Page 1

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit
Firewall with SSL & IPsec
VPN FVS336G Reference
Manual
NETGEAR, Inc.
350 East Plumeria Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
202-10257-05
v1.0
January 2010
Page 2

© 2007–2010 by NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved.
Technical Support
Please refer to the support information card that shipped with your product. By registering your product at
http://www.netgear.com/register, we can provide you with faster expert technical support and timely notices of
product and software upgrades.
NETGEAR, INC. Support Information
Phone: 1-888-NETGEAR, for US & Canada only. For other countries, see your Support information card.
E-mail: support@netgear.com
North American NETGEAR website:
http://www.netgear.com
Trademarks
NETGEAR and the NETGEAR logo are registered trademarks and ProSafe is a trademark of NETGEAR, Inc.
Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT ar e registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Other brand and product
names are registered trademarks or trademarks of their respective holders.
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, NETGEAR reserves the right to
make changes to the products described in this document without notice.
NETGEAR does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of the product(s) or circuit
layout(s) described herein.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Compliance Notice: Radio Frequency
Notice
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruct ions, may cause harmf ul interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try
to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
EU Regulatory Compliance Statement
The ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN is compliant with the following EU Council
Directives: 89/336/EEC and LVD 73/23/EEC. Compliance is verified by testing to the following standards: EN55022
Class B, EN55024 and EN60950-1.
ii
v1.0, January 2010
Page 3
Bestätigung des Herstellers/Importeurs
Es wird hiermit bestätigt, daß das ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN gemäß der im BMPTAmtsblVfg 243/1991 und Vfg 46/1992 aufgeführten Bestimmungen entstört ist. Das vorschriftsmäßige Betreiben
einiger Geräte (z.B. Testsender) kann jedoch gewissen Beschränkungen unterliegen. Lesen Sie dazu bitte die
Anmerkungen in der Betriebsanleitung.
Das Bundesamt für Zulassungen in der Telekommunikation wurde davon unterrichtet, daß dieses Gerät auf den Markt
gebracht wurde und es ist berechtigt, die Serie auf die Erfüllung der Vorschriften hin zu überprüfen.
Certificate of the Manufacturer/Importer
It is hereby certified that the ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN has been suppressed
in accordance with the conditions set out in the BMPT-AmtsblVfg 243/1991 and Vfg 46/1992. The operation of some
equipment (for example, test transmitters) in accordance with the regulations may, howe v er, be subject to certain
restrictions. Please refer to the notes in the operating instructions.
Federal Office for Telecommunications Approvals has been notified of the placing of this equipment on the market
and has been granted the right to test the series for compliance with the regulations.
Voluntary Control Council for Interference (VCCI) Statement
This equipment is in the second category (information equipment to be used in a residential area or an adjacent area
thereto) and conforms to the standards set by the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by Data Processing
Equipment and Electronic Office Machines aimed at preventing radio interference in such residential areas.
When used near a radio or TV receiver , it may become the cause of radio interference.
Read instructions for correct handling.
Additional Copyrights
AES Copyright (c) 2001, Dr. Brian Gladman, brg@gladman.uk.net, Worcester, UK.
All rights reserved.
TERMS
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted
subject to the following conditions:
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of
conditions, and the following disclaimer.
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of
conditions, and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials
provided with the distribution.
3. The copyright holder’s name must not be used to endorse or promote any products
derived from this software without his specific prior written permission.
This software is provided “as is” with no express or implied warranties of correctness or fitness
for purpose.
v1.0, January 2010
iii
Page 4
Open SSL Copyright (c) 1998–2000 The OpenSSL Project. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted
provided that the following conditions are met:
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of
conditions, and the following disclaimer.
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of
conditions, and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials
provided with the distribution.
3. All advertising materials mentioning features or use of this software must display the
following acknowledgment: “This product includes software developed by the OpenSSL
Project for use in the OpenSSL Toolkit (
4. The names “OpenSSL Toolkit” and “OpenSSL Project” must not be used to endorse or
promote products derived from this software without prior written permission. For written
permission, contact openssl-core@openssl.org.
5. Products derived from this software may not be called “OpenSSL” nor may “OpenSSL”
appear in their names without prior written permission of the OpenSSL Project.
6. Redistributions of any form whatsoever must retain the following acknowledgment: “This
product includes software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the OpenSSL
Toolkit (
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE OpenSSL PROJECT “AS IS,” AND ANY
EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE OpenSSL PROJECT OR ITS
CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL,
EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR
PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY
OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING
NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS
SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
This product includes cryptographic software written by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com). This
product includes software written by Tim Hudson (tjh@cryptsoft.com).
MD5 Copyright (C) 1990, RSA Data Security, Inc. All rights reserved.
License to copy and use this software is granted provided that it is identified as the “RSA Data
Security, Inc. MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm” in all material mentioning or referencing this
software or this function. License is also granted to make and use derivative works provided
that such works are identified as “derived from the RSA Data Security, Inc. MD5 MessageDigest Algorithm” in all material mentioning or referencing the derived work.
RSA Data Security, Inc. makes no representations concerning either the merchantability of
this software or the suitability of this software for any particular purpose. It is provided “as is”
without express or implied warranty of any kind.
These notices must be retained in any copies of any part of this documentation and/or
software.
http://www.openssl.org/).”
http://www.openssl.org/).”
iv
v1.0, January 2010
Page 5
PPP Copyright (c) 1989 Carnegie Mellon University. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms are permitted provided that the above
copyright notice and this paragraph are duplicated in all such forms and that any
documentation, advertising materials, and other materials related to such distribution and use
acknowledge that the software was developed by Carnegie Mellon University. The name of
the University may not be used to endor se or promote products derived from this software
without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS” AND WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTIBILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Zlib zlib.h -- interface of the 'zlib' general purpose compression library version 1.1.4, March 11th,
2002. Copyright (C) 1995-2002 Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler.
This software is provided 'as-is', without any express or implied warranty. In no event will the
authors be held liable for any damages arising from the use of this software. Permission is
granted to anyone to use this software for any purpose, including commercial applications,
and to alter it and redistribute it freely, subject to the following restrictions:
1. The origin of this software must not be misrepresented; you must not claim that you wrote
the original software. If you use this software in a product, an acknowledgment in the
product documentation would be appreciated but is not required.
2. Altered source versions must be plainly marked as such, and must not be misrepresented
as being the original software.
3. This notice may not be removed or altered from any source distribution.
Jean-loup Gailly: jloup@gzip.org; Mark Adler: madler@alu mni.caltech.edu
The data format used by the zlib library is described by RFCs (Request for Comments) 1950
to 1952 in the files ftp://ds.internic.net/rfc/rfc1950.txt
and rfc1952.txt (gzip format)
(zlib format), rfc1951.txt (deflate format)
Product and Publication Details
Model Number: FVS336G
Publication Date: January 2010
Product Family: VPN Firewall
Product Name: ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN
Home or Business Product: Business
Language: English
Publication Part Number: 202-10257-05
Publication Version Number 1.0
v1.0, January 2010
v
Page 6

vi
v1.0, January 2010
Page 7

Contents
ProSafe Dual WA N Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G
Reference Manual
About This Manual
Conventions, Formats, and Scope .................................................................................. xv
How to Print This Manual ................................................................................................xvi
Revision History ..................... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ... ... ................................xvi
Chapter 1
Introduction
Key Features ..................................................................................................................1-1
Dual WAN Ports for Increased Reliability or Outbound Load Balancing ..................1-2
Advanced VPN Support for Both IPsec and SSL .....................................................1-2
A Powerful, True Firewall with Content Filtering ......................................................1-3
Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink ...............................................1-3
Extensive Protocol Support ......................................................................................1-4
Easy Installation and Management ................................................................................1-4
Maintenance and Support ............................... ... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ........1-5
Package Contents ..........................................................................................................1-5
Front Panel Features ......................................................................................................1-6
Rear Panel Features ......................................................................................................1-7
Default IP Address, Login Name, and Password Location ........................... .................. 1-8
Qualified Web Browsers .................................................................................................1-8
Chapter 2
Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet
Understanding the Connection Steps .............................................................................2-1
Logging into the VPN Firewall .................. .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ..2-2
Navigating the Menus .....................................................................................................2-4
Configuring the Internet Connections ........................................................... ..................2-4
Automatically Detecting and Connecting ............................ ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ...............2-5
Manually Configuring the Internet Connection ... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ..2-7
v1.0, January 2010
vii
Page 8

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Configuring the WAN Mode (Required for Dual WAN) .... ....................................... ... ...2-11
Network Address Translation .................................................................................2-12
Classical Routing ...................................................................................................2-12
Configuring Auto-Rollover Mode ............................................................................2-13
Configuring Load Balancing ...................................................................................2-14
Configuring Dynamic DNS (Optional) ...........................................................................2-16
Configuring the Advanced WAN Options (Optional) ............................................... ...... 2-18
Additional WAN Related Configuration ..................................................................2-20
Chapter 3
LAN Configuration
Choosing the VPN Firewall DHCP Options ....................................................................3-1
Configuring the LAN Setup Options ...............................................................................3-2
Managing Groups and Hosts (LAN Groups) ...................................................................3-6
Viewing the LAN Groups Database .........................................................................3-7
Adding Devices to the LAN Groups Database ......................................................... 3-8
Changing Group Names in the LAN Groups Database ...........................................3-8
Configuring DHCP Address Reservation .................................................................3-9
Configuring Multi Home LAN IP Addresses ..................................................................3-10
Configuring Static Routes .............................................................................................3-11
Configuring Routing Information Protocol (RIP) ................. ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...3-13
Chapter 4
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
About Firewall Protection and Content Filtering .............................................................4-1
Using Rules to Block or Allow Specific Kinds of Traffic ..................................................4-2
About Services-Based Rules ...................................................................................4-3
Viewing the Rules ....................................................................................................4-8
Order of Precedence for Rules ................................................................................4-8
Setting the Default Outbound Policy ............................... .... ... ... ....... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..4-8
Creating a LAN WAN Outbound Services Rule .......................................................4-9
Creating a LAN WAN Inbound Services Rule ........................................................4-10
Modifying Rules ......................................................................................................4-11
Inbound Rules Examples .......................................................................................4-11
Outbound Rules Example ............................... ... .... ... ... ....................................... ...4-14
Configuring Other Firewall Features .............................................................................4-15
Attack Checks ....................... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ... ...................4-15
viii
v1.0, January 2010
Page 9

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Configuring Session Limits .....................................................................................4-17
Managing the Application Level Gateway for SIP Sessions ..................................4-18
Creating Services, QoS Profiles, and Bandwidth Profiles ............................................4-19
Adding Customized Services .................................................................................4-19
Setting Quality of Service (QoS) Priorities ............................................................. 4-21
Creating Bandwidth Profiles ...... ... ... ... ....................................................................4-22
Setting a Schedule to Block or Allow Specific Traffic ................................. ... ... ... .... ... ...4-24
Blocking Internet Sites (Content Filtering) ....................................................................4-25
Configuring Source MAC Filtering ................................................................................4-28
Configuring IP/MAC Address Binding ...........................................................................4-30
Configuring Port Triggering ...........................................................................................4-31
E-Mail Notifications of Event Logs and Alerts ......................................... ......................4-33
Administrator Tips .........................................................................................................4-33
Chapter 5
Virtual Private Networking Using IPsec
Considerations for Dual WAN Port Systems ..................................................................5-1
Using the VPN Wizard for Client and Gateway Configurations ...................................... 5-3
Creating Gateway to Gateway VPN Tunnels with the Wizard .................................5-3
Creating a Client to Gateway VPN Tunnel ...............................................................5-6
Testing the Connections and Viewing Status Information ............................................. 5-12
NETGEAR VPN Client Status and Log Information ............................................... 5-12
VPN Firewall VPN Connection Status and Logs .... ... ... ... .... ... ...... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...5-14
Managing VPN Policies .. .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... .............................5-15
Configuring IKE Policies ............................... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ... ...5-16
Configuring VPN Policies .......................................................................................5-18
Configuring Extended Authentication (XAUTH) ............................................................5-19
Configuring XAUTH for VPN Clients ......................................................................5-20
User Database Configuration .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ... ...................5-22
RADIUS Client Configuration .................................................................................5-22
Assigning IP Addresses to Remote Users (ModeConfig) .............................................5-24
Mode Config Operation ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... .............5-24
Configuring Mode Config Operation on the VPN Firewall ......................................5-25
Configuring the ProSafe VPN Client for ModeConfig ....................................... ......5-30
Configuring Keepalives and Dead Peer Detection .......................................................5-32
Configuring Keepalives ..........................................................................................5-32
v1.0, January 2010
ix
Page 10

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Configuring Dead Peer Detection ..........................................................................5-33
Configuring NetBIOS Bridging with VPN ......................................................................5-34
Chapter 6
Virtual Private Networking Using SSL
Understanding the Portal Options ...................................................................................6-1
Planning for SSL VPN ....................................................................................................6-2
Creating the Portal Layout ..............................................................................................6-3
Configuring Domains, Groups, and Users ......................................................................6-7
Configuring Applications for Port Forwarding ............................................ .....................6-7
Adding Servers ................................... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ..................6-8
Adding A New Host Name . ... .... ... ... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... ...............6-9
Configuring the SSL VPN Client ...................................................................................6-10
Configuring the Client IP Address Range . ...... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ......6-11
Adding Routes for VPN Tunnel Clients ........ ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....... ... ... ... .... ... ...6-12
Replacing and Deleting Client Routes ...................................................................6-12
Using Network Resource Objects to Simplify Policies ..................................................6-13
Adding New Network Resources ..........................................................................6-13
Configuring User, Group, and Global Policies ..............................................................6-15
Viewing SSL VPN Policies .....................................................................................6-16
Adding an SSL VPN Policy ....................................................................................6-17
Chapter 7
Managing Users, Authentication, and Certificates
Adding Authentication Domains, Groups, and Users .....................................................7-1
Creating a Domain ............................. .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ... ... ..7-1
Creating a Group .................................... ...................................... .... ... ... ... ...............7-5
Creating a New User Account ... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ... ... ..................7-6
Setting User Login Policies ............................. ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ..7-7
Changing Passwords and Other User Settings ......................... ....... ...... ...... ....... .....7-9
Managing Certificates ...................... ... ... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... ... .... ......7-11
Viewing and Loading CA Certificates .....................................................................7-12
Viewing Active Self Certificates ..............................................................................7-13
Obtaining a Self Certificate from a Certificate Authority ...................... ... ... ... .... ... ...7-14
Managing your Certificate Revocation List (CRL) .. ... ... ..........................................7-17
x
v1.0, January 2010
Page 11

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Chapter 8
VPN Firewall and Network Management
Performance Management ....................................... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ..8-1
Bandwidth Capacity .................................................................. ... .... ... ... ..................8-1
Features That Reduce Traffic ...................................................................................8-2
Features That Increase Traffic .................................................................................8-5
Using QoS to Shift the Traffic Mix ............................................................................8-7
Tools for Traffic Management .......... ... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ... ..... 8-8
Changing Passwords and Administrator Settings .... .... ... ... ... .... ... ..................................8-8
Enabling Remote Management Access .......................................................................8-10
Using the Command Line Interface ..............................................................................8-12
Using an SNMP Manager .............................................................................................8-13
Managing the Configuration File ...................................................................................8-14
Configuring Date and Time Service ..............................................................................8-17
Chapter 9
Monitoring System Performance
Enabling the Traffic Meter ...............................................................................................9-1
Activating Notification of Events and Alerts ....................................................................9-4
Viewing the Logs ............................................................................................................9-6
Viewing VPN Firewall Configuration and System Status ................................................ 9-8
Monitoring VPN Firewall Statistics ......... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ..9-9
Monitoring the Status of WAN Ports .............................................................................9-10
Monitoring Attached Devices ........................................................................................9-11
Viewing the DHCP Log .................................................................................................9-12
Monitoring Active Users ................... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... ..........9-13
Viewing Port Triggering Status .....................................................................................9-14
Monitoring VPN Tunnel Connection Status ........ ... ....... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...9-15
Viewing the VPN Logs ..................................................................................................9-16
Chapter 10
Troubleshooting
Basic Functions ............................................................................................................10-1
Power LED Not On .................................................................................................10-2
LEDs Never Turn Off ..............................................................................................10-2
LAN or WAN Port LEDs Not On .............................................................................10-2
Troubleshooting the Web Configuration Interface ........................................................10-3
v1.0, January 2010
xi
Page 12

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Troubleshooting the ISP Connection ............................................................................10-4
Troubleshooting a TCP/IP Network Using a Ping Utility ...............................................10-5
Testing the LAN Path to Your VPN Firewall ...........................................................10-5
Testing the Path from Your PC to a Remote Device ..............................................10-6
Restoring the Default Configuration and Password ............ ... .... ... ... ... ..........................10-7
Problems with Date and Time .......................................................................................10-7
Using the Diagnostics Utilities ......................................................................................10-8
Appendix A
Default Settings and Technical Specifications
Appendix B
Network Planning for Dual WAN Ports
What You Will Need to Do Before You Begin ................................................................ B-1
Cabling and Computer Hardware Requirements .................................................... B-3
Computer Network Configuration Requirements ...................................... ... .... ... ... . B-3
Internet Configuration Requirements ...................................................................... B-3
Where Do I Get the Internet Configuration Parameters? ........................................ B-4
Internet Connection Information Form .................................................................... B-4
Overview of the Planning Process ................................................................................. B-5
Inbound Traffic ........................................................................................................ B-5
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) ............................................................................. B-6
The Roll-over Case for Firewalls With Dual WAN Ports .......................................... B-6
The Load Balancing Case for Firewalls With Dual WAN Ports ............................... B-7
Inbound Traffic ............................................................................................................... B-7
Inbound Traffic to Single WAN Port (Reference Case) ........................................... B-7
Inbound Traffic to Dual WAN Port Systems ............................................................ B-8
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) .................................................................................... B-9
VPN Road Warrior (Client-to-Gateway) .................................................................B-11
VPN Gateway-to-Gateway ........... ...... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ...... .... ... .. B-13
VPN Telecommuter (Client-to-Gateway Through a NAT Router) .......................... B-16
Appendix C
Two Factor Authentication
Why do I need Two-Factor Authentication? ...................................................................C-1
What are the benefits of Two-Factor Authentication? ............................................. C-1
What is Two-Factor Authentication ......................................................................... C-2
NETGEAR Two-Factor Authentication Solutions ....................................................... .... C-2
xii
v1.0, January 2010
Page 13

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Appendix D
Related Documents
Index
v1.0, January 2010
xiii
Page 14

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
xiv
v1.0, January 2010
Page 15
About This Manual
The NETGEAR® ProSafe™ Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN Reference
Manual describes how to install, configure and troubleshoot a ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit
Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN. The information in this manual is intended for readers with
intermediate computer and networking skills.
Conventions, Formats, and Scope
The conventions, formats, and scope of this manual are described in the following paragraphs:
• Typographical Conventions. This manual uses the following typographical conventions:
Italic Emphasis, books, CDs, file and server names, extensions
Bold User input, IP addresses, GUI screen text
Fixed Command prompt, CLI text, code
italic URL links
• Formats. This manual uses the following formats to highlight special messages:
Note: This format is used to highlight information of importance or special interest.
Tip: This format is used to highlight a procedure that will save time or resources.
Warning: Ignoring this type of note may result in a malfunction or damage to the
equipment.
Danger: This is a safety warning. Failure to take heed of this notice may result in
personal injury or death.
v1.0, January 2010
xv
Page 16
ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
• Scope. This manual is written for the VPN firewall according to these specifications:
Product Version ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN
Manual Publication Date January 2010
For more information about network, Internet, firewall, and VPN technologies, see the links to the
NETGEAR website in Appendix D, “Related Documents.”
Note: Product updates are available on the NETGEAR, Inc. website at
http://kb.netgear.com/app/home.
How to Print This Manual
T o print this manual, your computer must have the free Adobe Acrobat reader installed in order to
view and print PDF files. The Acrobat reader is available on the Adobe websit e at
http://www.adobe.com.
Tip: If your printer supports printing two pages on a single sheet of paper, you can save
paper and printer ink by selecting this feature.
Revision History
Part Number
202-10257-01 1.0 October
202-10257-02 1.1 November
202-10257-03 1.2 June 2008 Updated to align with router firmware update.
xvi
Version
Number
Date Description
First publication
2007
Text corrections
2007
v1.0, January 2010
Page 17
ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
202-10257-04 1.3 March
2009
202-10257-05 1.0 January
2010
Added these corrections and topics for the March 2009 firmware
maintenance release:
• WIKID 2 factor authentication
• SIP AGL support
• DHCP Relay support
• Updated VPN configuration procedure topics
• Updated the Certificate management topic
• Corrected the firewall scheduling topic
Added the following new features for the January 2010 firmware
maintenance release:
• Connection reset and delay options on the WAN ISP Settings
screen (see “Manually Configuring the Internet Connection”).
• Support for DNS 3322 in the Dynamic DNS submenu (see
“Configuring Dynamic DNS (Optional)”).
• Support for an address range for inbound LAN rules on the Add
LAN WAN Inbound Service screen (see “Inbound Rules (Port
Forwarding)” and “Creating a LAN WAN Inbound Services Rule”).
• Support for new log options such as Resolved DNS Names and
VPN on the Firewall Logs & E-mail screen (see “Activating
Notification of Events and Alerts”).
In addition, made the following substantial changes to the book:
• Resized many screen captures for better viewing.
• Made various corrections.
• Made global stylistic changes for consistency and clarity.
• Added technical support information to page ii.
• Updated the bottom label image (Figure 1-3).
• Updated the qualified Web browsers in the “Qualified Web
Browsers” and “Computer Network Configuration Requirements”
sections.
• Updated the WAN1 ISP Settings screen (Figure 2-3) and the ISP
Type options in the
Connection” section.
• Updated the Dynamic DNS Configuration screen (Figure 2-12)
and the DDNS providers in the “Configuring Dynamic DNS
(Optional)” section.
• Reorganized Chapter 4, “Firewall Protection and Content
Filtering.”
• Updated the LAN Setup screen (Figure 3-1). Added DHCP Relay
information, LDAP information, and the Enable ARP Broadcast
paragraph to the “Configuring the LAN Setup Options” section.
• Updated the Add LAN WAN Inbound Service screen (Figure 4-3),
related screens in the “Inbound Rules Examples” section, and the
Inbound Rules table (Table 4-2) to show that a range of IP
addresses can be selected for the Send to LAN Server field.
• Updated the “Modifying Rules” section.
“Manually Configuring the Internet
v1.0, January 2010
xvii
Page 18
ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
202-10257-05
(continued)
1.0 January
2010
(continued)
• Updated the “Attack Checks” section and screen (Figure 4-8) to
show that you can specify an IP address that is allowed to
respond to a ping.
• Added the “Managing the Application Level Gateway for SIP
Sessions” section.
• Updated the “Creating Bandwidth Profiles” section, including
Figure 4-13 and Figure 4-14.
• Added the IKE Policies screen (Figure 5-20 and Figure 5-26) to
respectively the “The IKE Policies Screen” section and the
“Configuring an IKE Policy for Mode Config Operation” section.
• Added the Add IKE Policy screen (Figure 5-22) to “Configuring
XAUTH for VPN Clients” section.
• Updated the VPN-SSL Policies screen (Figure 6-8 and
Figure 6-9) to show the Related Policies Table and added a Note
to the “Viewing SSL VPN Policies” section.
• Revised the “Creating a Domain” secti on, added the
Authentication Protocols and Methods table (Table 7-1), and
revised the Domains screen (Figure 7-1).
• Revised the “Changing Passwords and Other User Settings”
section and replaced the Local Authentication screen with the
Edit User screen (Figure 7-9).
• Removed the “RADIUS Server External Authentication” section
(with its External Authentication screen) that has been
superseded by the “RADIUS Client Configuration” section and
the “Creating a Domain” section.
• Revised and corrected the “Performance Management” section.
• Updated the “Enabling Remote Management Access” section
and the Remote Management screen (Figure 8-3) to show the
extended secure HTTP management options.
• Updated the Firewall Logs & E-mail screen (Figure 9-2) to show
the new log options and revised Table 9-1.
• Added the (firewall) Logs screen (Figure 9-3).
• Revised and corrected the Router Status information in
Table 9-3.
• Added the “Monitoring VPN Firewall Statistics” section.
• Made screen reference corrections in Chapter 10,
“Troubleshooting.”
• Updated Appe
ndix D, “Related Documents.”
xviii
v1.0, January 2010
Page 19

Chapter 1
Introduction
The ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G connects your local
area network (LAN) to the Internet through one or two external broadband access devices such as
cable modems or DSL modems. Dual wide area network (WAN) ports allow you to increase
throughput to the Internet by using both ports together, or to maintain a backup connection in case
of failure of your primary Internet connection.
As a complete security solution, the FVS336G incorporates a powerful and flexible firewall to
safeguard your network, while providing advanced IPsec and SSL VPN technologies for secure
and simple remote connections.
The use of Gigabit Ethernet LAN and WAN ports ensures extremely high data transfer speeds
The FVS336G is a plug-and-play device that can be installed and configured within minutes.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• “Key Features” on this page
• “Package Contents” on page 1-5
• “Front Panel Features” on page 1-6
• “Rear Panel Features” on page 1-7
• “Default IP Address, Login Name, and Password Location” on page 1-8
• “Qualified Web Browsers” on page 1-8
Key Features
The FVS336G provides the following key features:
• Dual 10/100/1000 Mbps Gigabit Ethernet WAN ports for load balancing or failover p rotection
of your Internet connection, providing increased system reliability or increased throughput.
• Built-in four-port 10/100/1000 Mbps Gigabit Ethernet LAN switch for extremely fast data
transfer between local network resources.
• Advanced IPsec and SSL VPN support.
• Advanced stateful packet inspection (SPI) firewall with multi-NAT support.
1-1
v1.0, January 2010
Page 20

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
• Easy, web-based setup for installation and management.
• Front panel LEDs for easy monitoring of status and activity.
• Flash memory for firmware upgrade.
• Internal universal switching power supply.
Dual WAN Ports for Increased Reliability or Outbound Load Balancing
The FVS336G has two broadband WAN ports. The second WAN port allows you to connect a
second broadband Internet line that can be configured on a mutually-exclusive basis to:
• Provide backup and rollover if one line is inoperable, ensuring you are never disconnected.
• Load balance, or use both Internet lines simultaneously for outgoing traffic. The FVS336G
balances users between the two lines for maximum bandwidth efficiency.
See “Network Planning for Dual WAN Ports” on page B-1 for the planning factors to consider
when implementing the following capabilities with dual WAN port gateways:
• Single or multiple exposed hosts.
• V irtual private networks.
Advanced VPN Support for Both IPsec and SSL
The FVS336G supports IPsec and SSL virtual private network (VPN) connections.
• IPsec VPN delivers full network access between a central office and branch offices, or
between a central office and telecommuters. Remote access by telecommuters requires the
installation of VPN client software on the remote computer.
– IPsec VPN with broad protocol support for secure connection to other IPsec gateways and
clients.
– Bundled with the single-user license of the NETGEAR ProSafe VPN Client software
(VPN01L)
– Supports 25 concurrent IPsec VPN tunnels.
• SSL VPN provides remote access for mobile users to selected corporate resources without
requiring a pre-installed VPN client on their computers.
– Uses the familiar Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol, commonly used for e-commerce
transactions, to provide client-free access with customizable user portals and support for a
wide variety of user repositories.
1-2 Introduction
v1.0, January 2010
Page 21

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
– Browser based, platform-independent, remote access through a number of popular
browsers, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Apple Safari.
– Provides granular access to corporate resources based upon user type or group
membership.
– Supports 10 concurrent SSL VPN sessions.
A Powerful, True Firewall with Content Filtering
Unlike simple Internet sharing NAT routers, the FVS336G is a true firewall, using stateful packet
inspection (SPI) to defend against hacker attacks. Its firewall features include:
• Automatically detects and thwarts denial of service (DoS) attacks such as Ping of Death and
SYN Flood.
• Blocks unwanted traffic from the Internet to your LAN.
• Blocks access from your LAN to Internet locations or services that you specify as off-limits.
• Prevents objectionable content from reaching your PCs. You can control access to Internet
content by screening for Web services, Web addresses, and keywords within Web addresses.
You can configure the FVS336G to log and report attempts to access objectionable Internet
sites.
• Permits scheduling of firewall policies by day and time.
• Logs security events such as blocked incoming traffic, port scans, attacks, and administrator
logins. Y ou can configure the FVS336G to e-mail the log to you at specified intervals. You can
also configure the FVS336G to send immediate alert messages to your e-mail address or
e-mail pager whenever a significant event occurs.
Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink
With its internal 4-po rt 10/100/1000 Mbps switch and dual 10/100/1000 WAN ports, the FVS336 G
can connect to either a 10 Mbps standard Ethernet network, a 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet network, or
a 1000 Mbps Gigabit Ethernet network. The four LAN and two WAN interfaces are autosensing
and capable of full-duplex or half-duplex operation.
The FVS336G incorporates Auto Uplink
sense whether the Ethernet cable plugged into the port should have a “normal” connection such as
to a PC or an “uplink” connection such as to a switch or hub. That port will then configure itself to
the correct configuration. This feature eliminates the need to worry about crossover cables, as
Auto Uplink will accommodate either type of cable to make the right connection.
Introduction 1-3
TM
technology. Each Ethernet port will automatically
v1.0, January 2010
Page 22

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Extensive Protocol Support
The FVS336G supports the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and
Routing Information Protocol
Configuration Requirements” on page B-3.
• IP Address Sharing by NAT. The FVS336G allows many networked PCs to share an Internet
account using only a single IP address, which may be statically or dynamically assigned by
your Internet service provider (ISP). This technique, known as NAT, allows the use of an
inexpensive single-user ISP account.
• Automatic Configuration of Attached PCs by DHCP. The FVS336G dynamically assigns
network configuration information, including IP, gateway, and domain name server (DNS)
addresses, to attached PCs on the LAN using the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP). This feature greatly simplifies configuration of PCs on your local network.
• DNS Proxy. When DHCP is enabled and no DNS addresses are specified, the FVS336G
provides its own address as a DNS server to the attached PCs. The FVS336G obtains actual
DNS addresses from the ISP during connection setup and forwards DNS requests from the
LAN.
• PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE). PPPoE is a protocol for connecting remote hosts to the Internet
over a DSL connection by simulating a dial-up connection. This feature eliminates the need to
run a login program such as EnterNet or WinPOET on your PC.
• Quality of Service (QoS). Support for traffic prioritization.
(RIP). For further information about TCP/IP, refer to “Internet
Easy Installation and Management
You can install, configure, and operate the FVS336G within minutes after connecting it to the
network. The following features simplify installation and management tasks:
• Browser-Based Management. Browser-based configuration allows you to easily configure
your FVS336G from almost any type of personal computer, such as Windows, Macintosh, or
Linux. Online help documentation is built into the browser-based Web Management Interface.
• Auto Detection of ISP. The FVS336G automatically senses the type of Internet connection,
asking you only for the information required for your type of ISP account.
• VPN Wizard. The FVS336G includes the NETGEAR VPN Wizard to easily configure IPsec
VPN tunnels according to the recommendations of the Virtual Private Network Consortium
(VPNC) to ensure the IPsec VPN tunnels are interoperable with other VPNC-compliant VPN
routers and clients.
1-4 Introduction
v1.0, January 2010
Page 23

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
• SNMP. The FVS336G supports the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) to let you
monitor and manage log resources from an SNMP-compliant system manager. The SNMP
system configuration lets you change the system variables for MIB2.
• Diagnostic Functions. The FVS336G incorporates built-in diagnostic functions such as Ping,
Trace Route, DNS lookup, and remote reboot.
• Remote Management. The FVS336G allows you to login to the Web Management Interface
from a remote location on the Internet. For security, you can limit remote management access
to a specified remote IP address or range of addresses.
• Visual monitoring. The FVS336G’s front panel LEDs provide an easy way to monitor its
status and activity.
Maintenance and Support
NETGEAR offers the following features to help you maximize your use of the FVS336G:
• Flash memory for firmware upgrade.
• Technical support seven days a week, 24 hours a day, according to the terms identified in the
Warranty and Support information card provided with your product.
Package Contents
The product package should contain the following items:
• ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G appliance.
• One AC power cable.
• Rubber feet.
• One Category 5 (Cat5) Ethernet cable.
• Installation Guide, FVS336G ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN.
• Resource CD, including:
– Application Notes and other helpful information.
– ProSafe VPN Client Software—one user license.
• Warranty and Support Information Card.
Introduction 1-5
v1.0, January 2010
Page 24
ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
If any of the parts are incorrect, missing, or damaged, contact your NETGEAR dealer. Keep the
carton, including the original packing materials, in case you need to return the FVS336G for
repair.
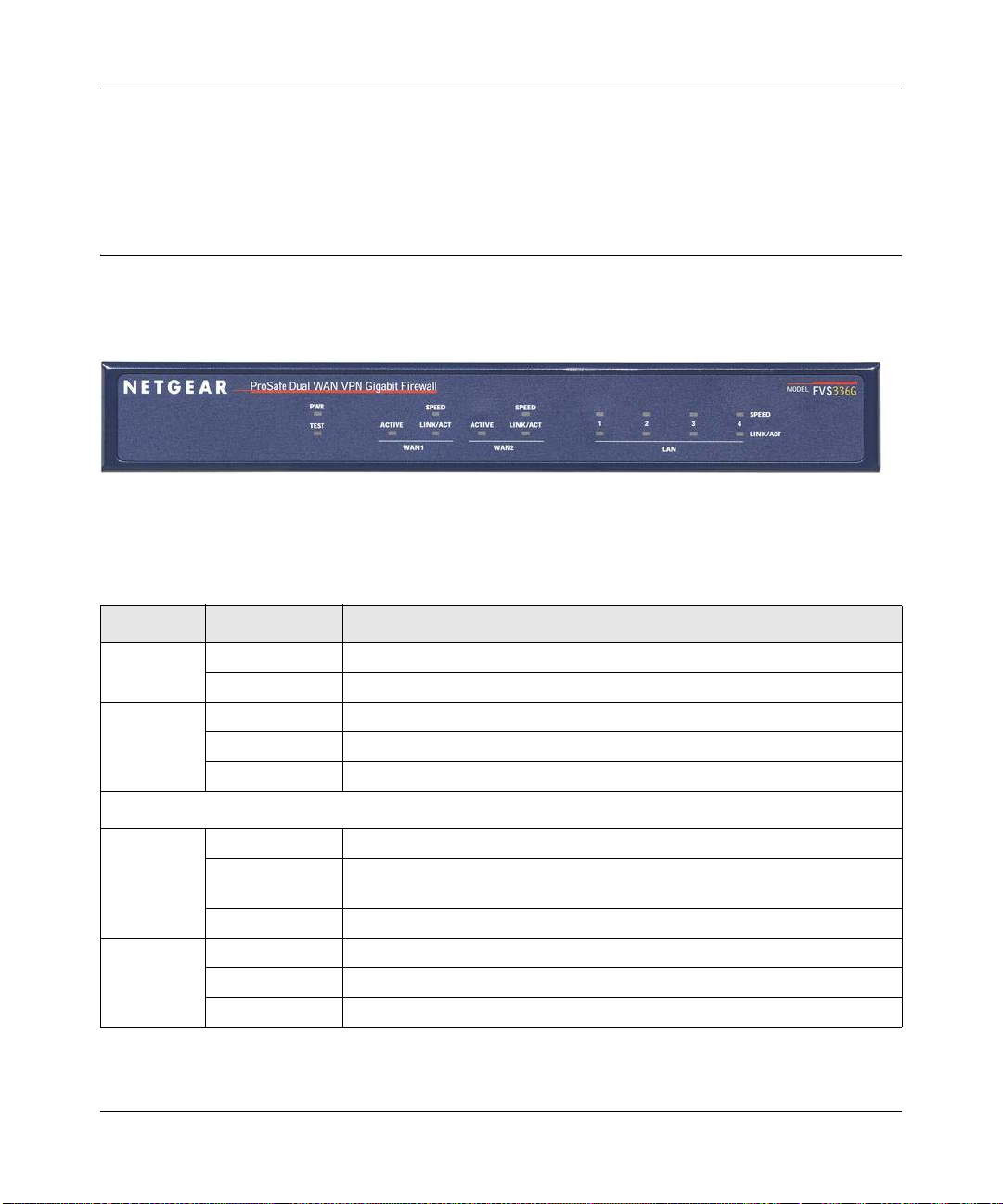
Front Panel Features
The FVS336G front panel shown below includes four groups of status indicator light-emitting
diodes (LEDs), including Power and Test, WAN1, WAN2, and the LAN lights:
Figure 1-1
The function of each LED is described in the following table:
Table 1-1. LED Descriptions
Object Activity Description
PWR
(Power)
TEST
WAN Ports
ACTIVE
SPEED
On (Green) Power is supplied to the FVS336G.
Off Power is not supplied to the FVS336G.
On (Amber) Test mode: The system is initializing or the initialization has failed.
Blinking (Amber) Writing to Flash memory (during upgrading or resetting to defaults).
Off The system has booted successfully.
On (Green) The WAN port has a valid Internet connection.
On (Amber) The Internet connection is down or not being used because the WAN port
is in standby for failover.
Off The WAN port is either not enabled or has no link.
On (Green) The WAN port is operating at 1,000 Mbps.
On (Amber) The WAN port is operating at 100 Mbps.
Off The WAN port is operating at 10 Mbps.
1-6 Introduction
v1.0, January 2010
Page 25

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Table 1-1. LED Descriptions (continued)
Object Activity Description
LINK/ACT
(Link and
Activity)
LAN Ports
SPEED
LINK/ACT
(Link and
Activity)
On (Green) The WAN port has detected a link with a connected Ethernet device.
Blinking (Green) Data is being transmitted or received by the WAN port.
Off The WAN port has no link.
On (Green) The LAN port is operating at 1,000 Mbps.
On (Amber) The LAN port is operating at 100 Mbps.
Off The LAN port is operating at 10 Mbps.
On (Green) The LAN port has detected a link with a connected Ethernet device.
Blinking (Green) Data is being transmitted or received by the LAN port.
Off The LAN port has no link.
Rear Panel Features
The rear panel of the FVS336G includes Gigabit Ethernet LAN and WAN connections, a cable
lock receptacle, power and reset switches, and an AC power connection.
Figure 1-2
Viewed from left to right, the rear panel contains the following elements:
• Factory Defaults button: Using a sharp object, press and hold this button for about ten seconds
until the front panel TEST light flashes to reset the FVS336G to factory default settings. All
configuration settings will be lost and the default password will be restored.
• LAN Ethernet ports: Four switched N-way automatic speed negotiating, Auto MDI/MDIX,
Gigabit Ethernet ports with RJ-45 connectors.
• WAN Ethernet ports: T wo independent N-way automatic speed negotiating, Auto MDI/MDIX,
Gigabit Ethernet ports with RJ-45 connectors.
• Cable security lock receptacle.
Introduction 1-7
v1.0, January 2010
Page 26
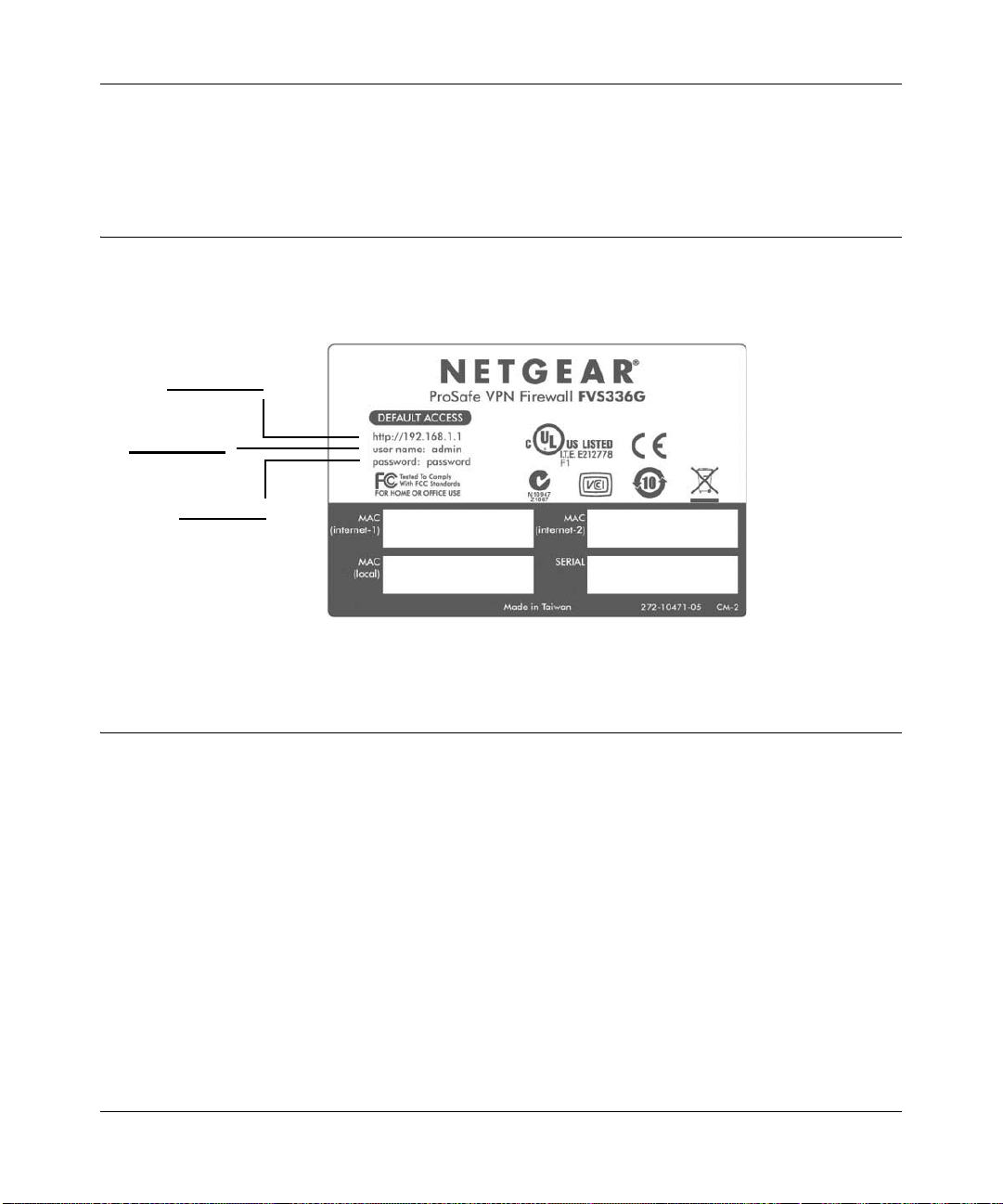
ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
IP Address
User Name
Password
• AC power receptacle: Universal AC input (100-240 VAC, 50-60 Hz).
• On/off power switch.
Default IP Address, Login Name, and Password Location
Check the label on the bottom of the FVS336G’s enclosure if you need a reminder of the following
factory default information:
Figure 1-3
Qualified Web Browsers
To configure the FVS336G, you must use a Web browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 6 or
higher, Mozilla Firefox 3 or higher, or Apple Safari 3 or higher with JavaScript, cookies, and you
must have SSL enabled.
Although these Web browsers are qualified for use with the FVS336G’s Web Management
Interface for configuring the FVS336G, SSL VPN users should choose a browser that supports
JavaScript, Java, cookies, SSL, and ActiveX to take advantage of the full suite of applications.
Note that Java is only required for the SSL VPN portal, not the Web Management Interface.
1-8 Introduction
v1.0, January 2010
Page 27

Chapter 2
Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet
The initial Internet configuration of the ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec
VPN FVS336G, hereafter referred to as the VPN firewall, is described in this chapter.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• “Understanding the Connection Steps” on this page
• “Logging into the VPN Firewall” on page 2-2
• “Navigating the Menus” on page 2-4
• “Configuring the Internet Connections” on page 2-4
• “Configuring the WAN Mode (Required for Dual WAN)” on page 2-11
• “Configuring Dynamic DNS (Optional)” on page 2-16
• “Configuring the Advanced WAN Options (Optional)” on page 2-18
Understanding the Connection Steps
Typically, six steps are required to complete the basic Internet connection of your VPN firewall.
1. Connect the VPN firewall physically to your network. Connect the cables and restart your
network according to the instructions in the installation guide. See the Installation Guide,
FVS336G ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN for complete steps. A
PDF of the Installation Guide is on the NETGEAR website at: http://kbserver.netgear.com.
2. Log in to the VPN Firewall. After logging in, you are ready to set up and configure your
VPN firewall. You can also change your password and enable remote management at this
time. See “Logging into the VPN Firewall” on page 2-2.
3. Configure the Internet connections to your ISP(s). During this phase, you will connect to
your ISPs. See “Configuring the Internet Connections” on page 2-4.
4. Configure the WAN mode (required for dual WAN operatio n). Select either dedicated
(single WAN) mode, auto-rollover mode, or load balancing mode. For load balancing, you can
also select any necessary protocol bindings. See “Configuring the WAN Mode (Required for
Dual WAN)” on page 2-11.
2-1
v1.0, January 2010
Page 28

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
5. Configure dynamic DNS on the WAN ports (optional). Configure your fully qualified
domain names during this phase (if required). See “Configuring Dynamic DNS (Optional)” on
page 2-16.
6. Configure the WAN options (optional). Optionally, you can enable each WAN port to
respond to a ping, and you can change the factory default MTU size and port speed. However ,
these are advanced features and changing them is not usually required. See “Configuring the
Advanced WAN Options (Optional)” on page 2-18.
Each of these tasks is detailed separately in this chapter. The configuration of firewall and VPN
features is described in later chapters.
Logging into the VPN Firewall
To connect to the VPN firewall, your computer needs to be configured to obtain an IP address
automatically from the VPN firewall by DHCP. For instructions on how to configure your
computer for DHCP, refer to the “Preparing Y our Network” document that you can access from the
link in Appendix D, “Related Documents.”
To connect and log in to the VPN firewall follow these steps:
1. Start any of the qualified browsers, as detailed in “Qualified Web Browsers” on page 1-8.
2. Enter https://192.168.1.1 in the address field. The Manager login features appear in the
browser.
Figure 2-1
3. In the User field, type admin
4. In the Password field, type password
Note that both entries are in lower case letters.
2-2 Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet
v1.0, January 2010
Page 29

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
5. Click Login. The Web Configuration Manager appears, displaying the Router Status screen:
Figure 2-2
Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet 2-3
v1.0, January 2010
Page 30
ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Navigating the Menus
The Web Configuration Manager menus are organized in a layered structure of main categories
and submenus:
• Main menu. The horizontal orange bar near the top of the page is the main menu, containing
the primary configuration categories. Clicking on a primary category changes the contents of
the submenu bar.
• Submenu. The horizontal grey bar immediately below the main menu is the submenu,
containing subcategories of the currently selected primary category.
• Tab. Immediately below the submenu bar, at the top of the menu active window, are one or
more tabs, further subdividing the currently selected subcategory if necessary.
• Option arrow . To the right of the tabs on some menus are one or more blue dots with an arrow
in the center . Clicking an option arrow brings up either a popup window or an ad vanced option
menu.
Tip: In the instructions in this guide, we may refer to a menu using the notation
primary | subcategory, such as Network Configuration | WAN Settings. In this
example, Network is the selected primary category (in the main menu) and
WAN Settings is the selected subcategory (in the submenu).
You can now proceed to the first configuration task, configuring the VPN firewall’s Internet
connections.
Configuring the Internet Connections
To set up your VPN firewall for secure Internet connections, you configure WAN ports 1 and 2.
The Web Configuration Manager offers two connection configuration options:
• Automatic detection and configuration of the network connection.
• Manual configuration of the network connection.
Each option is detailed in the sections following.
2-4 Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet
v1.0, January 2010
Page 31

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Automatically Detecting and Connecting
To automatically configure the WAN ports for connection to the Internet:
Figure 2-3
1. Select Network Configuration > WAN Settings from the menu. The WAN Settings tabs
appear, with the WAN1 ISP Settings screen in view.
2. Click Auto Detect at the bottom of the menu. Auto Detect will probe the WAN port for a
range of connection methods and suggest one that your ISP appears to support.
Note: When you click Auto Detect while the WAN port already has a connection,
you might lose the connection because the VPN firewall will enter its
detection mode.
Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet 2-5
v1.0, January 2010
Page 32

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Figure 2-4
a. If Auto Detect is successful, a status bar at the top of the screen will display the results.
b. If Auto Detect senses a connection method that requires input from you, it will prompt you
for the information. All methods with their required settings are detailed in the following
table.
Table 2-1. Internet connection methods
Connection Method Data Required
DHCP (Dynamic IP) No data is required.
PPPoE Login (Username, Password);
Account Name, Domain Name (sometimes required).
PPTP Login (Username, Password),
Local IP address, and PPTP Server IP address;
Account Name (sometimes required).
Fixed (Static) IP Static IP address, Subnet, and Gateway IP; DNS Server IP addresses.
c. If Auto Detect does not find a connection, you will be prompted to (1) check the physical
connection between your VPN firewall and the cable or DSL line, or to (2) check your
VPN firewall’s MAC address (For more information, see “Configuring the WAN Mode
(Required for Dual WAN)” on page 2-11 and “Troubleshooting the ISP Connection” on
page 10-4).
3. To verify the connection, click the WAN Status option arrow at the top right of the screen. A
popup window appears, displaying the connection status of WAN port 1 (see Figure 2-5 on
page 2-7).
2-6 Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet
v1.0, January 2010
Page 33

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Figure 2-5
The WAN Status window should show a valid IP address and gateway. If the configuration
was not successful, go to “Manually Configuring the Internet Connection” on page 2-7
following this section, or see “Troubleshooting the ISP Connection” on page 10-4.
Note: If the configuration process was successful, you are connected to the Internet
through WAN port 1. If you intend to use the dual WAN capabilities of the
VPN firewall, continue with the configuration process for WAN port 2.
4. Click the WAN2 ISP Settings tab.
5. Repeat the previous steps to automatically detect and configure the WAN2 Internet
connection.
6. Open the WAN Status window and verify a successful connection
If your WAN ISP configuration was successful, you can go to “Configuring the WAN Mode
(Required for Dual WAN)” on page 2-11.
If one or both automatic WAN ISP configurations failed, you can attempt a manual configuration
as described in the following section, or see “Troubleshooting the ISP Connection” on page 10-4.
Manually Configuring the Internet Connection
Unless your ISP automatically assigns your configuration automatically via DHCP, you will need
to obtain configuration parameters from your ISP in order to manually establish an Internet
connection. The necessary parameters for various connection types are listed in Table 2-1 on
page 2-6.
Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet 2-7
v1.0, January 2010
Page 34

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
To manually configure the WAN1 ISP settings:
1. Select Network Configuration > WAN Settings from the menu. The WAN Settings tabs
appear, with the WAN1 ISP Settings screen in view.
2. In the ISP Login options, choose one of these options:
Figure 2-6
• If your ISP requires an initial login to establish an Internet connection, click Yes (this is
the default).
• If a login is not required, click No and ignore the Login and Password fields.
3. If you clicked Yes, enter the ISP-provided Login and Password information.
4. In the ISP Type options, select the type of ISP connection you use from the three listed
options. By default, “Other (PPPoE)” is selected, as shown below.
Figure 2-7
(If your connection is PPPoE or PPTP, your ISP will require an initial login.)
5. If you have installed login software such as WinPoET or Ethernet, then your connection type
is PPPoE. If your ISP uses PPPoE as a login protocol:
a. Select Other (PPPoE).
2-8 Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet
v1.0, January 2010
Page 35

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
b. Configure the following fields:
• Account Name. Valid account name for the PPPoE connection.
• Domain Name. Name of your ISP’s domain or your domain name if your ISP has
assigned one. In most cases, you may leave this field blank.
• Idle Timeout. Select Keep Connected, to keep the connection always on. To logout
after the connection is idle for a period of time, click Idle Time and in the timeout
field enter the number of minutes to wait before disconnecting.
• Connection Reset. Select this checkbox to to specify a time when the PPPoE WAN
connection is reset, that is, the connection is disconnected momentarily and then reestablished. Enter the hour and minutes in the Disconnect Time fields to specify when
the connection should be disconnected. Enter the seconds in the Delay field to specify
the period after which the connection should be re-established.
6. If your ISP is Austria Telecom or any other ISP that uses PPTP as a login protocol:
a. Select PPTP.
b. Configure the following fields:
• Account Name (also known as Host Name or System Name). Enter the valid account
name for the PPTP connection (usually your e-mail name as assigned by your ISP).
Some ISPs require entering your full e-mail address here.
• Domain Name. Your domain name or workgroup name assigned by your ISP , or your
ISPs domain name. You may leave this field blank.
• Idle Timeout. Check the Keep Connected radio button to keep the connection
always on. To logout after the connection is idle for a period of time, click Idle Time
and enter the number of minutes to wait before disconnecting in the timeout field. This
is useful if your ISP charges you based on the amount of time you have logged in.
• My IP Address. IP address assigned by the ISP to make the connection with the ISP
server.
• Server IP Address. IP address of the PPTP server.
Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet 2-9
v1.0, January 2010
Page 36

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
7. Review the Internet (IP) Address options.
Figure 2-8
8. If your ISP has not assigned a static IP address, click Get dynamically from ISP. The ISP will
automatically assign an IP address to the VPN firewall using DHCP network protocol. The IP
address and subnet mask fields will be inactivated. As an option, you can select the following
checkboxes:
• Client Identifier. Select this checkbox if your ISP requires the Client Identifier
information to assign an IP address using DHCP.
• Vendor Class Identifier. Select this checkbox if your ISP requires the Vendor Class
Identifier information to assign an IP address using DHCP.
The ISP will automatically assign an IP address to the VPN firewall using DHCP network
protocol.
9. If your ISP has assigned a fixed (static) IP address, select Use Static IP Address, and
configure the following fields:
• IP Address. Enter the Static IP address assigned to you, that identifies the VPN firewall to
your ISP.
• Subnet Mask. Enter the mask provided by the ISP or your network administrator.
• Gateway IP Address. Enter the IP address of the ISP’s gateway, provided by the ISP or
your network administrator.
2-10 Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet
v1.0, January 2010
Page 37

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
10. Review the Domain Name Server (DNS) server options.
Figure 2-9
• If your ISP has not assigned any Domain Name Servers (DNS) addresses, click Get
dynamically from ISP.
• If your ISP (or your IT department) has assigned DNS addresses, click Use these DNS
Servers and enter the DNS server IP addresses provided to you in the fields.
11. Click Apply to save any changes to the WAN1 ISP Settings. (Or click Reset to discard any
changes and revert to the previous settings.)
12. Click Test to evaluate your entries.
The VPN firewall will attempt to connect to the NETGEAR website. If a successful
connection is made, NETGEAR’s website appears.
13. If you intend to use a dual WAN mode, click the WAN2 ISP Settings tab and configure the
WAN2 ISP settings using the same steps as WAN1.
Configuring the WAN Mode (Required for Dual WAN)
The dual WAN ports of the ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN can be
configured on a mutually exclusive basis for either auto-rollover (for increased system reliability)
or load balancing (for maximum bandwidth efficiency), or one port can be disabled.
• Auto-Rollover Mode. The selected WAN interface is made primary and the other is the
rollover link. As long as the primary link is up, all traffic is sent over the primary link. Once
the primary WAN interface goes down, the rollover link is brought up to send the traffic.
Traffic will automatically roll back to the original primary link once the original primary link
is back up and running again. If you want to use a redundant ISP link for backup purposes,
select the WAN port that will act as the primary link for this mode. Ensure that the backup
WAN port has also been configured and that you configure in the WAN Failure Detection
Method section of the WAN Mode screen to support Auto-Rollover.
Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet 2 -11
v1.0, January 2010
Page 38

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
• Load Balancing Mode. The VPN firewall distributes the outbound traffic equally among the
WAN interfaces that are functional.
Note: Scenarios could arise when load balancing needs to be bypassed for certain
traffic or applications. If certain traffic needs to travel on a specific WAN
interface, configure protocol binding rules for that WAN interface. The rule
should match the desired traffic.
• Single WAN Port Mode. The selected WAN interface is made primary and the other is
disabled.
Whichever WAN mode you choose, you must also choose either NAT or classical routing, as
explained in the following sections.
Network Address Translation
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows all PCs on your LAN to share a single public Internet
IP address. From the Internet, there is only a single device (the VPN firewall) and a single IP
address. PCs on your LAN can use any private IP address range, and these IP addresses are not
visible from the Internet.
• The VPN firewall uses NAT to select the correct PC (on your LAN) to receive any incoming
data.
• If you only have a single public Internet IP address, you MUST use NAT. (the default setting).
• If your ISP has provided you with multiple public IP addresses, you can use one address as the
primary shared address for Internet access by your PCs, and you can map incoming traffic on
the other public IP addresses to specific PCs on your LAN. This one-to-one inbound mapping
is configured using an inbound firewall rule.
Classical Routing
In classical routing mode, the VPN firewall performs routing, but without NAT. To gain Internet
access, each PC on your LAN must have a valid static Internet IP address.
If your ISP has allocated a number of static IP addresses to you, and you have assigned one of
these addresses to each PC, you can choose classical routing. Or, you can use classical routing for
routing private IP addresses within a campus environment. To learn the status of the WAN ports,
you can view the Router Status screen (see “Viewing VPN Firewall Configuration and System
Status” on page 9-8) or look at the LEDs on the front panel (see “Front Panel Features” on page 1-
6).
2-12 Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet
v1.0, January 2010
Page 39

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Configuring Auto-Rollover Mode
To use a redundant ISP link for backup purposes, ensure that the backup WAN port has already
been configured. Then select the WAN port that will act as the primary link for this mode and
configure the WAN Failure Detection Method to support Auto-Rollover.
When the VPN firewall is configured in Auto-Rollover mode, it uses the selected WAN Failure
Detection Method to check the connection of the primary link at regular intervals to detect its
routing status. Link failure is detected in one of the following ways:
• By sending DNS queries to a DNS server, or
• By sending a Ping request to an IP address, or
• None (no failure detection is performed).
From each WAN interface, DNS queries or Ping requests are sent to the specified IP address. If
replies are not received, after a specified number of retries, the corresponding WAN interface is
considered down.
To configure the dual WAN ports for Auto-Rollover:
1. Select Network Configuration > WAN Settings from the menu, and click the WAN Mode
tab. The WAN Mode screen is displayed
Figure 2-10
Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet 2 -13
v1.0, January 2010
Page 40

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
2. In the Port Mode section, select Auto-Rollover Using WAN port.
3. From the pull-down menu, choose which WAN port will act as the primary link for this mode.
4. In the WAN Failure Detection Method section, select one of the following detection failure
methods:
• DNS lookup using ISP DNS Servers. DNS queries are sent to the DNS server configured
on the WAN ISP screens (see “Configuring the Internet Connections” on page 2-4).
• DNS lookup using this DNS Server. Enter a public DNS server. DNS queries are sent to
this server through the WAN interface being monitored.
• Ping to this IP addresses. Enter a public IP address that will not reject the Ping request
and will not consider Ping traffic to be abusive. Queries are sent to this server through the
WAN interface being monitored.
5. Enter a Retry Interval in seconds. The DNS query or Ping is sent periodically after every test
period. The default test period is 30 seconds.
6. Enter the Failover after count. The WAN interface is considered down after the configured
number of queries have failed to elicit a reply. The rollover link is brought up after this. The
Failover default is 4 failures.
The default time to roll over after the primary WAN interface fails is 2 minutes (a 30-second
minimum test period for a minimum of 4 tests).
7. Click Apply to save your settings.
Once a rollover occurs, an alert will be generated (see “E-Mail Notifications of Event Logs and
Alerts” on page 4-33). When the VPN firewall detects that the failed primary WAN interface has
been restored, it will automatically rollover again to the primary WAN interface. Alternatively,
you can manually force traffic back on the original primary WAN interface by reapplying the
Auto-Rollover settings on the WAN Mode screen.
Configuring Load Balancing
To use multiple ISP links simultaneously, select Load Balancing. In Load Balancing mode, either
WAN port will carry any outbound protocol unless protocol binding is configured. When a
protocol is bound to a particular WAN port, all outgoing traffic of that protocol will be directed to
the bound WAN port. For example, if the HTTPS protocol is bound to WAN 1 an d the FTP
protocol is bound to WAN2, then the VPN firewall will automatically route all outbound HTTPS
traffic from the computers on the LAN through the WAN1 port. All outbound FTP traffic will be
routed through the WAN2 port.
2-14 Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet
v1.0, January 2010
Page 41

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Protocol binding
Protocol binding addresses two issues:
• Segregation of traffic between links that are not of the same speed.
High volume traffic can be routed through the WAN port connected to a high speed link and
low volume traffic can be routed through the WAN port connected to the low speed link.
• Continuity of source IP address for secure connections.
Some services, particularly HTTPS, will cease responding when a client’s source IP address
changes shortly after a session has been established.
To configure the dual WAN ports for load balancing with protocol binding:
1. Select Network >WAN Settings from the menu, and click the WAN Mode tab.
2. In the Port Mode section, select Load Balancing.
3. Click view protocol bindings (if required). The W AN1 Protocol Bindin gs screen is disp layed.
Figure 2-11
Enter the following data in the Add Protocol Binding section on screen:
a. Service. From the pull-down menu, choose the desired service or application to be
covered by this rule. If the desired service or application does not appear in the list, you
must define it using the Services screen (see “Adding Customized Services” on page 4-
19).
b. Source Network. These settings determine which computers on your network are affected
by this rule. Select the desired options:
• Any. All PCs and devices on your LAN.
Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet 2 -15
v1.0, January 2010
Page 42

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
• Single address. Enter the required address and the rule will be applied to that
particular PC.
• Address range. If this option is selected, you must enter the start and finish fields.
• Group 1-Group 8. If this option is selected, the devices assigned to this group will be
affected. (You may also assign a customized name to the group. See Edit Group
Names on the Groups and Hosts screen in the LAN Groups submenu.)
c. Dest ination Network. These settings determine which Internet locations are covered by
the rule, based on their IP address. Select the desired option:
• Any. All Internet IP address are covered by this rule.
• Single address. Enter the required address in the start field.
• Address range. If this option is selected, you must enter the start and finish fields.
4. Click Add to save this rule.
The new Protocol Binding Rule will be enabled and added to the Protocol Binding Table for
the WAN1 port.
5. Open the WAN2 Protocol Bindings tab and repeat the previous steps to set protocol bindings
for the WAN2 port.
Configuring Dynamic DNS (Optional)
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is an Internet service that allows routers with varying public IP addresses
to be located using Internet domain names. To use DDNS, you must setup an account with a
DDNS provider such as DynDNS.org, TZO.com, Oray .net, or 3322.or g. (Links to DynDNS, TZO,
Oray, and 3322 are provided for your convenience on the Dynamic DNS Configuration screen.)
The VPN firewall firmware includes software that notifies dynamic DNS servers of changes in the
WAN IP address, so that the services running on this network can be accessed by others on the
Internet.
If your network has a permanently assigned IP address, you can register a domain name and ha ve
that name linked with your IP address by public Domain Name Servers (DNS). However, if your
Internet account uses a dynamically assigned IP address, you will not know in advance what your
IP address will be, and the address can change frequently—hence, the need for a commercial
DDNS service, which allows you to register an extension to its domain, and restores DNS requests
for the resulting FQDN to your frequently-changing IP address.
After you have configured your account information in the VPN firewall, whenever your
ISP-assigned IP address changes, your VPN firewall will automatically contact your DDNS
service provider, log in to your account, and register your new IP address.
2-16 Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet
v1.0, January 2010
Page 43

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
You may need to use a fully qualified domain name (FQDN):
• For auto-rollover mode, you will need a FQDN to implement features such as exposed hosts
and virtual private networks regardless of whether you have a fixed or dynamic IP address.
• For load balancing mode, you may still need a FQDN either for convenience or if you have a
dynamic IP address.
Note: If your ISP assigns a private WAN IP address such as 192.168.x.x or 10.x.x.x, the
dynamic DNS service will not work because private addresses will not be routed
on the Internet.
To configure dynamic DNS:
1. Select Network Configuration > Dynamic DNS from the menu and click the Dynamic DNS
Configuration tab. The Dynamic DNS Configuration screen is displayed.
Figure 2-12
Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet 2 -17
v1.0, January 2010
Page 44

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
The Current WAN Mode section reports the currently configured WAN mode. (For example,
Single Port WAN1, Load Balancing or Auto Rollover.) Only those options that match the
configured WAN Mode will be accessible.
2. Select the tab for the DDNS service provider you will use.
3. Click the information or registration link in the upper right corner for registration information.
Figure 2-13:
4. Access the website of the DDNS service provider and register for an account (for example, for
dyndns.org, go to http://www.dyndns.org).
5. For each WAN port, click the Yes radio button for Change DNS to <your desired DDNS
service> and configure the active fields:
a. Enter the account information for the service you have chosen (for example, user name,
password, key, or domain).
b. If your DDNS provider allows the use of wild cards in resolving your URL, you may
select the Use wildcards checkbox to activate this feature. For example, the wildcard
feature will cause
yourhost.dyndns.org
*.yourhost.dyndns.org to be aliased to the same IP address as
c. If your WAN IP address does not change often, you may need to force a periodic update to
the DDNS service to prevent your account from expiring. If it appears, you can select the
Update every 30 days checkbox to enable a periodic update.
6. Click Apply to save your configuration.
Configuring the Advanced WAN Options (Optional)
To configure the Advanced WAN options:
1. Select Network Configuration > WAN Settings from the menu. The WAN1 ISP Settings
screen is displayed.
2. Click the Advanced link to the right of the tabs. The WAN1 Advanced Options screen is
displayed (see Figure 2-14 on page 2-19).
2-18 Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet
v1.0, January 2010
Page 45

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Figure 2-14
3. Edit the default information you want to change.
a. MTU Size. The normal MTU (Maximum Transmit Unit) value for most Ethernet
networks is 1500 Bytes, or 1492 Bytes for PPPoE connections. For some ISPs, you may
need to reduce the MTU. This is rarely required, and should not be done unless you are
sure it is necessary for your ISP connection.
b. Port Speed. In most cases, your VPN firewall can automatically determine the connection
speed of the WAN port. If you cannot establish an Internet connection and the WAN Link
or Speed LED blinks continuously, you may need to manually select the port speed.
AutoSense is the default.
If you know that the Ethernet port on your broadband modem supports 100BaseT, select
100BaseT Half_Duplex; otherwise, select 10BaseT Half_Duplex. Use the half-duplex
settings unless you are sure you need full duplex.
c. Router's MAC Address. Each computer or router on your network has a unique 32-bit
local Ethernet address. This is also referred to as the computer's MAC (Media Access
Control) address. The default is Use default address. However, if your ISP requires MAC
authentication, then select either of these options:
• Use this Computer's MAC address to have the VPN firewall use the MAC address of
the computer you are now using, or
• Use This MAC Address to manually type in the MAC address that your ISP expects.
The format for the MAC address is 01:23:45:67:89:AB (numbers 0-9 and either uppercase
or lowercase letters A-F). If you select Use This MAC Address and then type in a MAC
address, your entry will be overwritten.
4. Click Apply to save your changes.
Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet 2 -19
v1.0, January 2010
Page 46

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Additional WAN Related Configuration
• If you want the ability to manage the VPN firewall remotely, enable remote management at
this time (see “Enabling Remote Management Access” on page 8-10). If you enable remote
management, we strongly recommend that you change your password (see “Changing
Passwords and Administrator Settings” on page 8-8).
• At this point, you can set up the traffic meter for each WAN. See “Enabling the Traffic Meter”
on page 9- 1.
2-20 Connecting the FVS336G to the Internet
v1.0, January 2010
Page 47

Chapter 3
LAN Configuration
This chapter describes how to configure the advanced LAN features of your ProSafe Dual WAN
Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G.
This chapter contains the following sections
• “Choosing the VPN Firewall DHCP Options” on this page
• “Configuring the LAN Setup Options” on page 3-2
• “Managing Groups and Hosts (LAN Groups)” on page 3-6
• “Configuring Multi Home LAN IP Addresses” on page 3-10
• “Configuring Static Routes” on page 3-11
• “Configuring Routing Information Protocol (RIP)” on page 3-13
Choosing the VPN Firewall DHCP Options
By default, the VPN firewall will function as a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
server, allowing it to assign IP, DNS server, WINS Server, and default gateway addresses to all
computers connected to the VPN firewall’s LAN. The assigned default ga teway address is the
LAN address of the VPN firewall. IP addresses will be assigned to the attached PCs from a pool of
addresses that you must specify. Each pool address is tested before it is assigned to avoid duplicate
addresses on the LAN.
For most applications, the default DHCP and TCP/IP settings of the VPN firewall are satisfactory.
See the link to “TCP/IP Networking Basics” in Appendix D, “Related Documents” for information
about how to assign IP addresses for your network.
If another device on your network will be the DHCP server, or if you will manually configure the
network settings of all of your computers, clear the Enable DHCP server radio box by selecting
the Disable DHCP Server radio box. Otherwise, leave it checked.
Specify the pool of IP addresses to be assigned by setting the starting IP address and ending IP
address. These addresses should be part of the same IP address subnet as the VPN firewall’s LAN
IP address. Using the default addressing scheme, you should define a range between 192.168.1.2
and 192.168.1.100, although you may wish to save part of the range for devices with fixed
addresses.
3-1
v1.0, January 2010
Page 48

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
The VPN firewall will deliver the following parameters to any LAN device that requests DHCP:
• An IP address from the range you have defined.
• Subnet mask.
• Gateway IP address (the VPN firewall’s LAN IP address).
• Primary DNS server (the VPN firewall’s LAN IP address).
• WINS server (if you entered a WINS server address on the DHCP section of the LAN Setup
screen).
• Lease time (date obtained and duration of lease).
DHCP Relay options allow you to make the VPN firewall a dhcp relay agent. The DHCP Relay
Agent makes it possible for DHCP broadcast messages to be sent over routers that do not support
forwarding of these types of messages. The DHCP Relay Agent is therefore the routing protocol
that enables DHCP clients to obtain IP addresses from a DHCP server on a remote subnet, or
which is not located on the local subnet. If you have no configured DHCP Relay Agent, your
clients would only be able to obtain IP addresses from the DHCP server which is on the same
subnet. T o enable clients to obtain IP addresses from a DHCP server on a remote subnet, you have
to configure the DHCP Relay Agent on the subnet that contains the remote clients, so that it can
relay DHCP broadcast messages to your DHCP server.
When the DNS Proxy option is enabled, the VPN firewall will act as a proxy for all DNS requests
and communicate with the ISP’s DNS servers (as configured in the WAN settings screen). All
DHCP clients will receive the Primary/Secondary DNS IP along with the IP address where the
DNS Proxy is running, that is, the VPN firewall’s LAN IP address. When disabled, all DHCP
clients will receive the DNS IP addresses of the ISP excluding the DNS Proxy IP address. The
feature is particularly useful in Auto Rollover mode. For example, if the DNS servers for each
connection are different, then a link failure may render the DNS servers inaccessible. However,
when the DNS proxy is enabled, then clients can make requests to the VPN firewall and the VPN
firewall, in turn, sends those requests to the DNS servers of the active connection.
Configuring the LAN Setup Options
The LAN Setup screen allows configuration of LAN IP services such as DHCP and allows you to
configure a secondary or “multi-home” LAN IP setup in the LAN. The default values are suitable
for most users and situations. Disable the DNS Proxy if you are using a dual WAN configuration
with route diversity and failover. These are advanced settings most usually configured by a
network administrator.
3-2 LAN Configuration
v1.0, January 2010
Page 49

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Note: If you enable the DNS Relay feature, you will not use the VPN firewall as a DHCP
server but rather as a DHCP relay agent for a DHCP server somewhere else on
your network.
1. Go to Network Configuration > LAN Setup to display the LAN Setup screen.
Figure 3-1
2. In the LAN TCP/IP Setup section, configure the following settings:
• IP Address. The LAN address of your VPN firewall (factory default: 192.168.1.1).
LAN Configuration 3-3
v1.0, January 2010
Page 50

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Note: If you change the LAN IP address of the VPN firewall while connected
through the browser, you will be disconnected. You must then open a new
connection to the new IP address and log in again. For example, if you
change the default IP address 192.168.1.1 to 10.0.0.1, you must now enter
https://10.0.0.1 in your browser to reconnect to the Web Configuration
Manager.
• IP Subnet Mask. The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address.
Your VPN firewall will automatically calculate the subnet mask based on the IP address
that you assign. Unless you are implementing subnetting, use 255.255.255.0 as the subnet
mask.
3. In the DHCP section, select Disable DHCP Server, Enable DHCP Server, or DHCP Relay.
By default, the VPN firewall will function as a DHCP server, providing TCP/IP configuration
settings for all computers connected to the VPN firewall's LAN. If another device on your
network will be the DHCP server, or if you will manually configure all devices, click Disable
DHCP Server. If the VPN firewall will function as a DHCP relay agent, select DHCP Relay
and enter the IP address of the DHCP relay gateway in the Relay Gateway field.
If the DHCP server is enabled, enter the following parameters:
• Domain Name. (Optional) The DHCP will assign the entered domain to DHCP clients.
• Starting IP Address. Specifies the first of the contiguous addresses in the IP address pool.
Any new DHCP client joining the LAN will be assigned an IP address between this
address and the Ending IP Address. The IP address 192.168.1.2 is the default start address.
• Ending IP Address. Specifies the last of the contiguous addresses in the IP address pool.
The IP address 192.168.1.100 is the default ending address.
Note: The starting and ending DHCP addresses should be in the same subnet as
the LAN IP address of the VPN firewall (the IP address configured in the
LAN TCP/IP Setup section of the LAN Setup screen).
• Primary DNS Server. (Optional) If an IP address is specified, the VPN firewall will
provide this address as the primary DNS server IP address. If no address is specified, the
VPN firewall will provide its own LAN IP address as the primary DNS server IP address.
• Secondary DNS Server. (Optional) If an IP address is specified, the VPN firewall will
provide this address as the secondary DNS server IP address.
3-4 LAN Configuration
v1.0, January 2010
Page 51

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
• WINS Server. (Optional) Specifies the IP address of a local Windows NetBIOS Server if
one is present in your network.
• Lease Time. This specifies the duration for which IP addresses will be leased to clients.
If you will use a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) authentication server for
network-validated domain-based authentication, select Enable LDAP Information to enable
the DHCP server to provide LDAP server information. Enter the following parameters:
• LDAP Server. Specifies the name or the IP address of the device that hosts the LDAP
server.
• Search Base. Specifies the distinguished name (dn) at which to start the search, specified
as a sequence of relative distinguished names (rdn), connected with commas and without
any blank spaces. For most users, the search base is a variation of the domain name. For
example, if your domain is yourcompany.com, your search base dn might be as follows:
dc=yourcompany,dc=com.
• port. Specifies the port number that the LDAP server is using. Leave this field blank for
the default port.
4. In the Advanced Settings section, configure the following settings:
• Enable DNS Proxy. If the DNS proxy is enabled (which is the default setting), the DHCP
server will provide the VPN firewall’s LAN IP address as the DNS server for address
name resolution. If this box is unchecked, the DHCP server will provide the ISP’s DNS
server IP addresses. The VPN firewall will still service DNS requests sent to its LAN IP
address unless you disable DNS Proxy in the VPN firewall settings (see “Attack Checks”
on page 4- 15).
• Enable ARP Broadcast. If ARP broadcast is enabled (which is the default setting), the
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is broadcasted on the LAN so that IP addresses can be
mapped to physical addresses (that is, MAC addresses).
5. Click Apply to save your settings.
Note: Once you have completed the LAN setup, all outbound traffic is allowed and
all inbound traffic is discarded. To change these default traffic rules, refer to
Chapter 4, “Firewall Protection and Content Filtering.”
LAN Configuration 3-5
v1.0, January 2010
Page 52

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Managing Groups and Hosts (LAN Groups)
The Known PCs and Devices table on the LAN Groups screen contains a list of all known PCs
and network devices that are assigned dynamic IP addresses by the VPN firewall, or have been
discovered by other means. Collectively, these entries make up the LAN Groups Database.
The LAN Groups Database is updated by these methods:
• DHCP Client Requests. By default, the DHCP server in this VPN firewall is enabled, and
will accept and respond to DHCP client requests from PCs and other network devices. These
requests also generate an entry in the LAN Groups Database. Because of this, leaving the
DHCP server feature (on the LAN screen) enabled is strongly recommended.
• Scanning the Network. The local network is scanned using ARP requests. The ARP scan will
detect active devices that are not DHCP clients. However, sometimes the name of the PC or
device cannot be accurately determined, and will appear in the database as Unknown.
• Manual Entry. You can manually enter information about a network device.
Some advantages of the LAN Groups Database are:
• Generally, you do not need to enter either IP address or MAC addresses. Instead, you can just
select the desired PC or device.
• No need to reserve an IP address for a PC in the DHCP server. All IP address assignments
made by the DHCP server will be maintained until the PC or device is removed from the
database, either by expiry (inactive for a long time) or by you.
• No need to use a fixed IP on PCs. Because the address allocated by the DHCP server will
never change, you don't need to assign a fixed IP to a PC to ensure it always has the same IP
address.
• MAC level control over PCs. The LAN Groups Database uses the MAC address to identify
each PC or device. So changing a PC’s IP address does not affect any restrictions on that PC.
• Group and individual control over PCs.
– You can assign PCs to Groups and apply restrictions to each Group using the Firewall
Rules screen (see “Using Rules to Block or Allow Specific Kinds of Traffic” on page 4-2).
– You can also select the Groups to be covered by the Block Sites feature (see “Blocking
Internet Sites (Content Filtering)” on page 4-25).
– If necessary, you can also create Firewall Rules to apply to a single PC (see “Configuring
Source MAC Filtering” on page 4-28). Because the MAC address is used to identify each
PC, users cannot avoid these restrictions by changing their IP address.
3-6 LAN Configuration
v1.0, January 2010
Page 53

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
• A computer is identified by its MAC address—not its IP address. Hence, changing a
computer’s IP address does not affect any restrictions applied to that PC.
Viewing the LAN Group s Database
To view the LAN Groups Database, follow these steps:
1. Select Network Configuration > LAN Settings from the menu. The LAN Setup screen is
displayed.
2. Click the LAN Groups tab. The LAN Groups screen is displayed.
Figure 3-2
The Known PCs and Devices table lists the entries in the LAN Groups Database. For each
computer or device, the following fields are displayed:
• Name. The name of the PC or device. For computers that do not support the NetBIOS
protocol, this will be listed as “Unknown” (you can edit the entry manually to add a
meaningful name). If the computer was assigned an IP address by the DHCP server, then the
Name will be appended by an asterisk.
• IP Address. The current IP address of the computer. For DHCP clients of the VPN firewall,
this IP address will not change. If a computer is assigned a static IP addresses, you will need to
update this entry manually if the IP address on the computer has been changed.
• MAC Address. The MAC address of the PC’s network interface.
• Group. Each PC or device can be assigned to a single group. By default, a computer is
assigned to Group 1, unless a different group is chosen from the Group pull-down menu.
• Action. Allows modification of the selected entry by clicking Edit.
LAN Configuration 3-7
v1.0, January 2010
Page 54

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Adding Devices to the LAN Groups Database
To add devices manually to the LAN Groups Database, follow these steps:
1. In the Add Known PCs and Devices section, make the following entries:
• Name. Enter the name of the PC or device.
• IP Address Type. From the pull-down menu, choose how this device receives its IP
address. The choices are:
– Fixed (Set on PC). The IP address is statically assigned on the computer.
– Reserved (DHCP Client). Directs the VPN firewall’s DHCP server to always assign
the specified IP address to this client during the DHCP negotiation (see “Configuring
DHCP Address Reservation” on page 3-9).
Note: When assigning a reserved IP address to a client, the IP address selected
must be outside the range of addresses allocated to the DHCP server pool.
• IP Address. Enter the IP address that this computer or device is assigned in the IP
Address field. If the IP Address Type is Reserved (DHCP Client), the VPN firewall will
reserve the IP address for the associated MAC address.
• MAC Address. Enter the MAC address of the computer’s network interface in the MAC
Address field. The MAC address format is six colon-separated pairs of hexadecimal
characters (0-9 and A-F), such as 01:23:45:67:89:AB.
• Group. From the pull-down menu, select the LAN Group to which the computer will be
assigned. (Group 1 is the default group.)
2. Click Add. The device will be added to the Known PCs and Devices table.
3. (Optional) To enable DHCP Address Reservation after the entry is in the table, select the
checkbox for the new table entry and click Save Binding to bind the IP address to the MAC
address for DHCP assignment.
Changing Group Names in the LAN Groups Database
By default, the LAN Groups are named Group1 through Group8. You can rename these group
names to be more descriptive, such as Engineering or Marketing.
3-8 LAN Configuration
v1.0, January 2010
Page 55

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
To edit the names of any of the eight available groups:
1. From the LAN Groups tab, click the Edit Group Names link to the right of the tabs. The
Network Database Group Names screen appears.
Figure 3-3
2. Select the radio button next to any group name to make that name active for editing.
3. Type a new name in the field.
4. Select and edit other group names if desired.
5. Click Apply to save your settings.
Configuring DHCP Address Reservation
When you specify a reserved IP address for a device on the LAN (based on the MAC address of
the device), that computer or device will always receive the same IP address each time it accesses
the VPN firewall’s DHCP server. Reserved IP addresses should be assigned to servers or access
points that require permanent IP address settings. The Reserved IP address that you select must be
outside of the DHCP Server pool.
To reserve an IP address, manually enter the device on the LAN Groups screen, specifying
Reserved (DHCP Client), as described in “Adding Devices to the LAN Groups Database” on
page 3-8.
Note: The reserved address will not be assigned until the next time the PC contacts the
VPN firewall’s DHCP server. Reboot the PC or access its IP configuration and
force a DHCP release and renew.
LAN Configuration 3-9
v1.0, January 2010
Page 56

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Configuring Multi Home LAN IP Addresses
If you have computers on your LAN using different IP address ranges (for example, 172.16.2.0 or
10.0.0.0), you can add “aliases” to the LAN port, giving computers on those networks access to the
Internet through the VPN firewall. This allows the VPN firewall to act as a gateway to additional
logical subnets on your LAN. You can assign the VPN firewall an IP address on each additional
logical subnet.
To add a secondary LAN IP address:
1. Select Network Configuration > LAN Settings from the menu, and click the LAN Multihoming tab. The LAN Multi-homing screen is displayed.
Figure 3-4
The Available Secondary LAN IPs table lists the secondary LAN IP addresses added to the
VPN firewall.
• IP Address. The “alias,” an additional IP address hosted by the LAN port of the VPN
firewall. This address will be the gateway for computers on the secondary subnet.
• Subnet Mask. The IPv4 subnet mask that defines the range of the secondary subnet.
2. In the Add Secondary LAN IP Address section, enter the additional IP address and subnet
mask to be assigned to the LAN port of the VPN firewall.
3-10 LAN Configuration
v1.0, January 2010
Page 57

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
3. Click Add. The new Secondary LAN IP address will appear in the A vailable Secondary LAN
IPs table.
Note: IP addresses on these secondary subnets cannot be configured in the DHCP
server. The hosts on the secondary subnets must be manually configured with
IP addresses, gateway IP addresses, and DNS server IP addresses.
Tip: The secondary LAN IP address will be assigned to the LAN interface of the
VPN firewall and can be used as a gateway by computers on the secondary
subnet.
Configuring Static Routes
Static Routes provide additional routing information to your VPN firewall. Under normal
circumstances, the VPN firewall has adequate routing information after it has been configured for
Internet access, and you do not need to configure additional static routes. You should configure
static routes only for unusual cases such as multiple firewalls or multiple IP subnets located on
your network.
To add or edit a static route:
1. Select Network Configuration > Routing from the menu. The Routing screen is displayed.
Figure 3-5
LAN Configuration 3-11
v1.0, January 2010
Page 58

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
2. Click Add. The Add Static Route screen is displayed.
Figure 3-6
3. Enter a route name for this static route in the Route Name field (for identification and
management).
4. Select Active to make this route effective.
5. Select Private if you want to limit access to the LAN only. The static route will not be
advertised in RIP.
6. Enter the Destination IP Address to the host or network to which the route leads.
7. Enter the IP Subnet Mask for this destination. If the destination is a single host, enter
255.255.255.255.
8. Enter the Interface which is the physical network interface (WAN1, WAN2, or LAN) through
which this route is accessible.
9. Enter the Gateway IP Address through which the destination host or network can be reached
(must be a device on the same LAN segment as the VPN firewall).
10. Enter the Metric priority for this route. If multiple routes to the same destination exit, the
route with the lowest metric is chosen (value must be between 1 and 15).
11. Click Apply to save your settings.
The new static route will be added to the Static Routes table.
3-12 LAN Configuration
v1.0, January 2010
Page 59

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Configuring Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
RIP (Routing Information Protocol, RFC 2453) is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) that is
commonly used in internal networks (LANs). It allows a router to exchange its routing information
automatically with other routers, and allows it to dynamically adjust its routing tables and adapt to
changes in the network. RIP is disabled by default.
To configure RIP parameters:
1. Select Network Configuration > Routing from the menu.
2. Click the RIP Configuration link to the right of the tab. The RIP Configuration screen is
displayed.
Figure 3-7
3. From the RIP Direction pull-down menu, choose the direction in which the VPN firewall will
send and receive RIP packets. The choices are:
• None. The VPN firewall neither broadcasts its route table nor does it accept any RIP
packets from other routers. This effectively disables RIP.
LAN Configuration 3-13
v1.0, January 2010
Page 60

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
• Both. The VPN firewall broadcasts its routing table and also processes RIP information
received from other routers.
• Out Only. The VPN firewall broadcasts its routing table periodically but does not accept
RIP information from other routers.
• In Only. The VPN firewall accepts RIP information from other routers, but does not
broadcast its routing table.
4. From the RIP Version pull-down menu, choose the version from the following options:
• Disabled. The default section disables RIP versions.
• RIP-1. A classful routing that does not include subnet information. This is the most
commonly supported version.
• RIP-2. Supports subnet information. Both RIP-2B and RIP-2M send the routing data in
RIP-2 format:
– RIP-2B. Sends the routing data in RIP-2 format and uses subnet broadcasting.
– RIP-2M. Sends the routing data in RIP-2 format and uses multicasting.
5. Authentication for RIP2B/2M required? If you selected RIP-2B or RIP-2M, check the Yes
radio box to enable authentication, and enter the MD-5 keys to authenticate between devices in
the First Key Parameters and Second Key Parameters sections on the screen.
6. Click Apply to save your settings.
3-14 LAN Configuration
v1.0, January 2010
Page 61

Chapter 4
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
This chapter describes how to use the content filtering features of the ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit
Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G to protect your network.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• “About Firewall Protection and Content Filtering” on this page
• “Using Rules to Block or Allow Specific Kinds of Traffic” on page 4-2
• “Configuring Other Firewall Features” on page 4-15
• “Creating Services, QoS Profiles, and Bandwidth Profiles” on page 4-19
• “Setting a Schedule to Block or Allow Specific Traffic” on page 4-24
• “Blocking Internet Sites (Content Filtering)” on page 4-25
• “Configuring Source MAC Filtering” on page 4-28
• “Configuring IP/MAC Address Binding” on page 4-30
• “Configuring Port Triggering” on pa ge 4-31
• “Managing the Application Level Gateway for SIP Sessions” on page 4-18
• “E-Mail Notifications of Event Logs and Alerts” on page 4-33
• “Administrator Tips” on page 4-33
About Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
The VPN firewall provides you with Web content filtering options, plus browsing activity
reporting and instant alerts via e-mail. Network administrators can establish restricted access
policies based on time-of-day, Web addresses and Web address keywords. You can also block
Internet access by applications and services, such as chat or games.
A firewall is a special category of router that protects one network (the “trusted” network, such as
your LAN) from another (the untrusted network, such as the Internet), while allowing
communication between the two. You can further segment keyword blocking to certain known
groups (see “Managing Groups and Hosts (LAN Groups)” on page 3-6 to set up LAN Groups).
4-1
v1.0, January 2010
Page 62

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
A firewall incorporates the functions of a NAT (Network Address Translation) router, while
adding features for dealing with a hacker intrusion or attack, and for controlling the types of traffic
that can flow between the two networks. Unlike simple Internet sharing NAT routers, a firewall
uses a process called stateful packet inspection to protect your network from attacks and
intrusions. NAT performs a very limited stateful inspection in that it considers whether the
incoming packet is in response to an outgoing request, but true Stateful Packet Inspection goes far
beyond NAT.
Using Rules to Block or Allow Specific Kinds of Traffic
This section includes the following topics:
• “About Services-Based Rules” on page 4-3
• “Viewing the Rules” on page 4-8
• “Order of Precedence for Rules” on page 4-8
• “Setting the Default Outbound Policy” on page 4-8
• “Creating a LAN WAN Outbound Services Rule” on page 4-9
• “Creating a LAN WAN Inbound Services Rule” on page 4-10
• “Modifying Rules” on page 4-11
• “Inbound Rules Examples” on page 4-11
• “Outbound Rules Example” on page 4-14
Firewall rules are used to block or allow specific traffic passing through from one side to the other.
Inbound rules (WAN to LAN) restrict access by outsiders to private resources, selectively allowing
only specific outside users to access specific resources. Outbound rules (LAN to WAN) determine
what outside resources local users can have access to.
A firewall has two default rules, one for inbound traffic and one for outbound traffic. The default
rules of the VPN firewall are:
• Inbound. Block all access from outside except responses to requests from the LAN side.
• Outbound. Allow all access from the LAN side to the outside.
User-defined firewall rules for blocking or allowing traffic on the VPN firewall can be applied to
inbound or outbound traffic.
4-2 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 63

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
About Services-Based Rules
The rules to block traffic are based on the traffic’s category of service.
• Outbound Rules (service blocking). Outbound traffic is normally allowed unless the VPN
firewall is configured to disallow it.
• Inbound Rules (port forwarding). Inbound traffic is normally blocked by the VPN firewall
unless the traffic is in response to a request from the LAN side. The VPN firewall can be
configured to allow this otherwise blocked traffic.
• Customized Services. Additional services can be added to the list of services in the factory
default list. These added services can then have rules defined for them to either allow or block
that traffic (see “Adding Customized Services” on page 4-19).
• Quality of Service (QoS) priorities. Each service at its own native priority that impacts its
quality of performance and tolerance for jitter or delays. You can change this QoS priority if
desired to change the traffic mix through the system (see “Setting Quality of Service (QoS)
Priorities” on page 4-21).
Outbound Rules (Service Blocking)
The VPN firewall allows you to block the use of certain Internet services by PCs on your network.
This is called service blocking or port filtering.
The default policy can be changed to block all outbo und traffic and enable only specific servi ces to
pass through the VPN firewall. The following Outbound Rules table lists the configured rules for
outgoing traffic. An outbound rule is defined by the following fields:
Table 4-1. Outbound Rules
Item Description
Service Select the desired service or appli c ation to be covered by this rule. If the desired service
or application does not appear in the table, you must define it using the Services screen
(see “Adding Customized Services” on page 4-19).
Action Select the desired action for outgoing connections covered by this rule:
• BLOCK always
• BLOCK by schedule, otherwise Allow
• ALLOW always
• ALLOW by schedule, otherwise Block
Note: Any outbound traffic that is not blocked by rules you create will be allowed by the
default rule.
ALLOW rules are only useful if the traffic is already covered by a BLOCK rule. That is, you
wish to allow a subset of traffic that is currently blocked by another rule.
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-3
v1.0, January 2010
Page 64

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Table 4-1. Outbound Rules (continued)
Item Description
Select Schedule Select the desired time schedule (Schedule1, Schedule2, or Schedule3) that will be used
by this rule.
• This pull-down menu gets activated only when “BLOCK by schedule, otherwise Allow”
or “ALLOW by schedule, otherwise Block” is selected as Action.
• Use schedule screen to configure the time schedules (see “Setting a Schedule to Block
or Allow Specific Traffic” on page 4-24).
LAN Users Specifies which computers on your network are affected by this rule. Select the desired
options:
• Any – All PCs and devices on your LAN.
• Single address – Enter the required address and the rule will be applied to that
particular PC.
• Address range – If this option is selected, you must enter the start and finish fields.
• Groups – Select the Group to which this rule will apply. Use the LAN Groups screen
(under Network Configuration) to assign PCs to Groups. See “Managing Groups and
Hosts (LAN Groups)” on page 3-6.
WAN Users Specifies which Internet locations are covered by the rule, based on their IP address.
Select the desired option:
• Any – All Internet IP address are covered by this rule.
• Single address – Enter the required address in the start field.
• Address range – If this option is selected, you must enter the start and end fields.
QoS Priority Specifies the priority of a service which, in turn, determines the quality of that service for
the traffic passing through the VPN firewall. By default, the priority shown is that of th e
selected service. The user can change it accordingly. If the user does not make a
selection (leaves it as Normal-Service), then the native priority of the service will be
applied to the policy. See “Setting Quality of Service (QoS) Priorities” on page 4-21.
Log This determines whether packets covered by this rule are logged. Select the desired
action:
• Always – always log traffic considered by this rule, whether it matches or not. This is
useful when debugging your rules.
• Never – never log traffic considered by this rule, whether it matches or not.
Bandwidth
Profile
NAT IP Specifies whether the source IP address of the outgoing packets should be the WAN
NAT Single IP Is
On (interface)
Specifies the name of a bandwidth limiting profile. Using a bandwidth profile, bandwidth
consumed by different connections can be limited. If multiple connections correspond to
the same firewall rule, they will share the same bandwidth limiting. See “Creating
Bandwidth Profiles” on page 4-22.
interface address or a specified address, which should belong to the WAN subnet.
Specifies to which WAN interface the NAT IP address belongs. All outgoing packets will
be routed through the specified WAN interface only.
4-4 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 65

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Note: See “Configuring Source MAC Filtering” on page 4-28 for yet another way to
block outbound traffic from selected PCs that would otherwise be allowed by the
VPN firewall.
Inbound Rules (Port Forwarding)
When the VPN firewall uses Network Address Translation (NAT), your network presents only one
IP address to the Internet and outside users cannot directly address any of your local computers.
However, by defining an inbound rule you can make a local server (for example, a Web server or
game server) visible and available to the Internet. The rule tells the VPN firewall to direct inbound
traffic for a particular service to one local server based on the destination port number. This is al so
known as port forwarding.
Whether or not DHCP is enabled, how the PCs will access the server’s LAN address impacts the
inbound rules. For example:
• If your external IP address is assigned dynamically by your ISP (DHCP enabled), the IP
address may change periodically as the DHCP lease expires. Consider using dynamic DNS so
that external users can always find your network (see “Configuring Dynamic DNS (Optional)”
on page 2- 16).
• If the IP address of the local server PC is assigned by DHCP, it may change when the PC is
rebooted. To avoid this, use the Reserved IP address feature to keep the PC’s IP address
constant (see “Configuring DHCP Address Reservation” on page 3-9).
• Local PCs must access the local server using the server’s local LAN address. Attempts by
local PCs to access the server using the external WAN IP address will fail.
Note: See “Configuring Port Triggering” on page 4-31 for yet another way to allow
certain types of inbound traffic that would otherwise be blocked by the VPN
firewall.
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-5
v1.0, January 2010
Page 66

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Table 4-2. Inbound Rules
Item Description
Service Select the desired service or appli c ation to be covered by this rule. If the desired service
or application does not appear in the table, you must define it using the Services screen
(see “Adding Customized Services” on page 4-19).
Action Select the desired action for packets covered by this rule:
• BLOCK always
• BLOCK by schedule, otherwise Allow
• ALLOW always
• ALLOW by schedule, otherwise Block
Note: Any inbound traffic which is not allowed by rules you create will be blocked by the
Default rule.
Select Schedule Select the desired time schedule (Schedule1, Schedule2, or Schedule3) that will be used
by this rule (see “Setting a Schedule to Block or Allow Specific Traffic” on page 4-24).
• This pull-down menu gets activated only when “BLOCK by schedule, otherwise Allow”
or “ALLOW by schedule, otherwise Block” is selected as Action.
• Use schedule screen to configure the time schedules.
Send to LAN
Server
Translate to Port
Number
WAN
Destination IP
Address
LAN users This field appears only with NAT routing (not classical routing). Specifies which computers
WAN Users Specifies which Internet locations are covered by the rule, based on their IP addresses.
This field appears only with NAT routing (not classical routing). This LAN address or
range of LAN addresses determines which computer or computers on your network are
hosting this service rule. (You can also translate these addresses to a port number.)
Check this box and enter a port number to assign the LAN Server to a different service
port number. Inbound traffic to the service port will have the destination port number
modified to the port number configured here.
Specifies the destination IP address applicable to incoming traffic.
This is the public IP address that will map to the internal LAN server; it can either be the
address of the WAN1 or WAN2 ports or another public IP address
on your network are affected by this rule. Select the desired options:
• Any – All PCs and devices on your LAN.
• Single address – Enter the required address and the rule will be applied to that
particular PC.
• Address range – If this option is selected, you must enter the start and finish fields.
• Groups – Select the Group to which this rule will apply. Use the LAN Groups screen
(under Network Configuration) to assign PCs to Groups. See “Managing Groups and
Hosts (LAN Groups)” on page 3-6.
Select the desired option:
• Any – All Internet IP address are covered by this rule.
• Single address – Enter the required address in the start field.
• Address range – If this option is selected, you must enter the start and end fields.
.
4-6 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 67

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Table 4-2. Inbound Rules (continued)
Item Description
Log Specifies whether packets covered by this rule are logged. Select the desired action:
• Always – Always log traffic considered by this rule, whether it matches or not. This is
useful when debugging your rules.
• Never – Never log traffic considered by this rule, whether it matches or not.
Bandwidth
Profile
Bandwidth Limiting determines the way in which the data is sent to/from your host. The
purpose of bandwidth limiting is to provide a solution for limiting the outgoing/incoming
traffic, thus preventing the LAN users for consuming all the bandwidth of our internet link.
Bandwidth Limiting for outbound traffic will be done on the available WAN interface in the
single port and Auto-Failover modes. The limiting will be done on the user-specified
interface in Load Balancing mode. The bandwidth limiting for inbound traffic will be done
on the LAN interface for all WAN modes. See “Creating Bandwidth Profiles” on page 4-22.
Note: Some residential broadband ISP accounts do not allow you to run any server
processes (such as a Web or FTP server) from your location. Your ISP may
periodically check for servers and may suspend your account if it discovers any
active services at your location. If you are unsure, refer to the Acceptable Use
Policy of your ISP.
Remember that allowing inbound services opens holes in your VPN firewall. Enable only those
ports that are necessary for your network. We also recommend enabling the server’s application
security and configuring user password or privilege levels, if provided.
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-7
v1.0, January 2010
Page 68

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Viewing the Rules
To view the firewall rules: Select Security > Firewall from the menu. The LAN WAN Rules
screen is displayed (Figure 4-1 shows some examples).
Figure 4-1
Order of Precedence for Rules
As you define new rules, they are added to the tables in the LAN WAN Rules screen as the last
item in the table, as shown in Figure 4-1. For any traffic attempting to pass through the VPN
firewall, the packet information is subjected to the rules in the order shown in the Outbound
Services and Inbound Services rules tables, beginning at the top and proceeding to the bottom,
before applying the default rule. In some cases, the order of precedence of two or more rules may
be important in determining the disposition of a packet. For example, you should place the most
strict rules at the top (those with the most specific services or addresses). The Up and Down
buttons allow you to relocate a defined rule to a new position in the table.
Setting the Default Outbound Policy
The Default Outbound Policy is to allow all traffic to the Internet to pass through. Firewall rules
can then be applied to block specific types of traffic from going out from the LAN to the Internet
(Outbound). The default policy of Allow Always can be changed to block all outbound traffic
which then allows you to enable only specific services to pass through the VPN firewall.
4-8 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 69

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
To change the default outbound policy, follow these steps:
1. Go to the LAN WAN Rules screen, shown in Figure 4-1 on page 4-8.
2. Change the Default Outbound Policy by selecting Block Always from the pull-down menu.
3. Click Apply.
Creating a LAN WAN Outbound Services Rule
An outbound rule will block or allow the selected application from an internal IP LAN address to
an external WAN IP address according to the schedule created on the Schedule screen. You can
also tailor these rules to your specific needs (see “Administrator Tips” on page 4-33).
Note: This feature is for advanced administrators only! Incorrect configuration will cause
serious problems.
To create a new outbound service rule in the LAN WAN Rules screen:
1. Click Add under the Outbound Services table. The Add LAN WAN Outbound Service screen
is displayed.
Figure 4-2
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-9
v1.0, January 2010
Page 70

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
2. Configure the parameters based on the descriptions in Table 4-1 on page 4-3.
3. Click Apply to save your changes and reset the fields on this screen. The new rule will be
listed on the Outbound Services table.
Creating a LAN WAN Inbound Services Rule
This Inbound Services table lists all existing rules for inbound traf fic. If you have not defined any
rules, no rules will be listed. By default, all inbound traffic is blocked. Remember that allowing
inbound services opens holes in your VPN firewall. Only enable those ports that are necessary for
your network.
To create a new inbound service rule in the LAN WAN Rules screen:
1. Click Add under the Inbound Services table. The Add LAN WAN Inbound Service screen is
displayed.
Figure 4-3
2. Configure the parameters based on the descriptions in Table 4-2 on page 4-6.
3. Click Apply to save your changes and reset the fields on this screen. The new rule will be
listed in the Inbound Services table.
4-10 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 71

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Modifying Rules
To make changes to an existing outbound or inbound service rule on the the LAN WAN Rules
screen, in the Action column to the right of to the rule, click on of the following table buttons:
• edit. Allows you to make any changes to the rule definition of an existing rule. Depending on
your selection, either the Edit LAN WAN Outbound Service screen (identical to Figure 4-2 on
page 4-9) or Edit LAN WAN Inbound Service screen (identical to Figure 4-3 on page 4-10) is
displayed, containing the data for the selected rule.
• up. Moves the rule up one position in the table rank.
• down. Moves the rule down one position in the table rank.
To enable, disable, or delete one or more rules:
1. Select the checkbox to the left of the rule that you want to delete or disable or click the select
all table button to select all rules.
2. Click one of the following table buttons:
• enable. Enables the rule or rules. The “!” status icon changes from a grey circle to a green
circle, indicating that the rule is or rules are enabled. (By default, when a rule is added to
the table, it is automatically enabled.)
• disable. Disables the rule or rules. The “!” status icon changes from a green circle to a
grey circle, indicating that the rule is or rules are disabled.
• delete. Deletes the rule or rules.
Inbound Rules Examples
LAN WAN Inbound Rule: Hosting a Local Public Web Server
If you host a public W e b server on your local network, you can define a rule to allow inbound Web
(HTTP) requests from any outside IP address to the IP address of your Web server at any time of
day. In the example shown in Figu re 4-4 on page 4-12 , unrestricted access is provided from the
Internet to the local Web server at LAN IP address 192.168.1.99.
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-11
v1.0, January 2010
Page 72

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Figure 4-4
LAN WAN Inbound Rule: Allowing Videoconference from Restricted Addresses
If you want to allow incoming videoconferencing to be initiated from a restricted range of outside
IP addresses, such as from a branch office, you can create an inbound rule. In the example shown
in Figure 4-5, CU-SeeMe connections are allowed to a local host only from a specified range of
external IP addresses. Connections are blocked during the period specified by Schedule 1.
Figure 4-5
4-12 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 73

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
LAN WAN Inbound Rule: Setting Up One-to-One NAT Mapping
If you arrange with your ISP to have more than one public IP address for your use, you can use the
additional public IP addresses to map to servers on your LAN. One of these public IP addresses
will be used as the primary IP address of the VPN firewall. This address will be used to provide
Internet access to your LAN PCs through NAT. The other addresses are available to map to your
servers.
In the example shown in Figure 4-6, we have configured multi-NAT to support multiple public IP
addresses on one WAN interface. The inbound rule instructs the VPN firewall to host an
additional public IP address (10.1.0.5) and to associate this address with the Web server on the
LAN (at 192.168.1.1). We also instruct the VPN firewall to translate the incoming HTTP port
number (port 80) to a different port number (port 8080).
Figure 4-6
The following addressing scheme is used in this example:
• VPN firewall FVS336G
– WAN1 primary public IP address: 10.1.0.1
– WAN1 additional public IP address: 10.1.0.5
– LAN IP address 192.168.1.1
• Web server PC on the VPN firewall’s LAN
– LAN IP address: 192.168.1.11
– Port number for Web service : 8080
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-13
v1.0, January 2010
Page 74

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
To test the connection from a PC on the WAN side, type http://10.1.0.5. The home page of the
Web server should appear.
LAN WAN Inbound Rule: Specifying an Exposed Host
Specifying an exposed host allows you to set up a computer or server that is available to anyone on
the Internet for services that you have not yet defined.
To expose one of the PCs on your LAN as this host:
1. Create an inbound rule that allows all protocols.
2. Place the new rule below all other inbound rules.
Note: For security, NETGEAR strongly recommends that you avoid creating an exposed
host. When a computer on your LAN is designated as the exposed host, it loses
much of the protection of the firewall and is exposed to many exploits from the
Internet. If compromised, the computer can be used to attack your network.
Outbound Rules Example
Outbound rules let you prevent users from using applications such as Instant Messenger, Real
Audio, or other non-essential services.
LAN WAN Outbound Rule: Blocking Instant Messenger
To block Inst ant Messenger usage by employees during working hours, you can create an
outbound rule to block that application from any internal IP address to any external address
according to the schedule that you have created on the Schedule screen. See the example shown in
Figure 4-7 on page 4-1 5.
You can also have the VPN firewall log any attempt to use Instant Messenger during that blocked
period.
4-14 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 75

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Figure 4-7
Configuring Other Firewall Features
You can configure attack checks, set session limits, and manage the Application Level Gateway
(ALG) for SIP sessions.
Attack Checks
The Attack Checks screen allows you to specify whether or not the VPN firewall should be
protected against common attacks in the LAN and WAN networks. To enable the appropriate
Attack Checks for your environment:
1. Select Security > Firewall from the menu and click Attack Checks to display the Attack
Checks screen (see Figure 4-8 on page 4-16).
2. Check the boxes for the Attack Checks you wish to monitor. The various types of attack
checks are listed and defined below.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-15
v1.0, January 2010
Page 76

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Figure 4-8
The various types of attack checks listed on the Attack Checks screen are:
• WAN Security Checks
– Respond To Ping On Internet Ports. By default, the VPN firewall responds to an ICMP
Echo (ping) packet coming from the Internet or WAN side. Responding to a ping can be a
useful diagnostic tool when there are connectivity problems. If the ping option is enabled,
you can allow either any IP address or a specific IP address only to respond to a ping. You
can disable the ping option to prevent hackers from easily discovering the VPN firewall
via a ping.
– Enable Stealth Mode. In stealth mode, the VPN firewall will not respond to port scans
from the WAN or Internet, which makes it less susceptible to discovery and attacks.
– Block TCP Flood. A SYN flood is a form of denial of service attack in which an attacker
sends a succession of SYN requests to a target system. When the system responds, the
attacker does not complete the connection, thus saturating the server with half-open
connections. No legitimate connections can then be made.
When blocking is enabled, the VPN firewall will limit the lifetime of partial connections
and will be protected from a SYN flood attack.
4-16 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 77

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
• LAN Security Checks.
– Block UDP flood. A UDP flood is a form of denial of service attack in which the
attacking machine sends a large number of UDP packets to random ports to the victim
host. As a result, the victim host will check for the application listening at that port, see
that no application is listening at that port, and reply with an ICMP Destination
Unreachable packet.
When the victimized system is flooded, it is forced to send many ICMP packets,
eventually making it unreachable by other clients. The attacker may also spoof the IP
address of the UDP packets, ensuring that the excessive ICMP return packets do not reach
him, making the attacker’s network location anonymous.
If flood checking is enabled, the VPN firewall will not accept more than 20 simultaneous,
active UDP connections from a single computer on the LAN.
– Disable Ping Reply on LAN Ports. To prevent the VPN firewall from responding to ping
requests from the LAN, click this checkbox.
• VPN Pass through. When the VPN firewall is in NAT mode, all packets going to the Remote
VPN Gateway are first filtered through NAT and then encrypted per the VPN policy.
If a VPN client or gateway on the LAN side of the VPN firewall wants to connect to another
VPN endpoint on the WAN, with the VPN firewall between the two VPN end points, all
encrypted packets will be sent to the VPN firewall. Since the VPN firewall filters the
encrypted packets through NAT, the packets become invalid.
IPSec, PPTP, and L2TP represent different types of VPN tunnels that can pass through the
VPN firewall. T o allow the VPN traffic to pass through without filtering, enable those options
for the type of tunnel(s) that will pass through the VPN firewall.
Configuring Session Limits
To prevent one user or group from using excessive system resources, you can limit the total
number of IP sessions allowed through the VPN firewall for an individual or group. You can
specify the maximum number of sessions by either a percentage of maximum sessions or an
absolute number of maximum sessions. Session limiting is disabled by default.
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-17
v1.0, January 2010
Page 78

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
To configure session limits:
1. Select Security > Firewall > Session Limit to display the Session Limit screen.
Figure 4-9
2. Click Yes to enable Session Limits.
3. From the pull-down menu, select whether you will limit sessions by percentage or by absolute
number. The percentage is computed based on the total connection capacity of the device.
When setting a limit based on absolute number, note that some protocols (for example, FTP
and RSTP) create two sessions per connection.
4. Click Apply.
To monitor session limiting, return to this screen periodically and check the display of Total
Number of Packets Dropped due to Session Limit, which indicates that session limits have been
reached.
Managing the Application Level Gateway for SIP Sessions
The Application Level Gateway (ALG) facilitates multimedia sessions such as voice over IP
(VoIP) sessions that use the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) across the firewall and provides
support for multiple SIP clients. ALG support for SIP is disabled by default.
4-18 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 79

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
To enable ALG for SIP:
1. Select Security > Firewall > Advanced to display the Advanced screen.
Figure 4-10
2. Select the Enable SIP ALG checkbox.
3. Click Apply to save your settings.
Creating Services, QoS Profiles, and Bandwidth Profiles
When you create inbound and outbound firewall rules, you use firewall objects such as services,
QoS profiles, bandwidth profiles, and schedules to narrow down the firewall rules:
• Services. A service narrows down the firewall rule to an application and a port number. For
information about adding services, see “Adding Customized Services” on page 4-19.
• QoS profiles. A quality of service (QoS) profile defines the relative priority of an IP packet
for traffic that matches the firewall rule. For information about creating QoS profiles, see
“Setting Quality of Service (QoS) Priorities” on page 4-21.
• Bandwidth Profiles. A bandwidth profile allocates and limits traffic bandwidth for the LAN
users to which a firewall rule is applied. For information about creating bandwidth profiles,
see “Creating Bandwidth Profiles” on page 4-22.
Note: A schedule narrows down the period during which a firewall rule is applied. For
information about specifying schedules, see “Setting a Schedule to Block or Allow
Specific Traffic” on page 4-24.
Adding Customized Services
Services are functions performed by server computers at the request of client computers. For
example, Web servers serve Web pages, time servers serve time and date information, and game
hosts serve data about other players’ moves. When a computer on the Internet sends a request for
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-19
v1.0, January 2010
Page 80

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
service to a server computer, the requested service is identified by a service or port number. This
number appears as the destination port number in the transmitted IP packets. For example, a packet
that is sent with destination port number 80 is an HTTP (Web server) request.
The service numbers for many common protocols are defined by the Internet Engineering Task
Force (IETF) and published in RFC1700, “Assigned Numbers.” Service numbers for other
applications are typically chosen from the range 1024 to 65535 by the authors of the application.
Although the VPN firewall already holds a list of many service port numbers, you are not limited
to these choices. Use the Services screen to add additional services and applications to the list for
use in defining firewall rules. The Services screen shows a list of services that you have defined, as
shown in Figure 4-11.
To define a new service, you must first determine which port number or range of numbers is used
by the application. This information can usually be determined by contacting the publisher of the
application or from user groups or newsgroups. When you have the port number information, you
can enter it on the Services screen. You can configure up to 125 custom services.
To add a custom service:
1. Select Security > Services from the menu. The Services screen is displayed.
Figure 4-11
2. In the Add Custom Services section, enter a descriptive name for the service (this name is for
your convenience).
3. Select the Layer 3 transport protocol of the service: TCP, UDP, or ICMP.
4. For TCP or UDP services, enter the first port of the range that the service uses. For ICMP
services, enter the ICMP Type number.
5. For TCP or UDP services, enter the last port of the range that the service uses. If the service
only uses a single port number, enter the same number in both fields.
4-20 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 81

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
6. Click Add. The new custom service will be added to the Custom Services Table.
Modifying a Service
To edit the parameters of an existing service:
1. In the Custom Services Table, click the Edit button adjacent to the service you want to edit.
The Edit Service screen is displayed.
2. Modify the parameters you wish to change.
3. Click Apply to confirm your changes. The modified service is displayed in the Custom
Services Table.
Setting Quality of Service (QoS) Priorities
The QoS setting determines the priority of a service, which in turn determines the quality of that
service for the traffic passing through the VPN firewall. You can change the QoS Priority:
• On the Services screen in the Custom Services Table for customized services (see
Figure 4-11 on page 4-20).
• On the Add LAN WAN Outbound Services screen.
Figure 4-12
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-21
v1.0, January 2010
Page 82

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
The QoS priority definition for a service determines the queue that is used for the traffic passing
through the VPN firewall. A priority is assigned to IP packets using this service. Priorities are
defined by the “Type of Service (ToS) in the Internet Protocol Suite” standards, RFC 13 49. A ToS
priority for traffic passing through the VPN firewall is one of the following:
• Normal-Service. No special priority given to the traffic. The IP packets for services with this
priority are marked with a ToS value of 0.
• Minimize-Cost. Used when the data must be transferred over a link that has a low
transmission cost. The IP packets for this service priority are marked with a ToS value of 1.
• Maximize-Reliability. Used when data needs to travel to the destination over a reliable link
with little or no retransmission. The IP packets for this service priority are marked with a ToS
value of 2.
• Maximize-Throughput. Used when the volume of data transferred during an interval is
important even if the latency over the link is high. The IP packets for services with this priority
are marked with a ToS value of 4.
• Minimize-Delay. Used when the time required for the packet to reach the destination must be
short (low link latency). The IP packets for this service priority are marked with a ToS value
of 8.
Creating Bandwidth Profiles
To prevent one user or group from using excessive inbound or outbound bandwidth, you can
define a bandwidth profile to set a minimum and maximum bandwidth for an individual or group.
You can apply a defined profile in a firewall rule to limit specific protocols or all traffic (see
“Using Rules to Block or Allow Specific Kinds of Traffic” on page 4-2).
To create a bandwidth profile:
1. Select Security > Bandwidth Profile from the menu. The Bandwidth Profile screen is
displayed.
Figure 4-13
4-22 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 83

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
The List of Bandwidth Profiles table displays existing profiles.
2. T o create a new bandwidth profile, click Add. The Add Bandwidth Profile screen is displayed.
Figure 4-14
3. Enter the following information:
a. Enter a Profile Name. This name will become available in the firewall rules definition
menus.
b. From the Direction pull-down box, select whether the profile will apply to outbound,
inbound, or both outbound and inbound traffic.
c. Depen din g on the direction that you selected, enter the minimum and maximum
bandwidths to be allowed:
• Enter the Outbound Minimum Bandwidth and Outbound Maximum Bandwidth
in Kbps.
• Enter the Inbound Minimum Bandwidth and Inbound Maximum Bandwidth in
Kbps.
The minimum bandwidth can range from 0 Kbps to the maximum bandw idth that you
specify. The maximum bandwidth can range from 100 Kbps to 100,000 Kbps.
d. From the Type pull-down box, select whether the profile will apply to a group or
individual.
e. From the WAN pull-down box, specify the WAN interface (if in Load Balancing Mode)
for the profile.
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-23
v1.0, January 2010
Page 84

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
4. Click Apply. The new bandwidth profile will be added to the List of Bandwidth Profiles
table.
To edit a bandwidth profile:
1. Click the Edit link adjacent to the profile you want to edit. The Edit Bandwidth Profile screen
is displayed. (This screen shows the same fields as the Add New Bandwidth Profile screen.)
2. Modify the settings that you wish to change.
3. Click Apply. Yo ur modified profile is displayed in the Bandwidth Profile table.
To remove an entry from the table, select the profile and click delete.
To remove all the profiles, click select All and then click delete.
Setting a Schedule to Block or Allow Specific Traffic
Schedules define the timeframes under which firewall rules may be applied.
Figure 4-15
Three schedules, Schedule 1, Schedule 2 and Schedule3 can be defined, and any one of these can
be selected when defining firewall rules.
4-24 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 85

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
To invoke rules based on a schedule, follow these steps:
1. Select Security > Schedule to display the Schedule 1 screen.
2. Check the radio button for All Days or Specific Days. If you chose Specific Days, check the
radio button for each day you want the schedule to be in effect.
3. Check the radio button to schedule the time of day: All Day, or Specific Times. If you chose
Specific Times, enter the Start Time and End Time fields (Hour, Minute, AM/PM), which
will limit access during certain times for the selected days.
4. Click Apply to save your settings to Schedule 1.
5. Repeat these steps to set to a schedule for Schedule 2 and Schedule 3.
Blocking Internet Sites (Content Filtering)
To restrict internal LAN users from access to certain sites on the Internet, you can use the VPN
firewall’s Content Filtering and Web Components filtering. By default, these features are disabled;
all requested traffic from any website is allowed. If you enable one or more of these features and
users try to access a blocked site, they will see a “Blocked by NETGEAR” message.
Several types of blocking are available:
• Web Componen ts blocking. You can filter the following Web Component types: Proxy, Java,
ActiveX, and Cookies. For example, by enabling Java filtering, “Java” files will be blocked.
Certain commonly used web components can be blocked for increased security. Some of these
components are can be used by malicious Websites to infect computers that access them.
– Proxy. A proxy server (or simply, proxy) allows computers to route connections to other
computers through the proxy, thus circumventing certain firewall rules. For example, if
connections to a specific IP address are blocked by a firewall rule, the requests can be
routed through a proxy that is not blocked by the rule, rendering the restriction ineffective.
Enabling this feature blocks proxy servers.
– Java. Blocks java applets from being downloaded from pages that contain them. Java
applets are small programs embedded in web pages that enable dynamic functionality of
the page. A malicious applet can be used to compromise or infect computers. Enabling this
setting blocks Java applets from being downloaded.
– ActiveX. Similar to Java applets, ActiveX controls install on a Windows computer
running Internet Explorer. A malicious ActiveX control can be used to compromise or
infect computers. Enabling this setting blocks ActiveX applets from being downloaded.
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-25
v1.0, January 2010
Page 86

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
– Cookies. Cookies are used to store session information by websites that usually require
login. However, several websites use cookies to store tracking information and browsing
habits. Enabling this option filters out cookies from being created by a website.
Note: Many websites require that cookies be accepted in order for the site to be
accessed properly. Blocking cookies may interfere with useful functions
provided by these websites.
• Keyword Blocking (Domain Name Blocking). You can specify up to 32 words that, should
they appear in the website name (URL) or in a newsgroup name, will cause that site or
newsgroup to be blocked by the VPN firewall.
You can apply the keywords to on e or more groups. Requests from the PCs in the groups for
which keyword blocking has been enabled will be blocked. Blocking does not occur for the
PCs that are in the groups for which keyword blocking has not been enabled.
You can bypass Keyword blocking for trusted domains by adding the exact matching domain
to the Trusted Domains table. Access to the domains or keywords in the Trusted Domains
table by PCs, even those in the groups for which keyword blocking has been enabled, will still
be allowed without any blocking.
Keyword application examples:
• If the keyword “XXX” is specified, the URL <http://www.badstuff.com/xxx.html> is blocked,
as is the newsgroup alt.pictures.XXX.
• If the keyword “.com” is specified, only websites with other domain suffixes (such as .edu or
.gov) can be viewed.
• To block all Internet browsing access, enter the keyword “.”.
4-26 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 87

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
To enable Content Filtering:
1. Select Security > Block Sites to display the Block Sites screen.
Figure 4-16
2. Select Yes to enable content filtering.
3. Click Apply to activate the screen controls.
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-27
v1.0, January 2010
Page 88

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
4. Select any Web Compo nents you wish to block and click Apply.
5. Select the groups to which keyword blocking will apply, then click Enable to activate
keyword blocking (or disable to deactivate keyword blocking).
6. Enter your list of blocked keywords or domain names in the Blocked Keyword fields. After
each entry , click Add. The keyword or domain name will be added to the Blocked Keywords
table. (You can also edit an entry by clicking Edit in the Action column adjacent to the entry.)
7. In the Add T rusted Domain section of the screen, enter the name(s) of any domain for which
the keyword filtering will be bypassed and click Add. The trusted domain will appear in the
Trusted Domains table and will be exempt from filtering.
Configuring Source MAC Filtering
Source MAC filtering will drop or allow the Internet-bound traffic received from PCs with
specified MAC addresses.
• By default, the source MAC address filter is disabled. Traffic received from any MAC address
is allowed.
• When the source MAC address filter is enabled, outbound Internet traffic will be filtered using
the MAC Addresses table on this screen. You can choose to block MAC addresses in the table
or to allow only those addresses in the table.
Note: For additional ways of restricting outbound traffic, see “Outbound Rules
(Service Blocking)” on page 4-3
To enable MAC filtering and add MAC addresses to be blocked:
1. Select Security > Address Filter from the menu.
2. Select the Source MAC Filter tab to display the Source MAC Filter screen (see Figure 4-17
on page 4-29).
4-28 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 89

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Figure 4-17
3. Click Yes to enable Source MAC Filtering.
4. Select the action to be taken on outbound traffic from the listed MAC addresses:
– Block this list and permit all other MAC addresses.
– Permit this list and block all other MAC addresses.
5. Enter a MAC Address in the Add Source MAC Address checkbox and click Add. The MAC
address will appear in the MAC Addresses table. Repeat this process to add additional MAC
addresses.
A valid MAC address is six colon-separated pairs of hexadecimal digits (0 to 9 and a to f). For
example: 01:23:45:ab:cd:ef.
6. Click Apply to save your settings.
You can edit the MAC address by clicking Edit in the Action column adjacent to the MAC
address.
To remove an entry from the table, select the MAC address entry and click Delete.
T o select all the list of MAC addresses, click Select All. A checkmark will appear in the box to the
left of each MAC address in the MAC Addresses table
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-29
.
v1.0, January 2010
Page 90

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Configuring IP/MAC Address Binding
You can configure the VPN firewall to drop packets and generate an alert when a device appears to
have hijacked or spoofed another device’s IP address. An IP address can be bound to a specific
MAC address either by using a DHCP reserved address (see “Configuring DHCP Address
Reservation” on page 3-9) or by manually binding on the IP/MAC Binding screen.
To enable IP/MAC address binding enforcement and alerts:
1. Select Security > Address Filter from the menu.
2. Select the IP/MAC Binding tab to display the Source MAC Filter screen.
Figure 4-18
3. In the Email IP/MAC Violations section of the screen, check the Yes radio button to enable
IP/MAC address binding enforcement and alerts. E-mail alerts must be enabled (see “E-Mail
Notifications of Event Logs and Alerts” on page 4-33).
4. Click Apply.
5. To add a manual binding entry, enter the following data in the Add IP/MAC Bindings
section:
a. Enter a Name for the bound host device.
4-30 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 91

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
b. Enter the MAC Address and IP Address to be bound. A valid MAC address is six colon-
separated pairs of hexadecimal digits (0 to 9 and a to f). For example: 01:23:45:ab:cd:ef.
c. From the pull-down list, select whether dropped packets should be logged to a special
counter.
6. Click Apply. The specified binding will be added to the IP/MAC Bindings table.
To see the counter that shows the packets that were dropped because of IP-MAC binding
violations and to set the poll interval, click the Set Poll Interval link at the top of the IP/MAC
Binding screen.
Configuring Port Triggering
Port triggering allows some applications to function correctly that would otherwise be partially
blocked by the VPN firewall when it functions in NAT mode. Some applications require that when
external devices connect to them, they receive data on a specific port or range of ports. The VPN
firewall must send all incoming data for that application only on the required port or range of
ports. Using this feature requires that you know the port numbers used by the application.
Port triggering allows computers on the private network (LAN) to request that one or more ports
be forwarded to them. Unlike basic port forwarding which forwards ports to only one
preconfigured IP address, port triggering waits for an outbound request from the private network
on one of the defined outgoing ports. It then automatically sets up forwarding to the IP address that
sent the request. When the application ceases to transmit data over the port, the VPN firewall waits
for a timeout interval and then closes the port or range of ports, making them available to other
computers on the private network.
Once configured, port triggering operates as follows:
1. A PC makes an outgoing connection using a port number defined in the Port Triggering table.
2. The VPN firewall records this connection, opens the additional incoming port or ports
associated with this entry in the Port Triggering table, and associates them with the PC.
3. The remote system receives the PC’s request and responds using the different port numbers
that you have now opened.
4. The VPN firewall matches the response to the previous request, and forwards the response to
the PC.
Without port triggering, this response would be trea ted as a new connection request rather than a
response. As such, it would be handled in accordance with the inbound service rules.
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-31
v1.0, January 2010
Page 92

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Note these restrictions with port triggering:
• Only one PC can use a port triggering application at any time.
• After a PC has finished using a port triggering application, there is a time-out period before the
application can be used by another PC. This is required because the VPN firewall cannot be
sure when the application has terminated.
Note: For additional ways of allowing inbound traffic, see “Inbound Rules (Port
Forwarding)” on page 4-5.
To add a port triggering rule:
1. Select Security > Port Triggering to display the Port Triggering screen.
Figure 4-19
2. Enter a user-defined name for this rule in the Name field.
3. From the Enable pull-down menu, indicate if the rule is enabled or disabled.
4. From the Protocol pull-down menu, choose either TCP or UDP transport protocol.
5. In the Outgoing (Trigger) Port Range fields:
a. Enter the Start Port range (1 - 65534).
b. Enter the End Port range (1 - 65534).
6. In the Incoming (Response) Port Range fields:
a. Enter the Start Port range (1 - 65534).
b. Enter the End Port range (1 - 65534).
4-32 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 93

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
7. Click Add. The port triggering rule will be added to the Port Triggering Rules table.
T o check the status of the port triggering rules, click t he Status option arrow to the right of the tab
on the Port Triggering screen. The following data is displayed:
• Rule – The name of the port triggering rule.
• LAN IP Address – The IP address of the PC currently using this rule.
• Open Ports – The incoming ports associated with this rule. Incoming traffic using these ports
will be sent to the LAN IP address above.
• Time Remaining – The time remaining before this rule is released, and thus available for other
PCs. The timer is reset whenever incoming or outgoing traffic is received.
E-Mail Notifications of Event Logs and Alerts
The firewall logs can be configured to log and then e-mail denial of access, general attack
information, and other information to a specified e-mail address. For example, your VPN firewall
will log security-related events such as: accepted and dropped packets on different segments of
your LAN; denied incoming and outgoing service requests; hacker probes and login attempts; and
other general information based on the settings that you enter on the Firewall Logs & E-mail
screen. In addition, if you have set up content filtering on the Block Sites screen (see “Blocking
Internet Sites (Content Filtering)” on page 4-25), a log will be generated when someone on your
network tries to access a blocked site.
To configure e-mail or syslog notification, or to view the logs, see “Activating Notification of
Events and Alerts” on page 9-4.
Administrator Tips
Consider the following operational items:
• As an option, you can enable remote management if you have to manage distant sites from a
central location (see “Enabling Remote Management Access” on page 8-10).
• Although rules (see “Using Rules to Block or Allow Specific Kinds of Traffic” on page 4-2)
are the basic way of managing the traffic through your system, you can further refine your
control with the following optional features of the VPN firewall:
– Groups and hosts (see “Managing Groups and Hosts (LAN Groups)” on page 3-6)
– Services (see “About Services-Based Rules” on page 4-3)
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 4-33
v1.0, January 2010
Page 94

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
– Schedules (see “Setting a Schedule to Block or Allow Specific Traffic” on page 4-24)
– Block sites (see “Blocking Internet Sites (Content Filtering)” on page 4-25)
– Source MAC filtering (see “Configuring Source MAC Filtering” on page 4-28)
– Port triggering (see “Configuring Port Triggering” on page 4-31)
4-34 Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
v1.0, January 2010
Page 95

Chapter 5
Virtual Private Networking Using IPsec
This chapter describes how to use the IPsec virtual private networking (VPN) features of the
ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G to provide secure,
encrypted communications between your local network and a remote network or computer.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• “Considerations for Dual WAN Port Systems” on this page
• “Using the VPN Wizard for Client and Gateway Configurations” on page 5-3
• “Testing the Connections and Viewing Status Information” on page 5-12
• “Managing VPN Policies” on page 5-15
• “Configuring Extended Authentication (XAUTH)” on page 5-19
• “Assigning IP Addresses to Remote Users (ModeConfig)” on page 5-24
• “Configuring Keepalives and Dead Peer Detection” on page 5-32
• “Configuring NetBIOS Bridging with VPN” on page 5-34
Considerations for Dual WAN Port Systems
If both of the WAN ports of the VPN firewall are configured, you can enable either Auto-Rollover
mode for increased system reliability or Load Balancing mode for optimum bandwidth efficiency.
This WAN mode choice impacts how the VPN features must be configured.
The use of fully qualified domain names in VPN policies is mandatory when the WAN ports are in
load balancing or rollover mode; and is also required for the VPN tunnels to fail over. FQDN is
optional when the WAN ports are in load balancing mode if the IP addresses are static but
mandatory if the WAN IP addresses are dynamic.
Refer to “Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)” on page B-9 for more on the IP addressing
requirements for VPN in the dual WAN modes. For instructions on how to select and configure a
dynamic DNS service for resolving FQDNs, see “Configuring Dynamic DNS (Optional)” on
page 2-16. For instructions on WAN mode configuration, see “Configuring the WAN Mode
(Required for Dual WAN)” on page 2-11.
5-1
v1.0, January 2010
Page 96

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Rest of
Firewall
Functions
Firewall
WAN Port
Functions
Firewall
Rollover
Control
Firewall
WAN 1 Port
WAN 2 Port
Internet
Same FQDN required for both WAN ports
WAN Auto-Rollover: FQDN Required for VPN
Rest of
Firewall
Functions
Firewall
WAN Port
Functions
Load
Balancing
Control
Firewall
WAN 1 Port
WAN 2 Port
Internet
FQDN required for dynamic IP addresses
WAN Load Balancing: FQDN Optional for VPN
FQDN optional for static IP addresses
The diagrams and table below show how the WAN mode selection relates to VPN configuration.
Figure 5-1
Figure 5-2
Table 5-1 summariz es the WAN addressing requirements (FQDN or IP address) for your VPN
tunnel in either dual WAN mode.
Table 5-1. IP Addressing for VPNs in Dual WAN Port Systems
Configuration and WAN IP address Rollover Mode
VPN Road Warrior
(client-to-gateway)
VPN Gateway-to-Gateway Fixed FQDN required FQDN Allowed (optional)
VPN Telecommuter
(client-to-gateway through
a NAT router)
a. All tunnels must be re-established after a rollover using the new WAN IP address.
5-2 Virtual Private Networking Using IPsec
Fixed FQDN required FQDN Allowed (optional)
Dynamic FQDN required FQDN required
Dynamic FQDN required FQDN required
Fixed FQDN required FQDN Allowed (optional)
Dynamic FQDN required FQDN required
a
v1.0, January 2010
Load Balancing Mode
Page 97

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Using the VPN Wizard for Client and Gateway Configurations
You use the VPN Wizard to configure multiple gateway or client VPN tunnel policies.
The section below provides wizard and NETGEAR VPN Client configuration procedures for the
following scenarios:
• Using the wizard to configure a VPN tunnel between 2 VPN gateways
• Using the wizard to configure a VPN tunnel between a VPN gateway and a VPN client
Configuring a VPN tunnel connection requires that all settings and parameters on both sides of the
VPN tunnel match or mirror each other precisely, which can be a daunting task. The VPN Wizard
efficiently guides you through the setup procedure with a series of questions that will determine
the IPsec keys and VPN policies it sets up. The VPN Wizard will also set the parameters for the
network connection: Security Association, traffic selectors, authentication algorithm, and
encryption. The parameters used by the VPN wizard are based on the recommendations of the
VPN Consortium (VPNC), an organization that promotes multi-vendor VPN interoperability.
Creating Gateway to Gateway VPN Tunnels with the Wizard
Figure 5-3
Follow these steps to set up a gateway VPN tunnel using the VPN Wizard.
1. Select VPN > IPsec VPN from the menu.
2. Click the VPN Wizard tab to display the VPN Wizard screen (see Figure 5-4 on page 5-4).
To view the wizard default settings, click the VPN Wizard Default Values link. You can
modify these settings after completing the wizard.
Virtual Private Networking Using IPsec 5-3
v1.0, January 2010
Page 98

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
Figure 5-4
3. Select Gateway as your connection type.
4. Create a Connection Name. Enter a descriptive name for the connection. This name used to
help you manage the VPN settings; is not supplied to the remote VPN endpoint.
5. Enter a Pre-shared Key. The key must be entered both here and on the remote VPN gateway,
or the remote VPN client. This key must be a minimum of 8 characters and should not exceed
49 characters.
6. Choose which WAN port to use as the VPN tunnel end point.
Note: If you are using a dual WAN rollover configuration, after completing the
wizard, you must manually update the VPN policy to enable VPN rollover.
This allows the VPN tunnel to roll over when the WAN Mode is set to Auto
Rollover. The wizard will not set up the VPN policy with rollover enabled.
5-4 Virtual Private Networking Using IPsec
v1.0, January 2010
Page 99

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
7. Enter the Remote and Local WAN IP Addresses or Internet Names of the gateways which
will connect.
• Both the remote WAN address and your local WAN address are required.
Tip: T o assure tunnels stay active, after completing the wizard, manually edit the
VPN policy to enable keepalive which periodically sends ping packets to
the host on the peer side of the network to keep the tunnel alive.
• The remote WAN IP address must be a public address or the Internet name of the remote
gateway. The Internet name is the Fully Qualifi ed Domain Name (FQDN) as registered in
a Dynamic DNS service. Both local and remote endpoints should be defined as either
FQDN or IP addresses. A combination of IP address and FQDN is not allowed.
Tip: For DHCP WAN configurations, first, set up the tunnel with IP addresses.
Once you validate the connection, use the wizard to create new policies
using FQDN for the WAN addresses.
8. Enter the local LAN IP and Subnet Mask of the remote gateway in the Remote LAN IP
Address and Subnet Mask fields.
Note: The Remote LAN IP address must be in a different subnet than the Local LAN
IP address. For example, if the local subnet is 192.168.1.x, then the remote
subnet could be 192.168.10.x. but could not be 19 2.168.1.x. If this informatio n
is incorrect, the tunnel will fail to connect.
9. Click Apply to save your settings. The VPN Policies screen shows that the policy is enabled.
Figure 5-5
Virtual Private Networking Using IPsec 5-5
v1.0, January 2010
Page 100

ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN FVS336G Reference Manual
10. If you are connecting to another NETGEAR VPN firewall, use the VPN Wizard to configure
the second VPN firewall to connect to the one you just configured.
After both firewalls are configured, go to VPN > IPsec VPN > Connection Status to display the
status of your VPN connections.
Figure 5-6
The tunnel will automatically establish when both the local and target gateway policies are
appropriately configured and enabled,
Note: When using FQDN, if the dynamic DNS service is slow to update their servers
when your DHCP WAN address changes, the VPN tunnel will fail because the
FQDN does not resolve to your new address. If you have the option to
configure the update interval, set it to an appropriately short time.
Creating a Client to Gateway VPN Tunnel
Figure 5-7
5-6 Virtual Private Networking Using IPsec
v1.0, January 2010
 Loading...
Loading...