Page 1

SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCT INFORMATION
查询BR729供应商
Order this document by
M68000UMAD/AD
Communications and Advanced
Consumer Technologies Group
M68000
Addendum to
M68000
User Manual
August 7, 1997
This addendum to the
well as additional information. This document and other information on this product is maintained on the World
Wide Web at http://www.motorola.com/68000.
M68000UM/AD User’s Manual
, Revision 8, provides corrections to the original text as
OVERVIEW
This manual includes hardware details and programming information for the MC68HC000, the MC68HC001,
the MC68EC000, and the MC68SEC000. For ease of reading, the name M68000 MPUs will be used when
referring to all processors. Refer to M68000PM/AD,
information on the MC68000 instruction set.
The four microprocessors are very similar to each other and all contain the following features:
• Sixteen 32-Bit Data and Address Registers
• 16-Mbyte Direct Addressing Range
• Program Counter
• 6 Instruction Types
• Operations on Five Main Data Types
• Memory-Mapped Input/Output (I/O)
• 14 Addressing Modes
The following processors contain additional features:
• MC68HC001/MC68EC000/MC68SEC000
— Statically selectable 8- or 16-bit data bus
• MC68HC000/MC68EC000/MC68HC001/MC68SEC000
— Low power
M68000 Programmer's Reference Manual
, for detailed
This document contains information on a product under development. Motorola reserves the right to change or discontinue this product without notice.
1997 Motorola, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 2

2
The primary features of the MC68SEC000 embedded processor include the following:
• Direct Replacement for the MC68EC000
— Pin-for-pin compatibility with the MC68EC000 in the plastic QFP and TQFP packages
— Vast selection of existing third-party development tools for the MC68EC000 support the
MC68SEC000
— Software written for the MC68EC000 will run unchanged on the MC68SEC000
• Power Management
— Low-power HCMOS technology
— Static design allows for stopping the processor clock
— 3.3V or 5V operation
— Typical 0.5µA current consumption at 3.3V in sleep mode
• Software Strength
— Fully upward object-code compatible with other M68000 Family products
— M68000 architecture allows effective assembly code with a C compiler
• Upgrade
— Fully upward code-compatible with higher performance 680x0 and 68300 Family members
— ColdFire
®
code-compatible with minor modifications
1. MC68HC000
The primary benefit of the MC68HC000 is reduced power consumption. The device dissipates less power (by
an order of magnitude) than the NMOS MC68000.
The MC68HC000 is an implementation of the M68000 16/-32 bit microprocessor architecture. The
MC68HC000 has a 16-bit data bus implementation of the MC68000 and is upward code-compatible with the
MC68010 and the MC68020 32-bit implementation of the architecture.
1.1 MC68HC001
The MC68HC001 provides a functional extension to the MC68HC000 HCMOS 16-/32-bit microprocessor with
the addition of statically selectable 8- or 16-bit data bus operation. The MC68HC001 is object-code compatible
with the MC68HC000. You can migrate code written for the MC68HC001 without modification to any member
of the M68000 Family.
1.2 MC68EC000
The MC68EC000 is an economical high-performance embedded controller designed to suit the needs of the
cost-sensitive embedded-controller market. The HCMOS MC68EC000 has an internal 32-bit architecture that
is supported by a statically selectable 8- or 16-bit data bus. This architecture provides a fast and efficient
processing device that can satisfy the requirements of sophisticated applications based on high-level
languages.
The MC68EC000 is fully object-code compatible with the MC68000. You can migrate code written for the
MC68EC000 without modification to any member of the M68000 Family.
The MC68EC000 brings the performance level of the M68000 Family to cost levels previously associated with
8-bit microprocessors. The MC68EC000 benefits from the rich M68000 instruction set and its related high code
density with low memory bandwidth requirements.
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 3

. 4
1.3 MC68SEC000
The MC68SEC000 is a cost-effective static embedded processor engineered for low-power applications. In
addition to providing the substantial cost and performance benefits of the MC68EC000, the low-power mode
of the MC68SEC000 provides significant advantages in power consumption and power management. The
typical current consumption of the MC68SEC000 is only 0.5 µ A in static standby mode and 15.0mA in normal
3.3V operation. The MC68SEC000 operates in either 3.3V or 5.0V systems. The remarkably low power
consumption, small footprint packages, and static implementation are combined in the MC68SEC000 for lowpower applications such as portable measuring equipment, electronic games, and battery-operated hand-held
consumer products.
The HCMOS MC68SEC000’s static architecture is a direct replacement for the MC68EC000, which offers the
lowest cost entry point to 32-bit processing. The internal 32-bit architecture provides fast and efficient
processing that satisfies the requirements of sophisticated applications based on high-level languages.
All of the existing third-party developer tools widely available for the MC68EC000 will directly support the
MC68SEC000. You can find detailed descriptions of these tools in the
Source Catalog
High Performance Embedded Systems
MOTOROLA
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
3
Page 4
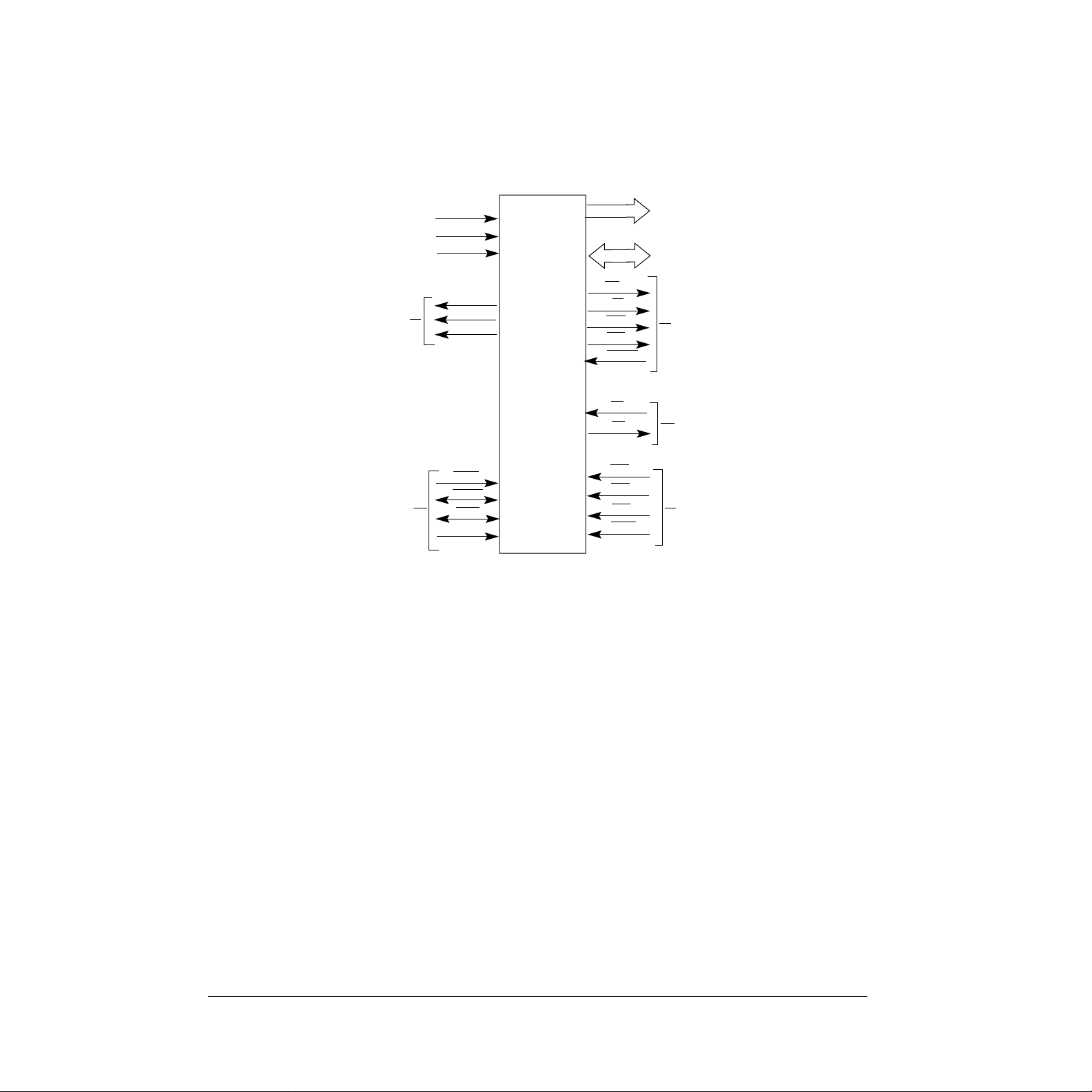
2.0 SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
Change Figure 3-3 on Page 3-2.
PROCESSOR
STATUS
SYSTEM
CONTROL
V
CC
GND
CLK
FC0
FC1
FC2
BERR
RESET
HALT
MODE
A23-A0
D15-D0
AS
R/W
UDS
LDS
DTACK
MC68SEC000
BR
BG
IPL0
IPL1
IPL2
AVEC
ADDRESS BUS
DATA BUS
ASYNCHRONOUS
BUS CONTROL
BUS ARBITRATION
CONTROL
INTERRUPT
CONTROL
Figure 1. Input and Output Signals (MC68EC000 and MC68SEC000)
2.1 Data Bus (D15-D0)
In Section 3.2 on page 3-4, replace “The MC68EC000 and MC68HC001 use D7-D0 in 8-bit mode, and D15D8 are undefined.” with “Using the MC68HC001, MC68EC000, and MC68SEC000 mode pin, you can
statically select either 8- or 16-bit modes for data transfer. The MC68EC000, MC68SEC000, and
MC68HC001 use D7-D0 in 8-bit mode. D15-D8 are undefined.”
2.2 Bus Arbitration Control
In Section 3.4 on page 3-5, the sentence “In the 48-pin version of the MC68008 and MC68EC000, no pin is
available for the bus grant acknowledge signal; this microprocessor uses a two-wire bus arbitration
scheme.” should read “In the 64-pin MC68EC000 and MC68SEC000, no pin is available for the bus grant
acknowledge signal. These microprocessors use a two-wire bus arbitration scheme.”
2.3 System Control
The Mode subsection heading of Section 3.6 on page 3-7 should read ‘‘Mode (MODE) (MC68HC001/
68EC000/68SEC000).’’
2.4 MC68SEC000 Low-Power Mode
Add the following to Sections 4 and 5, Bus Operation.
The MC68SEC000 has been redesigned to provide fully static- and low-power operation. This section
describes the recommended method for placing the MC68SEC000 into a low-power mode to reduce the
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 5

5
K
power consumption to its quiescent value
1
while maintaining the internal state of the processor. The
low-power mode described below will be routinely tested as part of the MC68SEC000 test vectors provided
by Motorola.
To successfully enter the low-power mode, the MC68SEC000 must first be in the supervisor mode. A
recommended method for entering the low-power mode is to use the TRAP instruction, which causes the
processor to begin exception processing, thus entering the supervisor mode. External circuitry should
accomplish the following steps during the trap routine:
1. Externally detect a write to the low-power address. You select this address which can be any address
in the 16 Mbyte addressing range of the MC68SEC000. A write to the low-power address can be
detected by polling A23–A0, R/W
, and FC2–FC0. When the low-power address is detected, R/W is
a logic low, and the function codes have a five (101) on their output, the processor is writing to the
low-power address in supervisor mode and user-designed circuitry should assert the
ADDRESS_MATCH signal shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
ADDRESS_MATCH
AS
D
Q
CK
AS
Q
CL
D
Q
CK
Q Q
CL
D
Q
CK
CPU_CLK
RESTART
RESET
SYSTEM_CLK
Figure 2. MC68SEC000 Low-Power Circuitry for 16-Bit Data Bus
ADDRESS_MATCH
RESTART
RESET
D
Q
AS AS AS
CK
Q
CL
D
Q
CK
Q
CL
D
Q
CK
Q
CL
SYSTEM_CLK
D
Q
CK
Q
Figure 3. MC68SEC000 Low-Power Circuitry for 8-Bit Data Bus
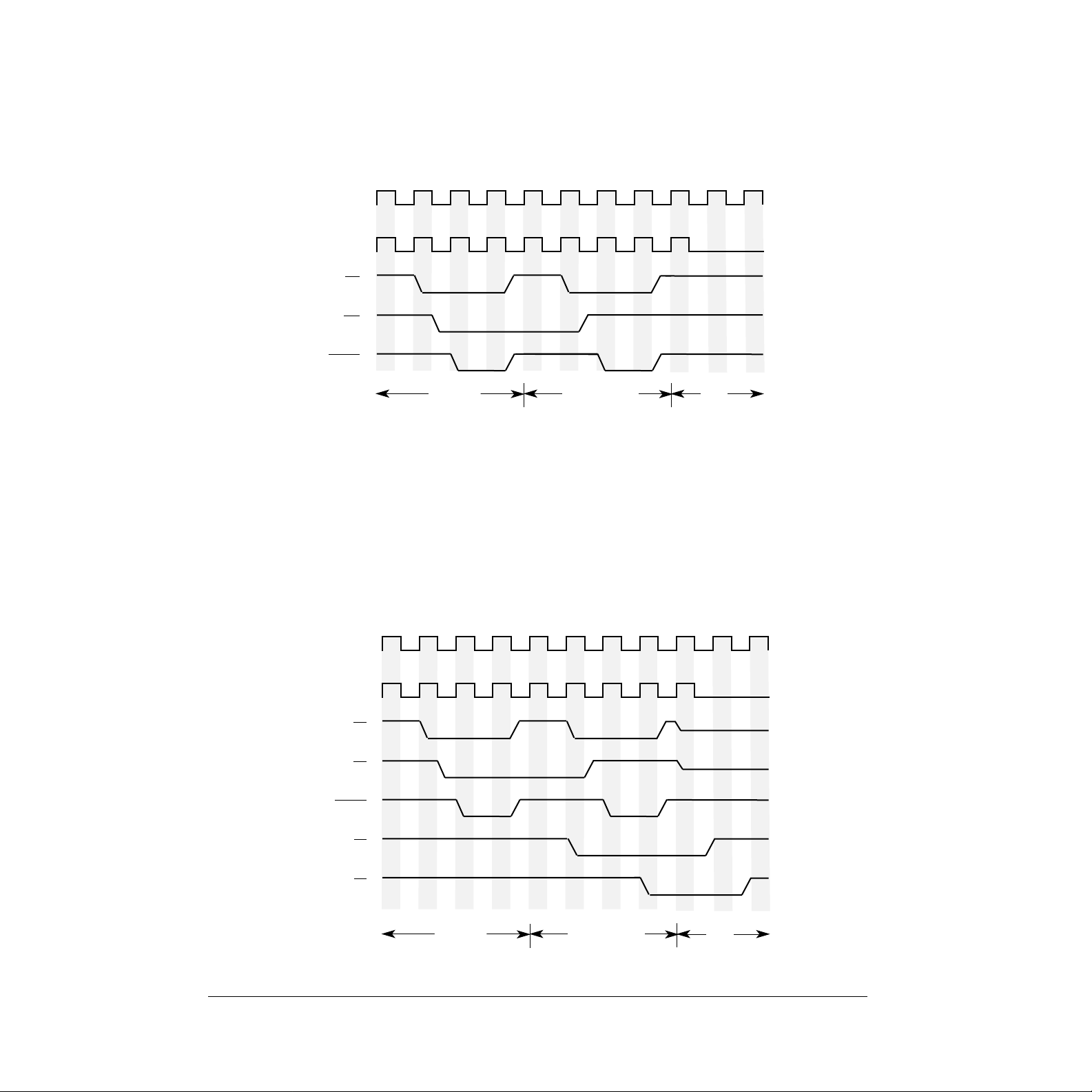
2. Execute the STOP instruction. The external circuitry shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3 will count the
number of bus cycles starting with the write to the low-power address and will stop the processor
clock on the first falling edge of the system clock after the bus cycle that reads the immediate data
of the STOP instruction. Figure 3 has one more flip-flop than Figure 2 because the MC68SEC000 in
CPU_CL
1.
The preliminary specification for the MC68SEC000’s current drain while in the low-po wer mode is Idd < 2 µ A for 3.3V operation and
Idd < 5 µ A for 5.0V operation.
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 6
6
ess
8-bit mode requires two bus cycles to fetch the immediate data of the STOP instruction. After the
processor clock is disabled, it is often necessary to disable the clock to other sections of your circuit.
This can be done, but be careful that runt clocks and spurious glitches are not presented to the
MC68SEC000. A timing diagram is shown in Figure 4.
CLK
CPU_CLK
AS
RW
DTACK
Write to
Low-Power
Address
S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7
Fetch Immediate
Data of STOP
Instruction
Stop
Figure 4. MC68SEC000 Clock Stop Timing for 16-Bit Data Bus
Note: While the MC68SEC000 is in the low-power mode, all inputs must be driven to V
pull-up or pull-down resistor.
DD
or V
, or have a
SS
3. This step is optional depending on whether your applications require the MC68SEC000 signals with
three-state capability to be placed into a high-impedance state. To place the MC68SEC000 into a
three-state condition, the proper method for arbitrating the bus (as described in 5.2 Bus Arbitration
in the
M68000 User’s Manual, Rev 8
)
s
hould be completed during the fetch of the status register data
for the STOP instruction. A timing diagram with the bus arbitration sequence is shown in Figure 5.
CLK
CPU_CLK
AS
RW
DTACK
BR
BG
Write to
Low-Power
Addr
S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7
Fetch Immediate
Data of STOP
Instruction
Stop
Figure 5. MC68SEC000 Clock Stop Timing with Bus Arbitration for 16-Bit Data Bus
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 7
7
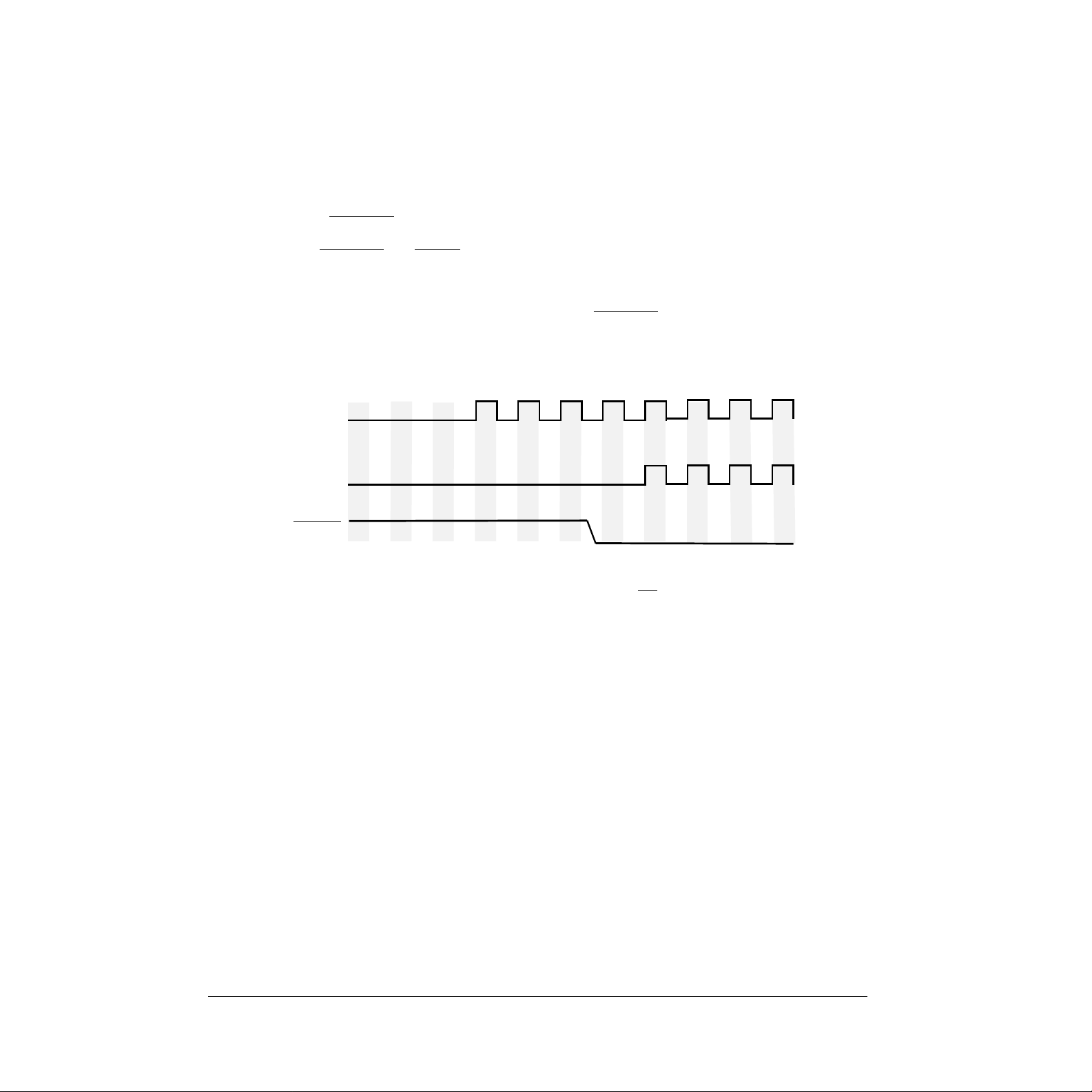
After the previous steps are completed, the MC68SEC000 will remain in the low-power mode until it
recognizes the appropriate interrupt . External logic will also have to poll IPLB2–IPLB0 to detect the proper
interrupt. When the correct interrupt level is received, the following steps will bring the processor out of the
low-power mode:
1. Restart the system clock if it was stopped.
2. Wait for the system clock to become stable.
3. Assert the RESTART signal. This will cause the processor’s clock to start on the next falling edge of
the system clock. Figure 6 shows the timing for bringing the processor out of the low-power mode.
Both the RESTART and RESET signals are subject to the asynchronous setup time as specified in
the Electrical Characteristics section of this addendum.
WARNING
The system clock must be stable before the RESTART
to prevent glitches in the clock. An unstable clock can cause unpredictable
results in the MC68SEC000.
signal is asserted
CLK
CPU_CLK
RESTART
Figure 6. MC68SEC000 Clock Start Timing
4. If the MC68SEC000 was placed in a three-state condition, the BR signal must be negated before the
processor can begin executing instructions.
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 8
8
°
°
An example trap routine is as follows:
TRAP_x MOVE.B #0,$low_power_address /* Write that causes ADDRESS_MATCH to assert */
STOP #$2000 /* STOP instruction with desired interrupt mask */
RTE /* Return from the exception */
The first instruction (MOVE.B #0,$low_power_address) writes a byte to the low-power address that will
cause the external circuitry to begin the sequence that will stop the processor’s clock. The second
instruction (STOP #$2000) loads the SR with the immediate data. This lets you set the interrupt that will
cause the processor to come out of the low-power mode. The final instruction (RTE) tells the processor to
return from the exception and resume normal processing.
3.0 MC68SEC000 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Add to the following table to Section 10.1.
3.1 MC68SEC000 MAXIMUM RATINGS
RATING SYMBOL VALUE UNIT
Supply Voltage V
Input Voltage V
Maximum Operating
Temperature Range
Commercial Extended "C" Grade
Storage Temperature Tstg –55 to 150
T
CC
in
A
–0.3 to 6.5 V
–0.5 to 6.5 V
T
to T
L
H
0 to 70
–40 to 85
C
C
3.2 CMOS CONSIDERATIONS
The following change should be made to Section 10.4, CMOS Considerations.
“Although the MC68HC000 and MC68EC000 is implemented with input protection diodes, care should be
exercised to ensure that the maximum input voltage specification is not exceeded.” should read “Although
the MC68HC000, MC68EC000, and MC68SEC000 are implemented with input protection diodes, be
careful not to exceed the maximum input voltage specification.”
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 9

9
4.0 MC68SEC000 AC ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Replace Figure 10-2 on page 10-6 with Figure 7.
DRIVE
TO 2.4 V
CLK
DRIVE TO
OUTPUTS(1) CLK
OUTPUTS(2) CLK
INPUTS(3) CLK
INPUTS(4) CLK
0.5 V
VALID
OUTPUT
DRIVE TO
DRIVE TO
n
2.4 V
0.5 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
A
B
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
INPUT
n + 1
VALID
OUTPUT
DC
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.0 V
n
0.8 V
VALID
INPUT
2.0 V
0.8 V
B
DC
2.0 V
0.8 V
A
2.0 V
0.8 V
VALID
OUTPUT
n+1
DRIVE
TO 2.4 V
DRIVE
TO 0.5 V
ALL SIGNALS(5)
2.0 V
0.8 V
E
F
2.0 V
0.8 V
NOTES:
1. This output timing is applicable to all parameters specified relative to the rising edge of the clock.
2. This output timing is applicable to all parameters specified relative to the falling edge of the clock.
3. This input timing is applicable to all parameters specified relative to the rising edge of the clock.
4. This input timing is applicable to all parameters specified relative to the falling edge of the clock.
5. This timing is applicable to all parameters specified relative to the assertion/negation of another signal.
LEGEND:
A. Maximum output delay specification.
B. Minimum output hold time.
C. Minimum input setup time specification.
D. Minimum input hold time specification.
E. Signal valid to signal valid specification (maximum or minimum).
F. Signal valid to signal invalid specification (maximum or minimum).
Figure 7. Drive Levels and Test Points for AC Specifications - applies to all parts
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 10

10
5.0 MC68SEC000 DC ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Add the following table to Section 10.13 on page 10-23.
(V
= 5.0 Vdc ± 5%, 3.3 Vdc ± 10%,; GND = 0 Vdc; T
CC
3.3 V 5.0 V
CHARACTERISTIC SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNIT
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input Leakage Current BERR, BR, DTACK, CLK, I PL2-IPL0, AVEC
MODE, HALT, RESET
Three-State (Off State) Input Current I
Output High Voltage V
Output Low Voltage
(IOL = 1.6 mA) HALT
(IOL = 3.2 mA) A23–A0, BG, FC2–FC0
(IOL = 5.0 mA) RESET
(IOL = 5.3 mA) AS, D15–D0, LDS, R/W, UDS
Current Dissipation* f = 0 Hz I
f=10MHz — 10 — 15 mA
f=16 MHz — 15 — 25 mA
f= 20 MHz — 20 — 30 mA
Capacitance (Vin = 0 V, T
= 25 ° C, Frequency = 1 MHz)** Cin — 20.0 — 20.0 pF
A
Load Capacitance HALT
All Others
= T
to T
A
L
2.0 V
IH
IL
Iin — 2.5
TSI
OH
V
OL
D
CL — 70
)
H
CC
GND 0.8 GND –
20
— 2.5 — 2.5 uA
2.4 — V
—
—
—
—
0.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
— 0.7 — 1.0 mA
130
2.0 V
CC
0.8 V
0.5
— 2.5
20
–0.75 — V
CC
—
—
—
—
0.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
—70
130
V
uA
V
pF
*During normal operation, instantaneous Vcc current requirements may be as high as 1.5A.
Currents listed are with no loading.
**Capacitance is periodically sampled rather than 100% tested.
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 11

11
6.0 MC68SEC000 AC ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS — CLOCK
TIMING (See Figure 2)
Add the following table and Figure 8 to Section 10.9 on page 10-9.
10MHz 16MHz 20MHz
NUM. CHARACTERISTIC SYMBOL MIN MAX min max min max UNIT
Frequency of Operation f 0 10.0 0 16.7 0 20.0 MHz
1 Cycle time tcyc 100 — 60 — 50 — ns
2,3 Clock Pulse Width t
4,5 Clock Rise and Fall Times t
Applies to 3.3V and 5V.
CL
t
CH
Cr
t
Cf
45
45
—
—
—
—
10
10
27
27
—
—
—
—
21
21
5
5
—
—
—
—
4
4
ns
ns
1
2
2.0 V
0.8 V
4 5
NOTE: Timing measurements are referenced to and from a low voltage of 0.8 V and a
high voltage of 2.0 V, unless otherwise noted. The voltage swing through this
range should start outside and pass through the range such that the rise or
fall will be linear between 0.8 V and 2.0 V.
3
Figure 8. MC68SEC000 Clock Input Timing Diagram
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 12

12
7.0 MC68SEC000 AC ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS — READ AND
WRITE CYCLES
Add the following table and Figures 9 and 10 to Section 10.16.
Applies to 3.3V and 5V.
(GND = 0 V; T
NUM CHARACTERISTIC
= T
A
to T
L
; see Figures 3 and 4)
H
10MHz 16MHz 20MHz
MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
UNIT
6 Clock Low to Address Valid — 35 — 30 — 25 ns
6A Clock High to FC Valid 0 35 0 30 0 25 ns
7 Clock High to Address, Data Bus High Impedance (Maximum)
—55—50—42ns
(Write)
8 Clock High to Address, FC Invalid (Minimum) 0—0—0—ns
1
Clock High to AS
9
2
Address Valid to AS
11
(Write)
2
FC Valid to AS
11A
1
Clock Low to AS
12
2
AS
13
14
14A
15
, LDS, UDS Negated to Address, FC Invalid 15 — 15 — 10 — ns
2
AS
(and LDS, UDS Read) Width Asserted 195 — 120 — 100 — ns
2
, UDS Width Asserted (Write) 95 — 60 — 50 — ns
LDS
2
, LDS, UDS Width Negated 105 — 60 — 50 — ns
AS
, LDS, UDS Asserted 3 35 3 30 3 25 ns
, LDS, UDS Asserted (Read)/ AS Asserted
20—15—10—ns
, LDS, UDS Asserted (Read)/ AS Asserted (Write) 45 — 45 — 40 — ns
, LDS, UDS Negated 3 35 3 30 3 25 ns
16 Clock High to Control Bus High Impedance — 55 — 50 — 42 ns
2
AS
17
18
20
20A
21
21A
22
, LDS, UDS Negated to R/W Invalid 15 — 15 — 10 — ns
1
Clock High to R/W
1
Clock High to R/W
2,6
Asserted to R/W Low (Write) — 10 — 10 — 10 ns
AS
2
Address Valid to R/W
2
FC Valid to R/W
2
Low to DS Asserted (Write) 50 — 30 — 25 — ns
R/W
High (Read) 0 35 0 30 0 25 ns
Low (Write) 0 35 0 30 0 25 ns
Low (Write) 0—0—0—ns
Low (Write) 50 — 30 — 25 — ns
23 Clock Low to Data-Out Valid (Write) — 35 — 30 — 25 ns
2
AS
25
26
27
28
28A Clock High to DTACK
, LDS, UDS Negated to Data-Out Invalid (Write) 30 — 15 — 10 — ns
2
Data-Out Valid to LDS
5
Data-In Valid to Clock Low (Setup Time on Read) 5—5—5—ns
2
, LDS, UDS Negated to DTACK Negated (Asynchronous Hold) 0 110 0 110 0 95 ns
AS
, UDS Asserted (Write) 30 — 15 — 10 — ns
Negated 0 110 0 110 0 95 ns
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 13

AC ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS — READ AND WRITE CYCLES (Continued)
13
±
NUM CHARACTERISTIC
29 AS
29A AS
30 AS
31
32 HALT
33 Clock High to BG
34 Clock High to BG
35 BR
36
38 BG
, LDS, UDS Negated to Data-In Invalid (Hold Time on Read) 0—0—0—ns
, LDS, UDS Negated to Data-In High Impedance (Read) — 150 — 90 — 75 ns
, LDS, UDS Negated to BERR Negated 0—0—0—ns
2,5
DTACK
Asserted to Data-In Valid (Setup Time on Read) — 65 — 50 — 42 ns
and RESET Input Transition Time 0 150 0 150 0 150 ns
Asserted — 35 — 30 — 25 ns
Negated — 35 — 30 — 25 ns
Asserted to BG Asserted 1.5 3.5 1.5 3.5 1.5 3.5 Clks
7
BR
Negated to BG Negated 1.5 3.5 1.5 3.5 1.5 3.5 Clks
Asserted to Control, Address, Data Bus High Impedance (AS
10MHz 16MHz 20MHz
MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
UNIT
—55—50—42ns
Negated)
39 BG
44 AS
47
48
Width Negated 1.5 — 1.5 — 1.5 — Clks
, LDS, UDS Negated to AVEC Negated 0 55 0 50 0 42 ns
5
Asynchronous Input Setup Time 5—5—5—ns
2,3
Asserted to DTACK Asserted 20 — 10 — 10 — ns
BERR
52 Data-In Hold from Clock High 0—0—0—ns
53 Data-Out Hold from Clock High (Write) 0—0—0—ns
55 R/W
56
58
58A
Asserted to Data Bus Impedance Change (Write) 20 — 10 — 0 — ns
4
HALT, RESET Pulse Width 10 — 10 — 10 — Clks
7
BR
Negated to AS, LDS, UDS, R/W Driven 1.5 — 1.5 — 1.5 — Clks
7
BR
Negated to FC Driven 1—1—1—Clks
Applies to 3.3V and 5V.
NOTES: 1. For a loading capacitance of less than or equal to 50 pF, subtract 5 ns from the value given in the maximum columns.
2. Actual value depends on clock period.
3. If #47 is satisfied for both DT
using the asynchronous input setup time (#47).
4. For power-up, the MC68SEC000 must be held in the reset state for 100 ms to allow stabilization of on-chip circuitry. After the
system is powered up, #56 refers to the minimum pulse width required to reset the controller.
5. If the asynchronous input setup time (#47) requirement is satisfied for DT
requirement can be ignored. The data must only satisfy the data-in to clock low setup time (#27) for the following clock cycle.
6. When AS
and R/W are equally loaded (
7. The minimum value must be met to guarantee proper operation. If the maximum value is exceeded, BG may be reasserted.
ACK and BERR, #48 may be ignored. In the absence of DTACK, BERR is an asynchronous input
ACK, the DTACK asserted to data setup time (#31)
20%), subtract 5 ns from the values given in these columns.
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 14
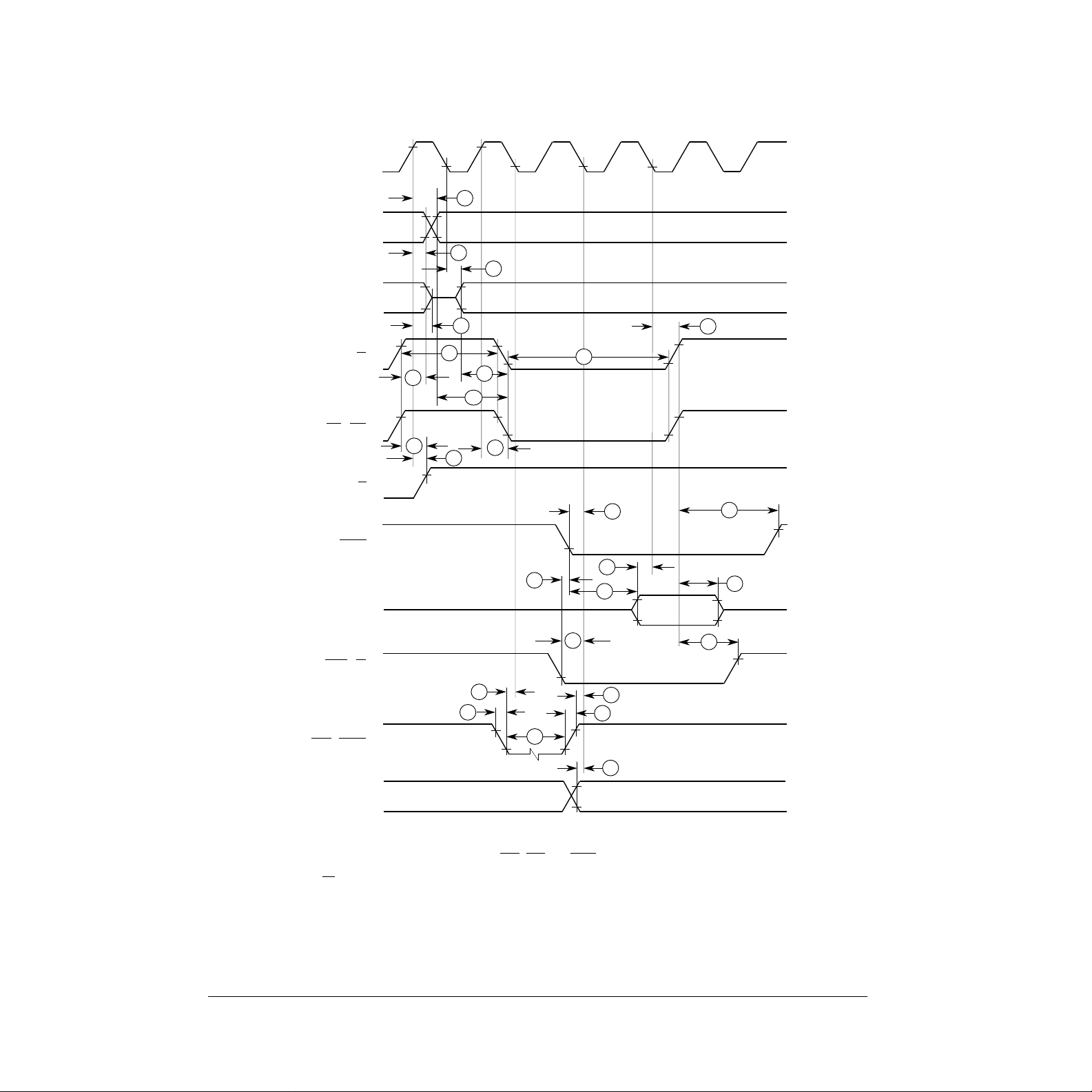
14
CLK
FC2–FC0
A23–A0
AS
LDS / UDS
R/W
S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6
6A
8
6
7
13
17
15
18
11
11A
9
14
47
S7
12
28
DTACK
47
32
31
27
29
30
47
47
48
DATA IN
BERR / BR
(NOTE 2)
47
32
HALT / RESET
ASYNCHRONOUS
INPUTS
(NOTE 1)
NOTES:
1. Setup time for the asynchronous inputs IPL2–IPL0 and AVEC (#47) guarantees their recognition at the
next falling edge of the clock.
2. BR need fall at this time only to insure being recognized at the end of the bus cycle.
3. Timing measurements are referenced to and from a low voltage of 0.8 V and a high voltage of 2.0 V,
unless otherwise noted. The voltage swing through this range should start outside and pass through the
range such that the rise or fall is linear between 0.8 V and 2.0 V.
56
Figure 9. MC68SEC000 Read Cycle Timing Diagram
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 15

15
CLK
FC2–FC0
A23–A0
AS
LDS / UDS
R/W
S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6
6A
8
6
7
13
17
15
18
11A
21A
21
9
11
20A
20
22
14
9
14A
47
S7
12
28
DTACK
DATA OUT
BERR / BR
(NOTE 2)
HALT / RESET
ASYNCHRONOUS
NOTES:
1. Timing measurements are referenced to and from a low voltage of 0.8 V and a high voltage of 2.0 V,
unless otherwise noted. The voltage swing through this range should start outside and pass through the
INPUTS
(NOTE 1)
range such that the rise or fall is linear between 0.8 V and 2.0 V.
2. Because of loading variations, R/W may be valid after AS even though both are initiated by the rising edge
of S2 (specification #20A).
55
26
23
7
47
32
48
47
47
32
56
47
53
25
30
MOTOROLA
Figure 10. MC68SEC000 Write Cycle Timing Diagram
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
Page 16

8.0 MC68SEC000 AC ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS — BUS
ARBITRATION
Add the following table and Figure 11 to Section 10.17.
16
(GND = 0 Vdc; T
NUM CHARACTERISTICp
7 Clock High to Address, Data Bus High Impedance (Maximum) — 55 — 50 — 42 ns
16 Clock High to Control Bus High Impedance — 55 — 50 — 42 ns
33 Clock High to BG
34 Clock High to BG
35 BR
36 BR
38 BG
39 BG
47 Asynchronous Input Setup Time 5—5—5—ns
58
58A
Asserted to Control, Address, Data Bus High Impedance (AS
1
1
= T
to T
A
Negated to AS, LDS, UDS, R/W Driven 1.5 — 1.5 — 1.5 — Clks
BR
; refer to Figure 13)
L
H
10MHz 16MHz 20MHz
MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX
Asserted 0 35 0 30 0 25 ns
Negated 0 35 0 30 0 25 ns
Asserted to BG Asserted 1.5 3.5 1.5 3.5 1.5 3.5 Clks
Negated to BG Negated 1.5 3.5 1.5 3.5 1.5 3.5 Clks
Negated)
Width Negated 1.5 — 1.5 — 1.5 — Clks
Negated to FC Driven 1—1—1—Clks
BR
—55—50—42ns
UNIT
Applies to 3.3V and 5V.
1. The minimum value must be met to guarantee proper operation. If the maximum value is exceeded, BG
may be reasserted.
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 17

STROBES
AND R/W
BR
36
17
35
BG
33
CLK
NOTE: Setup time to the clock (#47) for the asynchronous inputs BERR, BR, DTACK, IPL2-IPL0, and VPA
guarantees their recognition at the next falling edge of the clock.
38
3934
Figure 11. Bus Arbitration Timing
CLK
47
BR
35
BG
39
AS
33
38
34
36
58
LDS/UDS
DS
R/W
FC2–FC0
A23
A19–A0
D15
D7–D0
NOTE: Waveform measurements for all inputs and outputs are specified at: logic high 2.0 V, logic low = 0.8 V.
Figure 12. MC68SEC000 Bus Arbitration Timing Diagram
MOTOROLA
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
58A
Page 18

CLK
18
BR
BG
AS
DS
VMA
R/W
FC2-FC0
A23-A0
47
35
33
34
38
D15-D0
NOTES: Waveform measurements for all inputs and outputs are specified at: logic high 2.0 V, logic low = 0.8 V. This diagram also applies to the 68EC000.
Figure 13. Bus Arbitration Timing—Idle Bus Case
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 19

CLK
19
BR
BG
AS
DS
VMA
R/W
FC2-FC0
A23-A0
47
35
33
34
16
7
D15-D0
NOTE: Waveform measurements for all inputs and outputs are specified at: logic high 2.0 V, logic low = 0.8 V.
This diagram also applies to the 68EC000.
Figure 14. Bus Arbitration Timing - Active Bus Case
MOTOROLA
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
Page 20

CLK
BR
BG
47
35
33
20
3939
36
38
AS
DS
VMA
R/W
FC2-FC0
A23-A0
D15-D0
NOTES: Waveform measurements for all inputs and outputs are specified at: logic high 2.0 V, logic low = 0.8 V.
This diagram also applies to the 68EC000.
Figure 15. Bus Arbitration - Multiple Bus Request
58
57A
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
MOTOROLA
Page 21

9.0 MECHANICAL DATA
9.1 PIN ASSIGNMENTS
Add Figure 12 to Section 11.1.
The following defines the pin assignment and the package dimensions of the 64 lead QFP (FU package)
and 64 lead TQFP (PB package) for the MC68SEC000. Note that it is pin-to-pin compatible with the
MC68EC000.
R/W
DTACK
BG
BR
V
CC
CLK
GND
MODE
HALT
RESET
AVEC
BERR
IPL2
IPL1
IPL0
FC2
LDS
UDSASD0D1D2
64
148
MC68SEC000FU/PB
17 32
D4
D3
GNDD5D6D7D8D9D10
49
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
A23
A22
A21
V
CC
A20
A19
A18
A17
A16
A15
A14
3316
A13
MOTOROLA
FC1
A0A1A2
FC0
A3
A4
A5A6A7A8A9
GND
A10
A11
A12
Figure 16. 64-Lead Quad Flat Pack and 64-Lead Thin Quad Flat Pack
M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM
21
Page 22

10.0 PACKAGE DIMENSIONS - FU SUFFIX
This diagram replaces the one on Page 11-16
64 Lead Quad Flat Pack Case 840B-01
R
G
H
M
B S
A
D
C
DIM
MILLIMETERS INCHES
MIN MAX MIN MAX
A 16.95 17.45 0.667 0.687
B 13.90 14.10 0.547 0.555
C 16.95 17.45 0.667 0.687
D 13.90 14.10 0.547 0.555
G 0.30 0.45 0.012 0.018
H 0.80 BSC 0.031 BSC
K 2.15 2.45 0.085 0.096
L 0.13 0.23 0.005 0.009
M 2.00 2.40 0.79 0.094
R 12.00 REF 0.472 REF
S 12.00 REF 0.472 REF
L
K
22 M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM MOTOROLA
Page 23

11.0 PACKAGE DIMENSIONS - PB SUFFIX
Add the following to Section 11.2.
64 Lead Thin Quad Flat Pack Case 840F-02
G
B1A1
B
A
D1
C1
D
C
H
M
L
K
DIM
MILLIMETERS INCHES
MIN MAX MIN MAX
A 12.00 BSC 0.472 BSC
A1 6.00 BSC 0.236 BSC
B 10.00 BSC 0.394 BSC
B1 5.00 BSC 0.197 BSC
C 12.00 BSC 0.472 BSC
C1 6.00 BSC 0.236 BSC
D 10.00 BSC 0.394 BSC
D1 5.00 BSC 0.197 BSC
G 0.17 0.27 0.007 0.011
H 0.50 BSC 0.020 BSC
K --- 1.60 --- 0.063
L 0.09 0.20 0.004 0.008
M 1.35 1.45 0.053 0.057
MOTOROLA M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM 23
Page 24

12.0 PACKAGE/FREQUENCY AVAILABILITY
Replaces Section 11.1
The following tables identify the packages and operating frequencies available for the MC68HC000,
MC68HC001, MC68EC000, and the MC68SEC000.
MC68SEC000
PACKAGE
Quad Flat Pack (FU)
Thin Quad Flat Pack (PB)
MC68HC000
PACKAGE
Plastic DIP
Plastic Quad Pack (PLCC)
Plastic Quad (Gull Wing)**
Pin Grid Array, Solder Lead Finish**
Pin Grid Array, Gold Lead Finish**
Plastic Quad Pack (PLCC) 8,10,12,16,20 MHz 3
MC68HC001**
PACKAGE
Plastic Quad Pack (PLCC)
Plastic Quad (Gull Wing)
Pin Grid Array, Gold Lead Finish
FREQUENCY
10 MHz
16 MHz
20MHz
10 MHz
16 MHz
20MHz
FREQUENCY
8,10,12,16,20 MHz 3
8,10,12,16,20 MHz 3
8,10,12,16,20 MHz 3
8,10,12,16,20 MHz
FREQUENCY
8,10,12,16 MHz
8,10,12,16 MHz
8,10,12,16 MHz
8,10,12,16 MHz
VOLTAGE
3.3 V 5 V
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
VOLTAGE
VOLTAGE
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
5V
3
5V
✓
✓
✓
✓
MC68EC000
PACKAGE
Plastic Quad Pack (PLCC)
Plastic Quad Flat Pack
NOTE : ** not recommended for new designs
FREQUENCY
8 MHz
10 MHz
12 MHz
16 MHz
20 MHz
VOLTAGE
5V
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
24 M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM MOTOROLA
Page 25

ORDERING INFORMATION
Add the following to Section 11.
The following tables contains the ordering information for the MC68SEC000.
MC68SEC000 Ordering Information
PACKAGE BODY SIZE LEAD SPACING SPEED (IN MH Z) VOLTAGE SUFFIX
QFP 14.0 mm X 14.0mm 0.8mm
10/16/20 MHz 3.3V or 5.0V
TQFP 10.0mm x 10.0mm 0.5mm
MC68HC000 Ordering Information
PACKAGE BODY SIZE LEAD SPACING SPEED (IN MHZ) VOLTAGE SUFFIX
DIP 81.91mm X 20.57mm 2.54mm 8, 10, 12, 16
PLCC
25.57mm X 25.27mm 1.27mm
8, 10, 12, 16, 20 FN 0C to +70C
8, 10, 12, 16 CFN -40C to +85C
5.0V
MC68EC000 Ordering Information
PACKAGE BODY SIZE LEAD SPACING SPEED (IN MHZ) VOLTAGE SUFFIX
PLCC 25.57mm X 25.27mm 1.27mm 8, 10,12, 16, 20 5.0V FN 0C to +70C
PQFP 14.1mm X 14.1mm 0.8mm 8, 10,12, 16, 20 FU
FU 0C to +70C
CFU -40C to +85C
PB 0C to +70C
CPB -40C to +85C
P 0C to +70C
TEMPERATURE
RANGE
TEMPERATURE
RANGE
TEMPERATURE
RANGE
DOCUMENTATION
Add to Section 11.
The documents listed in the following table contain detailed information that pertain to the MC68SEC000
processor. You can obtain these documents from the Literature Distribution Centers listed on the last page
of this document.
MC68SEC000 Documentation
MC68SEC000 DOCUMENTATION DOCUMENT NUMBER
M68000 Family
Programmer’s Reference Manual
M68000 User’s Manual M68000UM/AD
High Performance Embedded Systems
Source Catalog‘‘
MC68EC000 Product Brief MC68EC000/D
MC68SEC000 Product Brief MC68SEC000/D
M68000PM/AD
BR729/D
MOTOROLA M68000 USER’S MANUAL ADDENDUM 25
Page 26

Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding
the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and
specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. "Typical" parameters can and do vary in different
applications. All operating parameters , including "Typicals" must be validated for each customer application by customer's technical experts. Motorola does not
convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Motorola products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in
systems intended for surgical implant into the body , or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or f or any other application in which the f ailure of the
Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buy er purchase or use Motorola products for an y such unintended
or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Motorola and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all
claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with
such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Motorola was negligent regarding the design or manuf acture of the part. Motorola and
are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer .
Literature Distribution Centers:
USA/EUROPE: Motorola Literature Distribution; P.O. Box 20912, Arizona 85036.
JAPAN: Nippon Motorola Ltd.; 4-32-1, Nishi-Gotanda, Shinagawa-ku, Tokyo 141 Japan.
ASIA-PACIFIC: Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd.; Silicon Harbour Center, No. 2 Dai King Street, Tai Po Industrial Estate,
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong.
SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCT INFORMATION
 Loading...
Loading...