Page 1

MSD Pro-Billet Chevrolet HEI Distributor
PN 8365
ONLINE PRODUCT REGISTRATION: Register your MSD product online and you’ll be entered
in our monthly 8.5mm Super Conductor Spark Plug Wire give-away! Registering your product
will help if there is ever a warranty issue with your product and helps the MSD R&D team create
new products that you ask for! Go to www.msdperformance.com/registration.
Important: Read these instructions before attempting the installation.
Parts Included:
1 - Pro-Billet Distributor, PN 8365
1 - Rotor, PN 84101
1 - Distributor Cap, PN 84111
1 - Coil Cover, PN 84022
1 - Digital HEAT Module, PN 83647
1 - Coil, PN 8225
1 - Advance Kit
1 - Gasket
WARNING: Before installing the MSD Distributor, disconnect the battery cables. When disconnect-
ing the battery cables, always remove the Negative (-) cable first and install it last.
TIMING FUNCTIONS
Before continuing with the installation, here are a few definitions you should be aware of:
Initial Timing: This is the base timing (also referred to as idle timing) of the engine before the
centrifugal advance begins.
1 - Tube of Gear Lubricant
1 - Vacuum Advance Lock-Out
2 - O-rings
1 - HEI Connector
2 - HEI Wiring Terminals
1 - HEI/Tach Connector
1 - Vacuum Advance Adjusting Kit
1 - Gray Tach Wire
Centrifugal Advance: The centrifugal (or mechanical) advance mechanism is made up of weights,
springs and an advance stop bushing. The amount and rate of advance that your distributor is capable
of is determined by the centrifugal timing. If you ever wish to lock out the centrifugal advance, refer
to the centrifugal advance section.
Note: MSD Distributors are supplied with the heavy (slow) advance springs and the 21° stop bushing
installed. This is to prevent detonation in certain applications. Review the information on pages
2-4 to determine the best advance curve for your application.
Total Timing: This is the total of the initial timing plus the centrifugal advance added together.
Example: 10° Initial + 25° centrifugal = 35° Total Timing. (When checking Total timing, disconnect
the vacuum canister and plug the vacuum source.)
Vacuum Advance: The vacuum advance will advance the timing up to 10° during partial throttle
driving (with 15 lbs of vacuum). The vacuum line should be routed to a ported vacuum outlet above
the throttle plates.
RPM LIMIT AND TACHOMETER INFORMATION
Tach Signal: The Pro-Billet HEI Distributor features a Gray Tach Output wire which provides a clean signal
for most tachometers and even some aftermarket fuel injection systems. The signal output
is a 12 volt square wave, 20° duty cycle. This wire is also responsible for programming the
built-in rev limiter.
M S D • W W W . M S D P E R F O R M A N C E . C O M • ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 5 2 0 0 • F A X ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 3 3 4 4
Page 2

2 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
PROGRAMMING THE REV LIMIT
The rev limiter of the HEAT module requires a tachometer to set the rev limit. The limit is programmed by running
the engine at half the desired rpm, then momentarily grounding the Gray tach output wire from the MSD. A
Gray jumper wire is supplied to connect to the tach with another tee-splice coming off to use for programming.
A switch may also be installed to ease adjustments of the limiter. The default rpm limit is 10,000 rpm.
CHOOSING AN ADVANCE CURVE
The function of the advance curve is to match the ignition timing to the burning rate of the fuel and speed
(rpm) of the engine. Any factor that changes the burning rate of the fuel or the engine speed can cause a
need for an ignition timing change. Figure 1 shows some of the factors that will affect engine timing.
FACTOR Advance Timing Retard Timing
For For
Cylinder Pressure Low High
Vacuum High Low
Energy of Ignition Low High
Fuel Octane High Low
Mixture (Air/Fuel) Rich Lean
Temperature Cool Hot
Combustion Chamber Shape Open Compact
Spark Plug Location Offset Center
Combustion Turbulence Low High
Load Light Heavy
Figure 1 Ignition Timing Factors.
As you can see from the chart, most factors will change throughout the range of the engine operation.
The timing mechanism of the distributor must make timing changes based on these factors.
Example: An engine has 11:1 compression with a high energy ignition. With the specifications given,
you will have to retard the timing for the high compression and high energy ignition. By comparing
the engine’s specifications against the chart, a usable timing guideline can be found. Engines with
a combination of items from both columns will require a timing that is set in the mid range.
Obviously a full technical explanation of correct ignition timing would be very complicated. The best
way to arrive at a suitable ignition curve for your engine is to use the Ignition Timing Factors Chart
as a guide and compare it to the Advance Graphs in Figure 4 until a suitable curve is found. When
selecting your advance curve, use detonation (engine ping) as an indicator of too much advance,
and a decrease in power as an indicator of too little advance.
TIPS ON SELECTING AN ADVANCE CURVE
• Use as much initial advance as possible without encountering excessive starter load.
• Start the centrifugal advance just above the idle rpm.
• The starting point of the centrifugal advance curve is controlled by the installed length and
tension of the spring.
• How quickly the centrifugal advance (slope) comes in is controlled by the spring stiffness. The
stiffer the spring, the slower the advance curve.
• The amount of advance is controlled by the advance bushing. The bigger the bushing, the
smaller the amount of advance.
M S D • W W W . M S D P E R F O R M A N C E . C O M • ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 5 2 0 0 • F A X ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 3 3 4 4
Page 3
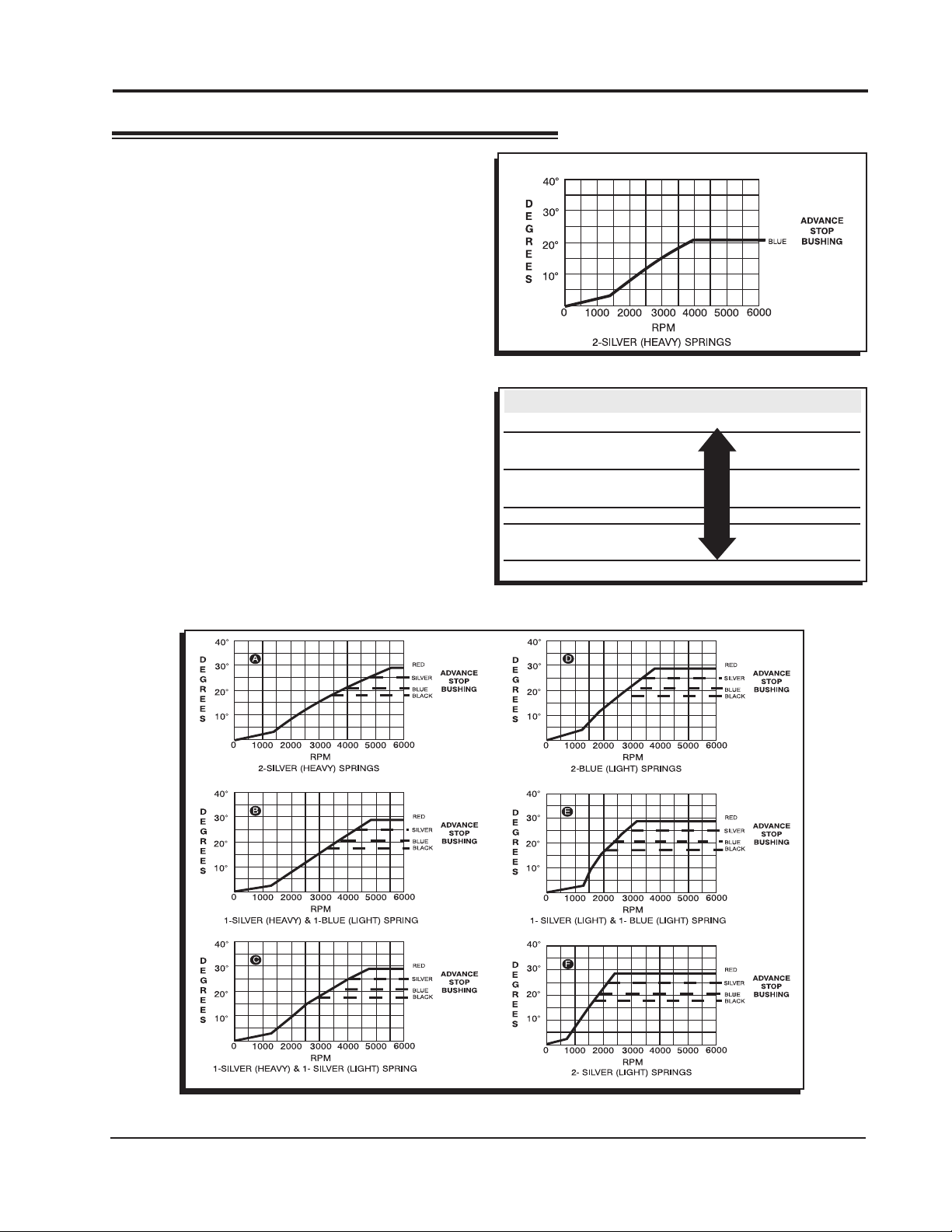
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS 3
CENTRIFUGAL ADVANCE CURVE
SELECTING THE ADVANCE SPRINGS
The rate, or how quick the advance comes in
is determined by the type of springs which are
installed on the distributor. The MSD distributors
are equipped with two Heavy Silver springs
installed. These will give you the slowest advance
curve possible (Figure 2). The parts kit contains
two additional sets of springs which can be used
to match the advance curve to your particular
application. Refer to the Spring Combination
Chart (Figure 3) for combinations that can be
achieved.
To change the springs, remove the cap and rotor
and use needlenose pliers to remove the springs.
Be sure the new springs seat in the groove on
the pin.
Timing Curve From Factory
Figure 2 The Factory Equipped Curve.
SPRING COMBINATION RATE OF ADVANCE FIGURE 4
2- Heavy Silver SLOWEST A
1- Heavy Silver B
1- Light Blue
1-Heavy Silver C
1-Light Silver
2- Light Blue D
1- Light Silver E
1- Light Blue
2- Light Silver FASTEST F
Figure 3 Spring Combination Chart.
Figure 4 Advance Curves.
M S D • W W W . M S D P E R F O R M A N C E . C O M • ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 5 2 0 0 • F A X ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 3 3 4 4
Page 4

4 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
SELECTING THE ADVANCE STOP
BUSHING
Three different advance stop bushings are supplied
in the distributor kit. The distributor comes with a
Blue (21°) bushing already installed. If a different
amount of centrifugal advance is desired, follow the
next procedure to change the bushings. The chart
in Figure 5 gives the size and approximate degrees
for the corresponding bushings.
CHANGING THE ADVANCE STOP
BUSHINGS
1. Remove the distributor cap and rotor.
2. Remove the locknut and washer on the bottom
of the advance assembly (Figure 6).
3. Remove the bushing and install the new one.
Install the washer and locknut.
LOCKING OUT THE CENTRIFUGAL
ADVANCE
1. Remove the advance components including the
springs, weights and the advance stop bushing
from the advance assembly.
2. Remove the roll-pin from the drive gear and
remove the gear from the shaft.
3. Slide the shaft two inches out of the housing.
4. Rotate the shaft 180° and insert the advance stop
bushing pin into the small hole on the advance
plate (Figure 7).
5. Install the locknut and washer to the advance stop
bushing pin. This locks the advance in place.
6. Install the drive gear and roll-pin.
BUSHING SIZE APPROXIMATE
CRANKSHAFT
DEGREES
Red-Smallest 28
Silver 25
Blue 21
Black-Largest 18
Figure 5 Advance Stop Bushing Chart.
Figure 6 Changing the Advance Stop Bushing.
Note: If you want to lock out the vacuum advance
of the Distributor, see page 7.
Figure 6 Locking Out the Centrifugal Advance.
Figure 7 Locking Out the Advance.
M S D • W W W . M S D P E R F O R M A N C E . C O M • ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 5 2 0 0 • F A X ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 3 3 4 4
Page 5

INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS 5
INSTALLING THE DISTRIBUTOR
1. Remove the existing distributor cap without
disconnecting any of the spark plug wires.
2. With the cap off, crank the engine until the
rotor is aimed at a fixed point on the engine or
firewall. Note this position by making a mark
(Figure 8).
3. Place the distributor cap back on and note
which plug wire the rotor is pointing to. MARK
THE SPARK PLUG WIRES and remove the
distributor cap.
4. Disconnect the wiring from the distributor.
5. Loosen the distributor hold down clamp and
slide the clamp out of the way.
6. Lift the distributor out of the engine. Note that
the rotor rotates as you lift the distributor out.
This is due to the helical cut gear and should
be taken into consideration when installing the
new distributor.
7. Install the gasket and apply a liberal amount of
the supplied lubricant to the distributor gear.
(The supplied O-rings can only be used if
the block has been modified as shown in
Figure 9.)
8. Install the distributor making sure that the
rotor comes to rest pointing at the same
fixed mark. If the distributor will not fully seat
with the rotor pointing to the marked position,
you may need to rotate the oil pump shaft
until the rotor lines up and the distributor fully
seats.
9. Position and tighten the hold down clamp onto
the distributor.
10. Install the distributor cap and spark plug wires
one at a time to ensure correct location.
11. Connect a switched 14-gauge wire from
a 12 volt source to the B+ terminal of the
Distributor Cap (Figure 10).
12. Page 7 shows how to set the rev limiter and
connect the tachometer.
Figure 8 Marking the Rotor Location.
Figure 9 Modified Block for use with O-Rings.
M S D • W W W . M S D P E R F O R M A N C E . C O M • ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 5 2 0 0 • F A X ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 3 3 4 4
Page 6

6 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
REMOVE MODULE AND
INSTALL HARNESS
BLACK
GROUND
TO ENGINE
GROUND
BLACK
GRAY
Figure 10 General Wire Installation.
M S D • W W W . M S D P E R F O R M A N C E . C O M • ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 5 2 0 0 • F A X ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 3 3 4 4
Figure 11 Wiring to an MSD Ignition Control.
Page 7

INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS 7
VACUUM ADVANCE LOCKOUT
If you do not want to use the vacuum advance canister,
MSD has supplied a lockout mechanism.
1. Remove the three Phillips screws that hold the
advance canister (Figure 12).
2. Remove the aluminum hex shaped spacer from
the housing.
3. Install the longer hex spacer supplied in the parts
bag in the threaded hole next to where the original
spacer was mounted. Use the same Phillips
screw.
4. Install the plastic cover to seal the distributor
HEX
SPACER
Figure 12 Removing the Vacuum Canister.
CANISTER
SCREWS
housing using the original advance hold down
screws (Figure 13).
LOCKOUT
Note: Do not forget to plug the original vacuum
COVER
advance hose.
VACUUM ADVANCE ADJUSTMENT
A kit is supplied that allows you to adjust the total
amount of vacuum advance.
TACHOMETER INFORMATION
The HEAT Digital HEI Module has a Gray wire that
provides a 12 volt square wave, 20° tachometer signal
that will trigger most tachometers. It is recommended
to connect this lead to your tach’s trigger input wire
VACUUM ADVANCE HOLE
(NOT USED)
Figure 13 Vacuum Lockout Installed.
and check its operation. If the tach requires a higher
voltage signal, connect its input wire to the Tach
terminal on the HEI Cap (Coil-/Tach).
No Rev Limit: To disable the rev limit function, cut and remove the
jumper shown in Figure 14.
PROGRAMMING THE REV LIMIT
A tachometer is required to set the rev limit. The limit is programmed
by running the engine at half the desired rpm, then momentarily
grounding the Gray tach output wire from the MSD. A Gray jumper
wire is supplied to connect to the tach with another tee-splice
coming off to use for programming. A switch may also be installed
to ease adjustments of the limiter (Figure 15). The default rpm limit
is 10,000 rpm. Note that the rpm limiter is extremely accurate and
due to the variety of tachometers available, there may be differences
in the displayed rpm.
1. Start the engine and bring the rpm to half the desired rev limit
(for a 6,000 rpm limit, raise the rpm to 3,000).
2. While holding the rpm steady, short the Gray tach wire to ground
for approximately one second. Note that the tach will go to zero
while grounded.
3. The tach will now display the programmed rev limit amount for
two seconds. If this value does not register on the tach, repeat
the procedure and try a different ground source.
LONGER
HEX SPACER
JUMPER
Figure 14 Disable the Rev Limit.
OPTIONAL
PROGRAMMING
SWITCH
TO
TACH
Figure 15 Setting the Rev Limiter.
JUMPER GRAY
M S D • W W W . M S D P E R F O R M A N C E . C O M • ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 5 2 0 0 • F A X ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 3 3 4 4
Page 8

Note: This rpm confirmation only displays when the HEI Gray wire is being used to trigger the
tachometer.
REV LIMITER VERIFICATION
The MSD HEAT HEI Module has an optional built-in Rev Limiter Verification feature. When the key
is in the On position (not cranking or running), an rpm signal is sent to the tachometer to verify the
unit's rev limit setting. With this function users can be sure of their rev limit settings before each drive
To enable this feature, follow the procedure below.
Note: It is important to note that this feature should not be used with EFI systems. When activated,
an rpm signal is sent to the tachometer. With an aftermarket EFI system, this could activate the
injectors causing a flooding situation.
ENABLE REV LIMIT VERIFICATION
1. With the ignition switch in the off position, ground the Gray tach output wire.
2. With the Gray wire connected to ground, turn the ignition on without starting the engine.
3. Hold the Gray tach output wire to ground for seven seconds. (AT LEAST five seconds.)
4. Release the wire from ground before ten seconds have passed.
5. To confirm the process has worked, cycle turn the key On. The tachometer should sweep to the
rpm limit set on the ignition.
To deactivate the verification feature, repeat the process.
Playback Tach: If you use a playback tach, be sure to check the high rpm value prior to turning the
key to the On position. When the key is in the On position, the rev limit will be displayed and may
override the tach memory.
Service
In case of malfunction, this MSD component will be repaired free of charge according to the terms of the warranty.
When returning MSD components for warranty service, Proof of Purchase must be supplied for verification. After
the warranty period has expired, repair service is based on a minimum and maximum fee.
All returns must have a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number issued to them before
being returned. To obtain an RMA number please contact MSD Customer Service at 1 (888) MSD-7859 or visit
our website at www.msdperformance.com/rma to automatically obtain a number and shipping information.
When returning the unit for repair, leave all wires at the length in which you have them installed. Be sure to include
a detailed account of any problems experienced, and what components and accessories are installed on the vehicle.
The repaired unit will be returned as soon as possible using Ground shipping methods (ground shipping is covered
by warranty). For more information, call MSD at (915) 855-7123. MSD technicians are available from 7:00 a.m. to
5:00 p.m. Monday - Friday (mountain time).
Limited Warranty
M
SD warrants this product to be free from defects in material and workmanship under its intended normal use*,
when properly installed and purchased from an authorized MSD dealer, for a period of one year from the date of
the original purchase. This warranty is void for any products purchased through auction websites. If found to be
defective as mentioned above, it will be repaired or replaced at the option of MSD. Any item that is covered under
this warranty will be returned free of charge using Ground shipping methods.
This shall constitute the sole remedy of the purchaser and the sole liability of MSD. To the extent permitted by
law, the foregoing is exclusive and in lieu of all other warranties or representation whether expressed or implied,
including any implied warranty of merchantability or fitness. In no event shall MSD or its suppliers be liable for special
or consequential damages.
*Intended normal use means that this item is being used as was originally intended and for the original application
as sold by MSD. Any modifications to this item or if it is used on an application other than what MSD markets the
product, the warranty will be void. It is the sole responsibility of the customer to determine that this item will work for
the application they are intending. MSD will accept no liability for custom applications.
M S D • W W W . M S D P E R F O R M A N C E . C O M • ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 5 2 0 0 • F A X ( 9 1 5 ) 8 5 7 - 3 3 4 4
© 2012 Autotr onic Controls C orpora tion
FRM30256 Revised 04/12 Printed in U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...