Page 1

www.DataSheet4U.com
ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE
OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE
RA13H1317M
135-175MHz 13W 12.5V MOBILE RADIO
DESCRIPTION
The RA13H1317M is a 13-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module
for 12.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the 135- to 175-MHz
range.
The battery can be connected directly to the drain of the
enhancement-mode MOSFET transistors. Without the gate
voltage (VGG=0V), only a small leakage current flows into the drain
and the RF input signal attenuates up to 60 dB. The output power
and drain current increase as the gate voltage increases. With a
gate voltage around 4V (minimum), output power and drain current
increases substantially. The nominal output power becomes
available at 4.5V (typical) and 5V (maximum). At VGG=5V, the
typical gate current is 1 mA.
This module is designed for non-linear FM modulation, but may
also be used for linear modulation by setting the drain quiescent
current with the gate voltage and controlling the output power with
the input power.
FEATURES
• Enhancement -Mode MOSFET Transistors
(IDD≅0 @ VDD=12.5V, VGG=0V)
• P
>13W, ηT>40% @ VDD=12.5V, VGG=5V, Pin=50mW
out
• Broadband Frequency Range: 135-175 MHz
• Low-Power Control Current IGG=1mA (typ) at VGG=5V
• Module Size: 66 x 21 x 9.88 mm
• Linear operation is possible by setting the quiescent drain current
with the gate voltage and controlling the output power with the
input power
BLOCK DIAGRAM
BLOCK DIAGRAM
1
1 RF Input (Pin)
2 Gate Voltage (VGG), Power Control
3 Drain Voltage (VDD), Battery
4 RF Output (P
5 RF Ground (Case)
2
)
out
3
4
5
ORDERING INFORMATION:
ORDER NUMBER SUPPLY FORM
RA13H1317M-E01
RA13H1317M-01
(Japan - Packed without desiccator)
Antistatic tray,
10 modules/tray
RA13H1317M
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
1/9
23 Dec 2002
Page 2
ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE
OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE
RA13H1317M
MAXIMUM RATINGS
(T
=+25°C, unless otherwise specified)
case
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS RATING UNIT
VDD Drain Voltage VGG<5V 17 V
VGG Gate Voltage VDD<12.5V, Pin=0mW 6 V
Pin Input Power 100 mW
P
Output Power
out
T
Operation Case Temperature Range -30 to +110 °C
case(OP)
T
Storage Temperature Range
stg
f=135-175MHz,
ZG=ZL=50Ω
20 W
-40 to +110 °C
The above parameters are independently guaranteed.
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(T
=+25°C, ZG=ZL=50Ω, unless otherwise specified)
case
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
f Frequency Range 135 175 MHz
P
Output Power 13 W
out
ηT Total Efficiency 40 %
2fo 2nd Harmonic -25 dBc
ρin Input VSWR 3:1 —
IGG Gate Current
— Stability
— Load VSWR Tolerance
VDD=12.5V
VGG=5V
Pin=50mW
VDD=10.0-15.2V, Pin=25-70mW,
P
<20W (VGG control), Load VSWR=3:1
out
VDD=15.2V, Pin=50mW, P
=13W (VGG control),
out
Load VSWR=20:1
1 mA
No parasitic oscillation —
No degradation or
destroy
—
All parameters, conditions, ratings, and limits are subject to change without notice.
RA13H1317M
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
2/9
23 Dec 2002
Page 3
OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
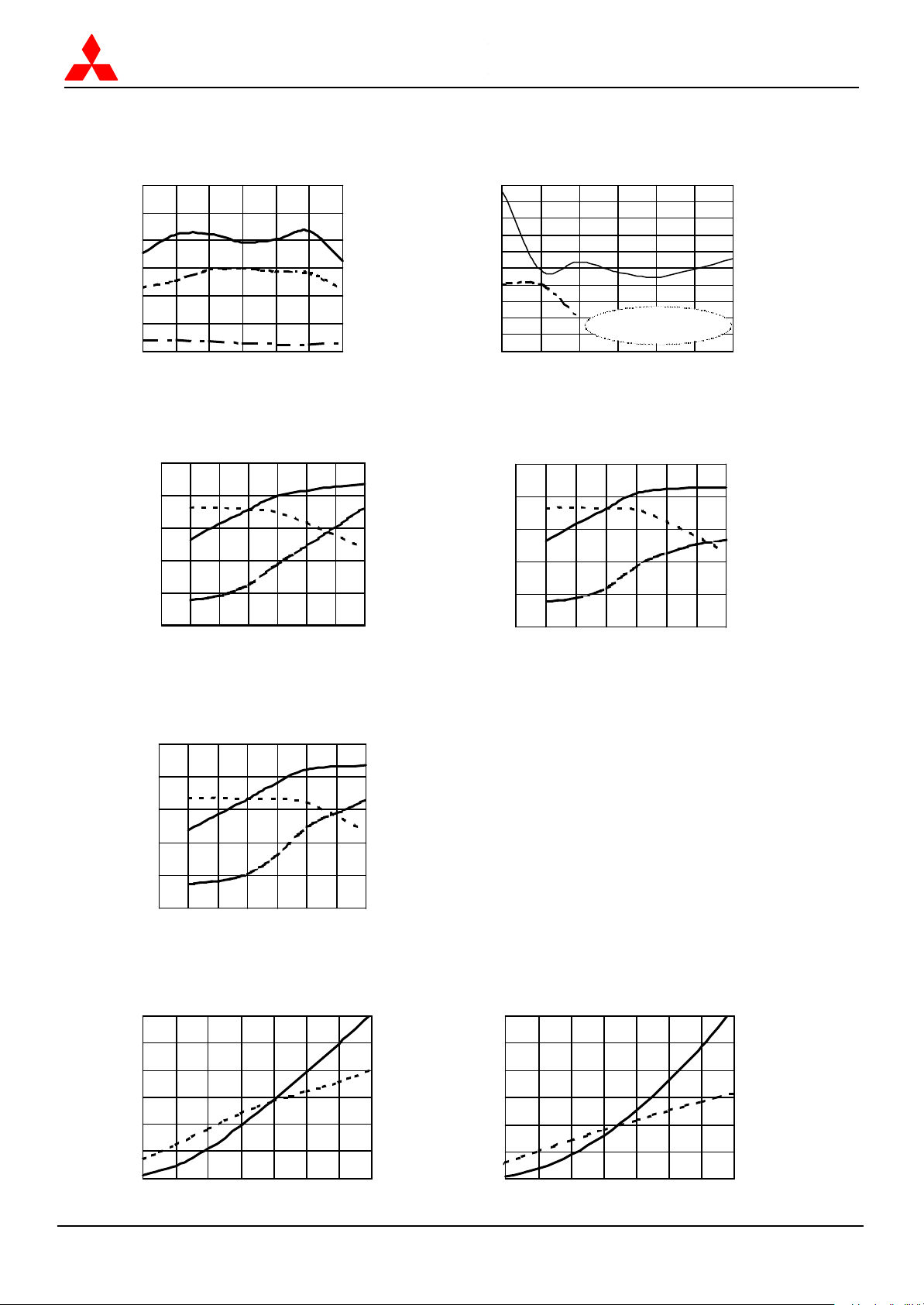
and INPUT VSWR versus FREQUENCY
OUTPUT POWER, POWER GAIN and
OUTPUT POWER, POWER GAIN and
DRAIN CURRENT versus INPUT POWER
DRAIN CURRENT versus INPUT POWER
OUTPUT POWER, POWER GAIN and
DRAIN CURRENT versus INPUT POWER
OUTPUT POWER and DRAIN CURRENT
OUTPUT POWER and DRAIN CURRENT
versus DRAIN VOLTAGE
versus DRAIN VOLTAGE
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE
OUTPUT POWER, TOTAL EFFICIENCY, 2nd, 3rd HARMONICS versus FREQUENCY
(W)
out
(-)
30
25
in
20
15
η
10
INPUT VSWR ρ
5
OUTPUT POWER P
0
125 135 145 155 165 175 185
ρ
in
FREQUENCY f(MHz)
50
40
30
(dBm)
out
20
P
OUTPUT POWER
10
POWER GAIN Gp(dB)
0
-15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 20
Gp
I
DD
INPUT POWER P in(dBm)
50
40
30
(dBm)
out
20
P
OUTPUT POWER
10
POWER GAIN Gp(dB)
0
-15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 20
Gp
IDD
INPUT POWER Pin(dBm)
ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE
(T
=+25°C, ZG=ZL=50Ω, unless otherwise specified)
case
120
P
out
P
out
f=175MHz,
VDD=12.5V,
VGG=5V
100
80
60
40
20
0
(%)
T
η
TOTAL EFFICIENCY
5
(A)
4
DD
3
2
1
DRAIN CURRENT I
0
5
(A)
4
DD
3
2
1
DRAIN CURRENT I
0
P
out
T
VDD=12.5V
Pin=50mW
f=135MHz,
VDD=12.5V,
VGG=5V
-20
-30
-40
-50
rd
HARMONICS (dBc)
-60
-70
125 135 145 155 165 175 185
50
40
30
(dBm)
out
20
P
OUTPUT POWER
10
POWER GAIN Gp(dB)
0
-15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 20
3
FREQUENCY f(MHz)
Gp
I
DD
INPUT POWER Pin(dBm)
VDD=12.5V
Pin=50mW
nd
2
below -60dBc
MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE
RA13H1317M
P
f=155MHz,
VDD=12.5V,
VGG=5V
5
out
(A)
4
DD
3
2
1
DRAIN CURRENT I
0
30
f=135MHz,
25
(W)
VGG=5V,
out
Pin=50mW
20
15
10
5
OUTPUT POWER P
0
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
DRAIN VOLTAGE VDD(V)
RA13H1317M
6
5
(A)
DD
P
out
I
DD
4
3
2
1
DRAIN CURRENT I
0
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
30
f=155MHz,
25
(W)
VGG=5V,
out
Pin=50mW
20
15
10
5
OUTPUT POWER P
0
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
DRAIN VOLTAGE VDD(V)
P
out
6
5
(A)
DD
4
3
I
DD
2
1
DRAIN CURRENT I
0
23 Dec 2002
3/9
Page 4

OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
OUTPUT POWER and DRAIN CURRENT
versus DRAIN VOLTAGE
OUTPUT POWER and DRAIN CURRENT
OUTPUT POWER and DRAIN CURRENT
versus GATE VOLTAGE
versus GATE VOLTAGE
OUTPUT POWER and DRAIN CURRENT
versus GATE VOLTAGE
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE
ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE
(T
=+25°C, ZG=ZL=50Ω, unless otherwise specified)
case
MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE
RA13H1317M
30
f=175MHz,
(W)
25
VGG=5V,
out
Pin=50mW
20
15
P
out
I
10
5
OUTPUT POWER P
0
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
DRAIN VOLTAGE VDD(V)
30
f=135MHz,
VDD=12.5V,
25
(W)
out
Pin=50mW
20
P
out
15
10
5
OUTPUT POWER P
0
1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5
GATE VOLTAGE VGG(V)
6
5
(A)
DD
4
DD
3
2
1
DRAIN CURRENT I
0
6
5
(A)
DD
4
3
I
DD
2
1
DRAIN CURRENT I
0
30
f=160MHz,
VDD=12.5V,
(W)
25
out
Pin=50mW
20
15
10
5
OUTPUT POWER P
0
6
5
P
out
(A)
DD
4
3
I
DD
2
1
DRAIN CURRENT I
0
1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5
GATE VOLTAGE VGG(V)
30
f=175MHz,
VDD=12.5V,
(W)
25
out
Pin=50mW
P
out
20
15
10
5
OUTPUT POWER P
0
1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5
GATE VOLTAGE VGG(V)
IDD
6
5
(A)
DD
4
3
2
1
DRAIN CURRENT I
0
RA13H1317M
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
4/9
23 Dec 2002
Page 5

OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
OUTLINE DRAWING (mm)
ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE
66.0 ±0.5
MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE
RA13H1317M
3.0 ±0.3
7.25 ±0.8
9.5 ±0.5 2.0 ±0.5
14.0 ±1 21.0 ±0.5
12.0 ±1
16.5 ±1
60.0 ±0.5
51.5 ±0.5
1 2 3 4
43.5 ±1
55.5 ±1
2-R2 ±0.5
17.0 ±0.5
5
4.0 ±0.3
Ø0.45 ±0.15
3.1 +0.6/-0.4
0.09 ±0.02
(50.4)
(9.88)
7.5 ±0.5
2.3 ±0.3
1 RF Input (Pin)
2 Gate Voltage (VGG)
3 Drain Voltage (VDD)
4 RF Output (P
)
out
5 RF Ground (Case)
RA13H1317M
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
5/9
23 Dec 2002
Page 6

OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
C1, C2: 4700pF, 22uF in parallel
Power
amplifier
5 4 3 2 1
ZG=50Ω
Z
=50Ω
C1
C2
3
TEST BLOCK DIAGRAM
Generator
Signal
Attenuator
EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
1
ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE
Power
Meter
Pre-
Attenuator
Directional
Coupler
2
- +
DC Power
Supply V
GG
DUT
+ -
DC Power
Supply V
MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE
RA13H1317M
Spectrum
Analyzer
Directional
Coupler
DD
1 RF Input (Pin)
2 Gate Voltage (VGG)
3 Drain Voltage (VDD)
4 RF Output (P
5 RF Ground (Case)
Attenuator
Meter
)
out
4
5
RA13H1317M
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
6/9
23 Dec 2002
Page 7

ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE
OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE
RA13H1317M
PRECAUTIONS, RECOMMENDATIONS, and APPLICATION INFORMATION:
Construction:
This module consists of an alumina substrate soldered onto a copper flange. For mechanical protection, a plastic cap
is attached with silicone. The MOSFET transistor chips are die bonded onto metal, wire bonded to the substrate, and
coated with resin. Lines on the substrate (eventually inductors), chip capacitors, and resistors form the bias and
matching circuits. Wire leads soldered onto the alumina substrate provide the DC and RF connection.
Following conditions must be avoided:
a) Bending forces on the alumina substrate (for example, by driving screws or from fast thermal changes)
b) Mechanical stress on the wire leads (for example, by first soldering then driving screws or by thermal expansion)
c) Defluxing solvents reacting with the resin coating on the MOSFET chips (for example, Trichlorethylene)
d) Frequent on/off switching that causes thermal expansion of the resin
e) ESD, surge, overvoltage in combination with load VSWR, and oscillation
ESD:
This MOSFET module is sensitive to ESD voltages down to 1000V. Appropriate ESD precautions are required.
Mounting:
Heat sink flatness must be less than 50 µm (a heat sink that is not flat or particles between module and heat sink may
cause the ceramic substrate in the module to crack by bending forces, either immediately when driving screws or later
when thermal expansion forces are added).
A thermal compound between module and heat sink is recommended for low thermal contact resistance and to reduce
the bending stress on the ceramic substrate caused by the temperature difference to the heat sink.
The module must first be screwed to the heat sink, then the leads can be soldered to the printed circuit board.
M3 screws are recommended with a tightening torque of 0.4 to 0.6 Nm.
Soldering and Defluxing:
This module is designed for manual soldering.
The leads must be soldered after the module is screwed onto the heat sink.
The soldering temperature must be lower than 260°C for a maximum of 10 seconds, or lower than 350°C for a maximum
of three seconds.
Ethyl Alcohol is recommend for removing flux. Trichlorethylene solvents must not be used (they may cause bubbles in
the coating of the transistor chips which can lift off the bond wires).
Thermal Design of the Heat Sink:
At P
=13W, VDD=12.5V, and Pin=50mW, each stage transistor operating conditions are:
out
Stage
1st
Pin
(W)
0.05 2.0 4.5 0.35
P
out
(W)
R
(°C/W)
th(ch-case)
IDD @ η
(A)
=40%
T
VDD
(V)
12.5
2nd 2.0 13.0 2.4 2.20
The channel temperatures of each stage transistor Tch = T
T
= T
ch1
T
ch2
+ (12.5V x 0. 35A – 2.0W + 0.05W) x 4.5°C/W = T
case
= T
+ (12.5V x 2.20A - 13.0W + 2.0W) x 2.4°C/W = T
case
+ (VDD x IDD - P
case
case
case
+ Pin) x R
out
+ 10.9°C
+ 39.6°C
th(ch-case)
are:
For long-term reliability, it is best to keep the module case temperature (T
temperature T
=60°C and P
air
=13W, the required thermal resistance R
out
) below 90°C. For an ambient
case
th (case-air)
= ( T
case
- T
) / ( (P
air
/ ηT ) - P
out
Pin ) of the heat sink, including the contact resistance, is:
R
th(case-air)
= (90°C - 60°C) / (13W/40% – 13W + 0.05W) = 1.53 °C/W
When mounting the module with the thermal resistance of 1.53 °C/W, the channel temperature of each stage transistor
is:
T
= T
= T
+ 40.9°C
air
+ 69.6°C
air
ch1
T
ch2
The 175°C maximum rating for the channel temperature ensures application under derated conditions.
+
out
RA13H1317M
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
7/9
23 Dec 2002
Page 8

ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE
OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
Electric Corporation puts the maximum effort into making semiconductor products better and more reliable, but
there is always the possibility that trouble may occur. Trouble with semiconductors may lead to personal injury, fire or property
to give due consideration to safety when making your circuit designs, with appropriate measures such
flammable material, or (iii) prevention against any
MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE
RA13H1317M
Output Power Control:
Depending on linearity, the following two methods are recommended to control the output power:
a) Non-linear FM modulation:
By the gate voltage (VGG).
When the gate voltage is close to zero, the RF input signal is attenuated up to 60 dB and only a small leakage
current flows from the battery into the drain.
Around VGG=4V, the output power and drain current increases substantially.
Around VGG=4.5V (typical) to VGG=5V (maximum), the nominal output power becomes available.
b) Linear AM modulation:
By RF input power Pin.
The gate voltage is used to set the drain’s quiescent current for the required linearity.
Oscillation:
To test RF characteristics, this module is put on a fixture with two bias decoupling capacitors each on gate and drain,
a 4.700 pF chip capacitor, located close to the module, and a 22 µF (or more) electrolytic capacitor.
When an amplifier circuit around this module shows oscillation, the following may be checked:
a) Do the bias decoupling capacitors have a low inductance pass to the case of the module?
b) Is the load impedance ZL=50Ω?
c) Is the source impedance ZG=50Ω?
Frequent on/off switching:
In base stations, frequent on/off switching can cause thermal expansion of the resin that coats the transistor chips and
can result in reduced or no output power. The bond wires in the resin will break after long-term thermally induced
mechanical stress.
Quality:
Mitsubishi Electric is not liable for failures resulting from base station operation time or operating conditions exceeding
those of mobile radios.
This module technology results from more than 20 years of experience, field proven in tens of millions of mobile radios.
Currently, most returned modules show failures such as ESD, substrate crack, and transistor burnout, which are
caused by improper handling or exceeding recommended operating conditions. Few degradation failures are found.
Keep safety first in your circuit designs!
Mitsubishi
damage. Remember
as (i) placement of substitutive, auxiliary circuits, (ii) use of nonmalfunction or mishap.
RA13H1317M
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
8/9
23 Dec 2002
Page 9

SALES CONTACT
JAPAN:
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
Semiconductor Sales Promotion Department
2-2-3 Marunouchi, Chiyoda-ku
Tokyo, Japan 100
Email: sod.sophp@hq.melco.co.jp
Phone: +81-3-3218-4854
Fax: +81-3-3218-4861
HONG KONG:
Mitsubishi Electric Hong Kong Ltd.
Semiconductor Division
41/F. Manulife Tower, 169 Electric Road
North Point, Hong Kong
Email: scdinfo@mehk.com
Phone: +852 2510-0555
Fax: +852 2510-9822
SINGAPORE:
Mitsubishi Electric Asia PTE Ltd.
Semiconductor Division
307 Alexandra Road
#3-01/02 Mitsubishi Electric Building,
Singapore 159943
Email: semicon@asia.meap.com
Phone: +65 64 732 308
Fax: +65 64 738 984
GERMANY:
Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V.
Semiconductor
Gothaer Strasse 8
D-40880 Ratingen, Germany
Email: semis.info@meg.mee.com
Phone: +49-2102-486-0
Fax: +49-2102-486-3670
FRANCE:
Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V.
Semiconductor
25 Boulevard des Bouvets
F-92741 Nanterre Cedex, France
Email: semis.info@meg.mee.com
Phone: +33-1-55685-668
Fax: +33-1-55685-739
ITALY:
Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V.
Semiconductor
Centro Direzionale Colleoni,
Palazzo Perseo 2, Via Paracelso
I-20041 Agrate Brianza, Milano, Italy
Email: semis.info@meg.mee.com
Phone: +39-039-6053-10
Fax: +39-039-6053-212
TAIWAN:
Mitsubishi Electric Taiwan Company, Ltd.
Semiconductor Department
9F, No. 88, Sec. 6
Chung Shan N. Road
Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Email: metwnssi@metwn.meap.com
Phone: +886-2-2836-5288
Fax: +886-2-2833-9793
U.S.A.:
Mitsubishi Electric & Electronics USA, Inc.
Electronic Device Group
1050 East Arques Avenue
Sunnyvale, CA 94085
Email: customerservice@edg.mea.com
Phone: 408-730-5900
Fax: 408-737-1129
CANADA:
Mitsubishi Electric Sales Canada, Inc.
4299 14th Avenue
Markham, Ontario, Canada L3R OJ2
Phone: 905-475-7728
Fax: 905-475-1918
U.K.:
Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V.
Semiconductor
Travellers Lane, Hatfield
Hertfordshire, AL10 8XB, England
Email: semis.info@meuk.mee.com
Phone: +44-1707-278-900
Fax: +44-1707-278-837
AUSTRALIA:
Mitsubishi Electric Australia,
Semiconductor Division
348 Victoria Road
Rydalmere, NSW 2116
Sydney, Australia
Email: semis@meaust.meap.com
Phone: +61 2 9684-7210
+61 2 9684 7212
+61 2 9684 7214
+61 3 9262 9898
Fax: +61 2 9684-7208
+61 2 9684 7245
RA13H1317M
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
9/9
23 Dec 2002
 Loading...
Loading...