Netgear FSM726 Installation Manual

700 Series Sof tware Manual
v2.1
NETGEAR, Inc.
4500 Great America Parkway
Santa Clara, CA 95054 USA
Phone 1-888-NETGEAR
202-10132-01
September 2005

© 2005 by NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
NETGEAR, Inc. NETGEAR, the Netgear logo, The Gear Guy and Everybody’s connecting are trademarks of Netgear,
Inc. in the United States and/or other countries. Other brand and product names are trademarks of their respective
holders. Information is subject to change without notice. All rights reserved.
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, NETGEAR reserves the right to
make changes to the products described in this document without notice. NETGEAR does not assume any liability that
may occur due to the use or application of the product(s) or circuit layout(s) described herein.
Customer Support
For assistance with installing and configuring your NETGEAR system or with questions or problems following
installation:
• Check the NETGEAR Web page at http://www.NETGEAR.com.
• Call Technical Support in No rth America at 1-888-NETGEAR. If you are outside North America, please refer to
the phone numbers listed on the Support Information Card that shipped with your switch.
• Email Technical Support at support@NETGEAR.com.
Defective or damaged merchandise can be returned to your point-of-purchase representative.
NETGEAR maintains a World Wide Web home page that you can access at the uniform resource locator (URL) http://
www.NETGEAR.com. A direct connection to the Internet and a Web browser such as Internet Explorer or Netscape are
required.
2

Contents
Chapter 1
About This Guide
Audience ................................... ................ ............. ................ ................. ................ ........1-1
Why the Document was Created ....................................................................................1-1
How to Use This Document ............................................................................................1-1
Typographical Conventions ............................................................................................1-2
Special Message Formats ..............................................................................................1-2
Features of the HTML Version of this Manual ................................................................1-3
How to Print this Manual .................................................................................................1-4
Chapter 2
Switch Management Overview
Management Access Overview ......................................................................................1-1
Protocols .................................................................................................................. 1-2
Virtual Terminal Protocols ..................................................................................1-3
SNMP Protocol ..................................................................................................1-3
SNMP Access ..........................................................................................................1-3
Chapter 3
Software Upgrade Procedure
Chapter 4
Administration Console Telnet Interface
Set Up Your Switch Using Direct Console Access .........................................................3-1
Introduction to the Command Menu Interface ................................................................3-3
Main Menu> System ......................................................................................................3-5
Main Menu> Status .........................................................................................................3-5
Main Menu> Status >Switch Statistics .....................................................................3-5
Main Menu> Status >Reset Statistics .......................................................................3-6
Main Menu> Status > MAC Address Table .............................................................3-6
Main Menu> Set-Up ........................................................................................................3-7
Main Menu> Set-Up> System Configuration .................................... ...... .......... ...... ..3-7
Main Menu> Set-Up> IP Configuration ....................................................................3-8
Main Menu> Set-Up> Port Configuration .................................................................3-9
Contents iii

Main Menu> Set-Up> GBIC ...................................................................................3-10
Main Menu> Tools ........................................................................................................3-11
Main Menu> Security ...................................................................................................3-12
Main Menu> Advanced .................................................................................................3-12
Main Menu> Advanced> Port Mirroring .................................................................3-14
Main Menu> Advanced> Port Trunking ..................................................................3-15
Main Menu> Advanced> Virtual Cable Tester ........... ............................................. 3-15
Main Menu> Advanced> Advanced Security .................. .......................................3-16
Main Menu> Advanced> Advanced Security> System Authentication ............3-16
Main Menu> Advanced> Advanced Security > Port-Based Authentication .....3-16
Main Menu> Advanced > Trusted MAC Address Table ...................................3-17
Main Menu > Advanced > MAC Address Lockdown Table ..............................3-17
Main Menu> Advanced> Advanced Tools ..............................................................3-18
Main Menu> Advanced> Advanced Tools> Software Upgrade .......................3-18
Main Menu> Advanced> Advanced Tools> Configuration Management .........3-19
Main Menu> Advanced> Traffic Management .......................................................3-19
Main Menu> Advanced> Traffic Management> Port Priority ...........................3-20
Main Menu> Advanced> Traffic Management> DiffServ .................................3-20
Main Menu> Advanced> Traffic Management> Broadcast Control .................3-21
Main Menu> Advanced> VLANS ...........................................................................3-21
Main Menu> Advanced> VLANS> VLAN Admin .............................................3-21
Main Menu> Advanced> VLANS> VLAN Membership .................... ... ... .... ... ...3-22
Main Menu> Advanced> VLANS> VLAN Ports ..............................................3-22
Main Menu> Advanced> Spanning Tree ................................................................3-23
Main Menu> Advanced> Spanning Tree> Bridge Settings .............................. 3-23
Main Menu> Advanced> Spanning Tree> Port Settings ..................................3-24
Main Menu> Advanced> MAC Address Manager ........................ .......................... 3-25
Main Menu> Advanced> MAC Address Manager> Aging Time ......................3-26
Main Menu> Advanced> MAC Address Manager> Static Addresses .............3-26
Main Menu> Advanced> Multimedia Support ........................................................3-27
Main Menu> Advanced> Multimedia Support> Enable/Disable IGMP ............3-27
Main Menu> Advanced> Multimedia Support> Static Multicast Administration 3-27
Main Menu> Advanced> Multimedia Support> Static Multicast Membership ..3-28
Main Menu> Advanced> SNMP .............................................................................3-29
Main Menu> Advanced> SNMP> Community Table .......................................3-29
iv Contents

Main Menu> Advanced> SNMP> Host Table ..................................................3-30
Main Menu> Advanced> SNMP> Trap Settings ........................................... ...3-30
Chapter 5
Web-Based Management Interface
Web Based Management Overview ............................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..4-2
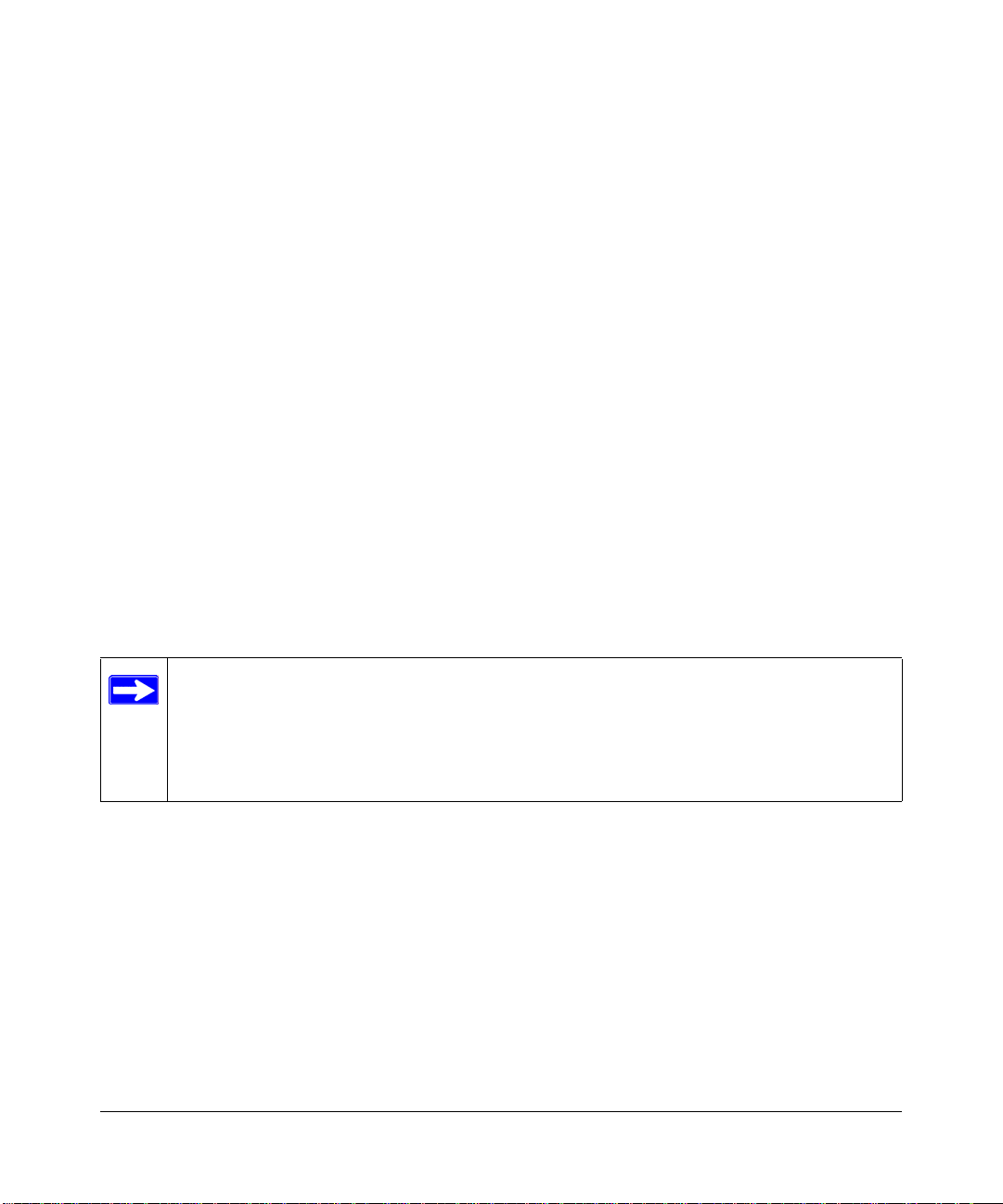
System Information .........................................................................................................4-3
Status Menus ..................................................................................................................4-4
Status > Switch Statistics .......... ... ... ... .... .......................................... ... ... ... ... .... ... .....4-5
Status > Port Statistics .............................................................................................4-7
Status > Error Statistics ............................................................................................4-8
Status > Most Active Ports .......................................................................................4-9
Status > Reset Statistics ........................................................................................4-10
Status > Port Settings ............................................................................................4-10
Status > MAC Address Table .................................................................................4-11
Set-up Menu .................................................................................................................4-12
Set-up> System Configuration ...............................................................................4-12
Set-up> IP Configuration ........................................................................................4-13
Set-up> Port Configuration ....................................................................................4-14
Set-up> GBIC .........................................................................................................4-15
Tools Menu ...................................................................................................................4-16
Tools> Save Configuration ....................................................................................4-16
Tools> Restore Factory Defaults ............................................................................4-17
Tools> Device Reset .............................................................................................4-18
Security> Passwords ....................................................................................................4-18
Advanced Options ........................................................................................................4-19
Advanced > Disable Advanced Alerting .................................................................4-22
Advanced > Port Mirroring .....................................................................................4-22
Advanced > Port Trunking ......................................................................................4-23
Advanced > Virtual Cable Tester ............................................................................4-23
Advanced> Advanced Security ..............................................................................4-24
Advanced > Advanced Security > System Authentication ...............................4-25
Advanced > Advanced Security > Port-Based Authentication ............... .... ... ...4-25
Advanced > Advanced Security > Trusted MAC Address Table ......................4-26
Advanced > Advanced Security > MAC Address Lockdown Table .................4-27
Advanced > Advanced Tools ....................................... ... .... ... ................................4-28
Contents v

Advanced > Advanced Tools > Software Upgrade .........................................4-29
Advanced > Advanced Tools > Configuration Management ............................4-30
Advanced > Traffic Management ...........................................................................4-31
Advanced > Traffic Management > Traffic Priority .............................. .............4-31
Advanced > Traffic Management > Broadcast Control ....................................4-32
Advanced> VLANS ................................................................................................4-32
Advanced> VLAN> Primary VLAN ..................................................................4-33
Advanced> VLAN> VLAN Ports ......................................................................4-34
Advanced> Spanning Tree .....................................................................................4-35
Advanced> Spanning Tree >Bridge Settings ...................................................4-35
Advanced> Spanning Tree > Port Settings ......................................................4-36
Advanced> MAC ....................................................................................................4-37
Advanced> MAC> Address Aging ...................................................................4-38
Advanced> MAC> Static Addresses ................................................................4-38
Advanced> Multimedia Support .............................................................................4-39
Advanced> Multimedia Support>Enable/Disable IGMP ..................................4-39
Advanced>Multimedia Support> Static Multicast Groups .......................... ... ...4-40
Advanced> SNMP ..................................................................................................4-40
Advanced> SNMP> Community Table ............................................................4-41
Advanced> SNMP> Host Table .......................................................................4-41
Advanced> SNMP> Trap Setting .....................................................................4-42
Chapter 6
Command Line Interface
Manual Syntax ................................................................................................................5-1
Entering the CLI ..............................................................................................................5-1
Help ................................................................................................................................5-2
Ping ................................................................................................................................5-2
Exit ...................................... ................ ............. ................ ................ ................ ...............5-3
Show ...................................... ................ ............. ................ ................ ................ ............5-3
Show DiffServ ........................... ... ... ... .... ... ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... ..5-4
Show Dot1x ........ .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... .......................................... ..5-4
Show Interfaces ................................. .......................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ........ 5-4
Show IP ........ .......................................... ... ... ... ... .... .......................................... ... ... ..5-5
Show Mac-Address-Table .................................. .... ... ... .......................................... ..5-5
Show Mirror ........ .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... .......................................... ..5-7
vi Contents

Show Multimedia ...... .......................................... .... ... ... ... .... .....................................5-7
Show Running-Config ..............................................................................................5-7
Show SNMP .... .......................................... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................... ... ..5-8
Show Spanning Tree .............................. ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .........................................5-9
Show System ..................... ... .... ... ... ... .... .......................................... ... ... ... ... .... ...... 5-10
Show Trunking .......................... ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .............5-11
Show VLAN .. ... ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... .... ... ................................5-11
Configure .................................. .......................................................................... ..........5-13
DiffServ ..................................................................................................................5-13
Dot1x ..................................... ................................. ............................. ................... 5-14
Exit .........................................................................................................................5-15
Interface ................................................................................................................. 5-15
CoS (Class or Service) ....................................................................................5-16
Exit .................................. .................... ................ ................... .................... ......5-16
Flow Control ............. .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... .............................5-17
Mirror ...............................................................................................................5-17
No .................................................................................................................... 5-18
Type ................................................................................................................5-18
Shutdown ......................................... ............................. ......................... .......... 5-18
Spanning Tree .................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .......................................5-19
Speed ..............................................................................................................5-19
Switchport ................................. .................................................... ................... 5-19
Trunking .................................................... .......................................... ............. 5-20
Mac-address-table .................................................................................................5-21
Multimedia ....................................... .................................... ................................ ... 5-22
No ..........................................................................................................................5-23
SNMP Server .........................................................................................................5-23
Spanning Tree .............................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ...5-26
System ................................................................................................................... 5-27
IP .....................................................................................................................5-28
IP-Filter ............................................................................................................ 5-28
IP-filter address .............. .......................................... .... ... ... ... .... ......................5-29
IP-Mode ........................................................................................................... 5-29
Mask ................................................................................................................ 5-29
Gateway ..........................................................................................................5-29
Contents vii

Save ................................................................................................................5-30
Restore ............................................................................................................ 5-30
Web .................................................................................................................5-30
Telnet ............................................................................................................... 5-30
Username ........................................................................................................ 5-31
Password ..................................... .................................................... ................ 5-31
Firmware boot ..................................................................................................5-31
Firmware TFTP-IP ...........................................................................................5-32
Firmware TFTP-File .........................................................................................5-32
RADIUS ........................................................................................................... 5-32
Reset ...............................................................................................................5-33
Stat-Reset .............................................................. .......................................... 5-34
VLAN ..................................... ................................. ............................. ................... 5-34
Appendix A
Virtual Local Area Network
VLAN Behavior in a 700 Series Managed Switch ......................................................... A-2
Appendix B
Cabling Guidelines
Fast Ethernet Cable Guidelines .................... ................... ................... .................... ....... B-1
Category 5 Cable ........................................................................................................... B-2
Category 5 Cable Specifications ............................................................................. B-2
Twisted Pair Cables ................................................................................................ B-3
Patch Panels and Cables .......... ... ... ... .... ... .............................................................. B-4
Using 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet over Category 5 Cable ....................................... B-5
Cabling ...................................... ............................................................. ................. B-5
Near End Cross Talk (NEXT) .................................................................................. B-6
Patch Cables ........................................................................................................... B-6
RJ-45 Plug and RJ-45 Connectors ......................................................................... B-6
Conclusion .............................................................................................................. B-8
Appendix C
802.1x Port-Based Authentication Overview
Understanding 802.1x Port Based Network Access Control .........................................C-1
Glossary
Index
viii Contents

Chapter 1
About This Guide
Thank you for purchasing the NETGEAR™ 700 Series Switches.
Audience
This reference manual assumes that the reader has basic-to-intermediate computer and Internet
skills. However, basic computer network, Internet, and wireless technology tutorial information is
provided in the Appendices.
This document describes configuration commands for the 700 Series Switches so ftw are. The
commands can be accessed from the CLI, telnet, and Web interfaces.
Why the Document was Created
This document was created primarily for system administrators configuring and operating a
system using 700 Series Switches software. It is intended to provide an understanding of the
configuration options of 700 Series Switches software.
It is assumed that the reader has an understanding of the relevant switch platforms. It is also
assumed that the reader has a basic knowledge of Ethernet and networking concepts.
How to Use This Document
This document describes configuration commands for the 700 Series Switches so ftw are. The
commands can be accessed from the CLI, telnet (CMI), and Web interfaces.
• Chapter 4, “Administration Console Telnet Interface” describes the CMI.
• Chapter 5, “Web-Based Management Interface” describes the Web interface.
• Chapter 6, “Command Line Interface” describes the CLI, which can be reached through the
telnet (CMI) interface.
About This Guide 1-1
700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Note: Refer to the release notes for the 700 Series Switches Software application level code. The
release notes detail the platform specific functionality of the Switching, SNMP, Config, and
Management packages.
Typographical Conventions
This guide uses the following typographical conventions:
Table 1. Typographical conventions
italics Emphasis.
bold times roman User input.
[Enter] Named keys in text are shown enclosed in square brackets. The notation [Enter]
is used for the Enter key and the Return key.
[Ctrl]+C Two or more keys that must be pressed simultaneously are shown in text linked
with a plus (+) sign.
SMALL CAPS
DOS file and directory names.
Special Message Formats
This guide uses the following formats to highlight special messages:
Note: This format is used to highlight information of importance or special interest.
This manual is written for the 700 Series Switches according to these specifications:
Table 1-1 . Manual Specifications
Product Version 700 Series Switches
Manual Publication Date September 2005
Note: Product updates are available on the NETGEAR, Inc. Web site at http://
www.netgear.com/support/main.asp.
1-2 About This Guide

Chapter 2
Switch Management Overview
This chapter gives an overview of switch management, including the methods you can use to
manage your NETGEAR 700 Series Switches. Topics include:
• Management Access Overview
• SNMP Access
• Protocols
Management Access Overview
Your NETGEAR 700 Series Switches gives you the flexibility to access and manage the switch
using any or all of the following methods:
• An administration console
• Web browser interface
• External Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)-based network-management
application
The administration console and We b browser interface support are embedded in the switch’s
firmware and available for immediate use. Each of these management methods has advantages.
Table 1-1 compares the three management methods.
Switch Management Overview 2-1
700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Table 2-1. Comparing Switch Management Methods
Management Method Advantages Disadvantages
Administration
console
Web browser
or Telnet
SNMP Agent • Communicates with switch functions at the
• Out-of-band access via direct cable
connection means network bottlenecks,
crashes, and downtime do not slow or
prevent access
• No IP address or subnet needed
• Menu or CLI based
• HyperTerminal access to full functionality
(HyperTerminal are built into Microsoft
Windows 95/98/NT/2000 operating
systems)
• Secure – make sure the switch is installed
in a secure area.
• Can be accessed from any location via the
switch’s IP address
• Ideal for configuring the switch remotely
• Compatible with Internet Explorer and
Netscape Navigator Web browsers
• Familiar browser interface
• Graphical data available
• Most visually appealing
• Menu or CLI interfaces available
Management Information Base (MIB) level
• Based on open standards
• Must be near switch or use dial-up
connection
• Not convenient for remote users
• Not graphical
• Security can be compromised (hackers
can attack if they know IP address)
• May encounter lag times on poor
connections
• Displaying graphical objects over a
browser interface may slow navigation
• Requires SNMP manager software
• Least visually appealing of all three
methods
• Limited amount of information
available
• Some settings require calculations
• Security can be compromised (hackers
need only know the community name)
For a more detailed discussion of the Administration Console, see Chapter 4. For a more detailed
discussion of the Web Browser Interface, see Chapter 5.
Protocols
Your NETGEAR 700 Series Switches supports the following protocols:
• V irtual terminal prot ocols, such as Telnet
•SNMP
2-2 Switch Management Overview
700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Virtual Terminal Protocols
A virtual terminal protocol is a software program, such as Telnet, that allows you to establish a
management session from a Macintosh, a PC, or a UNIX workstation. Because Telnet runs over
TCP/IP, you must have at least one IP address configured on a NETGEAR 700 Series Switches
before you can establish access to it with a virtual terminal protocol.
Terminal emulation differs from a virtual terminal protocol in that you must connect a terminal or
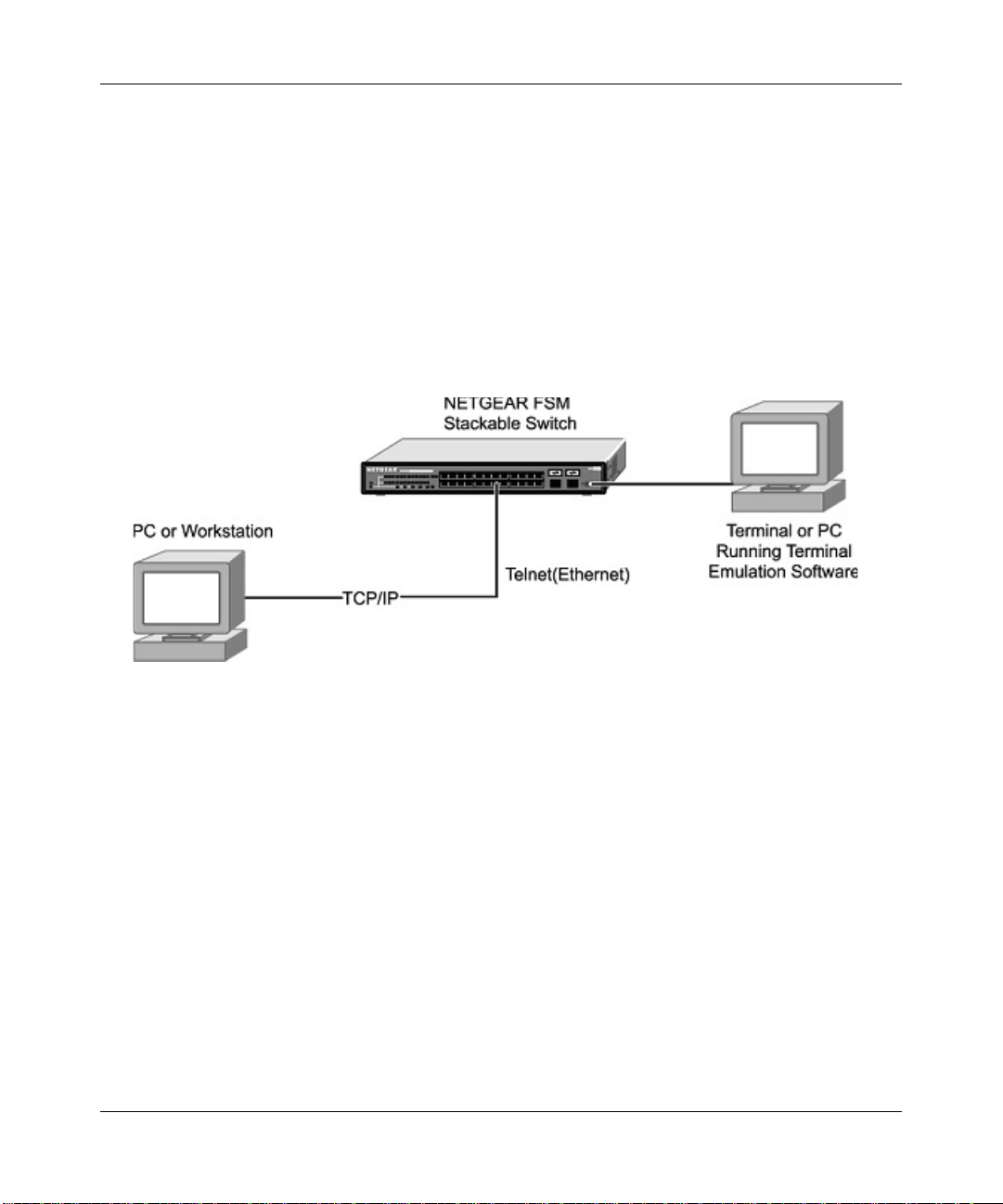
PC directly to the console port. Figure 2-1 shows a UNIX workstation connected to the system
through a virtual terminal protocol (Telnet), and a terminal connecting directly to the console port
through a null-modem cable.
Figure 2-1: Administration Console Access
SNMP Protocol
SNMP is the standard management protocol for multi-vendor IP networks. SNMP supports
transaction-based queries that allow the protocol to format messages and to transmit information
between reporting devices and data-collection programs. SNMP runs on top of the User Datagram
Protocol (UDP), offering a connectionless-mode service.
SNMP Access
With this access method, you can use an external SNMP-based application to manage your
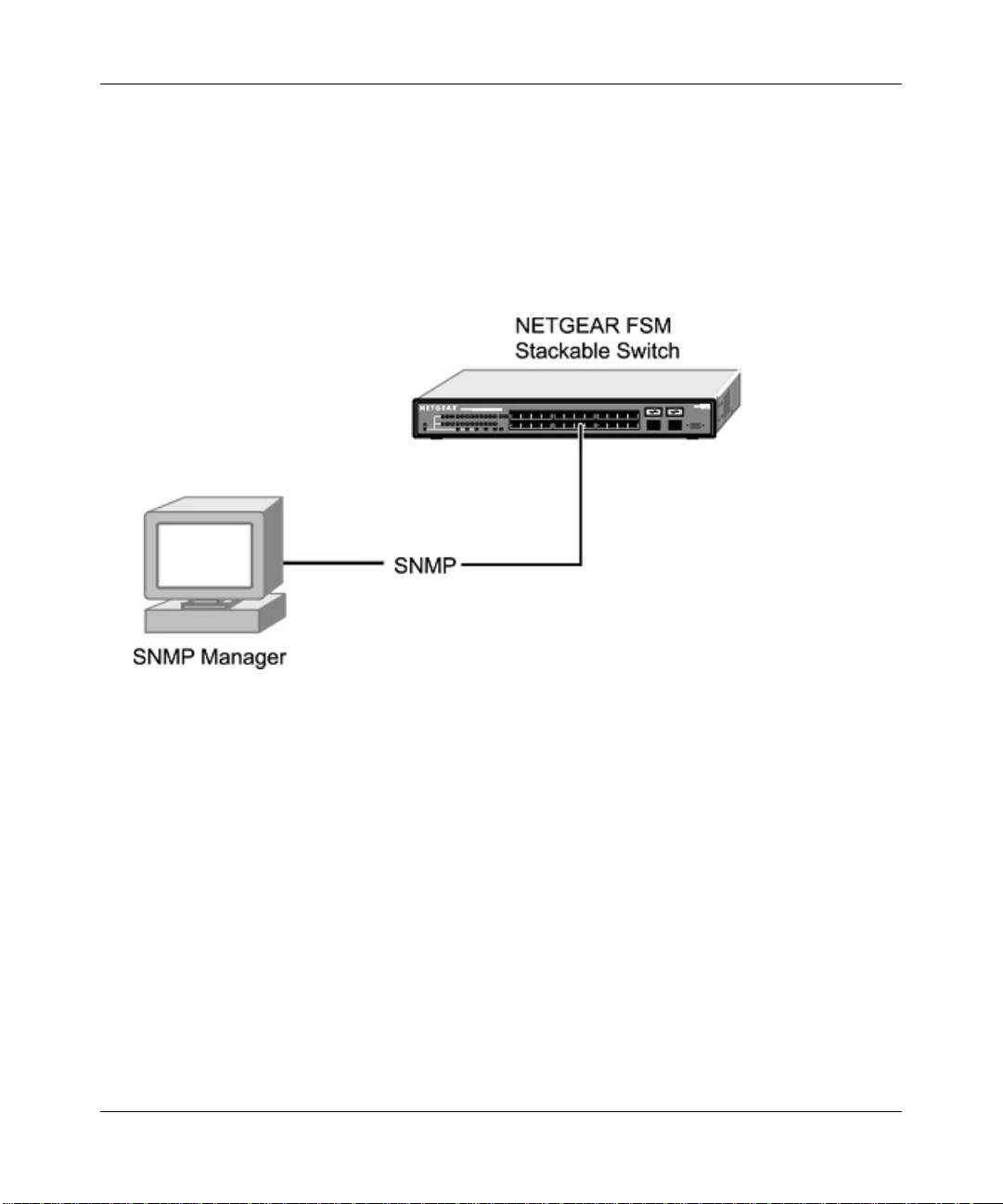
NETGEAR 700 Series Switches. Figure 2-2 shows an example of this management method.
Switch Management Overview 2-3
700 Series Software Manual v2.1
This management method requires the SNMP agent on the switch and the SNMP Network
Management Station to use the same community string and that the SNMP Network Management
Station is entered in the SNMP Host table on the switch. This management method, in fact, uses
two community strings: the GET community string and the SET community string. If the SNMP
Network management Station only knows the SET community string, it can read from and write to
the MIBs. However, if it only knows the GET community string, it can only read MIBs. The
default GET community string for the switch is ‘public’, and the host table is empty.
Figure 2-2: SNMP-Based Management Method
2-4 Switch Management Overview

700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Switch Management Overview 2-5
Chapter 3
Software Upgrade Procedure
As networking technology advances, NETGEAR will release new versions of the software that
runs the switch. These software releases will provide new capabilities that can extend the useful
life of your switch. This manual is updated whenever there is a change in either the first or second
positions of the software version number. The third position in the software version number
identifies bug fix and patch versions for which this manual is no t updated. The upgrade procedure
and the required equipment are described in this chapter.
IP address, Network Mask, and Default Gateway are not affected by upgrading the software. These
settings will be preserved in non-volatile memory (NVRAM).
The upgrade process is accomplished by having the switch boot from a TFTP server instead of its
own NVRAM. To initiate this sequence, the user must set the ‘Next Boot From’ configuration
parameter to ‘Boot from Net’, and then perform a ‘reset’. When the ‘Boot from Net’ option is set,
the switch will start using an image residing on a TFTP server on the network. Be sure that the
TFTP server residing on the network is accessible by the switch. Once completed, the software
version should be verified in the System page.
Note: It is highly recommended, though not necessary, to use a RS-232 serial port
connection to the switch during the software upgrade procedure. When using a Telnet
Session or Web interface alone, your connection to the switch will not be available until
the switch has completed its boot up and entered the Spanning Tree forwarding mode.
This can take up to three minutes.
The upgrade procedure below gives the exact steps to follow when using the Web interface. The
process is similar with either the CMI or CLI interfaces.
1. Select Advanced > Advanced Tools > Software Upgrade.
2. Select Next boot from: Net.
3. Verify information such as the IP address for the TFTP Server and the file name of the new
software image.
4. Save the setting in non-volatile memory. Press the Apply button and then go to the Tools >
Save Configuration to NVRAM option.
Software Upgrade Procedure 3-1

700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Restart the system via the Tools > Reset command. Bootstrap will retrieve the new software
5.
image then pass control to it. The system executes the new software image.
The previous software image in non-volatile memory will not be replaced by the new software
image. This enables you to return to the previous image if you do not like the new image.
6. Verify that the new software is loaded by going to the Advanced > Advanced Tools > Software
Upgrade screen and checking the Software Version.
Test your switch to make sure the new image is working correctly. If you decide to keep the
new image, go to Software Upgrade again. Select the Next boot from: Net & Save option.
7. Save the setting in non-volatile memory. Press the Apply button, and then go to the Tools >
Save Configuration to NVRAM option.
8. Restart the system via the Tools > Reset command
The new image should overwrite the old image in NVRAM. Verify it by going to the
Advanced > Advanced Tools > Software Upgrade screen and checking the Software Version.
Software Upgrade Procedure 3-2

700 Series Software Manual v2.1
3-3 Software Upgrade Procedure
Chapter 4
Administration Console Telnet Interface
The administration console is an internal, character-oriented, VT-100/ANSI menu-driven user
interface for performing management activities. Using this method, you can view the
administration console from a terminal, PC, Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation connected to
the switch’s console port. Figure 4-1 shows an example of this management method.
Figure 4-1: Administration Console Management Method
Set Up Your Switch Using Direct Console Access
The direct access management method is required when you initially set up your switch.
Thereafter, the convenience and additional features of the Web management access method
(described in Chapter 5) make it the best method to manage the switch.
Direct access to the switch console is achiev ed by connecting the switch’s console port to a
VT-100 or compatible terminal or to a PC, Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation equipped with
a terminal-emulation program. This connection is made using the null-modem cable supplied with
the switch.
Administration Console Telnet Interface 4-1
700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Examples of terminal-emulation programs include:
• HyperTerminal, which is included with Microsoft Windows operating systems
• ZTerm for the Apple Macintosh
• TIP for UNIX workstations
This example describes how to set up the connection using a HyperTerminal on a PC, but other
systems follow similar steps.
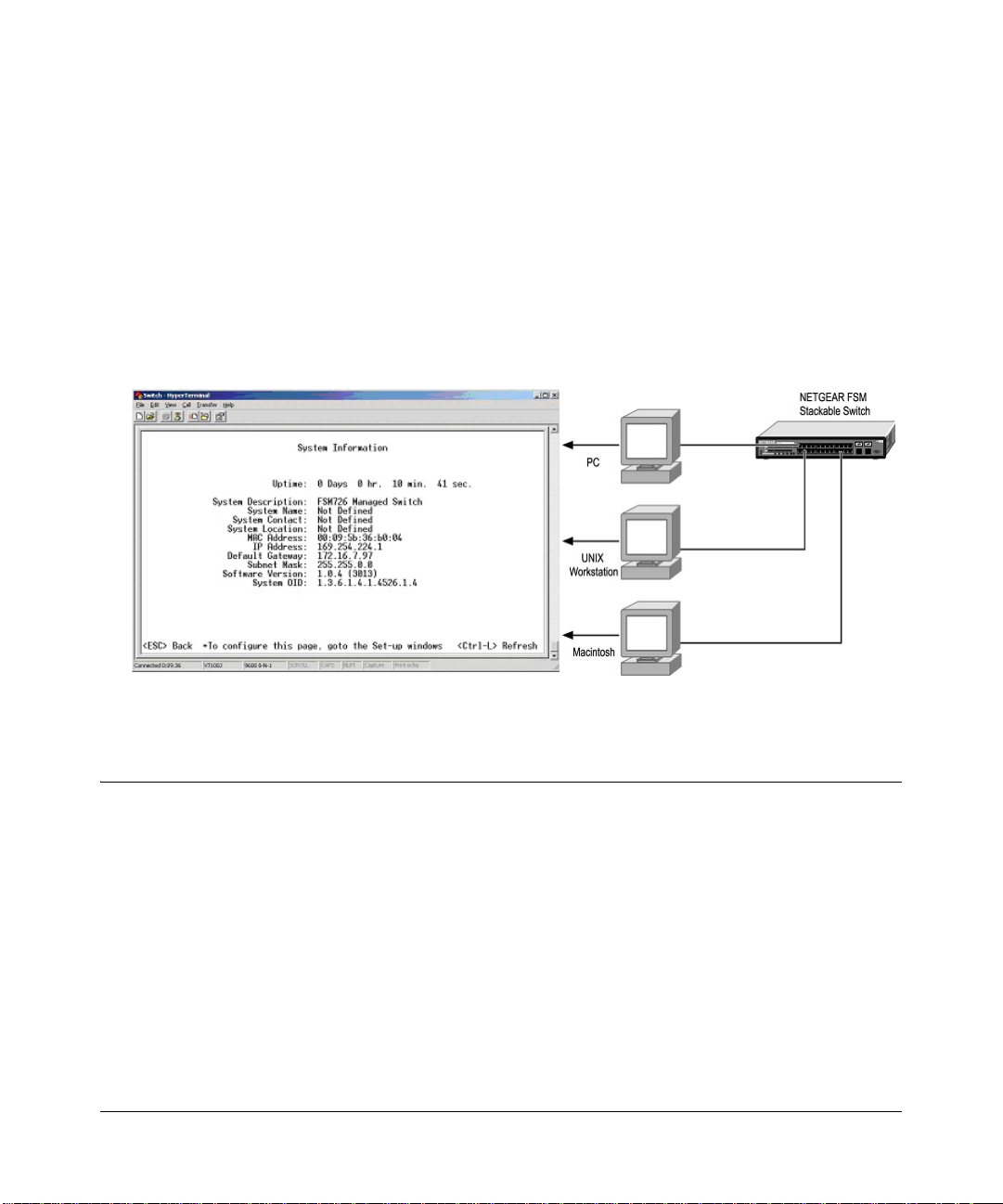
1. Click the Windows S tart button. Select Accessories and then Communications. HyperT erminal
should be one of the options listed in this menu. Select HyperTerminal
2. The following screen will appear. Enter a name for this connection. In the example below, the
name of the connection is FSM726. Click OK.
Figure 4-2: Connection Description
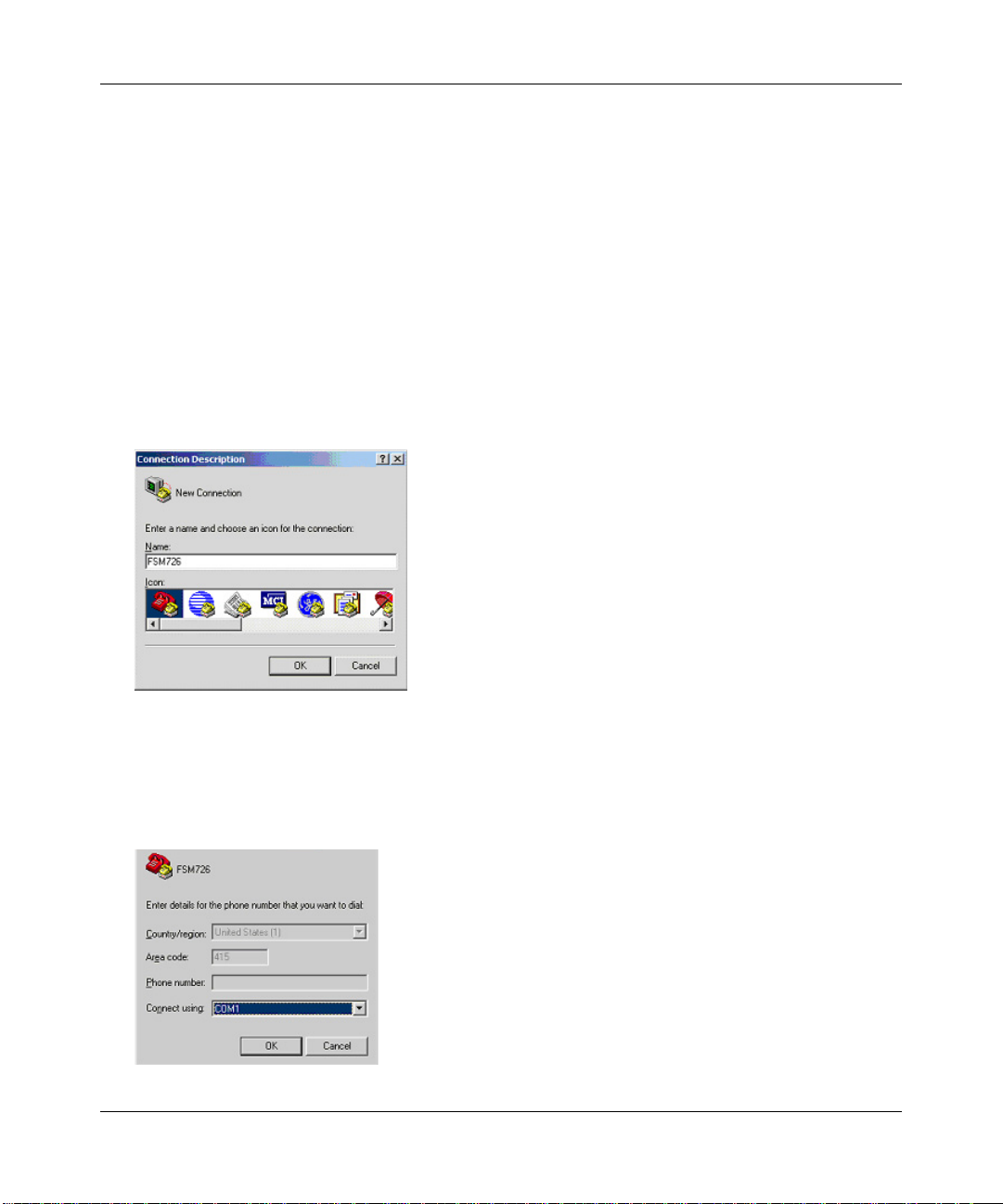
3.
The following screen will appear. In the bottom, drop down box labeled Connect Using, click
the arrow and choose the COM port to which the switch will connect. In the example below,
COM1 is the port selected. Click OK.
Figure 4-3: COM Port Selection
4-2 Administration Console Telnet Interface
700 Series Software Manual v2.1
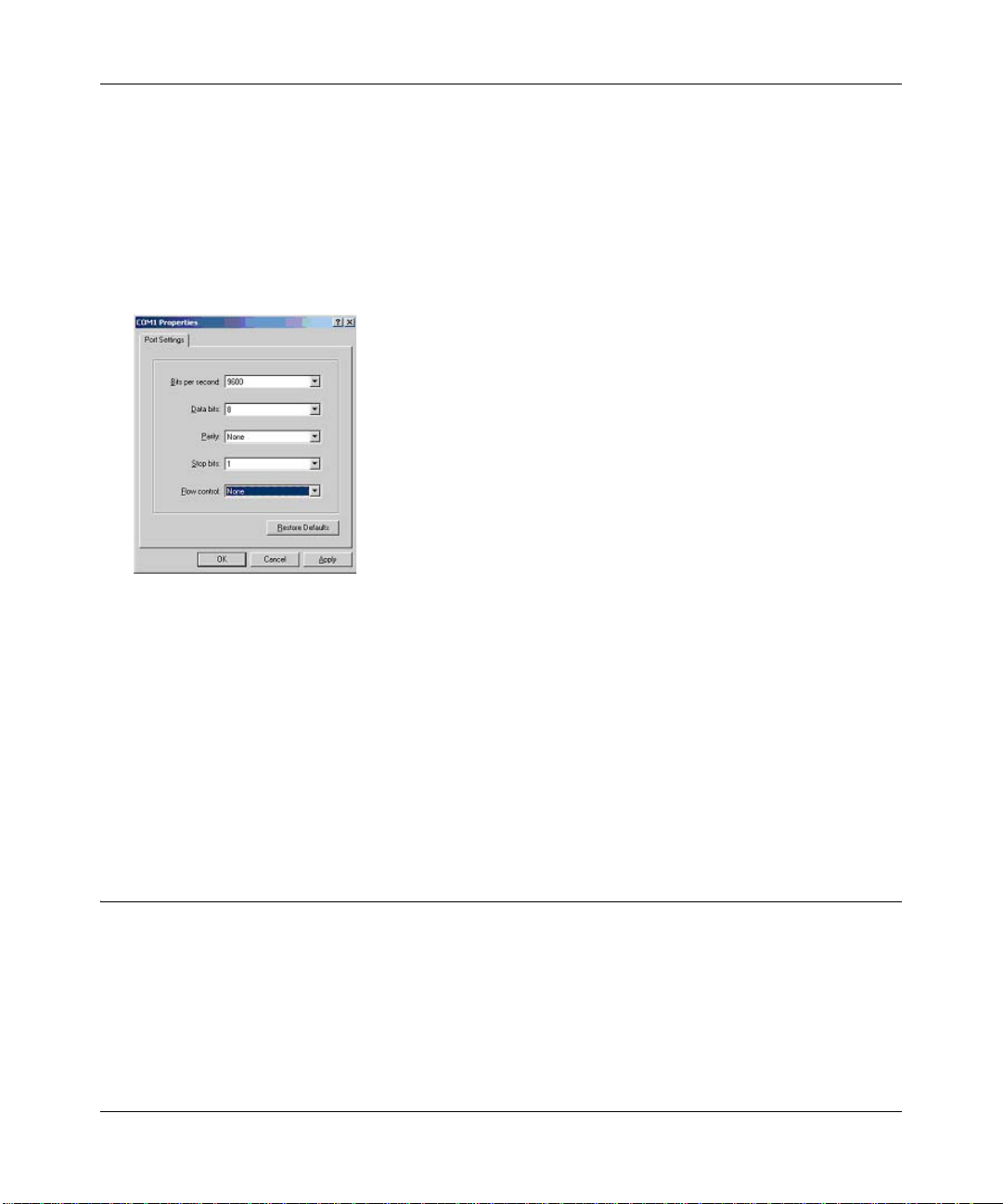
When the following screen appears, make sure that the port setting are as follows:
4.
Baud Rate: 9600
Data Bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop Bits: 1
Flow Control: None
Figure 4-4: Connection Settings
5.
Click OK.
The HyperTerminal window will open and you should be connected to the switch. If you do not
see the welcome screen or a system menu, press the return key.
In order to use the arrow keys when a tta ch ed to the U s er Inte rfa ce v ia a Telnet Session, make sure
the VT100 Arrows option is turned on. Under the terminal pull-down menu, choose Properties to
set this option.
Introduction to the Command Menu Interface
The switch offers a Command Menu Interface (CMI), which is a menu-driven method for
managing the switch, as well as a Command Line Interface (CLI), which uses text inputs to
manage the switch. The CLI is accessed through the CMI, but is not addressed in this chapter.
Chapter 6 discusses the CLI in detail.
Administration Console Telnet Interface 4-3

700 Series Software Manual v2.1
There are several characteristics to the CMI pages that are necessary to know before proceeding to
use it. The TAB key or the arrow keys may be used to move within menus and sub-screens. At the
bottom of every screen are some key commands available for that particular screen, as well as
some helpful information.
The common keystrokes and their definitions and intricacies are listed below:
ESC Return to the previous menu or screen, or abort editing
Tab Select field
Ctrl-L Refresh the screen
Ctrl-D Log off (password enabled)
Ctrl-M Move to field (Switch Statistics and Port Configuration menus only)
Ctrl-W Saves current configuration to Non-Volatile RAM (NVRAM)
Spacebar Toggles between possible settings for a field
Enter Select a menu item, edit a field, or accept a value after editing a field
Ctrl-X Delete a table entry
The main menu displays all the sub-menus that are available. Pressing ‘Enter’ when an option is
highlighted will confirm the choice of the specified sub-menu. The ‘hotkey’ or letter in front of
each menu option can also be typed to directly choose that option. As shown below, there are six
menu items to choose from:
Figure 4-5: Main Menu
To log out of the user interface, press Ctrl-D at any time during your telnet session. You will be
brought back to the login screen (password enabled) or Main Menu (password disabled).
4-4 Administration Console Telnet Interface

700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Main Menu> System
This screen displays the main menu System Information options. The user-definable options are:
System Name, System Contact, System Location, IP Address, Default Gateway, and Subnet Mask.
The System OID option is used for production testing.
Figure 4-6: System Information
Main Menu> Status
There are three Status sub-menus: Switch Statistics, Reset Statistics, and MAC Address Table.
Main Menu> Status >Switch Statistics
The Port-ID field allows you to choose a port to be observed. To get to the left side, use Ctrl-M to
move to that field. The screen displays basic statistics associated with the highlighted port.
Administration Console Telnet Interface 4-5

700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Figure 4-7: Switch Statistics
Main Menu> Status >Reset Statistics
The Reset Statistics menu allows you to reset the statistics counter to zero. When you choose this
option, a prompt will appear asking you for a confirmation. Once the confirmation is made, the
statistics counters will be reset to zero.
Figure 4-8: Reset Switch Statistics
Main Menu> Status > MAC Address Table
The MAC Address lookup table displays the MAC addresses that are currently in the address
database. When addresses are in the database, the packets intended for those addresses are
forwarded directly to those ports. You can filter out addresses in the table by port, VLAN, or MAC
address by entering a value in those fields, and selecting Query.
4-6 Administration Console Telnet Interface
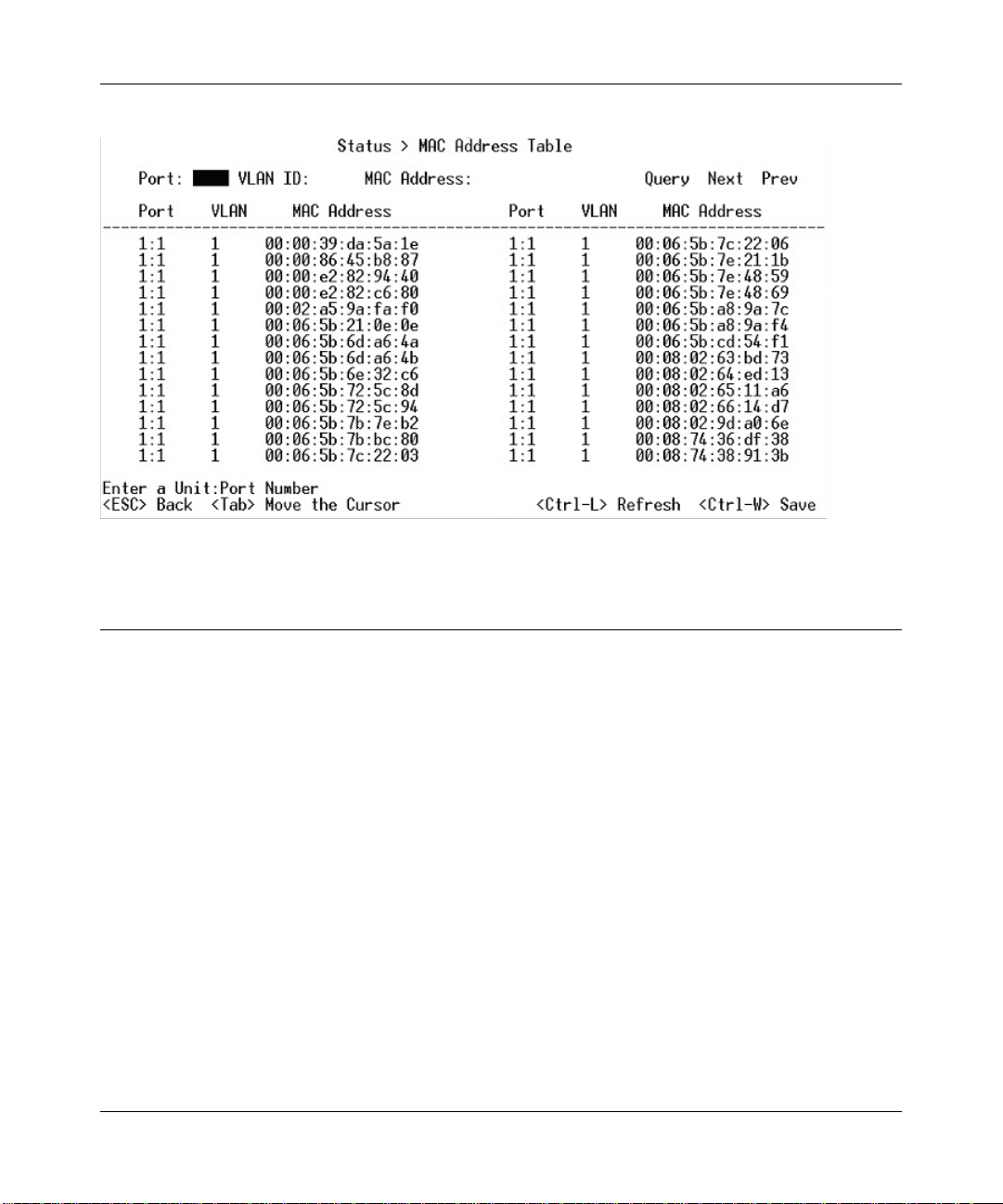
Figure 4-9: Address Manager: MAC Address Table
700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Main Menu> Set-Up
There are four sub-menus under the Set-Up menu:
• System Configuration
• IP Configuration
• Port Configuration
•GBIC
Main Menu> Set-Up> System Configuration
The System Configuration allows you to enter a number of system-related information for easy
reference in the future. Such items include System Name, Contact Person, and System Location.
The MAC address is also shown, but it is not user configurable.
Administration Console Telnet Interface 4-7

700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Figure 4-10: System Configuration
Main Menu> Set-Up> IP Configuration
This menu manages the IP related information of the system.
IP Assignment Mode. You can manually enter IP-related information:
• Bootstrap Protocol, which allows the switch to discover its own IP address from a BootP
server on the network
• DHCP, which allows the switch to accept DHCP broadcasts from a DHCP server and
automatically configures IP related information
The default setting is DHCP, to enable quick and easy set-up. However, since you need to know
the IP address of your switch to remotely manage it and DHCP assignments can change, change
the IP assignment mode from DHCP to manual after the switch has obtained its IP address.
Figure 4-11: Set-up Manager: IP Configuration
Note: In DHCP mode, if the switch fails to get a DHCP assignment, the switch defaults to
192.168.0.1 as its IP address.
If you are in the manual mode and need to configure the IP information, enter a site-specific IP
address, Gateway Address, and Network Mask (or subnet mask). Consult your netwo r k
administrator for the information.
Press Ctrl-W to save any changes to NVRAM.
4-8 Administration Console Telnet Interface
700 Series Software Manual v2.1
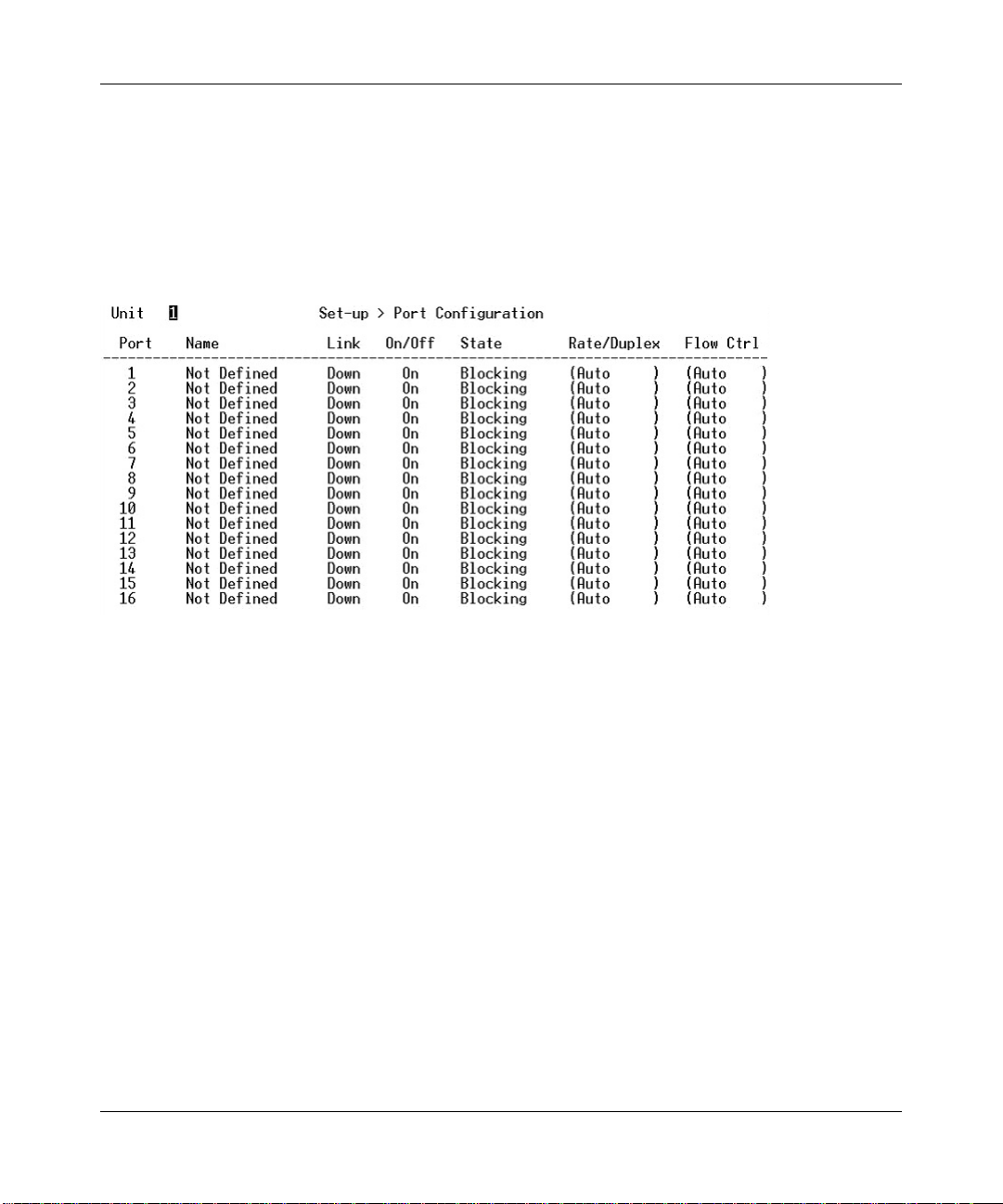
Main Menu> Set-Up> Port Configuration
On this page, you can set up the port characteristics related to link operations. All of the
parameters on this page are toggle settings. To change, or toggle, between options, press Ctrl-M to
move the curser to the ports field and simply press the space bar when the appropriate option is
highlighted. To modify ports 17 to 26, you must tab through ports 1 to 16. The comments field is
available for you to enter a description of the port.
Figure 4-12: Port Configuration
Port. The port number on the switch.
Name. The name of the port. This is a user-defined label.
Link. Indicates if the port is Up or Down.
On/Off. Indicates if the port is enabled or disabled by the Administrator.
Admin field. Allows you to Enable or Disable the port.
Stat e field. The State field displays the Spanning Tree State of the port (Blocking, Listening,
Learning, Forwarding, or Disabled). You can only observe the status of the ports; you cannot
modify this field. The Spanning Tree Protocol controls this field.
Rate/Duplex field. Indicates the speed and duplex for the port. The possible entries are
Auto-negotiation (Auto); 10 Mbps half duplex (10M Half); 10 Mbps full duplex (10M Full); 100
Mbps half duplex (100M Half); or 100 Mbps full duplex (100M Full).
Administration Console Telnet Interface 4-9

700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Enabling auto-negotiation on a port allows a port to sense the communication speed and negotiate
the duplex mode (full duplex or half duplex) automatically. The ports will select the highest
possible throughput. The port can auto-negotiate with any port that is compliant with IEEE 802.3u.
If the other port is not IEEE802.3u compliant, the port will default to half-duplex, 10 Mbps mode.
You can operate the communication speed and duplex mode manually.
Flow Control. Allows you to enable or disable Flow Control.
Flow control is a protocol that prevents packets from being dropped by reducing the amount of
traffic to a level that can be accommodated. If enabled on both ends of a connection, it will
prevent the sender from sending data until the receiver can accept it. This switch complies with
the IEEE802.3x flow control standard.
Main Menu> Set-Up> GBIC
This page allows you to choose the port type for the gigabit ports. The default is 1000BASE-T
(RJ-45).
Figure 4-13: GBIC Port Configuration
All of the parameters on this page are toggle settings. To change, or toggle, between options, press
Ctrl-M to move the curser to the ports field and simply press the space bar when the appropriate
option is highlighted.
If you want to use a GBIC, the settings on this page must be set accordingly. The switch
auto-detects if the media is copper or GBIC. This Auto-detect feature is enabled by default.
4-10 Administration Console Telnet Interface

700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Note: Enabling the GBIC connector for a Gigabit Ethernet port disables the built-in 1000BASE-T
port.
Main Menu> Tools
These system tools are provided:
• Save Configuration to NVRAM
• Restore Factory Values
• Reset Switch
After making changes to any of the information on the screens in the console interface, you must
save the changed settings to NVRAM. Save Configuration to NVRAM.
Figure 4-14: Save Settings to NVRAM & Restore Factory Values
• To Save Configuration to NVRAM, select the Save option, and press either ‘Enter’ or ‘Y’ to
save the configuration to NVRAM.
• To Restore Factory Values, select the Restore Factory Values to reset the switch parameters to
their original default settings. In order for changes to take effect, you must Reset the switch.
Note: Network IP settings (i.e. IP address, Gateway Address, Network Mask) will not be
affected by this command.
• To use the Reset Switch option, select it from the menu, which will restart the switch.
Resetting the switch is the equivalent of turning the power off and on. Resetting the switch
will clear the statistical counters to zero.
Administration Console Telnet Interface 4-11

700 Series Software Manual v2.1
Main Menu> Security
This screen allows you to enable or disable the web and/or telnet interfaces, as well as change the
user name and password. To use password protection, you must enable it. User names and
passwords are case sensitive and can be up to 20 characters long. The factory default password is
password in lower case letters.
Figure 4-15: Security
Note: Using telnet, you can only enable/disable the web interface. You cannot enable/disable the
telnet interface.
If you forget your password, contact NETGEAR technical support at 1-888-NETGEAR (in North
America).
Main Menu> Advanced
The Advanced page allows professional users to operate more complicated features of the device,
which include VLAN, Spanning Tree, Port Trunking, Multimedia support (IGMP), traffic
prioritization, SNMP, and port mirroring. These features are powerful and can degrade or disable a
network if improperly used. The submenus are introduced below.
• Port Mirroring: You can designate a port for monitoring traffic from one or more other ports or
of a single VLAN configured on the switch. The switch monitors the network activity by
copying all traffic from the specified monitoring sources to the designated monitoring port, to
which a network analyzer can be attached.
4-12 Administration Console Telnet Interface
 Loading...
Loading...