Page 1

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
µ MOTOROLA
nc...
I
MC68340
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Integrated Processor with DMA
User’s Manual
©MOTOROLA INC., 1992
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 2
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein to improve reliability, function or design. Motorola does not assume any
liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit described herein; neither does it convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of
others. Motorola products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or other
applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Motorola product could create a situation where personal
injury or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold
Motorola and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney
fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that
Motorola was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. Motorola and the are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an
Equal Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 3

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
PREFACE
The complete documentation package for the MC68340 consists of the MC68340UM/AD,
MC68340 Integrated Processor with DMA User’s Manual
Family Programmer’s Reference Manual,
Processor with DMA Product Brief
.
and the MC68340P/D,
, M68000PM/AD,
MC68340 Integrated
MC68000
MC68340 Integrated with DMA Processor User’s Manual
The
capabilities, registers, and operation of the MC68340; the
Reference Manual
Integrated Processor with DMA Product Brief
capabilities.
nc...
I
This user’s manual is organized as follows:
Section 1 Device Overview Section 8 Timer Modules
Section 2 Signal Descriptions Section 9 IEEE 1149.1 Test Access
Section 3 Bus Operation Port
Section 4 System Integration Module Section 10 Applications
Section 5 CPU32 Section 11 Electrical Characteristics
Section 6 DMA Controller Module Section 12 Ordering Information and
Section 7 Serial Module Mechanical Data
provides instruction details for the MC68340; and the
provides a brief description of the MC68340
68K FAX-IT
FAX 512-891-8593
cale Semiconductor,
The Motorola High-End Technical Publication Department provides a FAX number for you
to submit any questions and comments about this document. We welcome your
suggestions for improving our documentation or any questions concerning our products.
describes the programming,
MC68000 Family Programmer’s
MC68340
Frees
Please provide the part number and revision number (located in upper right-hand corner
on the cover), and the title of the document when submitting. When referring to items in
the manual please reference by the page number, paragraph number, figure number,
table number, and line number if needed. Reference the line number from the top of the
page.
When we receive a FAX between the hours of 7:30 AM and 5:00 PM EST, Monday
through Friday, we will respond within two hours. If the FAX is received after 5:00 PM or
on the weekend, we will respond within two hours on the first working day following receipt
of the FAX.
When sending a FAX, please provide your name, company, FAX number, and voice
number including area code (so we can talk to a real person if needed).
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 4

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
Section 1
Device Overview
1.1 M68300 Family.................................................................................................. 1-2
1.1.1 Organization.................................................................................................. 1-3
1.1.2 Advantages.................................................................................................... 1-3
1.2 Central Processor Unit..................................................................................... 1-3
1.2.1 CPU32............................................................................................................ 1-4
1.2.2 Background Debug Mode ........................................................................... 1-4
1.3 On-Chip Peripherals ........................................................................................ 1-5
1.3.1 System Integration Module ......................................................................... 1-5
1.3.1.1 External Bus Interface.............................................................................. 1-5
1.3.1.2 System Configuration and Protection ................................................... 1-6
1.3.1.3 Clock Synthesizer..................................................................................... 1-6
1.3.1.4 Chip Select and Wait State Generation............................................... 1-6
1.3.1.5 Interrupt Handling ..................................................................................... 1-6
1.3.1.6 Discrete I/O Pins........................................................................................ 1-6
1.3.1.7 IEEE 1149.1 Test Access Port................................................................ 1-7
1.3.2 Direct Memory Access Module................................................................... 1-7
1.3.3 Serial Module................................................................................................ 1-7
1.3.4 Timer Modules............................................................................................... 1-8
1.4 Power Consumption Management................................................................ 1-8
1.5 Physical.............................................................................................................. 1-9
1.6 Compact Disc-Interactive................................................................................ 1-9
1.7 More Information ............................................................................................... 1-10
Section 2
Signal Descriptions
2.1 Signal Index....................................................................................................... 2-2
2.2 Address Bus....................................................................................................... 2-4
2.2.1 Address Bus (A23–A0)................................................................................ 2-4
2.2.2 Address Bus (A31–A24) .............................................................................. 2-4
2.3 Data Bus (D15–D0) .......................................................................................... 2-4
2.4 Function Codes (FC3–FC0)............................................................................ 2-5
2.5 Chip Selects (
2.6 Interrupt Request Level (
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER'S MANUAL iii
CS3–CS0)................................................................................ 2-5
IRQ7, IRQ6, IRQ5, IRQ3)................................... 2-6
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 5

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev.1.0
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
2.7 Bus Control Signals ......................................................................................... 2-6
2.7.1 Data and Size Acknowledge (
2.7.2 Address Strobe (
2.7.3 Data Strobe (
2.7.4 Transfer Size (SIZ1, SIZ0).......................................................................... 2-7
2.7.5 Read/Write (R/
2.8 Bus Arbitration Signals .................................................................................... 2-7
2.8.1 Bu s Req ues t (
2.8.2 Bus Grant (
2.8.3 Bus Grant Acknowledge (
2.8.4 Read-Modify-Write Cycle (
2.9 Exception Control Signals .............................................................................. 2-8
2.9.1 Reset (
2.9.2 Halt (
2.9.3 Bus Error (
2.10 Clock Signals .................................................................................................... 2-8
2.10.1 System Clock (CLKOUT)............................................................................ 2-8
2.10.2 Crystal Oscillator (EXTAL, XTAL)............................................................... 2-9
2.10.3 External Filter Capacitor (XFC).................................................................. 2-9
2.10.4 Clock Mode Select (MODCK)..................................................................... 2-9
2.11 Instrumentation and Emulation Signals....................................................... 2-9
2.11.1 Instruction Fetch (
2.11.2 Instruction Pipe (
2.11.3 Breakpoint (
2.11.4 Freeze (FREEZE).......................................................................................... 2-10
2.12 DMA Module Signals ....................................................................................... 2-10
2.12.1 DMA Request (
2.12.2 DMA Acknowledge (
2.12.3 DMA Done (
2.13 Serial Module Signals..................................................................................... 2-11
2.13.1 Serial Crystal Oscillator (X2, X1)............................................................... 2-11
2.13.2 Serial External Clock Input (SCLK)........................................................... 2-11
2.13.3 Receive Data (RxDA, RxDB)....................................................................... 2-11
2.13.4 Transmit Data (TxDA, TxDB)....................................................................... 2-11
2.13.5 Clear to Send (
2.13.6 Request to Send (
2.13.7 Transmitter Ready (
2.13.8 Receiver Ready (
2.14 Timer Signals .................................................................................................... 2-12
2.14.1 Timer Gate (
2.14.2 Timer Input (TIN2, TIN1).............................................................................. 2-12
2.14.3 Timer Output (TOUT2, TOUT1)................................................................... 2-12
BG)............................................................................................... 2-7
RESET)............................................................................................... 2-8
HALT).................................................................................................... 2-8
BERR)........................................................................................... 2-8
BKPT)........................................................................................ 2-10
AS).................................................................................... 2-6
DS)........................................................................................... 2-7
W)........................................................................................... 2-7
BR).......................................................................................... 2-7
IFETCH).......................................................................... 2-9
IPIPE)............................................................................... 2-9
DREQ2, DREQ1)................................................................. 2-10
DACK2, DACK1)...................................................... 2-10
DONE2, DONE1)...................................................................... 2-10
CTSA, CTSB)..................................................................... 2-11
RTSA, RTSB)................................................................ 2-11
T≈RDYA)..................................................................... 2-11
R≈RDYA)......................................................................... 2-12
TGATE2, TGATE1)................................................................ 2-12
DSACK1, DSACK0)................................ 2-6
BGACK)............................................................. 2-7
RMC)................................................................. 2-8
iv MC68340 USER'S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 6

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
2.15 Test Signals ....................................................................................................... 2-13
2.15.1 Test Clock (TCK)........................................................................................... 2-13
2.15.2 Test Mode Select (TMS).............................................................................. 2-13
2.15.3 Test Data In (TDI).......................................................................................... 2-13
2.15.4 Test Data Out (TDO)..................................................................................... 2-13
2.16 Synthesizer Power (V
2.17 System Power and Ground (V
2.18 Signal Summary............................................................................................... 2-13
3.1 Bus Transfer Signals........................................................................................ 3-1
3.1.1 Bus Control Signals..................................................................................... 3-2
3.1.2 Function Code Signals ................................................................................ 3-3
3.1.3 Address Bus (A31–A0)................................................................................ 3-4
3.1.4 Address Strobe (
3.1.5 Data Bus (D15–D0) ...................................................................................... 3-4
3.1.6 Data Strobe (
3.1.7 Bus Cycle Termination Signals.................................................................. 3-4
3.1.7.1 Data Transfer and Size Acknowledge Signals
DSACK1 and DSACK0)..................................................................... 3-4
(
3.1.7.2 Bus Error (
3.1.7.3 Autovector (
3.2 Data Transfer Mechanism ............................................................................... 3-5
3.2.1 Dynamic Bus Sizing ..................................................................................... 3-5
3.2.2 Misaligned Operands................................................................................... 3-7
3.2.3 Operand Transfer Cases ............................................................................. 3-7
3.2.3.1 Byte Operand to 8-Bit Port, Odd or Even (A0 = X).............................. 3-7
3.2.3.2 Byte Operand to 16-Bit Port, Even (A0 = 0).......................................... 3-8
3.2.3.3 Byte Operand to 16-Bit Port, Odd (A0 = 1)........................................... 3-9
3.2.3.4 Word Operand to 8-Bit Port, Aligned..................................................... 3-9
3.2.3.5 Word Operand to 16-Bit Port, Aligned................................................... 3-10
3.2.3.6 Long-word Operand to 8-Bit Port, Aligned ........................................... 3-10
3.2.3.7 Long-Word Operand to 16-Bit Port, Aligned........................................ 3-12
3.2.4 Bus Operation................................................................................................ 3-14
3.2.5 Synchronous Operation with
3.2.6 Fast Termination Cycles .............................................................................. 3-15
3.3 Data Transfer Cycles........................................................................................ 3-16
3.3.1 Read Cycle..................................................................................................... 3-16
3.3.2 Write Cycle..................................................................................................... 3-18
3.3.3 Read-Modify-Write Cycle............................................................................. 3-19
DS)........................................................................................... 3-4
BERR)....................................................................................... 3-5
CCSYN
AS).................................................................................... 3-4
AVEC).................................................................................... 3-5
).......................................................................... 2-13
and GND)................................................ 2-13
CC
Section 3
Bus Operation
DSACK≈..................................................... 3-14
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER'S MANUAL v
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 7

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev.1.0
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
3.4 CPU Space Cycles........................................................................................... 3-21
3.4.1 Breakpoint Acknowledge Cycle ................................................................. 3-22
3.4.2 LPSTOP Broadcast Cycle ........................................................................... 3-23
3.4.3 Module Base Address Register Access.................................................... 3-27
3.4.4 Interrupt Acknowledge Bus Cycles............................................................ 3-27
3.4.4.1 Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle—Terminated Normally........................ 3-27
3.4.4.2 Autovector Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle............................................. 3-29
3.4.4.3 Spurious Interrupt Cycle.......................................................................... 3-30
3.5 Bus Exception Control Cycles ........................................................................ 3-32
3.5.1 Bus Errors....................................................................................................... 3-34
3.5.2 Retry Operation............................................................................................. 3-36
3.5.3 Halt Operation............................................................................................... 3-38
3.5.4 Double Bus Fault.......................................................................................... 3-39
3.6 Bus Arbitration ................................................................................................... 3-40
3.6.1 Bus Request................................................................................................... 3-43
3.6.2 Bus Grant........................................................................................................ 3-43
3.6.3 Bus Grant Acknowledge .............................................................................. 3-43
3.6.4 Bus Arbitration Control................................................................................. 3-44
3.6.5 Show Cycles.................................................................................................. 3-44
3.7 Reset Operation................................................................................................ 3-46
Section 4
System Integration Module
4.1 Module Overview.............................................................................................. 4-1
4.2 Module Operation............................................................................................. 4-2
4.2.1 Module Base Address Register Operation............................................... 4-2
4.2.2 System Configuration and Protection Operation .................................... 4-3
4.2.2.1 System Configuration.............................................................................. 4-5
4.2.2.2 Internal Bus Monitor................................................................................. 4-6
4.2.2.3 Double Bus Fault Monitor........................................................................ 4-6
4.2.2.4 Spurious Interrupt Monitor...................................................................... 4-6
4.2.2.5 Software Watchdog .................................................................................. 4-6
4.2.2.6 Periodic Interrupt Timer........................................................................... 4-7
4.2.2.6.1 Periodic Timer Period Calculation..................................................... 4-8
4.2.2.6.2 Using the Periodic Timer as a Real-Time Clock............................. 4-9
4.2.2.7 Simultaneous Interrupts by Sources in the SIM40............................. 4-9
4.2.3 Clock Synthesizer Operation...................................................................... 4-9
4.2.3.1 Phase Comparator and Filter................................................................. 4-11
4.2.3.2 Frequency Divider.................................................................................... 4-12
4.2.3.3 Clock Control ............................................................................................. 4-13
4.2.4 Chip Select Operation................................................................................. 4-13
4.2.4.1 Programmable Features.......................................................................... 4-14
vi MC68340 USER'S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 8

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
4.2.4.2 Global Chip Select Operation................................................................ 4-14
4.2.5 External Bus Interface Operation ............................................................... 4-15
4.2.5.1 Port A........................................................................................................... 4-15
4.2.5.2 Port B........................................................................................................... 4-16
4.2.6 Low-Power Stop ........................................................................................... 4-17
4.2.7 Freeze............................................................................................................. 4-17
4.3 Programming Model......................................................................................... 4-18
4.3.1 Module Base Address Register (MBAR)................................................... 4-20
4.3.2 System Configuration and Protection Registers ..................................... 4-21
4.3.2.1 Module Configuration Register (MCR).................................................. 4-21
4.3.2.2 Autovector Register (AVR)....................................................................... 4-23
4.3.2.3 Reset Status Register (RSR)................................................................... 4-23
4.3.2.4 Software Interrupt Vector Register (SWIV)........................................... 4-24
4.3.2.5 System Protection Control Register (SYPCR)..................................... 4-24
4.3.2.6 Periodic Interrupt Control Register (PICR)........................................... 4-26
4.3.2.7 Periodic Interrupt Timer Register (PITR)............................................... 4-27
4.3.2.8 Software Service Register (SWSR)...................................................... 4-28
4.3.3 Clock Synthesizer Control Register (SYNCR)........................................ 4-28
4.3.4 Chip Select Registers.................................................................................. 4-29
4.3.4.1 Base Address Registers.......................................................................... 4-30
4.3.4.2 Address Mask Registers.......................................................................... 4-31
4.3.4.3 Chip Select Registers Programming Example.................................... 4-33
4.3.5 External Bus Interface Control.................................................................... 4-33
4.3.5.1 Port A Pin Assignment Register 1 (PPARA1)....................................... 4-33
4.3.5.2 Port A Pin Assignment Register 2 (PPARA2)....................................... 4-34
4.3.5.3 Port A Data Direction Register (DDRA)................................................. 4-34
4.3.5.4 Port A Data Register (PORTA)................................................................ 4-34
4.3.5.5 Port B Pin Assignment Register (PPARB)............................................ 4-35
4.3.5.6 Port B Data Direction Register (DDRB)................................................. 4-35
4.3.5.7 Port B Data Register (PORTB, PORTB1).............................................. 4-35
4.4 MC68340 Initialization Sequence................................................................. 4-36
4.4.1 Startup............................................................................................................ 4-36
4.4.2 SIM40 Module Configuration ..................................................................... 4-36
4.4.3 SIM40 Example Configuration Code ........................................................ 4-38
Section 5
CPU32
5.1 Overview............................................................................................................. 5-1
5.1.1 Features.......................................................................................................... 5-2
5.1.2 Virtual Memory.............................................................................................. 5-2
5.1.3 Loop Mode Instruction Execution.............................................................. 5-3
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER'S MANUAL vii
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 9

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev.1.0
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
5.1.4 Vector Base Register.................................................................................... 5-4
5.1.5 Exception Handling ...................................................................................... 5-4
5.1.6 Addressing Modes........................................................................................ 5-5
5.1.7 Instruction Set................................................................................................ 5-5
5.1.7.1 Table Lookup and Interpolate Instructions........................................... 5-7
5.1.7.2 Low-Power STOP Instruction................................................................. 5-7
5.1.8 Processing States......................................................................................... 5-7
5.1.9 Privilege States ............................................................................................. 5-7
5.2 Architecture Summary..................................................................................... 5-8
5.2.1 Programming Model..................................................................................... 5-8
5.2.2 Registers......................................................................................................... 5-10
5.3 Instruction Set.................................................................................................... 5-11
5.3.1 M68000 Family Compatibility ..................................................................... 5-11
5.3.1.1 New Instructions........................................................................................ 5-11
5.3.1.1.1 Low-Power Stop (LPSTOP)................................................................ 5-11
5.3.1.1.2 Table Lookup and Interpolation (TBL).............................................. 5-12
5.3.1.2 Unimplemented Instructions ................................................................... 5-12
5.3.2 Instruction Format and Notation ................................................................. 5-12
5.3.3 Instruction Summary.................................................................................... 5-15
5.3.3.1 Condition Code Register ......................................................................... 5-20
5.3.3.2 Data Movement Instructions................................................................... 5-21
5.3.3.3 Integer Arithmetic Operations................................................................. 5-22
5.3.3.4 Logic Instructions ...................................................................................... 5-24
5.3.3.5 Shift and Rotate Instructions................................................................... 5-24
5.3.3.6 Bit Manipulation Instructions................................................................... 5-25
5.3.3.7 Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) Instructions.......................................... 5-26
5.3.3.8 Program Control Instructions .................................................................. 5-26
5.3.3.9 System Control Instructions .................................................................... 5-27
5.3.3.10 Condition Tests......................................................................................... 5-29
5.3.4 Using the TBL Instructions.......................................................................... 5-29
5.3.4.1 Table Example 1: Standard Usage ....................................................... 5-30
5.3.4.2 Table Example 2: Compressed Table.................................................. 5-31
5.3.4.3 Table Example 3: 8-Bit Independent Variable.................................... 5-32
5.3.4.4 Table Example 4: Maintaining Precision.............................................. 5-34
5.3.4.5 Table Example 5: Surface Interpolations ............................................. 5-36
5.3.5 Nested Subroutine Calls ............................................................................. 5-36
5.3.6 Pipeline Synchronization with the NOP Instruction................................ 5-36
5.4 Processing States............................................................................................. 5-36
5.4.1 State Transitions ........................................................................................... 5-37
5.4.2 Privilege Levels............................................................................................. 5-37
5.4.2.1 Supervisor Privilege Level...................................................................... 5-37
5.4.2.2 User Privilege Level ................................................................................. 5-39
viii MC68340 USER'S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 10

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
5.4.2.3 Changing Privilege Level........................................................................ 5-39
5.5 Exception Processing ...................................................................................... 5-39
5.5.1 Exception Vectors ......................................................................................... 5-40
5.5.1.1 Types of Exceptions................................................................................. 5-41
5.5.1.2 Exception Processing Sequence.......................................................... 5-41
5.5.1.3 Exception Stack Frame............................................................................ 5-42
5.5.1.4 Multiple Exceptions.................................................................................. 5-42
5.5.2 Processing of Specific Exceptions............................................................ 5-44
5.5.2.1 Reset........................................................................................................... 5-44
5.5.2.2 Bu s E r r or.. . . .... . . .... . . .... . . .... . . .... . . .... . . .... . . .... . . .... . . .... . .... . . ................................ 5-46
5.5.2.3 Address Error............................................................................................. 5-46
5.5.2.4 Instruction Traps........................................................................................ 5-47
5.5.2.5 Software Breakpoints............................................................................... 5-47
5.5.2.6 Hardware Breakpoints ............................................................................. 5-48
5.5.2.7 Format Error............................................................................................... 5-48
5.5.2.8 Illegal or Unimplemented Instructions.................................................. 5-48
5.5.2.9 Privilege Violations................................................................................... 5-49
5.5.2.10 Tracing........................................................................................................ 5-50
5.5.2.11 Interrupts..................................................................................................... 5-51
5.5.2.12 Return from Exception.............................................................................. 5-52
5.5.3 Fault Recovery............................................................................................... 5-53
5.5.3.1 Types of Faults.......................................................................................... 5-55
5.5.3.1.1 Type I—Released Write Faults........................................................... 5-55
5.5.3.1.2 Type II—Prefetch, Operand, RMW, and MOVEP Faults................. 5-56
5.5.3.1.3 Type III—Faults During MOVEM Operand Transfer....................... 5-57
5.5.3.1.4 Type IV—Faults During Exception Processing............................... 5-57
5.5.3.2 Correcting a Fault..................................................................................... 5-57
5.5.3.2.1 Type I—Completing Released Writes via Software....................... 5-57
5.5.3.2.2 Type I—Completing Released Writes via RTE ................................ 5-57
5.5.3.2.3 Type II—Correcting Faults via RTE.................................................... 5-58
5.5.3.2.4 Type III—Correcting Faults via Software .......................................... 5-58
5.5.3.2.5 Type III—Correcting Faults by Conversion and Restart................. 5-58
5.5.3.2.6 Type III—Correcting Faults via RTE................................................... 5-59
5.5.3.2.7 Type IV—Correcting Faults via Software......................................... 5-59
5.5.4 CPU32 Stack Frames.................................................................................. 5-60
5.5.4.1 Four-Word Stack Frame.......................................................................... 5-60
5.5.4.2 Six-Word Stack Frame............................................................................. 5-60
5.5.4.3 Bus Error Stack Frame............................................................................. 5-60
5.6 Development Support...................................................................................... 5-63
5.6.1 CPU32 Integrated Development Support ................................................ 5-63
5.6.1.1 Background Debug Mode (BDM) Overview........................................ 5-64
5.6.1.2 Deterministic Opcode Tracking Overview............................................ 5-64
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER'S MANUAL ix
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 11

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev.1.0
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
5.6.1.3 On-Chip Hardware Breakpoint Overview............................................. 5-64
5.6.2 Background Debug Mode ........................................................................... 5-65
5.6.2.1 Enabling BDM........................................................................................... 5-65
5.6.2.2 BDM Sources............................................................................................ 5-66
5.6.2.2.1 External
5.6.2.2.2 BGND Instruction.................................................................................. 5-66
5.6.2.2.3 Double Bus Fault.................................................................................. 5-66
5.6.2.3 Entering BDM............................................................................................ 5-66
5.6.2.4 Command Execution................................................................................ 5-67
5.6.2.5 BDM Registers........................................................................................... 5-67
5.6.2.5.1 Fault Address Register (FAR)............................................................. 5-67
5.6.2.5.2 Return Program Counter (RPC)......................................................... 5-67
5.6.2.5.3 Curre nt Instruction Program Counter (PCC).................................... 5-67
5.6.2.6 Returning from BDM................................................................................. 5-68
5.6.2.7 Serial Interface .......................................................................................... 5-68
5.6.2.7.1 CPU Serial Logic .................................................................................. 5-69
5.6.2.7.2 Development System Serial Logic.................................................... 5-71
5.6.2.8 Command Set ........................................................................................... 5-73
5.6.2.8.1 Command Format ................................................................................. 5-73
5.6.2.8.2 Command Sequence Diagram.......................................................... 5-74
5.6.2.8.3 Command Set Summary..................................................................... 5-75
5.6.2.8.4 Read A/D Register (RAREG/RDREG)................................................ 5-76
5.6.2.8.5 Write A/D Register (WAREG/WDREG).............................................. 5-77
5.6.2.8.6 Read System Register (RSREG)........................................................ 5-77
5.6.2.8.7 Write System Register (WSREG)....................................................... 5-78
5.6.2.8.8 Read Memory Location (READ)......................................................... 5-79
5.6.2.8.9 Write Memory Location (WRITE)........................................................ 5-79
5.6.2.8.10 Dump Memory Block (DUMP)............................................................ 5-80
5.6.2.8.11 Fill Memory Block (FILL)...................................................................... 5-82
5.6.2.8.12 Resume Execution (GO)...................................................................... 5-83
5.6.2.8.13 Call User Code (CALL)........................................................................ 5-83
5.6.2.8.14 Reset Peripherals (RST)...................................................................... 5-85
5.6.2.8.15 No Operation (NOP) ............................................................................. 5-85
5.6.2.8.16 Future Commands ................................................................................ 5-86
5.6.3 Deterministic Opcode Tracking .................................................................. 5-86
5.6.3.1 Instruction Fetch (
5.6.3.2 Instruction Pipe (
5.6.3.3 Opcode Tracking during Loop Mode.................................................... 5-88
5.7 Instruction Execution Timing........................................................................... 5-88
5.7.1 Resource Scheduling .................................................................................. 5-88
5.7.1.1 Microsequencer........................................................................................ 5-89
5.7.1.2 Instruction Pipeline ................................................................................... 5-89
BKPT Signal. ......................................................................... 5-66
IFETCH)...................................................................... 5-86
IPIPE)........................................................................... 5-87
x MC68340 USER'S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 12

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
5.7.1.3 Bus Controller Resources....................................................................... 5-89
5.7.1.3.1 Prefetch Controller................................................................................ 5-90
5.7.1.3.2 Write Pending Buffer............................................................................ 5-90
5.7.1.3.3 Microbus Controller .............................................................................. 5-91
5.7.1.4 Instruction Execution Overlap................................................................. 5-91
5.7.1.5 Effects of Wait States................................................................................ 5-92
5.7.1.6 Instruction Execution Time Calculation................................................ 5-92
5.7.1.7 Effects of Negative Tails.......................................................................... 5-93
5.7.2 Instruction Stream Timing Examples........................................................ 5-94
5.7.2.1 Timing Example 1—Execution Overlap................................................ 5-94
5.7.2.2 Timing Example 2—Branch Instructions.............................................. 5-95
5.7.2.3 Timing Example 3—Negative Tails....................................................... 5-96
5.7.3 Instruction Timing Tables............................................................................ 5-97
5.7.3.1 Fetch Effective Address........................................................................... 5-99
5.7.3.2 Calculate Effective Address .................................................................... 5-100
5.7.3.3 MOVE Instruction...................................................................................... 5-101
5.7.3.4 Special-Purpose MOVE Instruction....................................................... 5-101
5.7.3.5 Arithmetic/Logic Instructions ................................................................... 5-102
5.7.3.6 Immediate Arithmetic/Logic Instructions ............................................... 5-105
5.7.3.7 Binary-Coded Decimal and Extended Instructions............................ 5-106
5.7.3.8 Single Operand Instructions ................................................................... 5-107
5.7.3.9 Shift/Rotate Instructions........................................................................... 5-108
5.7.3.10 Bit Manipulation Instructions................................................................... 5-109
5.7.3.11 Conditional Branch Instructions ............................................................. 5-110
5.7.3.12 Control Instructions................................................................................... 5-111
5.7.3.13 Exception-Related Instructions and Operations.................................. 5-111
5.7.3.14 Save and Restore Operations ................................................................ 5-111
Section 6
DMA Controller Module
6.1 DMA Module Overview .................................................................................... 6-2
6.2 DMA Module Signal Definitions..................................................................... 6-4
6.2.1 DMA Request (
6.2.2 DMA Acknowledge (
6.2.3 DMA Done (
6.3 Transfer Request Generation......................................................................... 6-4
6.3.1 Internal Request Generation....................................................................... 6-4
6.3.1.1 Internal Request, Maximum Rate ........................................................... 6-5
6.3.1.2 Internal Request, Limited Rate............................................................... 6-5
6.3.2 External Request Generation..................................................................... 6-5
6.3.2.1 External Burst Mode ................................................................................. 6-5
DREQ≈)................................................................................ 6-4
DACK≈)...................................................................... 6-4
DONE≈)..................................................................................... 6-4
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER'S MANUAL xi
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 13

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev.1.0
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
6.3.2.2 External Cycle Steal Mode..................................................................... 6-5
6.4 Data Transfer Modes........................................................................................ 6-6
6.4.1 Single-Address Mode.................................................................................. 6-6
6.4.1.1 Single-Address Read............................................................................... 6-7
6.4.1.2 Single-Address Write ............................................................................... 6-9
6.4.2 Dual-Address Mode ..................................................................................... 6-12
6.4.2.1 Dual-Address Read .................................................................................. 6-12
6.4.2.2 Dual-Address Write.................................................................................. 6-14
6.5 Bus Arbitration ................................................................................................... 6-18
6.6 DMA Channel Operation................................................................................. 6-18
6.6.1 Channel Initialization and Startup ............................................................. 6-18
6.6.2 Data Transfers............................................................................................... 6-19
6.6.2.1 Internal Request Transfers...................................................................... 6-19
6.6.2.2 External Request Transfers..................................................................... 6-19
6.6.3 Channel Termination ................................................................................... 6-20
6.6.3.1 Channel Termination ............................................................................... 6-20
6.6.3.2 Interrupt Operation.................................................................................... 6-20
6.6.3.3 Fast Termination Option.......................................................................... 6-20
6.7 Register Description ......................................................................................... 6-22
6.7.1 Module Configuration Register (MCR)...................................................... 6-23
6.7.2 Interrupt Register (INTR).............................................................................. 6-26
6.7.3 Channel Control Register (CCR)............................................................... 6-26
6.7.4 Channel Status Register (CSR) ................................................................. 6-30
6.7.5 Function Code Register (FCR)................................................................... 6-32
6.7.6 Source Address Register (SAR)................................................................ 6-33
6.7.7 Destination Address Register (DAR)......................................................... 6-33
6.7.8 Byte Transfer Counter Register (BTC)...................................................... 6-34
6.8 Data Packing..................................................................................................... 6-35
6.9 DMA Channel Initialization Sequence ......................................................... 6-36
6.9.1 DMA Channel Configuration ...................................................................... 6-36
6.9.1.1 DMA Channel Operation in Single-Address Mode............................ 6-37
6.9.1.2 DMA Channel Operation in Dual-Address Mode............................... 6-37
6.9.2 DMA Channel Example Configuration Code.......................................... 6-38
Section 7
Serial Module
7.1 Module Overview.............................................................................................. 7-2
7.1.1 Serial Communication Channels A and B ............................................... 7-3
7.1.2 Baud Rate Generator Logic........................................................................ 7-3
7.1.3 Internal Channel Control Logic .................................................................. 7-3
7.1.4 Interrupt Control Logic................................................................................. 7-3
xii MC68340 USER'S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 14

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
7.1.5 Comparison of Serial Module to MC68681 ............................................. 7-4
7.2 Serial Module Signal Definitions................................................................... 7-4
7.2.1 Crystal Input or External Clock (X1).......................................................... 7-5
7.2.2 Crystal Output (X2)....................................................................................... 7-5
7.2.3 External Input (SCLK) .................................................................................. 7-6
7.2.4 Channel A Transmitter Serial Data Output (TxDA)................................. 7-6
7.2.5 Chan nel A Receiver Serial D ata Input (RxDA)........................................ 7-6
7.2.6 Channel B Transmitter Serial Data Output (TxDB)................................. 7-6
7.2.7 Chan nel B Receiver Serial D ata Input (RxDB)........................................ 7-6
7.2.8 Channel A Request-To-Send (
7.2.8.1
7.2.8.2 OP0.............................................................................................................. 7-6
7.2.9 Channel B Request-To-Send (
7.2.9.1
7.2.9.2 OP1.............................................................................................................. 7-7
7.2.10 Channel A Clear-To-Send (
7.2.11 Channel B Clear-To-Send (
7.2.12 Channel A Transmitter Ready (
7.2.12.1
7.2.12.2 OP6.............................................................................................................. 7-7
7.2.13 Channel A Receiver Ready (
7.2.13.1
7.2.13.2
7.2.13.3 OP4.............................................................................................................. 7-7
7.3 Operation............................................................................................................ 7-8
7.3.1 Baud Rate Generator................................................................................... 7-8
7.3.2 Transmitter and Receiver Operating Modes............................................ 7-8
7.3.2.1 Transmitter................................................................................................. 7-10
7.3.2.2 Receiver...................................................................................................... 7-11
7.3.2.3 FIFO Stack.................................................................................................. 7-12
7.3.3 Looping Modes ............................................................................................. 7-14
7.3.3.1 Automatic Echo Mode .............................................................................. 7-14
7.3.3.2 Local Loopback Mode............................................................................. 7-14
7.3.3.3 Remote Loopback Mode......................................................................... 7-14
7.3.4 Multidrop Mode............................................................................................. 7-15
7.3.5 Bus Operation................................................................................................ 7-17
7.3.5.1 Read Cycles............................................................................................... 7-17
7.3.5.2 Write Cycles ............................................................................................... 7-17
7.3.5.3 Interrupt Acknowledge Cycles................................................................ 7-17
7.4 Register Description and Programming....................................................... 7-17
7.4.1 Register Description ..................................................................................... 7-17
7.4.1.1 Module Configuration Register (MCR).................................................. 7-19
RTSA........................................................................................................... 7-6
RTSB........................................................................................................... 7-7
T≈RDYA...................................................................................................... 7-7
R≈RDYA...................................................................................................... 7-7
FFULLA....................................................................................................... 7-7
RTSA)...................................................... 7-6
RTSB)....................................................... 7-6
CTSA)........................................................... 7-7
CTSB)............................................................ 7-7
T≈RDYA)................................................. 7-7
R≈RDYA)..................................................... 7-7
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER'S MANUAL xiii
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 15

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev.1.0
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
7.4.1.2 Interrupt Level Register (ILR).................................................................. 7-21
7.4.1.3 Interrupt Vector Register (IVR)................................................................ 7-21
7.4.1.4 Mode Register 1 (MR1)............................................................................ 7-22
7.4.1.5 Status Register (SR)................................................................................. 7-24
7.4.1.6 Clock-Select Register (CSR) .................................................................. 7-26
7.4.1.7 Command Register (CR)......................................................................... 7-27
7.4.1.8 Receiver Buffer (RB)................................................................................. 7-30
7.4.1.9 Transmitter Buffer (TB)............................................................................. 7-30
7.4.1.10 Input Port Change Register (IPCR)........................................................ 7-31
7.4.1.11 Auxilia ry Control Regi ster (ACR)............................................................ 7-32
7.4.1.12 Interrupt Status Register (ISR)................................................................ 7-32
7.4.1.13 Interrupt Enable Register (IER)............................................................... 7-34
7.4.1.14 Input Port (IP)............................................................................................. 7-35
7.4.1.15 Output Port Control Register (OPCR).................................................... 7-35
7.4.1.16 Output Port Data Register (OP).............................................................. 7-37
7.4.1.17 Mode Register 2 (MR2)............................................................................ 7-37
7.4.2 Programming................................................................................................. 7-40
7.4.2.1 Serial Module Initialization ..................................................................... 7-40
7.4.2.2 I/O Driver Example.................................................................................... 7-40
7.4.2.3 Interrupt Handling ..................................................................................... 7-40
7.5 Serial Module Initialization Sequence ......................................................... 7-46
7.5.1 Serial Module Configuration ...................................................................... 7-46
7.5.2 Serial Module Example Configuration Code.......................................... 7-47
Section 8
Timer Modules
8.1 Module Overview.............................................................................................. 8-1
8.1.1 Timer and Counter Functions ..................................................................... 8-2
8.1.1.1 Prescaler and Counter............................................................................. 8-2
8.1.1.2 Timeout Detection..................................................................................... 8-2
8.1.1.3 Comparator................................................................................................ 8-2
8.1.1.4 Clock Selection Logic .............................................................................. 8-3
8.1.2 Internal Control Logic................................................................................... 8-3
8.1.3 Interrupt Control Logic................................................................................. 8-4
8.2 Timer Modules Signal Definitions ................................................................. 8-4
8.2.1 Timer Input (TIN1, TIN2).............................................................................. 8-5
8.2.2 Timer Gate (
8.2.3 Timer Output (TOUT1, TOUT2)................................................................... 8-6
8.3 Operating Modes.............................................................................................. 8-6
8.3.1 Input Capture/Output Compare .................................................................. 8-6
8.3.2 Square-Wave Generator ............................................................................. 8-8
TGATE1, TGATE2)................................................................ 8-6
xiv MC68340 USER'S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 16

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
8.3.3 Variable Duty-Cycle Square-Wave Generator........................................ 8-9
8.3.4 Variable-Width Single-Shot Pulse Generator......................................... 8-10
8.3.5 Pulse-Width Measurement.......................................................................... 8-12
8.3.6 Period Measurement.................................................................................... 8-13
8.3.7 Event Count................................................................................................... 8-14
8.3.8 Timer Bypass................................................................................................. 8-16
8.3.9 Bus Operation................................................................................................ 8-17
8.3.9.1 Read Cycles............................................................................................... 8-17
8.3.9.2 Write Cycles ............................................................................................... 8-17
8.3.9.3 Interrupt Acknowledge Cycles................................................................ 8-17
8.4 Register Description ......................................................................................... 8-17
8.4.1 Module Configuration Register (MCR)...................................................... 8-18
8.4.2 Interrupt Register (IR)................................................................................... 8-20
8.4.3 Control Register (CR)................................................................................... 8-20
8.4.4 Status Register (SR)..................................................................................... 8-23
8.4.5 Counter Register (CNTR)............................................................................ 8-25
8.4.6 Preload 1 Register (PREL1)........................................................................ 8-25
8.4.7 Preload 2 Register (PREL2)........................................................................ 8-26
8.4.8 Compare Register (COM)............................................................................ 8-26
8.5 Timer Module Initialization Sequence.......................................................... 8-27
8.5.1 Timer Module Configuration ....................................................................... 8-27
8.5.2 Timer Module Example Configuration Code ........................................... 8-28
Section 9
IEEE 1149.1 Test Access Port
9.1 Overview............................................................................................................. 9-1
9.2 TAP Controller ................................................................................................... 9-2
9.3 Boundary Scan Register................................................................................. 9-3
9.4 Instruction Register ........................................................................................... 9-9
9.4.1 EXTEST (000)............................................................................................... 9-10
9.4.2 SAMPLE/PRELOAD (001).......................................................................... 9-10
9.4.3 BYPASS (X1X, 101)..................................................................................... 9-11
9.4.4 HI-Z (100)....................................................................................................... 9-11
9.5 MC68340 Restrictions...................................................................................... 9-11
9.6 Non-IEEE 1149.1 Operation ........................................................................... 9-12
Section 10
Applications
10.1 Minimum System Configuration................................................................... 10-1
10.1.1 Processor Clock Circuitry .......................................................................... 10-1
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER'S MANUAL xv
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 17

11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev.1.0
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS (Concluded)
Paragraph Page
Number Title Number
10.1.2 Reset Circuitry............................................................................................. 10-3
10.1.3 SRAM Interface........................................................................................... 10-3
10.1.4 ROM Interface.............................................................................................. 10-4
10.1.5 Serial Interface ............................................................................................ 10-4
10.2 Memory Interface Information....................................................................... 10-5
10.2.1 Using an 8-Bit Boot ROM........................................................................... 10-5
10.2.2 Access Time Calculations ......................................................................... 10-6
10.2.3 Calculating Frequency-Adjusted Output................................................ 10-7
10.2.4 Interfacing an 8-Bit Device to 16-Bit Memory Using
Single-Address DMA Mode .................................................................. 10-10
10.3 Power Consumption Considerations .......................................................... 10-10
nc...
I
10.3.1 MC68340 Power Reduction at 5V .......................................................... 10-11
10.3.2 MC68340V (3.3 V) ..................................................................................... 10-13
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Section 11
Electrical Characteristics
11.1 Maximum Rating............................................................................................. 11-1
11.2 Thermal Characteristics................................................................................. 11-1
11.3 Power Considerations ................................................................................... 11-2
11.4 AC Electrical Specification Definitions....................................................... 11-2
11.5 DC Electrical Specifications......................................................................... 11-5
11.6 AC Electrical Specifications Control Timing.............................................. 11-6
11.7 AC Timing Specifications .............................................................................. 11-8
11.8 DMA Module AC Electrical Specifications ................................................. 11-19
11.9 Timer Module Electrical Specifications...................................................... 11-20
11.10 Serial Module Electrical Specifications...................................................... 11-22
11.11 IEEE 1149.1 Electrical Specifications......................................................... 11-25
Section 12
Ordering Information and Mechanical Data
12.1 Standard MC68340 Ordering Information................................................. 12-1
12.2 Pin Assignment............................................................................................... 12-2
12.2.1 144-Lead Ceramic Quad Flat Pack (FE Suffix) ..................................... 12-2
12.2.2 145-Lead Plastic Pin Grid Array (RP Suffix).......................................... 12-4
12.3 Package Dimensions ..................................................................................... 12-6
12.3.1 FE Suffix....................................................................................................... 12-6
12.3.2 RP Suffix....................................................................................................... 12-7
Index
xvi MC68340 USER'S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 18

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
Figure Page
Number Title Number
1-1 Block Diagram ......................................................................................................... 1-1
2-1 Functional Signal Groups..................................................................................... 2-1
3-1 Input Sample Window............................................................................................ 3-2
3-2 MC68340 Interface to Various Port Sizes.......................................................... 3-7
3-3 Long-Word Operand Read Timing from 8-Bit Port............................................ 3-11
3-4 Long-Word Operand Write Timing to 8-Bit Port................................................. 3-12
3-5 Long-Word and Word Read and Write Timing—16-Bit Port........................... 3-13
3-6 Fast Termination Timing........................................................................................ 3-15
3-7 Word Read Cycle Flowchart................................................................................. 3-16
3-8 Word Write Cycle Flowchart.................................................................................. 3-18
3-9 Read-Modify-Write Cycle Timing......................................................................... 3-19
3-10 CPU Space Address Encoding............................................................................ 3-21
3-11 Breakpoint Operation Flowchart.......................................................................... 3-24
3-12 Breakpoint Acknowledge Cycle Timing (Opcode Returned).......................... 3-25
3-13 Breakpoint Acknowledge Cycle Timing (Exception Signaled) ...................... 3-26
3-14 Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle Flowchart............................................................. 3-28
3-15 Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle Timing .................................................................. 3-29
3-16 Autovector Operation Timing................................................................................ 3-31
3-17 Bus Error without
3-18 Late Bus Error with
3-19 Retry Sequence...................................................................................................... 3-37
3-20 Late Retry Sequence ............................................................................................. 3-38
3-21
3-22 Bus Arbitration Flowchart for Single Request.................................................... 3-41
3-23 Bus Arbitration Timing Diagram—Idle Bus Case.............................................. 3-42
3-24 Bus Arbitration Timing Diagram—Active Bus Case......................................... 3-42
3-25 Bus Arbitration State Diagram.............................................................................. 3-45
3-26 Show Cycle Timing Diagram................................................................................ 3-46
3-27 Timing for External Devices Driving
3-28 Power-Up Reset Timing Diagram........................................................................ 3-48
HALT Timing............................................................................................................ 3-39
DSACK≈................................................................................... 3-35
DSACK≈................................................................................ 3-36
RESET...................................................... 3-47
4-1 SIM40 Module Register Block .............................................................................. 4-3
4-2 System Configuration and Protection Function................................................ 4-5
4-3 Software Watchdog Block Diagram.................................................................... 4-7
4-4 Clock Block Diagram for Crystal Operation....................................................... 4-10
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER'S MANUAL xvii
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 19

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev.1.0
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS (Continued)
Figure Page
Number Title Number
4-5 MC68340 Crystal Oscillator .................................................................................. 4-10
4-6 Clock Block Diagram for External Oscillator Operation................................... 4-11
4-7 Full Interrupt Request Multiplexer........................................................................ 4-16
4-8 SIM40 Programming Model.................................................................................. 4-19
5-1 CPU32 Block Diagram........................................................................................... 5-3
5-2 Loop Mode Instruction Sequence....................................................................... 5-3
5-3 User Programming Model ..................................................................................... 5-9
5-4 Supervisor Programming Model Supplement .................................................. 5-9
5-5 Status Register........................................................................................................ 5-10
5-6 Instruction Word General Format......................................................................... 5-12
5-7 Table Example 1 ..................................................................................................... 5-30
5-8 Table Example 2 ..................................................................................................... 5-31
5-9 Table Example 3 ..................................................................................................... 5-33
5-10 Exception Stack Frame.......................................................................................... 5-42
5-11 Reset Operation Flowchart.................................................................................... 5-45
5-12 Format $0—Four-Word Stack Frame.................................................................. 5-60
5-13 Format $2—Six-Word Stack Frame.................................................................... 5-60
5-14 Internal Transfer Count Register.......................................................................... 5-61
5-15 Format $C—BERR Stack for Prefetches and Operands.................................. 5-62
5-16 Format $C—BERR Stack on MOVEM Operand................................................ 5-62
5-17 Format $C—Four- and Six-Word BERR Stack.................................................. 5-63
5-18 In-Circuit Emulator Configuration ........................................................................ 5-64
5-19 Bus State Analyzer Configuration....................................................................... 5-64
5-20 BDM Block Diagram............................................................................................... 5-65
5-21 BDM Command Execution Flowchart................................................................. 5-68
5-22 Debug Serial I/O Block Diagram.......................................................................... 5-70
5-23 Serial Interface Timing Diagram.......................................................................... 5-71
5-24
5-25
5-26
5-27 Command-Sequence Diagram............................................................................ 5-75
5-28 Functional Model of Instruction Pipeline............................................................ 5-87
5-29 Instruction Pipeline Timing Diagram................................................................... 5-88
5-30 Block Diagram of Independent Resources ........................................................ 5-90
5-31 Simultaneous Instruction Execution.................................................................... 5-91
5-32 Attributed Instruction Times................................................................................... 5-92
5-33 Example 1—Instruction Stream ........................................................................... 5-95
5-34 Example 2—Branch Taken................................................................................... 5-95
5-35 Example 2—Branch Not Taken............................................................................ 5-96
5-36 Example 3—Branch Negative Tail...................................................................... 5-96
BKPT Timing for Single Bus Cycle...................................................................... 5-72
BKPT Timing for Forcing BDM............................................................................. 5-72
BKPT/DSCLK Logic Diagram.............................................................................. 5-72
xviii MC68340 USER'S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 20

11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS (Continued)
Figure Page
Number Title Number
6-1 DMA Block Diagram ............................................................................................... 6-1
6-2 Single-Address Transfers ..................................................................................... 6-3
6-3 Dual-Address Transfer........................................................................................... 6-3
6-4 DMA External Connections to Serial Module.................................................... 6-6
6-5 Single-Address Read Timing (External Burst).................................................. 6-8
6-6 Single-Address Read Timing (Cycle Steal)....................................................... 6-9
6-7 Single-Address Write Timing (External Burst)................................................... 6-10
6-8 Single-Address Write Timing (Cycle Steal) ....................................................... 6-11
6-9 Dual-Address Read Timing (External Burst—Source Requesting)............... 6-13
6-10 Dual-Address Read Timing (Cycle Steal—Source Requesting)................... 6-14
6-11 Dual-Address Write Timing (External Burst—Destination Requesting)........ 6-16
nc...
I
6-12 Dual-Address Write Timing (Cycle Steal—Destination Requesting) ............ 6-17
6-13 Fast Termination Option (Cycle Steal)................................................................ 6-21
6-14 Fast Termination Option (External Burst—Source Requesting).................... 6-22
6-15 DMA Module Programming Model...................................................................... 6-23
6-16 Packing and Unpacking of Operands................................................................. 6-35
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
7-1 Simplified Block Diagram...................................................................................... 7-1
7-2 External and Internal Interface Signals.............................................................. 7-5
7-3 Baud Rate Generator Block Diagram.................................................................. 7-8
7-4 Transmitter and Receiver Functional Diagram.................................................. 7-9
7-5 Transmitter Timing Diagram................................................................................. 7-10
7-6 Receiver Timing Diagram...................................................................................... 7-12
7-7 Looping Modes Functional Diagram................................................................... 7-15
7-8 Multidrop Mode Timing Diagram......................................................................... 7-16
7-9 Serial Module Programming Model .................................................................... 7-19
7-10 Serial Module Programming Flowchart.............................................................. 7-41
8-1 Simplified Block Diagram...................................................................................... 8-1
8-2 Timer Functional Diagram..................................................................................... 8-3
8-3 External and Internal Interface Signals.............................................................. 8-5
8-4 Input Capture/Output Compare Mode................................................................. 8-7
8-5 Square-Wave Generator Mode............................................................................ 8-8
8-6 Variable Duty-Cycle Square-Wave Generator Mode...................................... 8-10
8-7 Variable-Width Single-Shot Pulse Generator Mode........................................ 8-11
8-8 Pulse-Width Measurement Mode........................................................................ 8-12
8-9 Period Measurement Mode.................................................................................. 8-14
8-10 Event Count Mode.................................................................................................. 8-15
8-11 Timer Module Programming Model..................................................................... 8-18
9-1 Test Access Port Block Diagram.......................................................................... 9-2
9-2 TAP Controller State Machine.............................................................................. 9-3
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER'S MANUAL xix
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 21

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev.1.0
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS (Continued)
Figure Page
Number Title Number
9-3 Output Latch Cell (O.Latch)................................................................................... 9-7
9-4 Input Pin Cell (I.Pin)................................................................................................ 9-7
9-5 Active-High Output Control Cell (IO.Ctl1) ........................................................... 9-8
9 -6 Ac t i v e -Lo w O utp u t C ont r o l Ce l l (IO . C tl0 )............................................................ 9-8
9-7 Bidirectional Data Cell (IO.Cell) ........................................................................... 9-9
9-8 General Arrangement for Bidirectional Pins ...................................................... 9-9
9-9 Bypass Register...................................................................................................... 9-11
10-1 Minimum System Configuration Block Diagram............................................. 10-1
10-2 Sample Crystal Circuit ......................................................................................... 10-2
10-3 Statek Corporation Crystal Circuit..................................................................... 10-2
10-4 XFC and V
10-5 SRAM Interface ..................................................................................................... 10-3
10-6 ROM Interface........................................................................................................ 10-4
10-7 Serial Interface ...................................................................................................... 10-5
10-8 External Circuitry for 8-Bit Boot ROM ................................................................ 10-5
10-9 8-Bit Boot ROM Timing......................................................................................... 10-6
10-10 Access Time Computation Diagram.................................................................. 10-6
10-11 Signal Relationships to CLKOUT...................................................................... 10-7
10-12 Signal Width Specifications................................................................................ 10-8
10-13 Skew between Two Outputs ............................................................................... 10-9
10-14 Circuitry for Interfacing 8-Bit Device to 16-Bit Memory in
Single-Address DMA Mode .............................................................................. 10-10
10-15 MC68340 Current vs. Activity at 5 V.................................................................. 10-11
10-16 MC68340 Current vs. Voltage/Temperature.................................................... 10-12
10-17 MC68340 Current vs. Clock Frequency at 5 V................................................ 10-12
11-1 Drive Levels and Test Points for AC Specifications....................................... 11-4
11-2 Read Cycle Timing Diagram............................................................................... 11-11
11-3 Write Cycle Timing Diagram............................................................................... 11-12
11-4 Fast Termination Read Cycle Timing Diagram ............................................... 11-13
11-5 Fast Termination Write Cycle Timing Diagram................................................ 11-14
11-6 Bus Arbitation Timing—Active Bus Case ......................................................... 11-15
11-7 Bus Arbitration Timing—Idle Bus Case............................................................ 11-16
11-8 Show Cycle Timing Diagram.............................................................................. 11-16
11-9 IACK Cycle Timing Diagram............................................................................... 11-17
11-10 Background Debug Mode Serial Port Timing................................................. 11-18
11-11 Background Debug Mode FREEZE Timing..................................................... 11-18
11-12 DMA Signal Timing Diagram.............................................................................. 11-19
11-13 Timer Module Clock Signal Timing Diagram.................................................. 11-20
11-14 Timer Module Signal Timing Diagram.............................................................. 11-21
11-15 Serial Module General Timing Diagram.......................................................... 11-22
CCSYN
Capacitor Connections ........................................................ 10-3
xx MC68340 USER'S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 22

11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS (Concluded)
Figure Page
Number Title Number
11-16 Serial Module Asynchronous Mode Timing (X1)............................................ 11-23
11-17 Serial Module Asynchronous Mode Timing (SCLK–16X)............................ 11-23
11-18 Serial Module Synchronous Mode Timing Diagram..................................... 11-23
11-19 Test Clock Input Timing Diagram....................................................................... 11-25
11-20 Boundary Scan Timing Diagram....................................................................... 11-26
11-21 Test Access Port Timing Diagram...................................................................... 11-26
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER'S MANUAL xxi
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 23

11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev.1.0
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
Number Title Number
2-1 Signal Index............................................................................................................. 2-2
2-2 Address Space Encoding ..................................................................................... 2-5
2-3
2-4 SIZx Signal Encoding ............................................................................................ 2-7
2-5 Signal Summary..................................................................................................... 2-14
DSACK≈ Encoding................................................................................................. 2-6
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
3-1 SIZx Signal Encoding ............................................................................................ 3-3
3-2 Address Space Encoding ..................................................................................... 3-3
3-3
3-4
4-1 Clock Operating Modes ......................................................................................... 4-9
4-2 System Frequencies from 32.768-kHz Reference............................................ 4-13
4-3 Clock Control Signals ............................................................................................ 4-13
4-4 Port A Pin Assignment Register........................................................................... 4-15
4-5 Port B Pin Assignment Register........................................................................... 4-16
4-6 SHENx Control Bits ................................................................................................ 4-22
4-7 Deriving Software Watchdog Timeout ................................................................ 4-25
4-8 BMTx Encoding ....................................................................................................... 4-26
4-9 PIRQL Encoding...................................................................................................... 4-26
4-10 DDx Encoding......................................................................................................... 4-32
4-11 PSx Encoding.......................................................................................................... 4-32
5-1 Instruction Set.......................................................................................................... 5-6
5-2 Instruction Set Summary ....................................................................................... 5-16
5-3 Condition Code Computations............................................................................. 5-20
5 - 4 Da t a M o ve m en t Op e ra t io ns.................................................................................. 5-21
5-5 Integer Arithmetic Operations............................................................................... 5-23
5-6 Logic Operations..................................................................................................... 5-24
5-7 Shift and Rotate Operations.................................................................................. 5-25
5-8 Bit Manipulation Operations................................................................................. 5-25
5-9 Binary-Coded Decimal Operations..................................................................... 5-26
5-10 Program Control Operations................................................................................. 5-26
5-11 System Control Operations................................................................................... 5-28
5-12 Condition Tests....................................................................................................... 5-29
5-13 Standard Usage Entries ........................................................................................ 5-30
5-14 Compressed Table Entries................................................................................... 5-32
DSACK≈ Encoding................................................................................................. 3-5
DSACK≈, BERR, and HALT Assertion Results.................................................. 3-33
xxii MC68340 USER'S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 24

11/2/95 SECTION 1: OVERVIEW UM Rev 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF TABLES (Continued)
Table Page
Number Title Number
5-15 8-Bit Independent Variable Entries..................................................................... 5-33
5-16 Exception Vector Assignments............................................................................. 5-40
5-17 Exception Priority Groups...................................................................................... 5-43
5-18 Tracing Control........................................................................................................ 5-50
5-19 BDM Source Summary.......................................................................................... 5-67
5-20 Polling the BDM Entry Source.............................................................................. 5-68
5-21 CPU Generated Message Encoding................................................................... 5-70
5-22 Size Field Encoding ............................................................................................... 5-74
5-23 BDM Command Summary .................................................................................... 5-77
5-24 Register Field for RSREG and WSREG.............................................................. 5-79
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
6-1 FRZx Control Bits.................................................................................................... 6-24
6-2 SSIZEx Encoding ................................................................................................... 6-28
6-3 DSIZEx Encoding................................................................................................... 6-29
6-4 REQx Encoding....................................................................................................... 6-29
6-5 BBx Encoding and Bus Bandwidth...................................................................... 6-29
6-6 Address Space Encoding ..................................................................................... 6-32
7-1 FRZx Control Bits.................................................................................................... 7-20
7-2 PMx and PT Control Bits........................................................................................ 7-23
7-3 B/Cx Control Bits..................................................................................................... 7-24
7-4 RCSx Control Bits................................................................................................... 7-26
7-5 TCSx Control Bits................................................................................................... 7-27
7-6 MISCx Control Bits................................................................................................. 7-28
7-7 TCx Control Bits...................................................................................................... 7-29
7-8 RCx Control Bits...................................................................................................... 7-30
7-9 CMx Control Bits..................................................................................................... 7-38
7-10 SBx Control Bits...................................................................................................... 7-39
8-1 OCx Encoding......................................................................................................... 8-17
8-2 FRZx Control Bits.................................................................................................... 8-19
8-3 IEx Encoding............................................................................................................ 8-21
8-4 POTx Encoding....................................................................................................... 8-22
8-5 MODEx Encoding................................................................................................... 8-22
8-6 OCx Encoding......................................................................................................... 8-22
9-1 Boundary Scan Control Bits................................................................................. 9-4
9-2 Boundary Scan Bit Definitions............................................................................. 9-5
9-3 Instructions............................................................................................................... 9-10
10-1 Memory Access Times at 16.78 MHz................................................................ 10-7
10-2 Typical Electrical Characteristics....................................................................... 10-13
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER'S MANUAL xxiii
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 25
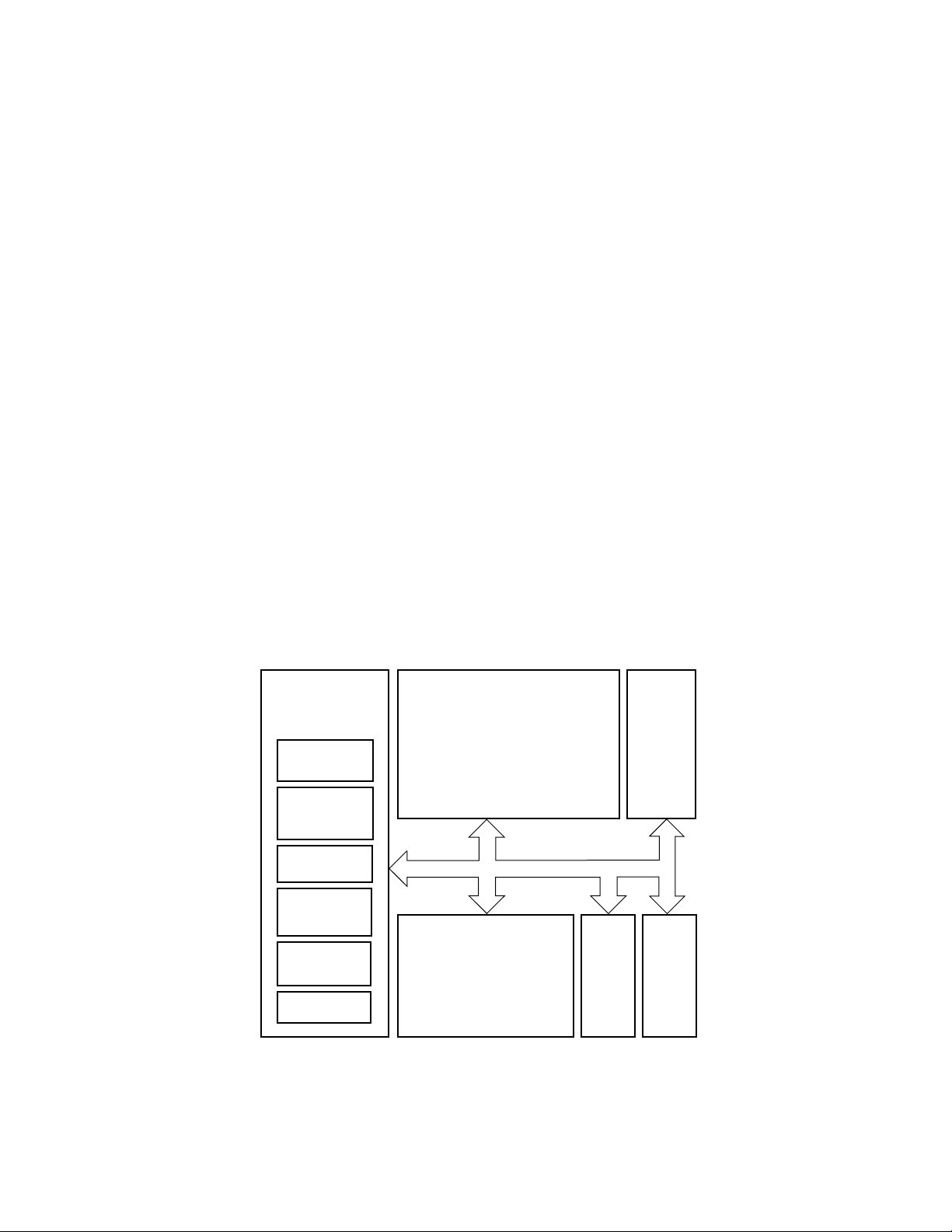
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
SECTION 1
DEVICE OVERVIEW
The MC68340 is a high-performance 32-bit integrated processor with direct memory
access (DMA), combining an enhanced M68000-compatible processor, 32-bit DMA, and
other peripheral subsystems on a single integrated circuit. The MC68340 CPU32 delivers
32-bit CISC processor performance from a lower cost 16-bit memory system. The
combination of peripherals offered in the MC68340 can be found in a diverse range of
microprocessor-based systems, including embedded control and general computing.
nc...
I
Systems requiring very high-speed block transfers of data can especially benefit from the
MC68340.
The MC68340's high level of functional integration results in significant reductions in
component count, power consumption, board space, and cost while yielding much higher
system reliability and shorter design time. The 3.3-V MC68340V is particularly attractive to
applications requiring a very tight power budget. Complete code compatibility with the
MC68000 and MC68010 affords the designer access to a broad base of established real time kernels, operating systems, languages, applications, and development tools—many
oriented towards embedded control.
SYSTEM
INTEGRATION
MODULE
(SIM40)
SYSTEM
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
PROTECTION
CHIP SELECTS
AND
WAIT STATES
CLOCK
SYNTHESIZER
EXTERNAL
BUS
INTERFACE
CPU32
68020– BASED
PROCESSOR
INTERMODULE BUS
TWO-
CHANNEL
SERIAL
I/O
BUS
ARBITRATION
IEEE TEST
TWO-CHANNEL DMA
CONTROLLER
TIMER
TIMER
Figure 1-1. Block Diagram
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 1-1
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 26

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
The primary features of the MC68340, illustrated in Figure 1-1, are as follows:
• High Functional Integration on a Single Piece of Silicon
• CPU32—MC68020-Derived 32-Bit Central Processor Unit
— Upward Object-Code Compatible with MC68000 and MC68010
— Additional MC68020 Instructions and Addressing Modes
— Unique Embedded Control Instructions
— Fast Two-Clock Register Instructions—10,045 Dhrystones
• Two-Channel Low-Latency DMA Controller for High-Speed Memory Transfers
— Single- or Dual-Address Transfers
— 32-Bit Addresses and Counters
— 8-, 16-, and 32-Bit Data Transfers
— 50 Mbyte/Sec Sustained Transfers (12.5 Mbyte/Sec Memory-to-Memory)
• Two-Channel Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (USART)
— Baud Rate Generators
— Modem Control
nc...
I
— MC68681/MC2681 Compatible
— 9.8 Mbits/Sec Maximum Transfer Rate
• Two Independent Counter/Timers
— 16-Bit Counter
— Up to 8-Bit Prescaler
— Multimode Operation
— 80-ns Resolution
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
• System Integration Module Incorporates Many Functions Typically Relegated to
External PALs, TTL, and ASIC, such as:
— System Configuration — External Bus Interface
— System Protection — Periodic Interrupt Timer
— Chip Select and Wait State Generation — Interrupt Response
— Clock Generation — Bus Arbitration
— Dynamic Bus Sizing — IEEE 1149.1 Boundary Scan (JTAG)
— Up to 16 Discrete I/O Lines — Power-On Reset
• 32 Address Lines, 16 Data Lines
• Power Consumption Control
— Static HCMOS Technology Reduces Power in Normal Operation
— Low Voltage Operation at 3.3 V ±0.3 V (MC68340V only)
— Programmable Clock Generator Throttles Frequency
— Unused Peripherals Can Be Turned Off
— LPSTOP Provides an Idle State for Lowest Standby Current
• 0–16.78 MHz or 0–25.16 MHz Operation
• 144-Pin Ceramic Quad Flat Pack (CQFP) or 145-Pin Plastic Pin Grid Array (PGA)
As a low voltage part, the MC68340V can operate with a 3.3-V power supply. MC68340 is
used throughout this manual to refer to both the low voltage and standard 5-V parts since
both are functionally equivalent.
1.1 M68300 FAMILY
The MC68340 is one of a series of components in the M68300 family. Other members of
the family include the MC68302, MC68330, MC68331, MC68332, and MC68333.
1-2 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 27

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
1.1.1 Organization
The M68300 family of integrated processors and controllers is built on an M68000 core
processor, an on-chip bus, and a selection of intelligent peripherals appropriate for a set of
applications. The CPU32 is a powerful central processor with nearly the performance of
the MC68020. A system integration module incorporates the external bus interface and
many of the smaller circuits that typically surround a microprocessor for address decoding,
wait-state insertion, interrupt prioritization, clock generation, arbitration, watchdog timing,
and power-on reset timing.
Each member of the M68300 family is distinguished by its selection of peripherals.
Peripherals are chosen to address specific applications but are often useful in a wide
variety of applications. The peripherals may be highly sophisticated timing or protocol
engines that have their own processors, or they may be more traditional peripheral
functions, such as UARTs and timers. Since each major function is designed in a
standalone module, each module might be found in many different M68300 family parts.
nc...
I
Driver software written for a module on one M68300 part can be used to run the same
module that appears on another part.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
1.1.2 Advantages
By incorporating so many major features into a single M68300 family chip, a system
designer can realize significant savings in design time, power consumption, cost, board
space, pin count, and programming. The equivalent functionality can easily require 20
separate components. Each component might have 16–64 pins, totaling over 350
connections. Most of these connections require interconnects or are duplications. Each
connection is a candidate for a bad solder joint or misrouted trace. Each component is
another part to qualify, purchase, inventory, and maintain. Each component requires a
share of the printed circuit board. Each component draws power—often to drive large
buffers to get the signal to another chip. The cumulative power consumption of all the
components must be available from the power supply. The signals between the CPU and
a peripheral might not be compatible nor run from the same clock, requiring time delays or
other special design considerations.
In a M68300 family component, the major functions and glue logic are all properly
connected internally, timed with the same clock, fully tested, and uniformly documented.
Power consumption stays well under a watt, and a special standby mode drops current
well under a milliamp during idle periods. Only essential signals are brought out to pins.
The primary package is the surface-mount quad flat pack for the smallest possible
footprint; pin grid arrays are also available.
1.2 CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT
The CPU32 is a powerful central processor that supervises system functions, makes
decisions, manipulates data, and directs I/O. A special debugging mode simplifies
processor emulation during system debug.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 1-3
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 28

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
1.2.1 CPU32
The CPU32 is an M68000 family processor specially designed for use as a 32-bit core
processor and for operation over the intermodule bus (IMB). Designers used the
MC68020 as a model and included advances of the later M68000 family processors,
resulting in an instruction execution performance of 4 MIPS (VAX-equivalent) at 25.16
MHz.
The powerful and flexible M68000 architecture is the basis of the CPU32. MC68000
(including the MC68HC000 and the MC68EC000) and MC68010 user programs will run
unmodified on the CPU32. The programmer can use any of the eight 32-bit data registers
for fast manipulation of data and any of the eight 32-bit address registers for indexing data
in memory. The CPU32 can operate on data types of single bits, binary-coded decimal
(BCD) digits, and 8, 16, and 32 bits. Peripherals and data in memory can reside anywhere
in the 4-Gbyte linear address space. A supervisor operating mode protects system-level
resources from the more restricted user mode, allowing a true virtual environment to be
developed.
Flexible instructions for data movement, arithmetic functions, logical operations, shifts and
rotates, bit set and clear, conditional and unconditional program branches, and overall
system control are supported, including a fast 32 × 32 multiply and 32-bit conditional
branches. New instructions, such as table lookup and interpolate and low power stop,
support the specific requirements of embedded control applications. Many addressing
modes complement these instructions, including predecrement and postincrement, which
allow simple stack and queue maintenance and scaled indexed for efficient table
accesses. Data types and addressing modes are supported orthogonally by all data
operations and with all appropriate addressing modes. Position-independent code is easily
written.
The CPU32 is specially optimized to run with the MC68340's 16-bit data bus. Most
instructions execute in one-half the number of clocks compared to the original MC68000,
yielding an overall 1.6 times the performance of the same-speed MC68000 and measuring
10,045 Dhrystones/sec
Like all M68000 family processors, the CPU32 recognizes interrupts of seven different
priority levels and allows the peripheral to vector the processor to the desired service
routine. Internal trap exceptions ensure proper instruction execution with good addresses
and data, allow operating system intervention in special situations, and permit instruction
tracing. Hardware signals can either terminate or rerun bad memory accesses before
instructions process data incorrectly.
@ 25.16 MHz (6,742 Dhrystones/sec @ 16.78 MHz).
The CPU32 offers the programmer full 32-bit data processing performance with complete
M68000 compatibility, yet with more compact code than is available with RISC
processors. The CPU32 is identical in all CPU32-based M68300 family products.
1.2.2 Background Debug Mode
A special operating mode is available in the CPU32 in which normal instruction execution
is suspended while special on-chip microcode performs the functions of a debugger.
1-4 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 29

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Commands are received over a dedicated, high-speed, full-duplex serial interface.
Commands allow the manual reading or writing of CPU32 registers, reading or writing of
external memory locations, and diversion to user-specified patch code. This background
debug mode permits a much simpler emulation environment while leaving the processor
chip in the target system, running its own debugging operations.
1.3 ON-CHIP PERIPHERALS
To improve total system throughput and reduce part count, board size, and cost of system
implementation, the M68300 family integrates on-chip, intelligent peripheral modules and
typical glue logic. These functions on the MC68340 include the SIM40, a DMA controller,
a serial module, and two timers.
The processor communicates with these modules over the on-chip intermodule bus (IMB).
This backbone of the chip is similar to traditional external buses with address, data, clock,
nc...
I
interrupt, arbitration, and handshake signals. Because bus masters (like the CPU32 and
DMA), peripherals, and the SIM40 are all on the chip, the IMB ensures that
communication between these modules is fully synchronized and that arbitration and
interrupts can be handled in parallel with data transfers, greatly improving system
performance. Internal accesses across the IMB may be monitored from outside of the
chip, if desired.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Each module operates independently. No direct connections between peripheral modules
are made inside the chip; however, external connections could, for instance, link a serial
output to a DMA control line. Modules and their registers are accessed in the memory
map of the CPU32 (and DMA) for easy access by general M68000 instructions and are
relocatable. Each module may be assigned its own interrupt level, response vector, and
arbitration priority. Since each module is a self-contained design and adheres to the IMB
interface specifications, the modules may appear on other M68300 family products,
retaining the investment in the software drivers for the module.
1.3.1 System Integration Module
The MC68340 SIM40 provides the external bus interface for both the CPU32 and the
DMA. It also eliminates much of the glue logic that typically supports the microprocessor
and its interface with the peripheral and memory system. The SIM40 provides
programmable circuits to perform address decoding and chip selects, wait-state insertion,
interrupt handling, clock generation, bus arbitration, watchdog timing, discrete I/O, and
power-on reset timing. A boundary scan test capability is also provided.
1.3.1.1 EXTERNAL BUS INTERFACE. The external bus interface (EBI) handles the
transfer of information between the internal CPU32 or DMA controller and memory,
peripherals, or other processing elements in the external address space. Based on the
MC68030 bus, the external bus provides up to 32 address lines and 16 data lines.
Address extensions identify each bus cycle as CPU32 or DMA initiated, supervisor or user
privilege level, and instruction or data access. The data bus allows dynamic sizing for 8- or
16-bit bus accesses (plus 32 bits for DMA). Synchronous transfers from the CPU32 or the
DMA can be made in as little as two clock cycles. Asynchronous transfers allow the
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 1-5
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 30

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
memory system to signal the CPU32 or DMA when the transfer is complete and to note
the number of bits in the transfer. An external master can arbitrate for the bus using a
three-line handshaking interface.
1.3.1.2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND PROTECTION. The M68000 family of
processors is designed with the concept of providing maximum system safeguards.
System configuration and various monitors and timers are provided in the MC68340.
Power-on reset circuitry is a part of the SIM40. A bus monitor ensures that the system
does not lock up when there is no response to a memory access. The bus fault monitor
can reset the processor when a catastrophic bus failure occurs. Spurious interrupts are
detected and handled appropriately. A software watchdog can pull the processor out of an
infinite loop. An interrupt can be sent to the CPU32 with programmable regularity for
DRAM refresh, time-of-day clock, task switching, etc.
1.3.1.3 CLOCK SYNTHESIZER. The clock synthesizer generates the clock signals used
by all internal operations as well as a clock output used by external devices. The clock
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
synthesizer can operate with an inexpensive 32768-Hz watch crystal or an external
oscillator for reference, using an internal phase-locked loop and voltage-controlled
oscillator. At any time, software can select clock frequencies from 131 kHz to 16.78 MHz
or 25.16 MHz, favoring either low power consumption or high performance. Alternately, an
external clock can drive the clock signal directly at the operating frequency. With its fully
static HCMOS design, it is possible to completely stop the system clock without losing the
contents of the internal registers.
1.3.1.4 CHIP SELECT AND WAIT STATE GENERATION. Four programmable chip
selects provide signals to enable external memory and peripheral circuits, providing all
handshaking and timing signals with up to 175-ns access times with a 25-MHz system
clock (265 ns
an address mask that determine the addressing characteristics of that chip select.
Address space and write protection can be selected for each. The block size can be
selected from 256 bytes up to 4 Gbytes in increments of 2
for either 8- or 16-bit transfers. Fast synchronous termination or up to three wait states
can be programmed, whether or not the chip select signals are used. External
handshakes can also signal the end of a bus transfer. A system can boot from reset out of
8-bit-wide memory, if desired.
@ 16.78 MHz). Each chip select signal has an associated base address and
n
. Accesses can be preselected
Frees
1.3.1.5 INTERRUPT HANDLING. Seven input signals are provided to trigger an external
interrupt, one for each of the seven priority levels supported. Seven separate outputs can
indicate the priority level of the interrupt being serviced. An input can direct the processor
to a default service routine, if desired. Interrupts at each priority level can be
preprogrammed to go to the default service routine. For maximum flexibility, interrupts can
be vectored to the correct service routine by the interrupting device.
1.3.1.6 DISCRETE I/O PINS. When not used for other functions, 16 pins can be
programmed as discrete input or output lines. Additionally, in other peripheral modules,
pins for otherwise unused functions can often be used for general input/output.
1-6 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 31

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
1.3.1.7 IEEE 1149.1 TEST ACCESS PORT. To aid in system diagnostics, the MC68340
includes dedicated user-accessible test logic that is fully compliant with the IEEE 1149.1
standard for boundary scan testability, often referred to as JTAG (Joint Test Action
Group).
1.3.2 Direct Memory Access Module
The most distinguishing MC68340 characteristic is the high-speed 32-bit DMA controller,
used to quickly move large blocks of data between internal peripherals, external
peripherals, or memory without processor intervention. The DMA module consists of two,
independent, programmable channels. Each channel has separate request, acknowledge,
and done signals. Each channel can operate in a single-address or a dual-address (flyby)
mode.
In single-address mode, only one (the source or the destination) address is provided, and
a peripheral device such as a serial communications controller receives or supplies the
nc...
I
data. An external request must start a single-address transfer. In this mode, each channel
supports 32 bits of address and 8, 16, or 32 bits of data.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
In dual-address mode, two bus transfers occur, one from a source device and the other to
a destination device. Dual-address transfers can be started by either an internal or
external request. In this mode, each channel supports 32 bits of address and 8 or 16 bits
of data (32 bits require external logic). The source and destination port size can be
selected independently; when they are different, the data will be packed or unpacked. An
8-bit disk interface can be read twice before the concatenated 16-bit result is passed into
memory.
Byte, word, and long-word counts up to 32 bits can be transferred. All addresses and
transfer counters are 32 bits. Addresses increment or remain constant, as programmed.
The DMA channels support two external request modes, burst transfer and cycle steal.
Internal requests can be programmed to occupy 25, 50, 75, or 100 percent of the data bus
bandwidth. Interrupts can be programmed to postpone DMA completion.
The DMA module can sustain a transfer rate of 12.5 Mbytes/sec in dual-address mode
and nearly 50 Mbytes/sec in single-address mode @ 25.16 MHz (8.4 and 33.3 Mbytes/sec
@ 16.78 MHz, respectively). The DMA controller arbitrates with the CPU32 for the bus in
parallel with existing bus cycles and is fully synchronized with the CPU32, eliminating all
delays normally associated with bus arbitration by allowing DMA bus cycles to butt
seamlessly with CPU bus cycles.
1.3.3 Serial Module
Most digital systems use serial I/O to communicate with host computers, operator
terminals, or remote devices. The MC68340 contains a two-channel, full-duplex USART.
An on-chip baud rate generator provides standard baud rates up to 76.8k baud
independently to each channel's receiver and transmitter. The module is functionally
equivalent to the MC68681/MC2681 DUART.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 1-7
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 32

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Each communication channel is completely independent. Data formats can be 5, 6, 7, or 8
bits with even, odd, or no parity and stop bits up to 2 in 1/16 increments. Four-byte receive
buffers and two-byte transmit buffers minimize CPU service calls. A wide variety of error
detection and maskable interrupt capability is provided on each channel. Full-duplex,
autoecho loopback, local loopback, and remote loopback modes can be selected.
Multidrop applications are supported.
A 3.6864-MHz crystal drives the baud rate generators. Each transmit and receive channel
can be programmed for a different baud rate, or an external 1× and 16× clock input can be
selected. Full modem support is provided with separate request-to-send (RTS) and clear to-send (CTS) signals for each channel. One channel also provides service request
signals. The two serial ports can sustain rates of 9.8 Mbps with a 25-MHz system clock in
1× mode, 612 kbps in 16× mode (6.5 Mbps and 410 kbps
@ 16.78 MHz).
1.3.4 Timer Modules
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Timers and counters are used in a system to monitor elapsed time, generate waveforms,
measure signals, keep time-of-day clocks, initiate DRAM refresh cycles, count events, and
provide “time slices” to ensure that no task dominates the activity of the processor. A
counter that counts clock pulses makes a timer, which is most useful when it causes
certain actions to occur in response to reaching desired counts.
The MC68340 has two, identical, versatile, on-chip counter/timers as well as a simple
timer in the SIM40. These general-purpose counter/timers can be used for precisely timed
events without the errors to which software-based counters and timers are susceptible —
e.g., errors caused by dynamic memory refreshing, DMA cycle steals, and interrupt
servicing. The programmable timer operating modes are input capture, output compare,
square-wave generation, variable duty-cycle square-wave generation, variable-width
single-shot pulse generation, event counting, period measurement, and pulse-width
measurement.
Each timer consists of a 16-bit countdown counter with an 8-bit countdown prescaler for a
composite 24-bit resolution. The two timers can be externally cascaded for a maximum
count width of 48 bits. The counter/timer can be clocked by the internal system clock
generated by the SIM40 (÷2) or by an external clock input. Either the processor or external
stimuli can trigger the starting and stopping of the counter. When a counter reaches a
predetermined value, either an external output signal can be driven, or an interrupt can be
made to the CPU32. The finest resolution of the timer is 80 ns with a 25-MHz system
clock (125 ns
@ 16.78 MHz).
1.4 POWER CONSUMPTION MANAGEMENT
The MC68340 is very power efficient due to its advanced 0.8-µ HCMOS process
technology and its static logic design. The resulting power consumption is typically
900 mW in full operation
comparable discrete component implementation the MC68340 can replace. For
applications employing reduced voltage operation, selection of the MC68340V, which
1-8 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
@ 25 MHz (650 mW @ 16.78 MHz)—far less than the
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 33

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
requires only a 3.3-V power supply, reduces current consumption by 40–60% in all modes
of operation (as well as reducing noise emissions).
The MC68340 has many additional methods of dynamically controlling power
consumption during operation. The frequency of operation can be lowered under software
control to reduce current consumption when performance is less critical. Idle internal
peripheral modules can be turned off to save power (5–10% each). Running a special low
power stop (LPSTOP) instruction shuts down the active circuits in the CPU and peripheral
modules, halting instruction execution. Power consumption in this standby mode is
reduced to about 350 µW. Processing and power consumption can be resumed by
resetting the part or by generating an interrupt with the SIM40's periodic interrupt timer.
1.5 PHYSICAL
The MC68340 is available as 0–16.78 MHz and 0–25.16 MHz, 0°C to +70°C and -40°C to
nc...
I
+85°C, and 5.0 V ±5% and 3.3 V ±0.3 supply voltages (reduced frequencies at 3.3 V)
Thirty-two power and ground leads minimize ground bounce and ensure proper isolation
of different sections of the chip, including the clock oscillator. A 144 pins are used for
signals and power. The MC68340 is available in a gull-wing ceramic quad flat pack
(CQFP) with 25.6-mil (0.001-in) lead spacing or a 15 × 15 plastic pin grid array (PPGA)
with 0.1-in pin spacing.
.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
1.6 COMPACT DISC-INTERACTIVE
The MC68340 was designed to meet the needs of many markets, including compact discinteractive (CD-I). CD-I is an emerging standard for a publishing medium that will bring
multimedia to a broad general audience—the consumer. CD-I players combine television
and stereo systems as output devices, with interactive control using a TV remote-controllike device to provide a multimedia experience selected from software “titles” contained in
compressed form on standard compact discs.
The highly integrated MC68340 is ideal as the central processor for CD-I players. It
provides the M68000 microprocessor code compatibility and DMA functions required by
CD-I Green Book
the
very cost-effective solution. The extra demands of full-motion video CD-I systems make
the best use of the MC68340 high performance. The MC68340 is CD-I compliant and has
been CD-I qualified. With its low voltage operation, the MC68340V is the only practical
choice for portable CD-I.
specification as well as many other useful on-chip functions for a
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 1-9
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 34

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
1.7 MORE INFORMATION
The following table lists available documentation related to the MC68340:
Document Number Document Name
BR1114/D
MC68340/D
MC68340UM/AD
M68000PM/AD
AN1063/D
AN453
BR573/D
BR729/D
nc...
I
BR1407/D
M68300 Integrated Processor Family
MC68340 Technical Summary
MC68340 User's Manual
M68000 Family Programmer's Reference Manual
DRAM Controller for the MC68340
Software Implementation of SPI on the MC68340
M68340 Evaluation System Product Brief
The 68K Source
3.3 Volt Logic and Interface Circuits
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
1-10 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 35

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
SECTION 2
SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS
This section contains brief descriptions of the MC68340 input and output signals in their
functional groups as shown in Figure 2-1.
A31/PORT A7/IACK7
A30/PORT A6/IACK6
A29/PORT A5/IACK5
A28/PORT A4/IACK4
A27/PORT A3/IACK3
A26/PORT A2/IACK2
A25/PORT A1/IACK1
A24/PORT A0
A23–A0
D15–D0
FC3–FC0
RESET
BERR
HALT
AS
DS
R/W
SIZ1
SIZ0
DSACK1
DSACK0
BR
BG
BGACK
RMC
IRQ7/PORT B7
IRQ6/PORT B6
IRQ5/PORT B5
IRQ3/PORT B3
CS3/IRQ4/PORT B4
CS2/IRQ2/PORT B2
CS1/IRQ1/PORT B1
CS0/AVEC
MODCK/PORT B0
PORT A
EXTERNAL
BUS
INTERFACE
BUS
ARBITRATION
PORT B
TMS
TCK
TDI
TEST
SYSTEM
INTEGRATION
MODULE
CLOCK
XTAL
EXTAL
TDO
TWO-CHANNEL
XFC
CLKOUT
DREQ1
IPIPE/DSO
FREEZE
BKPT/DSCLK
CPU32
CORE
DMA
CONTROLLER
DACK1
DONE1
DREQ2
IFETCH/DSI
IMB
DACK2
DONE2
SCLKX2X1
TWO-CHANNEL
SERIAL
I/O
OUTPUT
TIMER
MODULE
TIN1
TOUT1
TGATE1
PORT
TIMER
MODULE
TIN2
TGATE2
RxDA
TxDA
CTSA
RxDB
TxDB
CTSB
TxRDYA/OP6
RxRDYA/FFULLA/OP4
RTSB/OP1
RTSA/OP0
TOUT2
Figure 2-1. Functional Signal Groups
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 2-1
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 36

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
2.1 SIGNAL INDEX
The input and output signals for the MC68340 are listed in Table 2-1. The name,
mnemonic, and brief functional description are presented. For more detail on each signal,
refer to the signal paragraph. Guaranteed timing specifications for the signals listed in
Table 2-1 can be found in Section 11 Electrical Characteristics.
Table 2-1. Signal Index
Input/
Signal Name Mnemonic Function
Address Bus A23–A0 Lower 24 bits of the address bus Out
Address Bus/Port A7–A0/
Interrupt Acknowledge
Data Bus D15–D0 The 16-bit data bus used to transfer byte or word data I/O
Function Codes FC3–FC0 Identify the processor state and the address space of the
Chip Select 3–1/
Interrupt Request Level/
Port B4, B2, B1
Chip Select 0/Autovector CS0 Enables peripherals at programmed addresses or
Bus Request BR Indicates that an external device requires bus mastership In
Bus Grant BG Indicates that current bus cycle is complete and the
Bus Grant Acknowledge BGACK Indicates that an external device has assumed bus
Data and Size
Acknowledge
Read-Modify-Write Cycle RMC Identifies the bus cycle as part of an indivisible read-
Address Strobe AS Indicates that a valid address is on the address bus Out
Data Strobe DS During a read cycle, DS indicates that an external device
Size SIZ1, SIZ0 Indicates the number of bytes remaining to be transferred
Read/Write R/W Indicates the direction of data transfer on the bus Out
Interrupt Request Level/
Port B7, B6, B5, B3
Reset RESET System reset I/O
Halt HALT Suspends external bus activity I/O
Bus Error BERR Indicates an invalid bus operation is being attempted In
System Clock CLKOUT System clock out Out
Crystal Oscillator EXTAL, XTAL Connections for an external crystal or oscillator to the
External Filter Capacitor XFC Connection pin for an external capacitor to filter the circuit
A31–A24 Upper eight bits of the address bus, parallel I/O port, or
CS3–CS1 Enables peripherals at programmed addresses, interrupt
DSACK1,
DSACK0
IRQ7, IRQ6,
IRQ5, IRQ3
interrupt acknowledge lines
current bus cycle
priority level to the CPU32, or parallel I/O port
requests an automatic vector
MC68340 has relinquished the bus
mastership
Provides asynchronous data transfers and dynamic bus
sizing
modify-write operation
should place valid data on the data bus. During a write
cycle,
DS indicates that valid data is on the data bus.
for this cycle
Provides an interrupt priority level to the CPU32 or
becomes a parallel I/O port
internal oscillator circuit
of the phase-locked loop
Output
Out/I/O/Out
Out
Out/In/
I/O
Out/In
Out
In
In
Out
Out
Out
In/I/O
In, Out
In
2-2 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 37

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 2-1. Signal Index (Continued)
Input/
Signal Name Mnemonic Function
Clock Mode Select/
Port B0
Instruction Fetch/
Development Serial In
Instruction Pipe/
Development Serial Out
Breakpoint/Development
Serial Clock
Freeze FREEZE Indicates that the CPU32 has entered background debug
Transmit Data TxDA, TxDB Transmitter serial data output from the serial module Ou t
Clear-to-Send CTSA, CTSB Serial module clear-to-send inputs In
nc...
I
Request-to-Send/
OP1, OP0
MODCK Selects the source of the internal system clock upon reset
or becomes a parallel I/O port
IFETCH/DSI Indicates when the CPU32 is performing an instruction
word prefetch and when the instruction pipeline has been
flushed or provides background debug mode serial in
IPIPE/DSO Used to track movement of words through the instruction
pipeline or provides background debug mode serial out
BKPT/DSCLK Signals a hardware breakpoint to the CPU32 or provides
background debug mode serial clock
mode
RTSB, RTSA Channel request-to-send outputs or discrete outputs Out/Out
Output
In/I/O
Out/In
Out/Out
In/—
Out
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Serial Crystal Oscillator X1, X2 Connections for an external crystal to the serial module
internal oscillator circuit
Serial Clock SCLK External serial module clock input In
Transmitter Ready/OP6 T≈RDYA Indicates transmit buffer has a character or becomes a
parallel output
Receiver Ready/
FIFO Full/OP4
DMA Request DRE
DMA Acknowledge DACK2,
DMA Done DONE2,
Timer Gate TGATE2,
Timer Input TIN2, TIN1 Time reference input to timer In
Timer Output TOUT2,
Test Clock TCK Provides a clock for IEEE 1149.1 test logic In
Test Mode Select TMS Controls test mode operations In
Test Data In TDI Shifts in instructions and test data In
Test Data Out TDO Shifts out instructions and test data Out
Synchronizer Power V
R≈RDYA Indicates receive buffer has a character, the receiver
FIFO buffer is full or becomes a parallel output
Input that starts a DMA process In
Q2, DREQ1
Output that signals an access during DMA Out
DACK1
Bi-directional signal that indicates the last transfer I/O
DONE1
Counter enable input to timer In
TGATE1
Output waveform from timer Out
TOUT1
CCSYN
Quiet power supply to VCO; also used to control
synthesizer mode after reset.
Out/Out
Out/Out/Out
—
System Power Supply
and Ground
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 2-3
VCC, GND Power supply and ground to the MC68340 —
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 38

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
NOTE
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
The terms
to avoid confusion when dealing with a mixture of active-low
and active-high signals. The term
that a signal is active or true, independent of the level
represented by a high or low voltage. The term
negation
assert
indicates that a signal is inactive or false.
and
negate
are used throughout this section
assert
or
assertion
indicates
negate
or
2.2 ADDRESS BUS
The address bus signals are outputs that define the address of the byte (or the most
significant byte) to be transferred during a bus cycle. The MC68340 places the address on
the bus at the beginning of a bus cycle. The address is valid while
The address bus consists of the following two groups. Refer to Section 3 Bus Operation
for information on the address bus and its relationship to bus operation.
AS is asserted.
2.2.1 Address Bus (A23–A0)
These three-state outputs (along with A31–A24) provide the address for the current bus
cycle, except in the CPU address space.
2.2.2 Address Bus (A31–A24)
These pins can be programmed as the most significant eight address bits, port A parallel
I/O, or interrupt acknowledge signals. These pins can be used for more than one of their
multiplexed functions as long as the external demultiplexing circuit properly resolves
interaction between the different functions.
A31–A24
These pins can function as the most significant eight address bits.
Port A7–A0
These eight pins can serve as a dedicated parallel I/O port. See Section 4 System
Integration Module for more information on programming these pins.
IACK7– IACK1
The MC68340 asserts one of these pins to indicate the level of an external interrupt
during an interrupt acknowledge cycle. Peripherals can use the
of monitoring the address bus and function codes to determine that an interrupt
acknowledge cycle is in progress and to obtain the current interrupt level.
IACK≈ signals instead
2.3 DATA BUS (D15–D0)
This bidirectional, nonmultiplexed, parallel bus contains the data being transferred to or
from the MC68340. A read or write operation may transfer 8 or 16 bits of data (one or two
bytes) in one bus cycle. During a read cycle, the data is latched by the MC68340 on the
2-4 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 39

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
last falling edge of the clock for that bus cycle. For a write cycle, all 16 bits of the data bus
are driven, regardless of the port width or operand size. The MC68340 places the data on
the data bus approximately one-half clock cycle after
AS is asserted in a write cycle.
2.4 FUNCTION CODES (FC3–FC0)
These signals are outputs that indicate one of 16 address spaces to which the address
applies. Fifteen of these spaces are designated as either user or supervisor, program or
data, and normal or direct memory access (DMA) spaces. One other address space is
designated as CPU space to allow the CPU32 to acquire specific control information not
normally associated with read or write bus cycles. The function code signals are valid
while
nc...
I
2.5 CHIP SELECTS (CS3–CS0)
cale Semiconductor,
AS is asserted. See Table 2-2 for more information.
Table 2-2. Address Space Encoding
Function Code Bits
3210 Address Spaces
0000Reserved (Motorola)
0001User Data Space
0010User Program Space
0011Reserved (User )
0100Reserved (Motorola)
0101Supervisor Data Space
0110Supervisor Program Space
0111CPU Space
1 x x x DMA Space
These pins can be programmed to be chip select output signals, port B parallel I/O and
autovector input, or additional interrupt request lines. Refer to Section 4 System
Integration Module for more information on these signals.
Frees
CS3– CS0
The chip select output signals enable peripherals at programmed addresses. These
signals are inactive high (not high impedance) after reset.
CS0 is the chip select for a
boot ROM containing the reset vector and initialization program. It functions as the boot
chip select immediately after reset.
IRQ4, IRQ2, IRQ1
Interrupt request lines are external interrupt lines to the CPU32. These additional
interrupt request lines are selected by the FIRQ bit in the module configuration register.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 2-5
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 40

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Port B4, B2, B1, AVEC
This signal group functions as three bits of parallel I/O and the autovector input. AVEC
requests an automatic vector during an interrupt acknowledge cycle.
2.6 INTERRUPT REQUEST LEVEL (IRQ7, IRQ6, IRQ5, IRQ3)
These pins can be programmed to be either prioritized interrupt request lines or port B
parallel I/O.
IRQ7, IRQ6, IRQ5, IRQ3
IRQ7
interrupts. Refer to Section 5 CPU32 for more information on interrupt request lines.
Port B7, B6, B5, B3
These pins can be used as port B parallel I/O. Refer to Section 4 System Integration
nc...
I
Module for more information on parallel I/O signals.
, the highest priority, is nonmaskable. IRQ6–IRQ1 are internally maskable
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
2.7 BUS CONTROL SIGNALS
These signals control the bus transfer operations of the MC68340. Refer to Section 3
Bus Operation for more information on these signals.
2.7.1 Data and Size Acknowledge (DSACK1, DSACK0)
These two active-low input signals allow asynchronous data transfers and dynamic data
bus sizing between the MC68340 and external devices as listed in Table 2-3. During bus
cycles, external devices assert
During a read cycle, this signals the MC68340 to terminate the bus cycle and to latch the
data. During a write cycle, this indicates that the external device has successfully stored
the data and that the cycle may terminate.
DSACK1DSACK
1 1 Insert Wait States in Current Bus Cycle
1 0 Complete Cycle—Data Bus Port Size Is 8 Bits
0 1 Complete Cycle—Data Bus Port Size Is 16 Bits
0 0 Reserved—Defaults to 16-Bit Port Size Can Be
DSACK1 and/or DSACK0 as part of the bus protocol.
Table 2-3.
0
DSACK≈ Encoding
Result
Used for 32-Bit DMA Cycles
2.7.2 Address Strobe (AS)
AS is an output timing signal that indicates the validity of both an address on the address
bus and many control signals.
beginning of a bus cycle.
2-6 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
AS is asserted approximately one-half clock cycle after the
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 41

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
2.7.3 Data Strobe (DS)
DS is an output timing signal that applies to the data bus. For a read cycle, the MC68340
asserts
For a write cycle,
MC68340 asserts
write cycle.
DS and AS simultaneously to signal the external device to place data on the bus.
DS signals to the external device that the data to be written is valid. The
DS approximately one clock cycle after the assertion of AS during a
2.7.4 Transfer Size (SIZ1, SIZ0)
These output signals are driven by the bus master to indicate the number of operand
bytes remaining to be transferred in the current bus cycle as noted in Table 2-4.
Table 2-4. SIZx Signal Encoding
SIZ1 SIZ0 Transfer Size
nc...
I
0 1 Byte
1 0 Word
1 1 Three Byte
0 0 Long Word
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
2.7.5 Read/Write (R/W)
This active-high output signal is driven by the bus master to indicate the direction of a data
transfer on the bus. A logic one indicates a read from a slave device; a logic zero indicates
a write to a slave device.
2.8 BUS ARBITRATION SIGNALS
The following signals are the bus arbitration control signals used to determine the bus
master. Refer to Section 3 Bus Operation for more information on these signals.
2.8.1 Bus Request (BR)
This active-low input signal indicates that an external device needs to become the bus
master.
2.8.2 Bus Grant (BG)
Assertion of this active-low output signal indicates that the MC68340 has relinquished the
bus.
2.8.3 Bus Grant Acknowledge (BGACK)
Assertion of this active-low input indicates that an external device has become the bus
master.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 2-7
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 42

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
2.8.4 Read-Modify-Write Cycle (RMC)
This output signal identifies the bus cycle as part of an indivisible read-modify-write
operation. It remains asserted during all bus cycles of the read-modify-write operation to
indicate that bus ownership cannot be transferred.
2.9 EXCEPTION CONTROL SIGNALS
These signals are used by the MC68340 to recover from an exception.
2.9.1 Reset (RESET)
This active-low, open-drain, bidirectional signal is used to initiate a system reset. An
external reset signal (as well as a reset from the SIM40) resets the MC68340 and all
external devices. A reset signal from the CPU32 (asserted as part of the RESET
instruction) resets external devices; the internal state of the CPU32 is not affected. The
on-chip modules are reset, except for the SIM40. However, the module configuration
nc...
I
register for each on-chip module is not altered. When asserted by the MC68340, this
signal is guaranteed to be asserted for a minimum of 512 clock cycles. Refer to Section 3
Bus Operation for a description of bus reset operation and Section 5 CPU32 for
information about the reset exception.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
2.9.2 Halt (HALT)
This active-low, open-drain, bidirectional signal is asserted to suspend external bus
activity, to request a retry when used with
an output,
Operation for a description of the effects of
HALT indicates a double bus fault by the CPU32. Refer to Section 3 Bus
BERR, or to perform a single-step operation. As
HALT on bus operation.
2.9.3 Bus Error (BERR)
This active-low input signal indicates that an invalid bus operation is being attempted or,
when used with
3 Bus Operation for a description of the effects of
HALT, that the processor should retry the current cycle. Refer to Section
BERR on bus operation.
2.10 CLOCK SIGNALS
These signals are used by the MC68340 for controlling or generating the system clocks.
See Section 4 System Integration Module for more information on the various clocking
methods and frequencies.
2.10.1 System Clock (CLKOUT)
This output signal is the system clock output and is used as the bus timing reference by
external devices. CLKOUT can be varied in frequency or slowed in low power stop mode
to conserve power.
2-8 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 43

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
2.10.2 Crystal Oscillator (EXTAL, XTAL)
These two pins are the connections for an external crystal to the internal oscillator circuit.
If an external oscillator is used, it should be connected to EXTAL, with XTAL left open.
2.10.3 External Filter Capacitor (XFC)
This pin is used to add an external capacitor to the filter circuit of the phase-locked loop.
The capacitor should be connected between XFC and VCCSYN.
2.10.4 Clock Mode Select (MODCK)
This pin selects the source of the internal system clock during reset. After reset, it can be
programmed to be port B parallel I/O.
MODCK
The state of this active-high input signal during reset selects the source of the internal
nc...
I
system clock. If MODCK is high during reset, the internal voltage-controlled oscillator
(VCO) furnishes the system clock in crystal mode. If MODCK is low during reset, an
external clock source at the EXTAL pin furnishes the system clock output in external
clock mode.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Port B0
This pin can be used as a port B parallel I/O.
2.11 INSTRUMENTATION AND EMULATION SIGNALS
These signals are used for test or software debugging. See Section 5 CPU32 for more
information on these signals and background debug mode.
2.11.1 Instruction Fetch (IFETCH)
This pin functions as IFETCH in normal operation and as DSI in background debug mode.
IFETCH
This active-low output signal indicates when the CPU32 is performing an instruction
word prefetch and when the instruction pipeline has been flushed.
DSI
This development serial input signal helps to provide serial communications for
background debug mode.
2.11.2 Instruction Pipe (IPIPE)
This pin functions as IPIPE in normal operation and as DSO in background debug mode.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 2-9
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 44

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
IPIPE
This active-low output signal is used to track movement of words through the instruction
pipeline.
DSO
This development serial output signal helps to provide serial communications for
background debug mode.
2.11.3 Breakpoint (BKPT)
This pin functions as BKPT in normal operation and as DSCLK in background debug
mode.
BKPT
This active-low input signal is used to signal a hardware breakpoint to the CPU32.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
DSCLK
This development serial clock input helps to provide serial communications for
background debug mode.
2.11.4 Freeze (FREEZE)
Assertion of this active-high output signal indicates that the CPU32 has acknowledged a
breakpoint and has initiated background mode operation.
2.12 DMA MODULE SIGNALS
The following signals are used by the direct memory access (DMA) controller module to
provide external handshake for either a source or destination. See Section 6 DMA
Module for additional information on these signals.
2.12.1 DMA Request (DREQ2, DREQ1)
This active-low input is asserted by a peripheral device to request an operand transfer
between that peripheral and memory. The assertion of
The assertion level in external burst mode is level sensitive; in external cycle steal mode,
it is falling-edge sensitive.
DREQ≈ starts the DMA process.
2.12.2 DMA Acknowledge (DACK2, DACK1)
This active-low output is asserted by the DMA to signal to a peripheral that an operand is
being transferred in response to a previous transfer request.
2.12.3 DMA Done (DONE2, DONE1)
This active-low bidirectional signal is asserted by the DMA or a peripheral device during
any DMA bus cycle to indicate that the last data transfer is being performed.
active input in any mode. As an output, it is only active in external request mode. An
external pullup resistor is required even during operation in the internal request mode.
2-10 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
DONE≈ is an
Page 45

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
2.13 SERIAL MODULE SIGNALS
The following signals are used by the serial module for data and clock signals. See
Section 7 Serial Module for more information on these signals.
2.13.1 Serial Crystal Oscillator (X2, X1)
These pins furnish the connection to a crystal or external clock, which must be supplied
when using the baud rate generator. An external clock is connected to the X1 pin; X2 is
left floating.
2.13.2 Serial External Clock Input (SCLK)
This input can be used as the external clock input for channel A or channel B, bypassing
the baud rate generator.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
2.13.3 Receive Data (RxDA, RxDB)
These signals are the receiver serial data input for each channel. Data received on this
signal is sampled on the rising edge of the clock source, with the least significant bit
received first.
2.13.4 Transmit Data (TxDA, TxDB)
These signals are the transmitter serial data output for each channel. The output is held
high ('mark' condition) when the transmitter is disabled, idle, or operating in the local
loopback mode. Data is shifted out on this signal at the falling edge of the clock source,
with the least significant bit transmitted first.
2.13.5 Clear to Send (CTSA, CTSB)
These active-low signals can be programmed as the clear-to-send inputs for each
channel.
2.13.6 Request to Send (RTSA, RTSB)
These active-low signals can be programmed as request-to-send outputs or used as
discrete outputs.
RTSB, RTSA
When used for this function, these signals function as the request-to-send outputs.
OP1, OP0
When used for this function, these outputs are controlled by the value of bit 1 and bit 0,
respectively, in the output port data registers.
2.13.7 Transmitter Ready (T≈RDYA)
This active-low output can be programmed as the channel A transmitter ready status
indicator or used as a discrete output.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 2- 11
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 46

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
T≈RDYA
When used for this function, this signal reflects the complement of the status of bit 2 of
the channel A status register. This signal can be used to control parallel data flow by
acting as an interrupt to indicate when the transmitter contains a character.
OP6
When used for this function, this output is controlled by bit 6 in the output port data
registers.
2.13.8 Receiver Ready (R≈RDYA)
This active-low output signal can be programmed as the channel A receiver ready,
channel A FIFO full indicator, or a dedicated parallel output.
R≈RDYA
nc...
I
When used for this function, this signal reflects the complement of the status of bit 1 of
the interrupt status register. This signal can be used to control parallel data flow by
acting as an interrupt to indicate when the receiver contains a character.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
FFULLA
When used for this function, this signal reflects the complement of the status of bit 1 of
the interrupt status register. This signal can be used to control parallel data flow by
acting as an interrupt to indicate when the receiver FIFO is full.
OP4
When used for this function, this output is controlled by bit 4 in the output port data
registers.
2.14 TIMER SIGNALS
The following external signals are used by the timer modules. See Section 8 Timer
Modules for additional information on these signals.
2.14.1 Timer Gate (TGATE2, TGATE1)
These active-low inputs can be programmed to enable and disable the counters and
prescalers.
TGATE≈ can also be programmed as a simple input.
2.14.2 Timer Input (TIN2, TIN1)
These inputs can be programmed as clocks that cause events to occur in the counters
and prescalers.
2.14.3 Timer Output (TOUT2, TOUT1)
These outputs drive the various output waveforms generated by the timers.
2-12 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 47

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
2.15 TEST SIGNALS
The following signals are used with the on-board test logic defined by the IEEE 1149.1
standard. See Section 9 IEEE 1149.1 Test Access Port for more information on the use
of these signals.
2.15.1 Test Clock (TCK)
This input provides a clock for on-board test logic defined by the IEEE 1149.1 standard.
2.15.2 Test Mode Select (TMS)
This input controls test mode operations for on-board test logic defined by the IEEE
1149.1 standard.
2.15.3 Test Data In (TDI)
nc...
I
This input is used for serial test instructions and test data for on-board test logic defined
by the IEEE 1149.1 standard.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
2.15.4 Test Data Out (TDO)
This output is used for serial test instructions and test data for on-board test logic defined
by the IEEE 1149.1 standard.
2.16 SYNTHESIZER POWER (V
This pin supplies a quiet power source to the VCO to provide greater frequency stability. It
is also used to control the synthesizer mode after reset. See Section 4 System
Integration Module for more information.
CCSYN
2.17 SYSTEM POWER AND GROUND (V
These pins provide system power and ground to the MC68340. Multiple pins are provided
for adequate current capability. All power supply pins must have adequate bypass
capacitance for high-frequency noise suppression.
)
AND GND)
CC
2.18 SIGNAL SUMMARY
Table 2-5 presents a summary of all the signals discussed in the preceding paragraphs.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 2- 13
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 48

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 2-5. Signal Summary
Signal Name Mnemonic Input/Output Active State Three-State
Address Bus A23–A0 Out — Yes
Address Bus Port A7–A0/
Interrupt Acknowledge
Data Bus D15–D0 I/O — Yes
Function Codes FC3–FC0 Out — Yes
Chip Select 3/Interrupt Request
Level/Port B4, B2, B1
Chip Select 0/Autovector CS0 Out/In Low/Low No
Bus Request BR In Low —
Bus Grant BG Out Low No
Bus Grant Acknowledge BGACK In Low —
Data and Size Acknowledge DSACK1,
Read-Modify-Write Cycle RMC Out Low Yes
Address Strobe AS Out Low Yes
Data Strobe DS Out Low Yes
Size SIZ1, SIZ0 Out — Yes
Read/Write R/W Out High/Low Yes
Interrupt Request Level/
Port B7, B6, B5, B3
Reset RESET I/O Low No
Halt HALT I/O Low No
Bus Error BERR In Low —
System Clock CLKOUT Out — No
Crystal Oscillator EXTAL, XTAL In, Out — —
External Filter Capacitor XF C In — —
Clock Mode Select/Port B0 MODCK In/I/O —/— —
Instruction Fetch/
Development Serial In
Instruction Pipe/
Development Serial Out
A31–A24 Out/I/O/Out —/—/Low Yes
CS3–CS1 Out/In/I/O Low/Low/— No
In Low —
DSACK0
IRQ7, IRQ6,
IRQ5, IRQ3
IFETCH/DSI Out/In Low/— No/—
IPIPE/DSO Out/Out Low/— No/—
In/I/O Low/— —
Breakpoint/
Development Serial Clock
Freeze FREEZE Out High No
Receive Data RxDA, RxDB I n — —
2-14 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
BKPT/DSCLK In/In Low/— —/—
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 49

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 2-5. Signal Summary (Continued)
Signal Name Mnemonic Input/Output Active State Three-State
Transmit Data TxDA, TxDB Out — No
Clear-to-Send CTSA, CTSB In Low —
Request-to-Send/
OP1, OP0
Serial Clock SCLK In — —
Transmitter Ready/OP6 T≈RDYA Out/Out Low/— No
Receiver Ready/
FIFO Full/OP4
DMA Request DREQ2, DREQ1 In Low —
DMA Acknowledge DACK2, DACK1 Out Low No
DMA Done DONE2, DONE1 I/O Low No
nc...
I
Timer Gate TGATE2,
Timer Input TIN2, TIN1 In — —
Timer Output TOUT2, TOUT1 Out — Yes
Test Clock TCK In — —
Test Mode Select TMS In High —
Test Data In TDI In High —
Test Data Out TDO Out High —
Synchronizer Power V
System Power Supply and
Return
cale Semiconductor,
RTSB, RTSA Out/Out Low/— No
R≈RDYA Out/Out/Out Low/Low/— No
In Low —
TGATE1
CCSYN
VCC, GND – — —
–——
Frees
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 2- 15
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 50

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
SECTION 3
BUS OPERATION
This section provides a functional description of the bus, the signals that control it, and the
bus cycles provided for data transfer operations. It also describes the error and halt
conditions, bus arbitration, and reset operation. Operation of the external bus is the same
whether the MC68340 or an external device is the bus master; the names and
descriptions of bus cycles are from the viewpoint of the bus master. For exact timing
specifications, refer to Section 11 Electrical Characteristics.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
The MC68340 architecture supports byte, word, and long-word operands allowing access
to 8- and 16-bit data ports through the use of asynchronous cycles controlled by the
SIZ1/SIZ0 outputs and
word operands to be located in memory on word boundaries. The only type of transfer that
can be performed to an odd address is a single-byte transfer, referred to as an odd-byte
transfer. For an 8-bit port, multiple bus cycles may be required for an operand transfer due
to either misalignment or a word or long-word operand.
DSACK1/DSACK0 inputs. The MC68340 requires word and long-
3.1 BUS TRANSFER SIGNALS
The bus transfers information between the MC68340 and external memory or a peripheral
device. External devices can accept or provide 8 bits or 16 bits in parallel and must follow
the handshake protocol described in this section. The maximum number of bits accepted
or provided during a bus transfer is defined as the port width. The MC68340 contains an
address bus that specifies the address for the transfer and a data bus that transfers the
data. Control signals indicate the beginning and type of the cycle as well as the address
space and size of the transfer. The selected device then controls the length of the cycle
with the signal(s) used to terminate the cycle. Strobe signals, one for the address bus and
another for the data bus, indicate the validity of the address and provide timing information
for the data. Both asynchronous and synchronous operation is possible for any port width.
In asynchronous operation, the bus and control input signals are internally synchronized to
the MC68340 clock, introducing a delay. This delay is the time required for the MC68340
to sample an input signal, synchronize the input to the internal clocks, and determine
whether it is high or low. In synchronous mode, the bus and control input signals must be
timed to setup and hold times. Since no synchronization is needed, bus cycles can be
completed in three clock cycles in this mode. Additionally, using the fast-termination option
of the chip select signals, two-clock operation is possible.
Furthermore, for all inputs, the MC68340 latches the level of the input during a sample
window around the falling edge of the clock signal. This window is illustrated in Figure 3-1,
where tsu and th are the input setup and hold times, respectively. To ensure that an input
signal is recognized on a specific falling edge of the clock, that input must be stable during
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3-1
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 51

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
the sample window. If an input makes a transition during the window time period, the level
recognized by the MC68340 is not predictable; however, the MC68340 always resolves
the latched level to either a logic high or low before using it. In addition to meeting input
setup and hold times for deterministic operation, all input signals must obey the protocols
described in this section.
t
su
t
h
CLKOUT
EXT
nc...
I
SAMPLE WINDOW
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Figure 3-1. Input Sample Window
NOTE
The terms
assert
and
negate
are used throughout this section
to avoid confusion when dealing with a mixture of active-low
and active-high signals. The term
assert
or
assertion
indicates
that a signal is active or true independent of the level
represented by a high or low voltage. The term
negation
indicates that a signal is inactive or false.
negate
or
3.1.1 Bus Control Signals
The MC68340 initiates a bus cycle by driving the A31–A0, SIZx, FCx, and R/W outputs. At
the beginning of a bus cycle, SIZ1 and SIZ0 are driven with FC3–FC0. SIZ1 and SIZ0
indicate the number of bytes remaining to be transferred during an operand cycle
(consisting of one or more bus cycles). Table 3-1 lists the encoding of the SIZx signal.
These signals are valid while
the transfer during a bus cycle. Driven at the beginning of a bus cycle, R/
AS is asserted. R/W only transitions when a write cycle is preceded by a read cycle or
vice versa. The signal may remain low for consecutive write cycles. The
asserted at the beginning of the first bus cycle of a read-modify-write operation and
remains asserted until completion of the final bus cycle of the operation.
AS is asserted. The R/ W signal determines the direction of
W is valid while
RMC signal is
3-2 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 52

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 3-1. SIZx Signal Encoding
SIZ1 SIZ0 Transfer Size
0 1 Byte
1 0 Word
1 1 Three Bytes
0 0 Long Word
3.1.2 Function Code Signals
FC3–FC0 are outputs that indicate one of 16 address spaces to which the address
applies. Fifteen of these spaces are designated as either user or supervisor, program or
data, and normal or direct memory access (DMA) spaces. One other address space is
designated as CPU space to allow the CPU32 to acquire specific control information not
normally associated with read or write bus cycles. FC3–FC0 are valid while
asserted.
Function codes (see Table 3-2) can be considered as extensions of the 32-bit address
that can provide up to 16 different 4-Gbyte address spaces. Function codes are
automatically generated by the CPU32 to select address spaces for data and program at
both user and supervisor privilege levels, a CPU address space for processor functions,
and an alternate master address space. User programs access only their own program
and data areas to increase protection of system integrity and can be restricted from
accessing other information. The S-bit in the CPU32 status register is set for supervisor
accesses and cleared for user accesses to provide differentiation. Refer to 3.4 CPU
Space Cycles for more information.
Table 3-2. Address Space Encoding
Function Code Bits
3210 Address Spaces
0000Reserved (Motorola)
0001User Data Space
0010User Program Space
0011Reserved (User )
0100Reserved (Motorola)
0101Supervisor Data Space
0110Supervisor Program Space
0111CPU Space
1 x x x DMA Space
AS is
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3-3
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 53

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.1.3 Address Bus (A31–A0)
These signals are outputs that define the address of the byte (or the most significant byte)
to be transferred during a bus cycle. The MC68340 places the address on the bus at the
beginning of a bus cycle. The address is valid while
AS is asserted.
3.1.4 Address Strobe (AS)
This output timing signal indicates the validity of many control signals and the address on
the address bus.
a bus cycle.
AS is asserted approximately one-half clock cycle after the beginning of
3.1.5 Data Bus (D15–D0)
This bidirectional, nonmultiplexed, parallel bus contains the data being transferred to or
from the MC68340. A read or write operation may transfer 8 or 16 bits of data (one or two
nc...
I
bytes) in one bus cycle. During a read cycle, the data is latched by the MC68340 on the
last falling edge of the clock for that bus cycle. For a write cycle, all 16 bits of the data bus
are driven, regardless of the port width or operand size. The MC68340 places the data on
the data bus approximately one-half clock cycle after
AS is asserted in a write cycle.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
3.1.6 Data Strobe (DS)
DS is an output timing signal that applies to the data bus. For a read cycle, the MC68340
asserts
For a write cycle,
MC68340 asserts
write cycle.
DS and AS simultaneously to signal the external device to place data on the bus.
DS signals to the external device that the data to be written is valid. The
DS approximately one clock cycle after the assertion of AS during a
3.1.7 Bus Cycle Termination Signals
The following signals can terminate a bus cycle.
3.1.7.1 DATA TRANSFER AND SIZE ACKNOWLEDGE SIGNALS (
DSACK0). During bus cycles, external devices assert DSACK1 and/or DSACK0 as part
of the bus protocol. During a read cycle, this signals the MC68340 to terminate the bus
cycle and to latch the data. During a write cycle, this indicates that the external device has
successfully stored the data and that the cycle may terminate. These signals also indicate
to the MC68340 the size of the port for the bus cycle just completed (see Table 3-3). Refer
to 3.3.1 Read Cycle for timing relationships of
Additionally, the system integration module (SIM40) chip select address mask register can
be programmed to internally generate
eliminating logic required to generate these signals. However, if external
are returned earlier than indicated by the DD bits in the chip select address mask register,
the cycle will terminate sooner than programmed. Refer to Section 4 System Integration
Module for additional information. The SIM40 can alternatively be programmed to
generate a fast termination cycle, providing a two-cycle external access. Refer to 3.2.6
Fast Termination Cycles for additional information on these cycles.
DSACK1 and DSACK0.
DSACK1 and DSACK0 for external accesses,
DSACK1 AND
DSACK≈ signals
3-4 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 54

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.1.7.2 BUS ERROR (BERR). This signal is also a bus cycle termination indicator and
can be used in the absence of
be asserted in conjunction with
DSACK≈ to indicate a bus error condition. BERR can also
DSACK≈ to indicate a bus error condition, provided it
meets the appropriate timing described in this section and in Section 11 Electrical
Characteristics. Additionally,
BERR and HALT can be asserted together to indicate a
retry termination. Refer to 3.5 Bus Exception Control Cycles for additional information
on the use of these signals.
The internal bus monitor can be used to generate an internal bus error signal for internal
and internal-to-external transfers. If the bus cycles of an external bus master are to be
monitored, external
BERR generation must be provided since the internal bus error
monitor has no information about transfers initiated by an external bus master.
3.1.7.3 AUTOVECTOR (
AVEC).This signal can be used to terminate interrupt
acknowledge cycles, indicating that the MC68340 should internally generate a vector
(autovector) number to locate an interrupt handler routine.
nc...
I
externally or internally by the SIM40 (see Section 4 System Integration Module for
additional information).
AVEC is ignored during all other bus cycles.
AVEC can be generated either
3.2 DATA TRANSFER MECHANISM
The MC68340 supports byte, word, and long-word operands, allowing access to 8- and
16-bit data ports through the use of asynchronous cycles controlled by
DSACK0. The MC68340 also supports byte, word, and long-word operands, allowing
access to 8- and 16-bit data ports through the use of synchronous cycles controlled by the
fast termination capability of the SIM40.
3.2.1 Dynamic Bus Sizing
The MC68340 dynamically interprets the port size of the addressed device during each
bus cycle, allowing operand transfers to or from 8- and 16-bit ports. During an operand
cale Semiconductor,
transfer cycle, the slave device signals its port size (byte or word) and indicates
completion of the bus cycle to the MC68340 through the use of the
to Table 3-3 for
DSACK≈ encoding.
DSACK≈ inputs. Refer
DSACK1 and
Frees
Table 3-3.
DSACK1 DSACK0 Result
1
(Negated)1(Negated) Insert Wait States in Current Bus Cycle
1
(Negated)0(Asserted) Complete Cycle—Data Bus Port Size Is 8 Bits
0
(Asserted)1(Negated) Complete Cycle—Data Bus Port Size Is 16 Bits
0
(Asserted)0(Asserted)
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3-5
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
DSACK≈ Encoding
Reserved—Defaults to 16-Bit Port Size Can Be
Used for 32-Bit DMA cycles
Page 55

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
For example, if the MC68340 is executing an instruction that reads a long-word operand
from a 16-bit port, the MC68340 latches the 16 bits of valid data and runs another bus
cycle to obtain the other 16 bits. The operation from an 8-bit port is similar, but requires
four read cycles. The addressed device uses
instance, a 16-bit device always returns
the bus cycle is a byte or word operation).
Dynamic bus sizing requires that the portion of the data bus used for a transfer to or from
a particular port size be fixed. A 16-bit port must reside on data bus bits 15–0, and an 8-bit
port must reside on data bus bits 15–8. This requirement minimizes the number of bus
cycles needed to transfer data to 8- and 16-bit ports and ensures that the MC68340
correctly transfers valid data.
The MC68340 always attempts to transfer the maximum amount of data on all bus cycles;
for a word operation, it always assumes that the port is 16 bits wide when beginning the
bus cycle. The bytes of operands are designated as shown in Figure 3-2. The most
nc...
I
significant byte of a long-word operand is OP0, and OP3 is the least significant byte. The
two bytes of a word-length operand are OP0 (most significant) and OP1. The single byte
of a byte-length operand is OP0. These designations are used in the figures and
descriptions that follow.
DSACK≈ to indicate the port width. For
DSACK≈ for a 16-bit port (regardless of whether
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Figure 3-2 shows the required organization of data ports on the MC68340 bus for both
8- and 16-bit devices. The four bytes shown in Figure 3-2 are connected through the
internal data bus and data multiplexer to the external data bus. The data multiplexer
establishes the necessary connections for different combinations of address and data
sizes. The multiplexer takes the two bytes of the 16-bit bus and routes them to their
required positions. The positioning of bytes is determined by the SIZ1/SIZ0 and A0
outputs. The SIZ1/SIZ0 outputs indicate the number of bytes to be transferred during the
current bus cycle (see Table 3-1). The number of bytes transferred during a read or write
bus cycle is equal to or less than the size indicated by the SIZ1/SIZ0 outputs, depending
on port width. For example, during the first bus cycle of a long-word transfer to a word
port, the size outputs indicate that four bytes are to be transferred although only two bytes
are moved on that bus cycle.
The address line A0 also affects the operation of the data multiplexer. During an operand
transfer, A31–A1 indicate the word base address of that portion of the operand to be
accessed, and A0 indicates the byte offset from the base (i.e., either odd or even byte).
Figure 3-2 lists the bytes required on the data bus for read cycles. The entries shown as
OPn are portions of the requested operand that are read or written during that bus cycle
and are defined by SIZ1/SIZ0 and A0 for the bus cycle.
3-6 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 56

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
OPERAND
31
23
OP1OP0
OP0
15
OP2
OP1
OP0
OP3
OP2
OP1
OP0
70
Transfer Case
Case
A0SIZ0SIZ1
(a)
Byte to Byte
(b)
Byte to Word (Even)
(c)
Byte to Word (Odd)
(d)
Word to Byte (Aligned)
(e)
Word to Word (Aligned)
(f)
Long Word to Byte (Aligned)
(g)
Long Word to Word (Aligned)
NOTES:
nc...
I
1. Operands in parentheses are ignored by the MC68340 during read cycles.
2. A 3-byte to byte transfer does occur as the second byte transfer of a long-word to byte port transfer.
01X10
0100X
0110X
10010
1000X
00010
0000X
DSACK0DSACK1
Data Bus
D15 D7
D8
OP0
OP0
(OP0)
OP0
OP0
OP0
OP0 OP1
D0
(OP0)
(OP0)
OP0
(OP1)
OP1
(OP1)
Figure 3-2. MC68340 Interface to Various Port Sizes
3.2.2 Misaligned Operands
In this architecture, the basic operand size is 16 bits. Operand misalignment refers to
whether an operand is aligned on a word boundary or overlaps the word boundary,
determined by address line A0. When A0 is low, the address is even and is a word and
byte boundary. When A0 is high, the address is odd and is a byte boundary only. A byte
operand is properly aligned at any address; a word or long-word operand is misaligned at
an odd address.
At most, each bus cycle can transfer a word of data aligned on a word boundary. If the
MC68340 transfers a long-word operand over a 16-bit port, the most significant operand
cale Semiconductor,
word is transferred on the first bus cycle, and the least significant operand word is
transferred on a following bus cycle.
The CPU32 restricts all operands (both data and instructions) to be aligned. That is, word
Frees
and long-word operands must be located on a word or long-word boundary, respectively.
The only type of transfer that can be performed to an odd address is a single-byte
transfer, referred to as an odd-byte transfer. If a misaligned access is attempted, the
CPU32 generates an address error exception, and enters exception processing. Refer to
Section 5 CPU32 for more information on exception processing.
3.2.3 Operand Transfer Cases
The following cases are examples of the allowable alignments of operands to ports.
3.2.3.1 BYTE OPERAND TO 8-BIT PORT, ODD OR EVEN (A0 = X). The MC68340
drives the address bus with the desired address and the SIZx pins to indicate a single byte operand.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3-7
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 57

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
BYTE OPERAND
DATA BUS
CYCLE 1
OP0
7
0
D0D8D15 D7
(OP0)OP0
01X10
DSACK0DSACK1A0SIZ0SIZ1
For a read operation, the slave responds by placing data on bits 15–8 of the data bus,
asserting
DSACK0 and negating DSACK1 to indicate an 8-bit port. The MC68340 then
reads the operand byte from bits 15–8 and ignores bits 7–0.
For a write operation, the MC68340 drives the single-byte operand on both bytes of the
data bus because it does not know the port size until the
DSACK≈ signals are read. The
slave device reads the byte operand from bits 15–8 and places the operand in the
specified location. The slave then asserts
DSACK0 to terminate the bus cycle.
3.2.3.2 BYTE OPERAND TO 16-BIT PORT, EVEN (A0 = 0). The MC68340 drives the
nc...
I
address bus with the desired address and the SIZx pins to indicate a single-byte operand.
BYTE OPERAND
OP0
7
0
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
DATA BUS
CYCLE 1
OP0
(OP0)
D0D8D15 D7
0100X
DSACK0DSACK1A0SIZ0SIZ1
For a read operation, the slave responds by placing data on bits 15–8 of the data bus and
asserting
DSACK1 to indicate a 16-bit port. The MC68340 then reads the operand byte
from bits 15–8 and ignores bits 7–0.
For a write operation, the MC68340 drives the single-byte operand on both bytes of the
data bus because it does not know the port size until the
DSACK≈ signals are read. The
slave device reads the operand from bits 15–8 of the data bus and uses the address to
place the operand in the specified location. The slave then asserts
DSACK1 to terminate
the bus cycle.
3-8 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 58

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.2.3.3 BYTE OPERAND TO 16-BIT PORT, ODD (A0 = 1). The MC68340 drives the
address bus with the desired address and the SIZx pins to indicate a single-byte operand.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
BYTE OPERAND
DATA BUS
CYCLE 1
(OP0) OP0
OP0
7
0
D0D8D15 D7
0110X
DSACK0DSACK1A0SIZ0SIZ1
For a read operation, the slave responds by placing data on bits 7–0 of the data bus and
asserting
DSACK1 to indicate a 16-bit port. The MC68340 then reads the operand byte
from bits 7–0 and ignores bits 15–8.
For a write operation, the MC68340 drives the single-byte operand on both bytes of the
data bus because it does not know the port size until the
DSACK≈ signals are read. The
slave device reads the operand from bits 7–0 of the data bus and uses the address to
place the operand in the specified location. The slave then asserts
DSACK1 to terminate
the bus cycle.
3.2.3.4 WORD OPERAND TO 8-BIT PORT, ALIGNED. The MC68340 drives the address
bus with the desired address and the SIZx pins to indicate a word operand.
WORD OPERAND
DATA BUS
CYCLE 1
CYCLE 2
OP0 OP1
OP0
OP1
8
D0D8D15 D7
(OP1)
(OP1)
15 7 0
DSACK0DSACK1A0SIZ0SIZ1
10010
01110
For a read operation, the slave responds by placing the most significant byte of the
operand on bits 15–8 of the data bus and asserting
DSACK0 to indicate an 8-bit port. The
MC68340 reads the most significant byte of the operand from bits 15–8 and ignores bits
7–0. The MC68340 then decrements the transfer size counter, increments the address,
and reads the least significant byte of the operand from bits 15–8 of the data bus.
For a write operation, the MC68340 drives the word operand on bits 15–0 of the data bus.
The slave device then reads the most significant byte of the operand from bits 15–8 of the
data bus and asserts
DSACK0 to indicate that it received the data but is an 8-bit port.
The MC68340 then decrements the transfer size counter, increments the address, and
writes the least significant byte of the operand to bits 15–8 of the data bus.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3-9
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 59

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.2.3.5 WORD OPERAND TO 16-BIT PORT, ALIGNED. The MC68340 drives the
address bus with the desired address and the size pins to indicate a word operand.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
WORD OPERAND
DATA BUS
CYCLE 1
OP0 OP1
15 0
D0D8D15 D7
OP0 OP1
DSACK0DSACK1A0SIZ0SIZ1
1000X
For a read operation, the slave responds by placing the data on bits 15–0 of the data bus
and asserting
DSACK1 to indicate a 16-bit port. When DSACK1 is asserted, the
MC68340 reads the data on the data bus and terminates the cycle.
For a write operation, the MC68340 drives the word operand on bits 15–0 of the data bus.
The slave device then reads the entire operand from bits 15–0 of the data bus and asserts
DSACK1 to terminate the bus cycle.
3.2.3.6 LONG-WORD OPERAND TO 8-BIT PORT, ALIGNED. The MC68340 drives the
address bus with the desired address and the SIZx pins to indicate a long-word operand.
LONG-WORD OPERAND
DATA BUS
CYCLE 1
CYCLE 2
CYCLE 3
CYCLE 4
OP0
31 23 15 7
D15
OP0
OP1
OP2
OP3
D8
D7
OP1
(OP1)
(OP1)
(OP3)
(OP3)
OP2 OP3
0
DSACK0DSACK1A0SIZ0SIZ1D0
00010
11110
10010
01110
For a read operation, shown in Figure 3-3, the slave responds by placing the most
significant byte of the operand on bits 15–8 of the data bus and asserting
DSACK0 to
indicate an 8-bit port. The MC68340 reads the most significant byte of the operand (byte
0) from bits 15–8 and ignores bits 7–0. The MC68340 then decrements the transfer size
counter, increments the address, initiates a new cycle, and reads byte 1 of the operand
from bits 15–8 of the data bus. The MC68340 repeats the process of decrementing the
transfer size counter, incrementing the address, initiating a new cycle, and reading a byte
to transfer the remaining two bytes.
For a write operation, shown in Figure 3-4, the MC68340 drives the two most significant
bytes of the operand on bits 15–0 of the data bus. The slave device then reads only the
most significant byte of the operand (byte 0) from bits 15–8 of the data bus and asserts
DSACK0 to indicate reception and an 8-bit port. The MC68340 then decrements the
transfer size counter, increments the address, and writes byte 1 of the operand to bits
15–8 of the data bus. The MC68340 continues to decrement the transfer size counter,
increment the address, and write a byte to transfer the remaining two bytes to the slave
device.
3-10 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 60

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
S0 S2 S4 S0 S2 S4 S0 S2 S4 S0 S2 S4
CLKOUT
A31–A0
FC3–FC0
R/W
nc...
I
AS
DS
SIZ0
4 BYTES 3 BYTES 2 BYTES 1 BYTE
SIZ1
DSACK0
DSACK1
D15–D8
OP0
OP1
OP2
OP3
cale Semiconductor,
D7–D0
BYTE
READ
Frees
BYTE
READ
LONG-WORD OPERAND READ FROM 8-BIT BUS
BYTE
READ
BYTE
READ
Figure 3-3. Long-Word Operand Read Timing from 8-Bit Port
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 11
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 61

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
S2 S4
S0
CLKOUT
A31–A0
FC3–FC0
R/W
AS
DS
SIZ0
nc...
I
SIZ1
4 BYTES
S0 S2 S4 S0 S2 S4 S0 S2 S4
3 BYTES
2 BYTES
1 BYTE
DSACK0
DSACK1
D15–D8
D7–D0
OP0
(OP1)
WRITE WRITE WRITE WRITE
LONG-WORD OPERAND WRITE TO 8-BIT BUS
OP1
(OP1)
OP2 OP3
(OP3) (OP3)
Figure 3-4. Long-Word Operand Write Timing to 8-Bit Port
cale Semiconductor,
3.2.3.7 LONG-WORD OPERAND TO 16-BIT PORT, ALIGNED . Figure 3-5 shows both
long-word and word read and write timing to a 16-bit port.
Frees
LONG-WORD OPERAND
31 23 15 7 0
OP1OP0 OP2 OP3
DSACK0DSACK1A0SIZ0SIZ1
OP3
D0D8D15 D7
0000X
1000X
DATA BUS
CYCLE 1
CYCLE 2
3-12 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
OP0 OP1
OP2
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 62

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
S0 S2 S4 S0 S2 S4 S0 S2 S4 S0 S2 S4 S0 S2 S4 S0 S2
CLKOUT
A31–A0
FC3–FC0
R/W
AS
DS
SIZ0
nc...
I
SIZ1
DSACK0
DSACK1
4 BYTES
2 BYTES
2 BYTES
4 BYTES
2 BYTES 2 BYTES
S4
D15–D8
D7–D0
OP0
OP1
LONG WORD READ
FROM 16-BIT BUS
OP2
OP3
OP0
OP1
WORD READ
FROM 16-BIT BUS
OP0
OP1
LONG WORD WRITE TO
16-BIT BUS
OP2
OP0
OP1OP3
WORD
WRITE TO
16-BIT BUS
Figure 3-5. Long-Word and Word Read and Write Timing—16-Bit Port
cale Semiconductor,
The MC68340 drives the address bus with the desired address and drives the SIZx pins to
indicate a long-word operand. For a read operation, the slave responds by placing the two
DSACK1
Frees
most significant bytes of the operand on bits 15–0 of the data bus and asserting
to indicate a 16-bit port. The MC68340 reads the two most significant bytes of the operand
(bytes 0 and 1) from bits 15–0. The MC68340 then decrements the transfer size counter
by 2, increments the address by 2, initiates a new cycle, and reads bytes 2 and 3 of the
operand from bits 15–0 of the data bus.
For a write operation, the MC68340 drives the two most significant bytes of the operand
on bits 15–0 of the data bus. The slave device then reads the two most significant bytes of
the operand (bytes 0 and 1) from bits 15–0 of the data bus and asserts
DSACK1 to
indicate reception and a 16-bit port. The MC68340 then decrements the transfer size
counter by 2, increments the address by 2, and writes bytes 2 and 3 of the operand to bits
15–0 of the data bus.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 13
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 63

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.2.4 Bus Operation
The MC68340 bus is asynchronous, allowing external devices connected to the bus to
operate at clock frequencies different from the clock for the MC68340. Bus operation uses
the handshake lines (
transfers.
for valid data on a write cycle. Decoding the SIZx outputs and lower address line A0
provides strobes that select the active portion of the data bus. The slave device (memory
or peripheral) responds by placing the requested data on the correct portion of the data
bus for a read cycle or by latching the data on a write cycle; the slave asserts the
AS signals a valid address on the address bus, and DS is used as a condition
DSACK1/DSACK0 combination that corresponds to the port size to terminate the cycle.
Alternatively, the SIM40 can be programmed to assert the
internally and respond for the slave. If no slave responds or the access is invalid, external
control logic may assert
cycle.
AS, DS, DSACK1/DSACK0, BERR, and HALT) to control data
DSACK1/DSACK0 combination
BERR to abort the bus cycle or BERR with HALT to retry the bus
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
DSACK≈ can be asserted before the data from a slave device is valid on a read cycle.
The length of time that
any asynchronous system to ensure that valid data is latched into the MC68340. (See
Section 11 Electrical Characteristics for timing parameters.) Note that no maximum
time is specified from the assertion of
MC68340 can transfer data in a minimum of three clock cycles when the cycle is
terminated with
DSACK≈ is recognized. BERR and/or HALT can be asserted after DSACK≈ is
until
asserted.
asserted in any asynchronous system. If this maximum delay time is violated, the
MC68340 may exhibit erratic behavior.
BERR and or HALT must be asserted within the time specified after DSACK≈ is
DSACK≈, the MC68340 inserts wait cycles in clock-period increments
DSACK≈ may precede data must not exceed a specified value in
AS to the assertion of DSACK≈. Although the
3.2.5 Synchronous Operation with DSACK≈
Although cycles terminated with DSACK≈ are classified as asynchronous, cycles
terminated with
relative to clock edges. The devices that use these cycles must synchronize the response
to the MC68340 clock (CLKOUT) to be synchronous. Since the devices terminate bus
cycles with
The minimum cycle time for these cycles is also three clocks. To support systems that use
the system clock to generate
input setup time and the asynchronous input hold time are given. If the setup and hold
times are met for the assertion or negation of a signal such as
guaranteed to recognize that signal level on that specific falling edge of the system clock.
If the assertion of
data is latched into the MC68340 (for a read cycle) on the next falling clock edge if the
data meets the data setup time. In this case, the parameter for asynchronous operation
can be ignored. The timing parameters are described in Section 11 Electrical
Characteristics.
DSACK≈ can also operate synchronously in that signals are interpreted
DSACK≈, the dynamic bus sizing capabilities of the MC68340 are available.
DSACK≈ and other asynchronous inputs, the asynchronous
DSACK≈, the MC68340 is
DSACK≈ is recognized on a particular falling edge of the clock, valid
3-14 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 64

*
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
If a system asserts DSACK≈ for the required window around the falling edge of S2 and
obeys the proper bus protocol by maintaining
throughout the clock edge that negates
AS (with the appropriate asynchronous input hold
DSACK≈ (and/or BERR/HALT) until and
time), no wait states are inserted. The bus cycle runs at its maximum speed for bus cycles
terminated with
asserted after
the falling clock edge one clock cycle after
DSACK≈ (three clocks per cycle). When BERR (or BERR and HALT) is
DSACK≈, BERR (and HALT) must meet the appropriate setup time prior to
DSACK≈ is recognized. This setup time is
critical, and the MC68340 may exhibit erratic behavior if it is violated. When operating
synchronously, the data-in setup and hold times for synchronous cycles may be used
instead of the timing requirements for data relative to
DS.
3.2.6 Fast Termination Cycles
With an external device that has a fast access time, the chip select circuit fast termination
enable (FTE) can provide a two-clock external bus transfer. Since the chip select circuits
are driven from the system clock, the bus cycle termination is inherently synchronized with
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
the system clock. Refer to Section 4 System Integration Module for more information on
chip selects.When fast termination is selected, the DD bits of the corresponding address
mask register are overridden. Fast termination can only be used with zero wait states. To
use the fast termination option, an external device should be fast enough to have data
ready, within the specified setup time, by the falling edge of S4. Figure 3-6 shows the
DSACK≈ timing for a read with two wait states, followed by a fast termination read and
write. When using the fast termination option,
DS is asserted only in a read cycle, not in a
write cycle.
CLKOUT
AS
DS
R/W
S0 S2 SW SW S4 S0 S4 S0 S4 S0
S1 S3 S5 S1 S5 S1 S5SW*SW
Frees
DSACKx
D15–D0
* DSACKx only internally asserted for fast termination cycles.
TWO WAIT STATES IN READ
FAST
TERMINATION
READ
FAST
TERMINATION
WRITE
Figure 3-6. Fast Termination Timing
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 15
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 65

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.3 DATA TRANSFER CYCLES
The transfer of data between the MC68340 and other devices involves the following
signals:
• Address Bus A31–A0
• Data Bus D15–D0
• Control Signals
The address bus and data bus are parallel, nonmultiplexed buses. The bus master moves
data on the bus by issuing control signals, and the bus uses a handshake protocol to
ensure correct movement of the data. In all bus cycles, the bus master is responsible for
de-skewing all signals it issues at both the start and end of the cycle. In addition, the bus
master is responsible for de-skewing the acknowledge and data signals from the slave
devices. The following paragraphs define read, write, and read-modify-write cycle
operations. Each bus cycle is defined as a succession of states that apply to the bus
nc...
I
operation. These states are different from the MC68340 states described for the CPU32.
The clock cycles used in the descriptions and timing diagrams of data transfer cycles are
independent of the clock frequency. Bus operations are described in terms of external bus
states.
3.3.1 Read Cycle
During a read cycle, the MC68340 receives data from a memory or peripheral device. If
the instruction specifies a long-word or word operation, the MC68340 attempts to read two
bytes at once. For a byte operation, the MC68340 reads one byte. The section of the data
bus from which each byte is read depends on the operand size, address signal A0, and
the port size. Refer to 3.2.1 Dynamic Bus Sizing and 3.2.2 Misaligned Operands for
more information. Figure 3-7 is a flowchart of a word read cycle.
BUS MASTER
cale Semiconductor,
1. SET R/W TO READ
2. DRIVE ADDRESS ON A31–A0
3. DRIVE FUNCTION CODE ON FC3–FC0
Frees
4. DRIVE SIZE PINS FOR OPERAND SIZE
5. ASSERT AS AND DS
1. LATCH DATA
2. NEGATE AS AND DS
ADDRESS DEVICE
ACQUIRE DATA
1. DECODE ADDRESS
2. PLACE DATA ON D15–D0
3. DRIVE DSACKx SIGNALS
SLAVE
PRESENT DATA
TERMINATE CYCLE
1. REMOVE DATA FROM D15–D0
START NEXT CYCLE
2. NEGATE DSACKx
Figure 3-7. Word Read Cycle Flowchart
3-16 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 66

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
State 0—The read cycle starts in state 0 (S0). During S0, the MC68340 places a valid
address on A31–A0 and valid function codes on FC3–FC0. The function codes select the
address space for the cycle. The MC68340 drives R/
become valid, indicating the number of bytes requested for transfer.
W high for a read cycle. SIZ1/SIZ0
State 1—One-half clock later, in state 1 (S1), the MC68340 asserts
address on the address bus. The MC68340 also asserts
device uses R/
or both of the bytes (D15–D8 and D7–D0) are selected by SIZ1/SIZ0 and A0.
State 2—As long as at least one of the
of S2 (meeting the asynchronous input setup time requirement), data is latched on the
falling edge of S4, and the cycle terminates.
State 3—If
wait states instead of proceeding to states 4 and 5. To ensure that wait states are
nc...
I
inserted, both
input setup and hold times around the end of S2. If wait states are added, the MC68340
continues to sample
State 4—At the falling edge of state 4 (S4), the MC68340 latches the incoming data and
samples
State 5—The MC68340 negates
during S5 to provide address hold time for memory systems. R/
FC3–FC0 also remain valid throughout S5. The external device keeps its data and
DSACK≈ to get the port size.
W, SIZ1 or SIZ0, A0, and DS to place its information on the data bus. One
DSACK≈ signals is recognized on the falling edge
DSACK≈ is not recognized by the start of state 3 (S3), the MC68340 inserts
DSACK1 and DSACK0 must remain negated throughout the asynchronous
DSACK≈ on the falling edges of the clock until one is recognized.
AS and DS during state 5 (S5). It holds the address valid
DS during S1. The selected
DSACK≈ signals asserted until it detects the negation of AS or DS (whichever it detects
first). The device must remove its data and negate
clock period after sensing the negation of
asserted beyond this limit may be prematurely detected for the next bus cycle.
AS or DS. DSACK≈ signals that remain
DSACK≈ within approximately one
cale Semiconductor,
AS indicating a valid
W, SIZ1 and SIZ0, and
Frees
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 17
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 67

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.3.2 Write Cycle
During a write cycle, the MC68340 transfers data to memory or a peripheral device. Figure
3-8 is a flowchart of a word write cycle.
BUS MASTER SLAVE
ADDRESS DEVICE
1. SET R/W TO WRITE
2. DRIVE ADDRESS ON A31–A0
3. DRIVE FUNCTION CODE ON FC3–FC0
4. DRIVE SIZE PINS FOR OPERAND SIZE
5. ASSERT AS
6. PLACE DATA ON D15–D0
7. ASSERT DS
TERMINATE OUTPUT TRANSFER
1. DECODE ADDRESS
2. LATCH DATA FROM D15–D0
3. ASSERT DSACKx SIGNALS
ACCEPT DATA
nc...
I
State 0—The write cycle starts in S0. During S0, the MC68340 places a valid address on
A31–A0 and valid function codes on FC3–FC0. The function codes select the address
space for the cycle. The MC68340 drives R/
valid, indicating the number of bytes to be transferred.
State 1—One-half clock later during S1, the MC68340 asserts
address on the address bus.
cale Semiconductor,
State 2—During S2, the MC68340 places the data to be written onto D15–D0, and
samples
Frees
State 3—The MC68340 asserts
bus. As long as at least one of the
1. NEGATE DS AND AS
2. REMOVE DATA FROM D15–D0
START NEXT CYCLE
Figure 3-8. Word Write Cycle Flowchart
DSACK≈ at the end of S2.
DS during S3, indicating that data is stable on the data
TERMINATE CYCLE
1. NEGATE DSACKx
W low for a write cycle. SIZ1/SIZ0 become
AS, indicating a valid
DSACK≈ signals is recognized by the end of S2
(meeting the asynchronous input setup time requirement), the cycle terminates one clock
later. If
DSACK≈ is not recognized by the start of S3, the MC68340 inserts wait states
instead of proceeding to S4 and S5. To ensure that wait states are inserted, both
DSACK1 and DSACK0 must remain negated throughout the asynchronous input setup
and hold times around the end of S2. If wait states are added, the MC68340 continues to
sample
device uses R/
DSACK≈ on the falling edges of the clock until one is recognized. The selected
W, SIZ1/SIZ0, and A0 to latch data from the appropriate byte(s) of D15–D8
and D7–D0. SIZ1/SIZ0 and A0 select the bytes of the data bus. If it has not already done
so, the device asserts
DSACK≈ to signal that it has successfully stored the data.
3-18 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 68

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
State 4—The MC68340 issues no new control signals during S4.
State 5—The MC68340 negates
during S5 to provide address hold time for memory systems. R/
FC0 also remain valid throughout S5. The external device must keep
until it detects the negation of
negate
DSACK≈ within approximately one clock period after sensing the negation of AS
AS and DS during S5. It holds the address and data valid
W, SIZ1/SIZ0, and FC3–
DSACK≈ asserted
AS or DS (whichever it detects first). The device must
or DS. DSACK≈ signals that remain asserted beyond this limit may be prematurely
detected for the next bus cycle.
3.3.3 Read-Modify-Write Cycle
The read-modify-write cycle performs a read, conditionally modifies the data in the
arithmetic logic unit, and may write the data out to memory. In the MC68340, this
operation is indivisible, providing semaphore capabilities for multiprocessor systems.
During the entire read-modify-write sequence, the MC68340 asserts
nc...
I
an indivisible operation is occurring. The MC68340 does not issue a
BR signal during this operation. Figure 3-9 is an example of a functional timing
to a
diagram of a read-modify-write instruction specified in terms of clock periods.
S0 S2 S4 S2 S4 S0
CLK
OUT
A31–A30
FC3–FC0
SIZ1–SIZ0
R/W
S0
cale Semiconductor,
RMC
Frees
AS
RMC to indicate that
BG signal in response
DS
DSACKx
D15–D0
READ
INDIVISIBLE
CYCLE
WRITE
Figure 3-9. Read-Modify-Write Cycle Timing
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 19
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 69

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
State 0—The MC68340 asserts RMC in S0 to identify a read-modify-write cycle. The
MC68340 places a valid address on A31–A0 and valid function codes on FC3–FC0. The
function codes select the address space for the operation. SIZ1/SIZ0 become valid in S0
to indicate the operand size. The MC68340 drives R/
W high for the read cycle.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
State 1—One-half clock later during S1, the MC68340 asserts
address on the address bus. The MC68340 also asserts
State 2—The selected device uses R/
the data bus. Either or both of the bytes (D15–D8 and D7–D0) are selected by SIZ1/SIZ0
and A0. Concurrently, the selected device may assert
State 3—As long as at least one of the
(meeting the asynchronous input setup time requirement), data is latched on the next
falling edge of the clock, and the cycle terminates. If
start of S3, the MC68340 inserts wait states instead of proceeding to S4 and S5. To
ensure that wait states are inserted, both
throughout the asynchronous input setup and hold times around the end of S2. If wait
states are added, the MC68340 continues to sample the
edges of the clock until one is recognized.
State 4—At the end of S4, the MC68340 latches the incoming data.
State 5—The MC68340 negates
required to read in the operand(s), S0–S5 are repeated for each read cycle. When
finished reading, the MC68340 holds the address, R/
for the write portion of the cycle. The external device keeps its data and
asserted until it detects the negation of
must remove the data and negate
sensing the negation of
may be prematurely detected for the next portion of the operation.
Idle States—The MC68340 does not assert any new control signals during the idle states,
but it may internally begin the modify portion of the cycle at this time. S0–S5 are omitted if
no write cycle is required. If a write cycle is required, R/
S0 to prevent bus conflicts with the preceding read portion of the cycle; the data bus is not
driven until S2.
AS or DS. DSACK≈ signals that remain asserted beyond this limit
W, SIZ1/SIZ0, A0, and DS to place information on
DSACK≈ signals is recognized by the end of S2
DSACK1 and DSACK0 must remain negated
AS and DS during S5. If more than one read cycle is
AS or DS (whichever it detects first). The device
DSACK≈ within approximately one clock period after
DS during S1.
DSACK≈.
DSACK≈ is not recognized by the
DSACK≈ signals on the falling
W, and FC3–FC0 valid in preparation
W remains in the read mode until
AS indicating a valid
DSACK≈ signals
State 0—The MC68340 drives R/
to be performed, the address lines may change during S0.
State 1—In S1, the MC68340 asserts
State 2—During S2, the MC68340 places the data to be written onto D15–D0.
State 3—The MC68340 asserts
long as at least one of the
asynchronous input setup time requirement), the cycle terminates one clock later. If
DSACK≈ signals is recognized by the end of S2 (meeting the
W low for a write cycle. Depending on the write operation
AS, indicating a valid address on the address bus.
DS during S3, indicating stable data on the data bus. As
DSACK≈ is not recognized by the start of S3, the MC68340 inserts wait states instead of
3-20 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 70

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
proceeding to S4 and S5. To ensure that wait states are inserted, both DSACK1 and
DSACK0 must remain negated throughout the asynchronous input setup and hold times
around the end of S2. If wait states are added, the MC68340 continues to sample
DSACK≈ on the falling edges of the clock until one is recognized. The selected device
uses R/
W, DS, SIZ1/SIZ0, and A0 to latch data from the appropriate section(s) of D15–D8
and D7–D0. SIZ1/SIZ0 and A0 select the data bus sections. If it has not already done so,
the device asserts
DSACK≈ when it has successfully stored the data.
State 4—The MC68340 issues no new control signals during S4.
State 5—The MC68340 negates
during S5 to provide address hold time for memory systems. R/
AS and DS during S5. It holds the address and data valid
W and FC3–FC0 also
remain valid throughout S5. If more than one write cycle is required, states S0–S5 are
repeated for each write cycle. The external device keeps
the negation of
negate
nc...
I
or DS.
DSACK≈ within approximately one clock period after sensing the negation of AS
AS or DS (whichever it detects first). The device must remove its data and
DSACK≈ asserted until it detects
3.4 CPU SPACE CYCLES
FC3–FC0 select user and supervisor program and data areas. The area selected by FC3–
FC0 = $7 is classified as the CPU space. The breakpoint acknowledge, LPSTOP
broadcast, module base address register access, and interrupt acknowledge cycles
described in the following paragraphs use CPU space. The CPU space type, which is
encoded on A19–A16 during a CPU space operation, indicates the function that the
MC68340 is performing. On the MC68340, four of the encodings are implemented as
shown in Figure 3-10. All unused values are reserved by Motorola for additional CPU
space types.
CPU SPACE CYCLES
cale Semiconductor,
BREAKPOINT
ACKNOWLEDGE
Frees
LOW-POWER
STOP BROADCAST
FUNCTION
CODE
3
111
0
3
0
0
111
31
0
00000000
31
00000000
ADDRESS BUS
19 16
0000000000000000000 T0BKPT#
19 16 0
0
00000
111111111111111110
0
MODULE BASE
ADDRESS
REGISTER ACCESS
INTERRUPT
ACKNOWLEDGE
3
0
3
0
11 1
111
31
0
00000000
31
0
000000111111111100000000
111111111111
19
16
19 16
1111111111111111 1
CPU SPACE
TYPE FIELD
LEVEL
0
0
Figure 3-10. CPU Space Address Encoding
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 21
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 71

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.4.1 Breakpoint Acknowledge Cycle
The breakpoint acknowledge cycle allows external hardware to insert an instruction
directly into the instruction pipeline as the program executes. The breakpoint acknowledge
cycle is generated by the execution of a breakpoint instruction (BKPT) or the assertion of
BKPT pin. The T-bit state (shown in Figure 3-10) differentiates a software breakpoint
the
cycle (T = 0) from a hardware breakpoint cycle (T = 1).
When a BKPT instruction is executed (software breakpoint), the MC68340 performs a
word read from CPU space, type 0, at an address corresponding to the breakpoint number
(bits [2–0] of the BKPT opcode) on A4–A2, and the T-bit (A1) is cleared. If this bus cycle is
terminated with
illegal instruction exception processing. If the bus cycle is terminated by
MC68340 uses the data on D15–D0 (for 16-bit ports) or two reads from D15–D8 (for 8-bit
ports) to replace the BKPT instruction in the internal instruction pipeline and then begins
execution of that instruction.
When the CPU32 acknowledges a
background mode disabled, the CPU32 performs a word read from CPU space, type 0, at
an address corresponding to all ones on A4–A2 (BKPT#7), and the T-bit (A1) is set. If this
bus cycle is terminated by
processing. If this bus cycle is terminated by
data bus and continues execution of the next instruction.
The breakpoint operation flowchart is shown in Figure 3-11. Figures 3-12 and 3-13 show
the timing diagrams for the breakpoint acknowledge cycle with instruction opcodes
supplied on the cycle and with an exception signaled, respectively.
BERR (i.e., no instruction word is available), the MC68340 then performs
DSACK≈, the
BKPT pin assertion (hardware breakpoint) with
BERR, the MC68340 performs hardware breakpoint exception
DSACK≈, the MC68340 ignores data on the
NOTE
BKPT pin is sampled on the same clock phase as data
The
and is latched with data as it enters the CPU32 pipeline. If
BKPT is asserted for only one bus cycle and a pipeline flush
occurs before
ignored. To ensure detection of
can be asserted until a breakpoint acknowledge cycle is
recognized.
BKPT is detected by the CPU32, BKPT is
BKPT by the CPU32, BKPT
3-22 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 72

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.4.2 LPSTOP Broadcast Cycle
The low power stop (LPSTOP) broadcast cycle is generated by the CPU32 executing the
LPSTOP instruction. Since the external bus interface must get a copy of the interrupt
mask level from the CPU32, the CPU32 performs a CPU space type 3 write with the mask
level encoded on the data bus, as shown in the following figure. The CPU space type 3
cycle waits for the bus to be available, and is shown externally to indicate to external
devices that the MC68340 is going into LPSTOP mode. If an external device requires
additional time to prepare for entry into LPSTOP mode, entry can be delayed by asserting
HALT. The SIM40 provides internal DSACK≈ response to this cycle. For more information
on how the SIM40 responds to LPSTOP mode, see Section 4 System Integration
Module.
1514131211109876543210
—————————————I2I1I0
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
I2–I0—Interrupt Mask Level
The interrupt mask level is encoded on bits 2–0 of the data bus during an LPSTOP
broadcast.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 23
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 73

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
BREAKPOINT OPERATION FLOW
PROCESSOR
ACKNOWLEDGE BREAKPOINT
IF BREAKPOINT INSTRUCTION EXECUTED:
1. SET R/W TO READ
2. SET FUNCTION CODE TO CPU SPACE
3. PLACE CPU SPACE TYPE 0 ON A19–A16
4. PLACE BREAKPOINT NUMBER ON A2–A4
5. CLEAR T-BIT (A1)
nc...
I
6. SET SIZE TO WORD
7. ASSERT AS AND DS
IF BKPT PIN ASSERTED:
1. SET R/W TO READ
2. SET FUNCTION CODE TO CPU SPACE
3. PLACE CPU SPACE TYPE 0 ON A19–A16
4. PLACE ALL ONE'S ON A4–A2
5. SET T-BIT (A-1) TO ONE
6. SET SIZE TO WORD
7. ASSERT AS AND DS
IF BREAKPOINT INSTRUCTION EXECUTED AND
DSACKx IS ASSERTED:
1. LATCH DATA
2. NEGATE AS AND DS
3. GO TO (A)
IF BKPT PIN ASSERTED AND DSACKx IS ASSERTED:
1. NEGATE AS AND DS
2. GO TO (A)
IF BERR ASSERTED:
1. NEGATE AS AND DS
2. GO TO (B)
(A) (B)
IF BREAKPOINT INSTRUCTION EXECUTED:
1. PLACE REPLACEMENT OPCODE ON DATA BUS
2. ASSERT DSACKx
-OR-
1. ASSERT BERR TO INITIATE EXCEPTION PROCESSING
IF BKPT PIN ASSERTED:
1. ASSERT DSACKx
-OR-
1. ASSERT BERR TO INITIATE EXCEPTION PROCESSING
cale Semiconductor,
1. NEGATE DSACKx or BERR
Frees
IF BREAKPOINT INSTRUCTION EXECUTED:
1. PLACE LATCHED DATA IN INSTRUCTION PIPELINE
2. CONTINUE PROCESSING
IF BKPT PIN ASSERTED:
1. CONTINUE PROCESSING
EXTERNAL DEVICE
IF BREAKPOINT INSTRUCTION EXECUTED:
1. INITIATE ILLEGAL INSTRUCTION PROCESSING
IF BKPT PIN ASSERTED:
1. INITIATE HARDWARE BREAKPOINT PROCESSING
Figure 3-11. Breakpoint Operation Flowchart
3-24 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 74

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5
CLKOUT
A31–A20
A19–A16
A4–A1
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
A15–A5,A0
FC3–FC0
SIZ0
SIZ1
AS
DS
R/W
DSACKx
D7–D0
D15–D8
BERR
BREAKPOINT ENCODING (0000)
BREAKPOINT NUMBER/T-BIT
S0
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S0
CPU SPACE
Frees
HALT
BKPT
BREAKPOINT
OCCURS
READ
BREAKPOINT
ACKNOWLEDGE
INSTRUCTION WORD FETCH
FETCHED
INSTRUCTION
EXECUTION
Figure 3-12. Breakpoint Acknowledge Cycle Timing (Opcode Returned)
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 25
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 75

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5
CLKOUT
A31–A20
A19–A16
A4–A1
nc...
I
A15–A5, A0
FC3–FC0
SIZ0
SIZ1
AS
DS
R/W
DSACKx
D7–D0
cale Semiconductor,
D15–D8
BERR
S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S0
BREAKPOINT ENCODING (0000)
BREAKPOINT NUMBER/T-BIT
CPU SPACE
Frees
HALT
BKPT
BREAKPOINT
OCCURS
READ
BREAKPOINT
ACKNOWLEDGE
BUS ERROR ASSERTED
EXCEPTION
STACKING
Figure 3-13. Breakpoint Acknowledge Cycle Timing (Exception Signaled)
3-26 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 76

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.4.3 Module Base Address Register Access
All internal module registers, including the SIM40, occupy a single 4-Kbyte block that is
relocatable along 4-Kbyte boundaries. The location is fixed by writing the desired base
address of the SIM40 block to the module base address register using the MOVES
instruction. The module base address register is only accessible in CPU space at address
$0003FF00. The SFC or DFC register must indicate CPU space (FC3–FC0 = $7), using
the MOVEC instruction, before accessing the module base address register. Refer to
Section 4 System Integration Module for additional information on the module base
address register.
3.4.4 Interrupt Acknowledge Bus Cycles
The CPU32 makes an interrupt pending in three cases. The first case occurs when a
peripheral device signals the CPU32 (with
and the internally synchronized value on these signals indicates a higher priority than the
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
interrupt mask in the status register. The second case occurs when a transition has
occurred in the case of a level 7 interrupt. A recognized level 7 interrupt must be removed
for one clock cycle before a second level 7 can be recognized. The third case occurs if,
upon returning from servicing a level 7 interrupt, the request level stays at 7 and the
processor mask level changes from 7 to a lower level, a second level 7 is recognized. The
CPU32 takes an interrupt exception for a pending interrupt within one instruction boundary
(after processing any other pending exception with a higher priority). The following
paragraphs describe the types of interrupt acknowledge bus cycles that can be executed
as part of interrupt exception processing.
3.4.4.1 INTERRUPT ACKNOWLEDGE CYCLE—TERMINATED NORMALLY. When the
CPU32 processes an interrupt exception, it performs an interrupt acknowledge cycle to
obtain the number of the vector that contains the starting location of the interrupt service
routine. Some interrupting devices have programmable vector registers that contain the
interrupt vectors for the routines they use. The following paragraphs describe the interrupt
acknowledge cycle for these devices. Other interrupting conditions or devices that cannot
supply a vector number will use the autovector cycle described in 3.4.4.2 Autovector
Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle.
IRQ7–IRQ1) that the device requires service
Frees
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 27
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 77

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
The interrupt acknowledge cycle is a read cycle. It differs from the read cycle described in
3.3.1 Read Cycle in that it accesses the CPU address space. Specifically, the differences
are as follows:
1. FC3–FC0 are set to $7 (FC3/FC2/FC1/FC0 = 0111) for CPU address space.
2. A3, A2, and A1 are set to the interrupt request level, and the
IACK≈ strobe
corresponding to the current interrupt level is asserted. (Either the function codes
and address signals or the
IACK≈ strobes can be monitored to determine that an
interrupt acknowledge cycle is in progress and the current interrupt level.)
3. The CPU32 space type field (A19–A16) is set to $F (interrupt acknowledge).
4. Other address signals (A31–A20, A15–A4, and A0) are set to one.
5. The SIZ0/SIZ1 and R/W signals are driven to indicate a single-byte read cycle.
The responding device places the vector number on the least significant byte
of its data port (for an 8-bit port, the vector number must be on D15–D8; for a
16-bit port, the vector must be on D7–D0) during the interrupt acknowledge cycle.
nc...
I
The cycle is then terminated normally with
DSACK≈.
Figure 3-14 is a flowchart of the interrupt acknowledge cycle; Figure 3-15 shows the
timing for an interrupt acknowledge cycle terminated with
REQUEST INTERRUPT
1. SYNCHRONIZE IRQ7–IRQ1
2. COMPARE IRQ1–IRQ7 TO MASK LEVEL AND
WAIT FOR INSTRUCTION TO COMPLETE
3. PLACE INTERRUPT LEVEL ON A3–A1;
TYPE FIELD (A19–A16) = $F
4. SET R/W TO READ
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
1. PLACE VECTOR NUMBER ON LEAST
SIGNIFICANT BYTE OF DATA BUS
2. ASSERT DSACKx (OR AVEC IF NO VECTOR
NUMBER)
PROVIDE VECTOR NUMBER
5. SET FC3–FC0 TO 0111
6. DRIVE SIZE PINS TO INDICATE A ONE-BYTE
TRANSFER
7. ASSERT AS AND DS
8. ASSERT THE CORRESPONDING IACKx STROBE.
DSACK≈.
MC68340INTERRUPTING DEVICE
GRANT INTERRUPT
ACQUIRE VECTOR NUMBER
1. LATCH VECTOR NUMBER
RELEASE
1. NEGATE DSACKx
2. NEGATE DS AND AS
START NEXT CYCLE
Figure 3-14. Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle Flowchart
3-28 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 78

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
S0 S2 S4 S2 S4 S0
CLKOUT
A31–A4
0–2 CLOCKS*
S0 S1 S2
A3–A1
A0
FC3–FC0
nc...
I
SIZ0
SIZ1
R/W
AS
DS
DSACKx
D7–D0
D15–D8
cale Semiconductor,
IRQ7–IRQ1
INTERRUPT LEVEL
CPU SPACE
1 BYTE
VECTOR FROM 16-BIT PORT
VECTOR FROM 8-BIT PORT
Frees
IACK7–IACK1
*Internal Arbitration may take between 0–2 clock cycles.
READ
CYCLE
INTERNAL
ARBITRATION
WRITE
STACK
IACK CYCLE
Figure 3-15. Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle Timing
3.4.4.2 AUTOVECTOR INTERRUPT ACKNOWLEDGE CYCLE. When the interrupting
device cannot supply a vector number, it requests an automatically generated vector
(autovector). Instead of placing a vector number on the data bus and asserting
the device asserts
during an interrupt acknowledge cycle terminated by
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 29
AVEC to terminate the cycle. If the DSACK≈ signals are asserted
AVEC, the DSACK≈ signals and
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
DSACK≈,
Page 79

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
data will be ignored if AVEC is asserted before or at the same time as the DSACK≈
signals. The vector number supplied in an autovector operation is derived from the
interrupt level of the current interrupt. When
an interrupt acknowledge cycle, the MC68340 ignores the state of the data bus and
internally generates the vector number (the sum of the interrupt level plus 24 ($18)).
AVEC is asserted instead of DSACK≈ during
AVEC is multiplexed with CS0. The FIRQ bit in the SIM40 module configuration register
controls whether the
Section 4 System Integration Module for additional information).
during an interrupt acknowledge cycle. During all other cycles,
Additionally,
autovector register. Seven distinct autovectors can be used, corresponding to the seven
levels of interrupt available with signals
autovector operation.
3.4.4.3 SPURIOUS INTERRUPT CYCLE. Requested interrupts, whether internal or
nc...
I
external, are arbitrated internally. When no internal module (including the SIM40, which
responds for external requests) responds during an interrupt acknowledge cycle by
arbitrating for the interrupt acknowledge cycle internally, the spurious interrupt monitor
generates an internal bus error signal to terminate the vector acquisition. The MC68340
automatically generates the spurious interrupt vector number (24) instead of the interrupt
vector number in this case. When an external device does not respond to an interrupt
acknowledge cycle with
results in the CPU32 taking the spurious interrupt vector. If
MC68340 retries the interrupt acknowledge cycle instead of using the spurious interrupt
vector.
AVEC can be internally generated for external devices by programming the
cale Semiconductor,
AVEC/CS0 pin is used as an autovector input or as CS0 (refer to
AVEC is only sampled
AVEC is ignored.
IRQ7–IRQ1. Figure 3-16 shows the timing for an
AVEC or DSACK≈, a bus monitor must assert BERR, which
HALT is also asserted, the
Frees
3-30 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 80

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
S0 S2 S4 S2 S4
CLKOUT
A31–A4
0–2 CLOCKS*
S1
S0S0
S2
A3–A1
A0
FC3–FC0
nc...
I
SIZ0
SIZ1
R/W
AS
DS
DSACKx
D15–D0
cale Semiconductor,
AVEC
INTERRUPT LEVEL
CPU SPACE
1 BYTE
Frees
IRQ7–IRQ1
IACK7–IACK1
CYCLE
READ
* Internal Arbitration may take between 0–2 clocks.
ARBITRATION
INTERNAL
IACK
CYCLE
WRITE
STACK
Figure 3-16. Autovector Operation Timing
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 31
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 81

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.5 BUS EXCEPTION CONTROL CYCLES
The bus architecture requires assertion of DSACK≈ from an external device to signal that
a bus cycle is complete. Neither
•
DSACK≈/AVEC is programmed to respond internally.
• The external device does not respond.
• Various other application-dependent errors occur.
DSACK≈ nor AVEC is asserted in the following cases:
The MC68340 provides
within an appropriate period of time after the MC68340 asserts AS. This mechanism
allows the cycle to terminate and the MC68340 to enter exception processing for the error
condition.
external device for debugging purposes to cause single bus cycle operation, or, in
combination with
bus cycle for a retry or a bus error condition,
nc...
I
and negated with the rising edge of the MC68340 clock. This assures that when two
signals are asserted simultaneously, the required setup and hold time for both is met for
the same falling edge of the MC68340 clock. This or an equivalent precaution should be
designed into the external circuitry to provide these signals. Alternatively, the internal bus
monitor could be used. The acceptable bus cycle terminations for asynchronous cycles
are summarized in relation to
3-4):
• Normal Termination: DSACK≈ is asserted; BERR and HALT remain negated (case 1).
• Halt Termination:
HALT is also used for bus exception control. This signal can be asserted by an
BERR, a retry of a bus cycle in error. To properly control termination of a
BERR remains negated (case 2).
• Bus Error Termination:
DSACK≈ (case 3) or after DSACK≈ (case 4), and HALT remains negated; BERR is
negated at the same time as or after
• Retry Termination:
cale Semiconductor,
before
time as or after
DSACK≈ (case 5) or after DSACK≈ (case 6); BERR is negated at the same
BERR.
BERR when no device responds by asserting DSACK≈/ AVEC
DSACK≈, BERR, and HALT can be asserted
DSACK≈ assertion as follows (case numbers refer to Table
HALT is asserted at the same time as or before DSACKx, and
BERR is asserted in lieu of, at the same time as, or before
DSACK≈.
HALT and BERR are asserted in lieu of, at the same time as, or
DSACK≈, and HALT may be negated at the same time as or after
Frees
Table 3-4 lists various combinations of control signal sequences and the resulting bus
cycle terminations. To ensure predictable operation,
according to the specifications given in Section 11 Electrical Characteristics.
BERR
of the next bus cycle, that cycle may be terminated prematurely.
EXAMPLE A: A system uses a bus monitor timer to terminate accesses to an unpopulated
address space. The timer asserts
3-32 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
, and HALT may be negated after AS. If DSACK≈ or BERR remain asserted into S2
BERR after timeout (case 3).
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
BERR and HALT should be negated
DSACK≈
Page 82

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
EXAMPLE B: A system uses error detection and correction on RAM contents. The
designer may:
1. Delay DSACK≈ until data is verified and assert BERR and HALT simultaneously to
indicate to the MC68340 to automatically retry the error cycle (case 5), or if data is
valid, assert
DSACK≈ (case 1).
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
2. Delay
DSACK≈ until data is verified and assert BERR with or without DSACK≈ if
data is in error (case 3). This initiates exception processing for software handling of
the condition.
3. Return
DSACK≈ prior to data verification; if data is invalid, BERR is asserted on the
next clock cycle (case 4). This initiates exception processing for software handling of
the condition.
4. Return
DSACK≈ prior to data verification; if data is invalid, assert BERR and HALT
on the next clock cycle (case 6). The memory controller can then correct the RAM
prior to or during the automatic retry.
Table 3-4. DSACK≈, BERR, and HALT Assertion Results
Asserted on Rising
Edge of State
Case
Num
1 DSACK≈
2 DSACK≈
3 DSACK≈
4 DSACK≈
5 DSACK≈
6 DSACK≈
Control
Signal N N + 2 Result
Normal cycle terminate and continue.
Normal cycle terminate and halt; continue
when
HALT negated.
Terminate and take bus error exception,
possibly deferred.
Terminate and take bus error exception,
possibly deferred.
Terminate and retry when
Terminate and retry when
BERR
HALT
BERR
HALT
BERR
HALT
BERR
HALT
BERR
HALT
BERR
HALT
A
NA
NA
A
NA
A/S
NA/A
A
NA
A
NA
NA
NA/A
A
A/S
A
NA
NA
S
NA
X
S
NA
S
X
S
X
X
A
NA
X
S
S
X
A
A
HALT negated.
HALT negated.
NOTES:
N — Number of the current even bus state (e.g., S2, S4, etc.)
A — Signal is asserted in this bus state
NA — Signal is not asserted in this state
X — Don't care
S — Signal was asserted in previous state and remains asserted in this state
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 33
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 83

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.5.1 Bus Errors
BERR can be used to abort the bus cycle and the instruction being executed. BERR takes
precedence over
11 Electrical Characteristics . If
unpredictable operation of the MC68340. If
cycle, it may cause incorrect operation of that cycle. When
bus cycle, the MC68340 can enter exception processing immediately following the bus
cycle, or it can defer processing the exception.
The instruction prefetch mechanism requests instruction words from the bus controller
before it is ready to execute them. If a bus error occurs on an instruction fetch, the
MC68340 does not take the exception until it attempts to use that instruction word. Should
an intervening instruction cause a branch or should a task switch occur, the bus error
exception does not occur. The bus error condition is recognized during a bus cycle in any
of the following cases:
nc...
I
DSACK≈ and HALT are negated, and BERR is asserted.
•
DSACK≈ provided it meets the timing constraints described in Section
BERR does not meet these constraints, it may cause
BERR remains asserted into the next bus
BERR is issued to terminate a
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
HALT and BERR are negated, and DSACK≈ is asserted. BERR is then asserted
•
within one clock cycle (
BERR and HALT are asserted simultaneously, indicating a retry.
•
When the MC68340 recognizes a bus error condition, it terminates the current bus cycle in
the normal way. Figure 3-17 shows the timing of a bus error for the case in which
HALT remains negated).
DSACK≈ is not asserted. Figure 3-18 shows the timing for a bus error that is asserted
DSACK≈. Exceptions are taken in both cases. Refer to Section 5 CPU32 for details
after
of bus error exception processing.
In the second case, in which
asserted within the time specified for purely asynchronous operation, or it must be
asserted and remain stable during the sample window around the next falling edge of the
clock after
exhibit erratic behavior.
present on the bus, but it may not be valid. This sequence can be used by systems that
have memory error detection and correction logic and by external cache memories.
DSACK≈ is recognized. If BERR is not stable at this time, the MC68340 may
BERR is asserted after DSACK≈ is asserted, BERR must be
BERR has priority over DSACK≈. In this case, data may be
3-34 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 84

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
S0 S2
CLKOUT
A31–A0
FC3–FC0
nc...
I
R/W
AS
DS
DSACKx
D15–D0
BERR
cale Semiconductor,
READ CYCLE WITH BUS
ERROR
INTERNAL
PROCESSING
Figure 3-17. Bus Error without DSACK≈
S0 S2SW S4SW S4
STACK
WRITE
Frees
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 35
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 85

CLKOUT
A31–A0
FC3–FC0
R/W
AS
DS
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
S0 S2 S4 S0 S2 S4
nc...
I
3.5.2 Retry Operation
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
When both BERR and HALT are asserted by an external device during a bus cycle, the
MC68340 enters the retry sequence shown in Figure 3-19. A delayed retry, which is
similar to the delayed
The MC68340 terminates the bus cycle, places the control signals in their inactive state,
and does not begin another bus cycle until the
external logic. After a synchronization delay, the MC68340 retries the previous cycle using
the same access information (address, function code, size, etc.).
DSACKx
D15–D0
BERR
WRITE
CYCLE
INTERNAL
PROCESSING
STACK
WRITE
Figure 3-18. Late Bus Error with DSACK≈
BERR signal described previously, can also occur (see Figure 3-20).
BERR and HALT signals are negated by
BERR should be negated
before S2 of the retried cycle to ensure correct operation of the retried cycle.
3-36 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 86

CLKOUT
A31–A0
FC3–FC0
R/W
AS
DS
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
S0 S2 S0 S2SW S4SW S4
nc...
I
The MC68340 retries any read or write cycle of a read-modify-write operation separately;
cale Semiconductor,
RMC remains asserted during the entire retry sequence. Asserting BR along with BERR
and HALT provides a relinquish and retry operation. The MC68340 does not relinquish the
bus during a read-modify-write operation. Any device that requires the MC68340 to give
up the bus and retry a bus cycle during a read-modify-write cycle must assert only
Frees
and BR (HALT must not be included). The bus error handler software should examine the
DSACKx
D15–D0
BERR
HALT
DATA
IGNORED
RETRY
Figure 3-19. Retry Sequence
READ RERUNHALTREAD CYCLE WITH
BERR
read-modify-write bit in the special status word (see Section 5 CPU32) and take the
appropriate action to resolve this type of fault when it occurs.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 37
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 87

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
S0 S2 S4 S0 S2 S4
CLKOUT
A31–A0
FC3–FC0
R/W
AS
DS
DSACKx
nc...
I
D15–D10
BERR
HALT
WRITE
CYCLE
HALT
Figure 3-20. Late Retry Sequence
3.5.3 Halt Operation
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
When HALT is asserted and BERR is not asserted, the MC68340 halts external bus
activity at the next bus cycle boundary (see Figure 3-21).
terminate a bus cycle. Negating and reasserting
HALT in accordance with the correct
timing requirements provides a single-step (bus cycle to bus cycle) operation. Since
affects external bus cycles only, a program that does not require use of the external bus
may continue executing. The single-cycle mode allows the user to proceed through (and
debug) external MC68340 operations, one bus cycle at a time. Since the occurrence of a
bus error while
HALT is asserted causes a retry operation, the user must anticipate retry
WRITE
RERUN
HALT by itself does not
HALT
cycles while debugging in the single-cycle mode. The single-step operation and the
software trace capability allow the system debugger to trace single bus cycles, single
instructions, or changes in program flow.
When the MC68340 completes a bus cycle with
HALT asserted, D15–D0 is placed in the
high-impedance state, and bus control signals are negated (not high-impedance state);
the A31–A0, FCx, SIZx, and R/
W signals remain in the same state. The halt operation has
no effect on bus arbitration (see 3.6 Bus Arbitration). When bus arbitration occurs while
the MC68340 is halted, the address and control signals are also placed in the highimpedance state. Once bus mastership is returned to the MC68340, if
3-38 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
HALT is still
Page 88

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
asserted, the A31–A0, FCx, SIZx, and R/W signals are again driven to their previous
states. The MC68340 does not service interrupt requests while it is halted.
S0 S2 S4
CLKOUT
A31–A0
FC3–FC0
R/W
AS
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
DS
DSACKx
D15–D10
HALT
BR
BG
BGACK
READ
(ARBITRATION PERMITTED
HALT
WHILE THE PROCESSOR IS
HALTED)
S0 S2 S4
READ
S0
Figure 3-21. HALT Timing
Frees
3.5.4 Double Bus Fault
A double bus fault results when a bus error or an address error occurs during the
exception processing sequence for any of the following:
• A previous bus error
• A previous address error
• A reset
For example, the MC68340 attempts to stack several words containing information about
the state of the machine while processing a bus error exception. If a bus error exception
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 39
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 89

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
occurs during the stacking operation, the second error is considered a double bus fault.
When a double bus fault occurs, the MC68340 halts and asserts
operation can restart a halted MC68340. However, bus arbitration can still occur (see 3.6
Bus Arbitration). A second bus error or address error that occurs after exception
processing has completed (during the execution of the exception handler routine or later)
does not cause a double bus fault. A bus cycle that is retried does not constitute a bus
error or contribute to a double bus fault. The MC68340 continues to retry the same bus
cycle as long as the external hardware requests it.
Reset can also be generated internally by the halt monitor (see Section 5 CPU32).
HALT. Only a reset
3.6 BUS ARBITRATION
The bus design of the MC68340 provides for a single bus master at any one time, either
the MC68340 or an external device. One or more of the external devices on the bus can
have the capability of becoming bus master for the external bus, but not the MC68340
internal bus. Bus arbitration is the protocol by which an external device becomes bus
master; the bus controller in the MC68340 manages the bus arbitration signals so that the
MC68340 has the lowest priority. External devices that need to obtain the bus must assert
the bus arbitration signals in the sequences described in the following paragraphs.
Systems having several devices that can become bus master require external circuitry to
assign priorities to the devices so that, when two or more external devices attempt to
become bus master at the same time, the one having the highest priority becomes bus
master first. The sequence of the protocol is as follows:
1. An external device asserts
2. The MC68340 asserts
3. The external device asserts
The MC68340 does not place
state after reset or when the bus is granted to an external
master.
BR may be issued any time during a bus cycle or between cycles. BG is asserted in
response to
operand transfer. Additionally,
operation (when
receives
should begin whatever arbitration is required. When the external device assumes bus
mastership, it asserts
cycles) for which it is bus master. The following conditions must be met for an external
device to assume mastership of the bus through the normal bus arbitration procedure: 1) it
must have received
indicating that no other bus master has claimed ownership of the bus.
BR. To guarantee operand coherency, BG is only asserted at the end of an
RMC is negated) in response to a BR signal. When the requesting device
BG and more than one external device can be bus master, the requesting device
BGACK and maintains BGACK during the entire bus cycle (or
BG through the arbitration process, and 2) BGACK must be inactive,
BR.
BG to indicate that the bus is available.
BGACK to indicate that it has assumed bus mastership.
NOTE
CS3–CS0 in a high-impedance
BG is not asserted until the end of a read-modify-write
3-40 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 90

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Figure 3-22 is a flowchart showing bus arbitration for a single device. This technique
allows processing of bus requests during data transfer cycles. Refer to Figures 3-23 and
3-24 for bus arbitration timing diagrams.
BR is negated at the time that BGACK is asserted. This type of operation applies to a
system consisting of the MC68340 and one device capable of bus mastership. In a system
having a number of devices capable of bus mastership,
BR from each device can be wire-
ORed to the MC68340. In such a system, more than one bus request could be asserted
simultaneously.
if bus requests are still pending after the negation of
BG is negated a few clock cycles after the transition of BGACK. However,
BG, the MC68340 asserts another BG
within a few clock cycles after it was negated. This additional assertion of BG allows
external arbitration circuitry to select the next bus master before the current bus master
has finished using the bus. The following paragraphs provide additional information about
the three steps in the arbitration process. Bus arbitration requests are recognized during
normal processing,
nc...
I
HALT assertion, and a CPU32 halt caused by a double bus fault.
PROCESSOR REQUESTING DEVICE
REQUEST THE BUS
GRANT BUS ARBITRATION
1. ASSERT BG
TERMINATE ARBITRATION
1. NEGATE BG (AND WAIT FOR
BGACK TO BE NEGATED)
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
RE-ARBITRATE OR RESUME
PROCESSOR OPERATION
1. ASSERT BR
ACKNOWLEDGE BUS MASTERSHIP
1. EXTERNAL ARBITRATION DETERMINES
NEXT BUS MASTER
2. NEXT BUS MASTER WAITS FOR BGACK
TO BE NEGATED
3. NEXT BUS MASTER ASSERTS BGACK
TO BECOME NEW MASTER
4. BUS MASTER NEGATES BR
OPERATE AS BUS MASTER
1. PERFORM DATA TRANSFERS (READ AND
WRITE CYCLES) ACCORDING TO THE
SAME RULES THE PROCESSOR USES
RELEASE BUS MASTERSHIP
1. NEGATE BGACK
Figure 3-22. Bus Arbitration Flowchart for Single Request
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 41
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 91

CLKOUT
S3
A31–A0
D15–D0
AS
BR
BG
BGACK
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Figure 3-23. Bus Arbitration Timing Diagram—Idle Bus Case
CLKOUT
A31–A0
D15–D0
AS
DS
R/W
DSACK0,
DSACK1
S0 S1 S2
S4 S5
BR
BG
BGACK
Figure 3-24. Bus Arbitration Timing Diagram—Active Bus Case
3-42 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 92

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.6.1 Bus Request
External devices capable of becoming bus masters request the bus by asserting BR. This
signal can be wire-ORed to indicate to the MC68340 that some external device requires
control of the bus. The MC68340 is effectively at a lower bus priority level than the
external device and relinquishes the bus after it has completed the current bus cycle (if
one has started). If no
bus master once
processing if the arbitration circuitry inadvertently responds to noise or if an external
device determines that it no longer requires use of the bus before it has been granted
mastership.
BGACK is received while the BR is active, the MC68340 remains
BR is negated. This prevents unnecessary interference with ordinary
3.6.2 Bus Grant
The MC68340 supports operand coherency; thus, if an operand transfer requires multiple
bus cycles, the MC68340 does not release the bus until the entire transfer is complete.
nc...
I
Therefore, assertion of
• The minimum time for
synchronization (see Section 11 Electrical Characteristics).
BG is subject to the following constraints:
BG assertion after BR is asserted depends on internal
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
• During an external operand transfer, the MC68340 does not assert BG until after
the last cycle of the transfer (determined by SIZx and
• During an external operand transfer, the MC68340 does not assert
DSACK≈).
BG as long as
RMC is asserted.
• If the show cycle bits SHEN1–SHEN0 = 01, the MC68340 does not assert
an external master.
Externally, the
encoded network. The MC68340 is not affected by the method of arbitration as long as the
protocol is obeyed.
BG signal can be routed through a daisy-chained network or a priority-
BG to
3.6.3 Bus Grant Acknowledge
An external device cannot request and be granted the external bus while another device is
the active bus master. A device that asserts
negates
completed. Bus mastership is terminated at the negation of
Once an external device receives the bus and asserts
remains asserted after BGACK is asserted, the MC68340 assumes that another device is
requesting the bus and prepares to issue another
BGACK. BGACK should not be negated until all required bus cycles are
BGACK remains the bus master until it
BGACK.
BGACK, it should negate BR. If BR
BG.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 43
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 93

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.6.4 Bus Arbitration Control
The bus arbitration control unit in the MC68340 is implemented with a finite state machine.
As discussed previously, all asynchronous inputs to the MC68340 are internally
synchronized in a maximum of two cycles of the clock. As shown in Figure 3-25 input
signals labeled R and A are internally synchronized versions of
respectively. The BG output is labeled G, and the internal high-impedance control signal is
labeled T. If T is true, the address, data, and control buses are placed in the highimpedance state after the next rising edge following the negation of
signals are shown in positive logic (active high) regardless of their true active voltage
level. The state machine shown in Figure 3-25 does not have a state 1 or state 4.
State changes occur on the next rising edge of the clock after the internal signal is valid.
BG signal transitions on the falling edge of the clock after a state is reached during
The
which G changes. The bus control signals (controlled by T) are driven by the MC68340
immediately following a state change, when bus mastership is returned to the MC68340.
nc...
I
State 0, in which G and T are both negated, is the state of the bus arbiter while the
MC68340 is bus master. R and A keep the arbiter in state 0 as long as they are both
negated.
BR and BGACK
AS and RMC. All
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
The MC68340 does not allow arbitration of the external bus during the
For the duration of this sequence, the MC68340 ignores the
bus is required during an
RMC operation, BERR must be used to abort the RMC sequence.
BR input. If mastership of the
RMC sequence.
3.6.5 Show Cycles
The MC68340 can perform data transfers with its internal modules without using the
external bus, but, when debugging, it is desirable to have address and data information
appear on the external bus. These external bus cycles, called show cycles, are
distinguished by the fact that
strobe timing in show cycles.
After reset, show cycles are disabled and must be enabled by writing to the SHEN bits in
the module configuration register (see 4.3.2.1 Module Configuration Register (MCR)).
When show cycles are disabled, the A31–A0, FCx, SIZx, and R/
reflect internal bus activity. However,
external data bus remains in a high-impedance state. When show cycles are enabled,
indicates address strobe timing and the external data bus contains data. The following
paragraphs are a state-by-state description of show cycles, and Figure 3-26 illustrates a
show cycle timing diagram. Refer to Section 11 Electrical Characteristics for specific
timing information.
AS is not asserted externally. DS is used to signal address
W signals continue to
AS and DS are not asserted externally, and the
DS
3-44 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 94

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
+
RA B
VGT
STATE 0
RAB
RA
nc...
I
VGT
STATE 2
+
A
RA
GTV
STATE 5
RA
RA
R
GTV
STATE 6
RA
cale Semiconductor,
RA
+
RA
AB
VGT
STATE 3
R
R A
Frees
R - BUS REQUEST
A - BUS GRANT ACKNOWLEDGE
B - BUS CYCLE IN PROGRESS
G - BUS GRANT
T - THREE-STATE SIGNAL TO BUS CONTROL
V - BUS AVAILABLE TO BUS CONTROL
Figure 3-25. Bus Arbitration State Diagram
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 45
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 95

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
State 0—During state 0, the A31–A0 and FCx become valid, R/ W is driven to indicate a
show read or write cycle, and the SIZx pins indicate the number of bytes to transfer.
During a read, the addressed peripheral is driving the data bus, and the user must take
care to avoid bus conflicts.
State 41—One-half clock cycle later,
DS (rather than AS) is asserted to indicate that
address information is valid.
State 42—No action occurs in state 42. The bus controller remains in state 42 (wait states
will be inserted) until the internal read cycle is complete.
State 43—When
DS is negated, show data is valid on the next falling edge of the system
clock. The external data bus drivers are enabled so that data becomes valid on the
external bus as soon as it is available on the internal bus.
State 0—The A31–A0, FCx, R/
nc...
I
from the preceding cycle is valid through state 0.
S0 S42 S1S41 S43 S2
CLKOUT
A31–A0,
FC2–FC0,
SIZ1–SIZ0
R/W
AS, CS
DS
D15–D0
cale Semiconductor,
BKPT
Frees
W, and SIZx pins change to begin the next cycle. Data
S0
SHOW CYCLE
START OF EXTERNAL CYCLE
Figure 3-26. Show Cycle Timing Diagram
3.7 RESET OPERATION
The MC68340 has reset control logic to determine the cause of reset, synchronize it if
necessary, and assert the appropriate reset lines. The reset control logic can
independently drive three different lines:
1. EXTRST (external reset) drives the external
2. CLKRST (clock reset) resets the clock module.
3-46 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
RESET pin.
Page 96

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3. INTRST (internal reset) goes to all other internal circuits.
Synchronous reset sources are not asserted until the end of the current bus cycle,
whether or not
RMC is asserted. The internal bus monitor is automatically enabled for
synchronous resets; therefore, if the current bus cycle does not terminate normally, the
bus monitor terminates it. Only single-byte or word transfers are guaranteed valid for
synchronous resets. An external or clock reset is a synchronous reset source.
Asynchronous reset sources indicate a catastrophic failure, and the reset controller logic
immediately resets the system. Resetting the MC68340 causes any bus cycle in progress
to terminate as if
DSACK≈ or BERR had been asserted. In addition, the MC68340
appropriately initializes registers for a reset exception. Asynchronous reset sources
include power-up, software watchdog, double bus fault resets, and execution of the
RESET instruction.
If an external device drives
RESET low, RESET should be asserted for at least 590 clock
periods to ensure that the MC68340 resets. The reset control logic holds reset asserted
nc...
I
internally until the external
external
RESET is no longer being driven, it drives both internal and external reset low for
RESET is released. When the reset control logic detects that
an additional 512 cycles to guarantee this length of reset to the entire system. Figure 3-27
shows the
cale Semiconductor,
If reset is asserted from any other source, the reset control logic asserts RESET for 328
input clock periods plus 512 output clock periods, and until the source of reset is negated.
RESET timing.
1 CLOCK
RESET
590 CLOCK 512 CLOCK
PULLED EXTERNAL
DRIVEN BY MC68340
Figure 3-27. Timing for External Devices Driving RESET
Frees
After any internal reset occurs, a 14-cycle rise time is allowed before testing for the
presence of an external reset. If no external reset is detected, the CPU32 begins its vector
fetch.
Figure 3-28 is a timing diagram of the power-up reset operation, showing the relationships
between
RESET, V
, and bus signals. During the reset period, the entire bus three -
CC
states except for non-three-statable signals, which are driven to their inactive state. Once
RESET negates, all control signals are driven to their inactive state, the data bus is in read
mode, and the address bus is driven. After this, the first bus cycle for
processing begins.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 3- 47
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
RESET exception
Page 97

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
CLKOUT
VCO
LOCK
V
CC
RESET
BUS
CYCLES
NOTES:
1. Internal start-up time.
2. SSP read here.
3. PC read here.
nc...
I
4. First instruction fetched here.
BUS STATE
UNKNOWN
328
TCLKIN
××
512
TCLKOUT
ADDRESS AND
CONTROL SIGNALS
THREE-STATED
14 CLOCKS
≤
1
23 4
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Figure 3-28. Power-Up Reset Timing Diagram
When a RESET instruction is executed, the MC68340 drives the RESET signal for 512
clock cycles. The SIM40 registers and the module control registers in each internal
peripheral module (DMA, timers, and serial modules) are not affected. All other peripheral
module registers are reset the same as for a hardware reset. The external devices
connected to the
RESET signal are reset at the completion of the RESET instruction.
3-48 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 98

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
SECTION 4
SYSTEM INTEGRATION MODULE
The MC68340 system integration module (SIM40) consists of several functions that
control the system start-up, initialization, configuration, and the external bus with a
minimum of external devices. It also provides the IEEE 1149.1 boundary scan capabilities.
The SIM40 includes the following functions:
• System Configuration and Protection
• Clock Synthesizer
nc...
I
• Chip Selects and Wait States
• External Bus Interface
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
• Bus Arbitration
• Dynamic Bus Sizing
• IEEE 1149.1 Test Access Port
4.1 MODULE OVERVIEW
The SIM40 is essentially identical to the SIM implemented in the MC68330. The SIM40
has similar features to the SIM in the MC68331, MC68332, and MC68333. The periodic
interrupt timer, double bus fault monitor, software watchdog, internal bus monitor, and
spurious interrupt monitor are identical. However, many of the other features in the SIM's
differ in their use and details.
The system configuration and protection function controls system configuration and
provides various monitors and timers, including the internal bus monitor, double bus fault
monitor, spurious interrupt monitor, software watchdog timer, and the periodic interrupt
timer.
The clock synthesizer generates the clock signals used by the SIM40 and the other on chip modules, as well as CLKOUT used by external devices.
The programmable chip select function provides four chip select signals that can enable
external memory and peripheral circuits, providing all handshaking and timing signals.
Each chip select signal has an associated base address register and an address mask
register that contain the programmable characteristics of that chip select. Up to three wait
states can be programmed by setting bits in the address mask register.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 4-1
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 99

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
The external bus interface (EBI) handles the transfer of information between the internal
CPU32 and memory, peripherals, or other processing elements in the external address
space. See Section 3 Bus Operation for further information.
The MC68340 dynamically interprets the port size of an addressed device during each
bus cycle, allowing operand transfers to or from 8-, 16-, and 32-bit ports. The device
signals its port size and indicates completion of the bus cycle through the use of the
DSACK≈ inputs. Dynamic bus sizing allows a programmer to write code that is not bus -
width specific. For a discussion on dynamic bus sizing, see Section 3 Bus Operation.
The MC68340 includes dedicated user-accessible test logic that is fully compliant with the
IEEE 1149.1
associated with testing high-density circuit boards have led to the development of this
standard under the sponsorship of the IEEE Test Technology Committee and Joint Test
Action Group (JTAG). The MC68340 implementation supports circuit-board test strategies
based on this standard. Refer to Section 9 IEEE 1149.1 Test Access Port for additional
nc...
I
information.
Standard Test Access Port and Boundary Scan Architecture
. Problems
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
4.2 MODULE OPERATION
The following paragraphs describe the operation of the module base address register,
system configuration and protection, clock synthesizer, chip select functions, and the
external bus interface.
NOTE
The terms
to avoid confusion when dealing with a mixture of active-low
and active-high signals. The term
that a signal is active or true independent of the level
represented by a high or low voltage. The term
negation
assert
indicates that a signal is inactive or false.
and
negate
are used throughout this section
assert
or
assertion
indicates
negate
or
4.2.1 Module Base Address Register Operation
The module base address register (MBAR) controls the location of all internal module
registers (see 4.3.1 Module Base Address Register (MBAR)). The address stored in this
register is the base address (starting location) for all internal registers. All internal module
registers are contained in a single 4-Kbyte block (see Figure 4-1) that is relocatable along
4-Kbyte boundaries.
The location of the internal registers is fixed by writing the desired base address of the
4-Kbyte block to the MBAR using the MOVES instruction to address $0003FF00 in CPU
space. The source function code (SFC) and destination function code (DFC) registers
contain the address space values (FC3–FC0) for the read or write operand of the MOVES
instruction (see Section 5 CPU32 or M68000PM/AD,
Therefore, the SFC or DFC register must indicate CPU space (FC3–FC0 = $7), using the
MOVEC instruction, before accessing MBAR. The offset from the base address is shown
above each register diagram.
4-2 MC68340 USER’S MANUAL MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Programmer’s Reference Manual
).
Page 100

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
$FFFFFFFF
MC68340
RELOCATABLE
MODULE
BLOCK
MBAR
($0003FF00
nc...
I
FC=0111)
RAM
(TYPICAL)
NOTE: $XXXXX is the value contained in the MBAR bits BA31-BA12.
$XXXXXFFF
DMA
$XXXXX000
SERIAL PORTS
TIMER MODULES
SIM 40
$00000000
$FFF
$7BF
$780
$721
.
$700
$67F
$600
$07F
$000
Figure 4-1. SIM40 Module Register Block
4.2.2 System Configuration and Protection Operation
The SIM40 allows the user to control certain features of system configuration by writing
bits in the module configuration register (MCR). This register also contains read-only
status bits that show the state of the SIM40.
All M68000 family members are designed to provide maximum system safeguards. As an
cale Semiconductor,
extension of the family, the MC68340 promotes the same basic concepts of safeguarded
design present in all M68000 members. In addition, many functions that normally must be
provided by external circuits are incorporated in this device. The following features are
provided in the system configuration and protection function:
Frees
SIM40 Module Configuration
The SIM40 allows the user to configure the system to the particular requirements. The
functions include control of FREEZE and show cycle operation, the function of the
CS≈
signals, the access privilege of the supervisor/user registers, the level of interrupt
arbitration, and automatic vectoring for external interrupts.
Reset Status
The reset status register provides the user with information on the cause of the most
recent reset. The possible causes of reset include: external, power-up, software
watchdog, double bus fault, loss of clock, and RESET instruction.
MOTOROLA MC68340 USER’S MANUAL 4-3
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
 Loading...
Loading...