Page 1

Page 2

Page 3
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
(Always read these instructions before using this product.)
Before using this product, thoroughly read this manual and the relevant manuals introduced in this manual
and pay careful attention to safety and handle the products properly.
The precautions given in this manual are concerned with this product. For the safety precautions of the
system, refer to the User's Manual for each controller.
In this manual, the safety precautions are ranked as " WARNING" and " CAUTION".
WARNING
CAUTION
Note that the CAUTION level may lead to serious consequences according to the circumstances.
Always follow the precautions of both levels because they are important for personal safety.
Please save this manual to make it accessible when required and always forward it to the end user.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in miner or moderate injury or property damage.
[Design Instructions]
WARNING
● When data change, program change, or status control is performed from a personal computer to a running controller,
create an interlock circuit outside the programmable controller to ensure that the whole system always operates safely.
Furthermore, for the online operations performed from a personal computer to a controller, the corrective actions against a
communication error due to such as a cable connection fault should be predetermined as a system.
[Startup/Maintenance Instructions]
CAUTION
● The online operations performed from a personal computer to a running controller (Program change, operating status
change such as RUN-STOP switching, and remote control operation) have to be executed after the manual has been
carefully read and the safety has been ensured.
When changing a program while a controller is RUN, it may cause a program corruption in some operating conditions.
Fully understand the precautions described in the manuals and Help function of each controller before use.
A - 1
Page 4

CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
(1) Mitsubishi programmable controller ("the PRODUCT") shall be used in conditions;
i) where any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT, if any, shall not lead to any major or
serious accident; and
ii) where the backup and fail-safe function are systematically or automatically provided outside of the
PRODUCT for the case of any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT.
(2) The PRODUCT has been designed and manufactured for the purpose of being used in general
industries.
MITSUBISHI SHALL HAVE NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED
TO ANY AND ALL RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY BASED ON CONTRACT, WARRANTY, TORT,
PRODUCT LIABILITY) FOR ANY INJURY OR DEATH TO PERSONS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO
PROPERTY CAUSED BY the PRODUCT THAT ARE OPERATED OR USED IN APPLICATION NOT
INTENDED OR EXCLUDED BY INSTRUCTIONS, PRECAUTIONS, OR WARNING CONTAINED IN
MITSUBISHI'S USER, INSTRUCTION AND/OR SAFETY MANUALS, TECHNICAL BULLETINS AND
GUIDELINES FOR the PRODUCT.
("Prohibited Application")
Prohibited Applications include, but not limited to, the use of the PRODUCT in;
• Nuclear Power Plants and any other power plants operated by Power companies, and/or any other
cases in which the public could be affected if any problem or fault occurs in the PRODUCT.
• Railway companies or Public service purposes, and/or any other cases in which establishment of a
special quality assurance system is required by the Purchaser or End User.
• Aircraft or Aerospace, Medical applications, Train equipment, transport equipment such as Elevator
and Escalator, Incineration and Fuel devices, Vehicles, Manned transportation, Equipment for
Recreation and Amusement, and Safety devices, handling of Nuclear or Hazardous Materials or
Chemicals, Mining and Drilling, and/or other applications where there is a significant risk of injury to
the public or property.
Notwithstanding the above, restrictions Mitsubishi may in its sole discretion, authorize use of the
PRODUCT in one or more of the Prohibited Applications, provided that the usage of the PRODUCT is
limited only for the specific applications agreed to by Mitsubishi and provided further that no special
quality assurance or fail-safe, redundant or other safety features which exceed the general
specifications of the PRODUCTs are required. For details, please contact the Mitsubishi representative
in your region.
A - 2
Page 5
REVISIONS
The manual number is written at the bottom left of the back cover.
Print date Manual number
Oct., 2009 SH-080902ENG-A First edition
Apr., 2010 SH-080902ENG-B
Sep., 2010 SH-080902ENG-C
Model Addition
MELSEC-L series
Addition
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT, Section 3.4, Section 3.10
Correction
MANUALS, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL,
Section 1.1, Section 1.2, Section 2.1, Section 3.3, Section 3.4, Section 3.5,
Section 3.6, Section 3.7, Section 3.8, Section 3.9, Section 3.10, Section 3.12,
Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section 4.3, Section 4.4, Section 5.1, Section 5.2,
Section 6.2
Model Addition
MELSEC-FX series
Addition
Section 3.4, Section 3.10
Correction
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL,
Section 1.1, Section 1.2, Section 2.1, Section 3.1, Section 3.3, Section 3.4,
Section 3.5, Section 3.6, Section 3.7, Section 3.8, Section 3.9, Section 3.11,
Section 3.13, Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section 4.3, Section 4.4, Section 5.1,
Section 5.2, Section 6.2
Revision
Apr., 2011 SH-080902ENG-D
Nov., 2011 SH-080902ENG-E
Jun., 2012 SH-080902ENG-F
Nov., 2012 SH-080902ENG-G
Addition
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL
Correction
HOW TO READ THIS MANUAL, Section 1.1, Section 1.2, Section 2.1, Section 3.1,
Section 3.3, Section 3.4, Section 3.5, Section 3.6, Section 3.7, Section 3.8,
Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section 4.4, Section 5.1, Section 5.2, Section 6.2
Addition
MANUALS, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL,
Section 3.4.4
Correction
Section 1.1, Section 1.2, Section 2.1, Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.3,
Section 3.4, Section 3.5, Section 3.8, Section 3.9, Section 3.11, Section 3.13,
Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section 4.3, Section 4.4, Section 5.2, Section 6.1,
Section 6.2
Correction
Section 1.1, Section 1.2, Section 2.1, Section 3.4, Section 3.5, Section 3.8,
Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section 4.3, Section 4.4, Section 6.2
Correction
Section 1.2, Section 3.2, Section 3.4, Section 3.11, Section 5.2
A - 3
Page 6
Print date Manual number
Revision
Jun., 2013 SH-080902ENG-H
Dec., 2013 SH-080902ENG-I
Addition
Section 3.4.5
Correction
Section 2.1, Section 3.4.1, Section 3.4.4, Section 3.11
Addition
Section 3.4.6, Section 3.4.7
Correction
MANUALS, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL,
Section 3.4.2, Section 3.4.3, Section 3.4.4, Section 3.5.1, Section 3.6, Section 3.7,
Section 3.9, Section 3.11, Section 5.2
Japanese Manual Version SH-080763-J
This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any patent licenses.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation cannot be held responsible for any problems involving industrial property rights which may occur
as a result of using the contents noted in this manual.
© 2009 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
A - 4
Page 7

INTRODUCTION
Thank you for purchasing the Mitsubishi integrated FA software, MELSOFT series.
Before using the product, thoroughly read this manual to develop full familiarity with the functions and performance
to ensure correct use.
CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS ...................................................................................................................... A - 1
REVISIONS ........................................................................................................................................... A - 3
INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................................... A - 5
CONTENTS ........................................................................................................................................... A - 5
MANUALS.............................................................................................................................................. A - 7
HOW TO READ THIS MANUAL .......................................................................................................... A - 11
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL........................................................... A - 13
1OVERVIEW 1 - 1 to 1 - 10
1.1 MELSOFT iQ Works 1 - 2
1.2 Features 1 - 3
2 SCREEN CONFIGURATION 2 - 1 to 2 - 4
2.1 Screen Configuration 2 - 2
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR 3 - 1 to 3 - 60
3.1 Procedure of MELSOFT Navigator from Start to End 3 - 2
3.2 Starting MELSOFT Navigator 3 - 3
3.3 Creating Workspaces 3 - 4
3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram 3 - 8
3.4.1 System configuration to be created.............................................................................................. 3 - 8
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams......................................................................................3 - 9
3.4.3 Creating network configuration diagrams...................................................................................3 - 20
3.4.4 Creating CC-Link configuration diagrams...................................................................................3 - 22
3.4.5 Creating AnyWireASLINK configuration diagrams .....................................................................3 - 24
3.4.6 Creating Ethernet configuration diagrams ..................................................................................3 - 26
3.4.7 Creating CC IE Field configuration diagrams .............................................................................3 - 28
3.5 Creating Projects 3 - 30
3.5.1 Creating new projects.................................................................................................................3 - 30
3.5.2 Allocating projects to controllers................................................................................................. 3 - 35
3.6 Setting Parameters 3 - 38
3.7 Checking System Configuration 3 - 47
A - 5
Page 8

3.7.1 Checking system configuration .................................................................................................. 3 - 47
3.7.2 Checking power supply capacity and I/O points ........................................................................ 3 - 48
3.8 Editing Projects 3 - 49
3.8.1 Editing projects........................................................................................................................... 3 - 49
3.8.2 Utilizing existing projects (import) .............................................................................................. 3 - 50
3.9 Reading/Writing/Verifying Controller Data 3 - 53
3.10 Saving Workspaces 3 - 56
3.10.1 Saving workspaces with specified names .................................................................................. 3 - 56
3.10.2 Overwriting workspaces ............................................................................................................. 3 - 57
3.11 Printing Workspaces 3 - 58
3.12 Closing Workspaces 3 - 59
3.13 Exiting MELSOFT Navigator 3 - 60
4 USING SYSTEM LABELS 4 - 1 to 4 - 20
4.1 Registering System Labels in MELSOFT Navigator 4 - 2
4.1.1 Registering system labels in MELSOFT Navigator ...................................................................... 4 - 3
4.1.2 Assigning devices to system labels.............................................................................................. 4 - 5
4.1.3 Using system labels in GT Designer3 .......................................................................................... 4 - 8
4.2 Utilizing Existing Labels as System Labels 4 - 11
4.2.1 Registering labels as system labels ........................................................................................... 4 - 12
4.2.2 Using system labels in motion controller projects ...................................................................... 4 - 15
4.3 Using System Labels on another personal computer 4 - 17
4.4 Checking System Labels 4 - 19
5 CREATING SYSTEM BACKUP DATA 5 - 1 to 5 - 6
5.1 Setting Batch Read Password 5 - 2
5.2 Executing Batch Read Function 5 - 4
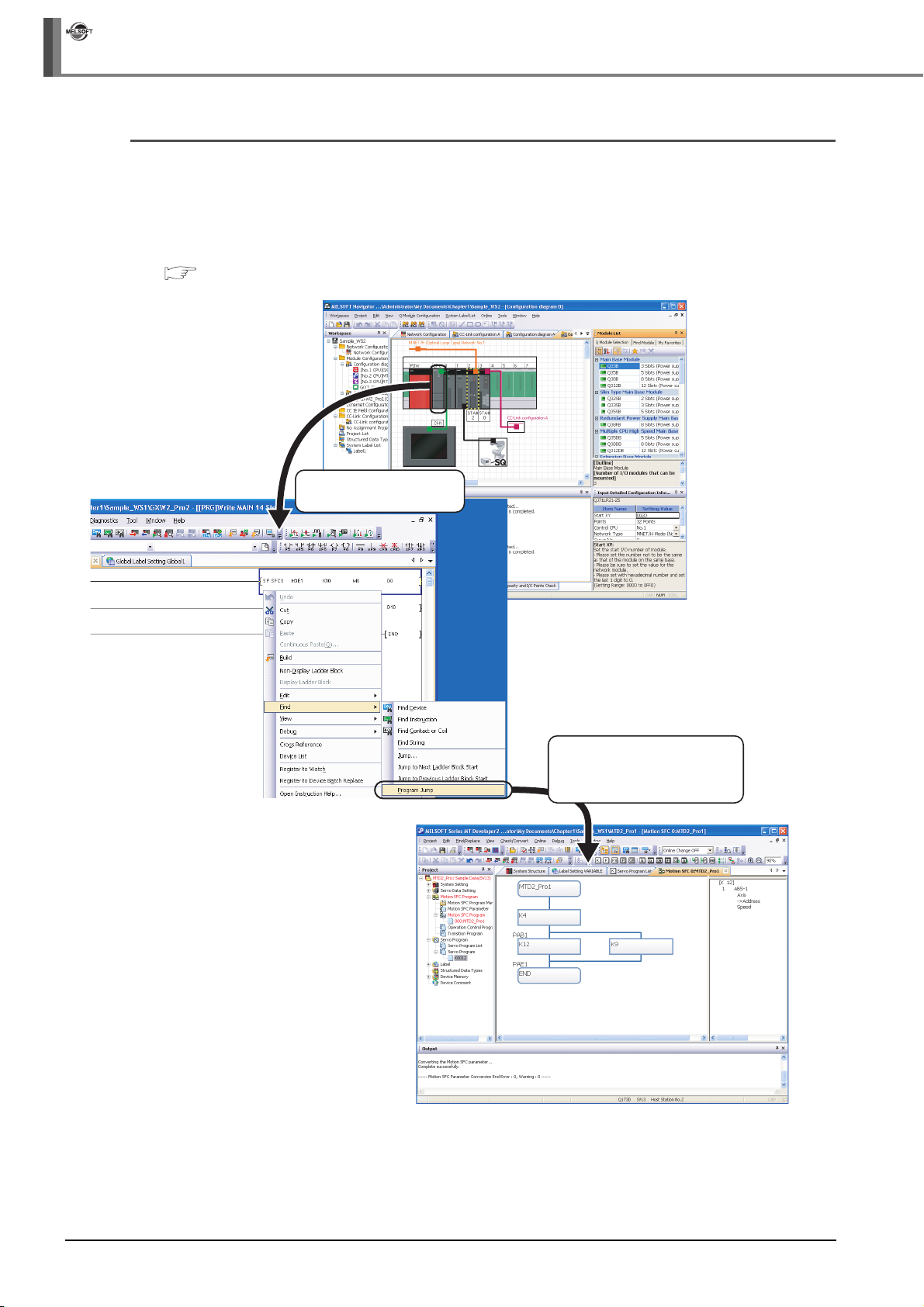
6 USING PROGRAM JUMP FUNCTION 6 - 1 to 6 - 5
6.1 Example of System Configuration 6 - 2
6.2 Program Jump Function 6 - 3
A - 6
Page 9
■ MANUALS
The manuals related to this product are shown below.
Refer to the following tables when ordering required manuals.
Related manuals
1) MELSOFT Navigator
For details of operations, refer to the Help function of MELSOFT Navigator.
2) GX Works2
Manual name
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
Explains the system configuration of GX Works2 and the functions common to a Simple project and
Structured project such as parameter setting, operation method for the online function. (Sold separately)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
Explains operation methods such as creating and monitoring programs in Simple project of GX Works2.
(Sold separately)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Structured Project)
Explains operation methods such as creating and monitoring programs in Structured project of GX
Works2. (Sold separately)
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual (Simple Project)
Explains fundamental operation methods such as creating, editing, and monitoring programs in Simple
project for users inexperienced with GX Works2. (Sold separately)
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual (Structured Project)
Explains fundamental operation methods such as creating, editing, and monitoring programs in
Structured project for users inexperienced with GX Works2. (Sold separately)
Manual number
(Model code)
SH-080779ENG
(13JU63)
SH-080780ENG
(13JU64)
SH-080781ENG
(13JU65)
SH-080787ENG
(13JZ22)
SH-080788ENG
(13JZ23)
A - 7
Page 10
3) GT Designer3
Manual name
GT Designer3 Version 1 Screen Design Manual (Fundamentals)
Explains the system configuration, screen configuration, basic operations for dialog boxes, methods
such as creating new project and transferring data to GOT, and convenient screen editing operations of
GT Designer3. (Sold separately)
GT Designer3 Version 1 Screen Design Manual (Functions) (1/2, 2/2)
Explains common settings, object function specifications, setting methods, and arranging methods of GT
Designer3. (Sold separately)
GT Designer3 (GOT2000) Screen Design Manual
Explains the system configuration, screen configuration, basic operations for dialog boxes, methods
such as creating new project and transferring data to GOT, and convenient screen editing operations of
GT Designer3. (Sold separately)
GOT1000 Series Connection Manual (Mitsubishi Products) for GT Works3
Explains Mitsubishi products that can be connected to GOT and their connection method.
(Sold separately)
GOT1000 Series Connection Manual (Non-Mitsubishi Products 1) for GT Works3
Explains non-Mitsubishi products that can be connected to GOT and their connection method.
(Sold separately)
GOT1000 Series Connection Manual (Non-Mitsubishi Products 2) for GT Works3
Explains non-Mitsubishi products that can be connected to GOT and their connection method.
(Sold separately)
GOT1000 Series Connection Manual (Microcomputer, MODBUS Products, Peripherals) for GT Works3
Explains the connection method between GOT and peripherals such as a bar code reader.
(Sold separately)
Manual number
(Model code)
SH-080866ENG
(1D7MB9)
SH-080867ENG
(1D7MC1)
SH-081220ENG
(1D7ML9)
SH-080868ENG
(1D7MC2)
SH-080869ENG
(1D7MC3)
SH-080870ENG
(1D7MC4)
SH-080871ENG
(1D7MC5)
GOT2000 Series Connection Manual (Mitsubishi Product) For GT Works3 Version1
Explains Mitsubishi products that can be connected to GOT and their connection method.
(Sold separately)
GOT2000 Series Connection Manual (Non Mitsubishi Product 1) For GT Works3 Version1
Explains non-Mitsubishi products that can be connected to GOT and their connection method.
(Sold separately)
GOT2000 Series Connection Manual (Non Mitsubishi Product 2) For GT Works3 Version1
Explains non-Mitsubishi products that can be connected to GOT and their connection method.
(Sold separately)
GOT2000 Series Connection Manual (Microcomputer, MODBUS Products, Peripherals) For GT Works3
Version1
Explains the connection method between GOT and peripherals such as a bar code reader.
(Sold separately)
GT Simulator3 Version 1 Operating Manual
Explains the system configuration, screen configuration, and operation methods of GT Simulator3 used
in GOT1000 series (GT16/GT15/GT11) and GOT-A900 series. (Sold separately)
GT SoftGOT1000 Version 3 Operating Manual for GT Works3
Explains the system configuration, screen configuration, and operation methods of monitoring software
GT Soft GOT1000. (Sold separately)
GT SoftGOT2000 Version1 Operating Manual
Explains the system configuration, screen configuration, and operation methods of monitoring software
GT Soft GOT2000. (Sold separately)
4) MT Developer2
Refer to the Help function of MT Developer2.
SH-081197ENG
(1D7MJ8)
SH-081198ENG
(1D7MJ9)
SH-081199ENG
(1D7MK1)
SH-081200ENG
(1D7MK2)
SH-080861ENG
(1D7MB1)
SH-080860ENG
(1D7MA9)
SH-081201ENG
(1D7MK3)
A - 8
Page 11
5) Motion Controllers
Manual name
Q173DCPU/Q172DCPU Motion controller Programming Manual (COMMON)
Explains the Multiple CPU system configuration, performance specifications, common parameters,
auxiliary/applied functions, and error lists. (Optional)
Q173DCPU/Q172DCPU Motion controller (SV13/SV22) Programming Manual (Motion SFC)
Explains the functions, programming, debugging, and error lists of Motion SFC. (Optional)
Q173DCPU/Q172DCPU Motion controller (SV13/SV22) Programming Manual (REAL MODE)
Explains the servo parameters, positioning instructions, device lists, and error lists. (Optional)
Q173DCPU/Q172DCPU Motion controller (SV22) Programming Manual (VIRTUAL MODE)
Explains the dedicated instructions, servo parameters, positioning instructions for mechanical system
program comprised of a virtual main shaft or mechanical module required to execute the synchronous
control, device lists, and error lists. (Optional)
Q173HCPU/Q172HCPU Motion controller Programming Manual (COMMON)
Explains the Multiple CPU system configuration, performance specifications, common parameters,
auxiliary/applied functions and error lists. (Optional)
Q173HCPU/Q172HCPU Motion controller (SV13/SV22) Programming Manual (Motion SFC)
Explains the functions, programming, debugging, and error lists of Motion SFC. (Optional)
Q173HCPU/Q172HCPU Motion controller (SV13/SV22) Programming Manual (REAL MODE)
Explains the servo parameters, positioning instructions, device list, and error lists. (Optional)
Q173HCPU/Q172HCPU Motion controller (SV22) Programming Manual (VIRTUAL MODE)
Explains the dedicated instructions, servo parameters, positioning instructions for mechanical system
program comprised of a virtual main shaft or mechanical module required to execute the synchronous
control, device lists, and error lists. (Optional)
Manual number
(Model code)
IB-0300134
(1XB928)
IB-0300135
(1XB929)
IB-0300136
(1XB930)
IB-0300137
(1XB931)
IB-0300111
(1XB911)
IB-0300112
(1XB912)
IB-0300113
(1XB913)
IB-0300114
(1XB914)
Q173HCPU/Q172HCPU Motion controller (SV43) Programming Manual
Explains the dedicated instructions to execute the positioning control by Motion program of EIA language
(G-code), servo parameters, positioning instructions, device list, and error lists. (Optional)
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV13/SV22) Programming Manual (Motion SFC)
Explains the Multiple CPU system configuration, performance specifications, functions, programming,
and error codes of the Motion SFC. (Optional)
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV13/SV22) Programming Manual (REAL MODE)
Explains the servo parameters, positioning instructions, device list, and error lists. (Optional)
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV22) Programming Manual (VIRTUAL MODE)
Explains the dedicated instructions, servo parameters, positioning instructions for mechanical system
program comprised of a virtual main shaft or mechanical module required to execute the synchronous
control, device lists, and error lists. (Optional)
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV43) Programming Manual
Explains the dedicated instructions to execute the positioning control by Motion program of EIA language
(G-code), Multiple CPU system configuration, performance specifications, functions, programming,
debugging, servo parameters, positioning instructions, device list, and error lists. (Optional)
6) RT ToolBox2
Manual name
CR750/700/500 series RT ToolBox2 / RT ToolBox2 mini User's Manual
Explains operation methods such as creating and monitoring programs, and connecting with robots.
IB-0300115
(1XB915)
IB-0300042
(1XB781)
IB-0300043
(1XB782)
IB-0300044
(1XB783)
IB-0300070
(1CT784)
Manual number
(Model code)
BFP-A8618
The Operating Manual is included on the DVD-ROM/CD-ROM of the software package in PDF file format.
Manuals in printed form are sold separately for single purchase. Order a manual by quoting the manual number
(model code) listed in the table above.
A - 9
Page 12
● Purpose of this manual
This manual explains the features and operations of iQ Platform supporting engineering environment
MELSOFT iQ Works.
Manuals and the Help function for reference are listed in the following table according to their
purpose.
For information such as the contents and number of each manual, refer to the list of 'Related
manuals'.
Purpose Manuals and HELP function for reference
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
Creating GX Works2 projects
Creating MT Developer2 projects Help function of MT Developer2
Creating GT Designer3 projects
Creating RT ToolBox2 projects CR750/700/500 series RT ToolBox2 / RT ToolBox2 mini User's Manual
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Structured Project)
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual (Simple Project)
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual (Structured Project)
GT Designer3 Version 1 Screen Design Manual (For GOT 1000 Series)
GT Designer3 (GOT2000) Screen Design Manual
Using system labels
Using data backup function
Using program jump function Motion controller programming manual of Q173D/Q172D, Q173H/Q172H, Q173/Q172
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Structured Project)
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual (Simple Project)
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual (Structured Project)
Help function of MT Developer2
A - 10
Page 13

■ HOW TO READ THIS MANUAL
This section explains how to read this manual according to your purpose when using MELSOFT iQ
Works.
Please use this manual with referring to the following descriptions.
1) To learn about the overview of MELSOFT iQ Works
Chapter 1 OVERVIEW
Chapter 1 explains the features of MELSOFT iQ Works.
2) To learn about the screen configuration of MELSOFT iQ Works
Chapter 2 SCREEN CONFIGURATION
Chapter 2 explains the screen configuration of MELSOFT Navigator.
3) To learn about the operating procedures of MELSOFT Navigator
Chapter 3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
Chapter 3 explains a sequence of the basic operation from start-up to creating and saving methods
of workspaces and projects.
4) To learn about the system labels
Chapter 4 USING SYSTEM LABELS
Chapter 4 explains the functions to utilize labels used in a project for controller projects in a
workspace.
5) To learn about the data backup
Chapter 5 CREATING SYSTEM BACKUP DATA
Chapter 5 explains the functions to read programmable controller projects, motion controller
projects, and GOT projects from respective controllers in batch and create their backup data using
MELSOFT Navigator.
6) To learn about the program jump function
Chapter 6 USING PROGRAM JUMP FUNCTION
Chapter 6 explains the function which can start motion SFC programs/servo programs, that are
linked with motion controller programs, using the SFCS and SVST instructions of ladder programs.
A - 11
Page 14
This explains notes requiring attention or useful functions relating to the information given on the
same page.
● Symbols used in this manual
The following shows the symbols used in this manual with descriptions and examples.
No. Symbol Description Example
[ ] Menu name on a menu bar [Workspace]
Toolbar icon
" " Item name in a workspace "Configuration diagram B"
" " Item name in a screen "Open Startup Screen at Start"
Button on a screen
- Keyboard key
Ctrl
A - 12
Page 15
■ GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL
This manual uses the generic terms and abbreviations listed in the following table to discuss the
software packages and programmable controller CPUs. Corresponding module models are also listed if
needed.
Generic term and abbreviation Description
Generic product name of the integrated development environment for SWnDND-IQWK-E/
MELSOFT Navigator
GX Works2
MT Developer2
GT Designer3
GX Developer
RT ToolBox2
Q series Generic term for MELSEC-Q series
SWnDNC-IQWK-E (iQ Platform supporting engineering environment MELSOFT iQ Works)
(n: version)
Generic product name for SWnDNC-GXW2-E
(n: version)
MELSOFT Navigator compatible GX Works2 is GX Works2Version 1.15R or later.
Generic product name for SWnDNC-MTW2-E
(n: version)
MELSOFT Navigator compatible MT Developer2 is MT Developer2 Version 1.09K or later.
Generic product name for SWnD5C-GTWK3-E
(n: version)
MELSOFT Navigator compatible GT Designer3 is GT Designer3 Version 1.05F or later.
Generic product name for SWnD5C-GPPW-E
(n: version)
MELSOFT Navigator compatible GX Developer is GX Developer Version 8.95Z or later.
Generic product name for 3D-11C-WINE/3D-12C-WINE
MELSOFT Navigator compatible RT ToolBox2 is RT ToolBox2 Version 2.00A or later.
L series Generic term for MELSEC-L series
FX series Generic term for MELSEC-F series
Controller Generic terms for programmable controller, motion controller, and GOT
Network Generic terms for CC-Link IE controller network, MELSECNET/H, and Ethernet
Personal computer
GOT
System configuration diagram Generic terms for network configuration and module configuration
GX Works2 project Projects that created/saved with GX Works2 (GX Works2 format project)
GX Developer project Projects that created/saved with GX Developer (GX Developer format project)
Generic term for personal computers on which Windows
Generic term for Mitsubishi Graphic Operation Terminal GOT1000 series and GOT2000
Series
®
operates
A - 13
Page 16

MEMO
A - 14
Page 17

1OVERVIEW
This chapter explains the features of MELSOFT iQ Works.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
1.1 MELSOFT iQ Works. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
1 - 1
Page 18
iQ Works
1 OVERVIEW
1.1 MELSOFT iQ Works
MELSOFT iQ Works is an integrated engineering software product which includes GX Works2, MT Developer2, GT
Designer3, and RT ToolBox2.
While sharing design information such as system designs and programming in the whole control system, the
system designing efficiency and the programming efficiency are improved, and thus the total programming cost is
reduced.
This manual explains the system management method using MELSOFT Navigator.
Q series, L series, and FX series are supported in MELSOFT Navigator, however, this manual explains the
operations of Q series.
MELSOFT iQ Works
GX Works2
(PLC programming and
maintenance software)
MT Developer2
(Motion programming and
maintenance software)
GT Designer3
(HMI screen creation software)
RT ToolBox2
(Robot total engineering
support software)
Share design information
among software products
MELSOFT Navigator
(System management software)
Design information
database
1 - 2
To start MELSOFT Navigator and engineering software products, select an item registered in the start menu by
following the procedures below.
• MELSOFT Navigator : Select [MELSOFT Application]
• GX Works2 : Select [MELSOFT Application]
• MT Developer2 : Select [MELSOFT Application]
• GT Designer3 : Select [MELSOFT Application]
• RT ToolBox2 : Select [MELSOFT Application]
⇒ [MELSOFT iQ Works] ⇒ [MELSOFT Navigator].
⇒ [GX Works2] ⇒ [GX Works2].
⇒ [MT Works2] ⇒ [MT Developer2].
⇒ [GT Works3] ⇒ [GT Designer3].
⇒ [RT ToolBox2] ⇒ [RT ToolBox2].
Page 19
1.2 Features
This section explains the features of MELSOFT iQ Works.
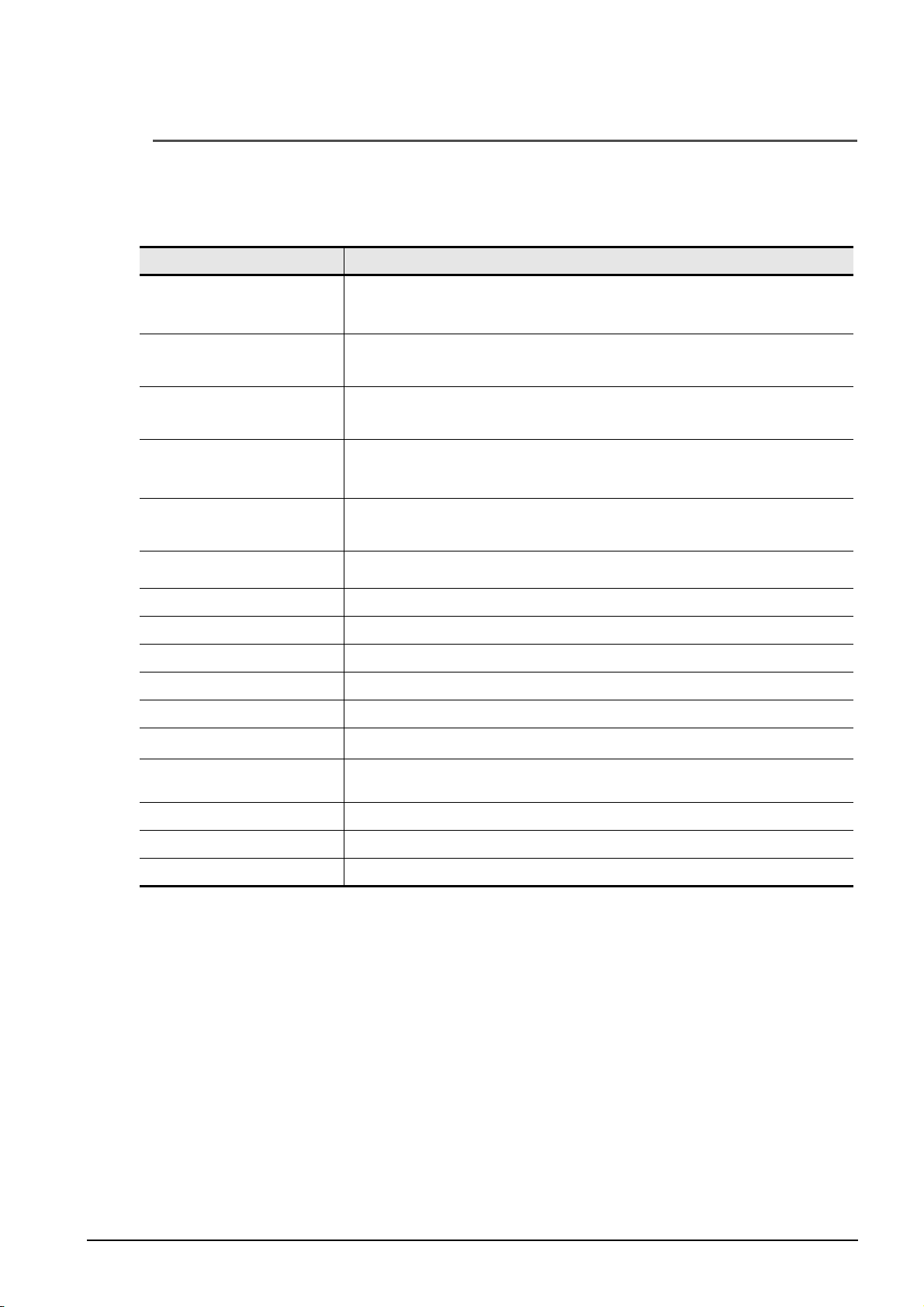
■ Project management using graphical system configuration diagrams
Projects are managed by using graphically displayed diagrams of the actual hardware equipment
configuration of the whole system, linking each equipment and the project.
1.2 Features
SCREEN
1
OVERVIEW
2
CONFIGURATION
Activate the Module Configuration
window by double-clicking a module
configuration diagram on the
Network Configuration window.
Activate the project linked
to the respective module by
double clicking a module on
the Module Configuration
window.
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
GOT project
Programmable controller project
1 - 3
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
Page 20
iQ Works
1 OVERVIEW
■ Improved project management efficiency
● Multiple project management using a workspace
Multiple project data (programmable controller projects, motion controller projects, GOT projects,
and robot controller projects) can be managed totally using a workspace.
Created date and modified date of each project can be confirmed with the project list.
Programmable controller
project
Motion controller project
GOT project
Robot controller project
1 - 4
Page 21
1.2 Features
■ Simplified parameter settings
Parameters, such as I/O assignment and network parameters, which require consistencies can be
set without opening related projects of each engineering software (GX Works2, MT Developer2,
and GT Designer3).
Parameters set to the project on CPU No. 1 can be utilized for the project on CPU No. 2 when
configuring multiple CPU system.
For the parameter setting function, refer to the following chapter.
Chapter 3
< I/O assignment/Network parameter >
Parameters are set
by reflecting them
to the project.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
< Multiple CPU parameter >
QCPU
(CPU No. 1)
Motion controller (CPU No. 2)
Multiple CPU parameter of CPU No. 1
Utilize
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
Multiple CPU parameter of CPU
No. 2 and other CPUs
1 - 5
Page 22
iQ Works
1 OVERVIEW
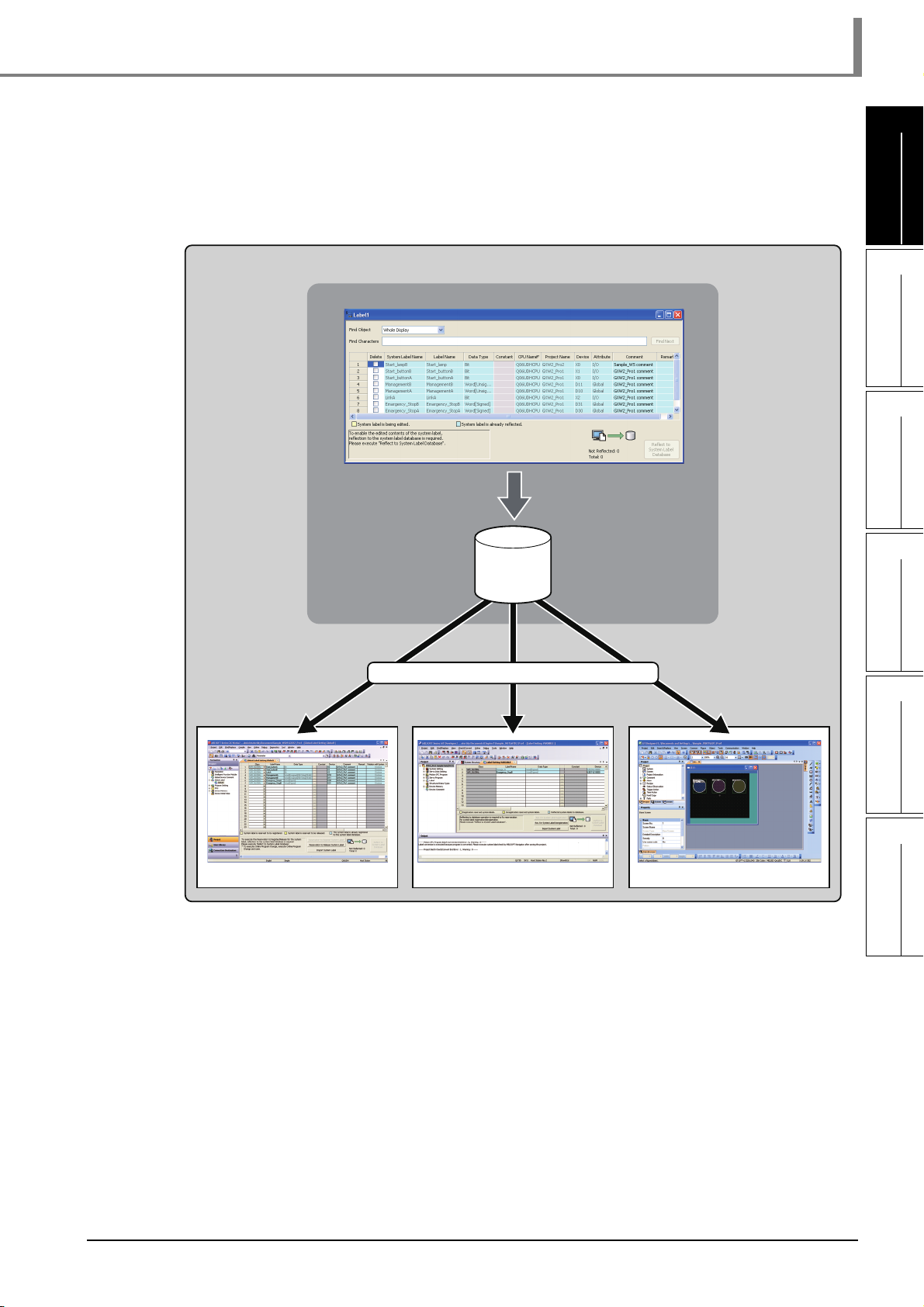
■ Improved programming efficiency using system labels
System labels are labels that can be used in any project within the workspace (within the
equipment configured in the network configuration diagram or module configuration diagram).
Programming (drawing) efficiency is improved by opening devices of programmable controller
projects and motion controller projects as system labels, and sharing them with multiple projects.
As the device assignment settings are changed in batch, device assignment changes are not
necessary on other projects or graphics.
For using system labels, refer to the following chapter.
Chapter 4
< Workspace >
System labels
(Valid within workspace)
< Programmable controller project >
Global labels
(Valid within project)
[Program (MAIN)]
Local labels
(Valid within program)
[Program (SUB)]
Local labels
(Valid within program)
< Programmable controller project >
Global labels
(Valid within project)
[Program (MAIN)]
Local labels
(Valid within program)
< GOT project >
< Motion controller project >
Labels
(Valid within project)
To use system labels in iQ Platform supporting engineering environment MELSOFT iQ Works,
utilize system labels registered in MELSOFT Navigator from projects (Top-down design method),
or register global labels defined in projects as system labels (Bottom-up design method).
1 - 6
Page 23
1.2 Features
● Top-down design method
Design system labels for accessing GOT or communicating between equipment after designing
network configuration in the upstream design.
In top-down design method, register system labels using MELSOFT Navigator, import them to
global labels of controller projects, and assign devices.
< Workspace >
MELSOFT Navigator
Register system labels
System label
database
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Programmable controller project
Use system labels in controller projects
Motion controller project GOT project
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
1 - 7
Page 24
iQ Works
1 OVERVIEW
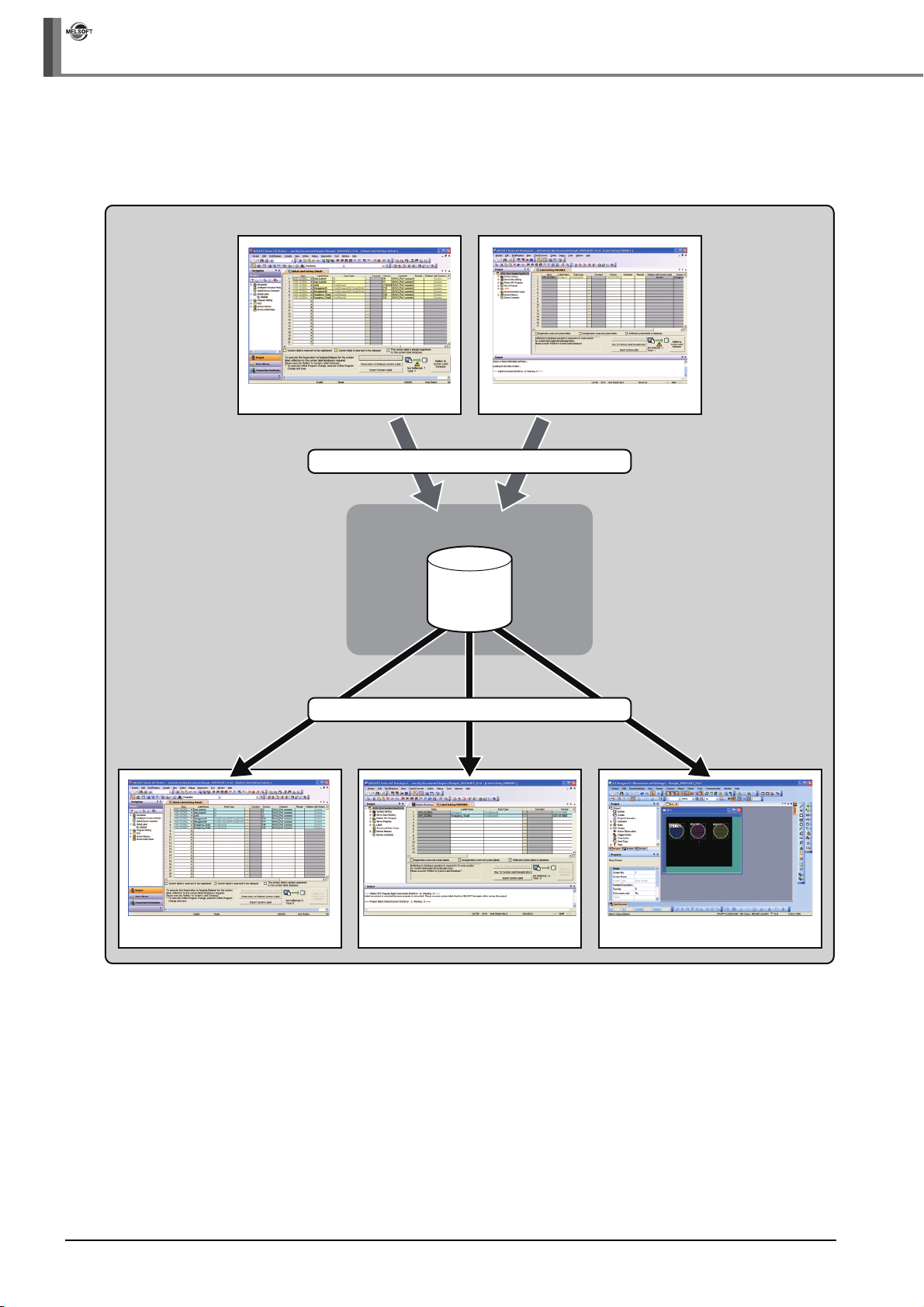
● Bottom-up design method
Design system labels for accessing GOT by using global labels which are registered in controller
projects as system labels, for a such case when configuring system by utilizing existing projects.
< Workspace >
Programmable controller project Motion controller project
Register global labels as system labels
Programmable controller project
MELSOFT Navigator
System label
database
Utilize system labels
Motion controller project GOT project
1 - 8
Page 25
1.2 Features
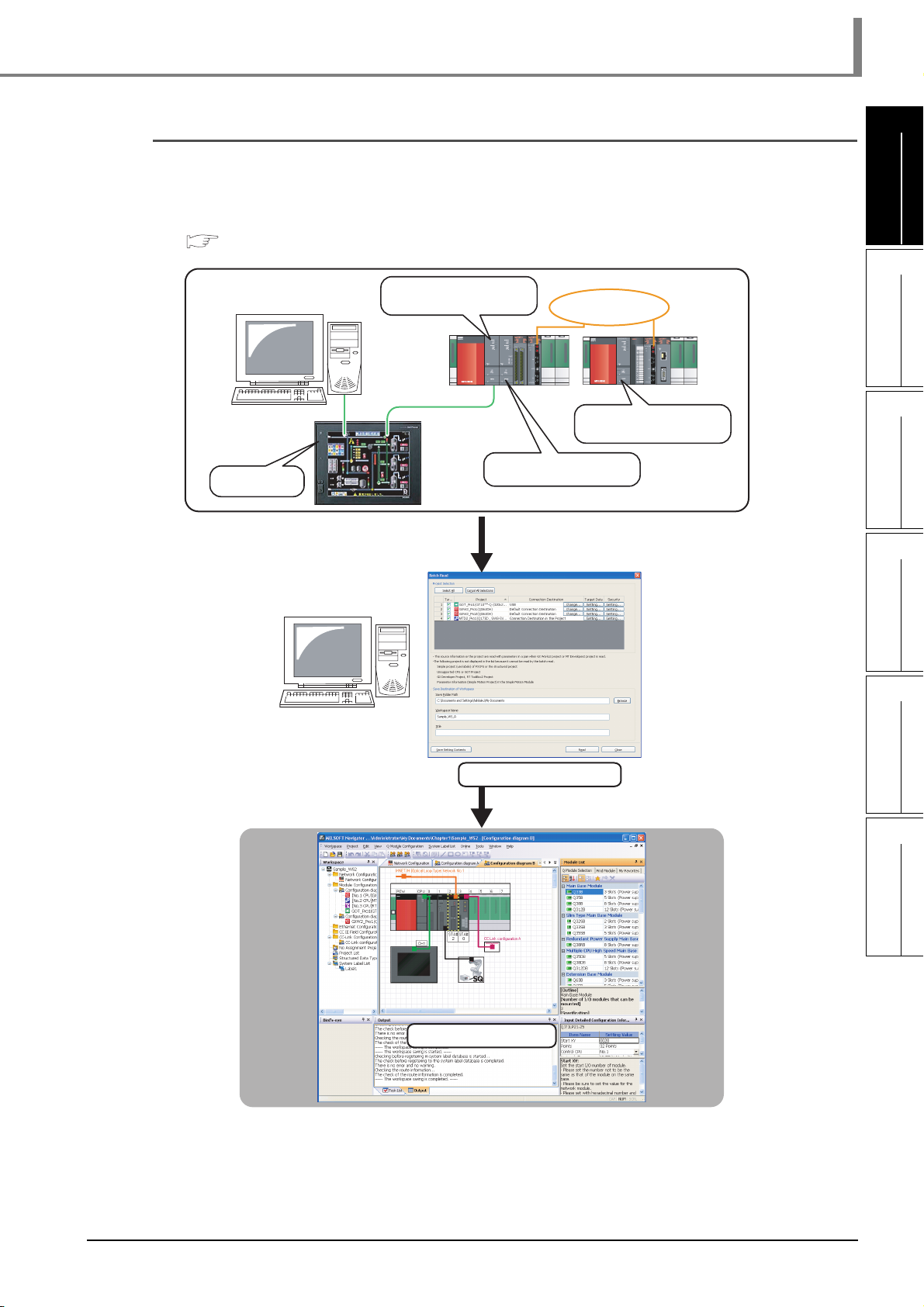
■ Simplified data backup operation
All controller projects in the workspace can be read and saved in batch without activating
respective engineering software (GX Works2, MT Developer2, and GT Designer3).
For the batch read function, refer to the following chapter.
Chapter 5
Programmable controller
GOT project
project
Motion controller project
MELSECNET/H
Programmable controller
project
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Create backup data in batch
MELSOFT Navigator
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
1 - 9
Page 26
iQ Works
1 OVERVIEW
■ Improved programming efficiency by linking with motion controller programs
A motion controller program, which corresponds to the motion dedicated programmable controller
instruction selected in the sequence program, can be activated by a simple mouse operation. This
function significantly improves programming efficiency.
For the program jump function, refer to the following chapter.
Chapter 6
Activate the programmable
controller project
The motion controller project
corresponds to the selected
motion dedicated programmable
controller instruction is activated.
1 - 10
Page 27

2 SCREEN CONFIGURATION
This chapter explains the screen configuration of MELSOFT Navigator.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
2.1 Screen Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
2 - 1
Page 28

iQ Works
2 SCREEN CONFIGURATION
2.1 Screen Configuration
The following explains the screen configuration.
Screen display
Title bar
Menu bar
Toolbar
Workspace
window
Configuration window
Bird's-eye
window
Status bar
Module Configuration
window
Output window
Task List window
Network Configuration
window
Module List
window
Input Detailed
Configuration
Information
window
Result of Power Supply Capacity and I/O Points Check window
Display contents
Name Description
Title bar Displays a title of product name, workspace path, and active window.
Menu bar Displays items of the basic menu.
Toolbar Displays tool buttons for functions executed frequently.
Workspace window Displays objects managed in a workspace in tree format.
Bird’s-eye window Displays a bird’s-eye view of the Network Configuration window.
Module Configuration window
Network Configuration window Set graphical network configuration.
Configuration window Set configurations and display them graphically.
Module List window Displays modules used in Q series/L series/FX series in list form.
Input Detailed Configuration
Information window
Output window
Task List window
Result of Power Supply Capacity
and I/O Points Check window
Status bar Displays information about the selected project.
Set details of graphical Q series/L series/FX series module configurations which are
allocated in the network configuration diagram.
Set I/O assignment and network parameters required in MELSOFT Navigator.
Displays messages and log outputs being processed in the parameter reflection process in
list form.
Displays a result of system configuration check, power supply capacity and I/O points
check or system label consistency check in list form.
Displays a result of power supply capacity and I/O points check.
2 - 2
Page 29

Help information of MELSOFT iQ Works can be displayed by pressing the key.
2.1 Screen Configuration
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
2 - 3
Page 30

iQ Works
2 SCREEN CONFIGURATION
MEMO
2 - 4
Page 31

3 OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
1
OVERVIEW
2
This chapter explains the methods for creating workspaces and system configurations using MELSOFT
Navigator.
3.1 Procedure of MELSOFT Navigator from Start to End . . . . . . 3-2
3.2 Starting MELSOFT Navigator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3.3 Creating Workspaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
3.5 Creating Projects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-30
3.6 Setting Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-38
3.7 Checking System Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-47
3.8 Editing Projects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-49
3.9 Reading/Writing/Verifying Controller Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-53
3.10 Saving Workspaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-56
3.11 Printing Workspaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-58
3.12 Closing Workspaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-59
3.13 Exiting MELSOFT Navigator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-60
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
3 - 1
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
Page 32

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.1 Procedure of MELSOFT Navigator from Start to End
This section explains the procedure of MELSOFT Navigator from start to end.
Start
Start MELSOFT Navigator
Create a workspace
Create a system configuration diagram
Create module configuration diagrams
Create a network configuration diagram
Create a CC-Link configuration
Create projects
Create new projects
Allocate the projects to the controllers
Set parameters
Check the system configuration
Check the system configuration
Check the power supply capacity and I/O points
Save the created workspace
Print the project
Close the workspace
*1
Edit the created projects
Edit the projects
Utilize an existing project
Perform controller data read/write/verification
3 - 2
Exit MELSOFT Navigator
Complete
*1 : Not supported by FXCPU.
Do not change the storage location and names of folders/files of a created workspace/project using the application
such as Windows
®
Explorer.
Page 33

3.2 Starting MELSOFT Navigator
This section explains a method for starting MELSOFT Navigator.
3.2 Starting MELSOFT Navigator
1
Select
1. Start MELSOFT Navigator from
Windows [Start] menu.
2. MELSOFT Navigator is activated.
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
●Double-clicking the icon on the desktop can also start MELSOFT Navigator.
Double-click the MELSOFT
Navigator icon.
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3 - 3
Page 34

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.3 Creating Workspaces
This section explains a method for creating a new workspace.
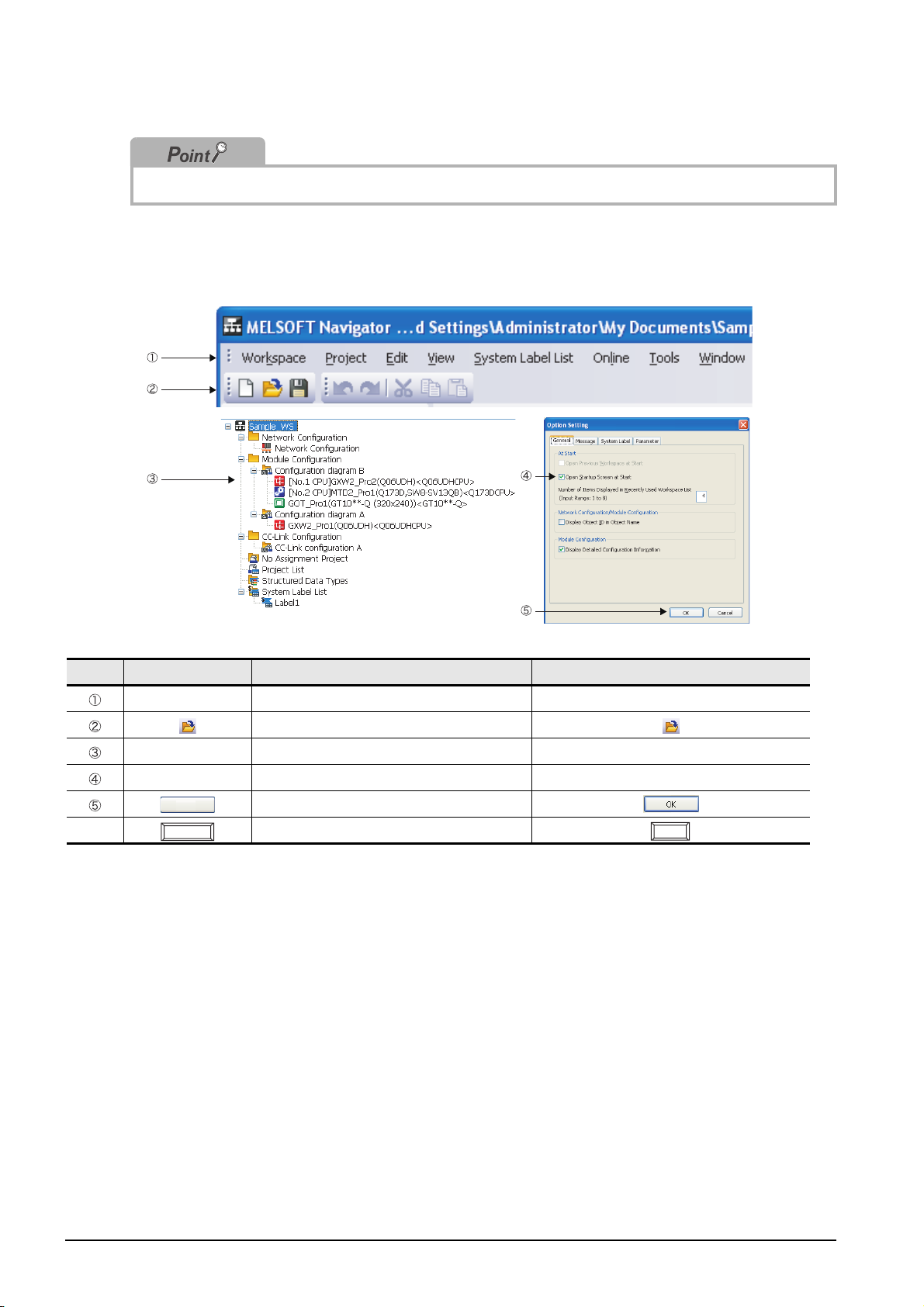
Select
1. Select [Workspace] ⇒ [New] ( ) in the
menu bar to display the "New
(Workspace)" dialog box.
2. Set "Save Folder Path", "Workspace
Name", and "Title" for the new
workspace.
After setting the items, click the
button.
Setting example
• Save Folder Path : C:\Documents and
Settings\
Administrator\
My Documents
• Workspace Name: Sample_WS
• Title (option) : Sample Data
(To the next page)
3. The "Choose a Default Configuration"
dialog box is displayed.
Select "Create Module Configuration" and
click the button.
Setting example
• Configuration : Q Series
Module Configuration
4. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button.
3 - 4
Page 35

3.3 Creating Workspaces
(From the previous page)
● Opening existing workspaces
Open an existing workspace by following the procedure below.
Select
5. The new workspace is created.
1. Select [Workspace] ⇒ [Open] ( )
in the menu bar to display the
"Open (Workspace)" dialog box.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
2. Select "Save Folder Path" and
"Workspace" for the workspace to
be opened.
The workspace folder copied by the
®
application such as Windows
can be selected.
After selecting the items, click the
button to open the workspace.
Setting example
• Save Folder Path : C:\Documents and
Settings\
Administrator\
My Documents
• Workspace Name: Sample_WS
Explorer
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3 - 5
Page 36

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
● Creating workspaces for motion system using templates
Workspaces for motion system can be created from templates consist of a combination of programmable controller
CPU and motion controller, which are used for multiple CPU system configuration.
The following shows the procedure to create a workspace for motion system using a template.
Select
1. Select [Tools] ⇒ [Motion Dedicated
Device Setting Support] in the menu
bar to display the "Select Motion
System Template" dialog box.
2. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button to display the "Select
Motion System Template" dialog box.
3. Select a workspace name in "Select
Template Workspace", and click the
button.
The "Motion Dedicated Device Setting
Support" dialog box is displayed.
Click
4. Set "Save folder path" and
"Workspace name" for the template
workspace.
After setting the items, click the
button.
Setting example
• Save Folder Path : C:\Documents and
Settings\
Administrator\
My Documents
• Workspace Name: WS_tmp1
3 - 6
(To the next page)
Page 37

(From the previous page)
3.3 Creating Workspaces
1
5. The workspace for motion system is
displayed.
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3 - 7
Page 38

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
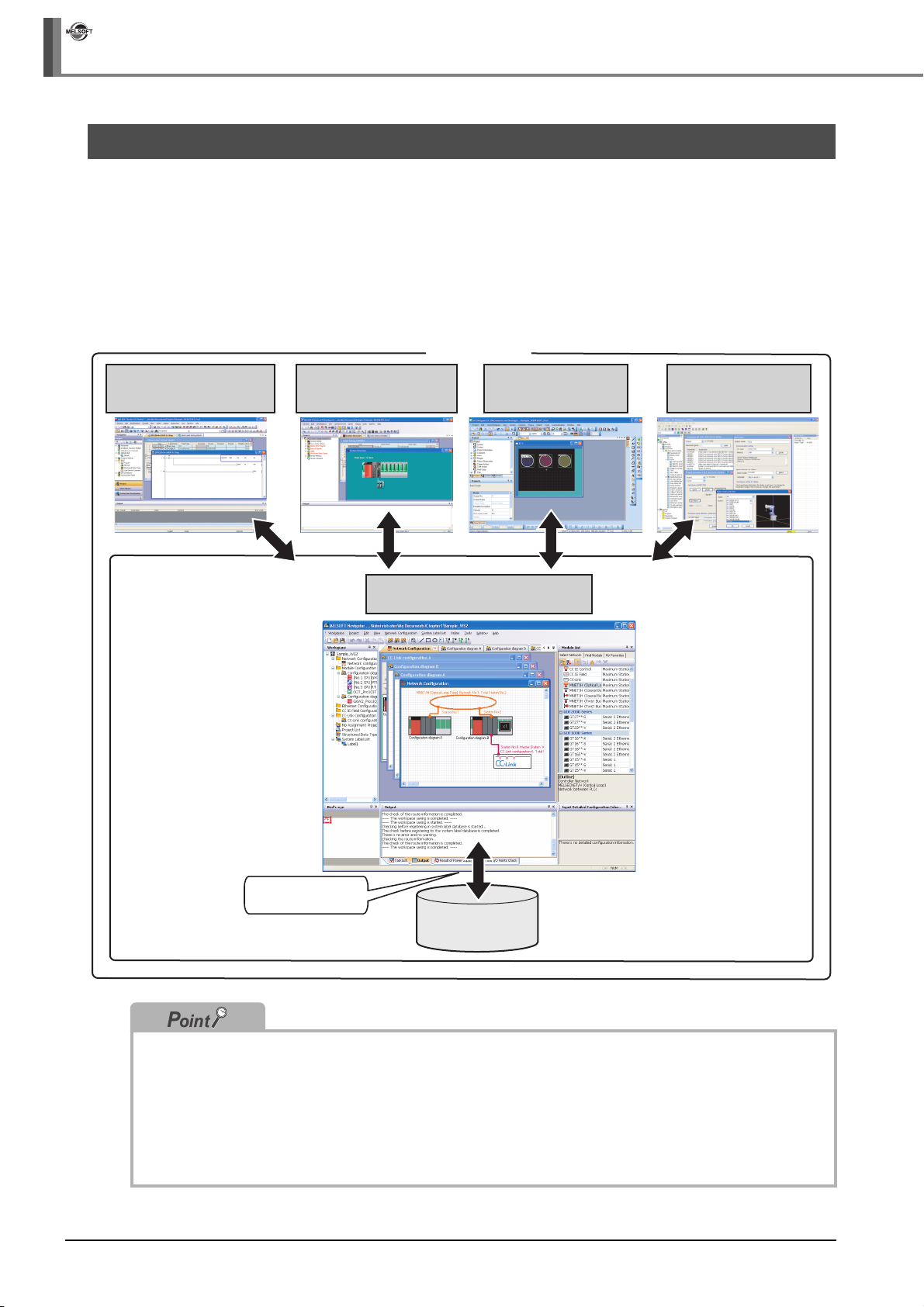
3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram
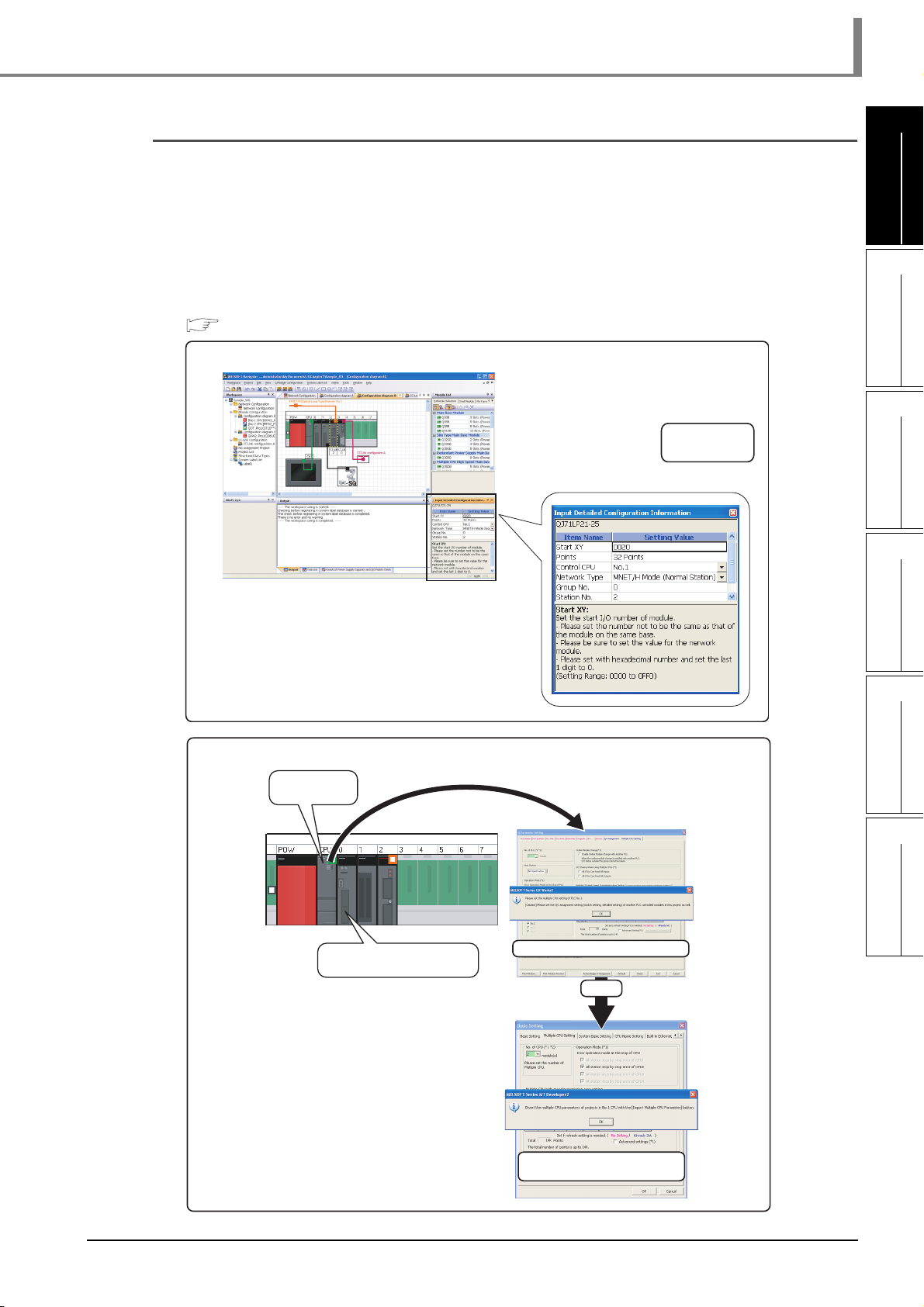
This section explains a method for creating a system configuration diagram.
Created module configuration diagrams are reflected to the network configuration diagram.
3.4.1 System configuration to be created
Create the following system configuration diagram.
< Configuration diagram A >
Base unit (Q35B)
QCPU
(Q62P)
Power supply
< Configuration diagram B >
Power supply
GOT
(GOT1000)
(Q06UDHCPU)
Base unit (Q38DB)
QCPU
(Q64P)
(Q06UDHCPU)
<CC-Link configuration A>
(QX40)
Input module
(QJ71LP21-25)
Network module
MELSECNET/H
(QH42P)
I/O module
Motion CPU
(Q173DCPU)
(Empty)
(Empty)
(Empty)
Station No. 1: Control station
Station No. 2: Normal station
(Empty)
(Empty)
(QJ61BT11N)
Master module
(QJ71LP21-25)
Network module
(Empty)
Module configuration diagrams
(Empty)
(AJ65SBTB1-8D)
CC-Link configuration
3 - 8
Remote I/O
station
3.4.1 System configuration to be created
Remote device
station
(AJ65BT-64DAV)
Remote device
(FR-A720-0.4K)
station
Network configuration diagram
Page 39

3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram
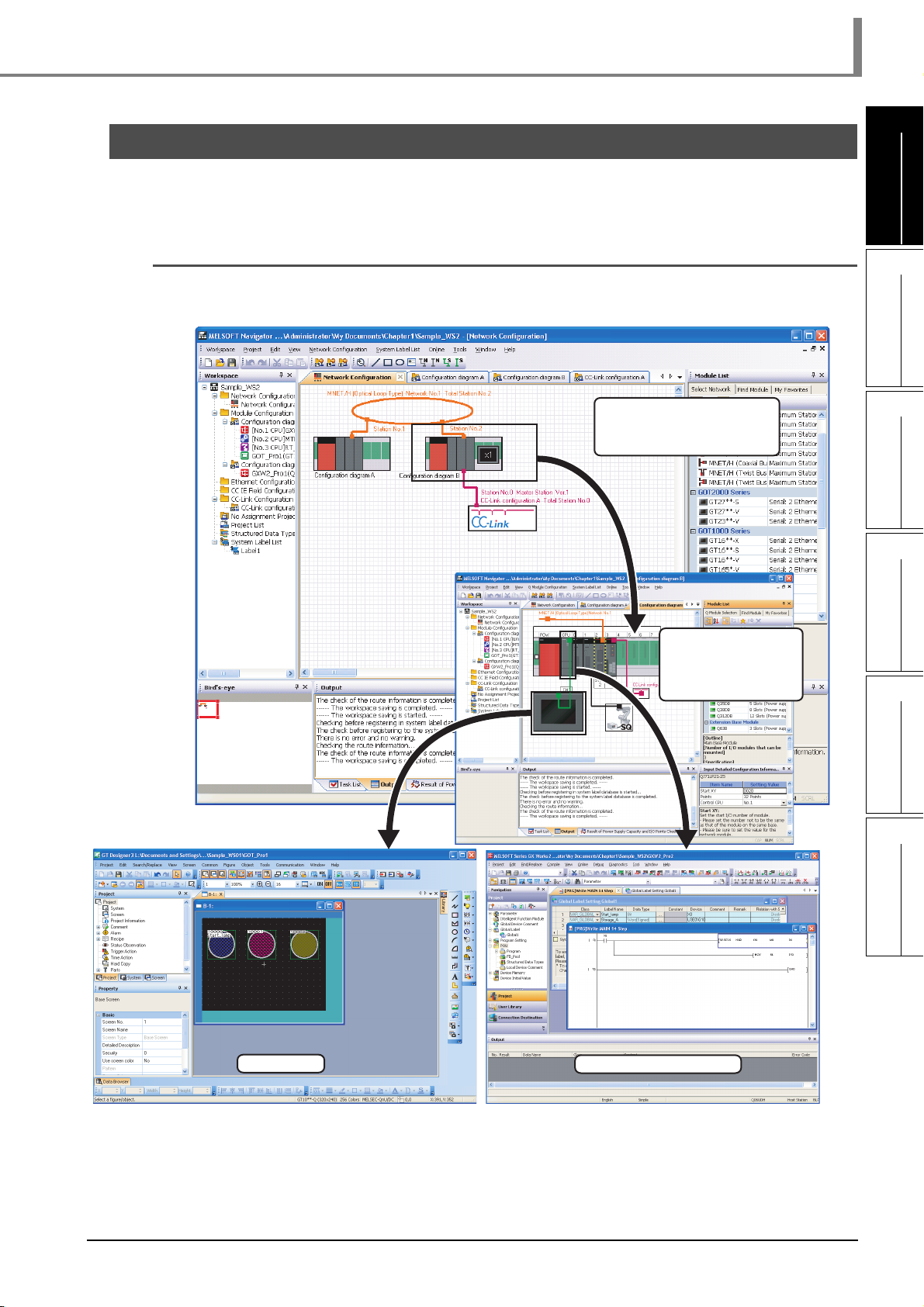
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams
Create module configuration diagrams by placing modules on the Module Configuration window.
1. Right-click "Q Module Configuration"
on the Workspace window, and select
[Module Configuration] ⇒ [Rename] in
the shortcut menu.
Select
2. Enter "Configuration diagram A" to
change the module configuration
diagram name.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Drag & drop
Drag & drop
3. Select the base unit ( ) from the
Module List window, and drag and drop
it onto the Module Configuration
window.
4. Select the power supply module
( ) from the Module List window,
and drag and drop it onto the base unit.
5. Select modules from the Module List
window, and drag and drop them onto
the base unit following the same
procedure in the step 4, and complete
the creation of "Configuration diagram
A".
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
(To the next page)
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams
3 - 9
Page 40

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
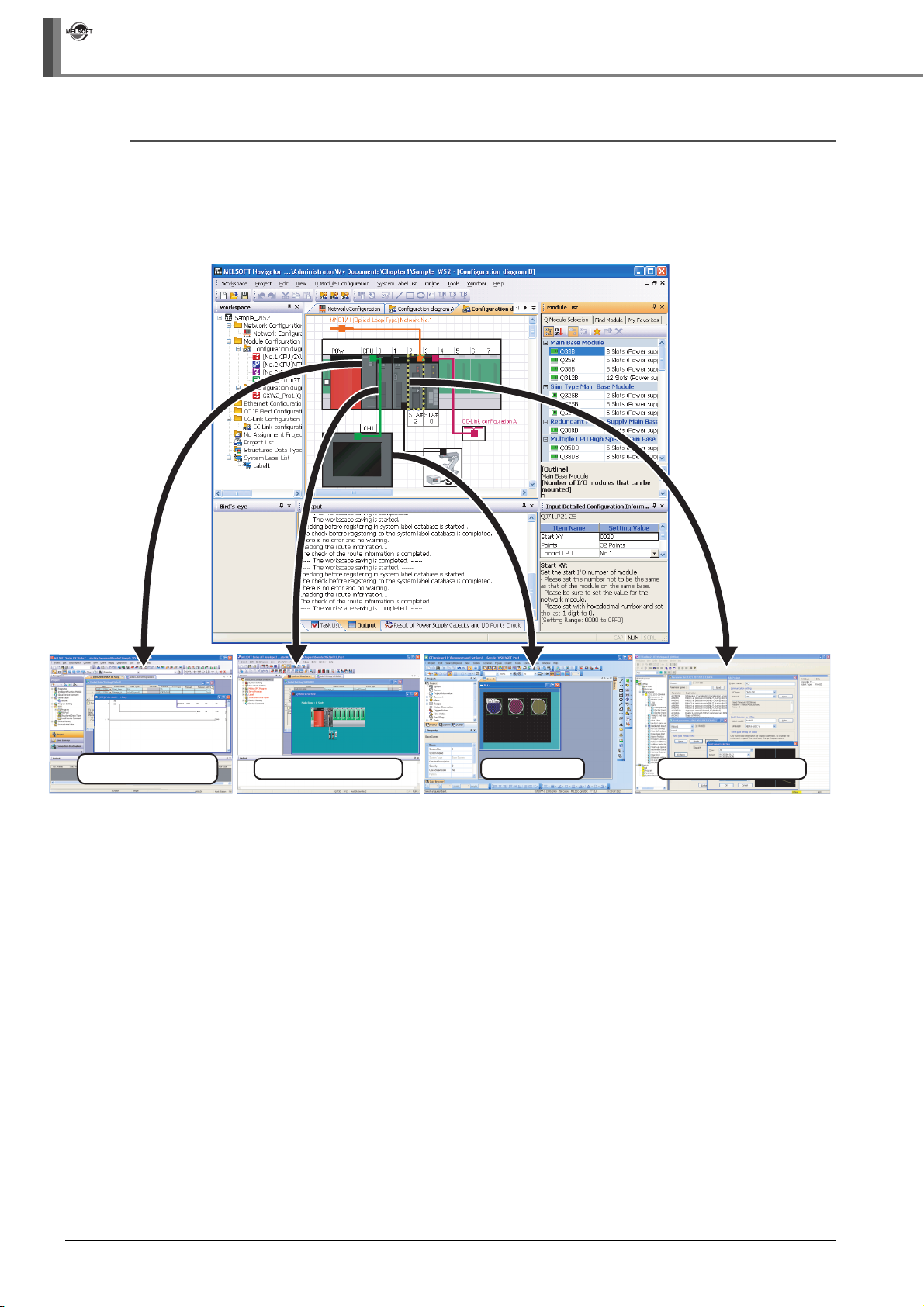
(From the previous page)
6. Select [Workspace] ⇒ [System
Configuration] ⇒ [New] ⇒ [Q Series
Module Configuration], and create a
Select
new module configuration diagram.
7. Change the module configuration name
to "Configuration diagram B" following
the same procedure in the step 1 and
step 2.
Drag & drop
8. Select modules from the Module List
window, and drag and drop them onto
the base unit following the same
procedure in the step 3 and step 4.
9. Select the GOT unit ( ) from
the Module List window, and drag and
drop it onto the Module Configuration
window.
10. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button.
3 - 10
(To the next page)
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams
Page 41

(From the previous page)
Drag & drop
Drag & drop
3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram
11. Select Serial Cable ( ) from
the Module List window, and drag and
drop it onto the connection port of the
GOT unit.
12. Drag and drop the edge of connection
line to the connection port of the
connection target CPU module.
The GOT unit is connected to the CPU
module.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams
3 - 11
Page 42

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
● Mounting modules
• When a module is dragged onto the base unit, the mountable area of the base unit is displayed in light green as
shown below.
Mountable slots
• If a module is not mounted properly, the whole module is displayed in pink as shown below.
● Connection lines
When a connection line is dragged and dropped onto the Module Configuration window, the connectable ports of
each controller are displayed as shown below.
Connectable ports
Drag & drop
● Connection points of GOT unit
By setting parameters on the Input Detailed Configuration Information window, I/F type and number of
connectable points of GOT unit can be changed.
3 - 12
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams
Page 43

3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram
■ Creating module configuration diagrams for L series
For L series, create module configuration diagrams refer to this section.
Basically, L series module configurations can be created in a similar way to Q series.
For operations that differ from Q series, refer to the Point in this section.
● System configuration to be created
Create the following system configuration.
<L module configuration diagram A>
(L61P)
Power supply
Ethernet (Network No.1)
LCPU
(L02CPU)
IP address :192.168.3.38
Input module
er (L6EC)
(LX40C6)
END cov
Module configuration diagrams
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
<L module configuration diagram B>
(L61P)
Power supply
GOT
(GOT1000)
(L6ADP-R2)
RS-232 adaptor
IP address :192.168.3.39
LCPU
(L02CPU)
L6EC)
(LX40C6)
Input module
END cover (
Network configuration diagram
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams
3 - 13
Page 44

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
● Creating module configuration diagrams
Create module configuration diagrams by placing modules on the Module Configuration window.
1. Right-click "Module Configuration" on
the Workspace window, and select
[Module Configuration] ⇒ [New] ⇒
[L Series Module Configuration] in the
Select
shortcut menu.
2. Right-click "L Module Configuration "
on the Workspace window, and select
[Module Configuration] ⇒ [Rename] in
the shortcut menu.
Drag & drop
Select
3. Enter "L module configuration diagram
A" to change the module configuration
diagram name.
4. Select modules from the Module List
window, and drag and drop them onto
the Module Configuration window
following the same procedure in the
step 4 through step11 in section 3.4.2.
3 - 14
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams
Page 45

3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram
● Creating L series module configurations
When creating workspaces, select "L Series Module Configuration" in the "Choose a Default Configuration" dialog
box.
For creating workspaces, refer to the following section.
3.3 Creating Workspaces
● Mounting modules
When a module is dragged onto the Module Configuration window, the mountable areas are displayed in light blue
as shown below.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
Mountable areas
● Deleting modules
When a module is deleted from the Module Configuration window, the modules next to the deleted module are
connected automatically as shown below.
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
Delete
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams
3 - 15
Page 46

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
● Mounting display module
Display module can be mounted on L series CPU modules.
Mount display module by following procedure below.
1. Right click the controller on the
Module Configuration window, and
select [Property] in the shortcut
menu.
Select
2. The "Properties" dialog box is
displayed.
Select "Installed" in the Display Module
tab and select the model name to be
mounted from "Select Model Name"
Setting example
• Select Model Name :L6DSPU
3. Click the button.
Display module is mounted on the
controller.
3 - 16
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams
Page 47

3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram
■ Creating module configuration diagrams for FX series
For FX series, create module configuration diagrams refer to this section.
Basically, FX series module configurations can be created in a similar way to Q series.
For operations that differ from Q series, and for main units, special blocks, and special adapters that
can be used in FX series, refer to the Point in this section.
● System configuration to be created
Create the following system configuration.
<FX Module configuration diagramA>
3UCPU)
FXCPU
(FX
IP address :192.168.3.38
Ethernet
special function block
Module configuration diagram
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Ethernet (Network No.1)
<FX Module configuration diagramB>
FXCPU
(FX3UCPU)
IP address :192.168.3.39
GOT
(GOT1000)
Ethernet
special function block
Network configuration diagram
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams
3 - 17
Page 48

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
● Creating module configuration diagrams
Create module configuration diagrams by placing modules on the Module Configuration window.
1. Right-click "Module Configuration" on
the Workspace window, and select
[Module Configuration] ⇒ [New] ⇒
[FX Series Module Configuration] in the
Select
shortcut menu.
2. Right-click "FX Module Configuration"
on the Workspace window, and select
[Module Configuration] ⇒ [Rename] in
the shortcut menu.
Select
Drag & drop
3. Enter "FX module configuration
diagramA" to change the module
configuration diagram name.
4. Select modules from the Module List
window, and drag and drop them onto
the Module Configuration window
following the same procedure in the
step 4 through step11 in section 3.4.2.
3 - 18
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams
Page 49

3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram
● Creating FX series module configurations
When creating workspaces, select "FX Series Module Configuration" in the "Choose a Default Configuration"
dialog box.
For creating workspaces, refer to the following section.
3.3 Creating Workspaces
● Mounting modules
When a module is dragged onto the Module Configuration window, the mountable areas are displayed in light blue
as shown below.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
Mountable area
● Supported CPU modules of FX series in MELSOFT Navigator
The following CPU modules of FX series are supported in MELSOFT Navigator.
• Main units
FX
3S, FX3G, FX3GC, FX3U, FX3UC
• Special block
Ethernet special function block (FX-ENET series)
• Special adapter
Ethernet communication special adapter (FX
For FX series, special blocks and special adapters are mounted to a main unit which combines power supply,
CPU, and I/O module. However, the following blocks and units can not be mounted: special blocks and special
units which do not contain related project or configuration software, and extension blocks which do not support a
function to check power supply capacity and I/O points.
● Parameters of special adapters
The parameters of special adapters can be set on the Input Detailed Configuration Information window.
The setting content is reflected to the parameter of a programmable controller project by performing parameter
reflection. For details of the parameter settings, refer to the following section.
Section 3.6 Setting Parameters
● Displaying module list window
The model name of special blocks of FX series compatible with MELSOFT Navigator are displayed on the Module
List window when the related software
When using special blocks install the related software
*1: The related software of FX-ENET series may be downloaded from MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC FA Global Website.
For the method of obtaining the related software, contact the store where you purchased the product.
are installed.
3U-ENET-ADP)
*1
of each module in advance.
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.4.2 Creating module configuration diagrams
3 - 19
Page 50

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.4.3 Creating network configuration diagrams
Create a network configuration diagram by placing and connecting the module configuration diagrams
on the Network Configuration window.
Double click
Drag & drop
1. Double-click "Network Configuration"
on the Workspace window to open the
Network Configuration window.
All module configuration diagrams created
on the Module Configuration windows are
displayed.
2. Drag and drop the module
configuration diagrams to desired
positions.
Drag & drop
3. Select MNET/H (Optical Loop Type)
( ) from the Module
List window, and drag and drop it onto
the Network Configuration window.
Drag & drop
(To the next page)
4. Select CC-Link ( ) from the
Module List window, and drag and drop
it onto the Network Configuration
window.
CC-Link configuration is added on the
Workspace window.
3 - 20
3.4.3 Creating network configuration diagrams
Page 51

3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram
(From the previous page)
Drag & drop
Drag & drop
5. Select Network Cable ( )
from the Module List window, and drag
and drop it onto the Network
Configuration window.
6. Drag and drop the edge of connection
line to the connection point of the
connection target module configuration
diagram.
CC-Link configuration is connected to the
module configuration diagram.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
● Adding Ethernet configuration
When adding Ethernet configuration by dragging and dropping from Module Configuration window onto the
Network Configuration window, select an Ethernet configuration from "Component Device"
Drag & drop
● Network Configuration window
• A Module Configuration window opens by double-clicking the module configuration diagram/CC-Link
configuration on the Network Configuration window/CC-Link configuration window.
For Ethernet/CC IE Field, each configuration window can be opened with the same operation as above.
• The whole system created on the Network Configuration window can be reviewed on the Bird’s-eye window.
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.4.3 Creating network configuration diagrams
3 - 21
Page 52

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.4.4 Creating CC-Link configuration diagrams
Create a configuration by placing modules on the CC-Link Configuration window.
1. Double-click "CC-Link Configuration"
on the Workspace window to open the
CC-Link Configuration window.
Double click
2. Right-click "CC-Link Configuration" on
the Workspace window, and select
[CC-Link Configuration] ⇒ [Rename] in
the shortcut menu.
Select
Drag & drop
3. Enter "CC-Link configuration A" to
change the CC-Link configuration
name.
4. Select AJ65SBTB1-8D ( )
from the Module List window, and drag
and drop it onto the CC-Link
Configuration window.
CC-Link configuration is added on the
Module configuration window.
5. Select modules to be connected from
the Module List window, and drag and
drop them onto the CC-Link
Configuration window following the
same procedure in the step 4.
3 - 22
3.4.4 Creating CC-Link configuration diagrams
Page 53

3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram
● Module display on configuration window
Check that the network modules on the Module Configuration window are connected to the network. If not, the
modules are not displayed on the configuration window.
● Detecting actual system configuration
The actual system configuration can be reflected to the CC-Link Configuration window by performing one of the
following operations.
• Click the button on the CC-Link Configuration window.
• Select [Online] ⇒ [Detect Now].
For the automatic detection of connected devices, refer to the following manual.
iQ Sensor Solution Reference Manual
● Verifying CC-Link configuration against the actual system configuration
The CC-Link configuration can be verified against the actual system configuration by performing one of the
following operations.
• Click the button on the CC-Link Configuration window.
• Select [Online] ⇒ [Verification of the Configuration with the Connected Module].
For the verification of the configuration with the connected modules, refer to the following manual.
iQ Sensor Solution Reference Manual
● Deleting CC-Link modules
The following shows a method for deleting CC-Link modules from CC-Link Configuration window.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
Select
Select
1. Select "Station No." or "Model
Name" of the CC-Link module to be
deleted.
2. Select [Edit] ⇒ [Delete] in the menu
bar to delete CC-Link module.
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.4.4 Creating CC-Link configuration diagrams
3 - 23
Page 54

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.4.5 Creating AnyWireASLINK configuration diagrams
Create a configuration by placing modules on the AnyWireASLINK Configuration window.
1. Select AnyWireASLINK master module
(QJ51AW12AL) from the Module List
window, and drag and drop it onto the
Module Configuration window.
The AnyWireASLINK configuration
Drag & drop
diagram is created.
2. Double-click "AnyWireASLINK
Configuration" on the Workspace
window to open the AnyWireASLINK
Configuration window.
Double click
3. Select the AnyWireASLINK slave
Drag & drop
4. Set the address to the added slave
*1: The address of the slave module can be set automatically.
For the address auto-input, refer to the following manual.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Intelligent Function Module)
module (B281PB-02U-CC20) from the
Module List window, and drag and drop
it onto the AnyWireASLINK
Configuration window.
The slave module is added on the "list of
modules", and the added slave module is
displayed on the "device map area".
module.
For the general-purpose AnyWireASLINK
module, set the I/O type, address, and
number of occupied I/O points.
*1
3 - 24
3.4.5 Creating AnyWireASLINK configuration diagrams
Page 55

3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram
● Detecting actual system configuration
The actual system configuration can be reflected to the AnyWireASLINK Configuration window by performing one
of the following operations.
• Click the button on the AnyWireASLINK Configuration window.
• Select [Online] ⇒ [Detect Now].
For the automatic detection of connected devices, refer to the following manual.
iQ Sensor Solution Reference Manual
● Verifying AnyWireASLINK configuration against the actual system configuration
The AnyWireASLINK configuration can be verified against the actual system configuration by performing one of
the following operations.
• Click the button on the AnyWireASLINK Configuration window.
• Select [Online] ⇒ [Verification of the Configuration with the Connected Module].
For the verification of the configuration with the connected modules, refer to the following manual.
iQ Sensor Solution Reference Manual
● Deleting AnyWireASLINK slave modules
The following shows a method for deleting AnyWireASLINK slave modules from AnyWireASLINK Configuration
window.
1. Select the row of the
AnyWireASLINK slave module to be
deleted. (Multiple rows can be
Select
selected.)
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Select
2. Select [Edit] ⇒ [Delete] in the menu
bar to delete AnyWireASLINK slave
module.
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.4.5 Creating AnyWireASLINK configuration diagrams
3 - 25
Page 56

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.4.6 Creating Ethernet configuration diagrams
Create a configuration by placing modules on the Ethernet Configuration window.
1. Right-click "Ethernet Configuration" on
the Workspace window, and select
[Ethernet Configuration] ⇒ [Rename] in
the shortcut menu.
Select
2. Enter "Ethernet configuration A" to
change the Ethernet configuration
name.
Double click
Drag & drop
3. Select an Ethernet built-in CPU to be
set as an own station and IP address of
Ethernet module.
4. Double-click "Ethernet Configuration"
on the Workspace window to open the
Ethernet Configuration window.
5. Select an Ethernet device
Module List window, and drag and drop
it onto the Ethernet Configuration
window.
*1
from the
3 - 26
*1: For the parameter processing of Ethernet devices, refer to the following manual.
iQ Sensor Solution Reference Manual
3.4.6 Creating Ethernet configuration diagrams
Page 57

3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram
● Module display on the configuration window
Check that the network modules on the Module Configuration window are connected to the network. If not, the
modules are not displayed on the configuration window.
● Detecting actual system configuration
The actual system configuration can be reflected to the Ethernet Configuration window by performing one of the
following operations.
• Click the button on the Ethernet Configuration window.
• Select [Online] ⇒ [Detect Now]
For the automatic detection of connected devices, refer to the following manual.
iQ Sensor Solution Reference Manual
● Reflecting communication settings of Ethernet devices
The communication settings of Ethernet devices can be reflected by performing the following operation.
• Select [Online] ⇒ [Communication Setting Reflection of Ethernet Device]
For the Communication Setting Reflection of Ethernet Device function, refer to the following manual.
iQ Sensor Solution Reference Manual
● Deleting Ethernet devices
The following shows a method for deleting Ethernet devices from Ethernet Configuration window.
1. Select the row of the Ethernet
device to be deleted. (Multiple rows
Select
can be selected.)
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Select
2. Select [Edit] ⇒ [Delete] in the menu
bar to delete Ethernet device.
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.4.6 Creating Ethernet configuration diagrams
3 - 27
Page 58

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.4.7 Creating CC IE Field configuration diagrams
Create a configuration by placing modules on the CC IE Field Configuration window.
1. Double-click "CC IE Field
Configuration" on the Workspace
window to open the CC IE Field
Configuration window.
Double click
Select
CC IE Field configuration diagram
created.
*1
is
2. Right-click "CC IE Field Configuration"
on the Workspace window, and select
[CC IE Field Configuration] ⇒
[Rename] in the shortcut menu .
3. Enter "CC IE Field configuration A" to
change the CC IE Field configuration
name.
4. Select a slave station
*1
from the
Module List window, and drag and drop
it onto the CC IE Field Configuration
Drag & drop
*1: For the parameter processing of slave station, refer to the following manual.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
● Module display on configuration window
Check that the network modules on the Module Configuration window are connected to the network. If not, the
modules are not displayed on the configuration window.
window.
3 - 28
3.4.7 Creating CC IE Field configuration diagrams
Page 59

3.4 Creating System Configuration Diagram
● Deleting slave stations of CC IE Field
The following shows a method for deleting slave stations from CC IE Field Configuration window.
1. Select the row of the slave station to
Select
be deleted. (Multiple rows can be
selected.)
2. Select [Edit] ⇒ [Delete] in the menu
bar to delete the slave station.
Select
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.4.7 Creating CC IE Field configuration diagrams
3 - 29
Page 60

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.5 Creating Projects
This section explains the methods for creating project data (programmable controller projects, motion
controller projects, GOT projects).
3.5.1 Creating new projects
■ Programmable controller projects
Create a new programmable controller project.
Select
1. Select [Project] ⇒ [New] ⇒ [GX
Works2 Project] in the menu bar to
display the "New (GX Works2 Project)"
dialog box.
2. Set "Project Name", "Title", "Project
Type", "PLC Series", "PLC Type", and
"Language" for the new project.
After setting the items, click the
button.
Setting example
• Project Name : GXW2_Pro1
• Title (option) : Sample Data
•Project Type
• Use Labels : Yes
• PLC Series : QCPU (Q mode)
• PLC Type : Q06UDH
• Language : Ladder
:
Simple Project
3 - 30
(To the next page)
3.5.1 Creating new projects
Page 61

(From the previous page)
3.5 Creating Projects
1
3. The new project is created.
Double click
Double-click the created project on the
Workspace window.
4. The programmable controller project is
activated.
For editing programmable controller
projects, refer to the following manuals.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating
Manual (Common)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating
Manual (Simple Project)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating
Manual (Structured Project)
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual
(Simple Project)
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual
(Structured Project)
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.5.1 Creating new projects
3 - 31
Page 62

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
■ Motion controller projects
Create a new motion controller project.
1. Select [Project] ⇒ [New] ⇒ [MT
Select
Developer2 Project] in the menu bar to
display the "New (MT Developer2
Project)" dialog box.
2. Set "Project Name", "Title", "CPU
Type", and "OS Type" for the new
project.
After setting the items, click the
button.
Double click
Setting example
• Project Name : MTD2_Pro1
• Title (option) : Sample Data
• CPU Type : Q173D
• OS Type : SW8-SV13QB
3. The new project is created.
Double-click the created project on the
Workspace window.
4. The motion controller project is
activated.
For editing motion controller projects, refer
to the Help function of MT Developer2.
3 - 32
3.5.1 Creating new projects
Page 63

3.5 Creating Projects
■ GOT projects
Create a new GOT project.
Select
1. Select [Project] ⇒ [New] ⇒ [GT
Designer3 Project] in the menu bar to
display the "New (GT Designer3
Project)" dialog box.
2. Set "Series", "GOT Type", and "Project
Name".
After setting the item, click the
button.
Setting example
• Series : GOT1000
• GOT Type : GT10**-Q (320 x 240)
• Project Name : GOT_Pro1
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Double click
3. The new project is created.
Double-click the created project on the
Workspace window.
4. The GOT project is activated.
For editing GOT projects, refer to the
following manuals.
GT Designer3 Version 1 Screen Design
Manual (Fundamentals)
GT Designer3 Version 1 Screen Design
Manual (Functions)
GT Designer3 (GOT2000) Screen Design
Manual
GT Simulator3 Version 1 Operating
Manual
GT SoftGOT1000 Version 3 Operating
Manual
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
GT SoftGOT2000 Version1 Operating
Manual
3.5.1 Creating new projects
3 - 33
Page 64

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
● Copying projects
The following shows a method for copying a project created in the workspace to create a new project.
1. Right-click the project name on the
Workspace window, and select [Add
Project Copy] in the shortcut menu
to display the "Add Project Copy"
dialog box.
2. Enter a project name for the copied
project, and click the button.
Setting example
• Project Name: GXW2_Pro2
3. The copied project is displayed in
the Workspace window.
● Changing project names
The following shows a method for changing a project name of an existing project.
• Right-click the project name on the
Workspace window, and select
[Change Project Name] in the
Right click
Select
● Deleting projects
The following shows a method for deleting a project. Once a project is deleted, it cannot be restored again.
Right click
shortcut menu to change the project
name.
• Right-click the project name on the
Workspace window, and select
[Delete Project] in the shortcut
menu to delete the project.
3 - 34
Select
3.5.1 Creating new projects
Page 65

3.5 Creating Projects
3.5.2 Allocating projects to controllers
Allocate projects in the workspace to controllers on the Module Configuration windows.
■ Allocating projects to controllers
The following figure shows controllers with the allocated projects.
Project name: GXW2_Pro1
< Configuration diagram A >
Base unit (Q35B)
Project name: GXW2_Pro2
QCPU
(Q62P)
Power supply
< Configuration diagram B >
(QX40)
Input module
(Q06UDHCPU)
(QJ71LP21-25)
Network module
MELSECNET/H
(Empty)
(Empty)
(Empty)
Base unit (Q38DB)
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
QCPU
(Q64P)
Power supply
GOT
(GOT1000)
● Allocating projects
A project cannot be allocated to a controller if a PLC type or a CPU type of the created project does not match with
the module name of the controller.
Check the module name of each controller and allocate projects.
Motion CPU
(Q06UDHCPU)
Project name: GOT_Pro1
(QH42P)
I/O module
(Q173DCPU)
(QJ71LP21-25)
Network module
Project name: MTD2_Pro1
(Empty)
(QJ61BT11N)
Master module
(Empty)
(Empty)
(Empty)
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.5.2 Allocating projects to controllers
3 - 35
Page 66

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
■ Batch allocation
Allocate projects in the workspace to all controllers on the Module Configuration windows.
1. Select [Workspace] ⇒ [Allocate Project
With The Controller] in the menu bar to
display the "Allocate Project With The
Controller" dialog box.
Select
Select
Click
2. Select a project name for each
controller.
After selecting the items, click the
button.
Setting example
Module name Project name
Q06UDHCPU GXW2_Pro1: Sample Data
Q06UDHCPU GXW2_Pro2: Sample Data
Q173DCPU MTD2_Pro1: Sample Data
GT10**-Q GOT_Pro1
3. The allocated projects are displayed
under the Module Configuration folder
on the Workspace window.
3 - 36
3.5.2 Allocating projects to controllers
Page 67

3.5 Creating Projects
■ Individual allocation
Allocate a project in the workspace to the controller selected on the Module Configuration window.
1. Right-click the controller on the Module
Configuration window, and select
[Allocate Project With The Controller] in
the shortcut menu to display the
"Allocate Project With The Controller"
dialog box.
Select
Select
Click
2. Select a project name for the selected
controller.
After selecting the item, click the
button.
Setting example
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Module name Project name
Q06UDHCPU GXW2_Pro1: Sample Data
3. The allocated project is displayed
under the Module Configuration folder
on the Workspace window.
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.5.2 Allocating projects to controllers
3 - 37
Page 68

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.6 Setting Parameters
This section explains a method for setting I/O assignment, network parameters, parameters of FX series
special adapters, and multiple CPU parameters for project data (programmable controller project, motion
controller project, GOT project).
■ Setting I/O assignment
I/O assignment for each controller can be set without opening respective parameter setting dialog
boxes.
Click
1. Click the module on "Configuration
diagram B".
The parameters are displayed on the Input
Detailed Configuration Information window.
2. Set the parameters on the Input
Detailed Configuration Information
window.
Setting example
• Start XY : 0000
• Points : 32 points
• Control CPU : CPU No. 2
For setting parameters, refer to user’s
manuals of each CPU.
3 - 38
Page 69

3.6 Setting Parameters
■ Setting network parameters
Network parameters for each controller can be set without opening respective parameter setting dialog
boxes.
Click
1. Click the network module (QJ71LP21-
25) on "Configuration diagram A".
The parameters are displayed on the Input
Detailed Configuration Information window.
2. Set the parameters on the Input
Detailed Configuration Information
window.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Setting example
• Start XY : 0010
• Points : 32 Points
• Control CPU : -
• Network Type : MNET/H Mode
(Control Station)
• Group No. : 0
•Station No. : 1
3. Set the parameters for "Configuration
diagram B" following the same
procedure in the step 1 and step 2.
Setting example
• Start XY : 0020
• Points : 32 Points
• Control CPU : No. 1
• Network Type : MNET/H Mode
(Normal Station)
• Group No. : 0
•Station No. : 2
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
For setting parameters, refer to user’s
manuals of each CPU.
3 - 39
Page 70

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
■ Setting parameters of FX series special adapter
The parameters of special adapters can be set without opening the parameter setting screen of
programmable controller project. The following shows an example when using FX3U-ENET-ADP.
Click
1. Click "FX3U-ENET-ADP" on "FX
module configuration diagram A".
The parameters are displayed on the Input
Detailed Configuration Information window.
2. Set the parameters on the Input
Detailed Configuration Information
window.
Setting example
• Station number: 1
• IP address : 192.168.3.38
• Channel : CH1
3. Set the parameters of "FX module
configuration diagram B" following the
same procedure in the step 1 and step
2.
Setting example
• Station number: 2
• IP address : 192.168.3.39
• Channel : CH1
For the reflection method for the set
parameters to a programmable controller
project, refer to the following section.
■ Reflecting parameters to projects
● Parameter initialization
When "Channel" has already been set to <<PLC System (2)>> tab of PLC parameter in the target program, the
settings of <<PLC System (2)>> tab will be initialized.
To retain the settings in the programmable controller project, backup the project before reflecting the parameters.
3 - 40
Page 71

3.6 Setting Parameters
■ Reflecting parameters to projects
Reflect parameters set in MELSOFT Navigator to projects.
1. Select [Workspace] ⇒ [Parameter] ⇒
Select
2. The message shown on the left is
[Batch Reflect] in the menu bar.
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
3. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button.
4. The parameters are reflected to the
projects.
Error or Warning is displayed when the
reflection result contains an error. Check
the error description on the Task List
window and correct the error.
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3 - 41
Page 72

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
■ Setting multiple CPU parameters
Set multiple CPU parameters by activating the multiple CPU settings of each controller project from
MELSOFT Navigator. Set the parameters on CPU No. 1, and utilize them for CPU No. 2.
The following is an example when utilizing parameters of programmable controller project for a
motion controller project.
For setting parameters on a motion controller project, follow the same procedure as described
below.
1. Select the CPU No. 1 controller on the
Select
Module Configuration window.
Select
2. Select [Q Module Configuration] ⇒
[Parameter] ⇒ [Multiple CPU
Parameter Setting] in the menu bar.
3. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button.
4. GX Works2 is activated and the
message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button.
3 - 42
(To the next page)
Page 73

3.6 Setting Parameters
(From the previous page)
Select
5. The "Q Parameter Setting" dialog box
is displayed.
For setting multiple CPU parameters, refer
to the following manual and function.
QCPU User’s Manual (Multiple CPU
System)
Help function of MT Developer2
6. Select [Project] ⇒ [Save] in the menu
bar of GX Works2.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Select
Select
7. Select the CPU No. 2 controller on the
Module Configuration window
8. Select [Q Module Configuration] ⇒
[Parameter] ⇒ [Multiple CPU
Parameter Setting] in the menu bar.
9. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
(To the next page)
Read the message and click the
button.
3 - 43
Page 74

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
(From the previous page)
10. MT Developer2 is activated and the
message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button.
11. The "Basic Setting" dialog box is
displayed.
Click the button to display
the "Open Project" dialog box.
Click
12. Check that the project name allocated
to the CPU No. 1 is selected, and click
the button.
13. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button to utilize the multiple CPU
parameter of CPU No.1 for CPU No. 2.
3 - 44
Page 75

3.6 Setting Parameters
● Verifying system configuration information with parameters
After parameters are reflected to projects, check for differences between parameters (system configuration
information) set in MELSOFT Navigator and parameters of project assigned to each controller.
1
Select
1. Select [Workspace] ⇒ [Parameter]
⇒ [Batch Verification of System
Configuration Information and
Parameters] in the menu bar.
2. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button.
3. The verification is executed.
Error or Warning is displayed when the
verification result contains an error.
Check the error description on the Task
List window and correct the error.
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3 - 45
Page 76

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
● Setting start XY in batch
Assign start XY consecutively to modules or empty slots in the order of slot number.
Resetting of start XY to each module is no longer required when replacing modules or changing number of points.
1. Select [Q Module Configuration] ⇒
[Start XY Batch Input] in the menu
bar.
Select
2. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
● Setting default points in batch
Set default to all points of modules or empty slots on the base unit.
Select
Read the message and click the
button.
3. The message on the left is
displayed, and start XY is set.
Click the button to complete
the start XY setting.
1. Select [Q Module Configuration] ⇒
[Default Points Batch Input] in the
menu bar.
2. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
3 - 46
Read the message and click the
button.
3. The message shown on the left is
displayed, and default points are
set.
Click the button to complete
the default point setting.
Page 77

3.7 Checking System Configuration
3.7 Checking System Configuration
This section explains a method for checking module configurations/CC-Link configurations of created system
configuration, power supply capacity, and I/O points.
3.7.1 Checking system configuration
Check module configurations of created system configuration and allocated status of projects.
1
OVERVIEW
2
1. Select [Workspace] ⇒ [Check] ⇒
[System Configuration] in the menu
bar.
Select
2. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button.
Error or Warning is displayed when the
check result contains an error. Check the
error description on the Task List window
and correct the error.
● Check target
System configuration check function checks the following items.
• Common to Q series/L series/FX series module configurations
•Unmounted modules
•Matching of project PLC type and CPU module model name of module configuration.
•Allocation of projects in the workspace to CPU modules or other modules of module configuration.
• Q series module configuration
•Power supply mounting condition
•CPU module configuration (multiple CPU system)
•Configuration of main base unit and extension base unit or GOT
•Number of mounted modules (For details, refer to the Help function of MELSOFT Navigator.)
•Consumption current within the range
•I/O points within the range
• L series module configuration
•Power supply and END cover mounting condition
•Consumption current within the range
•I/O points within the range
• AnyWireASLINK configuration, CC-Link configuration, Ethernet configuration, and CC IE Field configuration
•Equipment configuration of AnyWireASLINK configuration, CC-Link configuration, Ethernet configuration, and
CC IE Field configuration
Note that, CPU module versions, module versions, and GOT model names are not checked.
● GOT installation
When installing the first GOT at the position more than 13.2m in distance, a bus extension connector box is
required.
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.7.1 Checking system configuration
3 - 47
Page 78

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.7.2 Checking power supply capacity and I/O points
Check power supply capacity and I/O points of created system configuration.
This functions is not supported by FXCPU.
1. Select [Workspace] ⇒ [Check] ⇒
[Power Supply Capacity and I/O Points
of Q/L Module Configuration] in the
menu bar.
Select
2. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button to display the "Result of Power
Supply Capacity and I/O Points Check"
window.
3. Check for errors in the check result.
When an error exists in the check result
(items displayed in red), options of modules
for re-selection are displayed by clicking
"Total Output Current" or "Total I/O Points".
A message is displayed by clicking "Total
Voltage Drop".
Read the message and correct the module
configurations.
● "Total Output Current"
Values displayed under "Total Output Current" may be different from the total output current of module with latest
version.
For the total output current of module with latest version, check the latest manuals of each module.
3 - 48
3.7.2 Checking power supply capacity and I/O points
Page 79

3.8 Editing Projects
3.8 Editing Projects
This section explains a method for editing created projects and utilizing them for other workspace.
1
3.8.1 Editing projects
Activate the created project for editing.
The following is an example of activating a programmable controller project.
For activating a motion controller project or a GOT project, follow the same procedure as described
below.
1. On the Module Configuration window,
double-click the controller to which a
programmable controller project is
Double click
allocated.
2.
The programmable controller project is
activated.
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
For editing programmable controller
projects, refer to the following manuals.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating
Manual (Common)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating
Manual (Simple Project)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating
Manual (Structured Project)
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual
(Simple Project)
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual
(Structured Project)
● Activating projects
Projects can also be activated from the Workspace window or Project List window.
● Activating the related software
The related software is activated by double-clicking the module on the FX Series Module Configuration window.
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.8.1 Editing projects
3 - 49
Page 80

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.8.2 Utilizing existing projects (import)
Utilize a project created in other workspace using MELSOFT Navigator.
● Importing projects
Projects created using engineering software products (GX Works2, MT Developer2, GT Designer3, and RT
ToolBox2) and GX Developer can be imported to the workspace created using MELSOFT Navigator.
● Importing GX Developer projects
GX Developer projects are converted to GX Works2 format and imported to MELSOFT Navigator.
However, depending on the programmable controller type, some projects are not supported for import, or not
converted to GX Works2 format.
For details, refer to the Help function of MELSOFT Navigator.
In addition, a project imported in GX Developer format cannot be allocated to a controller etc. on the module
configuration window.
The following operation is an example of utilizing a GX Works2 project.
For utilizing MT Developer2 or GT Designer3 projects, follow the same procedure as described below.
Select
1. Select [Project] ⇒ [Import] in the menu
bar to display the "Import" dialog box.
2. Set "Save Folder Path" for the project
to be utilized, and double-click the
workspace name of the project to be
imported.
Setting example
•
Save Folder Path : C:\Documents and
Settings\Administrator\
My Documents
•Workspace
:
Sample
3 - 50
(To the next page)
3.8.2 Utilizing existing projects (import)
Page 81

(From the previous page)
3.8 Editing Projects
3. Selecting the workspace displays the
list of GX Works2 projects.
Select the project to be utilized, and click
the button.
Setting example
• Project Name: GXW2_ProC
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
4. The project is imported in the
Workspace window.
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.8.2 Utilizing existing projects (import)
3 - 51
Page 82

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
● Importing projects
Projects in several workspaces can be organized into one workspace.
For details, refer to the Help function of MELSOFT Navigator.
● Exporting projects
Export projects of an open workspace, and add them to a new or existing workspace by following the procedure
below.
1. Select [Project] ⇒ [Export] in the
menu bar to display the "Export"
dialog box.
Select
2. Set "Save Folder Path" and
"Workspace" for the project to be
saved.
Click the button to export the
workspace.
Setting example
•
Save Folder Path :
• Workspace
C:\Documents
and Settings\
Administrator\
My Documents
:
Sample_WS_A
3 - 52
3.8.2 Utilizing existing projects (import)
Page 83

3.9 Reading/Writing/Verifying Controller Data
3.9 Reading/Writing/Verifying Controller Data
This section explains a method for reading/writing/verifying project data (programmable controller project,
motion controller project, GOT project).
■ Programmable controller projects
Read/write/verify programmable controller project data.
1
OVERVIEW
2
Select
1. On the System Configuration window,
right-click the controller to which a
programmable controller project is
allocated, and select [Online] ⇒
[Read]/[Write]/[Verify] in the shortcut
menu.
The screen image on the left shows the
case when [Write] is selected. Perform the
same operation for [Read] and [Verify].
2. The "Online Data Operation" dialog box
is displayed.
For operating the "Online Data Operation"
dialog box, refer to the following manuals.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating
Manual (Common)
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating
Manual (Simple Project)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating
Manual (Structured Project)
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual
(Simple Project)
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual
(Structured Project)
3 - 53
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
Page 84

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
■ Motion controller projects
Read/write/verify motion controller project data.
1. On the System Configuration window,
right-click the controller to which a
motion controller project is allocated,
and select [Online] ⇒ [Read]/[Write]/
[Verify] in the shortcut menu.
The screen image on the left shows the
case when [Write] is selected. Perform the
same operation for [Read] and [Verify].
Select
2. The "Write to CPU" dialog box is
displayed.
For operating the "Read from CPU",
"Write to CPU", and "Verify with CPU"
dialog boxes, refer to the Help function of
MT Developer2.
3 - 54
Page 85

3.9 Reading/Writing/Verifying Controller Data
■ GOT projects
Read/write/verify GOT project data.
Select
1. On the System Configuration window,
right-click the controller to which a GOT
project is allocated, and select [Online]
⇒ [Read]/[Write]/[Verify] in the shortcut
menu.
The screen image on the left shows the
case when [Write] is selected. Perform the
same operation for [Read] and [Verify].
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
2. The "Communicate with GOT" dialog
box is displayed.
For operating the "Communicate with
GOT"
dialog box, refer to the following
manuals.
GT Designer3 Version 1 Screen
Design Manual (Fundamentals)
GT Designer3 (GOT2000) Screen
Design Manual
Connection manuals for GOT1000
series
(Mitsubishi Products),
(Non-Mitsubishi Products 1),
(Non-Mitsubishi Products 2),
(Microcomputer, MODBUS Products,
Peripherals)
Connection manuals for GOT2000
series
(Mitsubishi Products),
(Non-Mitsubishi Products 1),
(Non-Mitsubishi Products 2),
(Microcomputer, MODBUS Products,
Peripherals)
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
GT Simulator3 Version 1 Operating
Manual
GT SoftGOT1000 Version 3
Operating Manual
GT SoftGOT2000 Version1 Operating
Manual
3 - 55
Page 86

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.10 Saving Workspaces
This section explains a method for saving created workspaces.
3.10.1 Saving workspaces with specified names
Save an open workspace with a specified name.
1. Select [Workspace] ⇒ [Save As] in the
menu bar to display the "Save As
(Workspace)" dialog box.
Select
2. Set "Save Folder Path", "Workspace
Name", and "Title" for the workspace.
After setting the items, click the
button to save the project.
Setting example
• Save Folder Path : C:\Documents and
Settings\
Administrator\
My Documents
• Workspace Name: Sample_Workspace
• Title (option) : Sample Data
● Saving workspaces with compression/unpacking workspaces
Saving workspaces with compression makes the data passing easier. Also, unpacking workspaces saved with
compression and opening them.
For details, refer to HELP of MELSOFT Navigator.
3 - 56
3.10.1 Saving workspaces with specified names
Page 87

3.10 Saving Workspaces
3.10.2 Overwriting workspaces
Save an open workspace with the same name.
Select
• Select [Workspace] ⇒ [Save] ( ) in
the menu bar to overwrite and save the
workspace.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3.10.2 Overwriting workspaces
3 - 57
Page 88

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.11 Printing Workspaces
This section explains a method for printing a created workspace.
1. Select [Workspace] ⇒ [Print] in the
menu bar to display the "Print" dialog
box.
Select
2. Select items for print and click the
button to display the "Print"
dialog box.
3. Select a printer and click the
button.
3 - 58
● Print output target
By selecting "File" for "Target", data can be saved in a CSV format file or a text format file. For details, refer to the
Help function of MELSOFT Navigator.
Page 89

3.12 Closing Workspaces
This section explains a method for closing an open workspace.
3.12 Closing Workspaces
1
1. Select [Workspace] ⇒ [Close] in the
menu bar.
Select
2. Click the button to close the
workspace.
When the workspace has not been saved, the following message is displayed.
Click the button to save the workspace.
Click the button to close the workspace without saving it.
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
3 - 59
Page 90

iQ Works
3 OPERATING PROCEDURE OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
3.13 Exiting MELSOFT Navigator
This section explains a method for exiting MELSOFT Navigator.
• Select [Workspace] ⇒ [Exit] in the
menu bar to exit MELSOFT Navigator.
Select
When the workspace is being opened, the following message is displayed.
Click the button to close the workspace.
Click the button to abort the operation of exiting MELSOFT Navigator.
3 - 60
Page 91

4 USING SYSTEM LABELS
This chapter explains the methods for using system labels which are shared within workspace of
programmable controller projects, motion controller projects, and GOT projects.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4.1 Registering System Labels in MELSOFT Navigator. . . . . . . . 4-2
4.2 Utilizing Existing Labels as System Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
4.3 Using System Labels on another personal computer . . . . . 4-17
4.4 Checking System Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-19
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
4 - 1
Page 92

iQ Works
4 USING SYSTEM LABELS
4.1 Registering System Labels in MELSOFT Navigator
This section explains a method for using system labels with the top-down design method under the following
system configuration.
Programmable controller project
Register the system label.
System label name: Start_lamp
Data Type: Bit
Import
Assign the device.
Device: X0
Programmable controller project
GOT project
MELSOFT Navigator
Reflect
Utilize
System label name: Start_lamp
Data Type: Bit
Device: X0
GOT project
4 - 2
Page 93

4.1 Registering System Labels in MELSOFT Navigator
4.1.1 Registering system labels in MELSOFT Navigator
Create and register system labels in MELSOFT Navigator.
1. Right-click "Undefined_Name" under
"System Label List" on the Workspace
window, and select [System Label List]
⇒ [Rename] in the shortcut menu.
Select
2. Enter "Label1" and change the system
label name.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Double click
3. Double-click "Label1" on the
Workspace window.
The system label list window is displayed.
4. Set "System Label Name", "Data
Type", "Attribute", and "Comment" for
the system label to be registered.
Setting example
• System Label Name: Start_lamp
• Data Type : Bit
• Attribute (option)
• Comment (option) : Sample_WS
:
I/O
comment
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
(To the next page)
4.1.1 Registering system labels in MELSOFT Navigator
4 - 3
Page 94

iQ Works
4 USING SYSTEM LABELS
(From the previous page)
5. Click the button.
Click
6. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button. The system label is
registered to the system label database,
and the cell color turns light blue.
● Registering system labels
System labels can also be registered by saving the workspace after setting the system labels to be registered.
● Deleting system labels
Delete system labels registered in MELSOFT Navigator by following the procedure below.
1. Select the system label to be
deleted.
Select
2. Click the button to delete
Click
● Importing/Exporting system labels
System labels created in CSV format or text format can be imported to the workspace. Also, system labels created
in the workspace can be exported in CSV format or text format.
For details, refer to Help of MELSOFT Navigator.
the selected system label.
4 - 4
4.1.1 Registering system labels in MELSOFT Navigator
Page 95

4.1 Registering System Labels in MELSOFT Navigator
4.1.2 Assigning devices to system labels
Import system labels registered in MELSOFT Navigator to global labels of programmable controller
project and assign devices to system labels to be used in other projects.
For importing system labels to labels of motion controller project, follow the same procedure as
described below.
1. Double-click "GXW2_Pro2" on the
Workspace window to display the
programmable controller project.
Double click
2. Double-click "Global1" on the
Navigation window of GX Works2 to
display the Global Label Setting
window.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Select
Double click
Click
Click
3. Click the button on
the Global Label Setting window to
display the "Import System Labels to
Project" dialog box.
4. Select a system label to be imported,
and click the button.
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
(To the next page)
4.1.2 Assigning devices to system labels
4 - 5
Page 96

iQ Works
4 USING SYSTEM LABELS
(From the previous page)
5. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button to register system labels registered
in MELSOFT Navigator as global labels of
GX Works2.
6. Set a device to the imported system
label.
Setting example
•Device : X0
Click
7. Click the button.
8. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button to execute Build and Save the
project.
For the compilation, refer to the following
manuals.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating
Manual (Common)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating
Manual (Simple Project)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating
Manual (Structured Project)
4 - 6
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual
(Simple Project)
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual
(Structured Project)
(To the next page)
4.1.2 Assigning devices to system labels
Page 97

(From the previous page)
4.1 Registering System Labels in MELSOFT Navigator
9. The "Check before registering in
system label database" dialog box is
displayed.
Click
Contents to be registered are displayed in
red.
1
OVERVIEW
2
System label notification icon
Check the contents and click the
button.
10. The system label notification icon is
displayed on the status bar of
MELSOFT Navigator.
11. Select [Workspace] ⇒ [Save] in the
menu bar of MELSOFT Navigator to
save the workspace.
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
Select
The system label list of MELSOFT
Navigator is updated.
● Updating system labels
After checking registration of system labels to the system label database in the step 9, system labels of MELSOFT
Navigator can be updated by selecting [Workspace] ⇒ [System Label] ⇒ [Change Contents of System Label
Database] in the menu bar of MELSOFT Navigator and save the project.
● System labels of GX Works2.
• System labels imported to projects can be used as global labels.
• System labels cannot be used when using a project without labels in GX Works2.
Change project type from 'without labels' to 'with labels". For details of change project type, refer to the following
manual.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
4.1.2 Assigning devices to system labels
4 - 7
USING PROGRAM
6
JUMP FUNCTION
Page 98

iQ Works
4 USING SYSTEM LABELS
4.1.3 Using system labels in GT Designer3
Utilize system labels to which devices are assigned in a programmable controller project for a GOT
project.
In GOT projects, system label names can be specified when setting devices to created objects.
For drawing objects in GOT projects, refer to the following manuals.
• GT Designer3 Version 1 Screen Design Manual (Fundamentals)
• GT Designer3 Version 1 Screen Design Manual (Functions)
1. Double-click the project on the
Workspace window to open the GOT
project.
Double click
Double click
Click
2. The message shown on the left is
displayed when a GX Works2 or MT
Developer2 project is being opened.
Read the message and click the
button.
3. 4.Double-click the created object to
display the dialog box of the object.
4. Click to display the "Select CH No."
dialog box.
4 - 8
(To the next page)
4.1.3 Using system labels in GT Designer3
Page 99

4.1 Registering System Labels in MELSOFT Navigator
(From the previous page)
Select
Click
Click
5. Click the
button to display the "Import System
Labels to Project" dialog box.
6. Select a system label to be used and
click the button.
7. After the settings are completed, the
system label name is displayed on the
object.
1
OVERVIEW
2
SCREEN
CONFIGURATION
3
OPERATING PROCEDURE
OF MELSOFT NAVIGATOR
4
Select
8. Select [Project] ⇒ [Save] in the menu
bar.
9. The message shown on the left is
displayed.
Read the message and click the
button.
10. The system label is ready to be
referred.
USING SYSTEM
LABELS
5
CREATING SYSTEM
BACKUP DATA
6
USING PROGRAM
JUMP FUNCTION
4.1.3 Using system labels in GT Designer3
4 - 9
Page 100

iQ Works
4 USING SYSTEM LABELS
● Referencing system labels
• After saving GT Designer3 project by clicking
also be referred by selecting [Workspace] ⇒ [System Label] ⇒ [Route Information/Routing Parameters] in the
menu bar of MELSOFT Navigator to create the route information/routing parameters.
• An error which occurs when referring to system labels can be confirmed on the “System Label Update/Check”
screen in GT Designer3. For details, refer to the following manual.
GT Designer3 Version1 Screen Design Manual (Fundamentals)
button on the message in the step 9, system labels can
4 - 10
4.1.3 Using system labels in GT Designer3
 Loading...
Loading...