Page 1

MELSEC iQ-R
Motion Module
User's Manual (Network)
-RD78G4
-RD78G8
-RD78G16
-RD78G32
-RD78G64
-RD78GHV
-RD78GHW
Page 2

Page 3
WHEN USING A HUB WITH CC-Link IE TSN
WARNING
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions, resulting in
death or severe injury.
CAUTION
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions, resulting in
minor or moderate injury or property damage.
The dedicated TSN hub is required when modules on CC-Link IE TSN are configured in a star topology or hubs are
configured in a cascade topology.
Read the following carefully.
MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual (Startup)
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
(Read these precautions before using this product.)
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals carefully and pay full attention to safety to handle
the product correctly.
The precautions given in this manual are concerned with this product only. Refer to the MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration
Manual for a description of the PLC system safety precautions.
In this manual, the safety precautions are classified into two levels: " WARNING" and " CAUTION".
Under some circumstances, failure to observe the precautions given under " CAUTION" may lead to serious
consequences.
Observe the precautions of both levels because they are important for personal and system safety.
Make sure that the end users read this manual and then keep the manual in a safe place for future reference.
1
Page 4

[Design Precautions]
WARNING
● Configure safety circuits external to the programmable controller to ensure that the entire system
operates safely even when a fault occurs in the external power supply or the programmable controller.
Failure to do so may result in an accident due to an incorrect output or malfunction.
(1) Emergency stop circuits, protection circuits, and protective interlock circuits for conflicting
operations (such as forward/reverse rotations or upper/lower limit positioning) must be configured
external to the programmable controller.
(2) When the programmable controller detects an abnormal condition, it stops the operation and all
outputs are:
• Turned off if the overcurrent or overvoltage protection of the power supply module is activated.
• Held or turned off according to the parameter setting if the self-diagnostic function of the CPU
module detects an error such as a watchdog timer error.
(3) All outputs may be turned on if an error occurs in a part, such as an I/O control part, where the
CPU module cannot detect any error. To ensure safety operation in such a case, provide a safety
mechanism or a fail-safe circuit external to the programmable controller. For a fail-safe circuit
example, refer to "General Safety Requirements" in the MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration
Manual.
(4) Outputs may remain on or off due to a failure of a component such as a relay and transistor in an
output circuit. Configure an external circuit for monitoring output signals that could cause a
serious accident.
● In an output circuit, when a load current exceeding the rated current or an overcurrent caused by a
load short-circuit flows for a long time, it may cause smoke and fire. To prevent this, configure an
external safety circuit, such as a fuse.
● Configure a circuit so that the programmable controller is turned on first and then the external power
supply. If the external power supply is turned on first, an accident may occur due to an incorrect output
or malfunction.
● For the operating status of each station after a communication failure, refer to manuals relevant to the
network. Incorrect output or malfunction due to a communication failure may result in an accident.
2
Page 5

[Design Precautions]
WARNING
● When connecting an external device with a CPU module or intelligent function module to modify data
of a running programmable controller, configure an interlock circuit in the program to ensure that the
entire system will always operate safely. For other forms of control (such as program modification,
parameter change, forced output, or operating status change) of a running programmable controller,
read the relevant manuals carefully and ensure that the operation is safe before proceeding. Improper
operation may damage machines or cause accidents.
● Especially, when a remote programmable controller is controlled by an external device, immediate
action cannot be taken if a problem occurs in the programmable controller due to a communication
failure. To prevent this, configure an interlock circuit in the program, and determine corrective actions
to be taken between the external device and CPU module in case of a communication failure.
● Do not write any data to the "system area" and "write-protect area" of the buffer memory in the
module. Also, do not use any "use prohibited" signals as an output signal from the CPU module to
each module. Doing so may cause malfunction of the programmable controller system. For the
"system area", "write-protect area", and the "use prohibited" signals, refer to the user's manual for the
module used.
● If a communication cable is disconnected, the network may be unstable, resulting in a communication
failure of multiple stations. Configure an interlock circuit in the program to ensure that the entire
system will always operate safely even if communications fail. Failure to do so may result in an
accident due to an incorrect output or malfunction.
● To maintain the safety of the programmable controller system against unauthorized access from
external devices via the network, take appropriate measures. To maintain the safety against
unauthorized access via the Internet, take measures such as installing a firewall.
● Configure safety circuits external to the programmable controller to ensure that the entire system
operates safely even when a fault occurs in the external power supply or the programmable controller.
Failure to do so may result in an accident due to an incorrect output or malfunction.
(1) Machine homing is controlled by two kinds of data: a homing direction and a homing speed.
Deceleration starts when the proximity dog signal turns on. If an incorrect homing direction is set,
motion control may continue without deceleration. To prevent machine damage caused by this,
configure an interlock circuit external to the programmable controller.
(2) When the module detects an error, the motion slows down and stops or the motion rapidly stops,
depending on the stop group setting in parameter. Set the parameter to meet the specifications of
a positioning control system. In addition, set the homing parameter and positioning data within the
specified setting range.
(3) Outputs may remain on or off, or become undefined due to a failure of a component such as an
insulation element and transistor in an output circuit, where the module cannot detect any error. In
a system that the incorrect output could cause a serious accident, configure an external circuit for
monitoring output signals.
● If safety standards (ex., robot safety rules, etc.,) apply to the system using the module, drive unit and
servomotor, make sure that the safety standards are satisfied.
● Construct a safety circuit externally of the module or drive unit if the abnormal operation of the module
or drive unit differs from the safety directive operation in the system.
3
Page 6

[Design Precautions]
CAUTION
● Do not install the control lines or communication cables together with the main circuit lines or power
cables. Keep a distance of 100 mm or more between them. Failure to do so may result in malfunction
due to noise.
● During control of an inductive load such as a lamp, heater, or solenoid valve, a large current
(approximately ten times greater than normal) may flow when the output is turned from off to on.
Therefore, use a module that has a sufficient current rating.
● After the CPU module is powered on or is reset, the time taken to enter the RUN status varies
depending on the system configuration, parameter settings, and/or program size. Design circuits so
that the entire system will always operate safely, regardless of the time.
● Do not power off the programmable controller or reset the CPU module while the settings are being
written. Doing so will make the data in the flash ROM and SD memory card undefined. The values
need to be set in the buffer memory and written to the flash ROM and SD memory card again. Doing
so also may cause malfunction or failure of the module.
[Installation Precautions]
WARNING
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before mounting or removing the
module. Failure to do so may result in electric shock or cause the module to fail or malfunction.
[Installation Precautions]
CAUTION
● Use the programmable controller in an environment that meets the general specifications in the Safety
Guidelines included with the base unit. Failure to do so may result in electric shock, fire, malfunction,
or damage to or deterioration of the product.
● To mount a module, place the concave part(s) located at the bottom onto the guide(s) of the base unit,
push in the module, and fix it with screw(s). Incorrect interconnection may cause malfunction, failure,
or drop of the module.
● When using the programmable controller in an environment of frequent vibrations, fix the module with
a screw.
● Tighten the screws within the specified torque range. Undertightening can cause drop of the screw,
short circuit, or malfunction. Overtightening can damage the screw and/or module, resulting in drop,
short circuit, or malfunction.
● When using an extension cable, connect it to the extension cable connector of the base unit securely.
Check the connection for looseness. Poor contact may cause malfunction.
● When using an SD memory card, fully insert it into the SD memory card slot. Check that it is inserted
completely. Poor contact may cause malfunction.
● Securely insert an extended SRAM cassette or a battery-less option cassette into the cassette
connector of the CPU module. After insertion, close the cassette cover and check that the cassette is
inserted completely. Poor contact may cause malfunction.
● Do not directly touch any conductive parts of the module, SD memory card, extended SRAM cassette,
battery-less option cassette, or connector. Doing so can cause malfunction or failure of the module.
4
Page 7

[Wiring Precautions]
WARNING
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before installation and wiring.
Failure to do so may result in electric shock or cause the module to fail or malfunction.
● After installation and wiring, attach a blank cover module (RG60) to each empty slot and an included
extension connector protective cover to the unused extension cable connector before powering on the
system for operation. Failure to do so may result in electric shock.
[Wiring Precautions]
CAUTION
● Individually ground the FG and LG terminals of the programmable controller with a ground resistance
of 100 ohms or less. Failure to do so may result in electric shock or malfunction.
● Use applicable solderless terminals and tighten them within the specified torque range. If any spade
solderless terminal is used, it may be disconnected when the terminal screw comes loose, resulting in
failure.
● Check the rated voltage and signal layout before wiring to the module, and connect the cables
correctly. Connecting a power supply with a different voltage rating or incorrect wiring may cause fire
or failure.
● Connectors for external devices must be crimped or pressed with the tool specified by the
manufacturer, or must be correctly soldered. Incomplete connections may cause short circuit, fire, or
malfunction.
● Securely connect the connector to the module. Poor contact may cause malfunction.
● Do not install the control lines or communication cables together with the main circuit lines or power
cables. Keep a distance of 100 mm or more between them. Failure to do so may result in malfunction
due to noise.
● Place the cables in a duct or clamp them. If not, dangling cables may swing or inadvertently be pulled,
resulting in malfunction or damage to the modules or cables.
In addition, the weight of the cables may put stress on modules in an environment of strong vibrations
and shocks.
Do not clamp the extension cables with the jacket stripped. Doing so may change the characteristics
of the cables, resulting in malfunction.
● Check the interface type and correctly connect the cable. Incorrect wiring (connecting the cable to an
incorrect interface) may cause failure of the module and external device.
● Tighten the terminal screws or connector screws within the specified torque range. Undertightening
can cause drop of the screw, short circuit, fire, or malfunction. Overtightening can damage the screw
and/or module, resulting in drop, short circuit, fire, or malfunction.
5
Page 8

[Wiring Precautions]
CAUTION
● When disconnecting the cable from the module, do not pull the cable by the cable part. For the cable
with connector, hold the connector part of the cable. For the cable connected to the terminal block,
loosen the terminal screw. Pulling the cable connected to the module may result in malfunction or
damage to the module or cable.
● Prevent foreign matter such as dust or wire chips from entering the module. Such foreign matter can
cause a fire, failure, or malfunction.
● A protective film is attached to the top of the module to prevent foreign matter, such as wire chips,
from entering the module during wiring. Do not remove the film during wiring. Remove it for heat
dissipation before system operation.
● Programmable controllers must be installed in control panels. Connect the main power supply to the
power supply module in the control panel through a relay terminal block. Wiring and replacement of a
power supply module must be performed by qualified maintenance personnel with knowledge of
protection against electric shock. For wiring, refer to the MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual.
● For Ethernet cables to be used in the system, select the ones that meet the specifications in the user's
manual for the module used. If not, normal data transmission is not guaranteed.
[Startup and Maintenance Precautions]
WARNING
● Do not touch any terminal while power is on. Doing so will cause electric shock or malfunction.
● Correctly connect the battery connector. Do not charge, disassemble, heat, short-circuit, solder, or
throw the battery into the fire. Also, do not expose it to liquid or strong shock. Doing so will cause the
battery to produce heat, explode, ignite, or leak, resulting in injury and fire.
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before cleaning the module or
retightening the terminal screws, connector screws, or module fixing screws. Failure to do so may
result in electric shock.
6
Page 9
[Startup and Maintenance Precautions]
CAUTION
● When connecting an external device with a CPU module or intelligent function module to modify data
of a running programmable controller, configure an interlock circuit in the program to ensure that the
entire system will always operate safely. For other forms of control (such as program modification,
parameter change, forced output, or operating status change) of a running programmable controller,
read the relevant manuals carefully and ensure that the operation is safe before proceeding. Improper
operation may damage machines or cause accidents.
● Especially, when a remote programmable controller is controlled by an external device, immediate
action cannot be taken if a problem occurs in the programmable controller due to a communication
failure. To prevent this, configure an interlock circuit in the program, and determine corrective actions
to be taken between the external device and CPU module in case of a communication failure.
● Do not disassemble or modify the modules. Doing so may cause failure, malfunction, injury, or a fire.
● Use any radio communication device such as a cellular phone or PHS (Personal Handy-phone
System) more than 25 cm away in all directions from the programmable controller. Failure to do so
may cause malfunction.
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before mounting or removing the
module. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
● Tighten the screws within the specified torque range. Undertightening can cause drop of the
component or wire, short circuit, or malfunction. Overtightening can damage the screw and/or module,
resulting in drop, short circuit, or malfunction.
● After the first use of the product, do not perform each of the following operations more than 50 times
(IEC 61131-2/JIS B 3502 compliant).
Exceeding the limit may cause malfunction.
• Mounting/removing the module to/from the base unit
• Inserting/removing the extended SRAM cassette or battery-less option cassette to/from the
CPU module
• Mounting/removing the terminal block to/from the module
● After the first use of the product, do not insert/remove the SD memory card to/from the CPU module
more than 500 times. Exceeding the limit may cause malfunction.
● Do not touch the metal terminals on the back side of the SD memory card. Doing so may cause
malfunction or failure of the module.
● Do not touch the integrated circuits on the circuit board of an extended SRAM cassette or a batteryless option cassette. Doing so may cause malfunction or failure of the module.
● Do not drop or apply shock to the battery to be installed in the module. Doing so may damage the
battery, causing the battery fluid to leak inside the battery. If the battery is dropped or any shock is
applied to it, dispose of it without using.
● Startup and maintenance of a control panel must be performed by qualified maintenance personnel
with knowledge of protection against electric shock. Lock the control panel so that only qualified
maintenance personnel can operate it.
● Before handling the module, touch a conducting object such as a grounded metal to discharge the
static electricity from the human body. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
7
Page 10

[Startup and Maintenance Precautions]
CAUTION
● Before testing the operation, set a low speed value for the speed limit parameter so that the operation
can be stopped immediately upon occurrence of a hazardous condition.
● Confirm and adjust the program and each parameter before operation. Unpredictable movements
may occur depending on the machine.
● When using the absolute position system function, on starting up, and when the module or absolute
position motor has been replaced, always perform a homing.
● Before starting the operation, confirm the brake function.
● Do not perform a megger test (insulation resistance measurement) during inspection.
● After maintenance and inspections are completed, confirm that the position detection of the absolute
position detection function is correct.
● Lock the control panel and prevent access to those who are not certified to handle or install electric
equipment.
[Operating Precautions]
CAUTION
● When changing data and operating status, and modifying program of the running programmable
controller from an external device such as a personal computer connected to an intelligent function
module, read relevant manuals carefully and ensure the safety before operation. Incorrect change or
modification may cause system malfunction, damage to the machines, or accidents.
● Do not power off the programmable controller or reset the CPU module while the setting values in the
buffer memory are being written to the flash ROM in the module. Doing so will make the data in the
flash ROM and SD memory card undefined. The values need to be set in the buffer memory and
written to the flash ROM and SD memory card again. Doing so also may cause malfunction or failure
of the module.
● Note that when the reference axis speed is specified for interpolation operation, the speed of the
partner axis (2nd, 3rd, or 4th axis) may exceed the speed limit value.
● Do not go near the machine during test operations or during operations such as teaching. Doing so
may lead to injuries.
[Disposal Precautions]
CAUTION
● When disposing of this product, treat it as industrial waste.
● When disposing of batteries, separate them from other wastes according to the local regulations. For
details on battery regulations in EU member states, refer to the MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration
Manual.
8
Page 11

[Transportation Precautions]
CAUTION
● When transporting lithium batteries, follow the transportation regulations. For details on the regulated
models, refer to the MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual.
● The halogens (such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine), which are contained in a fumigant
used for disinfection and pest control of wood packaging materials, may cause failure of the product.
Prevent the entry of fumigant residues into the product or consider other methods (such as heat
treatment) instead of fumigation. The disinfection and pest control measures must be applied to
unprocessed raw wood.
9
Page 12

INTRODUCTION
Thank you for purchasing the Mitsubishi Electric MELSEC iQ-R series programmable controllers.
This manual describes the functions, programming, and troubleshooting of the relevant product listed below.
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals carefully and develop familiarity with the
functions and performance of the MELSEC iQ-R series programmable controller to handle the product correctly.
When applying the program examples provided in this manual to an actual system, ensure the applicability and confirm that it
will not cause system control problems.
Please make sure that the end users read this manual.
Relevant products
RD78G4, RD78G8, RD78G16, RD78G32, RD78G64, RD78GHV, RD78GHW
Symbols used in this manual are shown below.
• [RD78GH]: Symbols indicating that it corresponds to only RD78GH
COMPLIANCE WITH EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
Method of ensuring compliance
To ensure that Mitsubishi programmable controllers maintain EMC and Low Voltage Directives when incorporated into other
machinery or equipment, certain measures may be necessary. Please refer to one of the following manuals.
MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual
Safety Guidelines (This manual is included with the base unit.)
The CE mark on the side of the programmable controller indicates compliance with EMC and Low Voltage Directives.
Additional measures
To ensure that this product maintains EMC and Low Voltage Directives, please refer to one of the following manuals.
MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual
Safety Guidelines (This manual is included with the base unit.)
10
Page 13

CONTENTS
WHEN USING A HUB WITH CC-Link IE TSN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
INTRODUCTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
COMPLIANCE WITH EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
RELEVANT MANUALS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
TERMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
FUTURE SUPPORT PLANNED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
CHAPTER 1 FUNCTIONS 17
1.1 Cyclic Transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Communications using slave labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
1.2 Transient Transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Communications using the SLMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
1.3 Ethernet Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Connection with MELSOFT products and a GOT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Connecting SLMP-compatible devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.4 Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
IP filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Remote password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.5 RAS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Slave station disconnection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Master station duplication detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
IP address duplication error. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Time synchronization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
1.6 Others . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Slave station parameter automatic setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
CONTENTS
CHAPTER 2 PARAMETER SETTINGS 34
2.1 Setting Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2.2 Required Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Station Type. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Network No.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Station No./IP Address Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
2.3 Basic Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Network Topology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Communication Period Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Connection Device Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Slave Station Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2.4 Application Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Event Reception from Other Stations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Module Operation Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
2.5 "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Parameter setting of a slave station . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Connected/Disconnected Module Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Parameter processing of a slave station . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Command execution to slave stations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
11
Page 14

CHAPTER 3 TROUBLESHOOTING 49
3.1 Checking with LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3.2 Checking the Module Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Module Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
3.3 Checking the Network Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Communication Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Remote Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
3.4 Troubleshooting by Symptom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
3.5 List of Error Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
3.6 List of Parameter Nos. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
3.7 Event List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
APPENDICES 87
Appendix 1 Buffer Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
List of buffer memory addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Details of buffer memory addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Appendix 2 List of Link Special Relay (SB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Appendix 3 List of Link Special Register (SW) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Appendix 4 Port No.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
INDEX 98
REVISIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
WARRANTY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .101
TRADEMARKS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .102
12
Page 15

RELEVANT MANUALS
Manual name [manual number] Description Available
form
MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual (Network)
[IB-0300426ENG] (This manual)
MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual (Startup)
[IB-0300406ENG]
MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual (Application)
[IB-0300411ENG]
MELSEC iQ-R Programming Manual (Motion Module Instructions,
Standard Functions/Function Blocks)
[IB-0300431ENG]
For programs, refer to the following.
MELSEC iQ-R Programming Manual (Program Design)
e-Manual refers to the Mitsubishi Electric FA electronic book manuals that can be browsed using a dedicated
tool.
e-Manual has the following features:
• Required information can be cross-searched in multiple manuals.
• Other manuals can be accessed from the links in the manual.
• The hardware specifications of each part can be found from the product figures.
• Pages that users often browse can be bookmarked.
• Sample programs can be copied to an engineering tool.
Functions, parameter settings, troubleshooting, and buffer memory of
CC-Link IE TSN
Specifications, procedures before operation, system configuration, and
wiring of the Motion module
Functions, I/O signals, variables, labels, programming, and
troubleshooting of the Motion module
Instructions for the Motion module and standard functions/function blocks Print book
Print book
e-Manual
PDF
Print book
e-Manual
PDF
Print book
e-Manual
PDF
e-Manual
PDF
13
Page 16

TERMS
Unless otherwise specified, this manual uses the following terms.
Ter m Description
Authentication Class A class classified by CC-Link Partner Association (www.cc-link.org) from a function and performance of the
modulecorresponding to CC-Link IE TSN and a switching hub. There are two authentication Classes: A and B, and
authentication Class B for the RD78G(H).
Buffer memory A memory in an intelligent function module, where data (such as setting values and monitoring values) are stored.
CC-Link IE Includes the following network:
Conformance testing Testing performed for communications of a CC-Link or CC-Link IE product to ensure their high reliability.
Control CPU A CPU module that controls connected I/O modules and intelligent function modules. In a multiple CPU system, there are
CPU module The abbreviation for the MELSEC iQ-R series CPU module
Cyclic transmission A function by which data are periodically exchanged among stations on the network using slave labels
Data link A cyclic transmission and a transient transmission
Device Memory in a CPU module. There are two types of devices: a bit device and a word device.
Disconnection A process of stopping data link if a data link error occurs
Engineering tool A generic term for GX Works3 and MR Configurator2
Ethernet device A device supporting IP communication (such as personal computers)
Ethernet-equipped module The following modules when the Ethernet function is used:
General-purpose hub An authentication Class A hub authorized by CC-Link Partner Association
GOT A generic term for Mitsubishi Electric Graphic Operation Terminal GOT1000 and GOT2000 series
Grandmaster A source device or station to synchronize clocks in the time synchronization via PTP
GX Works3 The product name of the software package for the MELSEC programmable controllers
Intelligent function module A module that has functions other than input and output, such as an A/D converter module and D/A converter module
Label A label that represents a device in a given character string
Link scan (link scan time) Time required for all the stations on the network to transmit data. The link scan time depends on data volume and the number
Link device A device in a module on CC-Link IE
Link refresh Automatic data transfer between a link device of the Motion module and a device in a CPU module
Master station A station that controls the entire network. This station can perform cyclic transmission and transient transmission with all
Module label A label that represents one of memory areas (I/O signals and buffer memory areas) specific to each module in a given
Motion module A generic term for the RD78G(H)_
Network module Includes the following modules:
Priority A value that is assigned to devices or stations in a network to determine the grandmaster for time synchronization. The
PTP Precision Time Protocol. A predefined protocol for time synchronization between devices on a network.
RAS An abbreviation for Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability. This term refers to the overall usability of automated equipment.
RD78G Another term for the MELSEC iQ-R series Motion module (compatible with CC-Link IE TSN)
RD78GH
RD78G(H) A generic term for RD78G_, RD78GH_ (high performance version)
Remote station A station that exchanges I/O signals (bit data) and I/O data (word data) with another station by cyclic transmission. This
• CC-Link IE TSN
• CC-Link IE Controller Network ( MELSEC iQ-R CC-Link IE Controller Network User's Manual (Application))
• CC-Link IE Field Network ( MELSEC iQ-R CC-Link IE Field Network User's Manual (Application))
For details, refer to the CC-Link Partner Association home page. (www.cc-link.org)
multiple CPU modules and each connected module can be controlled by a different CPU module.
•RJ71EN71
• CPU module
of transient transmission requests.
stations. Only one master station can be used in a network.
character string. For the module used, GX Works3 automatically generates this label, which can be used as a global label.
• Ethernet interface module
• Module on CC-Link IE TSN
• CC-Link IE Controller Network module
• Module on CC-Link IE Field Network
• MELSECNET/H network module
• MELSECNET/10 network module
• RnENCPU (network part)
smaller the value, the higher the priority.
station can perform transient transmission.
14
Page 17

Term Description
Reserved address An IP address reserved for special purposes, defined by RFC 6890. This IP address cannot be used when the
programmable controller is connected via the global IP network.
Return A process of restarting data link when a faulty station recovers from an error
Routing A process of selecting paths for communication with other networks. There are two types of routing: dynamic routing that
RWr A remote register of the link device. This refers to word data input from a slave station to the master station. (For some areas
RWw A remote register of the link device. This refers to word data output from the master station to a slave station. (For some
RX Remote input of the link device. This refers to bit data input from a slave station to the master station. (For some areas in a
RY Remote output of the link device. This refers to bit data output from the master station to a slave station. (For some areas in
SB Link special relay. Bit data that indicates the operating status and data link status of a module on CC-Link IE.
Slave station • A generic term for a local station and remote station on CC-Link IE TSN
SLMP A Seamless Message Protocol. This protocol is used to access an SLMP-compatible device or a CPU module connected to
SW Link special register. Word data that indicates the operating status and data link status of a module on CC-Link IE.
Transient transmission A function of data communication unperiodically among nodes (station) on network.
Transient transmission group
No.
TSN hub An authentication Class B hub authorized by CC-Link Partner Association
auto-selects the communication routes, and static routing where communication routes are arbitrarily set.
in a local station, data are input in the opposite direction.)
areas in a local station, data are output in the opposite direction.)
local station, data are input in the opposite direction.)
a local station, data are output in the opposite direction.)
• A generic term for a local station, remote I/O station, remote device station, and intelligent device station on CC-Link IE
Field Network
an SLMP-compatible device from an external device such as a personal computer.
A function used to send message to the target station when requested by a link dedicated instruction or the engineering tool
Communication is available with station on another network via relay station, or gateway.
No. that is assigned for transient transmission to any given stations. By specifying a group of stations as transient
transmission target, data can be sent to the stations of the same group No.
15
Page 18

FUTURE SUPPORT PLANNED
The following model and functions are mentioned in this manual, but these are planned for a future support.
The information in this page might be changed for improvement without prior notice.
Model Description
RD78GH • RD78GHV
Function Description
Communication period setting Communication period interval setting (Do not set it in units of 1 s)
Station type Local station
Link refresh Refresh setting
Network connected device Standard station
• RD78GHW
[RD78GH]
Minimum communication period 31.25 s
16
Page 19
1 FUNCTIONS
No.1
No.2
No.1
No.2
→No.1
→No.2
→No.1
→No.2
Ô
Ó
RX
RY
RWr
RWw
No.2
No.2
←No.2
←No.2
RWr
RWw
0000H
0003H
No.1
0000H
0003H
←No.1
0000H
0003H
0000H
001FH
0000H
0003H
0000H
001FH
Ò
Õ
No.2No.1No.0
Slave label
Slave label
Slave label
Slave label
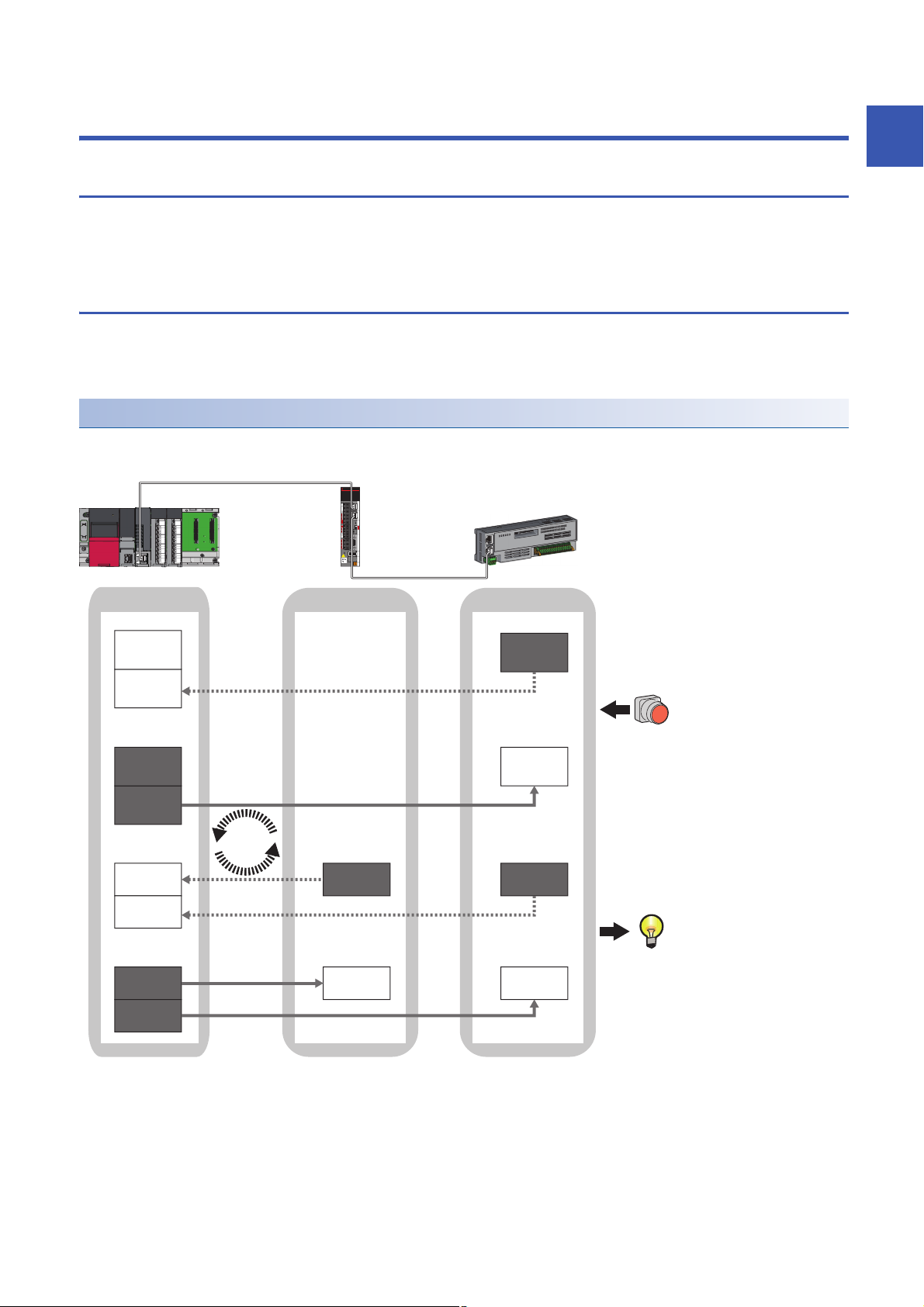
1.1 Cyclic Transmission
This allows data to be periodically exchanged among stations on the same network using slave labels.
• The slave labels can be assigned in "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings". ( Page 42 "CC-Link IE
TSN Configuration" Window)
Communications using slave labels
This allows I/O data to be exchanged in units of bits and in units of words in the master station and slave station.
Slave labels can be used in the motion control station only.
This function is available for the motion ST program only.
Master station and remote stations
1:1 communications between the master station and each remote station. Remote stations do not communicate with each
other.
1
No.0, No.1, No.2 Station No.0 (master station), Station No.1, Station No.2
No.1, No.2 Send range: to station No.1, Send range: to station No.2
No.1, No.2 Send range: from station No.1, Send range: from station No.2
• Output from the master station
The status data of the slave labels of the master station is stored in the link devices (RY, RWw) of each remote station by cyclic data transfer processing.
The status data of the link devices (RY, RWw) of the remote station are output to the external device.
• Input from the remote station
The status data of the external device is stored in the link devices (RX, RWr) of the remote station.
The status data of the link devices (RX, RWr) of the remote station is stored in the slave labels of the master station by cyclic data transfer processing.
1 FUNCTIONS
1.1 Cyclic Transmission
17
Page 20

1.2 Transient Transmission
(1)
(6)
(4) (6)
(4)
(3)(2)
(5)
(3)
This uses communications at any timing.
Page 18 Communications using the SLMP
Communications using the SLMP
By SLMP, data is read/written from the external device (1) such as a personal computer or HMI (Human Machine Interface) to
I/O module devices of the master station (2) and (3) and the buffer memory of the remote station.
The Motion module can create, send (4), relay (5), and receive (6) SLMP messages. For details on SLMP, refer to the
following.
SLMP Reference Manual
18
1 FUNCTIONS
1.2 Transient Transmission
Page 21

1.3 Ethernet Connection
Connection with MELSOFT products and a GOT
Programming and monitoring of the programmable controller with the engineering tool, and monitoring and testing of the
programmable controller from the GOT is performed via Ethernet. This function enables remote control using Ethernet's long-
distance connectivity and high-speed communications.
The section describes the methods of connecting the Motion module, MELSOFT product (such as engineering tool and MX
Component), and GOT.
: Connection available, : Connection not available
Connection method Purpose Availability Reference
Connection via hub
(Connection by specifying the IP
address)
Connection via hub
(Connection by specifying the network
No. and station No.)
For the procedures to connect the Motion module and GOT, refer to the following.
Manual for the GOT used
MELSOFT
product
To connect multiple MELSOFT products Page 19
To connect multiple MELSOFT products and GOTs
GOT
Connection via hub
1
Connection via hub
■Settings on the Motion module side
Sets the IP address of the Motion module using "Required Settings". ( Page 36 Station No./IP Address Settings)
When connecting by specifying the network No. and station No., set the network No. and station No. in "Required Settings".0
The Motion module can be connected to the MELSOFT product and GOT using the system dedicated connection, so no
settings are required in "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings".
1 FUNCTIONS
1.3 Ethernet Connection
19
Page 22
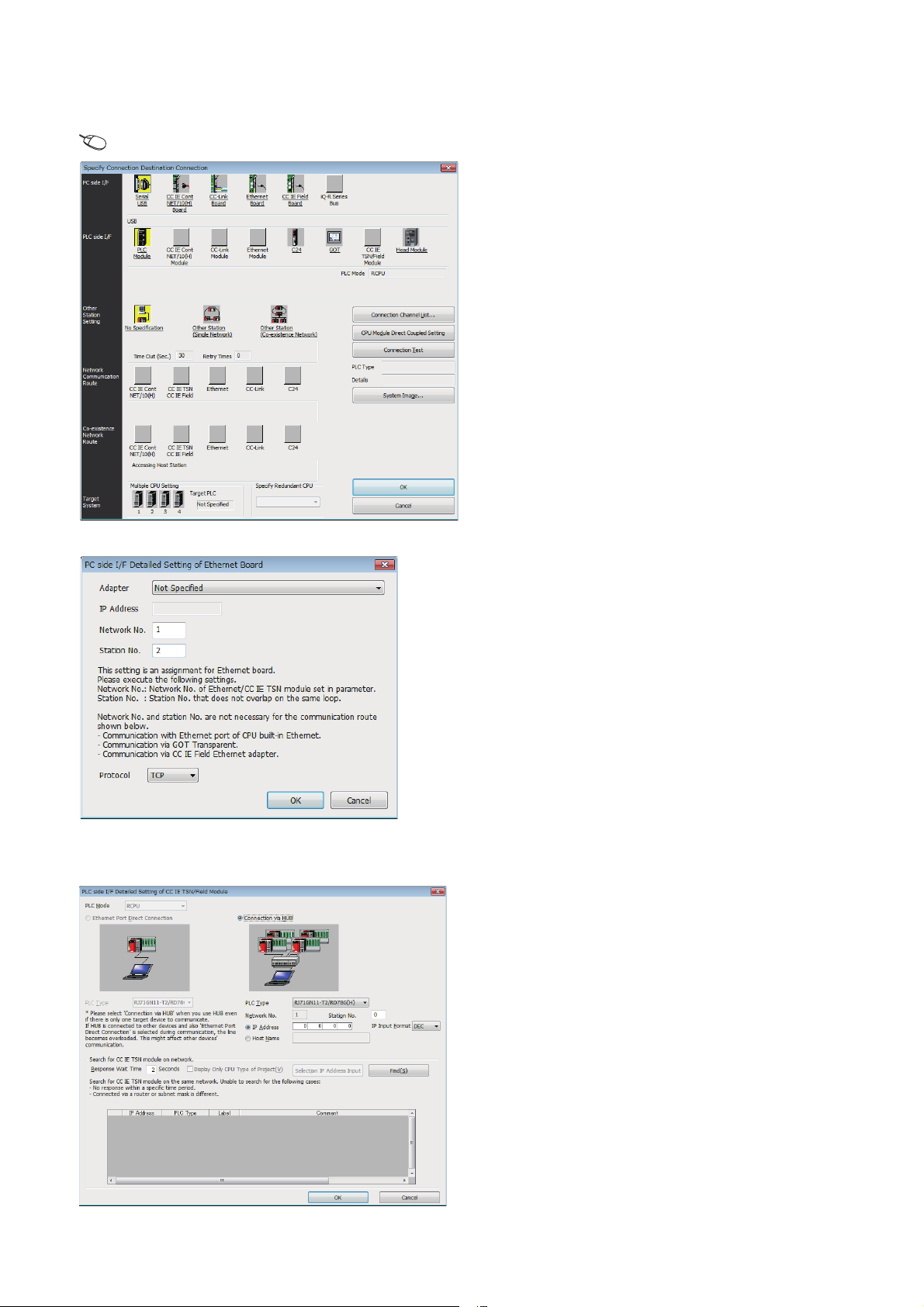
■Settings on the engineering tool side
Set in the "Specify Connection Destination Connection" window.
[Online] [Current Connection Destination]
1. Set "PC side I/F" to "Ethernet Board".
2. Double-click "Ethernet Board", and open the "PC side I/
F Detailed Setting of Ethernet Board" window.
3. Set the network No., station No., and protocol of the
personal computer.
TCP: A connection is established during communication.
Since data is exchanged while checking that the data has
correctly reached the communication destination, the data
reliability can be ensured. Note that the line load is larger
than UDP/IP communications.
UDP: Since a connection is not established during
communication and whether the communication destination
has correctly received the data is not checked, the line load is
lower. Note that the data reliability is lower than TCP/IP
communications.
4. Set the "PLC side I/F" to the module to be connected.
5. Double-click the icon set in step 4, and open the
detailed setting window.
6. Select "Connection via HUB" for the connection method,
and enter the station No. and IP address or host name
for the Motion module.
7. Specify "Other Station Setting" or "Network
Communication Route" if necessary.
20
1 FUNCTIONS
1.3 Ethernet Connection
Page 23
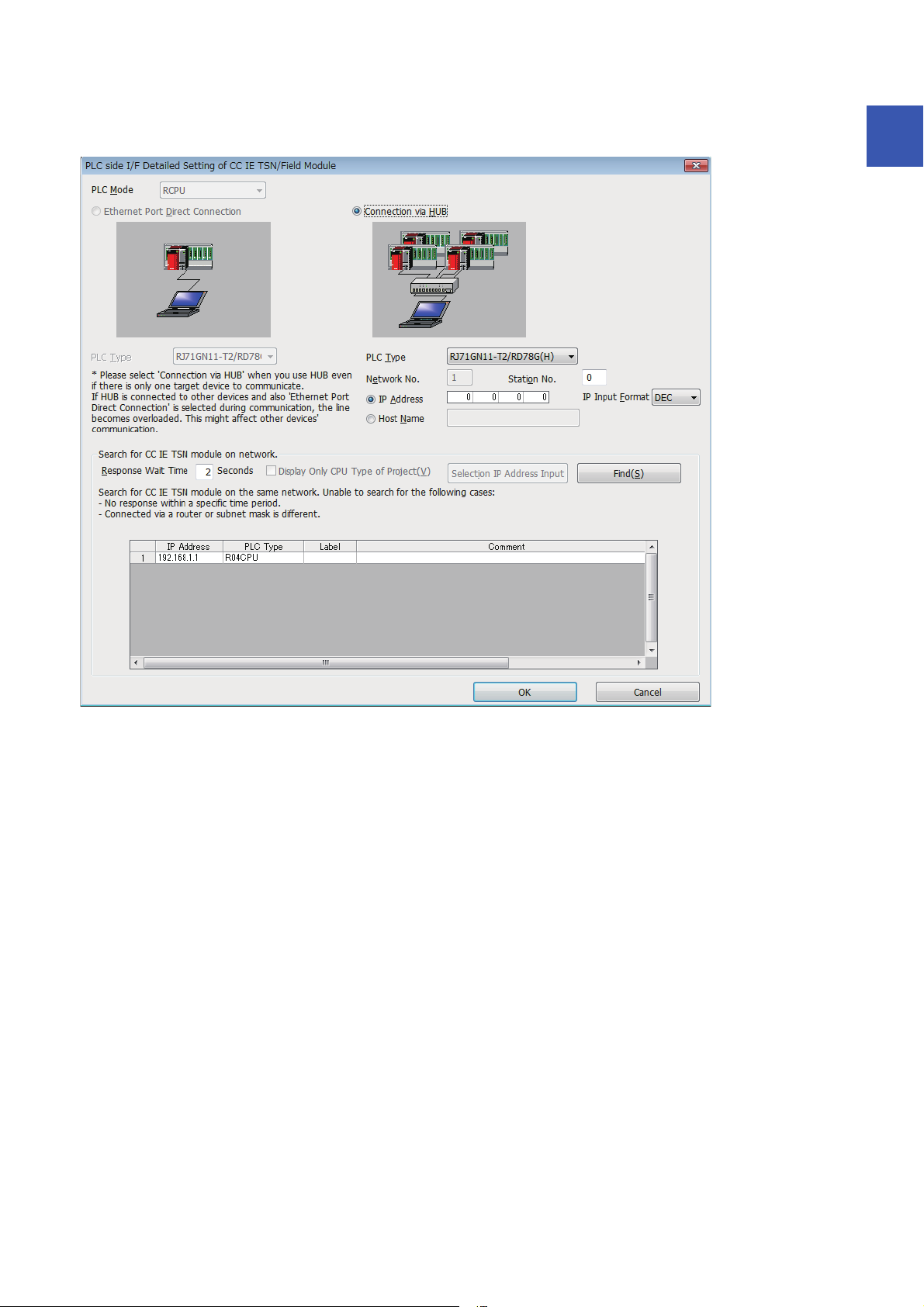
■Searching modules on the network
When connecting with a hub, a list of modules that can be searched for will appear by clicking the [Find] button on the detailed
setting window.
1
Search target modules are as follows.
• The control CPU of the Motion module connected to the same hub as the engineering tool
• The control CPU of the Motion module connected to cascade-connected hub
If the connected Motion module does not appear in the list after searching the modules on the network, check the following
items.
• Search cannot be performed if it is disabled with the IP filter.
• Modules connected via a router cannot be searched.
• If the module is connected via a wireless LAN, IP packet loss can prevent the Ethernet communication from stabilizing, and
may inhibit the module search.
• If there are modules with the same IP address in the list, review the IP address parameter settings for the Motion module.
• If the service processing load of the search-target CPU module is high, it may not be possible to search for the
corresponding module. If the search cannot be performed, increase the response waiting time in the search dialog, and
execute the search again.
1 FUNCTIONS
1.3 Ethernet Connection
21
Page 24

Connecting SLMP-compatible devices
Connect commercially available SLMP-compatible devices. A SLMP-compatible device can be introduced to the CC-Link IE
TSN system, resulting in easier linkage with an upper information network.
For details on SLMP, refer to the following.
SLMP Reference Manual
When the system structure is mixed with an Ethernet device, there are restrictions for the network topology
and connection order of the Ethernet device. (MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual (Startup))
22
1 FUNCTIONS
1.3 Ethernet Connection
Page 25

1.4 Security
No.0
HUB
(1) 192.168.1.1
(2) 192.168.1.5
Security for the network environment is structured by restricting access by each communication path that accesses the CPU
module. The following two access restriction methods can be used.
Page 23 IP filter
Page 25 Remote password
IP filter
Identifies the IP address of the access source, and prevents unauthorized access and data links.
By setting the IP address of the access source using the engineering tool, IP packets are allowed or blocked. (Allows or
blocks the IP packets received from the access source. IP packets sent from the own station are ignored.)
Use of this function is recommended when using in an environment connected to a LAN line.
1
When the "Allow" IP address is set to 192.168.1.1 using the IP filter of the master station No.0:
Only the Ethernet device (1) can access the master station, and the Ethernet device (2) cannot access the master station.
This function cannot be used when accessing via a network other than Ethernet or CC-Link IE TSN.
The IP filter is one method of preventing unauthorized access (such as program or data destruction) from an
external device. It does not completely prevent unauthorized access. Incorporate measures other than this
function if the programmable controller system's safety must be maintained against unauthorized access from
an external device. Mitsubishi shall not be held liable for any system problems that may occur from
unauthorized access.
Examples of measures for unauthorized access are given below.
• Install a firewall
1 FUNCTIONS
1.4 Security
23
Page 26

Setting method
Precautions
No.0
No.1: 192.168.1.1 No.2: 192.168.1.2
No.3: 192.168.1.3
1. Set the IP address to be allowed or blocked in the "IP Filter Settings" window of "Security" under "Application Settings".
(Page 41 Security) A warning is displayed in the following cases.
• When blocking the IP address of the slave station set in "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings" was
attempted
• When the slave station is not set in "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings", and the "Allow" target IP
address is not set in the "IP Filter Settings" window (because the IP filter is fully blocked)
2. Write the module parameters to the CPU module.
3. The IP filter is enabled when the CPU module power is turned off and on or reset.
Even if the connection was specified in "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings" or by a
program, access from the external device is either allowed or blocked according to the setting in the "IP Filter
Settings" window.
Setting Target
Allow or block should be set to all IP addresses that connect to the same network. Also, set allow or block to the IP address of
the slave station that is registered in "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings".
Register the setting details to the master station, and allow or block the IP packets received from the slave station of the
registered IP address.
Operation
Even for the slave station registered in "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings", a station with an IP address
set as blocked can become a disconnected station. As a result, cyclic transmission and transient transmission are not
performed. Such a station is also displayed as a disconnected station on the "CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics"
window. However, Ethernet devices are not displayed on the "CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics" window. (
Page 54 CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics)
When an IP packet is received from an IP address that is set as blocked, the denial is registered in the event history of the
master station.
( Page 84 Event List)
• Do not set the IP addresses of the master station or slave stations as blocked. When a slave station using line topology is
set as blocked, cyclic and transient transmissions cannot be performed on the slave stations that are connected after the
slave station set as blocked.
When the "Deny" IP address is set to 192.168.1.2 using the IP filter of the master station No.0:
Only the slave station No.1 can access the master station, and the slave station No.2 and slave station No.3 cannot access the master station.
• If there is a proxy server in the LAN line, block the IP address for the proxy server. If the IP address is allowed, it will not be
possible to prevent access from personal computers that access the proxy server.
• To block access from an external device to another station, block access to the connected station (station connected
directly to an external device) by using the IP filter.
24
1 FUNCTIONS
1.4 Security
Page 27

Remote password
Permits or prohibits access from the external device to the CPU module via Motion module. This function can prevent
unauthorized access of the CPU module from a remote location.
The remote password is one method of preventing unauthorized access (such as program or data destruction)
from an external device. It does not completely prevent unauthorized access. Incorporate measures other
than this function if the programmable controller system's safety must be maintained against unauthorized
access from an external device. Mitsubishi shall not be held liable for any system problems that may occur
from unauthorized access.
Examples of measures for unauthorized access are given below.
• Install a firewall
Number of settable modules
Up to eight modules can be set for remote passwords.
When using the multiple CPU system configuration, up to eight modules can be set for each CPU module.
1
1 FUNCTIONS
1.4 Security
25
Page 28
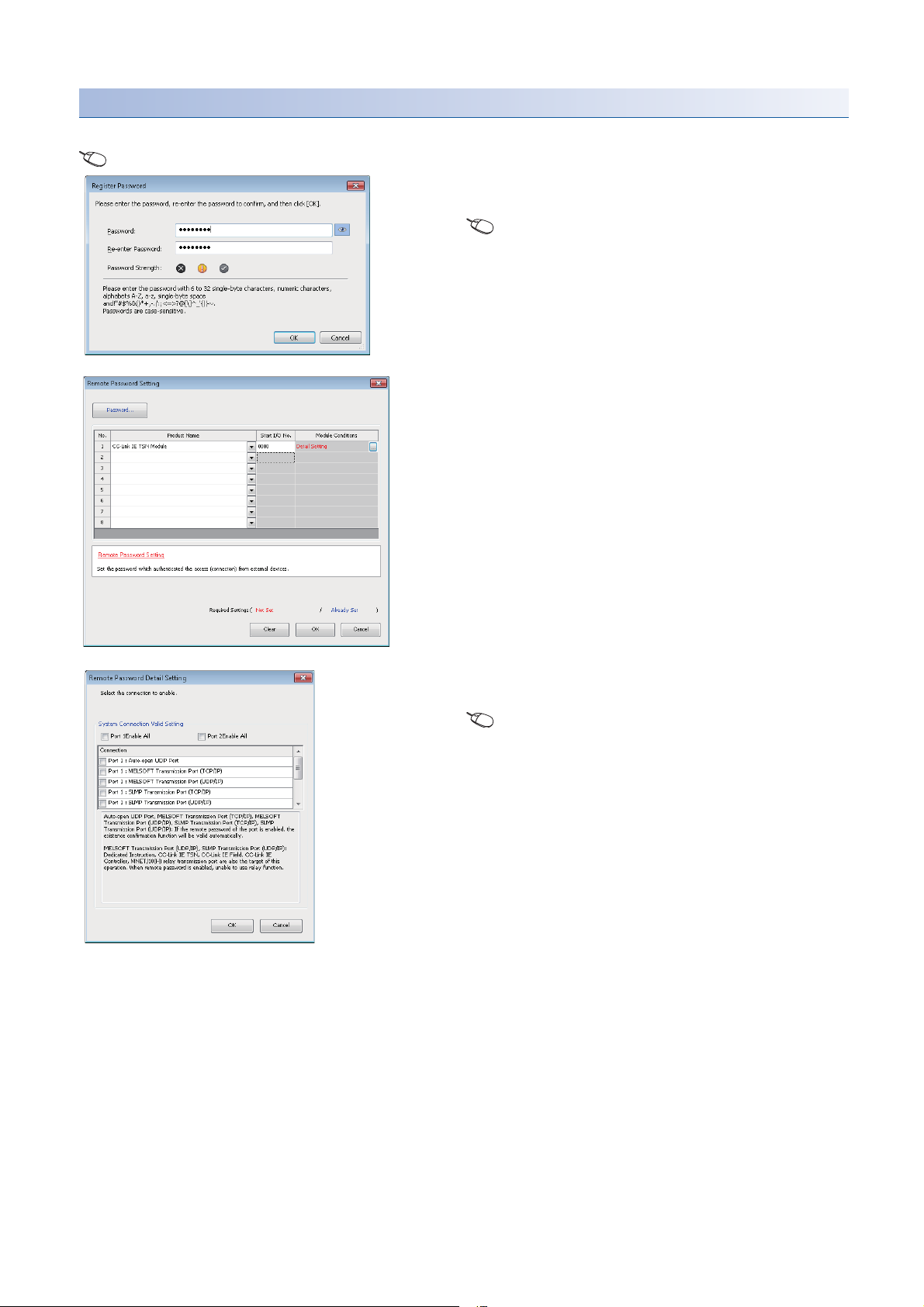
Setting method
Set on the "Remote Password Setting" window.
[Navigation window] [Parameter] [Remote Password]
1. Click the [Password] button, and register the remote
password on the "Register Password" window.
[Password] button
2. Select the module for which the remote password is to
be applied, and set the start I/O No..
3. Set the target connection on the "Remote Password
Detail Setting" window.
"Detail Setting" for the target module
4. Write the remote password to the CPU module.
5. The remote password is enabled when the CPU module
is reset or powered off and on.
■PING
This function uses the Ping command to perform an alive check of external devices whose access is permitted in UDP
communications. Therefore, if external devices do not respond to ping, an alive check error (event code 00906H) occurs.
When this function is used for UDP communications, check if the security setting of external devices (such as a firewall) is set
to respond to ping.
26
1 FUNCTIONS
1.4 Security
Page 29

Access permitted/prohibited processing operation
This section describes the processing for permitting or prohibiting access of the CPU module with remote password by the
external device.
■Access permit processing (Unlock processing)
The external device trying to communicate unlocks the remote password set for the connected Motion module.
If the password is not unlocked, the Motion module to which the external device is connected prohibits access, so an error
occurs in the external device.
The unlocking methods are shown below.
• SLMP dedicated command (Remote Password Unlock)
• Input password from engineering tool
■Access processing
Access to the specified station is possible when the remote password is correctly unlocked. Execute the arbitrary access.
■Access prohibit processing (Lock processing)
When access to the specified station ends, lock the remote password from the external device to disable subsequent access.
The locking methods are shown below.
• SLMP dedicated command (Remote Password Lock)
• Lock with engineering tool (executed automatically)
1
1 FUNCTIONS
1.4 Security
27
Page 30
Precautions
The following section lists the precautions for using remote password.
Ethernet
A
B
C
D
Enable/
Disable
Remote password
check
No remote password
parameter
Remote password
parameter
■Set connection
Set the remote password for the connection used for data communication with an external device that can execute the unlock/
lock processing.
■When remote password is set for UDP/IP connection
• Determine the external device to communicate with and perform data communication. (With UDP/IP, after the remote
password is unlocked, data can be exchanged with devices other than the unlocked external device too. Determine the
communication destination before starting use.)
• Always lock the remote password after data communication is finished. (If the remote password is not locked, the unlocked
state is held until timeout occurs.)
■TCP/IP close processing
If the TCP/IP is closed before the TCP/IP is locked, the CPU module will automatically start the lock processing.
■Remote password valid range
The remote password is valid only for access from the Motion module for which the parameters are set. When using multiple
CPU modules in a multiple CPU system, set a remote password for each CPU module for requiring a remote password.
The remote password is checked when accessing with path A or B.
The remote password is not checked when accessing with path C or D.
28
1 FUNCTIONS
1.4 Security
Page 31

1.5 RAS
No.0 No.1 No.2 No.0
No.0 No.1 No.2 No.0
No.0 No.1 No.0 No.2
This acronym stands for Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability. This function improves overall usability of automated
equipment.
Slave station disconnection
In star topology, the data link of the slave station where the error occurred is stopped, so the data link is connected only with
the normal slave stations. In line topology, the slave station where the error occurred and the stations beyond are
disconnected.
Master station duplication detection
If there are multiple master stations on one network, duplication is detected.
• When multiple master stations are simultaneously powered on, or when multiple master stations are simultaneously
connected, Master station duplication (error code 300FH) is detected in all master stations and cyclic transmission cannot
be performed in all stations. (Transient transmission available)
• If another master station is added to the network during data link, Master station duplication (error code 300FH) is detected
in the added master station and cyclic transmission cannot be performed. (Transient transmission available) Other stations
continue data link.
1
• If two networks are connected during data link, Master station duplication (error code 300FH) is detected in master stations
on both networks and cyclic transmission cannot be performed in all stations. (Transient transmission with IP address
specification is available)
1 FUNCTIONS
1.5 RAS
29
Page 32

IP address duplication error
Precautions
192.163.3.0 192.163.3.1 192.163.3.2 192.163.3.1
192.163.3.0 192.163.3.1 192.163.3.2 192.163.3.1
If one network has stations with the same IP address, duplication is detected.
• If there is already a station with the same IP address when adding a slave station, IP address duplication (error code
2160H) is detected in a station to be added and data link cannot be performed. (Other stations continue data link.)
When the slave station that has already been connected (linked up) with TSN hub is to be added to each TSN HUB, IP
address duplication is not detected in a station to be added. If IP address duplication (error code 1802H) is detected in the
master station, disconnect the relevant slave station from the network. Otherwise, multiple stations with the same IP address
will exist on the same network, possibly leading to transient transmission being sent to an unintended station.
• If the startup processing of cyclic transmission is executed by powering off and on the master station, when a station with
the same IP address is in the network, IP address duplication (error code 3021H) is detected in the master station and data
link cannot be performed.
• During cyclic transmission, IP address duplication is regularly checked in the master station. When there are overlapping IP
addresses, IP address duplication (error code 1802H) is detected in the master station and cyclic transmission cannot be
performed with the relevant slave station. (Other stations continue data link.)
• IP address duplication between an Ethernet device and a CC-Link IE TSN device, and IP address
duplication between Ethernet devices are not detected at cyclic transmission startup of the master station.
• Station No. duplication is not detected.
Methods of recovery from IP address duplication
If IP address duplication is detected in the master station (error codes 1802H, 3021H), change the IP address of the
corresponding station, and power off and on the master station, or reset it.
30
1 FUNCTIONS
1.5 RAS
Page 33

Time synchronization
Precautions
No.0 No.1 No.2
This synchronizes the time of all stations connected to CC-Link IE TSN with the time synchronization source (Motion module
of the master station).
Even if this function is not used, the time of the slave station is always automatically synchronized with the master station.
Setting method
It is set with the buffer memory. ( Page 90 Time synchronization)
If there is no device with a higher priority than the master station, the CPU modules on the same base
synchronize with the time of the Motion module in the master station, which becomes the time synchronization
source.
For the priority verification method and setting method, refer to the manual of the time synchronization device.
1
If "Connection Device Information" of "Basic Settings" is set as "Authentication Class B Only", use a CC-Link
IE TSN-compatible switching hub certified by the CC-Link Partner Association. A slave station connected to
an industrial switching hub that is not compatible with CC-Link IE TSN cannot perform data link.
• If this function is used, the time setting function (SNTP client) of the Ethernet-equipped module cannot be used. (
MELSEC iQ-R Ethernet User's Manual (Application))
• If multiple Motion modules are mounted to a CPU module on the same base, set time synchronization for only one Motion
module. If time synchronization is set for multiple, they are overwritten by the time that is synchronized later.
• When using the multiple CPU system configuration, the CPU module No.1 becomes the time synchronization source.
1 FUNCTIONS
1.5 RAS
31
Page 34

1.6 Others
No.0
GX Works3
No.2
ÒÓ
(A) (A)
No.0
No.2
Ö
Õ
(B)
Ô
SLMP
(A) (B) (A)
Slave station parameter automatic setting
Parameters of the slave station are saved in the master station, and the parameters will be automatically set when the slave
station is connected/returned.
If parameters are changed on the slave station side, saved parameters on the master station side are automatically updated.
Slave station parameter automatic setting from the master station
1. Parameters of the slave station set using the engineering tool are saved in the memory of the CPU module in the master
station or the SD memory card by writing.
2. When the slave station is connected/returned by power-on, saved parameters are automatically set from the master
station.
Save parameter (A) of the slave station to the CPU module on the master station.
When the slave station is returned/connected, saved parameter (A) is automatically set from the master station to the slave station.
Automatic update of saved parameter
1. If parameters on the slave station side are changed by the engineering tool or SLMP, the parameters of the slave station
that are saved in the memory of the CPU module or the SD memory card are automatically updated.
2. When the module of the slave station has been replaced, updated parameters are automatically set from the master
station by resetting the master station or turning its power off and on.
Parameter (A) of the slave station is changed to (B) by SLMP.
Saved parameter (A) of the CPU module on the master station is automatically updated to parameter (B).
• The master station starts data link with the slave station after parameters of the slave station are
automatically set.
• The slave station parameter automatic setting is also executed for slave stations set as reserved stations.
• The slave station is a CC-Link IE TSN module. (For checking if a module is compatible with automatic
32
1 FUNCTIONS
1.6 Others
update of saved parameter, refer to the manual of the module being used for the slave station.)
Page 35

Setting method
Precautions
Set in the "Parameter of Slave Station" window. ( Page 46 Parameter processing of a slave station)
• A slave station whose slave station parameter automatic setting abnormally ended does not start data link, and 'Execution
result of slave station parameter automatic setting function' (SW0160 to SW0167) turns on. Check 'Detailed execution
result of slave station parameter automatic setting' (SW0194) and the event history and perform corrective actions for
stored error codes.
• Do not disconnect the slave station that is currently executing an automatic update of saved parameters. Update of
parameter may fail.
• Do not turn off the master station that is currently executing an automatic update of saved parameters. Incorrect
parameters are automatically set in the slave station at the next power-on.
• If saved parameters are not in the CPU module when executing an automatic update of saved parameters, an error
response is returned to the relevant slave station.
• Check if the checkbox of "Parameter Automatic Setting" of the slave station is selected in "Network Configuration Settings"
under "Basic Settings".
• Check if the IP address of the slave station in the "Network Configuration settings" under "Basic Settings" matches the
actual IP address of the slave station.
1
1 FUNCTIONS
1.6 Others
33
Page 36

2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
This chapter describes the parameter settings required for communications between the Motion module and other stations.
2.1 Setting Parameters
1. Add the Motion module in the engineering tool.
[Navigation window] [Parameter] [Module Information] Right-click [Add New Module]
2. The required settings, basic settings, and application settings are included in the parameter settings. Select one of the
settings from the tree on the window shown below.
[Navigation window] [Parameter] [Module Information] Target Module [Module parameter (Network)]
3. After setting parameters, click the [Apply] button.
4. Write parameters to the CPU module using the engineering tool.
[Online] [Write to PLC]
5. The settings are reflected by resetting the CPU module or powering off and on the system.
The settings displayed on the required settings, basic settings, and application settings pages (default: ) are
the values that are displayed when the [Restore the Default Settings] button on each window of the
engineering tool is clicked.
34
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.1 Setting Parameters
Page 37

2.2 Required Settings
Set the station type or IP address of the Motion module.
Item Description Reference
Station Type Set the station type of the Motion module. Page 35 Station Type
Network No. Set the network No. of the Motion module. Page 36 Network No.
Station No./IP Address
Settings
Set the IP address of the Motion module. Page 36 Station No./IP Address Settings
2
Station Type
Set the station type of the Motion module.
Item Description Setting range
Station Type The Motion module is used as the master station.
Only one master station can be set in a network.
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.2 Required Settings
35
Page 38

Network No.
Precautions
Set the network No. of the own station of the Motion module.
Item Description Setting range
Network No. Set the network No. of the Motion module. 1 to 239
(Default: 1)
Set a network No. that does not duplicate any other network Nos.
In particular, when using an Ethernet-equipped module (CPU module) at default, the IP address is 192.168.3.39 and the
network No. is the third octet of the IP address, thus 3. Because setting the network No. of the Motion module to 3 causes
duplication, set another network No.
Station No./IP Address Settings
Set the station No. of the own station of the Motion module.
Item Description Setting range
Station No. The station No. of the master station is fixed to 0.
IP Address Set the IP address.
Do not set the following values.
• The third and fourth octets are all 0 or all 1.
• The host address bits are all 0 or all 1
• Reserved address
Subnet Mask Set the subnet mask.
Set the same value for the master station and slave station.
If the subnet mask is empty, the address class (class A, class B, class C) is determined from the
setting of "IP Address", and operation is done with the subnet mask according to the address
class.
The subnet mask for each class is as follows.
• Class A: 255.0.0.0
• Class B: 255.255.0.0
• Class C: 255.255.255.0
The IP address for each class is as follows.
• Class A: 0.x.x.x to 127.x.x.x
• Class B: 128.x.x.x to 191.x.x.x
• Class C: 192.x.x.x to 223.x.x.x
The host address for each class is the 0 section shown below.
• Class A: 255.0.0.0
• Class B: 255.255.0.0
• Class C: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway Set the default gateway. •Empty
0.0.0.1 to 223.255.255.254
(Default: 192.168.3.253)
•Empty
• 0.0.0.1 to 255.255.255.255
(Default: empty)
• 0.0.0.1 to 223.255.255.254
(Default: empty)
36
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.2 Required Settings
Page 39

2.3 Basic Settings
Set the network configurations, network topology, or other parameters for the Motion module.
2
Item Description Reference
Network Configuration
Settings
Refresh Settings Set link refresh ranges between the devices of the CPU module and the link special
Network Topology Select the network topology type according to the actual network configuration. Page 38 Network Topology
Communication Period Setting Set cycles of the cyclic transmission and transient transmission. Page 38 Communication Period
Connection Device
Information
Slave Station Setting Set items related to the slave station for data link error. Page 39 Slave Station Setting
Set the CC-Link IE configuration. Page 42 "CC-Link IE TSN
Configuration" Window
relay (SB), link special register (SW), and link devices of the Motion module, or
between the module label of the CPU module and the link special relay (SB) and
link special register (SW) of the Motion module.
Setting
Set the authentication Class of connected devices. Page 39 Connection Device
Information
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.3 Basic Settings
37
Page 40

Network Topology
Precautions
Select the network topology type according to the actual network configuration.
Setting is not required and can be left as "Line/Star" (default).
Communication Period Setting
Perform basic cycle setting.
Item Description Setting range
Basic Period
Setting
Multiple Cycle
*3
Setting
Setting in Units of 1s Select whether to set the basic cycle in increments of 1s. • Set
• Not set
(Default: Not set)
Communication Period Interval Setting
(Do Not Set it in Units of 1s)
Communication Period Interval Setting
(Set it in Units of 1s)
System Reservation Time Necessary time for the system to guarantee the
Cyclic Transmission Time Of communication cycle intervals, set the time to be allocated
Transient Transmission Time The value of "Communication Period Interval Setting" minus
Normal-Speed Select the "Normal-Speed" cycle for a basic cycle.
Low-Speed Select the "Low-Speed" cycle for a basic cycle.
*1
Select a communication cycle. • 125.00s
• 250.00s
• 500.00s
• 1000.00s
• 2000.00s
• 4000.00s
(Default: 1000.00s)
Input a communication cycle interval. 125.00s to 4000.00s (in
increments of 1s)
(Default: 1000.00s)
communication cycle interval.
When using an authentication class B/A device with a
communication speed of 100Mbps in the basic cycle, select
200s.
to cyclic transmission.
"Cyclic Transmission Time" and "System Reservation Time" is
displayed.
Secure 14.00s or more.
Setting is not required and can be left as "4".
Setting is not required and can be left as "16".
*2
• 20.00s
• 200.00s
(Default: 20.00s)
5.00s to 3966.00s (in
increments of 1s)
(Default: 500.00s)
14.00s to 3975.00s (in
increments of 1s)
(Default: 480.00s)
4 times
16 times
*1 An error will occur when a value outside the setting range is set.
*2 When the cyclic transmission time is 31.25 s or 62.5 s, no error will occur even though the calculation result of the transient
transmission is the lower limit value or less.
*3 The setting is invalid.
When the TSN hub is used, set TS0 to TS2. (Timeslot information from the setting values in "Communication
Period Setting")
Setting values of TS0 to TS2 can be checked with the buffer memory. ( Page 89 Timeslot information)
There are slave devises which does not correspond to some communication piriod setting . Check the specifications of each
devise.
38
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.3 Basic Settings
Page 41

Connection Device Information
Precautions
Set the information of the connected device.
Item Description Setting range
Authentication
Class Setting
Set the authentication Class of connected devices. • Authentication Class B only
• Mixture of Authentication Class B/A or
Authentication Class A Only
(Default: Authentication Class B only)
In the case of an "Authentication Class B Only" and a "Mixture of Authentication Class B/A or Authentication Class A Only"
system configuration, different restrictions apply. (MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual (Startup))
Slave Station Setting
Set items related to the slave station.
Item Description Setting range
Disconnection
Detection
Setting
Set the number of consecutive communication failures until a slave station in which a data link error has
occurred is considered disconnected.
•2 times
•4 times
•8 times
(Default: 4 times)
2
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.3 Basic Settings
39
Page 42

2.4 Application Settings
Set the event reception from other stations, module operation mode, and other settings for the Motion module.
Item Description Reference
Supplementary Cyclic Settings*1Set the station-based block data assurance and I/O maintenance settings.
Transient Transmission Group
No. Setting
Parameter Name
Dynamic Routing
Event Reception from Other Stations
Module Operation Mode Set the module operation mode of the Motion module. Page 41 Module Operation Mode
Security Set the security measures for access to the Ethernet device. Page 41 Security
Interlink Transmission Settings
*1 The setting is invalid.
*2 An error will occur when a value other than 0 is set.
*3 An error will occur when the setting is disabled.
*2
*1
*3
Set the transient transmission group No..
Set a name for the module parameter if desired.
Select whether to enable the dynamic routing function.
Select whether to obtain the history of events occurring in the other
stations.
*1
Set link device ranges when cyclic data are transferred from a station in
the own network to a station in a different network.
Page 40 Event Reception from Other Stations
Event Reception from Other Stations
Select whether to obtain the history of events occurring in the other stations.
Item Description Setting range
Event Reception from Other Stations Select whether to obtain the history of events occurring in the other stations. • Enable
•Disable
(Default: Enable)
40
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.4 Application Settings
Page 43

Module Operation Mode
Set the module operation mode of the Motion module.
Item Description Setting range
Module
Operation
Mode
Online
• Select this mode to connect the Motion module to the network for performing data link with other
stations.
Security
Set the security measures for access to the Ethernet device.
Item Description Setting range
IP Filter
Settings
IP Filter Settings
Up to 32 IP addresses can be set as an IP address to be allowed or denied by the IP filter.
Range specification as a single setting and specification of the IP addresses to be excluded from the set range are also
possible.
Item Description Setting range
Access from IP address below Select whether to allow or deny the access from the specified IP addresses. • Allow
Range Setting Select this item when specifying the IP addresses by range. (Default: Clear)
IP Address Set the IP addresses to be allowed or denied.
IP Address Excluded from Range When selecting "Range Setting", set the IP address to be excluded from the set range.
IP Filter Set whether to use the IP filter. • Not Use
•Use
(Default: Not Use)
IP Filter Settings Set the IP addresses to be allowed or denied.
• Deny
(Default: Allow)
0.0.0.1 to
When selecting "Range Setting", enter the start IP address (left field) and end IP address
(right field) of the range.
Up to 32 IP addresses can be set.
223.255.255.254
(Default: empty)
0.0.0.1 to
223.255.255.254
(Default: empty)
2
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.4 Application Settings
41
Page 44

2.5 "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" Window
Drag and drop the text.
List of stations
Network map
Set parameters of slave stations (the number of points and assignment of link devices) in the master station.
Perform either the parameter setting of slave stations or the detection of connected/disconnected devices.
Navigation window "Parameter" "Module Information" Target module "Module Parameter (Network)" "Basic
Settings" "Network Configuration Settings"
Parameter setting of a slave station
1. Select the module in "Module List" and drag it to the list of stations or the network map.
2. Set the required items.
3. Select [Close with Reflecting the Setting] and close the "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" window.
42
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.5 "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" Window
Page 45

Setting items
• Simple Display: Click the [Simple Display] button to display a narrow portion of items. Use for operation with default settings
or the minimum required settings. (Default)
• Detailed Display: Click the [Detailed display] button to display all items.
Simple
display
Assignment
No. The total number of slave stations set in the "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration"
Model Name The module model name is displayed.
STA# Enter the station No. of each slave station connected to the network.
Station Type
Motion
RX Setting Assign RX/RY points in increments of 16. ( Page 17 Communications using
RY Setting
RWw Setting Assign RWw/RWr points in increments of 4. ( Page 17 Communications
RWr Setting
LB Setting
Parameter Automatic
Setting
IP Address Set the IP address of a station that performs cyclic transmission. 0.0.0.1 to 223.255.255.254
Subnet Mask Set a subnet mask to identify a network address.
Default Gateway Set the default gateway address to connect to the external network. • 0.0.0.1 to 223.255.255.254 (When the
Reserved/Error Invalid
Station
Communication Period
Setting
Station Information ■Station-specific mode setting
*1
*1
Detailed
display
Method
*1
Control
Station
LW
Setting
Description Setting range
Select a link device assignment method.
Select "Points/Start" for the motion control station.
• Points/Start: Enter the Nos. of points and start Nos. of link devices.
• Start/End: Enter the start and end Nos.of link devices.
window is displayed.
To set a module where the profile is not registered, select it from the "General
CC-Link IE TSN Module" list or register the profile before setting the model name.
For how to register a profile, refer to the following.
GX Works3 Operating Manual
Station Nos. do not need to be set consecutively, but must be unique.
Set the station types. Select the station types same as those of the modules
connected to the network.
Use the device profile to allow selection of target stations for motion control. • Checked: Motion control target
*1
slave labels)
Modules with settings provided by device profile are automatically set from
selected models. (Excluding modules with a number of points that is not fixed)
using slave labels)
Modules with settings provided by device profile are automatically set from
selected models. (Excluding modules with a number of points that is not fixed)
*2
Assign LB points in increments of 16 and LW points in increments of 1.
Modules with settings provided by device profile are automatically set from
selected models. (Excluding modules with a number of points that is not fixed)
*2
Set whether to set the parameters of each slave station automatically.
This cannot be set for extension modules. However, the parameter automatic
setting of extension modules is interlocked with the settings of the connected
main module.
Set the same value for the master station and slave station. Even if a slave
station has a different subnet mask from the master station, it does not result in
an input error.
If 255.255.255.255 is set, leave it empty.
Set the slave station as a reserved station or error invalid station. No Setting
When multiple communication cycles are set, set the cycle of each slave station. Basic Period
Set the station-specific mode of the slave station. (Only when the slave station
supports the station-specific mode)
• Points/Start
• Start/End
(Default: Points/Start)
1 to 65 (Including the master station)
• Master station: Fixed to "0"
• Slave station: 1 to 64
(Default: Serial No. of added stations)
• Local Station
• Remote Station (Fixed other than the
Motion module)
(Default: Varies depending on the set module)
• Not checked: Not motion control target
(Default: Not checked)
• Number of points: No point, 16 to 16384
• Start: 0000H to 3FF0H
• End: 000FH to 3FFFH
(Default: Varies depending on the set module)
• Number of points: No point,4 to 8192
• Start: 0000H to 1FFCH
• End: 0003H to 1FFFH
(Default: Varies depending on the set module)
• Checked: Distribute parameters
• Not checked: Do not distribute parameters
(Default: Not checked)
(Default: The first to third octets have the
same values as the master station, the fourth
octet has a serial No. from 1 to 254)
0.0.0.1 to 255.255.255.255
(Default: The same value as subnet mask of
the master station which is set by the module
parameter)
address is inputted by decimal values)
• Empty (0.0.0.0)
The setting varies depending on the set
module.
2
*1 An error will occur when a value outside the setting range is set.
*2 An error will occur when the number of points are set.
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.5 "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" Window
43
Page 46

• Because a portion of the setting items are not displayed in simple display, when there are deficiencies in
setting items that are not displayed, the "Output" window may display a warning or error by selecting [Close
with Reflecting the Setting].
If a warning is displayed, switch to detailed display and correct the items.
• Stations which have the station No. can be set up to 64 stations, and up to 64 stations can be set the
network configuration settings. When using extended modules supporting the CANopen communication,
one module is counted as one station.
Connected/Disconnected Module Detection
1. Click the [Connected/Disconnected Module Detection] button.
2. When the [Execute] button is clicked according to the instruction on the window, connected slave stations are detected
and displayed on the "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" window.
3. Check items in the list of stations and change them as necessary. ( Page 43 Setting items)
4. Select [Close with Reflecting the Setting] and close the "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" window.
Detection of connected/disconnected devices cannot be executed in the following cases.
• Link Direct Device Setting" of the CPU parameter is not "Extended Mode (iQ-R Series Mode)".
• The actual system configuration is incorrect. (Such as IP address duplication)
• The master station does not perform data link.
44
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.5 "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" Window
Page 47

Connection/Disconnection/Replacement
Precautions
When the [Connected/Disconnected Module Detection] button is clicked while the saved CC-Link IE TSN configuration is
displayed, IP addresses of detected slave stations are compared with the saved IP addresses of slave stations and displayed
as follows by connection/disconnection/replacement.
IP address verification
result
Detected slave stations are in the
saved CC-Link IE TSN structure.
Slave stations in the saved CCLink IE TSN structure are not
detected.
Detected slave stations are not in
the saved CC-Link IE TSN
structure.
Operation Display When station Nos. of
detected slave stations are
not set
Replace When parameters between a detected slave station and a saved CC-
Link IE TSN structure mismatch, the parameters are replaced with the
parameters of the detected slave station.
When the model name, model version, and station type are
mismatched, the following settings are inherited.
• "Motion Control Station"
• "RX Setting", "RY Setting", "RWr Setting", "RWw Setting", "LB
Setting", "LW Setting"
• "IP Address" of the master station
• "Subnet Mask"
• "Default Gateway"
• "Reserved/Error Invalid Station" (however, if "Reserved Station" is
set, the setting will change to the default.)
• "Network Synchronous Communication"
• "Communication Period Setting"
If only the station No. is mismatched, only the station No. is reflected,
and all the settings are inherited.
(However, if the station No. of the detected device has not been set,
the station No. of the device before replacement is inherited.)
Disconnect • Modules other than extension modules: Setting of "Reserved/Error
Invalid Station" is changed to "Reserved Station".
• Extension modules: Are deleted.
Connect Detected slave stations are added. (Settings other than "IP Address",
"STA#", and "Station Type" are default)
When adding a device, the defaults other than IP address, station No.,
and station type are set.
(However, if the station No. of the detected device has not been set,
the station No. is also set to the default.)
Added slave stations are displayed in the list of stations in the following
order.
• Modules other than extension modules: In the order of IP addresses,
following disconnected slave stations.
• Extension modules: In the order of sub-IDs, following connected
main modules and extension modules.
The station No. takes over the
station No. of the saved CC-Link
IE TSN structure.
A station No. is automatically
numbered as the youngest
unused station No. in the range
from 1 to 120.
The order of automatic
numbering is the same as the
displayed order in the list of
stations (see left).
2
When the station No. is set in the slave station using the CC-Link IE TSN structure and parameters are written in CPU
modules, the station No. of the slave station is held in the master station. When parameters are not to be written in CPU
modules, they are saved in the CC-Link IE TSN structure as slave stations with the station No. not set.
Register the profile of the target device to detect in advance.
If the profile is not registered, the following may be displayed.
• "Model Name" is "General Remote Station", "General Local Station", or "General Extension Module".
• "Station Type" is "Remote Station", "Local Station", or "Extension Module".
For how to register a profile, refer to the following.
GX Works3 Operating Manual
• Even when the profile is registered, if modules that are not available for detection of connected/
disconnected devices are used, "Model Name" and "Station Type" are not displayed correctly.
• This function is not available for local stations.
• Data link faulty stations cannot be detected by this function.
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.5 "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" Window
45
Page 48

Parameter processing of a slave station
Reads and saves the parameters from the slave station, and writes the saved parameters to the slave station.
Also, automatically set parameters of the slave station from the master station. ( Page 32 Slave station parameter
automatic setting)
Navigation window “Parameter” “Module Information” Ta r ge t mo du l e “Module Parameter (Network)” “Basic
Settings” “Network Configuration Settings”
Select and right-click the slave station, and select "Parameter of Slave Station" to display the "Parameter of Slave Station"
window.
46
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.5 "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" Window
Page 49

Item Description
Target Module Information Information for the selected slave stations is displayed.
Method selection Select processing to be executed for selected slave stations.
• Parameter auto-setting: Automatically set contents of "Write Value/Setting Value" to the
slave station. ( Page 32 Slave station parameter automatic setting)
• Parameter read: Read parameters from the selected slave station.
• Parameter write: Write parameters to the selected slave station.
Parameter
Information
Processing option When there are options for processing selected by "Method Selection", setting items are
[Import] button Read contents of parameter processing created in a CSV file.
[Export] button Output contents of parameter processing set in this window to a CSV file.
[Clear All "Read Value"] button Click to clear all setting details that were read using "Parameter read".
[Clear All "Write Value/Setting Value"]
button
Click to clear all setting details that are written using "Parameter write".
displayed.
Procedure for clearing a saved parameter
When returning the saved parameters of a not-required slave station to the not-set status, perform the following procedure.
1. If the saved parameters are to be saved, output them in a CSV file using the [Export] button.
2. Delete not-required slave stations from the list of stations.
3. Select the same module as the deleted slave station in "Module List", and drag it to the list of stations or the network
map.
2
Conditions for clearing a saved parameter
Saved parameters of a slave station can be cleared under the following conditions.
When saved parameters are cleared, execute "Parameter auto-setting" or "Parameter read" in the "Parameter of Slave
Station" window and read the parameters of the slave station.
Item Operation Description
"CC-Link IE TSN
Configuration" window
"Parameter of Slave
Station" window
Module Parameter Manually delete "Network Configuration Settings" to apply. Parameters of "Network Configuration Settings" return to default.
System Parameter Divert system parameters from another project. Parameters of the slave station are not diverted.
Module Configuration Delete a module and check. Parameters are deleted together with the module.
Navigation window Delete a module.
Read from PLC Read module parameters that have a different network
Navigation window Import the data of a Motion module to take network
MELSOFT Navigator Reflect the parameter. Saved parameters are cleared.
Open the "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" window. When there is not a slave station with the station No. that matches
saved parameters in the "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" window,
saved parameters of the relevant slave station are skipped.
Skipped parameters of the slave station are cleared.
Reflect setting and close the window. Saved parameters of a slave station that is not in the actual system
configuration are cleared.
Execute detection of connected/disconnected devices. All saved parameters are cleared.
Change the function version in the "Properties" window. When the "Properties" window is closed, saved parameters are
cleared.
Open the "Parameter of Slave Station" window. Saved parameters that mismatch the relevant slave station are
skipped.
Clicking the [Close with Reflecting the Setting] button in the above
state clears the skipped saved parameters.
Change the "Setting Method of Basic/Application Settings"
under "Parameter Setting Method" in "Required Settings"
from "Parameter Editor" to "Program".
Change "Station Type" or set parameters that do not exist.
Parameters are overwritten.
configuration and the same start I/O No..
settings.
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.5 "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" Window
47
Page 50

Command execution to slave stations
The command to a slave station is executed.
Navigation window “Parameter” “Module Information” Ta r ge t mo du l e “Module Parameter (Network)” “Basic
Settings” “Network Configuration Settings”
Select and right-click the slave station, select "Command Execution of Slave Station" from "Online" to display the "Command
Execution of Slave Station" window.
Item Description
Target Module Information Information for the selected slave stations is displayed.
Method selection Select processing to be executed for selected slave stations.
• Error clear request
• Error history clear request
Command setting When there are command settings for processing selected by "Method selection", setting items are
Execution Result Execution results of the processing selected in "Method selection" are displayed.
[Save in the CSV file] button Outputs the contents of this window to a CSV file.
48
2 PARAMETER SETTINGS
2.5 "CC-Link IE TSN Configuration" Window
displayed.
Page 51

3 TROUBLESHOOTING
This chapter describes troubleshooting of CC-Link IE TSN.
3.1 Checking with LED
This section describes troubleshooting with the LEDs of the Motion module.
When the RUN LED turns off
When the RUN LED turns off after powering on the Motion module, check the following.
Check item Action
Is the Motion module mounted correctly? Securely mount the Motion module on the base unit.
When the ERR LED turns on or is flashing
When the ERR LED turns on or is flashing, check the following.
Check item Action
Does any error occur in the module
diagnostics?
Is a disconnected station displayed on the "CCLink IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics"
window?
Take the actions displayed on the window.
• Correct "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings" of the master station in accordance with
the slave station actually connected.
• Perform troubleshooting for the disconnected station when the D LINK LED turns off or is flashing. (
Page 49 When the D LINK LED turns off or is flashing)
3
When the D LINK LED turns off or is flashing
When the D LINK LED turns off or is flashing, check the following.
Check item Action
Is the master station operating normally? • If an error has occurred in the CPU module on the master station, eliminate the cause of the CPU
module error. ( MELSEC iQ-R CPU Module User's Manual (Application))
• If an error occurs in the Motion module, take action according to the module diagnosis procedure. (
Page 52 Checking the Module Status)
Is the master station connected to the network? Connect the master station to the network.
Does the IP address of each station match the
"Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic
Settings" of the master station?
In the "Network Configuration Settings" under
"Basic Settings", are the third and fourth octets of
the IP address of the master station duplicated
with those of any other stations?
In the "Network Configuration Settings" under
"Basic Settings", does the network address
(subnet mask part) of the IP address of the master
station match that of other stations?
Are the third and fourth octets of the IP address set
to all 0 or all 1?
Is the host address of the IP address set to all 0 or
all 1?
Is a reserved address set to the IP address?
Do the used Ethernet cables conform to the
Ethernet standard?
Is the switching hub used operating normally? • Use a switching hub that conforms to the standard. (MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual
Does the station-to-station distance meet the
specifications?
Does the cabling condition (bending radius) meet
the specifications?
Correct the setting of the IP address in "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings" of the
master station.
• Set IP addresses in a way that does not duplicate the third to fourth octets of the IP address in all
stations.
• Set the IP address and subnet mask to match the network addresses of all stations.
• Set the third and fourth octets of the IP address to values other than all 0 or all 1.
• Set the host address of the IP address to values other than all 0 or all 1.
• Set an IP address other than a reserved address.
Replace the cables with Ethernet cables which conform to the standard. (MELSEC iQ-R Motion
Module User's Manual (Startup))
(Startup))
• Power off and on the switching hub.
Set the station-to-station distance within range. (MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual
(Startup))
Refer to the manual for the Ethernet cable, and correct the bending radius.
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.1 Checking with LED
49
Page 52

Check item Action
Is any Ethernet cable disconnected? Replace the Ethernet cable.
Is the network in the ring topology configured? Configure the network to avoid the ring topology.
Has the time synchronization source station been
reset?
Is the time synchronization source station turned
off?
Is the time synchronization source station
operating normally?
Has any other station been reset? • Avoid unnecessary reset, since a station is disconnected while resetting.
Are other stations turned off? Power on other stations.
Are other stations connected to the Motion module
operating normally?
Is a network topology with restrictions used for
connection?
Are station Nos. unique? Change the duplicated station No..
Is the IP address duplicated with another station? Change the IP address of the duplicated station.
Are 65 or more slave stations connected? Change the connection of the slave stations to 64 stations or less.
Are Ethernet devices properly connected to a
network line?
Is the IP address of the slave station blocked by
the IP filter setting of the master station?
Is the IP address of the master station blocked by
the IP filter setting of the slave station?
Are time synchronization devices with time
synchronization priority of 0 to 15 connected?
• Since a station is temporarily disconnected after switching the time synchronization source, wait for it to
return.
• Avoid unnecessary disconnections or returns in a station that is the time synchronization source.
Check the manual of the module used for the time synchronization source station.
• Start other stations.
• Check if the modules on the other stations are performing data link using CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE
Field diagnostics. ( Page 54 Checking the Network Status)
• Check the operation status of modules on other stations. ( User's manual for the module used)
Correct the wiring. (MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual (Startup))
Correct the mixed structure of the Ethernet device. (MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual
(Startup))
Correct the "IP Filter Settings" under "Application Settings".
Remove time synchronization devices with time synchronization priority of 0 to 15, or change the priority
setting to between 16 and 255. ( Manual for the time synchronization devices used)
50
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.1 Checking with LED
Page 53

When the L ER LED turns on
When the L ER LED turns on, check the following.
Check item Action
Are the Ethernet cables used normally? • Use an Ethernet cable that conforms to the standard. ( MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's
Is the switching hub used operating normally? • Use a switching hub that conforms to the standard. ( MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual
Is there any source of noise near the module or
cables?
Manual (Startup))
• Set the station-to-station distance within range. ( MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual
(Startup))
• If the Ethernet cable is disconnected, reconnect it.
(Startup))
• Power off and on the switching hub.
Change the location of the module or cables.
When the LINK LED turns off
When the LINK LED turns off, check the following.
Check item Action
Do the used Ethernet cables conform to the
Ethernet standard?
Does the station-to-station distance meet the
specifications?
Does the cabling condition (bending radius) meet
the specifications?
Is any Ethernet cable disconnected? Replace the Ethernet cable.
Is the switching hub used operating normally? • Use a switching hub that conforms to the standard. ( MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual
Are other stations connected to the Motion module
operating normally?
Is the communication speed of connected devices
1Gbps?
Replace the cables with Ethernet cables which conform to the standard. ( MELSEC iQ-R Motion
Module User's Manual (Startup))
Set the station-to-station distance within range. ( MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual
(Startup))
Refer to the manual for the Ethernet cable, and correct the bending radius.
(Startup))
• Power off and on the switching hub.
Check the manual of the module used for the other stations and take action accordingly. ( User's
manual for the module used)
Connect devices which support a communication speed of 1Gbps.
3
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.1 Checking with LED
51
Page 54

3.2 Checking the Module Status
This section describes troubleshooting to check the status of the module by executing diagnostics and operation tests using
the engineering tool.
Module Diagnostics
The following items can be checked in the "Module Diagnostics" window for the Motion module.
Item Description
[Error Information] tab Displays the details of the errors currently occurring and the corrective actions for these errors.
"-" may be displayed in "Occurrence Data" of an error that occurred immediately after the power was turned on.
[Module Information List] tab Displays the LED information and individual information of the Motion module.
Supplementary
Function
Error Information
The details of the errors currently occurring and the corrective actions for these errors are displayed in the [Error Information]
tab.
CCIET/CCIEF
diagnostics
Enables checking the cause to resolve the problem when an error occurs in the CC-Link IE TSN. ( Page 54 Checking
the Network Status)
Item Description
Status Major: An error such as hardware failure or memory failure. The module stops operating.
Moderate: An error, such as parameter error, which affects module operation. The module stops operating.
Minor: An error such as communication failure. The module continues operating.
Error code Page 69 List of Error Codes
[Event History] button Click this button to check the history of errors that have occurred on the network, errors detected for each module, and
operations that have been executed. ( Page 84 Event List)
Detailed Information Displays up to three information items for each error, such as parameter information, operation source information, and
Cause Displays the detailed error causes.
Corrective Action Displays the actions to eliminate the error causes.
52
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.2 Checking the Module Status
system configuration information. ( Page 82 List of Parameter Nos.)
Page 55

Module Information List
The LED information and individual information of the Motion module are displayed in the [Module Information List] tab.
3
Item Description
LED information Displays the LED status of the Motion module.
Individual
information
Station Type Displays the station type set for the selected module.
Network No. Displays the network No. set for the selected module.
Station No. Displays the station No. set for the selected module.
Transient transmission group No. Displays the transient transmission group No. set for the selected module.
IP address Displays the IP address set for the selected module.
MAC address Displays the MAC address of the selected module.
P1 Communication Speed Displays the communication speed set using the auto-negotiation function.
P2 Communication Speed
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.2 Checking the Module Status
53
Page 56

3.3 Checking the Network Status
Precautions
This section describes troubleshooting to check the status of the network by executing diagnostics and operation tests using
the engineering tool.
CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics
For CC-Link IE TSN, perform status monitoring, operation tests, or others.
In the following cases, the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics cannot start.
• The Motion module is not connected to CPU modules specified on the "Specify Connection Destination Connection"
window.
• In CPU parameters of CPU modules specified on the "Specify Connection Destination Connection" window, "Link Direct
Device Setting" of "Memory/Device Setting" is not "Extended Mode (iQ-R Series Mode)".
Diagnostic items
When starting the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics by specifying "No Specification" in "Other Station Setting" on
the "Specify Connection Destination Connection" window, the following items can be used.
: Diagnosed : Diagnosed with restrictions
Item Overview Connection
destination of
engineering tool
Master station
Status
monitor
Operation
Te st
Remote Operation Operate remotely from the engineering tool to
Network map Check if any errors are being caused by the
devices and cables that configure the network. In
addition, check the operating status of each
station.
Data Unlinked Check that there is no station that is set on an
actual network.
Selected Station Communication
Status Monitor
Communication Test Check whether outgoing/incoming paths of
Check details of, or actions for, errors that
occurred in a selected station.
transient transmission between the own station
and the communication target are correct.
slave stations.
Page 57 "CC-Link IE TSN/
Page 62 Communication
*1
Reference
CC-Link IE Field
Diagnostics" window
Te st
Page 63 Remote Operation
*1 If the setting on the "Specify Connection Destination Connection" window of the engineering tool is as follows, remote operation cannot
54
be executed with "All Stations Specified".
Connection via Ethernet with the selections "Ethernet Board" for the personal computer-side I/F and "CC IE TSN/Field Module" for the
programmable controller-side I/F
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.3 Checking the Network Status
Page 57

Usage methods
Disconnected
station
This section describes how to use the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics.
■When "No Specification" is specified in "Other Station Setting" on the "Specify Connection
Destination Connection" window
1. Connect the engineering tool to the CPU module.
If a slave station cannot be monitored due to an error such as cable disconnection, directly connect the engineering tool to the
slave station.
2. Start the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics.
[Diagnostics] [CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics]
3. When the following window opens, select the Motion module to be diagnosed and click the [OK] button to start the CC-
Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics.
Modules are listed in the order configured in module information.
3
4. Select the station to be diagnosed from "Select Station" or in the network map.
• An icon indicating an error is displayed on the module icon of the station where an error occurs.
• A disconnected station that has performed data link is indicated with the "Disconnected Station" icon in the network map.
However, a disconnected station in following case is displayed on the right end of the area.
Stations displayed on the right end of the area.
• A station that was reconnected to a network after disconnecting/inserting the cable or powering off and on the system, and remains disconnected
• A disconnected station with the station icon deleted in the network map by clicking the [Update] button
• The "Error" icon is displayed on the icon of a cable where a communication error occurs. To check the details of the
communication error, click the neighboring stations of the "Error" icon.
When the station to be diagnosed cannot be selected, the status of network No. mismatch or duplication of
master stations cannot be checked using the CC-Link TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics. Check the error
details by directly connecting the engineering tool to the station where an error occurs, and opening the
"System Monitor" window.
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.3 Checking the Network Status
55
Page 58

5. The status of a station selected in "Network Status" is displayed in "Selected Station Communication Status Monitor".
( Page 57 "CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics" window)
The station status is displayed on the top of "Selected Station Communication Status Monitor".
If an error occurs, a button indicating the error such as [PORT2 Communication Error] is displayed in "Selected Station
Communication Status Monitor". Click the button to check the error details and actions.
6. Various tests and operations can be performed by clicking the "Operation Test" or "Selected Station Operation" on the
bottom left of the window. ( Page 62 Communication Test, Page 63 Remote Operation)
■When a setting other than "No Specification" is specified in "Other Station Setting" on the
"Specify Connection Destination Connection" window
1. Connect the engineering tool to the CPU module.
2. Start the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics.
[Diagnostics] [CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics]
The CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics cannot be started when "Other Station (Co-existence
Network)" has been specified in "Other Station Setting" on the "Specify Connection Destination Connection"
window and "CC-Link" or "C24" has been specified in "Co-existence Network Route".
3. Select the Motion module of the network No. to be diagnosed and click the [OK] button to start the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-
Link IE Field diagnostics.
4. Step 4 and later is the same procedure as when "No Specification" is specified in "Other Station Setting" on the "Specify
Connection Destination Connection" window. ( Page 55 When "No Specification" is specified in "Other Station
Setting" on the "Specify Connection Destination Connection" window)
56
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.3 Checking the Network Status
Page 59

"CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics" window
Network map
Disconnected station
status monitor
Item Description
Select
Diagnostics
Destination
Monitor
Status
[Update] button If the actual network configuration and network map of the "CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics" window are
[Legend] button Displays the meaning of icons displayed in the "CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics" window.
St. Info The display name of the slave station can be selected from "By Device Name", "By Station Type", "By Model Name", or
Module The Motion module under diagnostics is displayed.
[Change Module]
button
Select Station Selects the station No. of the station to be diagnosed.
[Start Monitoring]
button
[Stop Monitoring]
button
Allows to change the target Motion module when multiple Motion module are mounted.
A station to be diagnosed can also be selected by clicking the module icon displayed in the network map.
Starts monitoring the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics.
Stops monitoring the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics.
inconsistent, the network map update is executed so they are matched. A data link error may momentarily occur in all
the stations and outputs of the connected slave stations may turn off since all stations on the network will be
reconnected when executing the network map update. Set output data if needed.
"By IP Address".
"By Device Name" displays the information entered in "Alias" of "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic
Settings". The station type is displayed when the "Alias" is not entered.
3
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.3 Checking the Network Status
57
Page 60

Item Description
Network
Status
Selected Station Communication
Status Monitor
Operation
Te st
Selected
Station
Operation
Total Slave Stations
(Parameter)
Total Slave Stations
(Connected)
Communication Cycle
Interval Setting value
Number of Station
Errors Detected
Change IP Address
Display
Network map Indicates the CC-Link IE TSN structure and the status of each station. ( Page 59 Network map)
Data Unlinked Station
Monitor
[Communication Test]
button
[Remote Operation]
button
Displays the total number of slave stations set in "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings".
Stores the total number of slave stations (number of slave stations) that are actually connected by data link in the CCLink IE TSN.
The communication cycle interval set in "Communication Period Setting" under "Basic Settings" of the master station is
displayed. (s unit)
Indicates the number of error stations in the displayed network.
Allows to select from "DEC" or "HEX" for IP address display on the selected communication status monitor and
network map. (Default: Decimal)
If the status of each station is not displayed, check whether there are any duplications of master stations.
Displays a disconnected station that has been set in "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings" but has
not yet performed data link. Error invalid stations are also included.
However, even if a disconnected station had performed data link, disconnected stations in the following cases are
displayed in this area.
• A station that was reconnected to a network after disconnecting/inserting the cable or powering off and on the
system, and remains disconnected
• A disconnected station with the station icon deleted in the network map by clicking the [Update] button
Displays the St. info which is selected in "Station infomation switching" and the station No. on the station icon.
The "Other Modules" icon indicates a station that has not yet performed data link.
Icons other than the "Other Modules" icon indicate stations that had performed data link before disconnection.
For details on the displayed icon, click the [Legend] button.
Displays status of the station selected in "Network Status". ( Page 61 Selected Station Communication Status
Monitor)
Performs a communication test. ( Page 62 Communication Test)
Performs remote operation (such as RUN, STOP, or RESET operations) to the CPU module. (Page 63 Remote
Operation )
58
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.3 Checking the Network Status
Page 61

Network map
(2)
(3)
(4)
(1)
No.0 No.2 No.4
Engineering tool
■Icon
The module type and station No. are displayed with an icon.
• Click: Selection
• Right-click: Executes tests or debugging.
• keys on the keyboard: Move the
focus to the module to be diagnosed, and
determine it with the key.
No. Description
(1) Displays the station (own station) where the engineering tool is connected.
(2) Displays the station type and station No.. "?" is displayed when a station No. has not been set.
When the background of the text if colored, the relevant station may have been set as a reserved station or an error invalid station. Click the [Legend]
button to check the meaning of the background colors.
(3) Module status is displayed. Click the [Legend] button to check the meaning of the icon.
(4) An Ethernet port to which an Ethernet cable is connected is displayed.
■Network map
A network map is displayed according to the connection status.
Connection status Display of the network map
Line topology
3
Star topology
Engineering tool
No.0
Star and line mixed
Engineering tool
No.0
TSN HUB
Connection to P1
TSN HUB
No.2
No.2
No.3
No.4
No.4
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.3 Checking the Network Status
59
Page 62

In the following cases, the network map is displayed differently from the actual connection status.
Precautions
No.0
No.2
TSN HUB
Engineering tool
No.0
No.1
No.2
No.4
TSN HUB
TSN HUB
Engineering tool
Connection status Display of the network map
Two stations are connected through a switching hub. Branches are not displayed in the network map.
Switching hubs are in cascade connection. Only one branch is displayed.
Stations in offline mode are not displayed in the network map. In line topology, stations connected after a station in offline
mode are not displayed because they are disconnected.
60
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.3 Checking the Network Status
Page 63

Selected Station Communication Status Monitor
(2)
(4)
(1)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(3)
Displays status of the station selected in "Network Status".
■When a station where an error has occurred is selected
3
No. Description
(1) Indicates the station No. and operating status.
• Station No. No error (light blue): Normal operation
• Station No. Error (yellow): Error (Data link is continued)
• Station No. Error (red): Error (Data link is stopped)
(2) Displays the network type.
(3) Displays a MAC address.
(4) Displays an IP address.
(5) Click this button to check error details. Take actions following the description displayed in "Error Factor" and "Troubleshooting".
(6) The LED status of a module and communication status of P1 and P2 is displayed. ( MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual (Startup))
(7) Status of the cables connected to P1 and P2 is displayed.
■When a selected station is not available for communication status monitor
The information of devices are not displayed. The "Error details" window (detailed information, error factor, troubleshooting) is
displayed.
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.3 Checking the Network Status
61
Page 64

Communication Test
Precautions
This function checks if transient transmission can be performed from the own station to the communication target.
Depending on selection for "Communication Method" ("Network No./Station No." or "IP Address"), the range that can be
checked may vary.
Selection of "Communication Method" Communication target of transient transmission
Stations on the same network
Network No./Station No. Available for check
IP Address Available for check
Explain the procedure of the communication test.
1. Display the "Communication Test" window and select
"Network No./Station No." or "IP Address" from
"Communication Method".
[Diagnostics] [CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field
Diagnostics] [Communication Test] button
2. Enter values for "Target Station" and "Communication
Data Setting".
3. Click the [Execute Test] button to execute the
communication test. If an error occurs, take corrective
actions according to the error message.
Since this function uses ping, an error, “a communication test target station communication error” (error code D919H) occurs
if the communication target does not respond to ping. When executing this function, check if the security setting (such as
firewall) of the communication target is set to respond to ping. Moreover, if the target is set not to respond to ping in the
security settings (such as a firewall), it may take some time until a timeout error occurs on the engineering tool. For details on
when communication of the engineering tool is not allowed in the firewall settings of Windows, refer to the following.
GX Works3 Operating Manual
62
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.3 Checking the Network Status
Page 65

Remote Operation
This function executes remote operations (such as RUN, STOP, and RESET operations) to the station selected on the "CC-
Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics" window, from the engineering tool. (Remote operation for slave stations is
available only for RESET)
The displayed window varies depending on the station selected. For the operations with a module other than the Motion
module selected, refer to the manual for the module used.
Procedure
To perform remote operations, follow the steps below.
3
1. Select the module where the remote operations are
performed in the "CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field
Diagnostics" window.
2. Click the [Remote Operation] button in the "CC-Link IE
TSN/CC-Link IE Field Diagnostics" window, or right-click a
module icon in the "Network Status" and click [Remote
Operation].
The "Remote Operation" window is displayed.
3. Specify the target station in "Specify Execution Target".
• "Currently Specified Station": The remote operations are
performed only to the CPU module on the station selected in
the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics.
• "All Stations Specified": Remote operations are performed on
all stations under "Specify Target Network No.".
• "Specify Group No.": Among the stations for which a transient
transmission group No. has been set, remote operations are
performed only on the stations that are selected in "Specify
Group No.".
4. Select a remote operation (RUN, STOP, PAUSE, or
RESET) to be performed in "Operation".*
1
5. Click the [Execute] button to perform the remote operation.
*1 To perform remote RESET, set "Remote Reset Setting" under "Operation Related Setting" of "CPU Parameter" to "Enable" in advance.
For details on the remote operations, refer to the user's manual for the CPU module used.
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.3 Checking the Network Status
63
Page 66

3.4 Troubleshooting by Symptom
This section describes troubleshooting when a data link cannot be performed with the target station regardless of no error
occurring in the Motion module.
If an error has occurred in the Motion module, identify the error cause using the engineering tool. ( Page 54 Checking the
Network Status)
When cyclic transmission cannot be performed
The following lists the actions to be taken if cyclic transmission cannot be performed.
Check item Action
Is the D LINK LED of the Motion module turned on? Perform troubleshooting for when the D LINK LED turns off or is flashing.
Does the slave station support the link devices set in "Network Configuration
Settings" under "Basic Settings" of the master station?
Do the station types set in "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings"
of the master station match those set for the connected slave stations?
If "Connection Device Information" of "Basic Settings" sets as "Authentication Class
B Only", is a CC-Link IE TSN-compatible switching hub certified by the CC-Link
Partner Association being used?
When using an authentication class B/A device with a communication speed of
100Mbps in the basic cycle, is "System Reservation Time" in "Communication
Period Setting" under "Basic Settings" of the master station set to 20s?
Is " " displayed on the dot matrix LED of the Motion module? Set the module parameters.
When "Connected Device
Information" under "Basic
Settings" of the master station is
set to "Authentication Class B
Only"
Are authentication class A devices connected? Disconnect the authentication class A devices.
Is a general-purpose hub connected? Disconnect the general-purpose hub or replace it with a TSN hub.
( Page 49 When the D LINK LED turns off or is flashing)
Correct the link devices to be assigned to the slave station.
Check 'Station type match status of each station' (SB00E8) and 'Station
type match status' (SW00E8 to SW00EF) to correct the station type of
stations in which the station type does not match.
• Correct the used hub and the hub settings. For the setting method,
refer to the manual for the hub used.
• When using a CC-Link IE TSN-compatible switching hub certified by
the CC-Link Partner Association, check the precautions and
restrictions for system configuration on the CC-Link IE TSNcompatible switching hub list at the CC-Link Partner Association
website (www.cc-link.org).
• Correct the switching hub delay time according to the hub used. For
the switching hub delay time, refer to the manual for the hub used.
Set "System Reservation Time" to 200s.
64
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.4 Troubleshooting by Symptom
Page 67

Check item Action
When "Connected Device
Information" under "Basic
Settings" of the master station is
set to "Mixture of Authentication
Class B/A or Authentication
Class A Only"
Are 32 stations or more in total connected? Reduce the total number of station to 31 stations (master station: 1,
slave station: 30) or less.
Are nine or more authentication class B devices
connected to P1 or P2 of the master station?
Are authentication class A devices in line
topology?
Other than the master station, are
authentication class B devices in star topology?
In line topology plus star topology, are
authentication class A devices connected with
the master station in line topology?
Is the master station connected with
authentication class B devices via a generalpurpose hub?
Is an authentication class A device connected
between the master station and authentication
class B devices?
Are the master station and authentication class
A devices in line topology?
Are authentication class A devices connected
to each other?
Is a general Ethernet device connected to
places other than the end of the network?
Are an authentication class A device and a
general Ethernet device in line topology?
Do not use general-purpose hubs other than
the NZ2EHG-T8(N) or DT135TX.
Is a general-purpose hub in cascade
connection?
Reduce the number of authentication class B devices connecting to P1
or P2 of the master station to eight or less for each.
Do not connect authentication class A devices in line topology.
When connecting an authentication class B device and an authentication
class A device, connect them via a general-purpose hub.
Other than the master station, do not connect authentication class B
devices (via general-purpose hub) in star topology.
For line topology with the master station, connect only with
authentication class B devices.
When connecting the master station and an authentication class B
device, connect them in line topology without a general-purpose hub.
Connect the master station and an authentication class B device without
a general-purpose hub.
Connect the master station and an authentication class A device via a
general-purpose hub.
Connect the master station and an authentication class A device via a
general-purpose hub.
Connect authentication class A devices via a general-purpose hub. (Only
one device for each port of a general-purpose hub)
Connect a general Ethernet device at the end of the network.
Do not connect an authentication class A device and a general Ethernet
device. Even if a general Ethernet device is at the end of the network, do
not connect to it.
Use the NZ2EHG-T8(N) or DT135TX.
Do not connect it in cascade connection.
3
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.4 Troubleshooting by Symptom
65
Page 68

When transient transmission cannot be performed
The following lists the actions to be taken if transient transmission cannot be performed with the target station, and the
engineering tool cannot perform monitoring.
Check item Action
Is the D LINK LED of the Motion module turned off? Perform troubleshooting for when the D LINK LED turns off or is flashing.
( Page 49 When the D LINK LED turns off or is flashing)
Is the data link status of the target station normal? In the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics, identify the cause of
Is the network No. duplicated on the network? Change the duplicated network No..
Is " " displayed on the dot matrix LED of the Motion module? Set the module parameters.
When "Connected Device
Information" under "Basic
Settings" of the master station is
set to "Authentication Class B
Only"
When "Connected Device
Information" under "Basic
Settings" of the master station is
set to "Mixture of Authentication
Class B/A or Authentication
Class A Only"
Are authentication class A devices connected? Disconnect the authentication class A devices.
Is a general-purpose hub connected? Disconnect the general-purpose hub or replace it with a TSN hub.
Are 32 stations or more in total connected? Reduce the total number of station to 31 stations (master station: 1,
Are nine or more authentication class B devices
connected to P1 or P2 of the master station?
Are authentication class A devices in line
topology?
Other than the master station, are
authentication class B devices in star topology?
In line topology plus star topology, are
authentication class A devices connected with
the master station in line topology?
Is the master station connected with
authentication class B devices via a generalpurpose hub?
Is an authentication class A device connected
between the master station and authentication
class B devices?
Are the master station and authentication class
A devices in line topology?
Are authentication class A devices connected
to each other?
Is a general Ethernet device connected to
places other than the end of the network?
Are an authentication class A device and a
general Ethernet device in line topology?
Do not use general-purpose hubs other than
the NZ2EHG-T8(N) or DT135TX.
Is a general-purpose hub in cascade
connection?
the error and take action. ( Page 54 Checking the Network Status)
slave station: 30) or less.
Reduce the number of authentication class B devices connecting to P1
or P2 of the master station to eight or less for each.
Do not connect authentication class A devices in line topology.
When connecting an authentication class B device and an authentication
class A device, connect them via a general-purpose hub.
Other than the master station, do not connect authentication class B
devices (via general-purpose hub) in line topology.
For line topology with the master station, connect only with
authentication class B devices.
When connecting the master station and an authentication class B
device, connect them in line topology without a general-purpose hub.
Connect the master station and an authentication class B device without
a general-purpose hub.
Connect the master station and an authentication class A device via a
general-purpose hub.
Connect the master station and an authentication class A device via a
general-purpose hub.
Connect authentication class A devices via a general-purpose hub. (Only
one device for each port of a general-purpose hub)
Connect a general Ethernet device at the end of the network.
Do not connect an authentication class A device and a general Ethernet
device. Even if a general Ethernet device is at the end of the network, do
not connect to it.
Use the NZ2EHG-T8(N) or DT135TX.
Do not connect it in cascade connection.
If the above actions do not solve the problem, perform the following tests to check for an error.
• Communication test ( Page 62 Communication Test)
66
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.4 Troubleshooting by Symptom
Page 69

When a station is disconnected from the network
The following is the action to be taken when a station in data link is disconnected.
Check item Action
Is the ambient temperature for the module outside the specified range? Keep the ambient temperature within the specified range by taking action
such as removing heat source.
When a station repeats network initialization
The following lists the actions to be taken when a station in data link repeats network initialization.
Check item Action
Do the used Ethernet cables conform to the Ethernet standard? Replace the cables with Ethernet cables which conform to the standard. (
Is the station-to-station distance 100m or less? Change the station-to-station distance to 100m or less.
Does the cabling condition (bending radius) meet the specifications? Refer to the manual for the Ethernet cable, and if the bending radius exceeds
Is any Ethernet cable disconnected? If an Ethernet cable is disconnected, replace the Ethernet cable.
Is the switching hub used operating normally? • Use a switching hub that conforms to the standard. (MELSEC iQ-R
Is the station that is the time synchronization source normal? Check the manual of the module used for the time synchronization source
Are resets of other stations repeated? Avoid unnecessary reset since a station is disconnected while resetting.
Are other stations repeatedly powering on/off? Avoid unnecessary power-off, since a station is disconnected while turned off.
When using an authentication class B/A device with a communication speed
of 100Mbps in the basic cycle, is "System Reservation Time" in
"Communication Period Setting" under "Basic Settings" of the master station
set to 20s?
MELSEC iQ-R Motion Module User's Manual (Startup))
the specified range, correct the bending radius.
Motion Module User's Manual (Startup))
• Power off and on the switching hub.
station.
Set "System Reservation Time" to 200s.
3
When communication is unstable
When cyclic data transfer processing time or transmission delay time is long or when a transient transmission timeout
occurred, check the following items.
Check item Action
Is the L ER LED of the Motion module turned on? If turned on, perform troubleshooting for a case when the L ER LED is turned
on. ( Page 51 When the L ER LED turns on)
Is the ambient temperature for the module outside the specified range? Keep the ambient temperature within the specified range by taking action
Is any error shown in "Selected Station Communications Status Monitor" of
CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field diagnostics?
Is there any noise affecting the system? Change the placement and/or wiring of the modules so that the system is not
such as removing heat source.
If an error is identified at P1 or P2, perform a cable test and a module
communication test.
affected by noise.
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.4 Troubleshooting by Symptom
67
Page 70

When communications using the SLMP cannot be performed
When communications using the SLMP cannot be performed, check the following items.
Check item Action
Has the connection with the external device been opened? • If the connection with the external device is not opened, perform the open
Is the correct command format used for the command type, device
specification, address specification, and others?
Did the external device send a command? If the external device did not send a command, send a command to the
Was a response returned to the device that had sent the command? • If no response was returned, check if the correct IP address was specified
processing.
• If an error occurs, check and eliminate the error cause.
Correct the command format. ( SLMP Reference Manual)
Motion module.
in the command. If not, correct the IP address and send the command
again.
• If a response was returned, check the end and error codes to correct the
faulty area.
*1
If the above actions do not solve the problem, perform the module communication test to check for hardware failure. (
Page 53 Module Information List)
*1 If the connection of only the external device is closed due to communication cable disconnection, personal computer restart, or other
reasons, reopen the connection using the same port used before the error occurred. A connection is not closed if another Active open
request is received from the external device with a different IP address or a port No..
When communications with Ethernet devices cannot be performed
When communications with Ethernet devices cannot be performed, check the following items.
Check item Action
Is the firewall or proxy server setting enabled on the Ethernet device? Check and correct the settings on the Ethernet device.
Is a response to the Ping command (ICMP echo request) disabled?
Is the antivirus software on the Ethernet device blocking the communication? Check and correct the antivirus software settings on the Ethernet device.
• Is the security setting level of the antivirus software low?
• Is a response to the Ping command (ICMP echo request) disabled in the
firewall settings?
For details about when communication of the engineering tool is not allowed in the settings of Windows Firewall, refer to the
following.
GX Works3 Operating Manual
68
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.4 Troubleshooting by Symptom
Page 71

3.5 List of Error Codes
This section lists the error codes, error definitions and causes, and actions for the errors that occur in the processing for data
communication between the Motion module and external devices or occur by processing requests from the CPU module on
the own station.
Error codes are displayed in the [Error Information] tab in the "Module Diagnostics" window of the Motion module. ( Page
52 Error Information)
Error
code
1124H • The default gateway is not set correctly.
1128H The port No. is incorrect. Correct the port No..
1129H The port No. of the external device is not
112DH The data was sent to the connected device
112EH A connection could not be established in
1134H The external device does not send an ACK
1152H The IP address is not set correctly. Correct the IP addresses. Parameter
1155H • The specified connection was already
1157H • The specified connection was already
1158H • The receive buffer or send buffer is not
1166H Data was not sent correctly with TCP/IP. • Check the settings for connection with the external device.
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
information
• The gateway IP address is not set
correctly.
• The default gateway/gateway IP
address (network address after the
subnet mask) is different from that of the
IP address of the own node.
set correctly.
while the IP address setting of the device
set in the network configuration setting
was incorrect.
the open processing.
response in the TCP/IP communications.
closed in TCP/IP communications.
• Open processing is not performed.
closed in UDP/IP communications.
• Open processing is not performed.
sufficient.
• The window size of the external device
is not sufficient.
• Correct the default gateway IP address.
• Set the same network address as that of the IP address.
Correct the port No. of the external device.
• Correct the IP address of the connected device in the network
configuration setting.
• Check that the IP address class of the connected device is set to A, B, or C
in the network configuration setting.
• Check the operation of the external device.
• Check if the open processing has been performed in the external device.
• Correct the port No. of the Ethernet-equipped module, IP address/port No.
of the external device, and opening method.
• When a firewall is set in the external device, check if access is permitted.
• Check if the Ethernet cable is disconnected.
• Since there may be congestion of packets on the line, send data after a
certain period of time.
• Check if the connection cable is disconnected.
• Perform the open processing for the specified connection.
• Check if the open processing has been performed in the external device.
• Perform the open processing for the specified connection.
• Check if the open processing has been performed in the external device.
• Check the operation of the external device or switching hub.
• When the value of the "Receive Buffer Status Storage Area"
(Un\G6291486) is 0001H, reduce the frequency of data received from the
external device.
• Check the operation of the external device or switching hub.
• Since there may be congestion of packets on the line, send data after a
certain period of time.
• Check if the connection cable is disconnected.
• Check that there is no connection failure with the switching hub.
• Execute the communication test, and if the test was completed with an
error, take corrective action.
Parameter
information
• Parameter type
•I/O No.
• Parameter No.
• Network No.
• Station No.
information
• Parameter type
•I/O No.
• Parameter No.
• Network No.
• Station No.
3
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
69
Page 72

Error
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
code
1167H Unsent data found, but could not be sent. • Check the settings for connection with the external device.
• Check the operation of the external device or switching hub.
• Since there may be congestion of packets on the line, send data after a
certain period of time.
• Check if the connection cable is disconnected.
• Check that there is no connection failure with the switching hub.
• Execute the communication test, and if the test was completed with an
error, take corrective action.
1802H During data link, overlapping IP addresses
have been detected.
1811H A stop error has been detected in the CPU
module.
1830H Number of reception requests of transient
transmission (link dedicated instruction)
exceeded the upper limit of simultaneously
processable requests.
20E0H The module cannot communicate with the
CPU module.
2160H IP address duplication was detected. Check and correct the IP addresses.
2220H The parameter setting is corrupted. Check the detailed information of the error by executing module diagnostics
2221H The set value is out of the range. Check the detailed information of the error by executing module diagnostics
24C0H
to
24C3H
24C6H An error was detected on the system bus. • Take measures to reduce noise.
3009H The result when the value set in
300AH The set value that is set in the master
300BH The Announce frame send cycle
An error was detected on the system bus. • Take measures to reduce noise.
"Communication Period Interval Setting" in
"Communication Period Setting" under
"Basic Settings" of the master station is
multiplied by "Communication Period
Setting" of the slave station set in "Network
Configuration Settings" under "Basic
Settings" is out of the range.
station is out of the range.
parameter error was detected.
Change the IP address of devices with a duplicated IP address. Operation source
Check the error of the CPU module and take action using the module
diagnostics of the engineering tool.
Lower the transient transmission usage frequency, and retry the operation.
The hardware failure of the CPU module may have been occurred. Please
consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
using the engineering tool, and write the displayed parameter. If the same
error occurs again, the possible cause is a hardware failure of the module.
Please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
using the engineering tool, and correct the parameter setting corresponding
to the displayed parameter No..
• Reset the CPU module, and run it again. If the same error occurs again
even after taking the above, the possible cause is a hardware failure of the
module, base unit, or extension cable. Please consult your local Mitsubishi
representative.
• Reset the CPU module, and run it again. If the same error occurs again
even after taking the above, the possible cause is a hardware failure of the
module, base unit, or extension cable. Please consult your local Mitsubishi
representative.
Check the detailed information on module diagnostics of the engineering tool
and set the value of "Communication Period Setting" of the slave station
under "Basic Settings" within 16ms.
• Check the detailed information of the error by executing module
diagnostics using the engineering tool, and correct the parameter setting of
the master station corresponding to the displayed parameter No..
• If the same error occurs again, the possible cause is a hardware failure of
the module. Please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
• Check the Announce frame send cycle parameter setting value of the
device operating as the grandmaster. When the Motion module is
operating as the grandmaster, reset the CPU module, and run it again.
• If the same error occurs again even after taking the above measure, the
possible cause is a hardware failure of the module. Please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
information
information
• IP address
Parameter
information
• Parameter type
Parameter
information
• Parameter type
•I/O No.
• Parameter No.
• Network No.
• Station No.
System configuration
information
•I/O No.
• Base No.
•Slot No.
•CPU No.
Parameter
information
• Parameter type
•I/O No.
• Parameter No.
• Network No.
• Station No.
70
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
Page 73

Error
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
code
300CH A propagation delay send cycle parameter
error was detected.
300DH The Sync frame send cycle parameter
300FH Multiple master stations were detected in
3010H The value set in "Communication Period
3011H The value set in "Cyclic transmission time"
3013H The value set in "Transient Transmission
3021H At startup of data link, IP address
3060H The send/receive data size exceeds the
3121H The cyclic transmission setting information
3130H Devices with time synchronization priority
3135H Over the number of stations that can be
3136H An illegal ring topology was detected. Set a line topology or star topology and reset all stations.
3C00H
to
3C02H
error was detected.
the network.
Interval Setting" in "Communication Period
Setting" under "Basic Settings" of the
master station is smaller than the
communication cycle interval calculated by
the number of stations and points of slave
stations that was set in "Network
Configuration Settings" under "Basic
Settings".
in "Communication Period Setting" under
"Basic Settings" of the master station is
smaller than the cyclic transmission time
calculated by the number of stations and
points of slave stations set in "Network
Configuration Settings" under "Basic
Settings".
Time" in "Communication Period Setting"
under "Basic Settings" of the master
station is smaller than the transient
transmission time calculated using the
number of slave stations and the points of
slave stations set in "Network
Configuration Settings" under "Basic
Settings".
duplication among slave stations has been
detected.
allowable range.
received from the master station exceeds
the setting range.
of 0 to 15 have been connected.
connected.
A hardware failure has been detected. • Take measures to reduce noise.
• Check the propagation delay send cycle parameter setting value of the
device operating as the grandmaster. When the Motion module is
operating as the grandmaster, reset the CPU module, and run it again.
• If the same error occurs again even after taking the above measure, the
possible cause is a hardware failure of the module. Please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Check the Sync frame send cycle parameter setting value of the device
operating as the grandmaster. When the Motion module is operating as the
grandmaster, reset the CPU module, and run it again.
• If the same error occurs again even after taking the above measure, the
possible cause is a hardware failure of the module. Please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Connect only one master station on the same network.
• After taking the above action, power off and on or reset all stations where
the error was detected.
Set the value of "Communication Period Interval Setting" over the value in the
detailed information displayed by module diagnostics using "Communication
Period Setting" under "Basic Settings" of the master station.
Set the value of "Cyclic Transmission Time" over the value in the detailed
information displayed by module diagnostics using "Communication Period
Setting" under "Basic Settings" of the master station.
Set "Communication Period Interval Setting" and "Cyclic Transmission Time"
so that the value of "Transient Transmission Time" in "Communication Period
Setting" under "Basic Settings" of the master station is equal to or larger than
the value shown in SW0078.
Correct the IP addresses of the slave stations. Operation source
• Check and change the send data size of the Ethernet-equipped module or
the external device.
• If the same error code is displayed again, the possible cause is a hardware
failure of the error module or CPU module. Please consult your local
Mitsubishi representative.
Write the module parameter to the CPU module again. If the same error
occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your local Mitsubishi
representative.
Remove devices with time synchronization priority of 0 to 15, or change the
priority to between 16 and 255.
• Reduce the total number of stations to 31 stations (master station: 1, slave
station: 30) or less.
• Reduce the number of authentication class B devices to eight or less for
each port of the master station.
• Reset the CPU module, and run it again. If the same error occurs again
even after taking the above, the possible cause is a hardware failure of the
module, base unit, or extension cable. Please consult your local Mitsubishi
representative.
information
3
Parameter
information
• Parameter type
•I/O No.
• Parameter No.
information
• IP address
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
71
Page 74

Error
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
code
3C0FH
to
3C10H
3C13H
to
3C14H
3C2FH An error was detected in the memory. Reset the CPU module, and run it again. If the same error occurs again even
3E01H Network type of the own station is
3E02H A time synchronization error was detected. Reset the CPU module, and run it again. If the same error occurs again even
3E03H An error was detected in the memory. Reset the CPU module, and run it again. If the same error occurs again even
4000H to
4FFFH
C011H The port No. of the external device is not
C012H The port No. used in a connection already
C013H The port No. used in a connection already
C015H The data was sent to the connected device
C017H A connection could not be established in
C018H The specified IP address of the external
C032H The external device does not send an ACK
C035H The alive status of an external device
C037H • The receive buffer or send buffer is not
C038H Data was not sent correctly with UDP/IP. • Check the settings for connection with the external device.
C039H Data was not sent correctly with TCP/IP. • Check the settings for connection with the external device.
A hardware failure has been detected. • Take measures to reduce noise.
• Reset the CPU module, and run it again. If the same error occurs again
even after taking the above, the possible cause is a hardware failure of the
module, base unit, or extension cable. Please consult your local Mitsubishi
representative.
A hardware failure has been detected. Reset the CPU module, and run it again. If the same error occurs again even
after taking the above, the possible cause is a hardware failure of the error
module or CPU module. Please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
after taking the above, the possible cause is a hardware failure of the error
module. Please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
unexpected setting.
Errors detected by the CPU module ( MELSEC iQ-R CPU Module User's Manual (Application))
set correctly.
opened is set. (For TCP/IP)
opened is set. (For UDP/IP)
while the IP address setting of the device
set in the network configuration setting
was incorrect.
the open processing.
device is incorrect.
response in the TCP/IP communications.
could not be checked.
sufficient.
• The window size of the external device
is not sufficient.
Rewrite the module parameter using the engineering tool. If the same error
occurs again even after taking the above, the possible cause is a hardware
failure of the error module. Please consult your local Mitsubishi
representative.
after taking the above, the possible cause is a hardware failure of the error
module or CPU module. Please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
after taking the above, the possible cause is a hardware failure of the error
module or CPU module. Please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
Correct the port No. of the external device.
Correct the port Nos. of the Ethernet-equipped module and the external
device.
Correct the port Nos. of the Ethernet-equipped module and the external
device.
• Correct the IP address of the connected device in the network
configuration setting.
• Check that the IP address class of the connected device is set to A, B, or C
in the network configuration setting.
• Check the operation of the external device.
• Check if the open processing has been performed in the external device.
• When a firewall is set in the external device, check if access is permitted.
• Check if the Ethernet cable is disconnected.
Correct the specified IP address of the external device.
• Since there may be congestion of packets on the line, send data after a
certain period of time.
• Check if the connection cable is disconnected.
• Check the operation of the external device.
• Check if the connection cable is disconnected.
• Check the operation of the external device or switching hub.
• When the value of the 'Receive Buffer Status Storage Area'
(Un\G6291486) is 0001H, reduce the frequency of data received from the
external device.
• Check the operation of the external device or switching hub.
• Since there may be congestion of packets on the line, send data after a
certain period of time.
• Check if the connection cable is disconnected.
C
heck that there is no connection failure with the switching hub.
•
• Execute the PING test and communication status test, and if the test was
completed with an error, take the corrective action.
• Check the operation of the external device or switching hub.
• Since there may be congestion of packets on the line, send data after a
certain period of time.
• Check if the connection cable is disconnected.
• Check that there is no connection failure with the switching hub.
• Execute the PING test and communication status test, and if the test was
completed with an error, take the corrective action.
information
72
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
Page 75

Error
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
code
C040H • Sufficient data for the data length could
not be received.
• The remaining part of the message
divided at the TCP/IP level could not be
received.
C050H ASCII code data that cannot be converted
to binary code was received.
C051H • The number of read/write points from/to
C052H The number of read/write points from/to
C053H The number of read/write points from/to
C054H The number of read/write points from/to
C055H The read/write size from/to the file data of
C056H The read/write request exceeds the largest
C057H The request data length of the SLMP
C058H The request data length of the SLMP
C059H • The specified command and
C05AH The Ethernet-equipped module cannot
C05BH The Ethernet-equipped module cannot
C05CH • The received request data of the SLMP
the device of SLMP message is out of
the allowable range in the CPU module
(in units of words).
• The number of write points for the long
counter of SLMP message is not in twoword units.
the device of SLMP message is out of the
allowable range in the CPU module (in
units of bits).
the random device of SLMP message is
out of the allowable range in the CPU
module (in units of bits).
the random device of SLMP message is
out of the allowable range in the CPU
module (in units of words, double words).
SLMP message is out of the allowable
range.
address.
message does not match the number of
data in the character (a part of text).
message after the ASCII/binary conversion
does not match with the number of data in
the character (a part of text).
subcommand of the SLMP message are
incorrect
• A function that is not supported by the
target device was executed.
read/write data from/to the device specified
by the SLMP message.
read/write data from/to the device specified
by the SLMP message.
message is incorrect.
• The setting value of the communication
setting when the iQSS function is
executed is out of range.
the iQSS function is executed, the
When
•
items of communication setting which
cannot be set on the target device are
set.
• When the iQSS function is executed, the
required setting items have not been set
to the target device.
• Correct the data length of the communication data.
• Since there may be congestion of packets on the line, send the data again
from the external device after a random amount of time has passed.
Check if the ASCII code data that cannot be converted into binary code data
was sent from the external device.
Correct the number of read/write points and send the SLMP message to the
Ethernet-equipped module again.
Correct the number of read/write points and send the SLMP message to the
Ethernet-equipped module again.
Correct the number of read/write points and send the SLMP message to the
Ethernet-equipped module again.
Correct the number of read/write points and send the SLMP message to the
Ethernet-equipped module again.
Correct the read/write size and send the SLMP message to the Ethernetequipped module again.
• Correct the start address or the number of read/write points so that the
request does not exceed the largest address and send the data to the
Ethernet-equipped module again.
• If the access target and connection stations are modules of the MELSEC
iQ-R series, send the SLMP message again to the Ethernet-equipped
module using 003 and 002 of subcommands.
Check and correct the text or request data length, and send the SLMP
message to the Ethernet-equipped module again.
Check and correct the text or request data length, and send the SLMP
message to the Ethernet-equipped module again.
• Check that there are no errors in the specification of the command and
subcommand of the SLMP message.
• Check whether the function executed is supported by the target device.
• Check the version of the target device.
Correct the specification of the device to be read/written and send the SLMP
message to the Ethernet-equipped module again.
Correct the specification of the device to be read/written and send the SLMP
message to the Ethernet-equipped module again.
• Correct the request data and send the SLMP message to the Ethernetequipped module again.
• Correct the setting details of when the iQSS function is executed, and retry
the operation.
information
3
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
73
Page 76

Error
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
code
C05DH The "Monitor Request" command is
received before the monitor registration is
performed by the "Monitor Registration/
Clear" command of the SLMP message.
C05EH The time between reception of the SLMP
message by the Ethernet-equipped
module and the returned response from
the access destination exceeded the
monitoring timer value set in the SLMP
command.
C05FH This request cannot be executed to the
access destination specified by the SLMP
message.
C060H The request details for bit devices of the
C061H • The request data length of the SLMP
C06FH The network No. of request destination
C070H The device memory cannot be extended
C071H The number of device points for data read/
C072H The request details of the SLMP message
C073H The access destination of the SLMP
C075H The request data length for the label
C081H The termination processing for the
C087H IP address of the destination external
SLMP message is incorrect.
message does not match the No. of data
in the character (a part of text).
• The write data length specified by the
label write command is not even byte.
• When the iQSS function is executed,
incorrect frame is received.
specified by the SLMP request message is
not available for communications with the
station No. 121 or larger.
for the access destination specified by the
SLMP message.
write set for modules other than a
MELSEC iQ-R/Q/QnACPU is out of the
range.
are incorrect. (For example, a request for
data read/write in bit units has been issued
to a word device.)
message cannot issue this request. (For
example, the number of double word
access points cannot be specified for
modules other than a MELSEC iQ-R/Q/
QnACPU.)
access is out of range.
Ethernet-equipped module that is involved
with the reinitialization processing is being
performed, and arrival of link dedicated
instructions cannot be checked.
not be acquired.
device could
Register the monitoring data using "Monitor Registration/Clear" command
and perform monitoring.
• Increase the monitoring timer value.
• Check if the access destination is operating normally.
• Correct the network No. or request destination station No..
• If the access destination is a module with a different network No., correct
the routing parameter setting.
• If the access destination is a module with a different network No., check if
the network No. is not in use.
Correct the access destination.
Correct the request details and send the SLMP message to the Ethernetequipped module again.
• Check and correct the text or request data length, and send the SLMP
message to the Ethernet-equipped module again.
• Add one byte of dummy data, and specify the length as an even number of
bytes.
• Check the operating status and connection status of the target device at
the time the iQSS function is executed.
• Check the connection of the Ethernet cable and hub at the time the iQSS
function is executed.
• Check the line status of Ethernet at the time the iQSS function is executed.
• Reset the CPU module and device to be targets of the iQSS function, and
retry the operation.
For errors that occur when the iQSS function is executed, contact the
manufacturer of the target device if the above actions do not solve the
problem.
• If the SLMP3E or 4E frame is used, check that there is no error for the
network No. of request destination and station No..
• If the SLMP6E frame is used, check that there is no error for the network
number of request destination, station No., and extension station No..
• Correct the SLMP message to read/write data without the device memory
set for extension.
• Specify the extension of the device memory only for an Ethernet-equipped
module mounted station and a MELSEC iQ-R/Q/QnACPU via CC-Link IE
Controller Network, MELSECNET/H, or MELSECNET/10.
Correct the number of read/write points and send the SLMP message to the
Ethernet-equipped module again.
• Check if the data can be requested to the access destination.
• Correct the request details and send the SLMP message to the Ethernetequipped module again.
Correct the request details of the SLMP message.
• Correct the number of read/write points and send the SLMP message to
the Ethernet-equipped module again.
• Correct the label to shorten the label name and send the SLMP message
to the Ethernet-equipped module again.
Finish all the communications to perform the reinitialization processing of the
Ethernet-equipped module.
• Correct the IP address in the network station No. IP information setting.
• Check if the network or station No. of the external device is correctly
specified by using control data of the dedicated instruction.
• Check if the connection cable is disconnected.
information
74
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
Page 77

Error
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
code
C0B3H A request that cannot be processed was
issued from the CPU module.
C0D4H The number of relay stations to
communicate with other networks exceeds
the allowable range.
C0D8H The number of specified blocks exceeded
the range.
C0D9H The specified subcommand of the SLMP
message is incorrect.
C1A7H The specified network No. is incorrect. Correct the specified network No..
C1A9H The specified device No. is incorrect. Correct the specified device No..
C1CCH A response with a data length that exceeds
C200H The remote password is incorrect. Correct the remote password, and unlock/lock the remote password again.
C201H The remote password status of the port
C202H When another station was accessed, the
C203H An error has occurred when checking the
C204H The device is different from the one
C207H The file name has too many characters. Name the file with 255 characters or less.
C208H The password length is out of range. Set the password within 6 to 32 characters.
C612H The module processing was completed
C613H The module processing was completed
C615H The module processing was completed
C810H Remote password authentication has
C811H Remote password authentication has
C812H Remote password authentication has
C81
C814H Remote password authentication has
C815H Remote password authentication has
C816H The security function was activated and
C842H The routing setting is not set to reach to
the allowable range was received by the
SLMPSND.
used for communications is in the lock
status.
remote password could not be unlocked.
remote password.
requesting the remote password unlock
processing.
with an error.
with an error.
with an error.
failed when required.
failed when required.
failed when required.
H Remote password authentication has
3
failed when required.
failed when required.
failed when required.
remote password authentication cannot be
performed.
the destination network No..
• Correct the request details.
• Correct the network No. or request destination station No..
• Check if the specification (network No./station No.) for the communication
destination is correct.
• Check that the number of relay stations accessing the communication
destination is 7 or less.
• Correct the settings in the network station No. IP information setting for
the stations between the own station and the communication destination.
Correct the number of blocks.
Correct the subcommand.
• Execute again after correcting the request data to be within the range.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
After unlocking the remote password, perform communications.
When accessing another station, do not set the remote password on the relay
station or access station, or do not execute the remote password check on
them.
Correct the remote password, and unlock/lock the remote password again.
Request the lock processing of the remote password from the external device
that requested the unlock processing of the remote password.
• Execute the communication status test, and if the test was completed with
an error, take the corrective action.
• Execute the module communication test, and check that there is no failure
in the module.
• Execute the communication status test, and if the test was completed with
an error, take the corrective action.
• Execute the module communication test, and check that there is no failure
in the module.
• Execute the communication status test, and if the test was completed with
an error, take the corrective action.
• Execute the module communication test, and check that there is no failure
in the module.
Set a correct password and perform password authentication again.
Set a correct password and perform password authentication again one
minute later.
Set a correct password and perform password authentication again 5
minutes later.
Set a correct password and perform password authentication again 15
minutes later.
Set a correct password and perform password authentication again 60
minutes later.
Set a correct password and perform password authentication again 60
minutes later.
Set a correct password and perform password authentication again after a
certain period of time.
• Execute the link dedicated instruction again after correcting the target
network No./station No..
• Check that communication path to the destination network No. is set.
information
3
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
75
Page 78

Error
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
code
C844H Incorrect frame was received.
• Unsupported command
C900H Communication failed. Do not execute communication from multiple engineering tools to the same
C901H The size of the request data to the external
device or response data from the external
device exceeds the range supported for
communications.
C902H Communication was interrupted because
no response was returned from the
external device.
C903H Failed to send request to the external
device.
CA00H • Access to the flash ROM of the network
CA01H A firmware update file for the model that
CA02H A firmware update file with a file name or
CA03H The firmware update was performed while
CA04H Firmware update was performed for the
CA05H An error in the firmware data was detected
CA06H Firmware update was performed for the
CA07H A sequence error of firmware update was
CA08H Communications were not available
CA09H When a firmware update file is transferred
CA0AH Firmware update could not be performed
CF40H
module failed.
• At execution of firmware update, the
number of writes to the flash ROM has
exceeded 100000.
was different from the network module was
used.
file contents that were incorrect was used.
a firmware file with the version that does
not operate on the module was specified.
network module during data link.
during execution of the firmware update
function.
module during execution of a firmware
update.
detected.
between the firmware update tool and the
module.
to the target module, the user ID or
password for authentication is incorrect.
due to the disable setting of the firmware
update.
I
ncorrect frame was received. • Check the operating status and connection status of the target device.
• Replace the network module with a module of the version supporting the
function that has been executed.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
master station simultaneously.
Correct the size of the request data or response data to within 1500 bytes.
Execute the communication test, and if the test was completed with an error,
take corrective action.
• Correct the IP address of the external device.
• Check if the subnet mask of the external device matches the master
station.
• Execute firmware update again after resetting the module.
• If the same error occurs again, the number of writes to the flash ROM may
have exceeded 100000. Replace the module.
Check the target network module, and execute firmware update again after
resetting the module.
• Check if the file name of the firmware update file has been changed.
• Check if the firmware update file is damaged.
• After the above actions, execute firmware update again after resetting the
module.
Check that the firmware version that is appropriate for update, reset the
module and execute firmware update again.
Execute firmware update again after data link with other stations has been
stopped.
Execute firmware update again after resetting the module.
After the end of the firmware update, reset the module and execute firmware
update again.
• Check to see if multiple firmware update tools have been started, and
identical firmware updates for the same module have been executed.
• After the end of the firmware update, reset the module and execute
firmware update again.
• Check if the firmware update tool is mistakenly closed.
• Check if the switching hub and the cables are connected properly.
• Check if the communication load between the firmware update tool and the
module is too high.
• After the above actions, execute firmware update again after resetting the
module.
Enter the correct user ID and password, and execute the firmware update
again after resetting the module.
Clear the disable setting of the firmware update, and execute the firmware
update again.
• Check the connection of the Ethernet cable and hub.
• Check the line status of Ethernet.
• Reset the CPU module and target device, and retry the operation.
If the above actions do not solve the problem, contact the manufacturer of the
target device.
information
76
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
Page 79

Error
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
code
CF41H Incorrect frame was received. • Check the operating status and connection status of the target device.
• Check the connection of the Ethernet cable and hub.
• Check the line status of Ethernet.
• Reset the CPU module and target device, and retry the operation.
If the above actions do not solve the problem, contact the manufacturer of the
target device.
CF42H Incorrect frame was received. • Check the operating status and connection status of the target device.
CF43H An error has occurred. • Check the operating status of the external device.
CF44H Incorrect frame was received. • Check the operating status and connection status of the target device.
D0A3H Send processing of the transient
D203H The read data or write address of the
D205H The target station No. of transient
D20AH The target station No. of transient
D20BH There was no master station when the
D20CH There was no master station when the
D20DH Transmission completion wait timeout has
D20EH The header information of transient
D20FH In transient transmission, the command
D213H • The command of transient transmission
D
214H The data length of transient transmission is
transmission has failed.
transient transmission is incorrect.
transmission is incorrect.
transmission is incorrect.
specified master station was specified for
transient transmission.
current master station was specified for
transient transmission.
occurred in transient data transmission.
transmission is incorrect.
which cannot be requested to all or a
group of stations was executed with all
stations specification or group
specification.
is incorrect.
• The CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field
diagnostics was used for the network to
which the relay receiving station
belongs.
incorrect.
• Check the connection of the Ethernet cable and hub.
• Check the line status of Ethernet.
• Reset the CPU module and target device, and retry the operation.
If the above actions do not solve the problem, contact the manufacturer of the
target device.
• Check if there is any error in the line status.
If the above actions do not solve the problem, contact the manufacturer of the
target device.
• Check the connection of the Ethernet cable and hub.
• Check the line status of Ethernet.
• Reset the CPU module and target device, and retry the operation.
If the above actions do not solve the problem, contact the manufacturer of the
target device.
• Check the network status using the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field
diagnostics of the engineering tool, and take action.
• When the own station, target station, or relay station detected an error,
identify the cause of the error and take action.
• Correct the target station No. of transient data, and retry the operation.
• When the access destination is a module with a different network No.,
check if "Routing Setting" of "CPU Parameter" is correctly set.
Correct the read data or write address at the transient request source, and
retry the operation.
Correct the target station No. at the transient request source, and retry the
operation.
Correct the target station No. at the transient request source, and retry the
operation.
Correct the target station No. at the transient request source, and retry the
operation.
Correct the target station No. at the transient request source, and retry the
operation.
• Check the network status using the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field
diagnostics of the engineering tool, and take action.
• When the own station, target station, or relay station detected an error,
identify the cause of the error and take action.
• Lower the transient transmission usage frequency, and retry the operation.
• Check if the switching hub and the cables at the request source are
connected properly.
Correct the header information at the transient request source, and retry the
operation.
Check that the command can be requested to all or a group of stations at the
transient request source, and retry the operation.
• Correct the request command at the transient request source, and retry the
operation.
• Review the connection destination so that the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE
Field diagnostics is used for the network to which the relay sending station
ngs.
belo
Correct the data length at the transient request source, and retry the
operation.
information
3
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
77
Page 80

Error
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
code
D239H SLMP transmission failed. • Retry the operation after a while.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
D244H The transient data is incorrect. • Correct the transient data at the transient request source, and retry the
D25DH The transient data is incorrect. • Correct the transient data at the transient request source, and retry the
D273H The request data size of transient
D2D2H The IP address/port No. of the target
D2D3H Send processing of the transient
D602H Parameter error • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
D605H Parameter error • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
D619H Parameter error • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
D61AH Parameter error • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
D621H Parameter error • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
D622H Parameter error (error in the total number
D628H Parameter error (station type error) • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
D629H Parameter error (station No. range error) • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
D64
D642H Parameter error (gateway address setting) • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
transmission is incorrect.
station is incorrect.
transmission has failed.
of slave stations)
H Parameter error (IP address error) • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
1
operation.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
operation.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Correct the request command at the transient request source, and retry the
operation.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Execute again after correcting the port No. of the target station in the
setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Check the network status using the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field
diagnostics of the engineering tool, and take action.
• When the own station, target station, or relay station detected an error,
identify the cause of the error and take action.
• Correct the target IP address of transient data, and retry the operation.
• If the access destination is a module with a different network No., correct
the routing parameter setting.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
• Execute again after correcting the total number of slave stations.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Execute again after correcting the station type in the setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Execute again after correcting the station No. in the setting data so it is
within 1 to 120.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Execute again after correcting the IP address in the setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Execute again after correcting the gateway address setting in the setting
data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
information
78
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
Page 81

Error
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
code
D643H Parameter error (communication cycle
setting)
D644H Parameter error (cyclic transmission time
setting)
D645H Parameter error (transient transmission
D646H Parameter error (transmission path setting) • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
D647H Parameter error (time synchronization
D649H Parameter error (send timeslot setting) • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
D64AH Parameter error (number of data link error
D64BH Parameter error (number of occupied
D64DH Parameter error (parameter automatic
D64EH Parameter error (motion control station
D64FH Parameter error (cyclic frame cycle setting) • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
D65
D652H Parameter error (communication mode
D655H Network addresses of the master station
time setting)
setting)
detection)
stations)
setting)
setting)
1
H Parameter error (number of modules) • Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
setting)
and slave stations are incorrect.
• Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
• Execute again after correcting the communication cycle setting in the
setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
• Execute again after correcting the cyclic transmission time in the setting
data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
• Execute again after correcting the communication cycle setting or cyclic
transmission time in the setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Execute again after correcting the transmission path setting in the setting
data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
• Execute again after correcting the time synchronization setting in the
setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Execute again after correcting the send timeslot setting in the setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
• Execute again after correcting the number of data link error detection in the
setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
• Execute again after correcting the number of occupied stations in the
setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
• Execute again after correcting the parameter automatic setting in the
setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
• Execute again after correcting the motion control station setting in the
setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Execute again after correcting the cyclic frame cycle setting in the setting
data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Execute again after correcting the number of modules in the setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
• Write the network parameter to the CPU module again.
• Execute again after correcting the communication mode setting in the
setting data.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
Correct the IP address setting of the master station or slave stations.
information
3
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
79
Page 82

Error
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
code
D840H Number of transient requests exceeded
the upper limit of simultaneously
processable requests.
D841H The request data size of memory read/
write command is out of range.
D842H • Routing information to the destination
network No. is not registered.
• In transient transmission, the number of
relays to other networks exceeded
seven.
• The communication path is being
updated.
D843H The module operation mode is set to a
mode in which transient transmission
cannot be executed.
D844H Incorrect frame was received.
• Unsupported pre-conversion protocol
• Unsupported frame type
• Application header variable part
• Application header HDS
• Application header RTP
• Read command not requiring response
D902H The online test data is incorrect. • Correct the data at the station that started the online test, and retry the
D903H During execution of the communication
test, the test was retried.
D905H A communication monitoring timeout has
occurred in communication test.
D906H Transmission completion wait timeout has
occurred in communication test.
D909H The header information of transient
transmission is incorrect.
D90AH During execution of the communication
test, the test was retried.
D90BH The number of stations that communicate
in the network is out of the specification
range.
D90CH The communication destination specified
for the communication test is incorrect.
D912H Transient transmission sending failed. • Lower the transient transmission usage frequency, and retry the operation.
• Pause the transient transmission temporarily, and retry the operation.
• Lower the transient transmission usage frequency, and retry the operation.
Correct the read or write size specification at the transient request source,
and retry the operation.
• Correct the target network No. at the transient request source, and retry
the operation.
• Correct the communication path from the transient request source to the
destination, and retry the operation.
• When the dynamic routing is not used, or the module of the series other
than MELSEC iQ-R is included, retry the operation after correcting the
routing setting.
• Change the system configuration so that the number of relay stations is
seven or less.
• Transient transmission cannot be performed while the communication path
is being updated. Retry the operation.
After completion of the module communication test, retry the transient
transmission.
Correct the request data at the transient request source, and retry the
operation.
operation.
• If the error occurs again even after taking the above, please consult your
local Mitsubishi representative.
After completion of the communication test, retry the operation.
• Check the network status using the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field
diagnostics of the engineering tool, and take action. Then, retry the
operation.
• Check if "Routing Setting" of "CPU Parameter" is correctly set, and take
action.
• Check the network status using the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field
diagnostics of the engineering tool, and take action. Then, retry the
operation.
• Lower the transient transmission usage frequency, and retry the operation.
• Check if "Routing Setting" of "CPU Parameter" is correctly set, and take
action.
Correct the header information at the transient request source, and retry the
operation.
Check the network status using the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field
diagnostics of the engineering tool, and take action. Then, retry the
operation.
• Check the network status using the CC-Link IE TSN/CC-Link IE Field
diagnostics of the engineering tool, and take action.
• If the number of slave stations per network is more than 64, reduce it to 64
or less.
• Correct "Target Station" of communication test, and retry the operation.
• "Communication Test" cannot be executed for own station and relay
sending station. Set "Target Station" to other than own station and relay
transmission station.
• The communication destination is mounted on the same base unit (main
base unit and extension base unit) as th
Do not execute the communication test for station on the same base unit
(main base unit and extension base unit) as the connected station (own
station).
• Check if the switching hub and the cables are connected properly.
nnected station (own station).
e co
information
80
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
Page 83

Error
Error definition and causes Action Detailed
code
D913H
to
D917H
D919H No response from the target station of the
DA00H An error was detected in the network
DA10H
to
DA17H
DA19H An error was detected in the network
DB00H The station Nos. of 65 stations or more are
An error was detected in the network
module.
communication test.
module.
An error was detected in the network
module.
module.
specified.
Please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
• Correct the IP address, station No., or network No. for the target station of
the communication test.
• Check if the network configuration setting is correctly set in the master
station within the same network as the target station of the communication
test.
• When "IP Address" is selected for "Communication Method",
"Communication Test" cannot be executed for stations on networks
different from that of the connected station (own station). Change
"Communication Method" to "Network No./Station No.".
Please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
Please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
Please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
Check station Nos..
information
3
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.5 List of Error Codes
81
Page 84

3.6 List of Parameter Nos.
If there is an error in the parameter settings and the parameter No. is displayed, the corresponding parameter can be
identified.
It is displayed in "Detailed information" in the [Error Information] tab in the "Module Diagnostics" window of the Motion module.
( Page 52 Error Information)
Item Parameter No.
Required Settings Station Type Station Type 7100H
Network No. Network No. 7100H
Station No./IP Address
Setting
Basic Settings Network Configuration
Settings
Network Topology Network Topology A100H
Communication Period
Setting
Connection Device Information Authentication Class Setting A100H
Slave Station Setting Disconnection Detection Setting A100H
Station No. Station No. 7100H
IP Address IP Address A012H
Subnet Mask A012H
Default Gateway A013H
Total number of stations A100H
Simple Display,
Detailed Display
Detailed Display Motion Control Station A104H
Basic Period Setting Setting in Units of 1s A100H
STA# A104H
Station Type A104H
RX Setting A101H
RY Setting A101H
RWr Setting A101H
RWw Setting A101H
LB Setting A101H
LW Setting A101H
Parameter Automatic Setting A104H
PDO Mapping Setting A109H
IP Address A105H
Subnet Mask A105H
Default Gateway A105H
Reserved/Error Invalid Station A001H: Reserved Station
Network Synchronous Communication A045H
Communication Period Setting A108H
Station Information Alias A011H
Comment A011H
Station-specific mode
setting
Communication Period Interval Setting (Do Not
Set it in Units of 1s)
Communication Period Interval Setting (Set it in
Units of 1s)
Cyclic Transmission Time A100H
Transient Transmission Time A100H
A002H: Error Invalid
Station
A106H
A100H
A100H
82
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.6 List of Parameter Nos.
Page 85

Item Parameter No.
Application Settings Supplementary Cyclic
Settings
Event Reception from Other Stations Event Reception from Other Stations A016H
Module Operation Mode Module Operation Mode 7100H
Security IP Filter Settings IP Filter A03AH
Station-based Block Data Assurance A100H
I/O Maintenance
Settings
Output Hold/Clear Setting during CPU STOP A110H
Data Link Error Station Setting A110H
Output Mode upon CPU Error 7101H
IP Filter Settings Deny/Allow A03AH
Range Setting A03AH
IP Address A03AH
IP Address Excluded
from Range
A03AH
3
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.6 List of Parameter Nos.
83
Page 86

3.7 Event List
This section lists the events which occur in CC-Link IE TSN. The three event types are system, security, and operation.
The event type is displayed when the [Event History] button in the [Error Information] tab in the "Module Diagnostics" window
of the Motion module is clicked. ( Page 52 Error Information)
System
Event
Overview Cause
code
00100 Link-up Link-up has occurred when the network cable connected to the external device was
00141 CPU module time setting failure Setting of the time to the CPU module failed.
00403 Time synchronization completion The time synchronization has completed.
00404 Grandmaster selection (CC-Link IE TSN device) The CC-Link IE TSN device was selected as the grandmaster.
00405 Grandmaster selection (general-purpose device) The general-purpose device was selected as the grandmaster.
00500 <<Own station>> Network entry Own station enters the network.
00501 <<Another station>> Network entry Another station enters the network.
00502 Network entry in all stations All stations enter the network.
00510 <<Own station>> Data link restart (cyclic transmission
start)
00511 <<Another station>> Data link restart (cyclic
transmission start)
00512 All stations data link normalization (all-station cyclic
transmission start)
00541 Receive parameter error resolution A parameter error received from the master station/control station was resolved. (Normal
00542 <<Own station>> Receive frame error line status
caution level
00546 Slave station parameter match Parameters which backed up in the master station and parameters in a slave station are
00547 Slave station parameter mismatch Parameters which backed up in the master station and parameters in a slave station are
00800 Link-down Link-down occurred when a network cable connected to an external device was
00906 Alive check error The alive status of an external device could not be checked.
00907 Divided messages receive timeout error • Sufficient data for the data length could not be received.
00908 IP assembly timeout error An IP assembly timeout error has occurred. (The remaining part of the divided data could
00909 TCP specification port No. error The port No. used in a connection already opened is set. (For TCP/IP)
0090A UDP specification port No. error The port No. used in a connection already opened is set. (For UDP/IP)
00C00 <<Own station>> Disconnection from network Own station was disconnected from the network.
00C01 <<Another station>> Disconnection from network Another station was disconnected from the network.
00C02 Abnormal access response of another station • Abnormal response was returned from another station when accessing another
00C10 <<Own station>> Data link stop (cyclic transmission
stop)
00C11 <<Another station>> Data link stop (cyclic
transmission stop)
00C21 <<Another station>> Error occurrence An error has occurred in another station.
00C24 <<Another station>> Receive frame error occurrence A receive frame error has occurred at another station.
00C40 Slave station parameter automatic setting:
Interruption
connected.
Own station data link restarted.
Data link of another station restarted.
Data link returned to normal status at all stations.
parameter was received.)
A receive frame error (line status: caution level) has occurred.
matched by the slave station parameter management function.
not matched by the slave station parameter management function.
disconnected.
• The remaining part of the divided message could not be received.
not be received and a timeout has occurred.)
station.
• Abnormal response was returned to another station when accessed from another
station.
Own station data link was stopped.
Data link of another station was stopped.
An abnormal response was received from the slave station, and slave station parameter
automatic setting processing was interrupted.
For details on slave station response codes, refer to the manual for the slave station
used.
84
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.7 Event List
Page 87

Event
Overview Cause
code
00C41 Slave station parameter automatic setting: Parameter
update interruption
00C42 Slave station parameter automatic setting: System
error
00C43 Slave station parameter automatic setting:
Transmission timeout
00C44 Slave station parameter automatic setting: Receive
timeout
00C46 Slave station parameter automatic setting: SLMP
transmission error
00C47 Slave station parameter automatic setting: CPU
module access failure
00C48 Slave station parameter automatic setting: No target
station parameter
00C50 Time synchronization loss The time difference between the time notified from the grandmaster and the time of the
00C51 Time synchronization error The time synchronization loss occurred more than a fixed number.
00C52 Grandmaster switching (CC-Link IE TSN device) The device acting as the grandmaster station was disconnected, and then the CC-Link
00C53 Grandmaster switching (general-purpose device) The device acting as the grandmaster was disconnected, and then the general-purpose
00C54 Initialization sequence failed A communication error occurred in the initialization processing when control
00C55 Message disposal The request was discarded because there were too many requests to be processed.
00C56 Response timeout There was no response from the external device and timeout occurred.
00C57 Message disposal After response timeout, the response data from the external device was received.
00C58 SLMP response frame disposal The SLMP response frame was disposed of due to any of the following causes.
00C59 Specified port No. error There was a request for a port No. not open from the external device.
00C5A Specification IP address error Sending was performed the a device while the "IP Address" setting of the slave station
00C5B Connection establishment failed A connection could not be established in the open processing.
00C5C TCP connection timeout The external device does not send an ACK response in the TCP/IP communications.
00C5D Send processing execution disabled • The receive buffer or send buffer is not sufficient.
00C5E UDP/IP send failed Data was not sent correctly with UDP/IP due to either of the following causes.
00C5F TCP/IP send failed Data was not sent correctly with TCP/IP due to either of following causes.
00C60 IP address of the external device acquisition error Target IP address could not be acquired from the network No. and station No..
An abnormal response was received from the slave station, and parameter update
processing of slave station parameter automatic setting was interrupted.
For details on slave station response codes, refer to the manual for the slave station
used.
An error occurred while the slave station parameter automatic setting was executing.
Transmission timed out while communicating with the slave station parameter automatic
setting.
The specified period of time expired without receiving while communicating with the
slave station parameter automatic setting.
An error occurred while transmitting SLMP for the slave station parameter automatic
setting.
Access to the CPU module failed during slave station parameter automatic setting.
The slave station parameter file targeted during slave station parameter automatic
setting was not stored in the CPU module.
own station exceeded the allowable value.
IE TSN device was newly selected as the grandmaster.
device was newly selected as the grandmaster.
communications started.
• The request source of the received SLMP response frame is not clear.
• The received SLMP response frame has already returned an error response
according to the monitoring timeout.
• The SLMP communication load is high so that the received SLMP response frame
cannot be transferred.
set in "Network Configuration Settings" under "Basic Settings" of the master station was
incorrect.
• The window size of the external device is not sufficient.
• An error occurs in the external device.
• Failures of switching hubs and cables occur.
• Congestion of packets on the line
• An error occurs in the external device.
• Failures of switching hubs and cables occur.
• Congestion of packets on the line
3
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.7 Event List
85
Page 88

Security
Event
code
10200 Remote password lock The lock processing of the remote password was performed.
10201 Remote password unlock successful The unlock processing of the remote password was succeeded.
10202 Remote password unlock failed The unlock processing of the remote password has failed.
10300 Access from IP restricted with IP filter setting Accessed from IP address restricted with the IP filter setting.
Overview Cause
Operation
Event
code
24100 <<Own station>> Parameter change/new parameter
24307 Network No., station No., IP address setting/change
24F00 <<Another station>> CPU operating status change
Overview Cause
reception
execution
detection
Parameter was changed. Or new parameter was received at power-on.
Setting or change of the network No., station No., or IP address of the own station was
executed.
Operating status of the programmable controller CPU on another station was changed.
86
3 TROUBLESHOOTING
3.7 Event List
Page 89

APPENDICES
Appendix 1 Buffer Memory
The buffer memory is used to exchange data between the Motion module and the CPU module. Buffer memory values are
reset to default when the CPU module is reset or the system is powered off.
List of buffer memory addresses
P1 Name Initial
Address (decimal) Address
(hexadecimal)
0 to 57343 0 to DFFFH System area
98560 to 1245439 18100H to 1300FFH System area
1245440 to 1245441 130100H to 130101H Timeslot 0 information Cycle start offset (ns unit) 0 Read
1245442 130102H Cycle start offset (s unit)
1245443 130103H System area
1245444 to 1245445 130104H to 130105H Cycle end offset (ns unit) 0 Read
1245446 130106H Cycle end offset (s unit)
1245447 to 1245455 130107H to 13010FH System area
1245456 to 1245567 130110H to 13017FH Timeslot 1 to 7 information Same as Timeslot 0 information 0 Read
1245568 to 1245695 130180H to 1301FFH System area
1246180 to 1246719 1303E4H to 1305FFH System area
1247204 to 1247743 1307E4H to 1309FFH System area
1248228 to 1248767 130BE4H to 130DFFH System area
1249252 to 1249791 130FE4H to 1311FFH System area
1250276 to 1250815 1313E4H to 1315FFH System area
1251300 to 1252095 1317E4H to 131AFFH System area
1252096 131B00H Own station (network card)
1252097 131B01H Model type
1252098 131B02H Model code (lower 2 bytes) 1
1252099 131B03H Model code (upper 2 bytes) 1
1252100 131B04H Version 1
1252101 to 1252103 131B05H to 131B07H MAC address 1
1252104 131B08H Own station (controller)
1252105 131B09H Manufacturer code
1252106 131B0AH Model type
1252107 131B0BH Model code (lower 2 bytes)
1252108 131B0CH Model code (upper 2 bytes)
1252109 131B0DH Version
1252110 to 1252119 131B0EH to 131B17H Model name string
1252120 to 1252121 131B18H to 131B19H Vendor-specific device information
1252122 to 1252127 131B1AH to 131B1FH System area
1252128 to 1260543 131B20H to 133BFFH System area
1260544 to 1260559 133C00H to 133C0FH Communication path determination status (network No.1 to 239) 0 Read
1260560 to 1275135 133C10H to 1374FFH System area
1275136 137500H Time distribution interval setting of the CPU module 0 Read, write
1275137 137501H Time reflection setting to the CPU module 0 Read, write
1275138 to 1275903 137502H to 1377FFH System area
1275904 137800H Grandmaster information Grandmaster 0 Read
1275905 to 1275906 137801H to 137802H System area
1275907 to 1275909 137803H to 137805H Grandmaster MAC address 0 Read
information
information
Manufacturer code 0 Read
Controller information valid/invalid flag 0 Read
value
Read,
write
A
APPX
Appendix 1 Buffer Memory
87
Page 90

P1 Name Initial
Address (decimal) Address
value
(hexadecimal)
1275910 to 1275932 137806H to 13781CH System area
*1
1275933 13781DH Time synchronization setting PTP
disable
1275934 13781EH PTP
(P1)
1275935 13781FH PTP
(P2)
1275936 to 2102797 137820H to 20160DH System area
6291480 to 16777215 600018H to FFFFFFH System area
frame send source check enable/
*1
frame send source check result
*1
frame send source check result
0 Read, write
0Read
0Read
*1 PTP is the abbreviation for Precision Time Protocol.
• Do not write data to the system areas. Doing so may cause malfunction of the programmable controller
system.
• If the value in an area of one word becomes equal to or higher than 65536, the count stops at 65535
(FFFFH).
Read,
write
88
APPX
Appendix 1 Buffer Memory
Page 91

Details of buffer memory addresses
Timeslot information
■Timeslot 0 information (Un\G1245440 to Un\1245455)
Synchronous start offset (ns, s unit) of Timeslot 0 and synchronous end offset (ns, s unit) are stored.
Address Name Description
Un\G1245440 to Un\G1245441 Cycle start offset (ns unit) The ns digits of cycle start offset are stored.
Stored range: 0 to 999999999 (ns)
Un\G1245442 Cycle start offset (s unit) The s digits of cycle start offset are stored.
Un\G1245443 System area
Un\G1245444 to Un\G1245445 Cycle end offset (ns unit) The ns digits of cycle end offset are stored.
Un\1245446 Cycle end offset (s unit) The s digits of cycle end offset are stored.
Un\G1245447 to Un\G1245455 System area
■Timeslot 1 to 7 information (Un\G1245456 to Un\1245567)
Timeslot 1 to 7 information is stored in the same order as Timeslot 0 information.
Own station information
The information of the own station on the network is stored.
Stored range: 0 to 65535 (s)
Stored range: 0 to 999999999 (ns)
Stored range: 0 to 65535 (s)
■Own station (network card) information (Un\G1252096 to Un\G1252103)
Address Name Description
Un\G1252096 Manufacturer code The information of the own station is stored.
Un\G1252097 Model type
Un\G1252098 Model code (lower 2 bytes)
Un\G1252099 Model code (upper 2 bytes)
Un\G1252100 Version
Un\G1252101 to
Un\G1252103
MAC address The own station MAC address is stored.
(Also used in the CLPA conformance test.)
Un\G1252101: 5th byte, 6th byte of the MAC address
Un\G1252102: 3rd byte, 4th byte of the MAC address
Un\G1252103: 1st byte, 2nd byte of the MAC address
■Own station (controller) information (Un\G1252104 to Un\G1252121)
Address Name Description
Un\G1252104 Controller information valid/invalid flag Whether the value stored in the own station (controller)
Un\G1252105 Manufacturer code The information of the own station is stored.
Un\G1252106 Model type
Un\G1252107 Model code (lower 2 bytes)
Un\G1252108 Model code (upper 2 bytes)
Un\G1252109 Version
Un\G1252110 to
Un\G1252119
Un\G1252120 to
Un\G1252121
Model name string
Vendor-specific device information
information is valid or invalid is stored.
• 0: Invalid
• 1: Valid
A
APPX
Appendix 1 Buffer Memory
89
Page 92

Communication path determination status
■Communication path determination status (Un\G1260544 to Un\G1260559)
The determination information on the communication path for each network No. of the destination station is stored.
• 0: Path undetermined
• 1: Path determined
Address b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Un\1260544 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Un\1260558 Empty 239 238 237 236 235 234 233 232 231 230 229 228 227 226 225
Un\1260559 Empty
The numbers in the table indicate network Nos..
Time synchronization
■Time distribution interval setting of the CPU module (Un\G1275136)
The time distribution interval of the CPU module on the same base of the master station are set from the master station to the
slave station.
• 0001H to FFFEH: (Send using the set time interval (second))
• FFFFH: (Distribution stop)
■Time reflection setting to the CPU module (Un\G1275137)
• 0000H: Do not reflect the time to the CPU module.
• 0001H: Reflect the time to the CPU module.
Grandmaster information
The grandmaster status of the own station and MAC address are stored.
■Grandmaster (Un\G1275904)
When the own station is the grandmaster, "1" is stored.
• 1: Own station is the grandmaster
• 0: Another station is the grandmaster
■Grandmaster MAC address (Un\G1275907 to Un\G1275909)
The grandmaster MAC address is stored.
• Un\G1275907: 5th byte, 6th byte of the MAC address
• Un\G1275908: 3rd byte, 4th byte of the MAC address
• Un\G1275909: 1st byte, 2nd byte of the MAC address
Time synchronization setting
■PTP frame send source check enable/disable (Un\G1275933)
•1: Check
• 0: Do not check
■PTP frame send source check result (P1) (Un\G1275934)
• 1: Two or more send sources
• 0: One send source
■PTP frame send source check result (P2) (Un\G1275935)
• 1: Two or more send sources
• 0: One send source
90
APPX
Appendix 1 Buffer Memory
Page 93

MEMO
A
APPX
Appendix 1 Buffer Memory
91
Page 94

Appendix 2 List of Link Special Relay (SB)
The link special relay (SB) is turned on/off depending on various factors during data link. Any error status of the data link can
be checked by using or monitoring it in the program.
Application of link special relay (SB)
By using link special relay (SB), the status of CC-Link IE TSN can be checked from HMI (Human Machine Interfaces) as well
as the engineering tool.
Ranges turned on/off by users and by the system
The following ranges correspond to when the link special relay areas (SB) are assigned from SB0000 to SB0FFF.
• Turned on/off by users: SB0000 to SB001F
• Turned on/off by the system: SB0020 to SB0FFF
List of link special relay (SB)
The following table lists the link special relay areas (SB) when they are assigned from SB0000 to SB0FFF.
Do not turn on or off areas whose Nos. are not on the following list or ranges turned on/off by the system.
Doing so may cause malfunction of the programmable controller system.
No. Name Description
SB0006 Clear communication error
count
SB0014 Cyclic data receive status
clear
SB0040 Network type of own station Stores the network type of the own station.
SB0043 Module operation mode of
own station
SB0044 Station setting 1 of own
station
SB0046 Station No. setting status of
own station
SB0049 Data link error status of own
station
SB004A CPU minor error status of
own station
SB004B CPU moderate/major error
status of own station
SB004C CPU operating status of own
station
SB004D Received parameter error Stores the status of received parameter. (For the master station, this relay stores the parameter status of the
Clears the link special register areas related to communication errors (SW0074 to SW0077) to 0.
Off: Clear not requested
On: Clear requested (valid while on)
Clears the cyclic data receive status (SB0064).
While SB0014 is on, the cyclic data receive status does not turn on.
Off: Clear not requested
On: Clear requested (enabled while on)
On: CC-Link IE TSN
Stores the module operation mode of the own station.
Off: Online mode
On: Other than online mode
Stores the station type of the own station.
Off: Slave station (other than the master station)
On: Master station
Stores the station No. setting status.
Off: Station No. set
On: Station No. not set (local station only)
If parameters are set using the engineering tool, this relay is always off.
Stores the data link error status of the own station.
Off: Normal
On: Error
When this relay is turned on, the cause of the error can be checked with 'Cause of data link stop' (SW0049).
Depending on the link refresh timing, the update of 'Cause of data link stop' (SW0049) may be offset by one
sequence scan.
(Also used in the CLPA conformance test.)
Stores the minor error status of the CPU module on the own station.
Off: No minor error
On: Minor error
Stores the moderate/major error status of the CPU module on the own station.
Off: No moderate/major error
On: Moderate/major error
Stores the operating status of the CPU module on the own station.
Off: RUN
On: STOP, PAUSE, or moderate/major error
own station)
Off: Normal
On: Error
92
APPX
Appendix 2 List of Link Special Relay (SB)
Page 95

No. Name Description
SB0064 Cyclic data receive status Shows the receive status in the communication cycle in which the cyclic data from the slave station is set using
"Disconnection Detection Setting" in the master station.
Off: Cyclic data received
On: Cyclic data not received consecutively
(Conditions)
• Turns on when the cyclic data of one or more slave stations is not received consecutively.
• Stations that surpass the maximum station No. are ignored.
(Also used in the CLPA conformance test.)
SB006A PORT1 link-down status of
own station
SB0077 Parameter reception status Stores the status of parameter reception from the master station.
SB007E Type of IP Address Stores the type of IP address.
SB007F IP address setting status Stores the status of the IP address setting by parameter.
SB00B0 Data link error status of each
station
SB00B1 Data link error status of
master station
SB00E8 Station type match status of
each station
SB00F0 CPU operating status of each
station
SB00F1 CPU operating status of
master station
SB0100 CPU moderate/major error
status of each station
SB0101 CPU moderate/major error
status of master station
SB0111 CPU minor error status of
master station
Stores the link-down status of the own station P1 side.
Off: Link-up
On: Link-down
The time until link-up starts after power-on or Ethernet cable connection may vary. Normally link-up takes
several seconds. Depending on device status on the line, link-up processing is repeated and may increase the
time.
(Also used in the CLPA conformance test.)
Off: Reception completed
On: Reception not completed
Off: IPv4
On: IPv6
Off: No setting
On: Set
Stores the data link status of each station.
Off: All stations normal
On: Faulty station exists
When this relay is turned on, the status of each station can be checked with 'Data link status of each station'
(SW00B0 to SW00B7).
Depending on the link refresh timing, the update of 'Data link status of each station' (SW00B0 to SW00B7) may
be offset by one sequence scan.
Stores the data link status of the master station (master operating station).
Off: Normal
On: Error
Stores the station type match status of each station.
Off: Station type match in all stations
On: Station type mismatch exists
When this relay is turned on, the status of each station can be checked with 'Station type match status'
(SW00E8 to SW00EF).
Depending on the link refresh timing, the update of 'Station type match status' (SW00E8 to SW00EF) may be
offset by one sequence scan.
Stores the operating status of the CPU module on each station.
Off: All stations are at RUN or STEP-RUN state
On: Station at STOP or PAUSE state, or station with a moderate/major error exists.
When this relay is turned on, the status of each station can be checked with 'CPU operating status of each
station' (SW00F0 to SW00F7).
Depending on the link refresh timing, the update of 'CPU operating status of each station' (SW00F0 to
SW00F7) may be offset by one sequence scan.
Stores the operating status of the CPU module on the master station (master operating station).
Off: RUN
On: STOP state, PAUSE state, or moderate/major error
Stores the moderate/major error occurrence status of each station.
When the target station is master/local module, the occurrence status on the CPU module is stored.
Off: No station with a moderate/major error
On: Station with a moderate/major error exists
When this relay is turned on, the status of each station can be checked with 'CPU moderate/major error status
of each station' (SW0100 to SW0107).
Depending on the link refresh timing, the update of 'CPU moderate/major error status of each station' (SW0100
to SW0107) may be offset by one sequence scan.
Stores the moderate/major error occurrence status of the CPU module on the master station (master operation
station).
Off: No moderate/major error
On: Moderate/major error
Stores the minor error status of the CPU module on the master station.
Off: No minor errors occurring, or a moderate/major error is occurring
On: Minor error
A
APPX
Appendix 2 List of Link Special Relay (SB)
93
Page 96

Appendix 3 List of Link Special Register (SW)
b15 b2 b1 b0
SW0045
Not used
to
The link special register (SW) stores the information during data link as a numerical value. Faulty areas and causes can be
checked by using or monitoring the link special register (SW) in programs.
Application of link special register (SW)
By using link special register (SW), the status of CC-Link IE TSN can be checked from HMI (Human Machine Interfaces) as
well as the engineering tool.
Range where data is stored by users and range where data is stored by the system
The following ranges correspond to when the link special register areas (SW) are assigned from SW0000 to SW0FFF.
• Stored by users: SW0000 to SW001F
• Stored by the system: SW0020 to SW0FFF
List of link special register (SW)
The following table lists the link special register areas (SW) when they are assigned from SW0000 to SW0FFF.
Do not write any data to an area whose No. is not on the following list or ranges where data is stored by the
system. Doing so may cause malfunction of the programmable controller system.
No. Name Description
SW0040 Network No. Stores the network No. of the own station.
SW0042 Station No. Stores the station No. of the own station.
SW0043 Mode status of own
station
SW0045 Module type Stores the hardware status of the own station.
Range: 1 to 239
Range:
• Master station: 125
Stores the module operation mode setting or communication mode of the own station.
0: Online mode
2: Offline mode
Model type
00: Module
01: Board
10: HMI (Human Machine Interface)
SW0046 to
SW0047
SW0049 Cause of data link stop Stores the cause which stopped the data link of the own station.
IPv4 address Shows the IP address (IPV4) set in the own station.
SW0046
SW0047
(1): Third octet
(2): Fourth octet
(3): First octet
(4): Second octet
00H: At normal communication or power-on
02H: Monitoring time timeout
05H: No slave station (master station only)
13H: Own station Nos. duplication
14H: Master station duplication (master station only)
18H: Parameter error
19H: Parameter communication in progress
20H: CPU module moderate error, major error
60H: Illegal ring connection (master station only)
(Also used in the CLPA conformance test.)
(1)
(3)
(2)
(4)
94
APPX
Appendix 3 List of Link Special Register (SW)
Page 97

No. Name Description
SW004B CPU status of own
station
SW004C Parameter setting status Stores the status of parameter settings.
SW0058 Total number of slave
stations setting value
SW0059 Total number of slave
stations present value
SW005B Maximum data link
station No.
SW0060 Communication cycle
intervals
SW0061 System reserved time Stores the setting value of the system reserved time set with the module parameter of the master station. (Unit: s)
SW0062 Cyclic transmission time Stores the setting value of "Cyclic Transmission Time" of "Basic Settings". (Unit: s)
SW0063 Transient transmission
time
SW0064 Multiple cycle setting
(medium speed)
SW0065 Multiple cycle setting
(low speed)
SW0066 Connection status of own
station
SW0072 Communication cycle
intervals (Calculation
value)
SW0073 Cyclic transmission time
(Calculation value)
SW0074 PORT1 cable
disconnection detection
count
SW0075 PORT1 receive error
detection count
SW0076 PORT1 total number of
received data (lower 1
word)
SW0077 PORT1 total number of
received data (upper 1
word)
SW0078 Transient transmission
time (Calculation value)
Stores the status of the CPU module on the own station.
00H: No CPU module mounted
01H: STOP (normal)
02H: STOP (moderate/major error)
03H: STOP (minor error)
04H: RUN (normal)
05H: RUN (minor error)
07H: PAUSE
0EH: Reset in progress
0FH: Initial processing in progress
0: Normal
1 or greater: Error definition (Error code is stored.)
(Conditions)
• This register is enabled when 'Received parameter error' (SB004D) is on.
Stores the total number of slave stations that are set by the parameters.
Range: 1 to 64
Stores the total number of slave stations that are actually connected by data link.
Range: 1 to 64 (0 when own station is disconnected)
Stores the maximum station No. of the station where the data link is normally performed.
Range: 1 to 64 (0 when own station is disconnected)
(Conditions)
• This register is enabled when 'Data link error status of own station' (SB0049) is off.
Stores the setting value of the communication cycle intervals set with the module parameter of the master station.
(Unit: s)
Stores the setting value of "Transient Transmission Time" of "Basic Settings". (Unit: s)
Stores the setting value of the multiple cycle setting (medium speed) set with the module parameter of the master
station.
Stores the setting value of the multiple cycle setting (low speed) set with the module parameter of the master
station.
Stores the connection status of the own station.
00H: Normal (communication in progress on P1)
01H: Normal (communication in progress on P1)
10H: Normal (cable disconnected on P1)
11H: Disconnected (cable disconnected on P1)
12H: Disconnected (cable disconnected on P1)
21H: Disconnected (establishing line on P1)
22H: Disconnected (establishing line on P1)
Stores the communication cycle intervals that are calculated by the number of slave stations and the number of link
device points set in "Network Configuration Settings" of "Basic Settings". (Unit: s)
Stores the cyclic transmission time that are calculated by the number of slave stations and the number of link
device points set in "Network Configuration Settings" of "Basic Settings". (Unit: s)
Stores the cumulative count that was detected for cable disconnections at the P1 side.
When 'Clear communication error count' (SB0006) is turned on, the stored count is cleared.
When FFFFH (maximum value 65535) is counted, the value returns to 0 and the module continues to count.
Stores the cumulative count that error data was received at the P1 side.
The count stores only error data that is not transmitted to all stations.
When 'Clear communication error count' (SB0006) is turned on, the stored count is cleared.
When FFFFH (maximum value 65535) is counted, counting stops.
Stores the cumulative count that data was received at the P1 side.
When 'Clear communication error count' (SB0006) is turned on, the stored count is cleared.
When FFFFFFFFH (maximum value 4294967295) is
Stores the transient transmission time that are calculated by the number of slave stations and the number of link
device points set in "Network Configuration Settings" of "Basic Settings". (Unit: s)
nted, counting stops.
cou
A
APPX
Appendix 3 List of Link Special Register (SW)
95
Page 98

No. Name Description
16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17
48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33
64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49
SW00B1
SW00B2
SW00B3
SW00B0
16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17
48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33
64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49
SW00C9
SW00CA
SW00CB
SW00C8
16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17
48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33
64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49
SW00D1
SW00D2
SW00D3
SW00D0
16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17
48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33
64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49
SW00E9
SW00EA
SW00EB
SW00E8
SW00B0 to
SW00B3
SW00C8 to
SW00CB
Data link status of each
station
Parameter setting status Stores the status of parameter settings.
Stores the data link status of each station.
0: Data link normally operating station
1: Data link faulty station
• If multiple stations change from faulty to normal, because they are reconnected to the network one by one per
cycle, the time until the status changes to "0: Data link normally operating station" may vary by several seconds.
• If no response is received for several cycles, the station is determined to be a data link faulty station.
Each No. in the table represents a station No..
is fixed to 0.
(Conditions)
• Stations that surpass the maximum station No. are ignored.
(Also used in the CLPA conformance test.)
0: Station not set in the parameter
1: Station set in the parameter
Each No. in the table represents a station No..
is fixed to 0.
(Conditions)
• Stations that surpass the maximum station No. are ignored.
SW00D0 to
SW00D3
SW00E8 to
SW00EB
SW0160 to
SW0167
SW0194 Detailed execution result
96
APPX
Appendix 3 List of Link Special Register (SW)
Error invalid station
setting status
Station type match status Stores the match status between the station type set in the master station and that of the slave station.
Execution result of slave
station parameter
automatic setting
function
of slave station
parameter automatic
setting
Stores the error invalid station setting status of each station.
0: Station other than an error invalid station
1: Error invalid station
Each No. in the table represents a station No..
is fixed to 0.
(Conditions)
• Stations that surpass the maximum station No. are ignored.
0: Station type match
1: Station type mismatch
Each No. in the table represents a station No..
is fixed to 0.
(Conditions)
• This register is enabled only for the station in which 'Network connection status' (SW00B8 to SW00BF) is on and
is connected to the network.
When the slave station parameter automatic setting is completed with an error, the Bit of the target station is turned
on.
Off: Completed successfully
On: Completed with an error
When completed with an error, the error code is stored in the SW0194.
When the slave station parameter automatic setting is completed with an error, the error code is stored.
Page 99

Appendix 4 Port No.
A port No. for the system cannot be specified.
Port No. Applications
Decimal Hexadecimal
20 to 21 14H to 15H For system
161 to 162 A1H to A2H For system
5000 1388H Auto-open UDP port
5001 1389H MELSOFT transmission port (UDP/IP)
5002 138AH MELSOFT transmission port (TCP/IP)
5003 to 5009 138BH to 1391H For system
5010 1392H SLMP transmission port (UDP/IP)
5011 1393H SLMP transmission port (TCP/IP)
45237 to 61442 B0B5H to F002H For system
61448 F008H For system
61460 to 61464 F014H to F018H For system
61500 to 61501 F03CH to F03DH For system
62000 to 65534 F230H to FFFEH For system
A
APPX
Appendix 4 Port No.
97
Page 100

INDEX
C
Communication test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Control CPU. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Cyclic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
D
Data link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Diagnostic items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Diagnostics window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Disconnection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
E
Engineering tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Error information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
I
IP filter function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
IP filter settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
L
Link device. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Link refresh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Lock processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
U
Unlock processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
M
Master station. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
MELSOFT transmission port (UDP/IP) . . . . . . . . 97
Module information list. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
N
Network module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Network status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
R
RAS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Remote operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Return . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
S
Select diagnostics destination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Selected station communication status monitor . . 58
Slave station. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Supplementary function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
T
98
Transient transmission. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
 Loading...
Loading...