Motorola MCM69F618CTQ10R, MCM69F618CTQ12, MCM69F618CTQ8.5R, MCM69F618CTQ9, MCM69F618CTQ10 Datasheet
...
MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
64K x 18 Bit Flow–Through
BurstRAM Synchronous
Fast Static RAM
Order this document
by MCM69F618C/D
MCM69F618C
The MCM69F618C is a 1M–bit synchronous fast static RAM designed to provide a burstable, high performance, secondary cache for the 68K Family,
PowerPC, 486, i960, and Pentium microprocessors. It is organized as 64K
words of 18 bits each. This device integrates input registers, a 2–bit address
counter, and high speed SRAM onto a single monolithic circuit for reduced parts
count in cache data RAM applications. Synchronous design allows precise cycle
control with the use of an external clock (K). BiCMOS circuitry reduces the overall
power consumption of the integrated functions for greater reliability .
Addresses (SA), data inputs (DQx), and all control signals except output
enable (G
positive–edge–triggered noninverting registers.
Bursts can be initiated with either ADSP
addresses can be generated internally by the MCM69F618C (burst sequence
operates in linear or interleaved mode dependent upon the state of LBO
controlled by the burst address advance (ADV
Write cycles are internally self–timed and initiated by the rising edge of the
clock (K) input. This feature eliminates complex off–chip write pulse generation
and provides increased timing flexibility for incoming signals.
Synchronous byte write (SBx
chronous write enable SW
or to both bytes. The two bytes are designated as “a” and “b”. SBa
and SBb
are asserted with SW. Both bytes are written if either SGW is asserted or if all SBx
and SW are asserted.
For read cycles, a flow–through SRAM allows output data to simply flow freely
from the memory array .
The MCM69F618C operates from a 3.3 V power supply and all inputs and
outputs are L VTTL compatible and 5 V tolerant.
• MCM69F618C–8.5 = 8.5 ns Access / 12 ns Cycle
• Single 3.3 V + 10%, – 5% Power Supply
• ADSP
• Selectable Burst Sequencing Order (Linear/Interleaved)
• Internally Self–Timed Write Cycle
• Byte Write and Global Write Control
• 5 V Tolerant on all Pins (Inputs and I/Os)
• 100–Pin TQFP Package
) and Linear Burst Order (LBO) are clock (K) controlled through
or ADSC input pins. Subsequent burst
) and
) input pin.
), synchronous global write (SGW), and syn-
are provided to allow writes to either individual bytes
controls DQa
controls DQb. Individual bytes are written if the selected byte writes SBx
MCM69F618C–9 = 9 ns Access / 12 ns Cycle
MCM69F618C–10 = 10 ns Access / 15 ns Cycle
MCM69F618C–12= 12 ns Access / 16.6 ns Cycle
, ADSC, and ADV Burst Control Pins
TQ PACKAGE
TQFP
CASE 983A–01
The PowerPC name is a trademark of IBM Corp., used under license therefrom.
i960 and Pentium are trademarks of Intel Corp.
REV 2
2/18/98
Motorola, Inc. 1998
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
MCM69F618C
1
LBO
ADV
K
ADSC
ADSP
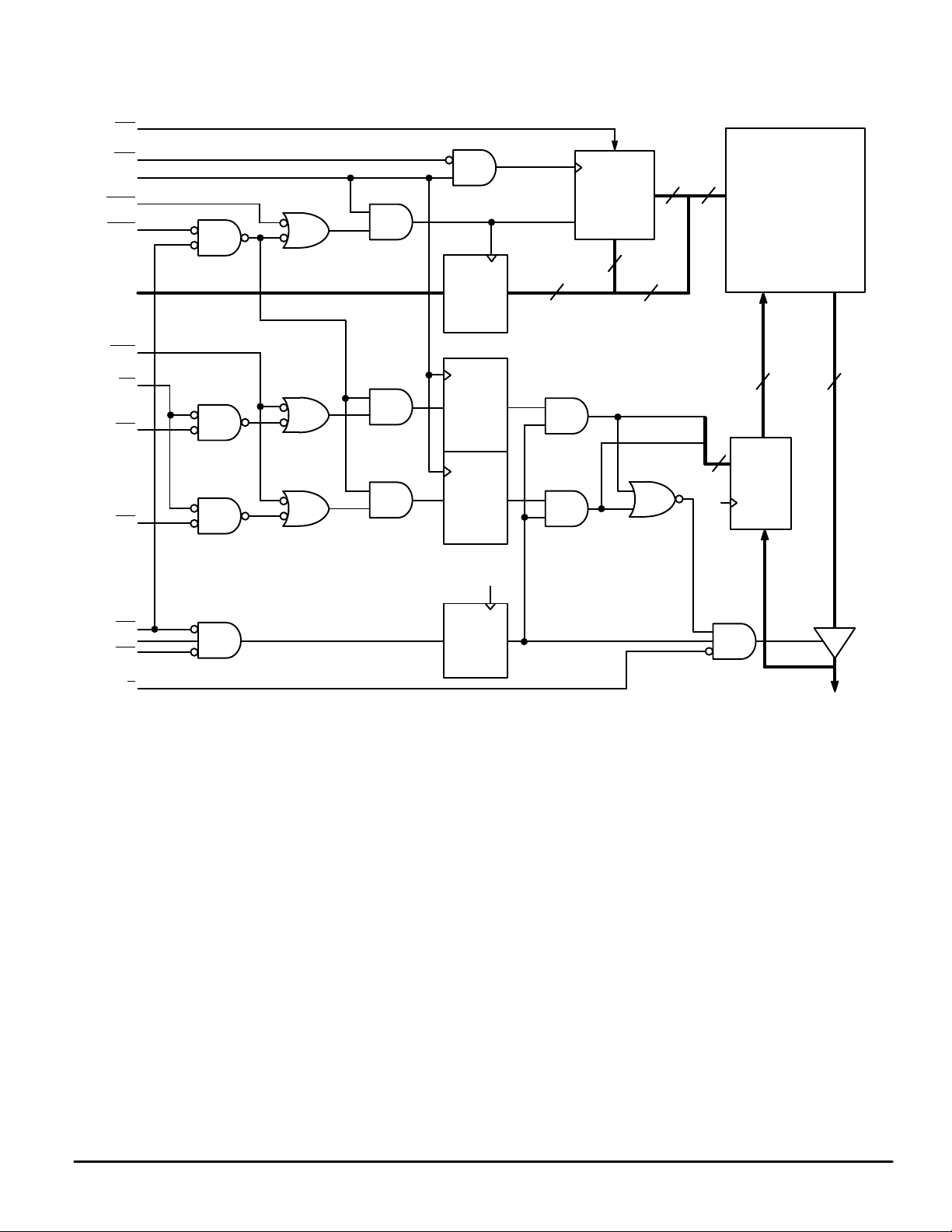
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
K2
BURST
COUNTER
CLR
2
16
64K x 18 ARRAY
SA
SA1
SA0
SGW
SW
SBa
SBb
SE1
SE2
SE3
G
ADDRESS
REGISTER
WRITE
REGISTER
a
WRITE
REGISTER
b
K2
ENABLE
REGISTER
16
2
14
18 18
2
DATA–IN
REGISTER
K
DQa, DQb
MCM69F618C
2
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
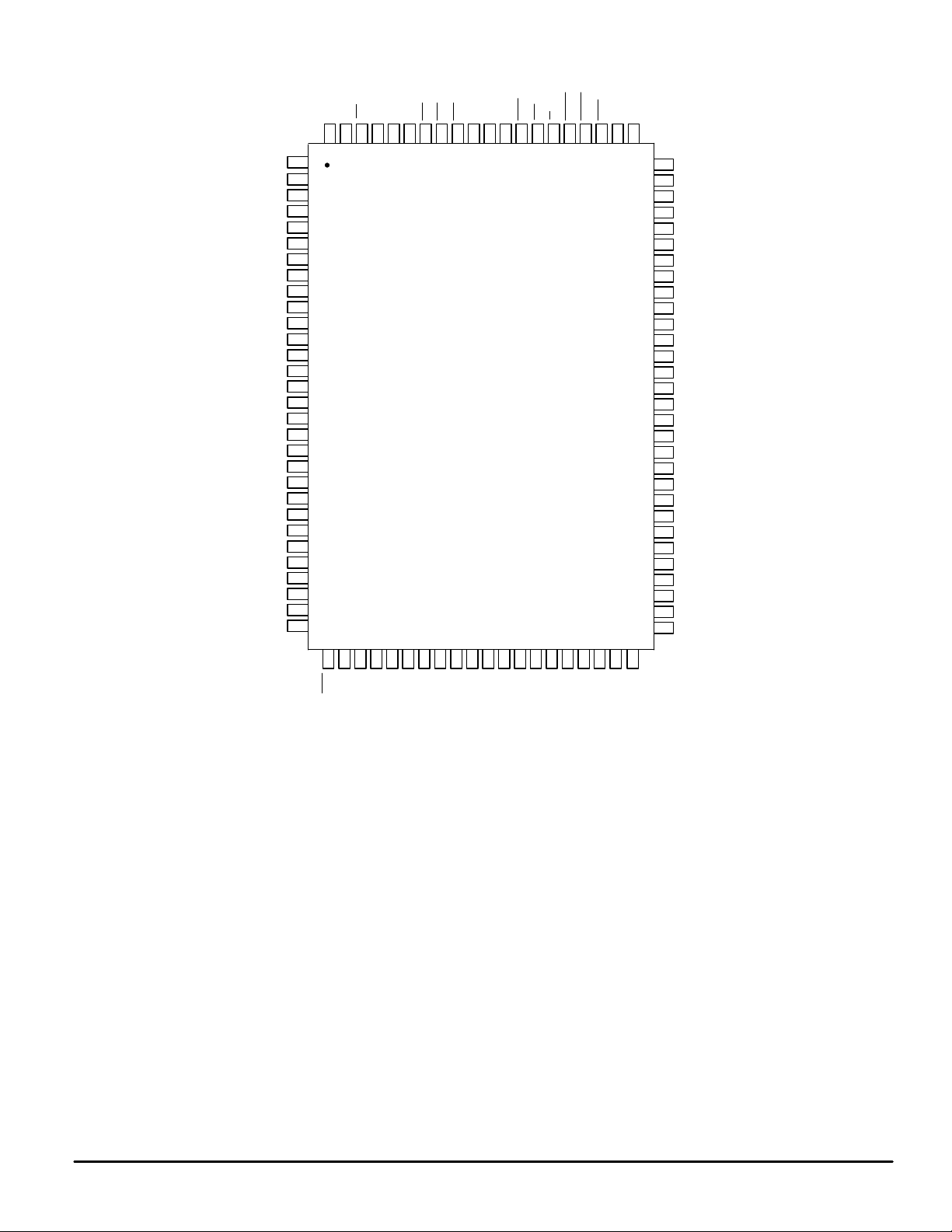
PIN ASSIGNMENT
NC
NC
NC
V
DD
V
SS
NC
NC
DQb
DQb
V
SS
V
DD
DQb
DQb
NC
V
DD
NC
V
SS
DQb
DQb
V
DD
V
SS
DQb
DQb
DQb
NC
V
SS
V
DD
NC
NC
NC
SASASE1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 32 33
SE2
NC
NC
SBb
94 9397 96 95 89 8892 91 90 86 8587100 99 98 81828384
37 3834 35 36 42 4339 40 41 45 4644
SBa
SE3
DD
VSSV
K
SGW
ADSC
ADV
SA
SA
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50494847
SA
NC
NC
V
DD
V
SS
NC
DQa
DQa
DQa
V
SS
V
DD
DQa
DQa
V
SS
NC
V
DD
NC
DQa
DQa
V
DD
V
SS
DQa
DQa
NC
NC
V
SS
V
DD
NC
NC
NC
ADSP
G
SW
SASASA
LBO
SA
SA1
SA0
SS
NCNCNC
DD
V
V
NC
SA
SASASA
SA
NC
NC
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
MCM69F618C
3
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Locations Symbol
85 ADSC Input Synchronous Address Status Controller: Initiates READ, WRITE or chip
84 ADSP Input Synchronous Address Status Processor: Initiates READ, WRITE or
83 ADV Input Synchronous Address Advance: Increments address count in
(a) 58, 59, 62, 63, 68, 69, 72, 73, 74
(b) 8, 9, 12, 13, 18, 19, 22, 23, 24
86 G Input Asynchronous Output Enable Input:
89 K Input Clock: This signal registers the address, data in, and all control signals
31 LBO Input Linear Burst Order Input: This pin must remain in steady state (this
32, 33, 34, 35, 44, 45, 46,
47, 48, 80, 81, 82, 99, 100
36, 37 SA1,SA0 Input Synchronous Address Inputs: these pins must be wired to the two LSBs
93, 94
(a) (b)
98 SE1 Input Synchronous Chip Enable: Active low to enable chip.
97 SE2 Input Synchronous Chip Enable: Active high for depth expansion.
92 SE3 Input Synchronous Chip Enable: Active low for depth expansion.
88 SGW Input Synchronous Global Write: This signal writes all bytes regardless of the
87 SW Input Synchronous Write: This signal writes only those bytes that have been
4, 11, 15, 20, 27, 41, 54,
61, 65, 70, 77, 91
5, 10, 17, 21, 26, 40, 55,
60, 67, 71, 76, 90
64 NC Input No Connection: There is no connection to the chip. For compatibility
1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 14, 16, 25, 28, 29, 30,
38, 39, 42, 43, 49, 50, 51, 52,
53, 56, 57, 66, 75, 78, 79, 95, 96
Type Description
deselect cycle.
chip deselect cycle (exception — chip deselect does not occur when
ADSP
is asserted and SE1 is high).
accordance with counter type selected (linear/interleaved).
DQx I/O Synchronous Data I/O: “x” refers to the byte being read or written
SA Input Synchronous Address Inputs: These inputs are registered and must
SBx Input Synchronous Byte Write Inputs: “x” refers to the byte being written (byte
V
DD
V
SS
NC — No Connection: There is no connection to the chip.
Supply Power Supply: 3.3 V + 10%, – 5%.
Supply Ground.
(byte a, b).
Low — enables output buffers (DQx pins).
High — DQx pins are high impedance.
except G
signal not registered or latched). It must be tied high or low.
Low — linear burst counter (68K/PowerPC).
High — interleaved burst counter (486/i960/Pentium).
meet setup and hold times.
of the address bus for proper burst operation. These inputs are
registered and must meet setup and hold times.
a, b). SGW
Negated high–blocks ADSP
status of the SBx
being used, tie this pin high.
selected using the byte write SBx
are being used, tie this pin low.
reasons, it is recommended that this pin be tied low for system designs
that do not have a sleep mode associated with the cache/memory
controller. Other vendors’ RAMs may have implemented this Sleep
Mode (ZZ) feature.
and LBO.
overrides SBx.
or deselects chip when ADSC is asserted.
and SW signals. If only byte write signals SBx are
pins. If only byte write signals SBx
MCM69F618C
4
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
 Loading...
Loading...