Page 1

NEC Storage Manager
Data Replication User’s Manual
(Function Guide)
IS015-9E
Page 2

© NEC Corporation 2001-2004
No part of the contents of this book may be reproduced or
transmitted in any form without permission of NEC Corporation.
The contents of this book may be modified without notice in the future.
Page 3

Preface
This manual describes how to use the data replication function provided by NEC Storage DynamicDataReplication
Ver2, NEC Storage RemoteDataReplication Ver2, and NEC Storage ReplicationControl.
The data replication function consists of the replication volume creation function provided in a disk array and
software to manage and operate it. It utilizes replication volume to make business operation more effective.
Refer to the “NEC Storage Manager Manual Guide” (IS901) for the overview of NEC Storage and the related
manuals. Refer to the “NEC Storage Manager Data Replication User’s Manual (Disaster Recovery System
Installation and Operation Guide)” (IS027) for the usage of the remote data replication functions provided by NEC
Storage RemoteDataReplication/DisasterRecovery and NEC Storage ReplicationControl/DisasterRecovery.
Remarks 1. This manual explains functions implemented by the following program products:
• NEC Storage Manager and NEC Storage BaseProduct
• NEC Storage DynamicDataReplication
• NEC Storage ReplicationControl
• NEC Storage RemoteDataReplication
2. This manual is applicable to the program products of the following versions:
• NEC Storage Manager Ver3.3
• NEC Storage BaseProduct Ver3.3
• NEC Storage ReplicationControl Ver3.3
3. The NEC Storage Manager is referred to as iSM or Storage Manager in the text of this manual.
Also, the NEC Storage series disk array subsystem is referred to as a disk array.
4. The following descriptions in the text of this manual refer to the corresponding products.
Storage Manager NEC Storage Manager
AccessControl NEC Storage AccessControl
DynamicDataReplication NEC Storage DynamicDataReplication
RemoteDataReplication NEC Storage RemoteDataReplication
RemoteDataReplication/DisasterRecovery NEC Storage RemoteDataReplication/DisasterRecovery
ReplicationControl NEC Storage ReplicationControl
SnapControl NEC Storage SnapControl
Description Corresponding Product
5. The following descriptions in the text of this manual refer to the corresponding manuals.
Description Corresponding Manual
User's Manual (UNIX) NEC Storage Manager User's Manual (UNIX) (IS001)
User's Manual NEC Storage Manager User's Manual (IS004)
Configuration Setting Tool User’s
Manual (GUI)
Data Replication User’s Manual
(Installation and Operation Guide for
Windows)
Data Replication Command Reference
NEC Storage Manager Configuration Setting Tool User’s
Manual (GUI) (IS007)
NEC Storage Manager Data Replication User’s Manual
(Installation and Operation Guide for Windows) (IS016)
NEC Storage Manager Data Replication Command
Reference (IS021)
Page 4
Description Corresponding Product
Data Replication User’s Manual (Disaster
Recovery System Installation and
Operation Guide)
Snapshot User’s Manual (Function
Guide)
6. Trademarks and registered trademarks
• Microsoft® and Windows® are trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and other countries.
• HP-UX is a registered trademark of Hewlett-Packard Co. in the United States.
• UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States and other countries.
• VERITAS, VxVM, VxFS, NetBackup, VERITAS Volume Manager, VERITAS File System, and
VERITAS NetBackup are trademarks or registered trademarks of VERITAS Software Corporation in
the United States and other countries.
• Legato NetWorker is a registered trademark of Legato Systems, Inc. in the United States.
• Sun is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
• Solaris is a trademark or a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States and
other countries.
• Linux is a trademark or registered trademark of Mr. Linus Torvalds in the United States and other
countries.
• AIX is a trademark of IBM Corporation.
Other product names and company names, etc. are trademarks or registered trademarks of the
associated companies.
7. In this document, matters to which careful attention needs to be paid will be described as follows:
Be sure to observe the contents.
If the indications are ignored and the system is improperly operated, settings which have been already
made might be affected.
NEC Storage Manager Data Replication User’s Manual
(Disaster Recovery System Installation and Operation
Guide) (IS027)
NEC Storage Manager Snapshot User’s Manual (Function
Guide) (IS030)
Type of Indication
Type Description
Describes contents which require special attention during operation.
The First Edition in March 2003
The Ninth Edition in November 2004
Page 5

Contents
Chapter 1 Data Replication Overview............................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Data Replication ..........................................................................................................................................................1
1.2 Examples of Applying Data Replication.....................................................................................................................2
1.2.1 Backup .................................................................................................................................................................2
1.2.2 Test Environment Setting ....................................................................................................................................4
1.2.3 Parallel Processing of Search Operation .............................................................................................................5
1.3 System Configuration .................................................................................................................................................. 6
Chapter 2 Data Replication ................................................................................................................................................8
2.1 Volume Classification .................................................................................................................................................8
2.2 Replication Operations ..............................................................................................................................................10
2.2.1 Replicate ............................................................................................................................................................ 10
2.2.2 Separate .............................................................................................................................................................10
2.2.3 Restore...............................................................................................................................................................11
2.3 Replication Operations and State Transitions ...........................................................................................................12
2.3.1 Replicate and State Transitions .........................................................................................................................13
2.3.2 Separate and State Transitions ..........................................................................................................................14
2.3.3 Restore and State Transitions ............................................................................................................................15
2.3.4 Activity State and Synchronous State ...............................................................................................................16
2.4 Copy Control State ....................................................................................................................................................17
2.5 Relationship between Copy Performance and Copy Control State...........................................................................19
2.6 RV Access Restriction...............................................................................................................................................20
2.7 Copy Faults and State Transitions............................................................................................................................. 21
2.8 Freeze of Disk Arrays................................................................................................................................................ 22
Chapter 3 Replication Management ................................................................................................................................ 23
3.1 Replication Management Overview .......................................................................................................................... 23
3.1.1 Operations and Authorization Levels ................................................................................................................23
3.1.2 Event Detection and Operation Message Output ..............................................................................................24
3.1.3 Notes on Operation............................................................................................................................................26
3.2 Explanation of Replication Screen ............................................................................................................................ 27
3.2.1 Replication Screen.............................................................................................................................................27
3.2.2 Configuration Display Area ..............................................................................................................................28
3.2.3 Replication Information Screen.........................................................................................................................30
3.2.4 Disk Array LINK Information Screen...............................................................................................................36
3.2.5 Menu Item List ..................................................................................................................................................39
3.2.6 Information Displayed on Execution Dialog.....................................................................................................41
3.3 Various Operations of Replication Management ......................................................................................................43
i
Page 6

3.3.1 Pair Setting/Unpair ............................................................................................................................................43
3.3.2 Replicate ............................................................................................................................................................ 50
3.3.3 Separate .............................................................................................................................................................54
3.3.4 Restore...............................................................................................................................................................58
3.3.5 Suspend/Resume Copy ......................................................................................................................................63
3.3.6 Change to Background Copy.............................................................................................................................68
3.3.7 RV Mode Change .............................................................................................................................................. 71
3.3.8 Forced Separate .................................................................................................................................................74
3.3.9 Forced Unpair....................................................................................................................................................78
3.3.10 Freeze/Defreeze .................................................................................................................................................82
3.3.11 Background Copy Level Change.......................................................................................................................83
3.3.12 Connection Screen.............................................................................................................................................85
3.3.13 CSV Output of Information List Display ..........................................................................................................91
3.3.14 Save Pair Setting Information ...........................................................................................................................93
3.3.15 Environment Setting ..........................................................................................................................................95
3.3.16 Refresh............................................................................................................................................................... 95
3.3.17 Record Screen Information................................................................................................................................96
3.3.18 Display Disk Array Properties...........................................................................................................................97
3.3.19 Display Link Properties ..................................................................................................................................... 98
3.3.20 Display Copy Fault List................................................................................................................................... 101
Chapter 4 Functions of ReplicationControl..................................................................................................................103
4.1 Command List .........................................................................................................................................................104
4.2 Operation Types ......................................................................................................................................................105
4.2.1 Direct Operation for a Disk Array...................................................................................................................106
4.2.2 Operations Linked with iSM ...........................................................................................................................109
4.3 Volume Types .........................................................................................................................................................111
4.4 Replication Operation File ......................................................................................................................................112
4.5 Volume List Creation/Display.................................................................................................................................113
4.5.1 Command Operations (Windows) ................................................................................................................... 113
4.5.2 Command Operations (UNIX) ........................................................................................................................119
4.5.3 GUI Operations (Windows) ............................................................................................................................124
4.6 Replication Operations ............................................................................................................................................140
4.6.1 Replicate Command ........................................................................................................................................140
4.6.2 Separate Command..........................................................................................................................................146
4.6.3 Restore Command ...........................................................................................................................................151
4.6.4 Copy Control State Change Command ...........................................................................................................157
4.6.5 Wait Command................................................................................................................................................161
4.6.6 Replication State Display Command............................................................................................................... 165
4.6.7 Specific Volume Name Display Command.....................................................................................................169
4.7 Pair Setting and Unpair Operations......................................................................................................................... 172
ii
Page 7

4.7.1 Logical Disk Information Display Command .................................................................................................172
4.7.2 Pair/Unpair Command.....................................................................................................................................175
4.8 Disk Array Operations.............................................................................................................................................178
4.8.1 Command for Displaying Information on the Replication Function...............................................................178
4.9 Disk Operations .......................................................................................................................................................181
4.9.1 File System Flush Command...........................................................................................................................181
4.9.2 Volume Mount Command ...............................................................................................................................183
4.9.3 Volume Unmount Command...........................................................................................................................185
4.9.4 Disk Signature Operation Command............................................................................................................... 187
4.9.5 Devices Scan Command..................................................................................................................................189
Index .........................................................................................................................................................................190
iii
Page 8

This page is intentionally left blank.
iv
Page 9
Chapter 1 Data Replication Overview
Chapter 1 Data Replication Overview
To manage an enormous amount of information accumulated in business in a unified way and promote effective
and efficient utilization of the information, a high-throughput, large-capacity, and high-reliability storage system is
required. Data Replication provides functions to build and manage such a storage system.
This chapter describes overview of Data Replication, hardware configuration, and software configuration.
1
.
1
D
a
t
a
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
1
.
1
D
a
t
a
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
1
.
1
D
a
t
a
R
e
p
l
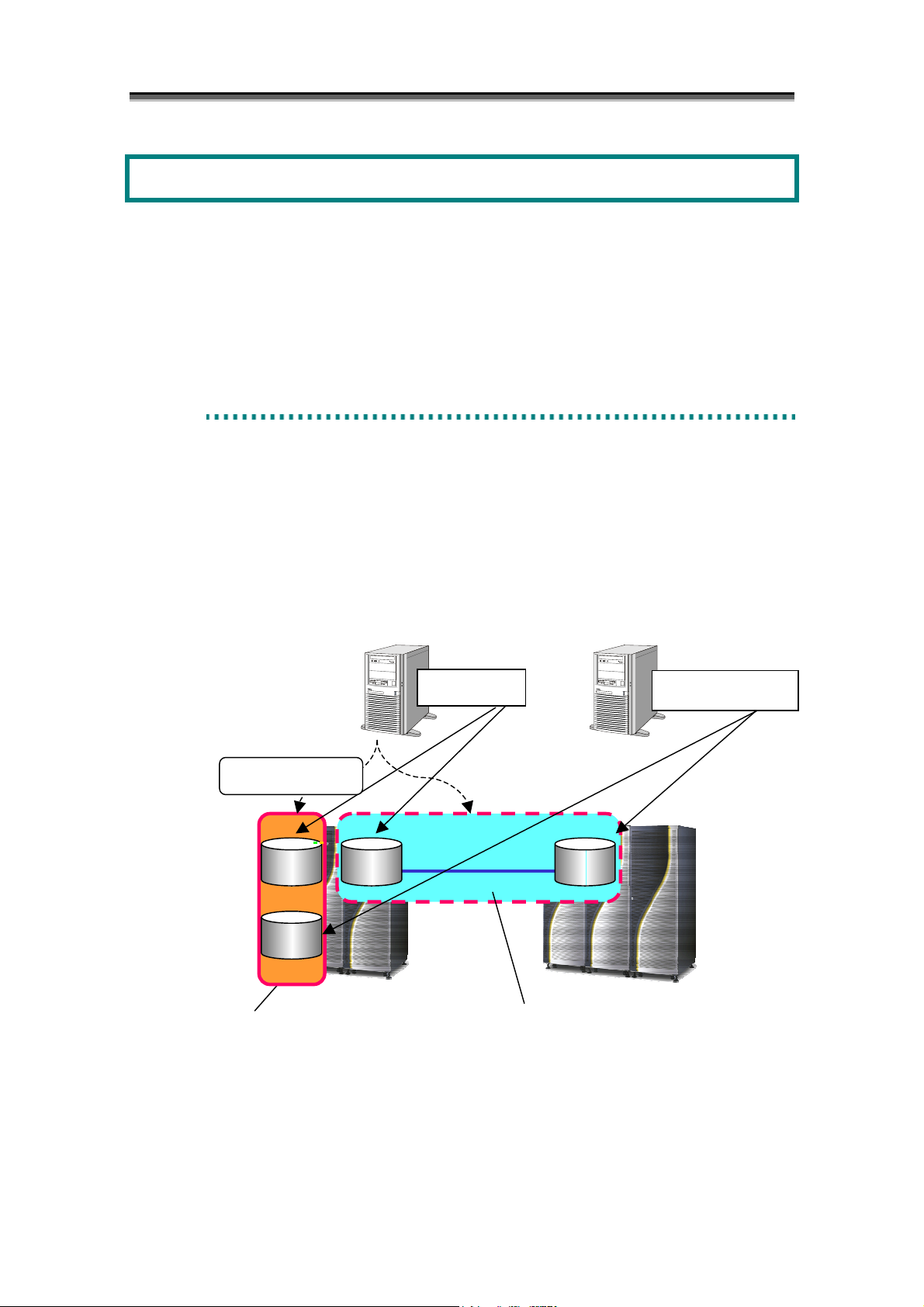
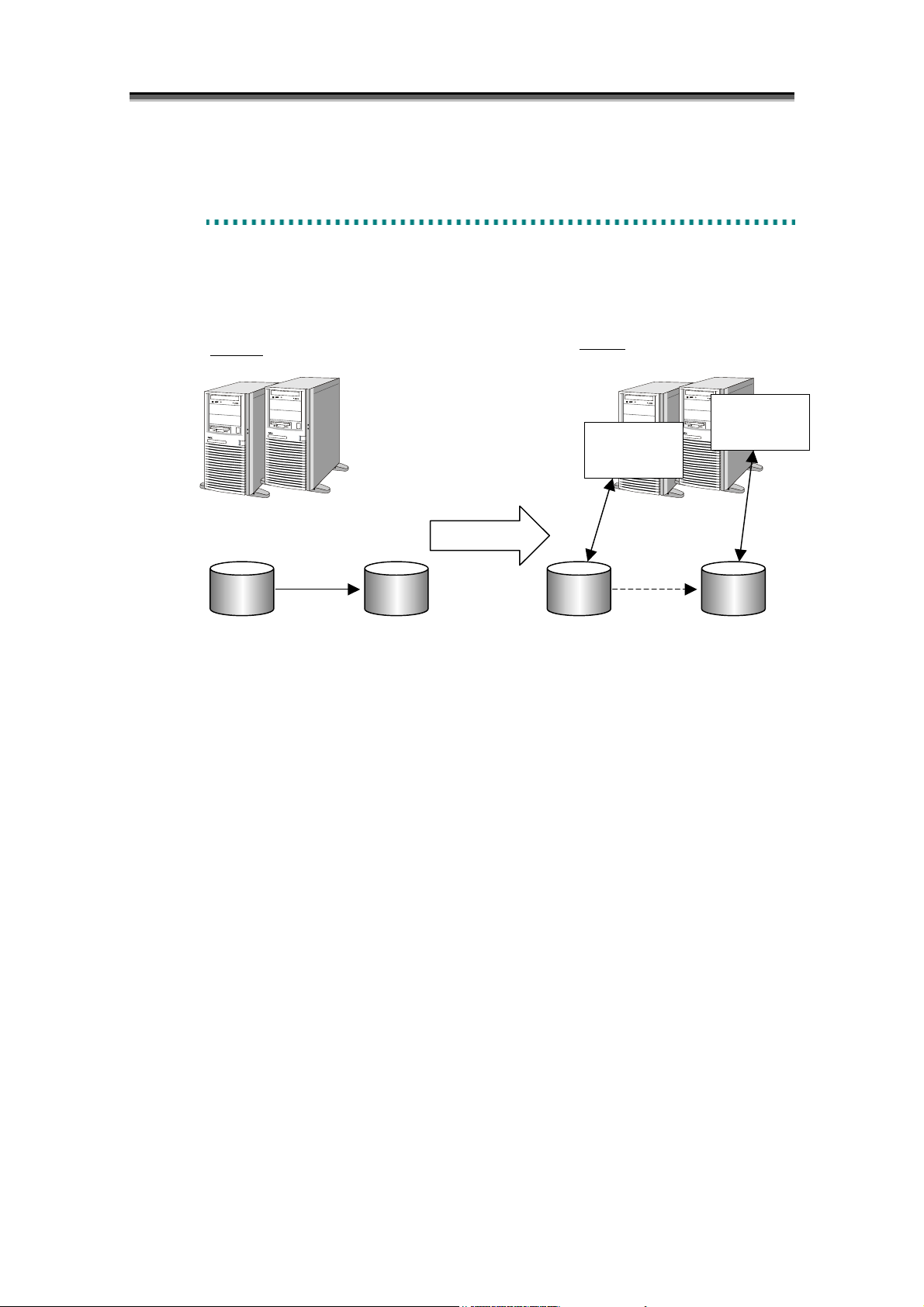
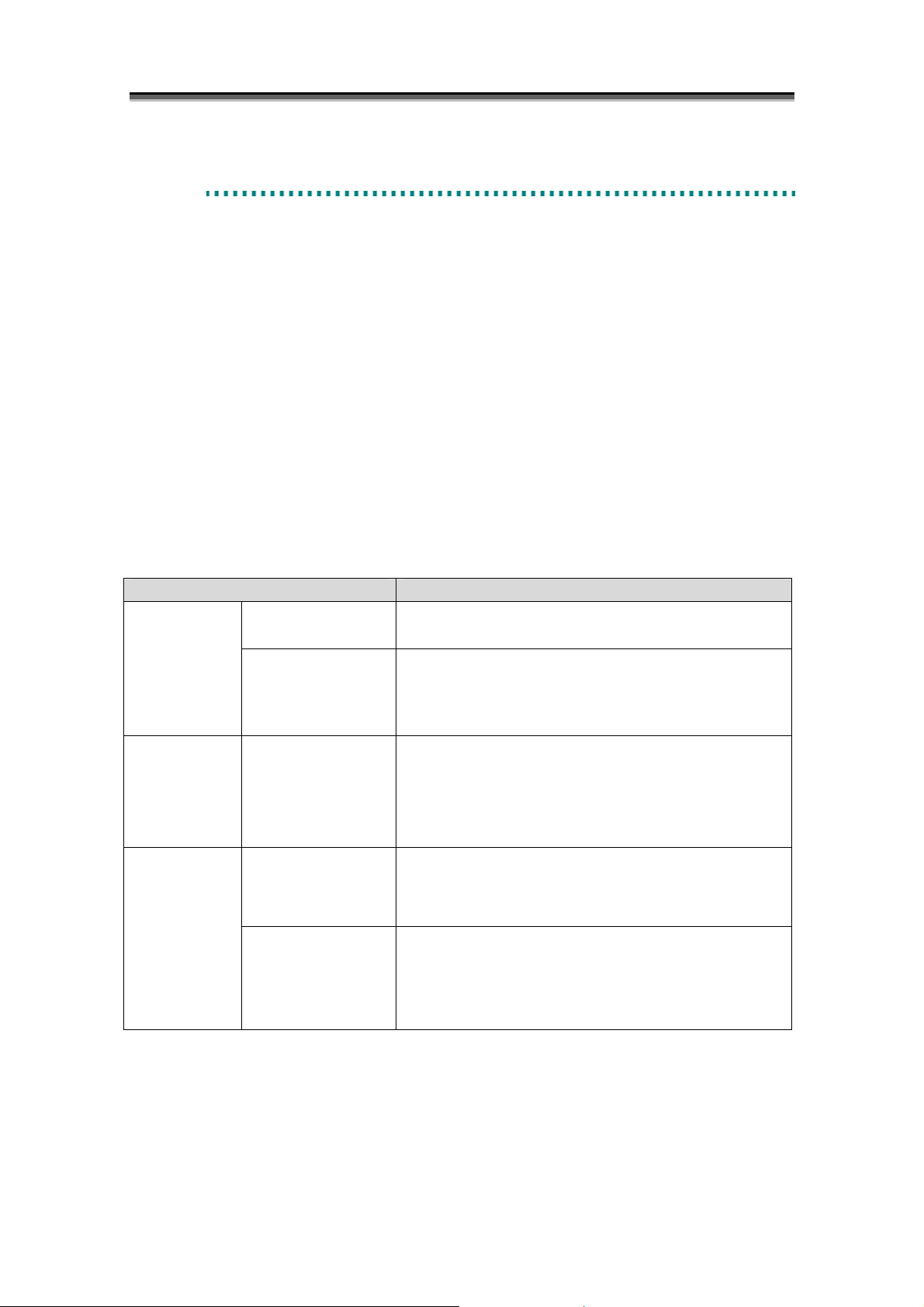
Data Replication is a function that creates Replication Volumes (RV) of a business volume (called
Master Volume (MV) in the data replication). It is installed in the disk array. Replication volumes
can be connected to or separated from the master volume at any time. Operations such as connection
and separation can be instructed from the business server and the iSM Client (e.g. Windows system).
The following two methods are provided to create replication volumes.
(1) Creating replication volumes within the same disk array (DDR: DynamicDataReplication)
(2) Creating replication volumes in different disk arrays (RDR: RemoteDataReplication)
Synchronize/Separate
Master Server
Operation
Master
(MV)
Replication
(RV)
DynamicDataReplication
Master
(MV)
Figure 1-1 Data Replication
Production Task
t
i
c
a
t
(Online)
RemoteDataReplication
i
o
n
i
o
n
Parallel Processing
(Backup/Search)
Replication
(RV)
1
Page 10

Chapter 1 Data Replication Overview
r
r
r
1
.
2
E
x
a
m
p
l
e
1
.
2
E
x
a
1
.
2
E
R
R
R
When you introduce Data Replication and use replication volumes which can be separated, you can get
the following benefits.
• The system down time during data backup is largely reduced. Lowered access performance to the
business database during data backup in system operation can be prevented.
• A test environment using the actual business data can be built more easily.
• Processing becomes more efficient due to parallel processing of data update tasks and data reference
tasks.
In this way, Data Replication makes system construction and system management easier and more
effective.
The following sections illustrate some applications of Data Replication.
x
e
e
e
a
p
p
p
m
m
l
i
l
i
l
i
c
c
c
p
p
a
a
a
s
l
e
s
l
e
s
t
i
o
t
i
o
t
i
o
n
o
o
o
n
n
f
A
p
p
l
y
i
n
g
D
a
t
a
f
A
p
p
l
y
i
n
g
f
A
p
p
l
y
i
n
g
D
D
a
a
t
a
t
a
1
.
2
.
1
B
a
c
k
u
p
1
.
2
.
1
B
a
c
1
.
2
.
1
B
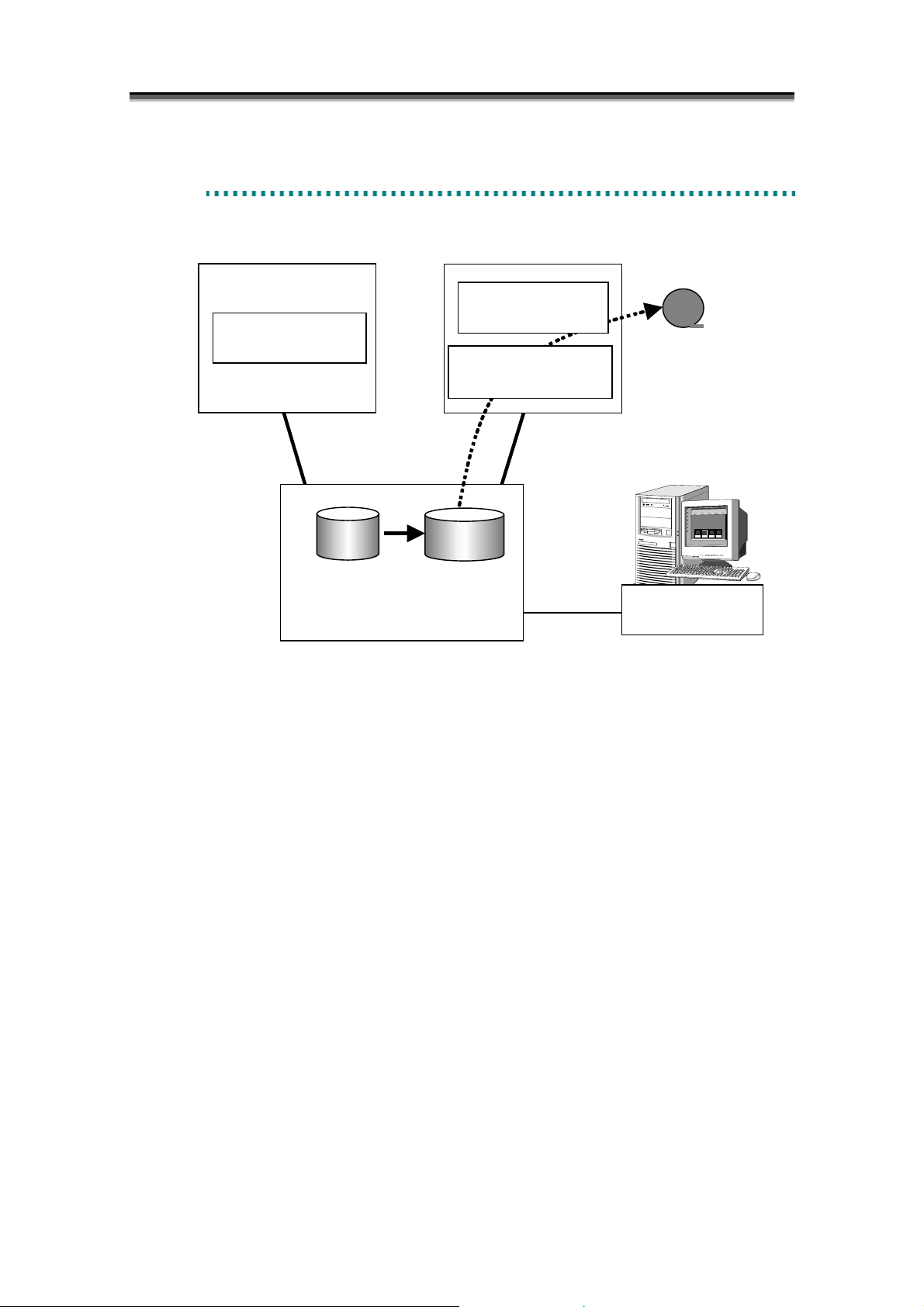
This section describes an application for backup using replication volumes.
[Backing Up from the Replication Volume to Magnetic Tape Media]
In this method, a replication volume of the master volume is backed up to the magnetic tape.
In this case, operations are suspended only for the time it takes to separate replication volumes from the
master volume. Therefore, the suspension time can be substantially reduced.
Because backup is done from the replication volume, it does not affect the master volume.
Master Serve
Production Task
k
a
c
Connect
u
p
k
u
p
Backup Serve
Maste
(MV)
Backup
Separate
Replication
(RV)
Figure 1-2 Backup from Replication Volume
Tape
2
Page 11
Chapter 1 Data Replication Overview
r
r
The procedure for backup from a replication volume is described below.
(1) During operation, the master volume (MV) and replication volume (RV) are connected.
(2) Suspend the production task and separate the replication volume (RV). Resume the task after
separation is complete.
(3) Use the separated replication volume (RV) to perform backup and the task in parallel. After
backup is complete, reconnect the replication volume (RV) (Reconnection takes only a short time
because only updated parts in the master volume are reflected to the replication volume (RV)).
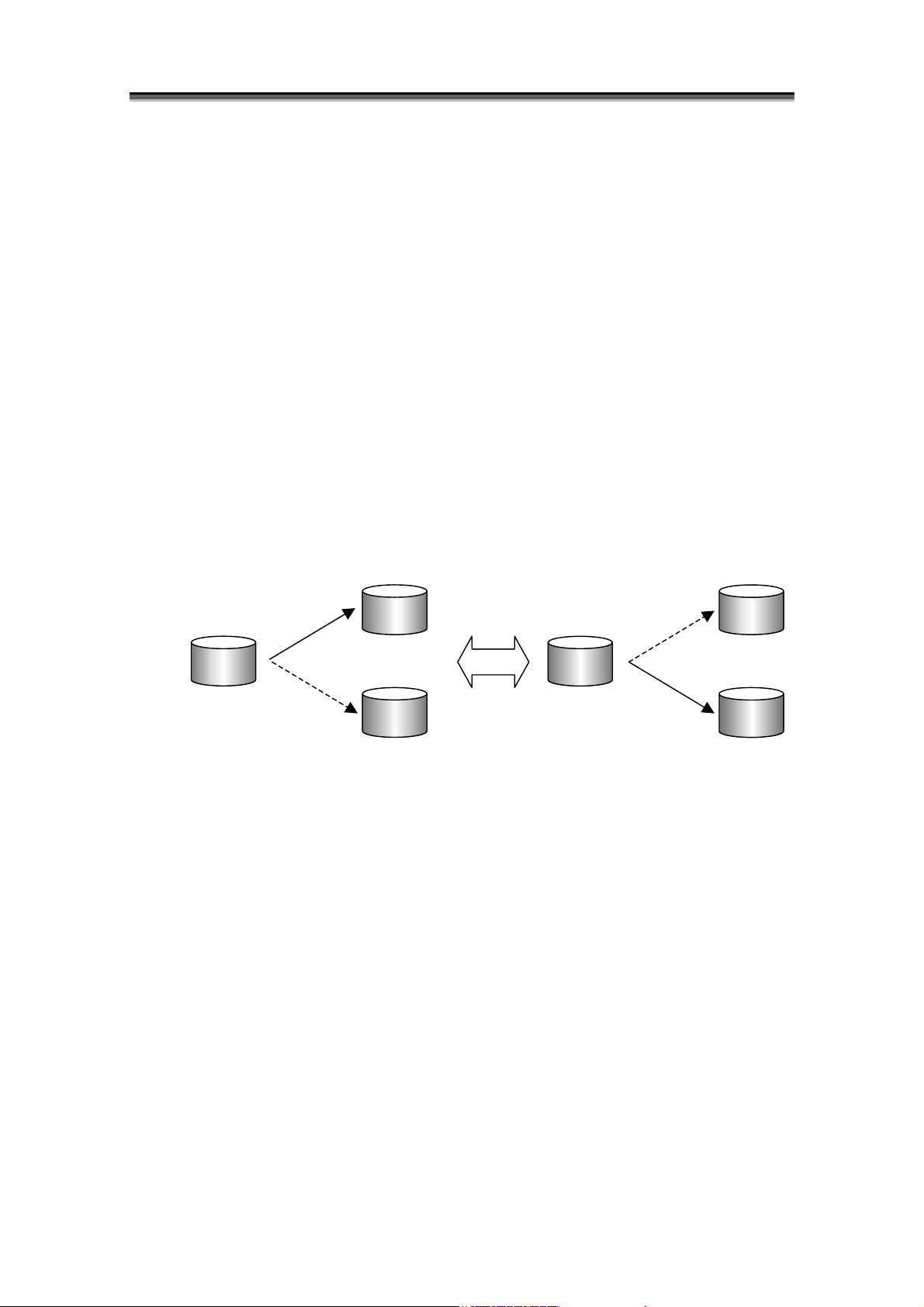
[Using the Replication Volume as Disk Backup]
In this method, the replication volume is used as backup of the master volume. In this case, you do
not have to manage the existing magnetic tapes because they are not used as storage media.
When the restoration instruction is complete, you can use the backup data even if the actual data
replication has not been completed. If data to be accessed is not restored to the master volume, the
data in the replication volume is accessed. The user does not have to be aware of using which of the
master volume or replication volume.
This reduces the data restoration time substantially.
Connect
Maste
(MV)
Separate
The procedure for using a replication volume for backup is described below.
(1) Connect the replication volume 1 (RV1) to the master volume.
(2) Suspend the production task and separate the replication volume 1 (RV1). Resume the task after
connecting the replication volume 2 (RV2).
(3) After that, use the replication volume 1 (RV1) and replication volume 2 (RV2) alternately to
perform backup.
Replication 1
(RV1)
Maste
(MV)
Replication 2
(RV2)
Figure 1-3 Using Replication Volume as Backup
Separate
Connect
Replication 1
(RV1)
Replication 2
(RV2)
3
Page 12
Chapter 1 Data Replication Overview
1
.
2
.
2
T
e
s
t
E
n
v
i
1
.
2
.
2
T
e
s
t
1
.
2
.
2
T
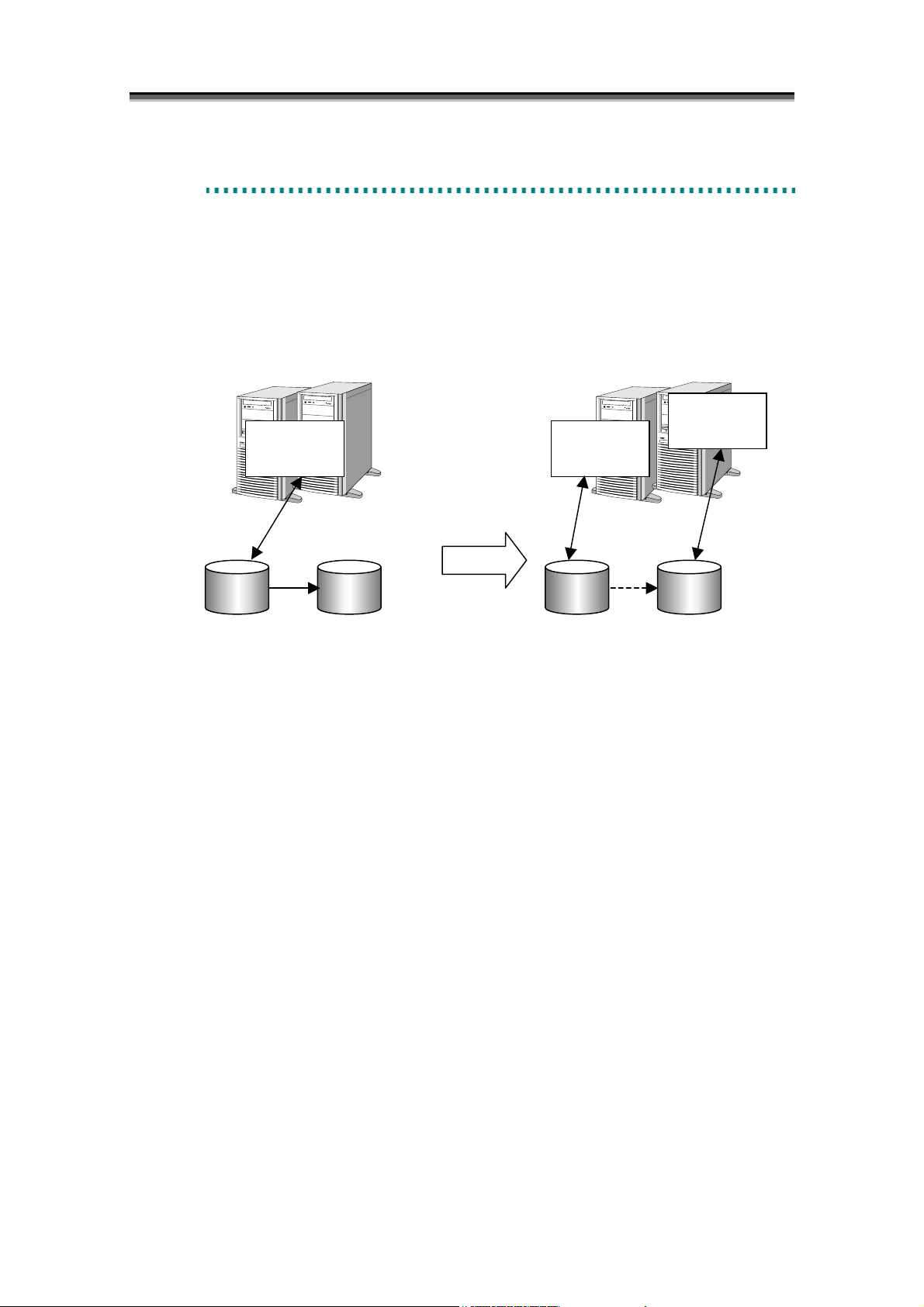
e
You can set the same environment as the production task environment easily by creating replication
volumes using the Data Replication function. You can evaluate an application program by using data
used in the production task, which makes evaluation of application programs more efficient.
Furthermore, in building an evaluation environment, operations are suspended only for the time which
takes to separate replication volumes from the master volume. Therefore, the suspension time can be
substantially reduced.
Production
Task
s
E
t
E
n
n
v
v
r
i
r
i
o
n
m
e
n
t
S
e
t
t
i
n
g
o
n
m
e
n
t
S
e
t
r
o
n
m
e
n
t
S
e
t
t
t
Production
i
n
i
n
Task
g
g
Test
Master
(MV)
Connect
The procedure for using a replication volume as a test environment is described below.
(1) Connect the master volume (MV) and replication volume (RV).
(2) Suspend the production task, separate the replication volume (RV), and then resume the task.
(3) Perform evaluation of the application program by using the separated replication volume (RV).
Replication
(RV)
Master
(MV)
Figure 1-4 Test Environment Setting
Separate
Replication
(RV)
4
Page 13
Chapter 1 Data Replication Overview
1
.
2
.
3
P
a
r
a
l
l
e
l
P
r
o
c
e
s
s
i
n
g
o
f
S
e
a
r
c
h
1
.
2
.
3
P
a
r
a
l
l
e
l
P
r
o
c
e
s
s
i
n
g
o
f
S
e
1
.
2
.
3
P
a
r
a
l
l
e
l
P
r
o
c
e
s
s
i
n
g
o
f
O
p
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
O
p
e
r
a
O
p
By creating replication volumes of the master database, you can separate the database and carry out
update tasks and search tasks using different volumes. This allows you to carry out database update
tasks without affecting database search tasks.
Nighttime
Master
(MV)
Master
Database
The procedure for parallel processing of search operation is described below.
(1) In the nighttime, suspend search tasks and connect the master volume (MV) and replication
(2) In the daytime, separate the master volume (MV) and replication volume (RV). Then perform
Connect
volume (RV).
update tasks and search tasks in parallel (RV contains data for the prior day).
t
e
r
a
t
Replication
Reflection of
Updated Parts
Figure 1-5 Parallel Processing of Search Task
i
o
i
o
(RV)
n
n
Daytime
Master
(MV)
Master
Database
a
S
e
a
Update Task
Separate
r
c
h
r
c
h
Data for Previous
Day
Search Task
Replication
(RV)
5
Page 14
Chapter 1 Data Replication Overview
1
.
3
S
y
s
t
e
m
1
1
.
3
S
y
s
t
.
3
S
y
s
e
t
e
m
m
C
C
C
o
o
o
n
n
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
u
t
r
a
t
f
i
g
i
o
n
i
o
n
Business Server
ReplicationControl
DB
• AccessControl
• DynamicDataReplication
• RemoteDataReplication
Disk Array
Figure 1-6 System Configuration
To install and use the Data Replication function, the following hardware devices are required.
• Disk array
Disk arrays on which the Data Replication function either with DynamicDataReplication or
RemoteDataReplication is installed are required.
• Management server
iSM is installed in the management server that monitors disk arrays. This server controls disk arrays
and the Data Replication function.
• Business server/backup server
Performs Data Replication operation or backup operation in cooperation with business.
Software to run Data Replication consists of the following components.
Backup Server
Backup Software
Tape Drive
ReplicationControl
Management
Server
Replication
LAN
Storage Manager
6
Page 15

Chapter 1 Data Replication Overview
• Storage Manager
Provides the disk array configuration and state display functions.
Installing DynamicDataReplication and/or RemoteDataReplication allows the replication
management function (hereinafter, referred to as the Replication Management) incorporated in iSM.
The Replication Management provides setting and operating functions such as state display, pair
setting, and replication operation for DynamicDataReplication or RemoteDataReplication.
• ReplicationControl
Provides commands for checking replication operations and replication states from the business
server and also provides library functions.
• AccessControl
The function to set the logical disks that can be accessed, for each business server.
• DynamicDataReplication
The function to realize data replication within the same disk array.
• RemoteDataReplication
The function to realize data replication in the different disk arrays.
7
Page 16

Chapter 2 Data Replication
Chapter 2 Data Replication
This chapter describes the types and state transitions of volumes that are necessary to perform operation using the
Data Replication function.
2
.
1
V
o
l
u
m
e
C
l
a
s
s
i
f
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
2
.
1
V
o
l
u
m
e
C
l
a
s
s
i
f
i
c
a
2
.
1
V
o
l
u
m
e
C
l
a
s
s
i
f
To create replication volumes using the Data Replication function, you must set the relation between
the original volume and the target volume (replication volume) first. In replication control, the
original volume is called MV (Master Volume), and replication volume is called RV (Replication
Volume). Furthermore, MV and RV are set as a pair.
In a disk array to which the Data Replication function is installed, the volume classification in the disk
array is categorized into the following three types. Figure 2-1 describes sample volume classification.
• Isolated Volume (IV)
Volume with no pair setting.
By specifying the pair setting to IV, you can set it to MV or RV.
• Master Volume (MV)
Volume with the pair setting. The original volume in the pair. Normally, volumes used in
operation are set as MVs.
To distinguish the uppermost MV from other MVs when multiple pairs are set in series hierarchically,
it is called the Primary Volume (PV).
• Replication Volume (RV)
Volume with the pair setting. The target volume in the pair. Normally, volumes used as backup or
in test operation are set as RVs.
The pair setting can be between the volumes within the same disk array, or between the volumes in
different disk arrays. To distinguish them, the former is called a Dynamic Replication Volume
(dRV) and the latter is called a Remote Replication Volume (rRV).
t
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
i
o
n
8
Page 17

Chapter 2 Data Replication
Volume A1/A2/B1 : IV
Volume A3 : MV (PV) of the pair A3/A4
Volume A4 : RV (dRV) of the pair A3/A4, and MV of the pair A4/B2
Volume B2 : RV (rRV) of the pair A4/B2
Disk Array A Disk Array B
FC
A1
IV
A3
MV
(PV)
A2
IV
A4
RV/MV
(dRV)
B1
IV
B2
RV
(rRV)
Pair Setting
Figure 2-1 Example of Volume Classification
9
Page 18

Chapter 2 Data Replication
2
.
2
R
e
p
R
R
R
S
S
S
e
e
e
e
e
e
e
e
p
p
p
p
p
p
p
p
l
2
.
2
2
.
2
The replication operations include Replicate that replicates data from MV to RV, Separate that
separates between MV and RV, and Restore that replicates data from RV to MV.
2
.
2
2
.
2
2
.
2
This operation copies data from MV to RV.
It is performed to replicate the latest data to the replication volume used in a test environment or search
tasks. When Replicate is executed, the data in MV is copied to RV. In addition, any update made to
MV after Replicate is reflected to RV.
2
.
2
2
.
2
2
.
2
R
R
.
1
.
1
.
1
.
2
.
2
.
2
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
O
p
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
s
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
O
p
e
r
a
t
i
l
l
a
a
l
l
a
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
O
p
e
r
i
c
a
t
e
a
a
a
a
t
e
t
e
t
e
t
e
t
e
i
c
i
c
r
a
r
r
a
o
t
i
o
n
n
s
s
This operation separates MV and RV.
It is performed to suspend data replication between MV and RV to use RV in a test environment or
search tasks.
When Separate is started, all the difference between the MV and RV contents at the point of starting
Separate is reflected into the RV, and then data replication is suspended and the RV is separated. The
updates made to MV after starting Separate are not reflected to RV and stored in the disk array as
update differences.
When executing Separate, you can determine when to make the RV available by choosing either of the
following:
• Separate for making RV available after completion of separation: Separate(completion)
Reflects all the difference between the MV and RV contents into the RV, and makes the RV available
after completion of separation.
Even though Separate is executed immediately after Replicate starts, RV cannot be used while the
difference between MV and RV is being reflected to RV. RV becomes available upon completion
of separation.
• Separate for immediately making RV available: Separate(immediate)
While reflecting the difference between the MV and RV contents into the RV, the Separate function
makes the RV available even during separation. You can instantly create RV and make it available
by executing Separate(immediate).
This function is available only for performing data replication in the same disk array. The product
“DynamicDataReplication Ver2“ is necessary for using the function.
10
Page 19
Chapter 2 Data Replication
2
.
2
.
3
R
e
s
t
o
r
e
2
.
2
.
3
R
e
s
2
.
2
.
3
R
This operation copies data from RV to MV.
It is performed to restore data from the backup volume (RV) when a failure occurs in MV.
When Restore is executed, the RV contents at the point of starting Restore are reflected copied into the
MV. At this time, you can determine whether to reflect the updated data of the MV into the RV by
choosing either of the following:
• Restore with RV being updated: Restore(update)
Restores the MV while automatically reflecting the updated data of the MV into the RV. Even after
the difference between MV and RV is resolved and Restore is completed, any data update made to
MV is reflected to RV.
• Restore without RV being updated: Restore(protect)
Restores the MV without reflecting the updated data of the MV into the RV. After the difference
between MV and RV is resolved and Restore is completed, Separate is automatically executed. The
Restore(protect) function enables you to save the RV data in the state before the restoration.
The product DynamicDataReplication Ver2 or RemoteDataReplication Ver2 is necessary for using
the function.
e
s
t
t
o
o
r
e
r
e
11
Page 20
Chapter 2 Data Replication
•
•
•
2
.
3
R
e
p
r
r
e
e
r
a
a
a
p
p
n
n
n
l
2
.
3
2
.
3
This section describes the replication operations and state transitions.
R
R
T
T
T
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
O
p
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
s
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
O
p
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
s
a
n
d
S
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
O
p
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
s
a
n
d
s
i
t
i
o
n
s
s
s
i
t
i
o
i
t
i
o
n
n
s
s
S
t
t
a
a
t
e
t
e
The pair setting is specified
but MV and RV are separated.
separated
• MV and RV can be
updated.
MV RV
Difference between MV and
RV is being reflected.
MV
Replicate
• RV cannot be updated.
rpl/exec
sep/exec
Separate
• As a rule, RV cannot
be updated.
rst/exec
Restore
• RV cannot be updated.
MV
RV
RV
The pair setting is specified
and synchronization has been
established.
sync
Updates to MV are reflected to RV.
• As a rule, access to RV is not
allowed.
rpl/sync
MV RV
rst/sync
When Restore(update) is
executed, updates to MV are
reflected to RV.
• When Restore(protect) is
executed, updates to MV are not
reflected to RV.
• As a rule, access to RV is not
allowed.
exec : Executing Replicate, Separate, or Restore
sync : Replicate or Restore synchronization state
rpl : replicate (Replicate)
rpl/exec ............. Executing synchronization
rpl/sync ............. Synchronization state
sep : separate (Separate)
sep/exec ............ Executing Separate
separated .......... Separate completion state
rst : restore (Restore)
rst/exec ............. Executing Restore
rst/sync ............. Synchronization state
Figure 2-2 Replication Operations and State Transitions
12
When Restore(protect) is executed,
Synchronous State (rst/sync) is
placed and then automatically
changed to Separated State
(separated).
Page 21
Chapter 2 Data Replication
2
.
3
.
1
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
e
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
T
r
a
n
s
i
t
i
o
n
s
2
.
3
.
1
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
e
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
T
r
a
n
s
i
t
i
2
.
3
.
1
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
e
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
T
r
a
n
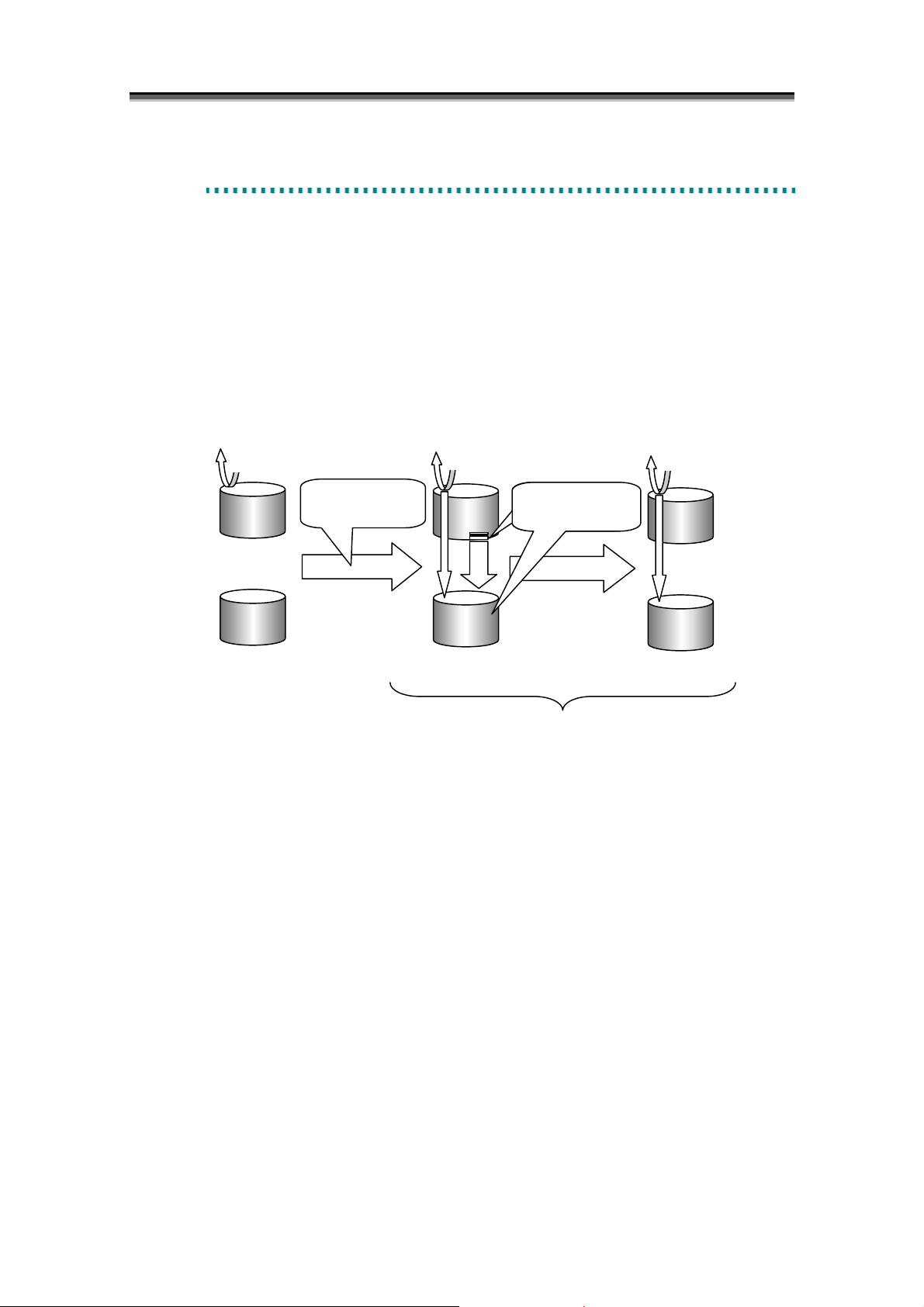
When Replicate is performed, data copy from MV to RV starts to reflect the content of MV to RV.
Any update to MV after Replicate is also reflected to RV.
After Replicate is started, the difference between MV and RV gradually decreases, and eventually the
content of MV at the beginning of Replicate is completely reflected to RV (The difference is zero).
The state from the beginning of Replicate to the content of MV is completely reflected to RV is called
the “Replicate execution”. The state where the difference between MV and RV is zero is called the
state synchronized by Replicate, or simply the “synchronous state“. Replicate execution and the state
synchronized by Replicate are collectively called the Replicate state.
Update to MV
Replicate
MV
RV
operation
starts
Update to MV
MV
RV
Until the
difference is zero
s
o
i
t
i
o
n
s
n
s
Update to MV
MV
RV
Synchronous Execution
Replicate State
Separate State
Synchronous State
Figure 2-3 Replicate and State Transitions
13
Page 22
Chapter 2 Data Replication
2
.
3
.
2
S
e
2
.
3
.
2
2
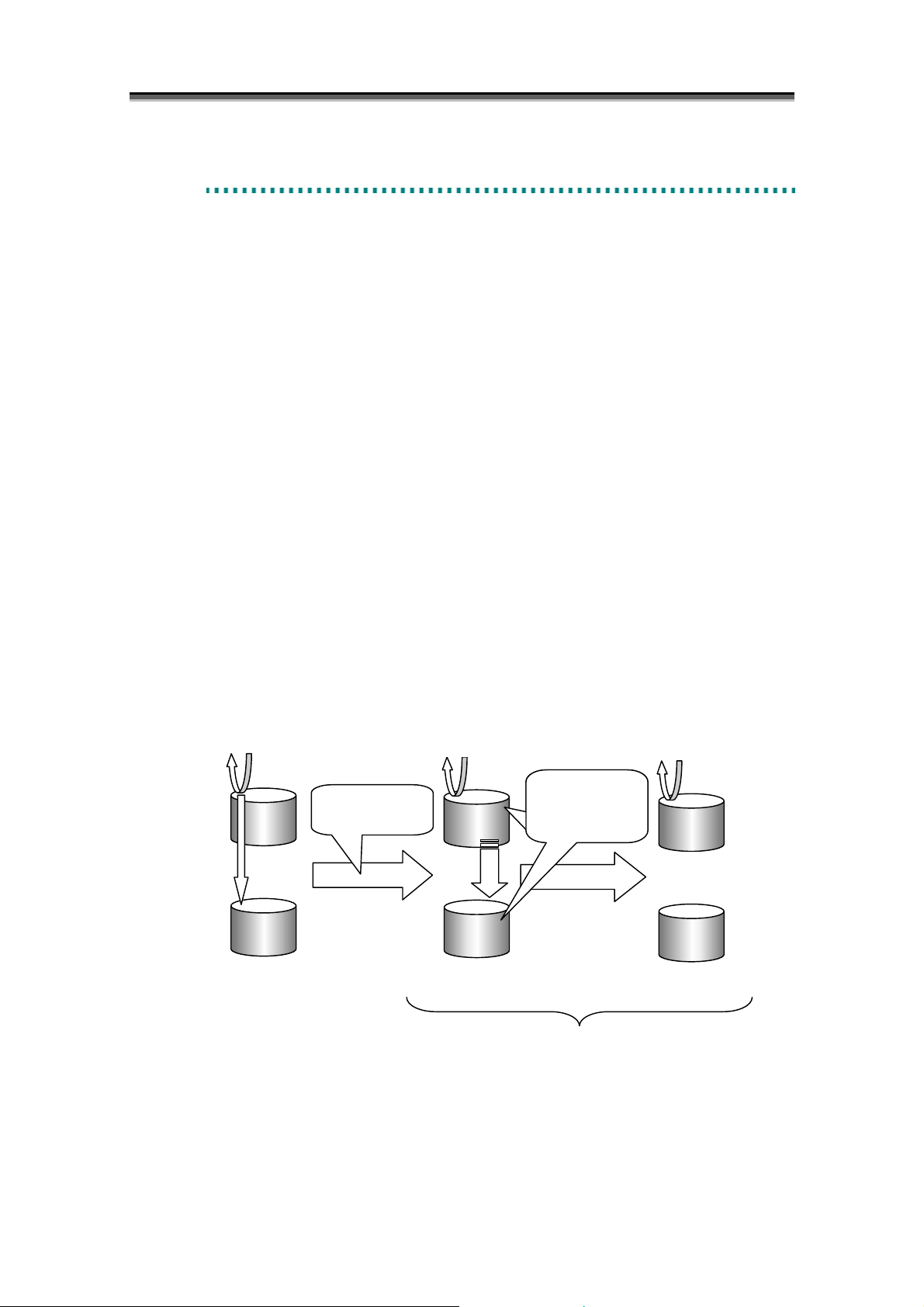
When Separate is performed, the difference between MV and RV at the time of executing the Separate
start instruction is reflected to RV and RV is separated. No update to MV after Separate is reflected to
RV.
After Separate is performed, data copy to RV is performed if the contents of MV and RV at the
beginning of Separate do not match, and all updates to MV before the Separate start instruction are
reflected to RV. The state from the beginning of Separate to the content of MV at the beginning of
Separate is completely reflected to RV is called the “Separate execution state“. The state where all
updates to MV are reflected to RV is called the state separated by Separate, or the “separated state“.
Separate execution and the separated state are collectively called the Separate state.
When Separate is executed under specification of immediate use of RV (Separate(immediate)), the RV
contents can be referred to or updated immediately after the Separate start instruction is issued,
regardless of whether or not all the MV contents have been reflected into the RV. This feature is
implemented as follows.
When an update/reference request for the RV is made and access to an area where difference copy from
the MV into RV is not completed is to be made, control is performed for copying the difference from
the MV into RV before permitting access to the area.
The updates made to MV until Separate is started are reflected to RV. The updates made to MV after
Separate is started are not reflected to RV and managed as update difference.
The updated states of MV and RV are managed in Separate State so that the difference between the MV
and RV contents is reflected when Replicate/Restore is executed.
.
3
.
2
Update to MV
S
S
e
e
p
p
p
a
a
a
r
a
t
e
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
T
r
a
n
s
i
t
i
o
n
s
r
a
t
e
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
T
r
a
n
s
i
t
i
r
a
t
e
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
T
r
a
n
Update to MV
s
o
i
t
i
o
n
s
n
s
Update to MV
Until the difference
between MV and
Synchronous State
MV
RV
Separate
operation starts
Separate Execution
Figure 2-4 Separate and State Transitions
MV
RV
14
RV is fully reflected
to RV
Separated State
Separate State
MV
RV
Page 23
Chapter 2 Data Replication
2
.
3
.
3
R
e
s
t
o
r
e
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
T
r
a
n
s
i
t
i
o
n
s
2
.
3
.
3
R
e
s
t
o
r
e
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
T
r
a
n
s
i
t
i
2
.
3
.
3
R
e
s
t
o
r
e
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
T
r
a
n
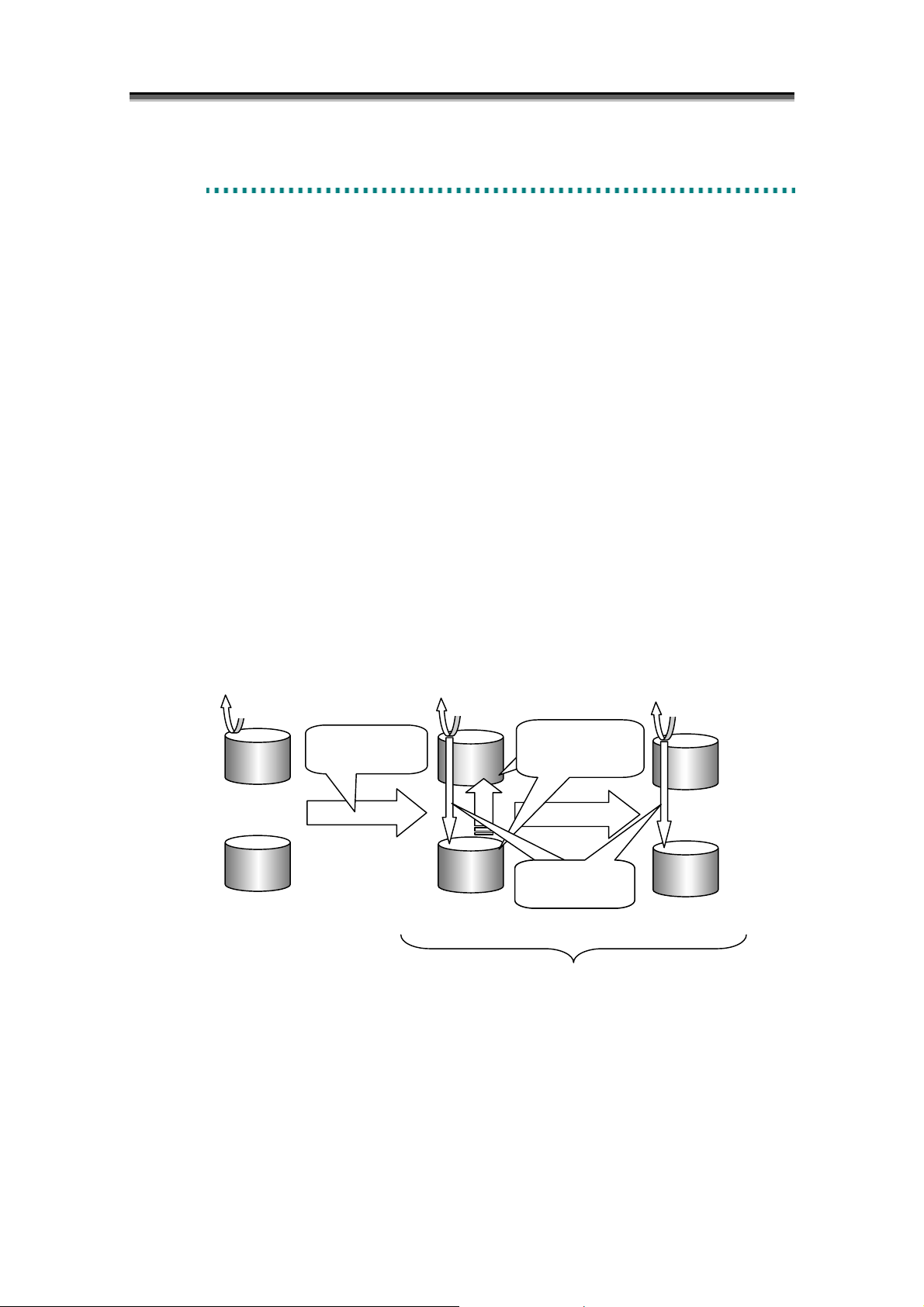
When Restore is performed, data copy from RV to MV starts to reflect the content of RV at the
beginning of Restore to MV. When Restore(update) is executed, any update to MV after Restore is
also reflected to RV.
After Restore is started, the difference between MV and RV gradually decreases, and eventually the
content of RV at the beginning of Restore is completely reflected to MV (The difference is zero). The
state from the beginning of Restore to the content of RV at the beginning of Restore is completely
reflected to MV is called the “Restore execution”. The state where the difference between MV and
RV is zero is called the state synchronized by Restore, or simply the “synchronous state“. Restore
execution and the state synchronized by Restore are collectively called the Restore state.
When Restore(protect) is executed, the updated data of the MV is not reflected into the RV. In this
case, the updated information of the MV is managed as the difference between the MV and RV contents
so that the difference can be reflected into the RV when Replicate/Restore is executed subsequently.
When the Synchronous State (sync) is placed after Restore(protect) is executed, it is automatically
changed to the Separated State (separated).
When data of MV is referred to during Restore execution, the user can refer to the content of RV
immediately after the instruction to start Restore even if the content of RV has not been completely
reflected to MV. This is done by obtaining data from RV when the area where difference copy from
RV to MV has not been completed is accessed in response to a reference request to MV.
Update to MV
MV
RV
Separate State
Restore
operation starts
Update to MV
MV
RV
Restore Execution
Until the
difference is zero
Only when
updating RV
o
s
i
t
i
o
Synchronous State
n
s
n
s
Update to MV
MV
RV
Restore State
Figure 2-5 Restore and State Transitions
15
Page 24
Chapter 2 Data Replication
2
.
3
.
4
A
c
t
i
v
i
t
y
S
t
a
t
e
a
n
d
S
2
.
3
.
4
A
c
t
i
v
i
t
y
S
t
a
t
e
a
2
.
3
.
4
A
c
t
i
v
i
t
y
S
t
a
t
S
t
a
t
e
S
t
S
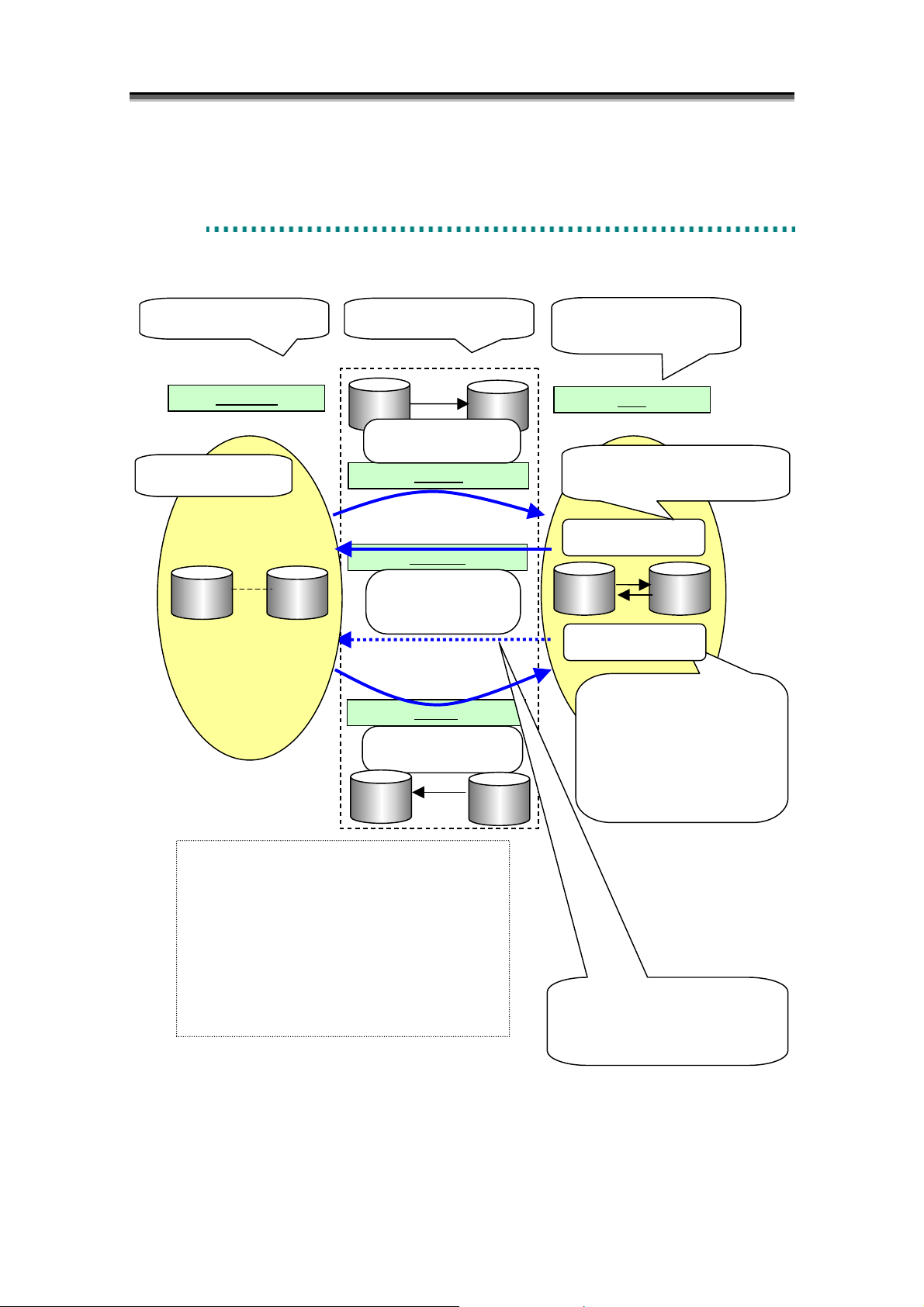
In data replication, Replicate, Restore, and Separate states are called “activity states”, or simply
“activities”.
The execution states indicating state transitions and the state in which the state transition is complete
are called “synchronous states”.
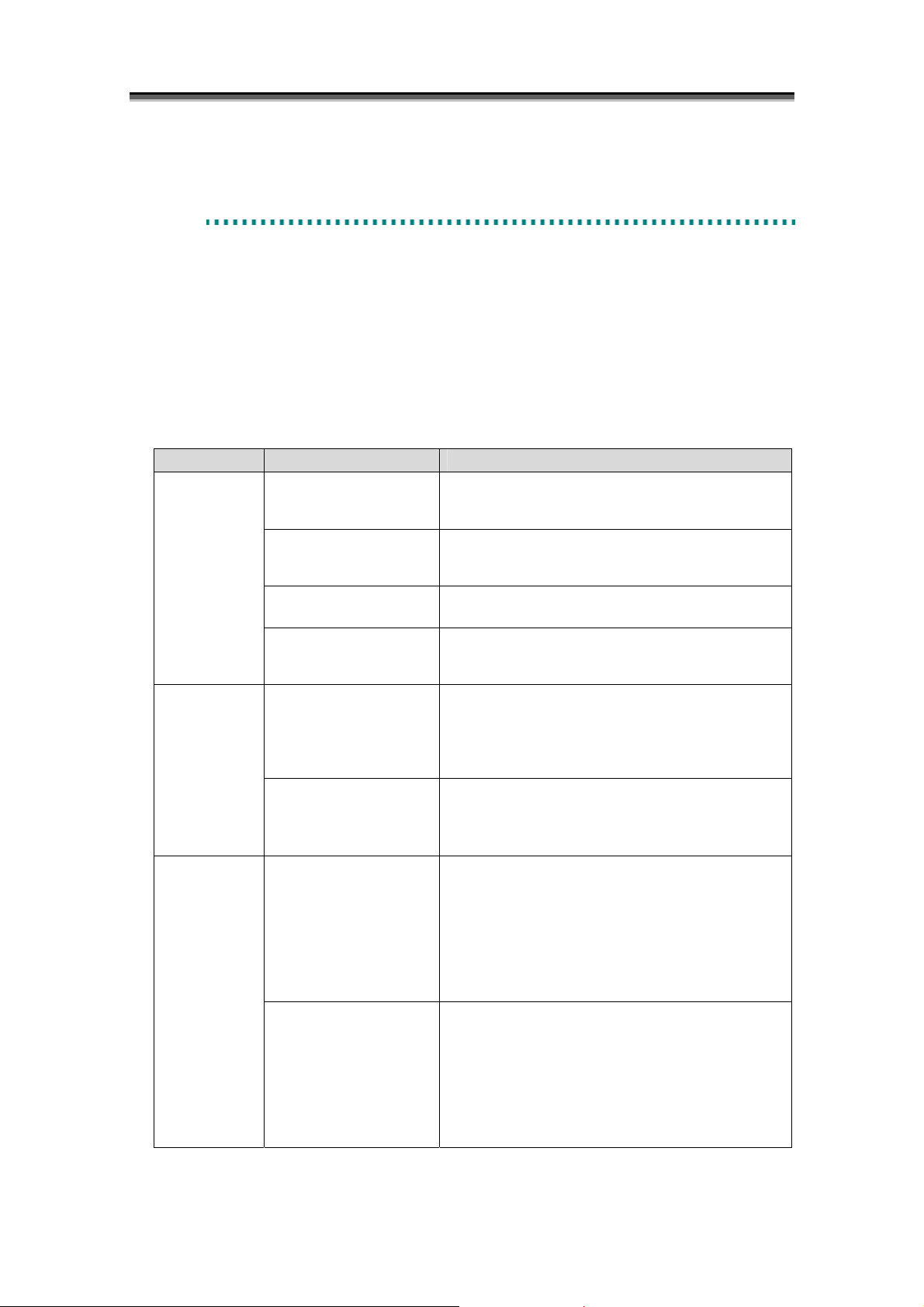
Table 2-1 shows the activity states and synchronous states which transit as a result of each replication
operation. For information on handling MV and RV access in the activity states, refer to 2.6 “RV
Access Restriction”.
Activity State Synchronous State Description
Separate State
Replicate State
Restore State
Separate Execution
(sep/exec)
Separated(separated)
Forced Separate(cancel)
Failure Separation (fault)
Synchronous Execution
(rpl/exec)
Synchronous State(rpl/sync)
Restore Execution(rst/exec)
Synchronous State(rst/sync)
a
t
e
t
a
t
e
Table 2-1 Activity State and Synchronous State
• Temporal state until the difference between MV and RV
• As a rule, read and write to RV are not allowed.
• Data copy between MV and RV is not performed. This
• Normally, read and write to RV are allowed.
• MV and RV are forcibly separated by Forced Separate.
• Read and write to RV are allowed.
• MV and RV are forcibly separated in the disk array due
• Read and write to RV are allowed.
• Reflection of the difference between MV and RV at
• Updates to MV is reflected to RV.
• As a rule, read and write to RV are not allowed.
• Reflection of the difference between MV and RV at
• Updates to MV is reflected to RV.
• As a rule, read and write to RV are not allowed.
• Reflection of the difference between MV and RV at
• When Restore(update) is executed, the updated data of
• When Restore(protect) is executed, the updated data of
• As a rule, read and write to RV are not allowed.
• Reflection of the difference between MV and RV at
• When Restore(update) is executed, the updated data of
• When Restore(protect) is executed, the updated data of
• As a rule, read and write to RV are not allowed.
n
e
a
n
becomes zero after Separate
state occurs immediately after the pair setting.
to a copy fault.
Replicate has not been completed (The difference is
being reflected from MV to RV).
Replicate has been completed.
Restore has not been completed (The difference is being
reflected from RV to MV).
the MV is reflected into the RV.
the MV is not reflected into the RV.
Restore has been completed.
the MV is reflected into the RV.
the MV is not reflected into the RV and the Separate
completion state is automatically entered.
d
d
y
S
y
S
y
n
n
n
c
c
c
h
h
h
r
o
n
o
u
s
o
u
u
s
s
r
o
n
o
r
o
n
16
Page 25
2
.
4
2
.
4
2
.
4
If the activity between volumes with the pair setting is the Replicate or Restore state, you can change the
copy method of data between MV and RV according to the load status of the disk array. The state to
which a transition is made by the instruction to change the copy method is called the “copy control state“.
There are the following two types of copy between MV and RV in the Replicate or Restore state.
• Copy for reflecting difference
Copy to reflect the content of MV (RV for Restore) at Replicate or Restore to RV (MV for Restore).
• Copy to reflect updates in MV to RV
Copy to reflect updates in MV to RV after Replicate or Restore. However, if Restore(protect) is
executed, the updated data of the MV is not reflected into the RV.
You can change the copy method and state by changing the copy control state.
There are the following copy states in the copy control states as shown in Table 2-2.
Copy Control State Copy State
Foreground Copy
Background Copy -
Suspend
C
o
p
y
C
C
o
o
Synchronous Copy
Mode
Semi-synchronous Copy
Mode
Suspend
Suspend due to a failure
p
p
C
y
C
y
C
Table 2-2 Copy Control State
Chapter 2 Data Replication
o
n
t
r
o
l
S
t
a
t
e
o
n
t
r
o
l
S
o
n
t
r
o
• Copy for reflecting difference is performed.
• Updates to MV are reflected RV sequentially.
• Copy for reflecting difference is performed.
• I/O of updates to MV is completed when data is written to MV,
and the data is copied to RV immediately after that.
• Can be set for a RemoteDataReplication pair.
• Copy for reflecting difference is performed.
• I/O of updates to MV is completed when data is written to MV,
and the data is accumulated as difference information. For the
accumulated difference, data is copied to RV asynchronously.
The copy interval to RV (Background Copy Level) can be
changed in units of disk arrays.
• Copy for reflecting difference is not performed.
• I/O of updates to MV is completed when data is written to MV,
and the data is accumulated as difference information.
Reflection to RV is not performed.
• Forcefully suspended in the disk array due to a copy fault.
• Copy for reflecting difference is not performed.
• I/O of updates to MV is completed when data is written to MV,
and the data is accumulated as difference information.
Reflection to RV is not performed.
t
l
S
t
a
a
t
e
t
e
17
Page 26
Chapter 2 Data Replication
py
Copy control states can be specified when Replicate or Restore is performed. You can also change the
copy control state you specified at Replicate or Restore as required.
When Restore with RV protection specified is executed, only copy for reflecting the difference is
executed, thus the updated data of the MV is not reflected into the RV. Therefore, specifying or
changing a copy control state (Synchronous Copy Mode, Semi-synchronous Copy Mode, or
Background Copy) has no effect.
There are the following five instructions to change the copy control state.
• Synchronous Copy instruction
• Semi-synchronous Copy instruction
• Resume instruction
• Background Copy instruction
• Suspend instruction
The Resume instruction changes Background Copy or Suspend to preceding Foreground Copy
(Synchronous Copy Mode, Semi-synchronous Copy Mode).
Figure 2-6 shows the state transition diagram of the copy control states.
Background Copy
Background
Copy Instruction
Foreground Copy
Sync Copy
Mode
Synchronous Copy or
Semi-synchronous
Copy or Resume
Background Copy Instruction
Suspend Instruction
Semi-
synchronous
Mode*
Co
Suspend Instruction
Copy Fault
* Semi-synchronous Copy Mode
can be used only for a
RemoteDataReplication pair
Synchronous Copy or
Semi-synchronous Copy
or Resume Instruction
Suspend
normal abnormal
Figure 2-6 State Transition Diagram of Copy Control State
18
Page 27
Chapter 2 Data Replication
2
.
5
R
e
l
a
t
i
o
n
s
h
i
p
b
e
t
w
e
e
n
C
o
p
y
2
.
5
R
e
l
a
t
i
o
n
s
h
i
p
b
e
t
w
e
e
n
C
p
p
p
y
y
y
C
o
o
C
C
C
2
.
5
R
e
l
a
t
i
o
n
s
h
i
p
b
e
t
w
e
e
n
P
e
r
f
o
r
m
a
n
c
e
a
n
d
C
P
e
r
f
o
r
m
a
n
c
e
a
n
P
e
r
f
o
r
m
a
n
c
e
S
t
a
t
e
S
t
S
t
If the copy control state is set to the Synchronized Copy state, the difference between MV and RV is
not accumulated because updates to MV are immediately reflected to RV. However, the write time to
MV is longer because it waits for reflection of the updates to RV. If the Copy Control state is set to
the Suspend state, the difference between MV and RV is accumulated because updates to MV are not
reflected to RV, but the write time to MV is the same as normal I/O.
In this way, there are correlations between the amount of accumulated differences in MV and RV and
write performance in different copy control states. The correlation for each copy control state is
shown in Table 2-3.
Copy Control State Difference between MV and RV Write Overhead to MV
a
t
e
a
t
e
Table 2-3 Correlations in Different Copy Control States
d
a
n
d
C
C
o
o
o
p
p
o
o
o
y
y
n
n
n
t
r
o
l
t
t
r
o
l
r
o
l
Foreground (Synchronous) Small Exists
Foreground
(Semi-synchronous)
Background
Suspend Large Does not exist
If the difference between MV and RV is large in the Replicate state, we recommend to select a copy
control state which gives the difference between MV and RV smaller in a system without sufficient
suspension time for Separate execution because the processing time of Separate increases. Also, we
recommend you to select a copy control state without write overhead to MV in a system where write
performance to MV must be maintained and improved.
19
Page 28
Chapter 2 Data Replication
2
.
6
R
V
A
c
c
e
s
s
2
.
6
R
V
A
c
c
2
.
6
R
V
A
In the Replicate state and Restore state, MV is synchronized with RV to always match the volume data
between MV and RV. Since the difference between MV and RV is reflected in the disk array
independently of the operating system or file system, however, the volume of RV may become
inconsistent. Therefore, the data replication function cannot impose access restrictions for MV, and
MV can be referred to and updated at any time. The function can impose access restrictions for RV
for activity state to prevent malfunction.
Table 2-4 shows the states which can be specified as RV access restrictions.
Access Restriction Description
Read/Write (R/W) RV is enabled for read/write.
Read Only (RO) RV is enabled only for reading.
Not Ready (NR) RV is disabled for read/write.
RV is not recognized by the
Not Available (NA)
operating system or the LU
(Logical Unit) is invalid.
e
c
c
e
Table 2-4 RV Access Restriction
s
s
s
s
R
R
R
e
e
e
s
s
s
t
r
i
c
t
i
o
n
t
r
i
c
t
t
r
i
c
t
rpl rst sep/exec separated
- -
∆
Note 2 ∆ Note 2 ∆ Note 2 ∆ Note 3
{ { {
∆
Note 4 ∆ Note 4 ∆ Note 4 ∆ Note 4
i
o
n
i
o
n
Activity State
∆
Note 1
{
-
{: Available ∆: Available with administrative restrictions -: Unavailable
rpl: Replicate state RW: Read/Write
rst: Restore state RO: Read Only
sep/exec: Separate execution NR: Not Ready
separated: Separated state NA: Not Available
Note 1: For Separate(immediate), “Read/Write (RW)” is set even during execution of Separate.
However, keep the following operational influence in mind:
1. Data is being copied from the MV into RV during Separate execution. Therefore, if the
I/O load on the RV is high, I/O performance on the MV side may lower.
Note 2: You can set “Read Only (RO)” to RV in the Replicate state, Restore state, or Separate
execution. In this case, note the following.
1. No update to MV should be done when RV is referred to in the Replicate state or Restore
state.
2. For updates to MV, I/O processing is done to the disk by the operating system control of
the file system. Even if the application has completed the update process to the disk, it
has not necessarily completed the update process to MV. Reflection of the update to RV
is processed in the disk array independent of the operating system.
Therefore, RV cannot be referred to normally because it is not consistent as a volume.
You can use it if consistency is assured in the specific operation.
20
Page 29

Chapter 2 Data Replication
Note 3: If “Read Only (RO)” is set for RV for which Separate was completed, keep the following
operational notes in mind.
<On the Windows system>
1. If NTFS is used as a file system, reference to the RV is disabled.
2. If FAT16/FAT32 is used as a file system, associate the file system with the drive by using
the mount command of the disk control operation commands or by starting [Disk
Management] (Windows).
3. If FAT16/FAT32 is used as a file system, an attempt to write to RV ends up with an error.
Therefore, do not use any application for automatically performing write operation for the
drive. Do not perform any operation (e.g., changing of a partition configuration) in
which write to RV is performed through [Disk Management] (Windows).
<On the UNIX system>
When mounting a file system, it is necessary to mount it by a read-only specification.
Note 4: The “Not Available (NA)” state has meaning when the VSS (Volume Shadow copy Service)
function is used. A transition to the Not Available state is automatically controlled by the
VSS function. The user need not perform the operation normally.
2
.
7
C
o
p
y
F
a
u
l
t
s
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
T
r
a
n
s
i
t
i
o
2
.
7
C
o
p
y
F
a
u
l
t
s
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
T
r
a
n
2
.
7
C
o
p
y
F
a
u
l
t
s
a
n
d
S
t
a
t
e
T
If copy operation between MV and RV is not performed normally due to a connection failure between
them, a transition to the following states may occur depending on the timing and type of the failure.
• Separate state due to a fault (failure separation)
Forcefully separated in the disk array due to a copy fault. The contents of MV and RV are
completely different.
To cancel the Separate state due to a failure, remove the cause of the copy fault and perform
restoration by using Replicate and Restore.
• Suspend state due to a fault (abnormal suspend)
Forcefully suspended in the disk array due to a copy fault in the Replicate or Restore state. Copy
between MV and RV is suspended.
To cancel the Suspend state due to a failure, change the copy control state as you do to cancel the
normal Suspend state after removing the cause of the copy fault (Refer to 2.4 “Copy Control State”).
s
r
a
n
s
n
i
t
i
o
n
i
t
i
o
n
s
s
s
21
Page 30

Chapter 2 Data Replication
2
.
8
F
r
e
2
.
8
2
.
8
If the power to the disk array is turned off for maintenance, access to the disk array is disabled,
disallowing to continue copy operation for the paired volumes in the disk array. In this situation, the
data replication function for the disk array stops replication operations of the whole disk array.
Freezing of replication operations for the disk array due to power down of the disk array is called
freezing of the disk array and the state is called the freeze state of the disk array.
When a disk array is in the freeze state, replication operations between volumes to which the pair
setting with the volume in the disk array is specified are also suspended, and the copy control state of
the pair becomes the freeze state.
When the pair is in the freeze state, no new replication operation can be performed.
For pairs in the freeze state, note the following.
• Freeze in the Separate state
If the pair goes into the freeze state in Separate execution, it transits to the Separate state due to a fault
(failure separation) when the following operation is performed.
<When updates to MV are done to the area where copy to RV has not been completed>
In this case, to use RV after the freeze state is cancelled, you must perform Replicate again to copy
data, and perform Separate.
• Freeze in the Replicate state
If the pair goes into the freeze state in the Replicate state, copy operation between MV and RV is
suspended. Copy operation is automatically resumed when the freeze state is cancelled.
• Freeze in the Restore state
If the pair goes into the freeze state in the Restore state, I/O terminates abnormally when reference or
update is performed to the area where copy from RV to MV has not been completed.
If the pair goes into the freeze state in the restored state, copy operation between MV and RV is
suspended.
Copy operation is automatically resumed when the freeze state is cancelled.
F
F
e
r
e
e
r
e
e
z
z
z
e
e
e
o
f
D
i
s
k
A
r
r
a
y
s
o
f
D
i
s
k
A
r
r
o
f
D
i
s
k
A
a
r
r
a
y
y
s
s
22
Page 31

Chapter 3 Replication Management
Chapter 3 Replication Management
This chapter describes various operations of Data Replication by the Graphical User Interface (GUI).
3
.
1
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t
3
.
1
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
M
a
n
a
g
e
u
u
g
t
t
t
h
h
h
e
m
m
o
o
o
r
i
r
i
r
i
3
.
1
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
M
a
n
a
O
v
e
r
v
i
e
w
O
v
e
r
v
e
e
e
e
i
r
v
r
a
r
a
r
a
O
v
This chapter describes an overview of various operations and the management method regarding data
replication that uses the replication management function.
3
.
1
.
1
O
3
3
.
1
.
1
.
1
.
1
p
O
p
O
p
e
w
i
t
e
w
i
o
n
s
a
n
d
A
t
i
o
n
s
a
t
i
o
n
s
n
a
n
d
d
u
A
A
e
e
z
z
z
n
n
a
a
a
t
t
t
i
o
n
t
i
o
n
t
i
o
n
L
e
v
e
l
s
L
e
v
L
e
v
e
e
l
s
l
s
Use the following functions to perform operations related to Data Replication through the iSM Client:
• State Monitoring
• Replication manager
• Configuration setting
Since operations performed from Replication manager includes important operations on volumes, the
operating authorization is set according to the following allowance levels.
However, when the server is disconnected by State Monitoring after displaying the Replication screen,
only the currently displayed state (the information gained while the server was connected) can be
referenced regardless of the operation authorization.
• L1: Allows only reference.
• L2: Allows replication-related operations (copy operations) in the administration level.
• L3: Allows all operations.
For information on how to set and log in, refer to the “User’s Manual” or “User’s Manual (UNIX)” in
accordance with your OS.
23
Page 32

Chapter 3 Replication Management
Table 3-1 lists the operations and state displays.
Table 3-1 List of Displays/Operations of Data Replication
Replication Management
Operation Item
Set Disk Array Name √ √ √ - - Set Logical Disk Name √ √ √ - - Link State - - √ - - Pair Setting/Unpair - - √ - - √
Replicate - - √ - √ √
Separate - - √ - √ √
Restore - - √ - √ √
Suspend/Resume Copy - - √ - √ √
Change to Background Copy - - √ - √ √
RV Mode Change - - √ - √ √
Forced Separate - - √ - √ √
Forced Unpair - - √ - - √
Freeze/Defreeze - - √ - - √
Background Copy Level Change - - √ - - √
Pair Batch Setting - √ - - - -
State
Monitoring
Configuration
Setting
Display
Operation Authorization
L1 L2 L3
√: Available - : Not available
L1: Allows only reference.
L2: Allows replication-related operations (copy operations) in the administration level.
L3: Allows all operations.
3
.
1
.
2
E
v
e
n
t
D
e
t
e
c
t
i
o
n
a
n
d
O
p
3
.
1
.
2
E
v
e
n
t
D
e
t
e
c
t
i
o
n
a
n
3
.
1
.
2
E
v
e
n
t
D
e
t
e
c
t
i
o
n
M
e
s
s
a
g
e
O
u
t
p
M
e
s
s
a
g
e
M
e
s
s
a
Events that occur in response to various operations performed on disk arrays and volumes can be
detected by the state monitoring and displayed in the iSM Client’s message display area as operation
messages.
By executing an environment setting beforehand, it is possible to detect events that occur as the result
of executing replication operation commands or other operations as well as performing replication
management operations, and it is also possible to confirm the events from operation messages.
Table 3-2 shows the replication-related events that can be confirmed as operation messages:
g
e
O
O
u
u
u
t
p
u
t
p
u
d
a
n
d
t
t
t
O
O
p
p
e
e
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
r
a
t
r
a
t
i
o
n
i
o
n
24
Page 33

Table 3-2 List of Replication-Related Events
Operation Target Operation
Disk array
Freeze
Chapter 3 Replication Management
Replication Management
Operation
{
Other Operations
∆
Defreeze
Change Background Copy level
Volume
{: Regular report ∆: Additional report performed according to an environment setting −: Not reported
Pair Setting/Unpair
Replicate
Synchronous State (rpl/sync)
Separate
Separated
Restore
Synchronous State (rst/sync)
Suspend/Resume Copy
Change to Background Copy
Change RV Mode
Change Copy Mode
Note: Replication management operations include operations performed together with the
ReplicationControl commands.
Regarding S2100 and A2100, the detection of events other than pair setting and unpairing events
may not be possible during the state monitoring.
Furthermore, the state monitoring monitors all the disk arrays’ volumes for a specified time
interval (default: 15 seconds) to detect events. Therefore, there is a time difference between
when an event actually occurred and when a message is output. Also, messages for each
detected event are displayed at the same time.
For information about an environment setting regarding the state monitoring’s event detection
time interval and operation message output control, refer to the “User’s Manual” or “User’s
Manual (UNIX)” in accordance with your OS.
{
{
{
{
∆ ∆
{
∆ ∆
{
∆ ∆
{
{
{
{
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
25
Page 34

Chapter 3 Replication Management
3
.
1
.
3
N
o
t
e
s
o
3
.
1
.
3
N
o
t
3
.
1
.
3
Note the following points when operating replication management:
[System Parameter Setting (on UNIX)]
For more information, refer to the “User’s Manual (UNIX)”.
[Messages at Start]
Immediately after iSM is started, replication-related device information is created internally.
Replication-related device information is recreated according to an information recreate instruction
from ReplicationControl.
Even if an attempt is made to display the Replication Screen at this timing, the screen cannot be
displayed because the device information cannot be obtained. If this happens, retry to display the
screen after a while.
[Action to Be Taken at Occurrence of Problems]
Refer to dialogs (messages) or help to take appropriate action.
N
o
e
t
e
s
s
n
o
n
o
n
O
O
O
p
p
p
e
e
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
r
a
t
r
a
t
i
o
n
i
o
n
26
Page 35

Chapter 3 Replication Management
3
.
2
E
x
p
l
a
n
a
t
i
o
n
o
f
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
S
c
r
e
e
n
3
.
2
E
x
p
l
a
n
a
t
i
o
n
o
f
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
S
c
r
3
.
2
E
x
p
l
a
n
a
t
i
o
n
o
f
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
S
To perform an operation, select the volumes you want to perform the operation to in the Volume List
Displayed on the Replication Information tab in the Replication Screen, and then click the [menu] on
the menu bar. You can also right-click the volume to display the menu.
3
.
2
.
1
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
S
c
r
e
e
n
3
.
2
.
1
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
S
c
r
3
.
2
.
1
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
The Replication Screen consists of the configuration display area (i) on the left part of the screen
displaying the configuration and state of the disk array and the information list display area (ii) on the
right part of the screen displaying the Volume List and disk array link configuration. When the
Replication Screen appears for the first time, it contains only the configuration display area (i) and the
information list display area (ii) is displayed by clicking the disk array icon. The information list
display area (ii) shows the selected disk array and the Volume List of the disk array connected with the
selected disk array by RemoteDataReplication.
S
c
e
r
e
e
e
n
n
c
e
r
e
e
e
n
n
(i)
(ii)
Figure 3-1 Example of Replication Screen
(i) For details, refer to 3.2.2 “Configuration Display Area”.
(ii) For details, refer to 3.2.3 “Replication Information Screen” and 3.2.4 “Disk Array LINK
Information Screen”.
* For details on the AT-group information screen, refer to the “Data Replication User’s Manual
(Disaster Recovery System Installation and Operation Guide)”.
27
Page 36

Chapter 3 Replication Management
3
.
2
.
2
C
o
n
f
i
g
u
3
.
2
.
2
C
o
n
3
.
2
.
2
C
The configuration display area is under the monitoring by the iSM and displays the list and the state of
the Disk Arrays that can use the Replication function, as well as the status of link among them.
o
n
f
f
r
i
g
u
r
i
g
u
r
a
a
a
t
i
o
n
D
i
s
p
l
a
y
A
r
e
a
t
i
o
n
D
i
s
p
l
a
y
t
i
o
n
D
i
s
p
A
l
a
y
A
r
e
a
r
e
a
Figure 3-2 Example of Configuration Display Area
28
Page 37

Disk Array icon
Icon Description
Chapter 3 Replication Management
, , , etc.
(in colors)
,
(dark gray)
, , , etc.
(light gray)
A disk array on which neither the DynamicDataReplication nor the RemoteDataReplication is installed
does not appear on the screen.
Indicates that the disk array is normally operating.
Indicates that the license capacity of the DynamicDataReplication,
RemoteDataReplication, or RemoteDataReplication/DisasterRecovery is
insufficient.
* If license capacity is insufficient, you cannot execute pair setting/unpair.
Indicates that the fault occurs in any link path between disk arrays.
Indicates that the copy fault or the fault in all link paths between disk arrays
occurs.
Indicates that the data replication function is frozen.
Indicates that the disk array to be linked is not directly monitored by Replication
manager when a link is established between disk arrays.
Indicates that the state monitoring is stopped.
If the Replication does not recognize the disk array of the link destination when the link is
established between disk arrays, the disk array name may be displayed as the address value
(Subsystem Absolute Address), which can uniquely identify the disk array not duplicated with other
disk arrays.
Each information screen to be explained in the following page or later may not be displayed depending
on the display items selected in the configuration display area and the state of disk array as follows.
Tabs in the information list display area cannot be selected when “iSM server” specified in the
configuration display area.
[Disk Array LINK Information] tab cannot be selected when the following disk arrays specified in the
configuration display area.
• Disk arrays not supporting RemoteDataReplication
• Disk arrays without RemoteDataReplication license
• Unmanaged disk arrays
[ATgroup Information] tab cannot be selected when the following disk arrays specified in the
configuration display area.
• Disk arrays not supporting RemoteDataReplication and RemoteDataReplication/Disaster Recovery
• Disk arrays without RemoteDataReplication and RemoteDataReplication/Disaster Recovery
29
Page 38

Chapter 3 Replication Management
license
• Unmanaged disk arrays
3
.
2
.
3
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
3
.
2
.
3
R
e
p
l
3
.
2
.
3
R
When click the [Replication Information] tab in the information list display area, the volume
information of the volumes in the selected disk array is displayed (refer to Figure 3-3 “Example of
Replication Information Screen”).
MV and RV are displayed in one line respectively (a total of two lines) for a pair and IV is displayed in
one line. If pair setting is performed for volumes, the states of the volumes are displayed in two lines
for one pair so as to check the states of MV and RV. IV is displayed in one line. To perform sort,
click the item name by which you want to sort. You can drag&drop an item to permute the order of
the items.
When pair setting and unpairing are performed, volume information is updated according to the order of
the last sort.
e
p
i
l
i
c
a
t
i
c
a
t
o
n
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
S
c
r
e
e
n
i
o
n
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
S
c
i
o
n
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
r
S
c
r
e
e
e
e
n
n
Figure 3-3 Example of Replication Information Screen
The Replication Information screen displays information regarding the following items.
30
Page 39

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(i) Classification
The volume types (volume attributes) are displayed.
Displayed Icon Description
(Green)
(Light Blue)
(White)
When the snapshot function is used, the base-volume (BV) used by snapshot is also displayed.
For snapshot, refer to the “Snapshot User’s Manual (Function Guide)”.
Displayed Icon Description
(Green)
(White)
(ii) Number
The logical disk number is displayed in hex digit.
It is the same as the logical disk number shown in the main screen (State Monitoring screen).
(iii) OS Type
Indicates the volume format.
When performing Replication operations, the OS type must be correctly specified.
Display Description
MV. Indicates Master Volume which is the volume of replication origin.
RV. Indicates Replication Volume which is the volume of replication target.
IV. Indicates Isolated Volume and is the volume except the replication object.
IV becomes MV or RV by operating pair setting.
Indicates the volume on which a copy fault occurs.
MV (MV/BV) having the BV attribute. Indicates the volume of replication
origin.
IV (BV) having the BV attribute. Indicates a volume which is not a replication
object. BV becomes MV (MV/BV) by operating pair setting.
A2 Indicates ACOS-2 format volume
A4 Indicates ACOS-4 format volume
AX Indicates AIX format volume
CX Indicates Solaris format volume
LX Indicates Linux format volume
NX Indicates HP-UX format volume
WN Indicates Windows format volume
31
Page 40

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(iv) Logical Disk Name
The identification name or identifier (see Note
It is the same as the logical disk name displayed in the main screen (State Monitoring screen) and
can be changed from the main screen (State Monitoring screen).
When the events given below have occurred when displaying the Replication Information screen, the
“Logical Disk Name” or “Paired Disk Name” field may show the unique volume number (Volume
Absolute Address) managed inside the disk array.
• The link failure has occurred.
• The Disk Array on the remote side is not managed by iSM or is in monitoring-stop state.
These events occur in a pair connected by RemoteDataReplication when the host to which a local
volume is connected cannot recognize the volume on the remote side. Also in such a case,
operations such as Forced Separate and Forced Unpair for local volumes are enabled.
) given for the logical disk is displayed.
(v) Pair Number
The logical disk number of paired volume is displayed in hex digit.
(vi) Pair Disk Name
The logical disk name of paired volume is displayed.
(vii) Activity State
The replication operation status is displayed.
Display Description
Replicate Indicates the status that copy is executing from MV to RV.
Separate Indicates the disconnection status of MV to RV.
Restore Indicates the status that copy is executing from RV to MV.
Restore (protect)
Indicates the state in which data is being copied from the RV into MV but the
updated data of the MV is not reflected into the RV.
32
Page 41

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(viii) Disk Array
The identification name given to the Disk Array including the volume indicated by “Pair Number”
is displayed.
It is the same as the Disk Array Name displayed in the main screen (State Monitoring screen), and
can be changed from the main screen (State Monitoring screen).
If the Replication does not recognize the link destination of the disk array when the link is
established between disk arrays, the disk array name may be displayed as the address value
(Subsystem Absolute Address), which can uniquely identify the disk array not duplicated with other
disk arrays.
(ix) Sync State
The transition status in activity state is displayed.
For more information, refer to 2.3 “Replication Operations and State Transitions”.
Display Description
Separating
Separated
Forced Separation
Fault
Sync Execution Indicates the status that difference exists while copy is executing.
Synchronized
Restoring
Restored
(synchronized)
Indicates the temporary status that difference between MV and RV is reducing to
zero during Separation Execution.
Indicates the status that the data copying is not processing between MV and RV.
It becomes this status right after pair setting.
Indicates the status that MV and RV are separated forcibly by the forced separate
instruction.
Indicates the status of forced separation inside the disk array due to copy fault
occurrence.
Indicates the status that reflection of the difference between the MV and RV at
the copy start instruction has been completed. Updates to the MV are reflected on
the RV sequentially for the pair in this state.
Indicates the status that difference between MV and RV is not reflected at the
time of restore execution.
Indicates the status that difference between MV and RV is reflected at the time of
restore execution. Updated MV content is reflected to RV.
33
Page 42

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(x) Copy Control State
The control status in copying is displayed.
For more information, refer to 2.4 “Copy Control State”.
Display Description
Foreground Copy Indicates the copy state in the synchronous or semi-synchronous mode.
Background Copy Indicates the asynchronous copy state by difference management.
Freeze Indicates that the data replication function is frozen.
Suspend Indicates that copy operation is suspended.
Abnormal Suspend Indicates that copy is forcibly suspended in the disk array due to a copy fault.
(xi) Copy Mode
The copy control state in the synchronous state during Replicate/Restore is displayed.
Display Description
Synchronous
Semi-synchronous
Background Copy
(xii) RV Mode
RV access restrictions are displayed. For more information, refer to 2.6 “RV Access
Restriction”.
Display Description
R/W Permit Indicates that the volume can be read and written from the host.
Read Only Indicates that the volume can be only read from the host.
Not Ready Indicates that the volume cannot be operated from the host.
Not Available Indicates that the volume cannot be operated from any host.
(xiii) Differential Quantity of Volume
Indicates the amount of difference after Separate (including the state right after pair setting) and
the amount of difference (the remaining amount) during synchronous execution.
Amount of difference may not change if I/O load is too heavy.
If a link failure occurs, amount of difference may not change. In this case, refer to 2.2.2 (2)
“Link fault” in the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for
Windows)”.
This mode completes copying to RV within the processing time of the command
for writing to MV.
This mode stops the command for writing to MV and immediately performs
copying to RV.
This mode performs copying to RV asynchronously after stopping the command
for writing to MV.
34
Page 43

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(xiv) Number of Pairs
Indicates the number of related pairs. This value is equal to “the number of volumes which make
up the pair link” minus 1.
An example of pair relations and Number of Pairs is shown below.
Number of Pairs Pair Relation
Some replication operations cannot be carried out while in the Replicate state, Restore state, or
Separate execution if the pair relation has multiple layers or if multiple RVs are connected to one
MV (Refer to the execution conditions of the operations). If the Number of Pairs is 2 or greater,
check the hierarchy in the Connection screen.
(xv) Capacity [GB]
Indicates the capacity of the logical disk.
(xvi) L D Se t Na me
Indicates the name of the LD Set to which the volume belongs.
(xvii) ATgroup Name
Indicates the name of the AT-group to which the volume belongs.
* For details on the AT-group, refer to the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Disaster Recovery
System Installation and Operation Guide)”.
1
2
2
35
Page 44

Chapter 3 Replication Management
3
.
2
.
4
D
i
s
k
A
r
r
3
.
2
.
4
D
i
s
k
3
.
2
.
4
D
When you click the [Disk Array LINK Information] tab in the information list display area, the link
information currently set between the disk arrays is displayed (refer to Figure 3-4 “Example of Disk
Array LINK Information Screen”).
To perform sort, click the item name by which you want to sort. You can drag&drop an item to
permute the order of the items.
i
s
k
A
A
a
r
r
r
r
a
a
y
y
y
L
I
N
K
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
S
c
r
e
e
n
L
I
N
K
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
S
c
r
L
I
N
K
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
S
c
e
r
e
e
e
n
n
Figure 3-4 Example of Disk Array LINK Information Screen
The Disk Array LINK Information screen displays information regarding the following items.
(i) LINK Number
Indicates the number of the linked disk arrays. The link number "0" is allocated to the first disk
array, and "1" to the second disk array (refer to Figure 3-5 “Replication Link Information”). The
icon shows the following path status.
Icon Description
(Green)
(Gray)
(Light Blue)
(Red)
Indicates the status of normal or link checking.
Indicates the offline status.
Indicates the status that the data replication function is frozen.
Indicates that a fault occurs.
36
Page 45

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(ii) LINK Disk Array Name
Indicates the identification name assigned to the linked disk array.
(iii) Path Number
Indicates the connection path number in the link.
If the link is connected via four paths, the path numbers are 0, 1, 2, and 3, respectively (refer to
Figure 3-5 “Replication Link Information”).
(iv) Path State
Display Description
Normal Indicates the normal status.
Offline Indicates that the link setting is unconfirmed during startup of the disk array.
Freeze Indicates that the Data Replication function in the target disk array is frozen.
Link Checking
Fault Indicates that the link is invalid due to a failure of communication in the link.
(v) Director Number
Indicates the replication director number (host director for the S2400 and 2800 series) that the link
is set.
Indicates that the link status is being checked due to a failure of communication
in the link. It transits to Normal or Fault after a certain time interval.
37
Page 46

Chapter 3 Replication Management
r
r
Figure 3-5 shows an example of two disk arrays connected to Disk Array 1 for using RDR. The
following shows an example of 3000/4000 series.
Director Number
Disk Array 1
Replication Director
Port Numbe
#05h
#0dh
#11h
Path Numbe
#0
#1
#0
#0
#1
#1
Path #00h
Path #01h
Path #02h
Path #03h
Path #00h
Path #01h
#00h
#01h
Figure 3-5 Replication Link Information
Disk Array 2
Disk Array 3
LINK Number
38
Page 47

Chapter 3 Replication Management
3
.
2
.
5
M
e
n
u
I
t
e
m
L
i
s
t
3
.
2
.
5
M
e
n
u
I
t
e
m
3
.
2
.
5
M
e
n
u
I
t
e
The list of menu bar items of Replication Management is shown below. For details, refer to
description on each menu item.
m
L
i
s
t
L
i
s
t
3.3.13 “CSV Output of Information List Display”
3.3.14 “Save Pair Setting Information”
Closes the Replication screen.
Shows or hides the status bar.
Shows or hides IVs.
3.4.8 “Display Copy Fault List”
3.4.5 “Record Screen Information”
3.4.3 “Environment Setting”
3.3.12 “Displaying Volume Connection State”
(when “Connection Screen” is displayed)
3.4.6 “Display Disk Array Properties” (when
Disk Array is selected from configuration
display area and “Properties” is displayed)
3.4.7 “Display Link Properties” (when
Director Port is selected from Disk Array
LINK Information Screen and “Properties” is
displayed)
3.4.4 “Refresh”
3.3.1 “Pair Setting/Unpair”
3.3.1 “Pair Setting/Unpair”
3.3.2 “Replicate”
3.3.3 “Separate”
3.3.4 “Restore”
3.3.5 “Suspend/Resume Copy”
3.3.5 “Suspend/Resume Copy”
3.3.6 “Change to Background Copy”
3.3.7 “RV Mode Change”
39
Page 48

Chapter 3 Replication Management
3.3.8 “Forced Separate”
3.3.9 “Forced Unpair”
3.3.10 “Freeze/Defreeze”
3.3.11 “Background Copy Level Change”
For details on operations related to the
AT-group, refer to the “Data Replication
User’s Manual (Disaster Recovery
System Installation and Operation
Guide)”.
Displays Help on the Replication screen.
Displays Help on the dialog list
regarding Replication screen.
40
Page 49

Chapter 3 Replication Management
3
.
2
.
6
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
D
i
s
p
l
a
y
e
d
o
n
3
.
2
.
6
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
D
i
s
p
l
a
y
e
d
3
.
2
.
6
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
D
i
s
p
l
a
D
i
a
l
o
g
D
i
a
D
i
a
The Execution dialog displayed for replication operations can be switched to [Summary] or [Details]
display mode for the volume-related information displayed.
In the description given below, the unpair execution dialog is used as an example. You can read
“operation” in the description as “Replicate”, “Restore”, etc. to be carried out.
Figure 3-6 shows an example of an Execution dialog information screen.
Items added when [Details] is selected
l
o
g
l
o
g
y
e
d
o
o
n
n
E
E
E
x
x
x
e
e
e
c
c
c
u
u
u
t
i
o
n
t
t
i
o
n
i
o
n
Figure 3-6 Example of Execution Dialog Information Screen
Information on the following items is displayed on the information screen of the execution dialog.
* Items (v), (vi), and (vii) are displayed only when [Details] is selected.
(i) Execution Result
Displays the execution result of the operation. Operation cannot be performed for a pair with
“Unexecutable”.
After the operation is executed, the execution results for the operation are displayed. To check
on the progress after the operation, close the execution dialog and check the progress on the
Connection Screen.
(ii) Unexecutable Information
Displays the reason why operation cannot be performed.
(iii) Activity State
Displays the execution state of the pair.
41
Page 50

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(iv) Logical Disk Name
Displays the logical disk name of MV.
(v) Copy Control State
Displays the control state during copy.
(vi) Sync State
Displays the transition status in the activity state.
(vii) Copy Mode
Displays the Synchronous/Semi-synchronous mode during copy operation.
(viii) Number
Displays the logical disk number of MV.
(ix) MV Disk Array Name
Displays the disk array name to which MV belongs.
(x) Pair Disk Name
Displays the logical disk name of RV.
(xi) Pair Number
Displays the logical disk number of RV.
(xii) RV Disk Array Name
Displays the disk array name to which RV belongs.
(xiii) ATgroup Name
Displays the name of the AT-group to which the volume belongs.
42
Page 51

Chapter 3 Replication Management
3
.
3
V
a
r
i
o
u
s
O
p
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
s
o
f
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
3
.
3
V
a
r
i
o
u
s
O
p
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
s
o
f
R
e
p
l
i
c
3
.
3
V
a
r
i
o
u
s
O
p
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
s
o
f
R
e
p
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t
M
a
n
a
g
e
M
a
n
a
3
.
3
.
1
P
a
i
r
3
.
3
.
1
1
P
P
PV
PV
3
.
3
.
To perform replication operations, you must set pairs beforehand.
To set a pair, set the original volume as MV and the target volume as RV. You can also use the
volume you have set as RV in another pair by setting it as MV.
You can set pairs freely within the following bounds.
• You can set up to three volumes of RVs (dRVs) or up to four volumes of RVs (including rRV) for
one MV at the same time.
• You can set RVs in up to 2 disk arrays for one PV.
• You can set DynamicDataReplication only for one layer in the disk array.
• You can set a pair only when the two volumes have the same capacity.
Figure 3-7 shows an example of the pair setting.
You may want to specify multiple pairs simultaneously, for example, when you initially build or rebuild
a replication environment. To specify pair environments at a time, use “Replication Setting” of “New
Setting” which is one of the configuration setting functions. For details, refer to the “Configuration
Setting Tool User’s Manual (GUI)” and 3.4.2 “Save Pair Setting Information”.
a
a
MV
MV
i
r
i
r
m
g
e
m
S
e
t
t
i
S
S
n
e
t
t
i
n
e
t
t
i
n
RV
MV
RV
RV
Figure 3-7 Example of Pair Setting
e
e
g
g
g
n
n
/
/
/
U
U
U
t
t
n
p
a
i
r
a
a
i
r
i
r
RV
n
n
p
p
a
l
i
c
a
n
t
i
o
n
t
i
o
n
43
Page 52

Chapter 3 Replication Management
[Operation Procedure]
Pair Setting
Do one of the following to display the Pair Setting screen.
y Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, and then select [Pair Setting].
y Right-click in the Replication Information screen, and then select [Pair Setting].
In pair setting, whether the selected volume can be set as MV is determined automatically. If the
selected volume is a volume for which pair setting cannot be performed as MV, the following prompt
appears.
Figure 3-8 Confirmation Screen
The possible causes are as follows:
Unexecutable condition Description
DDR/RDR
DDR
RDR
After checking the message, click the [Yes] button to display the Pair Setting screen. To select a
volume again on the Replication Information screen, click the [No] button.
Due to the description of the reason, the volume cannot be set as MV of
DDR and RDR.
Due to the description of the reason, the volume cannot be set as MV of
DDR.
Due to the description of the reason, the volume cannot be set as MV of
RDR.
44
Page 53

Figure 3-9 shows an example of the Pair Setting Screen.
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
Chapter 3 Replication Management
Figure 3-9 Example of Pair Setting Screen
After the Pair Setting, the copy operation such as Replicate, Restore etc. is available.
(i) Data Replication Mode
Select the method of setting pairs.
Radio Button Description
Dynamic Data Replication (within a Disk
Array)
Remote Data Replication (between Disk
Arrays)
(ii) Disk Array Name
On the MV part, displays the disk array name with the selected volume.
On the RV part, displays the disk array name for which pair setting of remote data replication
can be performed.
(iii) Object
To make only the selected volume the object of MV, check this (default).
To make all the volumes that can be used as MV the objects, uncheck this.
(iv) LD Set Name
You can narrow down object volumes for which pair setting can be performed by the LD Set
Name.
When the object volume for which pair setting can be performed is not registered in the LD
Set, LD Set Name cannot be used for narrowing down nor selected.
MV and RV use the volumes in the same Disk
Array.
MV and RV use the volumes in different Disk
Arrays.
45
Page 54

Chapter 3 Replication Management
d
N
d
ALL : All volumes become selectable objects.
LD Set Name : Volumes registered in the selected LD Set become selectable objects.
Undefined : Volumes not registered in the LD Set become selectable objects.
(v) Logical Disk
Select the Logical Disk which you want to set.
When you click the [Execute] button, the following message is displayed.
(i)
(ii)
Figure 3-10 Confirmation Screen
Unpair
Do one of the following to display the Unpair screen.
y Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, and then select [Unpair].
y Right-click in the Replication Information screen, and then select [Unpair].
Figure 3-11 shows an example of the Unpair screen.
Selecte
ot selecte
Cannot be
selected
Figure 3-11 Example of Unpair Screen
46
Page 55

Chapter 3 Replication Management
From the list, select a pair you want to unpair, and then click the [Execute] button.
You can select multiple executable pairs and execute them in a batch.
Unexecutable pairs cannot be selected.
(i) Selected Volume List
Displays the list of the pair (MV/RV) information selected in the Replication Information screen.
Volumes whose Execution Result is “Unexecutable” cannot be selected because they do not
satisfy the execution conditions.
For the “Unexecutable” volumes, do the following by referring to the Unexecutable Information.
Unexecutable Information Measure
Have Unpaired Execute it for a volume with the pair setting.
Replicated Change it to the Separated state and execute it again.
Restored Change it to the Separated state and execute it again.
Separating Execute it again in the Separated state.
Freeze Defreeze the Data Replication function and execute it again.
MV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for RV.
MV Monitoring
Suspended
RV Monitoring
Suspended
RV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for MV.
MV Outside iSM
Management
All Link Path Abnormal
Have been registered to
ATgroup
(ii) Summary Display/Details Display
For more information on this item, refer to 3.2.6 “Information Displayed on Execution Dialog”.
When you click the [Execute] button, the following message is displayed.
Change the disk array of MV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Change the disk array of RV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Execute it for a pair under the iSM management.
Refer to 2.2.2 (2) “Link fault” in the “Data Replication User’s
Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” to recover
from the failure.
Execute it for a pair that is not registered in the AT-group.
Or, execute it after deleting a volume from the AT-group.
Figure 3-12 Confirmation Screen
47
Page 56

Chapter 3 Replication Management
[Execution Conditions]
To Pair setting or Unpair, the following conditions must be satisfied.
Conditions for Pair setting
Volumes in which the pair setting is performed must satisfy the following conditions.
(i) The volume capacities of MV and RV match.
(ii) The specified RV is not set as RV for another pair.
(iii) If the specified MV is set as MV for another pair, the maximum number of simultaneous pairs is
not exceeded.
(iv) The volume formats match.
(v) The pair hierarchy does not form any loop.
(vi) When MV and RV exist in the same disk array and if RV is used to set another pair, a volume in
another disk array is specified.
(vii) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is monitored.
(viii) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is not in the Freeze state.
(ix) If the specified MV is registered in the AT-group, the MV and the specified RV are set as a DDR
pair.
(x) A volume having snapshot attributes other than BV is not set as MV.
(xi) A volume having snapshot attributes is not set as RV.
Do not execute Pair Setting for a reserved volume of the business server or for a volume specified as
a performance optimization work disk. The replication screen does not display the Volume List.
Conditions for Unpair
Volumes for unpair must satisfy the following conditions.
(i) The specified MV and RV are paired.
(ii) The specified MV and RV are in the Separated state.
(iii) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is monitored.
(iv) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is not in the Freeze state.
(v) The specified MV is not registered in the AT-group.
48
Page 57

Chapter 3 Replication Management
RV unmounted by the ReplicationControl function from a business server or backup server of
Windows may be set in the Not Ready state. In this case, even if the synchronous state of the pair
is “separated”, the RV mode is kept in the Not Ready state.
Make sure to change the RV set in the Not Ready state to the R/W Permit state by “RV mode
change” operation prior to unpair with the exception of the case where the logical disk of RV is used
by a business server or backup server in succession after unpair.
49
Page 58

Chapter 3 Replication Management
N
3
.
3
.
2
R
e
p
l
i
c
a
t
3
.
3
.
2
R
e
p
l
3
.
3
.
2
R
When you perform Replicate for volumes with the pair setting, copy from MV to RV starts.
[Operation Procedure]
Do one of the following to display the Replicate screen.
• Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select [Replicate].
• Right-click in the Replication Information screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select
[Replicate].
Figure 3-13 shows an example of the Replicate screen.
e
p
i
l
e
c
a
t
i
c
a
t
e
e
Cannot be
selected
(i)
(ii)
Selected
ot selected
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
Figure 3-13 Example of Replicate Screen
From the list, select a pair for which you want to perform the operation, and then click the [Execute]
button.
You can select multiple executable pairs and execute them in a batch.
Unexecutable pairs cannot be selected.
(i) Selected Volume List
Displays the list of the pair (MV/RV) information selected in the Replication Information screen.
Volumes whose Execution Result is “Unexecutable” cannot be selected because they do not
satisfy the execution conditions.
50
Page 59

Chapter 3 Replication Management
For the “Unexecutable” volumes, do the following by referring to the Unexecutable Information.
Unexecutable Information Measure
Have Unpaired Execute it for a volume with the pair setting.
Replicated Execute it for a volume in the Separate state.
Restored Execute it for a volume in the Separate state.
Being replicated by
other pair
Being restored by other
pair
Freeze Defreeze the Data Replication function and execute it again.
Being separated by other
pair
MV Monitoring
Suspended
RV Monitoring
Suspended
MV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for RV.
RV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for MV.
MV Outside iSM
Management
All Link Path Abnormal
Have been registered to
ATgroup
Snapshotting Execute it for a pair that is not operating snapshot.
Replicate is being executed in another layer. Execute it again after
Separate is complete.
Restore is being executed in another layer. Execute it again after
Separate is complete.
Separate is being executed in another layer. Execute it again after
Separate is complete.
Change the disk array of MV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Change the disk array of RV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Execute it for a pair under the iSM management.
Refer to 2.2.2 (2) “Link fault” in the “Data Replication User’s
Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” to recover
from the failure.
Execute it for a pair that is not registered in the AT-group.
(ii) Summary Display/Details Display
For more information on this item, refer to 3.2.6 “Information Displayed on Execution Dialog”.
(iii) Range
Normally, Only Difference is selected, which copies only the difference area of MV and RV.
You can also select All, which copies the entire area explicitly.
Radio Button Description
Only Difference Copies only the difference of the volumes.
All Copies the entire volume.
51
Page 60

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(iv) Copy Mode
You can specify the copy control state in Replicate Execution and the Synchronous state at the
same time as Replicate. The following copy modes can be specified.
Radio Button Description
Synchronous
Semi-synchronous
Background Copy
(v) RV Status
Specifies the access restrictions from the host until Replicate is complete.
Radio Button Description
Not Ready Operations for the volume cannot be performed from the host.
Read Only For the volume, only read can be performed from the host.
* Care should be taken to specify Read Only. Refer to 2.6 “RV Access Restriction”.
When you click the [Execute] button, the following message is displayed.
Changes the copy control state to the foreground copy
(Synchronous) mode.
Changes the copy control state to the foreground copy
(Semi-synchronous) mode. This can be specified for pairs
in different disk arrays.
Changes the copy control state to the Background Copy
state.
Figure 3-14 Confirmation Screen
[Execution Conditions]
To perform Replicate, the following conditions must be satisfied.
(i) The target MV is recognized by Replication Management as the Replication target disk.
(ii) The target MV and RV are paired.
(iii) The activity state of the target pair is Separate.
(iv) The Semi-synchronous Copy mode cannot be specified for pairs set in the same disk array.
The Semi-synchronous Copy mode can be specified only for pairs set in different disk arrays.
(v) The pair of the specified MV and the paired RV pair are not in the Restore state.
52
Page 61

(vi) The activity state of the pair of the specified MV and the paired upper MV is not in the Restore
state.
(vii) The activity state of the pair of the specified RV and the paired lower RV is not in the Restore
state.
(viii) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is not Freeze state.
(ix) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is monitored.
(x) The RV has been unmounted from the host.
(xi) The specified MV is not registered in the AT-group.
(xii) Separate is not being performed between the upper volume and the lower volume that are paired.
(xiii) Snapshot is not in operation.
Figure 3-15 illustrates the execution conditions of Replicate. (Each of (i) to (xiii) in the figure
corresponds to the respective number above.)
(vi) Not in the Restore state
(xii) Separate is not being
performed between the
upper volume and the
lower volume that are
paired.
(v) Not in the Restore state
(xiii) Snapshot is not in operation.
MV
Chapter 3 Replication Management
Target Pair
RV
MV
Target Pair
MV
Target Pair
MV
BV
Figure 3-15 Execution Conditions of Replicate
RV
SV
RV
MV
RV
RV
RV
(vii) Not in the Restore state
(xii) Separate is not being
(i) Replication Target Disk
(ii) Pair Setting
(iii) Separated
(iv) Semi-synchronous not
allowed for the same disk
array
(viii) Not in the Freeze state
(ix) Disk array monitored
(x) RV is unmounted from the
host.
(xi) The specified MV is not
registered in the AT-group.
performed between the
upper volume and the lower
volume that are paired.
53
Page 62

Chapter 3 Replication Management
N
d
3
.
3
.
3
S
e
p
a
r
a
t
3
.
3
.
3
S
e
p
3
.
3
.
3
S
If Separate is performed for paired volumes, MV is separated from RV and RV is made available. RV
cannot be reused until Separate is completed. However, it can be used for Separate(immediate).
[Operation Procedure]
Do one of the following to display the Separate screen.
• Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select [Separate].
• Right-click in the Replication Information screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select
[Separate].
Figure 3-16 shows an example of the Separate screen.
e
p
a
a
e
r
a
t
e
r
a
t
e
(i)
(ii)
Selected
Cannot be
selected
ot selecte
(iii)
(iv)
Figure 3-16 Example of Separate Screen
From the list, select a pair for which you want to perform the operation, and then click the [Execute]
button.
You can select multiple executable pairs and execute them in a batch.
Unexecutable pairs cannot be selected.
54
Page 63

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(i) Selected Volume List
Displays the list of the pair (MV/RV) information selected in the Replication Information screen.
Volumes whose Execution Result is “Unexecutable” cannot be selected because they do not
satisfy the execution conditions.
For the “Unexecutable” volumes, do the following by referring to the Unexecutable Information.
Unexecutable Information Measure
Have Unpaired Execute it for a volume with a volume of the Synchronous state.
Separated Execute it for a volume in the Synchronous state.
Restoring Execute it again when Restored is completed.
Suspend State Execute it again in the Synchronous state after copy is resumed.
Abnormal Suspend
Freeze Defreeze the Data Replication function and execute it again.
MV Monitoring
Suspended
RV Monitoring
Suspended
MV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for RV.
RV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for MV.
RV Forced Separate Execute it for a volume in the Synchronous state.
MV Outside iSM
Management
All Link Path Abnormal
Have been registered to
ATgroup
(ii) Summary Display/Details Display
For more information on this item, refer to 3.2.6 “Information Displayed on Execution Dialog”.
Refer to 2.2.2 “HW Fault Unique to Replication” in the “Data
Replication User’s Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for
Windows)” to recover from the failure.
Change the disk array of MV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Change the disk array of RV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Execute it for a pair under the iSM management.
Refer to 2.2.2 (2) “Link fault” in the “Data Replication User’s
Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” to recover
from the failure.
Execute it for a pair that is not registered in the AT-group.
55
Page 64

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(iii) RV Use Start Time
Determine when to make the RV available.
Radio Button Description
Separate End
Separate Start
* DynamicDataReplication Ver2 needs to be installed for using this function. The function is
available only for paired volumes in the same disk array.
(iv) Separated RV Status
Specifies the operation in response to a write request from the host after Separate is complete.
Radio Button Description
R/W Permit
Read Only Only read can be performed for a separated RV is complete from the host.
When you click the [Execute] button, the following message is displayed.
After Separate execution, the RV becomes available when the difference
between the MV and RV contents has been reflected into the RV
(Separate(completion)).
After Separate execution, the RV is immediately available while the
difference between the MV and RV contents is being reflected into the RV
(Separate(immediate)).
Read and write can be performed for a separated RV is complete from the
host.
Figure 3-17 Confirmation Screen
[Execution Conditions]
To perform Separate, the following conditions must be satisfied. RV cannot be reused until Separate
is completed. However, it can be used for Separate(completion).
(i) The target MV is recognized by Replication Management as the Replication target disk.
(ii) The target MV and RV are paired.
(iii) The target pair is not in the Restore Execution state.
(iv) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is not in the Freeze state.
(v) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is monitored.
(vi) The MV is unmounted from the host.
(vii) The specified MV is not registered in the AT-group.
(viii) Separate is not being performed between the upper volume and the lower volume that are paired.
56
Page 65

Chapter 3 Replication Management
Figure 3-18 illustrates the execution conditions of Separate. (Each of (i) to (viii) in the figure
corresponds to the respective number above.)
(i) Replication Target Disk
(ii) Pair Setting
(iii) Not in Restore execution
(iv) Not in the Freeze state
(v) Disk array monitored
(vi) MV is unmounted from the host.
(vii) The specified MV is not registered in the
Target Pair
MV
RV
Figure 3-18 Execution Conditions of Separate
AT-group.
(viii) Separate is not being performed
between the upper volume and the lower
volume that are paired.
57
Page 66

Chapter 3 Replication Management
N
3
.
3
.
4
R
e
s
t
o
r
e
3
.
3
.
4
R
e
s
3
.
3
.
4
R
When you perform Restore for volumes with the pair setting, copy from RV to MV starts.
[Operation Procedure]
Do one of the following to display the Restore screen.
• Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select [Restore].
• Right-click in the Replication Information screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select
[Restore].
Figure 3-19 shows an example of the Restore screen.
e
s
t
t
o
o
r
e
r
e
Selected
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
Figure 3-19 Example of Restore Screen
From the list, select a pair for which you want to perform the operation, and then click the [Execute]
button.
You can select multiple executable pairs and execute them in a batch.
Unexecutable pairs cannot be selected.
ot selected
Cannot be
selected
58
Page 67

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(i) Selected Volume List
Displays the list of the pair (MV/RV) information selected in the Replication Information screen.
Volumes whose Execution Result is “Unexecutable” cannot be selected because they do not
satisfy the execution conditions.
For the “Unexecutable” volumes, do the following by referring to the Unexecutable Information.
Unexecutable Information Measure
Have Unpaired Execute it for a volume with the pair setting.
Replicated Execute it for a volume in the Separate state.
Restored Execute it for a volume in the Separate state.
Being replicated by
other pair
Being restored by other
pair
Separating Execute it again in the Separated state.
Freeze Defreeze the Data Replication function and execute it again.
Being separated by other
pair
MV Monitoring
Suspended
RV Monitoring
Suspended
MV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for RV.
RV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for MV.
MV Outside iSM
Management
All Link Path Abnormal
Have been registered to
ATgroup
Replicate is being executed in another layer. Execute it again after
Separate is complete.
Restore is being executed in another layer. Execute it again after
Separate is complete.
Separate is being executed in another layer. Execute it again after
Separate is complete.
Change the disk array of MV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Change the disk array of RV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Execute it for a pair under the iSM management.
Refer to 2.2.2 (2) “Link fault” in the “Data Replication User’s
Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” to recover
from the failure.
Execute it for a pair that is not registered in the AT-group.
Snapshotting Execute it for a pair not in snapshot operation.
(ii) Summary Display/Details Display
For more information on this item, refer to 3.2.6 “Information Displayed on Execution Dialog”.
59
Page 68

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(iii) Active Mode
Specify a Restore operation mode.
Radio Button Description
RV Protection
RV Update Performs restoration while reflecting the updated data of the MV into the RV.
The default operation mode in (iii) is “RV Protection”.
Confirm the Restore operation mode before executing Restore.
“RV Update” needs to be selected for executing Restore in the same operation mode as for
Version1.4 or earlier.
If “RV Protection” is selected, selection of (v) Copy mode is not permitted.
(iv) Range
Normally, Only Difference is selected, which copies only the difference area of MV and RV.
You can also select All, which copies the entire area explicitly.
Radio Button Description
Performs restoration without reflecting the updated data of the MV into the
RV.
When the restoration is completed, Separate is automatically executed.
* To use this function for paired volumes located in the same disk array,
the DynamicDataReplication Ver2 is necessary, and to use this function
for paired volumes located in different disk arrays, the
RemoteDataReplication Ver2 is necessary.
When the restoration is completed, the state changes to Synchronous State
(rst/sync).
Only Difference Copies only the difference of the volumes.
All Copies the entire volume.
(v) Copy Mode
You can specify the copy control state in Restore Execution and the Synchronous state at the same
time as Restore. The following copy modes can be specified.
Radio Button Description
Synchronous
Semi-synchronous
Background Copy Changes the copy control state to the Background Copy state.
Changes the copy control state to the foreground copy (Synchronous)
mode.
Changes the copy control state to the foreground copy (Semi-synchronous)
mode. This can be specified for pairs in different disk arrays.
60
Page 69

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(vi) RV Status
Specifies the access restrictions from the host until Restore is complete.
Radio Button Description
Not Ready Operations for the volume cannot be performed from the host.
Read Only For the volume, only read can be performed from the host.
* Care should be taken to specify Read Only. Refer to 2.6 “RV Access
Restriction”.
When you click the [Execute] button, the following message is displayed.
Figure 3-20 Confirmation Screen
[Execution Conditions]
To perform Restore, the following conditions must be satisfied.
(i) The target MV is recognized by Replication Management as the Replication target disk.
(ii) The target MV and RV are paired.
(iii) The activity state of the target pair is Separate, but not Separate Execution.
(iv) The Semi-synchronous Copy mode cannot be specified for pairs set in the same disk array.
The Semi-synchronous Copy mode can be specified only for pairs set in different disk arrays.
(v) The activity state of the pair of the specified MV and the paired RV is Separate.
(vi) The activity state of the pair of the specified MV and the paired upper MV is Separate.
(vii) The activity state of the pair of the specified RV and the paired lower RV is Separate.
(viii) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is not in the Freeze state.
(ix) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is monitored.
(x) The MV and RV are unmounted from the host.
(xi) The specified MV is not registered in the AT-group.
(xii) Separate is not being performed between the upper volume, the lower volume, and the derived
volume that are paired.
(xiii) Snapshot is not in operation.
61
Page 70

Chapter 3 Replication Management
Figure 3-21 illustrates the execution conditions of Restore. (Each of (i) to (xiii) in the figure
corresponds to the respective number above.)
(vi) Separated
(xii) Separate is not
being performed
for an upper
volume.
MV
Target Pair
RV
MV
RV
MV
RV
(i) Replication Target Disk
(ii) Pair Setting
(iii) Separated
(iv) Semi-synchronous not
allowed for the same disk
array
(viii) Not in the Freeze state
(ix) Disk array monitored
(x) MV and RV are
unmounted from the host.
(xi) The specified MV is not
registered in the
AT-group.
(v) Separated
(xii) Separate is not being
performed for a derived
pair.
(xiii) Snapshot is not in operation.
(vii) Separated
Target Pair
MV
Target Pair
MV
BV
RV
RV
RV
(xii) Separate is not being
performed for a lower pair.
SV
Figure 3-21 Execution Conditions of Restore
62
Page 71

Chapter 3 Replication Management
d
N
3
.
3
.
5
S
u
s
p
e
n
d
/
R
e
s
u
m
e
C
o
p
y
3
.
3
.
5
S
u
s
p
e
n
d
/
R
e
s
u
m
e
C
3
.
3
.
5
S
u
s
p
e
n
d
/
R
e
s
u
m
You can suspend and resume copy operation in the Replicate or Restore state.
[Operation Procedure]
Suspend Copy
The Foreground Copy or Background Copy state is changed to the Suspend Copy state.
Do one of the following to display the Suspend Copy screen.
• Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select [Suspend Copy].
• Right-click in the Replication Information screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select
[Suspend Copy].
Figure 3-22 shows an example of the Suspend Copy screen.
e
C
o
o
p
p
y
y
Cannot be
selecte
(i)
(ii)
Selected
ot selected
Figure 3-22 Example of Suspend Copy Screen
From the list, select a pair for which you want to perform the operation, and then click the
[Execute] button.
You can select multiple executable pairs and execute them in a batch.
Unexecutable pairs cannot be selected.
63
Page 72

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(i) Selected Volume List
Displays the list of the pair (MV/RV) information selected in the Replication Information screen.
Volumes whose Execution Result is “Unexecutable” cannot be selected because they do not
satisfy the execution conditions.
For the “Unexecutable” volumes, do the following by referring to the Unexecutable Information.
Unexecutable Information Measure
Have Unpaired Execute it for a volume with the pair setting.
Already Suspended Execute it for a volume in the Replicate state, Restore state.
Separate State Execute it for a volume in the Replicate state or Restore state.
Freeze Defreeze the Data Replication function and execute it again.
MV Monitoring
Suspended
MV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for RV.
RV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for MV.
RV Forced Separate Execute it for a volume in the Synchronous state.
MV Outside iSM
Management
All Link Path Abnormal
Have been registered to
ATgroup
(ii) Summary Display/Details Display
For more information on this item, refer to 3.2.6 “Information Displayed on Execution Dialog”.
Resume Copy
The Suspend Copy or Background Copy state is changed to the Foreground Copy state.
Do one of the following to display the Resume Copy screen.
• Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select [Resume Copy].
• Right-click in the Replication Information screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select
[Resume Copy].
Change the disk array of MV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Execute it for a pair under the iSM management.
Refer to 2.2.2 (2) “Link fault” in the “Data Replication User’s
Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” to recover
from the failure.
Execute it for a pair that is not registered in the AT-group.
64
Page 73

Chapter 3 Replication Management
d
N
Figure 3-23 shows an example of the Resume Copy screen.
ot
selected
(i)
(ii)
Cannot be
selected
Selecte
(iii)
Figure 3-23 Example of Resume Copy Screen
From the list, select a pair for which you want to perform the operation, and then click the
[Execute] button.
You can select multiple executable pairs and execute them in a batch.
Unexecutable pairs cannot be selected.
(i) Selected Volume List
Displays the list of the pair (MV/RV) information selected in the Replication Information screen.
Volumes whose Execution Result is “Unexecutable” cannot be selected because they do not
satisfy the execution conditions.
For the “Unexecutable” volumes, do the following by referring to the Unexecutable Information.
65
Page 74

Chapter 3 Replication Management
Unexecutable Information Measure
Have Unpaired Execute it for a volume with the pair setting.
Foreground Copy State Execute it for a volume in the Suspend state.
Separate State Execute it for a volume in the Suspend state.
Freeze Defreeze the Data Replication function and execute it again.
MV Monitoring
Suspended
RV Monitoring
Suspended
MV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for RV.
RV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for MV.
RV Forced Separate Execute it for a volume in the Synchronous state.
MV Outside iSM
Management
All Link Path Abnormal
Have been registered to
ATgroup
(ii) Summary Display/Details Display
For more information on this item, refer to 3.2.6 “Information Displayed on Execution Dialog”.
(iii) Copy Mode
You can specify the copy control state when copy is resumed.
The following copy modes can be specified.
Radio Button Description
Change the disk array of MV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Change the disk array of RV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Execute it for a pair under the iSM management.
Refer to 2.2.2 (2) “Link fault” in the “Data Replication User’s
Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” to recover
from the failure.
Execute it for a pair that is not registered in the AT-group.
Synchronous
Semi-synchronous
Background Copy Changes the copy control state to the Background Copy state.
When you click the [Execute] button, the following message is displayed.
Changes the copy control state to the foreground copy (Synchronous)
mode.
Changes the copy control state to the foreground copy
(Semi-synchronous) mode. This can be specified for pairs in
different disk arrays.
Figure 3-24 Confirmation Screen
66
Page 75

Chapter 3 Replication Management
[Execution Conditions]
To perform operations of suspending/resuming copy, the following conditions must be satisfied.
(i) The target MV is recognized by Replication Management as the Replication target disk.
(ii) The target MV and RV are paired.
(iii) The activity state of the target pair is Replicate or Restore.
(iv) The Semi-synchronous Copy mode cannot be specified for pairs set in the same disk array.
The Semi-synchronous Copy mode can be specified only for pairs set in different disk arrays. (Can
be set only when copy is resumed.)
(v) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is not in the Freeze state.
(vi) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is monitored.
(In case of copy suspend, MV must be monitored)
(vii) The specified MV is not registered in the AT-group.
Figure 3-25 illustrates the execution conditions of operations of suspending/resuming copy. (Each of
(i) to (vii) in the figure corresponds to the respective number above.)
Figure 3-25 Execution Conditions of Suspend Copy and Resume Copy State Operation
Target Pair
MV
RV
(i) Replication Target Disk
(ii) Pair Setting
(iii) Replicate or Restore
(iv) Semi-synchronous not allowed
for the same disk array
(v) Not in the Freeze state
(vi) Disk array monitored
(vii) The specified MV is not
registered in the AT-group.
67
Page 76

Chapter 3 Replication Management
N
d
3
.
3
.
6
C
h
a
n
g
e
3
.
3
.
6
C
h
a
3
.
3
.
6
C
The copy control state is changed from the Replicate or Restore state to the Background Copy state.
[Operation Procedure]
Do one of the following to display the Change to Background Copy screen.
• Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select [Change to Background Copy].
• Right-click in the Replication Information screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select
[Change to Background Copy].
Figure 3-26 shows an example of the Change to Background Copy screen.
h
a
n
n
g
g
e
e
t
o
B
a
c
k
g
r
o
u
n
d
C
o
p
y
t
o
B
a
c
k
g
r
o
u
n
d
C
t
o
B
a
c
k
g
r
o
u
n
d
C
o
o
p
p
y
y
(i)
(ii)
ot selecte
Selected
Cannot be
selected
Figure 3-26 Example of Change to Background Copy Screen
From the list, select a pair for which you want to perform the operation, and then click the [Execute]
button.
You can select multiple executable pairs and execute them in a batch.
Unexecutable pairs cannot be selected.
(i) Selected Volume List
Displays the list of the pair (MV/RV) information selected in the Replication Information screen.
Volumes whose Execution Result is “Unexecutable” cannot be selected because they do not
satisfy the execution conditions.
For the “Unexecutable” volumes, do the following by referring to the Unexecutable Information.
68
Page 77

Chapter 3 Replication Management
Unexecutable Information Measure
Have Unpaired Execute it for a volume with the pair setting.
Separate State Execute it for a volume in the Replicate state or Restore state.
Already Background Copy
State
Freeze Defreeze the Data Replication function and execute it again.
MV Monitoring Suspended
RV Monitoring Suspended
MV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for RV.
RV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for MV.
RV Forced Separate Execute it for a volume in the Synchronous state.
MV Outside iSM
Management
All Link Path Abnormal
Have been registered to
ATgroup
(ii) Summary Display/Details Display
For more information on this item, refer to 3.2.6 “Information Displayed on Execution Dialog”.
When you click the [Execute] button, the following message is displayed.
Execute it for a volume in Foreground Copy.
Change the disk array of MV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Change the disk array of RV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Execute it for a pair under the iSM management.
Refer to 2.2.2 (2) “Link fault” in the “Data Replication User’s Manual
(Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” to recover from the
failure.
Execute it for a pair that is not registered in the AT-group.
Figure 3-27 Confirmation Screen
[Execution Conditions]
To perform changes to Background Copy, the following conditions must be satisfied.
(i) The target MV and RV are recognized by Replication Management as the Replication target disk.
(ii) The target MV and RV are paired.
(iii) The activity state of the target pair is Replicate or Restore.
(iv) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is not in the Freeze state.
(v) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is monitored.
(vi) The specified MV is not registered in the AT-group.
69
Page 78

Chapter 3 Replication Management
Figure 3-28 illustrates the execution conditions of changes to Background Copy. (Each of (i) to (vi) in
the figure corresponds to the respective number above.)
Target Pair
MV
Figure 3-28 Execution Conditions of Change to Background Copy
RV
(i) Replication Target Disk
(ii) Pair Setting
(iii) Replicate or Restore
(iv) Not in the Freeze state
(v) Disk array monitored
(vi) The specified MV is not
registered in the AT-group.
70
Page 79

Chapter 3 Replication Management
N
3
.
3
.
7
R
V
M
o
d
e
C
h
a
n
g
e
3
.
3
.
7
R
V
M
o
d
e
C
h
a
3
.
3
.
7
R
V
M
o
d
e
C
You can change the RV access restriction.
[Operation Procedure]
Do one of the following to display the RV Mode Change screen.
• Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select [RV Mode Change].
• Right-click in the Replication Information screen, point to [Volume Operation], and then select [RV
Mode Change].
Figure 3-29 shows is an example of the RV Mode Change screen.
h
a
n
n
g
g
e
e
(i)
(ii)
ot selected
Selected
(iii)
Figure 3-29 Example of RV Mode Change Screen
From the list, select a pair for which you want to perform the operation, and then click the [Execute]
button.
You can select multiple executable pairs and execute them in a batch.
Unexecutable pairs cannot be selected.
71
Page 80

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(i) Selected Volume List
Displays the list of the pair (MV/RV) information selected in the Replication Information screen.
Volumes whose Execution Result is “Unexecutable” cannot be selected because they do not
satisfy the execution conditions.
For the “Unexecutable” volumes, do the following by referring to the Unexecutable Information.
Unexecutable Information Measure
Have Unpaired Execute it for a volume with the pair setting.
Freeze Defreeze the Data Replication function and execute it again.
RV Outside iSM
Management
RV Monitoring
Suspended
MV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for RV.
RV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for MV.
All Link Path Abnormal
Have been registered to
ATgroup
(ii) Summary Display/Details Display
For more information on this item, refer to 3.2.6 “Information Displayed on Execution Dialog”.
(iii) RV Status
Specifies the operations for a write request from the host.
Radio Button Description
R/W Permit Read and write can be performed for a volume from the host.
* This cannot be executed in Replicate, Restore, or Separate execution (Refer
to Figure 3-28 “Execution Conditions of Change to Background Copy”).
Execute it for a pair under the iSM management.
Change the disk array of RV to the Monitored state and execute it
again.
Refer to 2.2.2 (2) “Link fault” in the “Data Replication User’s
Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)” to recover
from the failure.
Execute it for a pair that is not registered in the AT-group.
Not Ready Operations for the volume cannot be performed from the host.
Read Only For a volume, only read from the host can be performed.
* Care should be taken to specify Read Only. Refer to 2.6 “RV Access
Restriction”.
Not Available For a volume, access from the host is disabled.
72
Page 81

Chapter 3 Replication Management
When you click the [Execute] button, the following message is displayed.
Figure 3-30 Confirmation Screen
When it is performed for a volume in Replicate, Restore, or Separate execution, the following warning
message is displayed and the change of the RV mode of the volume is cancelled.
Figure 3-31 Warning Screen
[Execution Conditions]
To change the RV mode, the following conditions must be satisfied.
(i) The target RV is recognized by Replication Management as the Replication target disk.
(ii) The target MV and RV are paired.
(iii) In the Separated state (when R/W Permit is specified).
(iv) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is not in the Freeze state.
(v) The disk array where the specified RV is stored is monitored.
(vi) The specified RV is not registered in the AT-group.
Figure 3-32 illustrates the execution conditions of change of the RV mode. (Each of (i) to (vi) in the
figure corresponds to the respective number above.)
(i) Replication Target Disk
(ii) Pair Setting
(iii) Separate state (when R/W
Permit is specified)
Target Pair
MV
Figure 3-32 Execution Conditions of Change of RV Mode
RV
(iv) Not in the Freeze state
(v) Disk array in RV monitored
(vi) The specified RV is not
73
-
Page 82

Chapter 3 Replication Management
N
3
.
3
.
8
F
o
r
c
e
d
3
.
3
.
8
F
o
r
3
.
3
.
8
When a failure occurs in the connection between disk arrays and the normal Separate cannot be
performed on MV and RV, you can use Forced Separate to instruct Separate to MV and RV
individually.
Forced Separate forcibly separates MV and RV and makes RV available.
[Operation Procedure]
Do one of the following to display the Forced Separate screen.
• Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, point to [Forced Operation], and then select [Forced Separate].
• Right-click in the Replication Information screen, point to [Forced Operation], and then select
[Forced Separate].
Figure 3-33 shows an example of the Forced Separate screen.
F
o
c
r
c
e
e
d
d
S
S
S
e
e
e
p
p
p
a
a
a
r
a
t
e
a
a
t
e
t
e
r
r
(i)
(ii)
Figure 3-33 Example of Forced Separate Screen
From the list, select a pair for which you want to perform the operation, and then click the [Execute]
button.
You can select multiple executable pairs and execute them in a batch.
Unexecutable pairs cannot be selected.
Selected
Cannot be
selected
ot selected
74
Page 83

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(i) Selected Volume List
Displays the list of the pair (MV/RV) information selected in the Replication Information screen.
Volumes whose Execution Result is “Unexecutable” cannot be selected because they do not
satisfy the execution conditions.
For the “Unexecutable” volumes, do the following by referring to the Unexecutable Information.
Unexecutable Information Measure
Have Unpaired Execute it for a volume with the pair setting.
Separated Execute it for a volume in the Synchronous state.
MV Separated Complete Execute it for a volume in the Synchronous state.
Forced Separation Execute it for a volume in the Synchronous state.
MV Forced Separate Execute it for a volume in the Synchronous state.
MV Fault
MV Outside iSM
Management
MV Monitoring
Suspended
MV Freeze
MV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for RV.
RV Separate Complete Execute it for a volume in the Synchronous state.
RV Forced Separate Execute it for a volume in the Synchronous state.
RV Outside iSM
Management
RV Monitoring
Suspended
RV Freeze
RV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for MV.
Have been registered to
ATgroup
Refer to 2.2.2 “HW Fault Unique to Replication” in the “Data
Replication User’s Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for
Windows)” to recover from the failure.
After execution of RV Forced Separate, perform Forced Separate for
the volume in MV with the pair setting.
After execution of RV Forced Separate, perform Forced Separate for
the volume in MV with the pair setting.
After execution of RV Forced Separate, perform Forced Separate for
the volume in MV with the pair setting.
After execution of MV Forced Separate, perform Forced Separate for
the volume in RV with the pair setting.
After execution of MV Forced Separate, perform Forced Separate for
the volume in RV with the pair setting.
After execution of MV Forced Separate, perform Forced Separate for
the volume in RV with the pair setting.
Execute it for a volume that is not registered in the AT-group.
(ii) Summary Display/Details Display
For more information on this item, refer to 3.2.6 “Information Displayed on Execution Dialog”.
75
Page 84

Chapter 3 Replication Management
Figure 3-34 is displayed when MV is not under the iSM. Figure 3-35 is displayed when RV is not
under the iSM.
After execution, perform Forced Separate for MV or RV not separated.
Figure 3-34 Warning Screen for MV without under iSM
Figure 3-35 Warning Screen for RV without under iSM
When you click the [Yes] button, the following message is displayed.
Figure 3-36 Confirmation Screen
76
Page 85

Chapter 3 Replication Management
[Execution Conditions]
To perform Forced Separate, the following conditions must be satisfied.
(i) The target volume is recognized by Replication Management as the Replication target disk.
(ii) The target MV and RV are paired, or one of them is forcibly separated.
(iii) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is not in the Freeze state.
(iv) The disk array where the specified volume is stored is monitored.
(v) The specified MV or RV is not registered in the AT-group.
Figure 3-37 illustrates the execution conditions of Forced Separate. (Each of (i) to (v) in the figure
corresponds to the respective number above.)
Target Pair
MV
RV
Figure 3-37 Execution Conditions of Forced Separate
(i) Replication Target Disk
(ii) Pair Setting
(iii) Not in the Freeze state
(iv) Disk array monitored
(v) The specified MV or RV is not
registered in the AT-group
77
Page 86

Chapter 3 Replication Management
N
3
.
3
.
9
F
o
r
c
e
d
3
.
3
.
9
F
o
r
3
.
3
.
9
When a failure occurs in the disk array of MV or RV, monitoring is suspended and the normal Cancel
Pair may not be performed. In such a case, you can use Forced Unpair to unpair the pairs for MV and
RV separately.
[Operation Procedure]
Before performing Forced Unpair, you must separate MV and RV with Separate or Forced Separate.
Do one of the following to display the Forced Unpair screen.
• Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, point to [Forced Operation], and then select [Forced Unpair].
• Right-click in the Replication Information screen, point to [Forced Operation], and then select
[Forced Unpair].
Figure 3-38 shows an example of the Forced Unpair screen.
F
o
c
r
c
e
e
d
d
U
U
U
n
n
n
p
p
p
a
a
a
i
r
i
r
i
r
(i)
(ii)
Selected
Cannot be
selected
Figure 3-38 Example of Forced Unpair Screen
From the list, select a pair for which you want to perform the operation, and then click the [Execute]
button.
You can select multiple executable pairs and execute them in a batch.
Unexecutable pairs cannot be selected.
ot selected
78
Page 87

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(i) Selected Volume List
Displays the list of the pair (MV/RV) information selected in the Replication Information screen.
Volumes whose Execution Result is “Unexecutable” cannot be selected because they do not
satisfy the execution conditions.
For the “Unexecutable” volumes, do the following by referring to the Unexecutable Information.
Unexecutable Information Measure
Have Unpaired Execute it for a volume with the pair setting.
Separating Execute it again in the Separated state.
MV Separating Execute it again in the Separated state.
Replicate Execute it for a volume in the Separate state.
MV Replicate Execute it for a volume in the Separate state.
Restore Execute it for a volume in the Separate state.
MV Restore Execute it for a volume in the Separate state.
MV Outside iSM
Management
MV Monitoring
Suspended
MV Freeze
MV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for RV.
RV Separating Execute it again in the Separated state.
RV Replicate Execute it for a volume in the Separate state.
RV Restore Execute it for a volume in the Separate state.
RV Outside iSM
Management
RV Monitoring Suspended
RV Freeze
RV Force Unpaired Perform Forced Unpair for MV.
Have been registered to
ATgroup
(ii) Summary Display/Details Display
For more information on this item, refer to 3.2.6 “Information Displayed on Execution Dialog”.
After execution of RV Forced Unpair, perform Forced unpair for
the volume in MV with the pair setting.
After execution of RV Forced Unpair, perform Forced unpair for
the volume in MV with the pair setting.
After execution of RV Forced Unpair, perform Forced unpair for
the volume in MV with the pair setting.
After execution of MV Forced Unpair, perform Forced unpair for
the volume in RV with the pair setting.
After execution of MV Forced Unpair, perform Forced unpair for
the volume in RV with the pair setting.
After execution of MV Forced Unpair, perform Forced unpair for
the volume in RV with the pair setting.
Execute it for a volume that is not registered in the AT-group.
79
Page 88

Chapter 3 Replication Management
If Forced Unpair is performed for either MV or RV, the replication operations will not function
properly because inconsistency occurs in the recognized states of MV and RV. In this case,
perform Forced Unpair for MV or RV for which Unpair is not performed.
Figure 3-39 is displayed when MV is not under the iSM. Figure 3-40 is displayed when RV is not
under the iSM.
Figure 3-39 Warning Screen for MV without under iSM
Figure 3-40 Warning Screen for RV without under iSM
When you click the [Yes] button, the following message is displayed.
Figure 3-41 Confirmation Screen
80
Page 89

Chapter 3 Replication Management
[Execution Conditions]
To perform Forced Unpair, the following conditions must be satisfied.
(i) The target volume is recognized by Replication Management as the Replication target disk.
(ii) The target MV and RV are paired, or one of them is forcibly unpaired.
(iii) The target pair is in the Separated or Forced Separate state.
(iv) The disk array where the specified MV and RV are stored is not in the Freeze state.
(v) The disk array where the specified volume is stored is monitored.
(vi) The specified MV or RV is not registered in the AT-group.
Figure 3-42 shows the execution conditions for Forced Unpair. (Each of (i) to (vi) in this figure
correspond to the respective number above.)
(i) Replication Target Disk
(ii) Pair Setting, or one of them is
forcibly unpaired.
(iii) Separated or Forced Separate
state
Target Pair
MV
RV
(iv) Not in the Freeze state
(v) Disk array monitored
(vi) The specified MV or RV is not
registered in the AT-group
Figure 3-42 Execution Conditions of Forced Unpair
81
Page 90

Chapter 3 Replication Management
3
.
3
.
1
0
F
r
e
e
z
e
/
3
.
3
.
1
0
F
r
e
3
.
3
.
1
0
You can freeze or defreeze the Data Replication function of the disk array.
[Operation Procedure]
Do one of the following to display the Freeze/Defreeze screen.
• Select the disk array in the configuration display area, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, point to [System Operation], and then select [Freeze/Defreeze].
• Select the disk array in the configuration display area, right-click it, and then select [Freeze/Defreeze].
Figure 3-43 shows an example of the Freeze/Defreeze screen.
F
e
r
e
e
z
z
e
e
/
/
D
D
D
e
e
e
f
r
e
e
z
e
e
e
z
z
e
e
f
r
e
f
r
e
Figure 3-43 Example of Freeze/Defreeze Screen
(i) Freeze/Defreeze Execute
Button Description
Freeze Freezes (invalidates) the Data Replication function of the disk array.
Defreeze Defreezes (validates) the Data Replication function of the disk array.
When you click the [Execute] button, the following message is displayed.
Figure 3-44 Confirmation Screen
82
Page 91

Chapter 3 Replication Management
[Execution Conditions]
To perform Freeze/Defreeze, the following conditions must be satisfied.
(i) The target disk array is recognized by Replication Management.
(ii) The specified disk array is monitored.
When you perform Freeze, no replication operations can be performed in the disk array. Refer to 2.8
“Freeze of Disk Arrays”.
3
.
3
.
1
1
B
a
c
k
g
r
o
u
n
d
C
o
p
y
L
e
v
e
l
C
h
a
n
g
e
3
.
3
.
1
1
B
a
c
k
g
r
o
u
n
d
C
o
p
y
L
e
v
e
l
C
h
a
3
.
3
.
1
1
B
a
c
k
g
r
o
u
n
d
C
o
p
y
L
e
v
e
l
C
You can change the priority of Background Copy of the disk array.
[Operation Procedure]
Do one of the following to display the Background Copy Level Change screen.
• Select the disk array in the configuration display area, click [Operation] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, point to [System Operation], and then select [Background Copy Level Change].
• Select the disk array in the configuration display area, right-click it, and then select [Background
Copy Level Change].
Figure 3-45 shows an example of the Background Copy Level Change screen.
h
a
n
n
g
g
e
e
Figure 3-45 Example of Background Copy Level Change Screen
83
Page 92

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(i) Background Copy Level
Specifies the priority of copy operation when Background Copy is selected in Replicate and
Restore.
A higher priority results in faster copying for reflecting difference. (For more information, refer
to 2.4 “Copy Control State”.)
• Return Default Value
Restores the default value of the disk array.
• Change
You can specify the priority of the disk array.
When you click the [Execute] button, the following message is displayed.
Figure 3-46 Confirmation Screen
[Execution Conditions]
To perform operations of the copy control state, the following conditions must be satisfied.
(i) The target disk array is recognized by Replication Management.
(ii) The specified disk array is monitored.
84
Page 93

Chapter 3 Replication Management
3
.
3
.
1
2
C
o
n
n
e
c
t
i
o
n
S
c
r
e
e
n
3
.
3
.
1
2
C
o
n
n
e
c
t
i
o
n
S
c
3
.
3
.
1
2
C
o
n
n
e
c
t
i
o
n
The connection state of the volume is displayed.
[Operation Procedure]
Do one of the following to display the Volume Connection screen.
y Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, point to [View] on the menu bar of the
Replication screen, and then select [Connection Screen].
y Select a volume in the Replication Information screen, right-click it, and then select [Connection
Screen].
y Double-click a volume in the Replication Information screen.
Figure 3-47 shows an example of the Connection screen.
r
S
c
r
e
e
e
e
n
n
(vi)
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
Figure 3-47 Example of Connection Screen
This screen displays the pair selected in the Replication Information screen. If two or more volumes
are selected, all of them are displayed.
85
Page 94

Chapter 3 Replication Management
(i) Disk Array Name
Displays the name of the disk array where the volume exists.
The disk array name of the selected volume is highlighted.
(ii) Logical Disk Number, Format, Logical Disk Name
Displays them in the form of “(logical disk number) format:logical disk name (or VAA)”.
The logical disk number, format, and logical disk name of the selected volume is highlighted.
(iii) Copy Progress
Displays the progress of copy. This display disappears when copy is complete.
Progress may not change if I/O load is too heavy.
If a link failure occurs, Progress may not change. In this case, refer to 2.2.2 (2) “Link fault” in
the “Data Replication User’s Manual (Installation and Operation Guide for Windows)”.
(iv) Access Restrictions for RV
Displays the access restrictions for RV. There are the following modes.
Mode Description
R/W Permit Read and write can be performed for a volume from the host.
Read Only Only read can be performed for a volume from the host.
Not Ready Operations for a volume cannot be operated from the host.
Not Available Operations for a volume cannot be operated from any host.
(v) Operation Time Display
Displays the Start Time and End Time when operation for a volume is performed.
Displays the transition time at the forced separation or fault occurrence.
Displays the estimate of remaining time before copy completion during Replicate, Restore, or
Separate. However, “-“ is displayed for the time if the disk array to which MV belongs is not
recognized by replication management.
* The time is displayed at the forced separation only on the RV side even if replication
management does not recognize the disk array to which MV belongs.
Note: The estimate of remaining time may not be correct because it changes according to the
monitoring timing, the units, the status of lines and so on.
(vi) Differential Quantity of Volume
Displays “remaining amount/transfer rate” during synchronization.
86
Page 95

Chapter 3 Replication Management
[Connection Display of Paired Volumes]
Connections of volumes are displayed as pipes as shown below.
During copy operation, the color of the original disk moves through the pipe.
y For DynamicDataReplication
Replicate is executed : Replicate is complete :
Restore is executed : Restore is complete :
Separate is executed : Separate is complete :
y For RemoteDataReplication
Replicate is executed : Replicate is complete :
Restore is executed : Restore is complete :
Separate is executed : Separate is complete :
87
Page 96

Chapter 3 Replication Management
[Differential Quantity of Volume/Transfer Rate]
Displays the amount of difference and transfer rate during copy operation.
The unit of the amount of difference is variable (e.g. KB, MB, GB), and the unit of transfer rate is fixed
(MB/S).
Example of Display (Replicate)
Amount of Difference Transfer Rate
When Replication is complete (Amount of Difference=0), Amount of Difference and Transfer Rate
(MB/S) disappears.
After Replicate is complete
[Volume Color]
The Volume Color changes by layer and it becomes the layer color immediately after setting the pair or
when Separate has completed.
When volume colors of the pair match, it indicates synchronization.
Layer color
(i) PV: Yellowish green
(ii) 1st Layer: Light blue
(iii) 2nd Layer: Blue
(iv) 3rd Layer: Yellow
Example of Display
Yellowish green Light blue Blue Yellow
PV 1st Layer 2nd Layer 3rd Layer
88
Page 97

Chapter 3 Replication Management
In the pair connected by RemoteDataReplication, the remote disk array is not managed by iSM or, in
a monitoring stop, may be displayed like the above.
In the pair connected by RemoteDataReplication, when Remote Volume cannot be recognized from
the host computer which Local Volume has connected by having performed Forced Unpair to
Remote Volume etc., it may display like the above.
Case of the 2nd layer or more layer pair composition, when Forced Unpair is performed to the
volume of the 1st layer or the 2nd layer, the volume of upper layers may not be displayed.
[Copy Progress]
Displays the progress of Replicate, Restore, etc. as the change in volume.
Example of Display 1: Replicate
Replicate Execution
Replicate is complete
Turns to the same color when
synchronized.
89
Page 98

Chapter 3 Replication Management
b
Example of Display 2: Separate during Replicate
Replicate Execution
Separate Execution
Separate is executed.
Separate is complete.
Turns to the layer color
ecause Separate is complete.
[Others]
You can perform the replication operations by right-clicking the volume in the Connection screen. For
how to operate, refer to the items in 3.3.
3.3.2 “Replicate”
3.3.3 “Separate”
3.3.4 “Restore”
3.3.5 “Suspend/Resume Copy”
3.3.5 “Suspend/Resume Copy”
3.3.6 “Change to Background Copy”
3.3.7 “RV Mode Change”
3.3.8 “Forced Separate”
90
Page 99

Chapter 3 Replication Management
3
.
3
.
1
3
C
S
V
O
u
t
p
u
t
o
f
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
L
i
s
t
3
.
3
.
1
3
C
S
V
O
u
t
p
u
t
o
f
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
3
.
3
.
1
3
C
S
V
O
u
t
p
u
t
o
f
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
D
i
s
p
l
a
y
D
i
s
p
D
i
s
p
The replication information, the disk array LINK Information, and the AT-group information for the
specified disk array can be output to a file in CSV format.
This CSV file can be used as a data for spreadsheet software.
On the menu bar, do the following:
• Click [File], and then click [CSV Output of Information List Display].
Figure 3-48 shows an example of the CSV Output of Information List Display screen.
l
a
y
l
a
y
o
n
L
L
i
s
t
i
s
t
Figure 3-48 Example of CSV Output of Information List Display Screen
91
Page 100

Chapter 3 Replication Management
[CSV File Containing Information Display List]
This section shows an example of the CSV file that is created by executing the CSV output of
information display list.
In this file, the information displayed on the screen is written in the format in which each item is
separated by commas.
An example of the CSV file
Classification, Number, OS Type, Logical Disk Name, Pair Number, Paired Disk Name, Activity
State, Disk Array, Sync State, Copy Control State, Copy Mode, RV Mode, Differential Quantity of
Volume, Number of Pairs, Capacity [GB], LD Set name, ATgroup name
IV,0000h,WN,driveWN0,,,,,,,,,,,4.2,,
MV,0001h,WN,driveWN1,0001h,driveWN2,Replicate,Storage4300,Synchronized,Foreground
Copy,,,0 KB,1,4.2,WN:wos1,ATG0
RV,0002h,WN,driveWN2,0000h,driveWN1,Replicate,Storage4300,Synchronized,Foreground
Copy,Not Ready,,0 KB,1,4.2,,
MV,0003h,WN,driveWN3,0004h,driveWN4,Replicate,Storage4300,Synchronized,Foreground
Copy,,,3.7GB,1,4.2,,
RV,0004h,WN,driveWN4,0003h,driveWN3,Replicate,Storage4300,Synchronized,Foreground
Copy,Not Ready,,3.7 GB,1,4.2,,
IV,0005h,WN,driveWN5,,,,,,,,,,,4.2,WN:wos1,ATG1
IV,0006h,WN,driveWN6,,,,,,,,,,,4.2,WN:wos1,ATG2
MV,0007h,WN,driveWN7,0008h,driveWN8,Restore,Storage4300,Synchronized,Foreground
Copy,,,0 KB,1,4.2,,
RV,0008h,WN,driveWN8,0007h,driveWN7,Restore,Storage4300,Synchronized,Foreground
Copy,Not Ready,,0 KB,1,4.2,,
MV,0009h,WN,driveWN9,000ah,driveWNa,Separate,Storage4300,Forced Separation,,,,0
KB,1,4.2,,
RV,000ah,WN,driveWNa,0009h,driveWN9,Separate,Storage4300,Forced Separation,,R/W
Permit,,0 KB,1,4.2,,
IV,000bh,WN,driveWNb,,,,,,,,,,,4.2,,
MV,000ch,WN,driveWNc,000dh,driveWNd,Separate,Storage4300,Separated,,,,0
KB,1,4.2,WN:wos1,ATG3
RV,000dh,WN,driveWNd,000ch,driveWNc,Separate,Storage4300,Separated,,R/W Permit,,0
KB,1,4.2,,
92
 Loading...
Loading...