NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR TL082CP, TL082CMX, TL082CM Datasheet
April 1998
TL082
Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
General Description
These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset
voltage (BI-FET II
current yet maintain a large gain bandwidth product and fast
slew rate. In addition, well matched high voltage JFET input
devices provide very low input bias and offset currents. The
TL082 is pin compatible with the standard LM1558 allowing
designers toimmediatelyupgradethe overall performance of
existing LM1558 and most LM358 designs.
These amplifiers may be used in applications such as high
speed integrators, fast D/A converters, sample and hold circuits and many other circuits requiring low input offset voltage, low input bias current, high input impedance, high slew
rate and wide bandwidth. The devices also exhibit low noise
and offset voltage drift.
™
technology). They require low supply
Features
n Internally trimmed offset voltage: 15 mV
n Low input bias current: 50 pA
n Low input noise voltage: 16nV/
n Low input noise current: 0.01 pA/
n Wide gain bandwidth: 4 MHz
n High slew rate: 13 V/µs
n Low supply current: 3.6 mA
n High input impedance: 10
n Low total harmonic distortion A
=
R
L
BW=20 Hz−20 kHz
n Low 1/f noise corner: 50 Hz
n Fast settling time to 0.01%:2µs
10k, V
=
O
20 Vp − p,
12
Ω
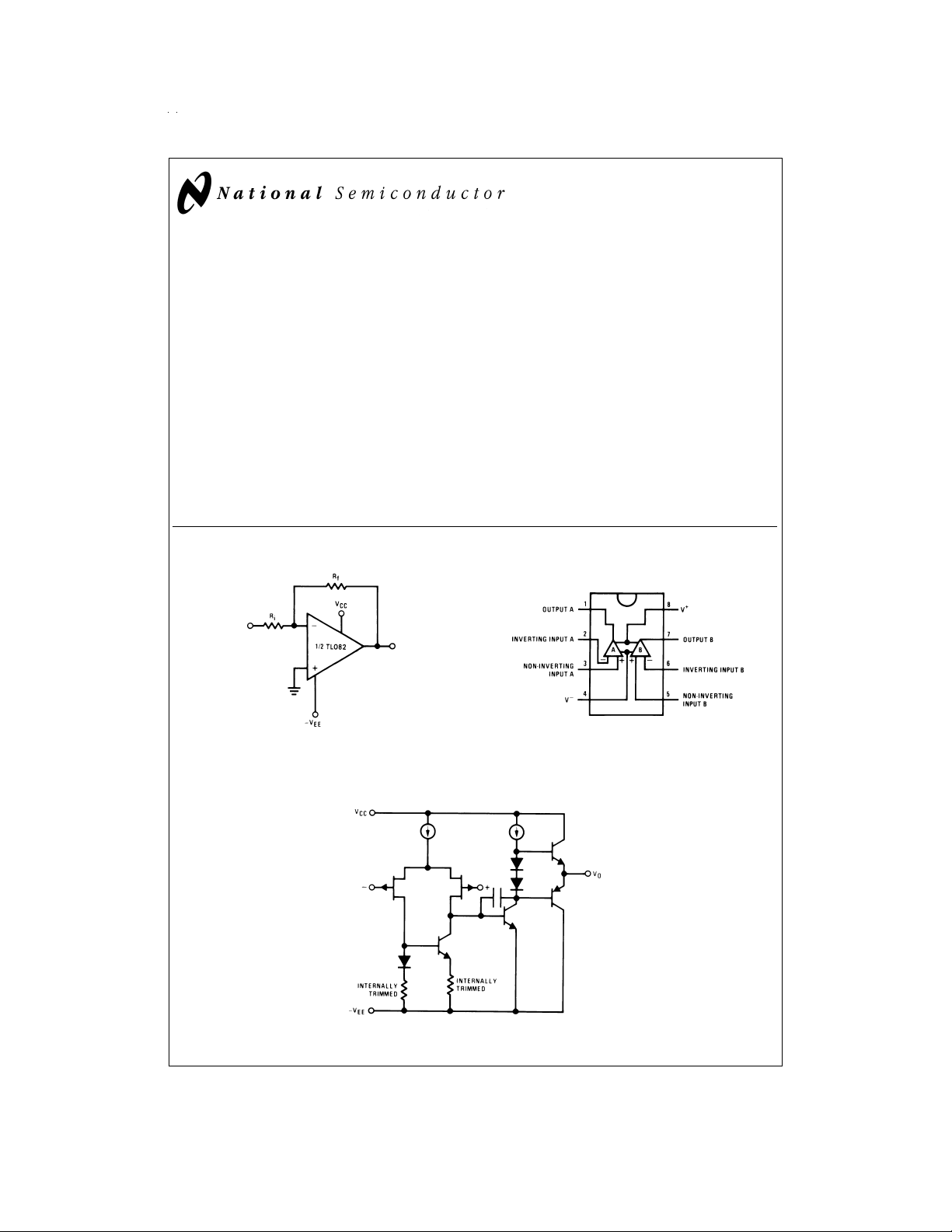
Typical Connection Connection Diagram
DIP/SO Package (Top View)
DS008357-1
Order Number TL082CM or TL082CP
See NS Package Number M08A or N08E
√
Hz
√
Hz
=
<
%
0.02
10,:
V
DS008357-3
Simplified Schematic
DS008357-2
BI-FET II™is a trademark of National Semiconductor Corp.
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS008357 www.national.com

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage
Power Dissipation (Note 2)
Operating Temperature Range 0˚C to +70˚C
T
j(MAX)
Differential Input Voltage
±
18V
150˚C
±
30V
Input Voltage Range (Note 3)
Output Short Circuit Duration Continuous
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temp. (Soldering, 10 seconds) 260˚C
ESD rating to be determined.
Note 1: “Absolute Maximum Ratings” indicate limits beyond which damage
to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the
device is functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits.
±
DC Electrical Characteristics (Note 5)
Symbol Parameter Conditions TL082C Units
Min Typ Max
V
OS
Input Offset Voltage R
=
S
10 kΩ,T
Over Temperature 20 mV
∆V
/∆T Average TC of Input Offset R
OS
=
10 kΩ 10 µV/˚C
S
Voltage
I
OS
I
B
R
IN
A
VOL
Input Offset Current T
Input Bias Current T
Input Resistance T
Large Signal Voltage Gain V
=
25˚C, (Notes 5, 6) 25 200 pA
j
T
≤ 70˚C 4 nA
j
=
25˚C, (Notes 5, 6) 50 400 pA
j
T
≤ 70˚C 8 nA
j
=
25˚C 10
j
=
±
S
=
±
V
O
Over Temperature 15 V/mV
=
V
O
V
CM
Output Voltage Swing V
Input Common-Mode Voltage V
±
S
=
±
S
Range −12 V
CMRR Common-Mode Rejection Ratio R
≤ 10 kΩ 70 100 dB
S
PSRR Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio (Note 7) 70 100 dB
I
S
Supply Current 3.6 5.6 mA
15V, T
10V, R
15V, R
15V
=
25˚C 5 15 mV
A
12
=
25˚C 25 100 V/mV
A
=
2kΩ
L
=
10 kΩ
L
±
±
±
12
13.5 V
11 +15 V
15V
Ω
AC Electrical Characteristics (Note 5)
Symbol Parameter Conditions TL082C Units
Min Typ Max
Amplifier to Amplifier Coupling T
SR Slew Rate V
GBW Gain Bandwidth Product V
e
n
i
n
Note 2: For operating at elevated temperature, the device must be derated based on a thermal resistance of 115˚C/W junction to ambient for the N package.
Note 3: Unless otherwise specified the absolute maximum negative input voltage is equal to the negative power supply voltage.
Note 4: The power dissipation limit, however, cannot be exceeded.
Note 5: These specifications apply for V
Note 6: The input bias currents are junction leakage currents which approximately double for every 10˚C increase in the junction temperature, T
production test time, the input bias currents measured are correlated to junction temperature. In normal operation the junction temperature rises above the ambient
temperature as a result of internal power dissipation, P
mended if input bias current is to be kept to a minimum.
Note 7: Supply voltage rejection ratio is measured for both supply magnitudes increasing or decreasing simultaneously in accordance with common practice.
V
S
www.national.com 2
Equivalent Input Noise Voltage T
Equivalent Input Noise Current T
S
=
±
6V to±15V.
=
±
15V and 0˚C ≤TA≤ +70˚C. VOS,IBand IOSare measured at V
=
D.Tj
=
25˚C, f=1Hz- −120 dB
A
20 kHz (Input Referred)
=
±
15V, T
S
=
±
15V, T
S
=
25˚C, R
A
f=1000 Hz
=
25˚C, f=1000 Hz 0.01 pA/
j
T
where θjAis the thermal resistance from junction to ambient. Use of a heat sink is recom-
A+θjAPD
=
25˚C 8 13 V/µs
A
=
25˚C 4 MHz
A
=
100Ω, 25 nV/
S
=
0.
CM
. Due to the limited
j
√
Hz
√
Hz
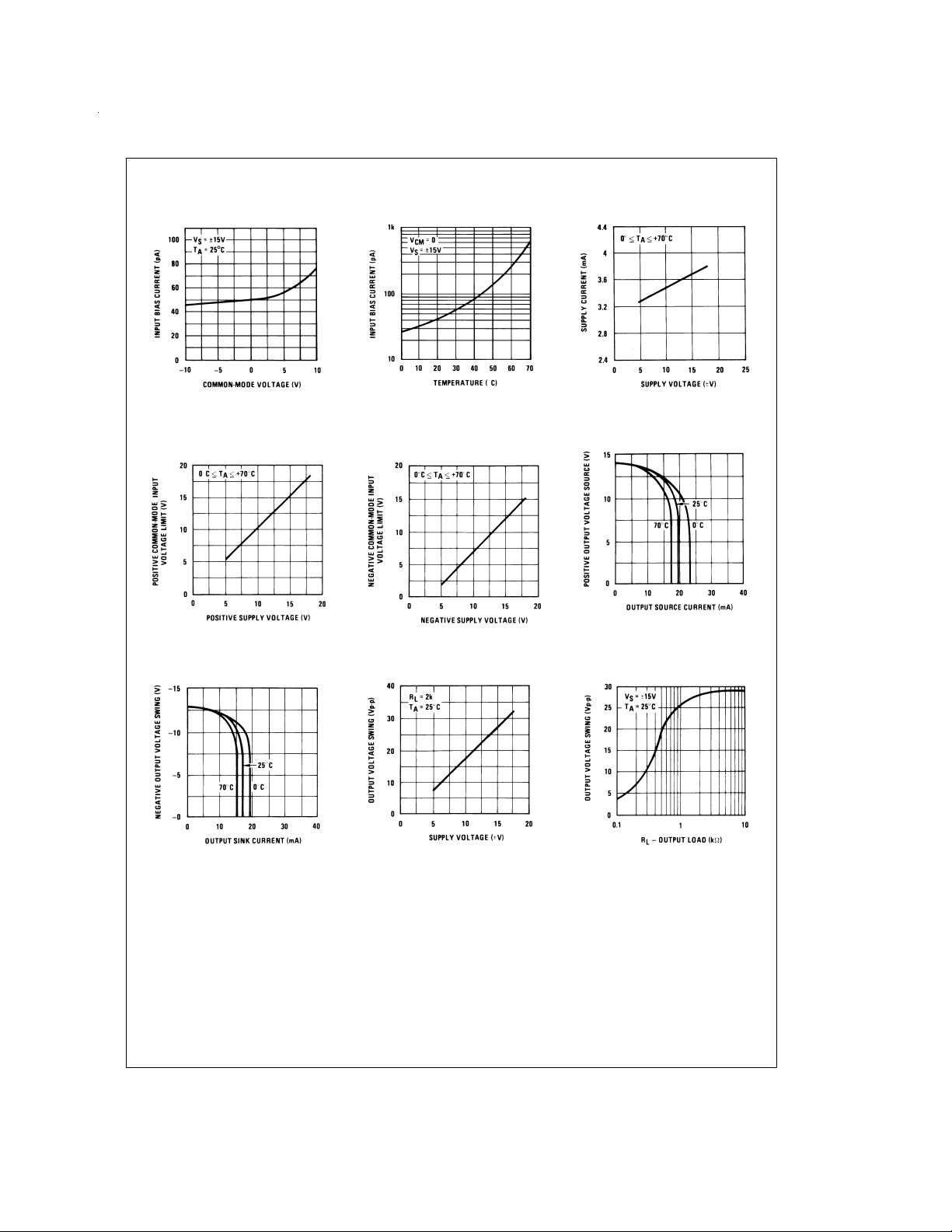
Typical Performance Characteristics
Input Bias Current
Positive Common-Mode Input
Voltage Limit
DS008357-18
DS008357-21
Input Bias Current
DS008357-19
Negative Common-Mode Input
Voltage Limit
Supply Current
DS008357-20
Positive Current Limit
DS008357-23
DS008357-22
Negative Current Limit
DS008357-24
Voltage Swing
DS008357-25
Output Voltage Swing
DS008357-26
www.national.com3
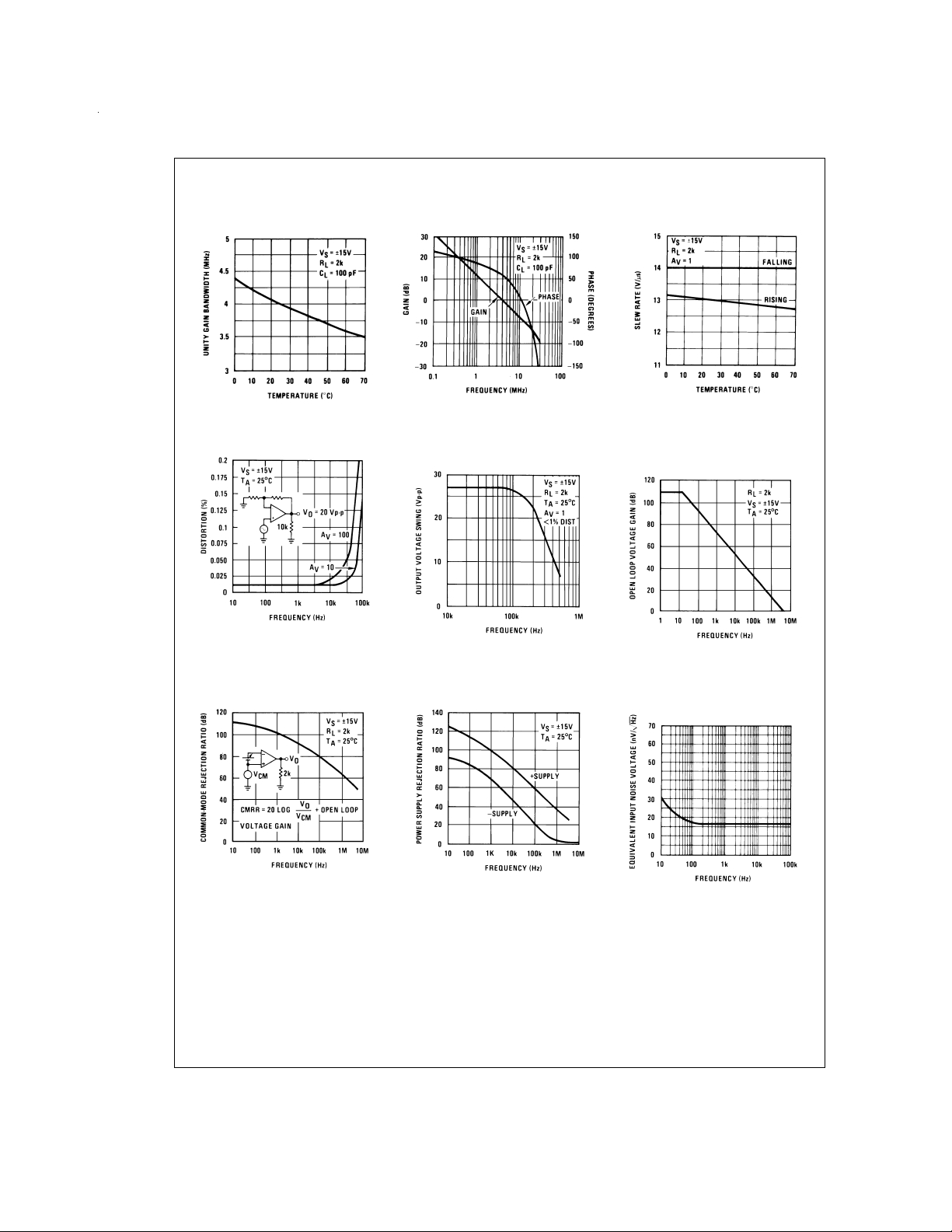
Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Gain Bandwidth
Distortion vs Frequency
DS008357-27
DS008357-30
Bode Plot
Undistorted Output
Voltage Swing
DS008357-28
DS008357-31
Slew Rate
DS008357-29
Open Loop Frequency
Response
DS008357-32
Common-Mode Rejection
Ratio
DS008357-33
www.national.com 4
Power Supply Rejection
Ratio
DS008357-34
Equivalent Input Noise
Voltage
DS008357-35
 Loading...
Loading...