Page 1

Page 2

Thank you for your purchase of Mitsubishi Transistor inverter FREQ,ROL-2200.
r
r
r--
This inverter is a variable frequency power supply unit used to control a squirrelcage induction motor.
IMPORTANT NOTE
This instruction manual describes handling, installation, operation and maintenance
of the inverter.
.Although it is easy to use the inverter,
cause unforeseen trouble. Before operating the inverter,
Your inverter is built to a high standard of quality and reliability.
Correct application and regular inspection,
operation.
-C 0 N T E N T S-
- INVERTER
HANDLING GUIDANCE
Q 1. CONSTRUCTICN
9 2. UNPACKING AND CHECKING
Q 3. INSTALLATION
3.1 Handling during transfer and installation
3.2 Environment
3.3 Mounting position and clearances
3.4 Inverter housed in enclosure
§ 4, WIRING
4.1 Main circuit
4.2 Control circuit
4.3 Terminals for wiring
4.4 Field wiring reference table
8 5. OPERATION
5.1 Operation modes
5.2 Pre-operation checks
5.3 Pre-operation settings and adjustments
5.4 Check points at test operation
8 6.
MAINTENANCE AND. INSPECTION
6.1 Caution for maintenance and inspection
6.2 Inspection points
improper
should give you long, trouble free,
use and mis-operation might
read this manual carefully.
\
...............
...............
...............
...............
...............
...............
...............
...............
...............
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
...............
...............
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
...............
...............
6
6
6’
7
8
8
12
15
17
20
20
20
21
24
27
27
27
Page 3

_--
.._-*
--.
.’
6.3 Method of measuring main circuit voltage;
current and output power
6.4 Measuring instrument, selection and usage
6.5 Transistor modules and diode modules
6.6 Parts replacement
Q 7. TROUBLESHOOTING
7.1 Troubleshooting
7.2 Protective functions
Q 8: SPECIFICATIONS
8.1 Block diagram
8.2 Terminals
8.3 Standard specifications
8.4 External dimensions
8.5 Selection of peripheral devices
8.6 Drip shield kit
. .
8.7 Overload protection
.................. 51
................ 51
...
..... . ... . ... ..... ‘31
...............
............... 36
............... 38 -’
............... 46
.... ..*........ 46
...............
................ 53
............... 58
...............
............... 65
.
.
...............
............... 68
34
44
64
66
0
r PARAMETER UNIT
Q 1.. INSTALLATION
8 2. OUTLINE OF FUNCTIONS
1 Q 3. FUNCTION KEY DESCRIPTIONS
Q 4. OPERATION
4.1 Operation modes
4.2 Operation with external signals
4.3 Operation with PU
4.4 Common setting errors
see also Page 92
Q 5. SETTINGS OF CONTROL VARIABLES (PARAMETERS)
5.1 Control functions and setting method
5.2 Examples of operation
. .
5.3 Caution (iIlega1 settings)
8 6. MONITOR
$3 7. DISPLAY
7.1 Alarm display
7.2 Indicator lamps
7.3 Characters appearing in readout
9 8. LIST OF FUNCTIONS NUMBERS
..I
. .
. .
‘,
.,.’
.I
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
....... . ....... 76
............... 77
............... 78
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
.: . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
. . . . . . .i. . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
.’
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . ...*. :...
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . * . . . . 1.;.
,,..,..........
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
I
Q
81
85
88
92
92
93
93
0
94
Page 4

(-
‘-was-
g 9. DETAILS OF EACH FUNCTION
8 10. PARAMETER UNIT SPECIFICATIONS
§ll. EXTERNAL DIMENSIONS AND CABLE DETAILS
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
112
113
Page 5
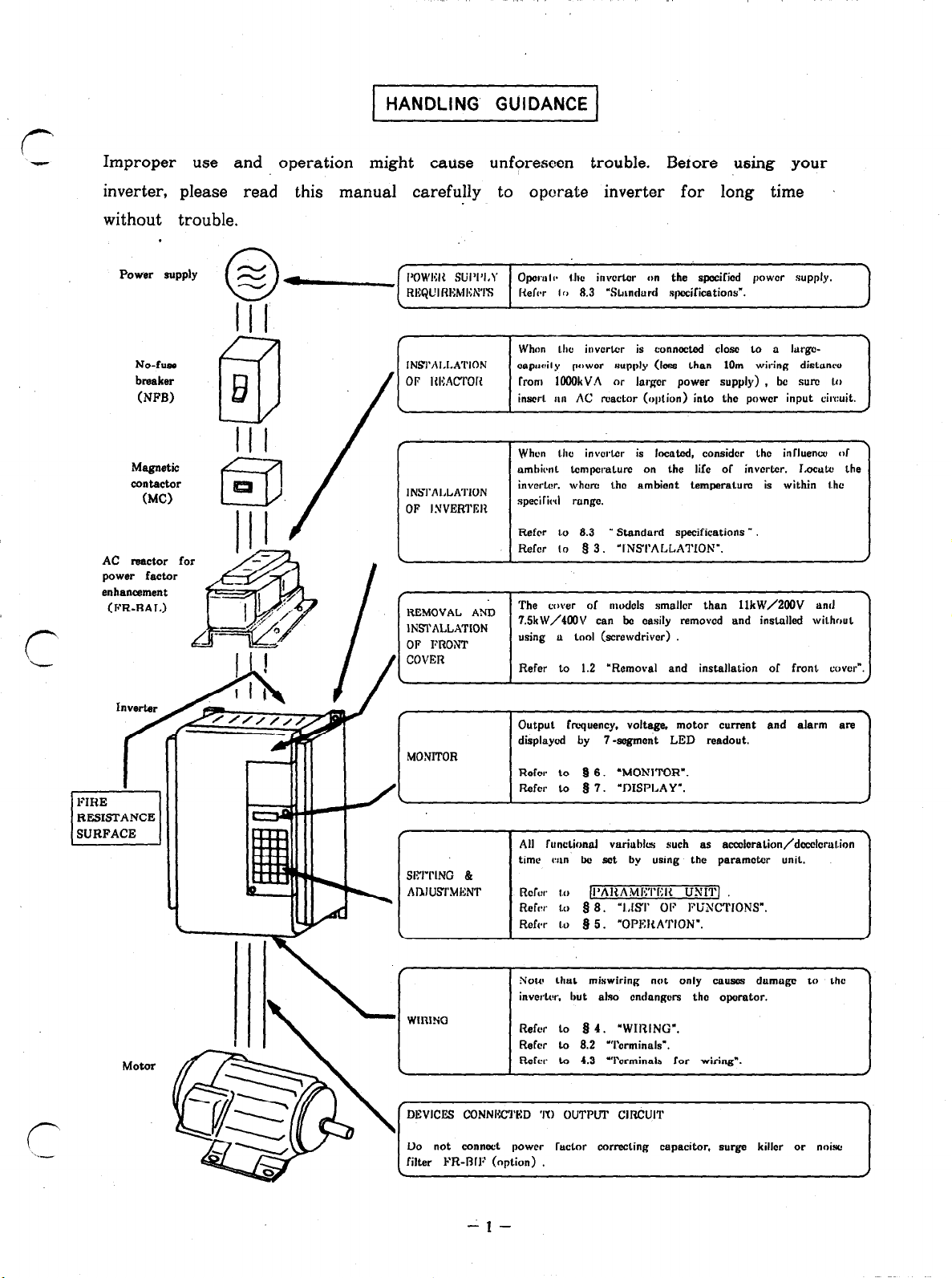
1 HANDLING GUIDANCE 1
Improper use and operation might cause unforeseen trouble. Betore using your
inverter, please read this manual carefully to operate inverter for long time
without trouble.
No-fuse
breaker
(NPB)
Magnetic
contactor
(MC)
AC reactor for
power factor
enhancement
,
INSI’ALLATION
OF I.VVERTRIZ
Rl?MOVAL AND
INSI’ALLATION
OF PRONT
MONITOR
When the icvcrtcr is connected close LO a lurgc-
capwily lwwcr supply (Ins than 1Om wiring distonw
lrom IOOOkVA or lorgcr power supply) , bc sure 1.0
inscrl. an AC reactor (option) inlo Lhc power input ciwuit.
When the invortcr is located, coasidcr the in&mu, 111
ambirnt temperature on the life of invcrtcr. I.ocutc the
invcrlcr. whcrc the ambient temperaturn is within l.hc
speGic~d range.
Refer
I -
1.0 8.3
Refer lo 93. ‘lNSThLLA1’ION”.
The cover of models smallcr than llkW/2OOV and
7SkW/4OOV can be easily removed and installed without
using u LOOI (screwdriver)
Refer to 1.2 ‘Removal and installation of front cover”.
Output frequency, voltage, motor current and alarm are
dbplaycd by 7-segment LED readout.
Rdcr LO 9 6. ‘MONlTOR”.
Rofcr to 8 7. “DISPLAY”.
” Standard specifications .
/
7
J
A
Mom
time wn bc set by using the paramctcr unit.
Not+ that mixwiring not only ~1~80s damogc to the
invcrtrr, but also cndongers the operator.
Refer lo I) 4. ‘WIRING”.
Refer LO 8.2 “Terminals’.
Refer to 4.3 “Terminals Ior wiring”.
‘DEVICES CONNlGI’I’E:D ‘I’0 OUTPUT CIRCUIT
Do not connect power Tactor correcting capacitor, surbw killer or n&c
filter FR-RIP (oplion) .
\.
\
J
Page 6
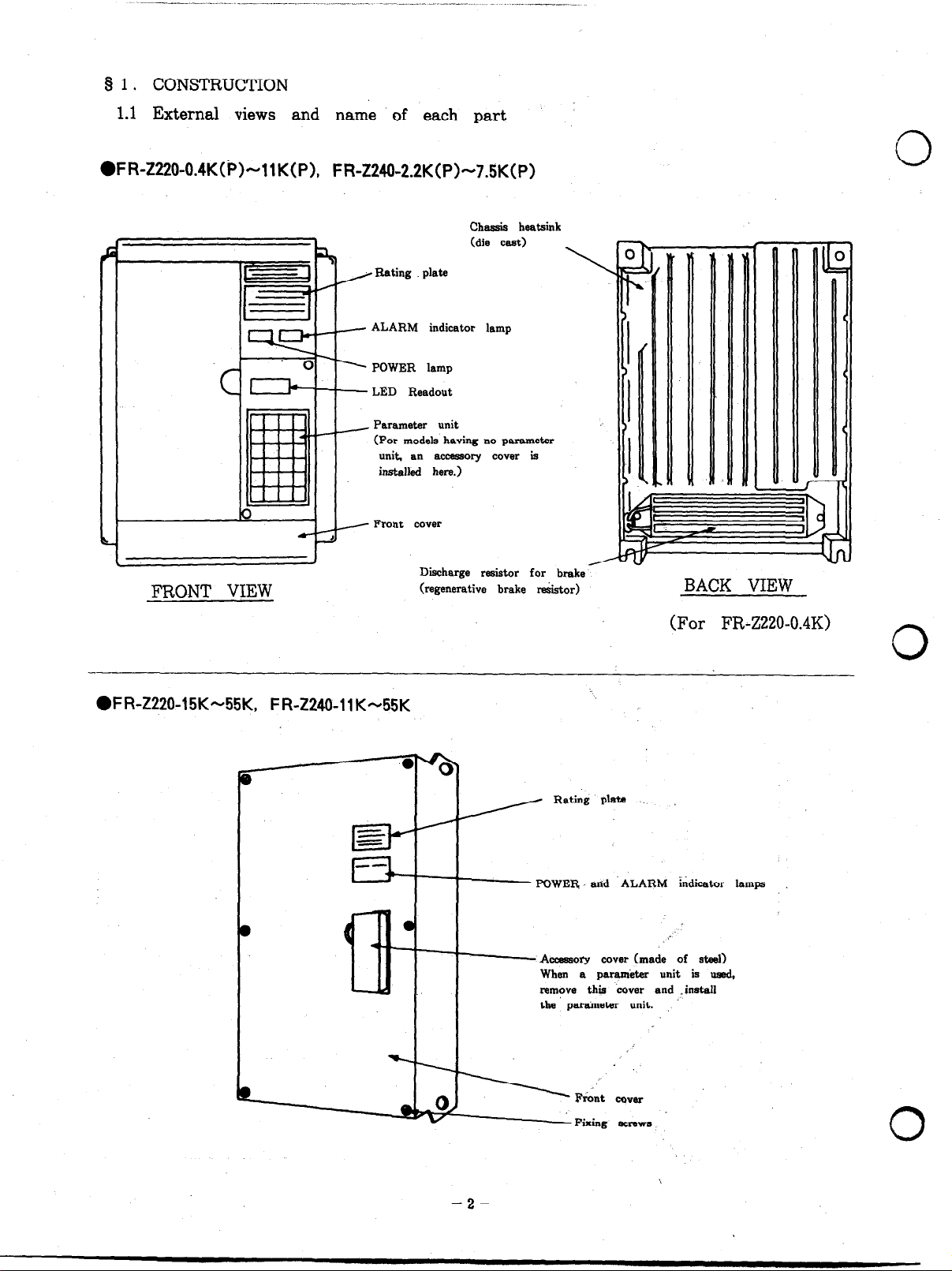
8 1. CONSTRUCTION
1.1 External views and name of each part
.FR-2220-0.4K(~)-11K0, FR-Z240-2.2K(P)-7.5KCP)
Chassis heatsink
(die cast)
, Rating plate
- ALARM indicator lamp
. POWER lamp
- LED Readout
- Parameter unit
(For models having no parameter
unit. an accessory cov*r is
installed hem.)
~~ -
FRONT VIEW
Discharge resistor for brake
(regenerative brake r&i&or)
0
\f--
BACK VIEW
l
FR-Z220-15K-55K, FR-Z240-llK-55K
(For FR-Z220-0.4K)
3
- POWER. atid ALARM indicator lamps
- A-ory cover (made of steel)
When a parameter unit is used,
remove this cover and .instaU
the paraineter unit.
0
Page 7

f-
/
1..2 Removal and installation of front cover
(FR-Z220-0.4K--11 K, FR-Z240-2.2K-7.5K)
How to remove the front cover (see Fig. 1 ) :
While pressing the white button at the top of the inverter, ease the cover
. . . ..3 .
forward and lift the plastic top cover
from the bottom location sockets.
How to attach the front cover (see Fig. 2 ) :
Insert the lugs at the bottom of the front cover into the sockets at the
chassis bottom and press the cover lightly against the chassis. Ensure white
button engages securely.
Inverter having no parameter unit is
equipped with an accessory cover. The
accessory cover can be removed by pulling it to the front while holding
the side wall lightly (Fig. 3 ) .
Fig. 1 Removal of front cover
Fig.
2 Installation of front cover
Fig. 3 Removal of access cover
CAUTION: 1 . After the front cover is installed, make sure it is held in
position securely,
2, The rating plate is stuck on. the front cover. Do not attach
the cover to another invertor.
3. When the parameter unit was removed for removal of the
r
--.
front cover, be sure to install it as instructed in 1.3.
-3-
Page 8
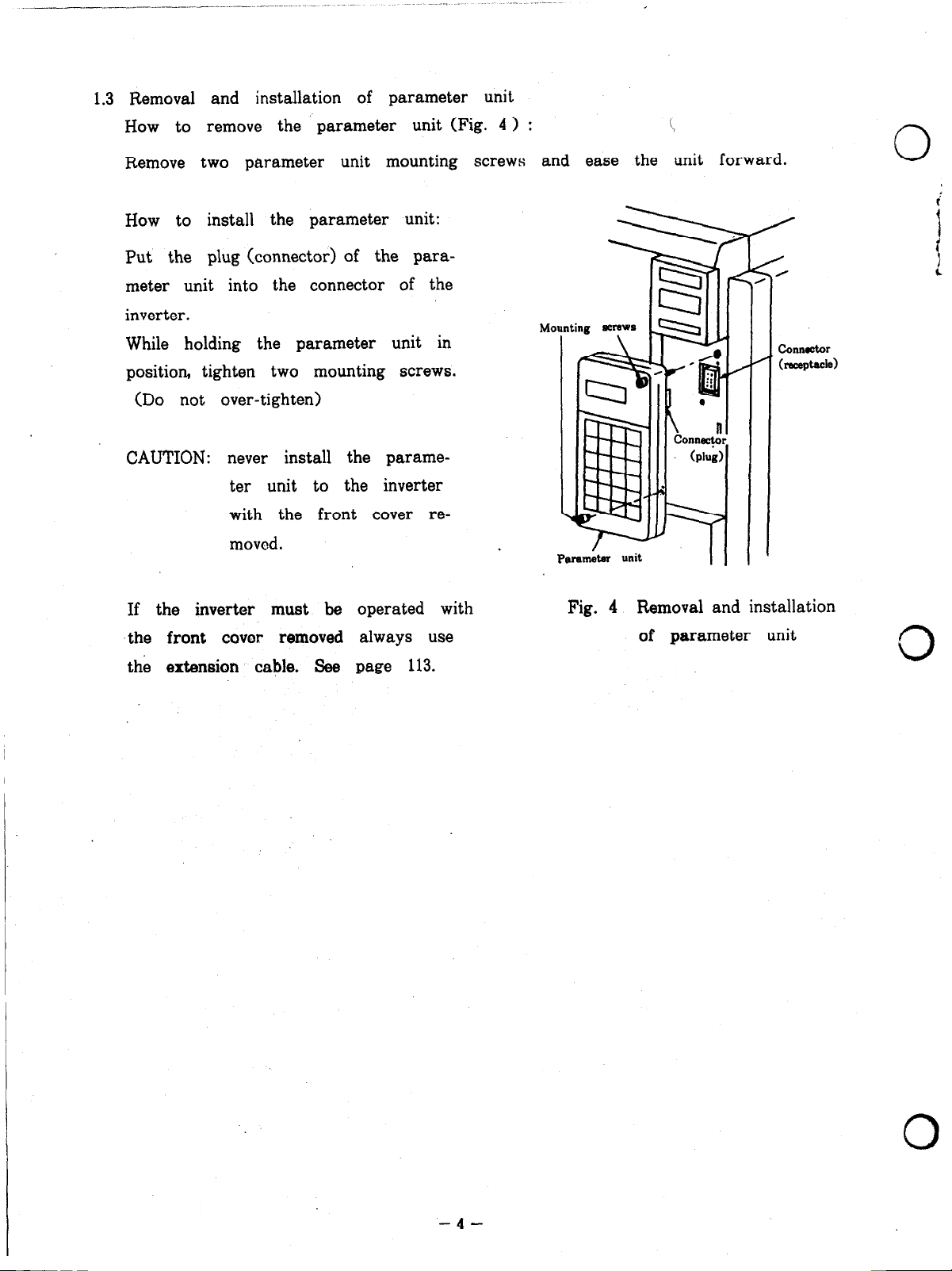
1.3 Removal and installation of parameter unit
How to remove the parameter unit (Fig. 4 > : i
Remove two parameter unit mounting screws and ease the unit forward.
How to install the parameter unit:
Put the plug (connector) of the para-
meter unit into the connector of the
inverter.
While holding the parameter unit in
position, tighten two mounting screws.
(Do not over-tighten)
CAUTION: never install the parame-
ter unit to the inverter
with the front cover removed.
If the inverter must be operated with
‘the front covw removed always use
the extension cable. See page 113.
Connector
hc%ptacle)
Fig. 4 Removal and installation
of parameter unit
0
-4-
0
Page 9
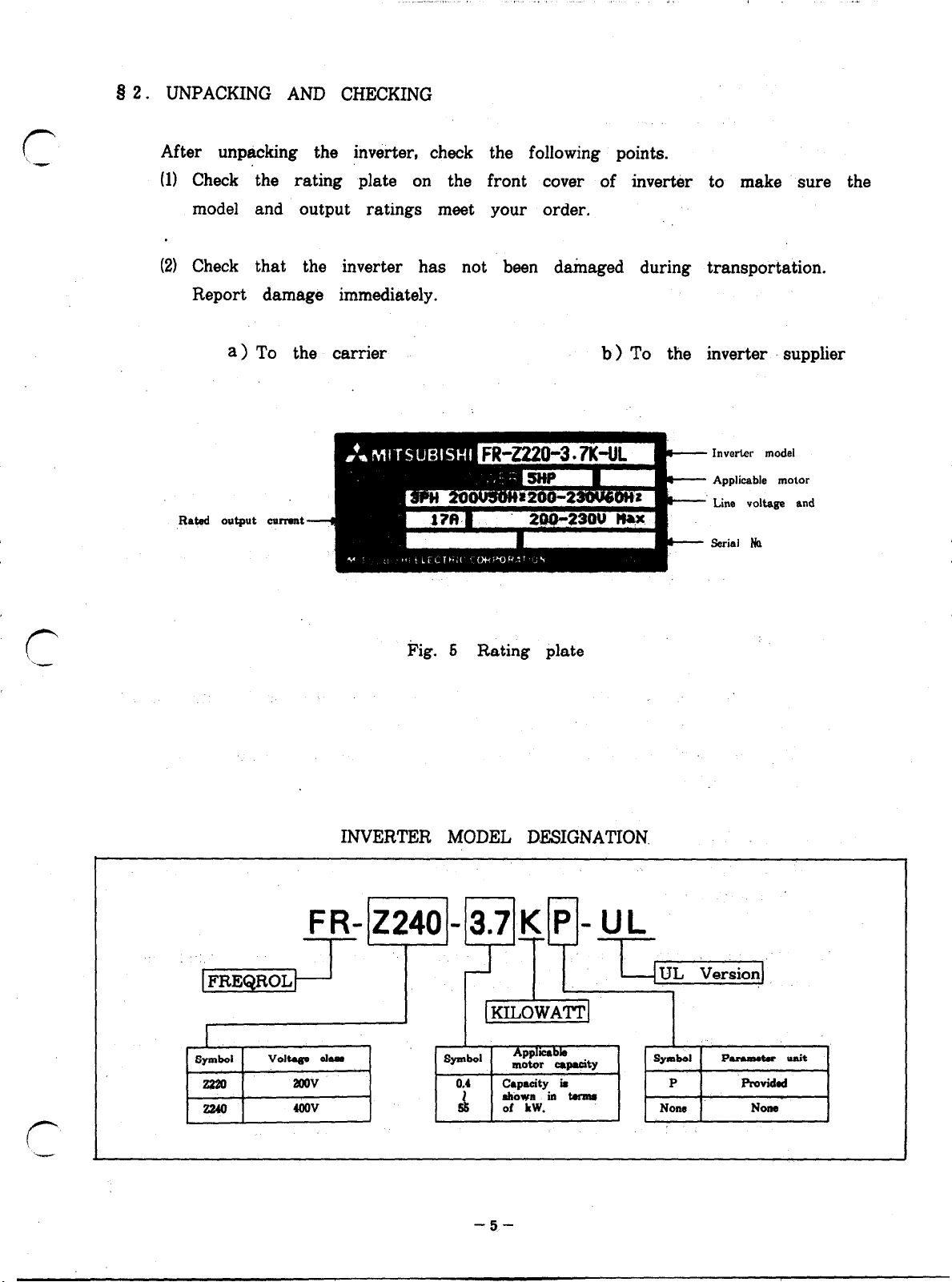
b 2. UNPACKING AND CHECKING
After unpacking the inverter, check the following points.
(11 Check the rating plate on the front cover of inverter to make sure the
model and output ratings meet your order.
(21 Check that the inverter has not been damaged during transportation.
Report damage immediately.
a > To the carrier b > To the inverter supplier
Invc&r model
Applicable motor
Line voltage and
Serial k
pcz@iJ-
I
SylllbOl
zm
2240
Volta@ clam
2OOV 0.4
4OOV 55 of LW. NOM
Pig. 5 Rating plate
INVERTER MODEL DESIGNATION.
FR-224003.7KP-UL
L < yI+-%q
KILOWATT
SpllbOl
Appl=bb
motor c8pacity
capacity k
akoun in Wnm
SyUlbOI
P Providad
ParalMtw unit
Nona
-5-
Page 10

8 3. INSTALLATION
3.1 Handling during unpacking and installation
Carefully handle the inverter when it is transferred and installed.
When the inverter is carried, do not hold it in such a manner that force
is exerted on only the front panel.
3.2 Environment
(1) Place the inverter in a clean and well-ventilated location.
Do not install the inverter . in direct sunlight, high temperature, high humidity, dense dust, corrosive gases, or hazardous areas.
If the inverter must .be used in an environment where dense dust or
corrosive gas arises, house it in an enclosure which does not allow
entrance of dust or gas. ..
Note: When the inverter is ..hous&d : in an enclosure, a suitable cooling
means should be used and/or the enclosure should be designed so
that temperature . around the inverter. do& not exceed the specified
“ambient t temperature“ listed under paragrapo 8.3.
(2) Install
(31 Cover the top and the bottom of the unit with drip shield kits (option)
when an inverter is wall-mounted. (See page 66)
Do not install the drip shield kits when the unit is mounted within
another cabinet.
3.3 Mounting position and- clearances
(1) Install
“FREQROL-Z200” face front.
th e inverter in a vibration free location.
th e inverter securely and vertically with bolts so that the letters
.
0
(2) Since the inverter generates heat, provide sufficient clearance around the
inverter to assure effective radiation of heat.
(31 When braking is repeated frequently, the surface temperature of the brake
discharge resistor (for models under FR-Z220/Z240-?.5K) , mounted at the
rear of the inverter, may become high (maximum approx. 150°C) .
Therefore, install the inverter on a non-flammable panel (such as metal
plate) .
-6-
.,
p
Page 11
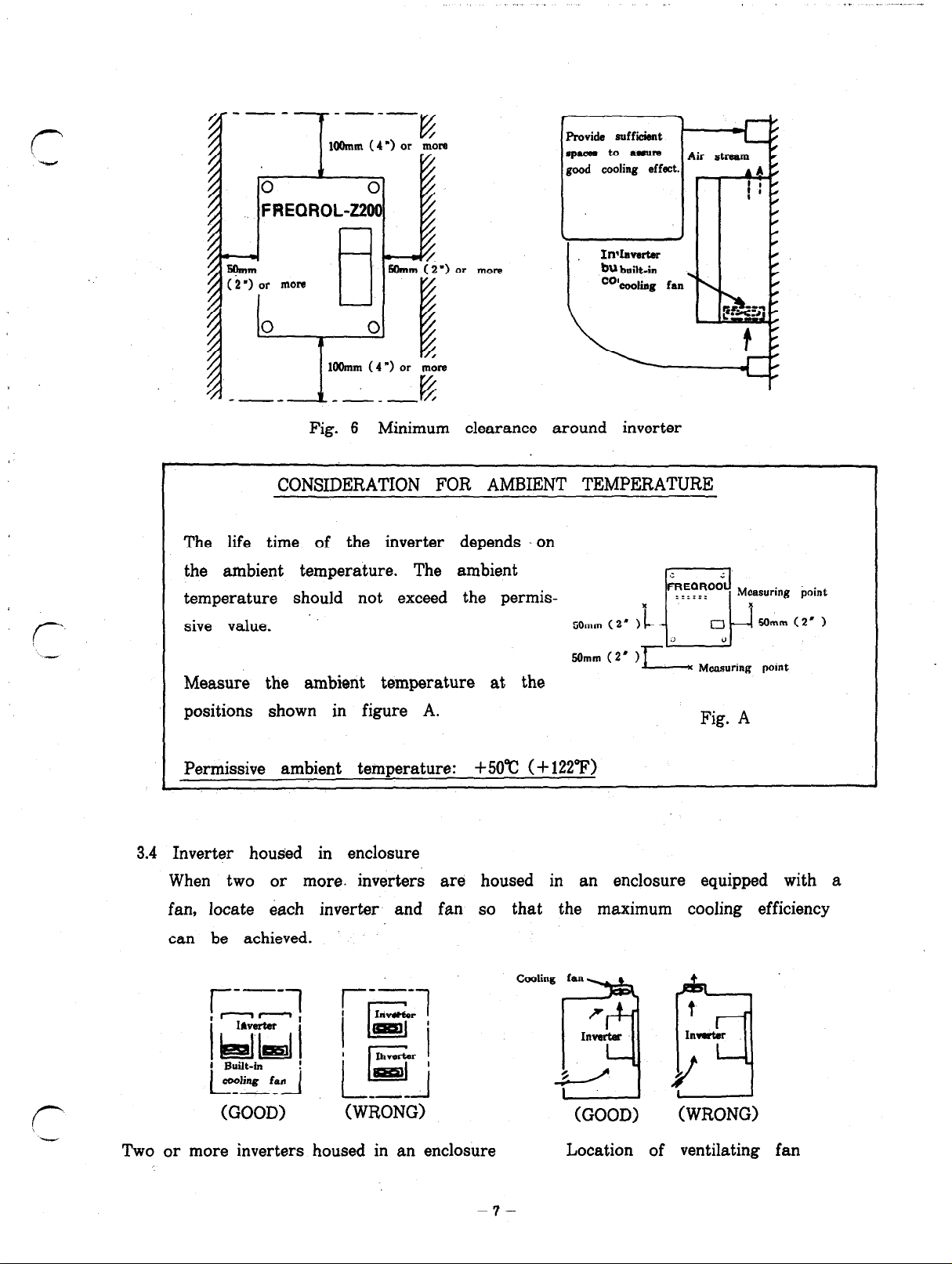
.,-
r
‘W
--- ----
1Wmm ( 4 ‘1 or mGre
0
FREQROL-2200
1OOmm (4”) or more 1OOmm (4”) or more
Fig. 6 Minimum clearance around inverter
CONSIDERATION FOR AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
The life time of the inverter depends on
I?
or mot-c
spaces to aaun spaces to aaun
good cooling effect. good cooling effect.
I
i
In*lw* In*lw*
Air stream r Air stream r
2 2
AA,: AA,:
1: / 1: /
/ /
0 0
/ /
/ /
/ /
I I
/ /
the ambient temperature. The ambient
temperature should not exceed the permissive value.
50mm (2’ 1
5Omm
(2’
)
Moamwing point
Measure the ambient temperature at the
positions shown in figure A.
Fig. A
Permissive ambient temperature: +5O”c (+ 122°F)
3.4 Inverter housed in enclosure
When two or more. inverters are housed in an enclosure equipped with a
fan, locate each inverter and fan so that the maximum cooling efficiency
can be achieved.
I--"1
i
Iawtter 1
II
lpeD i
r‘
(GOOD) (WRONG)
Two or more inverters housed in an enclosure
-?-
(GOOD)
(WRONG)
Location of ventilating fan
Page 12
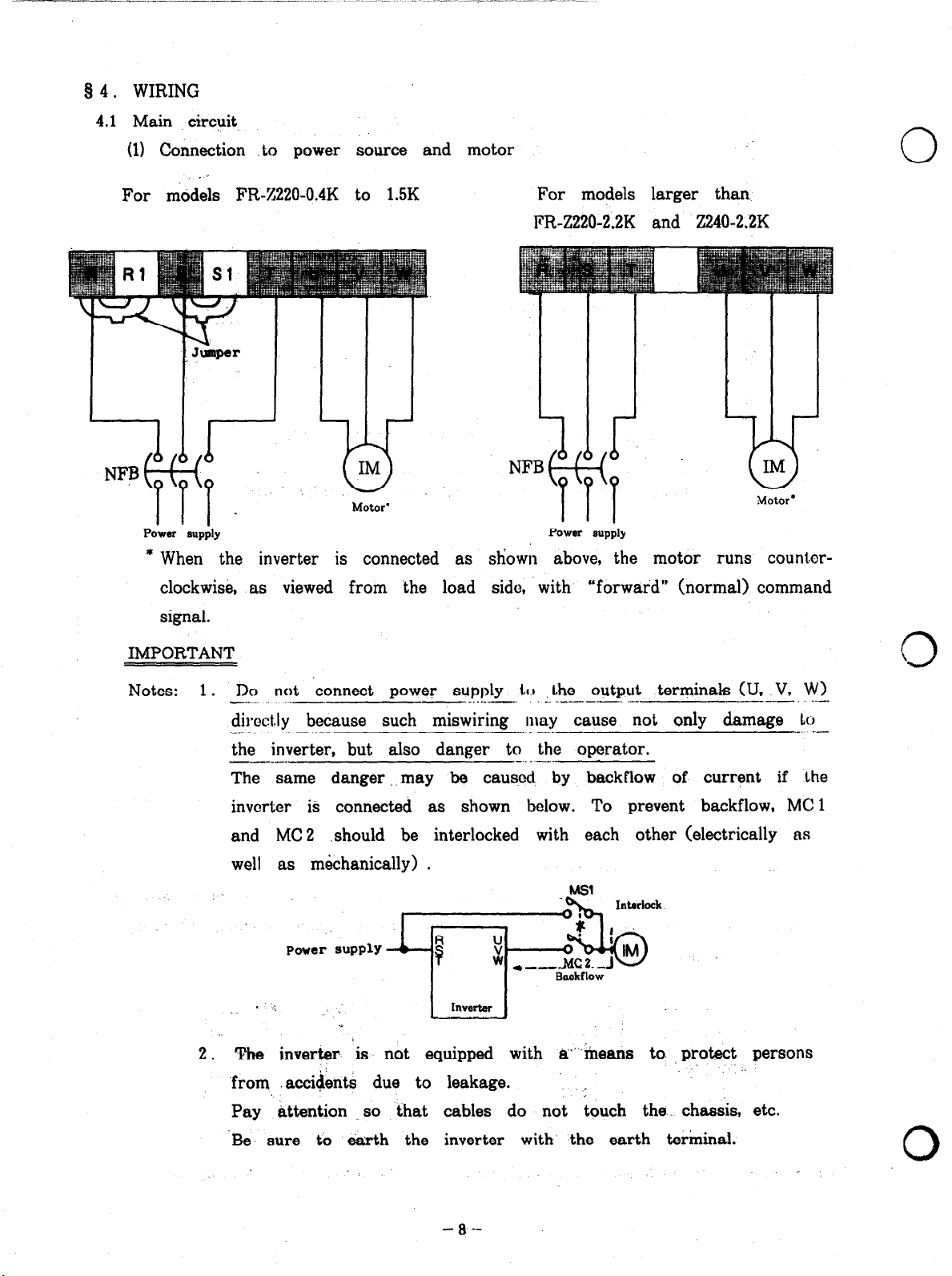
Q 4. WIRING
4.1 Main circuit.
(1) Connection to power source and motor
For models FR-%220-0.4K to 1.5K
For models larger than
PR-Z220-2.2K and Z240-2.2K
I I I
Power supply
* When the inverter is connected as
clockwise, as viewed from the load side, with “forward” (normal) command
signal.
shown above, the motor runs counber-
Power supply
0
IMPORTANT
Notes: 1 .
-._ _ ..-
--.- _ . --
------
2. The inverter is not equipped with a” means to. protect persons
-from .acci&nts due to leakage. ‘. .
DCJ not
directly because such miswiring n~ay cause not only damage
the inverter, but also danger to the operator.
The same danger ..may be caused by backflow of current if the
invorter is connected as shown below. To prevent backflow, MC 1
and MC 2 .should be interlocked with each other (electrically as
well as m&hanically) .
Pay attention so that cables do not touch the. chassis, etc.
‘connect power supply to the output terminals (II, V, W)
L __...____. _. ..__ ---. .-- ---- .--
Lo
-._ . _._.- -
-..-_
:’
_ .-
0
‘Be’ sure to earth the inverter with the earth terminal.
- 8 --
0
Page 13

r
3. If magnetic contactor (MC) is not inserted on the inverter primary
side and a power failure occurs for a short time (instantaneous
power failure) ,
time as the power source is restored.
If it is likbly that this automatic restart may cause damage to
the machine or persinnel, connect .(MC> so that restart is possible
only after’ safety is verified.
For a better understanding, refer to the following diagrams and
descriptions:
Para. 4.3 “Wiring diagram”
Para. 8.2 “Terminals for wiring”
Para: 8.1 “Block diagram”
the inverter will restart automatically at the same
(-
-.I
- CAUTION FOR WIRING OF PERIPHERAL DEVICES
When MC, NFB and other peripheral devices are being connected to the
inverter, cover the inverter to prevent wire chips, screws and other foreign
matter from entering into the inverter through slits and other openings of
the inverter.
(21 Connection of discharge resistor for increased braking (regenerative brake
resistor unit ****** option)
A built-in discharge resistor is been connected to terminals P and PR
-internally, .as standard. ’
However when braking operation is particularly frequent and may exceed
the thermal capacity of the built-in resistor, replace the built-in discharge
resistor with optional discharge resistor unit.
Apply this option with care, due to increased heat losses which have to
be dissipated.
- 9.’
Page 14
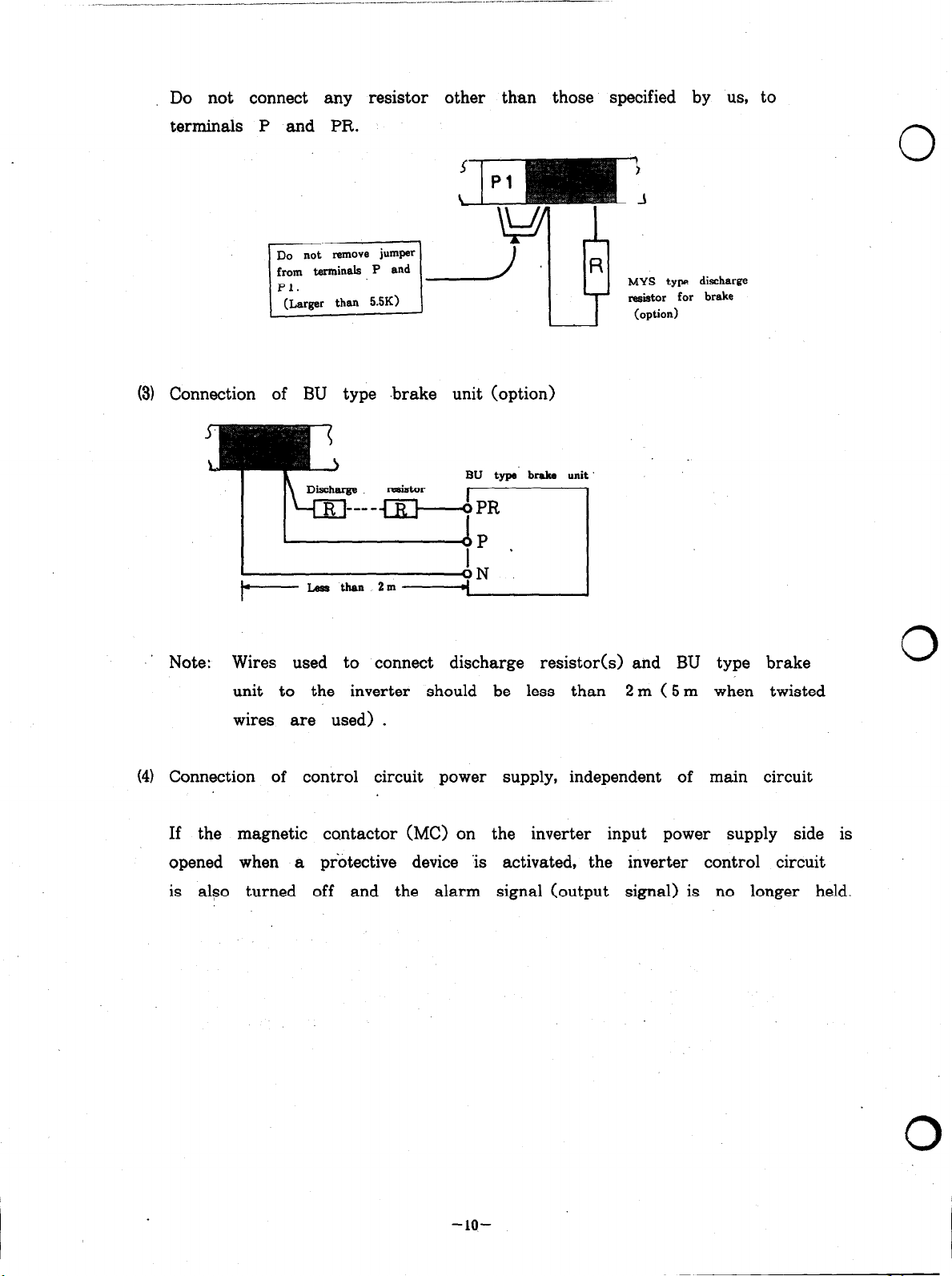
Do not connect any resistor other than those specified by us, to
terminals P and PR.
-
--* I3
(3)
Connection of BU type .brake unit (option)
BU type braka unit
\
Yh
LT
?
>
-J
MYS
type
resistor for
(option)
0
discharge
brake
.’ Note: Wires used to connect discharge resistor(s) and BU type brake
unit to the inverter should be less than 2 m (5 m when twisted
wires are used) .
(41 Connection of control circuit power supply, independent of main circuit
If the magnetic contactor (MC) on the inverter input power supply side is
opened when a protective device is activated, the inverter control circuit
is also turned off and the alarm signal (output signal) is no longer held.
0
I
0
-lO-
Page 15
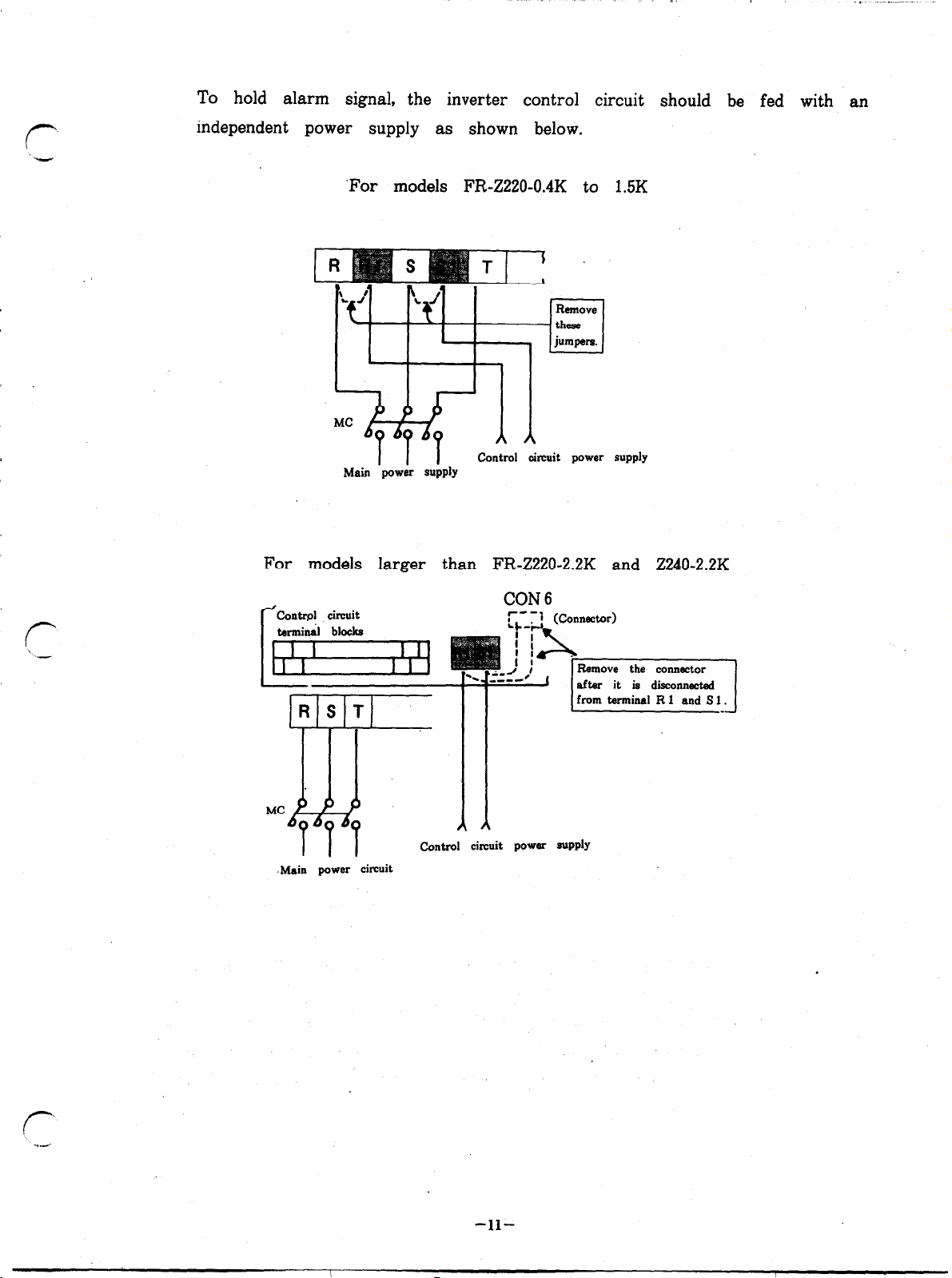
To hold alarm signal, the inverter control circuit should be fed with an
independent power supply as shown below.
r
‘v
‘For models FR-Z220-0.4K to 1.5K
RrmOW
these
jumpers.
Main ‘povJk
control oircuit
power supply
For models larger than FR-Z220-2.2K and Z240-2.2K
CON
6
from
tennina RI and Sl.
Control circuit power
.Main power circuit
SuPPlY
-ll-
Page 16
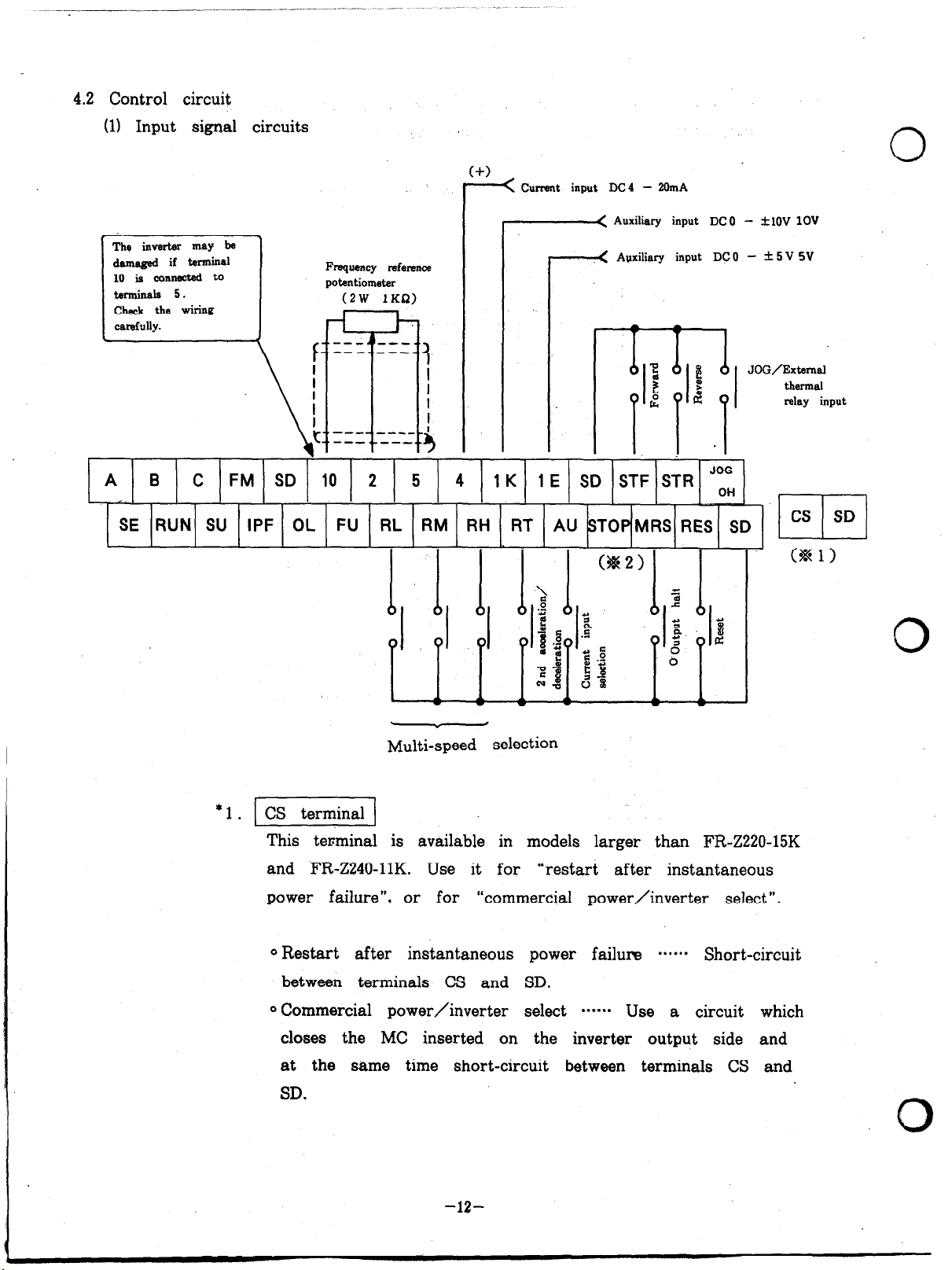
4.2 Control circuit
(1) Input signal circuits
0
c_( Current input DC4 - 20mA
-< Auxiliary input DC 0 - +lOV 1OV
darn4 if terminal
10 is connected to
Check the wiring
A B C FM SD 10 2 5 4
SE RUN SU IPF OL FU RL RM RH RT AU STOPMRS RES SD
Frequency reference
(2W 1KQ)
1 K 1 E SD STF STR JoG
___( Apxiliary input DC0 - f 5 V SV
CS SD
uzl
Multi-speed selection
This terminal is available in models larger than FR-Z220-15K
and FR-Z240-11K. Use it for
power failure”, or for
0 Restart after instantaneous power failure ****** Short-circuit
between terminals CS and SD.
0 Commercial power/inverter select ***-** Use a circuit which
closes the MC inserted on the inverter output side and
at the same time short-circuit between terminals CS and
SD.
“commercial power/inverter select “.
-12-
“restart after instantaneous
.O
Page 17

For details, refer to the technical information.
*2. STOP terminal
This terminal can be used to hold “start” signal.
1
’ f-
Note:
1 . Terminals SD and 5 are common terminals for input/output
signals, and insulated from each other.
,Do not connect these terminals to ground.
2. For signal wires connected to control circuit terminals of
inverter, use shielded wires or twisted wires.
These wires should be separated from cables for the main
circuit and high-voltage circuits (including 200V relay sequence
circuit) .
3. The speed reference signal is a faint current. To prevent miscontact, use two parallel connections of faint signal contacts or
twin contacts.
-13-
Page 18
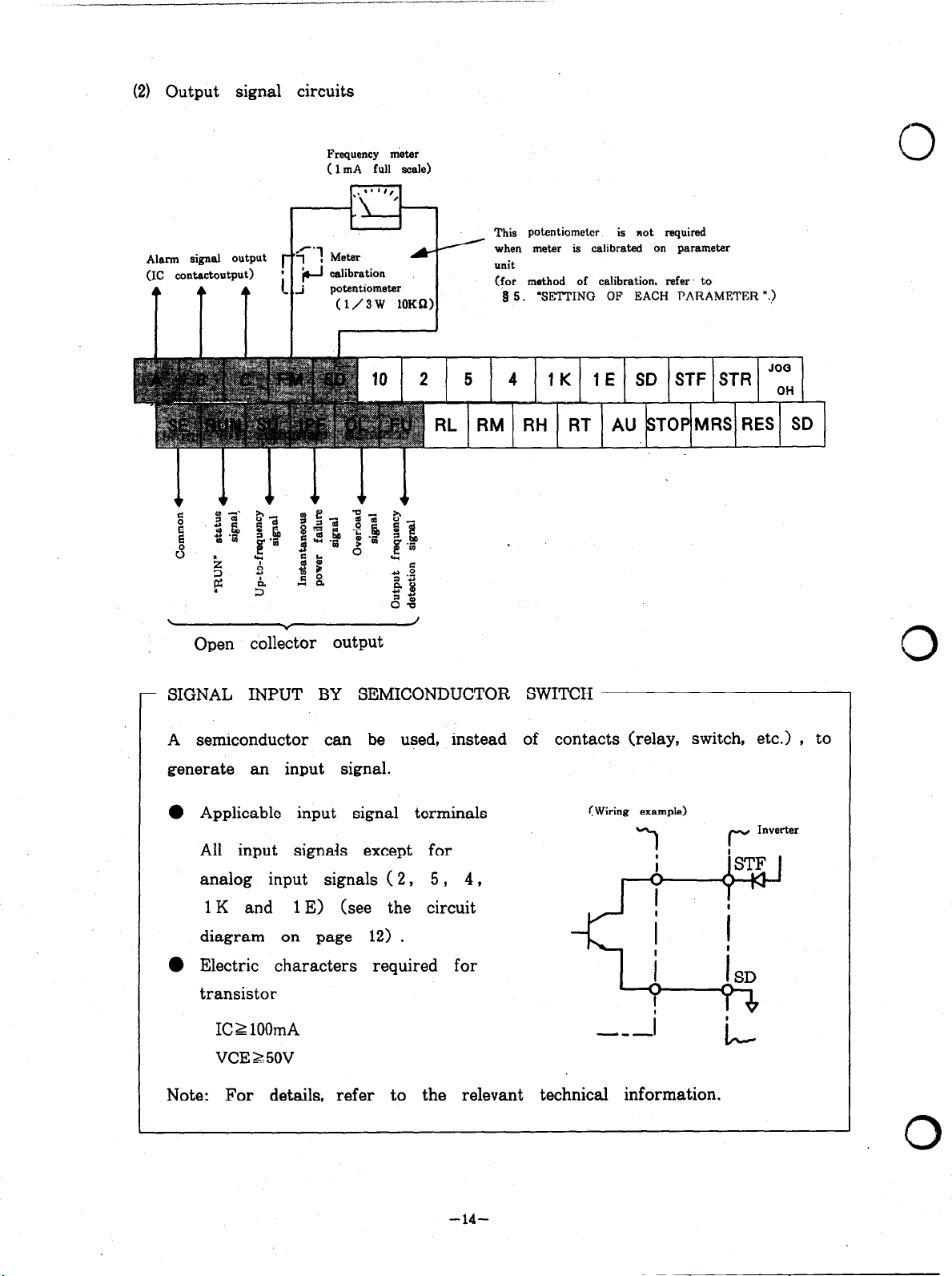
(21 Output signal circuits
Alarm signal output
(IC contactoutput)
.
Open collector output
Frequency nieter
( 1 mA full scale)
(1/3W lOKn>
Y
0
This potentiometer
when meter ie calibrated on parameter
(for method of calibration. refer. to
8 5. ‘SETTING OF EACH PARAMETER “.>
/
is not required
0
- SIGNAL INPUT BY SEMICONDUCTOR SWITCH
A semiconductor can be used, instead of contacts (relay, switch, etc.) , to
generate an input signal.
0 Applicable input signal terminals
All input signals except for
analog input signals ( 2, 5 , 4,
1 K and 1 E) (see the circuit
diagram on page 12) .
l
Electric characters required for
transistor
IC1 lOOmA
VCEZ 50V
Note: For details, refer to the relevant technical information.
(Wiring example)
A--
0
-14-
Page 19
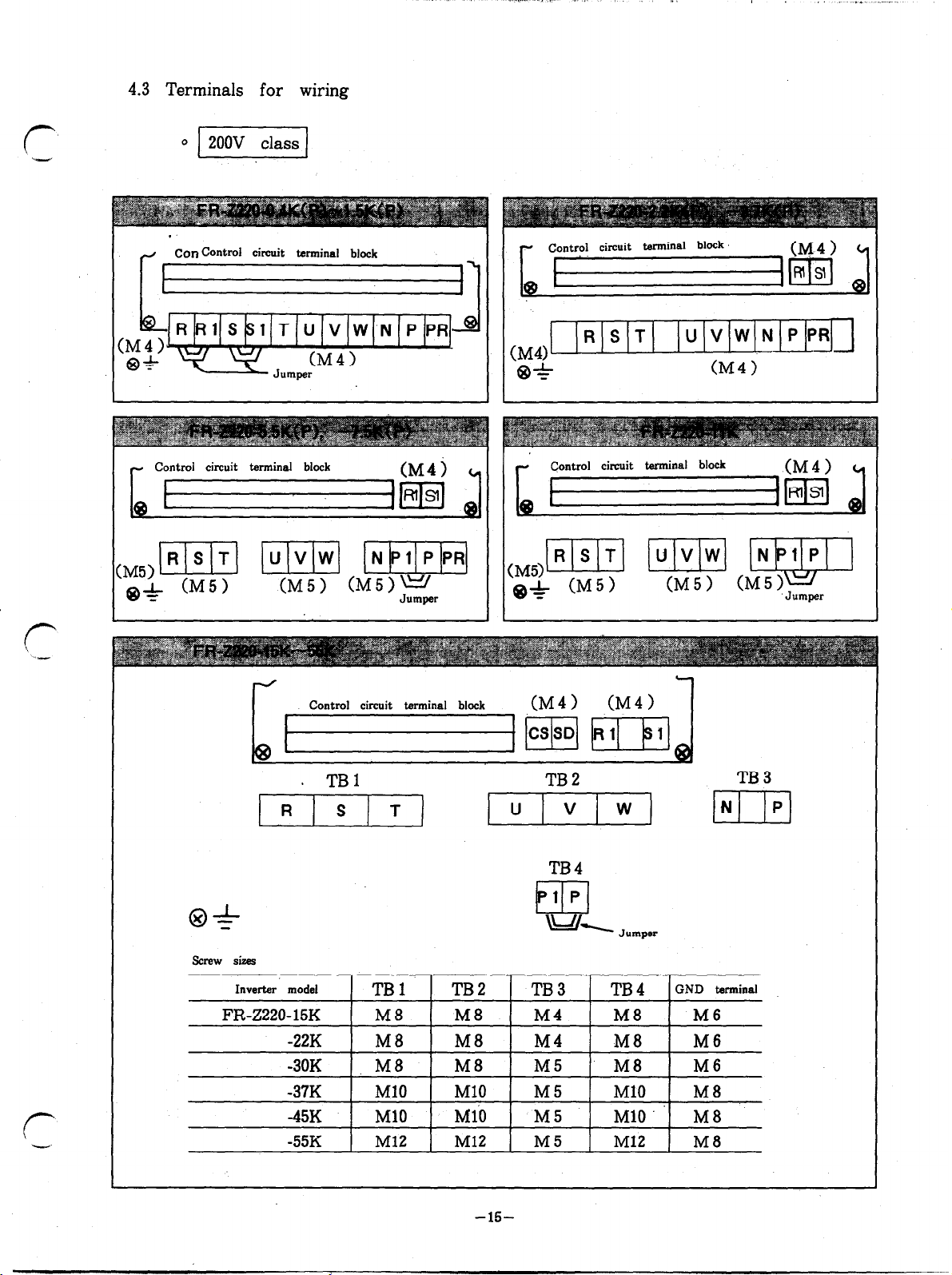
4.3 Terminals for wiring
Concontrd circuit terminal block
U VW N PPR
- Control circuit terminal block
Screw sizes
rc/
f=====jpqm
. TBl
Control circuit terminal block
(M51m w ,Mp
e+ CM51
v
(M4) (M4)
TB2
TB3
TB4
‘Jumper
Page 20
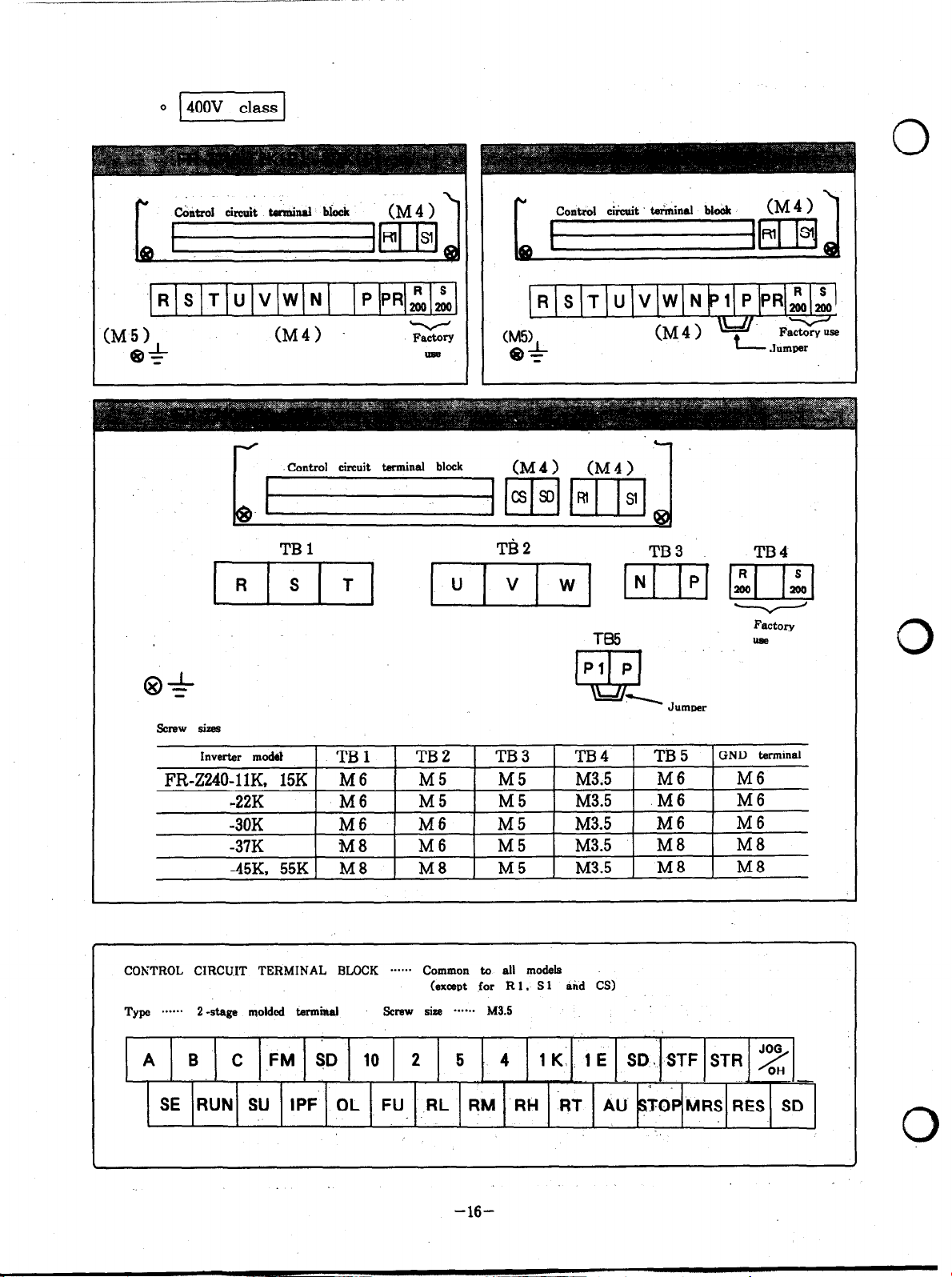
.RSTUVWN
PPRZA
R S ‘T U V W N 1 PPRz;i
CM51
e+
(M4)
J
-Control circuit tanninal block
TBl Tti2
screw sizes
Inverter model
TBl TB2 TB3
FR-Z240-llK, 15K M6
-22K M6 M5 M5
-3OK
-37K M8 M6 M5
-45K, 55K M8 M8 MS
Factory
use
(M5>
e+
(M4) (M4)
M 5
MS
M6 M6 MS
(M4)
c1
wc Faxse
TB3
TB4
TB5
M3.5 M6
M3.5 M6
M3.5 M 6
M3.5 M 8
GND terminal
M6
M6
M6
M8
M3.5 M8 M8
Jumper
TB4
Factory
ua?
0
CONTROL CIRCWT TERMINAL BLOCK ****+* Common to all models
(except
for Rl. Sl aid CS)
SE RUN SU IPF OL FU RL qM -RH -RT AU STOP
-16-
MRS RES SD
Page 21
(+-
-
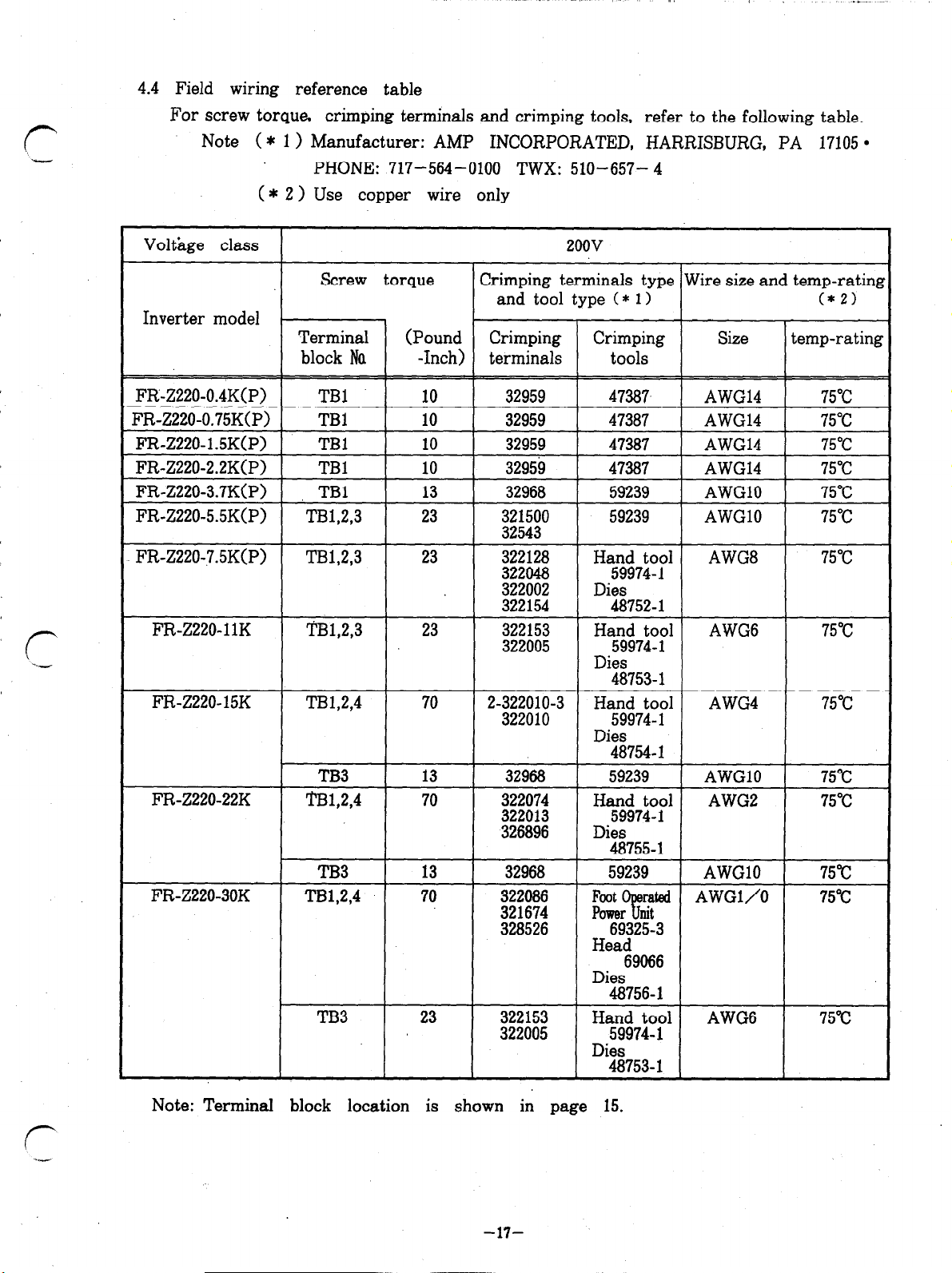
4.4 Field wiring reference table
For screw torque, crimping terminals and crimping tools, refer to the following table.
Note ( * 1) Manufacturer: AMP INCORPORATED, HARRISBURG, PA 17105
PHONE: 717-564-0100 TWX: 510-657- 4
( * 2 > Use copper wire only
Inverter model
l
FR-2220-15K
FR-2220-22K
FR-Z220-30K
Note: Terminal block location is shown in page 15.
TB1,2,4 70
TB3 13 32968 59239 AWGlO 75°C
TB1,2,4 70
TB3 13 32968 59239 AWGlO 75°C
TB1,2,4 70 EY: ;rr& 9 r$d AWGl/O 75°C
TB3 23 322153
2-;;;%;;-3 Hy9i70pl AWG4 75°C
48754- 1
E;; H%:7??
48755-l
328526 69325-3
Head
Dies
48756- 1
Hyg;70;l
322005
Dies
48753- 1
- Dies
AWG2 75°C
- 326896 Dies
69066
AWG6 75°C
-17-
Page 22
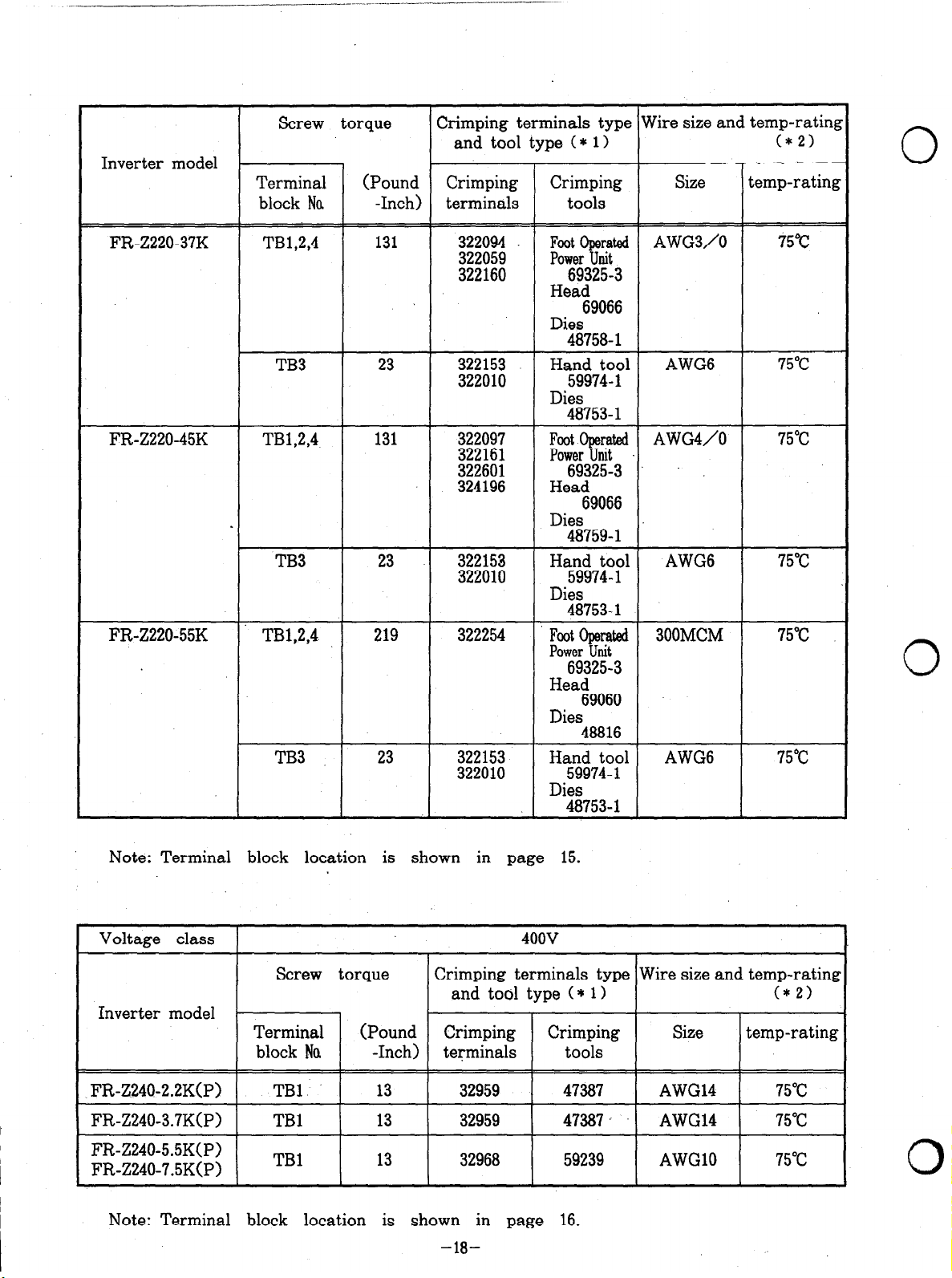
Inverter model
Screw torque
Terminal (Pound Crimping Crimping
block
Na
-Inch) terminals tools
Crimping terminals type Wire size and temp-rating
and tool type ( *
1)
(* 2)
0
Size temp-rating
FR-2220-37K
FR-Z220-45K TB1,2,4 131
FR-Z220-55K TB1,2,4 219
TB1,2,4
TB3 23
TB3 23
TB3
131
23
322094 Foot Operated AWGS/O 75°C
;E!
322153 AWG6 75°C
322010
Ei
322601 69325-3
324196 Head
E;
322254 Foot Operated 300MCM 75°C
Ei
Power Unit
69325-3
Head
69066
Dies
48758-l
Hygi70p1
Dies
48753- 1
Foot Operated AWG4/0
Power Unit
69066
Dies
48759-l
Hygi70y1 AWG6 75°C
Dies -
48753-l
Power Unit
69325-3
Head
69060
Dies
48816
Hygi70;l AWG6
Dies -
48753- 1
75°C
75°C
0
Note: Terminal block location is shown in page 15.
Inverter model
Note: Terminal block location is shown in page 16.
-18-
Page 23
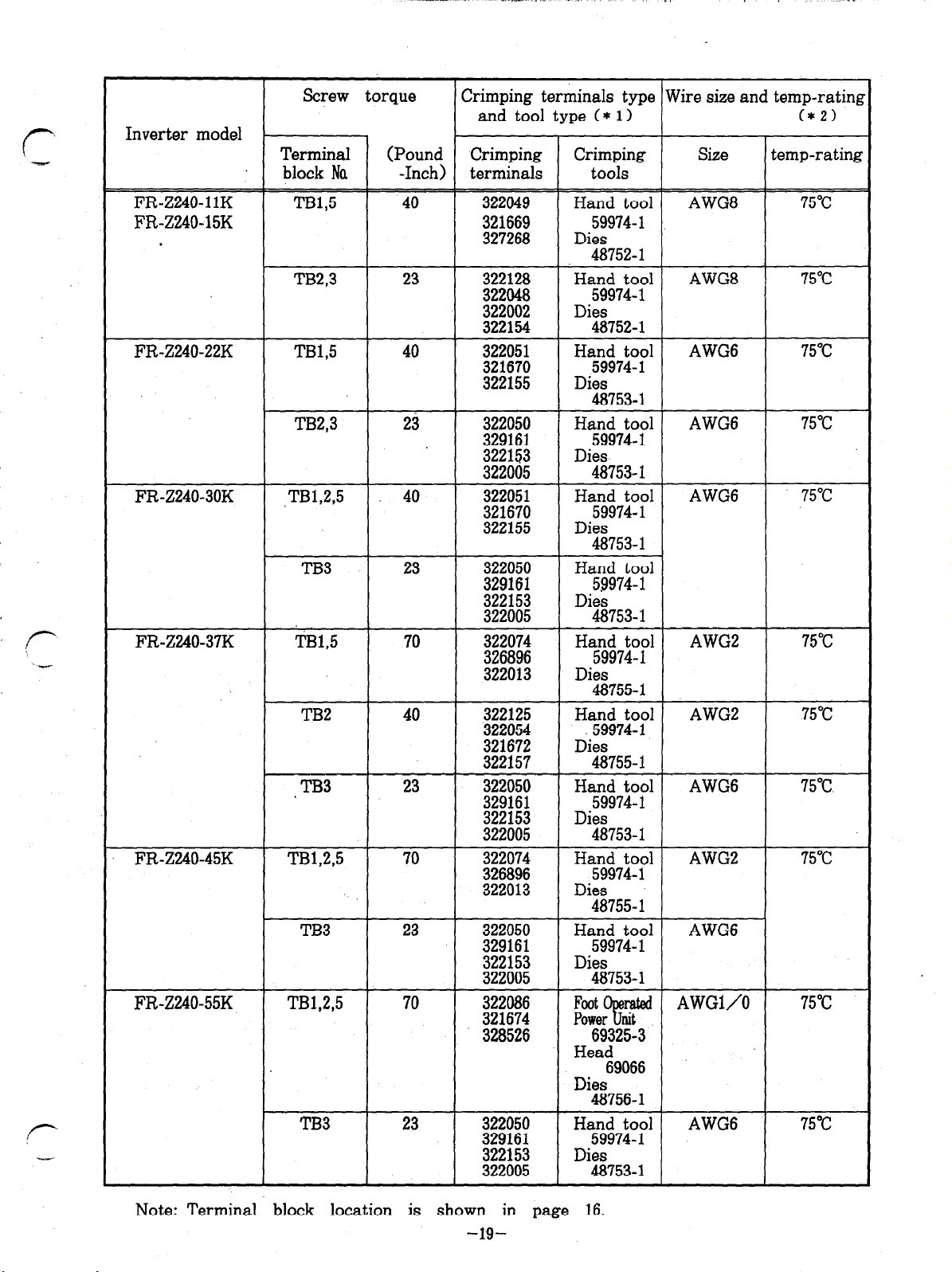
Inverter model
Screw torque
Crimping terminals type Wire size and temp-ratink
and tool type (*
Terminal (Pound Crimping
block
Na
-Inch) terminals tools
1)
(*2>
Crimping Size temp-rating
FR-Z240-11K TB1,5
40 322049 Hand tool AWG8
FR-ZZQO-15K
23
FR-Z240-22K
TB2,3
TB1,5 40
TB2,3 23
FR-Z240-30K ,TB1,2,5 40
TB3
FR-Z240-37K
TB1,5 70
TB2
?3
FR-Z240-45K TB1,2,5
TB3
FR-Z240-55K TB1,2,5
TB3
23
40
23
70
23
70
23
59974- 1
%E
Dies
48752- 1
Hand tool AWG8
Et!
59974-l
322002 Dies
322154
322051
48752-l
H”5”g&f;’
w Dies
48753-l
Hygi70~l AWG6
;I%
Dies
3;
322051
48753- 1
Hagngdg7F;l AWG6
%2 Dies -
48753-l
E%!
H”5”9d97;P’
Dies
;Ei;
E;i
48753- 1
Hyg;7~p1
322013 Dies
48755-l
EfE
7%7?P’
Dies -
x;
EE!i
322153
48755-l
“%$72’
Dies -
322005 48753-l
Ha;lgdgorl AWGZ
;;;:;;
322013 Dies -
48755- 1
Hsgngdg70yl AWG6
Ei!!
Dies
EE
48753-l
Foot rated AWGl/O
EE
77
Power nit
328526 69325-3
Head
69066
Dies
48756-l
Hand tool AWG6 75°C
!Ei!l
322153
322005
59974-l
Dies
48753-l
AWG6
AWG2
AWG2
AWG6
75°C
75°C
75°C
75°C
75°C
75°C
75°C
75°C
75°C
75°C
Note: Terminal block location is shown in page 16.
-19-
Page 24

Page 25

(2) Check that
(31 Check that h t s or -circuit and earth fault do not exist in the output circuit.
(4) Check that all screws, terminals and other fasteners. are tight.
CAUTION FOR INSULATION RESISTANCE TEST WITH MEGGER
th
ere is no short-circuit due to wire offcut, etc.
r
0 For insulation resistance test with megger, refer to Q 6 . 6.2, (3).
0 Never apply the test voltage to the control circuit terminals and across
the inverter terminals.
5.3 Pi-e-operation settings and adjustments
The inverter itself does not have control devices to set or adjust by operator,
(-
--
such as select switch and potentiometer. (As with previous models of FREQROL)
When settings (accelation/deceleration time, electronic thermal relay setting, etc.)
must be changed, the parameter unit (FR-PUO 1 > is used (for the initial settings,
refer to chapter
For methods of changing parameter setting, refer to the description “HANDLING
AND OPERATIGN OF PARAMETER UNIT”. (p. 69 - p. 113)
98.1.
r
-
-2l-
Page 26
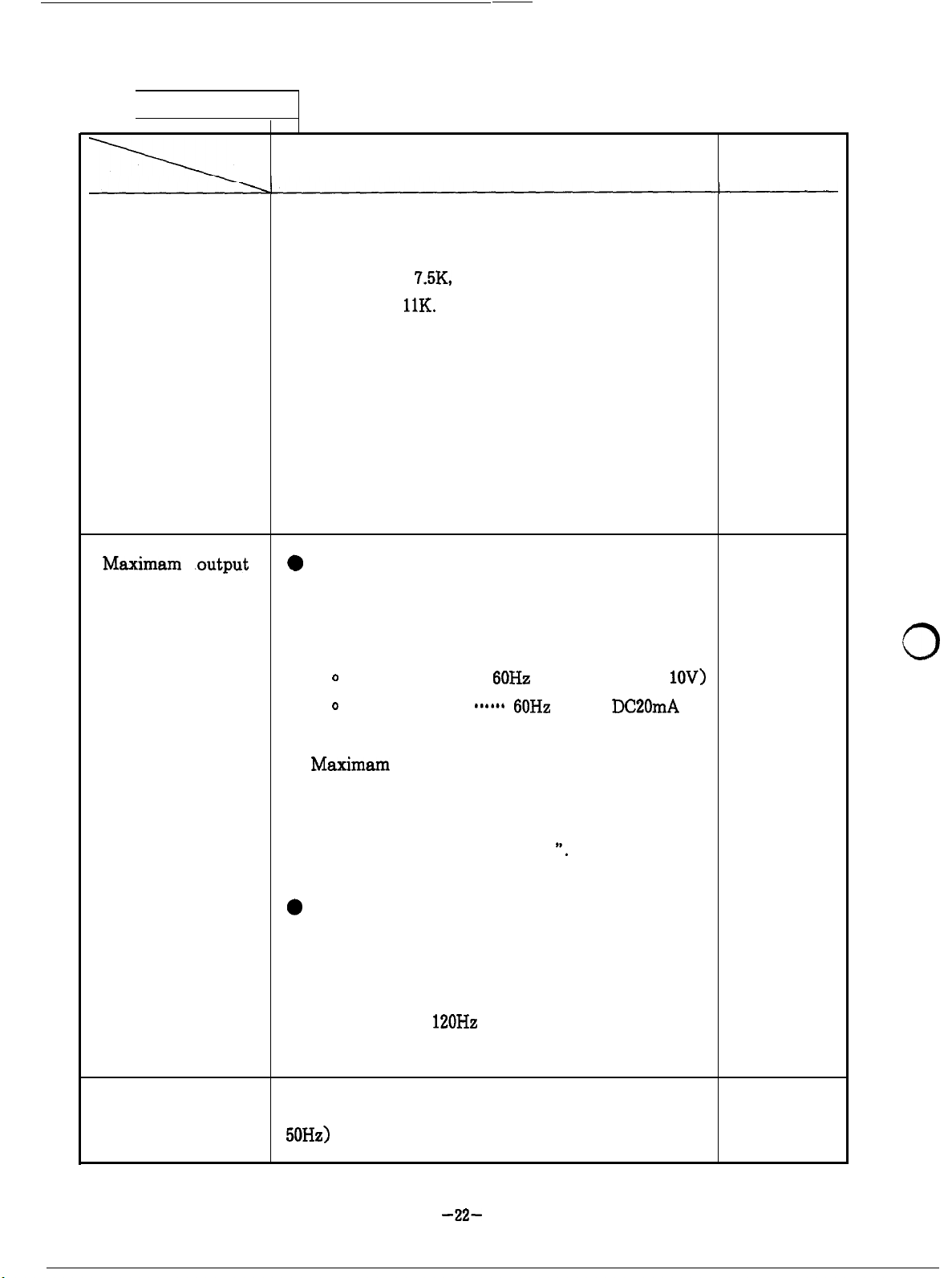
SETTING TABLE
Acceleration/
deceleration
time
Maximam .output
frequency
Description
When the inverter is shipped, acceleration/
deceleration time is set to 5 sec. for models P. 99
smaller than
larger than
The time setting can be changed on the
parameter unit.
Acceleration/deceleration time is the time in
which the inverter output frequency becomes
equal to the frequency at
reference signal voltage.
0
For operation with external signals
When the inverter is shipped, the maximum
7.5K,
and to 15 sec. for models
11K.
5 V of frequency
Refer to
P. 83
P. 83
P. 97
0
Electronic
thermal relay
inverter output frequency is set as follows:
---
6OHz
0
Voltage signal
0
Current signal
Maximam
changed by changing “frequency at 5 V
frequency reference input signal (or at 20mA
frequency reference signal)
0
For operation with parameter unit
The maximum output frequency can be
increased up to the maximum frequency
limit (set to
shipped) .
Setting should be based on current ‘value (at
50Hz)
indicated on the nameplate of the motor.
output frequency setting can be
--+-*- 60Hz
120Hz
when the inverter is
at DC 5 V (or
at
“.
DC20mA
lOV>
P. 83
P. 97
0
0
-22-
Page 27
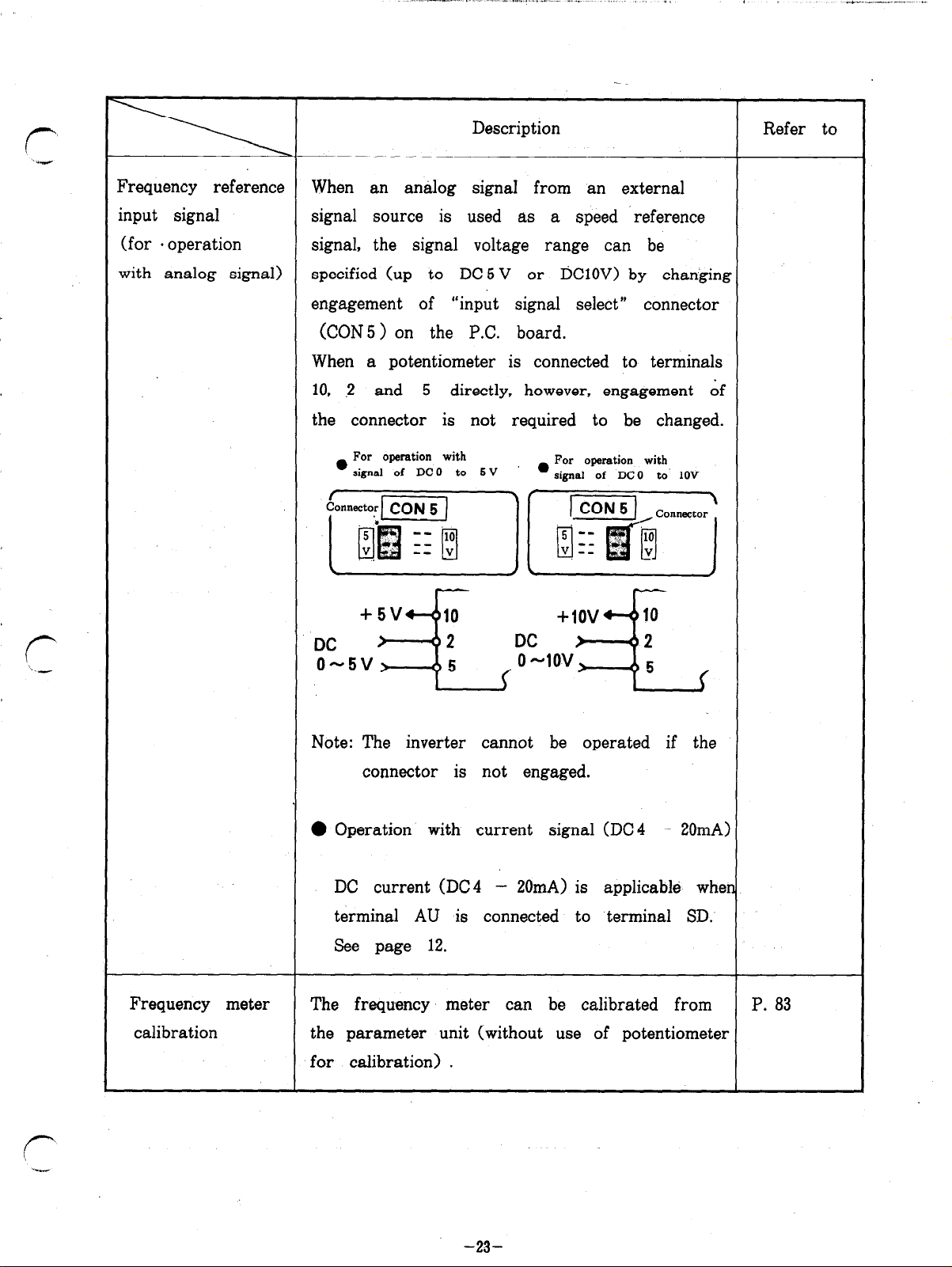
--..-.. ,.. .-. I. -.. . . . . . . . . - “._. I.. ., ,,
Description Refer to
4
*“c -...... --- .-
Frequency reference
input signal signal source is
When an analog signa from an external
used as a speed ‘reference
(for . operation signal, the signal voltage range can be
with analog signal)
specified (up to DC 5 V or DClOV) by changing
engagement of “input signal select” connector
(CON5 > on the P.C. board.
When a potentiometer is connected to terminals
10, 2 and 5 directly, however, engagement of
the connector is not required to be changed.
. 1”’ operation with
SIgnal Of DC O
;/f (;:,;yf (
tO
S V
For operation with
l
sipa] of DC0 b. 1OV
Frequency meter
calibration
Note: The inverter cannot be operated if the
connector is not engaged.
0 Operation with current signal (DC4 - 20mA)
DC current (DC4
- 20mA) is applicable when
terminal AU is connected to terminal SD.
See page 12.
The frequency meter can be calibrated from P. 83
the parameter unit (without use of potentiometer
for calibration) .
-23-
Page 28
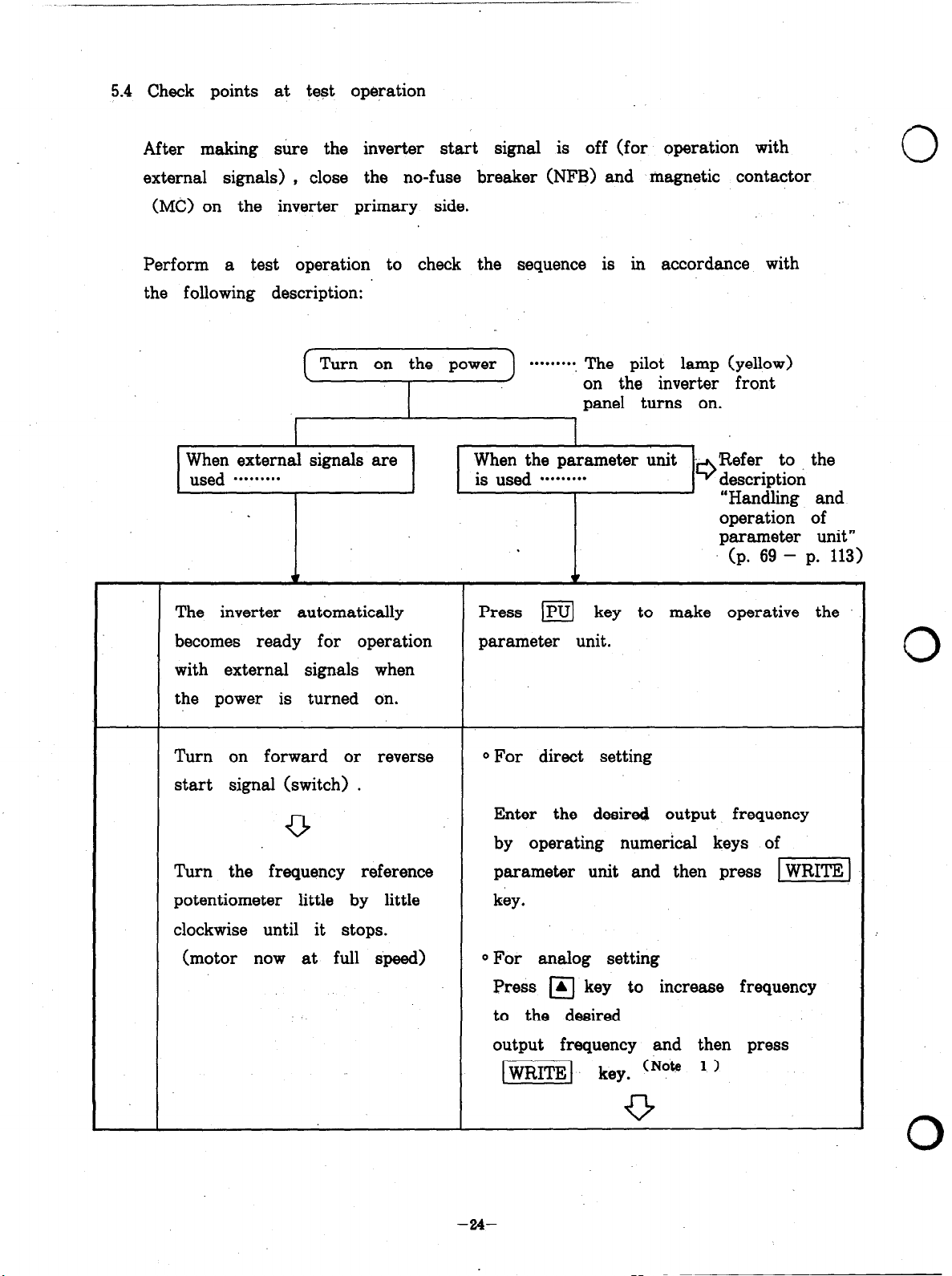
5.4 Check points at test operation
After making sure the inverter start signal is off (for operation with
external signals) ,
(MC) on the inverter primary side.
Perform a test operation to check the sequence is in accordance with
the following description:
When external signals are
. . . . . . . . .
used
The inverter automatically
close the no-fuse breaker (NFB) and magnetic contactor
Turn on the power
When the parameter unit Refer to the
is used
w
Press m key to make operative the
********‘. The pilot lamp (yellow)
on the inverter front
panel turns on.
. . . . . . . . . 9
‘I
description
“Handling and
operation of
parameter unit”
(p. 69 - p. 113)
0
becomes ready for operation
with external signals when
the power is turned on.
Turn on forward or reverse
start signal (switch) .
0
Turn the frequency reference
potentiometer little by little
clockwise until it stops.
(motor now at full speed)
parameter unit.
0 For direct setting
Enter the desired output frequency
by operating numerical keys of
parameter unit and then press
key.
0 For analog setting
Press m key to increase frequency
to the desired
output frequency and then press
-1 key. (Note * ’
pizeiq
0
-24-
-0
0
Page 29

Press I[ or @%$ key
(“MONITOR” function becomes
applicable automatically) .
.$g*
8-r:
ad
s
4
6
Turn the frequency reference Press -1 key. (Note 2,
potentiometer little by little
counter-clockwise to “zero”
position. (motor now stopped)
Change of frequency is not displayed if the parameter unit is not set
in “MONITOR” mode.
(Note 1) As the frequency displayed by the readout of parameter unit
increases, the motor speed increases.
(Note 2 > As the frequency displayed by the readout of parameter unit
decreases, the motor speed decreases.
When the output frequency reaches the “DC brake operating
1
:
L*
frequency”, the DC dynamic brake is activated and the motor
is stopped immediately (refer to “CAUTION” described below) .
f-
Check points:
(1) Check that the motor rotates in correct direction (for relationship
between motor phase sequence and direction of rotatiom, refer to
chapter 8 4. WIRING.)
(2)
Check that the motor does not generate unusual hums or vibration.
(3) Check that change of output frequency is displayed correctly.
(4) Check if “ALARM” lamp lights during acceleration or deceleration
(inverter trip) . If it lights, perform the following check:
l
Check if load is too heavy.
0 Increase acceleration/deceleration time.
-
l
Reduce amount of boost.
-25-
Page 30

CAUTION:
(11 If the forward (STF) and reverse (STR) start signals turn on at the same ’
time, the inverter will not start. If these signals turn on simultaneously
during operation, the motor is decelerated (the inverter output frequency
decreases) to a stop. _ .
(2) Durpng deceleration, the DC dynamic brake is actuated for 0.5 seconds when
the inverter output frequency decreases to less than the DC brake frequency
(below the start frequency, when speed reference signal voltage (or current)
is reduced gradually) .
During this DC dynamic braking period, the motor may generate a high-
pitched hum, but this is not a failure, nor a sign of trouble. This is
normal during DC braking.
(31, If “ALARM” lamp lights and the motor stops after coasting, check that the
motor has stopped completely and then reset the inveyter to shut off the
power, using the reset terminal.
0
0
.:
-26-
r
0
Page 31

8 6. MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
f-
%me-
The inverter is a piece of static equipment consisting mainly of semiconduct-
or elements.
To prevemt trouble with the inverter, due to high temperature, humidity, dust,
intense vibration, component deterioration, etc., it is very important to perform
periodic inspection.
6.1 Caution for maintenance and inspection
(1) Operator must check whether, power supply is ON or OFF by himself
to prevent misoperation by others.
(2) After the power
voltage for a while.
Before making an pnspection, check that the CHARGE lamp on the P.C.
board is off, and voltage across the inverter main circuit terminals P
is switched ’ off, the capacitor remains charged at high
and N is below DC30V, using a multimeter, etc.
6.2 Inspection points
This invertey is equipped with the power pilot lamp and error (alarm)
display function. .
It is advisable that you familiarize yourself with the error display definitions.
Also note the normal settings of the electronic thermal relay, acceleration/
deceleration time, etc.
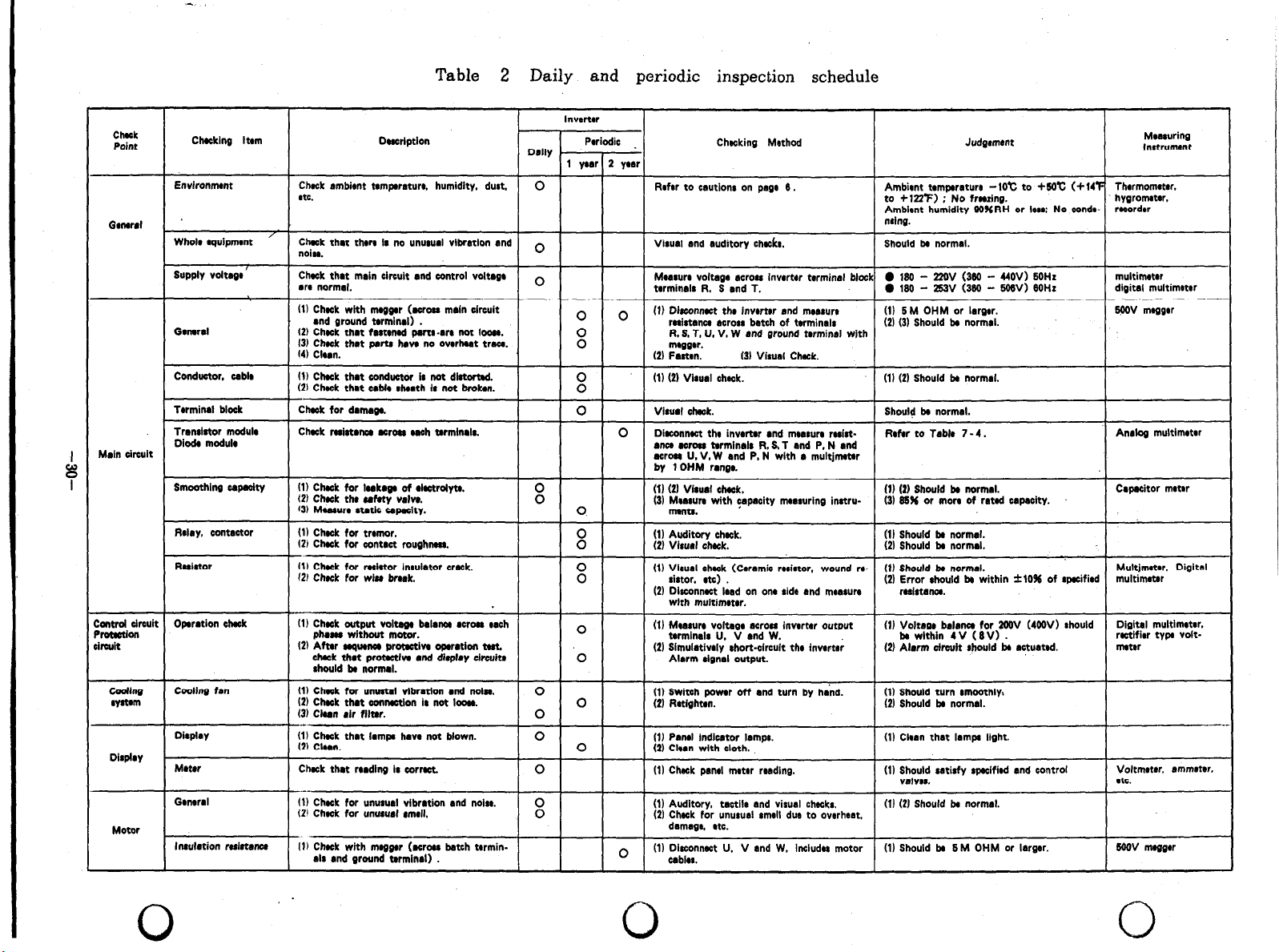
(1) Daily inspection
During daily operation, check the following:
(a) The motor operates properly.
(b) The environment is normal.
(cl The cooling system is normal.
(d) There is no unusual vibration and noise.
r
i-l
(e) There is no overheat and discoloration in any component of the
inverter .
-n-
Page 32

During operation, check inverter input/output voltage with a multimeter.
(2) Periodic inspection
Check the followings periodically with the inverter stopped:
(a) Check that the cooling system is in good condition.
Clean air filters, etc.
(b) Screws, bolts, nuts and other fasteners may become loose with time,
due to vibration, thermal expansion/retraction, etc.
Retighten loose screws or other fasteners.
(c) Check if conductors and insulators are not corroded. or damaged.
(d) Measure insukation resistances.
(e) Check the cooling fan, smoothing capacitor, contactors and relays for
condition.
0
Table 2 shows the standard daily and periodic inspection schedule.
(3) Insulation resistance test with megger
(a) Before checking insulation resistances of the external circuits with a
megger, disconnect wires (cables) from all inverter terminals so that
test voltage is not applied to the inverter circuits.
(b) Conduct the insulation resistance test on the inverter main circuit
only, as shown in Fig. 7.
Do not conduct the test on the control circuit of inverter.
(c) To check the control circuits for continuity, use a multimeter (high
resistance range> .
Do not use a megger or buzzer to check.
,
0
-28-
I
Page 33

Ground trrminsl
-m-m-)
---VW
Motor
Fig. 7
Insulation resistance test with megger
Page 34
Check
ammeter.
Point
Environnlwt
Gwwr*l ’
Whole rquipmont
supply voltage
Gmwd
Conductor. ublr
Tarmind block
Trrndstor module
Main circuit
t
:antrol circuit Operation chtok
WOtUtiW
:imuit
phi
mm
Dirplry
Motor
Diode module
Smoothing
AaIry. contactor
Rrirtor
CodInS fan
Dirplay
Meter
Guwral
Insulation rrrirtatwa
Checking Item
I
rpwity
Table 2 Daily and periodic inspection schedule
Dwcrlption
Check ambient temperature, humidity, dust.
etc.
/
Chmk that thrra ir no unutud vibration and O
noita.
Check that main circuit and control voltaS*
ore normal.
(11 Check with meggw (across main circuit
and ground tbrminal) .
(2) Chock that fastenad parts.rre not loom.
13) Chock that porta hrw no owrhut trau.
14) Clwn.
(1) Check that conductor is not dietort&.
(21 Chack that cable rhuth i# not broken.
Chnk for damago.
Check mist~nce acroa ah orminrls.
(1) Chack tar lukap of rlactrdytt.
(2) chuk
thr
‘3) Mwwn notit copuity.
(1) Chock for tramor.
(2i Cheek for contact roughen.
(1) Check for resistor insulator crack.
12) Check for wlrr break.
(1) Chrck output voltaga balmtea across wch
phases without motor.
(2) After nquana prouetiw operation tact.
chuk that protutlw and die& chita
should k normal.
(1) Cheek for unwtal vibration and noln.
(2)
Chuk that wmutlon h not loon.
(3) Ghan rlr flltar.
{:I Eh$ that Iamy have not blown.
Chack that wading Is corract. 0
(1) Check for unusual vibration and noisr.
(21 Chrcl: for unusurf rmrll.
(1) Check with nuggw (-roes batch trrmin-
elr and ground terminal) .
wfety VdW.
Inwrter
Dally .
0
O
8
0
0
0 (1) Panel indicator Iampc. (1) Clean that lamp light.
Periodic
1 ywr 2 year
Rnhr to cautions on paga 6. Ambirnt temperature -1O’c to +SaC (+14f Thrrmomrar.
Visual and auditory chock@. Should k normal.
Measure voltage (Iwo* inwrtrr terminal Mock 0 180 - 220; l:E 1 440:; ZO:
torminrlr R. 8 and T.
0 0
8
8
0
0 ment8.
8
8
0
0
0 (2) Should b normal.
0 (2) Clrrn with cloth.
HI Dlmomwct tha invutrr and mnrrure (1) 6M OHM or larger.
(2) Fasttm.
(1) (2) Visual ahack. (1) (21 should bb normal.
Viruel &ask. Should k normal.
0
Di@connect thr inwrtw and mratun resistanca mron hrmlnals R.S.T and P. N and
awon U. V. W and P. N with a multjmrtw
by 1 OHM ron~r
(1) (21 Vi8ual thack.
(3) Mea~un with capacity measuring instru- (3) 85% or man of rated wpacity.
(1) Auditory check. (II Should br normal.
(2) Visual c&k.
(1) Vl8url ahack (Ceramic rrsictor. wound R(2) Disconnect lrad on one sldr and measure
(1) Mearun volteg* acrow inwrtw output
(2) Simulativaly rhort-clreult the lnv&
(1) Switch poww off and turn by h&d. (1) Should turn wnwthly8
(2) Ratighan.
(II Chak panel meter reading.
(1) Auditory. tactile and visual checks. (1) (2J Should k normal.
(21 Check for unusual #mrll due to overheat,
(1) Clbl,nnwt U. V and W. Includrc motor
0
Chocking Method
to +122’F) ; No frnxing.
Ambirnt humidity SOURH or lass: No con&nrlng.
l 180 -
rrlstana across batch of terminals (2) (3) Should k normal.
R. S. T, LJ. V, W and around terminal with
mwg9.r.
sirtor. 9tc) .
with multim#rr.
twmlnalo U. V and W.
Alarm rlgnal output.
dsmsgr etc.
(3) Visual Chock.
Refer to Table 7-4.
(1) 0) Should k normal.
(21 Should k normal.
(1) Should k normal.
(2) ;~ti;~uld k within f10% of sceified multimater
(1) Voltage balona for 2OSV (4OOV) should
br wlthin 4V (8V) .
(2) Alarm &cult rhould k actuated.
(1) Should satisfy specified and control
VSIVU.
(1) Should ba 6M OHM or larger. MH)V mm
Judgment
Meaalurinp
lnstrumrnt
hygrometer.
rnordrr
multimeter
digital multimater
WOV mwgtr
An&S multimeter
Capwitor meter
Multjmmr. Digital
Digital multimrtrr.
rutlfior typ voltmeter
-
Voltmeter,
etc.
-_
0
.
0
Page 35

/ . 1.x. . ..^.
i..____-
_
-
6.3 Method of measuring main circuit voltage, current and output power
(1) Method of measuring voltage and current
Since the inverter power supply (input) , output voltage and current include
* high-harmonic components, date (measurement results) depend on instrument
and circuit used in measurement.
To measure voltafe and current with an instrument for commercial
frequency application, use the instrument in accordance with Table 3, and
the circuit shown .in Fig. 8.
3 -phase
power
SUPPlY
Input
VOltage
VwAi
Av
1 )
1
To
Output
voltage
output
current
motor
Fig. 8 Measuring points and instruments
Page 36

Table 3 Measuring points and measuring instruments
Measuring point Instrument
Line voltage
VI
Input current
11
Input power
P*
Input power
factor .
Pf,
Output voltage Across U and V,
VZ
Across R and S,
S and T, and T
and R
R, S and T line - Moving-iron
current
On R, S and T,
and across R and
S, and S and T
To be calculated from the equation shown below. after
line voltage, input current and input power and measured.
Pf, = &P1* I, X 100%
I
V and W, and W (moving-iron phases is * 1% or
and U
Remarks
(Criterion)
Moving-iron
c
type
c
type
Electrodynamic P*=W,, + WI?
8
type
’ Rectifier type Difference between
t
type is not less of maximum
acceptable) output voltage.
Commercial voltage
0 180 - 22OV
(360 --i 44OV)
50Hz
0 180 - 253V
(360 - 506V)
60Hz
0
0
Output current U, V and W line
I* current
Output power
PZ
Output power
factor
Converter output Across P and N
and across U
and V, and ,V
and W
: To be calculated from the equation shown below
Pf, = &IZ. I* X 100%
Moving-iron Current should be
c
type
type .
a Moving-coil
type (suoh
as multimeter)
equal to or less
than inverter rated
current.
Difference between
phases is 10% or
less.
Pz = wn + wtr On .U, V and W, e Electrodynamic
POWER lamp should
light.
1.35 X VI
Max. voltage during
regenerative braking
380v (73OV)
0
-32-
Page 37
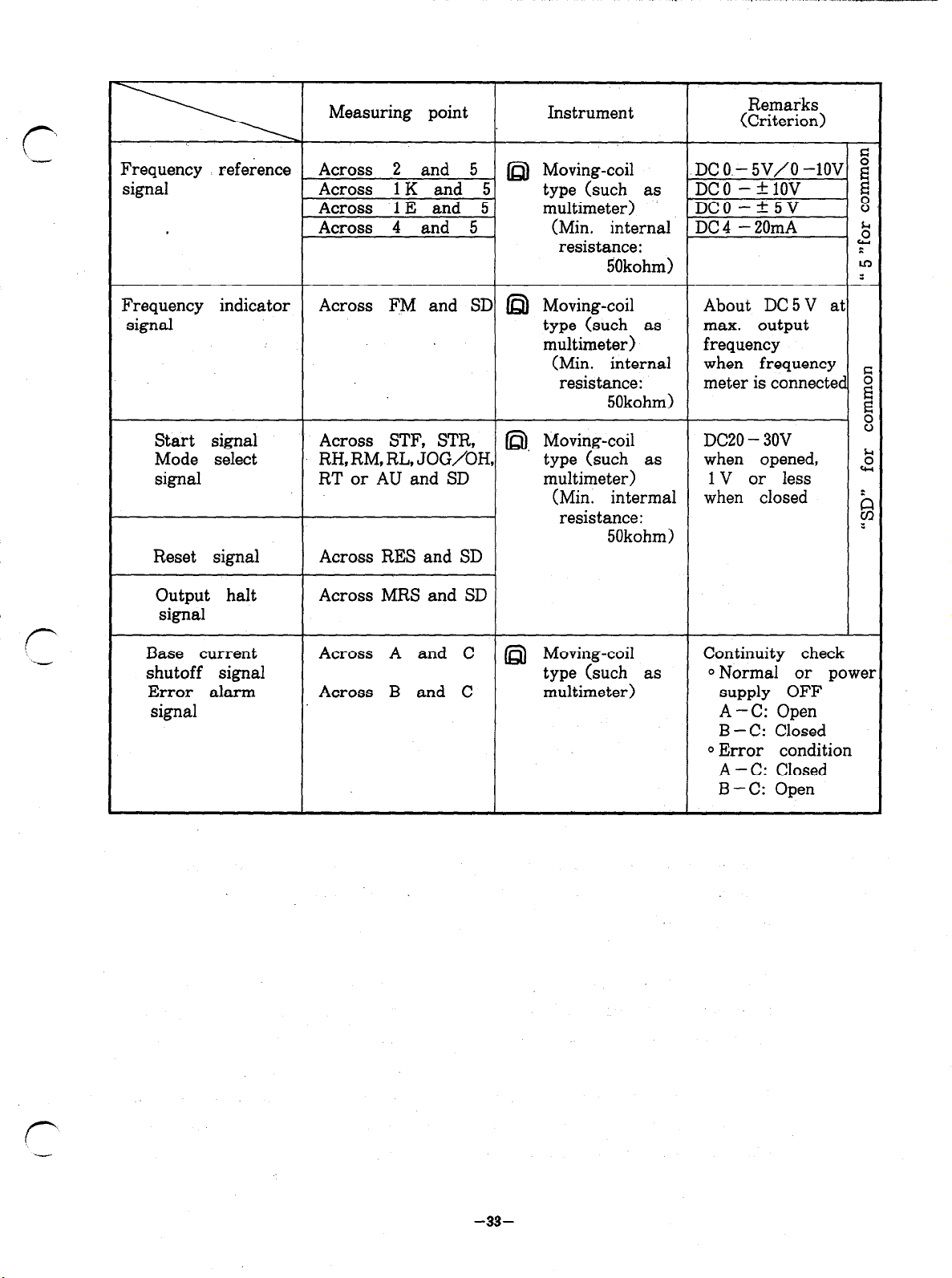
r
-
Measuring point
Frequency reference
signal Across 1 K and 5.
Across 2 and 5 _ n Moving-coil DC O.- 5V/O -lOV G E
Across 1 E and 5 multimeter) DC0
Across 4 and 5 (Min. internal DC 4 - 20mA
Instrument
type (such as
resistance:
5Okohm)
Remarks
(Criterion)
,DCO -klOV E
-+5v
8
5
:
m
:
Frequency indicator
signal
Start signal Across STF, STR,
Mode select
signal RT or AU and SD
Reset signal Across RES and SD
Output halt
signal
Base current
shutoff signal
Error alarm
signal
Across FM and SD D Moving-coil
RH, RM, RL, JOG/OH,
Across MRS and SD
Across A and C @) Moving-coil Continuity check
Across B and C
About DC5V at
type (such as max. output
multimeter)
(Min. internal when frequency
resistance: meter is connected 5
50kohm)
@), Moving-coil DC20 - 30V
type (such as when opened, k
multimeter) 1 V or less cy
(Min: intermal when closed
resistance:
50kohm)
type (such as ~Normal or power
multimeter)
frequency
supply OFF
A-C: Open
B - C: Closed
0 Error condition
A - C: Closed
B-C: Open
b
1
g
8
f-
-
-33-
Page 38

6.4 Mesuring instrument selection and usage
To observe the condition of insulation, voltage, current, signal level, waveform,
etc., select an adequate instrument and use it in accordance with the
following description:
(1) Measurements on main circuit
The measurements include power supply and output voltages and
current measurements, load (motor) continuity check, insulation check,
voltage and current waveform observation.
The followings are particularly important to be checked carefully with
the specified instrument(s):
0 Multfmeter
For continuity check with a multimeter, be careful of sneak path
0
circuit. Do not make continuity check for the inverter circuit transistor
module with the motor connected, and for the converter circuit diode
module with the power connected.
Make continuity check only for components to be checked with the
wiring to other components disconnected.
@ Voltmeter and ammeter
The input power supply voltage is sine-wave of the commercial
frequency. To measure the input voltage, any appropriate instrument
may be used.
Since the input and output current waveforms include various highharmonic components, use a moving-iron type ammeter, as it indicates
values in r.m.s., to measure the input and output currents.
0
To measure the output voltage, use a rectifier type voltmeter because
it reads nearly the basic wave
which is used as the reference value of torque generated by the motor.
component of the voltage waveform
0
Page 39

-_l__l___- II ..-..--- “.--“” ._..* - -..-... .._, ,.,..,_ ., ,
, . I...+
Anyway, it is important’ to record the instruments used and measurement
results, and to always use the same instruments at inspection.
0 Oscilloscope
To measure high voltage (4OOV or higher) , insulate the power supply
of oscilloscope and use a high-voltage probe or insulate the point to
be measured with a potential transformer or current transformer.
In the latter case, the potential transformer or current transformer
should have a capacity large enough to prevent magnetic saturation.
(21 Measurements on control circuits
The measurements on control circuits include measurements of frequency
reference signal, inverter
control voltage and observation of waveforms.
For accurate measurement, note the followings:
@ Voltage measurement and waveform observation
Since the currents of these signals are
faint and the impedances of
the circuits are high, use an instrument, input resistance of which is
as high as possible (lOOkohm to
1 Megohm) .
It is recommended to use a digital multimeter or oscilloscope in the
measurements.
Since input resistance of multimeter set in a low range is significantly
low, value read by multimeter may be lower than the true value.
0 Common line connection
f-
“,-
Connect the common terminal of instrument to an optimum point of
circuit (i.e. the common point nearest to the point measured) .
@ Instrument characteristics
For waveform observation, use’ an oscilloscope which has characteristics
that meet the waveform to be observed.
-35-
Page 40

The inverter base drive waveform can be observed, for example, with,
Instruments
5ooV megger
Multimeter
Voltmster
Ammeter
a 10MHz oscilloscope.
To measure transient waveform at rise of
signal (dv/dt or di/dt) , however, an oscilloscope of 200MHz or
larger frequency is required.
._
Table 4 Instruments and points to be measured
Measuring point
Main
..
circuit circuit ductivity
Control insulation Con- Voltage Current W aveform
0
0 0
?
0 ‘0
0
Measuring item
0 0
t
Description
Measure across batch of main circuit
terminals and ground.
(This does not apply to control circuit.)
Judges whether semiconductor element
is proper or not. Used to know
conductivity or resistance value.
0
Measure line and inverter output voltage.
Use a rectifier type.
Measure line and output current.
Use a moving-iron type.
0
Oscilloscope
Digital multimeter 0
0
0 0
1 ’ 1 ’ 1 ’ 1 transient voltage and current.
Used to observe waveform and measure
Used to measure circuit voltage instead
of multimeter.
6.5 Transistor modules and diode modules
To check transistor modules and diode modules, follow the procedure
described below.
(1) Preparation .
0 Disconnect the power supply cables (R, S, T) and motor ‘cables (II, V, W> .
l
Prepare a multimeter (set the multimeter to “ 1 OHM” resistance
measurement range) .
(21 Checking method
0
Alternate polarity of multimeter with the multimeter probes connected to
inverter terminals R, S, T, U, V, W; P and N and check for continuity
as listed in Table 5.
-36.-
0
Page 41

__~___.I.____----._-.lr--_ .-*,-. I ,, .r b (. , __,.._ -.~_l”ll_l-._----
Table 5 Checking the transistor modules and
diode modules
Normal conditidns Normal conditions
Notes: 1. Before measurement, check that the smoothing capacitor
been discharged.
2. “Discontinuity” means that the multimeter reading is almost
infinite. Due to electricity remaining in smqothing capacitor,
the multimeter may indicate “continuity” momentarily.
“Continuity” means that the multimeter reading is about
1 - lOOohm, depending on number of total modules, number
of modules connected in parallel, type of- modules, etc.
If all measurement results are almost same, the modules
are in good condition.
have
-37-
Page 42

P
TRl TR3 TR5
P
Dim
v
W
id6 TR 2
N
6.6 Parts replacement
The inverter consists of many esectronic ,parts such as. semiconductors.
The parts described below may deteriorate with time in electronical and
physical characteristics.
As preventive maintenance, therefore, these parts require to be replaced
0
periodically.
(11 Cooling fan
The service life of the bearings of the fan used to cool heatgenerating
parts such as main circuit semiconductors is ‘usually within a range from
10,000 to 35,000 hours. Hence, it ‘is necessary to replace the cooling fan
every 2 or 3 years.
If unusual noise and/or vibration is found during inspection, it is
necessary to replace thecooling fan.
Smoothing capacitor
For smoothing (rectification .of input power supply) , large-capacity aluminum
electric capacitors are used in the DC main circuit.
Its characteristics are, adversely affected by ripple current, etc.
When the invertey is used in normal air-conditioned environment, for
0
example, replace the capacitors about every 5 years.
0
Page 43

- ,_-. -.-.“*-*, .,._ < _ 4. . _. ._i .,_..___ ___I_-. I
When a capacitor is used for the period specified as life, it may
deteriorate suddenly.
It is necessary to check all smoothing capacitors yearly (several months
if life ‘is about to expire) .
.
Check the followings:
.
0 Case
. Side walls and bottom for deformation
0 Sealing plate
@ Pressure relief valve :
: For unusual warp and cracks
For excessive valve expansion and
operation
@ Appearance, crack in case, discoloration and leakage:
When capacitance of a capacitor is reduced below 85% of rated
capacitance, replace that capacitor.
To measure capacitance, use an
instrument available commercially.
(3) Relays
To prevent miscontact, it is necessary to replace relays in accordance
with the acumulated switching times.
For approximate interver parts replacement, refer to Table 6.
Other parts , having a relatively short service life, such as lamps. Replace
when deemed necessary as periodic inspection result will reveal.
Table 6 Inverter replacement parts
Part uame
Cooling fan
Standard interval 1
2 to 3 years
Replace (determine
Description
after checking)
Smoothing capacitor
5 years
Replace (determine
after checking)
Relays
Determine after checking
-39-
I
Page 44

Q 7. TROIJBLESHOOTING
If a fault occurs and the mverter does not work properly,, determine the
cause referring to the following troubleshooting list and apply the remedy.
If the cause cannot be determined in accordance with the list, the inverter
or its part(s) ,is likely to be defective.
For remedy of serious trouble or any inquiry, contact the nearest service
representative.
7.1 Troubleshooting
(1) Troubleshooting by indicator lamps’ of parameter unit
Indicator lamp. Possible cause Checkup Remedy
OVT: Overvoltage in DC
Regenerative output circuit fast? time (it should meet
overvoltage (across terminals load GDP (WK*) **a
shut off P and N) inertia) ‘.
(deceleration time
set improperly)
IPF:
Instantaneous failure of instantaneous
power failure power failure.
FIN: Heatsinks are Is cooling fan Replace cooling fan
Heatsink overheat overheated.
BE: ‘Brake transistor is Is brake operating Reduce load GD*
Brake transistor, defective. duty proper? (WK’) .
fault Reduce brake
Instantaneous power Determine the cause
.
Is ’ deceleration too Increase deceleration
stopped (for models
larger than 2.2K) ? Reduce. ambient
temperature.
Is ambient temperature too high?
. . .
‘operating duty.
‘0
OCl:
Acceleration ‘.- -
overcurrent Is outptt short-
Overcurrent Is acceleration too Prolong acceleration
ftist? --. : ,time.
circuited?
-4o-
0
Page 45
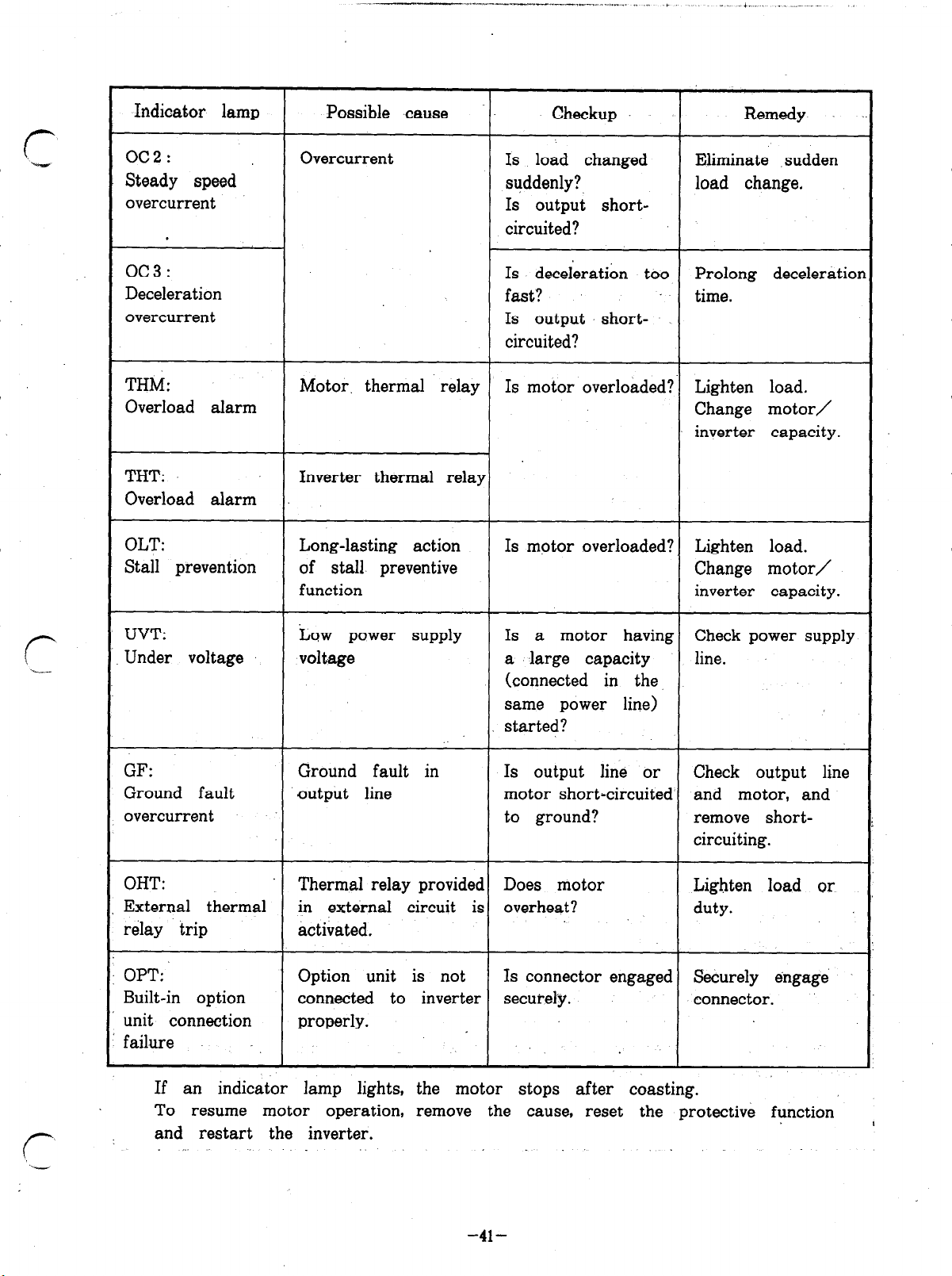
Indicator lamp
Possible cause
Checkup
Remedy
oc2:
Steady speed
overcurrent
oc3:
Deceleration
overcurrent
THM:
Overload alarm
THT:
Overload alarm
OLT:
Stall prevention
Overcurrent
Motor. thermal relay Is motor overloaded? Lighten load.
Inverter thermal relay
Long-lasting action
of stall preventive Change motor/
function inverter capacity.
Is load changed
suddenly?, load change,
Is output shortcircuited?
Is deceleration too
fast? time.
Is output shortcircuited?
Is motor overloaded? Lighten load.
Eliminate sudden
Prolong deceleratior
Change motor/
inverter capacity.
r
r‘
UVT:
Under voltage
GF:
Ground fault
overcurrent
OHT:
External thermal in external circuit is overheat?
relay trip activated.
OPT: Option unit is not
Built-in option connected to inverter securely. connector.
unit connection properly.
failure
If an indicator lamp lights, the motor stops after coasting.
To resume motor operation,
and restart the inverter.
,..
Low power supply Is a motor having Check power supply
voltage
Ground fault in
output line
Thermal relay provided Does motor Lighten load or
remove the cause, reset the protective function
a large capacity
(connected in the,
same power line)
started?
Is output line or Check output line
motor short-circuited and motor, and
to ground? remove short-
Is connector engaged Securely engage
.
line.
circuiting.
duty.
‘
-41-
Page 46
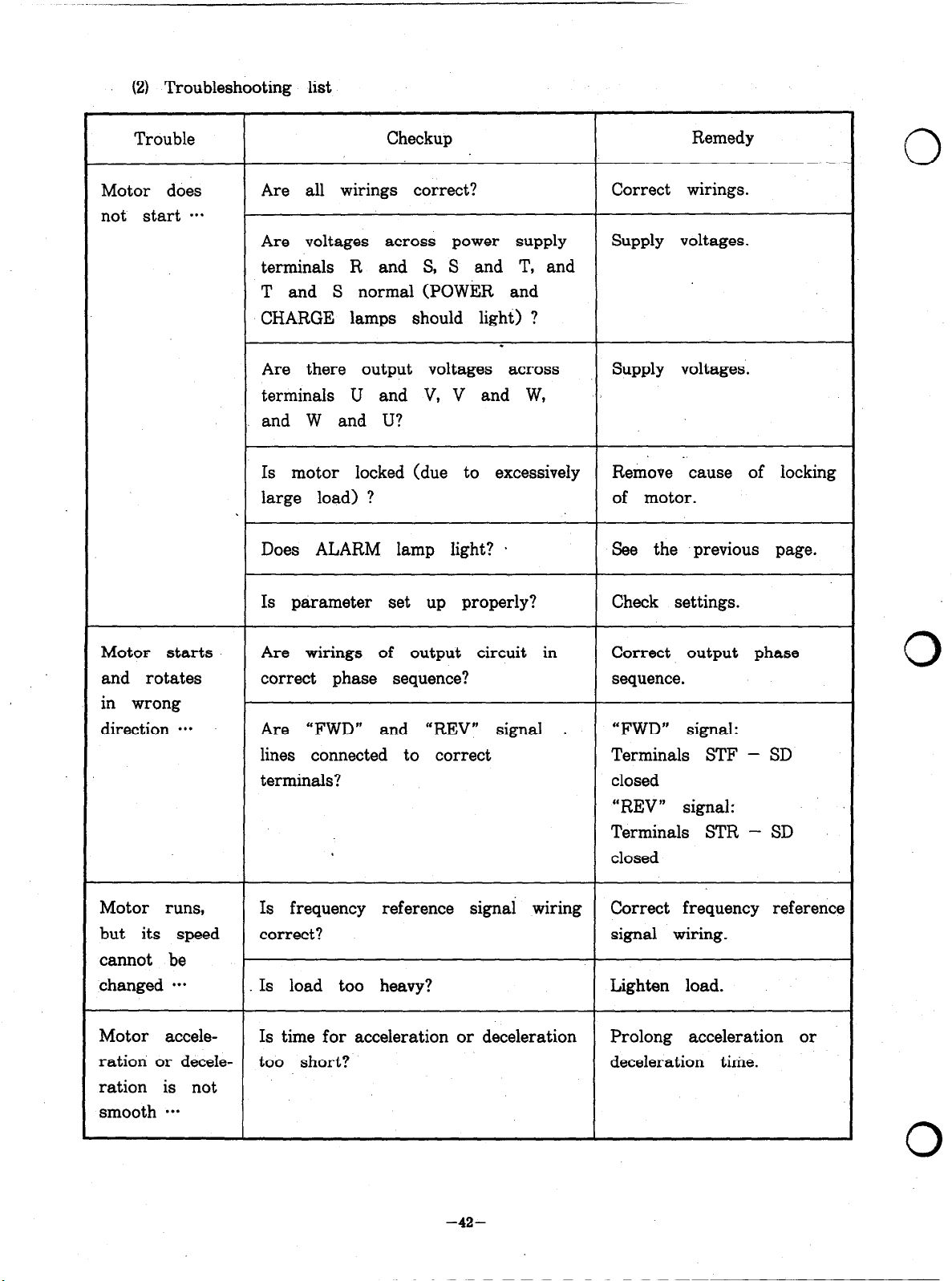
(2) Troubleshooting list
Trouble
Motor does
not start ***
Checkup
Are all wirings correct?
Are voltages across power supply
terminals R and S, S and T, and
T and S normal (POWER and
CHARGE lamps should light) ?
.
Are there output voltages across
terminals U and V, V and W,
and W and U?
Is motor locked (due to excessively
large load) ?
Does ALARM lamp light? *
Is parameter set up properly?
Remedy
0
Correct wirings.
Supply voltages.
Supply voltages.
Remove cause of locking
of motor.
See the previous page.
Check settings.
Motor starts
and rotates
in wrong
direction a*.
Motor runs,
but its speed
cannot be
changed ***
Motor accele-
ration or deceleration is not
smooth a**
Are wirings of output circuit in
correct phase sequence?
Are “FWD” and “REV” signal .
lines connected to correct
terminals?
Is frequency reference signai wiring
correct?
Is load too heavy?
Is time for acceleration or deceleration
too short?
Correct output phase
sequence.
“FWD” signal:
Terminals STF - SD
closed
“REV” signal:
Terminals STR - SD
closed
Correct frequency reference
signal wiring.
Lighten load.
Prolong acceleration or
deceleration time.
0
-42-
0
Page 47
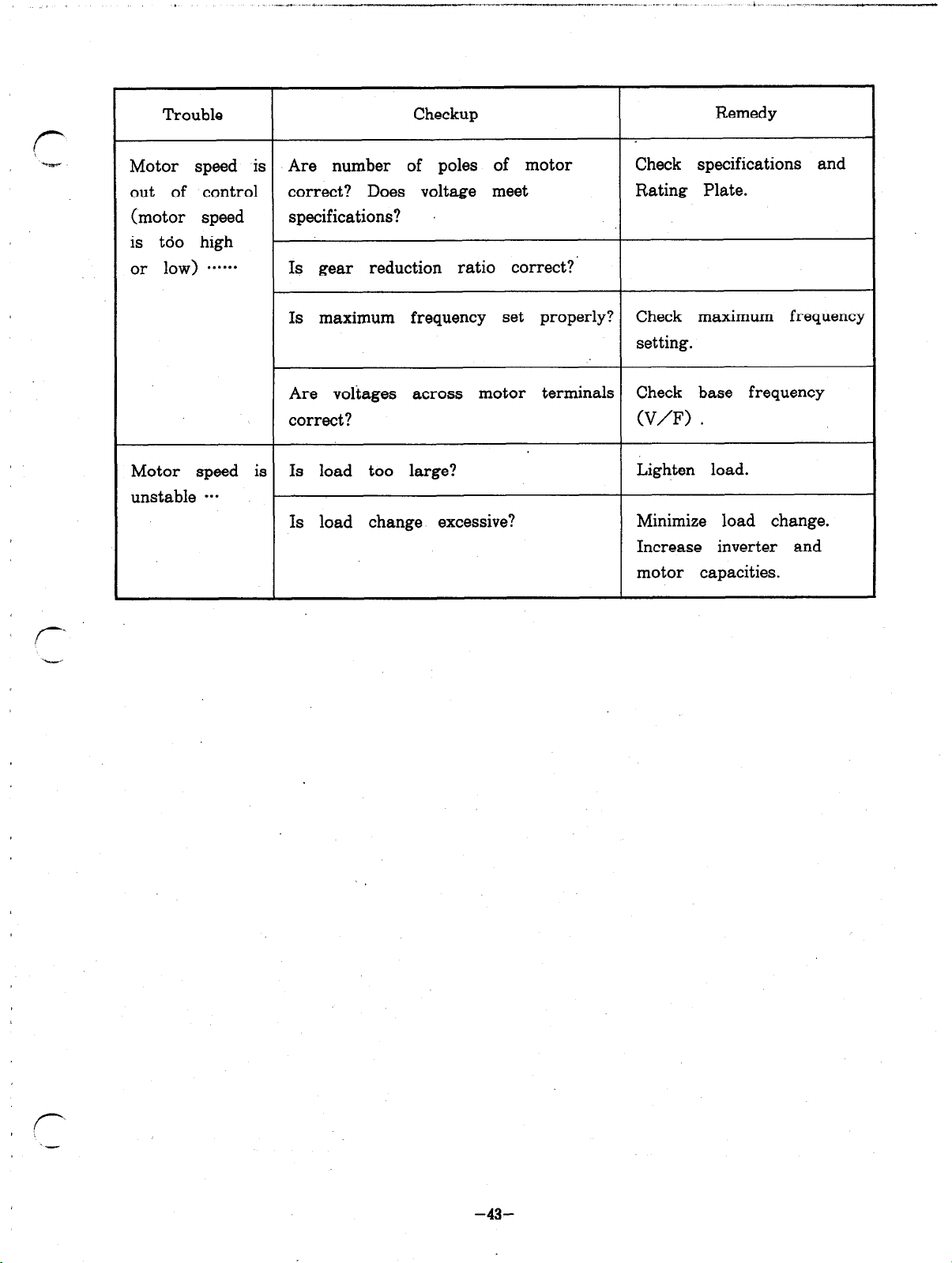
. -.e
. . d._ __-,- .---.
.--I-- “ll__ ,. .I.. e... - 1.
* .-. - .---
Trouble Checkup
Remedy
Motor speed is Are number of poles of motor Check specifications and
out of control correct? Does voltage meet Rating Plate.
(motor speed
specifications?
is too high
or low)
. . . . . .
Is gear reduction ratio correct?
Is maximum frequency set properly? Check maximum frequency
setting.
Are voltages across motor terminals Check base frequency
correct?
(V/F) .
Motor speed is Is load too large? Lighten load.
unstable *..
Is load change excessive? Minimize load change.
Increase inverter and
motor capacities.
-43-
Page 48

7.2’ Protective functions
The inverter is provided with the following protective functions for protection
from overcurrent or overvoltage.
. .
If a protective function is
is shut off and the motor stops after coasting. Its cause is displayed by
the readout of parameter unit (when parameter unit is used) .
For details, refer to the description “PARAMETER UNIT”. (p. 92)
Function Description
Overcurrent
stall prevention . rated current flows into the motor during
When 150% (Note*)
acceleration, this function stops increase of to prevent recurrence
frequency (inverter output) until load current of action of this
reduces to prevent - the inverter from
overcurrent tripping.
When 150% or more of the inverter rated
activated, the transistor base current (output)
Remedy
or more of the inverter
Prolong acceleration
time or reduce load
function.
0
current flows during normal (constantspeed) operation, this function reduces
frequency until load current reduces to
prevent inverter from overcurrent tripping.
After load current is reduced below 150%,
this function allows increase of frequency
up to the preset frequency.
Regenerative If converter output voltage is increased
overvoltage excessively by regenerative energy during
stall prevention motor deceleration, this function stops
decrease of frequency to prevent inverter
from overvoltage tripping.
Prolong deceleration
time.
0
-44-
Page 49

-._. . . . ..- -.,...... ^.l_l-- -,__,__-. _1 ,--,- ,,, ,,.--. +
.- ” .i< _... * ._._” _-____
Function
Overcurrent
shutoff
(OCl)
(OC2)
(OC3)
Description
Remarks
As soon as regenerative energy has
reduced, this function decreases frequency
again to allow deceleration to continue.
When 200% or more of the inverter
rated output current flows, this protective
The most possible
causes of overcurrent
function is activated to stop the inverter. shutoff include invertel
output short-circuit,
ground fault, excessivt
load inertia (GD’) ,
extremely short setting
of acceleration/
deceleration time,
Regenerative
overvoltage
shutoff :
(OVT)
When converter output voltage becomes
excessive, ‘due to regenerative energy from
the motor, this protective function is
activated to stop and hold transistor
start during motor
coasting, start of
special motor or
motor of capacity
larger than inverter
rating.
Restart after
examinating and
removing the cause.
This function is
activated mainly due
to short deceleration
time or negative
base current off.
load.
-ai-
Page 50
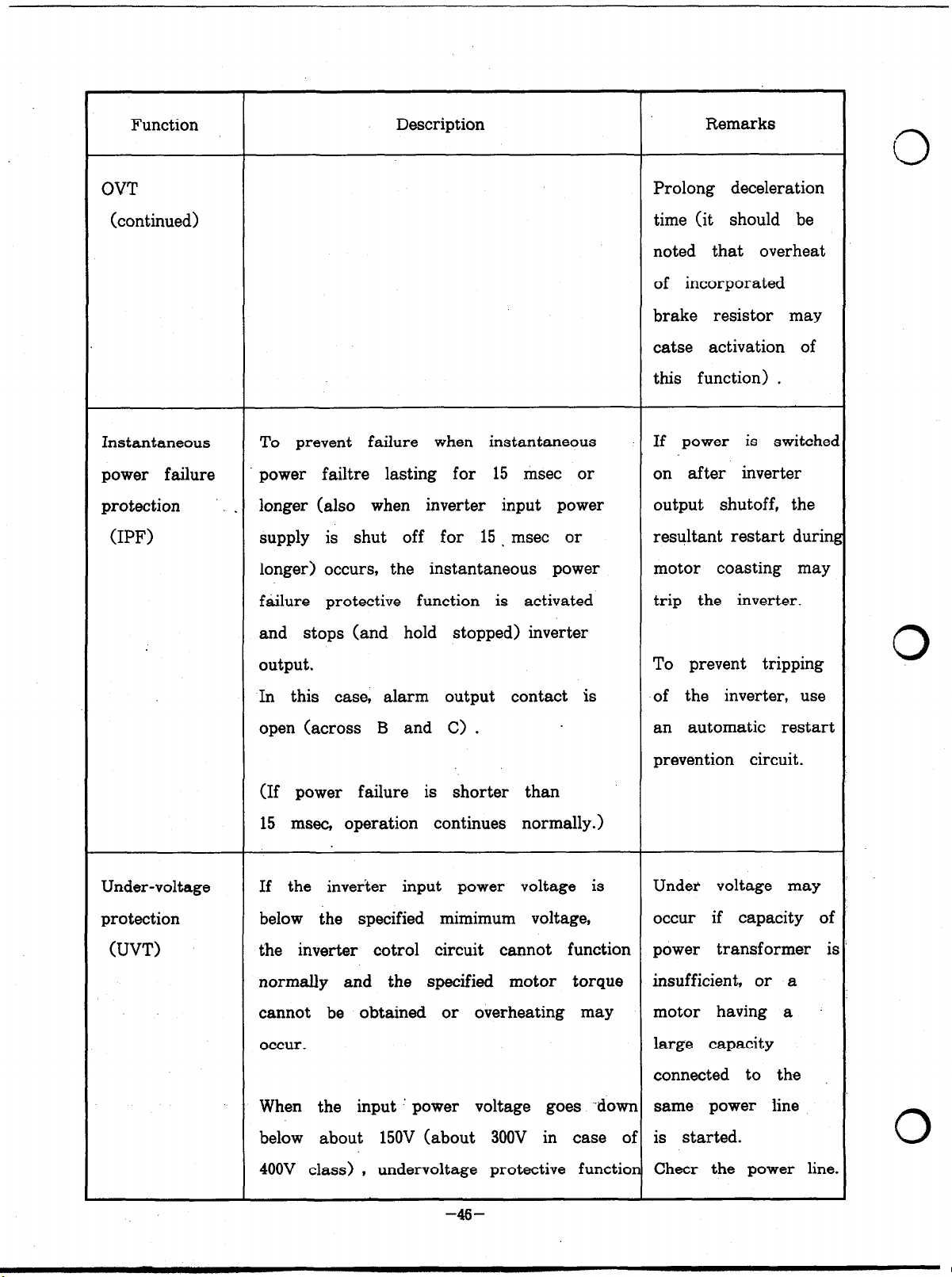
Function
Description
Remarks
OVT
(continued)
Instantaneous
power failure
protection .
(IPF)
Prolong deceleration
time (it should be
noted that overheat
of incorporated
brake resistor may
catse activation of
this function) .
To prevent failure when instantaneous If power is switchec
power failtre lasting for 15 msec or
longer (also when inverter input power
supply is shut off for 15 . msec or
longer) occurs, the instantaneous power
failure protective function is activated
and stops (and hold stopped) inverter
on after inverter
output shutoff, the
resultant restart durini
motor coasting may
trip the inverter.
Under-voltage
protection
(UVT)
output.
In this case, alarm output contact is
open (across B and C> .
(If power failure is shorter than
15 msec, operation continues normally.)
If the inverter input power voltage is
below the specified mimimum voltage,
the inverter cotrol circuit cannot function power transformer ir
normally and the specified motor torque
cannot be obtained or overheating may
occur.
When the input ’ power voltage goes -down same power line
To prevent tripping
of the inverter, use
an automatic restart
prevention circuit.
Under voltage may
occur if capacity of
insufficient, or a
motor having a
large capacity
connected to the
below about 150V (about 300V in case of is started.
400V class) , undervoltage protective function Cheer the power line
-46-
Page 51

f-
Function
Description
is activated and stops (and holds stopped)
inverter output.
Remarks
Brake transistor If trouble occurs with brake transistor,
fault detection
(BE)
Overload shutoff Electronic thermal relay in the inverter
(Electronic
thermal relay) under rated conditions, or motor over-
(THT)
(THM)
this function detects it and shuts off
inverter output.
detects overload of motor during operation of overload, and
heating at low speed, and activates this
protective function which stops (holds
stopped) inverter output.
Examine thermal
capacity of brake
resistor and regene-
rative braking duty
(%ED) and use
inverter having a
larger capacity, if
necessary.
Examine the cause
lighten load, change
operation pattern,
or use inverter
having a larger
r--
CkUTION
External overload protection must be
provided to protect the motor in
accordance with UL508 Par.144.3.
Heatsink overheat Models larger than 2.2K are equipped
protection with cooling far&) .
(FIN)
If the fan fails and the semiconductor
heatsinks overheat, temperature sensor is
activated to shut off (hold shut off)
inverter output.
capacity if necessary
Examine cooling fan
operation and ambient
temperature.
Page 52

Function
Description Remarks
0
Brake resistor
overheat exceeds the specified value, the brake
protection operation is stopped to protect the
Ground fault If ground fault occurs on the inverter Check if ground
current protectior output side (load side) and ground fault
(GF)
If regenerative brake energy from motor Prolong deceleration
time or change
operati-on sequence
brake resistor .from overheating.
When the brake resistor is cooled, the
brake operation restarts automatically.
_ current flows, the inverter output is
shut off.
to reduce. braking
duty.
fault occurs on the
load side (motor
power circuit) .
After removal of
the cause, restart
operation.
0
External thermal If externallyinstalled thermal relay for
relay trip protection of motor from overheat
(OHT)
Built-in option When an inverter built-in option unit Check connection
unit connection is used and not connected properly (connector engage-
failure
(OPT)
(or motor built-in thermal relay) is
activated (relay contact is opened) , the
inverter output is shut off and held
shut off.
This function is applicable when
,“external thermal signal input” function
is selected. (FUNCTION 46)
(misengagement
the inverter is shut off.
of conector, for example) , men0 of option unit.
Examine load and
motor duty to
determine the cause
of overheat.
_’
Page 53

-- “. ,..,.i-.“--
--- ,-,- -- _-._._ .,. . .._- _..* .I.. _ , I _, .~ . . __.~l__l
Note *: The stall prevention threshold level is set to “150%” of
inverter rated current when the inverter is shipped. This
setting can be changed by user (the overcurrent stall
prevention is activated at the threshold level set by user) .
Use this function parameter with care.
INDICATION AND DISPLAY OF PROTECTIVE FUNCTION
If a protecsive function is activated,
0 ALARM lamp lights,
and
0 Alarm information is dispkayed on the readout of parameter unit
(for details, refer to the description of
“PARAMETER UNIT”) . (p. 92)
HOW TO RESET THE INVERTER
If a protective function is activated, the inverter output is shut off
(held shut off) and the -motor stops after coasting.
To resume operation, the inverter should be reset by turning off and
then on again, or short-circuit between RESET terminals (RES and SD>
for at least O.lsec.
If terminals (RES and SD) are held closed, “Err.” appears (flickering) in
the readout * of the parameter unit, indicating that the inverter is in a
reset condition. Do not switch on and off repeatedly by the mains unit.
HOW TO HOLD AN ALARM OUTPUT SIGNAL
/
If the magnetic contactor on the power input side of the inverter is
opened when a protective function is actuated, the control circuit of
inverter is shut off from the power supply and the alarm signal cannot
be held on.
To hvld an alarm signal, an external circuit which holds an alarm signal
is used, or a separate power supply is provided for the control circuit
r
‘1
(refer to 4. WIRING, (5)) .
-4Q-
Page 54

ALARM HISTORY
The alarm information is stored In the memory (E’ROM) of inverter, and
not erased even when the power is turned off.
Since a maximum of 4 alarms can be stored in the memory, they can
be read one by one to identify the cause (for details, refer to the
description’ of “PARAMETER UNIT”) . (p. 89)
0
0
-5o-
0
Page 55

_x_
,*
..*-_..-
_IL_~~-_*--_--l-_II
,._-_
1. . .
..^
.c
--
..--
--
§ 8. SPECIFICATIONS
8.1 Block diagram
Factory use
Provided only
in 400V class
Forward run
Reverse run
stop
Multi- speed
selection
JOG/OH
select
2nd accel./
decel.
Output halt
Current
input
common
Reset
0
B..
t ATT
(Note 2 )
CPU
(Note 1)
PR.
I I
I ,I
G3
LSI
Custom -
made)
ALARM
-3
i
,
RA
s
(Note 3)
ii Jjg/y’
Common dr
DC 4 -2OmA >
DCOm+lOV>
DCOmk5V
> ‘lE
Notes:
-J
+1ov
Y
:onnector
14
T -
il K
Y
Parameter unit
FR-PUOl
1
--
1 . Terminal PR is provided in FR-Z220-0.4K to 7.5K,
and FR-Z24+2.2K to 7.5K.
-51-
-I
RUN
su
OL
IPF
FU
SE
i
Ground
Page 56

2. Terminal P 1 is provided in FR-Z220-5.5K to 55K, and
FR-Z240-5.5K to 55K.
3. Terminal CS is provided in models larger than FR-Z220-15K
and FR-Z240-11K.
*4 . For models larger than llK, built-in regenerative brake resistor
and brake transistor are not installed in the inverter. Fit
” BU ” brake option externally. on these larger models.
See page 53. P, P 1, PR, N.
0
0
-52-
0
Page 57

8.2 Terminals
. .-
__,....-_ .___ j. ,. _I” .-... c.“---....” __,-.-”
Symbol
STF
L
STR
Terminal name
AC power supply
input terminals
Inverter output
terminals
Converter output
terminals
Control power
supply terminals
Ground terminal
Forward
start input signal
terminal
Reverse
start input signal
terminal
Description
Connected to commercial power supply
Connected to three-phase squirrel-cage motor
Connected to optional BU type brake unit
(terminals P and N) or external regenerative
brake resistor (terminals P and PR)
Connected to power supply terminals (R and
S) in the inverter. When it is desirous to
hold alarm display, remove jumper wire from
terminals R and S and connect external
power supply to these terminals.
Inverter chassis grounding terminals
Motor starts rotating in forward
direction (normal run) when ,STF and SD
are short-circuited.
Motor starts rotating in reverse direction
when STR and SD are short-circuited.
STOP
RH,RM,RL
JOG/OH
Start signal selfhold terminal
Multi-speed
select terminals
JOG mode select or
external thermal
Start signal can be self-held ,when STOP
and SD are short-circuited. (p. 13)
A speed range can be selected from 7
different preset speed ranges. (p. 103)
JOG operation mode is selected when JOG
and SD are short-circuited.
To start and stop in JOG, use. signals
STF and SIR. (p. 106)
-53-
Page 58

Symbol
Terminal name
Description
JOG/OH
Continued)
RT
MRS
RES
AU
With external relay, it is possible to stop
inverter operation by a thermal contact
input signal.
2 nd acceleration/ 2 nd acceleration/deceleration time can be
deceleration time selected by short-circuiting, between RT and
select terminal SD.
Inverter output
shutoff, input
terminal
Reset signal, input
terminal
Current frequency
reference signal
select terminal
Shuts off transistor base current (inverter
output) to stop motor by. means of
magnetic brake, etc.
Inverter output is shut off when MRS and
SD are short-circuited.
To reset inverter after tripping, RES and
SD are* short-circuited for ‘more than O.lsec,
When AU and SD are short-circuited, DC
current ranging from 4 mA to 20mA can
be used as frequency reference signal.
0
0
SD
10
2
Instantaneous stop,
restart select
terminal
Common terminal .foi
contact input
Power supply
terminal for
frequency reference
Frequency reference
input signal
When CS and SD are held short-circuited,
operation is restarted automatically after
restoration following a power failure. (p. 12)
Common to contact input signal and
frequency indication
Insulated from common’ circuit of inverter
control circuit
DC 5 V or DClOV (selestabble by changing
position of connector) . See p. 23.
Permissible maximum load current: 1OmA
When 0 to 5 V signal ‘(or 0 to lOV> is
input, the output frequency is at a maximum
at 5 V (or lOV> of input voltage.
0
-54-
Page 59

..-...--- .s .I .-,-A.. .-. .- .-.. “.A..” “_. . ..,&.--
If-
1/ -
-‘w
Symbol
2
IContinued)
5
Terminal name
Common terminal fol
frequency reference
Description
The output frequency is directly proportional
to the input frequency reference signal
voltage. The frequency reference signal
voltage is within range from
ov to 5v
when connector (CON 5 > is engaged to m 5 V “,
and within range from
engaged to
” 1ov ” .
0 V to 1OV when
See p.23.
Input resistance : 1Okohm
Common to frequency reference input signal
Not insulated from common circuit of the
control circuit
Do not ground this terminal.
.K
1E
4
Auxiliary frequency
reference input signal
terminal
Auxiliary frequency
reference input signal
terminal
Current frequency
When DC0 to +lOV is input, the output
frequency becomes
-lOV*) .
The output frequency is proportional
maximum at +lOV (or
to the input frequency reference signal voltage.
The signal is added to signal on terminal 2.
Input resistance: 1Okohm
When DC0 to + 5 V is input, the output
frequency reaches a maximum at + 5 V (or
- 5 V * > . The output frequency is proportional
to the frequency reference signal voltage.
The signal is added to reference on terminal 2.
Input resistance: 1Okohm
Current signal ranging from DC4 mA to
r
-a.-.-
reference input
signal terminal
20mA is input.
Input rezistance: 2500hm
-55-
Page 60
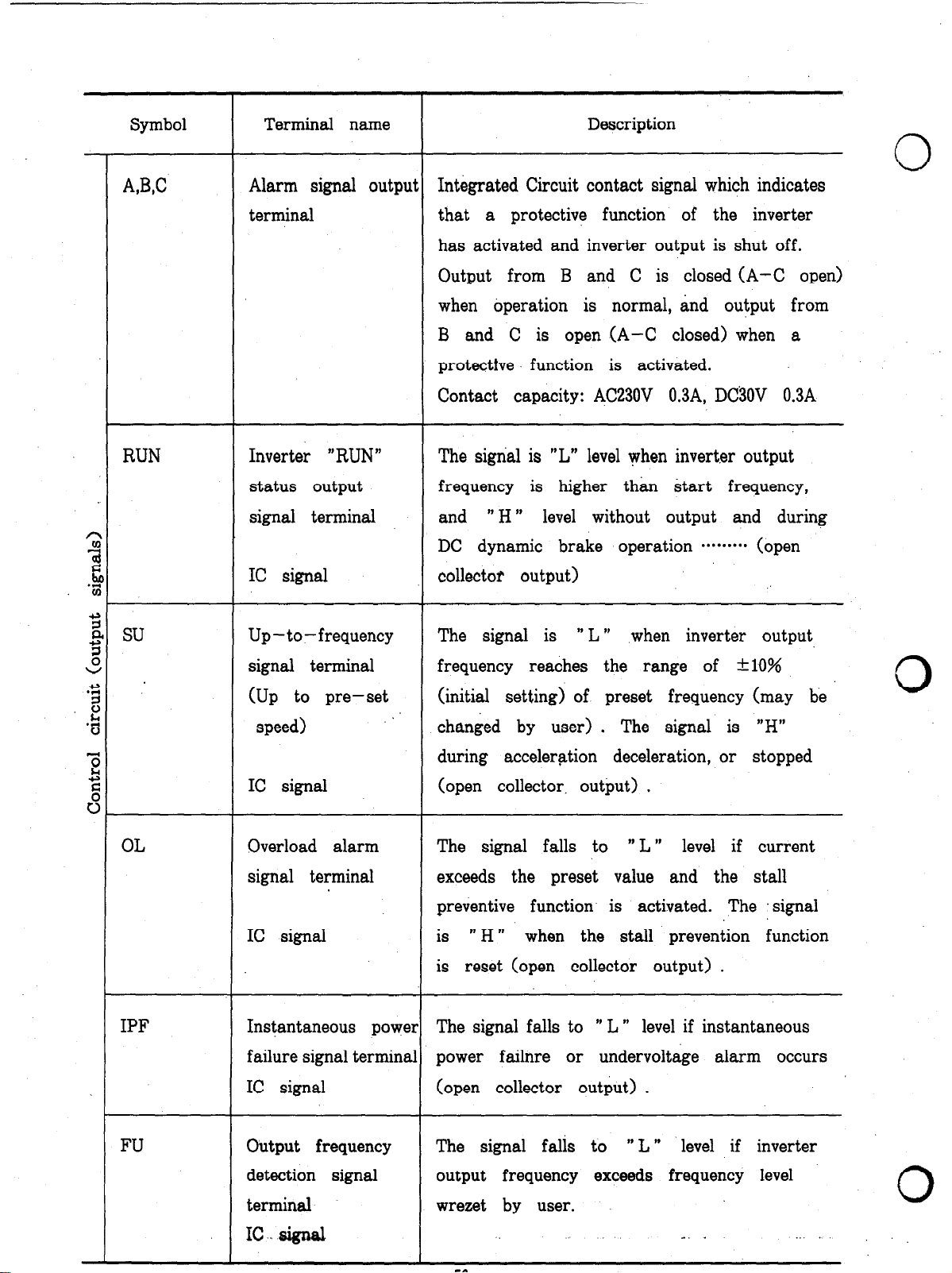
Symbol
-56-
A,W
Terminal name
Alarm signal outpui
terminal
Description
0
Integrated Circuit contact signal which indicates
that a protective function of the inverter
has activated and inverter output is shut off.
Output from B and C is closed (A-C open)
when operation is normal, and output from
B and C is open (A-C closed) when a
protectfve function is activated.
Contact capacity: AC230V 0.3A, DC3OV 0.3A
RUN
Inverter “RUN”
status output
signal terminal
IC signal
Up-to-frequency
signal terminal
(Up to pre-set
speed)
IC signal
Overload alarm
signal terminal
The signal is “L” level when invert.er output
frequency is higher than start frequency,
and ” H ” level without output and during
DC dynamic brake operation ********. (open
collector output)
The signal is ” L ”
frequency reaches the range of -tlO%
(initial setting) of preset frequency (may be
changed by user) . The signal is “H”
during acceleration deceleration, or stopped
(open collector, output) .
The signal falls to ” L ” level if current
exceeds the preset value and the stall
preventive function is activated. The signal
when inverter output
:
IPF
FU
IC signal
Instantaneous power
failure signal terminal
IC signal
Output frequency
detection signal
terminal
IC ,~ signal
is ” H ” when the stall prevention function
is reset (open collector output) .
The signal falls to ” L ” level if instantaneous
power failnre or undervoltage alarm occurs
(open collector output) .
The signal falls to ” L ” level if inverter
output frequency exceeds frequency level
wrezet by user.
0
Page 61

Symbol
Terminal name
Description
r
-
FU
(Continued)
SE
FM
*When function No.41 is set to ” 1 ” for forward and reverse operation
Common terminal for
open collector
output
IC signal
Terminal for
frequency indicator
and digital counter
The signal is ” H ” when inverter output
frequency is lower than the preset frequency
level (open collector output) .
This terminal is common to signals RUN,SU,
OLJPF and FU, and insulated from common
control circuit.
When inverter is shipped, the signal is set so
that about DC 5 V (FM-SD opened) is output
when inverter output frequency is 60Hz.
The output voltage is proportional to the
output frequency, and has pulse train waveform.
Initial setting: 1440Hz/60Hz
with analog speed reference signal, the inverter output frequency becomes
maximum when signal voltage is - 5 V (or -lOV> .
Note 1 : The. rated voltage and current of open collector output are DC24V
and O.lA respectively.
Page 62

8.3 Standard specifications
Voltage class 2oov
Model FR-ZZZO-
ipplicable motor capacity HP (kW)
0 Nominal output (kVA)
i?
*w
,.d Output, current (A)
Sk
9
8
f
5 Frequency range
5 Frequency Digital input
Maximum output voltage
C.1)
AC voltage and frequency
4
Permissive voltage
regulation
$
.
cn
Permissive frequency
k
regulation
B
fc
Power swdy capacity
(kVA) (‘2)
Control method Sinusoidal wave PWM control
Ei
d
0
ii
resolution Analog input I /lOOO of maximum frequency
,a
Frequency Digital setting
ii
2
accuracy Analog setting
E
z
Voltage/frequency Base frequency selectable within 50Hz - 360Hz
s
characteristics Constant torque or reduced torque pattern is selectable.
FR-Z220
-0.4K -0.75K -1.5K -2.2K -3.7K -5.5K -7.5K -1lK -15K -22K -3OK -37K -45K -55K
i/2 (0.4) 1 (0.75) 2 (1.5) 3 (2.2) 5 (3.7) 7.5 (5.5)
1.1 1.9 3.1 4.2 6.5 9.2
3 5 8 11 17 24
Three:phase, 2OOV 50H2, 200/220/23OV 60Hz
Three-phase, 2OOV 50H2, 200/220/23OV 60Hz
180 - 22OV 5OH2, 180 253V 60Hz
+5%
1
5
0.5 - 360Hz (starting frequency : 0.5 O.OlHz (less than 100Hz) , O.lHz (more
Max. 0.01% of preset output frequency (when set by parameter unit)
Max. *0.5% of maximum output frequency (at 25“C+lO”C)
2 5 4 5 5 5 g 12
-
10 (7:5)
12.6 17.6 23.3
33 46 61
17
lOHz,
than
15 (11) 20 (15) ‘($t$ 40 (30)
34 44 55 67
90 115 145 175
2b 28 34/41 52
adjustable)
lOOH&) . . . . when parameter
50 (371 60 (45) 75 (55)
82
215
66 80 100
unit is used.
0
0
0
Page 63

i
‘)
Voltage class
Model FR-2220-
Torque boost Manual and automatic torque boost
g
3
8
5 Braking brake
0
;,
torque
!s
Stall preventive function
i=i
E:
threshold current
2
Rated overload current, 150% for 1 min., 200% for 0.5sec.
s
Frequency reference DC0 - 5 V, 0 - lOV, 4 - 20mA
signal Auxiliary frequency reference signal : DC 0 - + 5 V, 0 - &lOV
Start signal
Acceleration/deceleration
E’
‘S
time
$ .
r;t
‘i;
a
iit
T;;i
g
‘3
2
%
0
2 nd acceleration/
deceleration time
Acceleration/deceleration
pattern
Multi-speed setting
Maximum and minimum Maximum frequency limit adjustable range : 0 - 36OHz
frequency limit setting Maximum frequency limit adjustable range : 0 - 60Hz
Regenerative Min. 150% Min. 100%
DC dynamic
brake
-0.4K I-0.75KI -1.5KI -2.2KI -3.7KI -5.5KI -7.5K) -1lK 1 -15K 1 -22K ) -3OK 1 -37K 1 -45K 1 -55K
(short time) (short time)
Operating frequency ( 0 - ,60Hz) , operating time ( 0 - 10sec) , voltage (torque) adjustable
Threshold current can be set.
Independent “forward start” and “reverse start”,
input) are applicable.
o 1
. - 3600sec. (acceleration and deceleration and times can be set independently)
0.1 - 3600sec. (acceleration and deceleration and times are set identically)
“Linear pattern” or “S pattern” can be selected.
Maximum 7 speed ranges can be set (adjustable within range from 0 Hz to 360Hz in
each speed range)
2oov
FR-Z220
Capacitor charge (min. 20%’ 3 )
and start signal self-holding ( 3 -wire
JOG mode operation JOG mode select terminal is available (‘4 ‘1 .
Reset signal External reset signal input terminal is available.
Page 64

Voltage class
200v
Model FR-Z220-
3 Output halt signal Output halt input signal termial is available.
‘2 Operation status output
Sk
9
3
I
8
I
Built-in optional units Maximum 2 cards. can be used.
signals “FU” (frequency detection) signals
Alarm output signal 1 C relay contact signal (AC 230V 0.3A, DC 30V 0.3A)
Protective, alarm and warnin Overcurrent shutoff (during acceleration, deceleration and normal operation) , regenerative
functions overvoltage shutoff, undervoltage protection, instantaneous power failure protection, overload
‘.
Ambient temperature -10°C to +5O“C (to be free from freezing)
Ambient humidity
%
2
Storage temperature (’ 7 > 1 -20°C to +65”C
E
‘5’ .
3
Protective structure
Atmosphere
Altitude, vibration
(JEM 1030)
-0.4K (-0.75KI -1.SK I-2.2K I-3.7K 1 -5.5K 1 -7.5K 1 -1lK 1 -15K 1 -22K 1 -3OK 1 -37K 1 -45K 1 -55K
‘RUN”, “SU” (up-to-frequency) , “ON” (overload) , “IPF” (instantaneous power failure) and
shutoff, (electronic terminal relay) , brake transistor fault detection
protection, output short-circuit protection, heatsink overheat protection 0 6 > , brake regenerative
resistor overheat protection (+5 >’ ,
9O%RH or less (to be free from condensation)
Indoor
Below 10OOm (3300ft)
0.6G or less (conforms to JIS 0911)
Enclosed type (IP20)
To be free from corrosive gases and. dense dust
stall prevention and overload alarm
FR-Z220
(‘5
4
Open type (wx>)
> , ground overcurrent
Weight (kg) kg (Lb)
Notes : l
1. If the line voltage decreases, output voltage over the line
l
2. Power supply capacity indicates the inverter input kVA and may change depending on power supply
impedance (including input reactor) .
* 3. This value may’ depend on motor loss.
* 4. JOG ,operation can be controlled not’ only with signal on JOG mode select terminal, but also parameter
unit.
* 5. This function is not provided for models FR-Z2WllK to 55K, and FR-Z2QO-11K to 55K.
0
0
v&age
cannot be guaranteed.
0
Page 65

Voltage class
Model FR-Z240-
Applicable motor
capacity HP (kW)
4OOV
FR-Z240
-2.2K -3.7K -5.5K -7.5K -1lK - 15K -22K
-3OK -37K
-45K -55K
3 (2.2) 5 (3.7) 7.5 (5.5) 10 (7.5) 15 (11) 20 (15) “$j5& 40 (30) 50 (37) 60 (45) 75 (55)
G Nominal output (kVA)
-2 Output current (A)
5 2.
P
Maximum output voltage
6
AC voltage and frequency
x
Permissive voltage
34
regulation
is
Permissive frequency
b
regulation
B
Power supply capacity 5 5
62
(kVA) (* 2 > ’
Control method
Frequency range
2
22
2
Frequency
5
resolution
8
2
2
=I’ Frequency
&
accuracy
2
Digital
input
Analog
input
Digital
setting
Analog
s
Voltage/frequency
characteristics
4.2 6.9 . 9.9
6
9
13
13
17
17.5 23.6 32.8
23 31 43
(. 1) Three-phase, 400V 5OH2, 400/440/46OV 60Hz
Three-phase, 400V 50Hz, 400/440/46OV 6OHz
360 -
440V 50Hz, 360 - 506V 60Hz
+5%
9
12
17
20 28 34/41 52 66 80 100
Sinusoidal wave PWM control
0.5 - 360Hz (starting frequency: 0.5 - lOHz, adjustable)
O.OlHz (less than 100Hz) , O.lHz (more than 1OOHz) . . ..when parameter unit is used.
1 /lOOO of maximum frequency
Max. 0.01% of preset output frequency (when set by parameter unit)
Max. +0.5% of maximum output frequency (at 25”C+lO”C)
Base frequency selectable within 50Hz - 360Hz
Constant torque
or reduced torque pattern is selectable.
43.4 54
57 71
65.5 84
86 110
Page 66

Voltage class
400v
Model FR-Z240-
-22K 1 -3.7K 1 -5.5K 1
Torque boost
g
‘I:
d
c
Braking brake
.r(
8
torque DC dynamic
iit
!ii
z
Stall preventive function
e
threshvld current
2
Rated overload current 150% for 1 min. , 200% for 0.5sec
u”
Frequency reference DC0 -
signal Auxiliary frequency reference signal: DC 0 - & 5 V, 0 - &lOV
Start signal
Acceleration/deceleration
do
3
5
74
‘S
8
time
0
2 nd acceleration/
8 deceleration time
ii?
Acceleration/deceleration
pattern
od
Multi-speed setting
2
Q)
.Maximum and minimum
frequency limit setting
JOG mode operation
Regenerative
brake
Manual and automatic torque boost
Min. 100% (short time)
Operating frequency ( 0 - 60Hz) , operating time ( 0 - 1Osec) , voltage (torque) adjustable
Threshold current can be set.
5 V, 0 - l.OV, 4 - 20mA
Independent “forward start” and .Yeverse start”,
input) are applicable.
o I
. - 36OOsec. (acceleration and deceleration times can be set independently)
0.1 - 36OOsec. (acceleration and deceleration times are set identically)
“Linear pattern” or “S pattern” can be selected.
Maximum 7 speed ranges can
each speed range)
Maximum frequency limit adjustable range: 0 - 360Hz
Maximum frequency limit adjustable range: 0 - 60Hz
JOG mode select terminal is available ( l 4 > ,
-7.5K -1lK -15K
FR-Z240
-22K
,
Capacitor charge (min. 20%*‘3 )
and start signal self-holding ( 3 -wire
be set (adjustable within range from 0 Hz to 360Hz in
1 -3OK 1 -37K 1 -45K 1 -55K
Frequency jump Maximum three frequency jump zones can be set.
Reset signal External reset signal input terminal is available.
0
0
0
Page 67
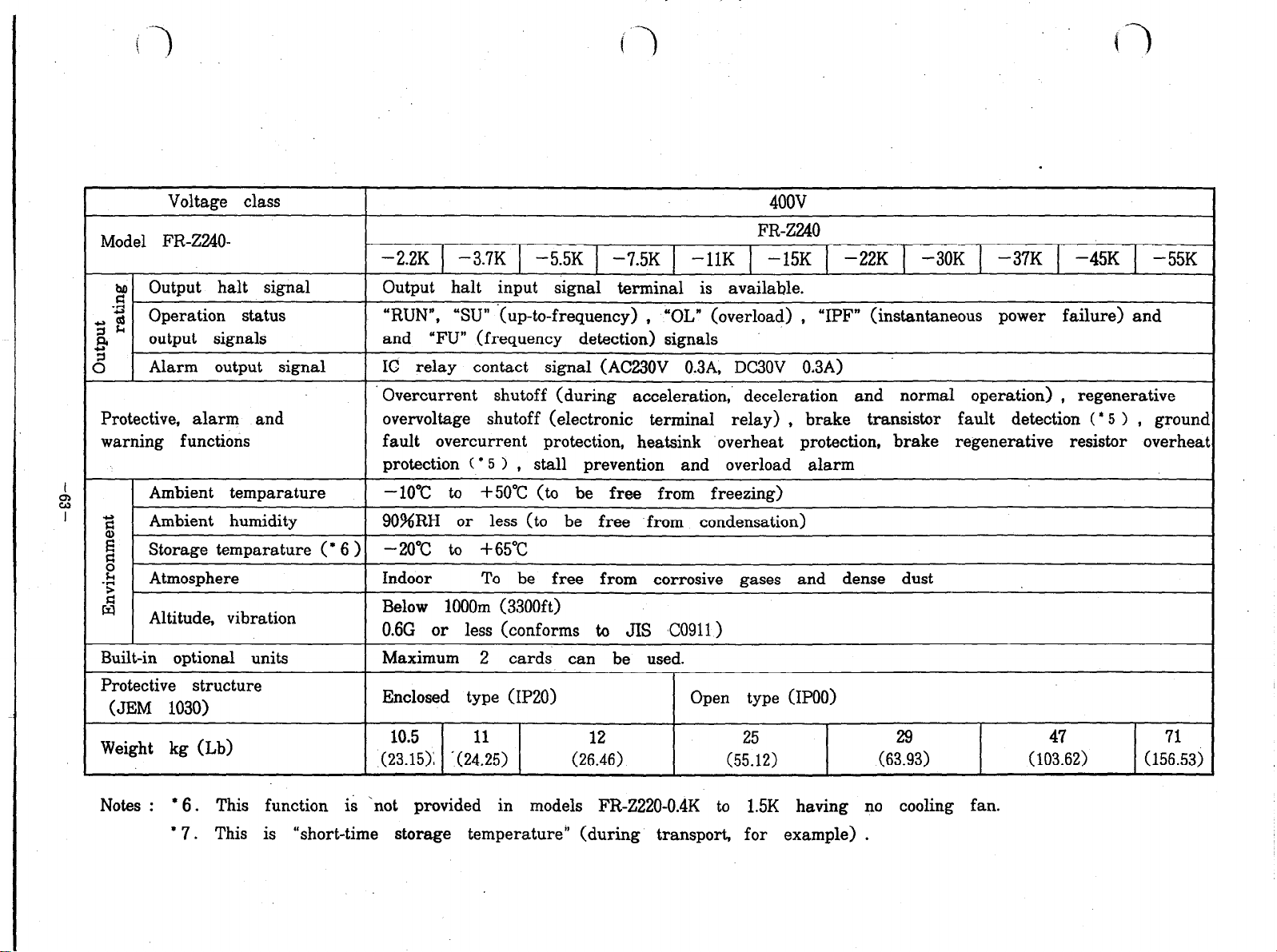
Voltage class 4oov
Model FR-Z240-
2 Output halt signal
5 .$ Operation status
i3
a
output signals and “FU” (frequency detection) signals
Alarm output signal IC relay contact signal (AC230V 0.3A, DC30V 0&3A)
-22K 1 -3.7K 1
Output halt input signal terminal is available.
“RUN”,
“SU” ‘(up-to-frequency) , ‘OL” (overload) ,
-5.5K 1 -7.5K 1 -1lK
Overcurrent shutoff (during acceleration,’ deceleration and normal operation) , regenerative
Protective, alarm and
warning functions
overvoltage shutoff (electronic terminal relay) ,
fault overcurrent protection, heatsink overheat protection, brake regenerative resistor overhee
protection ( * 5 > , stall prevention and overload alarm
Ambient temparature -10°C to +5O”C (to be free from freezing)
2
‘5’
I3
Ambient humidity 9O%RH or less (to be free from condensation)
ii!
Storage temparature ( l 6 )
2
Atmosphere
Altitude, vibration
-20°C to +65”C
Indoor
To be free from corrosive gases and dense dust
Below 1OOOm (3300ft)
0.6G or less (conforms to JIS CO911 >
Built-in optional units Maximum 2 cards can be used.
Protective structure
(JEM 1030)
Weight kg (Lb)
Enclosed type (IP20)
10.5 11
(23.15); '(24.25) (26.46) (55.12)
12
FR-2240
-15K 1 -22K 1 -3OK 1 -37K ] -45K 1 -55K
“IPF” (instantaneous power failure) and
brake transistor fault detection (* 5 > , groun
Open type (IPOO)
25
(632993)
47
(103.62) (156.53;
71
Notes :
l
6. This function is ‘not provided in models FR-Z220-0.4K to 1.5K having no cooling fan.
’ 7. This is
“short-time storage temperature” (during transport, for example) .
Page 68
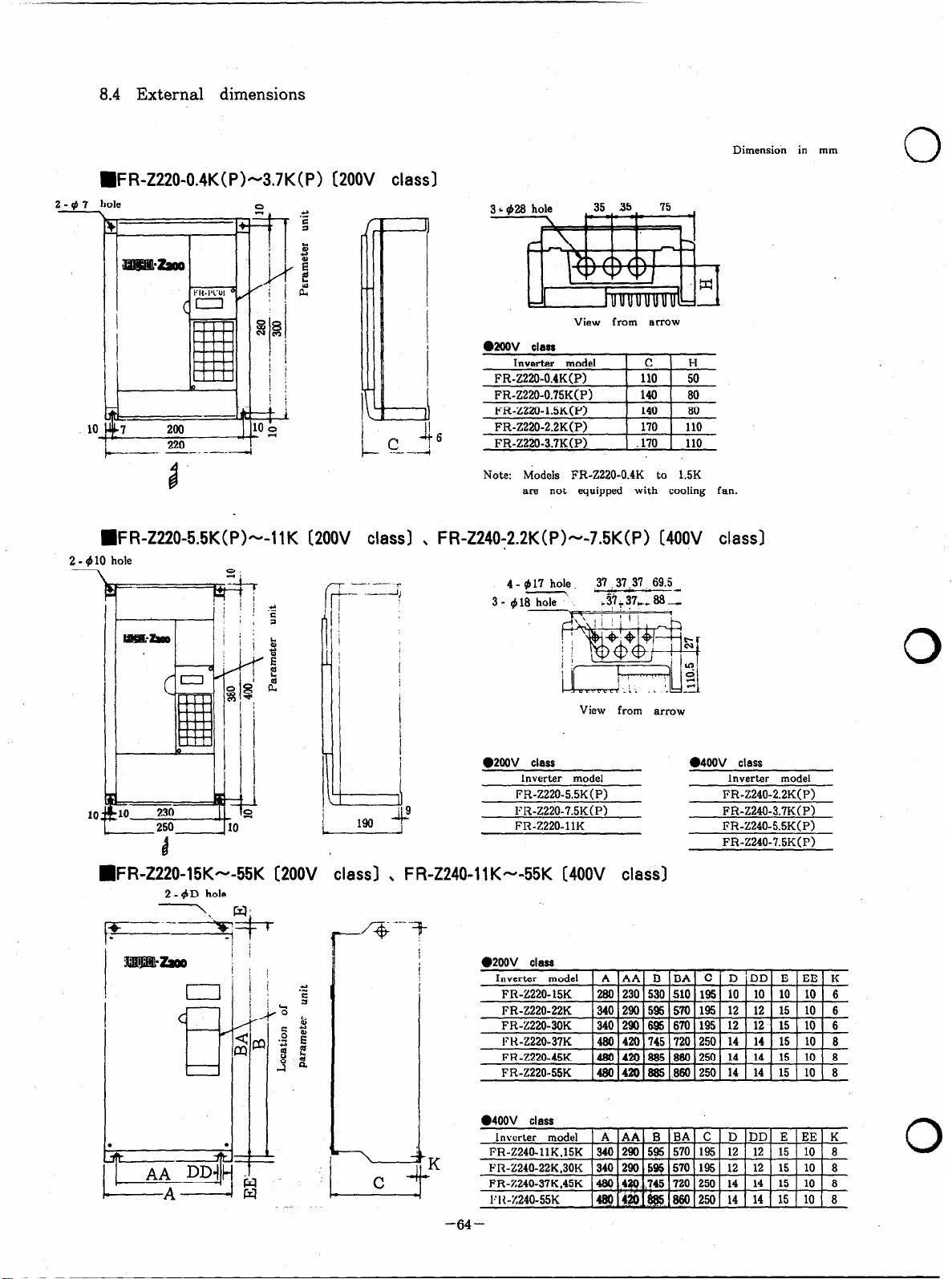
8.4 External dimensions
n
FR-Z220-0.4K(P)-3.7K(P) [2OOV class]
n
FR-Z220-5.5K(P)--1lK [2OOV class)
------- r
rt-- ----‘!
I! :
l
2QOV clan
Inverter model C H
FR-Z220-O.IK(P) 110 50
FR-Z220-O.EK(P) 140 80
FR-Z220-1.5K(P) 140 80
FR-Z220-2.2K(P) 170 110
FR-Z220-3.7K(P) ,170 110
Note: &dels FR-Z220-0.4K to 1.5K
are not equipped with cooling fan.
FR-Z240y2.2K(P)--7.5K(P) [4OOV class)
\
Dimension in mm
0
I
View from *rrow
l
2OOV class
lnverter model lnverter model
L
j 1wit”
n
FR-Z220-15K--55K 12OOV class1 , FR-Z240-11 K--55K [4OOV class]
PR-Z220-5.5K(P)
1%2220-7.5K(P)
FR-Z220-1lK
l
2WV clase
l
4OOV class
l
4WV class
FR-Z240-2.2K(P)
FR-Z240-3.7K(P)
FR-Z240-5.5K(P)
FR-Z240-7.5K(P)
0
K
0
-64-
Page 69
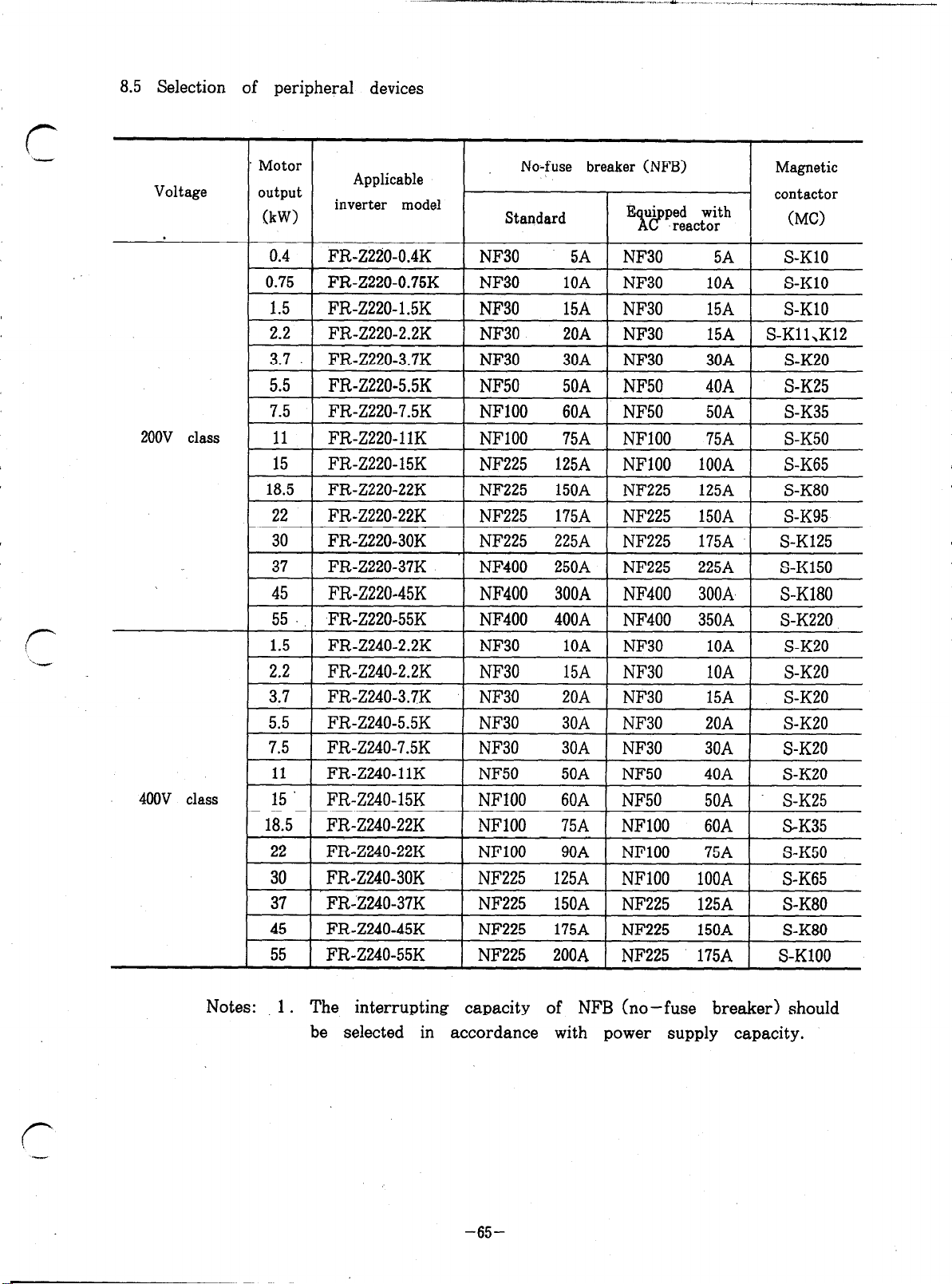
8.5 Selection of peripheral devices
inverter model
Notes: 1 . The interrupting capacity of NFB (no-fuse breaker) should
be selected in accordance with power supply capacity.
-65-
Page 70

8.6 Drip shield kits
\@f&$$$---y--
0
Markmg
(P--i
Marking
Marking : Part Na is stamped.
0
FR-Z220-11K i TD840A662G54 D784COlOG51 D784COllG51 D785C020H02 D783C501G51
FR-Z240-2.2K 1 TD840A662G54 D784COlOG51 D784COllG51
FR-Z240-3.7K i TD840A662G54 D784COlOG51 D784COllG51 D785C020H02 D783C501G51
FR-2240-5.5K ) TD840A662G54 D784COlOG51 D784COllG51 D785C020H02 D783C501G51
FR-Z240-7.5K j TD840A662G54 D784COlOG51 D784COllG51 D785C020H02 D783C501G51
-66-
D785C020H02 D783C501G51
0
Page 71
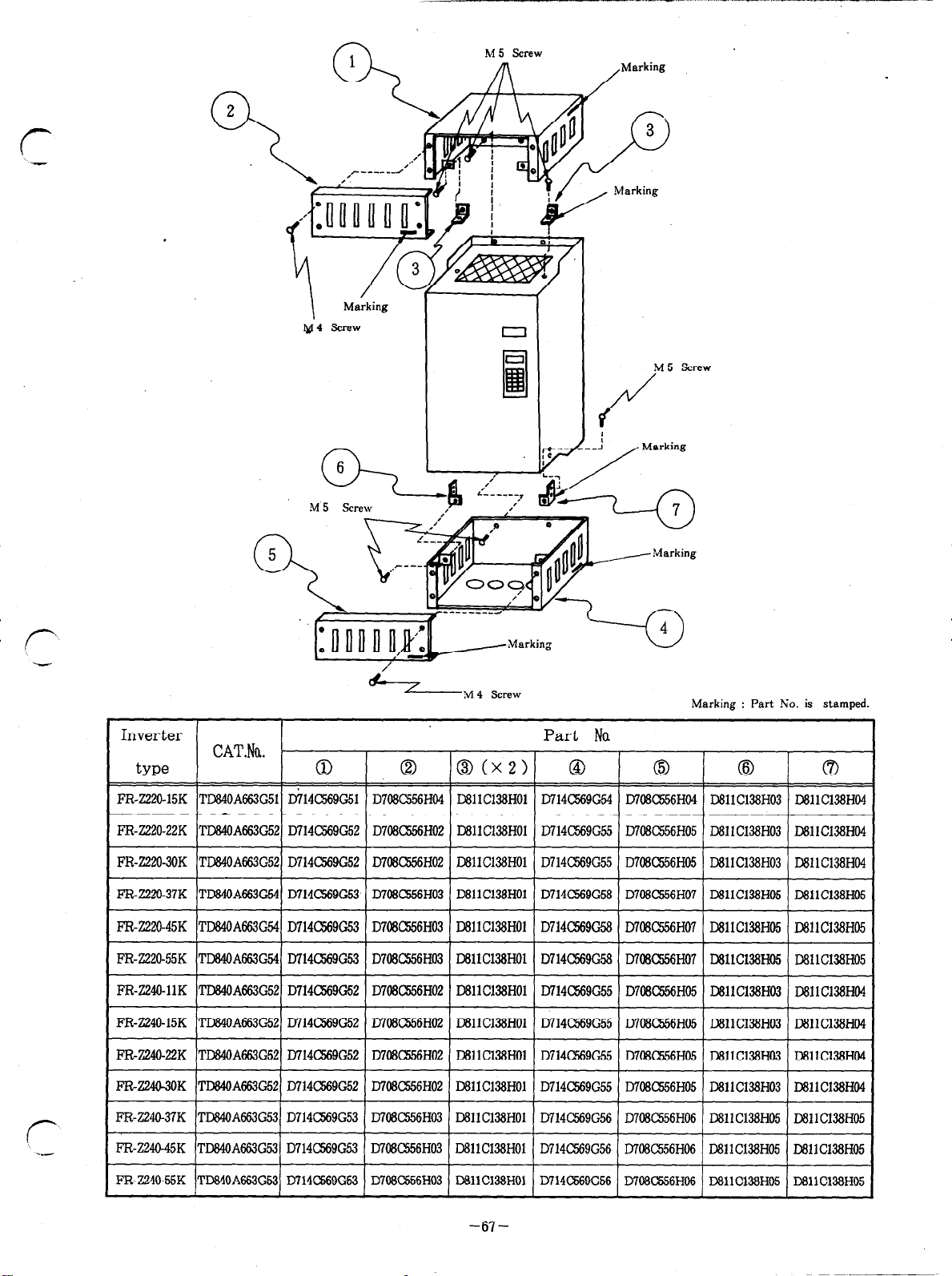
Marking
M4 screw
6
o-,
M 5 Scre
!W
Marking
1 Marking
-Marking
II
Marking : Part No. is stamped.
FR-Z220-37K TD84OA663G54 D714C569G53 D708C556HO3 D811C138HOl D714C569G58 D708C556HO7 lMlC138HO5 D811C138HO5
FR-Z220-45K TD84OA663G54 D714c569G53 D706CS56HO3 D311C138HO1 D714C569G58 D708C556H07 DEllC138HO5 D811Cl38HO5
E’R-Z220-55K TD84OA663G54 D714CS69G53 D708c556EfO3 D811C138HOl D714C569G58 MMS56H07 D811C138HO5 D811C138HO5
FR-Z24Q-1lK TlWOA663G52 D714cX69G52 D708c556HO2 iXllC138HOl D714CS69G55 D708CS56HO5 DSllC138HO3 D811C138HO4
FR-Z240-15K TD84OA663G52 D714CLi69G52 D708Ci56H02 D811C138HOl D714C569G55 D708c556HO5 D811C138HO3 lMlC138HO4
FR-2X40-22K TD84OA663G52 D714CS69G52 D7@3CX%HO2 D611C138HOl D714C569G55 D708cs56HO5 D811C138HO3 D811C138HO4
FR-Z24NOK TWA663G52 D714CS69G52 MWI556H02 D811C138HOl D714C569G55 D708C556H05 D811C138HO3 JXllC138Ho4
FR-Z240-37K TD84OA663G53 D714C569G53 D708CS56HO3 D811C138HOl D714CE69G56 MOW56H06 D811C138HO5 D811C138HO5
FR-Z240-45K TD84OA663G53 D714c569G53 D708cs56HO3 D811C138HOl D714C569G56 MW556HO6 D811C138HO5 D811C138HO5
FR-Z240-55K TD84OA663G53 D714C569G53 D708C556HO3 D811C138HOl D714C569G56 D708C556HO6 D811C138HO5 D811C138HO5
-67-
Page 72

8.7 Overload protection
External overload protection must be provided to protect the motor in
accordance with the National Electrical Code.
Note: The drive is suitable for use on a circuit capable of delivering 10,000
RMS Symmetrical Amps.
0
-68-
0
Page 73

1 PARAMETER UNIT 1
-69-
Page 74

PARAMETER UNIT
Parameter unit, model FR-PUOlE, is directly .attached to the inverter (FR-Z series) ,
or connected to the inverter with the cable (option) .
0
The parameter unit permits the operatior
variable (parameters) ,
In this manual, parameter unit is abbreviated, as “ PU ” .
§ 1. INSTALLATION
The PU can be directly attached to the inverter, or remotely installed and
connected to the inverter with the approved cable. It ‘can be attached or
connected even when the inverter is operating.
l
Direct attachment to inverter
and to monitor operation status through its readout.
(11 Connection
Engage the plug of PU with the receptacle
of inverter and gently press the PU against
the inverter.
to set (read and write) various control
0
(2) Securing the PU in position
Lightly tighten two screws to secure the PU
in position.
CAUTION: (11 The PU should be attached to the inverter with the front cover
installed on the inverter.
(2) Never operate the inverter with the PU with the front cover
removed. To prevent accidental damage to the inverter P.C.B and
the PU unit.
(3) If the inverter must be operated with the front cover removed,
always use the approved extension cable with the PU unit.
(41 Dangerous high voltages are present inside the inverter. Always
use with great care and attention.
-7o-
0
Page 75

ORemote installation using the approved cable connector
r.
‘-
Connection
(1)
Plug one end of the cable into the
receptacle of inverter, and the other end
into the PU.
Locking of plugs
The plug on the inverter side should be
locked with screws as shown to the left.
On the PU side, secure the cable so that
Fit the guides to the grooves.
CAUTION: (1) For cable, use only that specified by us (available as optional
accessory) .
(2) The cable plugs and sockets only fit in one position. Do not
the cable cannot be disconnected by its
own weight.
force plugs into sockets.
-71-
Page 76

8 2. OUTLINE OF FUNCTIONS
Selection of
operation mode used as control sour
(Parameter mode)
--_-------------------------
(External mode)
write) of control
variables
(Monitor/alter)
Parameter unit can b Keys of parameter
be used as control
source for inverter
Set control variable
Description
unit are operated.
quency reference potentiometer, START switch,
Change of setting
0.
settings (settings made at shipment)
e parameter can
Operation status can
be monitored.
Direction of rotation
-72-
Page 77

8 3. CONTROL DEVICES OF PARAMETER UNIT
“ONLY LIGHT FINGER PRESURE IS NECESSARY”
---DISPLAY (READOUT)
Frequency, motor current,
preset control variable,
alarm massage, etc. are
displayed by this 4 -digit
readout.
f
f%-PUOl E PARAMETER UNli
7MOUNTING SCREW
By loosening these two screws.
the unit can be separated from the inverter.
VARIABLE INDICATOR LAMP
Control variable to be monitored
_
r
motor current. etc.) is indicated.
i“
@
OPERATION MODE INDICATOR LAMPS
When an operation mode key (MONITOR,
SET, EXT OP. PU OP) is pressed. the
corresponding lamp lights.
OPERATION MODE KEYS
Operation mode can be selected from
I.
MONI’I’OH. WI’, EXT OP and PU OP.
Afler operation mode is selected. desired
control variable can bc set, read (checked)
or written (changed)
1
FliEQUI%‘CY ADJUST KEYS
While it is held down, frequency continously
increases or decreases. (Slowly at first,
progressively faster)
I
HIGH
I?
1-1
I
. . I
T I 1
\I I
\!
I
1 -
- 2nd or 3rd group function key (2 nd)
When setting of 2nd or 3 rd qroup function is read or written, this key is pressed. 3 rd group function
is selwted by SHIFT KEY after this key is pressed.
- SHIFT KEY
Variable (frequency, motor current, alarm message) to be monitored is shifted or 3rd group function is selected.
- CLEAR KEY
If wrong key is pressed during setting, it can be cancelled by pressing this key.
I
I
d
OPERATION KEYS
Motor rotating direction can be selected and
r
operation can be stopped.
-READ/WRITE KEYS
Variable setting can be read (checked) by
pmssing ml and written (changed) by
pressing [WRITE( after m key is pressed.
.FUNCTION/NUMERAL KEYS
Function No. of 1 st group function and
I
value or frequency can be specified.
-73-
Page 78

Key
Description
pzE?q
SET
I
IMONITOR
2nd
0,
piiiiiq This key is pressed to change variable to be monitored, to
A
tl
This key is pressed when external signals are used to control
the inverter. (Inverter always powers up in this mode)
This key is pressed when the PU (parameter unit) is used to
control the inverter.
This key is pressed to read (check) or write (change) setting of
variable.
This key is pressed to read frequency, motor current, output
v,oltage or alarm message (alarm code) .
2 nd or 3 rd group function can be selected.
select 3 rd group function, or to specify JOG mode.
This key is pressed to correct wrong ‘key operation, or erase
previous entry.
During operation with the PU, this key is pressed to increase
output frequency.
During operation with external signals, this key is pressed to
increase reading of externally connected frequency meter.
(Calibration mode)
0
.During operation with the PU, this key is pressed to decrease
output frequency.’
v
q
FWD
I
REV
El
lsTop[
pfiiFq
ml ”
During operation with external signals, this key is pressed to
decrease reading of externally connected frequency meter.
During operation with the PU, this key is pressed to make the
motor rotate in normal direcion.
During operation with the PU, this key is pressed to make the
motor rotate in opposite direction.
During operation with the PU, this key is pressed to stop the
motor.
This key is pressed to change setting of frequency or other
control variable.
This key is pressed to check setting of variable.
(Calibration mode)
l
” is used to specify decimal point.
0
~
-74-
0
Page 79

_cI_)__.“I_-_-
..__)_.
-*I--
_._
*.
Key
Description (Dual functions)
r‘
-+a.-
5
MID
q
6
LOW
f-
cl
” 0 ”
. . ..Numeral ” 0 ” is specified.
” BOOST ” . . ..Variable’ ” BOOST ”
,I ,t
1
. . ..Numeral ” 1 ” is specified.
” MAX ” . . ..Variable ” MAXIMUM FREQUENCY LIMIT ” is specified.
” 2 ”
. . ..Numeral ” 2 ” is specified.
” MIN ”
” 3 “
” V/F ” . . ..Variable “ V/F ” (base frequency) is selected.
” 4 ” . . ..Numeral ” 4 “ is specified.
” HIGH ” . . ..Variable ” HIGH SPEED ” is selected.
” 5 ”
“ MID ” . . ..Variable ” MIDDLE SPEED ” is selected.
” 6 ”
” LOW ” . . . . ” LOW SPEED ” is selected.
. . . *Variable ” MINIMUM FREQUENCY LIMIT ” is selected.
. . ..Numeral ” 3 ” is specified.
. . ..Numeral ” 5 “ is specified.
. . ..Numeral ” 6 ” is specified.
is selected.
” 7 ” . . ..Numeral ” 7 ” is specified.
“ ACCEL ” . . ..Variable ” ACCELERATION TIME ” is selected.
” 8 ”
. . ..Numeral
” D&EL ”
9
THM
q
.
” 9 ”
“ THM ” . . . .Variable ” ELECTRONIC THERMAL RELAY OPERATING
CURRENT ” is selected.
. . ..Variable ” DECELERATION TIME ” is selected.
. . ..Numeral ” 9 ” is specified.
” 8 ” is specified.
-75-
Page 80

3’4 . OPERATION
4.1 Operation mode
The inverter can be operated either with external signals, or with PU
(parameter unit) .
Selection of operation mode (exte;nal signal mode or parameter mode) can
be made by pressing key of PU.
It is possible to fix operation mode. (FUNCTION 79)
Operation with external signals
Tc-----J o see 4.2.
NFB
n
IWWrter
I
Motor
IM
0
0
Direct output
frequency
NFB
Inverter
FR-Z200
INITIAL OPERATION MODE
When the power is turned on (or CLEAR key is pressed to reset) ,
” external signal operation ” mode is automatically selected and the inverter
can be operated with external signals
. . ..the motor starts when START signal (STF-SD or STR-SD closed) is
Motor’
setting
see 4.3
0
3.
0
given.
0
-76-
Page 81
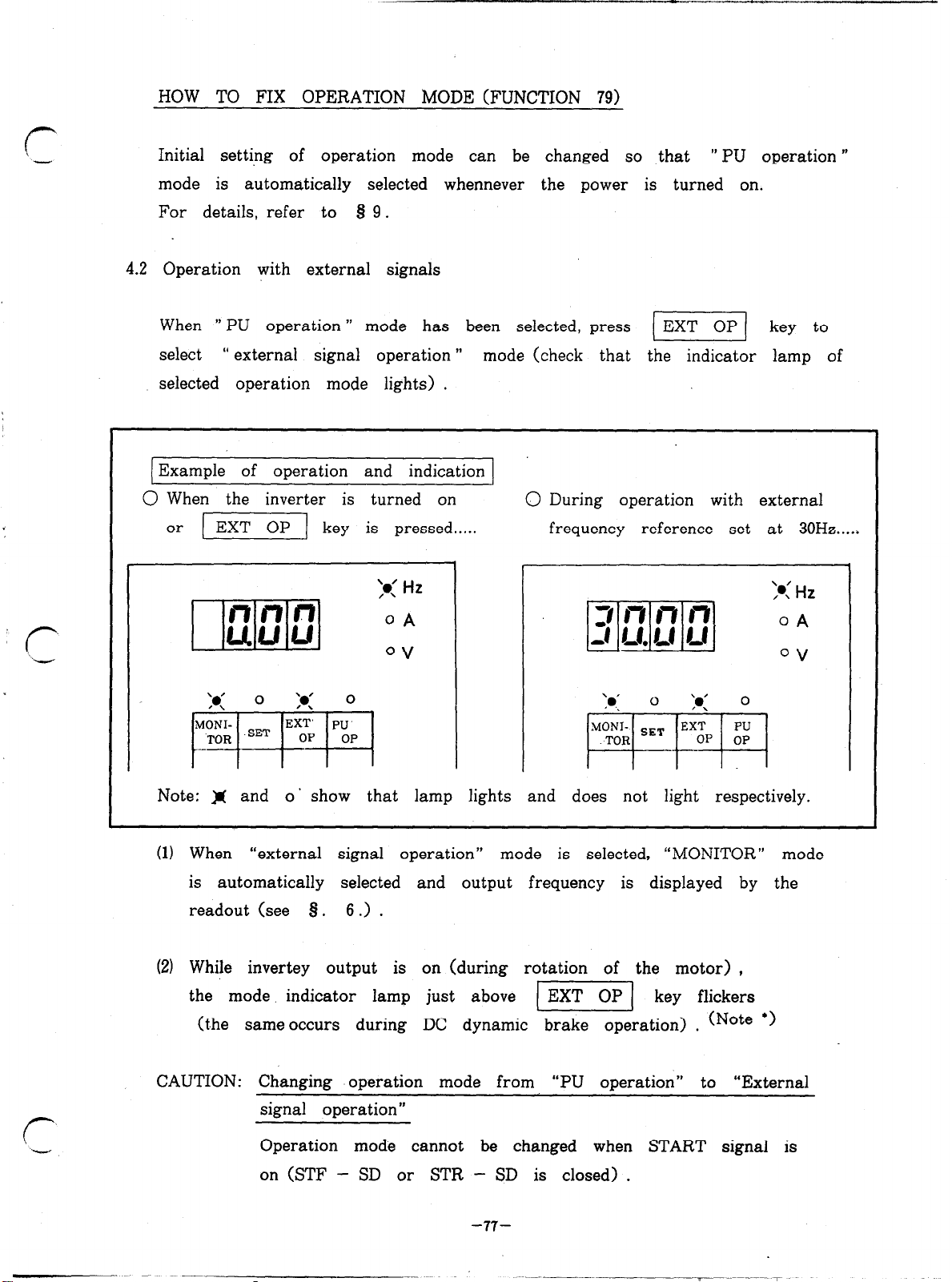
HOW TO FIX OPERATION MODE (FUNCTION 79)
Initial setting of operation mode can be changed so .that ” PU operation ”
mode is automatically selected whennever the power is turned on.
For details, refer to Q 9.
4.2 Operation with external signals
When ” PU operation ”
select
“ external signal operation ”
mode has been selected, press (EXTOP( key to
selected operation mode lights) .
Example of operation and indication
0 When the inverter is turned on
or 1 EXT OP 1 key is pressed.....
mode (check that the indicator lamp of
0 During operation with external
frequency reference set at 30Hz....,
I
Note: )I( and o’ show that lamp lights and does not light respectively.
(1) When
“external signal operation” mode is selected, “MONITOR” mode
is automatically selected and output frequency is displayed by the
readout (see Q. 6 .) .
(2) While invertey output is on (during rotation of the motor) ,
the mode. indicator lamp just above
pTiq key flickers
(t.he same occurs during DC dynamic brake operation) . (Note ‘)
CAUTION: Changing operation mode from “PU operation” to “External
signal operation”
Operation mode cannot be changed when START signal is
on GTF - SD or STR - SD is closed) .
-77-
Page 82

Before changing operation mode, START signal should be ,turned
off and it should be verified that the motor stops completely.
(Note l > The lamp does not flicker when a parameter unit of old
specification (Spec. Na BKO - C2128) is used.
4.3 Operation with PU
To operate the inverter with the PU, press op
After that, the inverter can be started ‘and stopped by pressing keys of
PU (without use of externally installed frequency reference potentiometer and
START switch) .
In this operation mode, it is also possible to jog the motor by pressing
keys of PU.
IMPORTANT ‘NOTE
If the inverter is turned off or reset, operation mode changes from
“PU operation” to “external signal operation” (initial mode setting) .
(1) DIRECT OUTPUT FREQUENCY SETTING
PU
cl
key.
3
(2) OUTPUT FREQUENCY SETTING, USING V OR A KEY (STEP
SETTING)
This method of setting corresponds to the method where externally
installed frequency reference potentiometer is used.
q
key is held down, frequency increases (or decreases) continuously.
Increase (or decrease) of frequency is slow immediately after key is
pressed, and becomes faster with time.
Note: If speed is being monitored, this setting should not be. tried (speed.
may not be displayed accurately) .
-78-
While
q
or
0
Page 83

f-
(31 JOG operation
To jog the motor, perform’ the following operation:
(-
PU
OP
q
The motor starts and runs only while m] or i-1 key is held
down.
@When the motor is started by pressing START key ((FWDI or [ml > ,
MONITOR mode is selected automatically and output frequency is displayed
l
While inverter output is on (during rotation of the motor) , the mode
indicator lamp just above
dynamic brake operation) .
Notes: 1 . MONITOR mode is not selected automatically when a parameter unit
2. The lamp dose not flicker when a parameter unit of previous
l
[ml l
of previous specification (Spec. No. BKO-C2128) is used.
specification (Spec. No. BKO-C2128) is used.
m (or Ill)
l$ fliekers (the same occurs during DC
cl
(Note 2 .>
(Note 1 >
Examples of operation and indication
OExample where 60Hz is set for desired output frequency (from start to 60Hz)
Set to 60Hz
P
x
OExample where speed is changed during operation (from 60Hz to 30Hz)
z
E
.s
8
6
2
g-Jm3
(Set to 60Hz)
fV
mj iQfjJ$fl: “A’
WEE
E
cl
Start stop
n n
pw9 or -,
REV
Set to 30Hz
SS
W=E
Pressing
m clears alternating display and sets to selected frequency.
-79-
Page 84

-.-
Note: Direct setting of output frequency is impossible while the MONITOR
c
1
mode indicator lamp is on.
To set output frequency, press
l
JOG operation
JOG mode selection Operation’
Key
hdicatig
0 0 0 b’ ,. 3: 0 0 ..’
NOTES: 1 . JOG mode cannot be selected while the motor is in operation.
press STOP key to stop the motor and then select JOG mode.
2 . To break JOG mode operation, press
3. Desired frequency and acceleration/deceleration time fo JOG mode
operation can be set by specifying the corresponding function
(control variable) . (FUNCTION 15 and 16)
key to break MONITOR mode.
*If the motor does not start,
check the starting frequency.
(FUNCTION 13)
You cannot jog at 5 Hz, if
” Min. Frequency ” is set higher
than 5
Reset 13 and 2 .
HZ.
(FUNCTION 2 )
0
When the inverter is shipped, the JOG frequency and acceleration/
deceleration time are set to 5 Hz and 0.5sec., respectively (it takes
0.04sec. for increaze of frequency up .to 5 Hz) .
0
-8O-
;
Page 85

4.4 Caution for operation
1. Selection of Operation mode cannot be changed during operation of
r
i-,
operation mode
2. Setting of speed
during speed RPM
setting (2) Speed should not be specified by operating A and
3. Digits of numerical
value and decimal
point 4 digits is entered, the first digit is ignored) .
the inverter.
Note that an operation mode indicator lamp flickers
during operation or the inverter.
When external start signal is on, operation mode cannot
be changed from ” PU operation ” to ” external signal
operation ” (t urn off the signal before changing operation
mode) .
(1) While speed being displayed in. RPM (see P. 901, desired
speed should be specified in terms of RPM.
V keys (step speed setting) .
q
(1) To specify numerical value, maximum 4 -digit numerals
can be entered (if a numerical value of more than
cl
r
Ex.: 12345 . . . .
(2) When ” 0. * * ” (*
entered, ” 0 ” should not be omitted.
” . * * ”
If
4.
Range of setting (1) Direct setting (reference
ten keys)
If a value above the pre-set frequency is entered ir
direct setting, an error occurs.
In this case, ‘press CLEAR key and eter correct
value below pre-set valve.
Range of setting . . . From the minimum frequency limit
to the maximum frequency limit
(When the product is shipped, the maximum
” 2345 ” is entered.
is for any numeral) must be
is entered, it is read as ” * * ” .
frequency is set by operating
0
and minimum frequency limits are set to
OHz and 120Hz respectively.)
-81-
Page 86

4.
Ex.: If ” 150Hz” is entered, error is displayed as shown
below.
mp=qqQy
This is because the maximum frequency (FUNCTION 1
is already pre-set to 120Hz.
(2) Step setting ( H and/or I‘r( key is pressed to
specify reference frequency)
Reference frequency can be set within the specified
range (from maximum frequency limit to minimum
frequency limit) .
If key is held down while frequency is at the
maximum or minimum limit value, the frequency
remains unchanged.
5. Conditions under
which reference (2) MONITOR mode is selected (step setting is possible
” External signal operation ” mode is selected.
(1)
\
3
frequency during MONITOR mode) .
(or speed) (3) Reference frequency (speed) is out of the specified
is unacceptable
(PU operation frequency. > (FUNCTION . 1 and 2 >
mode)
range. (Above or below pre-set max and min
0
-82-
0
Page 87

§ 5.
SETTING 0~ CONTROL VARIABLES (PARAMETERS)
(-
hS+V.”
The inverter has various control functions.
To assure the best performance
from your inverter and motor, these functions should be used with care and
thought for application to the driven machine.
These functions can be set, and setting can be checked or changed by
operating the PU.
Control functions and setting method
1 ” READ ” and ” WRITE ” of function . . . . See P.94
1 Change (write) 1
Basic control
[ ftztions 1 functions
Secondary functions
(operating conditions,
&C.)
3 rd Auxiliary functions
functions (calibration. etc.)
H~+KEJ.~ 1
( /ziq ) * piEq
Setting should be
changed after check.
[SET VALUEI l I-1
2
" ALL CLEAR " . . . . .
After pizq is pressed,
1
I I
Prohibition of parameter WRITE
I 3l
By performing the following operation, user’s settings
are reset to the initial settings (i.e., setting made at
shipment of inverter) .
llTTmKl
appears and flickers.
-83-
Page 88

4
Calibration of frequency meter . . . . . Calibration using PU
(11 Set the frequency for meter full-scale reading* * .
(2) Press m or mj key to start
0
the motor.
(3) Press the following keys to select CALIBRATION mode.
(41 While observing the pointer of frequency meter, press
reading ‘will increase or decrease.
(5) When the meter has been calibrated, ‘press -1 key.
(6) Press m] Key to stop the motor.
* * : For full-scale reading, ” output. frequency at 5 V of frequency
reference voltage ” is specified.
g; @ piJ [GEE]
0
v
When output frequency at 5 V of
frequency reference voltage is 60Hz.
I
A or ]rl key . . . .
0
Note: When ” prohibition of parameter WRITE ” has been set, frequency
meter cannot be calibrated.
IMPORTANT NOTE
This frequency inverter allows you access to multiple control variables which
must be used with care. It has been fully tasted to perform to it’s own
control parameters. But this may not be the case of the electric motor to
which it is to be applied.
If you require to increase the speed of any electric motor over it’s rated
nameplate speed, then you must check with the motor manufacturer first, that
the motor will operate safely and satisfactorily and- that you are not exceeding.
any electrical or mechanical design parameters of the motor.
If in doubt
ASK.
0
-a4-
Page 89
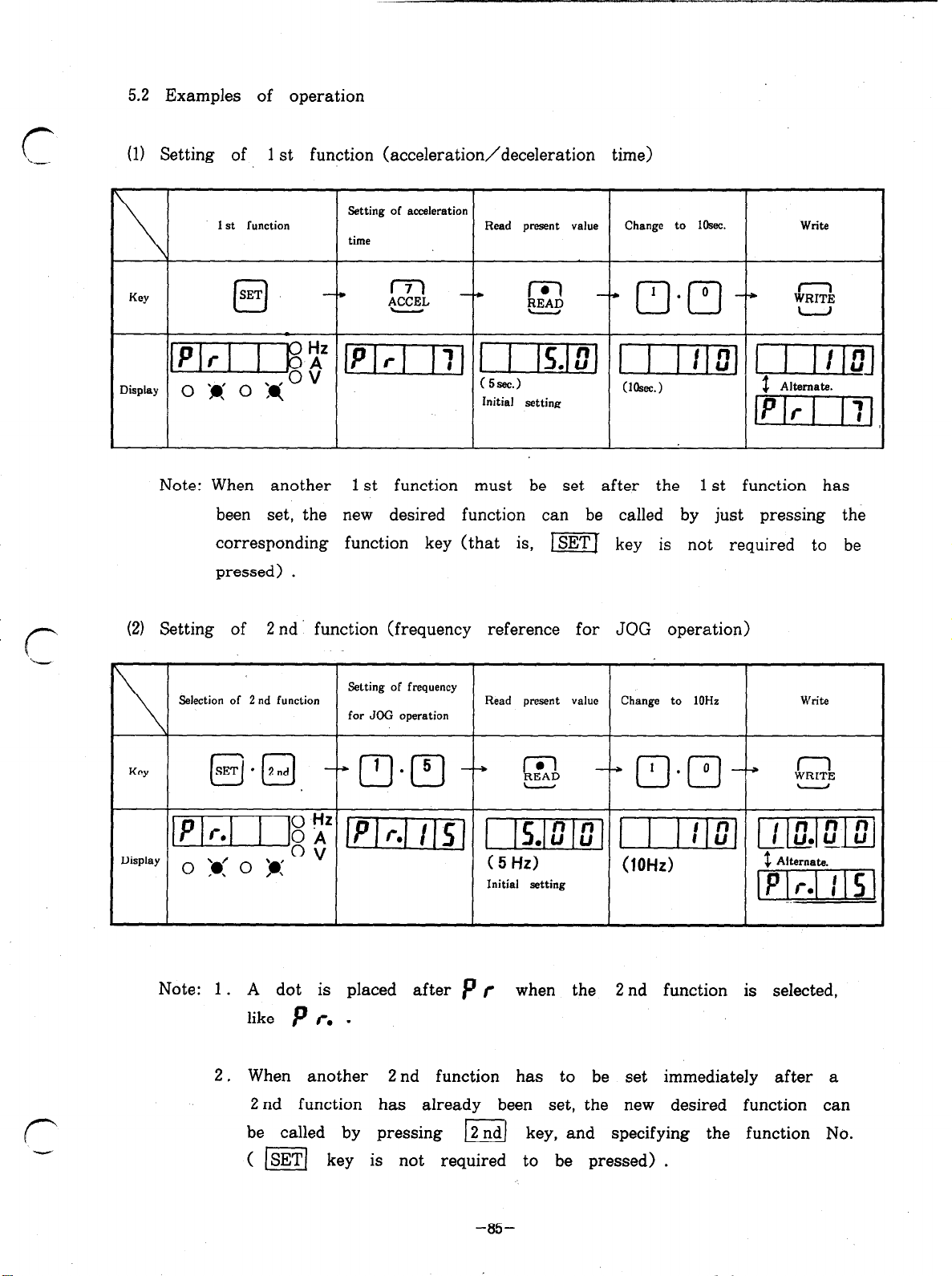
5.2 Examples of operation
(1) Setting of
Key 1 m -
Display
1 st function (acceleration/deceleration time)
Setting
.
time
of acceleration
Read
present value
Initial setting
Change to IOsec.
Note: When another 1 st function must be set after the 1 st function has
been set, the new desired function can be called by just pressing the
corresponding function
key
(that is, lsETJ key is not required to be
pressed) .
Write
(2) Setting of 2 nd’ function (frequency reference for JOG operation)
Setting of frequency
Read present value Change to 1OHz Write
for JOG operation
\
KCY
Selection of 2 nd function
@Ia.dj -
pjqy-q 1-j [I Irlo.lz_loi
Display
Note: 1 .
2. When another 2 nd function has to be set immediately after a
A dot is placed after p r when the 2 nd function is selected,
like p r. .
(5Hz)
Initial setting
(10Hd
.
2 nd function has already been set, the new desired function can
be called by pressing I 2 nd key, and specifying the function No.
( [=I key is not required to be pressed) .
-85-
Page 90

(3)
Setting of 3 rd function (examples of bias and gain settings for frequency
reference voltage signal) .
0
Display
Selection of 3 rd function
-
Bias
Note: Do not input frequency
reference signal across terminals
2 and 5.
3
Note: Do not input frequency
reference signal or used 5 V
input signal.
0
-at+
Page 91
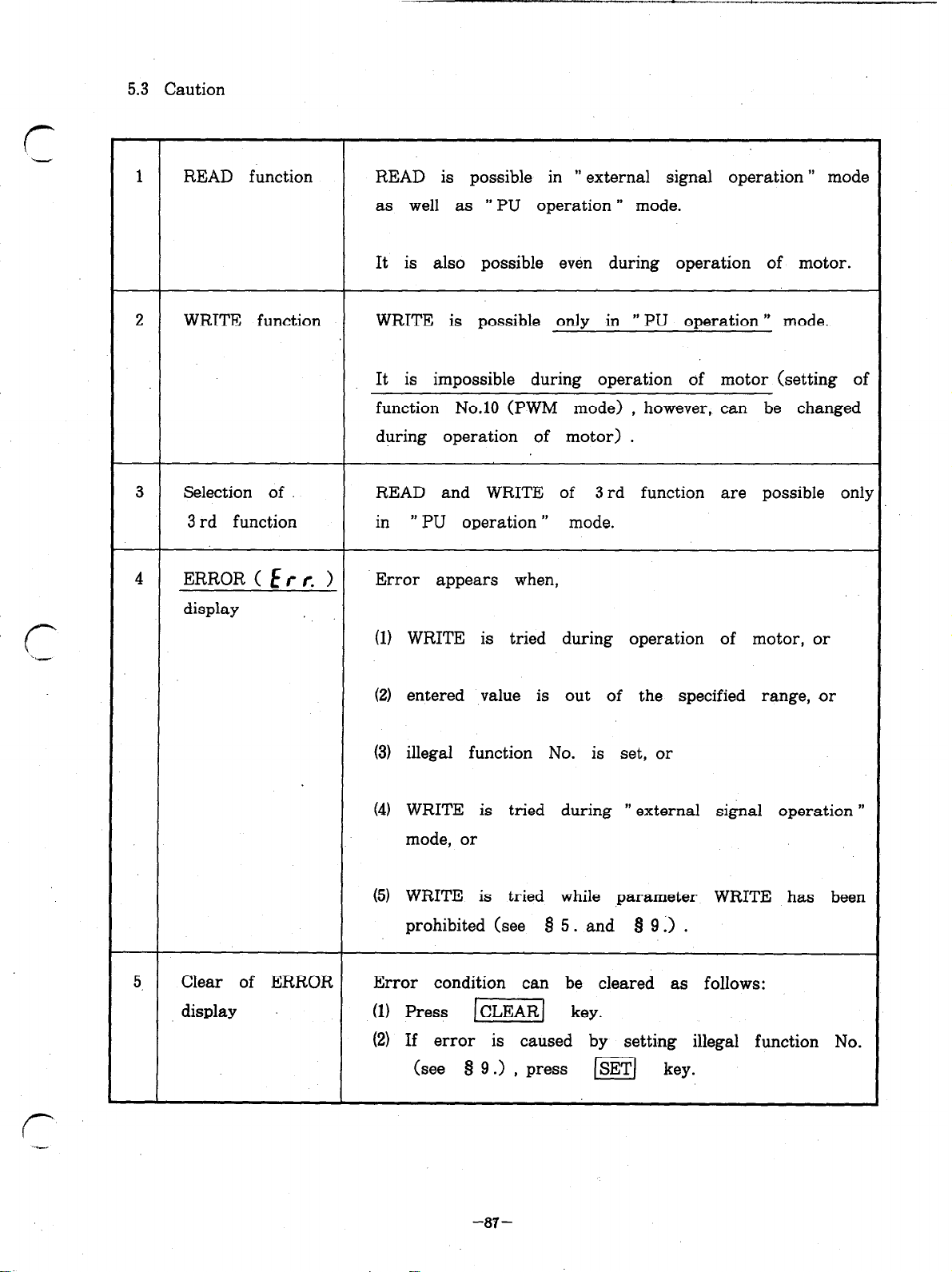
5.3 Caution
1 READ function READ is possible in
as well as ” PU operation ” mode.
It is also possible even during operation of motor.
2 WRITE function
3 Selection of READ and WRITE of 3 rd function are possible only
3 rd function
4
ERROR(Err. >
display
WRITE is possible only in ” PU operation ” mode.
It is impossible during operation of motor (setting of
function No.10 (PWM mode) , however, can be changed
during operation of motor) .
in ” PU operation ” mode.
Error appears when,
(11 WRITE is tried during operation of motor, or
” external sign-al operation ” mode
Clear of ERROR
5.
display
(21 entered value is out of the specified range, or
(3) illegal function No. is set, or
(41 WRITE is tried during ” external signal operation ”
mode, or
(51 WRITE is tried while parameter WRITE has been
prohibited (see 9 5. and Q 9 :> .
Error condition can be cleared as follows:
(11 Press
(2) If error is caused by setting illegal function No.
(see 8 9 .> , press m key.
[CLEAR] key.
-87-
Page 92
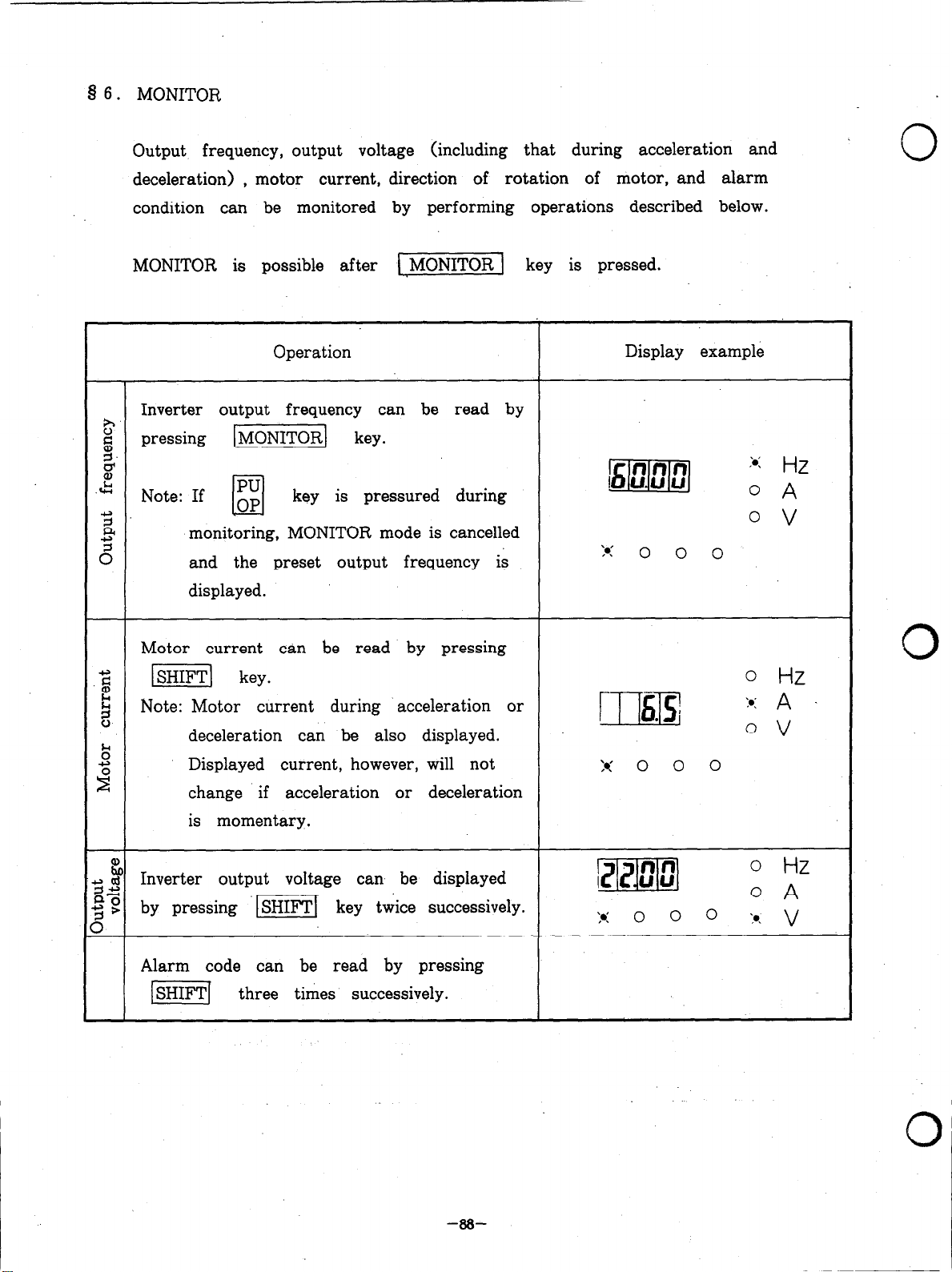
8 6. MONITOR
Output frequency, output voltage (including that during acceleration and
deceleration) ,
condition can be monitored by performing operations described below.
MONITOR is possible after -1 key is pressed.
Inverter output frequency can be read by
t?
pressing [MONITORI key.
s
=I.
B
&
Note: If g
s
a
3
monitoring, MONITOR mode is cancelled
and the preset output frequency is
displayed.
motor current, direction of rotation of motor, and alarm
Operation
key is pressured during
a
Display example
‘0’
,.
0 0 0
0
0 v
Motor current can
8 -1 key.
Note: Motor current during acceleration or
be
read by pressing
2
deceleration can be also displayed.
k
5
2
; 2 Inverter output voltage can be displayed
$? by pressing 1-l key twice successively.
>
Displayed current, however, will not
change if acceleration or deceleration
is momentary.
Alarm code can be read by pressing
[i5izFq three times successively.
.
. ,
h 0 0 0
[Plzlml
, , o o o
9.
0
0 Hz
0 Hz
o *
:a. v
-a8-
0
Page 93

c
Operation Display example
Notes: 1 . The function is capable of storing
0 Hz
r‘
--,-
a maximum of four alarm codes.
Stored alarm codes canbe read
one after another (see Q 7 for :K o o 0
alarm codes) .
How to read alarm codes
r -:--
Dsplay I
;or 1
I latest I alam alana
1
, alarm ’
-----J
s
.r(
.‘=
-2
8
E
A
-4
--‘~~-JGEJ---+piiG]
3rd ‘2nd 1 st
0
When
the latest alarm code appears
again.
0
When
the output frequency at that time
is displayed.
liikiij
IiiGiiiq
alarm
key is pressed,
key is pressed,
lm~ O *
0 v
(1) For the latest alarm, a dot
is placed by after E (see
an example shown above) .
(2) If no alarm has been stored,
the display is as shown
below.
2. Stored alarm codes are held even
after the inverter is turned off.
, ;,..
-89-
Page 94

Operation Display example
Speed RPM is displayed, instead of inverter) 0 When ” 4 ” is set for number
output frequency, when the following setting of motor poles . . . (In this
0
has been accomplished.
piq (2 pJ q l ][m\
- 0 v
2
-3
4
2
E”
J
Number of motor poles is set (within
range from 2 poles to 10 poles) .
Speed RPM which corresponds to
inverter output frequency is displayed.
Dis- When speed is monitored in
played N=
speed the label which indicates the
Note: Displayed speed RPM is in
proportion to output frequency.
120X f (Frequency)
P (Number of poles)
example, inverter output
frequency is assured to be
set at 30Hi previously.)
l
Unit used in display
terms of rpm or m/min,
unit (r-pm or m/min) should
be applied to the monitor
display unit over legend ” Hz”
0
a
8
c8
Speed of load (r-pm or m/min) is set
(within range from 11 to 9998) .
Speed at 60Hz of inverter output frequency
is set.
During ” PU operation ” or ” external
signal operation ” mode, direction of
rotation of the motor can be checked
through the MONITOR indicator lamp.
FORWARD . . . ” Hz ‘I (or ” A ” > lamp lights.
REVERSE . . . “Hz u (or ” A” > lamp flickers.
.o v
This lamp flickers when the
motor rotates in reverse
direction.
0
Page 95

Operation
Status of inverter during operation can be
monitored through the OPERATION MODE
Display example
indicator lamps (lamps just above
and
The lamp which corresponds to the selected
mode flickers during operation of motor.
g: keys) .
q
IEXT 0~1
During operation, either one of
these lamps flickers.
-91-
b
1.
I
Page 96

Q 7. DISPLAY
7.1 Alarm display
If failure occurs during operation
automatically.
Alarm code
Display Code
E
2c :
EcL’z EOCZ
E333
E”
UUT
UK? ETHM
EOC 1 Inverter output current exceeded the overcurrent limit during
acceleration.
Inverter output current exceeded the overcurrent limit during
constant -speed operation.
EOC3
EOVT .
Inverter output current exceeded the overcurrent limit, during
deceleration.
Braking regenerative power from motor exceeded the
regenerative overvoltage limt.
Electronic thermal relay in the inverter was activated (current
is below 150% of preset current) .
of the inverter, an alarm code is displayed.
Description
0
E:fl: ETHT Electronic thermal relay in the inverter was activated (current
is over 150% of preset current) .
E: ?f EIPF Instantaneous power failure protective function was activated.
E$: n EFIN
EbE EBE Brake transistor fault detection.
nl
c
E
ULI
ff’E EPE
U” tr EUVT Inverter input voltage fell below the specified limit.
E
c nr E GF
E
EOLT
Temperature of transistor heatsink exceeded the specified limit.
Stall preventive function was activated during constant -speed
operation and .stopped the motor.
Memory in the inverter is corrupted.
Overcurrent due to earth fault on the inverter output side.
0
EU”X: EOHT Externally installed thermal relay activated (overheat) .
EU”PT EOPT Built-in optional unit connection failure during operation.
-“rl-
-Jo--
0
Page 97

7.2 Indicator lamps in MONITOR mode
r
Y
‘k..-
Indication
0 Hz
OA
ov
7.3 Characters appearing in readout
The alphanumerics which appear in the readout are as listed below.
Latter Display
0
1
Frequency is
displayed.
Motor current
is displayed. flicker.
Output voltage
is displayed.
Jxttcr
A
B
Description
If stall preventive function is activated
during MONITOR mode,
all MODE lamps, other than that selected
Display
El
lzl
r
2
3 cl
4
5 El
6
7 cl 7
8.
9
.3
C
E
F
G
H
I
J
L
c
cl
El
III
c
cl
u’
ill
1.
cl
0
P
T
U
v
r
In
2
cl
El
r
I
cl
II
U
w
Cl
r
cl
-93-
Page 98

Q 8. LIST OF FUNCTIONS
Function No.
(parameter)
Torque boost (manual) 0 -30%
0
1 Max. frequency limit
2 Min. frequency limit
3 V/F (base frequency) 50 - 360Hz 50Hz
Fi
. ..4 1 st (high speed)
s
5
3
v-4
Multiispeed setting:
4
5 Multi-speed setting:
2 nd (middle speed)
Multi- speed setting:
6
3 rd (low speed)
7 Acceleration time
8 Deceleration time
Electronic thermal relay
9
(overheat)
10 PWM mode
11 DC dynamic brake time 0 -1Osec
Function Setting range
Initial
setting
See P.101
0 -120Hz 120Hz P.98
0 -6OHz
0 -360Hz 608~ P.103
0 -360Hz 30Hz
0 -360Hz
0.1 - 3600sec See P.99 P.99
0.1 - 3600sec See P.99 P.99
0 -999.9A
0 -15 3 P.104
OHz P.98
10Hz P.103
See P.99 P.99
0.5sec P.105
Refer to
P.101
P.102
P.103
0
12 DC dynamic brake voltage 0 -20%
13 Starting frequency
‘14 Load pattern selection
15 JOG frequency
JOG acceleration/
16
f3
.”
s
2 17 deceleration 2 nd acceleration/ time 0.1 - 3600sec 5 set
3 18 High - speed maximum
hl
20 Frequency at 5 V input voltage
21 Stall prevention level ’
22 2 nd stall prevention level
23 2 nd stall prevention level
24 Multi-speed setting: 4 th 0 -360Hz. 9999 9999
deceleration time
frequency limit
19 Base frequency voltage 0 -5oov, 9999 9999
(current)
(frequency)
0.5- 10Hz 0.5Hz P.106
0 (constant torque) o
1 (reduced torque)
0 -360Hz 5Hz P.106
O.l-3600sec 0.5sec P.106
120 - 360Hz 120Hz P-99
1 -360Hz 60Hz P.98
0 -200% 150%
0 -200%
0 -360Hz
See P.105 P-105
150% P.108
OHz P.108
P.102
P.100
P.102
P.107
P.103
0
-94-
0
Page 99

Function
(parameter)
25 Multi-,speed setting: 5 th 0 -360Hz, 9999 9999 P&103
26 Multi-speed setting: 6 th 0 -360Hz, 9999 9999 P.103
27 Multi-speed setting: 7 th 0 -360Hz, 9999 9999 P.103
Function Setting range
Intial
setting
Refer to
28 Multi-speed input
correction
29 Acceleration/deceleration
pattern selection
0,l 0 P.103
0,192
0 P.100
0.5 -360Hz, 9999
46
Exterrkl thermal relay signal o l loo 1ol
input
77 Parameter WRITE prohibition 0 1
tt,
,
-95-
0 P.109
0 P.97
Page 100

‘w&ion No.
&m.meter>
78 Reversing prevention
Operation mode selection
79
C- 1 Frequency meter calibration
Function Setting range
Initial
, setting
O,l
0,182
0 -360Hz 60Hz
0
0
Refer to
P.97
P.97
P.111
0
g c-2
-s
j c-3
2 c-4
c- 6 Gain for frequency reference
Least setting increments:
Note * :
Bias for frequency reference
voltage signal
Gain for frequency reference
voltage signal
Bias for frequency reference
current signal
current signal
Frequency . . . . . . . O.OlHz
Time- . . . . . . . O.lsec.
Current
%
Voltage
When a parameter unit of old specification (Spec. No. BKO-C2128)
used, the least setting increment of gain for frequency reference current
. . . . . . . O.lA
. ..*... 1%
. . . . . . . 1v
0 -120Hz OHz
1 -360Hz 60Hz
.O -12OHz
1 -360Hz*
OHz
60Hz
P.lll
P.lll
P.lll
P.111
is
0
signal is 1 Hz.
I
0
-90-
 Loading...
Loading...