Page 1

K8N Diamond
MS-7100 (v1.X) ATX Mainboard
G52-M7100XA
i
Page 2
Manual Rev: 1.2
Release Date: January 2005
FCC-B Radio Frequency Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is
operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation
of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which
case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Notice 1
The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Notice 2
Shielded interface cables and A.C. power cord, if any, must be used in order to
comply with the emission limits.
VOIR LA NOTICE D’INSTALLATION AVANT DE RACCORDER AU RESEAU.
Micro-Star International
MS-7100
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
(1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation
ii
Page 3

Copyright Notice
The material in this document is the intellectual property of MICRO-STAR
INTERNATIONAL. We take every care in the preparation of this document, but no
guarantee is given as to the correctness of its contents. Our products are under
continual improvement and we reserve the right to make changes without notice.
Trademarks
All trademarks are the properties of their respective owners.
AMD, Athlon™ 64 and Athlon™ FX are registered trademarks of AMD Corporation.
Intel® and Pentium® are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
PS/2 and OS®/2 are registered trademarks of International Business Machines
Corporation.
Microsoft is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Windows® 98/2000/NT/
XP are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
NVIDIA, the NVIDIA logo, DualNet, and nForce are registered trademarks or trademarks of NVIDIA Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Netware® is a registered trademark of Novell, Inc.
Award® is a registered trademark of Phoenix Technologies Ltd.
AMI® is a registered trademark of American Megatrends Inc.
Kensington and MicroSaver are registered trademarks of the Kensington Technology
Group.
PCMCIA and CardBus are registered trademarks of the Personal Computer Memory
Card International Association.
Revision History
Revision Revision History Date
V1.0 First release for PCB 1.X Dec. 2004
V1.1 First release for PCB 1.X Dec. 2004
V1.2 Release for PCB 1.X (Europe/Diamond) Jan. 2005
with nVIDIA nForce4 SLI
with nVIDIA nForce4 SLI (Platinum)
iii
Page 4

Technical Support
If a problem arises with your system and no solution can be obtained from the user’ s
manual, please contact your place of purchase or local distributor. Alternatively,
please try the following help resources for further guidance.
† Visit the MSI homepage & FAQ site for technical guide, BIOS updates, driver
updates, and other information: http://www.msi.com.tw & http://www.msi.
com.tw/program/service/faq/faq/esc_faq_list.php
† Contact our technical staff at: support@msi.com.tw
Safety Instructions
1. Always read the safety instructions carefully.
2. Keep this User’s Manual for future reference.
3. Keep this equipment away from humidity.
4. Lay this equipment on a reliable flat surface before setting it up.
5. The openings on the enclosure are for air convection hence protects the equipment from overheating. Do not cover the openings.
6. Make sure the voltage of the power source and adjust properly 110/220V before connecting the equipment to the power inlet.
7. Place the power cord such a way that people can not step on it. Do not place
anything over the power cord.
8. Always Unplug the Power Cord before inserting any add-on card or module.
9. All cautions and warnings on the equipment should be noted.
10. Never pour any liquid into the opening that could damage or cause electrical
shock.
11. If any of the following situations arises, get the equipment checked by a service
personnel:
† The power cord or plug is damaged.
† Liquid has penetrated into the equipment.
† The equipment has been exposed to moisture.
† The equipment has not work well or you can not get it work according to
User’s Manual.
† The equipment has dropped and damaged.
† The equipment has obvious sign of breakage.
12. Do not leave this equipment in an environment unconditioned, storage
temperature above 600 C (1400F), it may damage the equipment.
CAUTION: Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the
manufacturer.
iv
Page 5

CONTENTS
FCC-B Radio Frequency Interference Statement.........................................................ii
Copyright Notice..............................................................................................................iii
Revision History..............................................................................................................iii
Technical Support..........................................................................................................iv
Safety Instructions.........................................................................................................iv
English version......................................................................................................E1-1
1. Getting Started................................................................................................E1-3
2. Hardware Setup.............................................................................................E2-1
3. BIOS Setup......................................................................................................E3-1
French version.........................................................................................................F-1
German version.......................................................................................................G-1
v
Page 6

K8N Diamond
User’s Guide
Getting Started
English
E1-1
Page 7

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
E1-2
Page 8

Getting Started
Chapter 1. Getting
Started
Getting Started
Thank you for choosing the K8N Diamond (MS-7100) v1.X
ATX mainboard. The K8N Diamond mainboard is based on nVIDIA
nForce™4 SLI chipset for optimal system efficiency. Designed to fit
the advanced AMD® K8 Athlon 64 FX / Athlon 64 processor, the
K8N Diamond mainboard delivers a high performance and professional desktop platform solution.
®
E1-3
Page 9

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Mainboard Specifications
CPU
† Supports Socket-939 for AMD K8 Athlon 64 FX / Athlon 64 (Socket939) processor
† Supports up to 4000+ Athlon FX55 , or higher CPU
(For the latest information about CPU, please visit http://www.msi.com.tw/program/
products/mainboard/mbd/pro_mbd_cpu_support.php)
Chipset
† nVIDIA nForce4 SLI
- HyperTransport link to the AMD Athlon 64/Athlon 64 FX CPU
- HyperTransport supporting speed up to 1GHz (2000MT/s)
- Supports 2 PCI Express x16/ x1 interface
- Two independent SATA controllers, for four drives
- Dual Fast ATA-133 IDE controllers
- IEEE802.3 nVIDIA MAC for 1000BASE-T
Main Memory
† Supports dual channel, eight memory banks DDR 266/333/400, using four 184-
pin DDR DIMMs
† Supports a maximum memory size up to 4GB
† Supports 2.5v DDR SDRAM DIMM
(For the updated supporting memory modules, please visit http://www.msi.com.tw/
program/products/mainboard/mbd/pro_mbd_trp_list.php.)
Slots
† Two PCI Express x16 slots (supports PCI Express Bus specification v1.0a
compliant)
† 2nd PCI Express x16 slot (PCI_E3) is compatible with PCI Express x 1
† Three 32-bit Master PCI Bus slots, includes one orange slot which is reserved
as a communication slot.
† Support 3.3V/5V PCI bus Interface
On-Board IDE
† An IDE controller on the nVIDIA® nForce4 SLI chipset provides IDE HDD/CD-ROM
with PIO, Bus Master and Ultra DMA 66/100/133 operation modes
† Can connect up to 4 IDE devices
On-Board SATA
† NV RAID supports 4 SATA II ports (SATA1-4). Transfer rate is up to 300 MB/s.
Supports RAID 0, 0+1 and JBOD mode.
† Silicon Image’s SATARAID supports another 2 SATA II ports (SATA5/6). Transfer
rate is up to 300 MB/s. Supports RAID 0 & 1 mode.
E1-4
Page 10

Getting Started
USB Interface
† 10 USB ports
- Controlled by nForce4 SLI chipset
- 4 ports in the rear I/O, 6 ports via the external bracket
NV RAID (Software)
† Supports up to 4 SATA and 2 ATA133 Hard drives
-RAID 0 or 1, 0+1, JBOD is supported
-RAID function available for ATA133+SATA H/D or 4 SATA H/D drives
Silicon Image’s SATARAID (Software) (Optional)
† RAID 0 or 1 and multiple RAID groups are supported
† Support up to 2 SATA devices connected to a single controller
Dual LAN
† Supports dual LAN jacks
-1st LAN supports 10/100/1000 Fast Ethernet by nForce4 SLI
-2nd PCI Express LAN supports 10/100/1000 Fast Ethernet by Marvell
88E8053
IEEE 1394
† Supports up to three 1394 ports (rear panel x 1, pinheader x 2). Transfer rate
is up to 400Mbps
Audio
† Power by Creative Sound Bluster 24 bits H/W audio
-24-bit / 96~192 KHz audio quality
-Up to 100 db SNR clarity
-7.1 Channel output supported, Dolby Digital encoder
-Supports S/PDIF digital interface
-PCI 2.3 Specification compliant
On-Board Peripherals
† On-Board Peripherals include:
-1 floppy port supports 1 FDD with 360K, 720K, 1.2M, 1.44M and 2.88Mbytes
-1 serial port (COM1)
-1 parallel port supporting SPP/EPP/ECP mode
-1 Audio jack(5-in-1), coaxial/fiber SPDIF out
-1 D-Bracket 2 pinheader
-1 CD-In pinheader
-3 IEEE 1394 (Rear * 1 / Front * 2)
-10 USB1.1/2.0 ports (Rear * 4 / Front * 6)
-1 IrDA pinheader
E1-5
Page 11
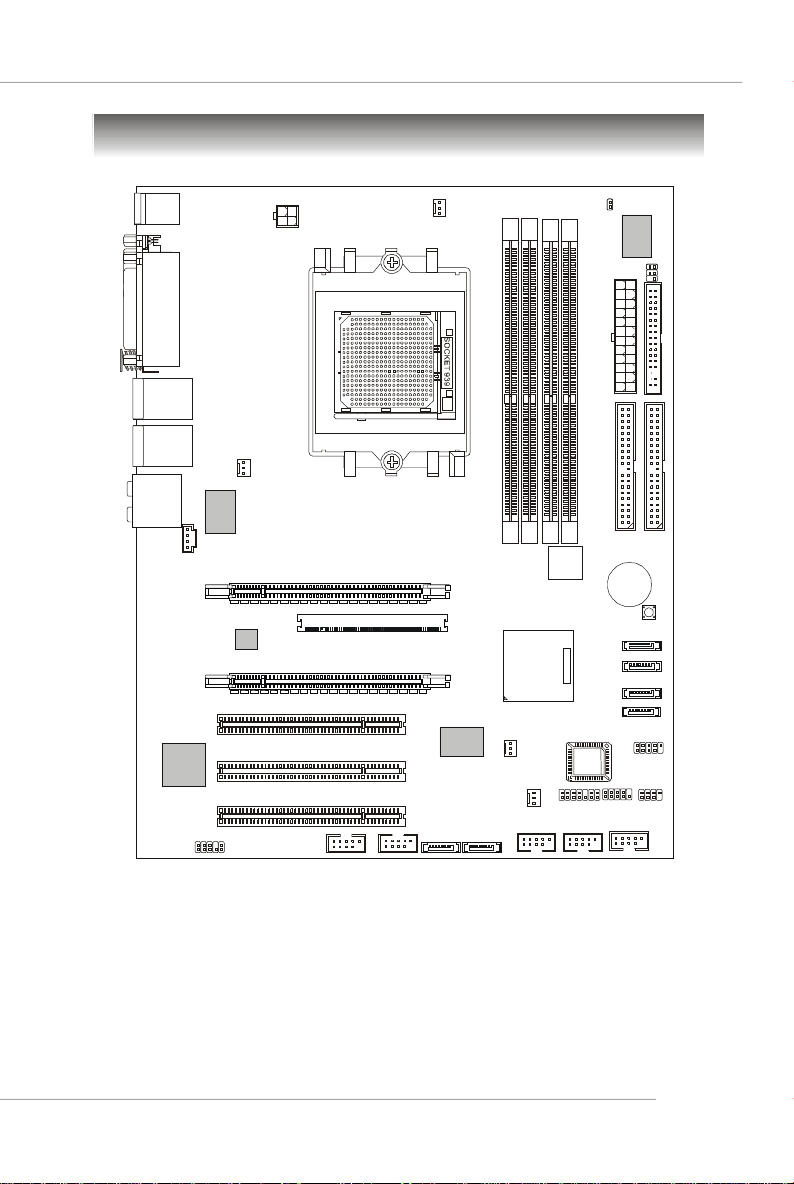
MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
BIOS
† The mainboard BIOS provides “Plug & Play” BIOS which detects the peripheral
devices and expansion cards of the board automatically.
† The mainboard provides a Desktop Management Interface (DMI) function which
records your mainboard specifications.
† Supports boot from LAN, USB Device 1.1 & 2.0, and SATA HDD.
Dimension
† ATX Form Factor (30.4 cm X 24.4 cm)
Mounting
† 9 mounting holes
MSI Reminds You...
To create a bootable RAID volume for a Windows 2000 environment,
Microsoft’s Windows 2000 Service Pack 4 (SP4) is required. As the
end user cannot boot without SP4, a combination installation CD must
be created before attempting to install the operating system onto the
bootable RAID volume.
To create the combination installation CD, please refer to the following website:
http://www.microsoft.com/windows2000/downloads/servicepacks/
sp4/HFdeploy.htm
E1-6
Page 12
S_FAN1
NB_FAN1
F
DD1
SATA3
SATA5
SATA6
SATA4
SATA1
SATA2
Winbond W
83627
T
H
F
CK8-04 SLI
BAT
T
+DIMM
1
J
PWR
1
PCI Slot 3
PCI Slot 2
PCI Slot 1
AUD1
JUSB3
JUSB1
Top : mouse
MSI
CoreCell
Bottom: keyboard
Top : Parallel Port
Bottom:
COM Port
1394 Port
SPDIF OUT
T: LAN jack
B: USB ports
T: LAN jack
B: USB ports
T:
Line-In
M:
Line-Out
B:
Mic
T:RS-Out
M:CS
-Out
B:SPDIF Out
88E1111-RCJ
Mainboard Layout
JPWR2
C_FAN1
Getting Started
2
3
4
JCI1
M
M
M
M
M
M
I
I
I
D
D
D
JIR1
2
1
E
E
D
D
I
I
JCD1
CREATIVE
Sound
Bluster
88E8053-NNC
PCI _E3
J1394_1
PCI _E1
PCI_E4
(SLI Connector)
J1394_2
VIA
VT6306
nVIDIA
S_FAN2
JUSB2
K8N Diamond (MS-7100 v1.X) ATX Mainboard
JLPC1
Sw1
S
JDB1
O
I
B
JFP1
JFP2
E1-7
Page 13

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
MSI motherboard
Packing Contents
MSI Driver/Utility CD
SATA RAID Driver
Diskette/ Creative
Audio Driver
SATA Cable/
Power Cable (Optional)
E1-8
SLI Switch card
Round Cable of
Floppy Disk
Back IO Shield
SLI bridge
1394 Cable
(Optional)
User’ s Guide/
Test Report
D-Bracket 2
(Optional)
Round Cable of
IDE Devices
Quick Guide
Page 14

Hardware Setup
Chapter 2. Hardware Setup
Hardware Setup
This chapter tells you how to install the CPU, memory modules,
and expansion cards, as well as how to setup the jumpers on the
mainboard. Also, it provides the instructions on connecting the peripheral devices, such as the mouse, keyboard, etc.
While doing the installation, be careful in holding the components and follow the installation procedures.
E2-1
Page 15
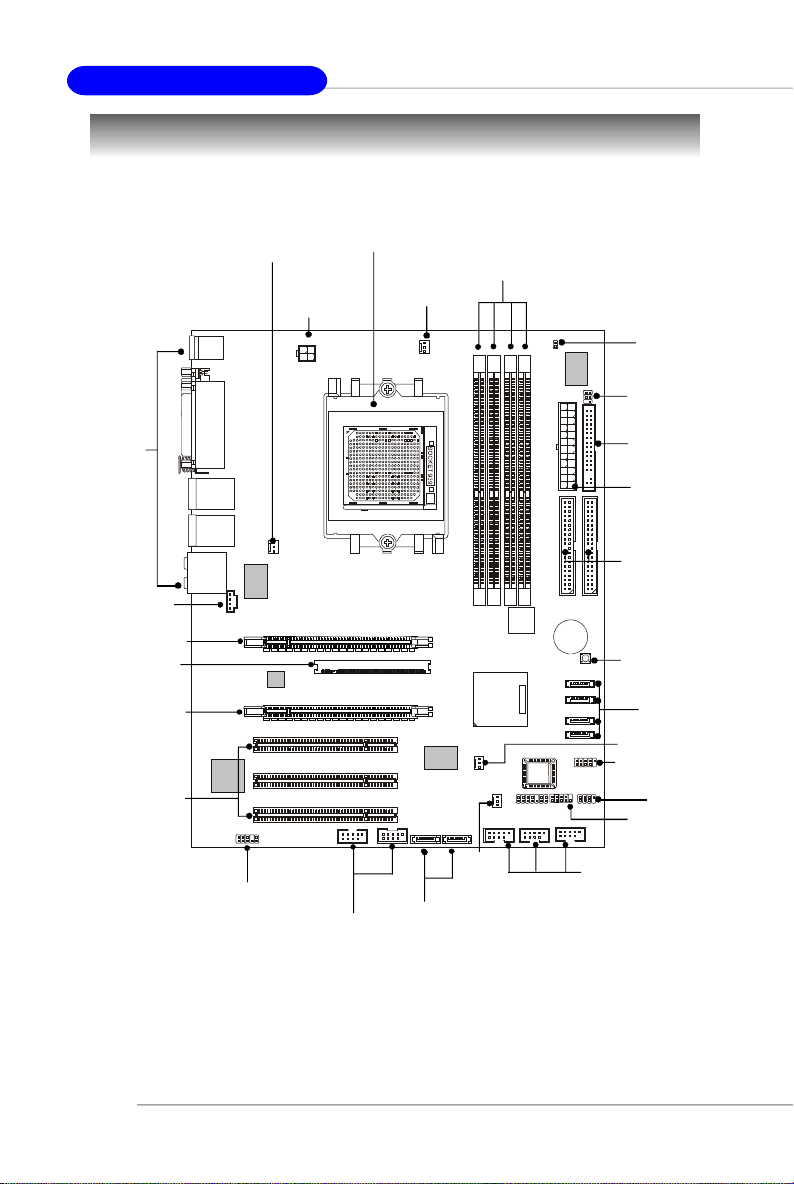
MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
B
A
T
T
+
Quick Components Guide
S_FAN1, E-2-16
JPWR2,
E-2-10
CPU, E-2-3
C_FAN1,
E-2-16
DDR DIMMs, E-2-7
JCI1, E-2-17
JIR1, E-2-20
Back Panel
I/O, E-2-12
JCD1, E-2-18
PCI_E1, E-2-28
PCI_E4,
E-2-24
PCI_E3, E-2-28
PCI Slot 1~3,
E-2-28
AUD1, E-2-20
J1394_1~2,
E-2-21
SFAN2,
p.2-16
SATA5~6,
E-2-18
S
O
I
B
JUSB1~3, E-2-19
FDD1, E-2-16
JPWR1, E-2-10
IDE1/2,E-2-17
SW1,
E-2-27
SATA1~4,
E-2-18
NB_FAN1, E-2-16
JDB1, E-2-21
JFP2, E-2-19
JFP1, E-2-19
E2-2
Page 16

Hardware Setup
Central Processing Unit: CPU
The mainboard supports AMD® Athlon64/ Athlon64 FX processors. The
mainboard uses a CPU socket called Socket-939 for easy CPU installation. When you
are installing the CPU, make sure the CPU has a heat sink and a cooling fan
attached on the top to prevent overheating. If you do not have the heat sink and
cooling fan, contact your dealer to purchase and install them before turning on the
computer.
For the latest information about CPU, please visit http://www.msi.com.tw/program/products/mainboard/mbd/pro_mbd_cpu_support.php.
MSI Reminds You...
Overheating
Overheating will seriously damage the CPU and system, always make
sure the cooling fan can work properly to protect the CPU from
overheating.
Replacing the CPU
While replacing the CPU, always turn off the ATX power supply or
unplug the power supply’s power cord from grounded outlet first to
ensure the safety of CPU.
Overclocking
This motherboard is designed to support overclocking. However, please
make sure your components are able to tolerate such abnormal setting,
while doing overclocking. Any attempt to operate beyond product specifications is not recommended. We do not guarantee the damages
or risks caused by inadequate operation or beyond product
specifications.
E2-3
Page 17
MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Gold arrow
Gold arrow
Gold arrow
Correct CPU placement
O
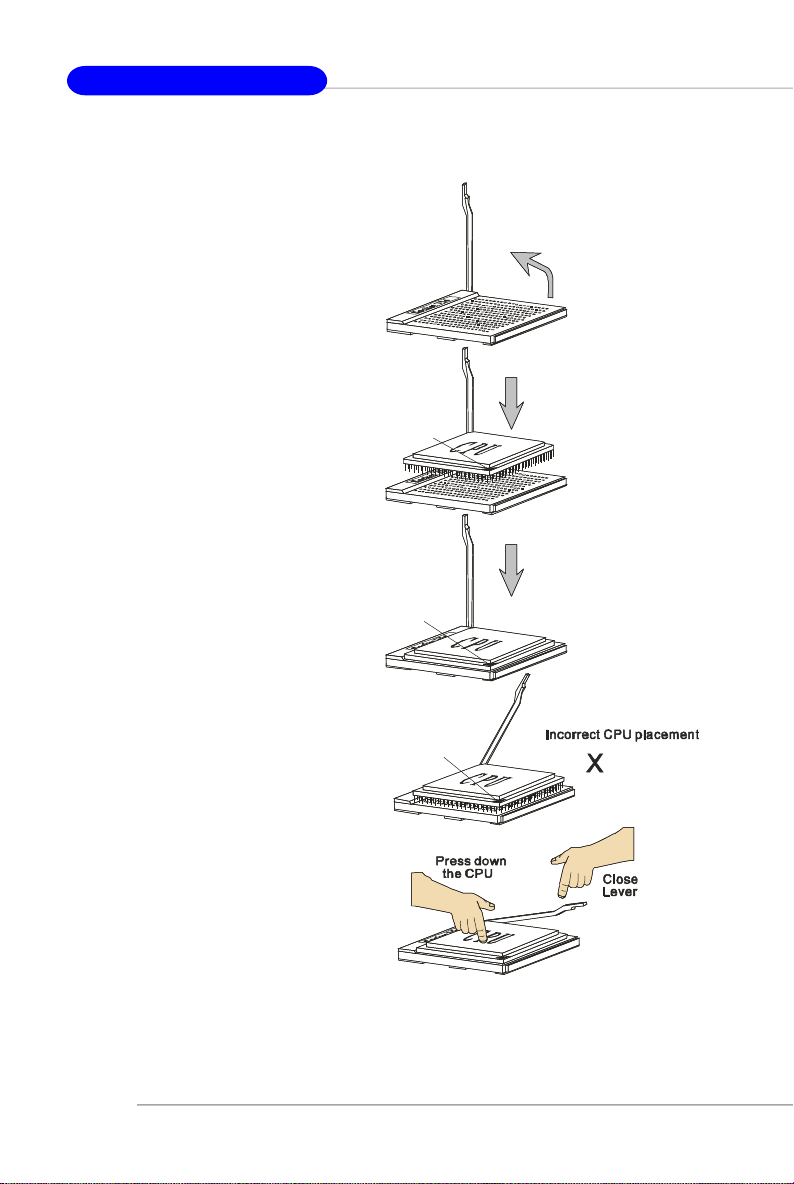
CPU Installation Procedures for Socket 939
1.Please turn off the power and
unplug the power cord before
installing the CPU.
2.Pull the lever sideways away
from the socket. Make sure to
raise the lever up to a 90-degree angle.
3.Look for the gold arrow on the
CPU. The gold arrow should point
as shown in the picture. The CPU
can only fit in the correct
orientation.Lower the CPU down
onto the socket.
4.If the CPU is correctly installed,
the pins should be completely
embedded into the socket and
can not be seen. Please note
that any violation of the correct
installation procedures may
cause permanent damages to
your mainboard.
Sliding
Plate
Open Lever
90 degree
5. Press the CPU down firmly into
the socket and close the lever.
As the CPU is likely to move while
the lever is being closed, always close the lever with your
fingers pressing tightly on top of
the CPU to make sure the CPU is
properly and completely embedded into the socket.
E2-4
Page 18
Hardware Setup
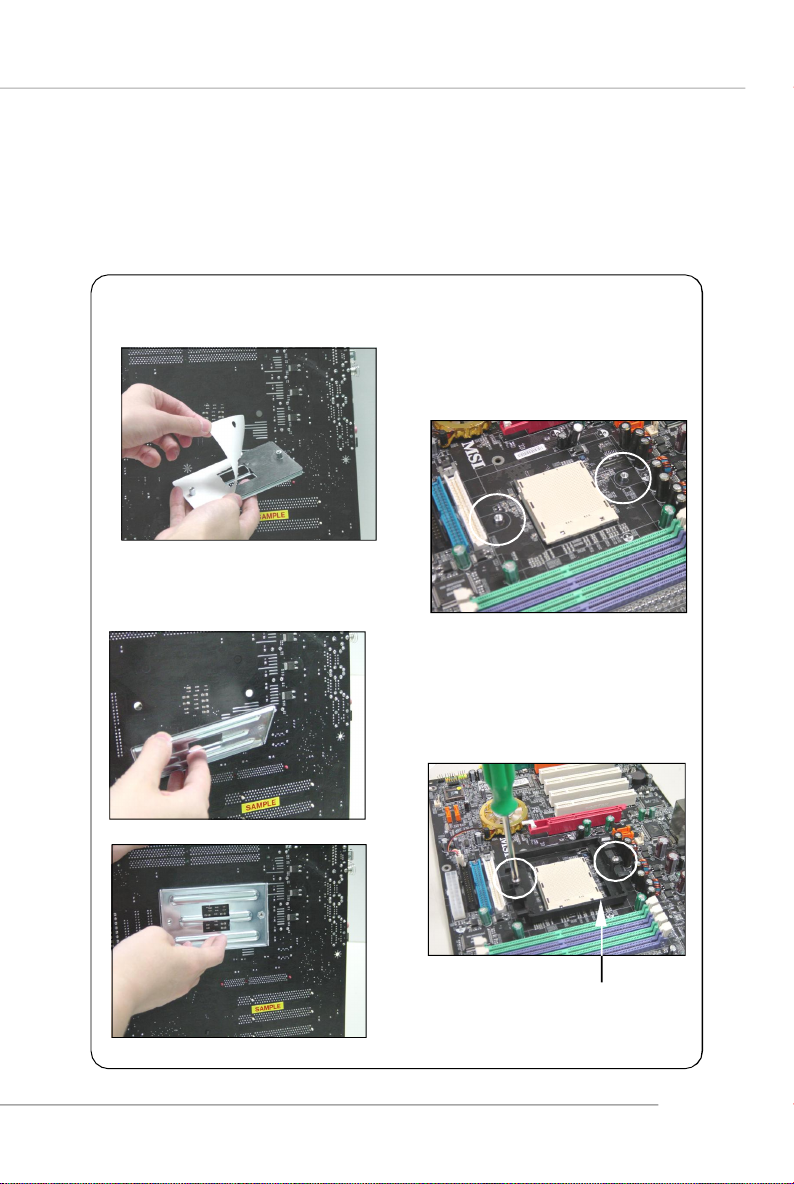
Installing AMD Athlon64/ Athlon64 FX CPU Cooler Set
When you are installing the CPU, make sure the CPU has a heat sink and
a cooling fan attached on the top to prevent overheating. If you do not have
the heat sink and cooling fan, contact your dealer to purchase and install them before
turning on the computer.
1.Detach the shield of the backplate’s
paster.
2.Turn over the mainboard, and install
the backplate to the proper position.
3.Turn over the mainboard again, and
place the mainboard on the flat
surface.
Locate the two screw holes of the
mainboard.
4.Align the retention mechanism and
the backplate.
Fix the retention mechanism and the
backplate with two screws.
retention mechanism
E2-5
Page 19
MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
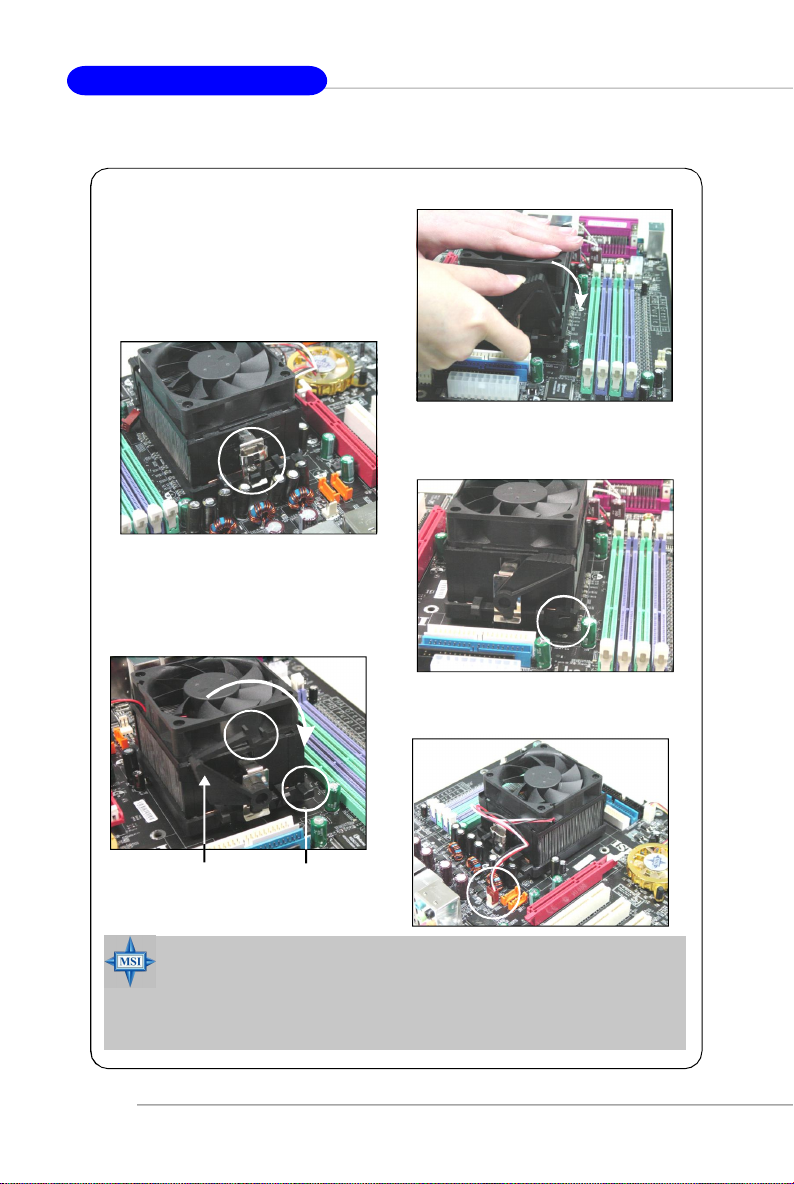
5.Position the cooling set onto the retention mechanism.
Hook one end of the clip to hook first,
and then press down the other end
of the clip to fasten the cooling set on
the top of the retention mechanism.
6.Locate the Fix Lever, Safety Hook
and the Fixed Bolt.
Lift up the intensive fixed lever.
Safety Hook
7.Fasten down the lever.
8.Make sure the safety hook completely
clasps the fixed bolt of the retention
mechanism.
9.Attach the CPU Fan cable to the CPU
fan connector on the mainboard.
E2-6
Fixed Lever
MSI Reminds You...
While disconnecting the Safety Hook from the fixed bolt, it is necessary to keep an eye on your fingers, because once the Safety Hook is
disconnected from the fixed bolt, the fixed lever will spring back instantly.
Fixed Bolt
Page 20

Hardware Setup
Memory
The mainboard provides 4 slots for 184-pin DDR SDRAM DIMM (Double In-Line
Memory Module) modules and supports the memory size up to 4GB. You can install
DDR266/ 333/400 modules on the DDR DIMM slots (DIMM1~4).
For the updated supporting memory modules, please visit http://www.msi.com.tw/
program/products/mainboard/mbd/pro_mbd_trp_list.php.
DIMM1~4
(from bottom to top)
Introduction to DDR SDRAM
DDR (Double Data Rate) SDRAM is similar to conventional SDRAM, but doubles
the rate by transferring data twice per cycle. It uses 2.5 volts as opposed to 3.3 volts
used in SDR SDRAM, and requires 184-pin DIMM modules rather than 168-pin DIMM
modules used by SDR SDRAM. High memory bandwidth makes DDR an ideal solution
for high performance PC, workstations and servers.
DIMM Module Combination
Install at least one DIMM module on the slots. Each DIMM slot supports up to a
maximum size of 1GB. Users can install either single- or double-sided modules to
meet their own needs. Please note that each DIMM can work respectively for
single-channel DDR, but there are some rules while using dual-channel
DDR (Please refer to the suggested DDR population table below). Users may install
memory modules of different type and density on different-channel DDR DIMMs.
However, the same type and density memory modules are necessary while
using dual-channel DDR, or instability may happen. Please refer to the following table
for detailed dual-channel DDR. Other combination not listed below will function as
single-channel DDR.
E2-7
Page 21
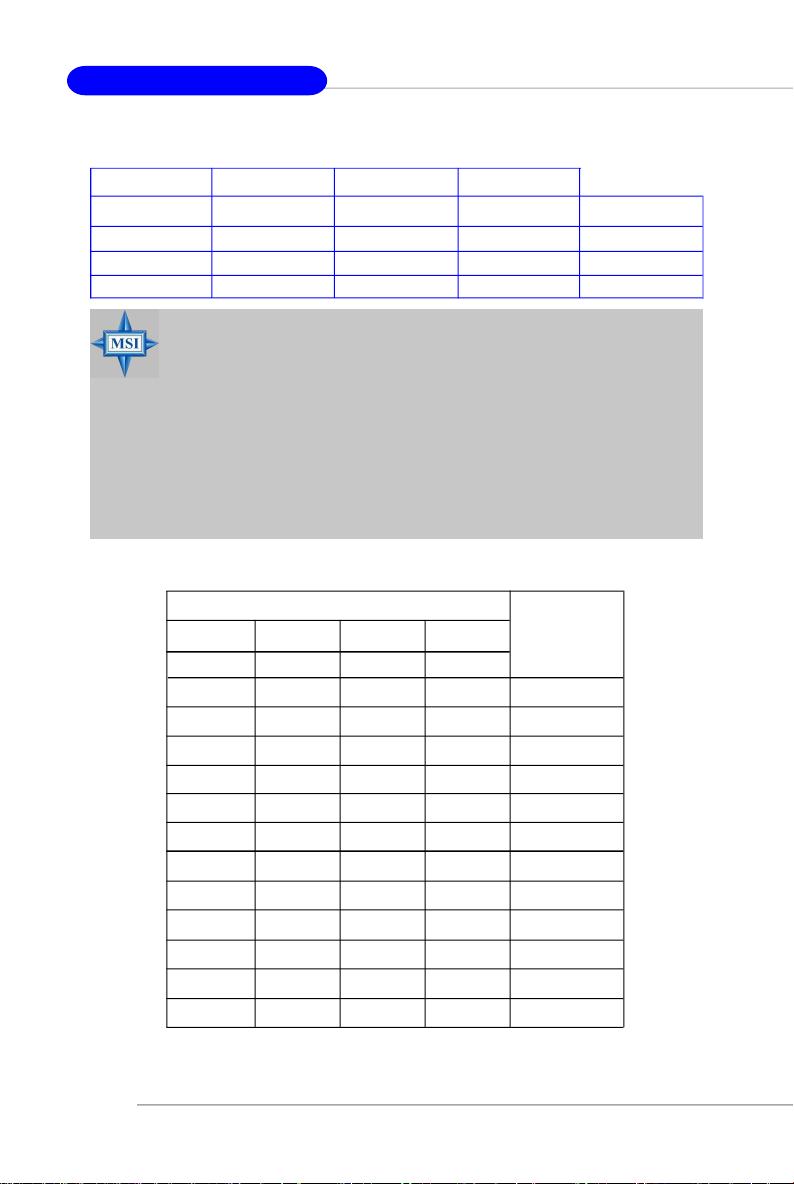
MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
GREEN
DIMM1 (Ch A) DIMM2 (Ch B) DIMM3 (Ch A) DIMM4 (Ch B) System Density
128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 256MB~2GB
128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 512MB~4GB
MSI Reminds You...
-Dual-channel DDR works ONLY in the 3 combinations listed in
-Please select the identical memory modules to install on the dual
-Always insert the memory modules into the GREEN slots first, and
-This mainboard DO NOT support the memory module installed
PURPLE
the table shown in the previous page.
channel, and DO NOT install three memory modules on three
DIMMs, or it may cause some failure.
it is strongly recommended not to insert the memory modules into
the PURPLE slots while the GREEN slots are left empty.
with more than 18 pieces of IC (integrated circuit).
GREEN
128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 256MB~2GB
PURPLE
Recommended Memory Combination List
DIMM Slots
Green Green
DIMM1
S
D
S D S
Purple
DIMM2 DIMM3 DIMM4
- -
-
-
-
S
-
DS -
D -
S
-
- - S S
D D
- -
S
D
S
D
- D D
S
D
Purple
-
-
-
-
-
S
D
Max Speed
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 333
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 333
E2-8
S: Single Side D: Double Side
Page 22
Hardware Setup
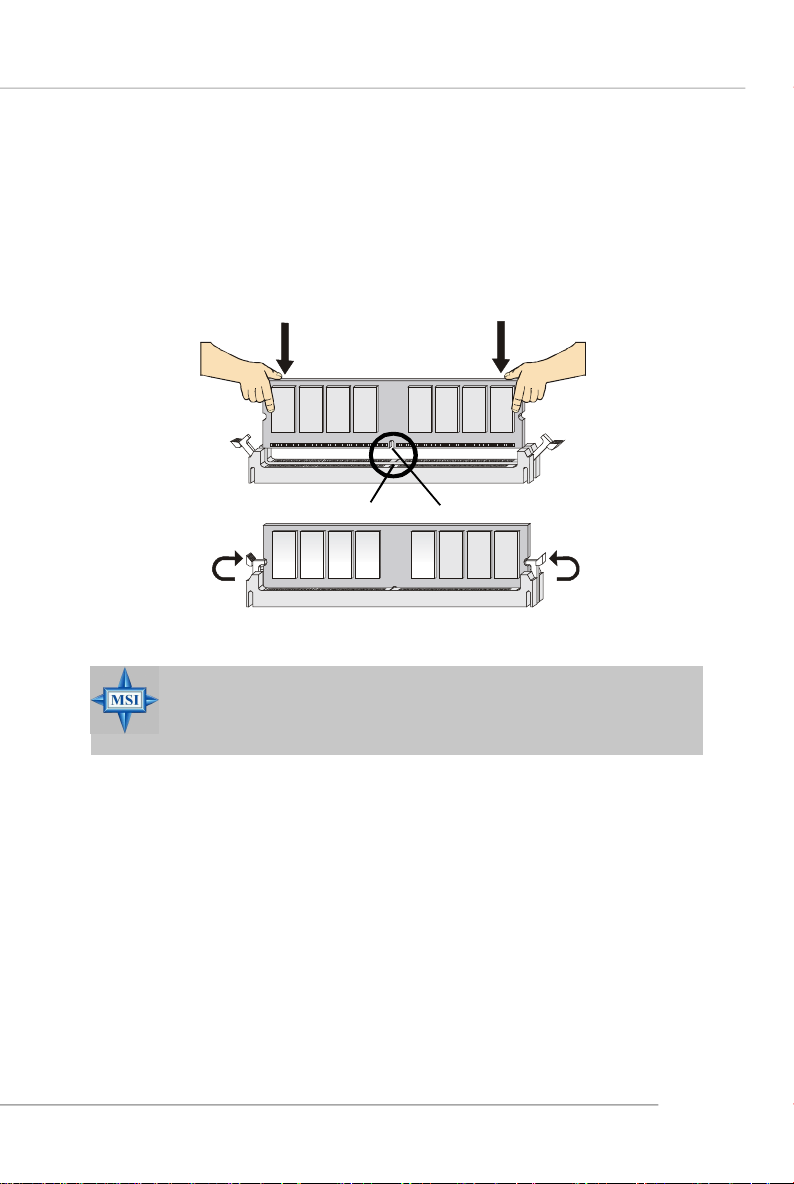
Installing DDR Modules
1. The DDR DIMM has only one notch on the center of module. The module will only
fit in the right orientation.
2. Insert the DIMM memory module vertically into the DIMM slot. Then push it in until
the golden finger on the memory module is deeply inserted in the socket.
3. The plastic clip at each side of the DIMM slot will automatically close.
Volt
MSI Reminds You...
You can barely see the golden finger if the module is properly inserted in the socket.
Notch
E2-9
Page 23
MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Power Supply
The mainboard supports ATX power supply for the power system. Before
inserting the power supply connector, always make sure that all components are
installed properly to ensure that no damage will be caused.
ATX 24-Pin Power Connector: JPWR1
This connector allows you to connect an SSI power supply. To connect the
SSI power supply, make sure the plug of the power supply is inserted in the proper
orientation and the pins are aligned. Then push down the power supply firmly into
the connector.
Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL
13 +3.3V
14 -12V
15 GND
16 PS-ON#
17 GND
18 GND
19 GND
20 -5V
21 +5V
22 +5V
23 +5V
24 GND
JPWR1
13
24 12
1
PIN SIGNAL
1 +3.3V
2 +3.3V
3 GND
4 +5V
5 GND
6 +5V
7 GND
8 PWR OK
9 5VSB
10 +12V
11 +12V
12 NC
ATX 12V Power Connector: JPWR2
This 12V power connector is used to provide power to the CPU.
4
3
MSI Reminds You...
1. These two connectors connect to the ATX power supply and have to
work together to ensure stable operation of the mainboard.
2. Power supply of 450 watts (and above) is highly recommended for
system stability.
3. For ATX 12V power connection, it should be greater than 18A.
4. For this model, you must use the power supply that with a -5V pin
supply.
E2-10
2
1
JPWR2
Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL
1 GND
2 GND
3 12V
4 12V
Page 24

Hardware Setup
Important Notification about Power Issue
NForce chipset is very sensitive to ESD (Electrostatic Discharge), therefore
this issue mostly happens while the users intensively swap memory modules under
S5 (power-off) states, and the power code is plugged while installing modules. Due
to several pins are very sensitive to ESD, so this kind of memory-replacement actions
might cause system chipset unable to boot. Please follow the following solution to
avoid this situation.
Unplug the AC power cable (shown in figure 1) or unplug the JPWR1 & JPWR2
power connectors (shown in figure 2 & figure 3) before the 1st installation or during
system upgrade procedure.
Unplug the JPWR1 power conn.
Figure 2:
Unplug the AC power cable
Figure 1:
Figure 3:
Unplug the JPWR2 power conn.
E2-11
Page 25
MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
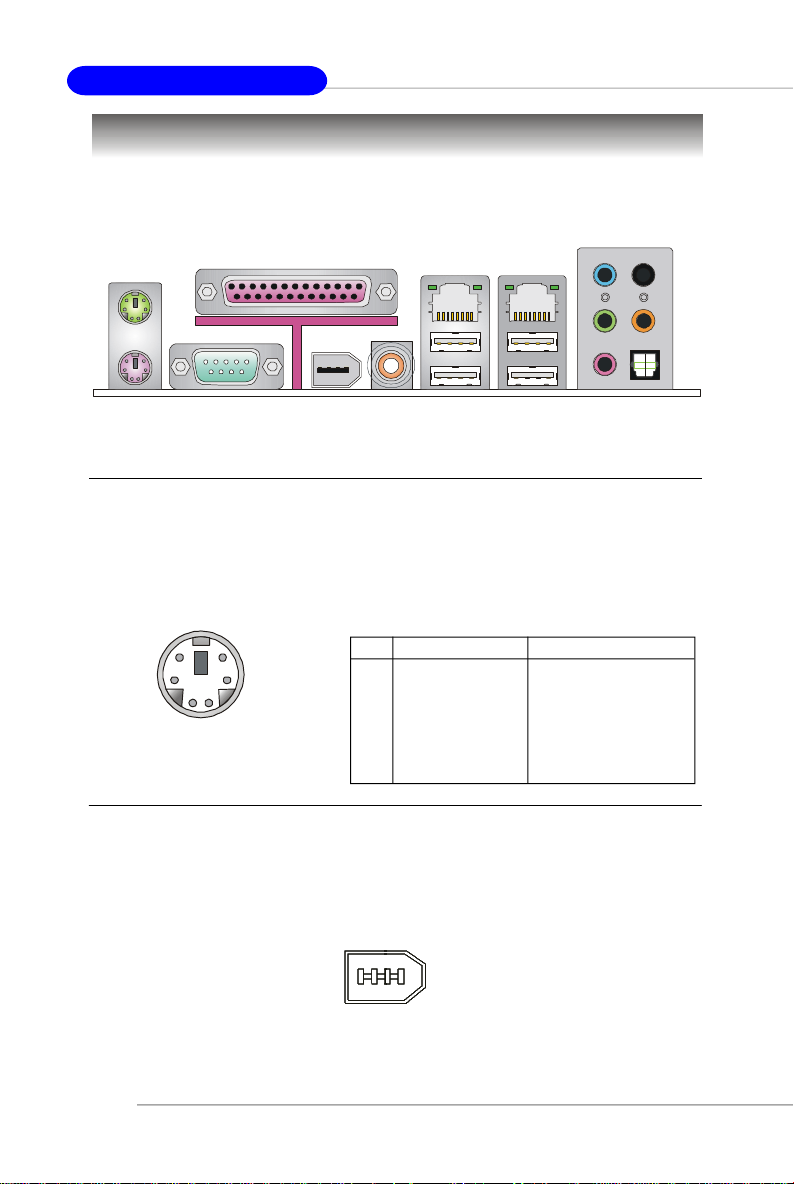
Back Panel
The back panel provides the following connectors:
Mouse
Parallel
LAN
LAN
L-In
RS-Out
Keyboard
COM Port
1394 Port
SPDIF
Out
(Coaxial)
USB Ports
L-Out
Mic
CS-Out
SPDIF Out
(Optical)
Mouse Connector (Green) / Keyboard Connector (Purple)
The mainboard provides a standard PS/2® mouse/keyboard mini DIN connector
for attaching a PS/2® mouse/keyboard. You can plug a PS/2® mouse/keyboard directly
into this connector. The connector location and pin assignments are as follows:
Pin Definition
6
4
2
PS/2 Mouse / Keyboard
(6-pin Female)
5
3
1
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 Mouse/Keyboard Data Mouse/Keyboard data
2 NC No connection
3 GND Ground
4 VCC +5V
5 Mouse/Keyboard Clock Mouse/Keyboard clock
6 NC No connection
IEEE1394 Port
The back panel provides one standard IEEE 1394 port. The IEEE1394 highspeed serial bus complements USB by providing enhanced PC connectivity for a
wide range of devices, including consumer electronics audio/video (A/V) appliances,
storage peripherals, other PCs, and portable devices.
E2-12
IEEE1394 Port
Page 26
Hardware Setup
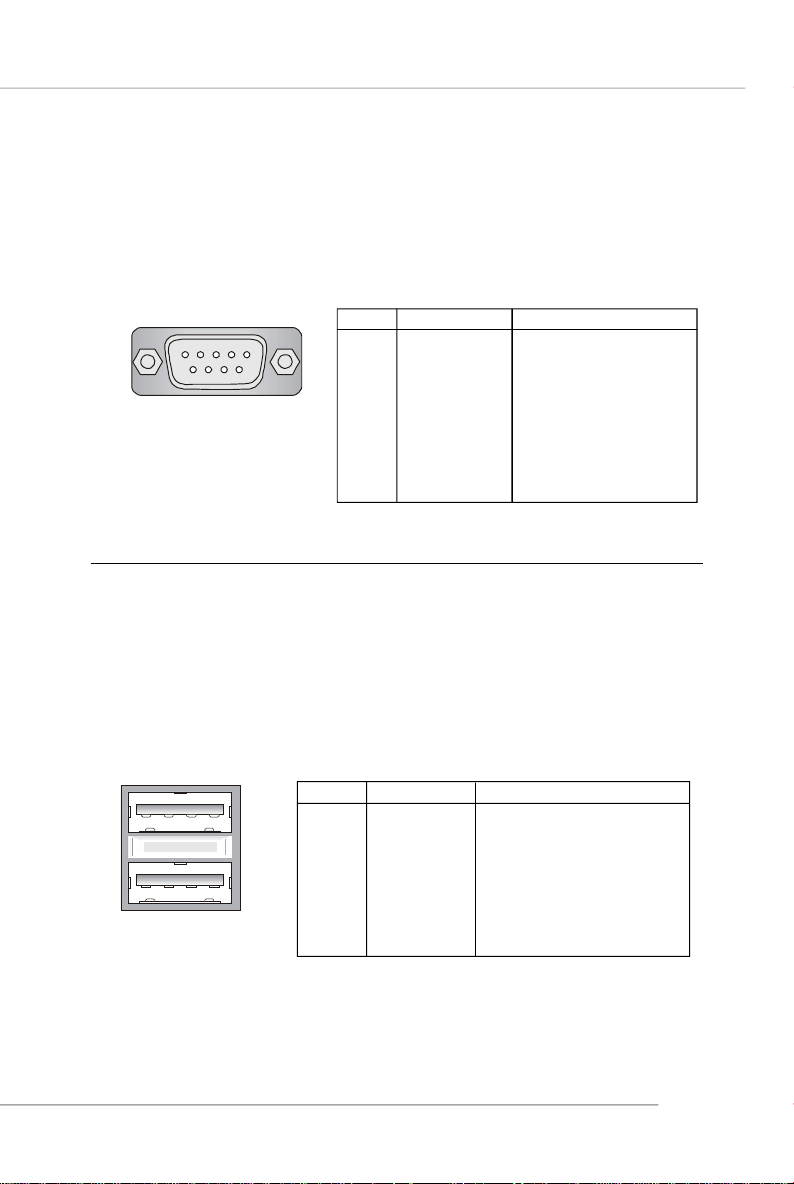
Serial Port Connector
The mainboard offers one 9-pin male DIN connector as the serial port. The port
is a 16550A high speed communication port that sends/receives 16 bytes FIFOs. You
can attach a serial mouse or other serial devices directly to the connector.
Pin Definition
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9
9-Pin Male DIN Connector
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 DCD Data Carry Detect
2 SIN Serial In or Receive Data
3 SOUT Serial Out or Transmit Data
4 DTR Data Terminal Ready)
5 GND Ground
6 DSR Data Set Ready
7 RTS Request To Send
8 CTS Clear To Send
9 RI Ring Indicate
USB Connectors
The mainboard provides two OHCI (Open Host Controller Interface) Universal
Serial Bus roots for attaching USB devices such as keyboard, mouse or other USBcompatible devices. You can plug the USB device directly into the connector.
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
USB Ports
USB Port Description
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 VCC +5V
2 -Data 0 Negative Data Channel 0
3 +Data0 Positive Data Channel 0
4 GND Ground
5 VCC +5V
6 -Data 1 Negative Data Channel 1
7 +Data 1 Positive Data Channel 1
8 GND Ground
E2-13
Page 27
MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
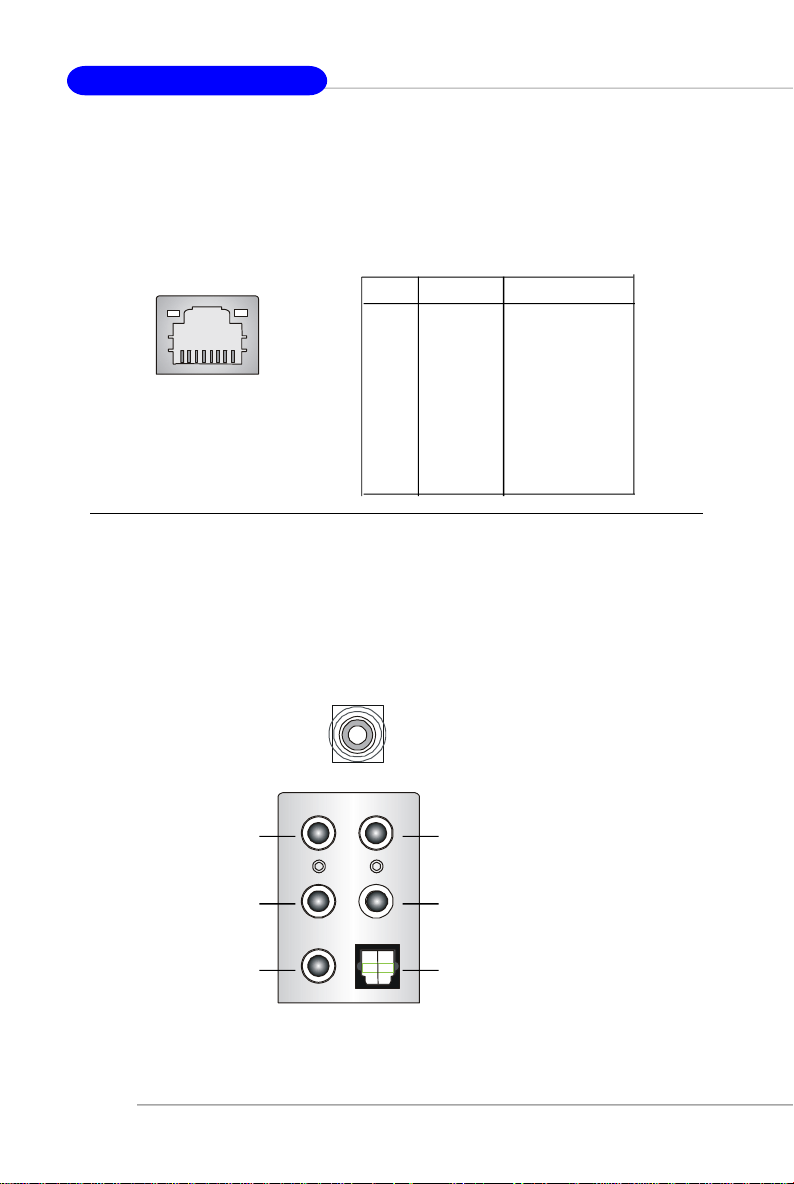
LAN (RJ-45) Jack
The mainboard provides 2 standard RJ-45 jacks for connection to single Local
Area Network (LAN). This Giga-bit LAN enables data to be transferred at 1000, 100
or 10Mbps. You can connect a network cable to either LAN jack.
Giga-bit LAN Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 D0P Differential Pair 0+
2 D0N Differential Pair 03 D1P Differential Pair 1+
RJ-45 LAN Jack
4 D2P Differential Pair 2+
5 D2N Differential Pair 26 D1N Differential Pair 17 D3P Differential Pair 3+
8 D3N Differential Pair 3-
Audio Port Connectors
The left 3 audio jacks are for 2-channel mode for stereo speaker output: Line
Out is a connector for Speakers or Headphones. Line In is used for external CD
player, Tape player, or other audio devices. Mic is a connector for microphones.
However, there is an advanced audio application provided by Creative CA0106 to
offer support for 7.1-channel audio operation and can turn rear audio connectors
from 2-channel to 4-/5.1-/7.1 channel audio.
E2-14
Line In
Line Out
MIC
S/PDIF Out-Coaxial
Rear Speaker Out
(in 7.1CH / 6CH)
Center/Subwoofer
Speaker Out
( in 7.1CH / 6CH)
S/PDIF Out-Optical
(in 7.1CH / 6CH)
Page 28
Hardware Setup
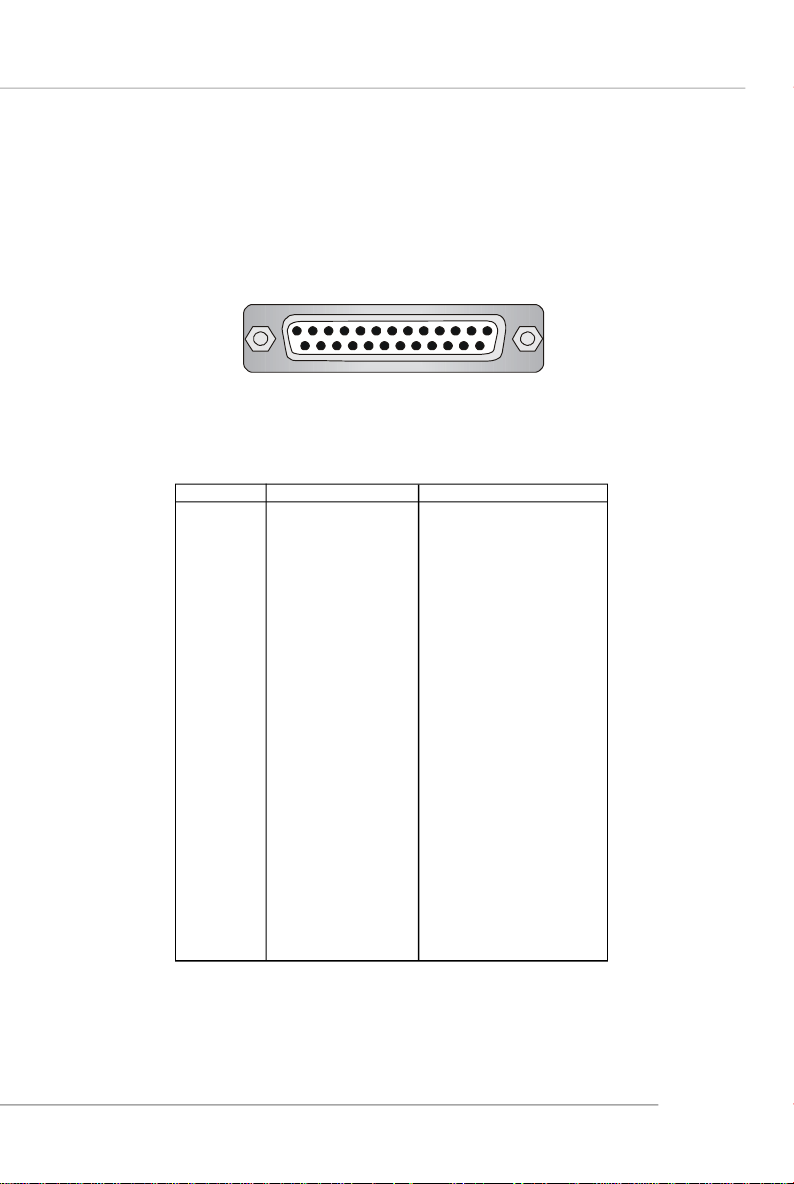
Parallel Port Connector: LPT1
The mainboard provides a 25-pin female centronic connector as LPT. A parallel
port is a standard printer port that supports Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) and Extended Capabilities Parallel Port (ECP) mode.
13 1
25
14
Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 STROBE Strobe
2 DATA0 Data0
3 DATA1 Data1
4 DATA2 Data2
5 DATA3 Data3
6 DATA4 Data4
7 DATA5 Data5
8 DATA6 Data6
9 DATA7 Data7
10 ACK# Acknowledge
11 BUSY Busy
12 PE Paper End
13 SELECT Select
14 AUTO FEED# Automatic Feed
15 ERR# Error
16 INIT# Initialize Printer
17 SLIN# Select In
18 GND Ground
19 GND Ground
20 GND Ground
21 GND Ground
22 GND Ground
23 GND Ground
24 GND Ground
25 GND Ground
E2-15
Page 29
MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Connectors
The mainboard provides connectors to connect to FDD, IDE HDD, case, LAN,
USB Ports, IR module and CPU/System FAN.
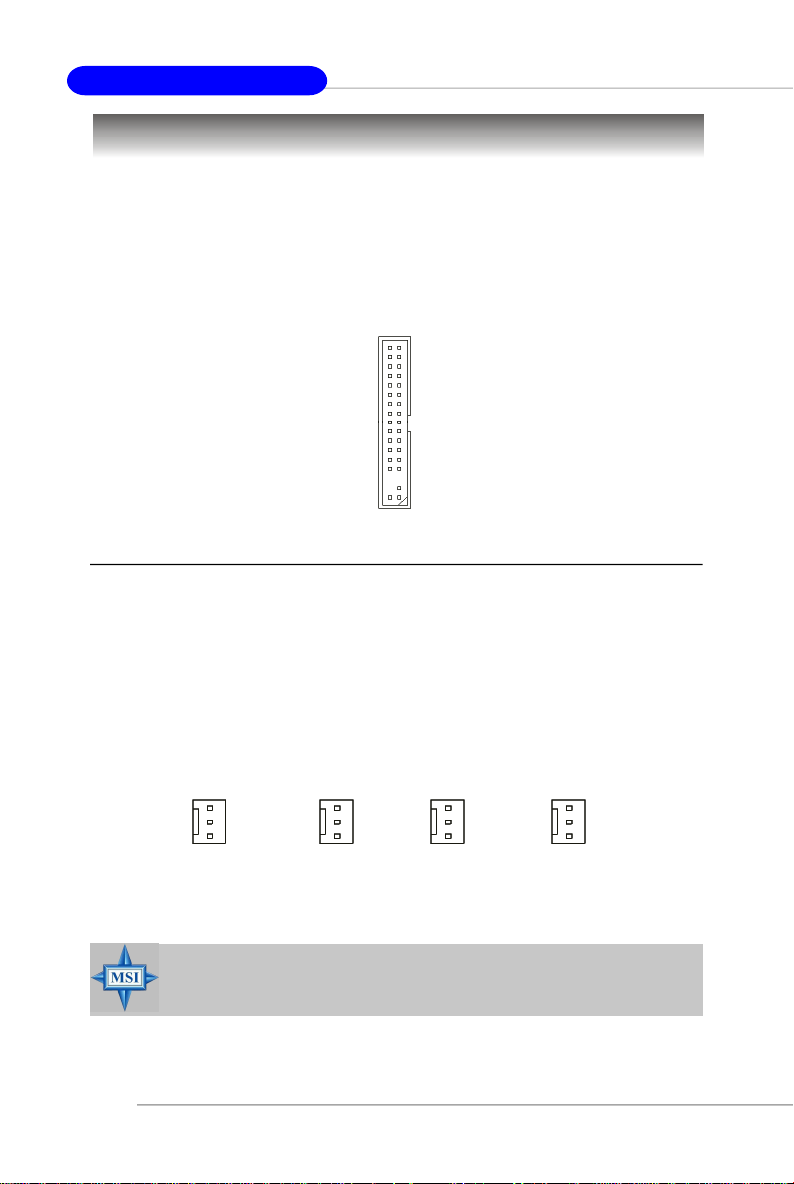
Floppy Disk Drive Connector: FDD1
The mainboard provides a standard floppy disk drive connector that supports
360K, 720K, 1.2M, 1.44M and 2.88M floppy disk types.
FDD1
Fan Power Connectors: C_FAN1 / S_FAN1 / S_FAN2 / NB_FAN1
The C_FAN1 (processor fan), S_FAN1 (system fan 1), S_FAN2 (system fan 2)
and NB_FAN1 (Chipset fan) support system cooling fan with +12V. These support
three-pin head connector. When connecting the wire to the connectors, always take
note that the red wire is the positive and should be connected to the +12V, the black
wire is Ground and should be connected to GND. If the mainboard has a System
Hardware Monitor chipset on-board, you must use a specially designed fan with
speed sensor to take advantage of the CPU fan control.
E2-16
GND
+12V
Sensor
C_FAN1
GND
+12V
S_FAN1
Sensor
GND
+12V
NC
GND
+12V
Sensor
S_FAN2 NB_FAN1
MSI Reminds You...
1.Always consult the vendors for proper CPU cooling fan.
2. Please refer to the recommended CPU fans at AMD® official website.
Page 30
Hardware Setup
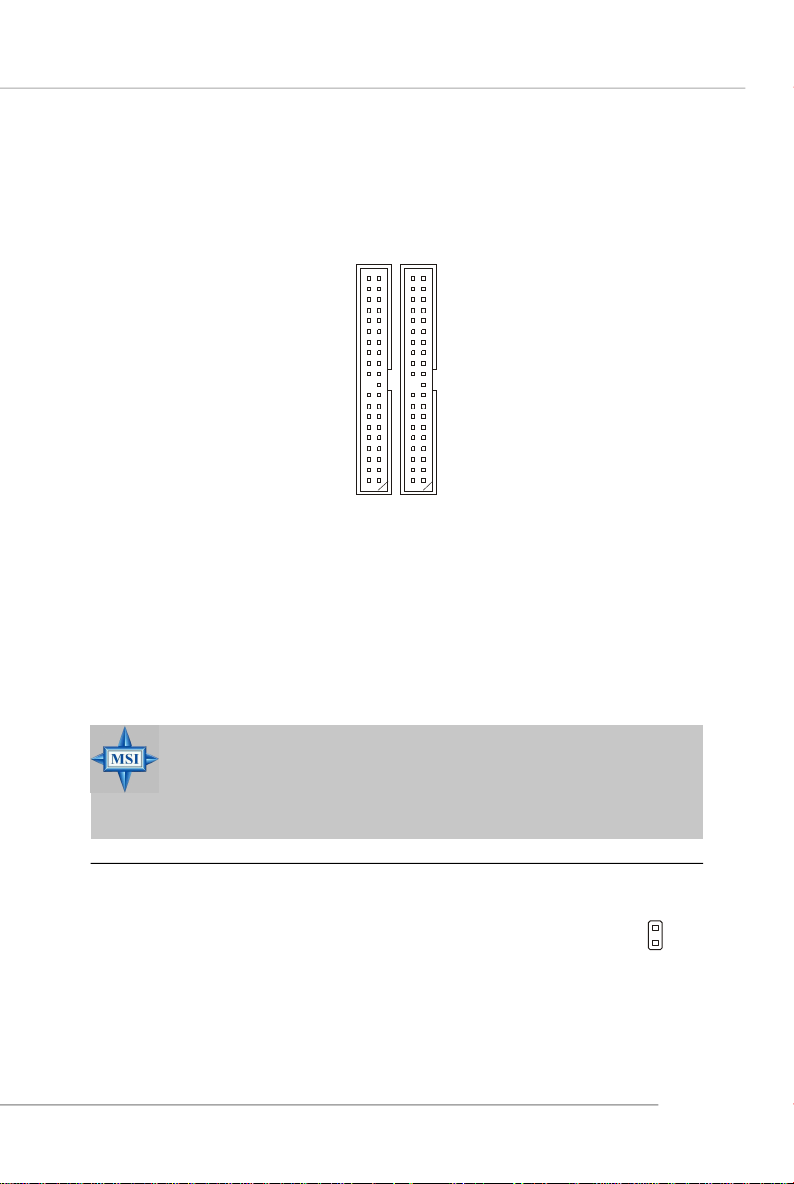
Hard Disk Connectors: IDE1 / IDE2
The mainboard has a 32-bit Enhanced PCI IDE and Ultra DMA 33/66/100/133
controller that provides PIO mode 0~4, Bus Master, and Ultra DMA 33/66/100/133
function. You can connect up to four hard disk drives, CD-ROM, or other devices.
IDE1IDE2
IDE1 (Primary IDE Connector)
The first hard drive should always be connected to IDE1. IDE1 can connect a
Master and a Slave drive. You must configure second hard drive to Slave mode by
setting the jumper accordingly.
IDE2 (Secondary IDE Connector)
IDE2 can also connect a Master and a Slave drive.
MSI Reminds You...
If you install two hard disks on cable, you must configure the second
drive to Slave mode by setting its jumper. Refer to the hard disk
documentation supplied by hard disk vendors for jumper setting
instructions.
Chassis Intrusion Switch Connector: JCI1
This connector is connected to a 2-pin chassis switch. If the
chassis is opened, the switch will be short. The system will record
this status and show a warning message on the screen. To clear
the warning, you must enter the BIOS utility and clear the record.
GND
CINTRU
2
1
JCI1
E2-17
Page 31

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Serial ATA/Serial ATA RAID Connectors controlled by
nForce4 SLI: SATA1 / SATA2 / SATA3 / SATA4;
Serial ATA/Serial ATA RAID Connectors controlled by
Silicon Image’s SATARAID: SATA5 / SATA6
The single chip of this mainboard is nForce4 SLI which supports four serial
ATA connectors SATA1~SATA4. Silicon Image’s SATARAID of this mainboard supports another two serial ATA connectors SATA5/ SATA6.
SATA1~SATA6 are high-speed Serial ATA interface ports. Each supports serial
ATA data rates of 300MB/s. Both connectors are fully compliant with Serial ATA 1.0
specifications. Each Serial ATA connector can connect to 1 hard disk device. Please
refer to the nVidia RAID Introduction & Silicon Image RAID Introduction for detail
software installation procedure.
SATA4
7
SATA5
1
1
7
SATA6
7
1
SATA3
SATA2
1
7
SATA1
Serial ATA cable
(optional)
Connect to serial ATA ports
MSI Reminds You...
Please do not fold the serial ATA cable in a 90-degree angle, which will
cause the loss of data during the transmission.
CD-In Connector: JCD1
The connector is for CD-ROM audio connector.
SATA1~ SATA6 Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
1 GND 2 TXP
3 TXN 4 GND
5 RXN 6 RXP
7 GND
Take out the dust cover and
connect to the hard disk
devices
R
JCD1
GND
GND
L
E2-18
Page 32

Hardware Setup
Front Panel Connectors: JFP1 / JFP2
The mainboard provides two front panel connectors for electrical connection
to the front panel switches and LEDs. JFP1 is compliant with Intel® Front Panel I/O
Connectivity Design Guide.
Power
Power
Switch
LED
Reset
Switch
10
9
JFP1
2
1
HDD
LED
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 HD_LED_P Hard disk LED pull-up
2 FP PWR/SLP MSG LED pull-up
3 HD_LED_N Hard disk active LED
4 FP PWR/SLP MSG LED pull-up
5 RST_SW_N Reset Switch low reference pull-down to GND
6 PWR_SW_P Power Switch high reference pull-up
7 RST_SW_P Reset Switch high reference pull-up
8 PWR_SW_N Power Switch low reference pull-down to GND
9 RSVD_DNU Reserved. Do not use.
JFP1 Pin Definition
JFP2 Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
1 GND 2 SPK3 SLED 4 BUZ+
5 PLED 6 BUZ7 NC 8 SPK+
JFP2
2
1
Speaker
Power
LED
8
7
Front USB Connectors: JUSB1 / JUSB2 / JUSB3
The mainboard provides three standard USB 2.0 pin headers JUSB1 & JUSB2
& JUSB3. USB 2.0 technology increases data transfer rate up to a maximum throughput
of 480Mbps, which is 40 times faster than USB 1.1, and is ideal for connecting highspeed USB interface peripherals such as USB HDD, digital cameras, MP3 players,
printers, modems and the like.
Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
2 10
1
JUSB1, JUSB2, JUSB3
(USB 2.0)
9
Connected to JUSB1, JUSB2, or JUSB3
(the USB pinheader in YELLOW color)
1 VCC 2 VCC
3 USB0- 4 USB15 USB0+ 6 USB1+
7 GND 8 GND
9 Key (no pin) 10 USBOC
USB 2.0 Bracket
(Optional)
E2-19
Page 33

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
MSI Reminds You...
Note that the pins of VCC and GND must be connected correctly, or it
may cause some damage.
Front Panel Audio Connector: AUD1
The AUD1 front panel audio connector allows you to connect to the front panel
audio and is compliant with Intel® Front Panel I/O Connectivity Design Guide.
Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 AUD_MIC Front panel microphone input signal
2 AUD_GND Ground used by analog audio circuits
3 AUD_MIC_BIAS Microphone power
10
4 AUD_VCC Filtered +5V used by analog audio circuits
9
5 AUD_FPOUT_R Right channel audio signal to front panel
6 AUD_RET_R Right channel audio signal return from front panel
7 HP_ON Reserved for future use to control headphone amplifier
8 KEY No pin
9 AUD_FPOUT_L Left channel audio signal to front panel
10 AUD_RET_L Left channel audio signal return from front panel
6 10
5
2
1
AUD1
MSI Reminds You...
If you don’t want to connect to the front audio header,
pins 5 & 6, 9 & 10 have to be jumpered in order to have
signal output directed to the rear audio ports. Otherwise,
the Line-Out connector on the back panel will not
function.
9
IrDA Infrared Module Header: JIR1
The connector allows you to connect to IrDA Infrared module. You must configure the setting through the BIOS setup to use the IR function. JIR1 is compliant with
Intel® Front Panel I/O Connectivity Design Guide.
JIR1 Pin Definition
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 NC 2 NC
3 VCC5 4 GND
5 IRTX 6 IRRX
E2-20
6 5
2 1
JIR1
Page 34

IEEE 1394 Connectors: J1394_1 / J1394_2
The mainboard provides two 1394 pin headers that allow you to connect IEEE
1394 ports via an external IEEE1394 bracket.
Pin Definition
2
1
10
9
J1394_1/ J1394_2
Foolproof Design
(the 1394 pinheader in GREEN color)
PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
1 TPA+ 2 TPA3 Ground 4 Ground
5 TPB+ 6 TPB7 Cable power 8 Cable power
9 Key (no pin) 10 Ground
IEEE1394 Bracket
(Optional)
Hardware Setup
D-Bracket™ 2 Connector: JDB1
The mainboard comes with a JDB1 connector for you to connect to D-Bracket™
2. D-Bracket™ 2 is a USB Bracket that supports both USB1.1 & 2.0 spec. It integrates
four LEDs and allows users to identify system problem through 16 various combinations of LED signals.
Pin Definition
Pin Signal
1 DBG1 (high for green color)
2
1
JDB1
10
9
2 DBR1 (high for red color)
3 DBG2 (high for green color)
4 DBR2 (high for red color)
5 DBG3 (high for green color)
6 DBR3 (high for red color)
7 DBG4 (high for green color)
8 DBR4 (high for red color)
9 Key
10 NC
E2-21
Page 35

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Connected to JDB1
Connected to JUSB1, JUSB2 or JUSB3
(the USB pinheader in YELLOW color)
D-Bracket™ 2 is an external USB bracket integrating four Diagnostic LEDs,
which use graphic signal display to help users understand their system. The LEDs
provide up to 16 combinations of signals to debug the system. The 4 LEDs can debug
all problems that fail the system, such as VGA, RAM or other failures. This special
feature is very useful for the overclocking users. These users can use the feature to
detect if there are any problems or failures.
D-Bracket™ 2 supports both USB 1.1 & 2.0 specification.
D-Bracket™ 2
Red
Green
D-Bracket™ 2
(Optional)
LEDs
1 2
3 4
E2-22
D-Bracket™ 2
1 2
3 4
Description
System Power ON
The D-LED will hang here if the processor is damaged or
not installed properly.
Early Chipset Initialization
Memory Detection Test
Testing onboard memory size. The D-LED will hang if the
memory module is damaged or not installed properly.
Page 36

Hardware Setup
Decompressing BIOS image to RAM for fast booting.
Initializing Keyboard Controller.
Testing VGA BIOS
This will start writing VGA sign-on message to the screen.
Processor Initialization
This will show information regarding the processor (like
brand name, system bus, etc...)
Testing RTC (Real Time Clock)
Initializing Video Interface
This will start detecting CPU clock, checking type of video
onboard. Then, detect and initialize the video adapter.
BIOS Sign On
This will start showing information about logo, processor brand name, etc...
Testing Base and Extended Memory
Testing base memory from 240K to 640K and extended
memory above 1MB using various patterns.
Assign Resources to all ISA.
Initializing Hard Drive Controller
This will initialize IDE drive and controller.
E2-23
Page 37

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
D-Bracket™ 2 Description
Initializing Floppy Drive Controller
This will initialize Floppy Drive and controller.
Boot Attempt
This will set low stack and boot via INT 19h.
Operating System Booting
NV SLI (Scalable Link Interface) connector: PCI_E4
The mainboard has a NV SLI connector to enable NV SLI technology. NV SLI
technology is a high performance technology that allows you to combine and scale
graphics performance by having two GPUs in a single system.
You can find a SLI switch card on the mainboard configured to NON-SLI mode
by manufacturer (fig.1). If you want to install two graphics cards with SLI mode for
your system, please follow the steps below:
non-SLI mode
Turn the latch to
loose the card
E2-24
Fig.1
1. Turn the latch either right or left and the SLI switch card will spring upward
instantly (refer to fig.2).
Fig.2
MSI Reminds You...
Please make sure to turn off the system before you remove the SLI
switch card.
Page 38

Hardware Setup
2. Remove the SLI switch card and rotate it 180 degrees to the other side (SLI
mode side). Then insert it with about 40 degrees into the NV SLI connector (fig.
3).
SLI mode
Fig.3
3. Press down the SLI switch card to parallel mainboard and use latch to fix the
SLI swithc card (fig.4). Before adding or removing NV SLI module, make sure
to unplug the power supply first.
Turn the latch
to fix the card
Fig.4
4. After configuring the card to NV SLI mode, you can install two graphic cards
in PCI Express x16 slots. With two cards installed, a bridge PCB is used to
connect the atop golden fingers of the both cards (fig.5). You only need to
connect a monitor to the first PCI Express card; although you have installed
two graphics cards, only the video outputs on the first card will work.
SLI bridge
Fig.5
MSI Reminds You...
1. Install one graphics card to first PCI Express x 16 slot (PCI_E1)
when non-SLI mode enabled.
2. When SLI mode was be enabled, to tear the sticker on the second ary PCI Express x 16 slot (PCI_E3) and install the second
graphics card to the slot (PCI_E3).
E2-25
Page 39

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
5. Finish hardware installation, reboot the computer and install the driver that
includes a configuration panel for Multi-GPU to graphics cards as below. Check the
Enable multi-GPU item to enable the SLI mode for the cards.(about the details of
multi-GPU setting, please refer to the manual within the graphic card you bought.)
Check the box.
6. Finally, you've to reboot the system and you’ll see a information that inform
you Multi-GPU has been enabled.
MSI Reminds You...
If you want to remove one graphics card and change the status from SLI
mode to normal, make sure that you have to unclick the "MultiGPU"
before removing the graphics card and change back to normal mode.
E2-26
Page 40

Hardware Setup
Button
The motherboard provides the following jumpers for you to set the computer’s
function. This section will explain how to change your motherboard’s function through
the use of button.
Clear CMOS Button: SW1
There is a CMOS RAM on board that has a power supply from external battery
to keep the system configuration data. With the CMOS RAM, the system can automatically boot OS every time it is turned on. If you want to clear the system configuration,
use the SW1 (Clear CMOS Button) to clear data. Press the button in the middle of the
connector top side to clear the data:
SW1
E2-27
Page 41

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Slots
The mainboard provides two PCI Express x16 slot and three 32-bit PCI bus
slots.
PCI Express Slots: PCI_E1 & PCI_E3
The PCI Express slots, as a high-bandwidth, low pin count, serial, intercon-
nect technology, support Intel highest performance desktop platforms utilizing the
AMD processor. You can insert the expansion cards to meet your needs. When
adding or removing expansion cards, make sure that you unplug the power supply
first.
PCI Express architecture provides a high performance I/O infrastructure for
Desktop Platforms with transfer rates starting at 2.5 Giga transfers per second over
a PCI Express x1 lane for Gigabit Ethernet, TV Tuners, 1394 controllers, and general
purpose I/O. Also, desktop platforms with PCI Express Architecture will be designed
to deliver highest performance in video, graphics, multimedia and other sophisticated
applications. Moreover, PCI Express architecture provides a high performance graphics
(PDF, 166Kb) infrastructure for Desktop Platforms doubling the capability of existing
AGP8x designs with transfer rates of 4.0 GB/s over a PCI Express x16 lane for
graphics controllers, while PCI Express x1 supports transfer rate of 250 MB/s.
PCI Express x16 slot
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) Slots: PCI1~3
The PCI slots allow you to insert the expansion cards to meet your needs.
When adding or removing expansion cards, make sure that you unplug the power
supply first. Meanwhile, read the documentation for the expansion card to make any
necessary hardware or software settings for the expansion card, such as jumpers,
switches or BIOS configuration.
The orange PCI slot (PCI3) also works as a communcation slot, which allows
you to insert the communcation card.
PCI Slots
E2-28
Page 42

Hardware Setup
PCI Interrupt Request Routing
The IRQ, acronym of interrupt request line and pronounced I-R-Q, are hardware lines over which devices can send interrupt signals to the microprocessor. The
PCI IRQ pins are typically connected to the PCI bus INT A# ~ INT D# pins as follows:
Order 1 Order 2 Order 3
PCI Slot 1 INT A# INT B# INT C#
PCI Slot 2 INT B# INT C# INT D#
PCI Slot 3 INT C# INT D# INT A#
E2-29
Page 43

BIOS Setup
Chapter 3. BIOS Setup
BIOS Setup
This chapter provides information on the BIOS Setup program and
allows you to configure the system for optimum use.
You may need to run the Setup program when:
² An error message appears on the screen during the sys-
tem booting up, and requests you to run SETUP.
² You want to change the default settings for customized
features.
MSI Reminds You...
1. The items under each BIOS category described in this chapter are
under continuous update for better system performance.
Therefore, the description may be slightly different from the latest
BIOS and should be held for reference only.
2. While booting up, the BIOS version is shown in the 1st line appearing after the memory counting. It is usually in the format:
example: W7100MS V1.0 011005
where:
1st digit refers to BIOS maker as A=AMI(R); W=AWARD(R)
2nd - 5th digit refers to the model number.
6th - 7th digit refers to the customer, MS=all standard customers.
V1.0 refers to the BIOS version.
011005 refers to the date this BIOS is released.
E3-1
Page 44

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Entering Setup
Power on the computer and the system will start POST (Power On Self Test)
process. When the message below appears on the screen, press <DEL> key to
enter Setup.
Press DEL to enter SETUP
If the message disappears before you respond and you still wish to enter
Setup, restart the system by turning it OFF and On or pressing the RESET button. You
may also restart the system by simultaneously pressing <Ctrl>, <Alt>, and <Delete>
keys.
Selecting the First Boot Device
You are allowed to select the 1st boot device without entering the BIOS setup
utility by pressing <F11>. When the same message as listed above appears on the
screen, press <F11> to trigger the boot menu.
The POST messages might pass by too quickly for you to respond in time. If
so, restart the system and press <F11> after around 2 or 3 seconds to activate the
boot menu similar to the following.
Select First Boot Device
Floppy : 1st Floppy
IDE-0 : IBM-DTLA-307038
CDROM : ATAPI CD-ROM DRIVE 40X M
[Up/Dn] Select [RETURN] Boot [ESC] cancel
The boot menu will list all the bootable devices. Select the one you want to boot
from by using arrow keys, then press <Enter>. The system will boot from the selected device. The selection will not make changes to the settings in the BIOS setup
utility, so next time when you power on the system, it will still use the original first
boot device to boot up.
MSI Reminds You...
The items under each BIOS category described in this chapter are
under continuous update for better system performance. Therefore,
the description may be slightly different from the latest BIOS and
should be held for reference only.
E3-2
Page 45

BIOS Setup
Control Keys
<↑> Move to the previous item
<↓> Move to the next item
<←> Move to the item in the left hand
<→> Move to the item in the right hand
<Enter> Select the item
<Esc> Jumps to the Exit menu or returns to the main menu from a
submenu
<+/PU> Increase the numeric value or make changes
<-/PD> Decrease the numeric value or make changes
<F7> Load BIOS Setup Defaults
<F9> Load High Performance Defaults
<F10> Save all the CMOS changes and exit
Getting Help
After entering the Setup menu, the first menu you will see is the Main Menu.
Main Menu
The main menu lists the setup functions you can make changes to. You can
use the arrow keys ( ↑↓ ) to select the item. The on-line description of the highlighted
setup function is displayed at the bottom of the screen.
Sub-Menu
If you find a right pointer symbol (as shown in the right view) appears to the
left of certain fields that means a sub-menu can be launched from this field. A submenu contains additional options for a field
parameter. You can use arrow keys ( ↑↓ ) to
highlight the field and press <Enter> to call up
the sub-menu. Then you can use the control keys
to enter values and move from field to field within
a sub-menu. If you want to return to the main
menu, just press the <Esc >.
General Help <F1>
The BIOS setup program provides a General Help screen. You can call up this
screen from any menu by simply pressing <F1>. The Help screen lists the appropriate
keys to use and the possible selections for the highlighted item. Press <Esc> to exit
the Help screen.
E3-3
Page 46

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
The Main Menu
Once you enter Phoenix-Award® BIOS CMOS Setup Utility, the Main Menu will
appear on the screen. The Main Menu allows you to select from twelve setup functions and two exit choices. Use arrow keys to select among the items and press
<Enter> to accept or enter the sub-menu.
Cell Menu
Use this menu to specify your settings for CPU/AGP frequency/voltage control and
overclocking.
Standard CMOS Features
Use this menu for basic system configurations, such as time, date etc.
Advanced BIOS Features
Use this menu to setup the items of AWARD® special enhanced features.
Advanced Chipset Features
Use this menu to change the values in the chipset registers and optimize your system’s
performance.
Integrated Peripherals
Use this menu to specify your settings for integrated peripherals.
Power Management Setup
Use this menu to specify your settings for power management.
PNP/PCI Configurations
This entry appears if your system supports PnP/PCI.
H/W Monitor
This entry shows your PC health status.
E3-4
Page 47

BIOS Setup
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Use this menu to load the default values set by the BIOS vendor for stable system
performance.
Load Optimized Defaults
Use this menu to load the default values set by the mainboard manufacturer specifically for optimal performance of the mainboard.
BIOS Setting Password
Use this menu to set the password for BIOS.
Save & Exit Setup
Save changes to CMOS and exit setup.
Exit Without Saving
Abandon all changes and exit setup.
E3-5
Page 48

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
nVidis RAID Config
nVidiaRAID Config
Press <Enter> to enter the sub-menu and the following screen appears:
RAID Enabled
This item is used to enable/disable the onchip RAID function. When you set to
enable and the following fields will be selectabled. Setting options: [Enabled],
[Disabled].
IDE Primary/ Secondary Master/Slave RAID
This feature allows users to enable or disable the RAID function for each IDE
hard disk drive. Settings: [Enabled], [Disabled].
SATA1/ SATA2/ SATA3/ SATA4 RAID
This feature allows users to enable or disable the RAID function for each
onchip SATA hard disk drive. The settings are: [Enabled], [Disabled].
E3-6
Page 49

Onboard Device
Onboard Device
Press <Enter> to enter the sub-menu and the following screen appears:
OnChip USB
This setting allows you to enable/disable the onboard USB controller. Selecting
[V1.1+V2.0] enables the system to support both USB 1.1 and 2.0 spec. Setting
options: [Disabled], [V1.1], [V1.1+V2.0].
USB KB/Storage Support
Select [Enabled] if you need to use a USB-interfaced keyboard or storage
device in the operating system. Setting options: [Enabled], [Disabled].
nVidia MAC LAN
Setting to [Auto] allows the BIOS to auto-detect the nVIDIA LAN controller and
enable it. Setting options: [Auto] and [Disabled].
BIOS Setup
OnBoard VIA 1394
This item allows you to enable/disable the onboard IEEE1394 controller. The
settings are: [Enabled], [Disabled].
Marvell GigaBit LAN
Setting to [Enabled] allows the BIOS to detect the Marvell LAN controller and
enable it. Setting options: [Enabled] and [Disabled].
OnBoard CREATIVE AUDIO
This setting controls the onboard Creative Audio chip. Setting options: [Enabled],
[Disabled].
OnBoard Sil3132 RAID
This setting controls the onboard Sil3132 RAID chip. Setting options: [Enabled],
[Disabled].
OnBoard Sil3132 Mode
This setting allows you to select either SATA and RAID mode for the onboard
Sil3132 RAID chip. Setting options: [SATA], [RAID].
E3-7
Page 50

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
H/W Monitor
This section shows the status of your CPU, fan, overall system status, etc.
Monitor function is available only if there is hardware monitoring mechanism onboard.
Chassis Intrusion Detect
The field enables or disables the feature of recording the chassis intrusion status
and issuing a warning message if the chassis is once opened. To clear the warning
message, set the field to [Reset]. The setting of the field will automatically return to
[Enabled] later. Setting options: [Enabled], [Reset], [Disabled].
Smart CPU Fan Target
System Temperature with CPU Temperature with CPU Fan. The BIOS povides the
Smart Fan system which can control the fan speed automatically depending on the
current temperature to keep it with in a specific range. Settings: [Enabled], [Disabled].
Smart CPU Fan Tolerance
You can select a fan tolerance value here for the specific range for the Smart CPU
Fan items. If the current temperatures of CPU fan reach to the maximum threshold
(the temperatures set in the Smart CPU Fan plus the tolerance values you set
here), the fans will speed up for cooling down. On the contrary if the current temperatures reach to the minimum threshold (the set temperatures minus the tolerance
values), the fans will slow down to keep the temperatures stable.
PC Health Status
Press <Enter> and the following sub-menu appears.
Current System/CPU Temperature, SYSTEM/CPU Fan Speed, Vcore, +3.3V,
+12V, +5.0V, Battery, +5VSB
These items display the current status of all of the monitored hardware devices/
components such as CPU voltage, temperatures and all fans’ speeds.
E3-8
Page 51

Cell Menu
The items in Cell Menu includes some important settings of CPU, AGP, DRAM
and overclocking functions.
MSI Reminds You...
Change these settings only if you are familiar with the chipset.
Current CPU / DDR Clock
These two items show the current clocks of CPU & DDR. Read-only.
BIOS Setup
DRAM Configuration
Press <Enter> to enter the sub-menu and the following screen appears:
Timing Mode
This field has the capacity to automatically detect all of the DRAM timing. If you
set this field to [Manual], the following fields will be selectable. The settings are:
[Auto], [Manual].
E3-9
Page 52

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
User Config mode
This field has the capacity to automatically detect all of the following 4 fields
default value.. If you set this field to [Manual], the following fields will be selectable.
The settings are: [Auto], [Manual].
S/W & H/W memory hole Remapping
This field enables software/hardware to remap the physical memory to the
address higher than 00E0. (This item only activities in 64-bit OS) Setting options:
[Disabled], [Enabled].
MTRR Mapping Mode
This field allows you to control the MTRR mapping Mode. Setting options:
[Disabled], [Continuous].
High Performance Mode
This field allows you to select the DDR timing setting. Setting to [Optimized] enables
DDR Memory Frequency automatically to be determined by SPD. Selecting [Manual]
allows users to configure these fields manually. Setting options: [Optimized], [Manual].
Aggressive timing
This item allows you to enable or disable the memory clock. When [Enabled] is selected,
the timing delay of memory will be shorten to increase the performance. Setting
options: [Enabled], [Disabled].
Dynamic Overclocking
Dynamic Overclocking Technology is the automatic overclocking function, included in
the MSITM’s newly developed CoreCell
TM
Technology. It is designed to detect the load
balance of CPU while running programs, and to adjust the best CPU frequency
automatically. When the motherboard detects CPU is running programs, it will speed
up CPU automatically to make the program run smoothly and faster. When the CPU is
temporarily suspending or staying in the low load balance, it will restore the default
settings instead. Usually the Dynamic Overclocking Technology will be powered only
when users' PC need to run huge amount of data like 3D games or the video process,
and the CPU frequency need to be boosted up to enhance the overall performance.
Setting options:
[Disabled] Disable Dynamic Overclocking function.
[Private] 1st level of overclocking, increasing the CPU frequency by 1%.
[Sergeant] 2nd level of overclocking, increasing the CPU frequency by 3%.
[Captain] 3rd level of overclocking, also the default value of "Load High
Performance Defaults", increasing the CPU frequency by 5%.
[Colonel] 4th level of overclocking, increasing the CPU frequency by 7%.
[General] 5th level of overclocking, increasing the CPU frequency by 9%.
[Commander] 6th level of overclocking, increasing the CPU frequency by 11%.
E3-10
Page 53

BIOS Setup
MSI Reminds You...
Even though the Dynamic Overclocking Technology is more stable
than manual overclocking, basically, it is still risky. We suggest user
to make sure that your CPU can afford to overclocking regularly first.
If you find the PC appears to be unstable or reboot incidentally, it's
better to disable the Dynamic Overclocking or to lower the level of
overclocking options. By the way, if you need to conduct overclocking
manually, you also need to disable the D.O.T Ranger first.
Adjust CPU FSB Frequency
This item allows you to select the CPU Front Side Bus clock frequency (in MHz).
Select the number between [200]~[400] for needed frequency.
HT Frequency
This setting specifies the maximum operating frequency of the link’s transmitter clock.
Setting options: [1x], [1.5x], [2x], [2.5x], [3x], [4x], [5x].
HT Width
This field allows you to set the HT Width between CPU & Chip.↑ mark means Chip to
CPU HT Width. And ↓ mark means CPU to Chip HT Width. Setting options: [ ↓ 8 ↑ 8], [
↓ 16 ↑ 8], [↓ 8 ↑16], [ ↓16 ↑16].
CPU Spread Spectrum
This setting is used to enable or disable the CPU Spread Spectrum feature. When
overclocking the CPU, always set it to [Disabled]. Setting options: [Center Spread],
[Disabled].
SATA Spread Spectrum
This setting is used to enable or disable the SATA Spread Spectrum feature. Setting
options: [Disabled], [Down Spread].
PCIE Spread Spectrum
This setting is used to enable or disable the CPU Spread Spectrum feature. When
overclocking the CPU, always set it to [Disabled]. Setting options: [Disabled], [Down
Spread].
PCIE Clock
This item allows you to select the PCIE Bus clock frequency (in MHz). Select the
number between [100]~[145] for needed frequency.
K8 CPU SSE/ SSE2 Instructions
This setting disables/enables the SSE/SSE2 Instructions. The Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) were introduced in the Pentium III processor. The SSE extensions consist of a new set of instructions and a new set of registers. These instructions and
registers are designed to allow Single-Instruction Multiple-Data (SIMD) computations
to be made on single-precision floating-point numbers.
E3-11
Page 54

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
The Streaming SIMD Extensions 2 (SSE2) were introduced in the Pentium 4 and Intel
Xeon processors. They consist of a new set of instructions that operate on the XXM
and MXCSR registers and perform SIMD operations on double-precision floatingpoint values and on integer values.Several of these new SSE/SSE2 instructions also
operate in the MMX registers. Setting options: [Enabled], [Disabled].
Cool’n’Quiet control
This feature is especially designed for AMD Athlon processor, which provides a CPU
temperature detecting function to prevent your CPU’s from overheating due to the
heavy working loading. Setting options: [Disabled], [Auto].
MSI Reminds You...
For the purpose of ensuring the stability of Cool'n'Quiet function, it is
always recommended to have the memories plugged in DIMM1.
Adjust CPU Ratio
This item lets you adjust the CPU ratio. Setting to [Startup] enables the CPU running at
the fastest speed which is detected by system. Setting options are: [Startup], [x4]~
[x25].
Adjust CPU VID
This item lets you adjust the CPU VID. Setting to [Startup] enables the CPU running at
the default VID which is detected by system. Setting options are: [Startup], [0.825V],
[0.850V],[0.875V],~, [1.550V].
CPU Voltage
This feature allows you to trim the voltage of CPU.
Memory Voltage
Adjusting the DDR voltage can increase the DDR speed. Any changes made to this
setting may cause a stability issue, so changing the DDR voltage for long-term
purpose is NOT recommended.
NF4 Voltage
NF4 voltage is adjustable in the field.
MSI Reminds You...
The settings shown in different color in CPU Voltage, Memory Voltage and NF4 Voltage help to verify if your setting is proper for your
system.
Gray: Default setting.
Yellow:High performance setting.
Red: Not recommended setting and the system may be
unstable.
Changing CPU Voltage and Memory Voltage and NF4 Voltage
may result in the instability of the system; therefore, it is NOT recommended to change the default setting for long-term usage.
E3-12
Page 55

BIOS Setup
Load Fail-Safe/Optimized Defaults
The two options on the main menu allow users to restore all of the BIOS
settings to the default Fail-Safe or Optimized values. The Optimized Defaults are the
default values set by the mainboard manufacturer specifically for optimal performance
of the mainboard. The Fail-Safe Defaults are the default values set by the BIOS
vendor for stable system performance.
When you select Load Fail-Safe Defaults, a message as below appears:
Pressing Y loads the BIOS default values for the most stable, minimal system
performance.
When you select Load Optimized Defaults, a message as below appears:
Pressing Y loads the default factory settings for optimal system performance.
E3-13
Page 56

Manuel d’utilisation
K8N Diamond
User’s Guide
French
F-1
Page 57

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
F-2
Page 58

Manuel d’utilisation
Chapter 1. Getting
Started
K8N Diamond
Manuel d’Utilisation
Félicitation vous venez d’acheter une carte mère ATX
K8N Diamond (MS-7100) v1.X basée sur le chipset nVIDIA
nForce™4 SLI offrant un système optimal. Destinées à
recevoir les processeurs AMD® K8 Athlon 64 FX / Athlon 64,
les K8N Diamond sont très performantes et offrent une solution adaptée tant aux particuliers qu’aux professionnels.
®
F-3
Page 59

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
Spécificités
CPU
† Supporte les processeurs AMD K8 Athlon 64 FX / Athlon 64 (Socket939)
† Supporte up to 4000+ Athlon FX55 , or higher CPU
(Pour les dernières informations relatives au CPU, veuillez visiter : http://www.msi.
com.tw/program/products/mainboard/mbd/pro_mbd_cpu_support.php)
Chipset
† nVIDIA nForce4 SLI
- HyperTransport link vers le CPU AMD Athlon 64/Athlon 64 FX
- HyperTransport supportant jusqu’à 1GHz (2000MT/s)
- Supporte l’interface 2 PCI Express x16/ x1
- Deux contrôleurs SATA indépendants pour quatre disques
- Contrôleur IDE ATA-133 Dual Fast
- IEEE802.3 nVIDIA MAC pour 1000BASE-T
Mémoire Principale
† Supporte le dual channel, huit banques de mémoire DDR 266/333/400, 4 DDR
DIMMs 184 broches
† Supporte jusqu’à 4GB
† Supporte DDR SDRAM DIMM 2.5v
(Pour une mise à jour sur les mémoires veuillez visiter : http://www.msi.com.tw/
program/products/mainboard/mbd/pro_mbd_trp_list.php.Référez-vous à la partie
du module de mémoire dans le rapport de test.)
Slots
† Deux slots PCI Express x16 (supporte les spécificités PCI Express Bus v1.0a)
† 2e slot PCI Express x16 (PCI_E3) compatible avec PCI Express x 1
† Trois slots PCI Bus Master 32-bit, incluant un slot orange réservé pour la
communication.
† Supporte l’interface PCI bus 3.3V/5V
IDE Intégré
† Un contrôleur IDE sur le chipset nVIDIA® nForce4 SLI procure les modes
opératoires IDE HDD/CD-ROM avec PIO, Bus Master et Ultra DMA 66/100/133
† Possibilité de connecter jusqu’à 4 matériels IDE
SATA Intégré
† NV RAID supporte 4 ports SATA II (SATA1-4). Taux de transfert jusqu’à 300 MB/
s. Supporte les modes RAID 0, 0+1 et JBOD.
† Silicon Image’s SATARAID supporte 2 autres ports SATA II (SATA5/6). Taux de
transfert jusqu’à 300 MB/s. Supporte le mode RAID 0 & 1.
F-4
Page 60

Manuel d’utilisation
Interface USB
† 10 ports USB
- Contrôlé par le chipset nForce4 SLI
- 4 ports I/O à l’arrière , 6 ports par le bracket externe
NV RAID (Software)
† Supporte jusqu’à 4 SATA et 2 disque durs ATA133
-RAID 0 ou 1, 0+1, JBOD supporté
-Fonction RAID disponible pour ATA133+SATA H/D ou 4 disques SATA H/D
Silicon Image’s SATARAID (Software) (Option)
† RAID 0 ou 1 ou multiples groupes RAID supporté
† Supporte jusqu’à 2 matériels SATA connecté à un seul contrôleur
LAN
† Supporte dual LAN jacks
-1er LAN supporte 10/100/1000 Fast Ethernet par nForce4 SLI
-2e LAN PCI Express supporte 10/100/1000 Fast Ethernet par Marvell
88E8053 .
IEEE 1394
† Supporte jusqu’à trois ports 1394 (panneau arrière x 1, connecteur x 2). Taux
de transfert jusqu’à 400Mbps
Audio
† Power par Creative Sound Bluster 24 bits H/W audio
-Qualité audio 24-bit / 96~192 KHz
-Clareté SNR jusqu’à 100 db
-Canaux 7.1 en sortie supportés, encodeur Dolby Digital
-Supporte l’interface digital S/PDIF
-Compatible avec les spécificités PCI 2.3
Périph ériques Intégrés
† Périphériques Intégrés Inclus:
-1 port floppy supportant 1 FDD avec 360K, 720K, 1.2M, 1.44M et 2.88Mbytes
-1 port série (COM1)
-1 port parallèle supportant les modes SPP/EPP/ECP
-1 Audio jack(5-in-1), coaxial/fibre SPDIF en sortie
-1 connecteur D-Bracket 2
-1 connecteur CD-In
-3 IEEE 1394 (Arrière* 1 / Avant * 2)
-10 ports USB1.1/2.0 (Arrière * 4 / Avant * 6)
-1 connecteur IrDA
F-5
Page 61

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
BIOS
† La carte mère procure un BIOS “Plug & Play” BIOS qui détecte
automatiquement les cartes d’extension ou les périphériques.
† La carte mère offre une interface Desktop Management Interface (DMI) qui
enregistre les spécificités de la carte mère.
† Supportes boot de LAN, Matériels USB 1.1 & 2.0,et SATA HDD.
Dimension
† Format ATX (30.4 cm X 24.4 cm)
Montage
† 9 trous de montage
MSI Vous Rappelle...
Pour créer un volume RAID bootable pour l’environnement Windows
2000, Le Service pack 4 Microsoft’s Windows 2000 (SP4) est
recommendé. comme l’utilisateur ne peut pas booter sans SP4, une
installation de combinaison CD doit être installé avant d’essayer
d’installer le système opératoire sur le volume RAID bootable.
Pour créer une installation de combinaison CD, merci de vous réferer
au site suivant:
http://www.microsoft.com/windows2000/downloads/servicepacks/
sp4/HFdeploy.htm
F-6
Page 62

S_FAN1
NB_FAN1
FDD
1
SATA3
SATA5
SATA6
SATA4
SATA1
SATA2
Win
bond W836
27THF
CK8-04 SLI
BATT+DI
MM
1
J
PWR
1
PCI Slot 3
PCI Slot 2
PCI Slot 1
AUD1
JUSB3
JUSB1
Top : mouse
MSI
CoreCell
123
444456678
910111212121314151616181818191717
(Optional)
(Optional)
(Optional)
(Optional)
(Optional)
Bottom: keyboard
Top : Parallel Port
Bottom:
COM Port
1394 Port (optional)
SPDIF OUT
T: LAN jack
B: USB ports
T: LAN jack (optional)
B: USB ports
T:
Line-In
M:
Line-Out
B:
Mic
T:RS-Out
M:CS
-Out
B:SPDIF Out
JCD1
88E1111-RCJ
88E8053-NNC
JPWR2
PCI _E3
Schéma
PCI _E1
(SLI Connector)
PCI_E4
C_FAN1
Manuel d’utilisation
2
3
4
JCI1
M
M
M
M
I
I
D
D
JIR1
2
E
D
I
Sw1
nVIDIA
M
M
I
D
1
E
D
I
CREATIVE
Sound
Bluster
Vt6306
S_FAN2
J1394_2
J1394_1
JUSB2
JLPC1
S
O
I
B
JFP1
VIA
Carte Mère ATX K8N Diamond (MS-7100 v1.X)
JDB1
JFP2
F-7
Page 63

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
Connecteur d’alimentation ATX 24 broches : JPWR1. Ce connecteur
1
vous permet de vous connecter à une alimentation ATX.
Connecteur d’alimentation ATX 12V : JPWR2. Ce connecteur
2
d’alimentation est utilisé pour alimenter le CPU.
Connecteur Floppy Disk Drive : FDD1. La carte mère procure un
3
connecteur floppy disk drive standard supportant les floppy disk drives de
360K, 720K, 1.2M, 1.44M et 2.88M.
Connecteur d’alimentation du ventilateur: C_FAN1, S_FAN1,
4
NB_FAN1 & S_FAN2. Ces connecteurs de ventilateurs supportent le +12V.
Connecteurs de disques durs ATA 133 : IDE1 & IDE2. Cette carte
5
mère possède un contrôleur 32-bit Enhanced PCI IDE et Ultra DMA 66/100/
133 qui procure les fonctions PIO mode 0~4, Bus Master et Ultra DMA 66/
100/133.
Connecteurs Serial ATA/ Serial ATA RAID contrôlés par le nForce4
6
SLI: SATA1 / SATA2 / SATA3 / SATA4. L’unique chip de cette carte mère
est nForce4 SLI qui supporte quatre connecteurs serial ATA SATA1 ~
SATA4. SATA1~SATA4 sont des ports d’interface Serial ATA haute vitesse.
Chacun supporte un taux de données serial ATA de 300MB/s.
Connecteurs Serial ATA/ Serial ATA RAID contrôlés par Silicon
7
Image’s SATARAID: SATA5 & SATA6 (uniquement pour K8N Neo4
Platinum/SLI) le Silicon Image’s SATARAID de cette carte mère supporte
deux autres connecteurs serial ATA SATA5/ SATA6. SATA5 & SATA6 sont
des ports d’interface Serial ATA haute vitesse. Chacun supporte un taux de
données serial ATA de 300MB/s.
F-8
8
Connecteur Switch Chassis Intrusion: JCI1. Ce connecteur est
connecté à un chassis switch 2 broches. Si le chassis est ouvert, le
système enregistrera la statut
Connecteurs Front Panel : JFP1 & JFP2. la carte mère procure deux
9
connecteurs front panel pour les connections éléctriques de l’interrupteur
en façade et des LEDs.
Power
Power
Switch
JFP1
LED
Reset
Switch
10
JFP2
9
2
1
HDD
LED
2
1
Speaker
Power
LED
8
7
Page 64

Manuel d’utilisation
Connecteur CD-In : JCD1. Le connecteur est destiné aux branchements
10
audio du CD-ROM.
Connecteur D-BracketTM 2: JDB1. La carte mère procure un connecteur
11
JDB1 permettant de se connecter au D-BracketTM 2.
Connecteurs Front USB: JUSB1, JUSB2 & JUSB3. Cette carte mère
12
procure trois connecteurs standards USB2.0: JUSB1, JUSB2 & JUSB3.
Connecteur Front Panel Audio: AUD1. Ce connecteur front panel audio
13
permet de vous connecter au front panel audio.
Connecteur Infra rouge IrDA : JIR1. Ce connecteur pemret la connec-
14
tion au module infrarouge IrDA. Vous devez configurer les paramètres du
BIOS pour utiliser la fonction IR. JIR1 est compatible avec Intel Front Panel I/
O Connectivity Design Guide.
Connecteur Clear CMOS: SW1. Le CMOS RAM intégré est alimenté par
15
une batteie extérieur qui garde les données de configuration du système.
Avec le CMOS RAM, le système peut automatiquement booter avec les
paramètres personnalisés du BIOS chaque fois que le PC est allumé. Si
vous souhaitez effacer la configuration du système, utilisez le SW1 (Clear
CMOS Button) pour effacer les données. Pressez le bouton dans le milieu
du coté supérieur du connecteur pour effacer les données.
Connecteurs IEEE 1394 : J1394_1 & J1394_2. la carte mère procure
16
deux connecteurs 1394 qui pemrmettent une connection aux ports IEEE
1394 par un bracket externel IEEE1394.
Slots PCI Express. Les slots PCI Express possèdent une large bande
17
passante, supportent les plateformes desktop AMD haute performances
utilisant le processeur AMD ainsi que les avantages de cette plateforme.
L’architecture PCI Express procure une infrastructure performante pour le
graphique et double la capacité de l’AGP 8X avec un taux de transfert de
données de 4.0 GB/s sur un PCI Express x16 pour contrôleur graphique
alors que le PCI Express x 1 supporte un taux de transfert de 250 MB/s.
Slots PCI: Vous pouvez insérer des cartes d’expansion selon vos
18
besoins. Lorsque vous ajoutez ou enlever une carte d’expansion, assurez-
vous que le PC n’est pas relié au secteur
Connecteur NV SLI (Scalable Link Interface): PCI_E4. La carte mère
19
possède un connecteur NV SLI pour activer la technologie NV SLI . La
technologie NV SLI est une technologie haute performance qui permet de
combiner les performances graphiques de deux GPUs dans un seul système.
F-9
Page 65

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
Central Processing Unit: CPU
La carte mère supporte les processeurs AMD® Athlon64/ Athlon64 FX. La carte
utilise un socket appelé Socket-939. Lors de l’installation du CPU, assurez-vous de
bien installer un dissipateur + ventilateur afin d’éviter la surchauffe. Si vous ne
savez pas le modèle qu’il vous faut, il est recommandé de prendre contact
avec votre revendeur.
Pour une mise à jour sur les informations relatives au CPU, veuillez visiter http:/
/www.msi.com.tw/program/products/mainboard/mbd/pro_mbd_cpu_support.php.
MSI Vous Rappelle...
Surchauffe
Une surchauffe peut sérieusement endommager le CPU et le système,
assurez vous toujours que le système de reffroidissement fonctionne
correctement pour protéger le CPU d’une surchauffe.
Remplacer le CPU
Avant de remplacer le CPU, éteignez toujours l’alimentation ATX ou
débranchez la prise pour assurer la sécurité du CPU.
Overclocking
Cette carte mère a été créée pour supporter l’overclocking. Assurez
vous que vos composants sont capables de tolérer de tels réglages,
avant d’overclocker le système. Tout essais au delà des spécifications
des produits n’est pas recommandé. Nous ne garantissons pas les
dommages causés par une mauvaises opération ou au delà des
spécifications du produit.
F-10
Page 66

Gold arrow
Gold arrow
Gold arrow
Correct CPU placement
O
CPU Installation Procedures for Socket 939
Manuel d’utilisation
1. Veuillez éteindre et débrancher
votr e PC avant l’installation du
CPU
2. Tirez le levier vers le haut.
Assurez-vous que celui-ci est
bien en position ouverte
maximum (angle de 90°)
3.Repérez la flèche dorée. La
flèche dorée doit se trouver
comme indiqué sur le dessin.
Le CPU ne peut être installé
que dans un seul sens. Mettre
le CPU sur le socket.
4.Si le CPU est correctement
installé alors les broches ne
sont plus visibles. Une
mauvaise installation pourrait
entraîner des dommages vis-à-
vis de la carte mère
Sliding
Plate
Open Lever
90 degree
5. Appuyez sur le CPU pendant
que vous abaissez le levier. Il
faut toujours exercer une
pression sur le CPU pour éviter
que ce dernier ne soit pas bien
fixé une fois le levier abaissé.
F-11
Page 67

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
Installation du ventilateur CPU AMD Athlon64/ Athlon64 FX
Quand vous installez votre CPU, assurez-vous que le CPU possède un
système de refroidissement pour prévenir les surchauffes.
1.Détacher la protection
2.Retourner la carte mère et installer la
plaque métallique
3.Retourner la carte mère et localiser
les deux trous de vis sur la carte
mère.
4.Aligner le méchanisme de rétention
et la plaque métallique.
Fixer le méchanisme de rétention et
la plaque métallique avec les vis..
F-12
retention mechanism
Page 68

Manuel d’utilisation
5.Positionner le ventilateur sur le
méchanisme de rétention.
Attacher un coté puis l’autre en
s’assurant que l’ensemble est bien
sécurisé
6.Localiser le levier de fixation et le
crochet de sécurité
Relever le levier.
Safety Hook
7.Abaisser le levier
8.S’assurer que le crochet est
sécurisé ( avec le méchanisme de
rétention).
9.Connectez le câble d’alimentation sur
le connecteur de la carte mère
prévu à cet effet
Fixed Lever
Fixed Bolt
MSI Vous Rapelle...
Lorsque vous déconnectez le crochet, il est nécessaire de garder un
oeil sur vos doigts car une fois le crochet déconnecté, celui-ci reprend
sa position initial du à son ressort.
F-13
Page 69

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
Mémoire
La carte mère procure 4 slots DDR DIMM (Double In-Line Memory Module) (184
broches) et supporte jusqu’à 4GB de mémoire. Vous pouvez installer les modules
DDR 266/333/
400 sur les slotsDDR DIMM (DIMM 1~4).
Pour les dernières mises à jours sur les modules de mémoires, veuillez visiter le site
suivant : http://www.msi.com.tw/program/products/mainboard/mbd/pro_mbd_trp_list.
php.
DIMM1~4
(Du bas vers le haut)
Introduction à la DDR SDRAM
La DDR SDRAM est similaire à la SDRAM conventionnelle mais double le taux de
transfert de données deux fois par cycle. Il utilise le 2.5v contrairement au 3.3v de
la SDR SDRAM.
Les modules de DDR possèdent 184 broches, contre 168 pour les modules
DIMM utilisé par SDR SDRAM. C’est une solution idéale pour les PC haute
performance, de travail et les serveurs.
DIMM Module Combination
Installez au moins un module DIMM sur les slots. Chaque slot DIMM supporte
une taille maximum d’ 1GB. Merci de noter que chaque DIMM fonctionnera
respectivement avec le single channell DDR mais certaines règles permettent d’utiliser
le dual channel DDR(merci de vous reporter au tavleau ci-contre). Vous pouvez
installer des modules simples ou doubles faces selon vos besoins. Vous pouvez
installer des mémoires de modules de différent type et de densité sur les différents
canaux DDR DIMMs. Les modules de mémoire de même type et densité sont requis
lors de l’utilisation dual-channel DDR, sinon une instabilité peut apparaître.
Merci de vous reférer au tableau suivant pour les détails sur le dual channel DDR.
D’autres combinaisons non référencées peuvent fonctionner en single channel DDR.
F-14
Page 70

Manuel d’utilisation
GREEN
DIMM1 (Ch A) DIMM2 (Ch B) DIMM3 (Ch A) DIMM4 (Ch B) System Density
128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 256MB~2GB
128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 512MB~4GB
MSI Vous Rappelle...
-Dual-channel DDR fonctionnent uniquement selon les 3
-Merci de choisir des modules de mémoire identiques pour
-Toujours insérer un module de mémoire dans les slots verts en
-- Cette carte mère ne supporte pas les modules de mémoire avec
PURPLE
combinaisons présentées dans le tableau ci-dessus.
l’installation en dual channel, et de ne pas pas installer 3 modules
de mémoires sur trois DIMMs sinon cela causera des dommages.
premier. Il est fortement recommendé de ne pas insérer de mod-
ule de mémoire dans les slots violets lorsque les slots verts sont
vides
plus de 18 IC (Circuit Intégré).
GREEN
128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 256MB~2GB
PURPLE
Combinaison entre les modules de mémoire
DIMM Slots
Vert Vert
DIMM1
S
D
S D S
Violet
DIMM2 DIMM3 DIMM4
- -
-
-
-
S
-
DS -
D -
S
-
- - S S
D D
- -
S
D
S
D
- D D
S
D
Violet
-
-
-
-
-
S
D
Vitesse Max
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 333
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 333
S: Single Side D: Double Side
F-15
Page 71

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
Installation des modules DDR
1. La DDR DIMM ne posséde qu’une encoche en son centre. Le module ne peut être
monté que dans le bon sens
2. Insérez le module de mémoire DIMM verticalement sur le slot. Puis appuyez dessus
3. Le clip en plastique situé de chaque coté du module va se fermer automatiquement
Volt
MSI Vous Rappelle...
La marque dorée doit ŕ peine ętre visible lorsque le module est
correctement installé.
Encoche
Panneau Arrière
Le panneau arrière procur eles connecteurs suivants :
Souris
Clavier
COM Port
Parallèle
1394 Port
SPDIF
Out
(Coaxial)
LAN
Ports USB
LAN
L-In
L-Out
Mic
RS-Out
CS-Out
SPDIF Out
(Optique)
F-16
Page 72

Manuel d’utilisation
Information Importante sur l’alimentation
Le chipset NForce est très sensible à l’ESD (Décharge Eléctrostatique). Ce
problème intevient la plupart du temps lorsque l’utilisateur change des modules de
mémoire lorsque le pc est en veille (S5) et que l’alimentation est toujours connectée.
Etant donné que les broches des modulmes de mémoire sont sensibles aux (ESD) le
remplacement de la mémoire dans ces conditions peut endomager le chipset et
l’empecher de booter correctement. Veuillez suivre les indications ci-dessous :
Débrancher le câble d’alimentation (voir fig. 1) ou débrancher les connecteurs
JPWR1 & JPWR2 (voir fig. 2 & 3) avant la première installation ou une mise à jour de
votre matériel.
Figure 1:
Débrancher l’alimentation
Débrancher l’alimentation JPWR1
Figure 2:
Débrancher l’alimentation JPWR2
Figure 3:
F-17
Page 73

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
Setup du BIOS
Allumez votre ordinateur, le système lance le processus de POST (Power
On Self Test). Quand le message ci-dessous apparaît à l’écran, appuyez sur le
bouton <DEL> pour entrer dans le setup.
Si le message disparaît avant que vous ne puissiez entrer dans le setup,
redémarrez votre ordinateur en appuyant sur le bouton RESET. Vous pouvez aussi
utiliser simultanément la combinaison de touches : <Ctrl>, <Alt>, et <Delete>.
Choix du premier élément de boot
Vous pouvez choisir le premier élément de boot sans entrer dans le setup,
pour cela il suffit d’appuyer sur la touche <F11> quand le message apparaît ŕ l’écran
(voir exemple ci-dessus).
Le message de POST passe trčs rapidement, si vous n’avez pas le temps
d’appuyer sur la touche <F11>, redémarrez votre PC et appuyez de nouveau sur
<F11> pendant 2 ou 3 secondes pour activer le menu de boot comme indiqué cidessous.
Floppy : 1st Floppy
IDE-0 : IBM-DTLA-307038
CDROM : ATAPI CD-ROM DRIVE 40X M
[Up/Dn] Select [RETURN] Boot [ESC] cancel
Le menu de boot va vous indiquer tous les éléments qui peuvent ętre selectionnés.
Choisir celui que vous voulez en utilisant les flčches pour vous déplacer et en
appuaynt sur <Enter> pour selectionner. Les systčme va alors booter ŕ partir de
cet élément. Cela ne change rien aux éléments du BIOS, le seul changement est
que lors du prochain démarrage, le boot se fera ŕ partir de cet élément.
Press DEL to enter SETUP
Select First Boot Device
Touches de Contrôle
<↑> Déplacement vers l’élement précédent
<↓> Déplacement vers l’élement suivant
<←> Déplacement vers l’élement de gauche
<→> Déplacement vers l’élement de droite
<Enter> Choisir l’élément
<Esc> Jumps to the Exit menu or returns to the main menu from a
<+/PU> Augmenter la valeur numérique
<-/PD> Diminuer la valeur numérique
<F7> Chargement du BIOS par défaut
<F9> Charger les valeurs du BIO S pour un système performant
<F10> Sauvegarde les changements et sortie de l’utilitaire
F-18
submenu
Page 74

Manuel d’utilisation
Menu Principal
Une fois entré dans Phoenix-Award® BIOS CMOS Setup Utility, le Menu
prinicpal appraît à l’écran. Utilisez les flèches pour vous diriger et appuyez sur
<Entrer> pour accéder aux sous-menus..
Standard CMOS Features
Cette fonction permet le paramétrage des éléments standards du BIOS.
Advanced BIOS Features
Cette fonction permet de paramétrer des éléments avancés du Bios.
Advanced Chipset Features
Cette option vous permet de paramétrer les éléments relatifs au registre
du chipset, permettant ainsi d’optimiser les performances de votre système.
Integrated Peripherals
Utilisez ce menu pour changer les choix relatifs aux périphériques intégrés.
Power Management Features
Utilisez ce menu afin de spécifier vos choix pour la gestion de l’energie.
PNP/PCI Configurations
Apparaît si votre système supporte PNP/PCI.
H/W/ Monitor
Voir les statuts des CPU, ventilateur, et alarme système.
Cell_Menu
Utilisez ce menu pour spécifier vos paramè tres pour la fréquence et le voltage des
CPU/DRAM/AGP.
F-19
Page 75

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Utilisez ce menu afin de charger les valeurs définies en usine pour le BIOS, offrant
ainsi des performances stables.
Load Optimized Defaults
Charge les paramètres optimum du BIOS sans affecter la stabilité du système.
BIOS Setting Password
Utilisez ce menu pour mettre un mot de passe BIOS.
Save & Exit Setup
Les modifications sont enregistrées dans le CMOS avant la sortie du setup
Exit Without Saving
Les modifications sont abandonnées avant la sorti du setup..
MSI Vous Rappelle...
Les descriptions de chaque catégorie du BIOS de ce chapitre sont
constamment mises à jour pour une meilleure performance du
système. La description peut par conséquent être légèrement
différente du dernier BIOS et doit uniquement servir de référence.
F-20
Page 76

Manuel d’utilisation
Configuration nVidiA RAID
Configuration nVidiaRAID
Appuyez sur <Enter> afin d’entrer dans le menu et que l’écran ci-dessous
apparaissent :
RAID Enabled
Cet élément est utiliser pour activer/désactiver la fonction RAID. En position
activer les différents champss eront accessibles. Les options : [Enabled],
[Disabled].
IDE Primary/ Secondary Master/Slave RAID
Cete fonction permet à l’utilisateur d’activer/désactiver la fonction RAID pour
chaque disque dur IDE. Options : [Enabled], [Disabled].
SATA1/ SATA2/ SATA3/ SATA4 RAID
Cette fonction permet à l’utilisateur d’activer/désactiver la fonction RAID pour
chaque disque SATA. Les options sont : [Enabled], [Disabled].
F-21
Page 77

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
H/W Monitor
Ce chapitre vous montre le statut du CPU, ventilateur, etc. Monitor function is
available only if there is hardware monitoring mechanism onboard.
Chassis Intrusion Detect
Active ou désactive le dispositif d’intrusion du boitîer. Lors d’une intrusion il y a un
message d’erreur qui apparaît. Pour éffacer ce message il faut choisir Reset. De
façon automatique, cet élément va se remettre en Enabled (actif). Les choix sont :
Enabled, Reset et Disabled.
Smart CPU Fan Target
Le BIOS Procure un système qui permet de contrôler la vitesse des ventilateurs en
fonction de la température. Paramètres: [Enabled], [Disabled].
Smart CPU Fan Tolerance
Vous pouvez choisir une valeur de tolérance pour le ventilateur. En effet si la
température du système dépasse celle que vous aurez indiqué, alors les ventilateurs
tourneront plus rapidement pour faire diminuer la température du système. A l’inverse
si la température descend en dessous du seuil indiqué alors les ventilateurs tourneront
moins vite tout en assurant la stabilité du système.
PC Health Status
Appuyez sur <Enter> et le menu apparaît.
Current System/CPU Temperature, SYSTEM/CPU Fan Speed, Vcore, +3.3V,
+12V, +5.0V, Battery, +5VSB
Ces éléments affichent les statuts des composants comme le CPU voltages,
temperatures et fan speeds.
F-22
Page 78

Manuel d’utilisation
Cell Menu
Ce Chapitre inclus des paramètres importants sur le CPU, AGP, DRAM et les
fonctions d’overclocking.
MSI Vous Rappelle...
Vous pouvez changer ces paramètres uniquement si vous êtes
familiarisés avec le chipset
Current CPU / DDR Clock
Ces deux fonctions montrent l’horloge du CPU & DDR. A lire uniquement
DRAM Configuration
Appuyez sur <Enter> pour faire apparaître le menu suivant :
Timing Mode
Ce champ a la capacité de détecter automatiquement le DRAM timing. En
sélectionnant [Manual], les champs suivants seront séléctionnables. Paramètres:
[Auto], [Manual].
F-23
Page 79

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
User Config mode
Ce paramètre permet de détecter automatiquement les 4 paramčtres ci-dessous.
En position [Manual], le champs sera selectionnable. Les choix : [Auto], [Manual].
S/W & H/W memory hole Remapping
Ce paramètre permet aux matériels/logiciels d’utiliser la mémoire à une adresse
supérieure à 00E0. (Uniquement valable avec un systčme d’exploitation 64-bit).
Les options: [Disabled], [Enabled].
MTRR Mapping Mode
Cet élément permet de contrôler le mode MTRR mapping. Les options : [Disabled],
[Continuous].
High Performance Mode
Cet élément vous permet de sélectionner le timing de la DDR. En position [Optimized]
cela active automatiquement Adjust DDR Memory Frequency pour ętre déterminé
par le SPD. Choisir [Manual] permet ŕ l’utilisateur de configurer manuellement les
différents champs. Options: [Optimized], [Manual].
Aggressive timing
Cet élément permet d’activer/désactiver le memory clock. En position [Enabled] le
timing mémoire est réduit pour augmenter les performances. Options: [Enabled],
[Disabled].
Dynamic Overclocking
Le DOT (Dynamic Overclocking Technology) est une fonction d’overclocking
automatique inclus dans les derniers produits équipés de la technologie CoreCell
TM
Cette fonction permet de détecter la charge de travail du CPU et d’adapter la fréquence
en conséquence. Normallement cette technologie DOT (Dynamic Overclocking
Technology) ne fonctionne que lors de l’utilisation de fonctions 3D (jeux...) lorsque le
CPU nécessite une augmentation de ses capacités.
Options :
.
[Disabled] Désactive la fonction d’overclocking dynamique.
[Private] 1er niveau d’overclocking, augmente la fréquence de 1%.
[Sergeant] 2ème niveau d’overclocking, augmente la fréquence de 3%.
[Captain] 3ème niveau d’overclocking, augmente la fréquence de 5%.
[Colonel] 4ème niveau d’overclocking, augmente la fréquence de 7%.
[General] 5ème niveau d’overclocking, augmente la fréquence de 9%.
[Commander] 6ème niveau d’overclocking, augmente la fréquence de 11%.
F-24
Page 80

Manuel d’utilisation
MSI Vous Rappelle...
Même si la fonction de DOT est un overclocking plus stable, cela
reste une opération risquée. Nous suggérons de vérifier que votre
CPU peut supporter cet overclocking. Si le PC devient instable ou
rebott, il est alors préférable de réduire le niveau d’overclocking ou
de désactiver la fonction. Pour un overclocking manuel, il est
nécessaire de désactiver en premier lieu cette fonction.
Adjust CPU FSB Frequency
Cet élément permet de sélectionner la fréquence FSB du CPU (en MHz). Choisir un
nombre entre [200]~[400] selon les besoins.
HT Width
Cet élément permet de régler le HT Width entre le CPU & Chip.La marque ↑ signifie Chip
vers CPU HT Width. Et la marque ↓ signifie CPU vers Chip HT Width. Options: [ ↓ 8 ↑ 8],
[ ↓ 16 ↑ 8], [↓ 8 ↑16], [ ↓16 ↑16].
CPU Spread Spectrum
Cet élément est utilisé pour activer/désactiver la fonction CPU Spread Spectrum. Lors
de l’overclocking CPU, toujours mettre en position [Disabled]. Options: [Center Spread],
[Disabled].
SATA Spread Spectrum
Cet élément est utilisé pour activer/désactiver la fonction SATA Spread Spectrum.
Options: [Disabled], [Down Spread].
PCIE Spread Spectrum
Cet élément est utilisé pour activer/désactiver la fonction CPU Spread Spectrum
feature. Lors de l’overclocking CPU, toujours mettre en possition [Disabled]. Options:
[Disabled], [Down Spread].
PCIE Clock
Cet élément permet de sélectionner la fréquence d’horloge du PCIE Bus clock (en
MHz). Choisir une valeur enrtre [100]~[145] selon les besoins.
K8 CPU SSE/ SSE2 Instructions
Cet élément active/désactive les instructions SSE/SSE2. Le SSE (Streaming SIMD
Extensions) est introduit avec les processeurs Pentium III. Les extensions SSE consistent en un nouveau jeu d’instructions pour le registre. Ces fonctions sont
développées pour des instructions simples ou multiples (SIMD).
F-25
Page 81

Carte Mère ATX MS-7100
Les SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) sont introduites avec les processeurs
Pentium 4 et Intel Xeon. Elles consistent en de nouveaux jeux d’instructions qui
fonctionnent avec les registres XXM et MXCSR pour améliorer les performances
SIMD des opérations en virgules flottantes et en valeurs intégrées. Plusieurs de ces
nouvelles instructions fonctionnent avec le registre MMX. Options: [Enabled],
[Disabled].
Cool’n’Quiet control
Cette fonction est spécialement prévue pour les CPU AMD Athlon, elle procure une
fonction de détection de la température afin d’éviter la surchauffe CPU.
Options: [Disabled], [Auto].
MSI Vous Rappelle...
Pour assurer la stabilité de la fonction Cool'n'Quiet, il est recommandé
de toujours avoir de la mémoire sur le DIMM1.
Adjust CPU Ratio
Cet élément permet d’ajuster le ratio CPU. En position [Startup] cela permet au CPU
de fonctionner à la vitesse la plsu rapide détectée par le système. Options :
[Startup], [x4]~[x25].
Adjust CPU VID
Cet élément permet d’ajuster le CPU VID. En position [Startup] cela permet au CPU
de fonctionner à la vitesse VID par défaut détectée par le système. Options :
[Startup], [0.825V], [0.850V],[0.875V],~, [1.550V].
CPU Voltage
Cette fonction permet de changer le voltage du CPU.
Memory Voltage
Modifier le voltage DDR peut augmenter la vitesse de la DDR. Toute modification peut
entraîner une instabilité, c’est pourquoi il ne faut pas faire de changements
pour une utilisation prolongée.
NF4 Voltage
Voltage NF4 modifiable ici.
MSI Vous Rappelle...
Les valeurs sont indiquées avec des couleurs (CPU Voltage,
Memory Voltage and NF4 Voltage) cela permet de vérifier si ils
fonctionnent correctement..
Gris: Paramè tre par défaut
Jaune:Paramè tre haute performance
Rouge:Paramètre non recommandé, le système pourraît être
instable.
Changer le CPU Voltage, Memory Voltage and NF4 Voltage
peut entraîner des instabilités, nous ne recommandons pas
l’utilisation à long terme du système avec des paramètres modifiés.
F-26
Page 82

K8N Diamond
User’s Guide
Benutzerhandbuch
German
G-1
Page 83

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
G-2
Page 84

Benutzerhandbuch
Chapter 1. Getting
Started
K8N Diamond
Benutzerhandbuch
Danke, dass Sie das K8N Diamond (MS-7100) V1.X ATX
Mainboard gewählt haben. Das K8N Diamond Mainboard basiert
auf dem nVIDIA® nForce™4 SLI Chipsatz und ermöglicht somit ein
optimales und effizientes System. Entworfen, um den
hochentwickelten AMD® K8 Athlon 64 FX / Athlon 64 Prozessor
aufzunehmen, stellt das Mainboard K8N Diamond die ideale Lösung
zum Aufbau eines professionellen Hochleistungsdesktopsystems dar.
G-3
Page 85

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Mainboard Spezifikationen
CPU
† Unterstützt den Sockel-939 für AMD K8 Athlon 64 FX / Athlon 64 (Sockel939)
Prozessoren
† Unterstützt Prozessoren bis hin zum 4000+ Athlon FX55, oder höher
(Die neuesten Informationen zu unterstützten Prozessoren finden Sie unter http://
www.msi.com.tw/program/products/mainboard/mbd/pro_mbd_cpu_support.php)
Chipsatz
† nVIDIA nForce4 SLI
- HyperTransport Link zur AMD Athlon 64/Athlon 64 FX CPU
- HyperTransport unterstützt Geschwindigkeiten bis hin zu 1GHz (2000MT/s)
- Bietet 2 PCI Express x16/ x1 Schnittstellen
- Zwei unabhängige SATA Kontroller, für vier Laufwerke
- Zwei Fast ATA-133 IDE Kontroller
- IEEE802.3 nVIDIA MAC für 1000BASE-T
Hauptspeicher
† Unterstützt Zweikanal DDR 266/333/400, auf acht Speicherbänken für vier 184-
Pin DDR DIMMs
† Unterstützt einen maximalen Speicherausbau von bis zu 4GB
† Unterstützt 2,5V DDR SDRAM DIMM
(Um den letzten Stand bezüglich der unterstützten Speichermodule zu erhalten,
besuchen Sie bitte http://www.msi.com.tw/program/products/mainboard/mbd/
pro_mbd_trp_list.php.)
Steckplätze
† Zwei PCI Express x16 Sockel (erfüllen die PCI Express Bus Spezifikation V1.0a)
† Der zweite PCI Express x16 slot (PCI_E3), kompatibel mit PCI Express x 1
† Drei 32-bit Master PCI Bus Slots, einschließlich eines orangefarbenen, der auch
als Kommunicationssockel dienen kann
† Unterstützt 3,3V/5V PCI- Bus
Onboard IDE
† Ein im nVIDIA® nForce4 SLI Chipsatz enthaltener IDE Kontroller bietet für den
Festplatten- und CD-ROM-Zugriff PIO, Bus Mastering und Betrieb mit Ultra DMA
66/100/133
† Bis zu vier IDE Geräte anschließbar
Onboard SATA
† NV RAID unterstützt 4 SATA II Anschlüsse (SATA1-4), mit einer
Datenü bertragunsrate von bis zu 300 MB/s. Unterstützt die RAID- Modi 0, 0+1
und JBOD.
† Silicon Image’s SATARAID unterst ützt weitere 2 SATA II Ports (SATA5/6), mit
einer Datenübertragunsrate von bis zu 300 MB/s. Unterstützt die RAID- Modi 0
und 1.
G-4
Page 86

Benutzerhandbuch
USB Schnittstellen
† 10 USB Anschlüsse
- Kontrolliert durch den nForce4 SLI Chipsatz
- 4 Anschlüsse im hinteren Ein-/Ausgabebereich, 6 Anschlüsse über ein
externes Slotblech
NV RAID (Software)
† Unterstützt bis zu 4 SATA und 2 ATA133 Festplatten
-Bietet RAID 0 oder 1, 0+1, sowie JBOD
-RAID Funktionalität verfügbar für ATA133+SATA H/D oder 4 SATA Festplatten
Silicon Image’s SATARAID (Software) (Optional)
† Unterstützt RAID 0 oder 1 und multiple RAID Gruppierungen
† Unterstützt bis zu 2 SATA Geräte an einem einzelnen Kontroller
Dual LAN
† Unterstütz zwei LAN Buchsen
-1ste LAN unterstützt 10/100/1000 Fast Ethernet durch den nForce4 SLI
-2ter PCI Express LAN Anschluss unterstützt 10/100/1000 Fast Ethernet
durch den Marvell 88E8053
IEEE 1394 (Optional)
† Unterstützt bis zu drei 1394 ports (1 am hinteren Anschlusspaneel, 2 als
Stifblöcke). Übertragunsrate von bis zu 400Mbps
Audio
† Leistung pur mit Creative Sound Blaster 24Bits Hardwäreaudiolösung
-24-Bit / 96~192 KHz Audioqualität
-Bis zu 100 DB SNR Klarheit
-7.1- Kanal Ausgabe unterstützt, Dolby Digital Encoder
-Unterstützt digitale S/PDIF Schnittstelle
-Erfüllt die Spezifikation PCI 2.3
Peripherieanschlüsse onboard
† hierzu gehören:
-1 Anschluss für 1 Diskettenlaufwerk mit 360 KB, 720 KB, 1,2 MB, 1,44 MB
oder 2,88 MB.
-1 Serielle Schnittstelle (COM1)
-1 Parallele Schnittstelle, die die Betriebsmodi SPP/EPP/ECP unterstützt.
-1 Audio Buchse(5-in-1), koaxial/Glasfaser SPDIF Ausgang
-1 D-Bracket 2 Stiftleistenanschluss
-1 CD-Eingang als Stiftleiste
-3 IEEE 1394 (1 hintere / 2 vordere)
-10 USB 1.1/2.0 Anschlüsse (4 hintere / 6 vordere)
-1 IrDA Stiftleiste
G-5
Page 87

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
BIOS
† Das Mainboard- BIOS verfügt über “ Plug & Play”- Funktionalität, mit der
angeschlossene Peripheriegeräte und Erweiterungskarten automatisch erkannt
werden.
† Das Mainboard stellt ein Desktop - Management - Interface (DMI) zur
Verfügung, welches automatisch die Spezifikationen Ihres Mainboards
aufzeichnet.
† Unterstützt Systemstart über LAN, von USB 1.1 und 2.0 Geräten und SATA
Festplatte.
Abmessungen
† ATX Form Faktor (30,4 cm X 24,4 cm)
Montage
† 9 Montagebohrungen
MSI weist darauf hin ...
Um ein bootfähiges RAID Laufwerk unter Windows 2000 zu erzeugen,
wird Microsoft’s Windows 2000 Service Pack 4 (SP4) benötigt. Da der
Endanwender nicht ohne SP4 booten kann, muss eine kombinierte
Installations- CD erstellt werden, befor der Versuch unternommen
werden kann, das Betriebssystem auf ein bootfähiges RAID Laufwerk
zu installieren.
Entnehmen Sie bitte folgender Website, wie Sie eine kombinierte
Installations- CD erstellen:
http://www.microsoft.com/windows2000/downloads/servicepacks/
sp4/HFdeploy.htm
G-6
Page 88

Mainboard Layout
S_FAN1
NB_FAN1
FDD
1
SATA3
SATA5
SATA6
SATA4
SATA1
SATA2
Winbond W83627THF
CK8-04 SLI
BATT+DIMM 1
JPWR1
PCI Slot 3
PCI Slot 2
PCI Slot 1
AUD1
JUSB3
JUSB1
MSI
CoreCell
123
444456678
910111212121314151616181818191717
(Optional)
(Optional)
(Optional)
(Optional)
(Optional)
Benutzerhandbuch
Oben : Maus
Unten: Tastatur
Oben : Parallele Schnittstelle
Unten:
COM Port
1394 Port (optional)
SPDIF Ausgang
O: LAN Buchse
U: USB Anschluss
T: LAN Buchse (optional)
B: USB Anschluss
:
OLine-In
M:
Line-Out
:
UMic
:RS-Out
O
88E1111-RCJ
M:CS
-Out
:SPDIF
UAusgang
JCD1
88E8053-NNC
CREATIVE
Sound
Bluster
JPWR2
PCI _E3
J1394_1
PCI _E1
PCI_E4
(SLI Anschluss)
J1394_2
C_FAN1
VIA
Vt6306
nVIDIA
S_FAN2
JUSB2
DIMM 2
JCI1
DIMM 3
DIMM 4
JIR1
IDE 2
IDE 1
Sw1
JDB1
BI OS
JFP1
JLPC1
JFP2
K8N Diamond
(MS-7100 V1.X) ATX Mainboard
G-7
Page 89

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
ATX 24-Pin Stromanschluss: JPWR1 Hier können Sie ein ATX Netzteil
1
anschließen
ATX 12V Stromanschluss: JPWR2 Dieser 12V Stromanschluss wird
2
verwendet, um die CPU mit Stromzu versorgen.
Anschluss des Diskettenlaufwerks: FDD1 Das Mainboard verf ügt
3
über einen Standardanschluss für Diskettenlaufwerke mit 360 KB, 720 KB,
1,2 MB, 1,44 MB oder 2,88 MB Kapazität.
Stromanschlüsse für Lüfter: C_FAN1, S_FAN1, NB_FAN1 & S_FAN2
4
Diese Anschlüsse unterstützen aktive Systemlüfter mit + 12V
ATA 133 Festplattenanschlüsse: IDE1 & IDE2. Das Mainboard besitzt
5
einen 32-Bit Enhanced PCI IDE und Ultra DMA 66/100/133 Kontroller, der die
PIO Modi 0- 4 bereitstellt, Bus Mastering beherrscht und Ultra DMA 66/100/
133 Funktionalität bietet.
Serial ATA Anschlüsse gesteuert durch den nForce4 SLI: SATA1 /
6
SATA2 / SATA3 / SATA4 Die Einchip- Lösung dieses Mainboards ist der
nForce4 SLI, der die vier Serial ATA Anschlüsse SATA1~SATA4 unterstützt.
SATA1~SATA4 sind Serial ATA Hochgeschwindigkeitsschnittstellen. Jede
unterstützt Serial ATA mit einem Datendurchsatz von 300 MB/s.
Serial ATA Anschlüsse gesteuert durch den Silicon Image’s
7
SATARAID: SATA5 & SATA6 Der auf diesem Mainboard vorhandene
Silicon Image’s SATARAID unterstützt zwei weitere Serial ATA Anschlüsse
SATA5/ SATA6.SATA5 & SATA6 sind Serial ATA Hochgeschwindigkeitsschnittstellen. Jede unterstützt Serial ATA mit einem Datendurchsatz von
300 MB/s.
G-8
Gehäusekontaktschalter: JCI1 Dieser Anschluss wird mit einem 2-
8
poligen Kontaktschalter verbunden. Wird das Gehäuse geöffnet, wird der
Schalter geschlossen.
Frontpaneel Anschlüsse: JFP1 & JFP2 Das Mainboard verfügt über
9
zwei Anschlüsse für das Frontpaneel, diese dienen zum Anschluss der
Schalter und LEDs des Frontpaneels.
System
System
Schalter
LED
Reset
Schalter
10
JFP2
9
2
JFP1
1
Festplatten
CD- Eingang: JCD1 Hier kann das Audiokabel des CD-ROM Laufwerkes
10
LED
2
1
Lautsprecher
System
LED
8
7
angeschlossen werden.
Page 90

Benutzerhandbuch
D-BracketTM 2 Connector: JDB1 Das Mainboard verfügt über einen JDB1
11
Anschluss, der den Anschluss der D-Bracket™ 2 ermöglicht.
USB Vorderanschlüsse: JUSB1, JUSB2 & JUSB3 Das Mainboard
12
verfügt über drei Standard- USB- 2.0- Anschlüsse in Form der Stift- Blöcke
JUSB1 & JUSB2 & JUSB3.
Audioanschluss des Frontpaneels: AUD1 Der Audio Vorderanschluss
13
AUD1 ermöglicht den Anschluss von Audioein- und -ausgängen eines
Frontpaneels.
Infrarotmodul Stifleiste: JIR1 Gestattet den Anschluss eines
14
Infrarotmoduls. Sie müssen im BIOS die notwendigen Einstellungen
vornehmen, um die IR Funktion nutzen zu können. JIR1 erfüllt die
Anforderungen des “Intel Front Panel I/O Connectivity Design Guide.”
Taster zur CMOS Löschung: SW1 Auf dem Mainboard gibt es einen
15
sogenannten CMOS Speicher (RAM), der über eine Batterie gespeist wird
und die Daten der Systemkonfiguration enthält. Er ermöglicht es dem
Betriebssystem, mit jedem Einschalten automatisch hochzufahren. Wollen
Sie die Systemkonfiguration löschen, verwenden Sie hierfür SW1 (Clear
CMOS Button- Taster zur CMOS Löschung). Drücken Sie den Knopf in der
Mitte der Oberseite, um die Daten zu löschen.
16
IEEE 1394 Anschlüsse: J1394_1 & J1394_2 Das Mainboard verfügt über
zwei 1394 Stiftblöcke, die den Anschluss von 1394 Ports über ein
externes IEEE1394 Slotblech ermöglichen.
PCI Express Sockel Die PCI Express Slots verwenden eine serielle
17
Anschlusstechnologie, die sich durch eine hohe Bandbreite und eine
niedrige Anzahl an Pins auszeichnet und die AMD’s Plattform für
Hochleistungsdesktops untersützt, indem Sie die Vorzüge dieser Plattform
mit AMD Prozessoren kombiniert. Die PCI Express Architektur bietet eine
Hochleistungsgrafikinfrastruktur für Desktopplattformen, die die
Leistungsfähigkeit bestehender AGP8x Designs mit Übertragungsraten von
4.0 Gbit/Sek über eine PCI Express 16-fach Leitung für Grafikkarten
verdoppelt, während PCI Express 1-fach Übertragungsraten von 250 MBit/
Sek unterstützt.
18
PCI Slots Die PCI Steckplätze ermöglichen Ihnen den Einsatz von PCI-
Karten, um das System Ihren Anforderungen anzupassen. Stellen Sie vor
dem Einsetzen oder Entnehmen von Karten sicher, dass Sie den
Netzstecker gezogen haben.
19
NV SLI (Scalable Link Interface) Anschluss: PCI_E4 Das Mainboard
verfügt über einen NV SLI Anschluss, um die NV SLI Technologie nutzen zu
k ö nnen. Bei der NV SLI Technologie handelt es sich um eine
Hochleistungstechnologie, die erlaubt, die Grafikleistung zu erhöhen und zu
skalieren, indem sie es ermöglicht zwei GPU’s in einem System zu verwenden.
.
G-9
Page 91

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Hauptprozessor: CPU
Das Mainboard unterstützt AMD® Athlon64/ Athlon64 FX Prozessoren. Hierbei
setzt das Mainboard den CPU Sockel 939 ein, um den CPU- Einbau zu erleichtern.
Achten Sie beim Einbau bitte darauf, dass die CPU immer mit einem Kühlkörper
mit aktivem Prozessorlüfter versehen sein muss, um Überhitzung zu
vermeiden. Verfügen Sie über keinen Kühler, setzen Sie sich bitte mit Ihrem Händler
in Verbindung, um einen solchen zu erwerben und danach zu installieren, bevor Sie
Ihren Computer anschalten.
(Um die neuesten Informationen zu unterstützten Prozessoren zu erhalten, besuchen
Sie bitte http://www.msi.com.tw/program/products/mainboard/mbd/
pro_mbd_cpu_support.php)
MSI Reminds You...
Überhitzung
Überhitzung beschädigt die CPU und das System nachhaltig, stellen
Sie stets eine korrekte Funktionsweise des CPU Kühlers sicher, um
die CPU vor Überhitzung zu schützen.
CPU Wechsel
Stellen Sie während eines CPU-Wechsels immer sicher, dass das
ATX Netzteil ausgeschaltet ist und ziehen Sie zuerst den Netzstecker,
um die Unversehrtheit Ihrer CPU zu gewährleisten
Übertakten
Dieses Motherboard wurde so entworfen, dass es Übertakten unterstützt.
Stellen Sie jedoch bitte sicher, dass die betroffenen Komponenten mit
den abweichenden Einstellungen während des Übertaktens zurecht
kommen. Von jedem Versuch des Betriebes außerhalb der
Produktspezifikationen kann nur abgeraten werden. Wir übernehmen
keinerlei Garantie für die Schäden und Risiken, die aus
unzulässigem oder Betrieb jenseits der Produktspezifikationen
resultieren.
G-10
Page 92

CPU Einbau Sockel 939
Goldener
Goldener
Goldener
Richtige Platzierung
O
1.Bitte Schalten Sie das System
aus und ziehen Sie den Netzstecker, bevor Sie die CPU
einbauen.
2.Ziehen Sie den Hebel leicht
seitlich weg vom Sockel,
heben Sie ihn danach bis zu
einem Winkel von ca. 90° an.
3.Suchen Sie nach einem
goldenen Pfeil. Der goldene
Pfeil sollte auf das Hebelgelenk
zeigen. Die CPU passt nur in
der korrekten Aus-richtung.
4.Ist die CPU korrekt installiert,
sollten die Pins an der
Unterseite vollständig versenkt
und nicht mehr sichtbar sein.
Beachten Sie bitte, dass jede
Abweichunng von der
richtigen Vorgehensweise
beim Einbau Ihr Mainboard
dauerhaft beschädigen kann.
Gleitplatte
Pfeil
Pfeil
Pfeil
Hebel fnen
鐪
90 Grad
Benutzerhandbuch
der CPU
Falsche Platzierung
der CPU
5. Drücken Sie die CPU fest in
den Sockel und drücken Sie
den Hebel wieder nach unten
bis in seine Ursprungsstellung.
Da die CPU während des
Schließens des Hebels dazu
neigt, sich zu bewegen,
sichern Sie diese bitte
während des Vorgangs durch
permanenten Fingerdruck von
oben, um sicherzustellen, dass
die CPU richtig und vollständig
im Sockel sitzt.
G-11
Page 93

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Installation des AMD Athlon64 / Athlon 64 FX CPU Kühlersets
Wenn Sie die CPU einbauen, stellen Sie bitte sicher, dass Sie auf der
CPU einen Kühlkörper mit aktiven Prozessorlüfter anbringen, um
Überhitzung zu vermeiden. Verfügen Sie über keinen aktiven Prozessorlüfter mit
Kühlkörper, setzen Sie sich bitte mit Ihrem Händler in Verbindung, um einen solchen
zu erwerben und zu installieren, bevor Sie Ihren Computer anschalten.
1. Ziehen Sie die Schutzfolie von der
Klebstoffschicht der Rückplatte ab
2. Drehen Sie das Mainboard um und
bringen Sie die Rückplatte an der
geeigneten Stelle an.
3. Drehen Sie das Mainboard wieder
auf die Vorderseite und legen Sie
es auf einer ebenen Fläche ab.
Machen Sie die zwei Bohrungen
auf dem Mainboard ausfinding.
4. Richten Sie den Rückhaltemechanismus und die Rückplatte
aufeinander aus.
Sichern Sie beide mit zwei
Schrauben gegeneinander.
G-12
Rückhaltemechanismus
Page 94

Benutzerhandbuch
5. Setzen Sie das Kühlerset auf
den Rückhaltemechanismus.
Haken Sie zuerst ein Ende des
Haltebügels ein, dann drücken
Sie das andere Ende des Bügels
herunter, um das Kühlerset auf
dem Rückhaltemechanismus zu
befestigen.
6. Machen Sie den
Sicherungshebel, den
Sicherungshaken und den
Sicherungsbolzen ausfindig.
Heben Sie den Sicherungshebel
Sicherungshaken
7. Drücken Sie den Sicherungshebel
herab.
8. Stellen Sie sicher, dass der
Sicher-ungshaken den
Sicherungsbolzen des
Rückhaltemechanismus voll-
9.Verbinden Sie das Stromkabel des
CPU Lüfters mit dem Anschluss auf
dem Mainboard.
Sicherungshebel
Sicherungsbolzen
MSI weist darauf hin...
Es besteht Verletzungsgefahr, wenn Sie den Sicherungs-haken vom
Sicherungsbolzen trennen. Sobald der Sicher-ungshaken gelöst
wird, schnellt der Sicherungshaken sofort zurück.
G-13
Page 95

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Speicher
Das Mainboard bietet Platz für vier 184-pin DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Double InLine Memory Module) und unterstützt den Speicherausbau auf bis zu 4GB. Sie können
DDR266/333 oder 400 Module in die DDR DIMM Sockel einsetzen (DDR 1- 4).
Um den letzten Stand bezüglich der unterstützten Speichermodule zu erhalten,
besuchen Sie bitte http://www.msi.com.tw/program/products/mainboard/mbd/
pro_mbd_trp_list.php
DIMM1~4
(von oben nach
unten)
Einführung zu DDR SDRAM
DDR (Double Data Rate) SDRAM entspricht konventionellem SDRAM,
verdoppelt aber die Datenrate, indem in jedem Taktzyklus zweimal Daten
übertragen werden. Es werden im Gegensatz zu den 3,3 Volt des SDR SDRAMS
2,5 Volt verwendet, und ebenso statt einem 168- Pin Modul ein 184- Pin Modul. Die
hohe Speicherbandbreite macht DDR zur idealen Lösung für Hochleistungs- PCs,
Workstations und Server.
DDR Speicherzusammensetzung
Setzen Sie mindestens ein Speichermodul in einen Stecksockel. Jeder DIMM
Sockel unterstützt einen Speicherriegel mit maximal 1 GB. Gemäß Ihren Anforderungen
können Sie entweder ein- oder doppelseitige Module verwenden. Bitte beachten Sie,
dass jedes DIMM jeweils im Einkanal- DDR- Betrieb verwendet werden kann,
jedoch einige Regeln beachtet werden müssen, falls Sie sie im
Zweikanalbetrieb verwenden wollen. (Entnehmen Sie bitte der Tabelle unten die
Vorschläge zur Speicherbestückung). Sie können Speicherriegel unterschiedlichen
Typs und unterschiedlicher Größe in unterschiedlichen Speicherkanälen verwenden.
Es kann jedoch zu Stabilitätsproblemen kommen, falls Sie nicht Module gleichen
Typs und gleicher Größe im Zweikanalbetrieb verwenden. Bitte entnehmen Sie
der folgenden Tabelle detailliert geeignete Zweikanalanordnungen. Abweichende
Speicherzusammenstellungen, die unten nicht aufgeführt sind, funktionieren als
Einkanalspeicher.
G-14
Page 96

Benutzerhandbuch
GRÜN
DIMM1 (Kan. A) DIMM2 (Kan. B) DIMM3 (Kan.A) DIMM4 (Kan. B)Systemkapazität
128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 256MB~2GB
128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 512MB~4GB
MSI weist darauf hin...
-Zweikanal DDR funktioniert NUR in den 3 Kombinationen
-Bitte wählen Sie identische Module, um sie paarweise in die
-Bestücken Sie immer zuerst die GRÜNEN Sockel, zudem ist es in
-Dieses Mainboard unterstüzt NICHT den Einbau von
VIOLET
aufgeführt in der vorangegangenen Liste.
Zweikanalslots einzusetzen und VERWENDEN SIE KEINE drei
Module in drei Sockeln, sonst kommt es zu unvorhersehbaren
Fehlern.
hohem Maße empfehlenswert, keine Speichermodule in die
VIOLETTEN Sockel einzusetzen, solange die GRÜNEN
unbestückt sind.
Speichermodulen, die mit mehr als 18 IC’s (Integrierte
Schaltkreise) bestückt sind.
GRÜN
128MB~1GB 128MB~1GB 256MB~2GB
VIOLET
Liste empfohlener Speicherzusammensetzungen
DIMM Slots
Green Green
DIMM1
E
D
E -
D -
E
Purple
DIMM2 DIMM3 DIMM4
- -
-
-
-
E
-
D-
E -
D -
E
-
- - E E
D D
- -
E
D
E
D
- D D
E
D
Purple
-
-
-
-
-
E
D
Max Speed
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 333
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 400
DDR 333
E: Einseitig D: Doppelseitig
G-15
Page 97

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
Vorgehensweise beim Einbau von DDR Modulen
1. DDR DIMMs haben nur eine Kerbe in der Mitte des Moduls. Sie passen nur in
einer Richtung in den Sockel.
2. Setzen Sie den DIMM- Speicherbaustein senkrecht in den DIMM- Sockel, dann
drücken Sie ihn hinein, bis die goldenen Kontakte tief im Sockel sitzen.
3. Die Plastikklammern an den Seiten des DIMM- Sockels schließen sich
automatisch.
Volt
MSI weist darauf hin...
Die goldenen Kontakte sind kaum noch sichtbar, wenn die Module
richtig eingesetzt sind.
Kerbe
Hinteres Anschlusspaneel
Das hintere Anschlusspaneel verfügt über folgende Anschlüsse:
Maus
Tastatur
COM Port
Parallel
1394 Port
SPDIF
Ausgang
(Coaxial)
LAN
USB Ports
LAN
L-In
L-Out
Mic
RS-Out
CS-Out
SPDIF
Ausgang
(Optisch)
G-16
Page 98

Benutzerhandbuch
Wichtiger Hinweis in Bezug auf Probleme mit der
Stromversorgung
Der NForce Chipsatz ist gegenüber statischen Entladungen sehr empfindlich,
deswegen kommt es zu diesem Problem vornehmlich, wenn der Nutzer häufig
Speichermodule im Modus S5 (Strom aus) austauscht, und das Stromkabel während
des Tausches eingesteckt ist. Da einige Pins sehr empfindlich auf statische
Entladungen reagieren, kann dies dazu führen, dass der Chipsatz nicht mehr hochfährt.
Beachten Sie bitte die folgende Lösung, um diese Situation zu vermeiden.
Ziehen Sie vor der ersten Installation oder bei der Aufrüstung des Systems das
Netzkabel (dargestellt in Abbildung 1 - Amerikanischer Netzstecker!) oder ziehen Sie
die Stromstecker JPWR1 & JPWR2 ab, wie in Darstellung 2 und 3 gezeigt).
Darstellung 1:
Ziehen des Netzsteckers (USA)
Darstellung 2:
Abziehen des Stromsteckers
JPWR1
Darstellung 3:
Abziehen des Stromsteckers
JPWR2
G-17
Page 99

MS-7100 ATX Mainboard
BIOS Setup
Nach dem Einschalten beginnt der Computer den POST (Power On Self Test Selbstüberprüfung nach Anschalten). Sobald die Meldung unten erscheint,
drücken Sie die Taste <Entf>(<Del>) um das Setup aufzurufen.
Wenn die Nachricht verschwindet, bevor Sie reagieren und Sie möchten
immer noch ins Setup, starten Sie das System neu, indem Sie es erst AUS- und
danach wieder ANSCHALTEN, oder die “RESET”-Taste am Gehäuse betätigen. Sie
können das System außerdem neu starten, indem Sie gleichzeitig die Tasten
<Strg>,<Alt> und <Entf> drücken (bei manchen Tastaturen <Ctrl>,<Alt> und <Del>).
Selecting the First Boot Device
Sie können das Laufwerk, von dem zuerst versucht werden soll, das
Betriebssytem zu laden, auch ohne Aufruf des BIOS wählen, indem Sie <F11> drücken,
sobald die obige Meldung erscheint. Sie rufen damit das Bootmenü auf.
Es kann geschehen, dass die POST Meldungen so schnell durchlaufen, dass Sie
nicht rechtzeitig reagieren können. Sollte dies der Fall sein, führen Sie einen Neustart
durch und drücken Sie 2 bis 3 Sekunden später <F11>, um das Bootmenü, wie im
Folgenden dargestellt, aufzurufen.
Floppy : 1st Floppy
IDE-0 : IBM-DTLA-307038
CDROM : ATAPI CD-ROM DRIVE 40X M
[Up/Dn] Select [RETURN] Boot [ESC] cancel
Press DEL to enter SETUP
Select First Boot Device
Das Bootmenü zeigt alle bootf ähigen Geräte an. W ählen Sie eines unter
Verwendung der Pfeiltasten aus und drücken Sie die Eingabetaste (<Enter>), das
System booted daraufhin von dem gewählten Gerät. Diese Auswahl ändert nicht
die Einstellungen im BIOS Setup Utility, so dass beim nächsten Hochfahren des
Systems erneut das dort ursprünglich festgelegte primäre Gerät zum Booten
herangezogen wird.
Steuertasten
G-18
<↑> Vorhergehender Menüpunkt
<↓> Nächster Menüpunkt
<←> Ein Eintrag nach links
<→> Ein Eintrag nach rechts
<Eingaber> Auswahl eines Eintrages
<Esc> Menü verlassen oder Aufruf des Hauptmenüs aus
Untermenü
<+/Bild auf>Hochzählen eines Wertes oder Ändern
<-/Bild ab> Herunterzählen eines Wertes oder Änderns
<F7> Wählt Standardwerte für den stabilsten Betrieb
<F9> Wählt Standardwerte für den leistungsmaxim. Betrieb
<F10> Speichern aller Änderungen im CMOS u.Verlassen d. BIOS
Page 100

Benutzerhandbuch
The Main Menu
Nachdem Sie das Phoenix-Award® BIOS CMOS Setup Utility, aufgerufen
haben, erscheint das Hauptmenü. Es weist zwölf Setup- Funktionen und zwei
Arten das Menü zu verlassen auf. Verwenden Sie die Pfeiltasten, um im Menü zu
navigieren und drücken Sie die Eingabetaste (<Enter>), um ein Untermenü
aufzurufen.
Cell Menu
Hier können Sie die Einstellungen bezüglich Frequenz und Spannung von CPU und
AGP sowie zur Übertaktung vornehmen.
Standard CMOS Features
In diesem Menü können Sie die Basiskonfiguration Ihres Systems anpassen, so z.B.
die Uhrzeit, das Datum usw.
Advanced BIOS Features
Verwenden Sie diesen Menüpunkt, AWARD® spezifische weitergehende
Einstellungen an Ihrem System vorzunehmen.
Advanced Chipset Features
Verwenden Sie dieses Menü, um die Werte in den Chipsatzregistern zu ändern
und die Leistungsfähigkeit Ihres Systems zu optimieren.
Integrated Peripherals
Verwenden Sie dieses Menü, um die Einstellungen für integrierte Peripheriegeräte
vorzunehmen.
Power Management Setup
Verwenden Sie dieses Menü , um die Einstellungen für die Stromsparfunktionen
vorzunehmen.
PNP/PCI Configurations
Dieser Eintrag erscheint, wenn Ihr System Plug and Play- Geräte am PCI-Bus
unterstützt.
G-19
 Loading...
Loading...