Page 1

3200 Master Series
MS-9656 (V1.X) Server Board
G52-96561X2
i
Page 2
Copyright Notice
The material in this document is the intellectual property of MICRO-STAR
INTERNATIONAL. We take every care in the preparation of this document, but no
guarantee is given as to the correctness of its contents. Our products are under
continual improvement and we reserve the right to make changes without notice.
Trademarks
All trademarks are the properties of their respective owners.
NVIDIA, the NVIDIA logo, DualNet, and nForce are registered trademarks or trade-
marks of NVIDIA Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
AMD, Athlon™ , Athlon™ XP, Thoroughbred™, and Duron™ are registered trademarks of AMD Corporation.
Intel® and Pentium® are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
PS/2 and OS®/2 are registered trademarks of International Business Machines
Corporation.
Windows® 95/98/2000/NT/XP are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Netware® is a registered trademark of Novell, Inc.
Award® is a registered trademark of Phoenix Technologies Ltd.
AMI® is a registered trademark of American Megatrends Inc.
Revision History
Revision Revision History Date
V1.1 Updating the Northbridge February 2008
Technical Support
If a problem arises with your system and no solution can be obtained from the user’ s
manual, please contact your place of purchase or local distributor. Alternatively,
please try the following help resources for further guidance.
Visit the MSI website at http://global.msi.com.tw/index.php?
func=faqIndex for FAQ, technical guide, BIOS updates, driver updates,
and other information.
Contact our technical staff at http://support.msi.com.tw/.
ii
Page 3

Safety Instructions
1. Always read the safety instructions carefully.
2. Keep this User’s Manual for future reference.
3. Keep this equipment away from humidity.
4. Lay this equipment on a reliable flat surface before setting it up.
5. The openings on the enclosure are for air convection hence protects the equipment from overheating. DO NOT COVER THE OPENINGS.
6. Make sure the voltage of the power source and adjust properly 110/220V before connecting the equipment to the power inlet.
7. Place the power cord such a way that people can not step on it. Do not place
anything over the power cord.
8. Always Unplug the Power Cord before inserting any add-on card or module.
9. All cautions and warnings on the equipment should be noted.
10. Never pour any liquid into the opening that could damage or cause electrical
shock.
11. If any of the following situations arises, get the equipment checked by service
personnel:
† The power cord or plug is damaged.
† Liquid has penetrated into the equipment.
† The equipment has been exposed to moisture.
† The equipment does not work well or you can not get it work according to
User’s Manual.
† The equipment has dropped and damaged.
† The equipment has obvious sign of breakage.
12. DO NOT LEAVE THIS EQUIPMENT IN AN ENVIRONMENT UNCONDITIONED, STORAGE TEMPERATURE ABOVE 600 C (1400F), IT MAY DAMAGE THE EQUIPMENT.
CAUTION: Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the
manufacturer.
iii
Page 4
FCC-B Radio Frequency Interference Statement
This equipment has been
tested and found to comply
with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the measures listed
below.
† Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
† Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
† Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
† Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for help.
Notice 1
The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Notice 2
Shielded interface cables and A.C. power cord, if any, must be used in order to
comply with the emission limits.
VOIR LA NOTICE D’ INSTALLATION AVANT DE RACCORDER AU RESEAU.
Micro-Star International
MS-9656
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
(1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
iv
Page 5

WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Statement
v
Page 6

vi
Page 7

vii
Page 8

CONTENTS
Copyright Notice..............................................................................................................ii
Trademarks.......................................................................................................................ii
Revision History..............................................................................................................ii
Technical Support...........................................................................................................ii
Safety Instructions.........................................................................................................iii
FCC-B Radio Frequency Interference Statement........................................................iv
WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Statement....................................v
Chapter 1 Getting Started.....................................................................................1-1
Mainboard Specifications...................................................................................1-2
Mainboard Layout................................................................................................1-4
Chapter 2 Hardware Setup....................................................................................2-1
Quick Components Guide....................................................................................2-2
CPU (Central Processing Unit)............................................................................2-3
Memory.................................................................................................................2-7
Power Supply......................................................................................................2-9
Back Panel I/O....................................................................................................2-10
Connector...........................................................................................................2-11
Jumper................................................................................................................2-18
Slot......................................................................................................................2-19
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup.............................................................................................3-1
Entering Setup.....................................................................................................3-2
The Menu Bar......................................................................................................3-4
Main......................................................................................................................3-5
Advanced............................................................................................................3-6
Boot....................................................................................................................3-20
Security..............................................................................................................3-23
Chipset...............................................................................................................3-24
Exit......................................................................................................................3-26
Appendix A Intel ICH9R SATA RAID.....................................................................A-1
ICH9R Introduction...............................................................................................A-2
BIOS Configuration..............................................................................................A-3
Installing Driver....................................................................................................A-9
Installing Software............................................................................................A-11
RAID Migration Instructions...............................................................................A-15
Degraded RAID Array........................................................................................A-22
viii
Page 9
Getting Started
Chapter 1
Getting Started
Thank you for choosing the 3200 Master Series (MS9656 V1.X), an excellent server board from MSI.
Based on the innovative Intel® 3210 / 3200 & ICH9R
chipsets for optimal system efficiency, the 3200 Master accommodates the latest Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 3000 series, Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® processor
3200 series, Wolfdale and Yorkfield processors in
LGA775 package and supports up to four 240-pin DDR2
667/800 DIMM slots to provide the maximum of 8GB
memory capacity.
In the entry-level and mid-range market segment, the
3200 Master Series can provide a high-performance
solution for today’s front-end and general purpose
server, as well as in the future.
1-1
Page 10

MS-9656 Server Board
Mainboard Specifications
Processor
- Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor 3000 series, Quad-Core Intel Xeon
processor 3200 series, Wolfdale and Yorkfield processors in LGA775
package
FSB
- 1333/ 1066/ 800 MHz
Chipset
- Northbridge: Intel 3210 / 3200 chipset
(NOTE: 3210 supports either two PCI Express x8 slots or one PCI
Express x16 slot. 3200 supports one PCI Express x8 slot.
Neither 3210 nor 3200 supports PCI Express graphics.)
- Southbridge: Intel ICH9R chipset
Memory
- 4 DDR2 667/800 DIMM slots (240pin / 1.8V)
- Up to 8GB memory capacity
LAN (Optional)
- For mainboards with IPMI chip:
Intel 82573V Gigabit Ethernet controller (LAN1) & Intel 82566DM
Gigabit Ethernet controller (LAN2)
- For mainboards without IPMI chip:
Intel 82573L Gigabit Ethernet controller (LAN1) & Intel 82566DM
Gigabit Ethernet controller (LAN2)
1-2
Floppy
- 1 floppy port
- Supports 1 FDD with 360KB, 720KB, 1.2MB, 1.44MB and 2.88MB
IDE
- 1 IDE port by ITE IT8213F
- Supports Ultra DMA 66/100/133 mode
- Supports PIO, Bus Master operation mode
SATA
- 6 SATAII ports by ICH9R
- Supports storage and data transfers at up to 300MB/s
RAID
- Supports RAID 0/ 1/ 0+1/ 5 or JBOD mode
Page 11

Graphics
- XGI Z7 graphics controller
- Onboard 16MB Video SDRAM
IPMI (Optional)
- Hitachi H8S/2168 IPMI microcontroller
Connectors
Back Panel
- 1 PS/2 mouse port
- 1 PS/2 keyboard port
- 2 USB 2.0 ports
- 1 serial port
- 1 VGA port
- 2 Gigabit LAN jacks
Onboard Connectors
- 3 proprietary front panel connectors (optional)
- 3 USB 2.0 connectors (6 ports)
- 1 serial port connector
- 1 TPM connector
- 1 SPI Flash ROM connector (for debugging)
- 1 chassis intrusion connector
Getting Started
Slots
- 1 PCI Express x16 slot (with x8 signal)
- 1 PCI Express x4 slot
- 4 PCI slots (supports 3.3V/ 5V PCI bus interface)
Regulations
- FCC, CE
Form Factor
- ATX form factor 12" x 9.6"
1-3
Page 12
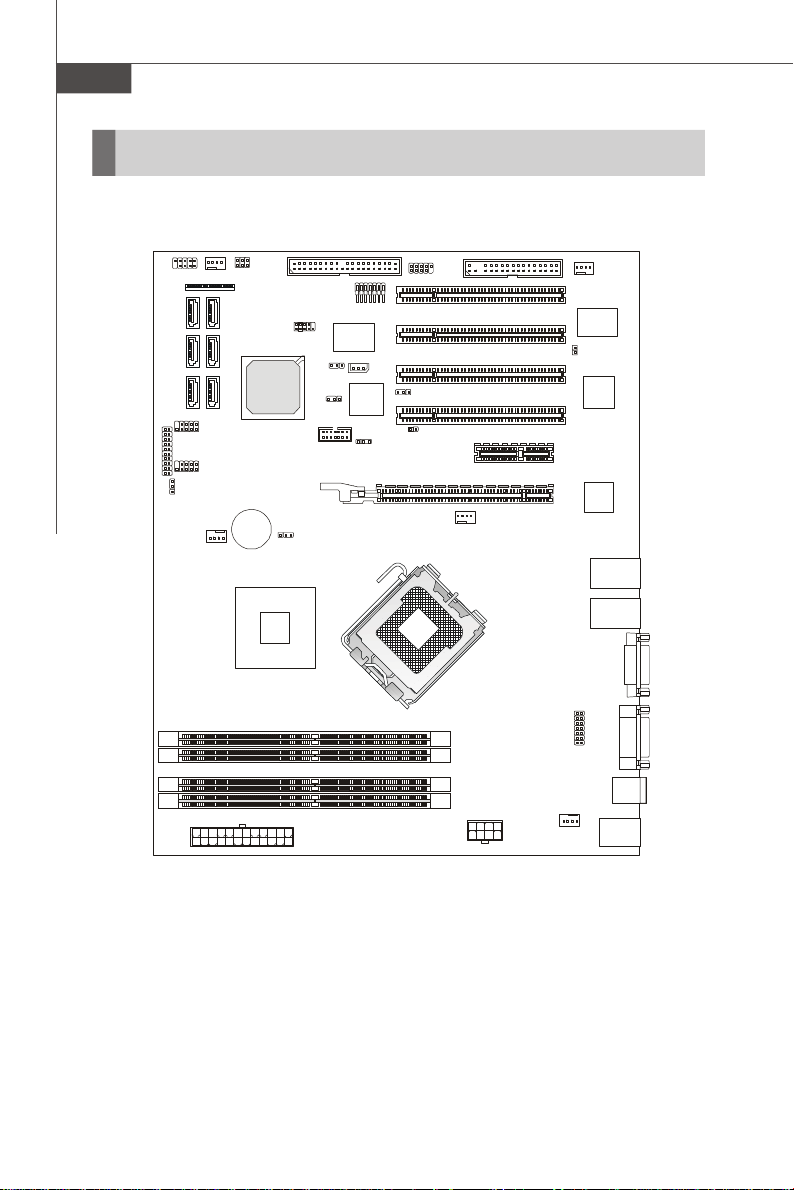
MS-9656 Server Board
JUSB1
T: Mouse
B: Keyboard
COM1
JLAN1
JLAN 2
SYS_FAN1
REAR_FAN1
JTPM1
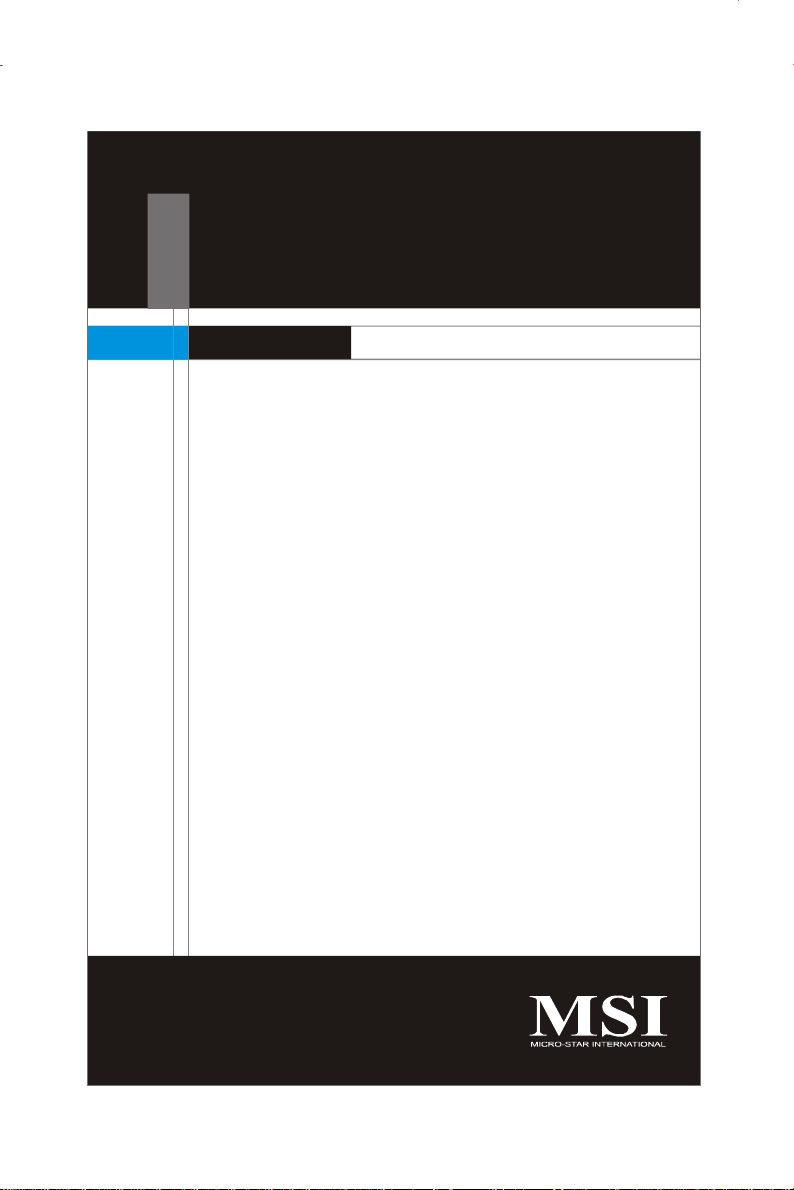
Mainboard Layout
COM2
JUSB3
JAPP3
JUSB2
J_VGA_EN1
SATA1 S ATA3 SATA5
FRONT_FAN1
SATA2 SATA4
SATA6
SYS_FAN2
FPC1
BATT
JAPP2
Intel
ICH9R
+
Intel
3210 / 3200
J_CMOS1
J_IDE1
JSPI1
J_BOOT3
J_SMBUS1
J1
ITE
IT8213F
J_IPMB1
J_BOOT1
BMC
Chip
J_BOOT2
JUSB4
J_ICMB1
FDD1
CPU_FAN1
DIMM_A1
DIMM_A2
DIMM_B1
DIMM_B2
PCIE1
PCIE2
PCI1
PCI2
PCI3
PCI4
JINT1
JAPP1
XGI
LAN
Chip
Z7
VGA 2
1-4
JPWR2
JPWR1
3200 Master Series (MS-9656 V1.X) Server Board
Page 13
Hardware Setup
Chapter 2
Hardware Setup
This chapter provides you with the information about
hardware setup procedures. While doing the installation,
be careful in holding the components and follow the
installation procedures. For some components, if you
install in the wrong orientation, the components will not
work properly.
Use a grounded wrist strap before handling computer
components. Static electricity may damage the
components.
2-1
Page 14
MS-9656 Server Board
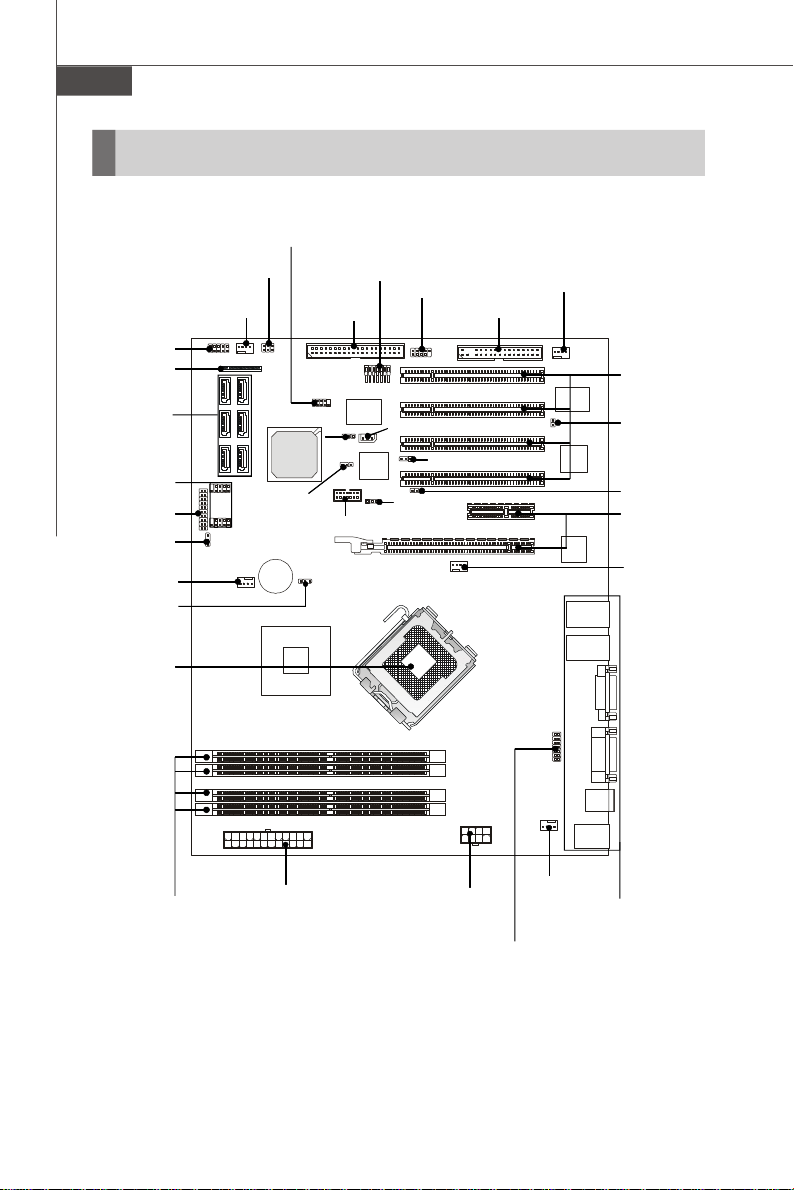
Quick Components Guide
JSPI1, p.2-12
JAPP2, p.2-14
FRONT_FAN1,
p.2-13
COM2, p.2-15
FPC1, p.2-13
SATA1~6,
p.2-12
JUSB2/3,
p.2-15
JAPP3, p.2-14
J_VGA_EN1,
p.2-18
SYS_FAN2,
p.2-13
J_CMOS1,
p.2-18
J_BOOT3,
p.2-18
J_SMBUS1,
p.2-17
JTPM1,
p.2-17
J_IDE1,
p.2-11
J1, p.2-16
JUSB4,
p.2-15
J_IPMB1, p.2-16
J_BOOT1,
p.2-16
FDD1,
p.2-11
J_ICMB1, p.2-16
SYS_FAN1,
p.2-13
PCI Slots,
p.2-19
JINT1,
p.2-13
J_BOOT2,
p.2-16
PCI Express
Slots, p.2-19
CPU_FAN1,
p.2-13
CPU, p.2-3
DIMM Slots,
2-2
p.2-7
JPWR2,
p.2-9
JPWR1,
p.2-9
JAPP1, p.2-14
REAR_FAN1,
p.2-13
Back Panel
I/O, p.2-10
Page 15
Hardware Setup
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
This mainboard supports dual-core Intel® Xeon® processor 3000 series, quad-core
Intel® Xeon® processor 3200 series, Wolfdale and Yorkfield processors in LGA775
package. When you install the CPU, make sure that you install the cooler to
prevent overheating. If you do not have the CPU cooler, consult your dealer
before turning on the computer.
Important
Overheating
Overheating will seriously damage the CPU and system. Always make sure
the cooling fan can work properly to protect the CPU from overheating. Make
sure that you apply an even layer of thermal paste (or thermal tape) between
the CPU and the heatsink to enhance heat dissipation.
Replaceing the CPU
While replacing the CPU, always turn off the power supply or unplug the
power supply’s power cord from the grounded outlet first to ensure the safety
of CPU.
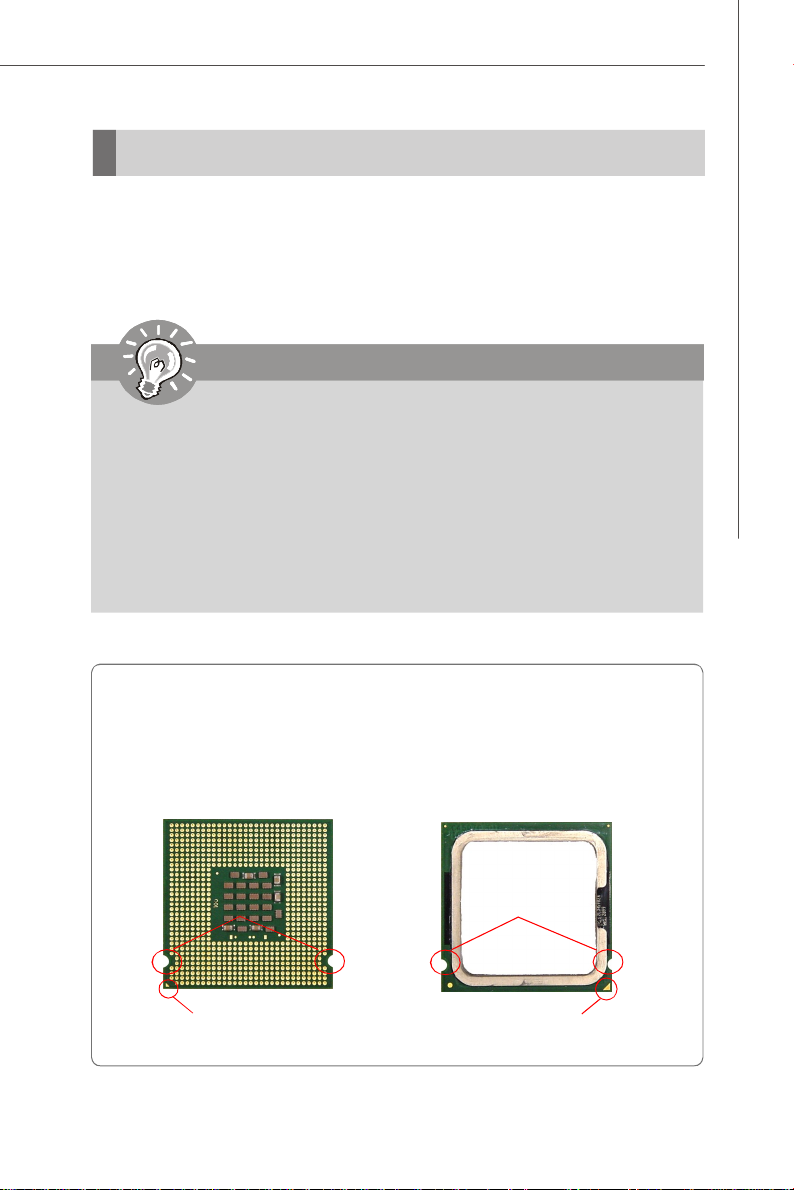
Introduction to LGA 775 CPU
The pin-pad side of LGA 775
CPU.
Alignment Key Alignment Key
Yellow triangle is the Pin 1 indicator
The surface of LGA 775 CPU.
Remember to apply some thermal paste on it for better heat
dispersion.
Yellow triangle is the Pin 1 indicator
2-3
Page 16
MS-9656 Server Board
CPU & Cooler Installation
When you are installing the CPU, make sure the CPU has a cooler attached on
the top to prevent overheating. Meanwhile, do not forget to apply some thermal
paste on CPU before installing the heat sink/cooler fan for better heat dispersion.
Follow the steps below to install the CPU & cooler correctly. Wrong installation will
cause the damage of your CPU & mainboard.
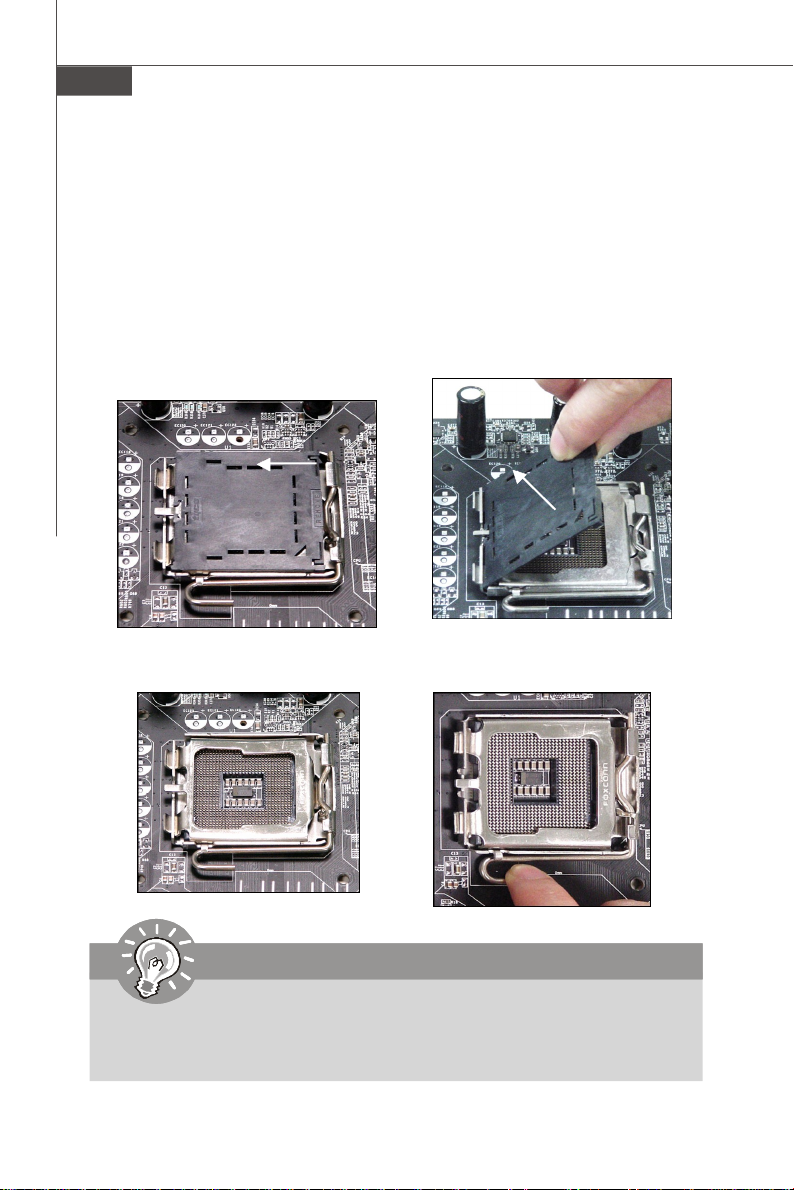
1.The CPU socket has a plastic cap
on it to protect the contact from
damage. Before you install the CPU,
always cover it to protect the socket
pin.
2.Remove the cap from lever hinge
side (as the arrow shows).
3.The pins of socket reveal.
4.Open the load lever.
Important
1.Confirm if your CPU cooler is firmly installed before turning on your system.
2. Do not touch the CPU socket pins to avoid damaging.
3. The availability of the CPU land side cover depends on your CPU packing.
2-4
Page 17
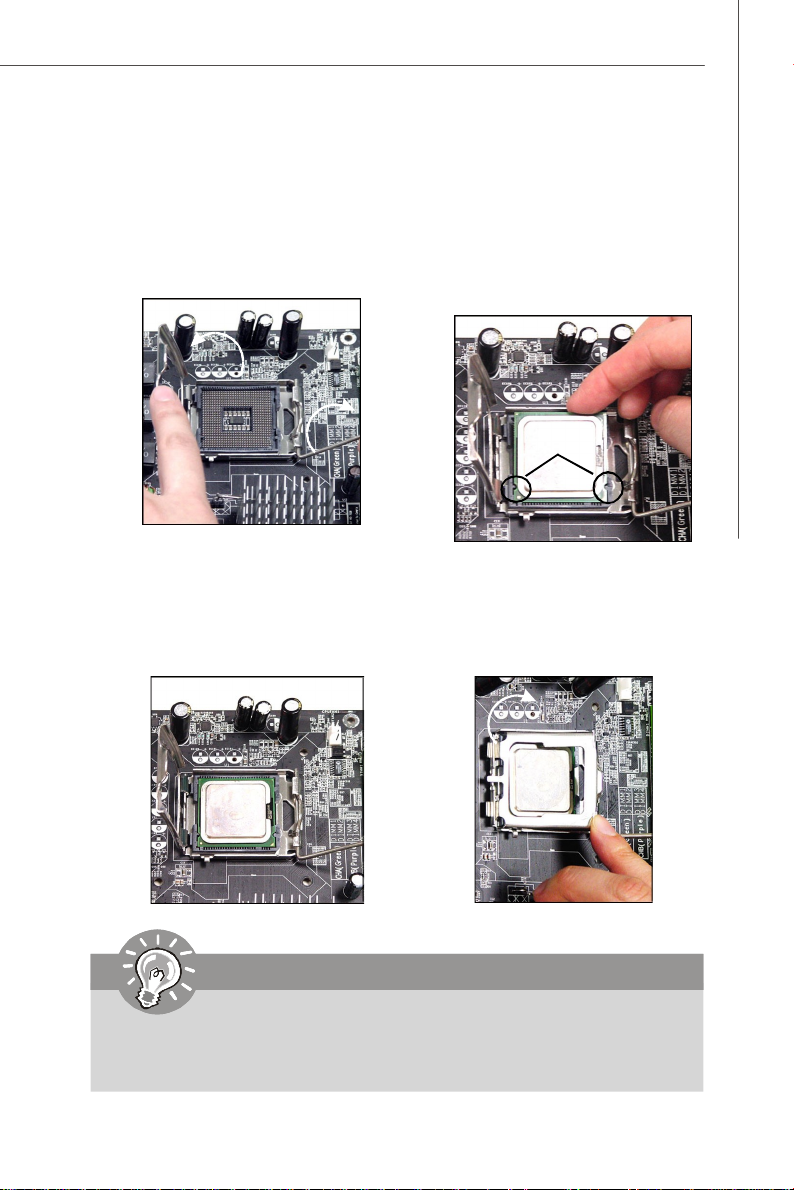
Hardware Setup
5.Lift the load lever up and open the
load plate.
7.Visually inspect if the CPU is
seated well into the socket. If not,
take out the CPU with pure vertical
motion and reinstall.
6.After confirming the CPU direction
for correct mating, put down the
CPU in the socket housing frame.
Be sure to grasp on the edge of
the CPU base. Note that the alignment keys are matched.
alignment
key
8.Cover the load plate onto the
package.
Important
Mainboard photos shown in this section are for demonstration of the CPU/
cooler installation only. The appearance of your mainboard may vary depending on the model you purchase.
2-5
Page 18
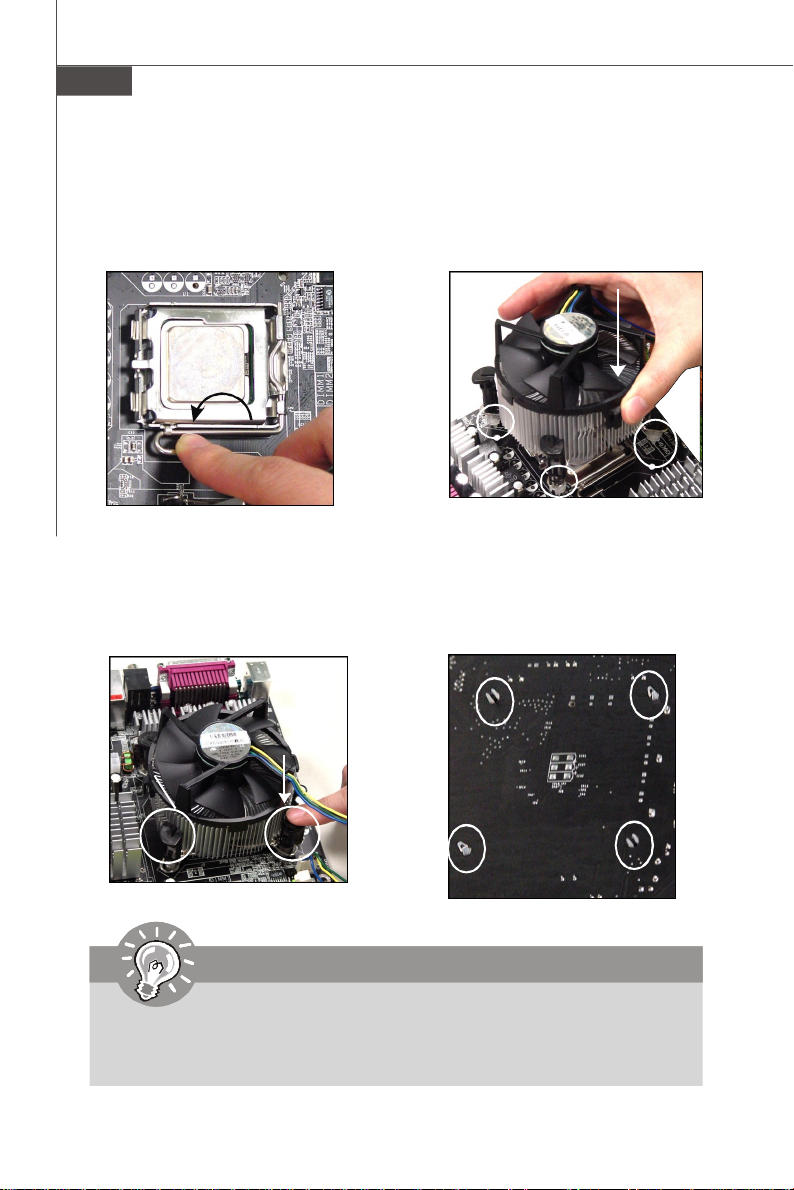
MS-9656 Server Board
9.Press down the load lever lightly
onto the load plate, and then secure the lever with the hook under
retention tab.
11.Press the four hooks down to fas-
ten the cooler. Then rotate the locking switch (refer to the correct direction marked on it) to lock the
hooks.
locking
switch
10. Align the holes on the mainboard
with the heatsink. Push down the
cooler until its four clips get
wedged into the holes of the
mainboard.
12.Turn over the mainboard to confirm that the clip-ends are correctly inserted.
Important
1. Read the CPU status in BIOS (Chapter 3).
2. Whenever CPU is not installed, always protect your CPU socket pin with the
plastic cap covered to avoid damage.
2-6
Page 19
Hardware Setup
Empty
Installed
Memory
These DIMM slots are intended for system memory modules.
DDR2
240-pin, 1.8V
64x2=128 pin 56x2=112 pin
Dual-Channel Mode Population Rule
In Dual-Channel mode, the memory modules can transmit and receive data with two
data bus lines simultaneously. Dual-Channel mode is enabled when the installed
memory capacities of both DIMM channels are equal. If different speed DIMMs are
used between channels, the slowest memory timing will be used.
Dual-Channel mode can be achieved with two, three or four DIMMs. To achieve DualChannel mode, the following conditions must be met:
* Matched DIMM configuration in each channel
* Same Density (128MB, 256MB, 512MB, etc.)
* Matched in both Channel A and Channel B memory channels
* Populate symmetrical memory slots (Slot 1 or Slot 2)
Configurations that do not match the above conditions will revert to Single-Channel
mode.
2 DIMMs
1GB
DIMM_A1
DIMM_A2
3 DIMMs
4 DIMMs
1GB
512MB
512MB
1GB
512MB
1GB
512MB
1GB
DIMM_B1
DIMM_B2
DIMM_A1
DIMM_A2
DIMM_B1
DIMM_B2
DIMM_A1
DIMM_A2
DIMM_B1
DIMM_B2
2-7
Page 20
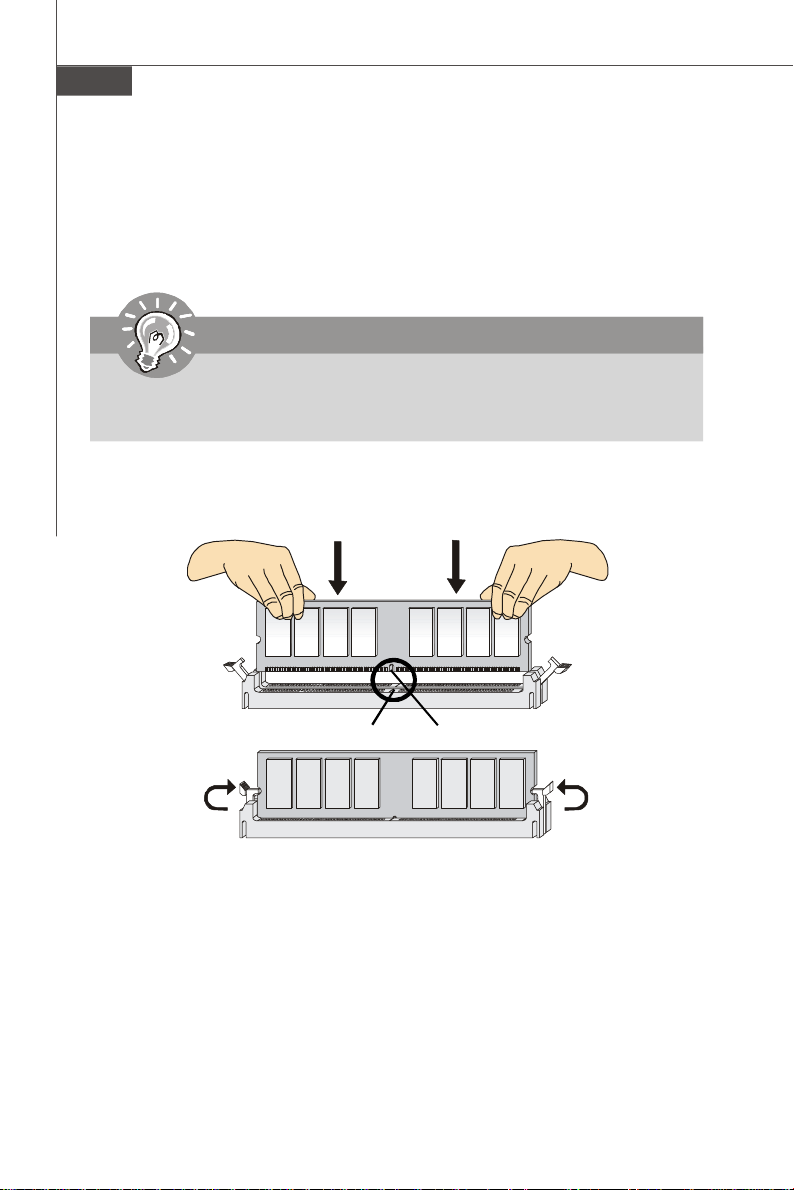
MS-9656 Server Board
Installing Memory Modules
1. The memory module has only one notch on the center and will only fit in the right
orientation.
2. Insert the memory module vertically into the DIMM slot. Then push it in until the
golden finger on the memory module is deeply inserted in the DIMM slot.
Important
You can barely see the golden finger if the memory module is properly inserted
in the DIMM slot.
3. The plastic clip at each side of the DIMM slot will automatically close.
2-8
Volt
Notch
Page 21
Hardware Setup
Power Supply
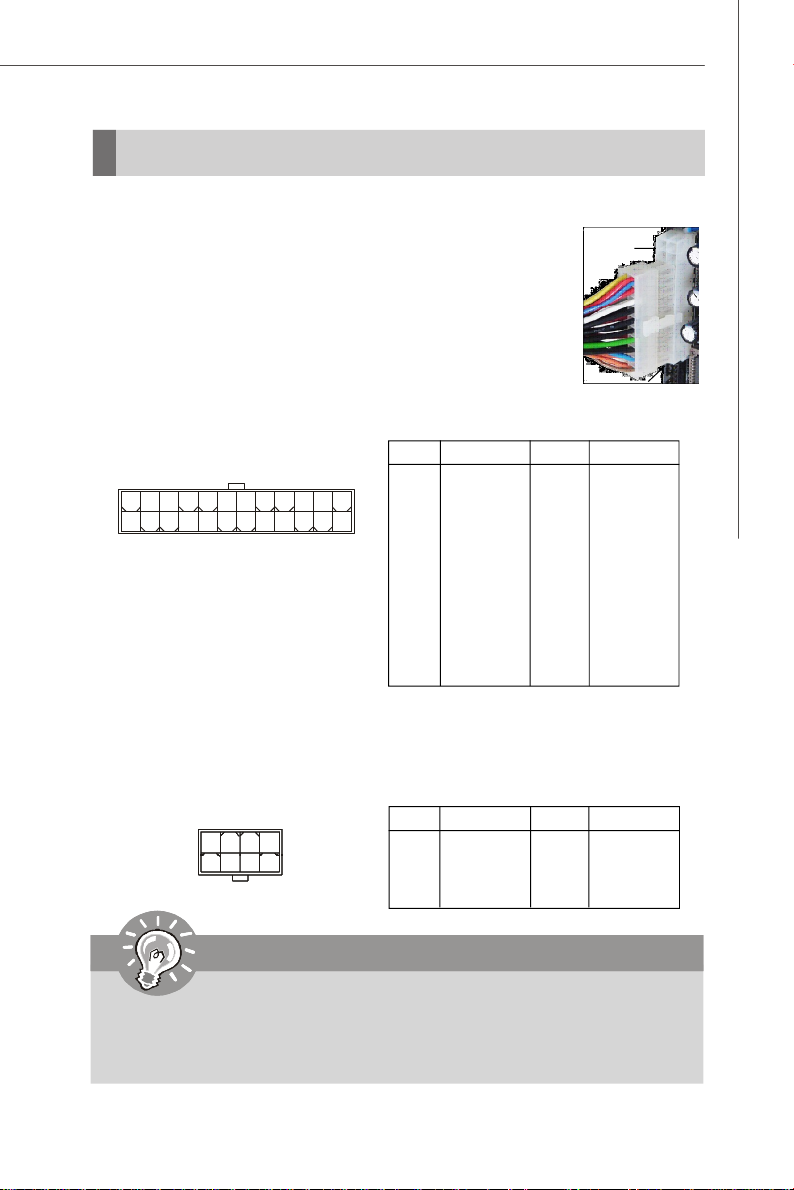
24-Pin System Power Connector: JPWR2
This connector allows you to connect a 24-pin power supply. To
connect the 24-pin power supply, make sure the power supply
connector is inserted in the proper orientation and the pins are
aligned. Then push down the power supply firmly into the connector.
You may use the 20-pin power supply as well. If you’d like to use the
20-pin power supply, please align your power supply connector
with pin 1 & pin 13. There is also a foolproof design on pin 11, 12, 23
& 24 to avoid wrong installation.
Pin Definition
JPWR2
24 13
PIN SIGNAL
1 +3.3V
2 +3.3V
3 GND
112
4 +5V
5 GND
6 +5V
7 GND
8 PWR OK
9 5VSB
10 +12V
11 +12V
12 +3.3V
PIN SIGNAL
13 +3.3V
14 -12V
15 GND
16 PS-ON#
17 GND
18 GND
19 GND
20 Res
21 +5V
22 +5V
23 +5V
24 GND
pin 12
pin 13
8-Pin CPU Power Connector: JPWR1
This connector provides 12V power output to the CPU.
Pin Definition
1
5
JPWR1
PIN SIGNAL
4
8
1 GND
2 GND
3 GND
4 GND
PIN SIGNAL
5 +12V
6 +12V
7 +12V
8 +12V
Important
1. Make sure that all connectors are connected to proper power supplies to
ensure stable operation of the mainboard.
2. Power supply of 350 watts (and above) is highly recommended for system
stability.
2-9
Page 22
MS-9656 Server Board
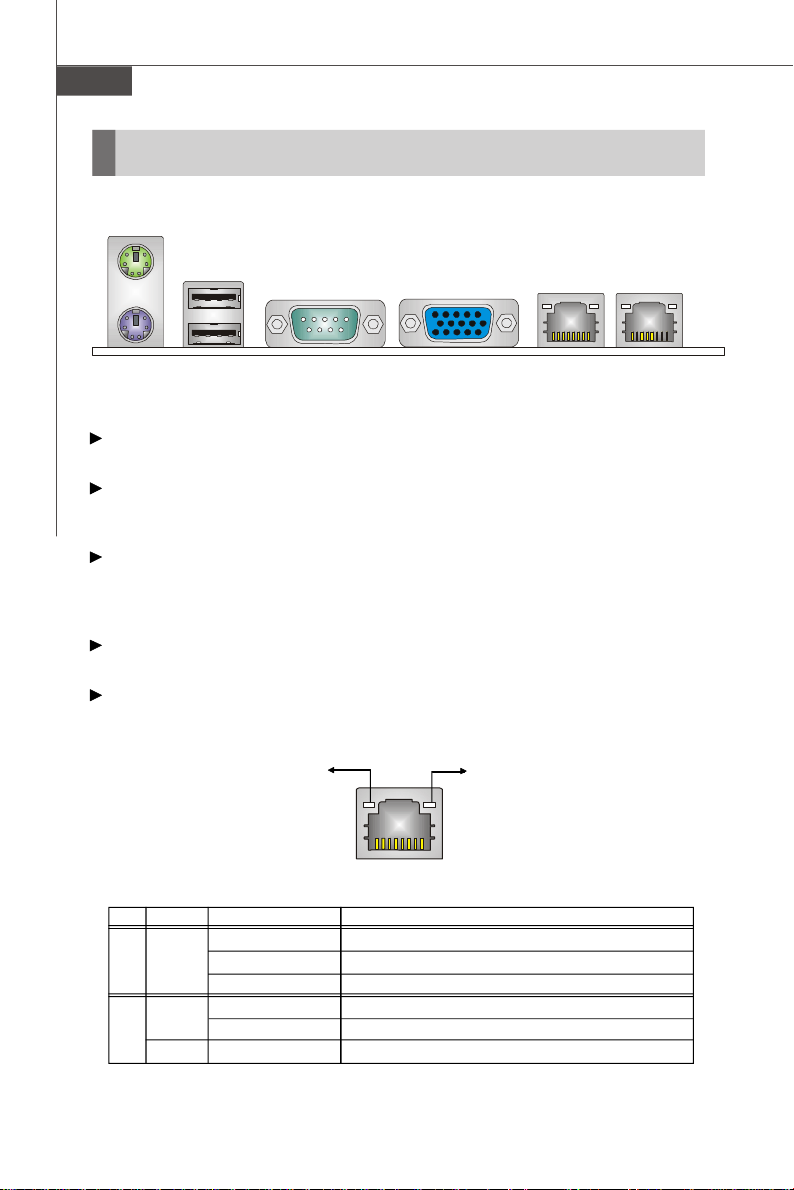
Back Panel I/O
Mouse
Keyboard
Serial PortUSB Ports VGA Port
LAN Jacks
Mouse/Keyboard
The standard PS/2® mouse/keyboard DIN connector is for a PS/2® mouse/keyboard.
USB Port
The USB (Universal Serial Bus) port is for attaching USB devices such as keyboard,
mouse, or other USB-compatible devices.
Serial Port
The serial port is a 16550A high speed communications port that sends/ receives 16
bytes FIFOs. You can attach a serial mouse or other serial devices directly to the
connector.
VGA Port
The DE-15 female connector is provided for monitor.
LAN
The standard RJ-45 LAN jack is for connection to the Local Area Network (LAN). You
can connect a network cable to it.
Link/Active Indicator
RJ-45 LAN Jack
LED Color LED State Condition
Off LAN link is not established.
Left Orange On (steady state) LAN link is established.
On (brighter & pulsing)The computer is communicating with another computer on the LAN.
Green Off 10 Mbit/sec data rate is selected.
Right On 100 Mbit/sec data rate is selected.
Orange On 1000 Mbit/sec data rate is selected.
Mode Indicator
2-10
Page 23
Hardware Setup
Connector
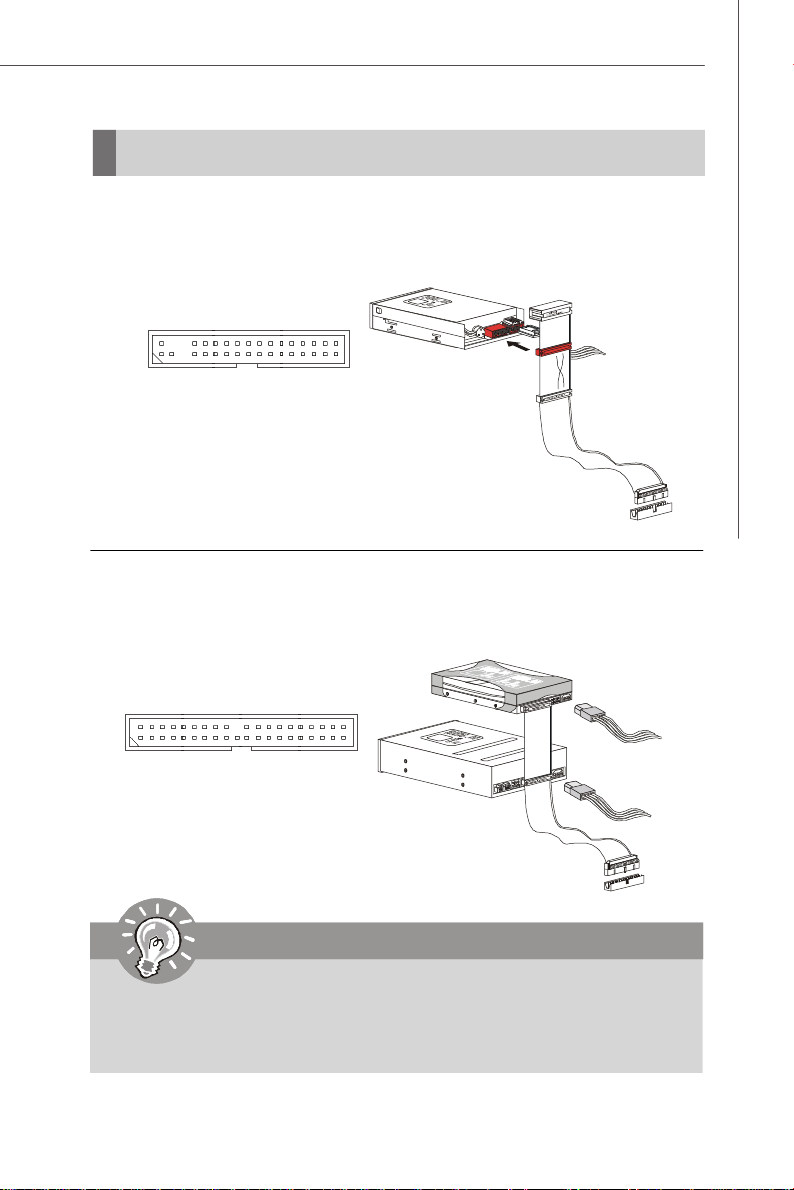
Floppy Disk Drive Connector: FDD1
This connector supports 360KB, 720KB, 1.2MB, 1.44MB or 2.88MB floppy disk drive.
FDD1
IDE Connector: J_IDE1
This connector supports IDE hard disk drives, optical disk drives and other IDE devices.
J_IDE1
Important
If you install two IDE devices on the same cable, you must configure the
drives separately to master / slave mode by setting jumpers. Refer to IDE
device’s documentation supplied by the vendors for jumper setting
instructions.
2-11
Page 24
MS-9656 Server Board
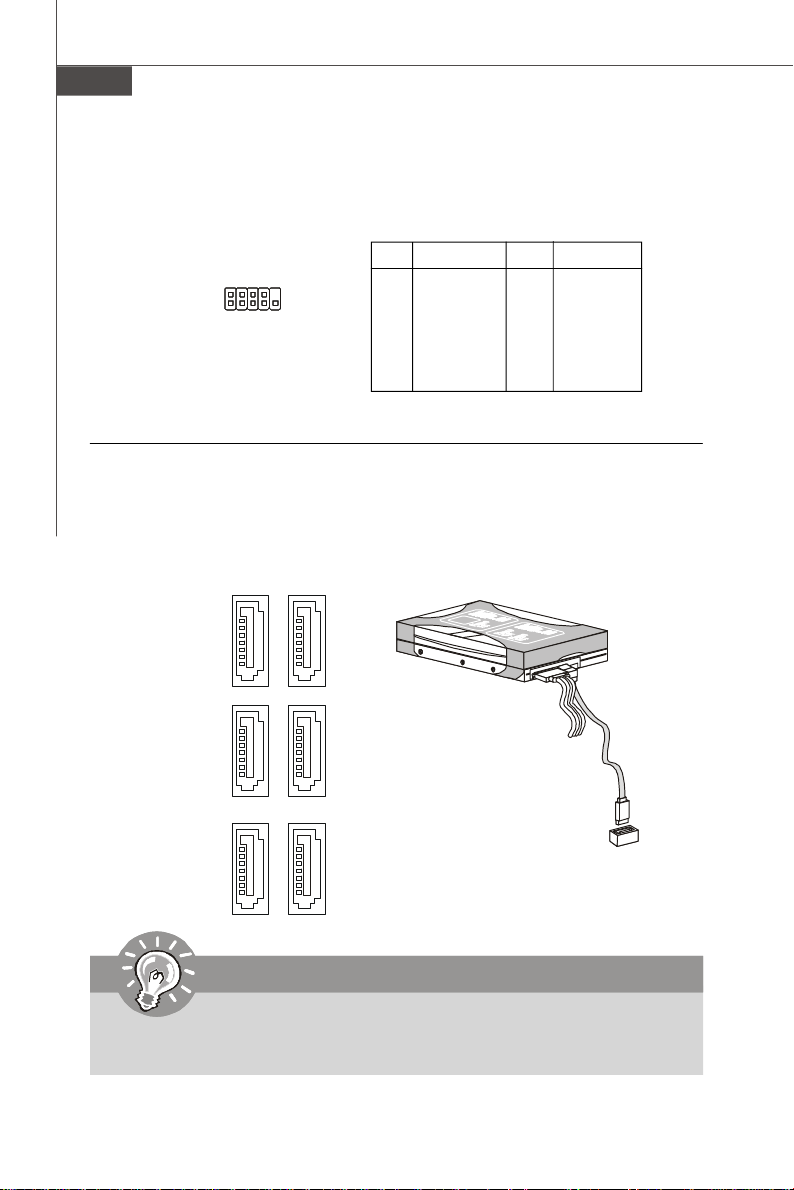
SPI Flash ROM Connector: JSPI1
This connector is used to flash SPI flash ROM.
Pin Definition
Pin Description Pin Description
1 VCC3_SB 2 VCC3_SB
3 SPI_MISO_F 4 SPI_MOSI_F
5 SPI_CS0_F# 6 SPI_CLK_F
7 GND 8 GND
9 SPI_HOLD# 10 NC
2
1
JSPI1
10
9
Serial ATA Connector: SATA1 ~ SATA6
This connector is a high-speed Serial ATA interface port. Each connector can connect to one Serial ATA device.
SATA2
SATA1
SATA3
SATA4
SATA5SATA6
Important
Please do not fold the Serial ATA cable into 90-degree angle. Otherwise,
data loss may occur during transmission.
2-12
Page 25
Hardware Setup
DVD/CD-ROM Connector: FPC1 (Optional)
This connector is designed to connect slim DVD/CD-ROM drive.
FPC1
Chassis Intrusion Switch Connector: JINT1
This connector connects to the chassis intrusion switch cable. If the chassis is
opened, the chassis intrusion mechanism will be activated. The system will record
this status and show a warning message on the screen. To clear the warning, you
must enter the BIOS utility and clear the record.
GND
1
2
CINTRU
JINT1
Fan Power Connector:
CPU_FAN1, SYS_FAN1/2, FRONT_FAN1, REAR_FAN1
The fan power connectors support system cooling fan with +12V. When connecting
the wire to the connectors, always note that the red wire is the positive and should
be connected to the +12V; the black wire is Ground and should be connected to GND.
If the mainboard has a System Hardware Monitor chipset onboard, you must use a
specially designed fan with speed sensor to take advantage of the CPU fan control.
C
S
O
E
N
N
T
+
S
G
R
1
O
N
O
2
R
D
V
L
CPU_FAN1,
SYS_FAN1,
FRONT_FAN1
SYS_FAN2,
REAR_FAN1
GND
+1 2V
SE NS OR
CONTROL
Important
1.Please refer to the recommended CPU fans at processor’s official website
or consult the vendors for proper CPU cooling fan.
2.Users are suggested to enter the BIOS Setup Utility to set up the Smart Fan
Control function.
2-13
Page 26

MS-9656 Server Board
Front Panel Connector: JAPP1, JAPP2, JAPP3 (Optional)
These are proprietary front panel connectors that provide I2C bus connection, serial
signal connection, and electrical connection to the front panel switches/LEDs.
JAPP1 Pin Definition
JAPP1
14 13
2 1
JAPP2
2
1
6
5
PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
1 +5VSB 2 GND
3 RESET+ 4 GND
5 POWER+ 6 GND
7 COM2 RXD 8 GND
9 COM2 TXD 10 NC
11 ATX PWR OK 12 GND
13 ID_LED+ 14 ID_LED-
JAPP2 Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL
1 +5VSB
2 GND
3 I2C_DATA
4 ID_LED+
5 I2C_CLK
6 ID_LED-
2-14
JAPP3
1
19
JAPP3 Pin Definition
2
20
PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
1 Power LED + 2 SYS_LED +
3 Power LED - 4 SYS_LED 5 Power Button + 6 LAN1_LED +
7 Power Button - 8 LAN1_LED 9 ID LED + 10 LAN2_LED +
11 ID LED - 12 LAN2_LED 13 ID Button + 14 Reset +
15 ID Button - 16 Reset 17 HDD LED + 18 HDD LED 19 +5VSB 20 +5VSB
Page 27

Hardware Setup
Serial Port Connector: COM2
This connector is a 16550A high speed communications port that sends/receives 16
bytes FIFOs. You can attach a serial device to it.
Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 DCD Data Carry Detect
COM2
19
2
2 SIN Serial In or Receive Data
3 SOUT Serial Out or Transmit Data
4 DTR Data Terminal Ready
5 GND Ground
6 DSR Data Set Ready
7 RTS Request To Send
8 CTS Clear To Send
9 RI Ring Indicate
Front USB Connector: JUSB2, JUSB3, JUSB4
This connector, compliant with Intel® I/O Connectivity Design Guide, is ideal for connecting high-speed USB interface peripherals such as USB HDD, digital cameras,
MP3 players, printers, modems and the like.
Pin Definition
9
10
2
1
JUSB2/3
JUSB4
1
2
10
9
PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
1 VCC 2 VCC
3 USB0- 4 USB15 USB0+ 6 USB1+
7 GND 8 GND
9 Key (no pin) 10 USBOC
USB 2.0 Bracket
(Optional)
Important
Note that the pins of VCC and GND must be connected correctly to avoid
possible damage.
2-15
Page 28

MS-9656 Server Board
BMC Connector: J_BOOT1, J_BOOT2, J_IPMB1, J_ICMB1, J1
These connectors are used to control the H8 BMC (Baseboard Management
Controller).
J_BOOT1
31
Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL
1 BOOT_TXD_CON
2 BOOT_RXD_CON
3 GND
J_IPMB1
1
Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL
1 IPMB_DATA
2 GND
3 IPMB_CLK
3
J1
13
14
Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
1 ETCK 2 GND
3 ETRST# 4 GND
5 ETDO 6 GND
7 H2C_RES# 8 3.3V DUAL
9 ETMS 10 GND
11 ETDI 12 GND
13 H8_RESET# 14 GND
J_BOOT2
1
Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL
1 Boot Mode
2 GND
J_ICMB1
Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL
1 BMC_RXD0
2 BMC_TXD0
3 ICMB_EN
1
2
13
2-16
Page 29

Hardware Setup
I2C Bus Connector: J_SMBUS1
The mainboard provides one I2C (also known as I2C) Bus connector for users to
connect System Management Bus (SMBus) interface.
Pin Definition
J_SMBUS1
1
PIN SIGNAL
1 SMB_ICH_ALERT#
2 SMB_ICH_CLK
3 SMB_ICH_DATA
TPM Connector: JTPM1 (Optional)
This connector connects to an optional TPM (Trusted Platform Module). Please refer
to the TPM security platform manual for more details.
JTPM1
13
14
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 LCLK LPC clock 2 3V dual/3V_STB 3V dual or 3V standby power
3 LRST# LPC reset 4 VCC3 3.3V power
5 LAD0 LPC address & data pin0 6 SIRQ Serial IRQ
7 LAD1 LPC address & data pin1 8 VCC5 5V power
9 LAD2 LPC address & data pin2 10 KEY No pin
11 LAD3 LPC address & data pin3 12 GND Ground
13 LFRAME# LPC Frame 14 GND Ground
1
2
2-17
Page 30

MS-9656 Server Board
Jumper
VGA Jumper: J_VGA_EN1
This jumper is used to enable or disable the onboard VGA controller.
3
1
DisableEnable
1
J_VGA_EN1
3
1
BIOS Recovery Jumper: J_BOOT3
Users can short connect pin#2-3 to recover the system BIOS with a Recovery
Floppy. When the system is done with the job, the buzzer will beep to remind the user
to set the jumper to its normal state (pin#1-2 short connected).
1
J_BOOT3
1
3
Normal
1
3
Recovery
Clear CMOS Jumper: J_CMOS1
There is a CMOS RAM onboard that has a power supply from an external battery to
keep the data of system configuration. With the CMOS RAM, the system can automatically boot OS every time it is turned on. If you want to clear the system configuration,
set the jumper to clear data.
1
J_CMOS1
1 3
Keep Data
1 3
Clear Data
Important
You can clear CMOS by shorting 2-3 pin while the system is off. Then return
to 1-2 pin position. Avoid clearing the CMOS while the system is on; it will
damage the mainboard.
2-18
Page 31

Hardware Setup
Slot
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) Express Slot
The PCI Express slot supports the PCI Express interface expansion card.
The standard PCI Express x16 slot supports up to 4.0 GB/s transfer rate.
But the onboard PCI Express x16 slot only supports x8 signal with up to
2.0 GB/s transfer rate.
The PCI Express x4 slot supports up to 1.0 GB/s transfer rate.
PCI Express x4 Slot
PCI Express x16 Slot
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) Slot
The PCI slot supports LAN card, SCSI card, USB card, and other add-on cards that
comply with PCI specifications.
32-bit PCI Slot
Important
When adding or removing expansion cards, make sure that you unplug the
power supply first. Meanwhile, read the documentation for the expansion
card to configure any necessary hardware or software settings for the expansion card, such as jumpers, switches or BIOS configuration.
2-19
Page 32

MS-9656 Server Board
PCI Interrupt Request Routing
The IRQ, acronym of interrupt request line and pronounced I-R-Q, are hardware lines
over which devices can send interrupt signals to the microprocessor. The PCI IRQ
pins are typically connected to the PCI bus pins as follows:
DEVICE Interrupt ID Select REQ / GNT
XGI Z7 PCI_PIRQ # 0 PCI_AD18
IT8213F PCI_PIRQ # 2 PCI_AD19 PCI_REQ# 2 / PCI_GNT# 2
PCI Slot 1 PCI_PIRQ # 0 PCI_AD20 PCI_REQ# 0 / PCI_GNT# 0
PCI_PIRQ # 1
PCI_PIRQ # 2
PCI_PIRQ # 3
PCI Slot 2 PCI_PIRQ # 3 PCI_AD21 PCI_REQ# 1 / PCI_GNT# 1
PCI_PIRQ # 0
PCI_PIRQ # 1
PCI_PIRQ # 2
PCI Slot 3 PCI_PIRQ # 2 PCI_AD22 PCI_REQ# 3 / PCI_GNT# 3
PCI_PIRQ # 3 or
PCI_PIRQ # 0 ARBITER_REQ# 1
PCI_PIRQ # 1 ARBITER_GNT# 1
PCI Slot 4 PCI_PIRQ # 1 PCI_AD23 ARBITER_REQ# 2
PCI_PIRQ # 2 &
PCI_PIRQ # 3 ARBITER_GNT# 2
PCI_PIRQ # 0
2-20
Page 33

Chapter 3
BIOS Setup
This chapter provides information on the BIOS Setup
program and allows you to configure the system for
optimum use.
You may need to run the Setup program when:
² An error message appears on the screen during the
system booting up, and requests you to run SETUP.
² You want to change the default settings for cus-
tomized features.
BIOS Setup
3-1
Page 34

MS-9656 Server Board
Entering Setup
Power on the computer and the system will start POST (Power On Self Test) process.
When the message below appears on the screen, press <Del> key to enter Setup.
Press Del to enter SETUP
If the message disappears before you respond and you still wish to enter Setup,
restart the system by turning it OFF and On or pressing the RESET button. You may
also restart the system by simultaneously pressing <Ctrl>, <Alt>, and <Delete> keys.
Important
1.The items under each BIOS category described in this chapter are under
continuous update for better system performance. Therefore, the description may be slightly different from the latest BIOS and should be held for
reference only.
2.Upon boot-up, the 1st line appearing after the memory count is the BIOS
version. It is usually in the format:
3-2
A9656IMS V1.0 101507 where:
1st digit refers to BIOS maker as A = AMI, W = AWARD, and P =
PHOENIX.
2nd - 5th digit refers to the model number.
6th digit refers to the chipset as I = Intel, N = nVidia, and V = VIA.
7th - 8th digit refers to the customer as MS = all standard customers.
V1.0 refers to the BIOS version.
101507 refers to the date this BIOS was released.
Page 35

BIOS Setup
Control Keys
<↑> Move to the previous item
<↓> Move to the next item
<←> Move to the item in the left hand
< →> Move to the item in the right hand
<Enter> Select the item
<Esc> Jumps to the Exit menu or returns to the main menu from a
submenu
<+/PU> Increase the numeric value or make changes
<-/PD> Decrease the numeric value or make changes
<F9> Load Optimized Defaults
<F8> Load Fail-Safe Defaults
<F10> Save all the CMOS changes and exit
Getting Help
After entering the Setup menu, the first menu you will see is the Main Menu.
Main Menu
The main menu lists the setup functions you can make changes to. You can use the
arrow keys ( ↑↓ ) to select the item. The on-line description of the highlighted setup
function is displayed at the bottom of the screen.
Sub-Menu
If you find a right pointer symbol (as shown in the right view)
appears to the left of certain fields that means a sub-menu
can be launched from this field. A sub-menu contains additional options for a field parameter. You can use arrow keys
( ↑↓ ) to highlight the field and press <Enter> to call up the sub-menu. Then you can
use the control keys to enter values and move from field to field within a sub-menu.
If you want to return to the main menu, just press the <Esc >.
General Help <F1>
The BIOS setup program provides a General Help screen. You can call up this screen
from any menu by simply pressing <F1>. The Help screen lists the appropriate keys
to use and the possible selections for the highlighted item. Press <Esc> to exit the
Help screen.
3-3
Page 36

MS-9656 Server Board
The Menu Bar
Main
Use this menu for basic system configurations, such as time, date etc.
Advanced
Use this menu to set up the items of special enhanced features.
Boot
Use this menu to specify the priority of boot devices.
Security
Use this menu to set supervisor and user passwords.
Chipset
This menu controls the advanced features of the onboard Northbridge and Southbridge.
Exit
This menu allows you to load the BIOS default values or factory default settings into
the BIOS and exit the BIOS setup utility with or without changes.
3-4
Page 37

BIOS Setup
Main
AMI BIOS, Processor, System Memory
These items show the firmware and hardware specifications of your system. Read
only.
System Time
This setting allows you to set the system time. The time format is <Hour> <Minute>
<Second>.
System Date
This setting allows you to set the system date. The date format is <Day>, <Month>
<Date> <Year>.
3-5
Page 38

MS-9656 Server Board
Advanced
For mainboards with IPMI chip
For mainboards without IPMI chip
3-6
Page 39

BIOS Setup
CPU Configuration
Execute Disable Bit Capability
Intel's Execute Disable Bit functionality can prevent certain classes of malicious
"buffer overflow" attacks when combined with a supporting operating system.
This functionality allows the processor to classify areas in memory by where
application code can execute and where it cannot. When a malicious worm
attempts to insert code in the buffer, the processor disables code execution,
preventing damage or worm propagation.
Core Multi-Processing
CMP (Core Multi Processing) is the ability to have many independent processing
cores on a single die, each with their own L1 Code & Data caches, Local APICs
& thermal controls, while having a shared L2 cache, power management & bus
interface. Intel multi-core architecture has a single Intel processor package that
contains two or more processor "execution cores," or computational engines to
enable enhanced performance and more-efficient simultaneous processing of
multiple tasks.
Intel(R) SpeedStep(tm) Tech
EIST (Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology) allows the system to dynamically
adjust processor voltage and core frequency, which can result in decreased
average power consumption and decreased average heat production.
3-7
Page 40

MS-9656 Server Board
IDE Configuration
SATA#1 Configuration, SATA#2 Configuration
These settings specify the operation modes of the SATA ports.
Configure SATA#1 ass
This setting specifies the function of the on-chip SATA controller.
Primary/Secondary/Third/Fourth/Fifth/Sixth IDE Master/Slave
3-8
Page 41

BIOS Setup
[Type] Press PgUp/<+> or PgDn/<-> to select
[LBA/Large Mode] Enabling LBA causes Logical Block Ad-
[Block(Multi-Sector Transfer)]Any selection except Disabled determines
[PIO Mode] Indicates the type of PIO (Programmed Input/
[DMA Mode] Indicates the type of Ultra DMA
[S.M.A.R.T.] This allows you to activate the S.M.A.R.T.
[32 Bit Data Transfer] Enables 32-bit communication between
Floppy Configuration
[Manual], [None] or [Auto] type. Note that the
specifications of your drive must match with
the drive table. The hard disk will not work
properly if you enter improper information for
this category. If your hard disk drive type is
not matched or listed, you can use [Manual] to
define your own drive type manually.
dressing to be used in place of Cylinders,
Heads and Sectors
the number of sectors transferred per block
Output)
(Self-Monitoring Analysis & Reporting
Technology) capability for the hard disks. S.
M.A.R.T is a utility that monitors your disk sta
tus to predict hard disk failure. This gives you
an opportunity to move data from a hard disk
that is going to fail to a safe place before the
hard disk becomes offline.
CPU and IDE card
Floppy A, Floppy B
This setting allows you to set the type of floppy drives installed.
3-9
Page 42

MS-9656 Server Board
Onboard LANs Configuration
GbE LAN1 (82573) Controller, GbE LAN2 (82566) Controller
These settings disable/enable the specified LAN controllers.
GbE LAN1 (82573) Boot ROM, GbE LAN2 (82566) Boot ROM
The items enable or disable the initialization of the onboard LAN Boot ROMs
during bootup. Selecting [Disabled] will speed up the boot process.
3-10
GbE Wake Up From S5
This field specifies whether the system will be awakened from power saving modes when activity or input signal of onboard LAN is detected.
Page 43

Super IO Configuration
Onboard Floppy Controller
This setting disables/enables the onboard floppy disk drive controller.
Serial Port 1 Address, Serial Port 2 Address
Select an address and a corresponding interrupt for the serial port 1/2.
BIOS Setup
3-11
Page 44

MS-9656 Server Board
Hardware Health Configuration (for mainboards without IPMI chip)
These items display the current status of all of the monitored hardware devices/
components such as voltages, temperatures and all fans’ speeds.
CPU FAN Mode Setting
This setting controls the Smart Fan feature. Smart Fan is an excellent feature
which will adjust the CPU/system fan speed automatically depending on the
current CPU/system temperature. Selecting [Smart Fan Mode] can prevent
the CPU from being damaged by overheating.
3-12
Front Fan PWM Output, System Fan1 & Fan2 PWM Output, Rear Fan
PWM Output
This setting allows users to control the fan speed by changing the duty
cycle of the fan PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) output.
Page 45

BIOS Setup
APM Configuration
Resume On Ring
An input signal on the serial Ring Indicator (RI) line (in other words, an incoming
call on the modem) awakens the system from a soft off state.
Resume On PME# of PCI Slots
When setting to [Enabled], this setting allows your system to be awakened from
the power saving modes through any PME (Power Management Event) on PCI
slots.
Resume On RTC Alarm
When [Enabled], your can set the date and time at which the RTC (real-time
clock) alarm awakens the system from suspend mode.
3-13
Page 46

MS-9656 Server Board
Event Log Configuration
View Event Log
Press [Enter] to view the contents of the DMI event log.
Mark All Events as Readd
Press [Enter] and a screen pops up, asking users to confirm whether or not to
clear all DMI event logs immediately. Press [Y] and [Enter], the BIOS will clear all
DMI event logs right away.
Clear Event Log
When this setting is set to [Yes], the DMI event log will be cleared at next POST
stage. Then, the BIOS will automatically set this option to [No].
3-14
Page 47

IPMI 2.0 Configuration (for mainboards with IPMI chip)
Status of BMC, BMC Firmware Version
These settings show the status of the BMC (Baseboard Management
Controller) chip and its firmware version. Read only.
View BMC System Event Log
Use this function to view system event logs recorded by BMC.
BIOS Setup
Clear BMC System Event Log
Use this function to clear system event logs recorded by BMC.
Set LAN Configuration
Channel Number, IP Address, MAC Address, Subnet Maskk
Use these settings to set up the channel number, IP address, MAC address,
and IP subnet mask for your system network.
3-15
Page 48

MS-9656 Server Board
BMC Watch Dog Timer Action
The system watch-dog timer is a hardware timer that generates either an NMI or
a reset when the software that it monitors does not respond as expected each
time the watch dog polls it.
Notify BMC FAN Type
This setting specifies the BMC fan type.
Remote Access Configuration
Remote Access
The setting enables/disables the remote access function. When set to [Enabled],
users may configure the following settings for remote access type and
parameters.
Serial Port Number, Base Address, IRQ, Serial Port Mode
Use these settings to configure ports for remote access.
Flow Control
Flow control is the process of managing the rate of data transmission between
two nodes. It’s the process of adjusting the flow of data from one device to
another to ensure that the receiving device can handle all of the incoming data.
This is particularly important where the sending device is capable of sending
data much faster than the receiving device can receive it.
Redirection After BIOS POST
This setting determines whether or not to keep terminals’ console redirection
running after the BIOS POST has booted.
3-16
Page 49

BIOS Setup
Terminal Type
To operate the system’s console redirection, you need a terminal supporting
ANSI terminal protocol and a RS-232 null modem cable connected between the
host system and terminal(s). This setting specifies the type of terminal device
for console redirection.
VT-UTF8 Combo Key Support
This setting enables/disables the VT-UTF8 combination key support for ANSI/
VT100 terminals.
Sredir Memory Display Delay
Use this setting to set the delay in seconds to display memory information.
Trusted Computing
TCG/TPM Support
This setting controls the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) designed by the Trusted
Computing Group (TCG). TPMs are special-purpose integrated circuits (ICs)
built into a variety of platforms to enable strong user authentication and machine attestation—essential to prevent inappropriate access to confidential
and sensitive information and to protect against compromised networks. TPM
Services is now a new feature set in Windows Server "Longhorn" and Windows Vista.
Clearing the TPM
When the TPM is cleared, all the keys you previously had stored on your vault
will be lost. You should create an archive of your TPM Keys before clearing the
TPM. To recover your TPM keys, you will need to restore your keys from an
archive.
3-17
Page 50

MS-9656 Server Board
TPM Enable/Disable Status
This setting displays the TPM enable/disable status. Read only.
TPM Owner Status
This setting shows the TPM ownership. Read only.
USB Configuration
Legacy USB Support
Set to [Enabled] if you need to use any USB 1.1/2.0 device in the operating
system that does not support or have any USB 1.1/2.0 driver installed, such as
DOS and SCO Unix.
USB 2.0 Controller Mode
This setting specifies the operation mode of the onboard USB 2.0 controller.
BIOS EHCI Hand-Off
This setting allows you to enable or disable a workaround for operating systems without EHCI (Enhanced Host Controller Interface) hand-off support. The
Enhanced Host Controller Interface (EHCI) specification describes the registerlevel interface for a Host Controller for the Universal Serial Bus (USB) Revision
2.0.
3-18
Page 51

BIOS Setup
USB Mass Storage Device Configuration
USB Mass Storage Reset Delay
This setting controls the number of seconds the POST waits for the USB
mass storage device after the start unit command is sent.
Emulation Type
This setting enables you to set the type of device you want the USB mass
storage device to emulate.
3-19
Page 52

MS-9656 Server Board
Boot
Boot Settings Configuration
3-20
Page 53

BIOS Setup
Quick Boot
Enabling this setting will cause the BIOS power-on self test routine to skip some
of its tests during bootup for faster system boot.
Quiet Boot
This BIOS feature determines if the BIOS should hide the normal POST messages with the motherboard or system manufacturer's full-screen logo.
When it is enabled, the BIOS will display the full-screen logo during the boot-up
sequence, hiding normal POST messages.
When it is disabled, the BIOS will display the normal POST messages, instead of
the full-screen logo.
Please note that enabling this BIOS feature often adds 2-3 seconds of delay to
the booting sequence. This delay ensures that the logo is displayed for a
sufficient amount of time. Therefore, it is recommended that you disable this
BIOS feature for a faster boot-up time.
AddOn ROM Display Mode
This item is used to determine the display mode when an optional ROM is
initialized during POST. When set to [Force BIOS], the display mode used by AMI
BIOS is used. Select [Keep Current] if you want to use the display mode of
optional ROM.
Bootup Num-Lock
This setting is to set the Num Lock status when the system is powered on.
Setting to [On] will turn on the Num Lock key when the system is powered on.
Setting to [Off] will allow users to use the arrow keys on the numeric keypad.
PS/2 Mouse Support
Select [Enabled] if you need to use a PS/2-interfaced mouse in the operating
system.
Wait For ‘F1’ If Error
When this setting is set to [Enabled] and the boot sequence encounters an
error, it asks you to press F1. If disabled, the system continues to boot without
waiting for you to press any keys.
Hit ‘DEL’ Message Display
Set this option to [Disabled] to prevent the message as follows:
It will prevent the message from appearing on the first BIOS screen when the
computer boots. Set it to [Enabled] when you want to run the BIOS Setup Utility.
Interrupt 19 Capture
Interrupt 19 is the software interrupt that handles the boot disk function. When
enabled, this BIOS feature allows the ROM BIOS of these host adaptors to
"capture" Interrupt 19 during the boot process so that drives attached to these
adaptors can function as bootable disks. In addition, it allows you to gain access to the host adaptor's ROM setup utility, if one is available.
Hit Del if you want to run setup
3-21
Page 54

MS-9656 Server Board
When disabled, the ROM BIOS of these host adaptors will not be able to "capture" Interrupt 19. Therefore, you will not be able to boot operating systems
from any bootable disks attached to these host adaptors. Nor will you be able to
gain access to their ROM setup utilities.
Boot Device Priority
1st Boot Device
The items allow you to set the sequence of boot devices where BIOS attempts
to load the disk operating system. First press <Enter> to enter the sub-menu.
Then you may use the arrow keys ( ↑↓ ) to select the desired device, then
press <+>, <-> or <PageUp>, <PageDown> key to move it up/down in the
priority list.
Removable Drives
1st Drive, 2nd Drive
This setting allows users to set the priority of the removable devices. First
press <Enter> to enter the sub-menu. Then you may use the arrow keys ( ↑↓ )
to select the desired device, then press <+>, <-> or <PageUp>, <PageDown>
key to move it up/down in the priority list.
3-22
Page 55

BIOS Setup
Security
Supervisor Password / Change Supervisor Password
Supervisor Password controls access to the BIOS Setup utility. These settings allow
you to set or change the supervisor password.
User Password / Change User Password / Clear User Password
User Password controls access to the system at boot. These settings allow you to
set, change, or clear the user password.
Chassis Intrusion
The field enables or disables the feature of recording the chassis intrusion status
and issuing a warning message if the chassis is once opened. To clear the warning
message, set the field to [Reset]. The setting of the field will automatically return to
[Enabled] later.
3-23
Page 56

MS-9656 Server Board
Chipset
North Bridge Configuration
3-24
Page 57

BIOS Setup
ECC Function
This setting enables/disables ECC (Error Correction Code) checking, a method
of checking the integrity of data in DRAM. ECC provides more elaborate error
detection than parity; ECC can detect multiple-bit errors and can locate and
correct single-bit errors.
Memory Remap Feature
The memory remapping feature allows for the segment of system memory that
was previously overwritten by the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)
configuration space to be remapped above the 4 GB address line.
South Bridge Configuration
USB 2.0 Controller
Set to [Enabled] if you need to use any USB 2.0 device in the operating system
that does not support or have any USB 2.0 driver installed, such as DOS and
SCO Unix.
Restore on AC Power Loss
This setting specifies whether your system will reboot after a power failure or
interrupt occurs. Available settings are:
[Power Off] Leaves the computer in the power off state.
[Power On] Leaves the computer in the power on state.
[Last State] Restores the system to the previous status before power
failure or interrupt occurred.
3-25
Page 58

MS-9656 Server Board
Exit
Save Changes and Exit
Save changes to CMOS and exit the Setup Utility.
Discard Changes and Exit
Abandon all changes and exit the Setup Utility.
Discard Changes
Abandon all changes and continue with the Setup Utility.
Load Optimal Defaults
Use this menu to load the default values set by the mainboard manufacturer specifically for optimal performance of the mainboard.
Load Failsafe Defaults
Use this menu to load the default values set by the BIOS vendor for stable system
performance.
3-26
Page 59

Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
Appendix A
Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
This appendix will assist users in configuring and enabling RAID functionality on platforms
The ICH9R RAID solution supports RAID level 0
(striping), RAID level 1 (mirroring), RAID level 5 (striping
with parity) and RAID level 10 (striping and mirroring).
A-1
Page 60

MS-9656 Server Board
ICH9R Introduction
The ICH9R provides a hybrid solution that combines 6 independent SATAII ports for
support of up to 6 Serial ATAII (Serial ATAII RAID) drives.
Serial ATAII (SATAII) is the latest generation of the ATA interface. SATA hard drives
deliver blistering transfer speeds up to 300MB/sec. Serial ATA uses long, thin cables,
making it easier to connect your drive and improving the airflow inside your PC. The
most outstanding features are:
1. Supports 300MB/s transfers with CRC error checking.
2. Supports Hot-plug-n-play feature.
3. Data handling optimizations including tagged command queuing, elevator
seek and packet chain command.
Intel® ICH9R offers RAID level 0 (Striping), RAID level 1 (Mirroring and Duplexing),
RAID level 5 (Block Interleaved Distributed Parity), RAID level 10 (A Stripe of Mirrors)
and Intel® Martix Storage Technology.
RAID 0 breaks the data into blocks which are written to separate hard drives. Spreading
the hard drive I/O load across independent channels greatly improves I/O performance.
RAID 1 provides data redundancy by mirroring data between the hard drives and
provides enhanced read performance. RAID 5 Provides data striping at the byte level
and also stripe error correction information. This results in excellent performance
and good fault tolerance. Level 5 is one of the most popular implementations of RAID.
RAID 10 Not one of the original RAID levels, multiple RAID 1 mirrors are created, and
a RAID 0 stripe is created over these. Intel Matrix RAID Technology is the advanced
ability for two RAID volumes to share the combined space of two hard drives being
used in unison.
Important
The least number of hard drives for RAID 0, RAID 1 or Matrix mode is 2. The
least number of hard drives for RAID 10 mode is 4. And the least number of
hard drives for RAID 5 mode is 3.
All the information/ volumes/ pictures listed in your system might differ from
the illustrations in this appendix.
A-2
Page 61

Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
BIOS Configuration
The Intel Matrix Storage Manager Option ROM should be integrated with the system
BIOS on all motherboards with a supported Intel chipset. The Intel Matrix Stroage
Manager Option ROM is the Intel RAID implementation and provides BIOS and DOS
disk services. Please use <Ctrl> + <I> keys to enter the “Intel(R) RAID for Serial ATA”
status screen, which should appear early in system boot-up, during the POST
(Power-On Self Test). Also, you need to enable the RAID function in BIOS to create,
delete and reset RAID volumes.
Using the Intel Matrix Stroage Manager Option ROM
1. Creating, Deleting and Resetting RAID Volumes:
The Serial ATA RAID volume may be configured using the RAID Configuration utility
stored within the Intel RAID Option ROM. During the Power-On Self Test (POST), the
following message will appear for a few seconds:
Important
The “Driver Model”, “Serial #” and “Size” in the following example might be
different from your system.
After the above message shows, press <Ctrl> and <I> keys simultaneously to enter
the RAID Configuration Utility.
Important
The following procedure is only available with a newly-built system or if you
are reinstalling your OS. It should not be used to migrate an existing system
to RAID.
A-3
Page 62

MS-9656 Server Board
After pressing the <Ctrl> and <I> keys simultaneously, the following window will
appear:
(1) Create RAID Volume
1. Select option 1 “Create RAID Volume” and press <Enter> key. The following
screen appears. Then in the Name field, specify a RAID Volume name and
then press the <TAB> or <Enter> key to go to the next field.
2. Use the arrow keys to select the RAID level best suited to your usage model
in RAID Level.
A-4
Page 63

Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
3. In the Disk field, press <Enter> key and the following screen appears. Use
<Space> key to select the disks you want to create for the RAID volume, then
click <Enter> key to finish selection.
4. Then select the strip value for the RAID array by using the “upper arrow” or
“down arrow” keys to scroll through the available values, and pressing the
<Enter> key to select and advance to the next field. The available values
range from 4KB to 128 KB in power of 2 increments. The strip value should be
chosen based on the planned drive usage. Here are some typical values:
RAID0 – 128KB
RAID10 – 64KB
RAID5 – 64KB
5. Then select the capacity of the volume in the Capacity field. The default
value is the maximum volume capacity of the selected disks.
A-5
Page 64

MS-9656 Server Board
Important
Since you want to create two volumes (Intel Matrix RAID Technology), this
default size (maximum) needs to be reduced. Type in a new size for the first
volume. As an example: if you want the first volume to span the first half of the
two disks, re-type the size to be half of what is shown by default. The second
volume, when created, will automatically span the remainder of two hard
drives.
6.Then the following screen appears for you to confirm if you are sure to
create the RAID volume. Press <Y> to continue.
7.Then the following screen appears to indicate that the creation is finished.
A-6
Page 65

Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
(2) Delete RAID Volume
Here you can delete the RAID volume, but please be noted that all data on RAID
drives will be lost.
Important
If your system currently boots to RAID and you delete the RAID volume in the
Intel RAID Option ROM, your system will become unbootable.
Select option 2 Delete RAID Volume from the main menu window and press
<Enter> key to select a RAID volume for deletion. Then press <Delete> key to
delete the selected RAID volume. The following screen appears.
Press <Y> key to accept the volume deletion.
A-7
Page 66

MS-9656 Server Board
(3) Reset Disks to Non-RAID
Select option 3 Reset Disks to Non-RAID and press <Enter> to delete the RAID
volume and remove any RAID structures from the drives. The following screen
appears:
Press <Y> key to accept the selection.
Important
1. You will lose all data on the RAID drives and any internal RAID structures
when you perform this operation.
2. Possible reasons to ‘Reset Disks to Non-RAID’ could include issues such
as incompatible RAID configurations or a failed volume or failed disk.
A-8
Page 67

Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
Installing Driver
Install Driver in Windows Vista / XP / 2003
† New Windows Vista / XP / 2003 Installation
The following details the installation of the drivers while installing Windows XP /
2003.
1. When you start installing Windows XP and older operating systems, you may
encounter a message stating, “Setup could not determine the type of one or
more mass storage devices installed in your system” . If this is the case, then
you are already in the right place and are ready to supply the driver. If this is
not the case, then press F6 when prompted at the beginning of Windows
setup.
2. Press the “ S” key to select “Specify Additional Device”.
3. You should be prompted to insert a floppy disk containing the Intel® RAID
driver into the A: drive.
Note: For Windows Vista you can use Floppy, CD/DVD or USB.
Important
Please follow the instruction below to make an “ Intel® RAID Driver” for
yourself.
1. Insert the MSI CD into the CD-ROM drive.
2. Click the “Browse CD” on the Setup screen.
3.Copy all the contents in \\IDE\Intel\ICH9R\Floppy to a formatted floppy
diskette.
4.The driver diskette for Intel® ICH9R RAID Controller is done.
4. For Windows Vista:
During the Operating system installation, after selecting the location to install
Vista click on “Load Driver” button to install a third party SCSI or RAID driver.
5. When prompted, insert the floppy disk or media (Floppy, CD/DVD or USB) you
created in step 3 and press Enter.
6. Select “Intel(R) ICH8R/ICH9R SATA RAID Controller” an press ENTER.
7. The next screen should confirm that you have selected the Intel® RAID
controller. Press ENTER again to continue.
8. You have successfully installed the Intel® Matrix Storage Manager driver, and
Windows setup should continue.
9. Leave the disk in the floppy drive until the system reboots itself. Windows
setup will need to copy the files from the floppy again after the RAID volume
is formatted, and Windows setup starts copying files.
† Existing Windows Vista/XP/2003 Driver Installation
1. Insert the MSI CD into the CD-ROM drive.
2. The CD will auto-run and the setup screen will appear.
3. Under the Driver tab, click on Intel IAA RAID Edition.
4. The drivers will be automatically installed.
A-9
Page 68

MS-9656 Server Board
† Confirming Windows Vista/XP/2003 Driver Installation
1. From Windows Vista/XP/2003, open the Control Panel from My Computer
followed by the System icon.
2. Choose the Hardware tab, then click the Device Manager tab.
3. Click the "+" in front of the SCSI and RAID Controllers hardware type. The
driver Intel(R) ICH9R SATA RAID Controller should appear.
A-10
Page 69

Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
Installing Software
Install Intel Matrix Storage Console
The Intel Application Accelerator RAID Edition driver may be used to operate the hard
drive from which the system is booting or a hard drive that contains important data.
For this reason, you cannot remove or un-install this driver from the system after
installation; however, you will have the ability to un-install all other non-driver
components.
Insert the MSI CD and click on the Intel Matrix Storage Manager to install the
software.
Click on this item
A-11
Page 70

MS-9656 Server Board
The InstallShield Wizard will begin automatically for installation showed as following:
Click on the Next button to proceed the installation in the welcoming window.
A-12
Page 71

Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
The window shows the components to be installed. Click Next button to continue.
After reading the license agreement in the following window, click Yes button to
continue.
A-13
Page 72

MS-9656 Server Board
The following window appears to show the Readme File Information. It shows the
system requirements and installation information.
Once the installation is complete, the following window appears.
A-14
Page 73

Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
RAID Migration Instructions
The Intel Matrix Storage Console offers the flexibility to upgrade from a single Serial
ATA (SATA) hard drive to RAID configuration when an additional SATA hard drive is
added to the system. This process will create a new RAID volume from an existing
disk. However, several important steps must be followed at the time the system is
first configured in order to take advantage of RAID when upgrading to a second
SATA hard drive:
1.BIOS must be configured for RAID before installing Windows on the single
SATA hard drive. Refer to On-Chip ATA Devices for properly setting of
the BIOS.
2.Install the Intel Application Accelerator RAID Driver during Windows Setup.
Refer to Installing Software for instructions on installing the driver during Windows Setup.
3.Install the Intel Matrix Storage Console after the operating system is installed.
To create a volume from an existing disk, complete the following steps:
Important
A Create from Existing Disk operation will delete all existing data from the
added disk and the data cannot be recovered. It is critical to backup all
important data on the added disk before proceeding. However, during the
migration process, the data on the source disk is preserved.
After the Intel Matrix Storage Console has been successfully installed and the system has rebooted, click on the Intel Application Accelerator shortcut link (Start --> All
Programs --> Intel Matrix Storage Manager --> Intel Matrix Storage Console)
and the following window will appear:
A-15
Page 74

MS-9656 Server Board
Create RAID Volume from Existing Disk
To create a RAID volume from an existing disk, choose Action --> Create RAID
Volume from Existing Hard Drive.
Note: The “Action” button only appears in advance mode. To enable the advance
mode, go to View --> Basic mode and click it.
The Create RAID Volume from Existing Hard Drive Wizard pops up to lead you
for the following procedure. Click Next to continue.
A-16
Page 75

Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
(1) Step 1: Configure Volume
Here you can configure the new RAID volume by entering the volume name, selecting
the RAID level and strip size.
† RAID Volume Name:
A desired RAID volume name needs to be typed in where the ‘ RAID_Volume1’ text
currently appears above. The RAID volume name has a maximum limit of 16 characters.
The RAID volume name must also be in English alphanumeric ASCII characters.
† RAID Level:
Select the desired RAID level:
RAID 0 (Performance) – A volume optimized for performance will allow you to
access your data more quickly.
RAID 1 (Redundancy) – A volume optimized for data redundancy will provide
you with a realtime duplicate copy of your data. Note:
Only half of the available volume space will be available for data storage.
RAID 5 (Useful) – RAID 5 can be used on three or more disks, with zero
or more spare-disks. The resulting RAID-5 device size
will be (N-1)*S, where N is the how many drive, S is the
size of the smallest drive in the array. If one of the disks
fail, all data are still intact. It can rebuild the disk from
the parity information. If spare disks are available, reconstruction will begin immediately after the device
failure. If two disks fail simultaneously, all data are lost.
RAID-5 can survive one disk failure, but not two or
more. Both read and write performance usually
increase, but can be hard to predict how much. Reads
are similar to RAID-0 reads, writes can be either rather
A-17
Page 76

MS-9656 Server Board
expensive (requiring read-in prior to write, in order to
be able to calculate the correct parity information), or
similar to RAID-1 writes. The write efficiency depends
heavily on the amount of memory in the machine, and
the usage pattern of the array. Heavily scattered writes
RAID 10 (Mirrored Stripes) – A RAID 1 array of two RAID 0 arrays.
† Strip Sizes:
Select the desired strip size setting. As indicated, the optimal setting is 128KB. Selecting any other option may result in performance degradation. Even though 128KB
is the recommended setting for most users, you should choose the strip size value
which is best suited to your specific RAID usage model. The most typical strip size
settings are:
4KB: For specialized usage models requiring 4KB strips
8KB: For specialized usage models requiring 8KB strips
16KB: Best for sequential transfers
32KB: Good for sequential transfers
64KB: Good general purpose strip size
128KB: Best performance for most desktops and workstations
(2) Select the source disk
Then select the source disk that you wish to use and then click “--->” to move it to the
Selected field. Then click Next to continue.
It is very important to note which disk is the source disk (the one containing all of the
information to be migrated) and which one is the target disk. On a RAID Ready
system, this can be determined by making a note during POST of which port the single
disk is attached to.
You can also use the Intel Application Accelerator RAID Edition utility before the
second disk is installed to verify the Port and serial number of the drive that contains
all the data.
are bound to be more expensive.
A-18
Page 77

Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
(3) Select Member Hard Drive(s)
Then select the member disk (the target disk) that you wish to use and then click “-
-->” to move it to the Selected field. Then click Next to continue.
Please note that the existing data on the selected hard drive(s) will be deleted
permanently. Do not forget to back up all the important data before continuing.
A-19
Page 78

MS-9656 Server Board
(4) Specify Volume Size
Specify the amount of available array space to be used by the new RAID volume. You
may enter the amount in the space or use the slider to specify. It is recommended you
use 100% of the available space for the optimized usage. For RAID 0 volume, if you
do not specify 100% of the hard drive space, the rest hard drive space will be
worked as RAID 1 volume, which is the new technology called Intel Matrix RAID. Then
click Next to continue.
(5) Start Creating RAID Volume from Existing Hard Drive Wizard
Before you continue the procedure of RAID volume creation from existing hard drive,
read the dialogue box below carefully. Please note that once you click Finish, the
existing data on the selected hard drive(s) will be deleted permanently and this
operation cannot be undone. It is critical that you backup all important data before
selecting Finish to start the migration process.
A-20
Page 79

Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
(6) Start Migration
The migration process may take up to two hours to complete depending on the size
of the disks being used and the strip size selected. A dialogue window will appear
stating that the migration process may take considerable time to complete, meanwhile
a popup dialogue at the taskbar will also show the migration status. While you can still
continue using your computer during the migration process, once the migration process starts, it cannot be stopped. If the migration process gets interrupted and your
system is rebooted for any reason, it will pick up the migration process where it left
off. You will be provided with an estimated completion time (the remaining time will
depend on your system) once the migration process starts.
The following screen appears if the migration process is completed successfully.
Then you have to reboot your system to use the full capacity of the new volume.
A-21
Page 80

MS-9656 Server Board
Degraded RAID Array
A RAID 1, RAID 5 or RAID 10 volume is reported as degraded when one of its hard
drive members fails or is temporarily disconnected, and data mirroring is lost. As a
result, the system can only utilize theremaining functional hard drive member. To reestablish data mirroring and restore data redundancy, refer to the procedure below
that corresponds to the current situation.
Missing Hard Drive Member
1. Make sure the system is powered off.
2. Reconnect the hard drive.
3. Reboot the system to Windows; the rebuild will occur automatically.
Failed Hard Drive Member
1. Make sure the system is powered off.
2. Replace the failed hard drive with a new one that is of equal or greater
capacity.
3. Reboot the system to Intel RAID Option ROM by press <Ctrl> and <I> keys
simultaneously during the Power-On Self Test (POST).
4. Select the port of the destination disk for rebuilding, and then press ENTER.
A-22
Page 81

Intel ICH9R SATA RAID
5. Exit Intel RAID Option ROM, and then reboot to Windows system.
6. When prompted to rebuild the RAID volume, click 'Yes'.
7. The Intel(R) Storage Utility will be launched. Right-click the new hard drive and
select 'Rebuild to this Disk'. The 'Rebuild Wizard' will be launched which will
guide you through the process of rebuilding to the new hard drive.
A-23
 Loading...
Loading...