MTD P25 Repair Manual

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
Professional Shop Manual
25cc 2-Cycle P25 Series Engines
NOTE: These materials are for use by trained technicians who are experienced in the service and repair of outdoor power
equipment of the kind described in this publication, and are n ot intended for use by untr ained or inexperienced individu als.
These materials are intended to provide supplemental information to assist the trained technician. Untrained or inexperienced individuals should seek the assistance of an experienced and trained professiona l. Read, understand, and follo w all
instructions and use common sense when working on powe r equipment. This includes the contents of the product’s Operators Manual, supplied with the equipment. No liability can be accepted for any inaccuracies or omission in this publication,
although care has been taken to make it as complete and a ccurate as possible at the time of pu blication. Howeve r, due to
the variety of outdoor power equipment and continuing product changes that occur over time, updates will be made to these
instructions from time to time. Therefore, it may be necessary to obtain the latest materials before servicing or repairing a
product. The company reserves the right to make changes at any time to this publication without prior notice and without
incurring an obligation to make such changes to previously published versions. Instructions, photographs and illustrations
used in this publication are for reference use only and may not depict actual model and component parts.
© Copyright 2010 MTD Products Inc. All Rights Reserved
www.mymowerparts.com

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
www.mymowerparts.com

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
Professional Shop Manual intent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Identifying engines. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Model and Serial Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Chapter 2: Maintenance 5
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Air filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Spark plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Spark arrestor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Fuel filer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Chapter 3: Troubleshooting 11
Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Steps to troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Identify factors that could cause the problem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Repairing the problem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Diagnostic tests. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Prime test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Compression testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Chapter 4: Ignition 19
Troubleshooting the Ignition System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Testing the module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Test the engine stop switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Flywheel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
www.mymowerparts.com
I

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
Chapter 5: Fuel system and carburetor 25
Fuel system troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Inspecting the fuel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Check the fuel/oil mixture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
To check the fuel in the carburetor:. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Test fuel for alcohol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Fuel filer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Fuel lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Fuel tank vent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Fuel tank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Carburetor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Troubleshooting the carburetor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Disassembly of the carburetor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Re-assembly of the carburetor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Carburetor insulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Chapter 6: Starters 41
Recoil Starter Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
The starter rope, pulley and springs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Chapter 7: Clutch and Upper Drive Shaft 47
Drive shaft assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Clutch removal/replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Chapter 8: Engine assembly 51
Theory of operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Engine disassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Engine Reassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
II
www.mymowerparts.com
For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
Introduction
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
Professional Shop Manual intent
This Manual is intended to provide service dealers with an introduction to the mechanical aspects of the 25cc
P25 series of 2-cycle engines.
Disclaimer: The information contained in this manual is correct at the time of writing. Both the product and the information about the product are subject to change without notice.
About the text format:
NOTE: is used to point out information that is relevant to the pro cedure, bu t doe s not fit as a step in the pr ocedure.
• Bullet points: indicate sub-steps or points.
! CA UTION! CA UTION
! WA RNIN G! WA RNIN G
! DANGER! DANGER
Disclaimer: This manual is intended for use by trained, professional technicians.
• Common sense in operation and safety is assumed.
• In no event shall MTD be liable for poor text interpretation or poor execution of the procedures described
in the text.
• If the person using this manual is uncomfortable with any procedures they encounter, they should seek
the help of a qualified technician or MTD Technical Supp ort.
Caution is used to point out potential danger to the technician, operator, bystanders, or surrounding property.
Warning indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not avoided, could result in death
or serious injury.
Danger indicates an imminently hazardous situation that, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury. This signal word is to be limited to the most extreme situations
Fasteners
• Most of the fasteners used on the engine are metric. Some are sized in fractional inches. For this reason ,
wrench sizes are frequently identified in the text, and measurements are given in U.S. and metric scales.
• If a fastener has a locking feature that has worn, replace the fastener or apply a small amount of releasable thread locking compound such as Loctite® 242 (blue).
• Some fasteners like cotter pins are single-use items that are not to be reused. Other fasteners such as
lock washers, retaining rings, and internal cotter pins (hairpin clips) may be reused if the do not show
signs of wear or damage. This manual leaves that decision to the judgement of the technician.
www.mymowerparts.com
1

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
P25 Series of engines
Assembly
Torque specifications may be noted in the text that covers assembly, they may also be summarized in tables
along with special instructions regarding locking or lubrication. Whichever method is more appropriate will be used.
In many cases, both will be used so that the manual is handy as a quick-reference guide as well as a step-by-step
procedure guide that does not require the user to hunt for information.
The level of assembly instructions provided will be determined by the complexity and of reassembly, and by the
potential for unsafe conditions to arise from mistakes made in assembly.
Some instructions may refer to other parts of the manual for subsidiary procedures. This avoids repeating the same
procedure two or three times in the manual.
Description
The P25 series of engines are used on a variety of
string trimmers. These engines have:
• 25cc’s of displacement.
• Piston ported/loop scavenged design.
• Cantilever crankshaft.
Figure 1.1
2
www.mymowerparts.com

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
Identifying engines
MTD currently has two cantilever crank, 2-cycle engines: the A31 and the P25.
NOTE: The starter is mounted between the engine and the drive shaft on all cantilever engines.
A31
Fuel tank
• 31 cc’s of displacement.
Introduction
Muffler
Figure 1.2
Air filter
Muffler
• Muffler on back side of engine.
• Fuel cap on top of engine.
• Air filter on rear of engine.
• Reed valve/loop scavenged design.
P25
• 25cc’s of displacement.
• Muffler on side of engine.
• fuel tank on bottom of engine.
• Air filter on side of engine.
Air filter
Figure 1.3
www.mymowerparts.com
3

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
P25 Series of engines
Model and Serial Numbers
The model (item) and serial number are on a little
white sticker with bar code. These are the numbers
needed when ordering parts. This sticker can be found on
the side of the engine.
Model number
Serial number
Figure 1.4
The model number is 41BD160G965. The break down of what the number mean is as follows:
41 ............................................................................................Hand held product
........B............................ ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ............................. Sales level
........... D.................................................................................. Product type
.................160 ..................................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... Unique Identifier
.........................G........... ... ... .................................................... Packaging code
.............................965 .............................................................Customer number
The serial number is 1H130DI1521. The serial number reads as follows:
1 ..............................................................................................Engineering level
...H........................................................................................... Month of production (H = August)
.....13 .......................................................................................Day of the month
.........0 ..................................................................................... Last digit of the year
...........D......................................................... ... ... .... ................Plant it was built in (MTD Southwest)
..............I ................................................................................. Assembly line number
.................1521 .......................................................................Number of unit built
4
www.mymowerparts.com

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
Maintenance
CHAPTER 2: MAINTENANCE
MAINTENANCE
The information in this manual applies to the P25 series of engines. Some basic principles may apply to other
engines produced by MTD and other manufacturers.
As the saying goes “an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure”. The same can be said about preventive
maintenance on outdoor power equipment. By changing the sp ark plu g and air filter at reco mmended inte rvals man y
failures can be avoided. Sometimes just clearing off yard debris that has collected through use can make th e difference between a properly running piece of equipment and the expensive inconvenience of unplanned repairs.
Air filter
A dirty air filter can reduce engine power, increase fuel consumption, increase CO emissions and make starting
more difficult.
The air filter should be cleaned every 10 hours of use (depending on area of use, dusty areas require more
frequent cleanings).
Press tab
Figure 2.1
Air filter cover
To clean/replace the air filter:
1. Remove the air filter cover by pressing in the tab on
the front side of the filter housing and swinging the
cover towards the rear of the engine. See Figure 2.1.
2. Pull the filter out. See Figure 2.2.
3. If the filter is crumbling or brittle, replace the filter.
4. Wash the air filter with warm soapy water. Let the filter air dry. DO NOT wring the filter out.
NOTE: Wringing the filter can tear it. Squeeze the filter, but
do not twist it.
5. Put a drop of oil to the filter and squeeze it through
out the filter.
Air filter
Figure 2.2
6. Insert the filter into air filter housing.
7. Install the air filter cover.
8. Test run the engine before returning it to service
www.mymowerparts.com
5
For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
P25 Series of engines
Spark plugs
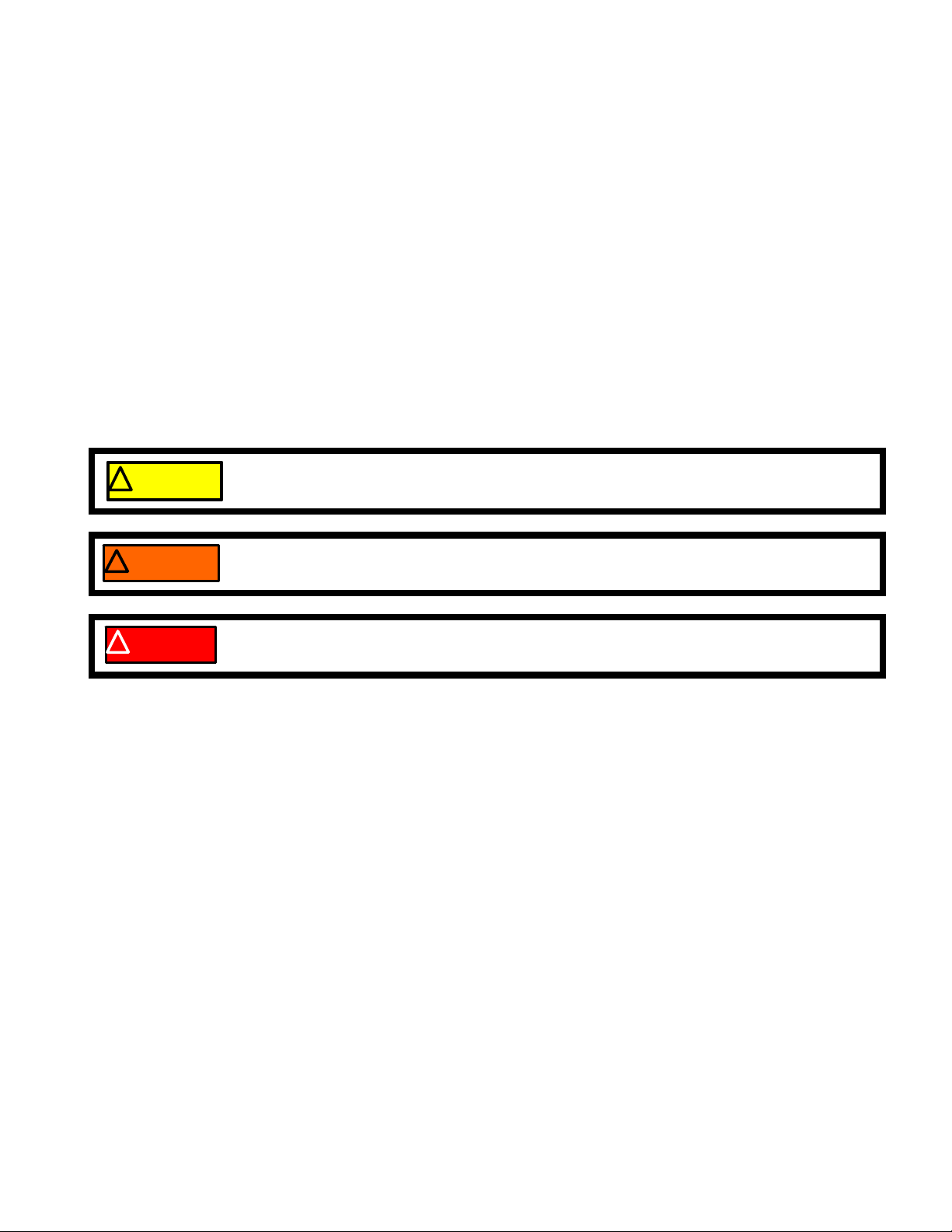
The spark plug used in the 2 5cc trimmer is a Champion RDJ7J (794-00055) gapped to 0.025” (0.655 mm).
See Figure 2.3.
Wear rate will vary with severity of use. If the edges
of the center electrode are rounded-off, or any other
apparent wear / damage occurs, replace the spark plug
before operating failure (no start) occurs.
Cleaning the spark plug:
NOTE: MTD does not recommend cleaning spark
plugs.
Center electrode
• Use of a wire brush may leave metal deposits
on the insulator that causes the spark plug to
short out and fail to spark.
• Use of abrasive blast for cleaning may cause
damage to ceramic insulator or leave blast
media in the recesses of the spark plug. When
the media comes loose during engine operation, severe and non-warrantable engine damage may result.
Inspection of the spark plug can provide indications of th e op er a ting con d ition of th e en gin e .
• Light tan colored deposits on insulator and electrodes is nor mal.
• Dry , black deposits on the insulator and electrodes indicate an over-rich fuel / air mixture (too much fuel or
not enough air)
• Wet, black deposits on the insulator and electrodes indicate the presence of oil in the combustion cha mber.
• Heat damaged (melted electrodes / cracked insulator / metal transfer deposits) may indicate detonation.
• A spark plug that is wet with fuel indicates that fuel is present in the combustion chamber, but it is not
being ignited.
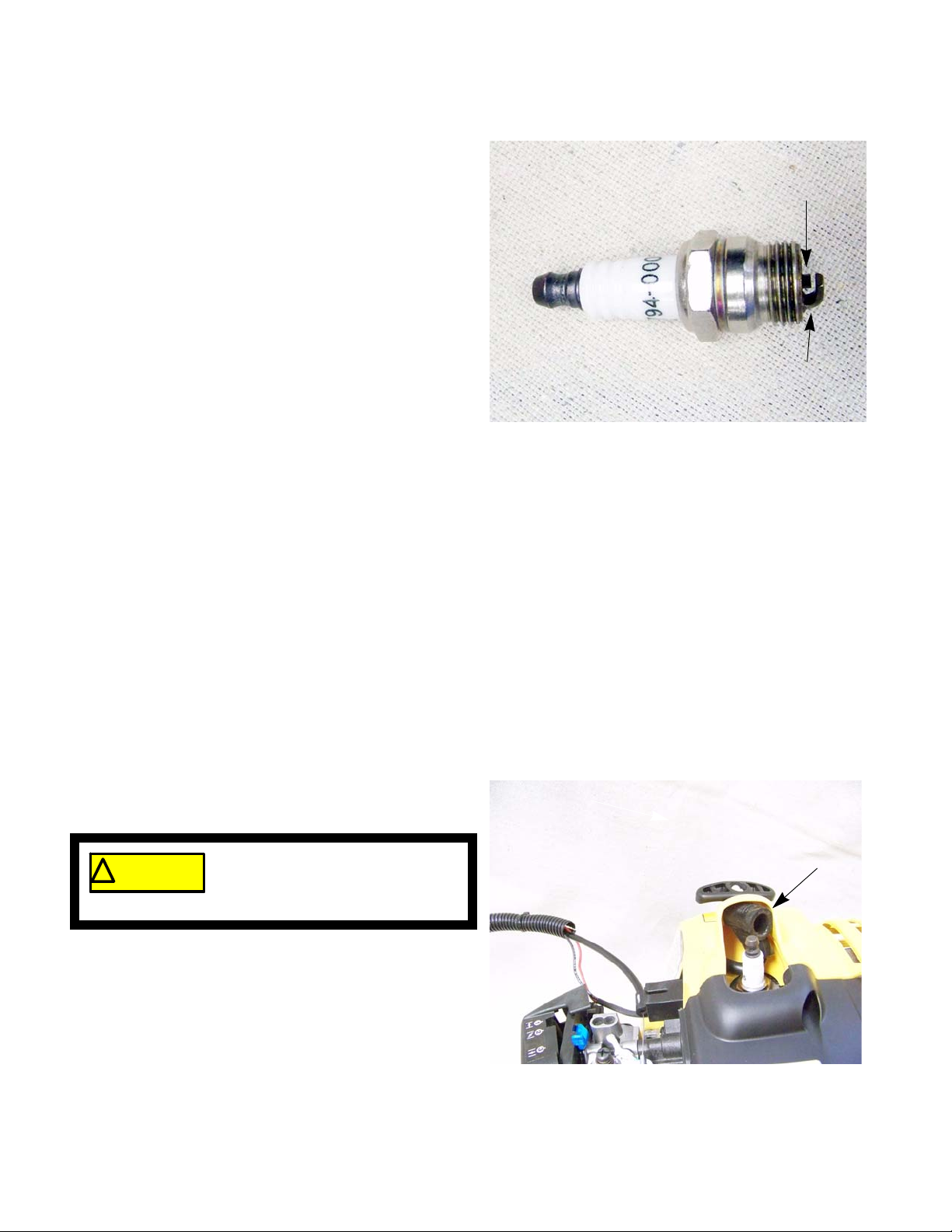
Spark plug removal and installation
To replace a spark plug:
1. Disconnect the spark plug wire.
Figure 2.3
Side electrode
Do not grab the spark plug wire with
! CAUTION! CAUTION
plug boot will weaken the spark of the spark plug.
2. Push the Spark plug wire boot into the starter housing. See Figure 2.4.
3. Remove the spark plug using a 5/8” spark plug
socket.
4. Gap a new plug at 0.025” (0.6 mm).
5. Install the spark plug and tighten to a torque of 160 220 in. lbs. (18 -25 Nm).
6. Re-connect the spark plug wire.
7. Test run the trimmer in a safe area before returning it to service.
6
pliers. Damage to the sparkplug
boot will result. A damaged spark
www.mymowerparts.com
Spark plug wire
Figure 2.4
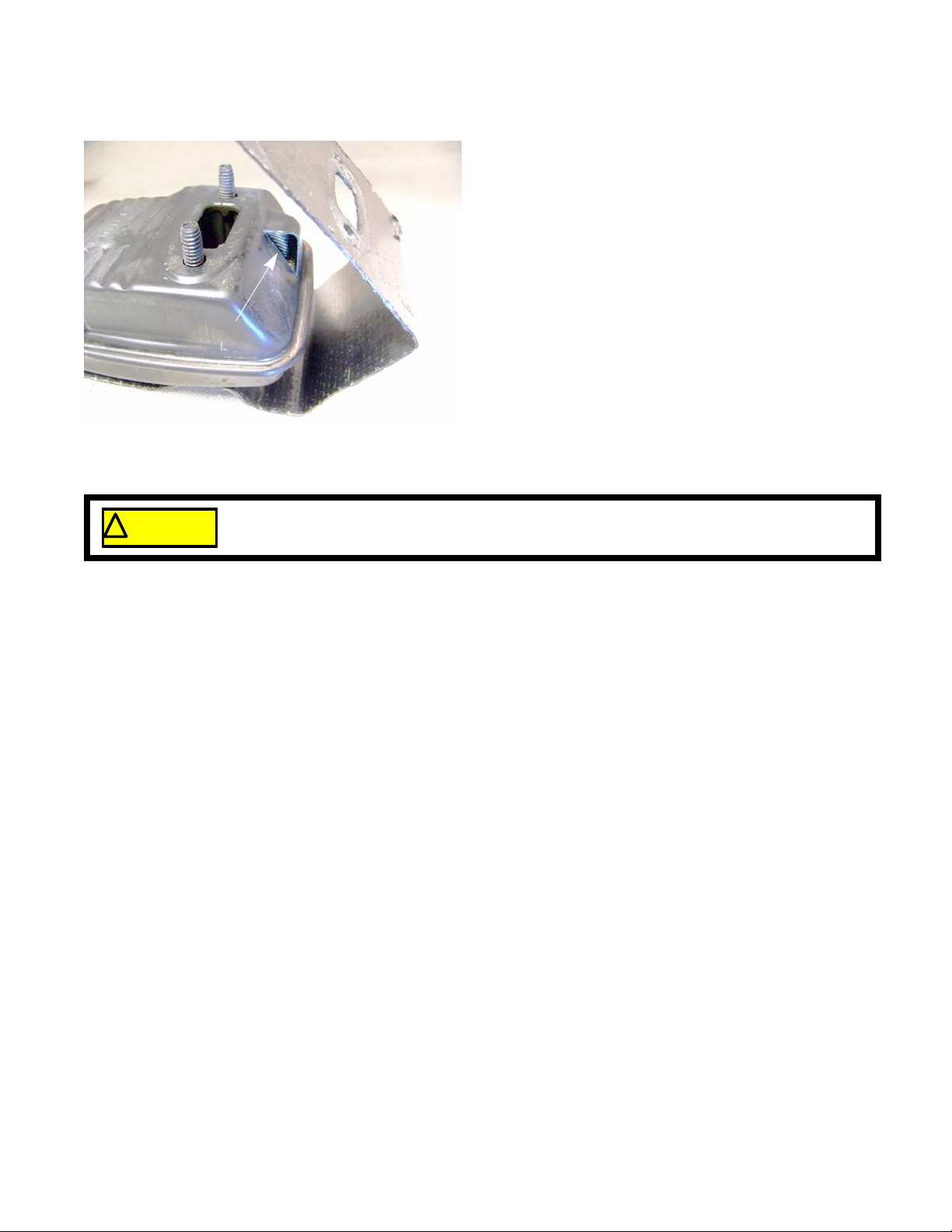
Spark arrestor
Spark arrestor screen
For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
Maintenance
A spark arrestor is a screen that is in the outlet of the
muffler. It’s job is to collect any sparks or hot embers that
are exiting the muffler. The spark arrestor will develop a
carbon build up over time. This build up will restrict the
exhaust flow, affecting engine performance.
The spark arrestor is part of the muffler and is not
accessible for cleaning. It should be inspected every 25
hours of use. When it develops a carbon build up, replace
the muffler.
NOTE: The spark arrestor also serves to keep blockages
out of the exhaust system. Typical blockages
include insect nests built during the dormant season.
Figure 2.5
! CA UTION! CA UTION
Do not return an engine to service without a working spark arrestor. Use of the engine or
equipment on unimproved land can start a fire if the spark arrestor has been removed.
www.mymowerparts.com
7

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
P25 Series of engines
Fuel filer
A dirty fuel filter can result in a lean run condition. The fuel filter should be inspected every 25 hours of use.
NOTE: The weighted fuel filter (clunk) keeps the filter submerged in the fuel at any angle of operation. The fil-
ter removes dirt and air bubbles from the fuel. Running the trimmer without the filter may allow air into
the fuel line creating a lean run condition at higher RPMs. This will cause a catastrophic failure of the
engine.
NOTE: St arting in 2012, EPA guidelines will mandate that all han dheld enginesproduced have low permeation
fuel lines. These fuel lines do not stand up to the removal/installation methods used in the field.
Because of this, the fuel filter and fuel lines are serviced with the fuel tank.
To inspect the fuel filter:
1. Bend a piece of wire to make a hook.
See Figure 2.6.
2. Remove the gas cap.
3. Stick the hook end of the wire into the fuel tank and
fish out the fuel filter. See Figur e 2.7.
4. Inspect the filter for signs of dirt or damage.
NOTE: If the filter is dirty or damaged, the whole
fuel tank assembly must be replaced.
5. Place the filter back inside the fuel tank.
NOTE: Pay close attention to the fuel line. If they
are discolored or brittle, replace the fuel t ank
assembly.
6. Test run the engine before returning it to service.
Figure 2.6
Fuel filter
Figure 2.7
8
www.mymowerparts.com

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
Maintenance
Storage
When storing a piece of gas powered equipment for longer than 4 weeks, the following procedures will prolong
the engine life and minimize issues such as hard starting after storage.
1. Run the engine until it is out of gas.
2. Open the air filter cover.
3. Spray some oil down the throat of the carburetor.
4. Close the air filter cover.
5. Pull the starter rope to turn the engine over a few time s.
Returning to service:
• When returning to service, fill the fuel tank with fresh fuel/oil mix.
• The engine should start normally.
www.mymowerparts.com
9

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
P25 Series of engines
10
www.mymowerparts.com
Definitions
For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
Troubleshooting
CHAPTER 3: TROUBLESHOOTING
Troubleshooting
Diagnosis
Introduction
Diagnosing an engine is an art form that is built on several factors. First and most importantly is a good understanding of how the engine works. The second is a skill set that has been honed by experience. Finally the use of
visual observations and a structured, systematic approach to troubleshooting a pr oblem.
The first part of this chapter will outline the steps of troubleshooting an engine so a technician can form a proper
diagnosis. The second half of this chapter will describe specific procedures and tests to preform while troubleshooting.
! CAUTION! CAUTION
Steps to troubleshooting
NOTE: The steps and the order of the steps that follow are a su ggested approach to troubleshooting the trim-
Define the problem
The first step in troubleshooting is to define the problem:
- The act of gathering information by performing tests and direct observations.
- A theory of what the problem is, based on the information gathered by troubleshooting.
The first two rules in troubleshooting are to cause no further harm to the engine and to prevent injuries. Always check for the proper fuel/oil mix before starting an engine. Check
attachments for damage and make sure they are firmly mounted .
mer engine. The technician does not necessarily have to follow them as described in this chapter
1. Crankshaft will not turn.
• Hard to pull rope, steady pressure
• Rope jerks back
• Rope will not pull at all
2. Crankshaft turns, no start
3. Starts, runs poorly
• Starts, then dies
• Runs with low power out put
• Makes unusual smoke when running
I. Black smoke, usually heavy
II. White smoke, usually heavy
III. Blue smoke. usually light
• Makes unusual sounds when running
I. Knock
II. Click
III. Chirp
IV. Unusual exhaust tone
www.mymowerparts.com
11

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
P25 Series of Engines
There are tools that the technician can use in order to define the problem, such as:
1. Interview the customer.
• Get a good description of their complaint.
• If it is an intermittent problem, verify what conditions aggravates the problem as best as possible.
• Get an accurate service history of the equipment.
• Find out how the customer uses and stores the equipment.
2. Direct observation:
• Do not take it that the customer is correct with their description of the problem. Try to duplicate the problem.
• Check the general condition of the equipment (visually).
I. Cleanliness of the equipment will indicate the level of care the equipment has received.
II. Make sure the engine and attachments are securely fastened.
III. The tune-up factors.
NOTE: Most hard starting and poor running conditions can be solved by preforming a tune-up.
a. Check the level and condition of the fuel.
b. Check the air filter and look for signs of dirt ingestion.
c. Check the ignition and “read” the spark plug.
d. Look for obvious signs of physical damage, bent blade, exhaust system blockage or cooling sys-
tem blockage.
5. Broken starter rope.
• Usually means the engine was hard to start.
• Makes it impossible to confirm any running or hard starting symptoms by direct observation.
• Some inference can be made from checking other factors of the general condition of the equipment.
12
www.mymowerparts.com

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
Identify factors that could cause the problem
This is the second step in the troubleshooting process.
1. Crankshaft will not turn.
Troubleshooting
• Hard to pull rope, steady pressure
pects are:
II. A parasitic load from a jammed attachment or drive shaft.
III. An internal drag from a scored or seized piston.
• Rope jerks back
pression stroke and is being driven back down by compression or combustion. The likely suspects are:
I. Compression that is unusually high.
a. a partial hydraulic lock.
II. Ignition timing is advanced.
a. Improper air gap.
b. Sheared or missing flywheel key.
c. The wrong flywheel or module is installed on the engine.
• Rope will not pull at all
I. A broken starter recoil (easy fix).
II. Complete hydraulic lock (easy fix).
III. External binding/jammed attachment (easy fix).
IV. Internal binding, cran kshaft, connecting rod or piston (unrepairable)
5. Crankshaft turns, no start.
• Most gasoline engine diagnosis involves isolating problems in the four critical factors an engine needs to
run properly:
I. Ignition
- This usually indicates that the piston is stopping before top dead center on the com-
-This is usually either a quick fix or a catastrophic failure. The likely suspects are:
- sufficient spark to start combustion in the cylinder, occurring at the proper time.
- This usually indicates a mechanical bind of some sort. the likely sus-
II. Compression
needs sufficient sealing to generate the vacuum needed to draw in and atomize the next intake
charge.
III. Fuel
IV. Flow
• Isolate the ignition system and compression from the fuel system by preforming a prime test.
I. Burns prime and dies. This would indicate a fuel system issue.
II. Does not burn prime. Not a fuel system issue. Check for an ignition, compression or flow problem.
• Compression or ignition problem
I. Check the engine stop and/or ignition switch.
II. Test the ignition system using a proper tester.
III. Replace the spark plug with a new one or a known good one.
IV. Check compression.
V. Check exhaust.
- correct type and grade of fresh gasoline; in sufficient q uantity, atomized ( tiny droplet s) and in
correct fuel/air proportions.
- if all of the above conditions are met, but the flow of air is constricted on the inlet or exhaust
side it will cause the engine to run poorly or not at all. This also includes ensuring the valves are
timed to open at the proper time.
- enough pressure in the cylinder to convert combustion into kinetic motion. It also
13
www.mymowerparts.com

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
P25 Series of Engines
6. Starts, runs poorly
• Starts, then dies
I. Run the engine with a spark tester in-line between the spar k plug wire and the spa rk plug or use an
oscilloscope and see if the spark goes away at the same time the engine dies.
II. Check choke operation.
a. Black smoke?
b. Wet plug?
III. Test for invisible damage to the air filter by starting the engine with the air filter removed.
IV. Prime test immediately af ter engine dies. If it restarts; this may indicate a problem with fuel flow to
the carburetor. Check the gas cap, fuel line, fuel filter, and the carburetor.
• Runs with low power output.
I. Look for unusual exhaust color (smoke).
II. Unusually hot muffler (may glow red).
a. Retarded ignition
II. Mechanical bind
a. A loose ignition module can drag on the flywheel or lock it up.
b. Parasitic external load. A bind in the equipment the engine is powering.
c. Internal drag from a scored piston or similar damage.
IV. Low compression/case leak
a. Check compression
• Engine hard to start.
• May start and run if prime test is used.
• May run well at high RPMs, but will not idle.
• “Sluggish” pick-up from lower RPMs.
II. Flow blockage
a. Exhaust blockage may idle, but performs poorly. It usually is accompanied by an unusual exhaust
sound.
NOTE: Just as a throttle on the carburetor controls the engine RPMs by limiting the amount of air an engine
can breathe in, an exhaust blockage will lim it eng in e pe rf or ma n c e by con str ictin g th e ot he r en d of the
system.
II. The muffler itself my be blocked.
III. The spark arrestor may be blocked.
14
IV. Intake blockage
a. An intake blockage up-stream of the carburetor will cause a rich fuel/air mixture and constrict the
amount of air that the engine can draw in, limiting performance. A blocked air filter is a common
cause of this.
VII. Makes unusual smoke when running
a. Black smoke
• Not enough air: air filter blockage or a partially closed choke.
, usually heavy usually indicates a rich air fuel mixture
www.mymowerparts.com

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
• Too much fuel: needle valve stuck or metering / emulsion issues with the carburetor.
b. Blue smoke,
• Too much oil in the fuel mix.
IX. Piston rings
a. Confirm with compression test.
b. Repair may not make economic sense.
X. Makes unusual noise when running.
•Knock
* Check for loose mounting of engine or driven implement
* Rotate crankshaft back-and-forth to check for loose connecting rod.
• Click
* Half-engine speed clatter, slightly heavier: wrist-pin.
* Rhythmic heavy-light engine speed click: piston slap
• Spark-knock
usually light.
Troubleshooting
* Advanced ignition timing
* Low oc tane fuel
* Over-heating engine (check for blocked cooling air flow)
* Carbon build-up in cylinder: glowing carbon chunks pre-igniting air fuel mix.
XI. Unusual exhaust tone
a. Splashy, blatty, wheezing or whistling.
• Splashy or blatty idle usually indicates a slightly rich condition.
• Whistling or wheezing may indicate an exhaust blockage, usually slightly muffled.
• Backfire
* On over-run: unburned fuel igniting past exhaust port. Mixture not burning completely in
combustion chamber. It may be too rich or it may be a spark plug or an ignition problem.
• Skip
* Usually ignition related.
NOTE: If the engine is run with no load at maximum RPM s, the rev limiter may be triggered causing the en gine
to skip at 7,900 RPM. This is a normal function of the rev limiter.
* Run the engine with a spark tester in-line between the spark plug wire and the spark plug
or use an oscilloscope and see if the spark goes away at the same time the engine dies.
XII. Engine RPMs surge (hunting)
a. The Ideal stoichiometric ratio/AFR (Air Fuel Ratio) for this engine is (12.5:1 - 13:1). An engine
that runs with an AFR greater than 13:1 is running lean. The engine RPMs will sink until they
reach a point that can be supported by the available fuel. This causes a momentary surge in
power until the available fuel is consumed, then the RPMs fall again, repeating the cycle.
• Too much air: look for an air leak in the intake tract
• Not enough fuel: look for fuel supply or carburetor problems
www.mymowerparts.com
15

For Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983
P25 Series of Engines
Repairing the problem
The third step in the diagnostic process is to repair the problem. This step consists of:
1. Form a diagnosis by using all of the information gathered from the troubleshooting that was performed.
2. Physically perform the repair.
The fourth, and hopefully final, step in the troubleshooting process is the follow through. This step consists of:
1. Thoroughly test the repaired equipment: confirming that the initial diagnosis was correct. If it was wrong, start
the troubleshooting process over again.
NOTE: Sometimes the engine will have multiple problems at the same time. By performing one repair, other
issues may show up that are unrelated to the first repair.
2. Delivery to customer: We are not just repairing equipment, we ar e re pairing custo m er s.
• Inoculate against recurring problem with education, e.g.... if the problem was caused by stale fuel, make
sure the customer is aware that fuel goes bad over time.
• Make sure the customer understands the repair, preventing “superstitious” come-backs.
Diagnostic tests
When troubleshooting an engine, the diagnostic tests are done in a specific order. The order is:
1. Compression testing
2. Ignition testing
3. Carburetor/fuel system testing.
NOTE: A prime test is a handy short cut. It will test compression and ignition in a single step. If the engine will
start from a prime test, the problem is in the fuel system. If the engine will not start with the prime, the
compression and ignition tests will need to be performed.
16
www.mymowerparts.com
 Loading...
Loading...