Page 1

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Software Administration Manual
350 East Plumeria Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
USA
October 2012
202-10484-05
v2.0
Page 2
GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
©2012 All rights reserved
No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated
into any language in any form or by any means without the written permission of NETGEAR, Inc.
NETGEAR, the NETGEAR logo, and Connect with Innovation are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of
NETGEAR, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. Information is subject to change
without notice. Other brand and product names are registered trademarks or trademarks of their respective
holders. ©2012 All rights reserved.
Technical Support
Thank you for choosing NETGEAR. To register your product, get the latest product updates, get support online, or
for more information about the topics covered in this manual, visit the Support website at
http://support.netgear.com
Phone (US & Canada only): 1-888-NETGEAR
Phone (Other Countries): Check the list of phone numbers at
http://support.netgear.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/984
Statement of Conditions
To improve internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, NETGEAR reserves the right to make changes
to the products described in this document without notice. NETGEAR does not assume any liability that may occur
due to the use, or application of, the product(s) or circuit layout(s) described herein.
Revision History
Publication Part Number Version Publish Date Comments
202-10484-05 v2.0 October 2012 Hardware/Software
Updates
202-10484-03 v1.0 November 2010 First publication
2
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 Switch Information and Setup
GS716T and GS724T Smart Switch Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Switch Management Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Connecting the Switch to the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Switch Discovery in a Network with a DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Switch Discovery in a Network without a DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Network Settings Configuration on the Administrative System . . . . . . . . .15
Web Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Smart Control Center Utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Network Utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Configuration Upload and Download . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Firmware Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Viewing and Managing Tasks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
User Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Web Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
SNMP Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Interface Naming Convention . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Chapter 2 System Information Features
Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
System Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
IP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
IPv6 Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
IPv6 Network Neighbor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Denial of Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
DNS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Green Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
License . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Show License . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
License Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
SNMPV1/V2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Trap Flags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
SNMP v3 User Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
LLDP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
LLDP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
LLDP Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
LLDP-MED Network Policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
3
Page 4

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
LLDP-MED Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Local Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Neighbors Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Services — DHCP Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
DHCP Filtering Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Interface Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Chapter 3 Switching Features
Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Port Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Flow Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Link Aggregation Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
LAG Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
LAG Membership . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
LACP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
LACP Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
VLAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
VLAN Membership Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Port VLAN ID Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Voice VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Voice VLAN Properties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Voice VLAN Port Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95
Voice VLAN OUI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Auto-VoIP Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Spanning Tree Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
STP Switch Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
CST Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
CST Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
CST Port Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Rapid STP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
MST Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
MST Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
STP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Multicast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Auto-Video Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .112
IGMP Snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
IGMP Snooping Querier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Address Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
MAC Address Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .128
Dynamic Address Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Static MAC Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .131
Multiple Registration Protocol Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
MRP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
MRP Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
MMRP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
MSRP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
4
Page 5

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
MSRP Reservation Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .139
Qav Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .141
MSRP Streams Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
802.1AS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
802.1AS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .145
802.1AS Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .147
802.1AS Statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .149
Chapter 4 Quality of Service Features
Class of Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Basic CoS Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .152
CoS Interface Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .153
Interface Queue Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .155
802.1p to Queue Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .156
DSCP to Queue Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .158
Differentiated Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .159
Defining DiffServ. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .159
DiffServ Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .160
Class Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .161
IPv6 Class Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .164
Policy Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .167
Service Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .170
Service Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .171
Chapter 5 Device Security
Management Security Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Change Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .174
RADIUS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175
Configuring TACACS+ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Authentication List Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Configuring Management Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
HTTP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Secure HTTP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .187
Certificate Download. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .188
Access Profile Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .190
Access Rule Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .192
Port Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
802.1X Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Port Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .195
Port Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .198
Traffic Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .200
MAC Filter Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .200
MAC Filter Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .202
Storm Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .203
Port Security Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .204
Port Security Interface Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .205
Security MAC Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .207
5
Page 6

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Protected Ports Membership . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
Configuring Access Control Lists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
ACL Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .210
MAC ACL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
MAC Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .212
MAC Binding Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
MAC Binding Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
IP ACL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
IP Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
IP Extended Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
IPv6 ACL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .222
IPv6 Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
IP Binding Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
IP Binding Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
Chapter 6 Monitoring the System
Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
Switch Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
Port Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
Port Detailed Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .233
EAP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
System Logs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
Memory Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
FLASH Log Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 244
Server Log Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
Trap Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .248
Event Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
Port Mirroring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
Multiple Port Mirroring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .250
Chapter 7 Maintenance
Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
Device Reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
Factory Default . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 254
Upload File From Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
TFTP File Upload . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .255
HTTP File Upload . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
Download File To Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
TFTP File Download. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
HTTP File Download . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .260
File Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
Dual Image Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
Dual Image Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 263
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
Ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .264
Ping IPv6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 266
Traceroute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267
6
Page 7

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Chapter 8 Help
Online Help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .269
User Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .270
Registration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .271
Appendix A Hardware Specifications and Default Values
GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches Specifications . . . . . . . . . 273
GS716T Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
GS724T Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
GS716T and GS724T Switch Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .274
GS716T and GS724T Switch Features and Defaults. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
Port Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .274
Traffic Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .275
Quality Of Service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .275
Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .275
System Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .276
Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .276
Other Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .277
Appendix B Configuration Examples
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 279
VLAN Example Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 281
Access Control Lists (ACLs). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
MAC ACL Example Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .282
Standard IP ACL Example Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .284
Differentiated Services (DiffServ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 285
Class. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .286
DiffServ Traffic Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .286
Creating Policies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .287
DiffServ Example Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .288
802.1X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290
802.1X Example Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
MSTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
MSTP Example Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .295
Appendix C Notification of Compliance
Index
7
Page 8

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
8
Page 9

1. Switch Information and Setup
The NETGEAR® GS716T and GS724T Smart Switch Software Administration Manual describes
how to configure and operate the GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches by using the
Web-based graphical user interface (GUI). This manual describes the software configuration
procedures and explains the options available within those procedures.
Document Organization
The GS716Tv2 and GS724Tv3 Software Administration Manual contains the following
chapters:
• Chapter 1, Switch Information and Setup, contains information about performing the
initial system configuration and accessing the user interface.
• Chapter 2, System Information Features, describes how to configure administrative
features such as SNMP, DHCP, and port information.
• Chapter 3, Switching Features, describes how to manage and monitor the layer 2
switching features.
• Chapter 4, Quality of Service Features, describes how to manage the Access Control
Lists (ACLs), and how to configure Differentiated Services and Class of Service features.
• Chapter 5, Device Security, contains information about configuring switch security
information such as port access control and RADIUS server settings.
• Chapter 6, Monitoring the System, describes how to view a variety of information about
the switch and its ports, and to configure how the switch monitors events.
• Chapter 7, Maintenance, describes features to help you manage the switch.
• Chapter 8, Help, describes how to access Online Help resources for the switch.
• Appendix A, Hardware Specifications and Default Values, contains hardware
specifications and default values on the GS716T and GS724T Smart Switches.
• Appendix B, Configuration Examples, contains examples of how to configure various
features on the GS716T and GS724T Smart Switches, such as VLANs and ACLs.
• Appendix C, Notification of Compliance contains regulatory information about the
GS716T and GS724T switch.
1
9
Page 10

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Note: Refer to the release notes for the GS716T and GS724T Gigabit
Smart Switches for information about issues and workarounds.
GS716T and GS724T Smart Switch Setup
This chapter provides an overview of starting your NETGEAR GS716T and GS724T Smart
Switch and accessing the user interface. It also leads you through the steps to use the Smart
Control Center utility. This chapter contains the following sections:
• Switch Management Interface on page 10
• Connecting the Switch to the Network on page 11
• Switch Discovery in a Network with a DHCP Server on page 12
• Switch Discovery in a Network without a DHCP Server on page 14
• Network Settings Configuration on the Administrative System on page 15
• Web Access on page 16
• Smart Control Center Utilities on page 17
• User Interfaces on page 23
• Interface Naming Convention on page 29
Switch Management Interface
The NETGEAR GS716T and GS724T Smart Switches contains an embedded Web server
and management software for managing and monitoring switch functions. The GS716T and
GS724T functions as a simple switch without the management software. However, you can
use the management software to configure more advanced features that can improve switch
efficiency and overall network performance.
Web-based management lets you monitor, configure, and control your switch remotely using
a standard Web browser instead of using expensive and complicated SNMP software
products. From your Web browser, you can monitor the performance of your switch and
optimize its configuration for your network. You can configure all switch features, such as
VLANs, QoS, and ACLs by using the Web-based management interface.
NETGEAR provides the Smart Control Center utility with this product. This program runs
®
under Microsoft
that discovers the switches on your network segment (L2 broadcast domain). When you
power up your switch for the first time, use the Smart Control Center to discover the switch
and view the network information that has been automatically assigned to the switch by a
DHCP server; or, if no DHCP server is present on the network, use the Smart Control Center
to discover the switch and assign static network information.
Windows® XP, Windows 2000, or Windows Vista® and provides a front end
10
Page 11

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
In addition to enabling NETGEAR switch discovery, the Smart Control Center provides
several utilities to help you maintain the NETGEAR switches on your network, such as
password management, firmware upgrade, and configuration file backup. For more
information, see Smart Control Center Utilities on page 17.
Connecting the Switch to the Network
To enable remote management of the switch through a Web browser or SNMP, you must
connect the switch to the network and configure it with network information (an IP address,
subnet mask, and default gateway). The switch has a default IP address of 192.168.0.239
and a default subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
Use one of the following three methods to change the default network information on the
switch:
• Dynamic assignment through DHCP—DHCP is enabled by default on the switch. If you
connect the switch to a network with a DHCP server, the switch obtains its network
information automatically. You can use the Smart Control Center to discover the
automatically-assigned network information. For more information, see Switch Discovery
in a Network with a DHCP Server on page 12.
• Static assignment through the Smart Control Center—If you connect the switch to a
network that does not have a DHCP server, you can use the Smart Control Center to
assign a static IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. For more information, see
Switch Discovery in a Network without a DHCP Server on page 14.
• Static assignment by connecting from a local host—If you do not want to use the Smart
Control Center to assign a static address, you can connect to the switch from a host
(administrative system) in the 192.168.0.0/24 network and change the settings by using
the Web-based management interface on the switch. For information about how to set
the IP address on the administrative system so it is in the same subnet as the default IP
address of the switch, see Network Settings Configuration on the Administrative System
on page 15.
11
Page 12

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Switch Discovery in a Network with a DHCP Server
This section describes how to set up your switch in a network that has a DHCP server. The
DHCP client on the switch is enabled by default. When you connect it to your network, the
DHCP server will automatically assign an IP address to your switch. Use the Smart Control
Center to discover the IP address automatically assigned to the switch.
To install the switch in a network with a DHCP server, use the following steps:
1. Connect the switch to a network with a DHCP server.
2. Power on the switch by connecting its power cord.
3. Install the Smart Control Center on your computer.
4. Start the Smart Control Center.
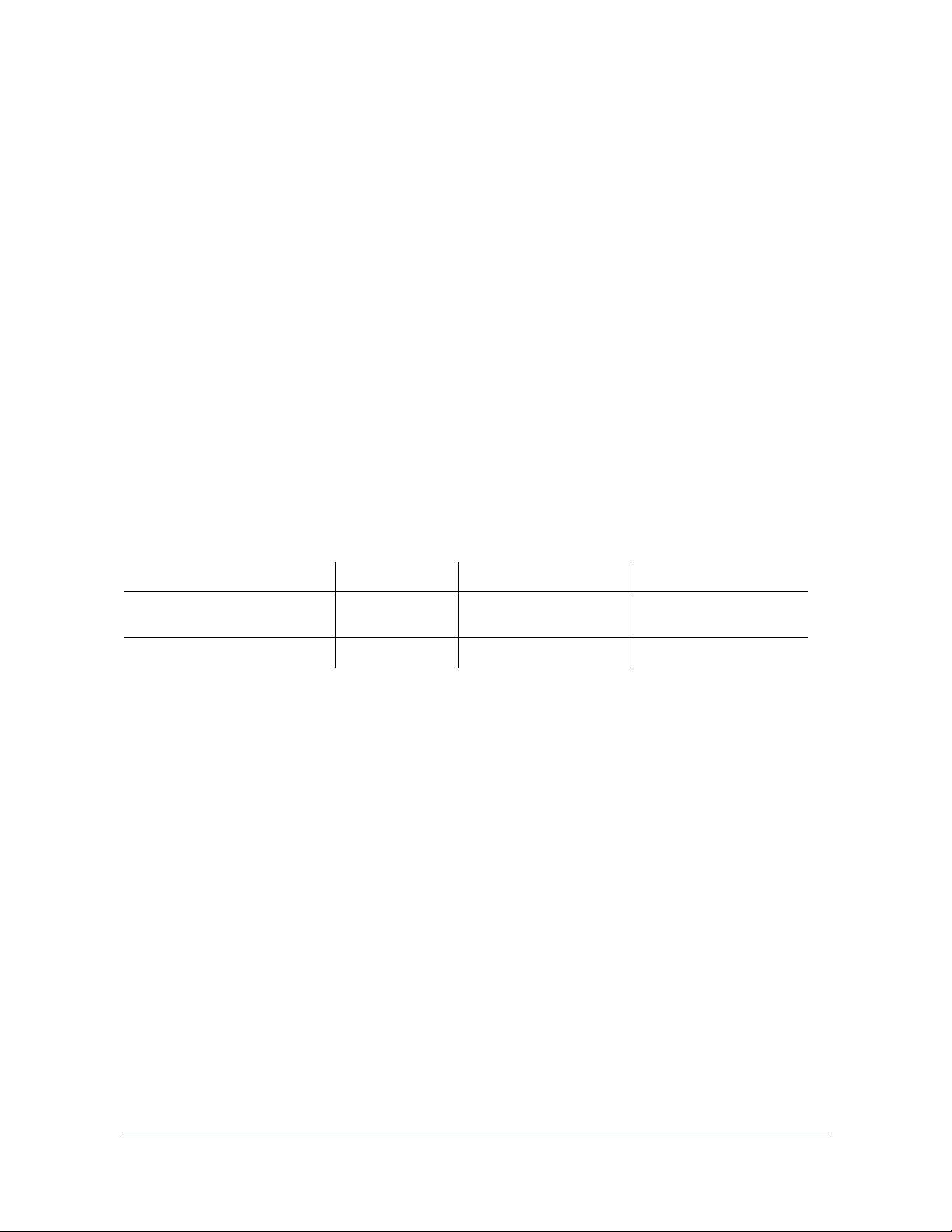
5. Click Discover for the Smart Control Center to find your switch. You should see a screen
similar to the one shown in the following figure.
Figure 1. Smart Switch Discovery
12
Page 13
GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
6. Make a note of the displayed IP address assigned by the DHCP server. You will need this
value to access the switch directly from a Web browser (without using the Smart Control
Center).
7. Select your switch by clicking the line that displays the switch, then click the
Web Browser Access button. The Smart Control Center displays a login window.
Use your Web browser to manage your switch. The default password is password. Then
use this page to proceed to management of the switch covered in Web Interface on
page 23.
13
Page 14
GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Switch Discovery in a Network without a DHCP Server
This section describes how to use the Smart Control Center to set up your switch in a
network without a DHCP server. If your network has no DHCP service, you must assign a
static IP address to your switch. If you choose, you can assign it a static IP address, even if
your network has DHCP service.
To assign a static IP address:
1. Connect the switch to your existing network.
2. Power on the switch by connecting its power cord.
3. Install the Smart Control Center on your computer.
4. Start the Smart Control Center.
5. Click Discover for the Smart Control Center to find your GS716T and GS724T switch. The
utility broadcasts Layer 2 discovery packets within the broadcast domain to discover the
switch. You should see a screen similar to Figure 1 on page 12.
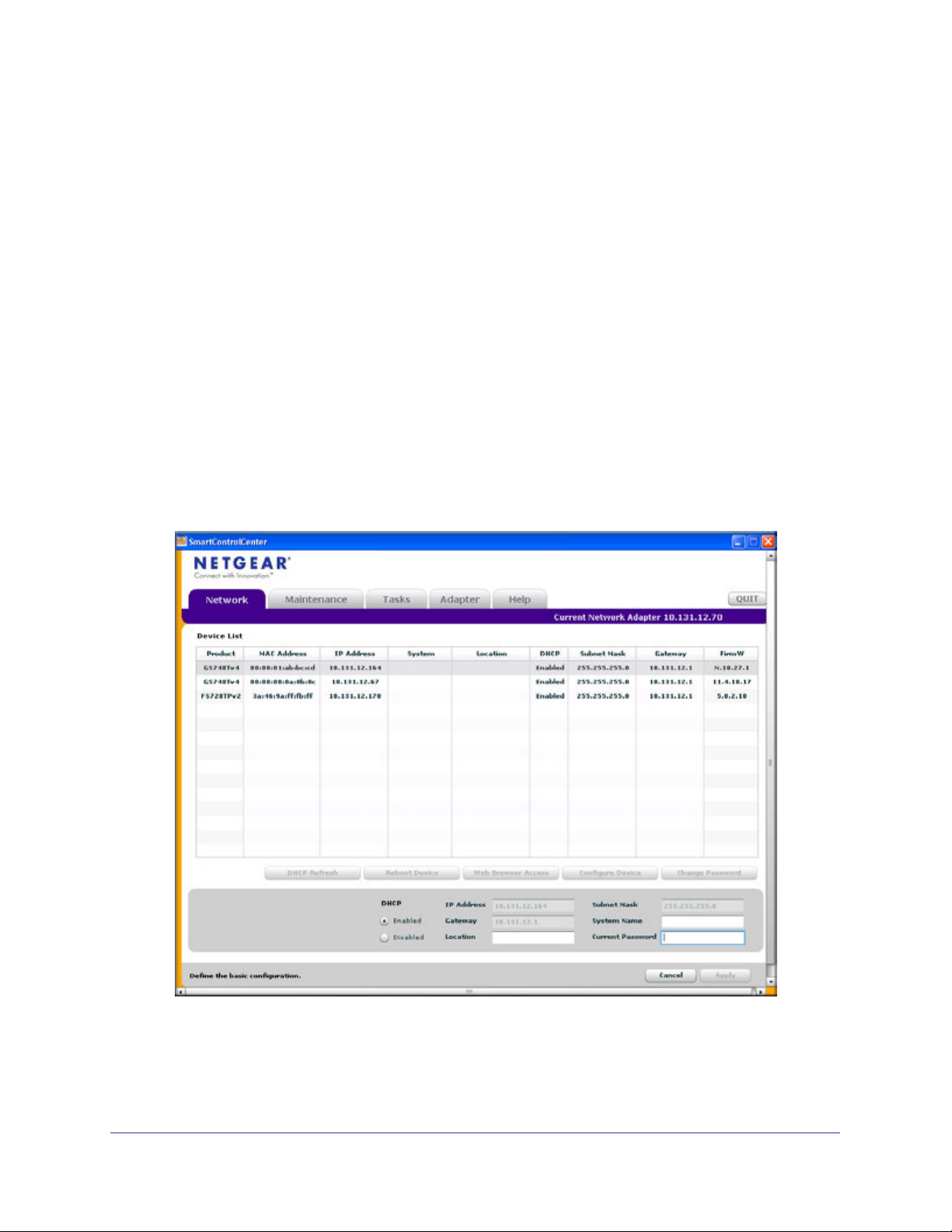
6. Select the switch, then click Configure Device. The page expands to display additional
.
fields at the bottom of the page, as the following figure shows.
7. Choose the Disabled radio button to disable DHCP.
14
Page 15
GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
8. Enter the static switch IP address, gateway IP address, and subnet mask for the switch, and
then type your password.
Tip: You must enter the current password every time you use the Smart
Control Center to update the switch setting. The default password is
password.
9. Click Apply to configure the switch with the network settings.
Please ensure that your PC and the switch are in the same subnet. Make a note of these
settings for later use.
Network Settings Configuration on the Administrative System
If you choose not to use the Smart Control Center to configure the network information on the
switch, you can connect directly to the switch from an administrative system, such as a PC or
laptop computer. The IP address of the administrative system must be in the same subnet as
the default IP address on the switch. For most networks, this means you must change the IP
address of the administrative system to be on the same subnet as the default IP address of
the switch (192.168.0.239).
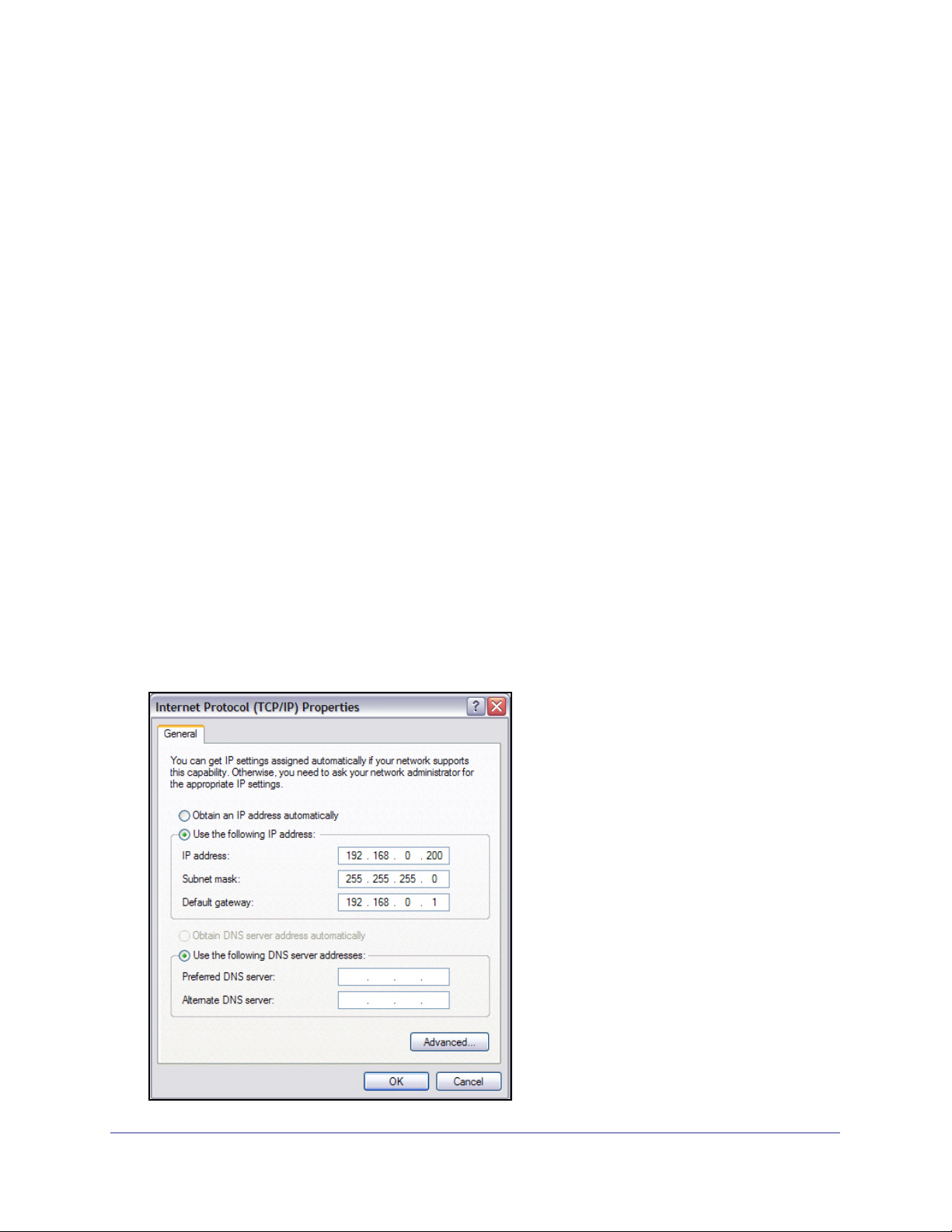
®
To change the IP address on an administrative system running a Microsoft
operating system, open the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) properties screen that you access
from the Local Area Connection properties, as shown in the following figure. You need
Windows Administrator privileges to change these settings.
Windows®
15
Page 16

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
WARNING:
When you change the IP address of your administrative system,
you will loose your connection to the rest of the network. Be sure
to write down your current network address settings before you
change them.
To modify the network settings on your administrative system:
1. On your PC, access the MS Windows operating system TCP/IP Properties.
2. Set the IP address of the administrative system to an address in the 192.168.0.0 network,
such as 192.168.0.200. The IP address must be different from that of the switch but within
the same subnet.
3. Click OK.
To configure a static address on the switch:
1. Use a straight-through cable to connect the Ethernet port on the administrative system
directly to any port on the GS716T and GS724T.
2. Open a Web browser on your PC and connect to the management interface as described in
Web Access on page 16.
3. Change the network settings on the switch to match those of your network (this procedure is
described in IP Configuration on page 33).
After you change the network settings on the switch, return the network configuration on your
administrative system to the original settings.
Web Access
To access the GS716T and GS724T management interface, use one of the following
methods:
• From the Smart Control Center, select the switch and click Web Browser Access.
• Open a Web browser and enter the IP address of the switch in the address field.
You must be able to ping the IP address of the GS716T and GS724T management interface
from your administrative system for Web access to be available. If you used the Smart
Control Center to set up the IP address and subnet mask, either with or without a DHCP
server, use that IP address in the address field of your Web browser. If you did not change
the IP address of the switch from the default value, enter 192.168.0.239 into the address
field.
16
Page 17

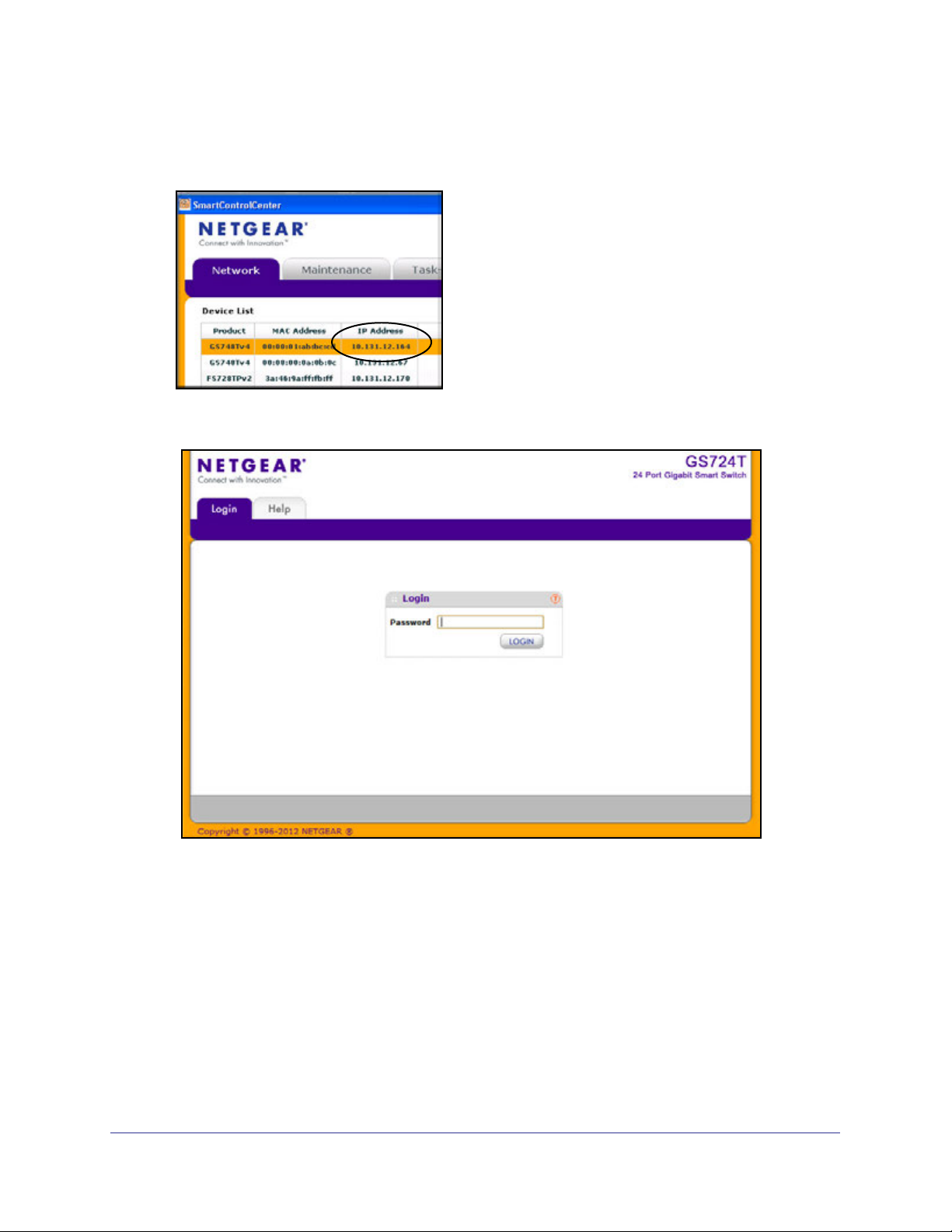
GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Clicking Web Browser Access on the Smart Control Center or accessing the switch directly
from your Web browser displays the login screen shown in the following figure.
Figure 2. Login Screen
Smart Control Center Utilities
In addition to device discovery and network address assignment, the Smart Control Center
includes several maintenance features. This section describes the following Smart Control
Center utilities:
• Network Utilities on page 17
• Configuration Upload and Download on page 19
• Firmware Upgrade on page 20
• Viewing and Managing Tasks on page 22
Network Utilities
From the Network tab, you can perform the following functions:
• DHCP Refresh—Forces the switch to release the current bindings and request new
address information from the DHCP server.
• Reboot Device—Reboots the selected device.
• Web Browser Access—Launches a Web browser and connects to the management
interface for the selected device.
17
Page 18

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
• Configure Device—Allows you to modify network information for the switch, including
the IP address, DHCP client mode, system name, and location. For more information
about this feature, see Configuring the Device .
• Change Password—Allows you to set a new password for the device. For more
information about this feature, see Changing the Switch Password .
Configuring the Device
To modify switch information:
1. Select the switch.
2. Click Configure Device. Additional fields appear on the screen.
3. To assign or update a static IP address, default gateway, or subnet mask, disable the DHCP
client and enter the new information. You can also specify a system name and location for
the switch.
4. Type the password in the Current Password field. You cannot apply the changes without a
valid switch password. The default password for the switch is password.
5. Click Apply to update the switch with the changes to the network information.
Changing the Switch Password
1. Select the switch.
2. Click Change Password. Additional fields appear on the screen.
3. Type the switch password in the Current Password field. The default password for the
switch is password.
4. Type the new password in the New Password and Confirm Password fields. The
password can contain up to 20 ASCII characters.
Click Apply to update the switch with the new password.
18
Page 19

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Configuration Upload and Download
When you make changes to the switch, the configuration information is stored in a file on the
switch. You can backup the configuration by uploading the configuration file from the switch
to an administrative system. You can download a saved configuration file from the
administrative system to the switch. The configuration file you download to the switch
overwrites the running configuration on the switch.
Configuration upload and download is useful if you want to save a copy of the current switch
configuration (Upload Configuration) before you make changes. If you do not like the
changes, you can use the Download Configuration option to restore the switch to the settings
in the saved configuration file.
To save a copy of the current switch configuration on your administrative system:
1. Click the Maintenance tab and select the device with the configuration to save.
2. Click Upload Configuration.
3. From the Browse for Folder window that appears, navigate to and select the folder where
you want to store the configuration file.
4. Click OK.
5. Enter the switch password and click Apply.
The file is uploaded to the administrative computer as a *.cfg file. You can open it and
view the contents with a text editor.
19
Page 20
GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To restore the configuration to a previously saved version:
1. Click the Maintenance tab and select the device with the configuration to restore.
2. Click Download Configuration.
3. From the Select a Configuration window that appears, navigate to and select the
configuration file to download to the switch.
4. Click Open.
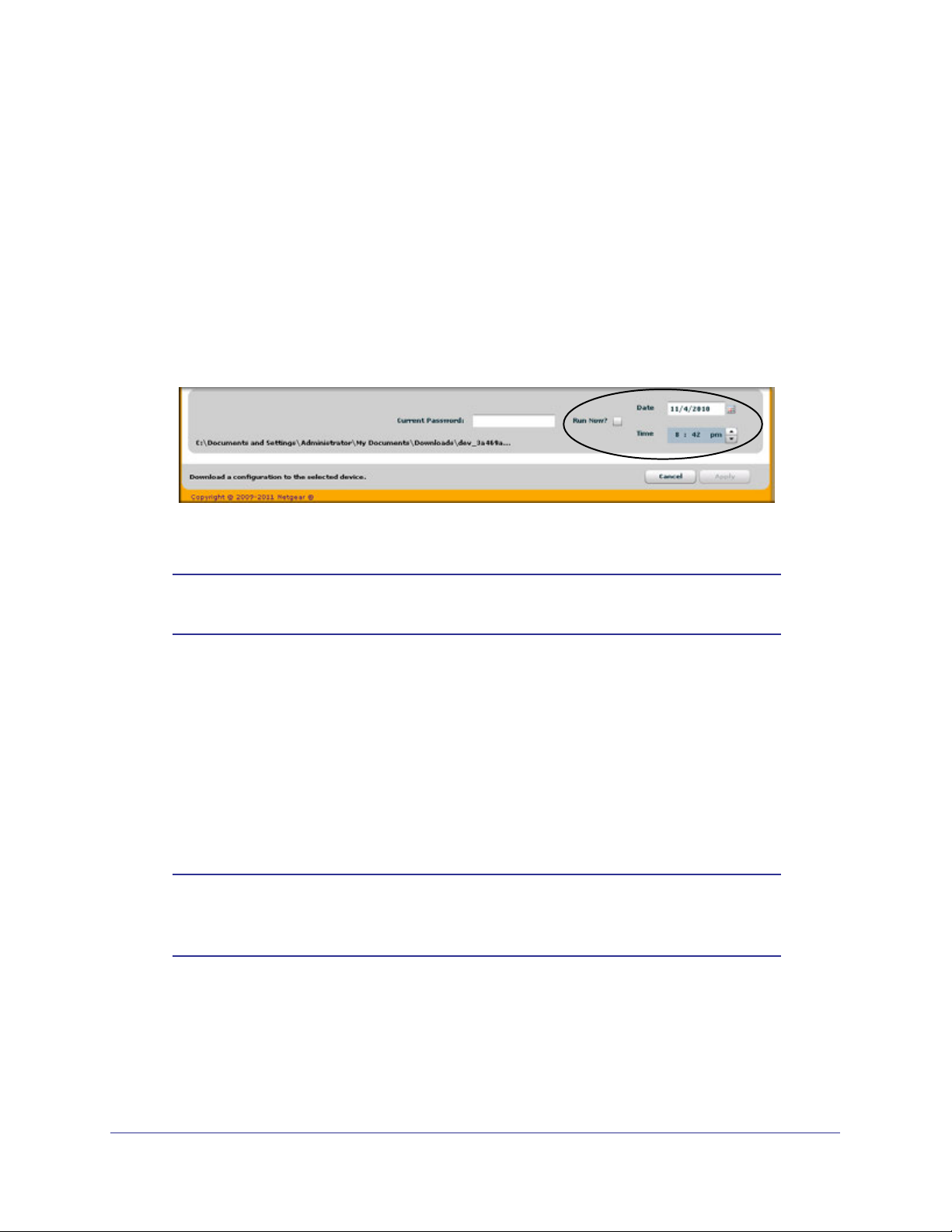
Optionally, you can schedule a different date and time to download the configuration file.
To delay the download process, clear the Run Now? check box and enter a date and
time to complete the download.
5. Enter the switch password and click Apply to begin the download process.
Note: Click the Tasks tab to view status information about the
configuration download.
Firmware Upgrade
The application software for the GS716T and GS724T Smart Switches is upgradable,
enabling your switch to take advantage of improvements and additional features as they
become available. The upgrade procedure and the required equipment are described in this
section. This procedure assumes that you have downloaded or otherwise obtained the
firmware upgrade and that you have it available as a binary file on your computer. This
procedure uses the TFTP protocol to implement the transfer from computer to switch.
Note: You can also upgrade the firmware using the TFTP Download and
HTTP Download features mentioned in this book. See HTTP File
Upload on page 256.
To upgrade your firmware:
1. Click the Maintenance tab, and then click the Firmware link directly below the tabs (see
Figure 1 on page 12).
2. Select the switch to upgrade and click Download Firmware.
20
Page 21

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
By default, the firmware is downloaded to primary storage and will be become the active
image after the download completes and the switch reboots. To download firmware to use
as a backup image, select the Secondary Storage option. To prevent the switch from
using the downloaded firmware as the active image, make sure the Run this FW after
download option is clear.
Note: NETGEAR recommends that you download the same image as the
primary and secondary image for redundancy.
3. From the Select new firmware window that appears, navigate to and select the firmware
image to download to the switch.
4. Click Open.
You can choose to schedule a later time to complete the download and installation by
clearing the Run Now? option and selecting a date and time to perform the firmware
download and installation. The scheduled firmware download appears in the Tasks list.
5. Enter the switch password to continue downloading the firmware.
6. Click Apply to download the firmware and upgrade the switch with the new image.
7. When the process is complete, the switch automatically reboots.
Note: Click the Tasks tab to view status information about the firmware
upgrade.
WARNING:
It is important that you do not power-off the administrative system
or the switch while the firmware upgrade is in progress.
21
Page 22
GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
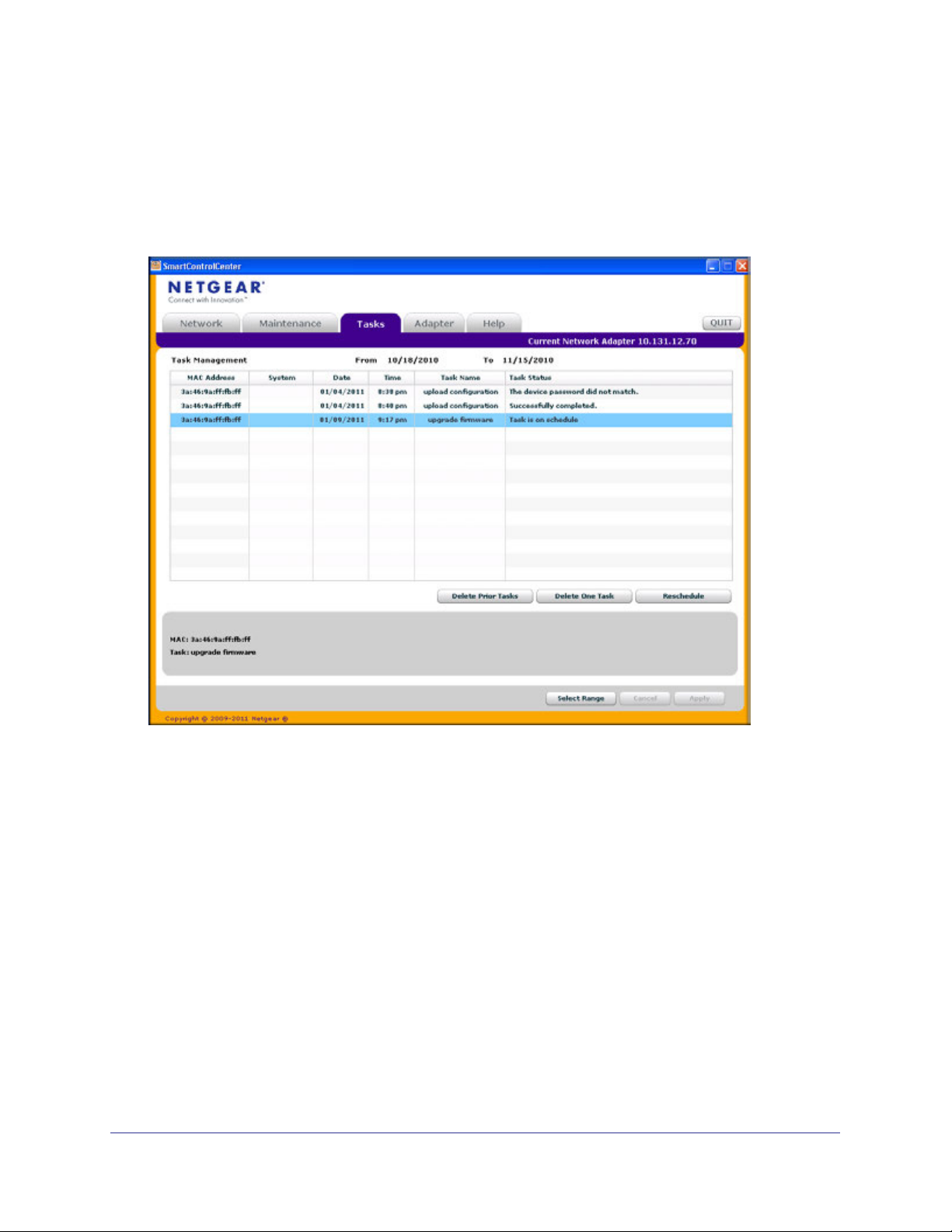
Viewing and Managing Tasks
From the Tasks tab, you can view information about configuration downloads and firmware
upgrades that have already occurred, are in progress, or are scheduled to take place at a
later time. You can also delete or reschedule selected tasks. Figure 3 shows the Tasks page.
Figure 3. Tasks Page
The following list describes the command buttons that are specific to the Tasks page:
• Delete Task—Remove a completed or schedule task from the list.
• Reschedule—Change the scheduled date and time for a pending firmware upgrade.
• Select Range—Select all tasks that occurred or are scheduled to occur within a certain
period of time.
22
Page 23

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
User Interfaces
The GS716T and GS724T Smart Switches software includes a set of comprehensive
management functions for configuring and monitoring the system by using one of the
following methods:
• Web user interface
• Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Each of the standards-based management methods allows you to configure and monitor the
components of the GS716T and GS724T Smart Switches software. The method you use to
manage the system depends on your network size and requirements, and on your
preference.
The GS716Tv2 and GS724Tv3 Software Administration Manual describes how to use the
Web-based interface to manage and monitor the system.
Web Interface
To access the switch by using a Web browser, the browser must meet the following software
requirements:
• HTML version 4.0, or later
• HTTP version 1.1, or later
• Java Runtime Environment 1.6 or later
Use the following procedures to log on to the Web interface:
1. Open a Web browser and enter the IP address of the switch in the Web browser
address field.
2. The factory default password is password. Type the password into the field on the login
screen, as shown in Figure 2 on page 17, and then click Login. Passwords are case
sensitive.
3. After the system authenticates you, the System Information page displays.
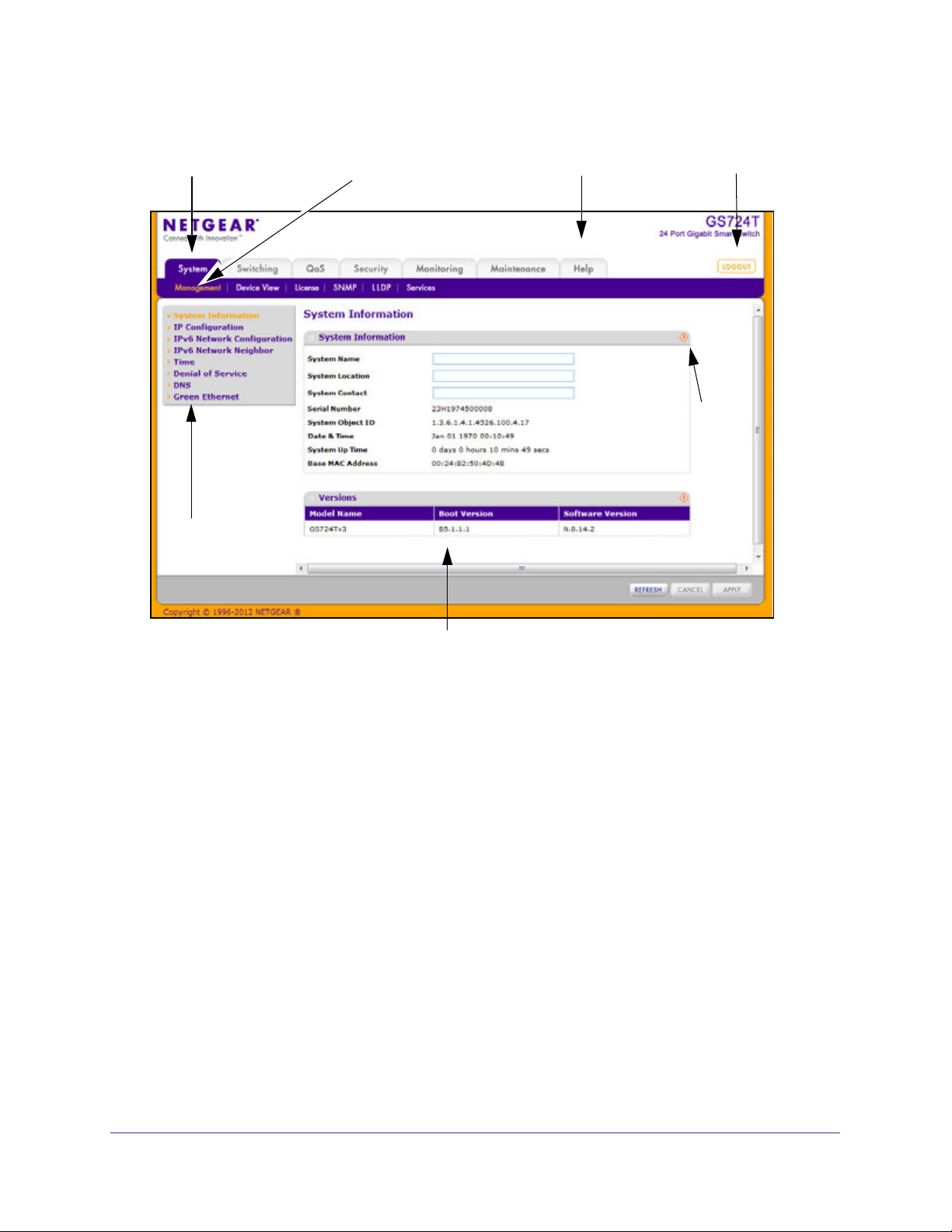
Figure 4 on page 24 shows the layout of the GS716T and GS724T switch Web interface.
23
Page 24
GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Navigation Tab Feature Link Logout Button
Page Menu
Help Link
Help
Page
Configuration and Status and Options
Figure 4. Administrative Page Layout
Navigation Tabs, Feature Links, and Page Menu
The navigation tabs along the top of the Web interface give you quick access to the various
switch functions. The tabs are always available and remain constant, regardless of which
feature you configure.
When you select a tab, the features for that tab appear as links directly under the tabs. The
feature links in the blue bar change according to the navigation tab that is selected.
The configuration pages for each feature are available as links in the page menu on the left
side of the page. Some items in the menu expand to reveal multiple configuration pages, as
Figure 5 on page 25 shows. When you click a menu item that includes multiple configuration
pages, the item becomes preceded by a down arrow symbol and expands to display the
additional pages.
24
Page 25

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Page Link
Configuration
Pages
Figure 5. Menu Hierarchy
Configuration and Status Options
The area directly under the feature links and to the right of the page menu displays the
configuration information or status for the page you select. On pages that contain
configuration options, you can input information into fields or select options from drop-down
menus.
Each page contains access to the HTML-based help that explains the fields and
configuration options for the page. Each page also contains command buttons.
The following table shows the command buttons that are used throughout the pages in the
Web interface:
Button Function
Add Clicking Add adds the new item configured in the heading row of a table.
Apply Clicking the Apply button sends the updated configuration to the switch. Configuration
changes take effect immediately.
Cancel Clicking Cancel cancels the configuration on the screen and resets the data on the screen
to the latest value of the switch.
Delete Clicking Delete removes the selected item.
Refresh Clicking the Refresh button refreshes the page with the latest information from the device.
Logout Clicking the Logout button ends the session.
25
Page 26

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Device View
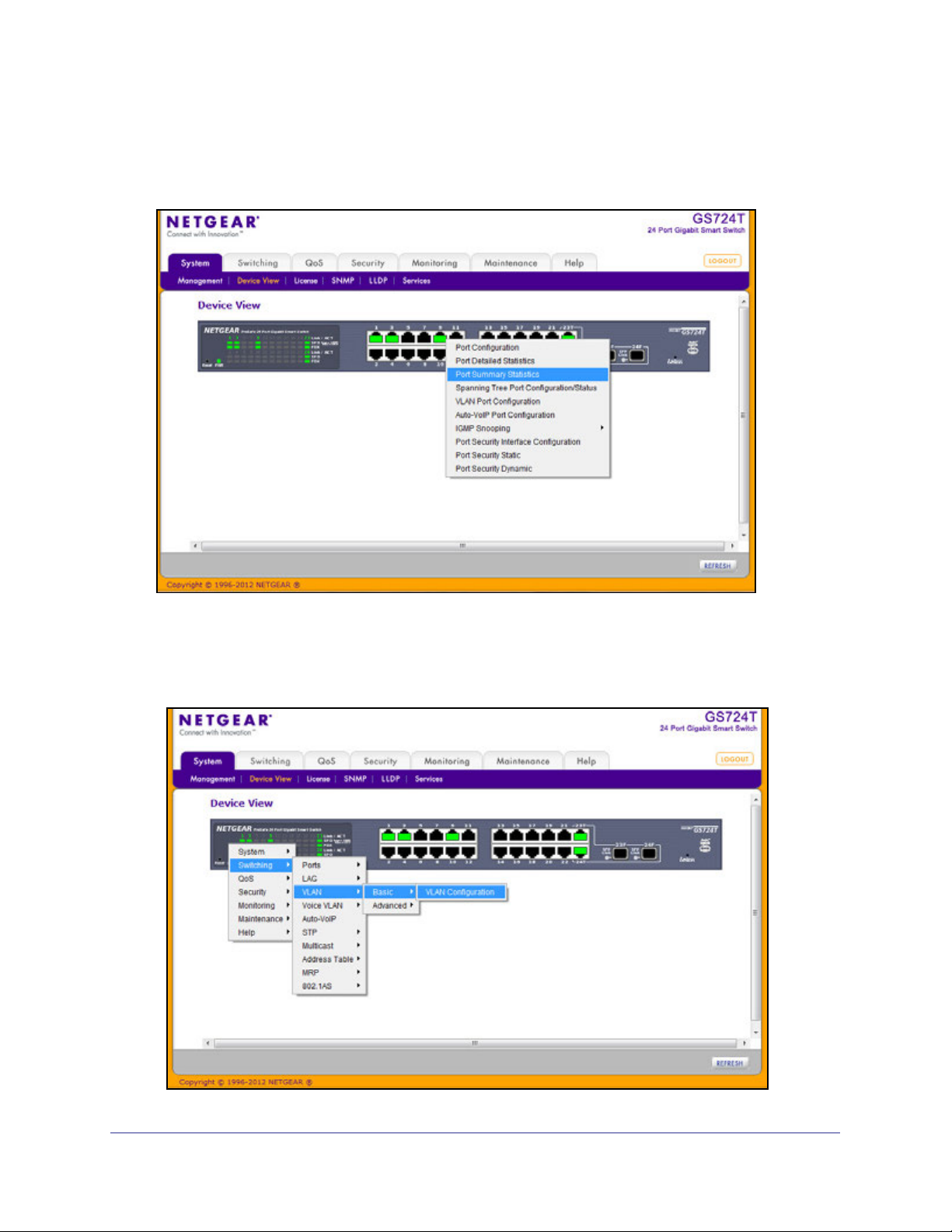
The Device View is a Java® applet that displays the ports on the switch. This graphic provides
an alternate way to navigate to configuration and monitoring options. The graphic also
provides information about device ports, current configuration and status, table information,
and feature components.
The Device View is available from the System
Device View page.
Depending upon the status of the port, the LED of the port illuminates either red, green, or
yellow:
• A red LED indicates that the link is disabled.
• A green LED indicates that the port is enabled and operating at a transfer rate of
1000 Mbps.
• A yellow LED indicates that the port is enabled and operating at a transfer rate of
10 Mbps/100 Mbps.
The following image shows the Device View of the GS716T.
The following image shows the Device View of the GS724T.
26
Page 27
GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Click the port you want to view or configure to see a menu that displays statistics and
configuration options. Click the menu option to access the page that contains the
configuration or monitoring options.
If you click the graphic, but do not click a specific port, the main menu appears, as the
following figure shows. This menu contains the same option as the navigation tabs at the top
of the page.
27
Page 28

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Help Page Access
Every page contains a link to the online help , which contains information to assist in
configuring and managing the switch. The online help pages are context sensitive. For
example, if the IP Addressing page is open, the help topic for that page displays if you click
Help. Figure 4 on page 24 shows the location of the Help link on the Web interface.
User-Defined Fields
User-defined fields can contain 1 to 159 characters, unless otherwise noted on the
configuration Web page. All characters may be used except for the following (unless
specifically noted in for that feature):
\ <
/ >|
* |
?
SNMP Management
The GS716T and GS724T Smart Switches software supports the configuration of SNMP
groups and users that can manage traps that the SNMP agent generates. The switches use
both standard public MIBs for standard functionality and private MIBs that support additional
switch functionality. All private MIBs begin with a “-” prefix. The main object for interface
configuration is in -SWITCHING-MIB, which is a private MIB. Some interface configurations
also involve objects in the public MIB, IF-MIB.
SNMP is enabled by default. The System
which is the page that displays after a successful login, displays the information you need to
configure an SNMP manager to access the switch.
Any user can connect to the switch using the SNMPv3 protocol, but for authentication and
encryption, the switch supports only one user which is admin; therefore there is only one
profile that can be created or modified.
To configure authentication and encryption settings for the SNMPv3 admin profile by using
the Web interface:
1. Navigate to the System
SNMP SNMPv3 User Configuration page.
2. To enable authentication, select an Authentication Protocol option, which is either MD5 or
SHA.
3. To enable encryption, select the DES option in the Encryption Protocol field. Then, enter
an encryption code of eight or more alphanumeric characters in the Encryption Key field.
4. Click Apply.
Management System Information Web page,
To access configuration information for SNMPv1 or SNMPv2, click System
SNMPv1/v2 and click the page that contains the information to configure.
28
SNMP
Page 29
GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Interface Naming Convention
The GS716T and GS724T Smart Switches supports physical and logical interfaces.
Interfaces are identified by their type and the interface number. All the physical ports 1–48
are Gigabit ports and the SFP Ports 47–50 support 1000M Speed fiber modules. Ports 47–48
are Combo ports and ports 49–50 will support dedicated SFP modules. The number of the
port is identified on the front panel. You can configure the logical interfaces by using the
software. The following table describes the naming convention for all interfaces available on
the switch.
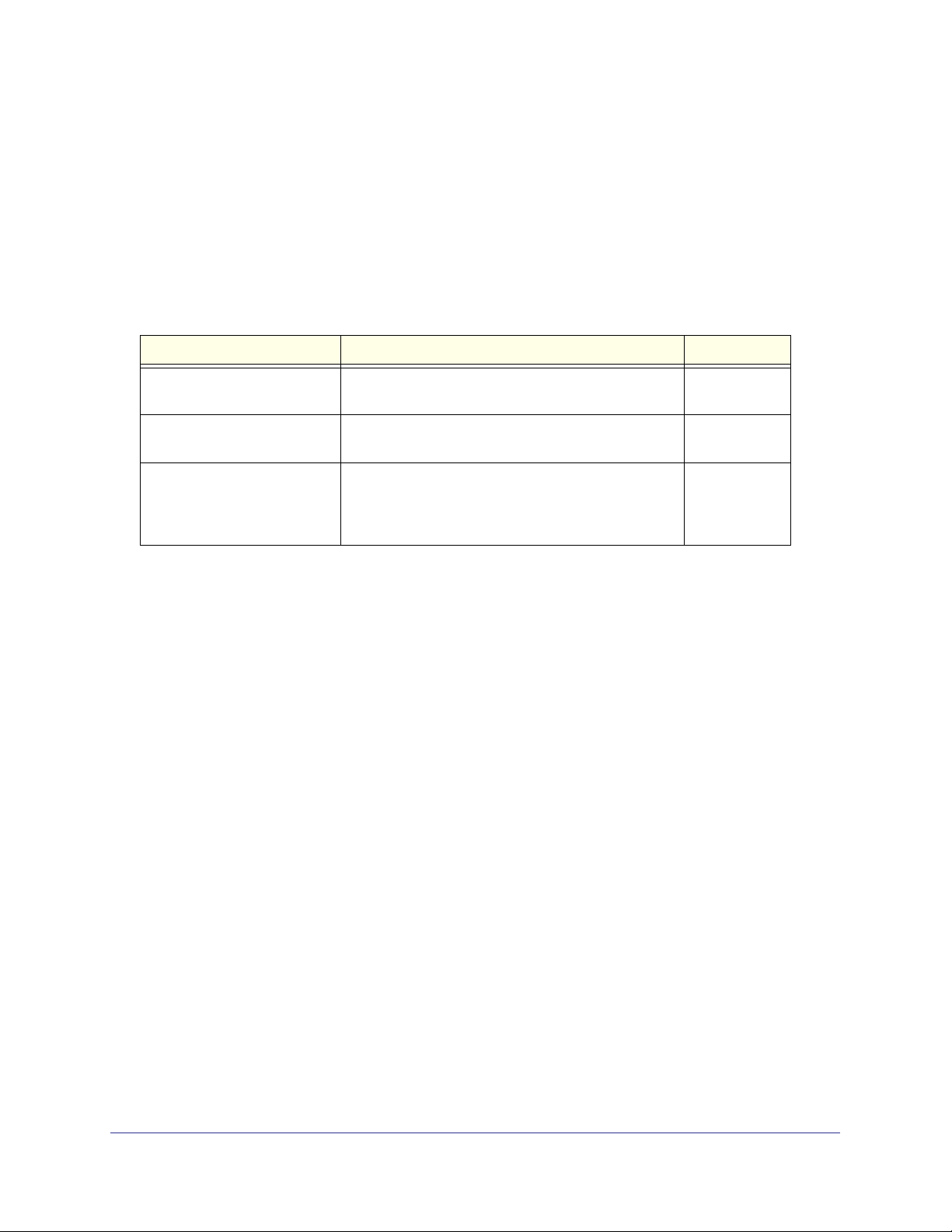
Interface Description Example
Physical The physical ports include Gigabit ports and are
numbered sequentially starting from one.
Link Aggregation Group (LAG) LAG interfaces are logical interfaces that are only
used for bridging functions.
CPU Management Interface This is the internal switch interface responsible for the
switch base MAC address. This interface is not
configurable and is always listed in the MAC Address
Table.
g1, g2, g3
l1, l2, l3
c1
29
Page 30

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
30
Page 31

2. System Information Features
Use the features in the System tab to define the switch’s relationship to its environment. The
System tab contains links to the following features:
• Management on page 31
• License on page 56
• SNMP on page 58
• LLDP on page 63
• Services — DHCP Filtering on page 76
Management
This section describes how to display the switch status and specify some basic switch
information, such as the management interface IP address, system clock settings, and DNS
information. From the Management link, you can access the following pages:
2
• System Information on page 32
• IP Configuration on page 33
• IPv6 Network Configuration on page 35
• IPv6 Network Neighbor on page 37
• Time on page 38
• Denial of Service on page 44
• DNS on page 47
• Green Ethernet on page 49
31
Page 32

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
System Information
After a successful login, the System Information page displays. Use this page to configure
and view general device information.
To display the System Information page, click System Management System Information.
A screen similar to the following displays.
To define system information:
1. Open the System Information page.
2. Define the following fields:
• System Name. Enter the name you want to use to identify this switch. You may use
up to 31 alphanumeric characters. The factory default is blank.
• System Location. Enter the location of this switch. You may use up to 31
alphanumeric characters. The factory default is blank.
• System Contact. Enter the contact person for this switch. You may use up to 31
alphanumeric characters. The factory default is blank.
3. Click Apply.
The system parameters are applied, and the device is updated.
32
Page 33

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
The following table describes the status information the System Page displays.
Field Description
Serial Number The serial number of the switch.
System Object ID The base object ID for the switch's enterprise MIB.
Date & Time The current date and time.
System Up Time Displays the number of days, hours, and minutes since the last system
restart.
Base MAC Address The universally assigned network address.
Model Name The model name of the switch.
Boot Version The boot code version of the switch.
Software Version The software version of the switch.
IP Configuration
Use the IP Configuration page to configure network information for the management
interface, which is the logical interface used for in-band connectivity with the switch through
any of the switch's front panel ports. The configuration parameters associated with the
switch's network interface do not affect the configuration of the front panel ports through
which traffic is switched or routed.
To access the page, click System
following displays.
Management IP Configuration. A screen similar to the
33
Page 34

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To configure the network information for the management interface:
1. Select the appropriate radio button to determine how to configure the network
information for the switch management interface:
• Dynamic IP Address (DHCP). Specifies that the switch must obtain the IP address
through a DHCP server.
• Dynamic IP Address (BOOTP). Specifies that the switch must obtain the IP address
through a BootP server.
• Static IP Address. Specifies that the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
must be manually configured. Enter this information in the fields below this radio
button.
2. If you selected the Static IP Address option, configure the following network information:
• IP Address. The IP address of the network interface. The factory default value is
192.168.0.239. Each part of the IP address must start with a number other than zero.
For example, IP addresses 001.100.192.6 and 192.001.10.3 are not valid.
• Subnet Mask. The IP subnet mask for the interface. The factory default value is
255.255.255.0.
• Default Gateway. The default gateway for the IP interface. The factory default value
is 192.168.0.254.
3. Specify the VLAN ID for the management VLAN.
The management VLAN is used to establish an IP connection to the switch from a
workstation that is connected to a port in the same VLAN. If not specified, the active
management VLAN ID is 1 (default), which allows an IP connection to be established
through any port.
When the management VLAN is set to a different value, an IP connection can be made
only through a port that is part of the management VLAN. It is also mandatory that the
port VLAN ID (PVID) of the port to be connected in that management VLAN be the same
as the management VLAN ID.
The management VLAN has the following requirements:
• Only one management VLAN can be active at a time.
• When a new management VLAN is configured, connectivity through the existing
management VLAN is lost.
• The management station should be reconnected to the port in the new management
VLAN.
Note: Make sure that the VLAN to be configured as the management
VLAN exists. And make sure that the PVID of at least one port that is
a port of the VLAN is the same as the management VLAN ID. For
information about creating VLANs and configuring the PVID for a
port, see VLANs on page 89.
34
Page 35

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
4. If you change any of the network connection parameters, click Apply to apply the changes
to the system.
5. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
IPv6 Network Configuration
Use the IPv6 Network Configuration page to configure the IPv6 network interface, which is
the logical interface used for in-band connectivity with the switch via all of the switch's
front-panel ports. The configuration parameters associated with the switch's network
interface do not affect the configuration of the front-panel ports through which traffic is
switched or routed.
To access the page, click System
Management IPv6 Network Configuration. A screen
similar to the following displays.
To access the switch over an IPv6 network, you must initially configure the switch with IPv6
information (IPv6 prefix, prefix length, and default gateway). IPv6 can be configured using
any of the following options:
• IPv6 Auto Configuration
• DHCPv6
When in-band connectivity is established, IPv6 information can be changed using any of the
following:
• SNMP-based management
• Web-based management
35
Page 36

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To configure the network information for an IPv6 network:
1. Admin Mode. Enable or disable the IPv6 network interface on the switch. The default
value is Enable.
2. IPv6 Address Auto Configuration Mode. The IPv6 address for the IPv6 network interface
is set in auto configuration mode if this option is enabled. The default value is Disable. Auto
configuration can be enabled only when DHCPv6 is not enabled on any of the management
interfaces.
3. Current Network Configuration Protocol. The IPv6 address for the IPv6 network interface
is configured by DHCPv6 protocol if this option is enabled. The default value is None.
DHCPv6 can be enabled only when IPv6 Auto config or DHCPv6 are not enabled on any of
the management interfaces.
4. DHCPv6 Client DUID. Identifier used to identify the client's unique DUID value. This option
only displays when DHCPv6 is enabled.
5. IPv6 Gateway. Specify the gateway for the IPv6 network interface. The gateway address is
in IPv6 global or link-local address format.
6. IPv6 Prefix/Prefix Length. Add the IPv6 prefix and prefix length to the IPv6 network
interface. The address is in the global address format.
7. EUI64. Specify whether format IPv6 address in EUI-64 format. The default value is False.
8. Click Add to add a new IPv6 address in global format.
9. Click Delete to delete a selected IPv6 address.
10. Click Apply to apply the changes to the system.
11. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
36
Page 37

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
IPv6 Network Neighbor
Use the IPv6 Network Neighbor page to configure the IPv6 Network Interface IPv6 Neighbor
Table.
To access the page, click System
Management IPv6 Network Neighbor. A screen similar
to the following displays.
Click Clear to delete all entries from the table. The table is repopulated as the IPv6 neighbors
are discovered on the network. Click Refresh to refresh the screen with most recent data.
The following table describes the information the IPv6 Network Interface Neighbor Table
displays
Field Description
IPv6 Address Specifies the IPv6 address of neighbor or interface.
MAC Address Specifies MAC address associated with an interface.
IsRtr Indicates whether the neighbor is a router. If the neighbor is a router, the value is
True. If the neighbor is not a router, the value is False.
37
Page 38

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Field Description
Neighbor State Specifies the state of the neighbor cache entry. The following are the states for
dynamic entries in the IPv6 neighbor discovery cache:
• Reachable. Positive confirmation was received within the last Reachable Time
milliseconds that the forward path to the neighbor was functioning properly. While
in REACH state, the device takes no special action as packets are sent.
• Stale. More than ReachableTime milliseconds have elapsed since the last positive
confirmation was received that the forward path was functioning properly. While in
STALE state, the device takes no action until a packet is sent.
• Delay. More than ReachableTime milliseconds have elapsed since the last positive
confirmation was received that the forward path was functioning properly. A packet
was sent within the last DELAY_FIRST_PROBE_TIME seconds. If no reachability
confirmation is received within DELAY_FIRST_PROBE_TIME seconds of entering
the DELAY state, send a neighbor solicitation message and change the state to
PROBE.
• Probe. A reachability confirmation is actively sought by resending neighbor
solicitation messages every RetransTimer milliseconds until a reachability
confirmation is received.
• Unknown. The switch cannot determine the state of the cache entry.
Last Updated.
Time since the address was confirmed to be reachable.
Time
GS716T and GS724T Smart Switches software supports the Simple Network Time Protocol
(SNTP). You can also set the system time manually
SNTP assures accurate network device clock time synchronization up to the millisecond.
Time synchronization is performed by a network SNTP server. GS716T and GS724T Smart
Switches software operates only as an SNTP client and cannot provide time services to other
systems.
Time sources are established by Stratums. Stratums define the accuracy of the reference
clock. The higher the stratum (where zero is the highest), the more accurate the clock. The
device receives time from stratum 1 and above since it is itself a stratum 2 device.
The following is an example of stratums:
• Stratum 0: A real-time clock is used as the time source, for example, a GPS system.
• Stratum 1: A server that is directly linked to a Stratum 0 time source is used. Stratum 1
time servers provide primary network time standards.
• Stratum 2: The time source is distanced from the Stratum 1 server over a network path.
For example, a Stratum 2 server receives the time over a network link, via NTP, from a
Stratum 1 server.
Information received from SNTP servers is evaluated based on the time level and server
type.
38
Page 39

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
SNTP time definitions are assessed and determined by the following time levels:
• T1: Time at which the original request was sent by the client.
• T2: Time at which the original request was received by the server.
• T3: Time at which the server sent a reply.
• T4: Time at which the client received the server's reply.
The device can poll Unicast server types for the server time.
Polling for Unicast information is used for polling a server for which the IP address is known.
SNTP servers that have been configured on the device are the only ones that are polled for
synchronization information. T1 through T4 are used to determine server time. This is the
preferred method for synchronizing device time because it is the most secure method. If this
method is selected, SNTP information is accepted only from SNTP servers defined on the
device using the SNTP Server Configuration page.
The device retrieves synchronization information, either by actively requesting information or
at every poll interval.
Time Configuration
Use the Time Configuration page to view and adjust date and time settings.
To display the Time Configuration page, click System
Configuration.
Management Time SNTP Global
39
Page 40

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To configure the time by using the CPU clock cycle as the source:
1. From the Clock Source field, select Local.
2. In the Date field, enter the date in the DD/MM/YYYY format.
3. In the Time field, enter the time in HH:MM:SS format.
Note: If you do not enter a date and time, the switch will calculate the date
and time using the CPU’s clock cycle.
When the Clock Source is set to Local, the Time Zone field is grayed out (disabled):
4. Click Apply to send the updated configuration to the switch. Configuration changes occur
immediately.
To configure the time through SNTP:
1. From the Clock Source field, select SNTP.
When the Clock Source is set to SNTP, the Date and Time fields are grayed out
(disabled). The switch gets the date and time from the network.
2. Use the menu to select the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) time zone in which the switch
is located, expressed as the number of hours.
3. Click Apply to send the updated configuration to the switch. Configuration changes take
effect immediately.
4. Use the SNTP Server Configuration page to configure the SNTP server settings, as
described in SNTP Server Configuration on page 42.
5. Click Refresh to refresh the page with the most current data from the switch.
6. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
The SNTP Global Status table on the Time Configuration page displays information about
the system’s SNTP client. The following table describes the SNTP Global Status fields.
Field Description
Version Specifies the SNTP Version the client supports.
Supported Mode Specifies the SNTP modes the client supports. Multiple modes may be
supported by a client.
Last Update Time Specifies the local date and time (UTC) the SNTP client last updated the
system clock.
Last Attempt Time Specifies the local date and time (UTC) of the last SNTP request or receipt
of an unsolicited message.
40
Page 41

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Field Description
Last Attempt Status Specifies the status of the last SNTP request or unsolicited message for both
unicast mode. If no message has been received from a server, a status of
Other is displayed. These values are appropriate for all operational modes:
• Other: None of the following enumeration values.
• Success: The SNTP operation was successful and the system time was
updated.
• Request Timed Out: A directed SNTP request timed out without
receiving a response from the SNTP server.
• Bad Date Encoded: The time provided by the SNTP server is not valid.
• Version Not Supported: The SNTP version supported by the server is
not compatible with the version supported by the client.
• Server Unsynchronized: The SNTP server is not synchronized with its
peers. This is indicated via the 'leap indicator' field on the SNTP
message.
• Server Kiss Of Death: The SNTP server indicated that no further
queries were to be sent to this server. This is indicated by a stratum field
equal to 0 in a message received from a server.
Server IP Address Specifies the IP address of the server for the last received valid packet. If no
message has been received from any server, an empty string is shown.
Address Type Specifies the address type of the SNTP Server address for the last received
valid packet.
Server Stratum Specifies the claimed stratum of the server for the last received valid packet.
Reference Clock Id Specifies the reference clock identifier of the server for the last received valid
packet.
Server Mode Specifies the mode of the server for the last received valid packet.
Unicast Sever Max Entries Specifies the maximum number of unicast server entries that can be
configured on this client.
Unicast Server Current
Entries
Specifies the number of current valid unicast server entries configured for
this client.
Click Refresh to refresh the page with the most current data from the switch.
41
Page 42

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
SNTP Server Configuration
Use the SNTP Server Configuration page to view and modify information for adding and
modifying Simple Network Time Protocol SNTP servers.
To display the SNTP Server Configuration page, click System Management Time SNTP
Server Configuration.
To configure a new SNTP Server:
1. Enter the appropriate SNTP server information in the available fields:
• Server Type. Specifies whether the address for the SNTP server is an IP address
(IPv4) or host name (DNS).
• Address. Enter the IP address or the host name of the SNTP server.
• Port. Enter a port number on the SNTP server to which SNTP requests are sent. The
valid range is 1–65535. The default is 123.
• Priority. Specifies the priority of this server entry in determining the sequence of
servers to which SNTP requests are sent. Enter a priority from 1–3, with 1 being the
default and the highest priority. Servers with lowest numbers have priority.
• Version. Enter the protocol version number that corresponds to the NTP version
running on the SNTP server. The range is 1–4, and the default version is SNTPv4.
2. Click Add.
3. Repeat the previous steps to add additional SNTP servers. You can configure up to three
SNTP servers.
4. To removing an SNTP server, select the check box next to the configured server to remove,
and then click Delete. The entry is removed, and the device is updated.
42
Page 43

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
5. To change the settings for an existing SNTP server, select the check box next to the
configured server and enter new values in the available fields, and then click Apply.
Configuration changes take effect immediately.
6. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
The SNTP Server Status table displays status information about the SNTP servers
configured on your switch. The following table describes the SNTP Global Status fields.
Field Description
Address Specifies all the existing Server Addresses. If no Server configuration exists, a
message saying “No SNTP server exists” flashes on the screen.
Last Update Time Specifies the local date and time (UTC) that the response from this server was
used to update the system clock.
Last Attempt Time Specifies the local date and time (UTC) that this SNTP server was last queried.
Last Attempt Status Specifies the status of the last SNTP request to this server. If no packet has been
received from this server, a status of Other is displayed:
• Other: None of the following enumeration values.
• Success: The SNTP operation was successful and the system time was
updated.
• Request Timed Out: A directed SNTP request timed out without receiving a
response from the SNTP server.
• Bad Date Encoded: The time provided by the SNTP server is not valid.
• Version Not Supported: The SNTP version supported by the server is not
compatible with the version supported by the client.
• Server Unsynchronized: The SNTP server is not synchronized with its
peers. This is indicated via the 'leap indicator' field on the SNTP message.
• Server Kiss Of Death: The SNTP server indicated that no further queries
were to be sent to this server. This is indicated by a stratum field equal to 0 in
a message received from a server.
Requests Specifies the number of SNTP requests made to this server since last agent
reboot.
Failed Requests Specifies the number of failed SNTP requests made to this server since last
reboot.
Click Refresh to refresh the page with the most current data from the switch.
43
Page 44

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Denial of Service
Use the Denial of Service (DoS) page to configure DoS control. The GS716T and GS724T
switch provide support for classifying and blocking specific types of DoS attacks. The type of
DoS attacks the switch can detect and prevent are described in DoS Configuration on
page 45.
Auto-DoS Configuration
The Auto-DoS Configuration page lets you automatically enable all the DoS features available
on the switch, except for TCP and UDP port attacks. See DoS Configuration on page 45 for
information about the types of DoS attacks the switch can monitor and block.
Note: When Auto-DoS is enabled, a port that is under attack is
automatically shut down and does not forward traffic. The port can
be enabled only manually by the admin user. A warning message is
logged to the buffered log and is sent to the Syslog server.
To access the Auto-DoS Configuration page, click System
Service
Auto-DoS Configuration.
Management Denial of
44
Page 45

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To configure the Auto-DoS feature:
1. Select a radio button to enable or disable Auto-DoS:
• Disable. Auto-DoS is disabled (default).
• Enable. Auto-DoS is enabled.
2. Click Apply to send the updated configuration to the switch. Configuration changes occur
immediately.
3. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
DoS Configuration
The DoS Configuration page lets you to select which types of DoS attacks for the switch to
monitor and block.
To access the DoS Configuration page, click System Management Denial of Service
DoS Configuration.
To configure individual DoS settings:
1. Select the types of DoS attacks for the switch to monitor and block and configure any
associated values, as the following list describes.
• Denial of Service SIP=DIP: Enable or disable this option by selecting the
corresponding line on the radio button. Enabling SIP=DIP DoS prevention causes the
switch to drop packets that have a source IP address equal to the destination IP
address. The factory default is disabled.
• Denial of Service First Fragment: IP Fragment Offset = 1. Enable or disable this
option by selecting the corresponding line on the radio button. Enabling First
Fragment DoS prevention causes the switch to drop packets that have an IP fragment
offset equal to 1. The factory default is disabled.
45
Page 46

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
• Denial of Service Min TCP Hdr Size: Specifies the Min TCP Hdr Size allowed. If
First TCP Fragment DoS prevention is enabled, then the switch will drop packets that
have a TCP header smaller than this configured Min TCP Hdr Size. The factory
default is 20.
• Denial of Service TCP Fragment: TCP Header size is smaller than the configured
value. Enable or disable this option by selecting the corresponding line on the radio
button. Enabling TCP Fragment DoS prevention causes the switch to drop packets
that have a TCP header smaller than the configured Min TCP Hdr Size. The factory
default is disabled.
• Denial of Service TCP Flag: Enable or disable this option by selecting the
corresponding line on the radio button. Enabling TCP Flag DoS prevention causes
the switch to drop packets that have TCP flag SYN set and TCP source port less than
1024 or TCP control flags set to 0 and TCP sequence number set to 0 or TCP flags
FIN, URG, and PSH set and TCP sequence number set to 0 or both TCP flags SYN
and FIN set. The factory default is disabled.
• Denial of Service L4 Port: Enable or disable this option by selecting the
corresponding line on the radio button. Enabling L4 Port DoS prevention causes the
switch to drop packets that have TCP/UDP source port equal to TCP/UDP destination
port. The factory default is disabled.
• Denial of Service ICMP: Enable or disable this option by selecting the corresponding
line on the radio button. Enabling ICMP DoS prevention causes the switch to drop
ICMP packets that have a type set to ECHO_REQ (ping) and a size greater than the
configured ICMP Pkt Size. The factory default is disabled.
• Denial of Service Mx ICMP Pkt Size: If ICMP DoS prevention is enabled and if the
ICMP echo request is carried in an unfragmented IPv4/IPv6 datagram and if the total
length (in the IP header) indicates a value greater than MAX ICMP Size configured +
IP header length, then the specified packet is dropped. The factory default is 512.
2. If you change any of the DoS settings, click Apply to apply the changes to the switch.
3. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
46
Page 47

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
DNS
You can use these pages to configure information about DNS servers the network uses and
how the switch operates as a DNS client.
DNS Configuration
Use this page to configure global DNS settings and DNS server information.
To access this page, click System
To configure the global DNS settings:
Management DNS DNS Configuration.
1. Specify whether to enable or disable the administrative status of the DNS Client.
• Enable. Allow the switch to send DNS queries to a DNS server to resolve a DNS
domain name. DNS is disabled by default.
• Disable. Prevent the switch from sending DNS queries.
2. Enter the DNS default domain name to include in DNS queries. When the system is
performing a lookup on an unqualified host name, this field is provided as the domain name
(for example, if default domain name is netgear.com and the user enters test, then test is
changed to test.netgear.com to resolve the name).
3. To specify the DNS server to which the switch sends DNS queries, enter an IP address in
standard IPv4 dot notation in the DNS Server Address and click Add. The server appears
in the list below. You can specify up to eight DNS servers. The precedence is set in the
order created.
4. To remove a DNS server from the list, select the check box next to the server you want to
remove and click Delete. If no DNS server is specified, the check box is global and will
delete all the DNS servers listed.
47
Page 48

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
5. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
6. Click Apply to send the updated configuration to the switch. Configuration changes take
effect immediately.
Host Configuration
Use this page to manually map host names to IP addresses or to view dynamic DNS
mappings.
To access this page, click System Management DNS Host Configuration.
To add a static entry to the local DNS table:
1. Specify the static host name to add. Each substring must be less than 64 characters in
length separated by a dot or space, and the length of the whole string must not exceed
158 characters.
2. Specify the IP address in standard IPv4 dot notation to associate with the host name.
3. Click Add. The entry appears in the list below.
4. To remove an entry from the static DNS table, select the check box next to the entry and
click Delete.
5. To change the host name or IP address in an entry, select the check box next to the entry
and enter the new information in the appropriate field, and then click Apply.
6. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
48
Page 49

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
The Dynamic Host Configuration table shows host name-to-IP address entries that the switch
has learned. The following table describes the dynamic host fields:
Field Description
Host Lists the host name you assign to the specified IP address.
Total Amount of time since the dynamic entry was first added to the table.
Elapsed Amount of time since the dynamic entry was last updated.
Type The type of the dynamic entry.
Addresses Lists the IP address associated with the host name.
Click Refresh to refresh the table with the most current data from the switch.
Click Clear to delete Dynamic Host Entries. The table will be repopulated with entries as they
are learned.
Green Ethernet
The Green Ethernet features allow the switch to reduce power consumption on a per-port
basis, except for the Combo ports (g15–16 for GS716T; g23–24 for GS724T). Each switch
can support one or more of the following features:
• Energy-detect Mode - When the Energy Detect mode is enabled and the port link is
down, the PHY automatically goes down for short period of time and then wakes up to
check link pulses. This mode reduces power consumption on the port when no link
partner is present.
• Short Cable Mode: With Short Cable mode enabled, the PHY goes into low power mode
when the cable length is less than a certain limit.
49
Page 50

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Green Ethernet Configuration
Use this page to configure the administrative mode for the Green Ethernet features available
on the switch. These features must also be enabled on each port to take advantage of the
possible power savings.
To access this page, click System
Management Green Ethernet Configuration.
To configure the Green Ethernet feature:
1. Enable or disable the Auto Power Down Mode.
• Enable. When the port link is down, the PHY will automatically go down for a short
period of time and then wake up to check link pulses. This allows the port to continue
to perform auto-negotiation while consuming less power when no link partner is
present.
• Disable. Provide full power to the port even if no link partner is present.
2. Enable or disable the Short Cable Mode.
• Enable. The switch performs a cable test when the port link is up. If the cable that
connects the port to its link partner has a length less than 10m, PHYs are placed in
low-power mode (nominal power).
• Disable. Do not perform an automatic cable test on a linked port or adjust the port
power based on the cable length.
3. Click Apply to send the updated configuration to the switch. Configuration changes take
effect immediately.
50
Page 51

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Green Ethernet Interface Configuration
Use this page to configure Green Ethernet features on a per-port basis. The Green Ethernet
modes must be administratively enabled on the switch for the mode enabled on the port to
take effect.
To access this page, click System
Management Green Ethernet Green Ethernet
Interface Configuration.
To configure the Green Ethernet Interface feature:
1. Select the check box next to the port to configure. You can select multiple ports to apply
the same setting to all selected ports. To configure all ports, select the check box in the
heading row.
2. Enable or disable the Auto Power-Down Mode.
• Enable. When the port link is down, the PHY automatically goes down for a short
period of time and then wake up to check link pulses. This behavior saves power
consumption when there is no link partner while still allowing the port to perform
auto-negotiation if a link partner does become present.
• Disable. The PHY remains up even if no link partner is present.
3. Enable or disable the Short Cable Mode.
• Enable. The switch performs a cable test on each cable connect to its ports. If the
cable is less than 10m in length, the port is placed in low power mode (nominal
power).
• Disable. Full transmit power is provided to all ports, regardless of cable length.
4. Click Apply to apply the change to the system. Configuration changes take effect
immediately.
5. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
51
Page 52

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Green Ethernet Detail
Use this page to configure Green Ethernet monitor and manage Green Ethernet features on
a specific port.
To access this page, click System Management Green Ethernet Green Ethernet
Detail.
52
Page 53

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To configure or view details about the Green Ethernet feature on a port:
1. Within the Local Device Information, select the port to view or configure from the
Interface menu.
2. Enable or disable the Energy Detect or Short Reach administrative modes on the interface.
3. If you make any changes to the Green Ethernet modes for the port, click Apply.
4. View the additional Green Ethernet information that displays for the port:
Field Description
Cumulative Energy Saved
on this port due to Green
Mode(s) (Watts * Hours)
Operational Status
(Energy Detect)
Reason Shows the Admin status, either Admin Down or Admin Up.
Operational Status
(Short Reach)
Reason Shows the reason why the port is either Active or Inactive.
Shows the energy savings per port, per hour.
Shows the Green Mode operational status, either Inactive or Active.
Shows the operational status of the port, either Active or Inactive.
5. Click Clear to reset the counters on the page to their default values.
6. Click Refresh to update the page with the current information.
53
Page 54

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Green Ethernet Statistics Summary
This page summarizes the Green Ethernet Summary settings currently in use.
To access this page, click System
Management Green Ethernet Green Ethernet
Statistics Summary.
The following table describes the information available on the Green Mode Statistics
Summary page.
Field Description
Current Power Consumption
by all ports in Stack
(mWatts)
Estimated Percentage
Power Saving per stack (%)
Cumulative Energy Saving
per Stack (Watts*Hours)
Unit Identifies the stack member number.
Green Features supported
on this unit
Interface Identifies the interface associated with the rest of the data in the row.
Estimated Power Consumption by all ports in the stack in mWatts.
Estimated Percentage Power saved on all ports in the stack due to Green
mode(s) enabled.
Estimated Cumulative Energy saved per stack in (Watts × Hours) due to all
green modes enabled.
List of Green Features supported on the given unit which could be one or
more of the following:
• Energy-Detect (Energy Detect)
• Short-Reach (Short Reach)
• Pwr-Usg-Est (Power Usage Estimates).
54
Page 55

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Field Description
Energy Detect Admin Mode Shows whether Energy Detect Mode is administratively enabled on the port.
Energy Detect Operational
Status
Short Reach Admin Mode Shows the administrative status of Short Reach Mode on the port. With short
Short Reach Operational
Status
Shows the current operational status of the Green Mode for the selected
port.
reach mode enabled, PHY goes into low power mode when cable length is
less than a given limit.
Indicates whether the port is in low-power mode due to the cable length.
Click Refresh to update the page with the most current data from the switch
55
Page 56

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
License
From the License link under the System tab, you can view information about the switch
license.The License link provides access to the following pages:
• Show License on page 56
• License Features on page 57
Show License
Use the Show License page to view information about the license key on the device. Some
features might require a special license in order to be active. If a license is not active, the
feature associated with the license is not available and cannot be configured.
To display the License Key page, click System > License > Show License. A screen similar
to the following displays.
The following table describes the non-configurable fields on the License Key page.
Field Description
License Date The date the license is purchased.
License Copy The number of licenses that exist on the switch.
License Status Indicates whether the license is active or inactive. If a license is inactive, a
license should be purchased and downloaded to the switch. The license is not
activated until the switch reboots.
Description A description of the license key status. If the license is inactive, this field
provides information about why it is inactive.
56
Page 57

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
License Features
Use the License Features page to view information about the features on the device that
require an active license.
To display the License Features page, click System > License > License Features. A
screen similar to the following displays.
57
Page 58

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
SNMP
From SNMP link under the System tab, you can configure SNMP settings for SNMP V1/V2
and SNMPv3.
From the SNMP link, you can access the following pages:
• SNMPV1/V2 on page 58
• Trap Flags on page 61
• SNMP v3 User Configuration on page 62
SNMPV1/V2
The pages under the SNMPV1/V2 menu allow you to configure SNMP community
information, traps, and trap flags.
Community Configuration
To display this page, click System SNMP SNMP V1/V2 Community Configuration.
By default, two SNMP Communities exist:
• Private, with Read/Write privileges and status set to Enable.
• Public, with Read Only privileges and status set to Enable.
These are well-known communities. Use this page to change the defaults or to add other
communities. Only the communities that you define using this page will have access to the
switch using the SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c protocols. Only those communities with read/write
level access can be used to change the configuration using SNMP.
58
Page 59

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Use this page when you are using the SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c protocol.
To configure SNMP communities:
1. To add a new SNMP community, enter community information in the available fields
described below, and then click Add.
• Management Station IP. Specify the IP address of the management station.Together,
the Management Station IP and the Management Station IP Mask denote a range of
IP addresses from which SNMP clients may use that community to access this
device. If either (Management Station IP or Management Station IP Mask) value is
0.0.0.0, access is allowed from any IP address. Otherwise, every client’s address is
ANDed with the mask, as is the Management Station IP Address; and, if the values
are equal, access is allowed. For example, if the Management Station IP and
Management Station IP Mask parameters are 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0, then any
client whose address is 192.168.1.0 through 192.168.1.255 (inclusive) will be allowed
access. To allow access from only one station, use a Management Station IP Mask
value of 255.255.255.255, and use that machine’s IP address for Client Address.
• Management Station IP Mask. Specify the subnet mask to associate with the
management station IP address.
• Community String. Specify a community name. A valid entry is a case-sensitive
string of up to 16 characters.
• Access Mode. Specify the access level for this community by selecting Read/Write or
Read Only from the menu.
• Status. Specify the status of this community by selecting Enable or Disable from the
pull down menu. If you select Enable, the Community Name must be unique among
all valid Community Names or the set request will be rejected. If you select Disable,
the Community Name will become invalid.
2. To modify an existing community, select the check box next to the community, change the
desired fields, and then click Apply. Configuration changes take effect immediately.
59
Page 60

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
3. To delete a community, select the check box next to the community and click Delete.
4. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
Trap Configuration
This page displays an entry for every active Trap Receiver. To access this page, click System
SNMP SNMP V1/V2 Trap Configuration.
To configure SNMP trap settings:
1. To add a host that will receive SNMP traps, enter trap configuration information in the
available fields described below, and then click Add.
• Recipients IP. The address in x.x.x.x format to receive SNMP traps from this device.
• Version. The trap version to be used by the receiver from the menu.
• SNMP v1: Uses SNMP v1 to send traps to the receiver.
• SNMP v2: Uses SNMP v2 to send traps to the receiver.
• Community String. The community string for the SNMP trap packet to be sent to the
trap manager. This may be up to 16 characters and is case sensitive.
• Status. Select the receiver’s status from the menu:
• Enable: Send traps to the receiver.
• Disable: Do not send traps to the receiver.
2. To modify information about an existing SNMP recipient, select the check box next to the
recipient, change the desired fields, and then click Apply. Configuration changes take effect
immediately.
3. To delete a recipient, select the check box next to the recipient and click Delete.
4. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
60
Page 61

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Trap Flags
The pages in the Trap Manager folder allow you to view and configure information about
SNMP traps the system generates.
Use the Trap Flags page to enable or disable traps the switch can send to an SNMP
manager. When the condition identified by an active trap is encountered by the switch, a trap
message is sent to any enabled SNMP Trap Receivers, and a message is written to the trap
log.
To access the Trap Flags page, click System
SNMP SNMP V1/V2 Trap Flags.
To configure the trap flags:
1. From the Authentication field, enable or disable activation of authentication failure
traps by selecting the corresponding button. The factory default is Enable.
2. From the Link Up/Down field, enable or disable activation of link status traps by selecting
the corresponding button. The factory default is Enable.
3. From the Spanning Tree field, enable or disable activation of spanning tree traps by
selecting the corresponding button. The factory default is Enable.
4. If you make any changes to this page, click Apply to send the updated configuration to the
switch. Configuration changes take effect immediately.
5. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
61
Page 62

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
SNMP v3 User Configuration
Use this page to configure user access for management of the switch using SNMP v3.
To access this page, click System
SNMP SNMP V3 User Configuration.
The SNMPv3 Access Mode is a read-only field that shows the access privileges for the user
account. The admin account always has Read/Write access, and all other accounts have
Read Only access.
To configure SNMPv3 settings for the user account:
1. In the Authentication Protocol field, specify the SNMPv3 Authentication Protocol setting
for the selected user account. The valid Authentication Protocols are None, MD5, or
SHA. If you select:
• None: The user will be unable to access the SNMP data from an SNMP browser.
• MD5 or SHA: The user login password will be used as SNMPv3 authentication
password, and you must therefore specify a password. The password must be eight
characters in length.
2. In the Encryption Protocol field, choose whether to encrypt SNMPv3 packets transmitted by
the switch.
• None. Do not encrypt the contents of SNMPv3 packets transmitted from the switch.
• DES. Encrypt SNMPv3 packets using the DES encryption protocol.
3. If you selected DES in the Encryption Protocol field, enter the SNMPv3 Encryption Key here.
Otherwise, this field is ignored. Valid keys are 0 to 15 characters long.
4. Click Apply to send the updated configuration to the switch. Configuration changes take
effect immediately.
5. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
62
Page 63

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
LLDP
The IEEE 802.1AB-defined standard, Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), allows stations
on an 802 LAN to advertise major capabilities and physical descriptions. This information is
viewed by a network manager to identify system topology and detect bad configurations on
the LAN.
From the LLDP link, you can access the following pages:
• LLDP Configuration on page 63
• LLDP Port Settings on page 65
• LLDP-MED Network Policy on page 66
• LLDP-MED Port Settings on page 67
• Local Information on page 68
• Neighbors Information on page 72
LLDP is a one-way protocol; there are no request/response sequences. Information is
advertised by stations implementing the transmit function, and is received and processed by
stations implementing the receive function. The transmit and receive functions can be
enabled/disabled separately per port. By default, both transmit and receive are enabled on all
ports. The application is responsible for starting each transmit and receive state machine
appropriately, based on the configured status and operational state of the port.
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol-Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) is an
enhancement to LLDP with the following features:
• Auto-discovery of LAN policies (such as VLAN, Layer 2 Priority, and DiffServ settings),
enabling plug and play networking.
• Device location discovery for creation of location databases.
• Extended and automated power management of Power over Ethernet endpoints.
• Inventory management, enabling network administrators to track their network devices
and determine their characteristics (manufacturer, software and hardware versions,
serial/asset number).
LLDP Configuration
Use the LLDP Configuration page to specify LLDP and LLDP-MED parameters that are
applied to the switch.
To display the LLDP Configuration page, click System > LLDP > Basic > LLDP
Configuration.
Note: You can also access the LLDP Configuration page by clicking
System > LLDP > Advanced > LLDP Configuration.
63
Page 64

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To configure global LLDP settings:
1. Configure the following LLDP properties.
• TLV Advertised Interval. Specify the interval at which frames are transmitted. The
default is 30 seconds, and the valid range is 5–32768 seconds.
• Hold Multiplier. Specify multiplier on the transmit interval to assign to Time-to-Live
(TTL). The default is 4, and the range is 2–10.
• Reinitializing Delay. Specify the delay before a reinitialization. The default is 2
seconds, and the range is 1–10 seconds.
• Transmit Delay. Specify the interval for the transmission of notifications. The default
is 5 seconds, and the range is 5–3600 seconds.
2. To change the LLDP-MED properties in the Fast Start Duration field, specify the number of
LLDP packets sent when the LLDP-MED Fast Start mechanism is initialized, which occurs
when a new endpoint device links with the LLDP-MED network connectivity device. The
default value is 3, and the range is from 1–10.
3. Click Apply to apply the new settings to the system.
4. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
5. Click Refresh to update the screen with the current information.
64
Page 65

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
LLDP Port Settings
Use the LLDP Port Settings page to specify LLDP parameters that are applied to a specific
interface.
To display the LLDP Port Settings page, click System
Settings.
To configure LLDP port settings:
LLDP Advanced LLDP Port
1. Change the LLDP port settings described below:
• Interface. Specifies the port to be affected by these parameters.
• Admin Status. Select the status for transmitting and receiving LLDP packets:
• Tx Only: Enable only transmitting LLDP PDUs on the selected ports.
• Rx Only: Enable only receiving LLDP PDUs on the selected ports.
• Tx and Rx: Enable both transmitting and receiving LLDP PDUs on the selected
ports. This is the default value.
• Disabled: Do not transmit or receive LLDP PDUs on the selected ports.
• Management IP Address. Choose whether to advertise the management IP address
from the interface. The possible field values are:
• Stop Advertise: Do not advertise the management IP address from the interface.
• Auto Advertise: Advertise the current IP address of the device as the
management IP address.
• Notification. When notifications are enabled, LLDP interacts with the Trap Manager
to notify subscribers of remote data change statistics. The default is Disabled.
65
Page 66

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
• Optional TLV(s). Enable or disable the transmission of optional type-length value
(TLV) information from the interface. The TLV information includes the system name,
system description, system capabilities, and port description. The default is enabled.
To configure the System Name, see Management on page 31. To configure the Port
Description, see Ports on page 79.
2. If you make any changes to the page, click Apply to apply the new settings to the system.
3. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
LLDP-MED Network Policy
This page displays information about the LLPD-MED network policy TLV transmitted in the
LLDP frames on the selected local interface.
To display this page, click System LLDP Advanced LLDP-MED Network Policy.
From the Interface menu, select the interface with the information to view. The following table
describes the LLDP-MED network policy information that displays on the screen.
Field Description
Network Policy Number Specifies the policy number.
Application Specifies the media application type associated with the policy, which can
only be Voice.
The application information is displayed only if a network policy TLV has
been transmitted from the port.
VLAN ID Specifies the VLAN ID associated with the policy.
66
Page 67

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Field Description
VLAN Type Specifies whether the VLAN associated with the policy is tagged or
untagged.
User Priority Specifies the priority associated with the policy.
DSCP
Specifies the DSCP associated with a particular policy type.
Click Refresh to refresh the page with the most current data from the switch.
LLDP-MED Port Settings
Use this page to enable LLDP-MED mode on an interface and configure its properties.
To display this page, click System
LLDP Advanced LLDP-MED Port Settings.
To configure LLDP-MED settings for a port:
1. From the Port field, select the port to configure.
2. From the LLDP-MED Status field, enable or disable the LLDP-MED mode for the selected
interface.
3. From the Notification field, specify whether the port should send a topology change
notification if a device is connected or removed.
67
Page 68

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
4. From the Transmit Optional TLVs field, specify whether the port should transmit optional type
length values (TLVs) in the LLDP PDU frames. If enabled, the following LLDP-MED TLVs
are transmitted:
• MED Capabilities
• Network Policy
• Location Identification
• Extended Power via MDI: PSE
• Extended Power via MDI: PD
• Inventory
5. Click Apply to send the updated configuration to the switch. These changes occur
immediately and the configuration will be saved.
6. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
Local Information
Use the LLDP Local Information page to view the data that each port advertises through
LLDP.
To display the LLDP Local Device Information page, click System Advanced LLDP
Local Information.
68
Page 69

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
If LLDP or LLDP-MED is enabled on one or more ports, the Device Information table
displays information about the device that is transmitted in TLVs, as the following table
describes:
Field Description
Chassis ID Subtype The type of information used to identify the GS716T and GS724T in the
Chassis ID field.
Chassis ID The hardware platform identifier for the GS716T and GS724T.
System Name The user-configured system name for the GS716T and GS724T.
System Description The device description, which includes information about the product model
and platform.
System Capabilities The primary function(s) the GS716T and GS724T supports.
The Port Information table provides information about the LLDP and LLDP-MED status of
each port, as the following table describes:
Field Description
Interface Select the interface with the information to display.
Port ID Subtype Identifies the type of data displayed in the Port ID field.
Port ID Identifies the physical address of the port.
Port Description Identifies the user-defined description of the port. To configure the Port
Description, see Ports on page 79.
Advertisement Displays the advertisement status of the port.
Click Refresh to refresh the page with the most current data from the switch.
69
Page 70

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To view additional details about a port, click the name of the port in the Interface column of
the Port Information table.
A popup window displays information for the selected port.
The following table describes the detailed local information that displays for the selected port.
Field Description
Managed Address
Address SubType Displays the type of address the management interface uses, such as an IPv4
address.
Address Displays the address used to manage the device.
Interface SubType Displays the port subtype.
Interface Number Displays the number that identifies the port.
MAC/PHY Details
70
Page 71

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Field Description
Auto-Negotiation Supported Specifies whether the interface supports port-speed auto-negotiation. The
possible values are True or False.
Auto-Negotiation Enabled Displays the port speed auto-negotiation support status. The possible values
are True (enabled) or False (disabled).
Auto Negotiation Advertised
Capabilities
Operational MAU Type Displays the Medium Attachment Unit (MAU) type. The MAU performs
MED Details
Capabilities Supported Displays the MED capabilities enabled on the port.
Current Capabilities Displays the TLVs advertised by the port.
Device Class Network Connectivity indicates the device is a network connectivity device.
Network Policies
Application Type Specifies the media application type associated with the policy.
VLAN ID Specifies the VLAN ID associated with the policy.
VLAN Type Specifies whether the VLAN associated with the policy is tagged or untagged.
User Priority Specifies the priority associated with the policy.
DSCP
Displays the port speed auto-negotiation capabilities such as 1000BASE-T
half-duplex mode or 100BASE-TX full-duplex mode.
physical layer functions, including digital data conversion from the Ethernet
interface collision detection and bit injection into the network.
Specifies the DSCP associated with a particular policy type.
71
Page 72

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Neighbors Information
Use the LLDP Neighbors Information page to view the data that a specified interface has
received from other LLDP-enabled systems.
To display the LLDP Neighbors Information page, click System > LLDP > Advanced >
Neighbors Information.
The following table describes the information that displays for all LLDP neighbors that have
been discovered.
Field Description
MSAP Entry Displays the Media Service Access Point (MSAP) entry number for the
remote device.
Local Port Displays the interface on the local system that received LLDP information
from a remote system.
Chassis ID Subtype Identifies the type of data displayed in the Chassis ID field on the remote
system.
Chassis ID Identifies the remote 802 LAN device's chassis.
Port ID Subtype Identifies the type of data displayed in the remote system’s Port ID field.
Port ID Identifies the physical address of the port on the remote system from which
the data was sent.
System Name Identifies the system name associated with the remote device. If the field is
blank, the name might not be configured on the remote system.
Click Refresh to update the information on the screen with the most current data.
To view additional information about the remote device, click the link in the MSAP Entry field.
72
Page 73

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
A popup window displays information for the selected port.
Field Description
Port Details
Local Port Displays the interface on the local system that received LLDP information
from a remote system.
MSAP Entry Displays the Media Service Access Point (MSAP) entry number for the
remote device.
Basic Details
Chassis ID Subtype Identifies the type of data displayed in the
system.
Chassis ID Identifies the remote 802 LAN device's chassis.
Port ID Subtype Identifies the type of data displayed in the remote system’s
Port ID Identifies the physical address of the port on the remote system from which
the data was sent.
Port Description Identifies the user-defined description of the port.
System Name Identifies the system name associated with the remote device.
System Description Specifies the description of the selected port associated with the remote
system.
Chassis ID field on the remote
Port ID field.
System Capabilities Specifies the system capabilities of the remote system.
73
Page 74

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Field Description
Managed Addresses
Address SubType Specifies the type of the management address.
Address Specifies the advertised management address of the remote system.
Interface SubType Specifies the port subtype.
Interface Number Identifies the port on the remote device that sent the information.
MAC/PHY Details
Auto-Negotiation Supported Specifies whether the remote device supports port-speed auto-negotiation.
The possible values are True or False
Auto-Negotiation Enabled Displays the port speed auto-negotiation support status. The possible values
are True or False
Auto Negotiation Advertised
Capabilities
Operational MAU Type Displays the Medium Attachment Unit (MAU) type. The MAU performs
MED Details
Capabilities Supported Specifies the supported capabilities that were received in MED TLV from the
Current Capabilities Specifies the advertised capabilities that were received in MED TLV from the
Device Class Displays the LLDP-MED endpoint device class. The possible device classes
Hardware Revision Displays the hardware version advertised by the remote device.
Firmware Revision Displays the firmware version advertised by the remote device.
Displays the port speed auto-negotiation capabilities.
physical layer functions, including digital data conversion from the Ethernet
interface collision detection and bit injection into the network.
device.
device.
are:
• Endpoint Class 1 Indicates a generic endpoint class, offering basic LLDP
services.
• Endpoint Class 2 Indicates a media endpoint class, offering media
streaming capabilities as well as all Class 1 features.
• Endpoint Class 3 Indicates a communications device class, offering all
Class 1 and Class 2 features plus location, 911, Layer 2 switch support
and device information management capabilities.
Software Revision Displays the software version advertised by the remote device.
Serial Number Displays the serial number advertised by the remote device.
Model Name Displays the model name advertised by the remote device.
Asset ID
Displays the asset ID advertised by the remote device.
74
Page 75

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Field Description
Location Information
Civic Displays the physical location, such as the street address, the remote device
has advertised in the location TLV. For example, 123 45th St. E. The field
value length range is 6–160 characters.
Coordinates Displays the location map coordinates the remote device has advertised in
the location TLV, including latitude, longitude and altitude.
ECS ELIN Displays the Emergency Call Service (ECS) Emergency Location
Identification Number (ELIN) the remote device has advertised in the location
TLV. The field range is 10–25.
Unknown Displays unknown location information for the remote device.
Network Policies
Application Type Specifies the media application type associated with the policy advertised by
the remote device.
VLAN ID Specifies the VLAN ID associated with the policy.
VLAN Type Specifies whether the VLAN associated with the policy is tagged or untagged.
User Priority Specifies the priority associated with the policy.
DSCP Specifies the DSCP associated with a particular policy type.
LLDP Unknown TLVs
Type Displays the unknown TLV type field.
Value
Displays the unknown TLV value field.
75
Page 76

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Services — DHCP Filtering
DHCP Filtering is a useful feature that can be employed as a security measure against
unauthorized DHCP servers. A known attack is when an unauthorized DHCP server
responds to a client that is requesting an IP address. The server configures the gateway for
the client to be equal to the IP address of the server. At that point, the client sends all of its IP
traffic destined to other networks to the unauthorized machine. This gives the attacker the
possibility of snooping traffic for passwords or employing a man-in-the-middle attack. DHCP
Filtering works by allowing the administrator to configure each port as either a trusted port or
an untrusted port. The port that has the authorized DHCP server should be configured as a
trusted port. Any DHCP responses received on a trusted port are forwarded. All other ports
should be configured as untrusted. Any DHCP (or BootP) responses received are discarded.
From the Services link, you can access the following pages:
• DHCP Filtering Configuration on page 76
• Interface Configuration on page 77
DHCP Filtering Configuration
Use the DHCP Filtering Configuration page to enable or disable the DHCP Filtering feature
on the switch.
To access the DHCP Filter Configuration page, click System Services DHCP Filtering
Configuration.
To configure global DHCP filtering settings:
1. In the Admin Mode field, select Enable or Disable to turn the DHCP Filtering feature on
or off.
2. Click Apply to apply the change to the system. Configuration changes take effect
immediately.
3. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
76
Page 77

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Interface Configuration
Use the DHCP Filtering Interface Configuration page to view and configure each port as a
trusted or untrusted port. Any DHCP responses received on a trusted port are forwarded. If a
port is configured as untrusted, any DHCP (or BootP) responses received on that port are
discarded.
To access the DHCP Filtering Interface Configuration page, click System
Filtering
Interface Configuration.
Services DHCP
To configure DHCP filtering settings for an interface:
1. To configure DHCP filtering settings for a physical port, click PORTS.
2. To configure DHCP filtering settings for a Link Aggregation Group (LAG), click LAGS.
3. To configure DHCP filtering settings for both physical ports and LAGs, click ALL.
4. Select the check box next to the port or LAG to configure. You can select multiple ports and
LAGs to apply the same setting to the selected interfaces. Select the check box in the
heading row to apply the same settings to all interfaces.
5. Choose the trust mode for the selected port(s) or LAG(s).
• Enable: Any DHCP responses received on this port are forwarded. The port
connected downstream from the authorized DHCP server should be configured as a
trusted port. Any DHCP responses received on a trusted port are forwarded. All other
ports should be configured as untrusted. Any DHCP (or BootP) responses received
are discarded.
• Disable: Any DHCP (or BootP) responses received on this port are discarded. Ports
connected to hosts should be configured as untrusted. This is the default value.
6. Click Apply to apply the change to the system. Configuration changes take effect
immediately.
7. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
77
Page 78

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
78
Page 79

3. Switching Features
Use the features in the Switching tab to define Layer 2 features. The Switching tab contains
links to the following features:
• Ports on page 79
• Link Aggregation Groups on page 83
• VLANs on page 89
• Voice VLAN on page 94
• Auto-VoIP Configuration on page 98
• Spanning Tree Protocol on page 99
• Multicast on page 112
• Address Table on page 128
• Multiple Registration Protocol Configuration on page 132
• 802.1AS on page 145
3
Ports
The pages on the Ports tab allow you to view and monitor the physical port information for
the ports available on the switch. From the Ports link, you can access the following pages:
• Port Configuration on page 80
• Flow Control on page 82
79
Page 80

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Port Configuration
Use the Port Configuration page to configure the physical interfaces on the switch.
To access the Port Configuration page, click Switching
Ports Port Configuration.
To configure port settings:
1. To configure settings for a physical port, click PORTS.
2. To configure settings for a Link Aggregation Group (LAG), click LAGS.
3. To configure settings for both physical ports and LAGs, click ALL.
80
Page 81

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
4. Select the check box next to the port or LAG to configure. You can select multiple ports and
LAGs to apply the same setting to the selected interfaces. Select the check box in the
heading row to apply the same settings to all interfaces.
5. Configure or view the settings:
• Description. Enter the description string to be attached to a port. The string can be
up to 64 characters in length.
• Port Type. For most ports this field is blank. Otherwise, the possible values are:
• Probe: Indicates that the port is a monitoring (destination) port. For additional
information about port monitoring see Port Mirroring on page 250.
• Mirrored: The port is a source port and mirrors traffic to the probe port. For
additional information about port monitoring see Port Mirroring on page 250.
• LAG: Indicates that the port is a member of a Link Aggregation trunk. For more
information see Link Aggregation Groups on page 83.
• Admin Mode. Use the menu to select the port control administration state, which can
be one of the following:
• Enable: The port can participate in the network (default).
• Disable: The port is administratively down and does not participate in the network.
• Port Speed. Use the menu to select the port’s speed and duplex mode. If you select
Auto, the duplex mode and speed will be set by the auto-negotiation process. The
port’s maximum capability (full duplex and 1000 Mbps) will be advertised. Otherwise,
your selection will determine the port’s duplex mode and transmission rate. The
factory default is Auto.
• Physical Status. Indicates the physical port’s speed and duplex mode
• Link Status. Indicates whether the Link is up or down.
• Link Trap. This object determines whether or not to send a trap when link status
changes. The factory default is Enable.
• Enable: Specifies that the system sends a trap when the link status changes.
• Disable: Specifies that the system does not send a trap when the link status
changes.
• Maximum Frame Size. Specifies the maximum Ethernet frame size the interface
supports. The size includes the Ethernet header, CRC, and payload. Any change to
the maximum frame size is immediately applied to all interfaces.
• MAC Address. Displays the physical address of the specified interface.
• PortList Bit Offset. Displays the bit offset value which corresponds to the port when
the MIB object type PortList is used to manage in SNMP.
• ifIndex. The ifIndex of the interface table entry associated with this port. If the
interface field is set to All, this field is blank.
6. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
7. If you make any changes to the page, click Apply to apply the changes to the system.
81
Page 82

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Flow Control
IEEE 802.3x flow control works by pausing a port when the port becomes oversubscribed
and dropping all traffic for small bursts of time during the congestion condition. This can lead
to high-priority and/or network control traffic loss. When IEEE 802.3x flow control is enabled,
lower speed switches can communicate with higher speed switches by requesting that the
higher speed switch refrains from sending packets. Transmissions are temporarily halted to
prevent buffer overflows.
To display the Flow Control page, click Switching
Ports, and then click the Flow Control
link.
To configure global flow control settings:
1. From the Global Flow Control (IEEE 802.3x) Mode field, enable or disable IEEE 802.3x
flow control on the system. The factory default is Disable.
• Enable. The switch sends pause packets if the port buffers become full.
• Disable. The switch does not send pause packets if the port buffers become full.
2. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
3. If you change the mode, click Apply to apply the changes to the system.
The GS716T and GS724T supports two combo ports using 1000M SFP modules. Each
combo port can operate in either ‘copper’ or ‘fiber’ mode. When a cable is plugged into the
RJ-45 port, copper mode is used. When a SFP module is plugged in, fiber mode is used.
The system automatically detects the media that is in use on a combo port and operates
accordingly. The SFP transceiver takes precedence over the RJ-45 copper port.
82
Page 83

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
In particular, the following behavior of combo port mechanism is followed:
1. When SFP transceiver is present in (plugged into) the SFP slot and optical link is
established via the SFP transceiver the combo port mechanism will use the SFP
transceiver and shut down the RJ-45 copper port regardless of the state of the latter
(that is, regardless of the copper port link being up or down);
2. If (and while) the optical link is down (SFP transceiver is not present in the SFP slot or fiber
cable is unplugged from SFP transceiver or optical link is shut down on the other side of the
fiber cable, etc.), then the combo port mechanism will use the RJ-45 copper port.
It is possible to switch between the RJ-45 copper port and the SFP transceiver without a
system reboot or reset.
Link Aggregation Groups
Link aggregation groups (LAGs), which are also known as port-channels, allow you to
combine multiple full-duplex Ethernet links into a single logical link. Network devices treat the
aggregation as if it were a single link, which increases fault tolerance and provides load
sharing. You assign the LAG VLAN membership after you create a LAG. The LAG by default
becomes a member of the management VLAN.
A LAG interface can be either static or dynamic, but not both. All members of a LAG must
participate in the same protocols. A static port-channel interface does not require a partner
system to be able to aggregate its member ports.
Static LAGs are supported. When a port is added to a LAG as a static member, it neither
transmits nor receives LAGPDUs. The GS716T and GS724T Smart Switches supports eight
LAGs.
From the LAGs link, you can access the following pages:
• LAG Configuration on page 84
• LAG Membership on page 85
• LACP Configuration on page 87
• LACP Port Configuration on page 88
83
Page 84

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
LAG Configuration
Use the LAG (Port Channel) Configuration page to group one or more full-duplex Ethernet
links to be aggregated together to form a link aggregation group, which is also known as a
port-channel. The switch treats the LAG as if it were a single link.
To access the LAG Configuration page, click Switching
LAG Basic LAG Configuration.
To configure LAG settings:
1. Select the check box next to the LAG to configure. You can select multiple LAGs to
apply the same setting to the selected interfaces. Select the check box in the heading
row to apply the same settings to all interfaces.
2. Configure or view the following settings:
• LAG Name. Specify the name you want assigned to the LAG. You may enter any
string of up to 15 alphanumeric characters. A valid name has to be specified in order
to create the LAG
• Description. Specify the Description string to be attached to a LAG. It can be up to 64
characters in length.
• LAG ID. Displays the number assigned to the LAG. This field is read-only.
• Link Trap. Specify whether you want to have a trap sent when link status changes.
The factory default is Disable, which will cause the trap to be sent.
• Admin Mode. Select Enable or Disable from the menu. When the LAG (port channel)
is disabled, no traffic will flow and LAGPDUs will be dropped, but the links that form
the LAG (port channel) will not be released. The factory default is Enable.
• STP Mode. Select the Spanning Tree Protocol Administrative Mode associated with
the LAG.
84
Page 85

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
• LAG Type. Specifies whether the LAG is configured as a Static or LACP port. When
the LAG is static, it does not transmit or process received LAGPDUs, for example the
member ports do not transmit LAGPDUs and all the LAGPDUs it may receive are
dropped. The default is Static.
• Active Ports. A listing of the ports that are actively participating members of this Port
Channel. A maximum of 8 ports can be assigned to a port channel.
• LAG State. Indicates whether the link is Up or Down.
3. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
4. If you make any changes to this page, click Apply to send the updated configuration to the
switch. Configuration changes take effect immediately.
LAG Membership
Use the LAG Membership page to select two or more full-duplex Ethernet links to be
aggregated together to form a link aggregation group (LAG), which is also known as a
port-channel. The switch can treat the port-channel as if it were a single link.
To access the LAG Membership page, click Switching
LAG Basic LAG Membership.
85
Page 86

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To add ports to a LAG:
1. From the LAG ID field, select the LAG to configure.
2. Optionally, in the LAG Name field, enter the name you want assigned to the LAG. You may
enter any string of up to 15 alphanumeric characters. A valid name has to be specified to
create the LAG.
3. Click the orange bar to display the ports.
4. Click the box below each port to include in the LAG. The following figure shows an example
of how to configure LAG1 with ports g1–g4 as members.
5. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
6. If you make any changes to this page, click Apply to send the updated configuration to the
switch. Configuration changes take effect immediately.
7. To view the ports that are members of the selected LAG, click Current Members.
86
Page 87

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
LACP Configuration
To display the LACP Configuration page, click Switching LAG Advanced LACP
Configuration.
To configure LACP:
1. From the LACP System Priority field, specify the device’s link aggregation priority
relative to the devices at the other ends of the links on which link aggregation is
enabled. A higher value indicates a lower priority. You can change the value of the
parameter globally by specifying a priority from 0–65535. The default value is 32768.
2. Click Refresh to reload the page and display the most current information.
3. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
4. If you make any changes to this page, click Apply to send the updated configuration to the
switch. Configuration changes take effect immediately.
87
Page 88

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
LACP Port Configuration
To display the LACP Port Configuration page, click Switching LAG Advanced LACP
Port Configuration.
To configure LACP port priority settings:
1. Select the check box next to the port to configure. You can select multiple ports to apply
the same setting to all selected ports.
Note: You cannot select ports that are not participating in a LAG
2. Configure the LACP Priority value for the selected port. The field range is 0–255. The
default value is 128.
3. Configure the administrative LACP Timeout value.
• Long. Specifies a long timeout value.
• Short. Specifies a short timeout value.
4. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
5. If you make any changes to this page, click Apply to send the updated configuration to the
switch. Configuration changes take effect immediately.
88
Page 89

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
VLANs
Adding Virtual LAN (VLAN) support to a Layer 2 switch offers some of the benefits of both
bridging and routing. Like a bridge, a VLAN switch forwards traffic based on the Layer 2
header, which is fast, and like a router, it partitions the network into logical segments, which
provides better administration, security and management of multicast traffic.
By default, all ports on the switch are in the same broadcast domain. VLANs electronically
separate ports on the same switch into separate broadcast domains so that broadcast
packets are not sent to all the ports on a single switch. When you use a VLAN, users can be
grouped by logical function instead of physical location.
Each VLAN in a network has an associated VLAN ID, which appears in the IEEE 802.1Q tag
in the Layer 2 header of packets transmitted on a VLAN. An end station may omit the tag, or
the VLAN portion of the tag, in which case the first switch port to receive the packet may
either reject it or insert a tag using its default VLAN ID. A given port may handle traffic for
more than one VLAN, but it can only support one default VLAN ID.
From the VLAN link, you can access the following pages:
• VLAN Configuration on page 89
• VLAN Membership Configuration on page 90
• Port VLAN ID Configuration on page 92
VLAN Configuration
Use the VLAN Configuration page to define VLAN groups stored in the VLAN membership
table. The GS716T and GS724T supports up to 256 VLANs. VLAN 1 is created by default,
and all ports are untagged members.
To display the VLAN Configuration page, lick Switching
Configuration.
VLAN Basic VLAN
89
Page 90

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To configure VLANs:
1. To add a VLAN, configure the VLAN ID, name, and type, and then click Add.
• VLAN ID. Specify the VLAN Identifier for the new VLAN. (You can enter data in this
field only when you are creating a new VLAN.) The range of the VLAN ID is 1–4093.
• VLAN Name. Use this optional field to specify a name for a non-default VLAN. It can
be up to 32 alphanumeric characters long, including blanks. The default is blank.
VLANs 1–3 cannot be renamed.
• VLAN Type. This field identifies the type of the VLAN you are configuring. The switch
is preconfigured with three VLANS that have a VLAN Type of Default. VLAN 1 is the
Default VLAN, VLAN 2 is the Voice VLAN, and VLAN 3 is the Auto-Video VLAN.
These VLANs cannot be changed or deleted. When you create a VLAN on this page,
its type will always be Static.
2. To delete a VLAN, select the check box next to the VLAN ID and click Delete. You cannot
delete the default VLANs.
3. To modify settings for a VLAN, select the check box next to the VLAN ID, change the
desired information, and then click Apply. Configuration changes occur immediately.
4. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
5. To reset the VLAN settings on the switch to the factory defaults, select the Reset
Configuration check box, and click OK in the popup message to confirm. If the
Management VLAN is set to a non-default VLAN (VLAN 1), it is automatically set to 1 after a
Reset Configuration.
VLAN Membership Configuration
Use this page to configure VLAN Port Membership for a particular VLAN. You can select the
Group operation through this page.
To display the VLAN Membership Configuration page, click Switching VLAN Advanced
VLAN Membership.
90
Page 91

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To configure VLAN membership:
1. From the VLAN ID field, select the VLAN to which you want to add ports.
2. Click the orange bar below the VLAN Type field to display the physical ports on the switch.
3. Click the lower orange bar to display the LAGs on the switch.
4. To select the port(s) or LAG(s) to add to the VLAN, click the square below each port or LAG.
You can add each interface as a tagged (T) or untagged (U) VLAN member. A blank square
means that the port is not a member of the VLAN.
• Tagged: Frames transmitted from this port are tagged with the port VLAN ID.
• Untagged: Frames transmitted from this port are untagged. Each port can be an
untagged member of only one VLAN. By default, all ports are an untagged member of
VLAN 1.
In the following figure, ports g6, g7, g8, and LAG 1 are being added as tagged members
to VLAN 99.
91
Page 92

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
5. Use the Group Operations field to select all the ports and configure them. Possible values
are:
• Untag All: Select all the ports on which all frames transmitted from this VLAN will be
untagged. All the ports will be included in the VLAN.
• Tag All: Select the ports on which all frames transmitted for this VLAN will be tagged.
All the ports will be included in the VLAN.
• Remove All: This selection has the effect of excluding all ports from the selected
VLAN.
6. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
7. If you make any changes to this page, click Apply to send the updated configuration to the
switch. Configuration changes take place immediately.
Port VLAN ID Configuration
The Port PVID Configuration screen lets you assign a port VLAN ID (PVID) to an interface.
There are certain requirements for a PVID:
• All ports must have a defined PVID.
• If no other value is specified, the default VLAN PVID is used.
To access the Port PVID Configuration page, click Switching
PVID Configuration.
VLAN Advanced Port
92
Page 93

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To configure PVID information:
1. To configure PVID settings for a physical port, click PORTS.
2. To configure PVID settings for a Link Aggregation Group (LAG), click LAGS.
3. To configure PVID settings for both physical ports and LAGs, click ALL.
4. Select the check box next to the interfaces to configure. You can select multiple interfaces to
apply the same setting to the selected interfaces. Select the check box in the heading row to
apply the same settings to all interfaces.
5. Configure the PVID to assign to untagged or priority tagged frames received on this port.
6. In the Acceptable Frame Type field, specify how you want the port to handle untagged and
priority tagged frames. Whichever you select, VLAN tagged frames will be forwarded in
accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN standard. The factory default is Admit All.
• VLAN Only: The port will accept only VLAN-tagged frames and will discard any
untagged or priority tagged frames it receives.
• Admit All: Untagged and priority tagged frames received on the port will be accepted
and assigned the value of the Port VLAN ID for this port.
7. In the Ingress Filtering field, specify how you want the port to handle tagged frames:
• Enable: A tagged frame will be discarded if this port is not a member of the VLAN
identified by the VLAN ID in the tag. In an untagged frame, the VLAN is the Port
VLAN ID specified for the port that received this frame.
• Disable: All frames are forwarded in accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
standard. The factory default is Disable.
8. Specify the default 802.1p priority assigned to untagged packets arriving at the port. Possible
values are 0–7.
9. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
10. If you make any changes to this page, click Apply to send the updated configuration to the
switch. Configuration changes take place immediately.
93
Page 94

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Voice VLAN
Configure the Voice VLAN settings for ports that carry traffic from IP phones. The Voice
VLAN feature can help ensure that the sound quality of an IP phone is safeguarded from
deteriorating when the data traffic on the port is high.
From the VLAN link, you can access the following pages:
• Voice VLAN Properties on page 94
• Voice VLAN Port Setting on page 95
• Voice VLAN OUI on page 96
Voice VLAN Properties
To display the Voice VLAN Properties page, click Switching Voice VLAN Basic
Properties.
To configure Voice VLAN:
1. From the Voice VLAN Status field, enable or disable Voice VLAN on the switch. If the
switch does not handle traffic from IP phones, the status should be disabled.
2. From the Voice VLAN ID field, select the VLAN to use for voice traffic on the switch. The
VLAN must already exist on the switch. For information about how to create VLANs, see
VLAN Configuration on page 89.
3. From the Class of Service field, set the CoS tag value to be reassigned for packets
received on the Voice VLAN when Remark CoS is enabled.
4. From the Remark CoS field, select Enable or Disable to reassign the CoS tag value to
packets received on the Voice VLAN.
94
Page 95

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
5. From the Voice VLAN Aging Time field, specify the amount of time after the last IP phone’s
OUI is aged out for a specific port. The port will age out after the bridge and voice aging
time.
6. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
7. If you make any changes to this page, click Apply to send the updated configuration to the
switch.
Voice VLAN Port Setting
To display the Voice VLAN Port Setting page, click Switching Voice VLAN Advanced
Port Setting.
To configure Voice VLAN port settings:
1. Select the check box next to the port to configure. You can select multiple check boxes
to apply the same setting to all selected ports.
2. From the Voice VLAN Mode menu, specify whether to enable or disable Voice VLAN on the
selected port.
3. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
4. If you make any changes to this page, click Apply to send the updated configuration to the
switch.
Note: The Membership field displays whether the current operational
status of the voice VLAN on the interface is active or not active.
95
Page 96

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Voice VLAN OUI
The Organizational Unique Identifier (OUI) identifies the IP phone manufacturer. The switch
comes preconfigured with the following OUIs:
• 00:01:E3: SIEMENS
• 00:03:6B: CISCO1
• 00:12:43: CISCO2
• 00:0F:E2: H3C
• 00:60:B9: NITSUKO
• 00:D0:1E: PINTEL
• 00:E0:75: VERILINK
• 00:E0:BB: 3COM
• 00:04:0D: AVAYA1
• 00:1B:4F: AVAYA2
You can select an existing OUI or add a new OUI and description to identify the IP phones on
the network.
To display the Voice VLAN OUI page, click Switching
Voice VLAN Advanced OUI.
96
Page 97

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
To configure OUI settings:
1. To add a new OUI prefix, type the VOIP OUI prefix in the Telephony OUI(s) field,
provide a description of the prefix, and click Add. The OUI prefix must be in the format
AA:BB:CC.
2. To delete an OUI prefix from the list, select the check box next to the OUI prefix and click
Delete.
3. To modify information for an entry in the OUI list, select the check box next to the OUI prefix,
update the OUI prefix or description, and then click Apply.
4. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
5. Click Restore Defaults to restore the list to the preconfigured OUIs.
97
Page 98

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Auto-VoIP Configuration
The Auto-VoIP automatically makes sure that time-sensitive voice traffic is given priority over
data traffic on ports that have this feature enabled. Auto-VoIP checks for packets carrying the
following VoIP protocols:
• Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
• H.323
• Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP)
VoIP frames that are received on ports that have the Auto-VoIP feature enabled are marked
with CoS Traffic Class 3.
Use the Auto-VoIP Configuration menu to configure the Auto-VoIP parameters. Interface
specifies all the configurable Auto-VoIP interfaces. Traffic Class displays the Traffic Class on
which the received VoIP frames are marked.
To display the Auto-VoIP Configuration page, click Switching
Auto-VoIP.
To enable Auto-VoIP:
1. Auto-VoIP Mode. Select the Auto-VoIP administrative mode for the interface. This
selector lists the two options for administrative mode: Enable and Disable. The
administrative mode of Auto-VoIP is disabled by default.
2. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to
the latest value of the switch.
3. If you make any configuration changes, click Apply to send the updated configuration to the
switch. Configuration changes occur immediately.
98
Page 99

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
Spanning Tree Protocol
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides a tree topology for any arrangement of bridges.
STP also provides one path between end stations on a network, eliminating loops. Spanning
tree versions supported include Common STP, Multiple STP, and Rapid STP.
Classic STP provides a single path between end stations, avoiding and eliminating loops. For
information on configuring Common STP, see CST Port Configuration on page 103.
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) supports multiple instances of Spanning Tree to
efficiently channel VLAN traffic over different interfaces. Each instance of the Spanning Tree
behaves in the manner specified in IEEE 802.1w, Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP), with slight
modifications in the working but not the end effect (chief among the effects, is the rapid
transitioning of the port to ‘Forwarding’). The difference between the RSTP and the traditional
STP (IEEE 802.1D) is the ability to configure and recognize full-duplex connectivity and ports
which are connected to end stations, resulting in rapid transitioning of the port to ‘Forwarding’
state and the suppression of Topology Change Notification. These features are represented
by the parameters ‘pointtopoint’ and ‘edgeport’. MSTP is compatible to both RSTP and STP.
It behaves appropriately to STP and RSTP bridges. A MSTP bridge can be configured to
behave entirely as a RSTP bridge or a STP bridge.
Note: For two bridges to be in the same region, the force version should
be 802.1s and their configuration name, digest key, and revision
level should match. For additional information about regions and
their effect on network topology, refer to the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
The Spanning Tree folder contains links to the following features:
• STP Switch Configuration on page 100
• CST Configuration on page 102
• CST Port Configuration on page 103
• CST Port Status on page 105
• Rapid STP on page 106
• MST Configuration on page 107
• MST Port Configuration on page 109
• STP Statistics on page 111
99
Page 100

GS716T and GS724T Gigabit Smart Switches
STP Switch Configuration
The Spanning Tree Switch Configuration/Status page contains fields for enabling STP on the
switch.
To display the Spanning Tree Switch Configuration/Status page, click Switching > STP >
Basic
STP Configuration.
To configure STP settings on the switch:
1. From the Spanning Tree State field, specify whether to enable or disable Spanning
Tree operation on the switch.
2. From the STP Operation Mode field, Specifies the Force Protocol Version parameter for the
switch. Options are:
• STP (Spanning Tree Protocol): IEEE 802.1D
• RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol): IEEE 802.1w
• MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol): IEEE 802.1s
3. Specify the configuration name and revision level.
• Configuration Name. Name used to identify the configuration currently being used. It
may be up to 32 alphanumeric characters.
• Configuration Revision Level. Number used to identify the configuration currently
being used. The values allowed are between 0 and 65535. The default value is 0.
100
 Loading...
Loading...