
查询LM12434CIWM供应商
July 1995
LM12434/LM12
with Serial I/O and Self-Calibration
LM12434/LM12ÀLÓ438 12-Bit
a
Sign Data Acquisition
System with Serial I/O and Self-Calibration
General Description
The LM12434 and LM12ÀLÓ438 are highly integrated Data
Acquisition Systems. Operating on 3V to 5V, they combine a
fully-differential self-calibrating (correcting linearity and zero
errors) 13-bit (12-bit
(ADC) and sample-and-hold (S/H) with extensive analog
and digital functionality. Up to 32 consecutive conversions,
using two’s complement format, can be stored in an internal
32-word (16-bit wide) FIFO data buffer. An internal 8-word
instruction RAM can store the conversion sequence for up
to eight acquisitions through the LM12
multiplexer. The LM12434 has a four-channel multiplexer, a
differential multiplexer output, and a differential S/H input.
The LM12434 and LM12
a
sign resolution and in a supervisory ‘‘watchdog’’ mode
that compares an input signal against two programmable
limits.
Acquisition times and conversion rates are programmable
through the use of internal clock-driven timers. The differential reference voltage inputs can be externally driven for absolute or ratiometric operation.
All registers, RAM, and FIFO are directly accessible through
the high speed and flexible serial I/O interface bus. The
serial interface bus is user selectable to interface with the
following protocols with zero glue logic: MICROWIRE/
TM
PLUS
, Motorola’s SPI/QSPI, Hitachi’s SCI, 8051 Family’s
Serial Port (Mode 0), I
Port.
An evaluation kit for demonstrating the LM12434 and
ÀLÓ
LM12
438 is available.
TRI-STATEÉis a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
MICROWIRE/PLUS
Windows
TM
is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
É
a
sign) analog-to-digital converter
ÀLÓ
438’s eight-input
ÀLÓ
438 can also operate with 8-bit
2
C and the TMS320 Family’s Serial
is a trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
Key Specifications
e
f
8 MHzÀL, f
CLK
Y
Resolution 12-bitasign or 8-bitasign
Y
13-bit conversion time 5.5 msÀ7.3 msÓ(max)
Y
9-bit conversion time 2.6 msÀ3.5 msÓ(max)
Y
13-bit Through-put rate
Y
Comparison time (‘‘watchdog’’ mode)
Y
Serial Clock 10 MHzÀ6 MHzÓ(max)
Y
Integral Linearity Error
Y
VINrange GND to V
Y
Power dissipation 45 mWÀ20 mWÓ(max)
Y
Stand-by mode
power dissipation 25 mW
Y
Supply voltage LM12L438 3.3Vg10%
Features
Y
Three operating modes: 12-bitasign, 8-bitasign,
and ‘‘watchdog’’ comparison mode
Y
Single-ended or differential inputs
Y
Built-in Sample-and-Hold
Y
Instruction RAM and event sequencer
Y
8-channel (LM12ÀLÓ438) or 4-channel (LM12434)
multiplexer
Y
32-word conversion FIFO
Y
Programmable acquisition times and conversion rates
Y
Self-calibration and diagnostic mode
Y
Power down output for system power management
Y
Read while convert capability for maximum through-put
e
CLK
140k samples/s
LM12434/8 5V
rate
Applications
Y
Data Logging
Y
Portable Instrumentation
Y
Process Control
Y
Energy Management
Y
Robotics
6 MHz
Ó
À
105k sample/sÓ(min)
À
1.4 ms
1.8 msÓ(max)
g
1 LSB (max)
À
16.5 mWÓ(typ)
g
A
10%
À
L
Ó
438 12-Bit
a
a
Sign Data Acquisition System
Connection Diagrams
28-Pin PLCC Package
*Pin names in ( ) apply to the LM12434
TL/H/11879– 1
Order Number LM12434CIWM, LM12438CIWM, or
Order Number LM12434CIV, LM12438CIV, or
LM12L438CIV
See NS Package Number V28A
C
1995 National Semiconductor Corporation RRD-B30M85/Printed in U. S. A.
TL/H/11879
28-Pin Wide Body SO Package
TL/H/11879– 2
LM12L438CIWM
See NS Package Number M28B

Table of Contents
1.0 FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAMS АААААААААААААААААААААААА3
2.0 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS АААААААААААААААААА5
2.1 Ratings ААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААА5
2.1.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings ААААААААААААААААА5
2.1.2 Operating Ratings ААААААААААААААААААААААААА5
2.2 Performance Characteristics ААААААААААААААААААААА5
2.2.1 Converter Static Characteristics ААААААААААААА5
2.2.2 Converter Dynamic Characteristics АААААААААА6
2.2.3 DC CharacteristicsААААААААААААААААААААААААА8
2.2.4 Digital DC CharacteristicsААААААААААААААААААА9
2.3 Digital Switching Characteristics ААААААААААААААААА10
2.3.1 Standard Interface Mode АААААААААААААААААА10
2.3.2 8051 Interface ModeАААААААААААААААААААААА11
2.3.3 TMS320 Interface ModeААААААААААААААААААА12
2
2.3.4 I
C Bus Interface ААААААААААААААААААААААААА13
2.4 Notes on Specifications АААААААААААААААААААААААА14
3.0 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ААААААААААААААА15
4.0 TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS ÀÀÀ19
5.0 PIN DESCRIPTIONS АААААААААААААААААААААААААААА23
6.0 OPERATIONAL INFORMATION АААААААААААААААААА27
6.1 Functional Description ААААААААААААААААААААААААА27
6.2 Internal User-Accessible Registers АААААААААААААА31
6.2.1 Instruction RAM АААААААААААААААААААААААААА31
6.2.2 Configuration Register АААААААААААААААААААА38
6.2.3 InterruptsАААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААА38
6.2.4 Interrupt Enable Register АААААААААААААААААА39
6.2.5 Interrupt Status Register АААААААААААААААААА39
6.2.6 Limit Status Register АААААААААААААААААААААА40
6.2.7 Timer ААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААА40
6.2.8 FIFOАААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААА40
6.3 Instruction SequencerАААААААААААААААААААААААААА41
7.0 DIGITAL INTERFACE ААААААААААААААААААААААААААА43
7.1 Standard Interface Mode ААААААААААААААААААААААА43
7.1.1 Examples of Interfacing to the HPC 46XXX’s
MICROWIRE/PLUS
TM
and 68HC11’s SPI ÀÀÀ50
7.2 8051 Interface ModeААААААААААААААААААААААААААА59
7.2.1 Example of Interfacing to the 8051АААААААААА62
7.3 TMS320 Interface ModeАААААААААААААААААААААААА66
7.3.1 Example of Interfacing to the TMS320C3x ÀÀÀ69
2
7.4 I
C Bus Interface АААААААААААААААААААААААААААААА74
7.4.1 Example of Interfacing to an I
2
C ControllerÀÀÀ76
8.0 ANALOG CONSIDERATIONS АААААААААААААААААААА77
8.1 Reference Voltage АААААААААААААААААААААААААААА77
8.2 Input Range АААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААА77
8.3 Input Current ААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААА77
8.4 Input Source Resistance ААААААААААААААААААААААА77
8.5 Input Bypass Capacitance АААААААААААААААААААААА77
8.6 Input Noise ААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААА77
8.7 Power Supply Consideration АААААААААААААААААААА77
8.8 PC Board Layout and Grounding ConsiderationÀÀÀÀ78
2

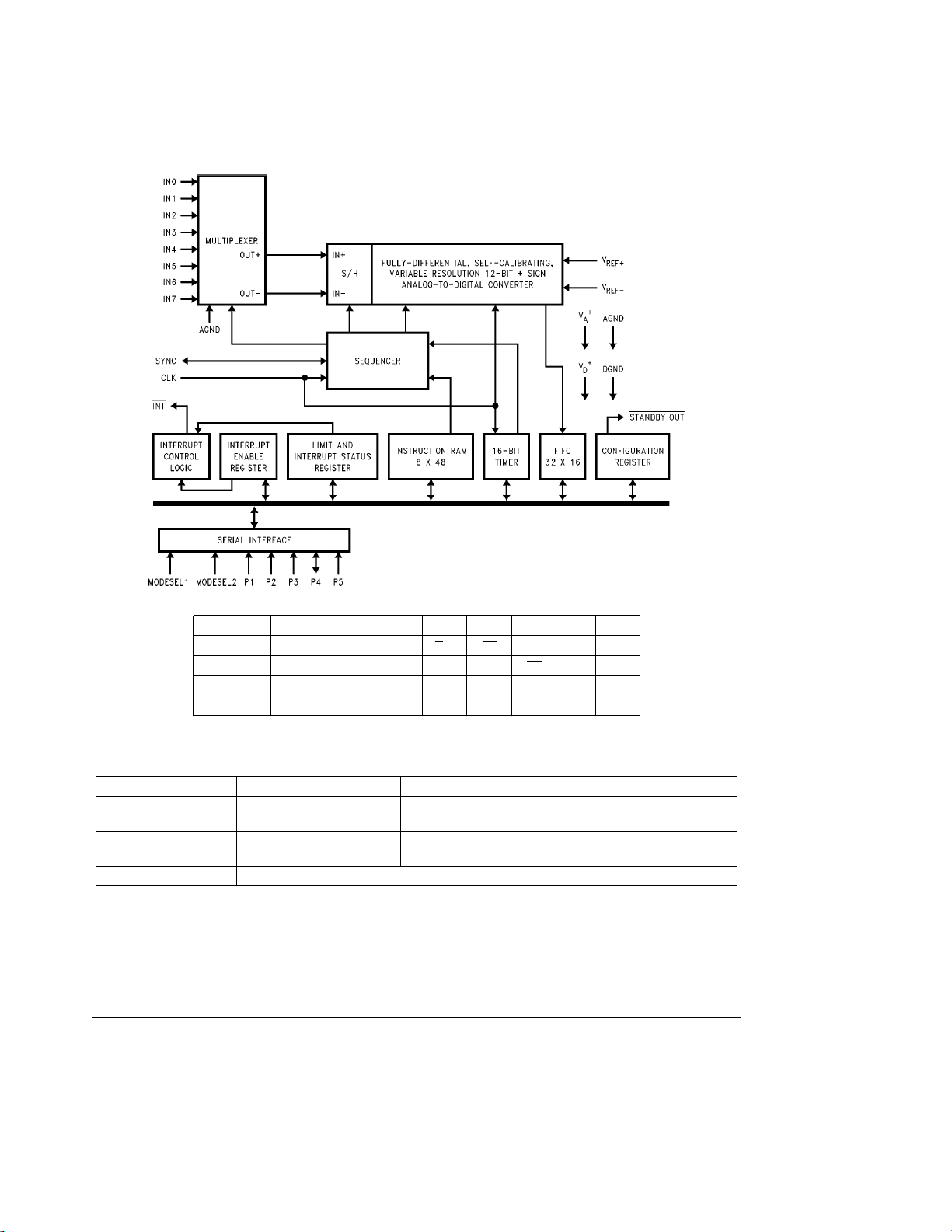
1.0 Functional Diagrams
LM12434
INTERFACE MODESEL1 MODESEL2 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5
Standard 0 1 R
8051 0 0 1* 1* CS RXD TXD
I2C 1 0 SAD0 SAD1 SAD2 SDA SCL
TMS320 1 1 FSR FSX DX DR SCLK
*Internal pull-up
/F CS
DI DO SCLK
Ordering Information (LM12434)
Part Number Package Type NSC Package Number Temperature Range
LM12434CIV 28-Pin PLCC V28A
LM12434CIWM 28-Pin Wide Body SO M28B
3
b
40§Ctoa85§C
b
40§Ctoa85§C
TL/H/11879– 3
1.0 Functional Diagrams (Continued)
LM12
ÀLÓ
438
INTERFACE MODESEL1 MODESEL2 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5
Standard 0 1 R/F CS DI DO SCLK
8051 0 0 1* 1* CS RXD TXD
I2C 1 0 SAD0 SAD1 SAD2 SDA SCL
TMS320 1 1 FSR FSX DX DR SCLK
*Internal pull-up
Ordering Information (LM12ÀLÓ438)
Part Number Package Type NSC Package Number Temperature Range
LM12438CIV 28-Pin PLCC V28A
LM12L438CIV
LM12438CIWM 28-Pin Wide Body SO M28B
LM12L438CIWM
LM12438 Eval Evaluation Board and WindowsÉbased software
4
b
40§Ctoa85§C
b
40§Ctoa85§C
TL/H/11879– 4

2.0 Electrical Specifications
2.1 RATINGS
2.1.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings (Notes1&2)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales
Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (V
a
A
Voltage at Input and Output Pins
except IN0–IN3 (LM12434)
and IN0 – IN7 (LM12
Voltage at Analog Inputs IN0– IN3 (LM12434)
and IN0–IN7 (LM12
a
a
b
V
V
l
A
AGNDbDGND
l
l
D
l
Input Current at Any Pin (Note 3)
Package Input Current (Note 3)
Power Dissipation (T
V Package
a
and V
) 6.0V
D
ÀLÓ
438)
ÀLÓ
438) GNDb5V to V
e
25§C) (Note 4)
A
b
0.3V to V
a
a
a
300 mV
300 mV
g
g
0.3V
a
5V
5mA
20 mA
WM Package
Storage Temperature
b
65§Ctoa150§C
Soldering Information, Lead Temperature (Note 19)
V Package, Vapor Phase (60 seconds)
Infrared (15 seconds)
WM Package, Vapor Phase (60 seconds)
Infrared (15 seconds)
ESD Susceptibility (Note 5) 1.5 kV
2.2 PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS All specifications apply to the LM12434, LM12438, and LM12L438 unless otherwise
noted. Specifications in braces
2.2.1 Converter Static Characteristics The following specifications apply to the LM12434 and LM12
a
e5VÀ
V
D
8.0 MHzÀ6 MHzÓ,R
À
1.25VÓcommon-mode voltage, and minimum acquisition time unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply for T
T
J
3.3VÓ, AGNDeDGNDe0V, V
e
T
to T
MIN
MAX
ÀÓ
apply only to the LM12L438.
e
25X, source impedance for V
S
; all other limits T
e
T
A
e
4.096VÀ2.5VÓ,V
a
REF
e
25§C. (Notes 6, 7, 8 and 9)
J
Symbol Parameter Conditions
ILE Positive and Negative Integral After Auto-Cal (Notes 12, 17)
Linearity Error
TUE Total Unadjusted Error After Auto-Cal (Note 12)
Resolution with No Missing Codes After Auto-Cal (Note 12) 13 Bits
DNL Differential Non-Linearity After Auto-Cal
Zero Error After Auto-Cal (Notes 13, 17)
Positive Full-Scale Error After Auto-Cal (Notes 12, 17)
Negative Full-Scale Error After Auto-Cal (Notes 12, 17)
DC Common Mode Error (Note 14)
ILE 8-BitaSign and ‘‘Watchdog’’ (Note 12)
Mode Positive and Negative
Integral Linearity Error
TUE 8-BitaSign and ‘‘Watchdog’’ Mode After Auto-Zero
Total Unadjusted Error
8-BitaSign and ‘‘Watchdog’’ Mode
Resolution with No Missing Codes
2.1.2 Operating Ratings (Notes1&2)
Temperature Range (T
LM12434CIV/LM12
ÀLÓ
LM12434CIWM, LM12
Supply Voltage
a
a
V
,V
A
D
a
a
b
V
V
l
A
AGDNDbDGND
l
l
D
l
Analog Inputs Range GND
V
Input Voltage 1VsV
a
REF
V
Input Voltage 0VsV
b
REF
b
REF
a
V
V
and V
V
a
REF
Common Mode
REF
Range (Note 16) 0.1 V
REF
REF
b
REF
e
0V, 12-bitasign conversion mode, f
b
s
25X, fully-differential input with fixed 2.048V
b
Typical Limits Units
(Note 10) (Note 11) (Limit)
g
g
g
s
T
min
438CIV
ÀLÓ
438CIWMb40§CsT
b
40§CsT
3.0V to 5.5V
s
V
IN
REF
s
V
b
REF
a
s
A
0.35
g
1 LSB
g
0.2
g
0.2
g
0.2
g
0.2
g
2
0.15
1/2
g
g
g
g
g
g
À
g
g
g
REF
1VsV
REF
s
V
REFCM
ÀLÓ
438 for V
1 LSB (max)
1 LSB (max)
1 LSB (max)
2 LSB (max)
2 LSB (max)
3.5 LSB (max)
Ó
4.0
1/2 LSB (max)
1/2 LSB (max)
9 Bits (max)
A
s
s
a
a
s
A
A
a
0.6 V
T
max
s
85§C
s
85§C
100 mV
100 mV
s
V
s
V
b
s
V
a
A
CLK
A
)
a
A
a
A
1V
a
A
a
A
e
e
e
5

2.0 Electrical Specifications (Continued)
2.2.1 Converter Static Characteristics The following specifications apply to the LM12434 and LM12
a
e5VÀ
V
D
8.0 MHzÀ6 MHzÓ,R
À
1.25VÓcommon-mode voltage, and minimum acquisition time unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply for T
e
T
J
3.3VÓ, AGNDeDGNDe0V, V
T
to T
MIN
e
25X, source impedance for V
S
; all other limits T
MAX
e
A
Symbol Parameter Conditions
DNL 8-BitaSign and ‘‘Watchdog’’ Mode
Differential Non-Linearity
8-BitaSign and ‘‘Watchdog’’ Mode After Auto-Zero
Zero Error
e
4.096VÀ2.5VÓ,V
a
REF
e
T
25§C. (Notes 6, 7, 8 and 9) (Continued)
J
REF
a
and V
REF
REF
b
e
0V, 12-bitasign conversion mode, f
b
s
25X, fully-differential input with fixed 2.048V
Typical Limits Units
(Note 10) (Note 11) (Limit)
g
g
8-BitaSign and ‘‘Watchdog’’ Positive
and Negative Full-Scale Error
8-BitaSign and ‘‘Watchdog’’ Mode
DC Common Mode Error
Multiplexer Channel-to-Channel
Matching
V
a
IN
V
b
IN
b
V
a
IN
b
V
a
IN
Non-Inverting GND V (min)
Input Range
Inverting GND V (min)
Input Range
V
Differential Input Voltage Range
b
IN
V
Common Mode Input Voltage Range GND V (min)
b
IN
g
g
2
a
a
e
PSS Power Supply Zero Error V
Sensitivity Full-Scale Error V
(Note 15) Linearity Error
C
REF
C
IN
2.2.2 Converter Dynamic Characteristics The following specifications apply only to the LM12434 and LM12438 for V
a
V
D
throughput rate
2.048V
for T
V
/V
REF
a
Input Capacitance 85 pF
b
REF
Selected Multiplexer Channel Input
Capacitance
e
5V, AGNDeDGNDe0V, V
e
T
J
133.3 kHz, R
e
T
MIN
to T
À
1.25VÓcommon-mode voltage, and minimum acquisition time unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply
e
A
e
S
; all other limits T
MAX
e
a
REF
25X, source impedance for V
4.096V, V
e
T
A
J
A
REF
REF
e
25§C. (Notes 6, 7, 8 and 9)
Symbol Parameter Conditions
e
V
5Vg10%,
D
e
4.096V, V
a
e
0V, 12-bitasign conversion mode, f
b
REF
a
and V
REF
REF
e
b
b
Typical Limits Units
(Note 10) (Note 11) (Limit)
g
GNDg0.25
s
25X, fully-differential input with fixed
CLK Duty Cycle 50 %
40 % (min)
60 % (max)
t
C
t
A
Conversion Time 13-Bit Resolution,
Sequencer State S5
9-Bit Resolution,
Sequencer State S5
Acquisition Time Sequencer State S7
(Figure 10)
(Figure 10)
(Figure 10)
44 (t
21 (t
(Programmable) Minimum for 13-Bits 9 (t
Maximum for 13-Bits (D
Minimum for 9-Bits
e
15) 39 (t
(Figure 10)
2(t
Maximum for 9-Bits (De15) 2 (t
) 44 (t
CLK
) 21 (t
CLK
) 9(t
CLK
) 39 (t
CLK
) 2(t
CLK
) 32 (t
CLK
)a50 ns (max)
CLK
)a50 ns (max)
CLK
)a50 ns (max)
CLK
)a50 ns (max)
CLK
)a50 ns (max)
CLK
)a50 ns (max)
CLK
ÀLÓ
438 for V
0.1
g
1/2 LSB (max)
g
1/2 LSB (max)
g
1/2 LSB (max)
0.15
0.05
g
1/8 LSB
0.05 LSB
a
V
A
a
V
A
a
b
V
A
a
V
A
a
V
A
0.05
g
g
1.0 LSB (max)
g
1.5 LSB (max)
0.2 LSB
75 pF
CLK
e
t
CLK
A
CLK
V (max)
V (max)
V (min)
V (max)
V (max)
A
e
8.0 MHz,
CLK Period
a
e
e
e
A
a
e
6

2.0 Electrical Specifications (Continued)
2.2.2 Converter Dynamic Characteristics The following specifications apply only to the LM12434 and LM12438 for V
a
e
V
5V, AGNDeDGNDe0V, V
D
throughput rate
2.048V common-mode voltage, and minimum acquisition time unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply for T
e
T
T
J
MIN
to T
e
MAX
133.3 kHz, R
; all other limits T
e
25X, source impedance for V
S
Symbol Parameter Conditions
t
t
Auto-Zero Time Sequencer State S2
Z
Full Calibration Time Sequencer State S2
CAL
Throughput Rate (Note 18)
t
‘‘Watchdog’’ Mode Comparison Time Sequencer States S6, S4,
WD
SNR Signal-to-Noise Ratio, V
Differential Input f
SNR Signal-to-Noise Ratio, V
Single-Ended Input f
SINAD Signal-to-NoiseaDistortion Ratio, V
Differential Input f
SINAD Signal-to-NoiseaDistortion Ratio, V
Single-Ended Input f
THD Total Harmonic Distortion, V
Differential Input f
THD Total Harmonic Distortion, V
Distortion, Single-Ended Input f
ENOB Effective Number of Bits, V
Differential Input f
ENOB Effective Number of Bits, V
Single-Ended Input f
SFDR Spurious Free Dynamic Range, V
Differential Input f
SFDR Spurious Free Dynamic Range, V
Single-Ended Input f
A
REF
e
4.096V, V
a
e
e
T
25§C. (Notes 6, 7, 8 and 9) (Continued)
J
REF
e
b
REF
(Figure 10)
(Figure 10)
(Figure 10)
and S5
e
g
4.096V (Note 20)
IN
e
1 kHz 79 dB
IN
e
f
10 kHz 79 dB
IN
e
f
62 kHz 70 dB
IN
e
4.096 V
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
p-p
1 kHz 71 dB
10 kHz 71 dB
62 kHz 67 dB
g
4.096V (Note 20)
1 kHz 79 dB
10 kHz 78 dB
62 kHz 67 dB
4.096 V
p-p
1 kHz 71 dB
10 kHz 70 dB
62 kHz 64 dB
g
4.096V (Note 20)
1 kHz
10 kHz
62 kHz
4.096 V
p-p
1 kHz
10 kHz
62 kHz
g
4.096V (Note 20)
1 kHz 12.6 Bits
10 kHz 12.2 Bits
62 kHz 12.1 Bits
4.096 V
p-p
1 kHz 11.3 Bits
10 kHz 11.2 Bits
62 kHz 10.8 Bits
g
4.096V (Note 20)
1 kHz 90 dBc
10 kHz 86 dBc
62 kHz 76 dBc
4.096V V
1 kHz 90 dBc
p-p
10 kHz 85 dBc
62 kHz 72 dBc
0V, 12-bitasign conversion mode, f
and V
a
s
25X, fully-differential input with fixed
b
REF
Typical Limits Units
(Note 10) (Note 11) (Limit)
76 (t
4944 (t
) 76 (t
CLK
) 4944 (t
CLK
)a50 ns (max)
CLK
CLK
142 140
11 (t
) 11 (t
CLK
b
90 dBc
b
85 dBc
b
71 dBc
b
88 dBc
b
82 dBc
b
67 dBc
)a50 ns (max)
CLK
e
CLK
)a50 ns (max)
a
A
8.0 MHz,
A
kHz
(min)
e
e
7

2.0 Electrical Specifications (Continued)
2.2.2 Converter Dynamic Characteristics The following specifications apply only to the LM12434 and LM12438 for V
a
e
V
5V, AGNDeDGNDe0V, V
D
throughput rate
2.048V common-mode voltage, and minimum acquisition time unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply for T
e
T
T
J
MIN
to T
e
MAX
133.3 kHz, R
; all other limits T
e
S
Symbol Parameter Conditions
IMD Two Tone Intermodulation Distortion V
Differential Input f
IMD Two Tone Intermodulation Distortion V
Single Ended Input f
Multiplexer Channel-to-Channel Crosstalk V
t
PU
t
WU
2.2.3 DC Characteristics The following specifications apply to the LM12434 and LM12ÀLÓ438 for V
AGND
otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply for T
Power-Up Time 10 ms
Wake-Up Time (Note 22) 2 ms
e
DGNDe0V, V
REF
a
e
4.096VÀ2.5VÓ,V
and 8)
Symbol Parameter Conditions
a
I
D
a
I
A
I
ST
a
V
Supply Current f
D
a
V
Supply Current f
A
Stand-By Supply Current (I
D
Multiplexer ON-Channel Leakage Current V
Multiplexer OFF-Channel Leakage Current V
e
4.096V, V
a
REF
25X, source impedance for V
e
e
T
A
25§C. (Notes 6, 7, 8 and 9) (Continued)
J
b
REF
e
IN
e
19.190 kHz
1
e
f
19.482 kHz
2
e
IN
e
19.190 kHz
1
e
f
19.482 kHz
2
e
IN
e
f
IN
f
CROSSTALK
LM12434 MUXOUT Only
and LM12438 MUX
plus Converter (Note 21)
e
0V, f
b
REF
e
e
T
A
a
a
a
I
) Stand-By Mode Selected
A
T
J
e
8 MHzÀ6 MHz
CLK
e
f
SCLK
e
f
SCLK
e
8 MHzÀ6 MHz
CLK
e
f
SCLK
e
f
Stopped 5À5
CLK
e
f
8 MHzÀ6 MHz
CLK
e
f
SCLK
e
f
Stopped 1.4À0.8
CLK
e
f
8 MHzÀ6 MHz
CLK
a
e
5.5V
A
ON-Channel
OFF-Channel
ON-Channel
OFF-Channel
a
e
5.5VÀ3.3V
A
ON-Channele5.5VÀ3.3V
OFF-Channele0V 0.1 1.0À3.0ÓmA (max)
ON-Channel
OFF-Channel
e
0V, 12-bitasign conversion mode, f
and V
a
REF
s
25X, fully-differential input with fixed
b
REF
CLK
Typical Limits Units
(Note 10) (Note 11) (Limit)
g
4.096V (Note 20)
4.096 V
pp
4.096 V
PP
5 kHz
e
40 kHz
e
8.0 MHzÀ6 MHzÓand minimum acquisition time unless
CLK
to T
MIN
; all other limits T
MAX
b
82 dBc
b
80 dBc
b
90 dBc
a
e
V
A
D
e
e
T
A
25§C. (Notes 6, 7
J
Typical Limits Units
(Note 10) (Note 11) (Limit)
Ó
Stopped 2.0À1.4
10 MHzÀ8 MHz
Ó
Ó
4.0À2.0
2.8À2.2
Ó
Ó
5.0À2.5ÓmA (max)
Ó
4.0À3.5ÓmA (max)
Stopped
Ó
10 MHzÀ8 MHz
e
e
e
e
e
e
Ó
Ó
5.5V
0V 0.1 1.0À3.0ÓmA (max)
0V
5.5V 1.0À3.0ÓmA (max)
Ó
Ó
0V
5.5VÀ3.3V
Ó
120À50
1.4À0.8
Ó
Ó
Ó
Ó
1.0À3.0ÓmA (max)
a
e
e5VÀ
a
A
8.0 MHz,
A
3.3V],
mA (max)
mA (max)
mA (max)
mA (max)
mA (max)
e
e
8

2.0 Electrical Specifications (Continued)
2.2.3 DC Characteristics The following specifications apply to the LM12434 and LM12
e
AGND
DGNDe0V, V
otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply for T
and 8) (Continued)
REF
a
e
4.096VÀ2.5VÓ,V
REF
A
e
b
e
T
J
0V, f
e
e
8.0 MHzÀ6 MHzÓand minimum acquisition time unless
CLK
T
to T
MIN
MAX
Symbol Parameter Conditions
R
ON
Multiplexer ON-Resistance LM12434
e
V
5V 650 1000 X(max)
IN
e
V
2.5V 700 1000 X(max)
IN
e
V
0V 630 1000 X(max)
IN
ÀLÓ
438 for V
; all other limits T
Typical Limits Units
(Note 10) (Note 11) (Limit)
Multiplexer Channel-to-Channel LM12434
R
matching V
ON
2.2.4 Digital DC Characteristics The following specifications apply to the LM12434 and LM12ÀLÓ438 for V
À
3.3VÓ, AGNDeDGNDe0V, unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply for T
e
limits T
e
T
A
25§C. (Notes 6, 7 and 8)
J
e
5V
IN
e
V
2.5V
IN
e
V
0V
IN
Symbol Parameter Conditions
a
a
e
V
IN(1)
V
IN(0)
I
IN(1)
I
IN(0)
C
IN
V
OUT(1)
V
OUT(0)
I
OUT
Logical ‘‘1’’ Input Voltage V
Logical ‘‘0’’ Input Voltage V
Logical ‘‘1’’ Input Current V
Logical ‘‘0’’ Input Current V
A
a
A
IN
IN
All Digital Inputs 6 pF
Logical ‘‘1’’ Output Voltage V
Logical ‘‘0’’ Output Voltage V
TRI-STATEÉOutput Leakage Current V
I
OUT
I
OUT
I
OUT
V
a
A
a
A
OUT
OUT
e
V
5.5VÀ3.6V
D
a
e
e
V
4.5VÀ3.0V
D
e5VÀ
e
e
eb
eb
e
e
e
e5VÀ
Ó
3.3V
0V
a
e
V
4.5VÀ3.0V
D
360 mA 2.4 V (min)
10 mA 4.25À2.9
a
e
V
4.5VÀ3.0V
D
1.6 mA
0V
Ó
3.3V
g
1.0%
g
1.0%
g
1.0%
A
Typical Limits Units
(Note 10) (Note 11) (Limit)
Ó
Ó
0.005 1.0 mA (max)
b
0.005
Ó
Ó
b
0.05
0.05 3.0 mA (max)
a
A
e
T
A
g
g
g
e
e
T
T
J
MIN
a
e
e5VÀ
V
D
e
25§C. (Notes 6, 7
J
3.3V],
3.0% (max)
3.0% (max)
3.0% (max)
a
a
e
e
V
A
D
to T
; all other
MAX
2.0 V (min)
0.8 V (max)
b
1.0 mA (max)
Ó
V (min)
0.4 V (max)
b
3.0 mA (max)
5V
9

2.0 Electrical Specifications (Continued)
2.3 DIGITAL SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS The following specifications apply to the LM12434 and LM12
ae5VÀ
e
V
D
Boldface limits apply for T
2.3.1 Standard Mode Interface (MICROWIRE/PLUS
Symbol
(See
Figure
t
1
t
2
t
3
t
4
t
5
t
6
t
7
t
8
*CLK is the main clock input to the device, pin number 24 in PLCC package or pin number 2 in SO package.
3.3VÓ, AGNDeDGNDe0V, CL(load capacitance) on output linese80 pF unless otherwise specified.
Below) (Note 10) (Note 11) (Limit)
e
e
T
T
A
J
MIN
to T
, all other limits for T
MAX
TM
, SCI and SPI/QSPI)
Parameter Conditions
e
e
T
A
25§C. (Notes 6, 7, and 9)
J
Typical Limits Units
SCLK (Serial Clock) Period 100À125
CS Set-Up Time to First
Clock Transition
DI Valid Set-Up Time to Data
Capture Transition of SCLK
DI Valid Hold Time to Data
Capture Transition of SCLK
DO Hold Time from Data Shift
Transition of SCLK
À30Ó
25
0 ns (min)
40 ns (min)
À
70
120
CS Hold Time from Last SCLK
Transition in a Read or Write Cycle 25 ns (min)
(Excluding Burst Read Cycle)
CS Inactive to CS Active Again
3
SCLK Idle Time between the
End of the Command Byte
Transfer and the Start of the (min)*
3
Data Transfer in Read Cycles
ÀLÓ
Ó
Ó
438 for V
ns (min)
ns (min)
ns (max)
CLK Cycle
(min)*
CLK Cycle
a
A
TL/H/11879– 18
10

2.0 Electrical Specifications (Continued)
2.3 DIGITAL SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS The following specifications apply to the LM12434 and LM12
ae5VÀ
e
V
D
Boldface limits apply for T
2.3.2 8051 Interface Mode
Symbol
(See
Figure
t
9
t
10
t
11
t
12
t
13
t
14
t
15
t
16
*CLK is the main clock input to the device, pin number 24 in PLCC package or pin number 2 in SO package.
3.3VÓ, AGNDeDGNDe0V, CL(load capacitance) on output linese80 pF unless otherwise specified.
Below) (Note 10) (Note 11) (Limit)
e
e
T
T
to T
A
J
MIN
, all other limits for T
MAX
Parameter Conditions
e
e
T
A
25§C. (Notes 6, 7, and 9) (Continued)
J
Typical Limits Units
TXD (Serial Clock Period) 125À250
CS Set-Up Time to First
Clock Transition
Data in Valid Set-Up Time to
TXD Clock High
Data in Valid Hold Time
from TXD Clock High
Data Out Hold Time
from TXD Clock High
À40Ó
25
40 ns (min)
À90Ó
40
À
70
120
CS Hold Time from Last TXD
High in a Read or Write Cycle 25À50
Ó
(Excluding Burst Read Cycle)
CS Inactive to CS Active Again
3
SCLK Idle Time between the
End of the Command Byte
Transfer and the Start of the (min)*
3
Data Transfer in Read Cycles
Ó
Ó
ÀLÓ
438 for V
ns (min)
ns (min)
ns (min)
ns (max)
ns (min)
CLK Cycle
(min)*
CLK Cycle
a
A
TL/H/11879– 21
11

2.0 Electrical Specifications (Continued)
2.3 DIGITAL SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS The following specifications apply to the LM12434 and LM12
ae5VÀ
e
V
D
Boldface limits apply for T
2.3.3 TMS320 Interface Mode
Symbol
(See
Figure
t
22
t
23
t
24
t
25
t
26
t
27
t
28
t
29
3.3VÓ, AGNDeDGNDe0V, CL(load capacitance) on output linese80 pF unless otherwise specified.
Below) (Note 10) (Note 11) (Limit)
e
e
T
T
to T
A
J
MIN
, all other limits for T
MAX
Parameter Conditions
e
e
T
A
25§C. (Notes 6, 7, and 9) (Continued)
J
Typical Limits Units
SCLK (Serial Clock) Period 125À167
FSX Set-Up Time to SCLK High 30À50
FSX Hold Time from SCLK High 10 ns (min)
Data in (DX) Set-Up
Time to SCLK Low
Data in DX Hold Time from
SCLK Low
0 ns (min)
À
30
120
FSR High from SCLK High 80À100
FSR Low from SCLK Low 120 ns (max)
SCLK High to Data
Out (DR) Change
90 ns (max)
ÀLÓ
Ó
Ó
Ó
Ó
438 for V
ns (min)
ns (min)
ns (min)
ns (max)
a
A
TL/H/11879– 23
12

2.0 Electrical Specifications (Continued)
2.3 DIGITAL SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS The following specifications apply to the LM12434 and LM12
ae5VÀ
e
V
D
Boldface limits apply for T
2
2.3.4 I
C Bus Interface
The switching characteristics of the LM12434/8 for I2C bus interface fully meets or exceeds the published specifications of the
2
I
C bus. The following parameters given here are the timing relationships between SCL and SDA signals related to the
LM12434/8. They are not the I
Symbol
(See
Figure
t
17
t
18
t
19
t
20
t
21
3.3VÓ, AGNDeDGNDe0V, CL(load capacitance) on output linese80 pF unless otherwise specified.
Below) (Note 10) (Note 11) (Limit)
e
e
T
T
to T
A
J
MIN
2
C bus specifications.
, all other limits for T
MAX
Parameter Conditions
e
e
T
A
25§C. (Notes 6, 7, and 9) (Continued)
J
Typical Limits Units
SCL (Clock) Period 2500À10000
Data in Set-Up Time to SCL High 30 ns (min)
Data Out Stable after SCL Low 900À1400
SDA Low Set-Up Time to SCL
Low (Start Condition)
SDA High Hold Time after SCL
High (Stop Condition)
ÀLÓ
438 for V
Ó
ns (min)
Ó
ns (max)
40 ns (min)
40 ns (min)
a
A
TL/H/11879– 22
13

2.0 Electrical Specifications (Continued)
2.4 NOTES ON SPECIFICATIONS
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is
functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. For guaranteed specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. The guaranteed
specifications apply only for the test conditions listed. Some performance characteristics may degrade when the device is not operated under the listed test
conditions.
Note 2: All voltages are measured with respect to GND, unless otherwise specified. GND specifies either AGND and/or DGND and V
a
.
or V
D
Note 3: When the input voltage (V
5 mA. The 20 mA maximum package input current rating allows the voltage at any four pins, with an input current of 5 mA, to simultaneously exceed the power
supply voltages.
Note 4: The maximum power dissipation must be derated at elevated temperatures and is dictated by T
junction to ambient thermal resistance), and T
or the number given in the Absolute Maximum Ratings, whichever is lower. For this device, T
H
JA
package, when board mounted, is 70
) at any pin exceeds the power supply rails (V
IN
(ambient temperature). The maximum allowable power dissipation at any temperature is PD
A
C/W and in the WM package, when board mounted, is 60§C/W.
§
IN
k
GND or V
a
IN
Jmax
l
e
a
(V
or V
)), the current at that pin should be limited to
A
D
(maximum junction temperature), HJA(package
Jmax
150§C, and the typical thermal resistance (HJA) of the V
Note 5: Human body model, 100 pF discharged through a 1.5 kX resistor.
Note 6: Two on-chip diodes are tied to each analog input through a series resistor, as shown below. Input voltage magnitude up to 5V above V
GND will not damage the part. However, errors in the A/D conversion can occur if these diodes are forward biased by more than 100 mV. As an example, if V
, the full-scale input voltage must bes4.6 VDCto ensure accurate conversions.
4.5 V
DC
a
specifies either V
e
max
(T
Jmax
a
or 5V below
A
a
and/
A
b
TA)/
a
A
is
a
Note 7: V
conversion/comparison accuracy. Refer to Section 8.0 for a detailed discussion on grounding the DAS.
Note 8: Accuracy is guaranteed when operating the LM12434/LM12
Note 9: With the test condition for V
Note 10: Typicals are at T
Note 11: Limits are guaranteed to National’s AOQL (Average Output Quality Level).
Note 12: Positive integral linearity error is defined as the deviation of the analog value, expressed in LSBs, from the straight line that passes through positive full-
scale and zero. For negative integral linearity error the straight line passes through negative full-scale and zero. (See
Note 13: Zero error is a measure of the deviation from the mid-scale voltage (a code of zero), expressed in LSB. It is the average value of the code transitions
b
between
Note 14: The DC common-mode error is measured with both the inverted and non-inverted inputs shorted together and driven from 0V to 5V
measured value is referred to the resulting output value when the inputs are driven with a 2.5V
a
and V
A
must be connected together to the same power supply voltage and bypassed with separate capacitors at each Vapin to assure
D
e
A
1to0and0toa1 (see
ÀLÓ
b
V
a
REF(VREF
25§C and represent most likely parametric norm.
Figure 6
).
) given asa4.096V, the 12-bit LSB is 1 mV and the 8-bit/‘‘Watchdog’’ LSB is 19 mV.
b
REF
438 at f
CLK
e
8 MHzÀ6 MHzÓ.
À
1.65VÓsignal.
Note 15: Power Supply Sensitivity is measured after Auto-Zero and/or Auto-Calibration cycle has been completed with V
Note 16: V
Note 17: The device self-calibration technique ensures linearity and offset errors as specified, but noise inherent in the self-calibration process will result in a
repeatability uncertainty of
Note 18: The Throughput Rate is for a single instruction repeated continuously while reading data during conversions with a serial clock frequency f
À
8 MHzÓ. Sequencer states 0 (1 clock cycle), 1 (1 clock cycle), 7 (9 clock cycles) and 5 (44 clock cycles) are used (see
conversion. The Throughput Rate is f
Note 19: See AN-450 ‘‘Surface Mounting Methods and their Effect on Product Reliability’’ for other methods of soldering surface mount devices.
Note 20: Each input referenced to the other input sees a
done by applying two sine waves with 180
Note 21: Multiplexer channel-to-channel crosstalk is measured by placing a sinewave with a frequency of f
frequency of f
generated by doing a FFT on these samples. The crosstalk is then calculated by subtracting the amplitude of the frequency component at 40 kHz from the
amplitude of the fundamental frequency at 5 kHz.
Note 22: Interrupt 7 is set to return an out-of-standby flag 10 ms (typ) after the device is requested to come out of standby mode. However, characterization has
shown the devices will perform to their rated specifications in 2 ms.
(Reference Voltage Common Mode Range) is defined as (V
REFCM
g
0.10 LSB.
(MHz)/N, where N is the number of clock cycles/conversion.
CLK
g
4.096V (8.192 V
CROSSTALK
phase shift and 4.096 V
§
e
40 kHz on the remaining channels. 8192 conversions are performed on the channel with the 5 kHz signal. A special response is
(between GND and V
p-p
a
V
REF
b
A
)/2. See
a
) to the inputs.
a
REF
) sine wave. However the voltage at each input stays within the supply rails. This is
p-p
TL/H/11879– 5
Figures 5b
and5c).
a
a
and V
and4.
A
Figures 3
Figure 10
e
5 kHz on one channel and another sinewave with a
IN
at the specified extremes.
D
) for a total of 56 clock cycles per
SCLK
À
3.3VÓ. The
e
10 MHz
14
3.0 Electrical Characteristics
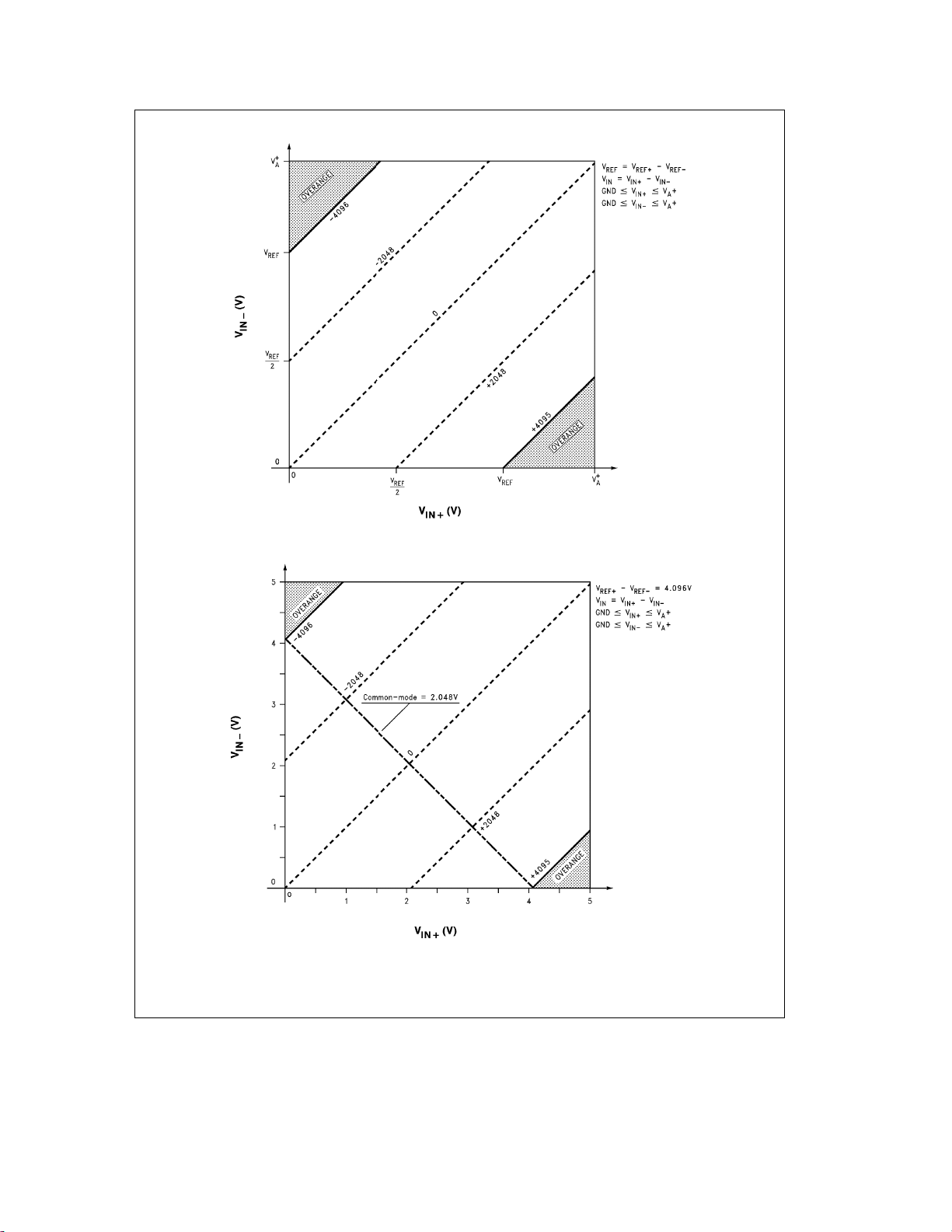
FIGURE 1. Output Digital Code vs the Operating Input Voltage Range (General Case)
FIGURE 2. Output Digital Code vs the Operating Input Voltage Range for V
REF
e
TL/H/11879– 6
TL/H/11879– 7
4.096V
15

3.0 Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
FIGURE 3. V
FIGURE 4. V
Operating Range (General Case)
REF
Operating Range for V
REF
TL/H/11879– 8
a
e
5V
A
TL/H/11879– 9
16

3.0 Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
FIGURE 5a. Transfer Characteristic
FIGURE 5b. Simplified Error Curve vs Output Code without Auto-Calibration or Auto-Zero Cycles
TL/H/11879– 10
TL/H/11879– 11
17

3.0 Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
FIGURE 5c. Simplified Error Curve vs Output Code after Auto-Calibration Cycle
TL/H/11879– 13
FIGURE 6. Offset or Zero Error Voltage
TL/H/11879– 12
18

4.0 Typical Performance Characteristics
The following curves apply for 12-bitasign mode after auto-calibration unless otherwise specified. The performance for 8-bit
sign and ‘‘watchdog’’ modes is equal to or better than shown. (Note 9)
Linearity Error Change
vs CLK Frequency
Linearity Error Change
vs Temperature
Linearity Error Change
vs Reference Voltage
a
Linearity Error Change
vs Supply Voltage
Full-Scale Error Change
vs Reference Voltage
Zero Error Change
vs Temperature
Full-Scale Error Change
vs CLK Frequency
Full-Scale Error
vs Supply Voltage
Zero Error Change
vs Reference Voltage
Full-Scale Error Change
vs Temperature
Zero Error Change
vs CLK Frequency
Zero Error Change
vs Supply Voltage
TL/H/11879– 14
19

4.0 Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
a
The following curves apply for 12-bit
sign and ‘‘watchdog’’ modes is equal to or better than shown. (Note 9)
sign mode after auto-calibration unless otherwise specified. The performance for 8-bit
a
Analog Supply Current
vs Temperature
The following curves apply to the LM12L438 in 12-bitasign mode after auto-calibration unless otherwise specified. R
e
T
A
100 kHz.
25§C, V
a
a
e
e
V
A
3.3V, V
D
REF
e
Unipolar Spectral Response with
10 kHz Sine Wave at 0 dB
*Digital Supply Current
vs Clock Frequency
*Free-running conversion and SPI mode data
read at 200 ns SCLK period.
2.5V, f
CLK
e
6 MHz, f
SCLK
e
8 MHz, V
Unipolar Spectral Response with
20 kHz Sine Wave at 0 dB
*Digital Supply Current
vs Temperature
e
2.5Vx0 dB, Sampling Rate
IN
TL/H/11879– 15
e
50X,
S
e
The following curves apply for 12-bitasign mode after auto-calibration unless otherwise specified. R
a
a
e
V
A
e
V
5V, V
D
e
4.096V, f
REF
CLK
Unipolar Special Response
with 41.2 kHz Sine Wave
at 0 dB Reading Data
during Conversion f
e
8 MHz, f
SCLK
SCLK
e
e
10 MHz, V
10 MHz
e
4.096Vx0 dB, Sampling Ratee100 kHz.
IN
Unipolar Special Response
with 41.2 kHz Sine Wave
at 0 dB Reading Data
between Conversions
20
TL/H/11879– 84
e
50X,T
S
TL/H/11879– 55
e
25§C,
A

4.0 Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
a
The following curves apply for 12-bit
e
R
S
Sampling Rate
50X,T
e
A
e
133.3 kHz.
25§C, V
a
A
Unipolar Signal-to-Noise Ratio
vs Input Frequency
sign mode after auto-calibration unless otherwise specified.
a
e
e
V
5V, V
D
e
4.096V, f
REF
Unipolar Signal-to-Noise
a
CLK
Distortion
e
8 MHz, f
vs Input Frequency
SCLK
e
10 MHz, V
Unipolar Total
Harmonic Distortion
vs Input Frequency
e
4.096Vx0 dB,
IN
Unipolar Spurious Free
Dynamic Range
vs Input Frequency
Unipolar Spectral Response
with 40.283 kHz
Sine Wave at 0 dB
Unipolar Spectral Response
with 62.256 kHz
Sine Wave at 0 dB
Unipolar Spectral Response
with 1.025 kHz
Sine Wave at 0 dB
Unipolar Spectral Response
with 40.283 kHz
Sine Wave at
Unipolar Two Tone Spectral
Response with f1
e
f2
b
0.5 dB
e
19.190 kHz and
19.482 kHz Sine Wave
Unipolar Spectral Response
with 10.010 kHz
Sine Wave at 0 dB
Unipolar Spectral Response
with 40.283 kHz
Sine Wave at
b
1.0 dB
TL/H/11879– 17
TL/H/11879– 24
21

4.0 Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
a
The following curves apply for 12-bit
e
R
S
Sampling Rate
50X,T
e
A
e
133.3 kHz.
25§C, V
a
A
Bipolar Signal-to-Noise Ratio
vs Input Frequency
sign mode after auto-calibration unless otherwise specified.
a
e
e
V
5V, V
D
e
4.096V, f
REF
Bipolar Signal-to-Noise
a
Distortion vs
CLK
e
8 MHz, f
Input Frequency
SCLK
e
10 MHz, V
e
g
IN
Bipolar Total Harmonic
Distortion vs Input Frequency
4.096Vx0 dB,
Bipolar Spurious Free
Dynamic Range
vs Input Frequency
Bipolar Spectral Response
with 40.283 kHz
Sine Wave at 0 dB
Bipolar Spectral Response
with 62.25 kHz
Sine Wave at 0 dB
Bipolar Spectral Response
with 1.025 kHz
Sine Wave at 0 dB
Bipolar Spectral Response
with 40.283 kHz
Sine Wave at
Bipolar Two Tone Spectral
Response with f1
e
f2
b
0.5 dB
e
19.190 kHz and
19.482 kHz Sine Waves
Bipolar Spectral Response
with 10.010 kHz
Sine Wave at 0 dB
Bipolar Spectral Response
with 40.283 kHz
Sine Wave at
b
1.0 dB
TL/H/11879– 25
TL/H/11879– 26
22

5.0 Pin Descriptions
TABLE I. LM12ÀLÓ438 Pin Description
Pin Number
PLCC SO
Pkg. Pkg.
1 7 DGND Digital ground. This is the device’s digital supply ground connection. It should be connected
2 8 IN0 These are the eight analog inputs to the multiplexer. For each conversion to be performed, the
3 9 IN1 active channels are selected according to the instruction RAM programming. Any individual
4 10 IN2 channel can be selected for a single-ended conversion referenced to AGND, or any pair of
5 11 IN3 channels, whether adjacent or non adjacent, can be selected as a fully differential input pairs.
6 12 IN4
7 13 IN5
8 14 IN6
9 15 IN7
10 16 V
11 17 V
12 18 AGND Analog ground. This is the device’s analog supply ground connection. It should be connected
13 19 V
14 20 DGND Digital ground. See above definition.
15 21 V
16 22 voltage range is
17 23 P5 P1 –P5 are the multi-function serial interface input or output pins that have different assignments
18 24 P4 Serial interface input/output: Standard: DO
19 25 P3 Serial interface input: Standard: DI
Pin Name Description
through a low resistance and low inductance ground return to the system power supply.
a
REF
Positive reference input. The operating voltage range for this input is 1VsV
Figures 3
and4). In order to achieve 12-bit performance this pin should be by passed to AGND
at least with a parallel combination of a 10 mF and a 0.1 mF (ceramic) capacitor. The capacitors
should be placed as close to the part as possible.
b
REF
Negative reference input. The operating voltage range for this input is 0 VsV
b
1V (See
Figures 3
and4). In order to achieve 12-bit performance, this pin should be bypassed
to AGND at least with a parallel combination of a 10 mF and a 0.1 mF (ceramic) capacitor. The
capacitors should be placed as close to the part as possible.
through a low resistance and low inductance ground return to the system power supply.
a
A
Analog supply. This is the supply connection for the analog circuitry. The device operating supply
voltage range is
a
3.0V toa5.5V. Accuracy is guaranteed only if the V
connected to the same potential. In order to achieve 12-bit performance, this pin should be
bypassed to AGND at least with a parallel combination of a 10 mF and a 0.1 mF (ceramic)
capacitor. The capacitors should be placed as close to the part as possible.
a
D
Digital supply. This is the supply connection for the analog circuitry. The device operating supply
a
3.0V toa5.5V. The device accuracy is guaranteed only if the V
are connected to the same potential. In order to achieve 12-bit performance this pin should be
by passed to DGND at least with a parallel combination of a 10 mF and a 0.1 mF (ceramic)
capacitor. The capacitors should be placed as close to the part as possible.
depending on the selected mode.
Serial interface input: Standard: SCLK
8051: TXD
2
I
C: SCL
TMS320: DR
8051: RXD
I2C: SDA
TMS320: DR
8051: CS
2
I
C: SAD2
TMS320: DX
a
a
s
V
REF
a
and V
A
REF
A
b
s
V
REF
a
are
D
a
and V
A
(See
a
D
a
23

5.0 Pin Descriptions (Continued)
TABLE I. LM12
Pin Number
PLCC SO
Pin Name Description
Pkg. Pkg.
20 26 P2 Serial interface input: Standard: CS
21 27 P1 Serial interface input: Standard: R/F (Clock rise/fall)
22 28 MODESEL2 Serial mode selection inputs. The logic states of these inputs determine the operation of
23 1 MODESEL1 the serial mode as shown below. The standard mode covers the National’s MICROWIRE,
Motorola’s SPI and Hitachi’s SCl protocols.
MODESEL1, MODESEL2: 01 Standard mode
24 2 CLK The device main clock input. The operating range of clock frequency is 0.05 MHz to
10.0 MHz. The device accuracy is guaranteed only for the clock frequencies indicated in
the specification tables.
25 3 INT Interrupt output. This is an active low output. An interrupt is generated any time a non-
masked interrupt condition takes place. There are seven different conditions that can
generate an interrupt. (Refer to Section 6.2.4). The interrupt is set high (inactive) by reading
the interrupt status register. This output can drive up to 100 pF of capacitive loads. An
external buffer should be used for driving higher capacitive loads.
26 4 SYNC Synchronization input/output. SYNC is an input if the Configuration Register’s SYNC I/O bit
is ‘‘0’’ and output when the bit is ‘‘1’’. When sync is an input, a rising edge on this pin
causes the internal S/H to hold the input signal and a conversion cycle or a comparison
cycle (depending on the programmed instruction) to be started. (The conversion or
comparison actually begins on the rising edge of the CLK immediately following the rising
edge of sync.) When output, it goes high at the start of a conversion or a comparison cycle
and returns low when the cycle is completed. At power up the SYNC pin is set as an input.
When used as an output it can drive up to 100 pF of capacitive loads. An external buffer
should be used for driving higher capacitive loads.
27 5 STANDBYOUT Stand-by output. This is an active low output. STANDBYOUT will be activated when the
LM12ÀLÓ438 is put into stand-by mode through the Configuration Register’s stand-by bit. It
is used to force any other devices in the system (signal conditioning circuitry, for example)
to go into power-down mode. This is done by connecting the ‘‘shutdown’’, ‘‘powerdown’’,
‘‘standby’’, etc. pins of the other ICs to STANDBYOUT
ICs do not have the power-down inputs, STANDBYOUT
through an electronic switch. Note that the logic polarity of the STANDBYOUT
opposite to that of the stand-by bit in the Configuration Register.
28 6 V
a
D
Digital supply. See above definition.
LM12434 Pin Description. (Same as LM12
LM12434 Pin Description (Same As LM12
6 12 MUXOUT
7 13 MUXOUT
8 14 S/H IN
9 15 S/H IN
b
b
a
Multiplexer outputs. These are the LM12434’s externally available analog MUX output pins.
a
Analog inputs are directed to these outputs based on the Instruction RAM programming.
Sample-and-hold inputs. These are the inverting and non-inverting inputs of the sampleand-hold. LM12434 allows external analog signal conditioning circuits to be placed
between MUX outputs and S/H inputs.
ÀLÓ
438 Pin Description (Continued)
8051: 1
2
I
C: SAD1
TMS320: FSX
8051: 1
2
I
C: SAD0
TMS320: FSR
00 8051
10 I
2
11 TMS320
ÀLÓ
438 with the exceptions of the following pins.)
ÀLÓ
438 with the exception of the following pins.)
C
. In those cases where the peripheral
can be used to turn off their power
is the
24
 Loading...
Loading...