Page 1
查询UPD6121供应商查询UPD6121供应商
DATA SHEET
DATA SHEET
MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
µ
PD6121, 6122
REMOTE CONTROL TRANSMISSION CMOS IC
The µPD6121, 6122 are infrared remote control transmission ICs using the NEC transmission format that are ideally
suited for TVs, VCRs, audio equipment, air conditioners, etc. By combining external diodes and resistors, a maximum
of 65,536 custom codes can be specified. These ICs come in small packages, thus facilitating the design of light
and compact remote control transmitters.
The NEC transmission format consists of leader codes, custom codes (16 bits), and data codes (16 bits). It can
be used for various systems through decoding by a microcontroller.
FEATURES
• Low-voltage operation: VDD = 2.0 to 3.3 V
• Low current dissipation: 1 µA Max. (at standby)
• Custom codes: 65,536 (set by external diodes and resistors)
• Data codes:
• µPD6121: 32 codes (single input), 3 codes (double input), expandable up to 64 codes through SEL pin
• µPD6122: 64 codes (single input), 3 codes (double input), expandable up to 128 codes through SEL pin
• µPD6121, 6122 are transmission code-compatible (NEC transmission format) with the µPD1913C
Note
6102G
• Pin compatibility:
• µPD6121G-001 is pin-compatible with the µPD1943G (However, capacitance of capacitor connected to
oscillator pin and other parameters vary)
• µPD6122G-001 is pin-compatible with the µPD6102G (However, capacitance of capacitor connected to
oscillator pin and other parameters vary)
• Standard products (Ver. I, Ver. II specifications)
, and 6120C
Note
.
Note
, 1943G
Note
*
*
,
*
Note Provided for maintenance purpose only
• When using this product (in NEC transmission format), please order custom codes from NEC.
• New custom codes for the
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Document No. U10114EJ6V0DS00 (6th edition)
(Previous No. IC-1813)
Date Published October 1995 P)
Printed in Japan
µPD6121G-002, µPD6122G-002 cannot be ordered.
The mark shows revised points.
*
©
©
1994
1994
Page 2
ORDERING INFORMATION
*
Part number Package Description
µPD6121G-001 20-pin plastic SOP (375 mil) Standard (Ver I spec.)
µPD6121G-002 20-pin plastic SOP (375 mil) Standard (Ver II spec.)
µPD6122G-001 24-pin plastic SOP (375 mil) Standard (Ver I spec.)
µPD6122G-002 24-pin plastic SOP (375 mil) Standard (Ver II spec.)
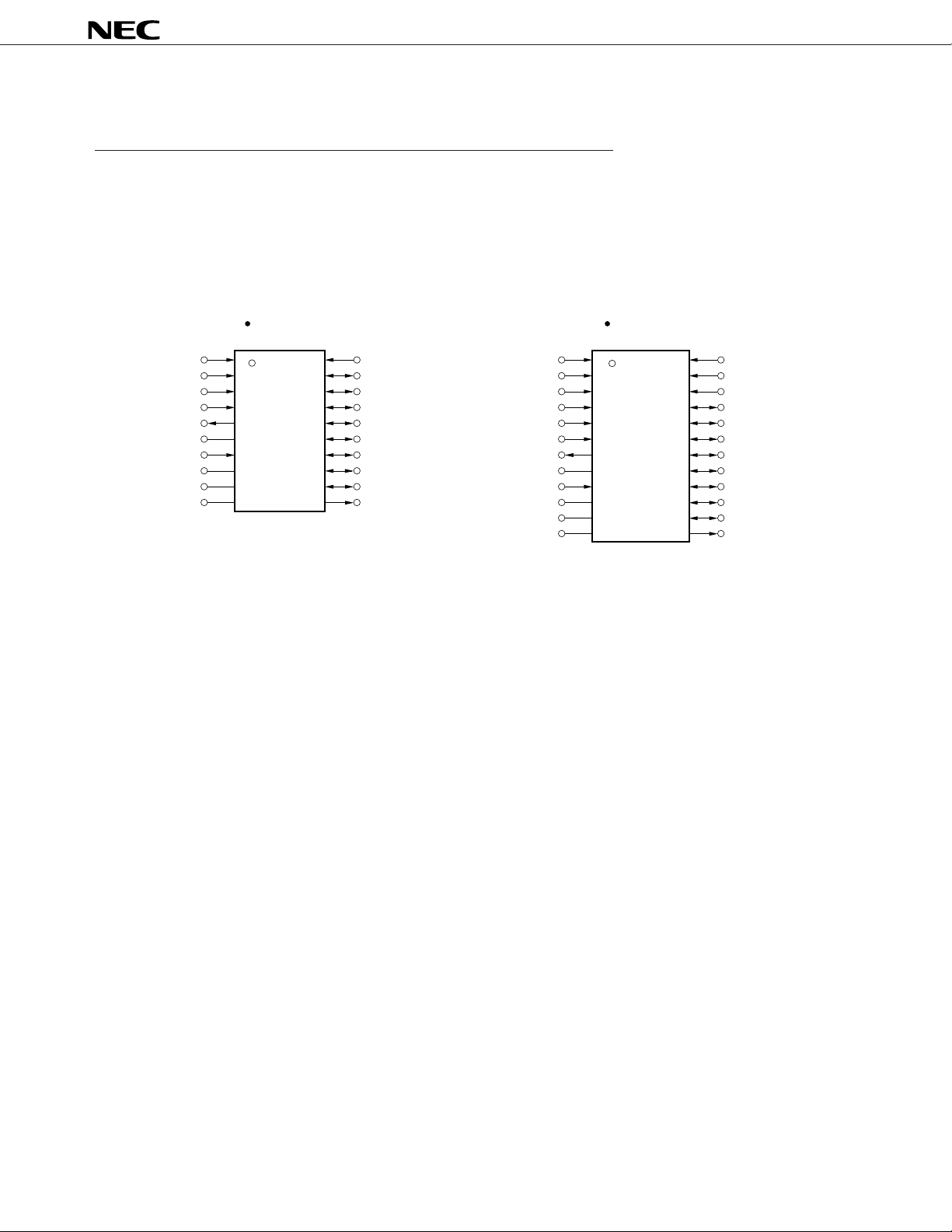
PIN CONFIGURATION (Top View)
µ
PD6121, 6122
µPD6121
KI
KI
KI
KI
REM
V
SEL
OSCO
OSCI
V
0
1
2
3
DD
SS
1
2
µPD6121G-002
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
20
19
µPD6121G-001
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
CCS
KI/O
KI/O
KI/O
KI/O
KI/O
KI/O
KI/O
KI/O
LMP
2
KI
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
KI
KI
KI
KI
KI
REM
V
SEL
3
4
5
6
7
DD
OSCO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11 14OSCI
SS
12 13V
PIN IDENTIFICATIONS
CCS : Custom code selection input REM : Remote output
KI0 - KI7 : Key input SEL : SEL input
0 - KI/O7 : Key input/output VDD : Power supply pin
KI/O
LMP : Lamp output VSS : GND pin
OSCI, OSCO: Resonator connection pin
µPD6122
24
23
22
µPD6122G-001
µPD6122G-002
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
KI
1
KI
0
CCS
KI/O
KI/O
KI/O
KI/O
KI/O
KI/O
KI/O
KI/O
LMP
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
Page 3
µ
PD6121, 6122
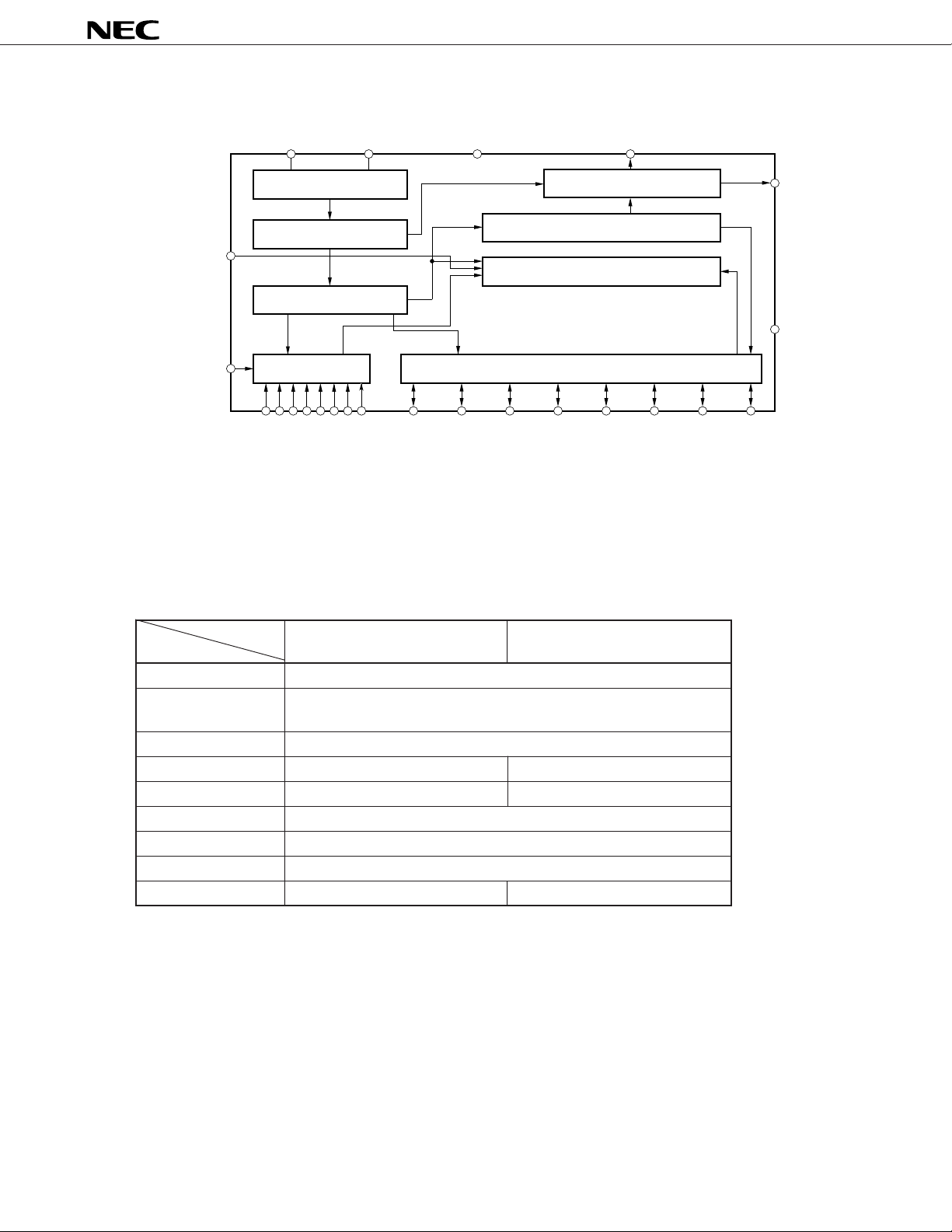
BLOCK DIAGRAM
OSCO OSCI VDD LMP
SEL
CCS
Note µPD6121: KI0 - KI3
µPD6122: KI0 - KI7
Key input circuit
Oscillator
Frequency divider
Timing generator
Note
KI0 – KIn
*
Output circuit
Controller
Data register
Key input/output circuit
KI/O1KI/O0
KI/O2
REM
SS
V
KI/O7KI/O6KI/O5KI/O4KI/O3
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PRODUCTS
Part number
Item
Operating voltage VDD = 2.0 to 3.3 V
Current consumption 1 µA MAX.
(at standby)
Custom codes 65,536 (16-bit setting)
Data codes 32 x 2 64 x 2
No. of KI pins 4 8
No. of KI/O pins 8
SEL pin Provided
Transmission format NEC transmission format
Package 20-pin plastic SOP (375 mil) 24-pin plastic SOP (375 mil)
µPD6121 µPD6122
3
Page 4

µ
PD6121, 6122
1. PIN FUNCTIONS
(1) Key input pins (KI0 to KI7), key input/output pins (KI/O0 to KI/O7)
A pull-down resistor is placed between key input pins and a VSS pin. When several keys are pressed
simultaneously, the transmission of the corresponding signals is inhibited by a multiple-input prevention circuit.
In the case of double-key input, transmission is inhibited if both keys are pressed simultaneously (within 36 ms
interval); if not pressed simultaneously, the priority of transmission is first key, then second key.
When a key is pressed, the custom code and data code reading is initiated, and 36 ms later, output to REM output
is initiated. Thus if the key is pressed during the initial 36 ms, one transmission is performed. If a key is kept
pressed for 108 ms or longer, only leader codes are consecutively transmitted until the key is released.
Keys can be operated intermittently at intervals as short as 126 ms (interval between two on’s), making this an
extremely fast-response system.
(2) Resonator connection pins (OSCI, OSCO)
The oscillator starts operating when it receives a key input. Use a ceramic resonator with a frequency between
400 and 500 kHz.
(3) Power-supply pin
The power supply voltage is supplied by two 3-V batteries. A broad range of operating power supply voltage is
allowed, from 2.0 to 3.3 V. The supply current falls below 1 µA when the oscillator is inactive when no keys are
pressed.
(4) REM output pin
The REM output pin outputs the transmission code, which consists of the leader code, custom code (16 bits),
and data code (16 bits) (Refer to 2. NEC TRANSMISSION FORMAT (REM OUTPUT)).
(5) SEL input pin
By controlling D
data codes, respectively. By connecting the SEL pin to VDD or VSS, D7 is set to “0” or “1”, respectively.
This pin has high-impedance input, therefore be sure to connect it either to V
(6) CCS input pin
By placing a diode between the CCS pin and the KI/O pin, it is possible to set a custom code. When a diode
is connected, the corresponding custom code is “1”, and when not connected, it is “0”.
(7) LMP output pin
The LMP pin outputs a low-level signal while the REM pin outputs a transmission code.
7 of the data code with this pin, the µPD6121 and µPD6122 can transmit 64 and 128 different
DD or VSS.
4
Page 5
µ
PD6121, 6122
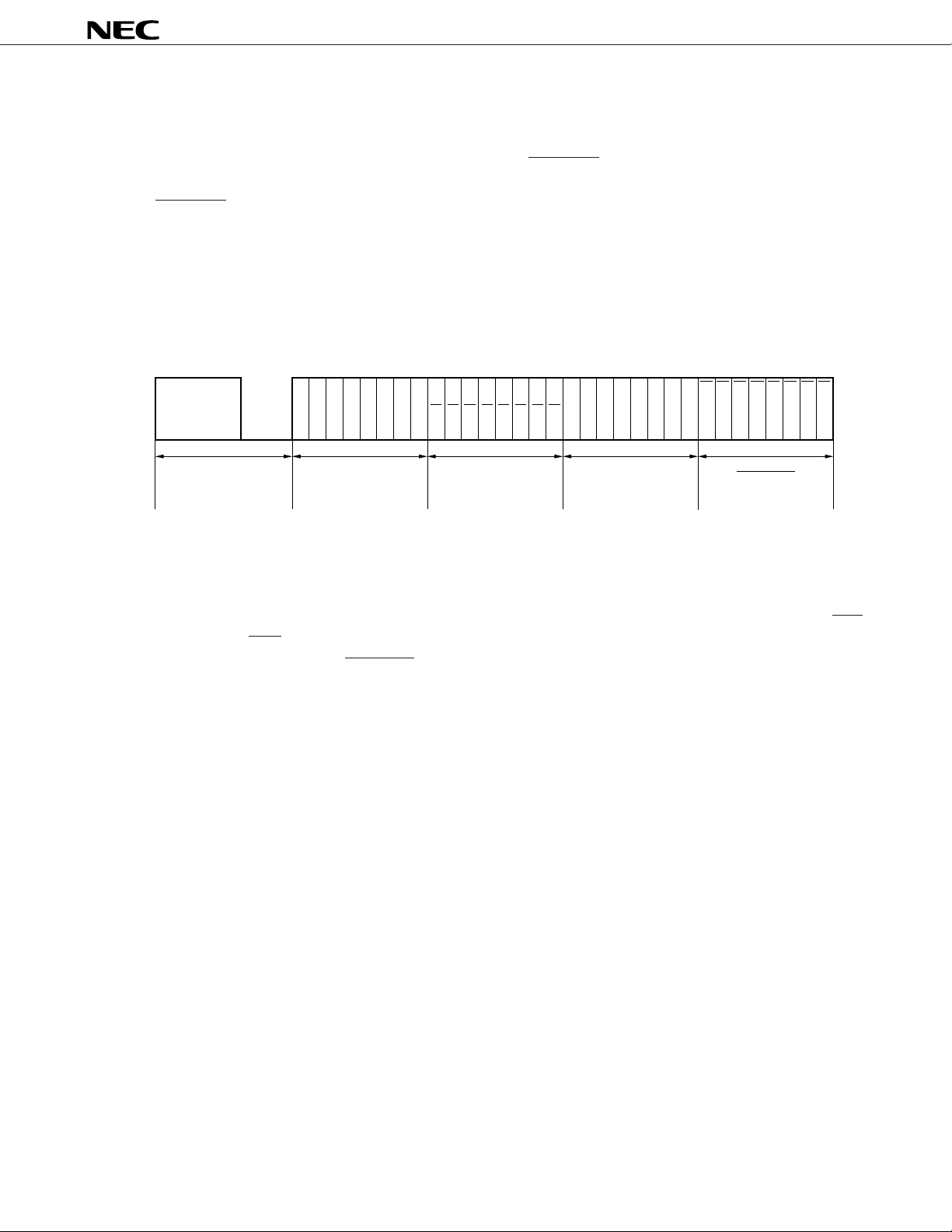
2. NEC TRANSMISSION FORMAT (REM OUTPUT)
The NEC transmission format consists of the transmission of a leader code, 16-bit custom codes (Custom
Code, Custom Code’), and 16-bit data codes (Data Code, Data Code) at one time, as shown in Figure 2-1.
Also refer to 4. REMOTE OUTPUT WAVEFORM.
Data Code is the inverted code of Data Code.
The leader code consists of a 9-ms carrier waveform and a 4.5-ms OFF waveform and is used as leader for
the ensuing code to facilitate reception detection.
Codes use the PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) method, and the signals “1” and “0” are fixed by the interval
between pulses.
Figure 2-1. REM Output Code
C0C1C2C3C4C5C6C7C0’C1’C2’C3’C4’C5’C6’C7’
Custom Code Custom Code’ Data Code Data CodeLeader Code
=======
C0C1C2C3C4C5C6C
or
or or or or or or or
C
C
0
1C2C3C4C5C6C7
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D
=
7
7
Cautions 1. Use any of the possible 256 kinds of custom codes specified with 00xxH (diode not
connected), as desired. If intending to use custom codes other than 00xxH, please consult
NEC in order to avoid various types of errors from occurring between systems.
2. When receiving data in the NEC transmission format, check that the 32 bits made up of the
16-bit custom code (Custom Code, Custom Code’) and the 16-bit data code (Data Code, Data
Code) are fully decoded, and that there are no signals with the 33rd bit and after (be sure
to check also Data Code).
5
Page 6
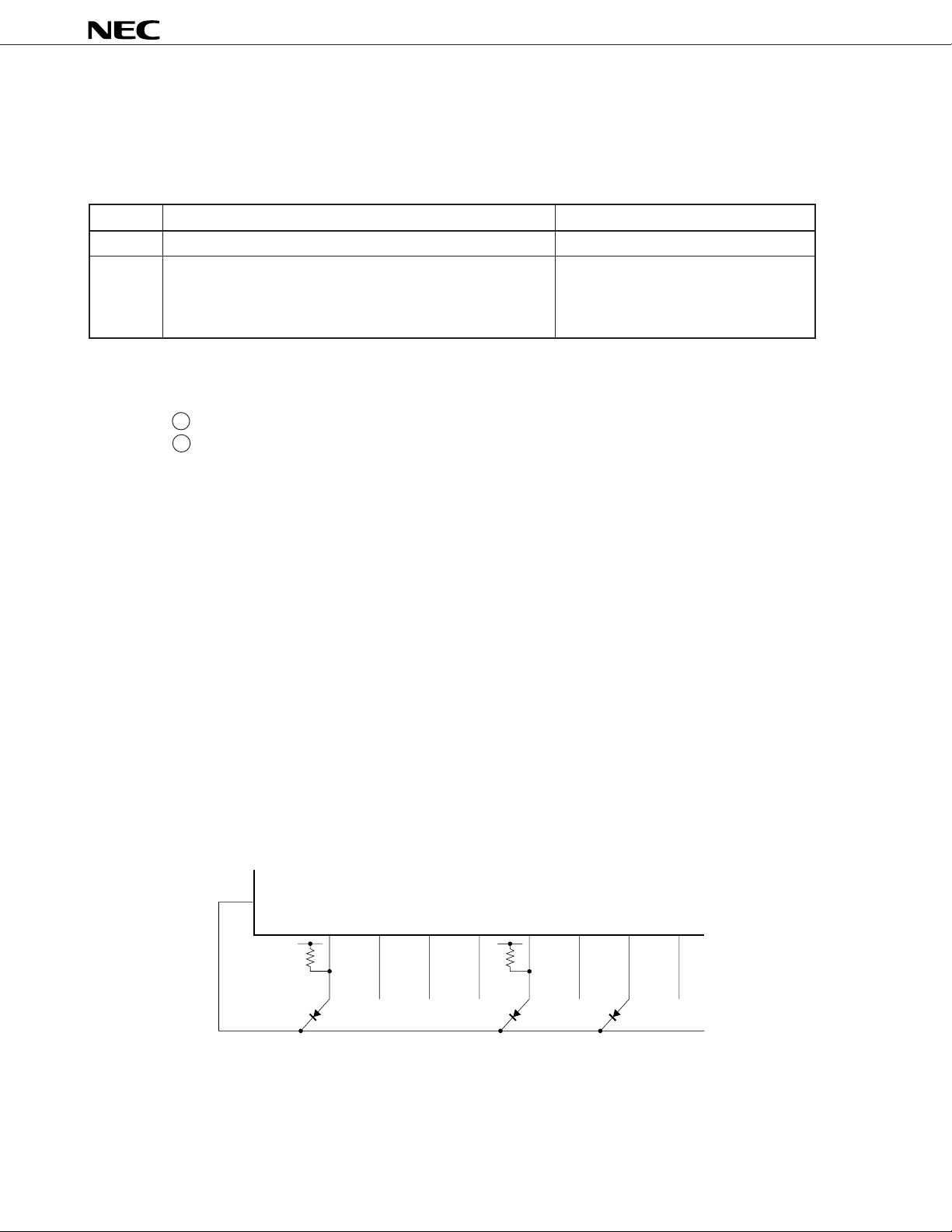
3. CUSTOM CODE (CUSTOM CODE, CUSTOM CODE’) SETTING
*
The custom code is set in two different ways depending on whether Ver I or Ver II specifications are employed.
Figure 3-1. Custom Code Setting
µ
PD6121, 6122
Higher 8 bits of custom code
Ver I
Ver II
Remark The µPD6121-001 has Ver I specifications and is pin-compatible with the µPD1943G, and the µPD6122-
A custom code setting example is shown below.
Fixed by external diode bit
C0, C1, C2 ... Fixed by connecting CCS pin and either one of
pins KI/O0 to KI/O7
C3 to C7 ... Fixed by absence or presence of external pull-up
resistor for KI/O6, KI/O7
001 has Ver I specifications and is pin-compatible with the µPD6102G.
If used as pin-compatible products, please note the following points.
1 Connect the SEL pin to V
2 Change the capacitance of the capacitor connected to the resonator connection pin (Refer to
9. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS).
DD.
3.1 Standard versions with Ver I specs. (µPD6121-001, µPD6122-001)
*
Each of the higher 8 bits of the custom code is set to “1” when a diode is connected between the CCS pin and
the corresponding KI/O pin, and is set to “0” when no diode is connected. If a pull-up resistor is connected to
the KI/O pin corresponding to one of the lower 8 bits of the custom code’, the bit is first set to “1”. Based on the
1’s information of the lower 8 bits of the custom code’, the corresponding bit of the higher 8 bits of the custom
code is then captured and not inverted. The non-inverted value is finally overwritten to the corresponding bit of
the lower 8 bits of the custom code’. The inverse occurs when no pull-up resistor is connected.
It follows from the above that the custom code can be set in 65,536 different ways depending on whether or not
a diode and/or pull-up resistor are present.
Please refer to Figure 3-2 Example of Custom Code Setting for Ver I Specifications (
001).
Lower 8 bits of custom code’
Fixed by external pull-up resistor bit
Fixed by external pull-up resistor (KI/O0 to
KI/O5) bit
µPD6121-001, 6122-
Figure 3-2. Example of Custom Code Setting for Ver I Specifications (
Configuration example
6
CCS
µPD6121-001, 6122-001)
KI/O
0
KI/O1KI/O2KI/O3KI/O4KI/O5KI/O6KI/O
V
V
DD
DD
7
Page 7
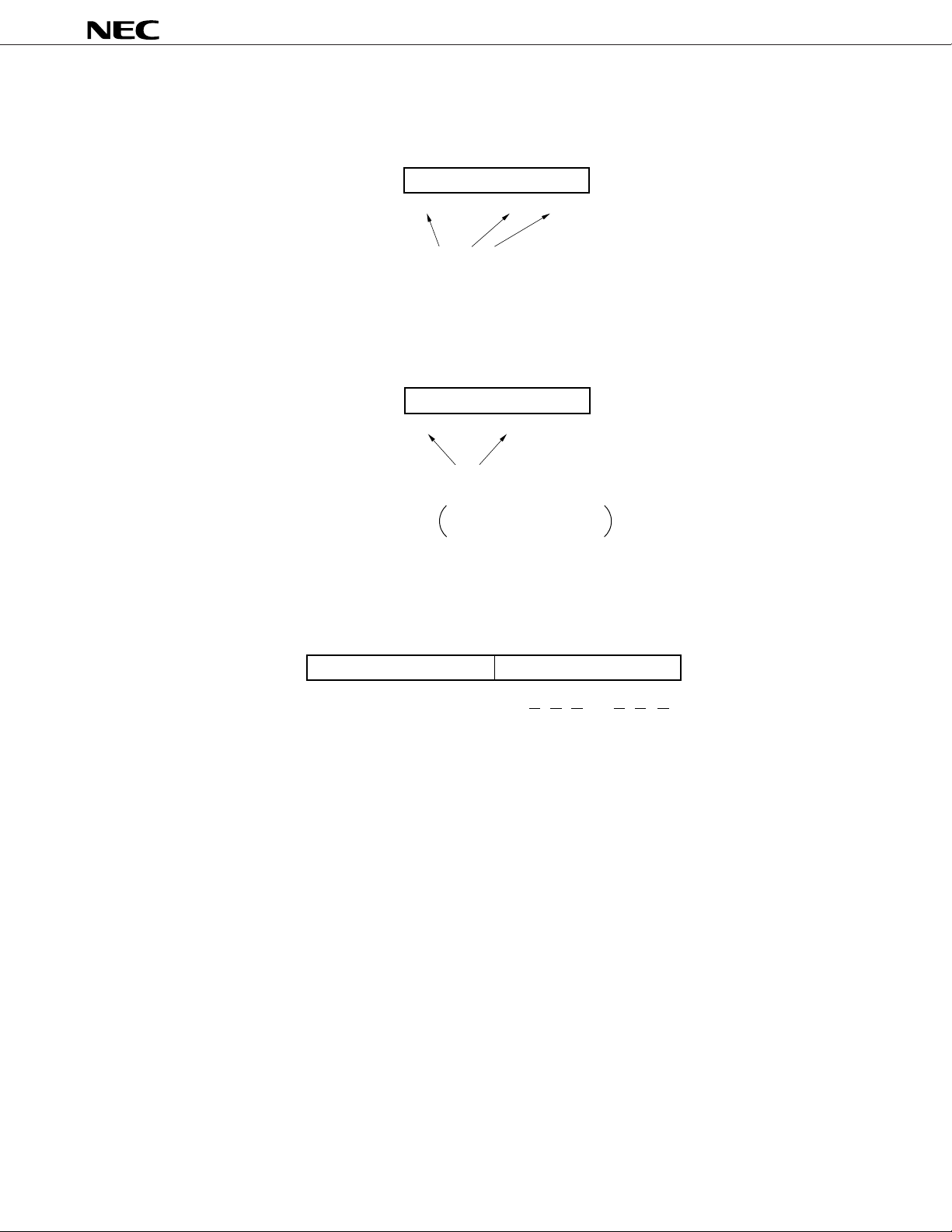
µ
PD6121, 6122
The higher 8 bits of the custom code are determined by the diode connected to the CCS pin and KI/O pin.
Set custom code
Higher 8 bits of custom code
10001010
C
0C1C2C3C4C5C6C7
Set to “1” by diode
The inversion/non-inversion of the lower 8 bits of the custom code’ is determined by the pull-up resistor
connected to the KI/O pin.
Set custom code
Lower 8 bits of custom code’
10001000
0
to C
’
’
0
to C7
7
C
0’C1’C2’C3’C4’C5’C6C7
Set to “1” by pull-up resistor,
that is, bit for non-inversion of custom code is set
1: Non-inversion for C
0: Inversion for C
When the above-described setting is done, the following custom code is output.
Custom code
Higher 8 bits of custom code
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
C
1
2
3
4
5
C
C
C
C
6
C
C
Lower 8 bits of custom code’
1111101
1
0
0
’
7
C
C1’C2’C3’C4’C5’C6’C7’
C
C0 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7
Remark Codes are transmitted from the LSB.
7
Page 8
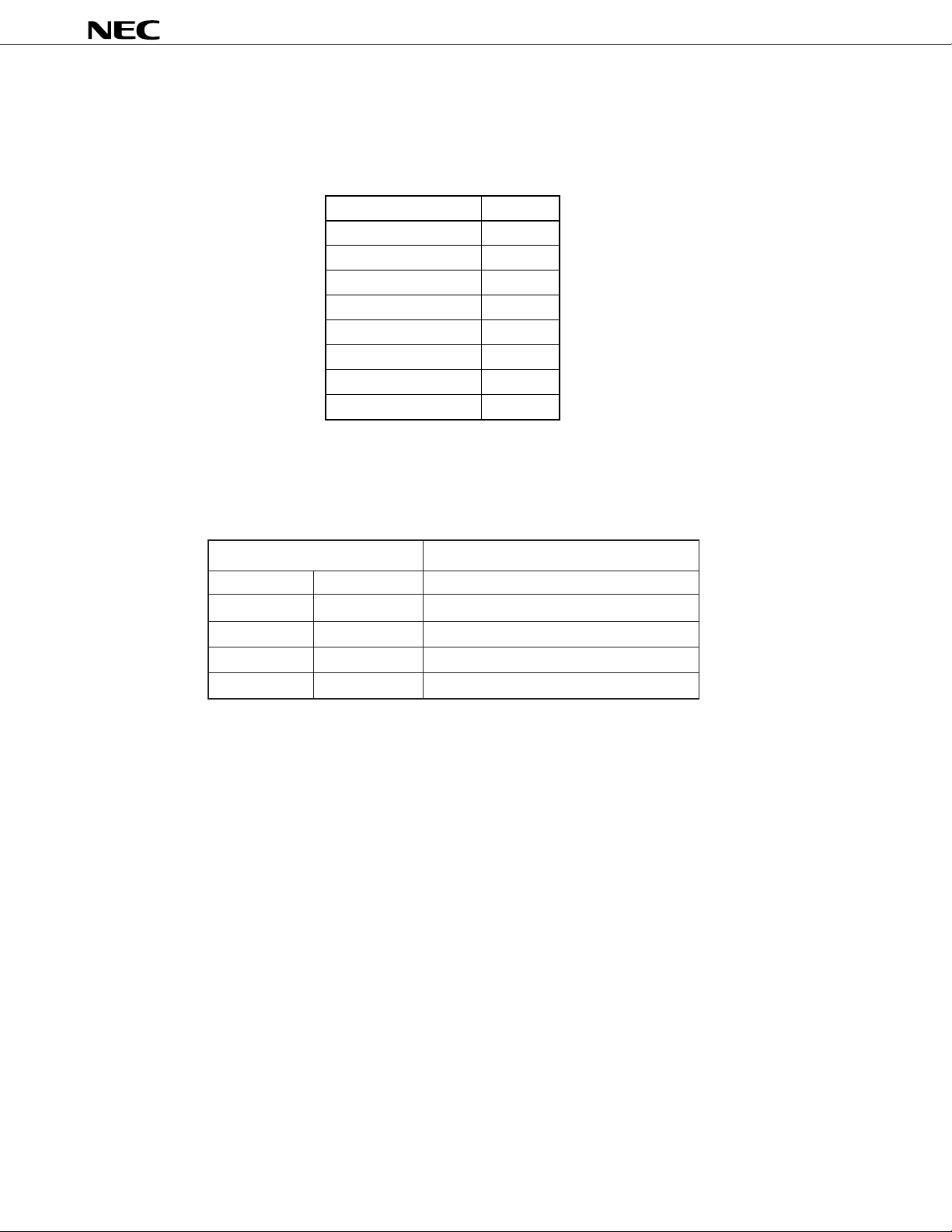
3.2 Standard versions with Ver II specs. (µPD6121-002, 6122-002)
*
In Ver II, the CCS pin does not have the external diode reading function.
The allocation of C
2, C1 and C0 of the higher 8 bits of the custom code is done by connecting the CCS pin
to any one of the KI/O0 to KI/O7 pins, as shown below.
µ
PD6121, 6122
Pin connected to CCS pin
KI/O0
KI/O1
KI/O2
KI/O3
KI/O4
KI/O5
KI/O6
KI/O7
When CCS pin is open, (C
*
The allocation of C
whether a pull-up resistor is provided.
7, C6, C5, C4 and C3 of the higher 8 bits of the custom code is as follows depending on
Pull-up Resistor C7 to C3 of Higher 8 bits of Custom Code
KI/O6 KI/O7 C7 C6 C5 C4 C3
Not Provided Not Provided 0 0 0 0 0
Not Provided Provided 1 0 0 1 1
Provided Not Provided 1 0 0 0 0
C2
C1
C0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
2 C1 C0) = (0 0 0)
Provided Provided 1 1 1 0 1
Caution In Ver II, it is not possible to set all custom codes.
Also, new custom codes cannot be ordered for Ver II products; therefore, Ver I products should
be used if new custom codes are required.
8
Page 9
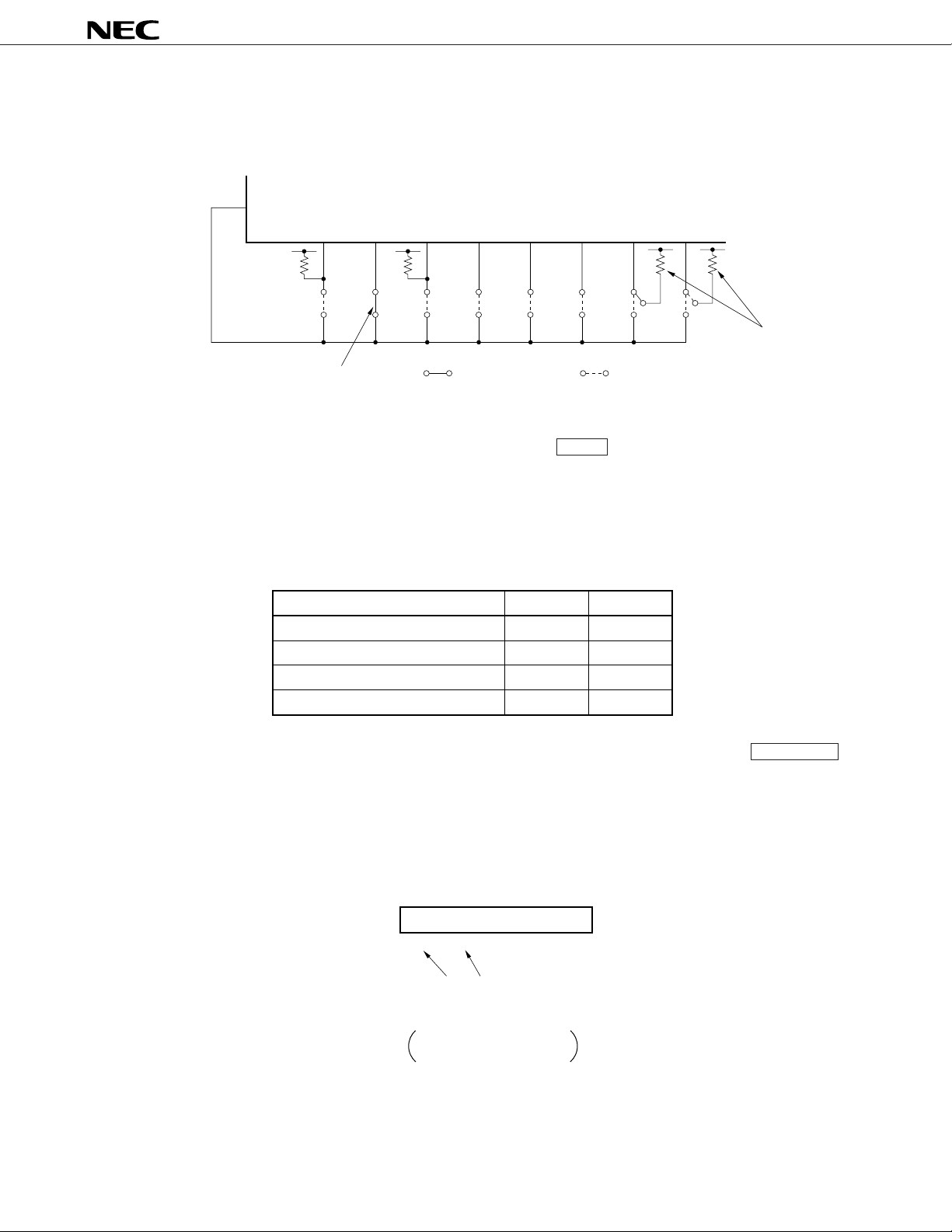
µ
PD6121, 6122
Figure 3-3. Example of Custom Code Setting for Ver II Specifications (µPD6121-002, 6122-002)
Configuration Example
CCS
0
KI/O
V
DD
KI/O1KI/O2KI/O3KI/O4KI/O5KI/O6KI/O
V
DD
7
V
V
DD
DD
ROM3 selector
Connection of any one line
2, C1 and C0 of the higher 8 bits of the custom code are fixed by connecting the CCS pin to KI/O0 to KI/
C
: Connected : Not connected
O7. Therefore, in the configuration example, they become 1 0 0 .
C
0 C1 C2
C7, C6, C5, C4 and C3 of the higher 8 bits of the custom code are selected and fixed by the pull-up resistor
connected to KI/O
6 and KI/O7 in four channels.
C
7
C
6
C
5
C
4
C
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
3
Pull-up resistor
KI/O
6
Disconnected
Disconnected
Connected
Connected
KI/O
7
Disconnected
Connected
Disconnected
Connected
In this configuration example, C3 to C7 of the higher 8 bits of the custom code become 1 1 0 1 1 .
C3 C4 C5 C6 C7
The inversion/non-inversion of the lower 8 bits of the custom code’ is fixed by the bit of the external pullup resistor of KI/O0 to KI/O5.
*
*
Caution C
External setting (Refer to Configuration Example)
Bit for non-inversion of custom code is set
6’ and C7’ are fixed to 0.
Lower 8 bits of custom code’
101000
0’C1’C2’C3’C4’C5
C
00
C
6
’
Pull-up resistor bit
0
, KI/O2)
(KI/O
0
1: Non-inversion for C
0: Inversion for C0 to C
to C
7
’
7
’
C
7
9
Page 10

µ
PD6121, 6122
As noted above, setting the pull-up resistor and connection, produces the following custom code.
Custom code
Higher 8 bits of custom code
*
C
C
0
1C2C3C4C5C6C7
Lower 8 bits of custom code’
1
10001001011001
1
0
’
C1’C2’C3’C4’C5’C6’C7’
C
C
0
1C2C3C4 C5 C6 C7
C
Remark Codes are transmitted from the LSB.
10
Page 11

µ
PD6121, 6122
4. REMOTE OUTPUT WAVEFORM (NEC TRANSMISSION FORMAT:
ONE-SHOT COMMAND TRANSMISSION MODE)
• When fOSC = 455 kHz
(1) Remote (REM) output (from stage 2 , transmission occurs only when key is kept depressed)
REM output
58.5 to 76.5 ms
108 ms 108 ms
1 2
(2) Magnification of stage 1
3
REM output
9 ms
Leader Code
4.5 ms
13.5 ms
(3) Magnification of waveform 3
REM output
(4) Magnification of waveform 2
REM output
Custom Code
8 bits
9 ms
13.5 ms
9 ms
11.25 ms
Leader Code
Custom Code’
18 ms to 36 ms
58.5 ms to 76.5 ms
2.25 ms
8 bits
4.5 ms
Data Code
8 bits
0.56 ms
1.125 ms
2.25 ms
01 100
0.56 ms
Stop Bit
Data Code
8 bits
27 ms
Stop Bit
1 bit
(5) Carrier waveform (Magnification of HIGH period of codes)
REM output
8.77 µs
26.3 µs
9 ms or 0.56 ms
Carrier frequency: fc = fosc/12 = 38 kHz
Remark If a key is kept depressed, the second and subsequent times, only the leader code and the stop
bit are transmitted, which allows power savings for the infrared-emitting diode. If a command is
issued continuously in the same way the second and subsequent times as the first time, refer to
7. ONE-SHOT/CONTINUOUS COMMAND TRANSMISSION MODE.
11
Page 12

5. KEY DATA CODES (SINGLE INPUT)
*
KEY
K1
K2
K3
K4
K5
K6
K7
K8
K9
K10
K11
K12
K13
K14
K15
K16
K17
K18
K19
K20
K21
K22
K23
K24
K25
K26
K27
K28
K29
K30
K31
K32
KEY
K33
K34
K35
K36
K37
K38
K39
K40
K41
K42
K43
K44
K45
K46
K47
K48
K49
K50
K51
K52
K53
K54
K55
K56
K57
K58
K59
K60
K61
K62
K63
K64
CONNECTION
KI0 KI1 KI2 KI3 KI/O
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
CONNECTION
KI4 KI5 KI6 KI7 KI/O
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
KI/O0
*
KI/O1
*
KI/O2
*
KI/O3
*
KI/O4
*
KI/O5
*
KI/O6
*
KI/O7
*
KI/O0
*
KI/O1
*
KI/O2
*
KI/O3
*
KI/O4
*
KI/O5
*
KI/O6
*
KI/O7
*
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7
00000000/1
10000000/1
01000000/1
11000000/1
00100000/1
10100000/1
01100000/1
11100000/1
00010000/1
10010000/1
01010000/1
11010000/1
00110000/1
10110000/1
01110000/1
11110000/1
00001000/1
10001000/1
01001000/1
11001000/1
00101000/1
10101000/1
01101000/1
11101000/1
00011000/1
10011000/1
01011000/1
11011000/1
00111000/1
10111000/1
01111000/1
11111000/1
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7
00000010/1
10000010/1
01000010/1
11000010/1
00100010/1
10100010/1
01100010/1
11100010/1
00010010/1
10010010/1
01010010/1
11010010/1
00110010/1
10110010/1
01110010/1
11110010/1
00001010/1
10001010/1
01001010/1
11001010/1
00101010/1
10101010/1
01101010/1
11101010/1
00011010/1
10011010/1
01011010/1
11011010/1
00111010/1
10111010/1
01111010/1
11111010/1
Note Bit D7 is “0” when the SEL pin is connected to V DD, and “1” when it is connected to VSS.
DATA CODE
DATA CODE
Note
µPD1913C
µPD6120C
µPD1913C
µPD6120C
µPD1913C
µPD6120C
µPD1943G
µPD1913C
µPD6120C
µPD6121G
µPD1943G
µPD1913C
µPD6120C
µPD6121G
µPD1943G
µPD1913C
µPD6120C
µPD6121G
µPD1943G
µPD1913C
µPD6120C
µPD6121G
µPD1943G
µPD1913C
µPD6120C
µPD6121G
µPD1943G
µPD1913C
µPD6120C
µPD6121G
µPD1943G
µPD1913C
µPD6120C
µPD6121G
µPD1943G
µPD1913C
µPD6120C
µPD6121G
NOTES
Unavailable
Unavailable
Unavailable
NOTES
Unavailable
Unavailable
Unavailable
Unavailable
Unavailable
Unavailable
Unavailable
Unavailable
µ
PD6121, 6122
• µPD6121
• µPD6122
• µPD6122
only
12
Page 13

µ
PD6121, 6122
6. DOUBLE-INPUT OPERATION
All keys are provided with a multiple-input prevention circuit. When two or more keys are pressed simultaneously, no signal is transmitted; but when the keys K21 and K22, K21 and K23, or K21 and K24 are pressed
together, D5 is set to “1”. However, the way keys are pressed determines the priority: If K22/K23/K24 are pressed
126 ms or longer after K21 is pressed, transmission is performed in this mode.
Double-input key operation is ideally suited for tape recording error prevention applications.
Double-Input Operation Key Codes
KEY D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7
K21 + K22 10101100/1
K21 + K23 01101100/1
K21 + K24 11101100/1
Double-Input Operation Timing
1 Double-input transmission
push
2 No operation
push
3 No operation
push
K21
K21
K21
K21 code transmission
t > 126 ms
K21 code transmission
36 ms < t < 126 ms
K22/K23/K24
–36 ms < t < 36 ms
K22/K23/K24
push
push
No transmission
5
+ K22/K23/K24 code transmission
D
K22/K23/K24
push
Transmission stop
4 No operation
K22/K23/K24
push
t > 126 ms
K22/K23/K24 code transmission
K21
push
Transmission stop
13
Page 14

µ
PD6121, 6122
7. ONE-SHOT/CONTINUOUS COMMAND TRANSMISSION MODE
7.1 One-shot Command Transmission Mode
In order to reduce the average transmission current, the µPD6120C, 6121G, and 6122G transmit data only
once, and thereafter transmit just the leader code and stop bit indicating that a key is depressed. As a result,
this transmission method (one-shot command transmission mode) has the following characteristics.
Advantages
• Average transmission current is reduced to 1/3 to 1/4 compared with continuous command transmission mode
• Reduced software load for reception program (not all commands are processed all the time)
• This mode distinguishes when a key is pressed several times successively and when a key is kept depressed.
Disadvantages
• If a command is not read the first time, it cannot be read a second time
• If a signal transmission is interrupted while continuous commands are executed, subsequent commands cannot
be executed.
Moreover, when f
3 % of the peak current.
IAVE = (9 ms + 0.56 ms)/108 ms x 1/3 (duty) = 2.95 % (first command is ignored)
OSC = 455 kHz, the average current to the infrared-emitting diode is roughly equivalent to
7.2 Continuous Command Transmission Mode
A continuous command transmission mode for transmitting data a second or more times is also available.
As shown in Figure 7-2, it is possible to continuously transmit commands for all the keys or for individual key
output lines simply by adding a diode D and connecting it to KI
In this case, the average transmission current is larger than that in the one-shot command transmission mode.
OSC = 455 kHz, the average current to the infrared-emitting diode is roughly equivalent to 9 % of the
When f
peak current.
IAVE = (9 ms + 0.56 ms x 33)/108 ms x 1/3 (duty) = 8.48 %
Cautions 1. If the double input key (K21-K24) is used in the continuous command transmission mode,
double-input key transmission is not performed (D
2. When the voltage drop of the REM output is large, the signal is not transmitted accurately.
Therefore, keep the REM output current within 1 mA.
Figure 7-1 shows the continuous command transmission mode.
0 or KI/O.
5 does not become 1).
14
Page 15

Figure 7-1. Continuous Command Transmission Mode (When fOSC = 455 kHz)
µPD6120C, 6121G, 6122G
(1)
REM output
µ
PD6121, 6122
58.5 to 76.5 ms
LMP output
(2) µPD1913C, 1943G, 6102G
1 to K20, K33 to K52 (KO0 to KO4)
1 K
REM output
67.5 ms 38 ms
105.5 ms
LMP output
2 K21 to K32, K53 to K64 (KO5 to KO7)
108 ms
Note
31.5 to 49.5 ms
Average transmission
current ratio
TYP
= 8.48 % x I
I
Average transmission
current ratio
TYP
= 8.68 % x I
I
peak
(LED)
peak
(LED)
REM output
Note
20 ms
Average transmission
current ratio
TYP
= 10.47 % x I
I
peak
(LED)
67.5 ms
87.5 ms
LMP output
Note In the case of the µPD1913C, 1943G and 6102G, the transmission repeat cycle (T) varies depending
on the key.
Remark I
TYP = IAVE x Ipeak (LED)
IAVE = (9 ms + 0.56 ms x 33)/T ms x 1/3 (duty)
15
Page 16

Figure 7-2. Application Circuit for Continuous Command Transmission Mode
1 Continuous command transmission for all keys
REM output is input to KI0 with diode D.
Ceramic resonator
455 kHz
220 pF
OSCO OSCI V
CCS
KI3KI1KI/O0KI/O1KI/O2KI/O3KI/O4KI/O5KI/O6KI/O
KI
2KI0
220 pF
DD
µPD6121G-001
µPD6121G-002
DD
V
V
100 Ω
DD
Transmission
display
LMP
Note 1
47 µF
REM
V
SS
7
Diode D
Key matrix
+
82 Ω
2.2 kΩ
12 kΩ
Custom code selection resistor
µ
PD6121, 6122
Custom code selection diode
2 Continuous command transmission for key output lines
REM output is input to KI/O with diode D.
Ceramic resonator
455 kHz
220 pF
OSCO OSCI V
CCS
KI3KI1KI/O0KI/O1KI/O2KI/O3KI/O4KI/O5KI/O6KI/O
220 pF
µPD6121G-001
µPD6121G-002
KI
2KI0
DD
V
Custom code selection diode
100 Ω
DD
V
DD
Transmission
display
LMP
47 µF
REM
V
Diode D
+
82 Ω
2.2 kΩ
SS
12 kΩ
7
Custom code selection resistor
Continuous command transmission can be performed for keys whose KI/O output lines have received diode
D input
Note 2
.
Notes 1. Double-key transmission cannot be performed.
*
2. If the KI/O5 output line (double-input key) is in the continuous command transmission mode,
double-input key transmission is not performed (D
5 does not become 1).
Caution When the voltage drop of the REM output is large, the signal is not transmitted accurately.
Therefore, keep the REM output current within 1 mA.
16
Page 17

8. APPLICATION CIRCUIT EXAMPLE
(1) Example application circuit using µPD6121
µ
PD6121, 6122
Ceramic resonator
455 kHz
OSCO OSCI V
SEL
CCS
0
KI
KI
3
KI/O
+
DD
µPD6121G-001
0
V
DD
V
3V
DD
(2) Example application circuit using µPD6122
Ceramic resonator
455 kHz
+
3V
LMP
REM
V
KI/O
Infrared-emitting diode
SE303A-C
SE307-C
SE313
SE1003-C
2SC2001, 3616
2SD1513, 1616
2SD1614
SS
7
Custom code selection resistor
Key matrix
8 x 4 = 32 keys
Custom code selection diode
=
OSCO OSCI V
SEL
CCS
0
KI
KI
7
DD
µPD6122G-001
KI/O
0
V
DD
V
LMP
DD
REM
V
KI/O
Infrared-emitting diode
SE303A-C
SE307-C
SE313
SE1003-C
2SC2001, 3616
2SD1513, 1616
2SD1614
SS
7
Custom code selection resistor
Key matrix
8 x 8 = 64 keys
Custom code selection diode
17
Page 18

(3) Application circuit example, receive side
*
Microcomputer
µ
PD6121, 6122
Preamplifier
(amplification, waveform shaping)
IN OUT INT
PIN photo diode
PH302C
PH310
PH320
µPC2800A, 2801A
µPC2803
µPC2804
Shield case
Note The µPC2801A’s active level is high.
Note
Key input
Display
Control
Communications
17K series
75X series
75XL series
78K series
18
Page 19

9. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Absolute Maximum Ratings (TA = 25 °C)
Parameter Symbol Ratings Unit
Supply voltage VDD –0.3 to +6.0 V
Input voltage VI –0.3 to VDD + 0.3 V
Power dissipation PD 250 mW
Operating ambient temperature TA –20 to +75 ˚C
Storage temperature Tstg –40 to +125 ˚C
Recommended Operating Conditions (TA = –20 to +75 °C)
Parameter Symbol MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Supply voltage VDD 2.0 3.0 3.3 V
Oscillation frequency fOSC 400 455 500 kHz
Input voltage VI 0VDD V
Custom code select pull-up resistor RUP 160 200 240 kΩ
µ
PD6121, 6122
DC Characteristics (TA = 25 °C, VDD = 3.0 V)
Parameter Symbol Condition MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Supply current 1 IDD1 fOSC = 455 kHz 0.1 1 mA
Supply current 2 IDD2 fOSC = STOP 1 µA
REM output current High IOH1 VO = 1.5 V –5 –8 mA
REM output current Low IOL1 VO = 0.3 V 15 30 µA
LMP output current High IOH2 VO = 2.7 V –15 –30 µA
LMP output current Low IOL2 VO = 0.3 V 1 1.5 mA
KI input current High I IH1 VI = 3.0 V 10 30 µA
KI input current Low IIL1 VI = 0 V –0.2 µA
KI, SEL input voltage High VIH1 2.1 3.0 V
KI, SEL input voltage Low VIL1 0 0.9 V
KI/O input voltage High VIH2 1.3 V
KI/O input voltage Low VIL2 0.4 V
KI/O input current High IIH2 VI = 3.0 V 2 7 µA
KI/O input current Low IIL2 VI = 0 V –0.2 µA
KI/O output current High IOH3 VO = 2.5 V –1.0 –2.5 mA
KI/O output current Low IOL3 VO = 1.7 V 35 100 µA
CCS input voltage High VIH3 1.1 V
CCS input current High IIH3 Pull-up, VI = 3.0 V 0.2 µA
CCS input current Low IIL3 Pull-up, VI = 0 V –3 –8 µA
CCS input current High IIH4 Pull-down, VI = 3.0 V 10 30 µA
CCS input current Low IIL4 Pull-down, VI = 0 V –0.2 µA
19
Page 20

Recommended Ceramic Resonators (TA = –20 to +75 °C, VDD = 2.0 to 3.3 V)
• µPD6121, 6122
µ
PD6121, 6122
Maker Product
Murata Seisakusho Corp. CSB455E 220 220 2.0 3.3
CSB480E 220 220 2.0 3.3
Toko Corp. CRK455 120 300 2.0 3.3
Kyocera Corp. KBR-455BTLR 220 220 2.0 3.3
Recommended constant [pF] Operating voltage [V]
C1 C2 MIN. MAX.
Example of external circuit
OSCI OSCO
C2C1
V
DD
Caution If using an oscillation circuit, wire the area enclosed in the dotted line in the figure in the manner
indicated below in order to avoid negative effects such as from stray capacitance of wires.
• Keep wiring as short as possible.
• Do not cross other signal lines. Do not design wiring close to lines with large fluctuating
current.
• Make sure that the connection point of the oscillation circuit’s capacitor has the same
potential as V
DD.
• Do not extract signals from the oscillation circuit.
20
Page 21

µ
PD6121, 6122
10. PACKAGE DRAWINGS
(1) Package for the µPD6121
20 PIN PLASTIC SOP (375 mil)
110
A
*
1120
detail of lead end
P
H
G
F
E
B
C
M
D
NOTE
Each lead centerline is located within 0.12 mm (0.005 inch) of
its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition.
M
I
J
K
L
N
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A
13.00 MAX.
B
0.78 MAX.
C
1.27 (T.P.)
D 0.40 0.016
E
F
G
H
I
J
K 0.15
L 0.8±0.2 0.031
M
N
P3° 3°
+0.10
–0.05
0.125±0.075
2.9 MAX.
2.50
10.3±0.3
7.2
1.6
+0.10
–0.05
0.12
0.15
+7°
–3°
0.512 MAX.
0.031 MAX.
0.050 (T.P.)
+0.004
–0.003
0.005±0.003
0.115 MAX.
0.098
+0.012
0.406
–0.013
0.283
0.063
+0.004
0.006
–0.002
+0.009
–0.008
0.005
0.006
+7°
–3°
P20GM-50-375B-4
21
Page 22

(2) Package for the µPD6122
*
24 PIN PLASTIC SOP (375 mil)
24 13
112
G
µ
PD6121, 6122
detail of lead end
P
A
H
I
J
F
E
C
DM
NOTE
Each lead centerline is located within 0.12 mm (0.005 inch) of
its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition.
M
K
B
L
N
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
15.54 MAX.
A
0.78 MAX.
B
1.27 (T.P.)
C
D 0.40 0.016
E
F
G
H
I
J
K 0.15
L 0.8±0.2 0.031
M
N
P3° 3°
+0.10
–0.05
0.1±0.1
2.9 MAX.
2.50
10.3±0.3
7.2
1.6
+0.10
–0.05
0.12
0.15
+7°
–3°
0.612 MAX.
0.031 MAX.
0.050 (T.P.)
+0.004
–0.003
0.004±0.004
0.115 MAX.
0.098
+0.012
0.406
–0.013
0.283
0.063
+0.004
0.006
–0.002
+0.009
–0.008
0.005
0.006
+7°
–3°
P24GM-50-375B-3
22
Page 23

µ
PD6121, 6122
11. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS
The following conditions (see table below) must be met when soldering this product.
For more details, refer to the NEC document SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE MOUNTING TECHNOLOGY
MANUAL (IEI-1207).
Please consult an NEC sales representative in case an other soldering process is used, or in case soldering
is done under different conditions.
Table 11-1. Soldering Conditions for Surface Mounting
µPD6121G-001: 20-pin plastic SOP (375 mil)
µPD6121G-002: 20-pin plastic SOP (375 mil)
µPD6122G-001: 24-pin plastic SOP (375 mil)
µPD6122G-002: 24-pin plastic SOP (375 mil)
Soldering Process Soldering Conditions Symbol
Infrared ray reflow Peak temperature of package surface: 230 °C, IR30-00-1
Reflow time: 30 seconds or less (210 °C or higher),
Number of reflow processes: 1
VPS Peak temperature of package surface: 215 °C, VP15-00-1
Reflow time: 40 seconds or less (200 °C or higher),
Number of reflow processes: 1
Wave soldering Solder temperature: 260 °C or lower, WS60-00-1
Reflow time: 10 seconds or less, Number of reflow processes: 1
Preheat temperature: 120 °C or lower (at package surface)
Partial heating Pin temperature: 300 °C or lower, —
Time: 3 seconds or less (per device side)
Caution Do not apply more than one soldering method at any one time, except for the partial heating
method.
*
23
Page 24

APPENDIX. REMOTE CONTROL TRANSMISSION IC AND MICROCONTROLLER LIST
*
• Single-function remote control transmission ICs (NEC transmission format)
µ
PD6121, 6122
Part number
Parameter
Operating voltage VDD = 2.0 to 3.3 V
Operating clock fOSC = 400 to 500 kHz ceramic resonator
Transmission format Leader 16-bit custom code 8-bit data code 8-bit data code
Modulation method PPM 0 ····· 1 ·····
Custom code 16-bit setting
Data code 32 x 2 64 x 2
No. of keys 32 64
Package 20-pin SOP (375 mil) 24-pin SOP (375 mil)
Cautions 1. New custom codes are not available for the following standard products.
µPD6121 µPD6122
38-kHz carrier modulation (fosc = 455 kHz)
µPD6121G, 6122G Ver II standard products (-002)
2. If products other than listed in Caution 1 are used, please contact NEC for custom codes.
24
Page 25

µ
PD6121, 6122
• Single-Function 4-bit Single-Chip Microcontroller
Part number µPD6133 µPD6134 µPD6604
Parameter
ROM capacity 512 x 10 bits 1002 x 10 bits
RAM capacity 32 x 4 bits
Oscillator Ceramic oscillator RC oscillator
S0 (S-IN) Read with P01 register (left shift instruction excluded, standby cancellation
function provided)
S1/LED (S-OUT) I/O (standby cancellation function provided)
Key matrix (without Di) 8 x 6 = 48 keys
Timer clock fX/8, fX/16
Stack Also usable for RAM RF (1 level)
Carrier frequency fX, fX/8, fX/12, high level
fX/2, fX/16, fX/24 (software specified)
Instruction execution time 8 µs (fX = 1 MHz)
Operating frequency fX = 300 kHz to 1 MHz
Power supply voltage VDD = 1.8 to 3.6 V
*
Note 1
Operating ambient temperature TA = –40 to +85 °C
Charge/discharge function (NOP) Not provided (NOP instruction provided)
Low voltage detector Low level is output to RESET pin at detection
Package • 20-pin plastic SOP • 20-pin plastic SOP • 20-pin plastic SOP
• 20-pin plastic shrink DIP •
PROM version µPD61F35 (flash EEPROMTM)
Note 2
20-pin plastic shrink SOP
Notes 1. Under development
2. This product’s pin configuration is the same as that of the 20-pin µPD6133, 6134, and 6604, but the package
is a 24-pin SOP shrink DIP package.
Caution If using the NEC transmission format, please contact NEC for the custom code.
25
Page 26

• 4-Bit Single-Chip Microcontroller for Programmable Remote Control Transmission
*
Part number µPD6600 µPD6600A µPD6124 µPD6124A µPD6125A
Parameter
ROM capacity 512 x 10 bits 1002 x 10 bits
RAM capacity 32 x 5 bits
Oscillator Ceramic oscillator
S0 (S-IN) Read with left shift instruction
S1/LED (S-OUT) Output
µ
PD6121, 6122
Key matrix (without Di) 8 x 4 = 32 keys
Timer clock fX/8
Stack Also usable for RAM (3 levels)
Carrier frequency fX/8, fX/12 (mask option)
Instruction execution time 16 µs (fX = 500 kHz)
Operating frequency fX = 400 kHz to 500 kHz
Power supply voltage
Operating ambient temperature TA = –20 to +75 °C
Charge/discharge function (NOP) Provided
Low voltage detector Not provided Low level is Not provided Low level is Not provided
Package • 20-pin plastic SOP
PROM version µPD61P24 (one-time PROM) —
VDD = 2.0 to 3.6 V VDD = 2.2 to 3.6 V VDD = 2.0 to 6.0 V VDD = 2.2 to 5.5 V
output to ouput to
S-OUT pin S-OUT pin
at detection at detection
• 20-pin plastic shrink DIP
8 x 8 = 64 keys
VDD = 2.0 to 6.0 V
• 24-pin plastic
SOP
• 24-pin plastic
shrink DIP
Caution If using the NEC transmission format, please contact NEC for the custom code.
26
Page 27

µ
PD6121, 6122
NOTES FOR CMOS DEVICES
1 PRECAUTION AGAINST ESD FOR SEMICONDUCTORS
Note: Strong electric field, when exposed to a MOS device, can cause destruction
of the gate oxide and ultimately degrade the device operation. Steps must
be taken to stop generation of static electricity as much as possible, and
quickly dissipate it once, when it has occurred. Environmental control must
be adequate. When it is dry, humidifier should be used. It is recommended
to avoid using insulators that easily build static electricity. Semiconductor
devices must be stored and transported in an anti-static container, static
shielding bag or conductive material. All test and measurement tools
including work bench and floor should be grounded. The operator should
be grounded using wrist strap. Semiconductor devices must not be touched
with bare hands. Similar precautions need to be taken for PW boards with
semiconductor devices on it.
2 HANDLING OF UNUSED INPUT PINS FOR CMOS
Note: No connection for CMOS device inputs can be cause of malfunction. If no
connection is provided to the input pins, it is possible that an internal input
level may be generated due to noise, etc., hence causing malfunction. CMOS
devices behave differently than Bipolar or NMOS devices. Input levels of
CMOS devices must be fixed high or low by using a pull-up or pull-down
circuitry. Each unused pin should be connected to VDD or GND with a
resistor, if it is considered to have a possibility of being an output pin. All
handling related to the unused pins must be judged device by device and
related specifications governing the devices.
3 STATUS BEFORE INITIALIZATION OF MOS DEVICES
Note: Power-on does not necessarily define initial status of MOS device. Produc-
tion process of MOS does not define the initial operation status of the
device. Immediately after the power source is turned ON, the devices with
reset function have not yet been initialized. Hence, power-on does not
guarantee out-pin levels, I/O settings or contents of registers. Device is not
initialized until the reset signal is received. Reset operation must be
executed immediately after power-on for devices having reset function.
27
Page 28

µ
PD6121, 6122
The application circuits and their parameters are for references only and are not intended for use in actual
design-in's.
No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without the prior written
consent of NEC Corporation. NEC Corporation assumes no responsibility for any errors which may appear in this
document.
NEC Corporation does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights or other intellectual
property rights of third parties by or arising from use of a device described herein or any other liability arising
from use of such device. No license, either express, implied or otherwise, is granted under any patents,
copyrights or other intellectual property rights of NEC Corporation or others.
While NEC Corporation has been making continuous effort to enhance the reliability of its semiconductor devices,
the possibility of defects cannot be eliminated entirely. To minimize risks of damage or injury to persons or
property arising from a defect in an NEC semiconductor device, customer must incorporate sufficient safety
measures in its design, such as redundancy, fire-containment, and anti-failure features.
NEC devices are classified into the following three quality grades:
“Standard“, “Special“, and “Specific“. The Specific quality grade applies only to devices developed based on
a customer designated “quality assurance program“ for a specific application. The recommended applications
of a device depend on its quality grade, as indicated below. Customers must check the quality grade of each
device before using it in a particular application.
Standard: Computers, office equipment, communications equipment, test and measurement equipment,
audio and visual equipment, home electronic appliances, machine tools, personal electronic
equipment and industrial robots
Special: Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.), traffic control systems, anti-disaster
systems, anti-crime systems, safety equipment and medical equipment (not specifically designed
for life support)
Specific: Aircrafts, aerospace equipment, submersible repeaters, nuclear reactor control systems, life
support systems or medical equipment for life support, etc.
The quality grade of NEC devices in “Standard“ unless otherwise specified in NEC's Data Sheets or Data Books.
If customers intend to use NEC devices for applications other than those specified for Standard quality grade,
they should contact NEC Sales Representative in advance.
Anti-radioactive design is not implemented in this product.
28
M4 94.11
 Loading...
Loading...