphanumeric characters.
Default 0.0.0.0
Format config snmpcommunity ipmask <ipmask> <name>
7-18 Switching Commands
Page 73

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config snmpcommunity mode
This command activates or deactivates an SNMP community. If a community is enabled, an
SNMP manager associated with this community manages the switch according to its access right.
If the community is disabled, no SNMP requests using this community are accepted. In this case
the SNMP manager associated with this community cannot manage the switch until the Status is
changed back to Enable.
Default The default private and public communities are enabled by
default. The four undefined communities are disabled by default.
Format config snmpcommunity mode <enable|disable>
<name>
show snmptrap
This command displays SNMP trap receivers. Trap messages are sent across a network to an
SNMP Network Manager. These messages alert the manager to events occurring within the switch
or on the network. Six trap receivers are simultaneously supported.
Format show snmptrap
SNMP Trap Name The community string of the SNMP trap packet sent to the trap
manager. This may be up to 16 alphanumeric characters. This
string is case sensitive.
IP Address The IP address to receive SNMP traps from this device. Enter 4
numbers between 0 and 255 separated by periods.
Status A pull down menu that indicates the receiver's status(enabled or
disabled) and allows the administrator/user to perform actions on
this user entry:
Enable - send traps to the receiver
Disable - do not send traps to the receiver.
Delete - remove the table entry.
config snmptrap create
This command adds an SNMP trap name. The maximum length of name is 16 case-sensitive
alphanumeric characters.
Default The default name for the six undefined community names is
Delete.
Format config snmptrap create <name> <ipAddr>
Switching Commands 7-19
Page 74

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config snmptrap delete
This command deletes trap receivers for a community.
Format config snmptrap delete <name> <ipaddr>
config snmptrap ipaddr
This command assigns an IP address to a specified community name. The maximum length of
name is 16 case-sensitive alphanumeric characters.
Note: IP addresses in the SNMP trap receiver table must be unique. If you make multiple entries
using the same IP address, the first entry is retained and processed. All duplicate entries are
ignored.
Format config snmptrap ipaddr <ipaddrold> <name>
<ipaddrnew>
config snmptrap mode
This command activates or deactivates an SNMP trap. Enabled trap receivers are active (able to
receive traps). Disabled trap receivers are inactive (not able to receive traps).
Format config snmptrap mode <enable|disable> <name>
<ipaddr>
show trapflags
This command displays trap conditions. Configure which traps the switch should generate by
enabling or disabling the trap condition. If a trap condition is enabled and the condition is detected,
the switch's SNMP agent sends the trap to all enabled trap receivers. The switch does not have to
be reset to implement the changes. Cold and warm start traps are always generated and cannot be
disabled.
Format show trapflags
Authentication Flag May be enabled or disabled by selecting the corresponding line
on the pull-down entry field. The factory default is enabled. Indicates whether authentication failure traps will be sent.
Link Up/Down Flag May be enabled or disabled by selecting the corresponding line
on the pull-down entry field. The factory default is enabled. Indicates whether link status traps will be sent. Multiple Users Flag.
7-20 Switching Commands
Page 75

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Multiple Users Flag May be enabled or disabled by selecting the corresponding line
on the pull-down entry field. The factory default is enabled. Indicates whether a trap will be sent when the same user ID is logged
into the switch more than once at the same time (either via telnet
or serial port).
Spanning Tree Flag May be enabled or disabled by selecting the corresponding line
on the pull-down entry field. The factory default is enabled. Indicates whether spanning tree traps will be sent.
Broadcast Storm Flag May be enabled or disabled by selecting the corresponding line
on the pull-down entry field. The factory default is enabled. Indicates whether broadcast storm traps will be sent.
config trapflags authentication
This command enables or disables the Authentication Flag.
Default enable
Format
config trapflags authentication
<enable|disable>
config trapflags bcaststorm
This command enables or disables the broadcast storm trap. When enabled, broadcast storm traps
are sent only if the broadcast storm recovery mode setting associated with the port is enabled (see
“config switchconfig broadcast” on page 24).
Default enable
Format config trapflags bcaststorm <enable|dis-
able>
config trapflags linkmode
This command enables or disables Link Up/Down traps for the entire switch. When enabled, link
traps are sent only if the Link Trap flag setting associated with the port is enabled (see “config port
linktrap” on page 27).
Default enable
Format
Switching Commands 7-21
config trapflags linkmode <enable|disable>
Page 76

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config trapflags multiusers
This command enables or disables Multiple User traps. When the traps are enabled, a Multiple
User Trap is sent when a us er logs in to the terminal interface (EIA 232 or telnet) and there is an
existing terminal interface session.
Default enable
Format
config trapflags multiusers <enable|disable>
config trapflags stpmode
This command enables or disables the sending of new root traps and topology change notification
traps.
Default enable
Format config trapflags stpmode <enable|disable>
show telnet
This command displays telnet settings.
Format show telnet
Telnet Login Timeout (minutes) This object indicates the number of minutes a telnet sess ion is
allowed to remain inactive before being logged off.A zero means
there will be no timeout. May be specified as a number from 0 to
160. The factory default is 5.
Maximum Number of Telnet Sessions Selectable from a pull-down menus for values of from 0
to 5. This object indicates the number of simultaneous telnet sessions allowed. The factory default is 5.
Allow New Telnet Sessions Indicates that new telnet sessions will not be allowed when set to
no. The factory default value is yes.
config telnet maxsessions
This command specifies the maximum number of telnet sessions that can be established. A value
of 0 indicates that no telnet session can be established. The range is 0 to 5.
Default 5
Format config telnet maxsessions <0-5>
7-22 Switching Commands
Page 77

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config telnet mode
This command regulates new telnet sessions. If sessions are enabled, new telnet sessions can be
established until there are no more sessions available. If sessions are disabled, no new telnet
sessions are established. An established session remains active until the session is ended or an
abnormal network error ends it.
Default enable
Format config telnet mode <enable|disable>
config telnet timeout
This command sets the telnet session timeout value, in minutes. A session is active as long as the
session has been idle for the value set. A value of 0 indicates that a session remains active
indefinitely. the time is a decimal value from 0 to 160.
Note: Changing the timeout value for active sessions does not become ef fective until the session is
reaccessed. Any keystroke will also activate the new timeout duration.
Default 5
Format config telnet timeout <0-160>
show forwardingdb agetime
This command displays the timeout for address aging. In an IVL system, the [fdbid|all] parameter
is required. In an SVL system, the [fdbid|all] parameter is not used and will be ignored if entered.
Default all
Format show forwardingdb agetime [fdbid|all]
Forwarding DB ID Fdbid (Forwarding database ID) indicates the forwarding data-
base whose aging timeout is to be shown. The all option is used to
display the aging timeouts associated with all forwarding databases. This field displays the forwarding database ID in an IVL
system. This field will not be displayed in an SVL system.
Agetime displays the address aging timeout for the associated forwarding
database in IVL. In an SVL system, this will display the system's
address aging timeout value in seconds.
Switching Commands 7-23
Page 78

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config forwardingdb agetime
This command configures the forwarding database address aging timeout. In an IVL system, the
[fdbid/all] parameter is required. In an SVL system, the [fdbid/all] parameter is not used and will
be ignored if entered.
Default The default value for <10-1,000,000> is 300 seconds
Format config forwardingdb agetime <10-1,000,000>
[fdbid/all]
Seconds The <seconds> parameter must be within the range of 10 to
1,000,000 seconds.
Forwarding Database ID Fdbid (Forwarding database ID) indicates which forwarding data-
base's aging timeout is being configured. All is used to configure
all forwarding database's agetime. In an SVL system, the [fdbid/
all] parameter is not used and will be ignored if entered.
Device Configuration Commands
This section describes device configuration commands.
show switchconfig
This command displays switch configuration information.
Format show switchconfig
Broadcast Storm
Recovery Mode
May be enabled or disabled by selecting the corresponding line
on the pull-down entry field. The factory default is disabled.
802.3x Flow Control Mode May be enabled or disabled by selecting the corresponding line
on the pull-down entry field. The factory default is disabled.
config switchconfig broadcast
This command enables or disables broadcast storm recovery mode. If the mo de is enabled,
broadcast storm recovery with high and low thresholds is implemented.
7-24 Switching Commands
Page 79

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
The threshold implementation follows a percentage pattern. If the broadcast traffic on any Ethernet
port exceeds the high threshold percentage (as represented in “Broadcast Storm Recovery
Thresholds” table) of the link speed, the switch discards the broadcasts traffic until the broadcast
traffic returns to the low threshold percentage or less. The full implementation is depicted in the
“Broadcast Storm Recovery Thresholds” table.
Table 2. Broadcast Storm Recovery Thresholds
Link Speed High Low
10M 20 10
100M 5 2
1000M 5 2
Format config switchconfig broadcast <enable/dis-
able>
config switchconfig flowcontrol
This command enables or disables 802.3x flow control for the switch.
Note: This command only applies to full-duplex mode ports.
Default enable
Format config switchconfig flowcontrol <enable/dis-
able>
Switching Commands 7-25
Page 80

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
show port
This command displays port information.
Format show port <slot.port|all>
Slot.Port The physical slot and physical port.
Type If not blank, this field indicates that this port is a special type of
port. The possible values are:
Mon - this port is a monitoring port. Look at the Port Monitoring
screens to find out more information.
Lag - this port is a member of a Lag. Look at the Lag screens to
find out more information.
Probe - this port is a probe port. Look at the Port Mirroring
screens to find out more information.
Admin Mode Selects the Port control administration state. The port must be
enabled in order for it to be allowed into the network. - May be
enabled or disabled by selecting the corresponding line on the
pull-down entry field. The factory default is enabled.
Physical Mode Selects the desired port speed and duplex mode. If auto-negotia-
tion support is selected, then the duplex mode and speed will be
set from the auto-negotiation process. Note that the port's maximum capability (full duplex -100M) will be advertised. Otherwise, this object will determine the port's duplex mode and
transmission rate. The factory default is Auto.
Physical Statu s Indicates the port speed and duplex mode.
Link Status Indicates whether the Link is up or down.
Link Trap This object determines whether or not to send a trap when link
status changes. The factory default is enabled.
LACP Mode Displays whether LACP is enabled or disabled on this port.
config port adminmode
This command enables or disables a port.
Default enable
Format config port adminmode <slot.port|all>
<enable|disable>
7-26 Switching Commands
Page 81

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config port linktrap
This command enables or disables link status traps by interface.
Note: This command is valid only when the Link Up/Down Flag is enabled (see “config trapflags
linkmode” on page 21).
Format config port linktrap < slot.port|all>
<enable|disable>
config port physicalmode
This command sets the speed and duplex setting for the interface.
Format config port physicalmode <slot.port|all>
<100h|100f|10h|10f>
Acceptable values are:
100h 100BASE-T half-duplex
100f 100BASE-T full duplex
10h 10BASE-T half duplex
10f 100BASE-T full duplex
config port lacpmode
This command enables or disables Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) on a port. The
possible values for <mode> are enable and disable. The default value is disable.
Format config port lacpmode <slot.port/all>
<enable/disable>
config port autoneg
This command enables or disables automatic negotiation on a port. The possible values for
<mode> are enable and disable. The default value is enable.
Format config port autoneg <slot.port/all> <enable/
disable>
Switching Commands 7-27
Page 82

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
show lag
This command displays an overview of all link aggregations (LAGs) on the switch.
Format show lag <logical slot.port|all>
Logical Slot.Port The logical slot and the logical port.
Lag Name The name of this lag. You may enter any string of up to 15 alpha-
numeric characters.
Link State Indicates whether the Link is up or down.
Admin Mode May be enabled or disabled by selecting the corresponding line
on the pull-down entry field. The factory default is enabled.
Link Trap Mode This object determines whether or not to send a trap when link
status changes. The factory default is enabled.
STP Mode The Spanning Tree Protocol Administrative Mode associated
with the port or lag. The possible values are:
Disable - Spanning tree is disabled for this port.
Enable - Spanning tree is enabled for this port.
Mbr Ports A listing of the ports that are members of this lag, in slot.port
notation. There can be a maximum of 8 ports assigned to a given
lag.
Port Speed
config lag create
This command configures a new LAG and generates a logical slot and port number for it. Display
this number using the “show lag” on page 28.
Note: Before including a port in a LAG, set the port physical mode. See “config port
physicalmode” on page 27.
Format config lag create <name>
config lag addport
This command adds one port to the LAG. The first interface is a logical slot and port number of a
configured LAG.
Note: Before adding a port to a LAG, set the physical mode of the port. See “config port
physicalmode” on page 27.
7-28 Switching Commands
Page 83

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Format config lag addport <logical slot.port>
<slot.port>
config lag deleteport
This command deletes one or more ports from the LAG. The first interface is a logical slot and port
number of a configured LAG, and the second interface is a valid slot and port number that is a
member of any LAG or all (to delete all ports in the specified LAG).
Format config lag deleteport <logical slot.port>
<slot.port|all>
config lag adminmode
This command enables or disables a LAG. The interface is a logical slot and port for a configured
LAG. The option all sets every configured LAG with the same administrative mode setting.
Format config lag adminmode <logical slot.port|all>
<enable|disable>
config lag linktrap
This command enables or disables link trap notifications for the LAG. The interface is a logical
slot and port for a configured LAG. The option all sets every configured LAG with the same
administrative mode setting.
Default enable
Format config lag linktrap <logical slot.port|all>
<enable|disable>
config lag name
This command defines a name for the LAG. The interface is a logical slot and port for a configured
LAG, and name is an alphanumeric string up to 15 characters. This command is used to modify the
name that was associated with the LAG when it was created.
Format config lag name <logical slot.port|all>
<name>
Switching Commands 7-29
Page 84

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config lag deletelag
This command deletes an existing lag from the configuration. The interface is a logical slot and
port for a configured LAG. The all option removes all configured LAGs.
Format config lags deletelag <logical
slot.port|all>
config lag stpmode
This command sets the STP mode for a specific LAG. This is the value specified for STP Mode on
the Port Configuration Menu. 802.1D mode is the default. The interface is a logical slot and port
for a configured LAG. The all option sets all configured LAGs with the same option.
Format config lag stpmode <logical slot.port|all>
<off|802.1d|fast>
The mode is one of the following:
802.1d IEEE 802.1D-compliant STP mode is used
fast Fast STP mode is used
off STP is turned off
show vlan summary
This command displays a list of all configured VLANs.
Format show vlan summary
VLAN ID There is a VLAN Identifier (VID) associated with each VLAN.
The range of the VLAN ID is 1 to 4094.
VLAN Name A string associated with this VLAN as a convenience. It can be
up to 16 alphanumeric characters long, including blanks. The
default is blank. VLAN ID 1 always has a name of `Default`. This
field is optional.
VLAN Type What type of VLAN this is. A VLAN can be the Default VLAN,
(VLAN ID = 1), a static VLAN, one that is configured and permanently defined, or a Dynamic VLAN, one that is created by
GVRP registration. In order to change a VLAN from Dynamic to
Static, select Static from the Vlan Type pull-down entry field.
Once the VLAN is selected, click on Submit. This will change the
VLAN type to Static.
7-30 Switching Commands
Page 85

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
show vlan detailed
This command displays detailed information, including interface information, for a specific
VLAN.
Format config vlan detailed <vlan id>, where the ID is a
valid VLAN identification number
VLAN ID There is a VLAN Identifier (VID) associated with each VLAN.
The range of the VLAN ID is 1 to 4094.
VLAN Name A string associated with this VLAN as a convenience. It can be
up to 16 alphanumeric characters long, including blanks. The
default is blank. VLAN ID 1 always has a name of `Default`. This
field is optional.
VLAN Type What type of VLAN this is. A VLAN can be the Default VLAN,
(VLAN ID = 1), a static VLAN, one that is configured and permanently defined, or a Dynamic VLAN, one that is created by
GVRP registration. In order to change a VLAN from Dynamic to
Static, select Static from the Vlan Type pull-down entry field.
Once the VLAN is selected, click on Submit. This will change the
VLAN type to Static.
Slot.Port Indicates by slot id and port number which port is controlled by
the fields on this line. It is possible to set the parameters for all
ports by using the selectors on the top line.
Current Determines the degree of participation of this port in this VLAN.
The permissible values are:
Include - This port is always a member of this VLAN. This is
equivalent to registration fixed in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
Exclude - This port is never a member of this VLAN. This is
equivalent to registration forbidden in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
Autodetect - Specifies to allow the port to be dynamically regis-
tered in this VLAN via GVRP. The port will not participate in this
VLAN unless a join request is received on this port. This is
equivalent to registration normal in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
Configured Determines the configured degree of participation of this port in
this VLAN. The permissible values are:
Include - This port is always a member of this VLAN. This is
equivalent to registration fixed in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
Exclude - This port is never a member of this VLAN. This is
equivalent to registration forbidden in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
Switching Commands 7-31
Page 86

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Autodetect - Specifies to allow the port to be dynamically registered in this VLAN via GVRP. The port will not participate in this
VLAN unless a join request is received on this port. This is
equivalent to registration normal in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
Tagging Select the tagging behavior for this port in this VLAN.
Tagged - specifies to transmit traffic for this VLAN as tagged
frames.
Untagged - specifies to transmit traffic for this VLAN as
untagged frames.
config vlan create
This command creates a new VLAN and assigns it an ID. The ID is a valid VLAN identification
number (ID 1 is reserved for the default VLAN) VLAN range is 2-4094.
Format config vlan create <2-4094>
config vlan delete
This command deletes an existing VLAN. The ID is a valid VLAN identification number (ID 1 is
reserved for the default VLAN) VLAN range is 2-4094.
Format config vlan delete <2-4094>
config vlan name
This command changes the name of a VLAN. The name is an
alphanumeric string of up to 16 characters, and the ID is a valid
VLAN identification number. ID range is 1-4094.
Default The name for VLAN ID 1 is always Default. The name for other
VLANs is defaulted to a blank string.
Format config vlan name <name> <2-4094>
config vlan makestatic
This command changes a dynamically created VLAN (one that is created by GVRP registration) to
a static VLAN (one that is permanently configured and defined). The ID is a valid VLAN
identification number. VLAN range is 2-4094.
7-32 Switching Commands
Page 87

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Format config vlan makestatic <2-4094>
config vlan participation
This command configures the degree of participation for a specific interface in a VLAN. The ID is
a valid VLAN identification number, and the interface is a valid interface number or all.
Format config vlan participation
<exclude|include|auto> <1-4094>
<slot.port|all>
Participation options are:
include The interface is always a member of this VLAN. This is equiva-
lent to registration fixed.
exclude The interface is never a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent
to registration forbidden.
auto The interface is dynamically registered in this VLAN by GVRP.
The interface will not participate in this VLAN unless a join
request is received on this interface. This is equivalent to registration normal.
config vlan port tagging
This command configures the tagging behavior for a specific interface in a VLAN. If tagging is
enabled, traffic is transmitted as tagged frames. If tagging is disabled, traffic is transmitted as
untagged frames. The ID is a valid VLAN identification number. The interface is a valid port
number or all.
Format config vlan port tagging <enable|disable>
<1-4094> <slot.port|all>
show vlan port
This command displays VLAN port information.
Format show vlan port <slot.port>
Slot.Port Indicates by slot id and port number which port is controlled by
the fields on this line. It is possible to set the parameters for all
ports by using the selectors on the top line.
Switching Commands 7-33
Page 88

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Port VLAN ID The VLAN ID that this port will assign to untagged frames or pri-
ority tagged frames received on this port. The value must be for
an existing VLAN. The factory default is 1.
Acceptable Frame Types Specifies the types of frames that may be received on this port.
The options are 'VLAN only' and 'Admit All'. When set to
'VLAN only', untagged frames or priority tagged frames received
on this port are discarded. When set to 'Admit All', untagged
frames or priority tagged frames received on this port are
accepted and assigned the value of the Port VLAN ID for this
port. With either option, VLAN tagged frames are forwarded in
accordance to the 802.1Q VLAN specification.
Ingress Filtering May be enabled or disabled by selecting the corresponding line
on the pull-down entry field. When enabled, the frame is discarded if this port is not a member of the VLAN with which this
frame is associated. In a tagged frame, the VLAN is identified by
the VLAN ID in the tag. In an untagged frame, the VLAN is the
Port VLAN ID specified for the port that received this frame.
When disabled, all frames are forwarded in accordance with the
802.1Q VLAN bridge specification. The factory default is disabled.
GVRP
config vlan port pvid
This command changes the VLAN ID per interface.
Default 1
Format config vlan port pvid <1-4094>
<slot.port|all>
config vlan port acceptframe
This command sets the frame acceptance mode per interface. For VLAN Only mode, untagged
frames or priority frames received on this interface are discarded. For Admit All mode, untagged
frames or priority frames received on this interface are accepted and assigned the value of the
interface VLAN ID for this port. With either option, VLAN tagged frames are forwarded in
accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Specification. VLAN ID range is 1-4094.
Default Admit All
7-34 Switching Commands
Page 89

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Format config vlan port acceptframe <all|vlan>
<slot.port|all>
config vlan port ingressfilter
This command enables or disables ingress filtering. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames received
with VLAN IDs that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving interface are admitted
and forwarded to ports that are members of that VLAN.
Default disable
Format config vlan port ingressfilter <enable|dis-
able> <slot.port|all>
show protocol
This command displays the Protocol-Based VLAN information for either the entire system, or for
the indicated Group.
Format show protocol detailed <groupid/all>
Group Name
This field displays the group name of an entry in the Protocolbased VLAN table.
Group ID This field displays the group identifier of the protocol group.
Protocol(s) This field indicates the type of protocol(s) for this group.
VLAN This field indicates the VLAN associated with this Protocol
Group.
Interface(s) This field lists the Slot.Port interface(s) that are associated with
this Protocol Group.
config protocol create
This command adds protocol-based VLAN group to the system. The <groupName> is a character
string of 1 to 16 characters. When it is created, the protocol group will be assigned a unique
number that will be used to identify the group in subsequent commands.
Format config protocol create <groupname>
config protocol delete
This command removes the protocol-based VLAN group that is iden tified by this <groupid>.
Format config protocol delete <groupid>
Switching Commands 7-35
Page 90

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config protocol protocol add
This command adds the <protocol> to the protocol-based VLAN identified by <groupid>. A group
may have more than one protocol associated with it. Each interface an d protocol combination can
only be associated with one group. If adding a protocol to a group causes any conflicts with
interfaces currently associated with the group, this command will fail and the protocol will not be
added to the group. The possible values for protocol are
Default none
Format config protocol protocol add <groupid> <protocol>
ip, arp, and ipx.
config protocol protocol remove
This command removes the <protocol> from this protocol-based VLAN group that is identified
by this
<groupid>. The possible values for protocol are ip, arp, and ipx.
Default none
Format config protocol protocol remove <groupid> <protocol>
config protocol vlan add
This command attaches a <vlan> to the protocol-based VLAN identified by <groupid>. A group
may only be associated with one VLAN at a time, however the VLAN association can be changed.
Default none
Format config protocol vlan add <groupid> <vlan>
config protocol vlan remove
This command removes the <vlan> from this protocol-based VLAN group that is identified by
this
<groupid>.
Default none
Format config protocol vlan remove <groupid> <vlan>
7-36 Switching Commands
Page 91

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config protocol interface add
This command adds the physica l <slot.port> interface to the protocol-based VLAN identified by
<groupid>. If <all> is selected, all physical interfaces will be added to this protocol group. A
group may have more than one interface associated with it. Each interface and protocol
combination can only be associated with one group. If adding an interface to a group ca uses any
conflicts with protocols currently associated with the group, this command will fail and the
interface(s) will not be added to the group.
Default none
Format config protocol interface add <groupid> <slot.port/
all>
config protocol interface remove
This command removes the <interface> from this protocol-based VLAN group that is identified
by this
<groupid>. If <all> is selected, all ports will be removed from this protocol group.
Default none
Format config protocol interface remove <groupid>
<slot.port/all>
show garp info
This command displays Generic Attributes Registration Protocol (GARP) information.
Format show garp info
GMRP Admin Mode
This displays the administrative mode of GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP) for the system.
GVRP Admin Mode This displays the administrative mode of GARP VLAN Registra-
tion Protocol (GVRP) for the system.
show garp interface
This command displays Generic Attributes Registration Protocol (GARP) information for one or
all interfaces.
Format show garp interface <slot.port/all>
Interface
Switching Commands 7-37
This displays the slot.port of the interface that this row in the
table describes.
Page 92

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Join Timer Specifies the interval between the transmission of GARP PDUs
registering (or re-registering) membership for an attribute. Current attributes are a VLAN or multicast group. There is an
instance of this timer on a per-Port, per-GARP participant basis.
Permissible values are 10 to 100 centiseconds (0.1 to 1.0 seconds). The factory default is 20 centiseconds (0.2 seconds). The
finest granularity of specification is 1 centisecond (0.01 seconds).
Leave Timer Specifies the period of time to wait after receiving an unregis-
tered request for an attribute before deleting the attribute. Current
attributes are a VLAN or multicast group. This may be considered a buffer time for another station to assert registration for the
same attribute in order to maintain uninterrupted service. There is
an instance of this timer on a per-Port, per-GARP participant
basis. Permissible values are 20 to 600 centiseconds (0.2 to 6.0
seconds). The factory default is 60 centiseconds (0.6 seconds).
The finest granularity of specification is 1 centisecond (0.01 seconds).
LeaveAll Timer This Leave All Time controls how frequently LeaveAll PDUs are
generated. A LeaveAll PDU indicates that all registrations will
shortly be deregistered. Participants will need to rejoin in order to
maintain registration. There is an instance of this timer on a perPort, per-GARP participant basis. The Leave All Period Timer is
set to a random value in the range of LeaveAllTime to
1.5*LeaveAllTime. Permissible values are 200 to 6000 centiseconds (2 to 60 seconds). The factory default is 1000 centiseconds
(10 seconds). The finest granularity of specification is 1 centisecond (0.01 seconds).
Port GMRP Mode Indicates the GMRP administrative mode for the port. It may be
enabled or disabled. If this parameter is disabled, Join Time,
Leave Time and Leave All Time have no effect. The factory
default is disabled.
Port GVRP Mode Indicates the GVRP administrative mode for the port. It may be
enabled or disabled. If this parameter is disabled, Join Time,
Leave Time and Leave All Time have no effect. The factory
default is disabled.
7-38 Switching Commands
Page 93

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config garp gmrp adminmode
This command enables or disables GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP) on the system.
The default value is disable.
Format config garp gmrp adminmode <enable/disable>
config garp gmrp interfacemode
This command enables or disables GARP Multicast Registration Protocol on a selected interface.
The <slot.port> parameter identifies the interface on which to configure the mode. If an interface
which has GARP enabled is enabled for routing or is enlisted as a member of a LAG, GARP
functionality will be disabled on that interface. GARP functionality will subsequently be reenabled if routing is disabled and LAG membership is removed from an interface that has GARP
enabled.
Default disable
Format config garp gmrp interfacemode <slot.port/all>
<enable/disable>
config garp gvrp adminmode
This command enables or disables GVRP.
Default disable
Format config garp gvrp adminmode <enable|disable>
config garp gvrp interfacemode
This command enables or disables GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol) for a specific
port. If GVRP is disabled, Join Time, Leave Time and Leave All Time have no effect.
Default disable
Format config garp gvrp interfacemode
<slot.port|all> <enable|disable>
Switching Commands 7-39
Page 94

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config garp jointimer
This command sets the GVRP join time per port and per GARP. Join time is the interval between
the transmission of GARP Protocol Data Units (PDUs) registering (or re-registering) membership
for a VLAN or multicast group.
This command has an effect only when GVRP is enabled. The time is from 10 to 100
(centiseconds)
Default 20 centiseconds (0.2 seconds)
Format config garp jointimer <slot.port/all> <10-
100>
config garp leavetimer
This command sets the GVRP leave time per port. Leave time is the time to wait after receiving an
unregister request for a VLAN or a multicast group before deleting the VLAN entry. This can be
considered a buffer time for another station to assert registration for the same attribute in order to
maintain uninterrupted service.time is 20 to 600 (centiseconds).
Note: This command has an effect only when GVRP is enabled.
Default 60 centiseconds (0.6 seconds)
Format config garp leavetimer <slot.port/all> <20-
600>
config garp leavealltimer
This command sets how frequently Leave All PDUs are generated per port. A Leave All PDU
indicates that all registrations will be unregistered. Participants would need to rejoin in order to
maintain registration. The value applies per port and per GARP participation. The time may range
from 200 to 6000 (centiseconds).
Note: This command has an effect only when GVRP is enabled.
Default 1000 centiseconds (10 seconds)
Format config garp leavealltimer <slot.port/all>
<200-6000>
7-40 Switching Commands
Page 95

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
show igmpsnooping
This command displays IGMP Snooping information. Configured information is displayed
whether or not IGMP Snooping is enabled. Status information is only displayed when IGMP
Snooping is enabled.
Format show igmpsnooping
Admin Mode This indicates whether or not IGMP Snooping is active on the
switch.
Query Interval Tim e This displays the IGMP Query Interval Time. This is the amount
of time a switch will wait for a report for a particular group on a
particular interface before it sends a query on that interface. This
value may be configured
Max Response Time This displays the amount of time the switch will wait after send-
ing a query on an interface because it did not receive a report for a
particular group on that interface. This value may be configured.
Multicast Router Present
Expiration Time If a query is not received on an interface within this amount of
time, the interface is removed from the list of interfaces with multicast routers attached. This value may be configured.
Interfaces Enabled for
IGMP Snooping This is the list of interfaces on which IGMP Snooping is enabled.
The following status values are only displayed when IGMP Snooping is enabled.
Multicast Control
Frame Count This displays the number of multicast control frames that are pro-
cessed by the CPU.
Data Frames Forwarded
by the CPU
This displays the number of data frames that are forwarded by the
CPU.
config igmpsnooping adminmode
This command enables or disables IGMP Snooping on the system. The default value is disable.
Format config igmpsnooping adminmode <enable/disable>
Switching Commands 7-41
Page 96

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
config igmpsnooping groupmembershipinterval
This command sets the IGMP Group Membership Interval time on the system. The Group
Membership Interval time is the amount of time in seconds that a switch will wait for a report from
a particular group on a particular interface before deleting the interface from the entry. This value
must be greater than the IGMP Maximum Response time value. The range is 1 to 3600 seconds.
Default 260 seconds
Format config igmpsnooping groupmembershipinterval <1-3600>
config igmpsnooping maxresponse
This command sets the IGMP Maximum Response time on the system. The Maximum Response
time is the amount of time in seconds that a switch will wait after sending a query on an interface
because it did not receive a report for a particular group in that interface. This value must be less
than the IGMP Query Interval time value. The range is 1 to 3600 seconds.
Default 10 seconds
Format config igmpsnooping maxresponse <1-3600>
config igmpsnooping mcrtrexpiretime
This command sets the Multicast Router Present Expiration time on the system. This is the amount
of time in seconds that a switch will wait for a query to be received on an interface before the
interface is removed from the list of interfaces with multicast routers attached. The range is 0 to
3600 seconds. A value of 0 indicates an infinite timeout, i.e. no expiration.
Default 0
Format config igmpsnooping mcrtrexpiretime <0-3600>
config igmpsnooping interface mode
This command enables or disables IGMP Snooping on a selected interface. The <slot.port/all>
parameter identifies the interface on which to configure the mode. If an interface which has IGMP
Snooping enabled is enabled for routing or is enlisted as a member of a LAG, IGMP Snooping
functionality will be disabled on that interface. IGMP Snooping functionality will subsequently be
re-enabled if routing is disabled or LAG membership is removed from an interface that has IGMP
Snooping enabled.
Default disable
7-42 Switching Commands
Page 97

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Format config igmpsnooping interface mode <slot.port/all>
<enable/disable>
show mfdb table
This command displays the Multicast Forwarding Database (MFDB) information. If the command
is entered with no parameter, the entire table is displayed. This is the same as entering the optional
all parameter. The user can display the table entry for one MAC Address by specifying the MAC
address a an optional parameter.
Format show mfdb table [macaddr/all]
Mac Address
Type This displays the type of the entry. S tatic entries are those th at are
Component The component that is responsible for this entry in the Multicast
Description The text description of this multicast table entry.
Interfaces The list of interfaces that are designated for forwarding (Fwd:)
Forwarding Interfaces The resultant forwarding list is derived from combining all the
A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and
or filtering information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for example
01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will be
displayed as 8 bytes. In an SVL system, the MAC address will be
displayed as 6 bytes.
configured by the end user. Dynamic entries are added to the
table as a result of a learning process or protocol.
Forwarding Database. Possible values are IGMP Snooping,
GMRP, and Static Filtering.
and filtering (Flt:).
component’s forwarding interfaces and removing the interfaces
that are listed as the static filtering interfaces.
show mfdb gmrp
This command displays the GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP) entries in the
Multicast Forwarding Database (MFDB) table.
Format show mfdb gmrp
Mac Address A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and
or filtering information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for example
01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will be
Switching Commands 7-43
Page 98

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
displayed as 8 bytes. In an SVL system, the MAC address will be
displayed as 6 bytes.
Type This displays the type of the entry. S tatic entries are those th at are
configured by the end user. Dynamic entries are added to the
table as a result of a learning process or protocol.
Description The text description of this multicast table entry.
Interfaces The list of interfaces that are designated for forwarding (Fwd:)
and filtering (Flt:).
show mfdb igmpsnooping
This command displays the IGMP Snooping entries in the Multicast Forwarding Database
(MFDB) table.
Format show mfdb igmpsnooping
Mac Address
Type This displays the type of the entry. S tatic entries are those th at are
Description The text description of this multicast table entry.
Interfaces The list of interfaces that are designated for forwarding (Fwd:)
A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and
or filtering information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for example
01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will be
displayed as 8 bytes. In an SVL system, the MAC address will be
displayed as 6 bytes.
configured by the end user. Dynamic entries are added to the
table as a result of a learning process or protocol.
and filtering (Flt:).
show mfdb staticfiltering
This command displays the Static Filtering entries in the Multicast Forwarding Database (MFDB)
table.
Format show mfdb staticfiltering
Mac Address
7-44 Switching Commands
A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and
or filtering information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for example
01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will be
displayed as 8 bytes. In an SVL system, the MAC address will be
displayed as 6 bytes.
Page 99

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Type This displays the type of the entry. S tatic entries are those th at are
configured by the end user. Dynamic entries are added to the
table as a result of a learning process or protocol.
Description The text description of this multicast table entry.
Interfaces The list of interfaces that are designated for forwarding (Fwd:)
and filtering (Flt:).
show mfdb stats
This command displays the Multicast Forwarding Database (MFDB) statistics.
Format show mfdb stats
Total Entries
Most MFDB Entries
Ever Used This displays the largest number of entries that have been present
Current Entries This displays the current number of entries in the Multicast For-
This displays the total number of entries that can possibly be in
the Multicast Forwarding Database table.
in the Multicast Forwarding Database table. This value is also
known as the MFDB high-water mark.
warding Database table.
show mirroring
This command displays the Port Mirroring information for the system.
Format show mirroring
Port Mirroring Mode Indicates whether the Port Mirroring feature is enabled or dis-
abled. The possible values are enable and disable.
Probe Port Slot.Port Is the slot.port that is configured as the probe port. If this value
has not been configured, 'Not Configured' will be displayed.
Mirrored Port Slot.Port Is the slot.port that is configured as the mirrored port. If this
value has not been configured, 'Not Configured' will be displayed.
config mirroring create
This command configures a probe port and a mirrored port for Port Mirroring. The first slot.port is
the probe port and the second slot.port is the mirrored port. If this command is executed while port
mirroring is enabled, it will have the effect of changing the probe and mirrored port values.
Switching Commands 7-45
Page 100

7000 Series L3 Managed Switch Reference Manual for Software v2.0
Format config mirroring create <slot.port>
<slot.port>
config mirroring delete
This command removes the port mirroring designation from both the probe port and the mirrored
port and removes the probe port from all VLANs. The port must be manually re-added to any
desired VLANs.
Format config mirroring delete
config mirroring mode
This command configures the Port Mirroring mode. The possible values are enable and disable.
The default value is disable. The probe and mirrored ports must be configured before port
mirroring can be enabled. If enabled, the probe port will mirror all traffic received and transmitted
on the physical mirrored port. It is not necessary to disable port mirroring before modifying the
probe and mirrored ports.
Default disable
Format config mirroring mode <enable|disable>
show macfilter
This command displays the Static MAC Filtering information for all Static MAC Filters. If <all> is
selected, all the Static MAC Filters in the system are displayed. If a macaddr is entered, a vlan
must also be entered and the Static MAC Filter information will be displayed only for that MAC
address and VLAN.
Format show macfilter <macaddr vlan/all>
MAC Address
VLAN ID Is the VLAN ID of the static MAC filter entry.
Source Port(s) Indicates the source port filter set's slot and port(s).
Destination Port(s) Indicates the destination port filter set's slot and port(s).
7-46 Switching Commands
Is the MAC Address of the static MAC filter entry.
 Loading...
Loading...