查询COP87L88EGN-XE供应商
COP688EG/COP684EG/COP888EG/COP884EG/
COP988EG/COP984EG 8-Bit Microcontroller
with UART and Three Multi-Function Timers
General Description
The COP8TMfeature family of microcontrollers use an 8-bit
single-chip core architecture fabricated with National Semiconductor’s M
COP888EG/COP884EG are members of this expandable
8-bit core processor family of microcontrollers. (Continued)
Key Features
Y
Full duplex UART
Y
Three 16-bit timers, each with two 16-bit registers
supporting
Ð Processor Independent PWM mode
Ð External Event counter mode
Ð Input Capture mode
Y
Quiet design (low radiated emissions)
Y
8k bytes on-board ROM
Y
256 bytes on-board RAM
Additional Peripheral Features
Y
Idle Timer
Y
Multi-Input Wake-Up (MIWU) with optional interrupts (8)
Y
Two analog comparators
Y
WATCHDOGTMand clock monitor logic
Y
MICROWIRE/PLUSTMserial I/O
I/O Features
Y
Memory mapped I/O
Y
Software selectable I/O options (TRI-STATEÉOutput,
Push-Pull Output, Weak Pull-Up Input, High Impedance
Input)
Y
Schmitt trigger inputs on ports G and L
2
CMOSTMprocess technology. The
August 1996
Y
Packages:
Ð 28 SO or 28 DIP, each with 24 I/O pins
Ð 40 DIP with 36 I/O pins
Ð 44 PQFP with 40 I/O pins
Ð 44 PLCC with 40 I/O pins
CPU/Instruction Set Features
Y
1 ms instruction cycle time
Y
Fourteen multi-source vectored interrupts servicing
Ð External Interrupt with selectable edge
Ð Idle Timer T0
Ð Three Timers (each with 2 Interrupts)
Ð MICROWIRE/PLUS
Ð Multi-Input Wake-Up
Ð Software Trap
Ð UART (2)
Ð Default VIS (default interrupt)
Y
Versatile and easy to use instruction set
Y
8-bit Stack Pointer (SP) stack in RAM
Y
Two 8-bit Register Indirect Data Memory Pointers
(B and X)
Fully Static CMOS
Y
Two power saving modes: HALT and IDLE
Y
Low current drain (typicallyk1 mA)
Y
Single supply operation: 2.5V to 6.0V
Y
Temperature ranges: 0§Ctoa70§C,b40§Ctoa85§C,
b
55§Ctoa125§C
Development Support
Y
Emulation and OTP devices
Y
Real time emulation and full program debug offered by
MetaLink Development System
COP688EG/COP684EG/COP888EG/COP884EG/COP988EG/COP984EG
8-Bit Microcontroller with UART and Three Multi-Function Timers
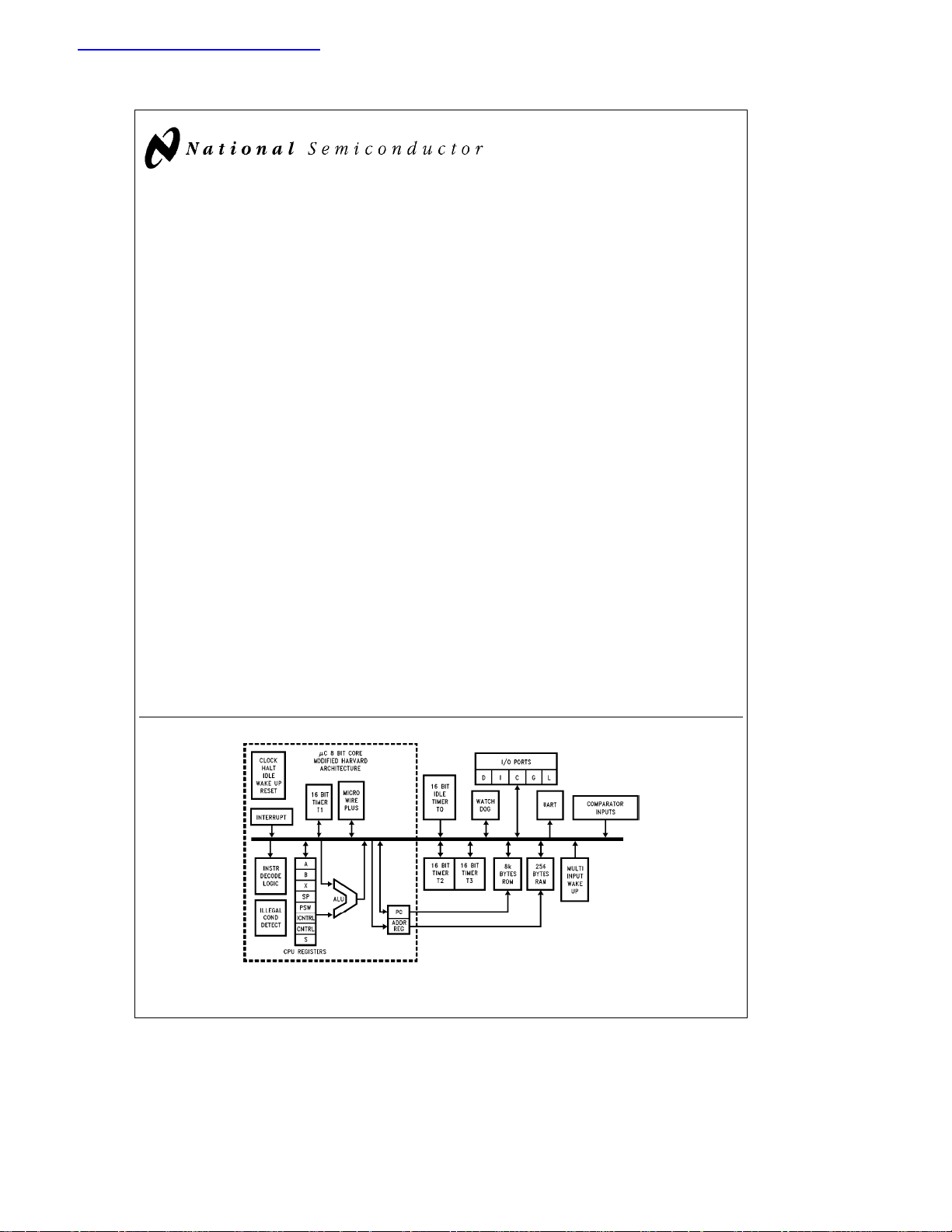
Block Diagram
TRI-STATEÉis a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
MICROWIRE/PLUS
IBM
É
iceMASTER
C
1996 National Semiconductor Corporation RRD-B30M106/Printed in U. S. A.
TM
,PCÉ, PC-ATÉand PC-XTÉare registered trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation.
,M2CMOSTM, COPSTMmicrocontrollers, MICROWIRETMand WATCHDOGTMare trademarks of National Semiconductor Corporation.
TM
is a trademark of MetaLink Corporation.
TL/DD11214
FIGURE 1. Block Diagram
TL/DD/11214– 1
http://www.national.com
General Description (Continued)
They are fully static parts, fabricated using double-metal silicon gate microCMOS technology. Features include an 8-bit
memory mapped architecture, MICROWIRE/PLUS serial
I/O, three 16-bit timer/counters supporting three modes
(Processor Independent PWM generation, External Event
counter, and Input Capture mode capabilities), full duplex
UART, two comparators, and two power savings modes
(HALT and IDLE), both with a multi-sourced wakeup/interrupt capability. This multi-sourced interrupt capability may
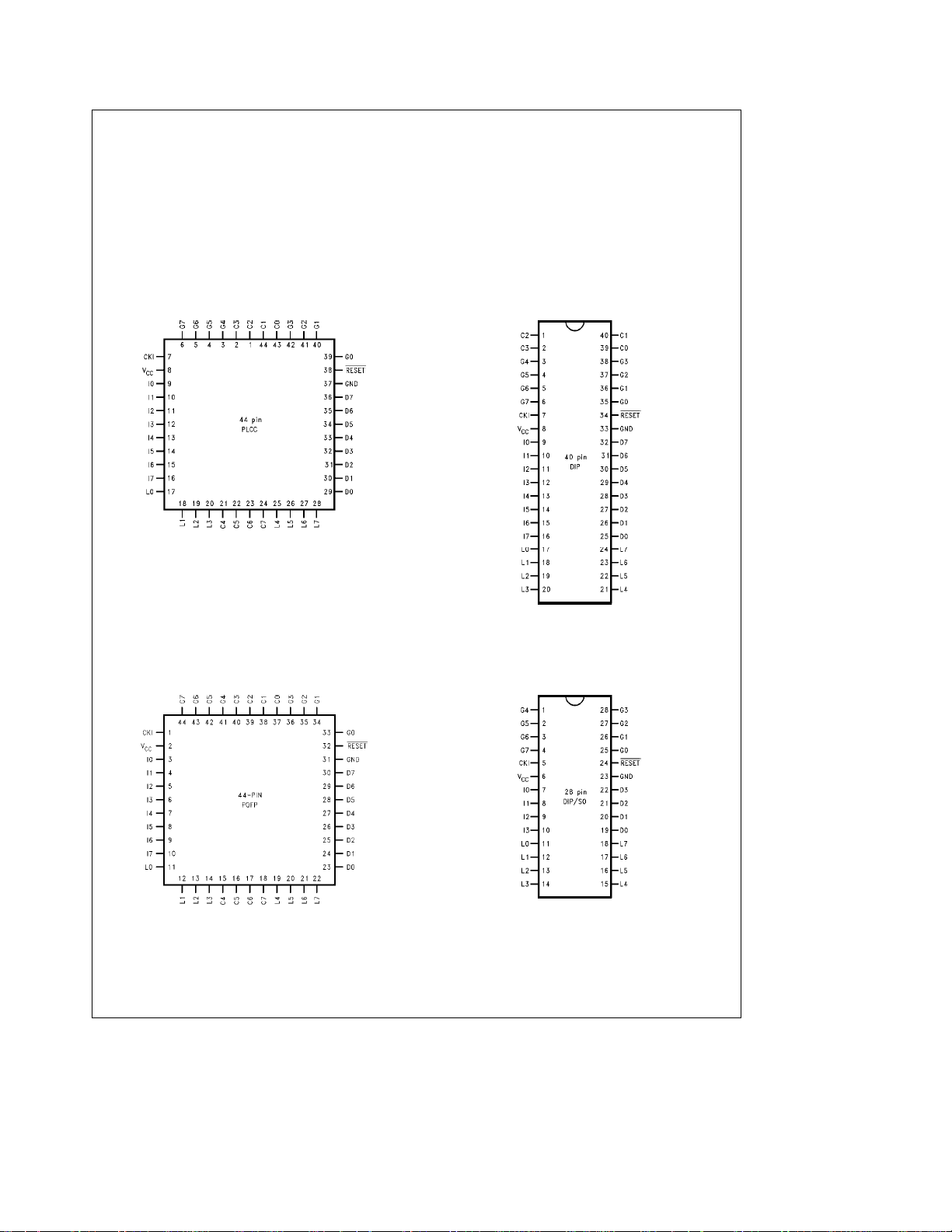
Connection Diagrams
Plastic Chip Carrier
also be used independent of the HALT or IDLE modes.
Each I/O pin has software selectable configurations. The
device operates over a voltage range of 2.5V to 6V. High
throughput is achieved with an efficient, regular instruction
set operating at a maximum rate of 1 ms per instruction.
Low radiated emissions are achieved by gradual turn-on
output drivers and internal I
logic and crystal oscillator.
smoothing filters on the chip
CC
Dual-In-Line Package
Top View
TL/DD/11214– 2
Order Number COP888EG-XXX/V
See NS Plastic Chip Package Number V44A
Molded Plastic Quad Flat Package
TL/DD/11214– 30
Top View
Order Number COP888EG-XXX/VEJ
See NS Package Number VEJ44A
FIGURE 2a. Connection Diagrams
Top View
TL/DD/11214– 3
Order Number COP888EG-XXX/N
See NS Molded Package Number N40A
Dual-In-Line Package
TL/DD/11214– 4
Top View
Order Number COP884EG-XXX/WM
or COP884EG-XXX/N
See NS Molded Package Number M28B or N28A
http://www.national.com 2
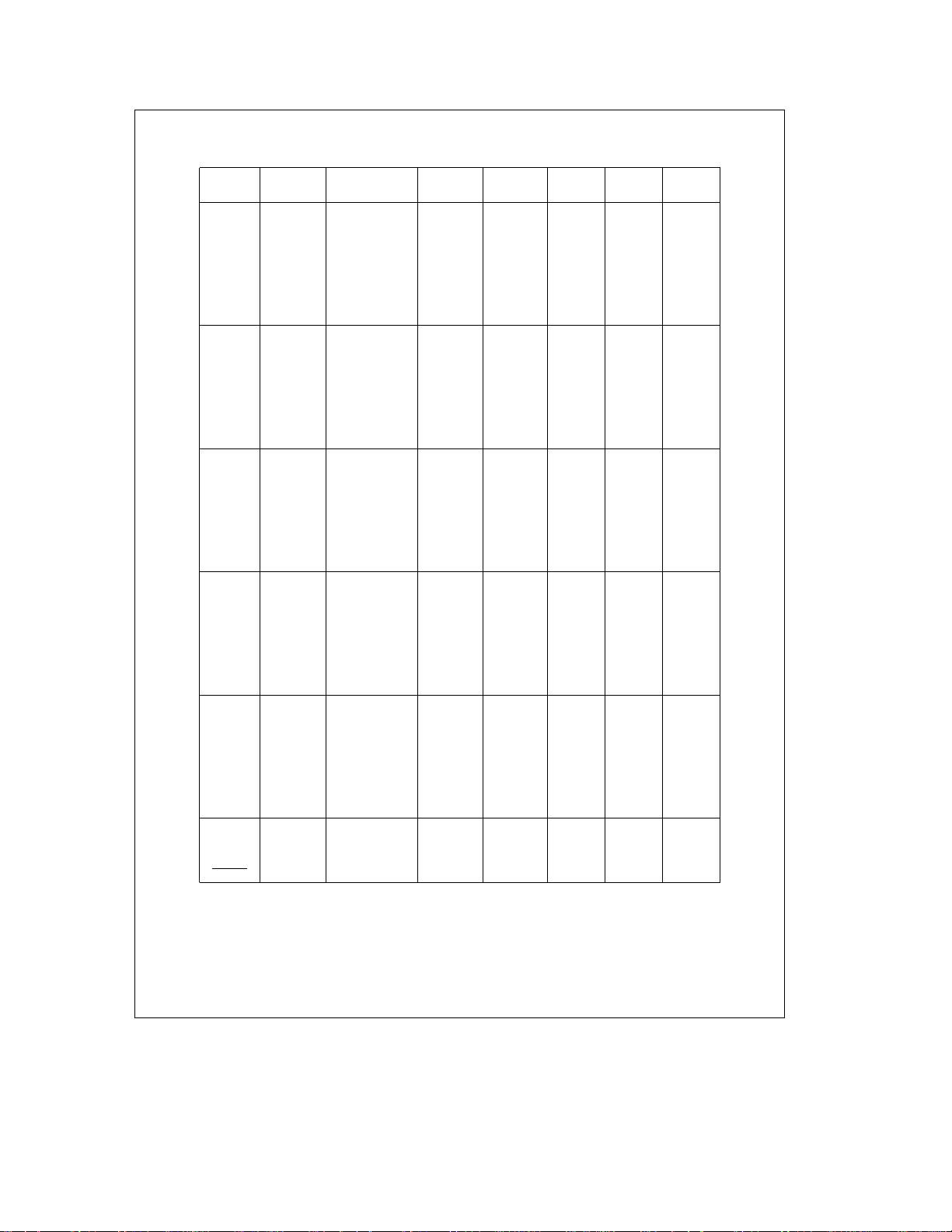
Connection Diagrams (Continued)
Pinouts for 28-, 40- and 44-Pin Packages
Port Type Alt. Fun Alt. Fun
L0 I/O MIWU 11 17 17 11
L1 I/O MIWU CKX 12 18 18 12
L2 I/O MIWU TDX 13 19 19 13
L3 I/O MIWU RDX 14 20 20 14
L4 I/O MIWU T2A 15 21 25 19
L5 I/O MIWU T2B 16 22 26 20
L6 I/O MIWU T3A 17 23 27 21
L7 I/O MIWU T3B 18 24 28 22
G0 I/O INT 25 35 39 33
G1 WDOUT 26 36 40 34
G2 I/O T1B 27 37 41 35
G3 I/O T1A 28 38 42 36
G4 I/O SO 1 3 3 41
G5 I/O SK 2 4 4 42
G6 I SI 3 5 5 43
G7 I/CKO HALT Restart 4 6 6 44
D0 O 19 25 29 23
D1 O 20 26 30 24
D2 O 21 27 31 25
D3 O 22 28 32 26
D4 O 29 33 7
D5 O 30 34 8
D6 O 31 35 9
D7 O 32 36 10
I0 I 7 9 9 27
I1 I COMP1IN
I2 I COMP1IN
I3 I COMP1OUT 10 12 12 30
I4 I COMP2IN
I5 I COMP2IN
I6 I COMP2OUT 15 15 5
I7 I 16 16 6
C0 I/O 39 43 37
C1 I/O 40 44 38
C2 I/O 1 1 39
C3 I/O 2 2 40
C4 I/O 21 15
C5 I/O 22 16
C6 I/O 23 17
C7 I/O 24 18
V
CC
GND 23 33 37 31
CKI 5 7 7 1
RESET
28-Pin 40-Pin 44-Pin 44-Pin
DIP/SO DIP PLCC PQFP
b
a
b
a
8101028
9111129
13 13 3
14 14 4
6882
24 34 38 32
http://www.national.com3
Absolute Maximum Ratings
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales
Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (V
Voltage at Any Pin
Total Current into V
)7V
CC
Pin (Source) 100 mA
CC
b
0.3V to V
CC
a
0.3V
DC Electrical Characteristics 98XEG: 0
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Operating Voltage COP98XEG 2.5 4.0 V
Power Supply Ripple (Note 1) Peak-to-Peak 0.1 V
Supply Current (Note 2)
e
CKI
10 MHz V
CKIe4 MHz V
e
CKI
4 MHz V
e
CKI
1 MHz V
HALT Current (Note 3) V
IDLE Current
e
CKI
10 MHz V
CKIe4 MHz V
e
CKI
1 MHz V
Input Levels
RESET
Logic High 0.8 V
Logic Low 0.2 V
CKI (External and Crystal Osc. Modes)
Logic High 0.7 V
Logic Low 0.2 V
All Other Inputs
Logic High 0.7 V
Logic Low 0.2 V
Hi-Z Input Leakage V
Input Pullup Current V
G and L Port Input Hysteresis 0.35 V
Output Current Levels
D Outputs
Source V
Sink V
All Others
Source (Weak Pull-Up Mode) V
Source (Push-Pull Mode) V
Sink (Push-Pull Mode) V
TRI-STATE Leakage V
Note 1: Rate of voltage change must be less then 0.5 V/ms.
Note 2: Supply current is measured after running 2000 cycles with a square wave CKI input, CKO open, inputs at rails and outputs open.
Note 3: The HALT mode will stop CKI from oscillating in the RC and the Crystal configurations. Test conditions: All inputs tied to V
outputs and set high. The D port set to zero. The clock monitor and the comparators are disabled.
COP98XEGH 4.0 6.0 V
e
6V, t
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
V
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
V
CC
CC
V
CC
CC
V
CC
CC
V
CC
CC
V
CC
CC
c
e
6V, t
c
e
4V, t
c
e
4V, t
c
e
6V, CKIe0 MHz
e
4V, CKIe0 MHz
e
6V, t
c
e
6V, t
c
e
4V, t
c
e
6V
e
6V, V
e
4V, V
e
2.5V, V
e
4V, V
e
2.5V, V
e
4V, V
e
2.5V, V
e
4V, V
e
2.5V, V
e
4V, V
e
2.5V, V
e
6.0V
Total Current out of GND Pin (Sink) 110 mA
Storage Temperature Range
Note:
Absolute maximum ratings indicate limits beyond
b
65§Ctoa140§C
which damage to the device may occur. DC and AC electrical specifications are not ensured when operating the device at absolute maximum ratings.
s
CsT
§
e
e
e
e
e
e
e
IN
OH
OH
OL
OL
OH
OH
OH
OH
OL
OL
a
70§C unless otherwise specified
A
CC
1 ms 12.5 mA
2.5 ms 5.5 mA
2.5 ms 2.5 mA
10 ms 1.4 mA
k
0.7 8 mA
k
0.3 4 mA
1 ms 3.5 mA
2.5 ms 2.5 mA
10 ms 0.7 mA
CC
CC
CC
b
1
e
0V
e
3.3V
e
1.8V
e
1V 10 mA
e
0.4V 2.0 mA
e
2.7V
e
1.8V
e
3.3V
e
1.8V
e
0.4V 1.6 mA
e
0.4V 0.7 mA
b
40
b
0.4 mA
b
0.2 mA
b
10
b
2.5
b
0.4 mA
b
0.2 mA
b
1
CC
CC
CC
a
1 mA
b
250 mA
CC
b
100 mA
b
33 mA
a
1 mA
, L and G0-G5configured as
CC
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
http://www.national.com 4
s
DC Electrical Characteristics 98XEG: 0
CsT
§
a
70§C unless otherwise specified (Continued)
A
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Allowable Sink/Source
Current per Pin
D Outputs (Sink) 15 mA
All others 3mA
Maximum Input Current T
without Latchup (Note 5)
RAM Retention Voltage, V
r
e
25§C
A
500 ns Rise
and Fall Time (Min)
g
100 mA
2V
Input Capacitance 7pF
Load Capacitance on D2 1000 pF
s
AC Electrical Characteristics 98XEG: 0
CsT
§
a
70§C unless otherwise specified
A
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
s
Instruction Cycle Time (tc)4V
Crystal, Resonator, 2.5V
R/C Oscillator 4V
s
V
6V 1 DC ms
CC
k
s
V
4V 2.5 DC ms
CC
s
s
V
6V 3 DC ms
CC
k
s
2.5V
V
4V 7.5 DC ms
CC
Inputs
t
SETUP
t
HOLD
4VsV
2.5V
4VsV
2.5V
Output Propagation Delay (Note 6) R
t
PD1,tPD0
SO, SK 4VsV
2.5VsV
All Others 4V
2.5V
MICROWIRETMSetup Time (t
MICROWIRE Hold Time (t
MICROWIRE Output Propagation Delay (t
)20ns
UWS
)56ns
UWH
) 220 ns
UPD
s
6V 200 ns
CC
k
s
V
4V 500 ns
CC
s
6V 60 ns
CC
k
s
V
4V 150 ns
CC
e
L
s
e
2.2k, C
CC
V
CC
s
V
100 pF
L
s
6V 0.7 ms
k
4V 1.75 ms
CC
s
6V 1 ms
k
4V 2.5 ms
CC
Input Pulse Width
Interrupt Input High Time 1 t
Interrupt Input Low Time 1 t
Timer Input High Time 1 t
Timer Input Low Time 1 t
c
c
c
c
Reset Pulse Width 1 ms
Note 5: Pins G6 and RESET are designed with a high voltage input network for factory testing. These pins allow input voltages greater than VCCand the pins will
have sink current to V
resistance to V
Note 6: The output propagation delay is referenced to the end of the instruction cycle where the output change occurs.
when biased at voltages greater than VCC(the pins do not have source current when biased at a voltage below VCC). The effective
CC
is 750X (typical). These two pins will not latch up. The voltage at the pins must be limited to less than 14V.
CC
http://www.national.com5
Absolute Maximum Ratings
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales
Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (V
Voltage at Any Pin
Total Current into V
DC Electrical Characteristics 888EG:
)7V
CC
Pin (Source) 100 mA
CC
b
0.3V to V
CC
a
0.3V
b
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Operating Voltage 2.5 6 V
Power Supply Ripple (Note 1) Peak-to-Peak 0.1 V
Supply Current (Note 2)
e
CKI
10 MHz V
e
CKI
4 MHz V
CKIe4 MHz V
e
CKI
1 MHz V
HALT Current (Note 3) V
e
6V, t
CC
e
6V, t
CC
e
4.0V, t
CC
e
4.0V, t
CC
e
6V, CKIe0 MHz
CC
e
V
4.0V, CKIe0 MHz
CC
c
c
IDLE Current
e
CKI
10 MHz V
e
CKI
4 MHz V
CKIe1 MHz V
CC
CC
CC
e
e
e
6V, t
6V, t
4.0V, t
c
c
Input Levels
RESET
Logic High 0.8 V
Logic Low 0.2 V
CKI (External and Crystal Osc. Modes)
Logic High 0.7 V
Logic Low 0.2 V
All Other Inputs
Logic High 0.7 V
Logic Low 0.2 V
Hi-Z Input Leakage V
Input Pullup Current V
CC
CC
e
6V
e
6V, V
G and L Port Input Hysteresis 0.35 V
Output Current Levels
D Outputs
Source V
Sink V
All Others
Source (Weak Pull-Up Mode) V
Source (Push-Pull Mode) V
Sink (Push-Pull Mode) V
TRI-STATE Leakage V
Note 1: Rate of voltage change must be less then 0.5 V/ms.
Note 2: Supply current is measured after running 2000 cycles with a crystal/resonator oscillator, inputs at rails and outputs open.
Note 3: The HALT mode will stop CKI from oscillating in the RC and the Crystal configurations. Test conditions: All inputs tied to V
as outputs and set high. The D port set to zero. The clock monitor and the comparators are disabled.
e
4V, V
CC
e
V
2.5V, V
CC
e
4V, V
CC
e
V
2.5V, V
CC
e
4V, V
CC
e
V
2.5V, V
CC
e
4V, V
CC
e
V
2.5V, V
CC
e
4V, V
CC
e
V
2.5V, V
CC
e
6.0V
CC
Total Current out of GND Pin (Sink) 110 mA
Storage Temperature Range
Note:
Absolute maximum ratings indicate limits beyond
b
65§Ctoa140§C
which damage to the device may occur. DC and AC electrical specifications are not ensured when operating the device at absolute maximum ratings.
s
40§CsT
e
1 ms 12.5 mA
e
2.5 ms 5.5 mA
e
c
e
c
e
1 ms 3.5 mA
e
2.5 ms 2.5 mA
e
c
e
IN
e
OH
OH
e
OL
e
OL
e
OH
OH
e
OH
OH
e
OL
e
OL
a
85§C unless otherwise specified
A
CC
2.5 ms 2.5 mA
10 ms 1.4 mA
k
110mA
k
0.5 6 mA
10 ms 0.7 mA
0V
3.3V
e
1.8V
CC
CC
CC
b
2
b
40
b
0.4 mA
b
0.2 mA
CC
CC
CC
a
2 mA
b
250 mA
CC
1V 10 mA
0.4V 2.0 mA
2.7V
e
3.3V
e
1.8V
1.8V
b
10
b
2.5
b
0.4 mA
b
0.2 mA
b
100 mA
b
33 mA
0.4V 1.6 mA
0.4V 0.7 mA
b
2
a
2 mA
,L,C,andG0-G5configured
CC
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
http://www.national.com 6
DC Electrical Characteristics 888EG:
b
40§CsT
s
a
85§C unless otherwise specified (Continued)
A
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Allowable Sink/Source
Current per Pin
D Outputs (Sink) 15 mA
All others 3mA
Maximum Input Current T
without Latchup
RAM Retention Voltage, V
r
e
25§C
A
500 ns Rise
and Fall Time (Min)
g
100 mA
2V
Input Capacitance 7pF
Load Capacitance on D2 1000 pF
AC Electrical Characteristics 888EG:
b
40§CsT
s
a
85§C unless otherwise specified
A
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Instruction Cycle Time (tc)
s
4V
2.5V
s
V
6V 1 DC ms
CC
k
s
V
4V 2.5 DC ms
CC
s
s
V
6V 3 DC ms
CC
k
s
V
4V 7.5 DC ms
CC
Crystal, Resonator, 4V
R/C Oscillator 2.5V
Inputs
t
SETUP
t
HOLD
4VsV
2.5V
4VsV
2.5V
Output Propagation Delay (Note 4) R
t
PD1,tPD0
SO, SK 4VsV
2.5V
All Others 4V
2.5V
MICROWIRETMSetup Time (t
MICROWIRE Hold Time (t
MICROWIRE Output Propagation Delay (t
)20ns
UWS
)56ns
UWH
) 220 ns
UPD
s
6V 200 ns
CC
k
s
V
4V 500 ns
CC
s
6V 60 ns
CC
k
s
V
4V 150 ns
CC
e
L
s
e
2.2k, C
CC
s
V
V
CC
s
V
100 pF
L
s
6V 0.7 ms
k
4V 1.75 ms
CC
s
6V 1 ms
k
4V 2.5 ms
CC
Input Pulse Width
Interrupt Input High Time 1 t
Interrupt Input Low Time 1 t
Timer Input High Time 1 t
Timer Input Low Time 1 t
Reset Pulse Width 1 ms
e
t
Instruction cycle time.
c
Note 4: The output propagation delay is referenced to the end of the instruction cycle where the output change occurs.
c
c
c
c
http://www.national.com7
Absolute Maximum Ratings
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales
Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (V
Voltage at Any Pin
Total Current into V
DC Electrical Characteristics 688EG:
)7V
CC
Pin (Source) 100 mA
CC
b
0.3V to V
CC
a
0.3V
b
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Operating Voltage 4.5 5.5 V
Power Supply Ripple (Note 1) Peak-to-Peak 0.1 V
Supply Current (Note 2)
e
CKI
10 MHz V
e
CKI
4 MHz V
HALT Current (Note 3) V
e
5.5V, t
CC
e
5.5V, t
CC
e
5.5V, CKIe0 MHz
CC
IDLE Current
e
CKI
10 MHz V
e
CKI
4 MHz V
CC
CC
e
e
5.5V, t
5.5V, t
Input Levels
RESET
Logic High 0.8 V
Logic Low 0.2 V
CKI (External and Crystal Osc. Modes)
Logic High 0.7 V
Logic Low 0.2 V
All Other Inputs
Logic High 0.7 V
Logic Low 0.2 V
Hi-Z Input Leakage V
Input Pullup Current V
CC
CC
e
e
5.5V
5.5V, V
G and L Port Input Hysteresis 0.35 V
Output Current Levels
D Outputs
Source V
Sink V
All Others
Source (Weak Pull-Up Mode) V
Source (Push-Pull Mode) V
Sink (Push-Pull Mode) V
TRI-STATE Leakage V
Note 1: Rate of voltage change must be less then 0.5 V/ms.
Note 2: Supply current is measured after running 2000 cycles with a crystal/resonator oscillator, inputs at rails and outputs open.
Note 3: The HALT mode will stop CKI from oscillating in the RC and the Crystal configurations. Test conditions: All inputs tied to V
as outputs and set high. The D port set to zero. The clock monitor and the comparators are disabled.
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
e
e
e
e
e
e
4.5V, V
4.5V, V
4.5V, V
4.5V, V
4.5V, V
5.5V
Total Current out of GND Pin (Sink) 110 mA
Storage Temperature Range
Note:
Absolute maximum ratings indicate limits beyond
b
65§Ctoa140§C
which damage to the device may occur. DC and AC electrical specifications are not ensured when operating the device at absolute maximum ratings.
s
55§CsT
e
c
e
c
e
c
e
c
e
IN
OH
OL
OH
OH
OL
a
125§C unless otherwise specified
A
CC
1 ms 12.5 mA
2.5 ms 5.5 mA
k
10 30 mA
1 ms 3.5 mA
2.5 ms 2.5 mA
CC
CC
CC
b
5
0V
e
3.3V
e
1V 9 mA
e
2.7V
e
3.3V
e
0.4V 1.4 mA
b
35
b
0.4 mA
b
9
b
0.4 mA
b
5
CC
CC
CC
a
5 mA
b
400 mA
CC
b
140 mA
a
5 mA
,L,C,andG0-G5configured
CC
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
http://www.national.com 8
DC Electrical Characteristics 688EG:
b
55§CsT
s
a
125§C unless otherwise specified (Continued)
A
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Allowable Sink/Source
Current per Pin
D Outputs (Sink) 12 mA
All others 2.5 mA
Maximum Input Current T
without Latchup
RAM Retention Voltage, V
r
e
25§C
A
500 ns Rise
and Fall Time (Min)
g
100 mA
2V
Input Capacitance 7pF
Load Capacitance on D2 1000 pF
AC Electrical Characteristics 688EG:
b
55§CsT
s
a
125§C unless otherwise specified
A
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Instruction Cycle Time (tc)
Crystal, Resonator, V
R/C Oscillator V
t
4.5V 1 DC ms
CC
t
4.5V 3 DC ms
CC
Inputs
t
SETUP
t
HOLD
Output Propagation Delay (Note 4) R
t
PD1,tPD0
SO, SK V
All Others V
MICROWIRE Setup Time (t
MICROWIRE Hold Time (t
MICROWIRE Output Propagation Delay (t
)20ns
UWS
)56ns
UWH
) 220 ns
UPD
t
V
4.5V 200 ns
CC
t
V
4.5V 60 ns
CC
L
CC
CC
e
t
t
e
2.2k, C
100 pF
L
4.5V 0.7 ms
4.5V 1 ms
Input Pulse Width
Interrupt Input High Time 1 t
Interrupt Input Low Time 1 t
Timer Input High Time 1 t
Timer Input Low Time 1 t
Reset Pulse Width 1 ms
Note 4: The output propagation delay is referenced to the end of instruction cycle where the output change occurs.
c
c
c
c
http://www.national.com9
Comparators AC and DC Characteristics V
CC
e
5V, T
e
25§C
A
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Input Offset Voltage 0.4VsV
b
V
CC
1.5V
IN
g
10
s
Input Common Mode Voltage Range 0.4 V
Low Level Output Current V
High Level Output Current V
e
0.4V 1.6 mA
OL
e
4.6V 1.6 mA
OH
DC Supply Current Per Comparator
(When Enabled)
Response Time TBD mV Step, TBD mV
Overdrive, 100 pF Load
1 ms
g
25 mV
b
1.5 V
CC
250 mA
FIGURE 2. MICROWIRE/PLUS Timing
TL/DD/11214– 5
http://www.national.com 10
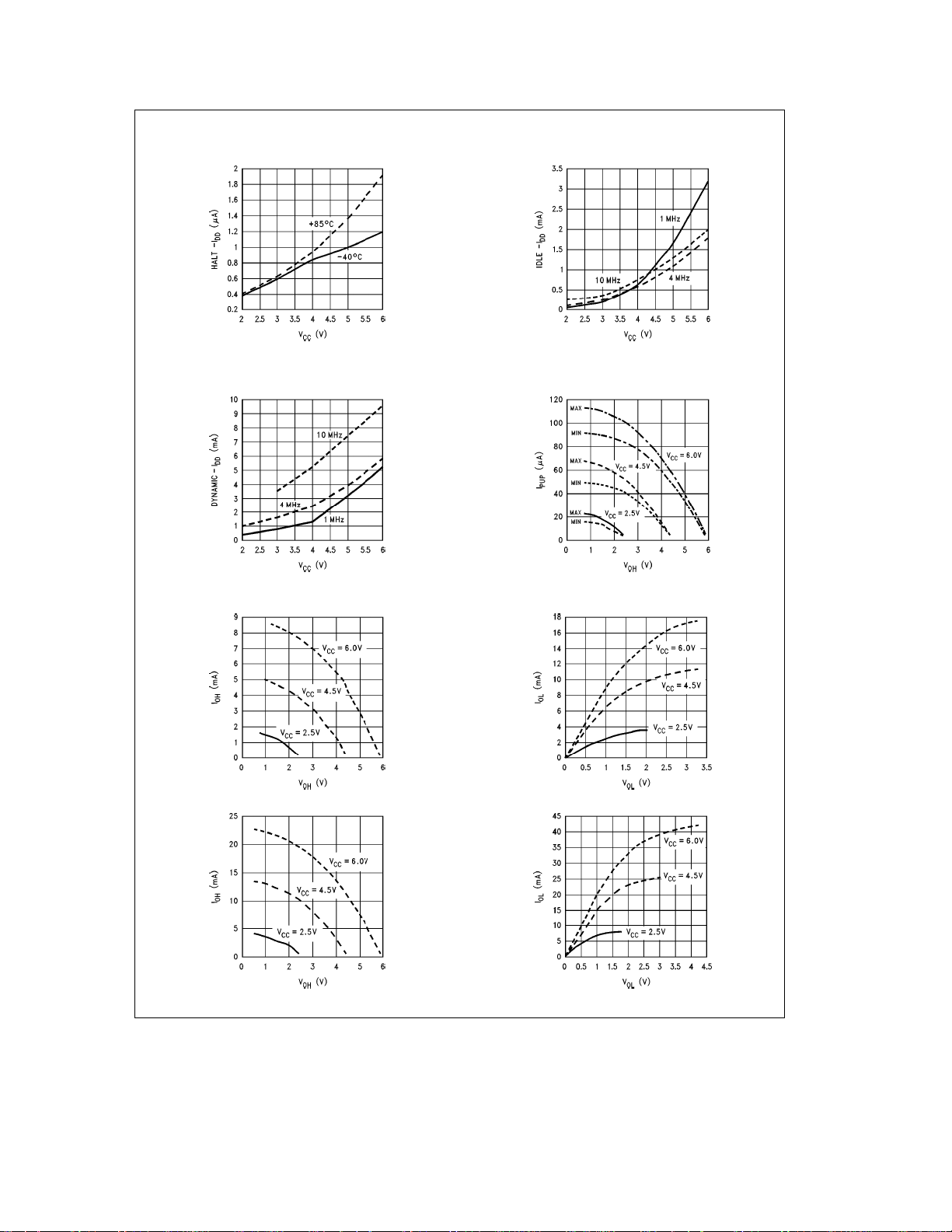
Typical Performance Characteristics (
HaltÐI
DD
b
40§CsT
s
a
85§C)
A
IdleÐIDD(Crystal Clock Option)
TL/DD/11214– 7
DynamicÐIDDvs V
(Crystal Clock Option)
CC
TL/DD/11214– 9
Port L/C/G Push-Pull Source Current
Port D Source Current
TL/DD/11214– 11
TL/DD/11214– 8
Port L/C/G Weak Pull-Up
Source Current
TL/DD/11214– 10
Port L/C/G Push-Pull Sink Current
TL/DD/11214– 12
Port D Sink Current
TL/DD/11214– 13
TL/DD/11214– 14
http://www.national.com11
Pin Descriptions
VCCand GND are the power supply pins.
CKI is the clock input. This can come from an R/C generated oscillator, or a crystal oscillator (in conjunction with
CKO). See Oscillator Description section.
RESET
is the master reset input. See Reset Description
section.
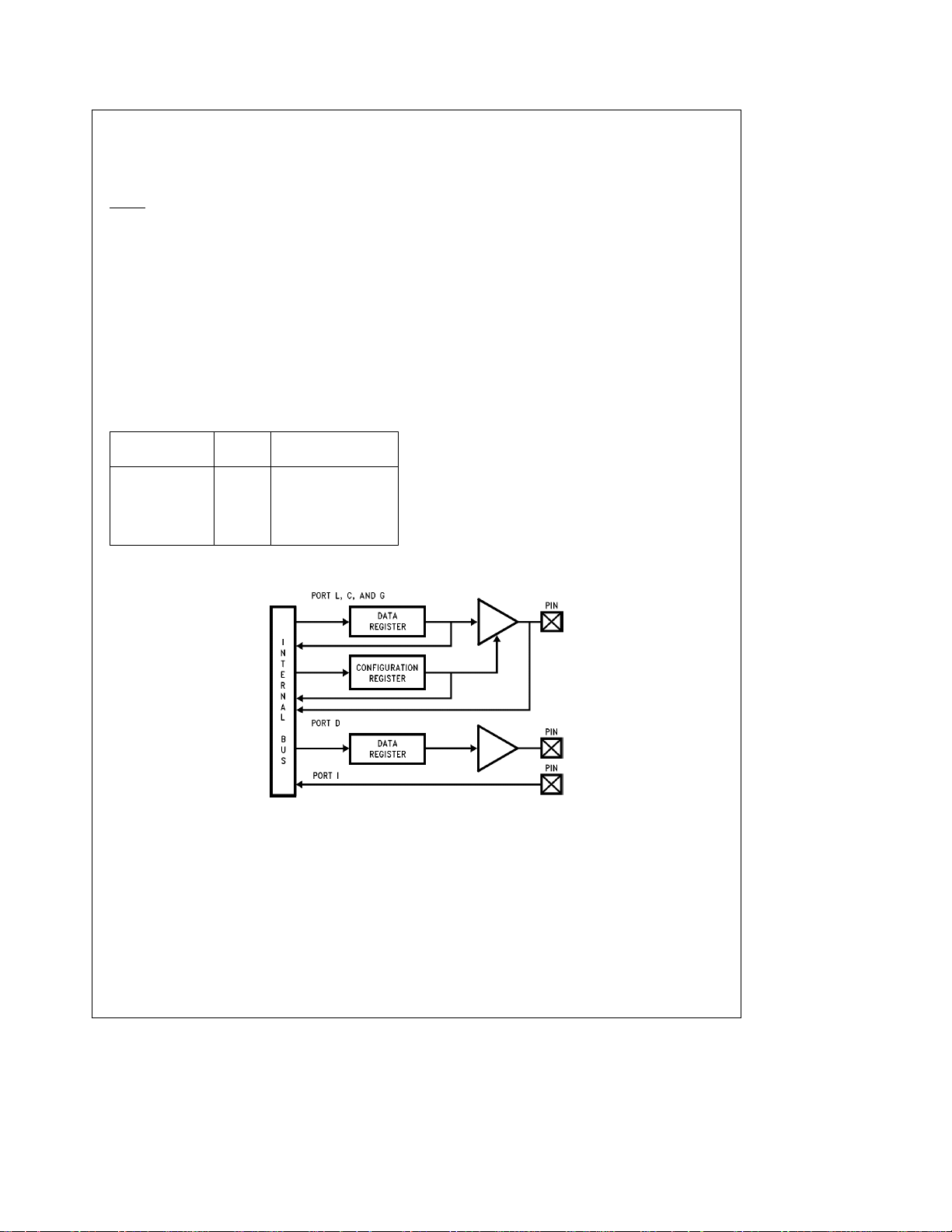
The device contains three bidirectional 8-bit I/O ports (C, G
and L), where each individual bit may be independently configured as an input (Schmitt trigger inputs on ports L and G),
output or TRI-STATE under program control. Three data
memory address locations are allocated for each of these
I/O ports. Each I/O port has two associated 8-bit memory
mapped registers, the CONFIGURATION register and the
output DATA register. A memory mapped address is also
reserved for the input pins of each I/O port. (See the memory map for the various addresses associated with the I/O
ports.)
Figure 3
DATA and CONFIGURATION registers allow for each port
bit to be individually configured under software control as
shown below:
CONFIGURATION DATA
Register Register
shows the I/O port configurations. The
Port Set-Up
0 0 Hi-Z Input
(TRI-STATE Output)
0 1 Input with Weak Pull-Up
1 0 Push-Pull Zero Output
1 1 Push-Pull One Output
PORT L is an 8-bit I/O port. All L-pins have Schmitt triggers
on the inputs.
The Port L supports Multi-Input Wake Up on all eight pins.
L1 is used for the UART external clock. L2 and L3 are used
for the UART transmit and receive. L4 and L5 are used for
the timer input functions T2A and T2B. L6 and L7 are used
for the timer input functions T3A and T3B.
The Port L has the following alternate features:
L0 MIWU
L1 MIWU or CKX
L2 MIWU or TDX
L3 MIWU or RDX
L4 MIWU or T2A
L5 MIWU or T2B
L6 MIWU or T3A
L7 MIWU or T3B
Port G is an 8-bit port with 5 I/O pins (G0, G2 –G5), an input
pin (G6), and two dedicated output pins (G1 and G7). Pins
G0 and G2 –G6 all have Schmitt Triggers on their inputs. Pin
G1 serves as the dedicated WDOUT WATCHDOG output,
while pin G7 is either input or output depending on the oscillator mask option selected. With the crystal oscillator option
selected, G7 serves as the dedicated output pin for the CKO
clock output. With the single-pin R/C oscillator mask option
selected, G7 serves as a general purpose input pin but is
also used to bring the device out of HALT mode with a low
to high transition on G7. There are two registers associated
with the G Port, a data register and a configuration register.
Therefore, each of the 5 I/O bits (G0, G2 – G5) can be individually configured under software control.
FIGURE 3. I/O Port Configurations
http://www.national.com 12
TL/DD/11214– 6
Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Since G6 is an input only pin and G7 is the dedicated CKO
clock output pin (crystal clock option) or general purpose
input (R/C clock option), the associated bits in the data and
configuration registers for G6 and G7 are used for special
purpose functions as outlined below. Reading the G6 and
G7 data bits will return zeros.
Note that the chip will be placed in the HALT mode by writing a ‘‘1’’ to bit 7 of the Port G Data Register. Similarly the
chip will be placed in the IDLE mode by writing a ‘‘1’’ to bit 6
of the Port G Data Register.
Writing a ‘‘1’’ to bit 6 of the Port G Configuration Register
enables the MICROWIRE/PLUS to operate with the alternate phase of the SK clock. The G7 configuration bit, if set
high, enables the clock start up delay after HALT when the
R/C clock configuration is used.
Config Reg. Data Reg.
G7 CLKDLY HALT
G6 Alternate SK IDLE
Port G has the following alternate features:
G0 INTR (External Interrupt Input)
G2 T1B (Timer T1 Capture Input)
G3 T1A (Timer T1 I/O)
G4 SO (MICROWIRE
G5 SK (MICROWIRE Serial Clock)
G6 SI (MICROWIRE Serial Data Input)
Port G has the following dedicated functions:
G1 WDOUT WATCHDOG and/or Clock Monitor dedicat-
ed output
G7 CKO Oscillator dedicated output or general purpose
input
Port C is an 8-bit I/O port. The 40-pin device does not have
a full complement of Port C pins. The unavailable pins are
not terminated. A read operation for these unterminated
pins will return unpredicatable values.
PORT I is an eight-bit Hi-Z input port. The 28-pin device
does not have a full complement of Port I pins. The unavailable pins are not terminated i.e., they are floating. A read
operation for these unterminated pins will return unpredictable values. The user must ensure that the software takes
this into account by either masking or restricting the accesses to bit operations. The unterminated Port I pins will draw
power only when addressed.
Port I1–I3 are used for Comparator 1. Port I4 –I6 are used
for Comparator 2.
The Port I has the following alternate features.
I1 COMP1
I2 COMP1aIN (Comparator 1 Positive Input)
I3 COMP1OUT (Comparator 1 Output)
I4 COMP2bIN (Comparator 2 Negative Input)
I5 COMP2
I6 COMP2OUT (Comparator 2 Output)
Port D is an 8-bit output port that is preset high when
RESET
goes low. The user can tie two or more D port out-
puts (except D2) together in order to get a higher drive.
Note: Care must be exercised with the D2 pin operation. At RESET, the
external loads on this pin must ensure that the output voltages stay
above 0.8 V
keep the external loading on D2 to less than 1000 pF.
CC
TM
Serial Data Output)
b
IN (Comparator 1 Negative Input)
a
IN (Comparator 2 Positive Input)
to prevent the chip from entering special modes. Also
Functional Description
The architecture of the device is modified Harvard architecture. With the Harvard architecture, the control store program memory (ROM) is separated from the data store memory (RAM). Both ROM and RAM have their own separate
addressing space with separate address buses. The architecture, though based on Harvard architecture, permits
transfer of data from ROM to RAM.
CPU REGISTERS
The CPU can do an 8-bit addition, subtraction, logical or
shift operation in one instruction (t
There are six CPU registers:
A is the 8-bit Accumulator Register
PC is the 15-bit Program Counter Register
PU is the upper 7 bits of the program counter (PC)
PL is the lower 8 bits of the program counter (PC)
B is an 8-bit RAM address pointer, which can be optionally
post auto incremented or decremented.
X is an 8-bit alternate RAM address pointer, which can be
optionally post auto incremented or decremented.
SP is the 8-bit stack pointer, which points to the subroutine/
interrupt stack (in RAM). The SP is initialized to RAM address 06F with reset.
S is the 8-bit Data Segment Address Register used to extend the lower half of the address range (00 to 7F) into 256
data segments of 128 bytes each.
All the CPU registers are memory mapped with the exception of the Accumulator (A) and the Program Counter (PC).
PROGRAM MEMORY
The program memory consists of 8192 bytes of ROM.
These bytes may hold program instructions or constant data
(data tables for the LAID instruction, jump vectors for the
JID instruction, and interrupt vectors for the VIS instruction).
The program memory is addressed by the 15-bit program
counter (PC). All interrupts in the devices vector to program
memory location 0FF Hex.
DATA MEMORY
The data memory address space includes the on-chip RAM
and data registers, the I/O registers (Configuration, Data
and Pin), the control registers, the MICROWIRE/PLUS SIO
shift register, and the various registers, and counters associated with the timers (with the exception of the IDLE timer).
Data memory is addressed directly by the instruction or indirectly by the B, X, SP pointers and S register.
The data memory consists of 256 bytes of RAM. Sixteen
bytes of RAM are mapped as ‘‘registers’’ at addresses 0F0
to 0FF Hex. These registers can be loaded immediately,
and also decremented and tested with the DRSZ (decrement register and skip if zero) instruction. The memory
pointer registers X, SP, B and S are memory mapped into
this space at address locations 0FC to 0FF Hex respectively, with the other registers being available for general usage.
The instruction set permits any bit in memory to be set,
reset or tested. All I/O and registers (except A and PC) are
memory mapped; therefore, I/O bits and register bits can be
directly and individually set, reset and tested. The accumulator (A) bits can also be directly and individually tested.
Note: RAM contents are undefined upon power-up.
) cycle time.
c
http://www.national.com13
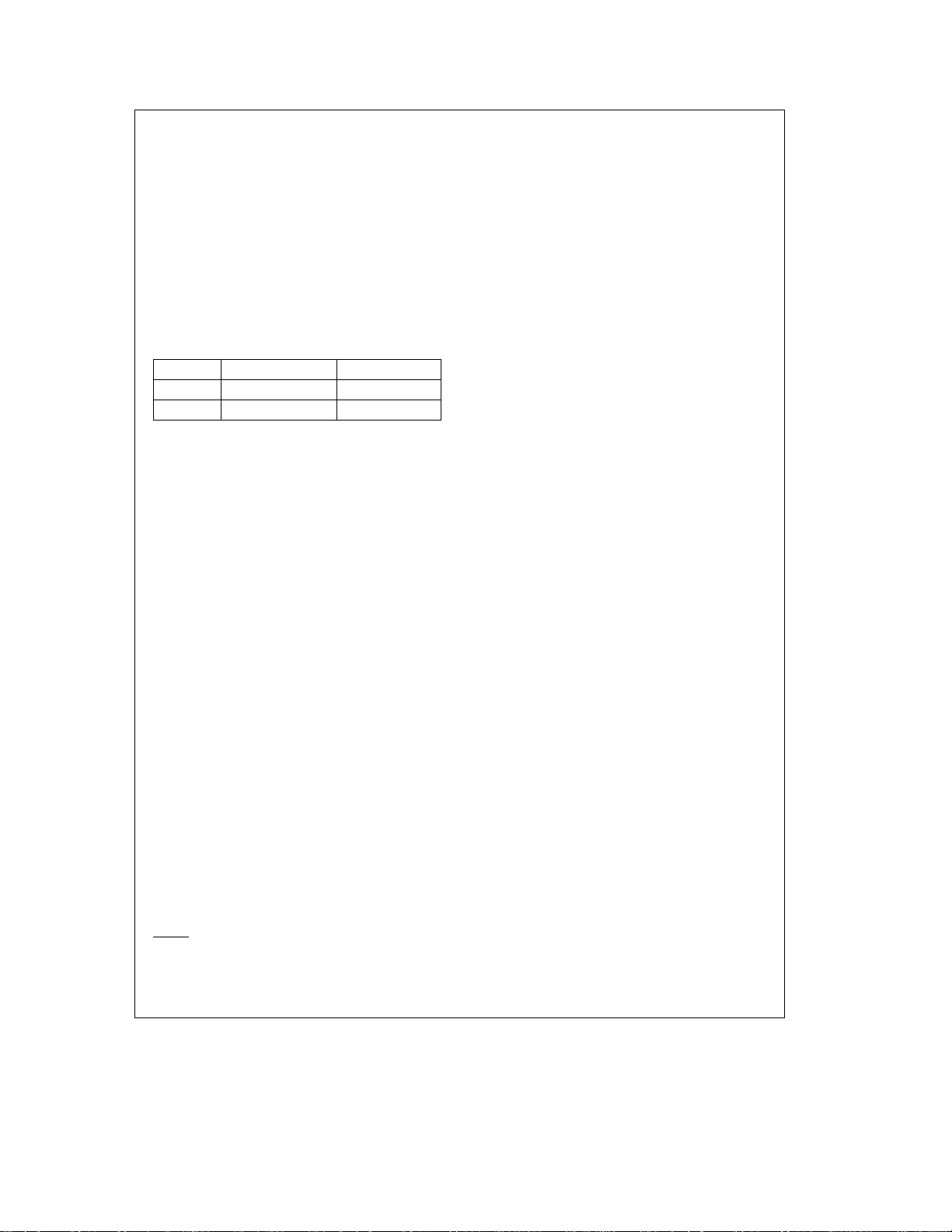
Data Memory Segment RAM Extension
Data memory address 0FF is used as a memory mapped
location for the Data Segment Address Register (S).
The data store memory is either addressed directly by a
single byte address within the instruction, or indirectly relative to the reference of the B, X, or SP pointers (each contains a single-byte address). This single-byte address allows
an addressing range of 256 locations from 00 to FF hex.
The upper bit of this single-byte address divides the data
store memory into two separate sections as outlined previously. With the exception of the RAM register memory from
address locations 00F0 to 00FF, all RAM memory is memory mapped with the upper bit of the single-byte address being equal to zero. This allows the upper bit of the single-byte
address to determine whether or not the base address
range (from 0000 to 00FF) is extended. If this upper bit
equals one (representing address range 0080 to 00FF),
then address extension does not take place. Alternatively, if
this upper bit equals zero, then the data segment extension
register S is used to extend the base address range (from
0000 to 007F) from XX00 to XX7F, where XX represents the
8 bits from the S register. Thus the 128-byte data segment
extensions are located from addresses 0100 to 017F for
data segment 1, 0200 to 027F for data segment 2, etc., up
to FF00 to FF7F for data segment 255. The base address
range from 0000 to 007F represents data segment 0.
Figure 4
illustrates how the S register data memory extension is used in extending the lower half of the base address
range (00 to 7F hex) into 256 data segments of 128 bytes
each, with a total addressing range of 32 kbytes from XX00
to XX7F. This organization allows a total of 256 data segments of 128 bytes each with an additional upper base segment of 128 bytes. Furthermore, all addressing modes are
available for all data segments. The S register must be
changed under program control to move from one data segment (128 bytes) to another. However, the upper base segment (containing the 16 memory registers, I/O registers,
control registers, etc.) is always available regardless of the
contents of the S register, since the upper base segment
(address range 0080 to 00FF) is independent of data segment extension.
The instructions that utilize the stack pointer (SP) always
reference the stack as part of the base segment (Segment
0), regardless of the contents of the S register. The S register is not changed by these instructions. Consequently, the
stack (used with subroutine linkage and interrupts) is always
located in the base segment. The stack pointer will be intitialized to point at data memory location 006F as a result of
reset.
The 128 bytes of RAM contained in the base segment are
split between the lower and upper base segments. The first
112 bytes of RAM are resident from address 0000 to 006F
in the lower base segment, while the remaining 16 bytes of
RAM represent the 16 data memory registers located at addresses 00F0 to 00FF of the upper base segment. No RAM
is located at the upper sixteen addresses (0070 to 007F) of
the lower base segment.
Additional RAM beyond these initial 128 bytes, however, will
always be memory mapped in groups of 128 bytes (or less)
at the data segment address extensions (XX00 to XX7F) of
the lower base segment. The additional 128 bytes of RAM
are memory mapped at address locations 0100 to 017F
hex.
*Reads as all ones.
FIGURE 4. RAM Organization
TL/DD/11214– 15
Reset
The RESET input when pulled low initializes the microcontroller. Initialization will occur whenever the RESET
pulled low. Upon initialization, the data and configuration
registers for ports L, G and C are cleared, resulting in these
Ports being initialized to the TRI-STATE mode. Pin G1 of the
G Port is an exception (as noted below) since pin G1 is
dedicated as the WATCHDOG and/or Clock Monitor error
output pin. Port D is set high. The PC, PSW, ICNTRL,
CNTRL, T2CNTRL and T3CNTRL control registers are
cleared. The UART registers PSR, ENU (except that TBMT
bit is set), ENUR and ENUI are cleared. The Comparator
Select Register is cleared. The S register is initialized to
zero. The Multi-Input Wakeup registers WKEN, WKEDG and
WKPND are cleared. The stack pointer, SP, is initialized to
6F Hex.
The device comes out of reset with both the WATCHDOG
logic and the Clock Monitor detector armed, with the
WATCHDOG service window bits set and the Clock Monitor
bit set. The WATCHDOG and Clock Monitor circuits are inhibited during reset. The WATCHDOG service window bits
being initialized high default to the maximum WATCHDOG
service window of 64k t
being initialized high will cause a Clock Monitor error following reset if the clock has not reached the minimum specified
frequency at the termination of reset. A Clock Monitor error
will cause an active low error output on pin G1. This error
output will continue until 16 t
the clock frequency reaching the minimum specified value,
at which time the G1 output will enter the TRI-STATE mode.
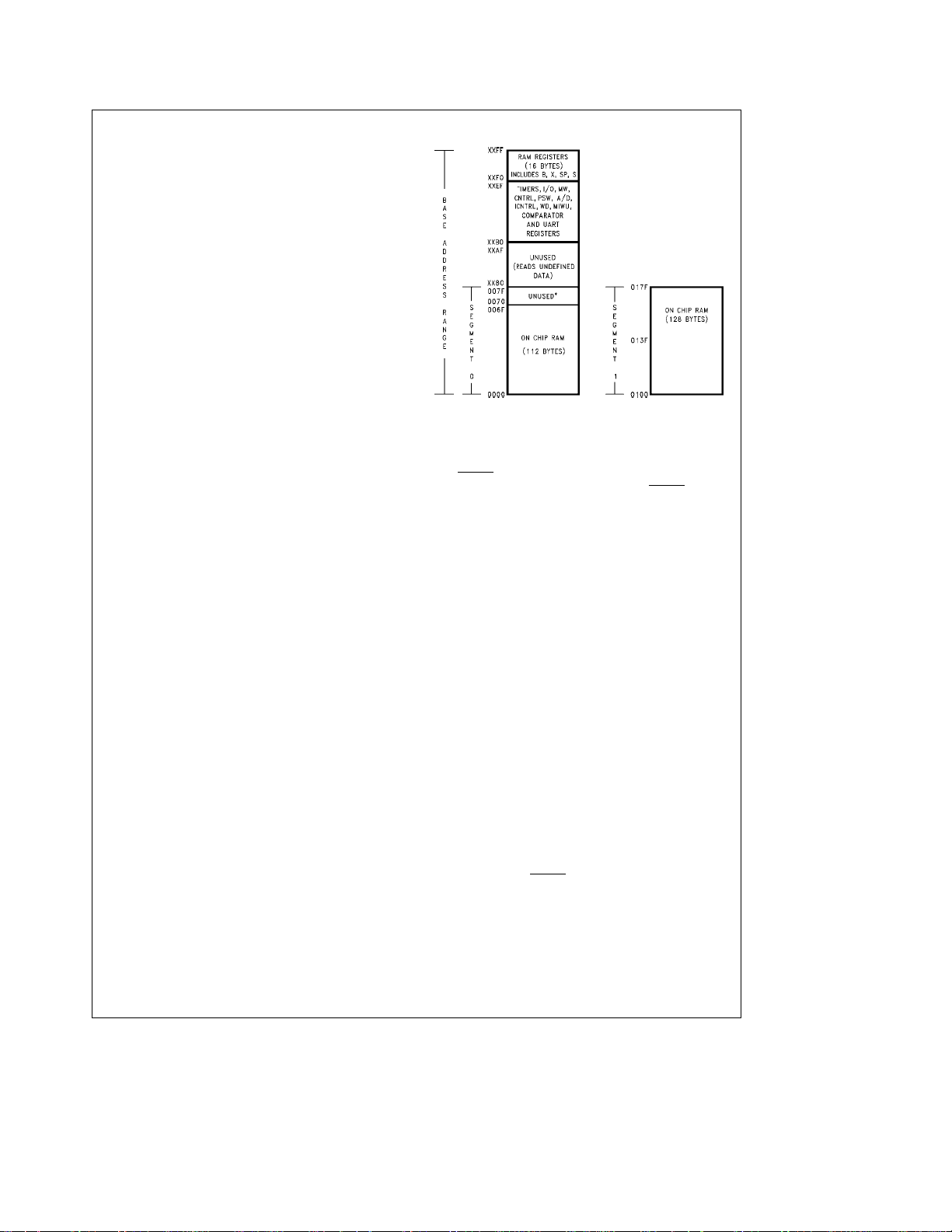
The external RC network shown in
to ensure that the RESET
supply to the chip stabilizes.
clock cycles. The Clock Monitor bit
C
–32 tCclock cycles following
C
Figure 5
pin is held low until the power
input is
should be used
http://www.national.com 14
Reset (Continued)
TABLE A. Crystal Oscillator Configuration, T
R1 R2 C1 C2 CKI Freq
(kX)(MX) (pF) (pF) (MHz)
0 1 30 30 – 36 10 V
0 1 30 30 – 36 4 V
0 1 200 100– 150 0.455 V
e
25§C
A
Conditions
e
5V
CC
e
5V
CC
e
5V
CC
RCl5cPower Supply Rise Time
TL/DD/11214– 16
FIGURE 5. Recommended Reset Circuit
Oscillator Circuits
The chip can be driven by a clock input on the CKI input pin
which can be between DC and 10 MHz. The CKO output
clock is on pin G7 (crystal configuration). The CKI input frequency is divided down by 10 to produce the instruction
cycle clock (1/t
Figure 6
CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR
CKI and CKO can be connected to make a closed loop
crystal (or resonator) controlled oscillator.
Table A shows the component values required for various
standard crystal values.
R/C OSCILLATOR
By selecting CKI as a single pin oscillator input, a single pin
R/C oscillator circuit can be connected to it. CKO is available as a general purpose input, and/or HALT restart input.
Table B shows the variation in the oscillator frequencies as
functions of the component (R and C) values.
).
c
shows the Crystal and R/C oscillator diagrams.
TL/DD/11214– 18
TABLE B. RC Oscillator Configuration, T
R C CKI Freq Instr. Cycle
(kX) (pF) (MHz) (ms)
3.3 82 2.2 to 2.7 3.7 to 4.6 V
5.6 100 1.1 to 1.3 7.4 to 9.0 V
6.8 100 0.9 to 1.1 8.8 to 10.8 V
Note: 3ksRs200k
50 pF
sCs
200 pF
e
25§C
A
Conditions
e
5V
CC
e
5V
CC
e
5V
CC
Control Registers
CNTRL Register (Address XÊ00EE)
The Timer1 (T1) and MICROWIRE/PLUS control register
contains the following bits:
SL1 & SL0 Select the MICROWIRE/PLUS clock divide
IEDG External interrupt edge polarity select
MSEL Selects G5 and G4 as MICROWIRE/PLUS
T1C0 Timer T1 Start/Stop control in timer
T1C1 Timer T1 mode control bit
T1C2 Timer T1 mode control bit
T1C3 Timer T1 mode control bit
T1C3 T1C2 T1C1 T1C0 MSEL IEDG SL1 SL0
Bit 7 Bit 0
e
by (00
(0
2, 01e4, 1xe8)
e
Rising edge, 1eFalling edge)
signals SK and SO respectively
modes 1 and 2
Timer T1 Underflow Interrupt Pending Flag in
timer mode 3
FIGURE 6. Crystal and R/C Oscillator Diagrams
TL/DD/11214– 17
http://www.national.com15
 Loading...
Loading...