Page 1

4Mpps Capable High-Speed Counter Module
User's Manual
-QD64D2
-GX Configurator-CT (SW0D5C-QCTU-E)
Page 2

Page 3
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
(Read these precautions before use.)
Before using this product, please read this manual carefully and pay full attention to safety to handle the
product correctly.
The precautions given in this manual are concerned with this product. For the safety precautions of the
programmable controller system, please read the User's Manual for the CPU module.
In this manual, the safety precautions are classified into two levels: " WARNING" and " CAUTION".
WARNING
CAUTION
Note that the CAUTION level may lead to a serious consequence according to the circumstances.
Always follow the precautions of both levels because they are important to personal safety.
Please save this manual to make it accessible when required and always forward it to the end user.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in minor or moderate injury or property damage.
[DESIGN PRECAUTIONS]
WARNING
Do not write data to "read-only area" or "reserved area" in the buffer memory of the intelligent
function module. Also do not turn ON/OFF the "reserved" signal in I/O signals to the programmable
controller CPU.
Doing any of these operations may cause a malfunction of the programmable controller system.
When a transistor for external output fails, the output may be ON or OFF status.
Create a circuit for monitoring output signal that may lead to serious accident.
CAUTION
Do not install the control lines and/or pulse input wiring together with the main circuit or power lines,
and also do not bring them close to each other.
Keep a distance of 150mm (5.91 inch) or more between them.
Failure to do so may cause a malfunction due to noise.
[INSTALLATION PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
Use the programmable controller in the environment conditions given in the general specifications of
the User's Manual for the CPU module.
Failure to do so may cause an electric shock, fire, malfunction, or damage to or deterioration of the
product.
A - 1
Page 4
[INSTALLATION PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
While pressing the installation lever located at the bottom of the module, fully insert the module fixing
projection into the fixing hole in the base unit and press the module using the hole as a fulcrum.
Incorrect module mounting may cause a malfunction, failure, or drop of the module.
In an environment of frequent vibrations, secure the module with screws.
The screws must be tightened within the specified torque range.
If the screw is too loose, it may cause a drop, short circuit, or malfunction.
Excessive tightening may damage the screw and/or the module, resulting in a drop, short circuit or
malfunction.
Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply used by the system before mounting or
removing the module.
Failure to do so may cause damage to the product.
Do not directly touch any conductive part or electronic part of the module.
Doing so may cause a malfunction or failure of the module.
[WIRING PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
For wiring and connection, properly crimp or solder the connector with the tools specified by the
manufactures and attach the connector to the module securely.
Be careful to prevent foreign matter such as dust or wire chips from entering the module.
Failure to do may cause a fire, failure or malfunction.
A protective film is attached to the module top to prevent foreign matter such as wire chips from
entering the module during wiring.
Do not remove the film during wiring.
Be sure to remove it for heat dissipation before system operation.
Be sure to place the cables connected to the module in a duct or clamp them.
If not, dangling cables may swing or inadvertently be pulled, resulting in damage to the module and/
or cables, or malfunctions due to poor cable connection.
When disconnecting the cable, do not pull it by holding the cable part.
Disconnect the cable with connector with holding the connector plugged into the module.
Pulling the cable part with the cable still connected to the module may cause a malfunction or
damage to the module and/or cable.
A - 2
Page 5
[WIRING PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
Always ground the shielded cable on the module side.
Failure to do may cause a malfunction.
Correctly wire cables to the module after checking the rated voltage and terminal layout of the
product.
Connecting a voltage different from the rated voltage or incorrect wiring may result in a fire or failure.
[STARTUP/MAINTENANCE PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
Do not disassemble or remodel each of the modules.
Doing so may cause failure, malfunctions, personal injuries and/or a fire.
Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply used by the system before mounting or
removing the module.
Not doing so may result in a failure or malfunction of the module.
Do not mount/remove the module onto/from the base unit more than 50 times (IEC 61131-2
compliant), after the first use of the product.
Doing so may cause malfunctions.
Do not touch the terminal while the power is ON. Failure to do may cause a malfunction.
Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply used by the system when cleaning the
module or retightening the terminal or module fixing screws.
Not doing so may result in a failure or malfunction of the module.
If the screw is too loose, it may cause a drop, short circuit or malfunction.
Excessive tightening may damage the screw and/or the module, resulting in a drop, short circuit or
malfunction.
Before handling the module, touch a grounded metal object to discharge the static electricity from
the human body.
Not doing so may result in a failure or malfunction of the module.
[DISPOSAL PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
When disposing of this product, treat it as industrial waste.
A - 3
Page 6

CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
(1) Mitsubishi programmable controller ("the PRODUCT") shall be used in conditions;
i) where any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT, if any, shall not lead to any major
or serious accident; and
ii) where the backup and fail-safe function are systematically or automatically provided outside of
the PRODUCT for the case of any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT.
(2) The PRODUCT has been designed and manufactured for the purpose of being used in general
industries.
MITSUBISHI SHALL HAVE NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO ANY AND ALL RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY BASED ON CONTRACT,
WARRANTY, TORT, PRODUCT LIABILITY) FOR ANY INJURY OR DEATH TO PERSONS OR
LOSS OR DAMAGE TO PROPERTY CAUSED BY the PRODUCT THAT ARE OPERATED OR
USED IN APPLICATION NOT INTENDED OR EXCLUDED BY INSTRUCTIONS, PRECAUTIONS,
OR WARNING CONTAINED IN MITSUBISHI'S USER, INSTRUCTION AND/OR SAFETY
MANUALS, TECHNICAL BULLETINS AND GUIDELINES FOR the PRODUCT.
("Prohibited Application")
Prohibited Applications include, but not limited to, the use of the PRODUCT in;
• Nuclear Power Plants and any other power plants operated by Power companies, and/or any
other cases in which the public could be affected if any problem or fault occurs in the PRODUCT.
• Railway companies or Public service purposes, and/or any other cases in which establishment of
a special quality assurance system is required by the Purchaser or End User.
• Aircraft or Aerospace, Medical applications, Train equipment, transport equipment such as
Elevator and Escalator, Incineration and Fuel devices, Vehicles, Manned transportation,
Equipment for Recreation and Amusement, and Safety devices, handling of Nuclear or
Hazardous Materials or Chemicals, Mining and Drilling, and/or other applications where there is a
significant risk of injury to the public or property.
Notwithstanding the above, restrictions Mitsubishi may in its sole discretion, authorize use of the
PRODUCT in one or more of the Prohibited Applications, provided that the usage of the PRODUCT
is limited only for the specific applications agreed to by Mitsubishi and provided further that no
special quality assurance or fail-safe, redundant or other safety features which exceed the general
specifications of the PRODUCTs are required. For details, please contact the Mitsubishi
representative in your region.
A - 4
Page 7
REVISIONS
* The manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover.
Print date *Manual number Revision
Dec., 2008 SH(NA)-080726ENG-A First edition
Apr., 2010 SH(NA)-080726ENG-B
Correction
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS,GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS,
Chapter 1, Section 2.1,Section 2.2, Section 4.4.1, Section 5.3.4, Section 6.2.1
Addition
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT, Compliance with the EMC and
Low Voltage Directives, Section 2.3
Japanese Manual Version SH-080725-D
This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any licenses. Mitsubishi
Electric Corporation cannot be held responsible for any problems involving industrial property rights which may occur as a
result of using the contents noted in this manual.
2008 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
A - 5
Page 8

INTRODUCTION
Thank you for purchasing the Mitsubishi programmable controller MELSEC-Q series.
Before using the product, please read this manual carefully to develop full familiarity with the functions and
performance of the Q series programmable controller to ensure correct use.
CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 1
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 4
REVISIONS •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••A - 5
INTRODUCTION •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 6
CONTENTS••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 6
Compliance with the EMC and Low Voltage Directives •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 9
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 10
PACKING LIST•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 10
CHAPTER1 OVERVIEW 1 - 1 to 1 - 3
1.1 Features •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 1 - 2
CHAPTER2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION 2 - 1 to 2 - 9
2.1 Applicable Systems•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••2 - 1
2.2 About Use of the QD64D2 with Redundant CPU •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••2 - 5
2.3 About Use of the QD64D2 on the MELSECNET/H Remote I/O Station •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••2 - 6
2.4 How to Check the Function Version/Serial No./Software Version •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••2 - 7
CHAPTER3 SPECIFICATIONS 3 - 1 to 3 - 28
3.1 Performance Specifications••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 1
3.1.1 Relation of phase difference between phase A and phase B•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••3 - 2
3.1.2 Derating chart ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••3 - 3
3.2 Function List •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••3 - 5
3.3 I/O Signals to the Programmable Controller CPU •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 6
3.3.1 List of I/O signals ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••3 - 6
3.3.2 Functions of I/O signals •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 8
3.4 Buffer Memory Assignment ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 15
3.4.1 List of buffer memory assignment•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 15
3.4.2 Details of the buffer memory •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 19
3.5 Specifications of I/O Interfaces with External Device •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 24
3.5.1 Electrical specifications of I/O signals ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 24
3.5.2 Signal layout for external device connector •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 25
3.5.3 List of I/O signal details •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 26
3.5.4 Interface for external device••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 27
3.6 Connectable Encoders••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 28
A - 6
Page 9

CHAPTER4 PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE OPERATION 4 - 1 to 4 - 12
4.1 Handling Precautions •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 1
4.2 Procedures before Operation •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••4 - 2
4.3 Part Names •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 3
4.4 Wiring ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 5
4.4.1 Wiring precautions ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••4 - 5
4.4.2 Example of wiring the module and an encoder•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 7
4.4.3 Example of wiring a controller and an external input terminal ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••4 - 8
4.4.4 Example of wiring with an external output terminal ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 9
4.5 Intelligent Function Module Switch Setting •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 10
CHAPTER5 FUNCTIONS 5 - 1 to 5 - 31
5.1 Pulse Input and Count Methods ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 1
5.1.1 Types of the pulse input method •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••5 - 1
5.2 Selecting a Counter Format••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 3
5.2.1 Selecting the linear counter ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 4
5.2.2 Selecting the ring counter •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••5 - 5
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••5 - 8
5.3.1 Using the coincidence output function •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 9
5.3.2 Using the continuous comparison function ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 13
5.3.3 Using the coincidence output test function ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 22
5.3.4 Coincidence detection interrupt function•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 24
5.4 Using the Preset Function••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 27
5.5 Using the Latch Counter Function ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 29
5.6 Response Delay Time ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 31
CHAPTER6 UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-CT) 6 - 1 to 6 - 20
6.1 Utility Package Functions •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••6 - 1
6.2 Installing and Uninstalling the Utility Package••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 3
6.2.1 Handling precautions ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 3
6.2.2 Operating environment ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 5
6.3 Utility Package Operation ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 7
6.3.1 Common utility package operations ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 7
6.3.2 Operation overview •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••6 - 9
6.3.3 Starting the Intelligent function module utility •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 11
6.4 Initial Setting ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 14
6.5 Auto Refresh ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 16
6.6 Monitoring/Test •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 18
6.6.1 Monitoring/test ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 18
CHAPTER7 PROGRAMMING 7 - 1 to 7 - 18
7.1 Programming Procedure •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 1
A - 7
Page 10

7.2 For Use in Normal System Configuration ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••7 - 3
7.2.1 Before creating a program •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••7 - 4
7.3 Programming Example when GX Configurator-CT is Used •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 6
7.4 Programming Example when GX Configurator-CT is not Used•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 12
7.5 Program Example when the Coincidence Detection Interrupt Function is Used ••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 17
CHAPTER8 TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 1 to 8 - 13
8.1 Error Processing and Recovery Methods •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 1
8.1.1 Checking error description using System Monitor of GX Developer ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 1
8.1.2 When the RUN LED turns OFF••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 3
8.1.3 When the RUN LED and ERR.LED turn ON•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 3
8.1.4 When the RUN LED and FUSE LED turn ON •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 3
8.2 When the QD64D2 does not Start Counting•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 4
8.3 When the QD64D2 does not Normally Count •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 4
8.4 When the Counter Value Coincidence No.1 (X02) or Counter Value Coincidence No.2 (X05) does not
Turn ON/OFF •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 5
8.4.1 When selecting the coincidence output function ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 5
8.4.2 When selecting the continuous comparison function•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 5
8.5 When the Counter Value Coincidence No.1 (X02) or Counter Value Coincidence No.2 (X05) are Turned
ON, but the Coincidence Output No.1 Terminal (EQU1) and Coincidence Output No.2 Terminal (EQU2)
do not Turn ON ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 6
8.6 When the Coincidence Detection Interrupt does not Occur •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 6
8.7 When the Coincidence Output Test Function Cannot be Executed •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 7
8.8 When the Preset Cannot be Executed••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 8
8.8.1 When the preset cannot be executed by the preset command (Y04)••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 8
8.8.2 When the preset cannot be executed by the preset input terminal (PRST)••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 8
8.9 When the Latch Counter Function Cannot be Executed ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 9
8.9.1 When the latch counter function cannot be executed by the latch counter execution command
(Y07) •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 9
8.9.2 When the latch counter function cannot be executed by the latch counter input terminal (LATCH)
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 9
8.10 When the Error Code (Un\G18)/Warning Code (Un\G19) Cannot be Reset ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 9
8.11 Action and Handling of Errors •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 10
8.11.1 Error code list •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 10
8.11.2 Warning code list •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 13
APPENDICES App - 1 to App - 2
Appendix 1 External Dimensions •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• App - 1
Appendix 2 Difference with the QD62D ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• App - 1
INDEX Index - 1 to Index - 2
A - 8
Page 11

Compliance with the EMC and Low Voltage Directives
(1) For programmable controller system
To configure a system meeting the requirements of the EMC and Low Voltage
Directives when incorporating the Mitsubishi programmable controller (EMC and Low
Voltage Directives compliant) into other machinery or equipment, refer to Chapter 9
"EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES" of the QCPU User's Manual (Hardware
Design, Maintenance and Inspection).
The CE mark, indicating compliance with the EMC and Low Voltage Directives, is
printed on the rating plate of the programmable controller.
(2) For the product
For the compliance of this product with the EMC and Low Voltage Directives, refer to
Section 4.4.1 Wiring precautions.
A - 9
Page 12
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
This manual describes the type QD64D2 4Mpps capable high-speed counter module
using the following generic terms and abbreviations, unless otherwise specified.
Generic term and
abbreviation
QD64D2 Abbreviation for the type QD64D2 4Mpps capable high-speed counter module
CH
Coincidence signal No. m Generic term for the coincidence signal No. 1 and the coincidence signal No. 2
Coincidence output No. m Generic term for the coincidence output No. 1 and the coincidence output No. 2
Continuous comparison
No.m
Continuous comparison
No.1 point n
Continuous comparison
No.2 point n
Continuous comparison
No.m point n setting
Comparison point
External coincidence output
power supply terminal
Personal computer Generic term for IBM-PC/AT-compatible personal computer
GX Developer
GX Works2
GX Configurator-CT Abbreviation for GX Configurator-CT (SW0D5C-QCTU-E) of counter module setting/monitor tool
QCPU (Q mode)
Redundant CPU Generic term for the Q12PRHCPU and Q25PRHCPU
Windows Vista
Windows XP
Generic term for CH1 and CH2
Generic term for the continuous comparison No. 1 and the continuous comparison No. 2
Generic term for the continuous comparison No. 1 point 1 to the continuous comparison No. 1 point 16
Generic term for the continuous comparison No. 2 point 1 to the continuous comparison No. 2 point 16
Generic term for the continuous comparison No. 1 point n setting and the continuous comparison No. 2 point
n setting
Generic term for the coincidence output No. m point setting and the continuous comparison No. m point n
setting
Generic term for external coincidence output power supply 12/24V terminal and external coincidence output
power supply GND (0V) terminal
Product name for MELSEC software packerge
Generic term for the Q00JCPU, Q00CPU, Q01CPU, Q02CPU, Q02HCPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU,
Q25HCPU, Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU, Q25PHCPU, Q12PRHCPU, Q25PRHCPU, Q00UJCPU,
Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, Q02UCPU, Q03UDCPU, Q04UDHCPU, Q06UDHCPU, Q10UDHCPU,
Q13UDHCPU, Q20UDHCPU, Q26UDHCPU, Q03UDECPU, Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDEHCPU,
Q10UDEHCPU, Q13UDEHCPU, Q20UDEHCPU, Q26UDEHCPU, Q50UDEHCPU and Q100UDEHCPU
Generic term for the following:
Microsoft Windows Vista Home Basic Operating System,
Microsoft Windows Vista Home Premium Operating System,
Microsoft Windows Vista Business Operating System,
Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate Operating System,
Microsoft Windows Vista Enterprise Operating System
Generic term for the following:
Microsoft Windows XP Professional Operating System,
Microsoft Windows XP Home Edition Operating System
Description
PACKI N G LIST
The following are included in the package.
Model Product name Quantity
QD64D2 Type QD64D2 4Mpps capable high-speed counter module 1
SW0D5C-QCTU-E GX Configurator-CT Version 1 (single license product) (CD-ROM) 1
SW0D5C-QCTU-EA GX Configurator-CT Version 1 (volume license product) (CD-ROM) 1
A - 10
Page 13
1
OVERVIEW
CHAPTER1 OVERVIEW
This User's Manual describes the specifications, handling, and programming methods for
the type QD64D2 4Mpps capable high-speed counter module used together with the
MELSEC-Q series CPU module.
The QD64D2 has the following input methods.
1
OVERVIEW
2
•1 multiple of 1 phase pulse
input
•1 multiple of 2 phases pulse
input
•2 multiples of 1 phase pulse
input
•2 multiples of 2 phases pulse
input
For details of the input methods, refer to Section 5.1.
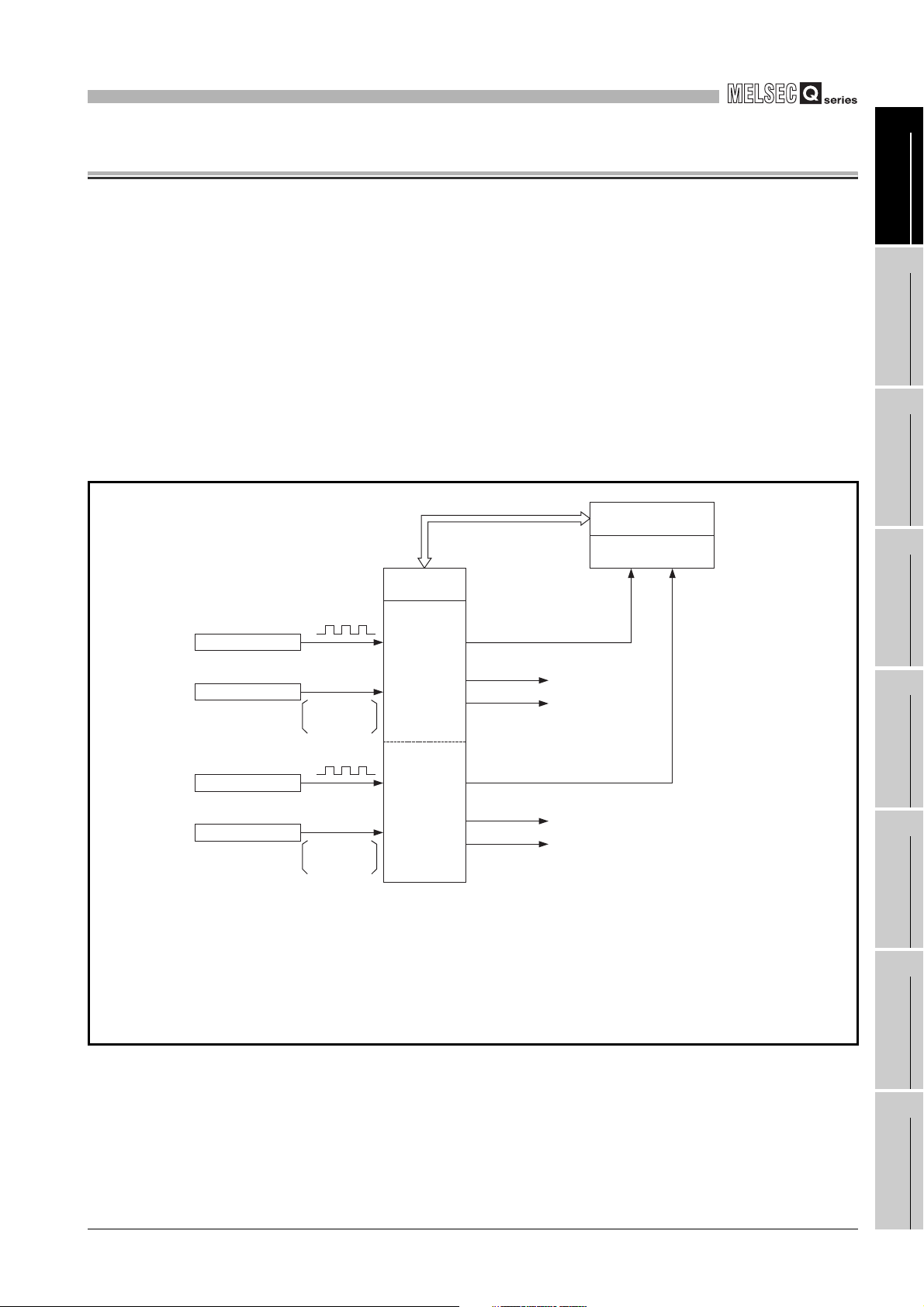
Figure 1.1 shows the general operation of the QD64D2.
Reading/writing
3)
I/O signal and
buffer memory
QD64D2
Pulse
Encoder
External
control signal
Controller
Preset
Latch counter
Pulse
Encoder
External
control signal
Controller
Preset
Latch counter
1)
2)
1)
2)
CH1
CH2
4)
5)
4)
5)
Coincidence signal
output (2 points)
Coincidence signal
output (2 points)
•CW/CCW
•4 multiples of 2 phases pulse
input
Programmable
controller CPU
QCPU (Q mode)
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
1) Pulses to be input to the QD64D2 are counted.
2) Preset value and count value can be latched with external control signal.
3) Status of the I/O signal and buffer memory of the QD64D2 can be checked with the sequence
program.
Also, start/stop of a count, preset, and coincidence output can be performed.
4) When a counter value matches with the set value, an interrupt request can be issued to the
programmable controller CPU.
5) The present value is compared with comparison point setting value and the coincidence signal can
be output.
Figure 1.1 General operation of the QD64D2
1 - 1
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 14

1
OVERVIEW
1.1 Features
This section describes the features of the QD64D2.
(1) Counting at the maximum counting speed of 4Mpps is possible. (In 4
multiples of 2 phases)
Since the QD64D2 can be used for high-resolution encoder (e.g. linear scale), the
equipment can improve position detection accuracy and a workpiece can be moved at
high-speed.
(2) Wide range of expression on counting (from -2147483648 to 2147483647)
Count values can be stored in 32-bit signed binary.
(3) Pulse input selection
Pulse input can be selected from 1 multiple of 1 phase, 2 multiples of 1 phase, 1
multiple of 2 phases, 2 multiples of 2 phases, 4 multiples of 2 phases, and CW/CCW.
(4) Counter format selection
Either of the following counter formats can be selected.
(a) Linear counter format
From -2147483648 to 2147483647 can be counted and an overflow can be
detected when the count range is overrun.
(b) Ring counter format
Counts are repeatedly executed between the ring counter upper limit value and
ring counter lower limit value.
(5) Coincidence detection
The QD64D2 can compare the present value and comparison point, notify the
comparison result with input signal, and start an interrupt program when they match.
It also mounts 2-point external coincidence output for each channel, which permits
controlling external devices at high-speed.
According to application, select the coincidence output function or continuous
comparison function.
(a) Coincidence output function
Set 1 as the coincidence detection point for each point to compare it with the
present value.
Reset the coincidence output signal or change the coincidence detection point
with the sequence program.
Controlling equipment according to the operating status, such as change of the
coincidence detection point according to condition, is possible.
1 - 2
1.1 Features
Page 15
1
OVERVIEW
(b) Continuous comparison function
(6) Mounting the coincidence output test function (when using the
continuous comparison function)
By using the coincidence output test function, wiring of the coincidence output
terminals (EQU1, EQU2) and operations can be checked without count operation.
(7) Preset function
The present value when the preset command (Y04) is input or the preset input
terminal (PRST) is turned ON can be overwritten to preset value.
Set from 1 to 16 as the coincidence detection point for each point to compare it
with the present value (Only 1 point can be compared simultaneously).
Whenever a coincidence is detected, the coincidence output signal is reset or the
coincidence detection point is changed automatically.
If this function is used when the coincidence detection point is predetermined, the
sequence program can be reduced, which brings improvement in takt time.
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
(8) Latch counter function
The present value when the latch counter execution command (Y07) is input or the
latch counter input terminal (LATCH) is turned ON can be latched.
(9) Executing the preset function/latch counter function with external
control signal
Since the QD64D2 is independent of scan time of the programmable controller CPU,
disparity in a span before executing the preset function/latch counter function can be
lessen.
(10)Fuse blown at external output part is detectable.
The QD64D2 can detect fuse blown at external output part and notify it with the blown
fuse detection flag (X1F) and LED display on it.
(11)Easy setting using GX Configurator-CT
The QD64D2 setting can be performed on screen by using GX Configurator-CT sold
separately. Thus, the number of sequence programs results in decreasing and
checking a setting status or operation status of modules easily.
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
1.1 Features
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
1 - 3
Page 16
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
CHAPTER2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
This chapter describes system configurations for the QD64D2.
2.1 Applicable Systems
This section describes the applicable systems.
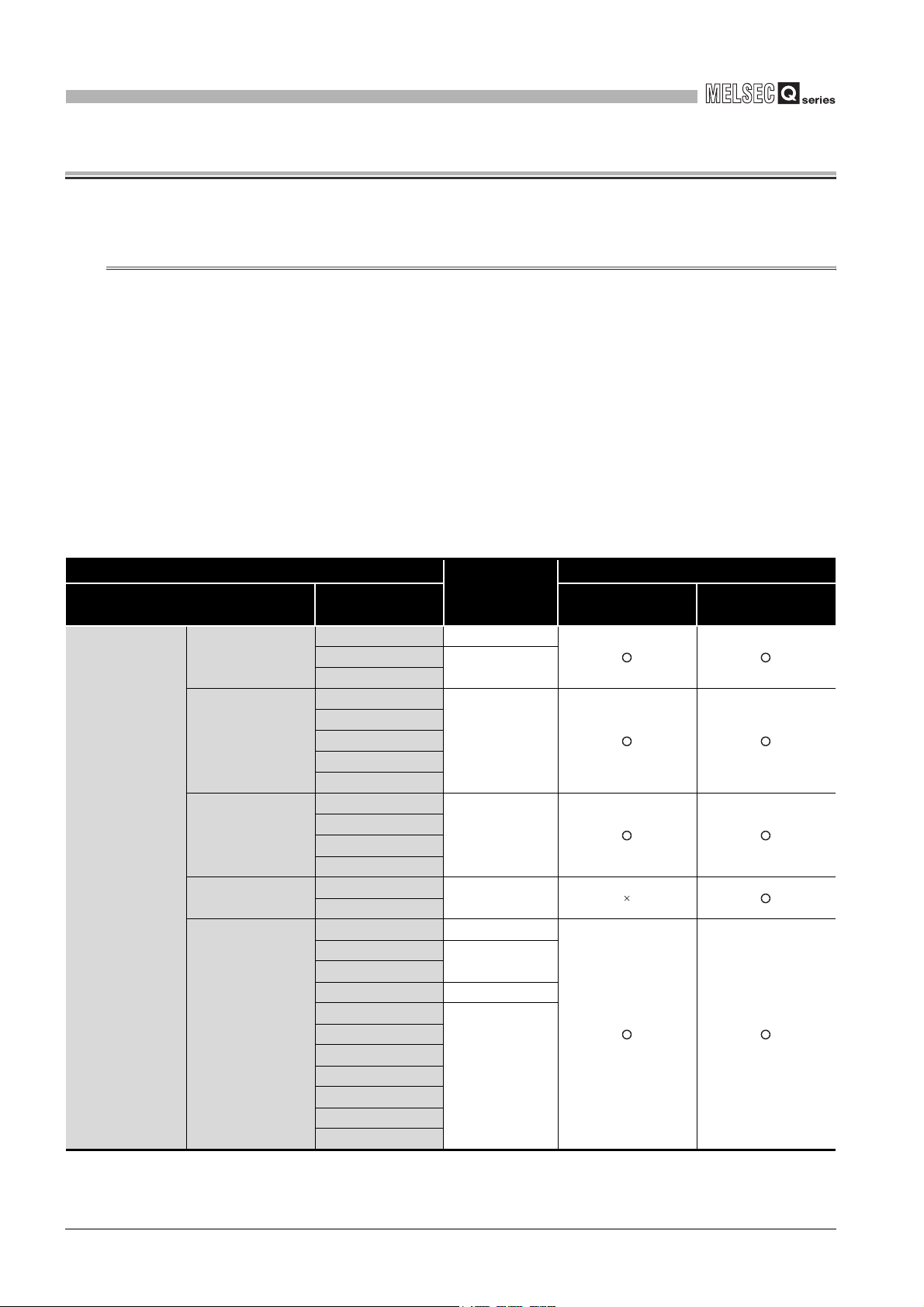
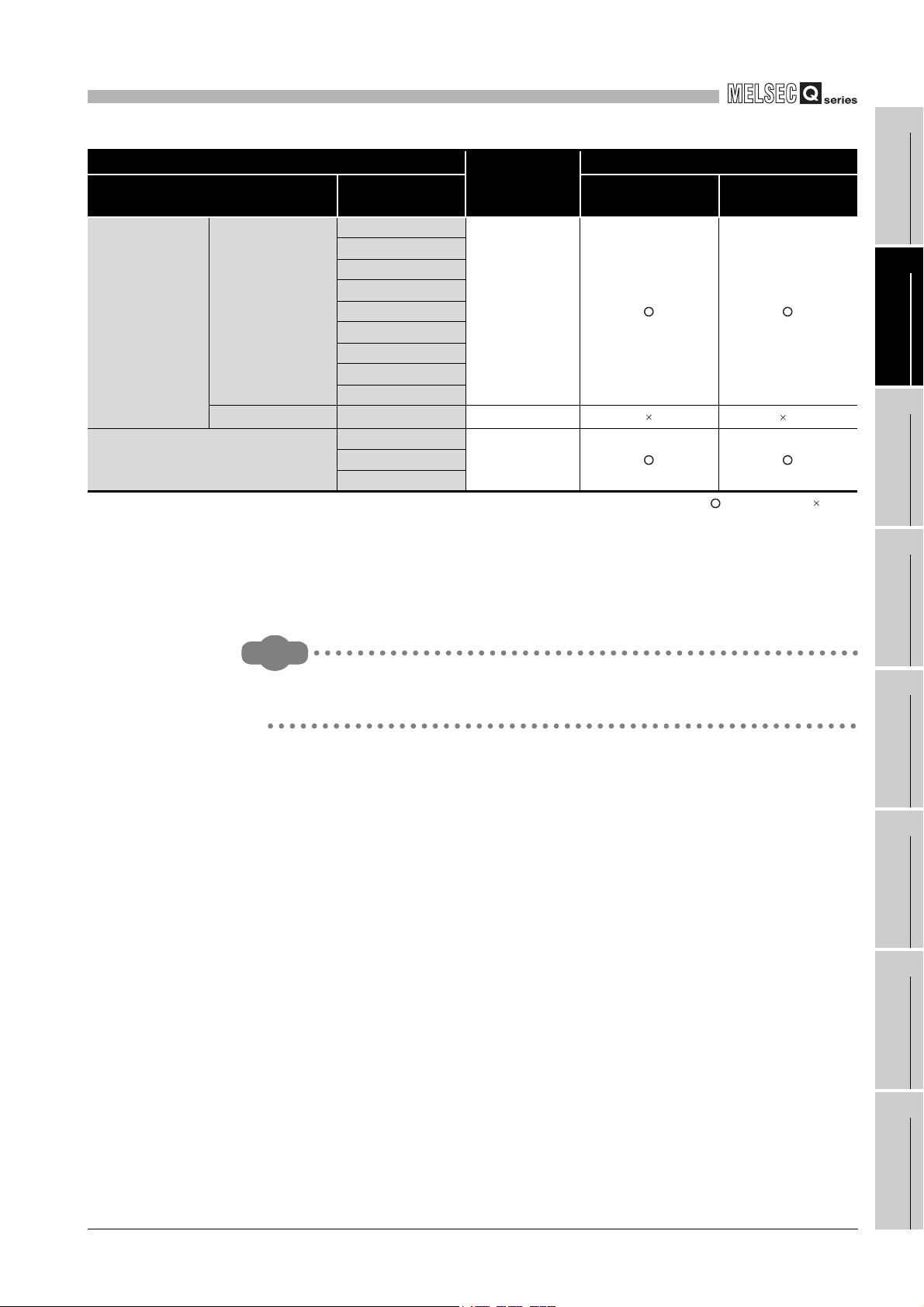
(1) Applicable modules and base units, and No. of modules
(a) When mounted with a CPU module
The table below shows the CPU modules and base units applicable to the
QD64D2 and quantities for each CPU model.
Depending on the combination with other modules or the number of mounted
modules, power supply capacity may be insufficient.
Pay attention to the power supply capacity before mounting modules, and if the
power supply capacity is insufficient, change the combination of the modules.
Programmable
controller CPU
Table 2.1 Applicable modules and the number of mountable modules
Applicable CPU module
CPU type CPU model Main base unit
Basic model
*3
QCPU
High Performance
model QCPU
Process CPU
Redundant CPU
Universal model
QCPU
Q00JCPU Up to 8
Q00CPU
Q01CPU
Q02CPU
Q02HCPU
Q06HCPU
Q12HCPU
Q25HCPU
Q02PHCPU
Q06PHCPU
Q12PHCPU
Q25PHCPU
Q12PRHCPU
*4
Q25PRHCPU
Q00UJCPU Up to 8
Q00UCPU
Q01UCPU
Q02UCPU Up to 36
Q03UDCPU
Q04UDHCPU
Q06UDHCPU
Q10UDHCPU
Q13UDHCPU
Q20UDHCPU
Q26UDHCPU
No. of
modules
Up to 24
Up to 64
Up to 64
Up to 53
Up to 24
Up to 64
*1
Base unit
*2
Extension base
unit
2 - 1
2.1 Applicable Systems
Page 17
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Applicable CPU module
CPU type CPU model Main base unit
Programmable
controller CPU
C Controller module
Table 2.1 Applicable modules and the number of mountable modules (Continued)
No. of
*1
Q03UDECPU
Q04UDEHCPU
Q06UDEHCPU
Universal model
QCPU
Safety CPU QS001CPU N/A
* 1 Limited within the range of I/O points for the CPU module.
* 2 Can be installed to any I/O slot of a base unit.
* 3 For the coincidence detection interrupt function, use the Basic model QCPU of function version B
* 4 The coincidence detection interrupt function is not supported.
* 5 Connection of extension base units is not available with any safety CPU.
Q10UDEHCPU
Q13UDEHCPU
Q20UDEHCPU
Q26UDEHCPU
Q50UDEHCPU
Q100UDEHCPU
Q06CCPU-V
Q06CCPU-V-B
Q12DCCPU-V
or later.
Up to 64
Up to 64
modules
Base unit
*2
Extension base
: Applicable : N/A
unit
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
*5
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
Remark
For the use of the C Controller module, refer to C Controller Module User's
Manual.
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
8
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
2.1 Applicable Systems
TROUBLESHOOTING
2 - 2
Page 18
T
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
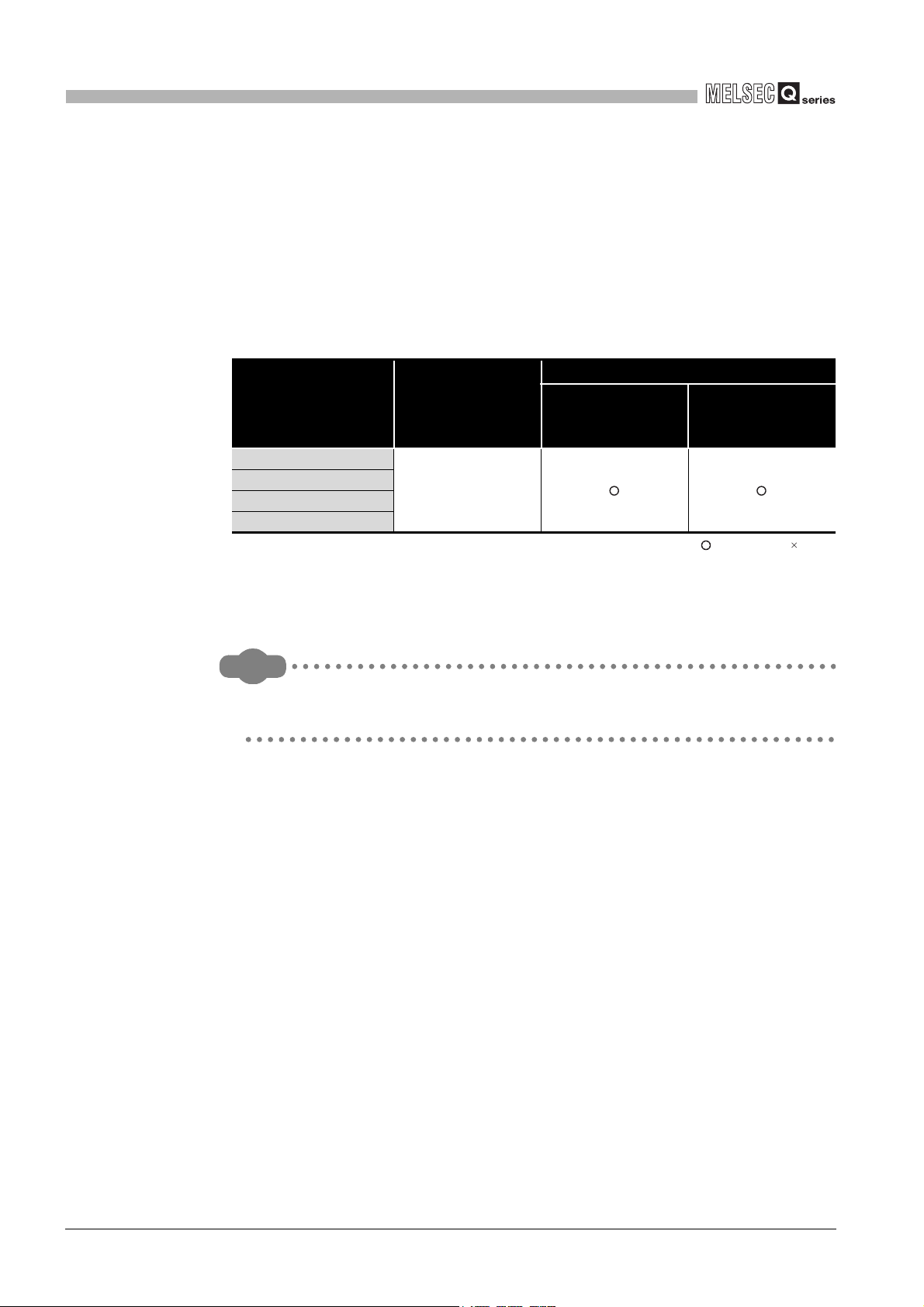
(b) Mounting to a MELSECNET/H remote I/O station
The following table shows network modules that can be mounted to the QD64D2,
the number of mountable network modules, and applicable base units.
The QD64D2 module can be mounted into any I/O slots
unit.
However, the power capacity may be insufficient depending on the combination
with the other mounted modules and the number of mounted modules.
Be sure to check the power capacity when mounting the modules.
Table 2.2 Mountable network modules, No. of mountable modules, and mountable base unit
Mountable network
module
QJ72LP25-25
QJ72LP25G
QJ72LP25GE
QJ72BR15
* 1 Limited within the range of I/O points for the network module.
* 2 Can be installed to any I/O slot of a base unit.
* 3 The coincidence detection interrupt function is not supported.
*3
Up to 64
Number of
mountable
modules
*1
*1
Applicable base unit
Main base unit on
the remote I/O
station
on the applicable base
*2
Extension base unit
on the remote I/O
station
: Applicable : N/A
Remark
The Basic model QCPU or C Controller module cannot create the MELSECNET/
H remote I/O network.
2 - 3
2.1 Applicable Systems
Page 19
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
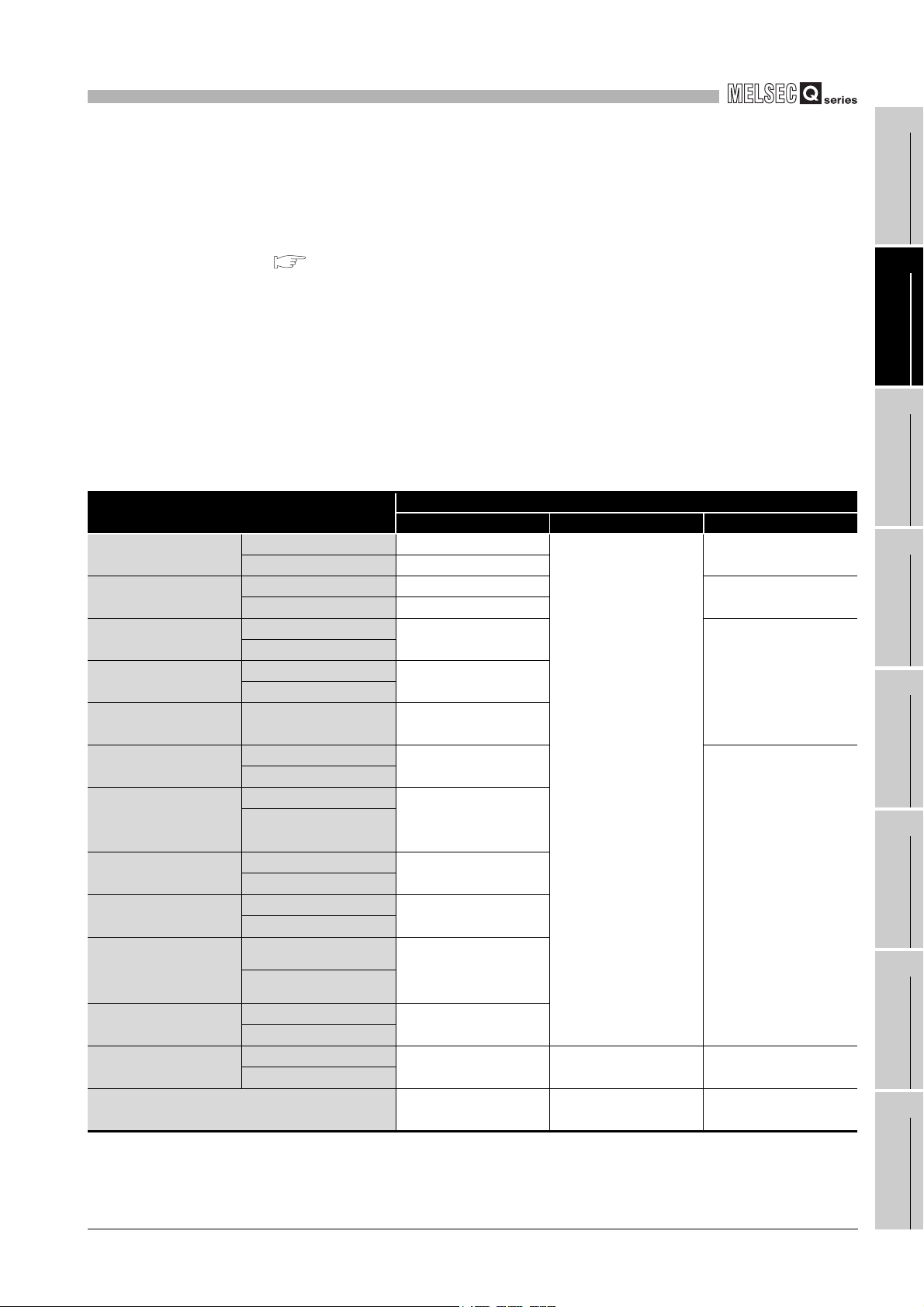
(2) Support of the multiple CPU system
The QD64D2 of first released version to function version B supports multiple CPU
system.
When using the QD64D2 in a multiple CPU system, refer to the following manual first.
QCPU User's Manual (Multiple CPU System)
(a) Intelligent function module parameters
Write intelligent function module parameters to only the control CPU of the
QD64D2.
(3) Supported software packages
Relation between the system using the QD64D2 and software package is shown in
the following table.
GX Developer is necessary when using the QD64D2.
Table 2.3 Software package version
Item
Q00J/Q00/Q01CPU
Q02/Q02H/Q06H/
Q12H/Q25HCPU
Q02H/Q06HCPU
Q12PH/Q25PHCPU
Q12PRH/
Q25PRHCPU
Q00UJ/Q00U/
Q01UCPU
Q02U/Q03UD/
Q04UDH/
Q06UDHCPU
Q10UDH/
Q20UDHCPU
Q13UDH/
Q26UDHCPU
Q03UDE/Q04UDEH/
Q06UDEH/Q13UDEH/
Q26UDEHCPU
Q10UDEH/
Q20UDEHCPU
Q50UDEH/
Q100UDEHCPU
When mounted to the MELSECNET/H remote I/
O station
Single CPU system Version 7 or later
Multiple CPU system Version 8 or later
Single CPU system Version 4 or later
Multiple CPU system Version 6 or later
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Redundant system Version 8.45X or later
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Software version
GX Developer GX Configurator-CT GX Works2
Version 1.10N or later
Version 1.08J or later
Version 8.68W or later
Version 7.10L or later
Version 8.76E or later
Version 1.28AE or later
Version 8.48A or later
Version 8.76E or later
Version 8.62Q or later
Version 8.68W or later
Version 8.76E or later
Use prohibited Use prohibited Version 1.31H or later
Version 6 or later Version 1.28AE or later Use prohibited
Use prohibited
Version 1.08J or later
1
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
8
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
(4) Connector
The connector is not included with the QD64D2.
Purchase it with reference to Section 4.3.
2.1 Applicable Systems
TROUBLESHOOTING
2 - 4
Page 20

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.2 About Use of the QD64D2 with Redundant CPU
This section explains how to use the QD64D2 with the Redundant CPU.
(1) GX Configurator-CT
GX Configurator-CT cannot be used when accessing the Redundant CPU via an
intelligent function module on an extension base unit from GX Developer.
Connect a personal computer with a communication path indicated below.
1 2
Main base unit
Extension base unit
(GX Configurator-CT cannot be used.)
Connecting directly to a programmable controller CPU
1
Connecting to a programmable controller CPU via an intelligent function module
2
(Ethernet module, MELSECNET/H module, or CC-Link module) on the main base unit
Figure 2.1 Communication path which GX Configrator-CT can use
(2) Restrictions when using the Redundant CPUs
The coincidence detection interrupt function is not available.
2 - 5
2.2 About Use of the QD64D2 with Redundant CPU
Page 21

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.3 About Use of the QD64D2 on the MELSECNET/H Remote I/O
Station
1
This section explains how to use the QD64D2 on the MELSECNET/H remote I/O station.
(1) Number of QD64D2 that can be installed when the remote I/O station is
used
Refer to Section 2.1 concerning the number of the QD64D2 that can be installed
when the remote I/O station is used.
(2) Limitations when using the remote I/O station
(a) The coincidence detection interrupt function cannot be used.
(b) When the QD64D2 is used on the MELSECNET/H remote I/O station, a delay will
occur due to the link scan time. Therefore, fully verify that there will be no problem
with controllability in the target system.
(Example) When processing is executed using the counter value input by a
sequence program, variations will occur due to a delay in the link scan time.
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
2.3 About Use of the QD64D2 on the MELSECNET/H Remote I/O Station
2 - 6
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 22
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
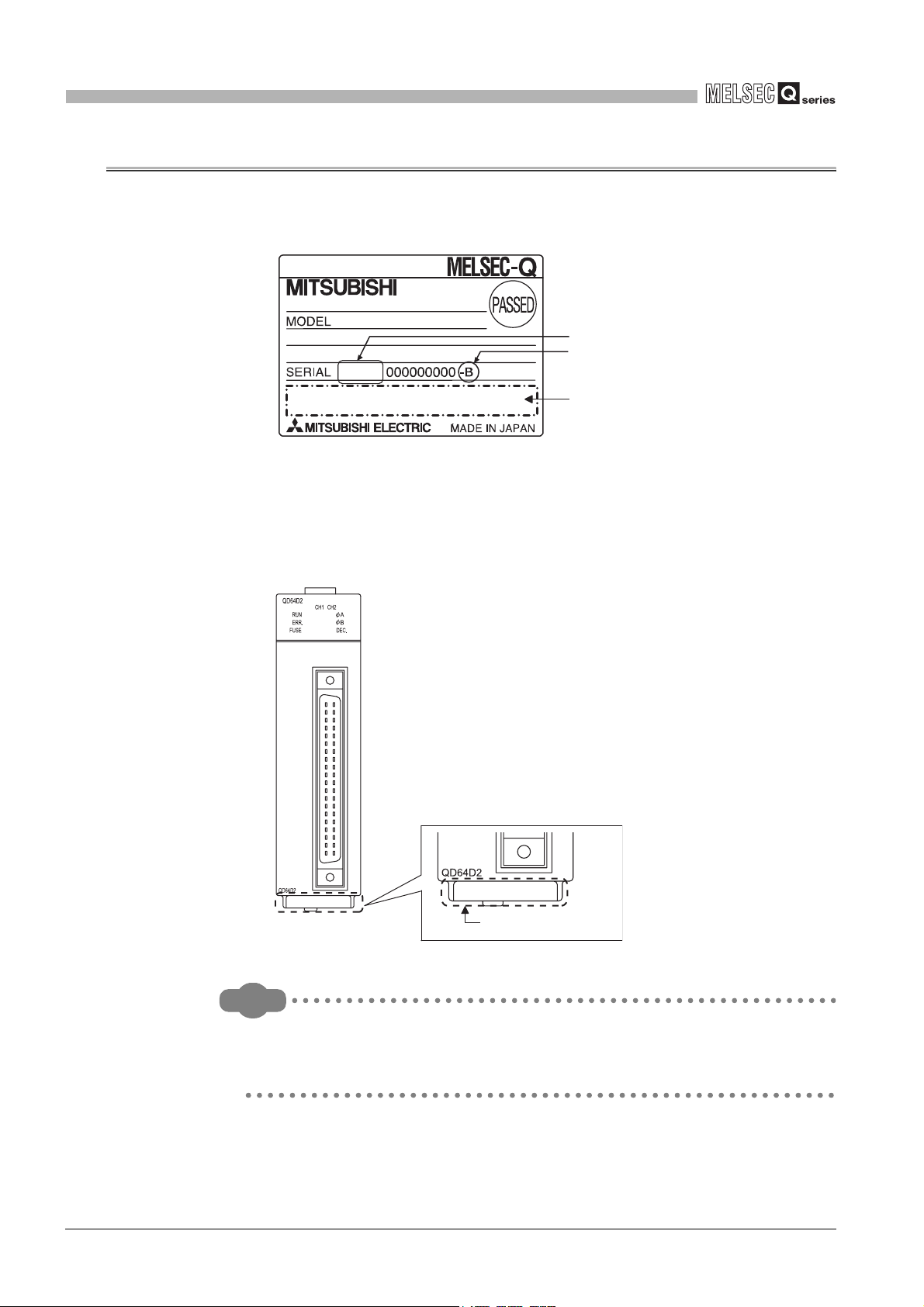
2.4 How to Check the Function Version/Serial No./Software Version
(1) Checking the rating plate on the module side
The rating plate is situated on the side face of the QD64D2.
Serial No. (Upper 6 digits)
function version
100812
Relevant regulation
Figure 2.2 Checking the serial No. and function version (rating plate)
(2) Checking on the front of the module
The serial No. on the rating plate is also indicated on the front of the module (lower
part).
standards
2 - 7
100812000000000-B
Serial number
Figure 2.3 Display on the front of the module
Remark
The serial number is displayed on the front of the module from August 2008
production. Products manufactured during switching period may not have the
serial number on the front of the module.
2.4 How to Check the Function Version/Serial No./Software Version
Page 23
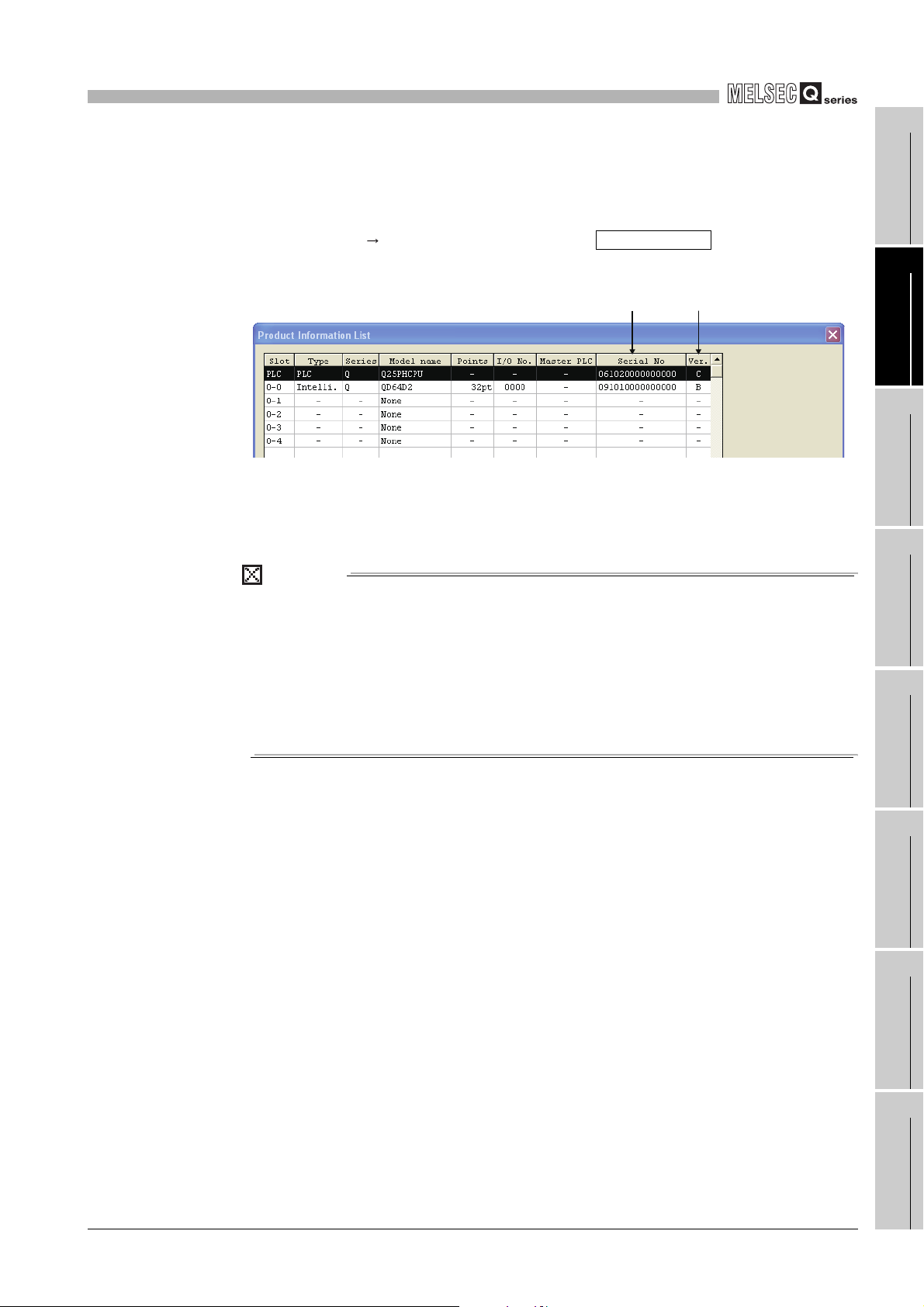
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(3) Confirming the serial number on the system monitor (Product
Information List)
To display the screen for checking the serial number and function version, select
[Diagnostics] [System monitor] and click the Product Inf. List button in GX
Developer.
1
OVERVIEW
2
Serial
number
Figure 2.4 System monitor
(a) Production number display
Since the QD64D2 does not support the production number display, "-" is
displayed.
Function
version
POINT
The serial No. displayed in the Product Information List of GX Developer may be
different from the one on the rating plate and the front of the module.
• The serial No. on the rating plate and the front of the module indicates the
management information of the product.
• The serial No. in the Product Information List of GX Developer indicates
the functional information on the product, which is updated when a new
function is added.
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
2.4 How to Check the Function Version/Serial No./Software Version
2 - 8
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 24
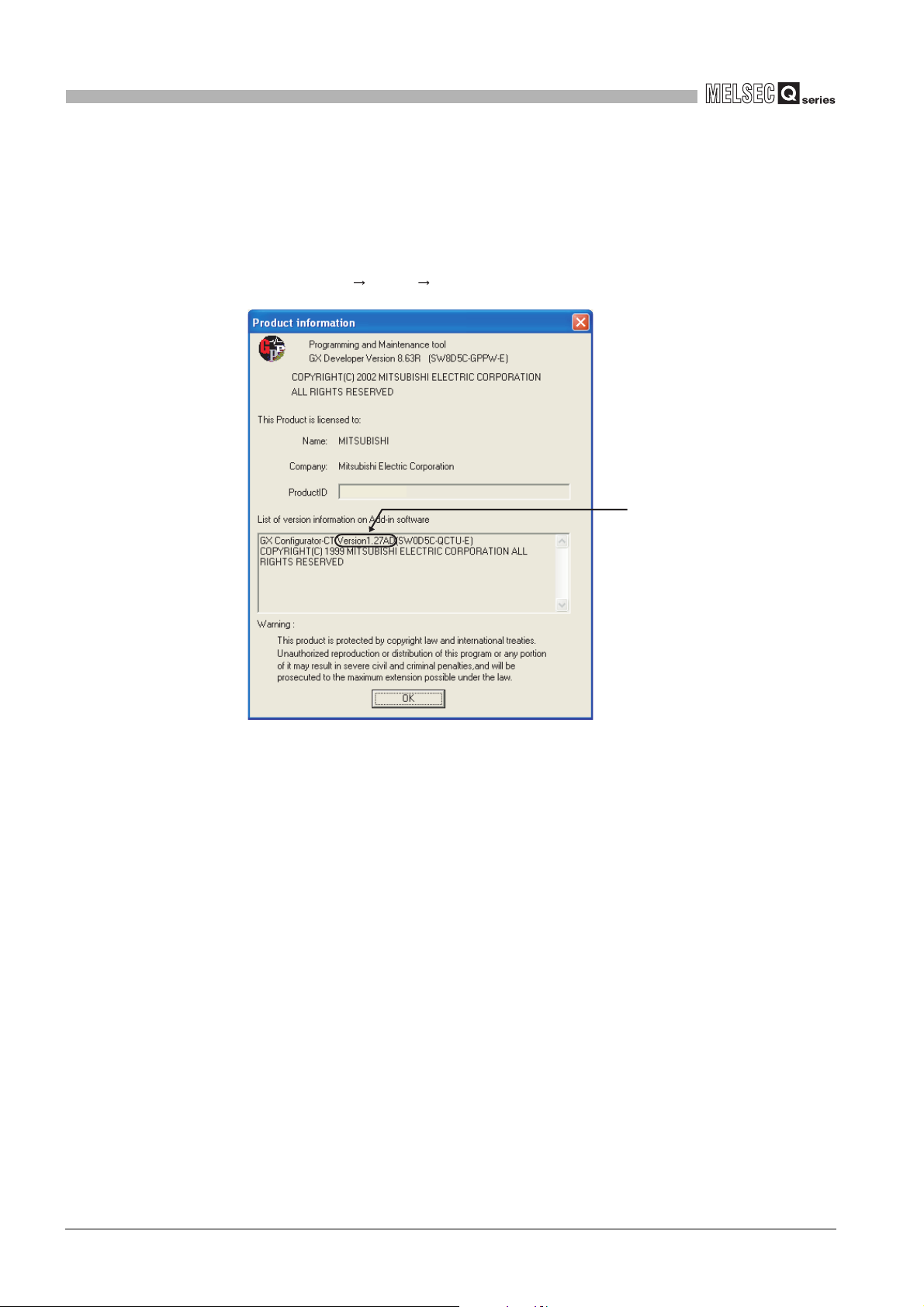
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(4) Checking the software version of GX Configurator-CT
The software version of GX Configurator-CT can be checked GX Developer's
"Product information" screen.
[Operating procedure]
GX Developer [Help] [Product information]
Software version
(In the case of GX Developer Version 8)
Figure 2.5 [Product information] screen of GX Developer
2 - 9
2.4 How to Check the Function Version/Serial No./Software Version
Page 25
3
SPECIFICATIONS
CHAPTER3 SPECIFICATIONS
This chapter describes the performance specifications of the QD64D2, I/O signals to the
programmable controller CPU, specifications of the buffer memory.
For general specifications of the QD64D2, refer to the User's Manual for the CPU module.
3.1 Performance Specifications
The following table shows the performance specifications of the QD64D2.
Table 3.1 Performance specifications of the QD64D2
Item Specifications
Number of channels 2 channels
Count
input
signal
Phase 1-phase input, 2-phase input
Signal level ( A, B)
Counting speed (max.)
*1 *2
Counting range 32-bit signed binary (-2147483648 to 2147483647)
Typ e
(AM26LS31 (manufactured by Texas Instruments Incorporated) or equivalent)
EIA Standard RS-422-A Differential line driver level
4 multiples of 2 phases : 4Mpps
2 multiples of 1 phase, 2 multiples of 2 phases: 2Mpps
1 multiple of 1 phase, 1 multiple of 2 phases, CW/CCW: 1Mpps
Addition method, subtraction method
linear counter format, ring counter format
preset counter function, latch counter function
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
1
Counter
Minimum count pulse
width
(Duty ratio 50 %)
(Minimum phase difference for 2-phase input: 0.25 s)
Comparison range 32-bit signed binary
Coincide
nce
detection
External
input
External
output
Number of occupied I/O points 32 points (I/O assignment: Intelligent 32 points)
5VDC internal current consumption 0.53 A
Weight 0.16 kg
Comparison result
Interrupt With coincidence detection interrupt function
Preset
Count value latch
Coincidence output
Derating Applied (refer to Section 3.1.2 )
* 1 Note that counting a pulse whose phase difference between phase A and phase B is small may
result in a count error.
For the relation of phase difference between phase A and phase B, refer to Section 3.3.1.
* 2 The maximum counting speed is determined in the pulse input mode.
Counting speed cannot be changed.
0.5 0.5
0.25
For details, refer to Section 3.1.1
Setting value < Count value
Setting value = Count value
Setting value > Count value
24VDC 2 to 5mA
Transistor (sinking type) output: 2 points/channel
12/24VDC 0.5 A/point 2 A/common
3.1 Performance Specifications
(Unit: s)
3 - 1
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
8
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 26
3
SPECIFICATIONS
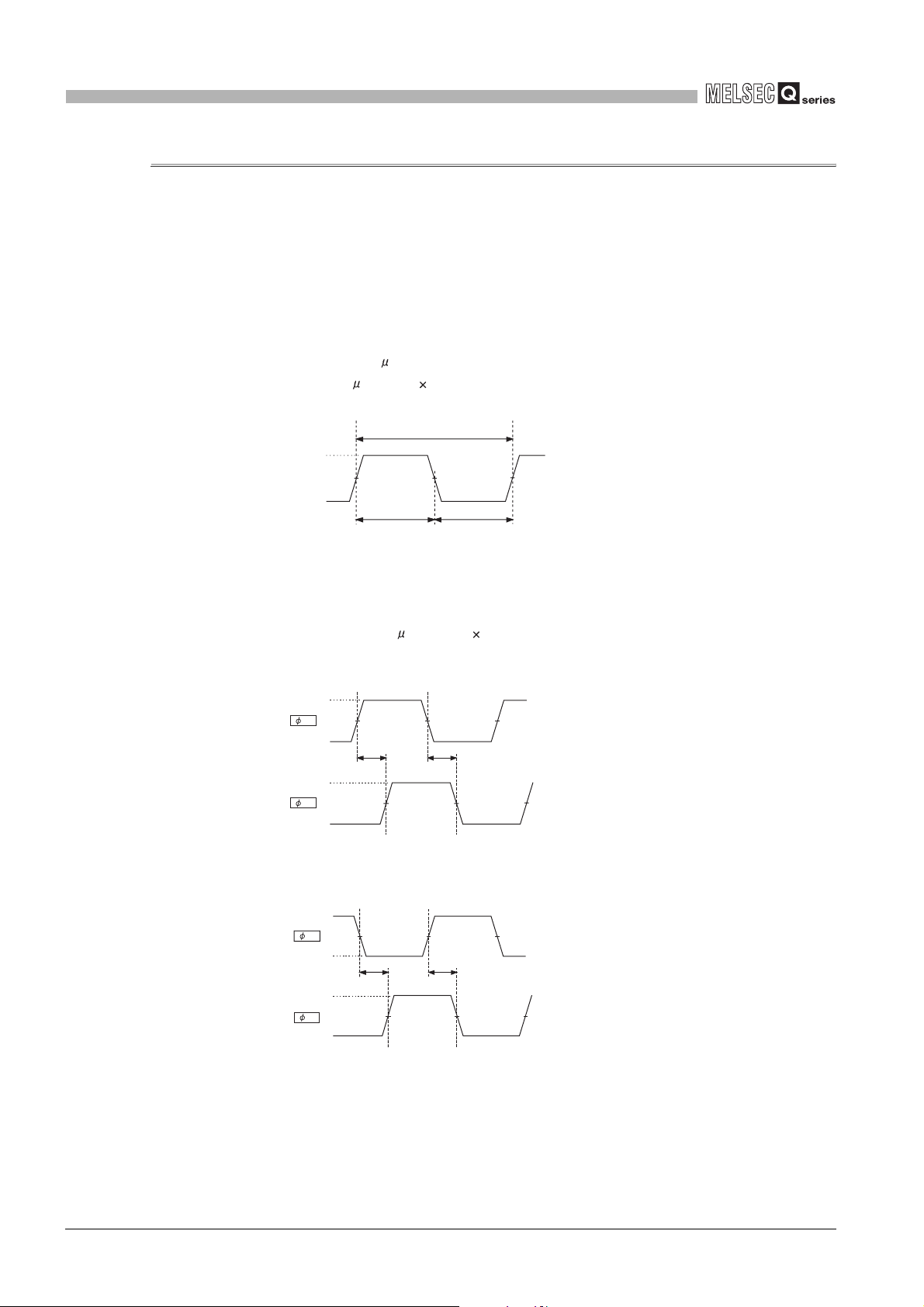
3.1.1 Relation of phase difference between phase A and phase B
The relation indicated below is for each pulse input mode at the maximum counting speed.
Pulse input waveform that does not reach to the maximum counting speed is also
applicable.
(a) At 1-phase input
Pulse input waveform at 1-phase input input needs to satisfy the following
conditions (duty ratio of 50%).
t (=t
H+tL) = 1.0 s
t
H, tL = 0.5 s (= 0.5 t)
Differential
voltage
H level
0.1V
L level
Figure 3.1 Pulse input waveform at 1-phase input
t
-0.1V
t
H
t
0.1V
L
(b) At 2-phase input
Pulse input waveform at 2-phase input needs to satisfy both the condition at 1phase input and the condition below.
t
1, t2, t3, t4 = 0.25 s (= 0.25 t)
Differential
voltage
H level
-0.1V
0.1V
0.1V
A
L level
Differential
voltage
H level
B
L level
Figure 3.2 Pulse input waveform at 2-phase input 1
0.1V -0.1V
t1
0.1V
t2
3 - 2
Differential
voltage
H level
A
L level
Differential
voltage
H level
B
L level
Figure 3.3 Pulse input waveform at 2-phase input 2
-0.1V
t3
0.1V -0.1V
0.1V
t4
-0.1V 0.1V
3.1 Performance Specifications
3.1.1 Relation of phase difference between phase A and phase B
Page 27
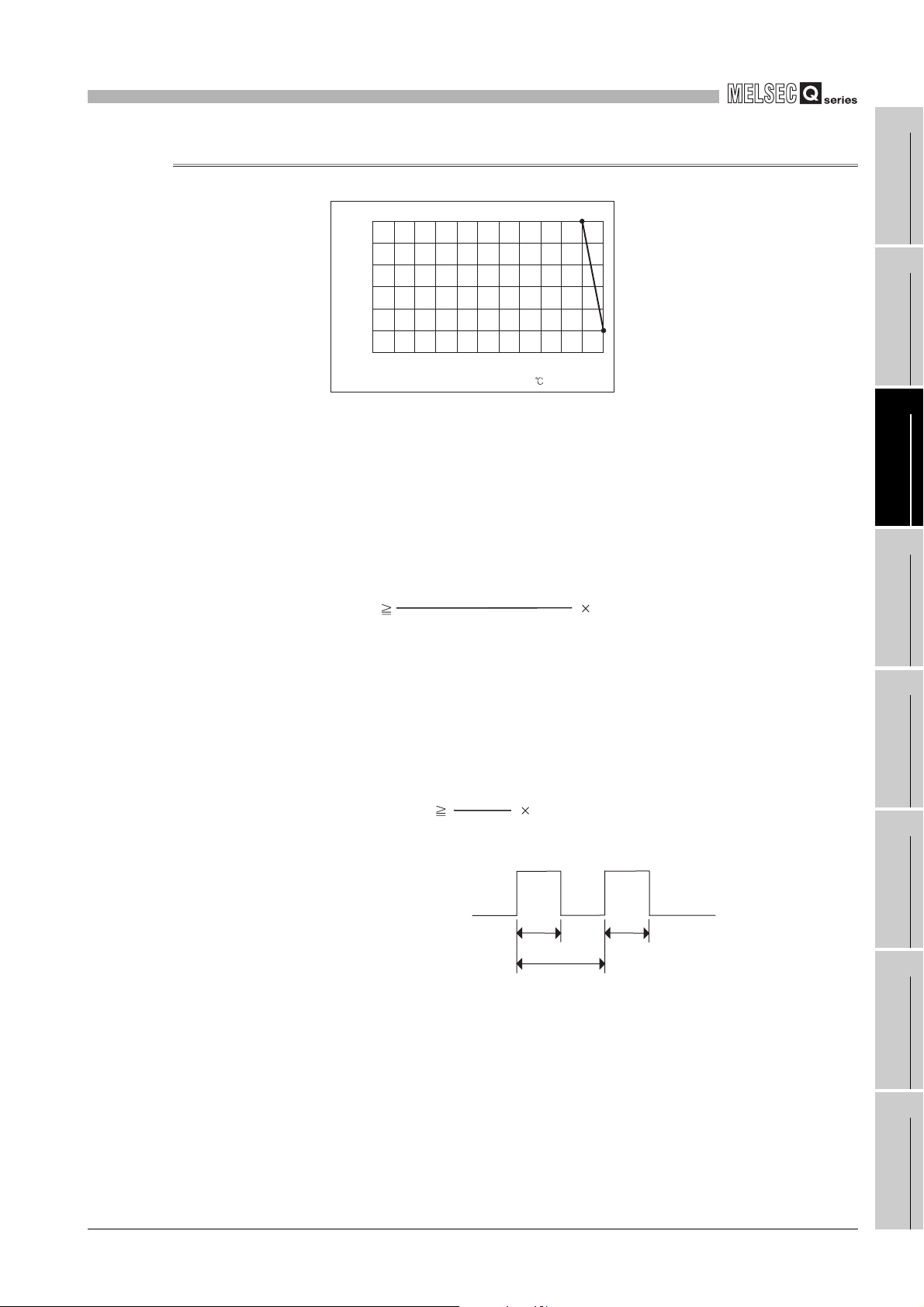
3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.1.2 Derating chart
100
90
80
70
ON ratio (%)
60
50
40
This section explains conditions for each counter value comparison function selection.
(1) When all channels are the coincidence output function
Take care so that the ratio of the number of points that external coincidence output
(ON) is executed to the number of external coincidence output points of the module (4
points) does not exceed the ON ratio in Figure 3.4.
ON ratio [%]
0 1020304050
Ambient temperature( )
Figure 3.4 Derating chart
The number of points that
external coincidence output
(ON) is executed
4 (point)
55
100 [%]
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
(2) When all channels are the continuous comparison function
Take care so that the ratio of continuous comparison No. m ON time setting (Un\G52,
Un\G102) (t1) to the time from start of coincidence output to the next coincidence
output (t2) in Figure 3.5 may not exceed the ON ratio in Figure 3.4.
(For interval of the continuous comparison No. m point n setting that decides t2, refer
to Section 5.3.2.)
ON
OFF
t1[ms]
t2[ms]
100 [%]
t1
t2
t1
ON ratio [%]
Coincidence output No. m terminal
Figure 3.5 Relationship between ON time setting in the case of the continuous comparison function (t1) and the time from start of
coincidence output to the next coincidence output (t2)
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
8
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
3.1 Performance Specifications
3.1.2 Derating chart
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 3
Page 28

3
ON ratio [%]
SPECIFICATIONS
(3) When (CH1 or CH2) is the coincidence output function and (CH2 or CH1)
is the continuous comparison function
Take care so that the addition of the ratio of above (1) "When all channels are the
coincidence output function" in the CH where the coincidence output function is set
and a value when the ratio of above (2) "When all channels are the continuous
comparison function" in the CH where the continuous comparison function is set is
divided by 2 may not exceed the ON ratio in Figure 3.4
Ratio of above (1) "When all channels are the
coincidence output function" [%]
The number of points that external
coincidence output (ON) is executed
(
4 (point)
(
100 [%]
Ratio of above (2) "When all channels are the
continuous comparison function" [%]
+
t1[ms]
(
+
t2[ms]
2
100 [%]
(
2
3 - 4
3.1 Performance Specifications
3.1.2 Derating chart
Page 29
3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.2 Function List
The following table shows the functions of the QD64D2.
I/O numbers (X/Y) and buffer memory addresses in Description describe only for channel
1.
For I/O numbers (X/Y) of channel 2 and buffer memory addresses, refer to Section 3.3.1.
Table 3.2 Function list of the QD64D2
Function
Linear counter function
Ring counter function
Coincidence output
function
Counter
value
comparison
function
Preset function Overwrites present value to an arbitrary value. Section 5.4
Latch counter function Latches the present value. Section 5.5
Continuous comparison
function
Coincidence detection
interrupt function
*1
Coincidence output
test function
* 1 The functions can be used in combination.
However, as for the following functions, select either of them.
Counts within the range from -2147483648 to 2147483647.
An overflow occurs when a count exceeds the count range.
Repeats a count between the ring counter upper limit value
and the lower limit value.
Compares preset coincidence detection point of an arbitrary
channel with the present counter value and outputs the
counter value coincidence.
Compares any of preset coincidence detection points of an
arbitrary channel with the present counter value and
outputs the counter value coincidence during the set time
after the coincidence.
Checks wiring of coincidence output.
This function can be used only when the continuous
comparison function is selected.
Generates an interrupt signal to the programmable
controller CPU when a coincidence is detected, and starts
an interrupt program.
• Linear counter function, ring counter function
• Coincidence output function, continuous comparison function
Description Reference
Section 5.2.1
Section 5.2.2
Section 5.3.1
Section 5.3.2
Section 5.3.3
Section 5.3.4
1
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
3.2 Function List
3 - 5
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 30

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3 I/O Signals to the Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.1 List of I/O signals
The following table shows the I/O signals from the QD64D2 to the programmable
controller CPU.
Note that I/O numbers (X/Y) mentioned in this and the subsequent chapters are assumed
when the QD64D2 is mounted to the null I/O slot on the main base unit.
(1) List of input signals (Signal direction: QD64D2 Programmable
controller CPU)
Table 3.3 List of input signals
I/O
number
X00 Module READY X10 Reserved
X01
Counter value large No.1 X11
Signal name
I/O
number
Counter value large No.1
Signal name
X02 Counter value coincidence No.1 X12 Counter value coincidence No.1
X03 Counter value small No.1 X13 Counter value small No.1
X04 Counter value large No.2 X14 Counter value large No.2
X05 Counter value coincidence No.2 X15 Counter value coincidence No.2
X06 Counter value small No.2 X16 Counter value small No.2
X07 Reserved X17 Reserved
X08 External preset request detection X18 External preset request detection
X09
X0A
X0B Reserved X1B Reserved
X0C Reserved X1C Reserved
X0D Error occurrence X1D Error occurrence
X0E Warning occurrence X1E Warning occurrence
X0F Reserved X1F Blown fuse detection flag
CH1
During continuous comparison No.1
execution
During continuous comparison No.2
execution
*1
*1
* 1 The signals are used only for the continuous comparison function.
X19
X1A
CH2
During continuous comparison No.1
execution
During continuous comparison No.2
execution *1
*1
POINT
The reserved signals above are for system use, not for users. If used (turning ON/
OFF) by a user, the functions of the QD64D2 are not guaranteed.
3 - 6
3.3 I/O Signals to the Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.1 List of I/O signals
Page 31

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(2) List of output signals (Signal direction: Programmable controller CPU
QD64D2)
Table 3.4 List of output signals
I/O
number
Y00 Reserved --- Y10 Reserved ---
Signal name
Operation
timing
I/O
number
Signal name
Operation
timing
1
OVERVIEW
2
Y01
Y02
Y03
Y04 Preset command Y14 Preset command
Y05 Subtraction count command Y15 Subtraction count command
Y06 Count enable command Y16 Count enable command
Y07
Y08
Y09
Y0A
Y0B
Y0C
Y0D Error reset command Y1D Error reset command
Coincidence signal No.1 reset
command
Coincidence signal No.2 reset
command
Coincidence output enable
command
Latch counter execution
CH1
command
External preset request
detection reset command
Continuous comparison No.1
execution command
Continuous comparison No.2
execution command
Coincidence output No.1 test
command
Coincidence output No.2 test
command
*1
*1
*1
*2
*2
Y11
Y12
Y13
Y17
Y18
*2
*2
Y19
Y1A
Y1B
Y1C
Coincidence signal No.1 reset
command
Coincidence signal No.2 reset
command
Coincidence output enable
command
Latch counter execution
CH2
command
External preset request
detection reset command
Continuous comparison No.1
execution command
Continuous comparison No.2
execution command
Coincidence output No.1 test
command
Coincidence output No.2 test
command
*1
*1
*1
*2
*2
*2
*2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Y0E
Reserved ---
Y0F Y1F
* 1 The signal is only used for the coincidence output function.
* 2 The signal is only used for the continuous comparison function.
Y1E
POINT
(1) The reserved signals above are for system use, not for users. If used (turning
ON/OFF) by a user, the functions of the QD64D2 are not guaranteed.
(2) Definitions of the expression in Operation timing are as follows.
•
ON time should be 2ms or longer.
•
ON time and OFF time should be 2ms or longer.
:Enabled while the signal is ON.
:Enabled when the signal is turned from OFF to ON.
3.3 I/O Signals to the Programmable Controller CPU
Reserved ---
3.3.1 List of I/O signals
3 - 7
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 32

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3.2 Functions of I/O signals
The following indicates the details of I/O signals of the QD64D2.
In this section, I/O numbers (X/Y) and buffer memory addresses are listed only for channel
1.
For I/O numbers and buffer memory addresses used for channel 2, refer to Section 3.3.1
and Section 3.4.1.
(1) Module READY(X00)
• Turns ON at reset or power-on of the programmable controller CPU when the
QD64D2 is ready for counting, and the counting process is executed.
• Turns OFF when a watchdog timer error or an error which affects the system
(Error code: 810 to 860) occurs.
• When the module READY (X00) is OFF, the counting is not executed.
• Use this signal for an interlock of a sequence program.
Operation by the QD64D2
Operation by the sequence program
QD64D2 status
Module READY
(X00)
Figure 3.6 Operation of the module READY (X00)
In
preparation
Ready
ON
Watchdog timer error or an error
that affects the system
OFF
3 - 8
3.3 I/O Signals to the Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.2 Functions of I/O signals
Page 33

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(2) Counter value large No.1 (X01), counter value coincidence No.1 (X02),
counter value small No.1 (X03)
counter value large No.2 (X04), counter value coincidence No.2 (X05),
counter value small No.2 (X06)
The signals notify a comparison result in the counter value comparison function
(coincidence output function, continuous comparison function).
In (a) and (b) below, operations of the counter value large No.1 (X01), the counter
value coincidence No.1 (X02) and the counter value small No.1 (X03) are explained.
For the counter value large No.2 (X04), the counter value coincidence No.2 (X05),
and the counter value small No.2 (X06), operations are the same except that I/O
numbers (X/Y) and buffer memory addresses of the point used for comparison are
different.
(a) Operation when used for the coincidence output function (Refer to Section 5.3.1.)
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
Counter value
large
No.1(X01)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
* The counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) remains ON until the coincidence signal No.1 reset command (Y01) is
turned ON.
Immediately after power-on or reset
of the programmable controller CPU
Coincidence output
No.1 point setting
(Un\G6 and 7)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Counter value large
No.1 (X01)
Counter value coincidence
No.1 (X02)
Counter value small
No.1 (X03)
Coincidence signal No.1
reset command
(Y01)
Coincidence output No.1 point
<
Coincidence output No.1 point
=
Coincidence output No.1 point
>
setting
(Un\G6 and 7)
setting
(Un\G6 and 7)
setting
(Un\G6 and 7)
Operation by the QD64D2
Operation by the sequence program
0
01
ON
OFF
ON
t*
OFF OFF ON
OFF ON* OFF
ON OFF OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
Counter value
coincidence
No.1(X02)
100
100 101 1029998
ON
OFF
Counter value
small
No.1(X03)
ON
OFF
ON
t*
OFF
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
* t 2ms
Figure 3.7 Operation of the counter value large No.1 (X01), the counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) and the counter value small
No.1 (X03) when using the coincidence output function
3.3 I/O Signals to the Programmable Controller CPU
3 - 9
3.3.2 Functions of I/O signals
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 34

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(b) Operation when used for the continuous comparison function (Refer to Section
5.3.2.)
Continuous comparison
No.1 execution command
(Y09)
During continuous
comparison No.1
execution (X09)
Continuous comparison
No.1 point monitor
during comparison
(Un\G86)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Continuous comparison No.1 point
<
n setting
(Un\G54 to 85)
Continuous comparison No.1 point
=
n setting
(Un\G54 to 85)
Continuous comparison No.1 point
>
n setting
(Un\G54 to 85)
Counter value
large
No.1(X01)
OFF OFF ON
OFF ON* OFF
ON OFF OFF
Counter value
coincidence
No.1(X02)
Counter value
small
No.1(X03)
* The counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) remains ON for the preset time of the continuous comparison No.1
ON time setting (Un\G52).
Usage condition of the following operation diagram
Continuous comparison No.1 start point setting (Un\G50): 1 (point 1)
Continuous comparison No.1 repeat point setting (Un\G51): 3 (point 3)
Continuous comparison No.1 point 1 setting (Un\G54 and 55): 100
Continuous comparison No.1 point 2 setting (Un\G56 and 57): 10000
Continuous comparison No.1 point 3 setting (Un\G58 and 59): 20000
Operation by the QD64D2
Operation by the sequence program
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
01 12 3
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Counter value
large No.1 (X01)
Coincidence output
No.1 terminal
(EQU1)
Counter value
coincidence No.1
(X02)
Counter value
small No.1 (X03)
012
ON
10000 10001 10002
9999
98
99 100 101 102
ON
ON
t1*1
ON
t2*2
OFF OFF OFF
9998
ON ON
OFF
ON ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON ON
*1 t1 = Continuous comparison No.1 ON time setting (Un\G52)
*2 t1 < t2 < (t1+1ms)
19998 19999 20000 20001
OFF
OFF
OFF
20002
OFF
ON
OFF
Figure 3.8 Operation of the counter value large No.1 (X01), the counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) and the counter value small
No.1 (X03) when using the continuous comparison function
3 - 10
3.3 I/O Signals to the Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.2 Functions of I/O signals
Page 35

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(3) External preset request detection (X08)
• Turns ON when the preset input terminal (PRST) is turned ON.
• To turn OFF the external preset request detection (X08), turn ON the external
preset request detection reset command (Y08).
• The preset cannot be executed while the external preset request detection (X08)
is ON.
Preset value setting
Preset input terminal
External preset request detection
External preset request
detection reset command
(Un\G4 and 5)
(PRST)
(X08)
(Y08)
Operation by the QD64D2
Operation by the sequence program
100
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
t*
OFF
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Figure 3.9 Operation of the external preset request detection (X08)
0 100
*t 2ms
(4) During continuous comparison No.1 execution (X09), during continuous
comparison No.2 execution (X0A)
• Turns ON during execution of the continuous comparison function. (Refer to
Section 5.3.2.)
(5) Error occurrence (X0D)
• Turns ON when an error occurs.
• To turn OFF the error occurrence (X0D), fix the cause of the error and then turn
ON the error reset command (Y0D).
Operation by the QD64D2
Operation by the sequence program
Error reset command
(Y0D)
Error code
(Un\G18)
Error occurrence
(X0D)
Figure 3.10 Operation of the error occurrence (X0D)
0 100 0
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
t*
* t 2ms
(6) Warning occurrence (X0E)
• Turns ON when a warning occurs.
• To turn OFF the warning occurrence (X0E), fix the cause of the warning and then
turn ON the error reset command (Y0D).
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
Operation by the QD64D2
Operation by the sequence program
Error reset command
(Y0D)
Warning code
(Un\G19)
Warning occurrence
(X0E)
Figure 3.11 Operation of the warning occurrence (X0E)
0 31 0
ON
ON
t*
OFF
3.3 I/O Signals to the Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.2 Functions of I/O signals
OFF
* t 2ms
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 11
Page 36

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(7) Blown fuse detection flag (X1F)
• Turns ON when a fuse blown of the external coincidence output part is detected.
• Even if the fuse is blown, the signal does not turn ON unless a voltage is applied
to the external coincidence output power supply terminal.
• For actions when a fuse is blown, refer to Section 8.1.4.
External coincidence output
power supply terminal
External coincidence output
part fuse status
Blown fuse detection flag
Error code
(Un\G18)
Error occurrence
(X0D)
Figure 3.12 Operation of the blown fuse detection flag (X1F)
(X1F)
ON
Normal
0
.
Operation by the QD64D2
OFF
Fuse blown
ON
OFF
860
ON
(8) Coincidence signal No.1 reset command (Y01), coincidence signal No.2
reset command (Y02)
• Use the signals for the coincidence output function. (Refer to Section 5.3.1.)
• Turn ON the coincidence signal No.1 reset command (Y01) to reset the counter
value coincidence No.1 (X02).
• Turn ON the coincidence signal No.2 reset command (Y02) to reset the counter
value coincidence No.2 (X05).
• Turn OFF the signal after the resetting is completed.
(9) Coincidence output enable command (Y03)
• Use the signal for the coincidence output function. (Refer to Section 5.3.1.)
• Turn ON the coincidence output enable command (Y03) to enable output from
the coincidence output No.1 terminal (EQU1) and the coincidence output No.2
terminal (EQU2) of the external device connector when the count value coincides
with the comparison point.
Operation by the QD64D2
Counter value coincidence No.1
Counter value coincidence No.2
Coincidence output enable command
Coincidence output No.1 terminal
Coincidence output No.2 terminal
Figure 3.13 Operation of the coincidence output enable command (Y03)
(X02)
(X05)
(Y03)
(EQU1)
(EQU2)
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
3 - 12
3.3 I/O Signals to the Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.2 Functions of I/O signals
Page 37

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(10)Preset command (Y04)
• Turn ON the preset command (Y04) to execute the preset function (Refer to
Section 5.4).
• Check that the present value (Un\G12 and 13) has been changed, then turn OFF
the preset command (Y04).
• While the external preset request detection (X08) is ON, the preset cannot be
executed by the preset command (Y04).
Preset value setting
(Un\G4 and 5)
Preset command
(Y04)
Operation by the QD64D2
100
ON
t *
OFF
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Figure 3.14 Operation of the preset command (Y04)
1000
* t 2ms
(11)Subtraction count command (Y05)
• Turn ON to execute the subtraction count at 1-phase input mode.
• In the 1-phase pulse input mode, the subtraction count is executed when the
phase B pulse or the subtraction count command (Y05) is turned ON.
• When the pulse input mode is 1 multiple of 1 phase, counting is executed as
shown below.
• For the addition count, check that the phase B pulse and the subtraction count
command (Y05) are turned OFF.
A
B
Subtraction count command
Figure 3.15 Operation of the subtraction count command (Y05) (when the pulse input mode is 1 multiple of 1 phase)
(Y05)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
ON ON
OFF
ON
99 98 9710099
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
(12)Count enable command (Y06)
• Turn ON the count enable command (Y06) to start the count operation.
• When the pulse input mode is 1 multiple of 1 phase, counting is executed as
shown below.
A
B
Count enable command
(Y06)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Figure 3.16 Operation of the count enable command (Y06) (when the pulse input mode is 1 multiple of 1 phase)
3.3 I/O Signals to the Programmable Controller CPU
ON
210
3.3.2 Functions of I/O signals
3 - 13
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 38

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(13)Latch counter execution command (Y07)
• When the latch counter execution command (Y07) is turned from OFF to ON, the
present value (Un\G12 and 13) is stored in the latch count value (Un\G14 and
15).
• Turn OFF the latch counter execution command (Y07) after the present value
(Un\G12 and 13) is stored in the latch count value (Un\G14 and 15).
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Latch counter execution command
(Y07)
Operation by the QD64D2
04123
ON
OFF
t* t*
ON
OFF
Latch count value
(Un\G14 and 15)
Figure 3.17 Operation of the latch counter execution command (Y07)
031
* t 2ms
(14)External preset request detection reset command (Y08)
• Turn ON to turn OFF the external preset request detection (X08).
(15)Continuous comparison No.1 execution command (Y09), continuous
comparison No.2 execution command (Y0A)
• Turn ON to execute the continuous comparison function. (Refer to Section 5.3.2.)
(16)Coincidence output No.1 test command (Y0B), coincidence output No.2
test command (Y0C)
• Turn ON to execute the coincidence output test function. (Refer to Section 5.3.3.)
(17)Error reset command (Y0D)
• Turn ON to reset the error and warning.
• After fixing the cause of the error, reset the error code so that the newly detected
errors can be checked.
3 - 14
3.3 I/O Signals to the Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.2 Functions of I/O signals
Page 39
3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4 Buffer Memory Assignment
3.4.1 List of buffer memory assignment
The following table shows the buffer memory assignment of the QD64D2. For details of
each buffer memory, refer to Section 3.4.2.
Table 3.5 List of buffer memory assignment
Address
(decimal
notation)
CH1 CH2
0 200
1 201 (H)
2 202
3 203 (H)
4 204
5 205 (H)
6 206
7 207 (H)
8 208
9 209 (H)
10 210 Coincidence output No.1 point change request
11 211 Coincidence output No.2 point change request
12 212
13 213 (H)
14 214
15 215 (H)
16 216 Overflow detection flag
17 217 External I/O status monitor
19 219 Warning code
20 220
to to
49 249
50 250 Continuous comparison No.1 start point setting
51 251
52 252 Continuous comparison No.1 ON time setting
53 253 Reserved ---- ---- ---54 254 Continuous comparison No.1 point 1
55 255 (H)
56 256 Continuous comparison No.1 point 2
57 257 (H)
58 258 Continuous comparison No.1 point 3
59 259 (H)
Ring counter lower limit value
Ring counter upper limit value
Preset value setting
Coincidence output No.1 point setting
Coincidence output No.2 point setting
Present value
Latch count value
Reserved ---- ---- ----
Continuous comparison No.1 repeat point
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
Setting contents
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
* 1 Initial value which is set when the module is powered on or the programmable controller CPU is
reset.
* 2 Read and write a value in 32-bit signed binary format. (Make sure to use a value in units of 2
words.)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
Initial
value
*1
0
0
0
Read/
write
Read/write
are
enabled.
Read only
Read/write
are
enabled.
Read/write
are
enabled.
Remarks
Only used for the ring counter function.
Only used for the coincidence output
function.
Only used for the linear counter
function.
Only used for the continuous
comparison function.
Only used for the continuous
comparison function.
----
----
----18 218 Error code
1
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
8
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
3.4 Buffer Memory Assignment
3.4.1 List of buffer memory assignment
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 15
Page 40

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.5 List of buffer memory assignment (Continued)
Address
(decimal
notation)
CH1 CH2
60 260 Continuous comparison No.1 point 4
61 261 (H)
62 262 Continuous comparison No.1 point 5
63 263 (H)
64 264 Continuous comparison No.1 point 6
65 265 (H)
66 266 Continuous comparison No.1 point 7
67 267 (H)
68 268 Continuous comparison No.1 point 8
69 269 (H)
70 270 Continuous comparison No.1 point 9
71 271 (H)
72 272 Continuous comparison No.1 point 10
73 273 (H)
74 274 Continuous comparison No.1 point 11
75 275 (H)
76 276 Continuous comparison No.1 point 12
77 277 (H)
78 278 Continuous comparison No.1 point 13
79 279 (H)
80 280 Continuous comparison No.1 point 14
81 281 (H)
82 282 Continuous comparison No.1 point 15
83 283 (H)
84 284 Continuous comparison No.1 point 16
85 285 (H)
86 286
87 287
to to
99 299
100 300 Continuous comparison No.2 start point setting
101 301 Continuous comparison No.2 repeat point setting
102 302 Continuous comparison No.2 ON time setting
103 303 Reserved ---- ---- ---104 304 Continuous comparison No.2 point 1
105 305 (H)
106 306 Continuous comparison No.2 point 2
107 307 (H)
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
Continuous comparison No.1 point monitor
during comparison
Reserved ---- ---- ----
*2
setting
*2
setting
Setting contents
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
* 1 Initial value which is set when the module is powered on or the programmable controller CPU is
reset.
* 2 Read and write a value in 32-bit signed binary format. (Make sure to use a value in units of 2
words.)
Initial
value
*1
0
0
0
Read/write Remarks
Read/write
are enabled.
Read only
Read/write
are enabled.
Read/write
are enabled.
Only used for the continuous
comparison function.
Only used for the continuous
comparison function.
Only used for the continuous
comparison function.
3 - 16
3.4 Buffer Memory Assignment
3.4.1 List of buffer memory assignment
Page 41

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.5 List of buffer memory assignment (Continued)
Address
(decimal
notation)
CH1 CH2
108 308 Continuous comparison No.2 point 3
109 309 (H)
110 310 Continuous comparison No.2 point 4
111 311 (H)
112 312 Continuous comparison No.2 point 5
113 313 (H)
114 314 Continuous comparison No.2 point 6
115 315 (H)
116 316 Continuous comparison No.2 point 7
117 317 (H)
118 318 Continuous comparison No.2 point 8
119 319 (H)
120 320 Continuous comparison No.2 point 9
121 321 (H)
122 322 Continuous comparison No.2 point 10
123 323 (H)
124 324 Continuous comparison No.2 point 11
125 325 (H)
126 326 Continuous comparison No.2 point 12
127 327 (H)
128 328 Continuous comparison No.2 point 13
129 329 (H)
130 330 Continuous comparison No.2 point 14
131 331 (H)
132 332 Continuous comparison No.2 point 15
133 333 (H)
134 334 Continuous comparison No.2 point 16
135 335 (H)
136 336
137 337
to to
199 399
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
*2
setting
Continuous comparison No.2 point monitor
during comparison
Reserved ---- ---- ----
Setting contents
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
(L)
* 1 Initial value which is set when the module is powered on or the programmable controller CPU is
reset.
* 2 Read and write a value in 32-bit signed binary format. (Make sure to use a value in units of 2
words.)
Initial
value
*1
0
Read/write Remarks
Read/write
are enabled.
Read only
Only used for the continuous
comparison function.
1
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
3.4 Buffer Memory Assignment
3.4.1 List of buffer memory assignment
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 17
Page 42

3
SPECIFICATIONS
POINT
• The reserved areas in the above table and areas not mentioned in the
table are for system use, not for users. If written by a user, the functions
of the QD64D2 are not guaranteed.
• All data in the buffer memory of the QD64D2 are initialized when the
module is powered on or the programmable controller CPU is reset. To
save the necessary data, use the FROM/DFRO/TO/DTO instructions in
the sequence program or make setting with the utility package for writing/
reading of the buffer memory data.
• Since the buffer memory contents are automatically updated by count
operation, the latest count value can be read from the buffer memory.
3 - 18
3.4 Buffer Memory Assignment
3.4.1 List of buffer memory assignment
Page 43

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.2 Details of the buffer memory
This section describes details of the QD64D2 buffer memory.
In this section, I/O numbers (X/Y) and buffer memory addresses are listed for channel 1
and coincidence output No.1. For I/O numbers and buffer memory addresses used for
channel 2 and coincidence output No.2, refer to Section 3.3.1 and Section 3.4.1.
(1) Ring counter lower limit value (Un\G0 and 1)
Ring counter upper limit value (Un\G2 and 3)
• This area is used for setting a count range for the ring counter. (Refer to Section
5.2.2.)
• Setting range: -2147483648 to 2147483647
Operation by the QD64D2
Count enable command
(Y06)
Ring counter lower limit value
(Un\G0 and 1)
Ring counter upper limit value
(Un\G2 and 3)
*1 Setting value of the ring counter upper limit value (Un\G2 and 3) and the ring counter lower
limit value (Un\G0 and 1) becomes effective when the count enable command (Y06) is turned
from OFF to ON.
*2 It does not become effective until the count enable command (Y06) is turned from OFF to ON.
Figure 3.18 Timing chart for the ring counter lower limit value (Un\G0 and 1) and ring counter upper limit value (Un\G2 and 3)
ON
*1
200 1000
*2
*1
2001000
*2
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
(2) Preset value setting (Un\G4 and 5)
• This area is used for setting a preset value for the counter. (Refer to Section 5.4.)
• Setting range: -2147483648 to 2147483647
• The setting value becomes effective when the preset command (Y04) or the
preset input terminal (PRST) is turned from OFF to ON.
Operation by the QD64D2
Preset value setting
(Un\G4 and 5)
Preset command
(Y04)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Figure 3.19 Timing chart for the preset value setting (Un\G4 and 5)
ON
100
OFF
t*
1000
* t 2ms
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
8
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
3.4 Buffer Memory Assignment
3.4.2 Details of the buffer memory
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 19
Page 44

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(3) Coincidence output No.1 point setting (Un\G6 and 7)
Coincidence output No.1 point change request (Un\G10)
Coincidence output No.2 point setting (Un\G8 and 9)
Coincidence output No.2 point change request (Un\G11)
• This area is used for setting the comparison point (the value used to compare
with the present value) used for the coincidence output function.
• Setting procedure
1) Write any comparison point to the coincidence output No.1 point setting (Un\G
6 and 7).
Setting range: -2147483648 to 2147483647
2) Write "1" (Change request) to the coincidence output No.1 point change
request (Un\G10).
3) The comparison point written to the coincidence output No.1 point setting
(Un\G6 and 7) becomes effective, and the coincidence output No.1 point
change request (Un\G10) changes from "1" to "0" (No change request).
4) The comparison between the set comparison point and the present value is
executed.
Note) If a value other than "1" is written to the coincidence output No.1 point
change request, the comparison point written to the coincidence output No.1
point setting does not become effective.
For the comparison point, a value previously set in the coincidence output
No.1 point setting is used.
For example, the default value of the coincidence output No.1 point setting is
"0". If "10000" is written to the coincidence output No.1 point setting, the
default value of "0" is used for the comparison point unless "1" is written to
the coincidence output No.1 point change request.
• The above procedure is described as an example of the coincidence output No.1.
To set the coincidence output No.2, replace the coincidence output No.1 setting
(Un\G6 and 7) and the coincidence output No.1 point change request (Un\G10)
with the coincidence output No.2 point setting (Un\G8 and 9) and the coincidence
output No.2 point change request (Un\G11).
Operation by the QD64D2
Coincidence output No.1 point change request
Coincidence output No.1 point 1 setting
Figure 3.20 Timing chart for the coincidence output No.1 point setting (Un\G6 and 7) and the coincidence output No.1 point change
(Un\G10)
(Un\G6 and 7)
*1 When the coincidence output No.1 point setting (Un\G6 and 7) becomes
effective, the QD64D2 writes "0" to the coincidence output No.1 point change
request (Un\G10).
request (Un\G10)
*1
0
1
0010
*1
200100
• For details of the operation, refer to Section 5.3.1.
3 - 20
3.4 Buffer Memory Assignment
3.4.2 Details of the buffer memory
Page 45

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(4) Present value (Un\G12 and 13)
• Present value of the counter is stored in this area.
• Setting range: -2147483648 to 2147483647
• An example when the pulse input mode is CW/CCW is shown below.
Count enable command
(Y06)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Figure 3.21 Timing chart of the present value (Un\G12 and 13)
(5) Latch count value (Un\G14 and 15)
• The latched value of the present value (Un\G12 and 13) is stored in this area.
(Refer to Section 5.5.)
• When one of the following conditions is satisfied, the present value (Un\G12 and
13) is stored in the latch count value (Un\G14 and 15).
A
B
ON
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
210
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
1) When turning from OFF to ON the latch counter execution command (Y07)
2) When turning from OFF to ON the latch counter input terminal (LATCH)
• Setting range: -2147483648 to 2147483647
Operation by the QD64D2
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Latch counter execution command
Figure 3.22 Timing chart for the latch count value (Un\G14 and 15)
(Y07)
Latch count value
(Un\G14 and 15)
04123
t* t*
031
* t 2ms
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
3.4 Buffer Memory Assignment
3.4.2 Details of the buffer memory
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 21
Page 46

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(6) Overflow detection flag (Un\G16)
• Overflow occurrence status of the counter is stored in this area. (Refer to Section
5.2.1.)
0: No detection
1: Overflow occurred
• Overflow occurs when the count value exceeds the range of -2147483648 to
2147483647.
• The overflow detection flag (Un\G16) can be cleared by the preset command
(Y04) or the preset input terminal (PRST).
Operation by the QD64D2
A
B
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Overflow detection flag
(Un\G16)
Preset value setting
(Un\G4 and 5)
Preset command
(Y04)
Error code
(Un\G18)
Figure 3.23 Timing chart for the overflow detection flag (Un\G16) (when the pulse input mode is 1 multiple of 1 phase)
2147483646 2147483647
0
0 100
0
1
2
1
0
ON
0
(7) External I/O status monitor (Un\G17)
• The I/O status of the external device connector is stored in this area.
• Storage contents is as follows.
b15 b8 b7 b0
0000000
Reserved: Fixed to 0
00
Storage item
Preset input status
Latch counter input status
Phase A input status
Phase B input status
Coincidence output No.1 output status *1
Coincidence output No.2 output status *1
Addition/subtraction status
Definition
0:OFF
1:ON
0: During addition
1: During
subtraction
3 - 22
Figure 3.24 Storage contents of the external I/O status monitor (Un\G17)
• Storage item marked with "*1" turns to "1" (ON) regardless of applying a voltage
to the external coincidence output power supply terminal.
• It takes up to 2ms until actual I/O status is reflected to the external I/O status
monitor (Un\G17).
3.4 Buffer Memory Assignment
3.4.2 Details of the buffer memory
Page 47

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(8) Error code (Un\G18)
• Error code of the detected error is stored in this area.
• For operations when multiple errors occur concurrently, refer to POINT in Section
8.11.1.
(9) Warning code (Un\G19)
• Warning code of the detected error is stored in this area.
• For operations when multiple warnings occur concurrently, refer to POINT in
Section 8.11.2.
(10)Continuous comparison No.1 start point setting (Un\G50)
Continuous comparison No.2 start point setting (Un\G100)
• This area is used for setting a start point number of comparison for the
continuous comparison function.
• Setting range: 1 to 16
• For details of setting and operation, refer to Section 5.3.2.
(11)Continuous comparison No.1 repeat point setting (Un\G51)
Continuous comparison No.2 repeat point setting (Un\G101)
• This area is used for setting a repeat point number of comparison for the
continuous comparison function.
• Setting range: 1 to 16
• For details of setting and operation, refer to Section 5.3.2.
(12)Continuous comparison No.1 ON time setting (Un\G52)
Continuous comparison No.2 ON time setting (Un\G102)
• This area is used for setting ON time of the coincidence output terminal and the
counter value coincidence.
• Setting range: 1 to 10 (Unit: ms)
• For determination of ON time, refer to Section 5.3.2 (4).
• For details of setting and operation, refer to Section 5.3.2.
1
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
(13)Continuous comparison No.1 point n setting (Un\G54 to 85)
Continuous comparison No.2 point n setting (Un\G104 to 135)
• This area is used for setting a continuous comparison point for the continuous
comparison function.
• Setting range: -2147483648 to 2147483647
• For details of setting and operation, refer to Section 5.3.2.
(14)Continuous comparison No.1 point monitor during comparison (Un\G86)
Continuous comparison No.2 point monitor during comparison
(Un\G136)
• Point number (1 to 16) which is currently in comparison with the present value is
stored in this area.
• For details of setting and operation, refer to Section 5.3.2.
3.4 Buffer Memory Assignment
3.4.2 Details of the buffer memory
3 - 23
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 48

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.5 Specifications of I/O Interfaces with External Device
3.5.1 Electrical specifications of I/O signals
(1) Input specifications
Table 3.6 Input specifications of the QD64D2
Signal name
Phase A pulse input
Phase B pulse input
Preset input
Latch counter input
External coincidence
output power supply
12/24V
Rated input
voltage/
current
•RS-422-A compliant differential receiver
(AM26C32 (manufactured by Texas Instruments Incorporated) or equivalent)
IT+ differential input ON voltage (H level threshold voltage) 0.1V
V
VIT- differential input OFF voltage (L level threshold voltage) -0.1V
Vhys Hysteresis voltage (V
(A current type line driver cannot be used.)
24VDC
/5mA
24VDC
/5mA
12 or 24VDC
/8mA
(TYP 24VDC)
Operating
voltage range
IT+ - VIT-) 60mV
21.6 to 26.4VDC
21.6 to 26.4VDC
10.2 to 30VDC ---- ----
ON voltage/
current
21.6 to 26.4VDC
/2 to 5mA
21.6 to 26.4VDC
/2 to 5mA
OFF voltage/
current
5VDC or less
/0.1mA or less
5VDC or less
/0.1mA or less
Input
resistance
Approx.
10k
Approx.
10k
Approx.
3.9k
Response
time
OFF ON
0.5ms or
less
ON OFF
1.0ms or
less
OFF ON
0.5ms or
less
ON OFF
1.0ms or
less
----
Signal name
Coincidence output
No.1
Coincidence output
No.2
3 - 24
3.5 Specifications of I/O Interfaces with External Device
3.5.1 Electrical specifications of I/O signals
(2) Output specifications
Table 3.7 Output specifications of the QD64D2
Rated load
voltage
12/24VDC 10.2 to 30VDC
Operating load
voltage range
Maximum load
current/rush
current
0.5A/point
2A/common
Maximum
voltage drop at
ON
1.5VDC
Leakage
current
at OFF
0.1mA
or less
Response
time (rated
load,
resistance
load)
OFF ON
0.05ms or
less
ON OFF
0.1ms or
less
Page 49

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.5.2 Signal layout for external device connector
The specifications of the connector section, which is the I/O interface for the QD64D2 and
external device, are shown below.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.8 Signal layout for external device connector
Terminal layout
B20
B19
B18
B17
B16
B15
B14
B13
B12
B11
B10
B09
B08
B07
B06
B05
B04
B03
B02
B01
Front view of the module
A20
A19
A18
A17
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A09
A08
A07
A06
A05
A04
A03
A02
A01
Figure 3.25 Appearance of the QD64D2
CH1 CH2
Terminal
number
B20 NC A20 NC
B19 PULSE A + A19 PULSE A +
B18 PULSE A - A18 PULSE A -
B17 PULSE B + A17 PULSE B +
B16 PULSE B - A16 PULSE B -
B15 PULSE COM A15 PULSE COM
B14 NC A14 NC
B13 PRST COM A13 PRST COM
B12 PRST A12 PRST
B11 NC A11 NC
B10 NC A10 NC
B09 LATCH COM A09 LATCH COM
B08 LATCH A08 LATCH
B07 NC A07 NC
B06 NC A06 NC
B05 EQU1 A05 EQU1
B04 EQU2 A04 EQU2
B03 12V/24V A03 12V/24V
B02 0V A02 0V
B01 NC A01 NC
Signal name
Terminal
No.
Signal name
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
8
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
3.5 Specifications of I/O Interfaces with External Device
3.5.2 Signal layout for external device connector
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 25
Page 50

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.5.3 List of I/O signal details
The details of each signal for the QD64D2 external device connector are shown below.
Table 3.9 Details of each signal for external device connector
Termin al
Signal name
Phase A pulse input + B19 A19 PULSE A + •Inputs + (plus) side of phase A pulse.
Phase A pulse input - B18 A18 PULSE A - •Inputs - (minus) side of phase A pulse.
Phase B pulse input + B17 A17 PULSE B + •Inputs + (plus) side of phase B pulse.
Phase B pulse input - B16 A16 PULSE B - •Inputs - (minus) side of phase B pulse.
Pulse input common B15 A15
Preset input common B13 A13
Preset input 24V B12 A12 PRST
Latch counter input
common
Latch counter input
24V
Coincidence output
No.1
Coincidence output
No.2
External coincidence
output power supply
12/24V
External coincidence
output power supply
GND(0V)
number
CH1 CH2
B09 A09
B08 A08 LATCH
B05 A05 EQU1
B04 A04 EQU2
B03 A03 12V/24V
B02 A02 0V
Symbol Signal details
PULSE
COM
PRST
COM
LATCH
COM
•Common for pulse input
•It is common between channels.
•Common for preset input
•It is separated between channels.
•Turn ON to execute the preset by the external signal.
•When the preset input terminal (PRST) is turned ON, the present
value (Un\G12 and 13) is changed to the preset value setting (Un\G4
and 5).
•Common for latch counter input
•It is separated between channels.
•Turn ON to latch the present value (Un\G12 and 13) by the external
signal.
•When the latch counter input terminal (LATCH) is turned ON, the
present value (Un\G12 and 13) is latched and stored in the latch
count value (Un\G14 and 15).
Executes the coincidence output when a coincidence of the count
value is detected while using the coincidence output function or the
continuous comparison function.
•Supplies 12V or 24V when executing the external coincidence output.
•It is common between channels.
•Inputs 0V when executing the external coincidence output.
•It is also used as a common for external coincidence output.
•It is common between channels.
3 - 26
3.5 Specifications of I/O Interfaces with External Device
3.5.3 List of I/O signal details
Page 51

3
SPECIFICATIONS
1
3.5.4 Interface for external device
The following table shows the list of external device interface of the QD64D2.
I/O
classification
Input
Table 3.10 List of external device interface of the QD64D2
Terminal
Internal circuit
number Signal name
CH1 CH2
+5V
+5V
Isolator
(Isolating
element)
Isolator
(Isolating
element)
+5V
Line
receiver
+5V
Line
receiver
27k
1/10W
27k
1/10W
27k
1/10W
27k
1/10W
4.7k
1/10W
4.7k
1/10W
4.7k
1/10W
4.7k
1/10W
B19 A19 Phase A pulse input +
100
1/2W
B18 A18 Phase A pulse input -
B17 A17 Phase B pulse input +
100
1/2W
B16 A16 Phase B pulse input -
B15, A15 Pulse input common
10k
1/3W
B12 A12 Preset input 24V
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
Output
To blown fuse
detection circuit
1k
1/10W
1k
1/10W
10k
1/3W
FUSE
B13 A13 Preset input common
B08 A08 Latch counter input 24V
B09 A09 Latch counter input common
B05 A05 Coincidence output No.1
B04 A04 Coincidence output No.2
B03, A03
B02, A02
External coincidence output power supply
12/24V
External coincidence output power supply
GND (0V)
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
3.5 Specifications of I/O Interfaces with External Device
3.5.4 Interface for external device
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 27
Page 52

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6 Connectable Encoders
The encoders connectable to the QD64D2 are described below.
• Line driver output type encoders
(Check that the encoder output voltage meets the specifications of the QD64D2.)
3 - 28
3.6 Connectable Encoders
Page 53

PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
4
OPERATION
CHAPTER4 PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
OPERATION
1
This chapter describes the operating procedures before operation, part names, settings,
and wiring of the QD64D2.
4.1 Handling Precautions
This section describes precautions on handling the QD64D2.
(1) Do not drop the module case and/or connector or apply a strong impact
to it.
(2) Do not remove the printed-circuit board of the module from the case.
Doing so will cause a failure.
(3) Be careful to prevent foreign matter such as dust or wire chips from
entering the module.
Failure to do may cause a fire, failure or malfunction.
(4) A protective film is attached to the module top to prevent foreign matter
such as wire chips from entering the module during wiring.
Do not remove the film during wiring.
Be sure to remove it for heat dissipation before system operation.
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
(5) Tighten the screws such as module fixing screws within the following
ranges.
Table 4.1 Tightening torque range of module fixing screw
Screw Tightening torque range
Module fixing screw (M3)
Connector screw of module (M2.6) 0.20 to 0.29 N•m
* 1 The module can be easily fixed onto the base unit using the hook at the top of the module.
However, it is recommended to secure the module with the module fixing screw if the module is
subject to significant vibration.
(6) When mounting the module to the base unit, insert the module fixing
projection into the fixing hole in the base unit, and mount the module
with using the hole as a supporting point.
Incorrect module mounting may cause a malfunction, failure, or drop of
the module.
*1
0.36 to 0.48 N•m
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
4.1 Handling Precautions
TROUBLESHOOTING
4 - 1
Page 54

PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
4
OPERATION
4.2 Procedures before Operation
The following flowchart shows the procedures for operating the QD64D2.
Start
Module mounting
Mount the QD64D2 to the specified slot.
Wiring
Wire external devices to the QD64D2.
Intelligent function module switch setting
Set the switches with GX Developer
(refer to Section 4.5).
Section 4.5
Use GX Configurator-CT?
No
No
Make the initial setting?
Yes
Initial setting
Create a sequence program for writing
initial values with the FROM/TO
instruction.
Programming
Create and a program for counter
processing with the FROM/TO instruction
and check it.
Yes
No
Initial setting
Make initial settings with
GX Configurator-CT (refer to Section 6.4).
No
Auto refresh setting
Make the auto refresh setting with
GX Configurator-CT (refer to Section 6.5).
Programming
Create and a program for counter
processing without the FROM/TO
instruction and check it.
Make the initial setting?
Yes
Make the auto refresh setting?
Yes
Section 6.4
Section 6.5
4 - 2
Operation
Figure 4.1 Procedures before operation
4.2 Procedures before Operation
Page 55

PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
)
4
OPERATION
4.3 Part Names
The following explains the part names of the QD64D2.
(Connector terminal number) (Connector terminal number
1)
2)
B20
A20
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
B01
3)
Figure 4.2 Appearance of the QD64D2
Table 4.2 Part names
Name Description
Indicates operating status of the QD64D2.
RUN
ERR.
FUSE
1)
LED indicator
A_CH1 to CH2
B_CH1 to CH2
DEC._CH1 to CH2
2) External device connector (40 pins)
3) Serial number plate Indicates the serial No. of the QD64D2.
ON: Normal operation
OFF: Watchdog timer error
Indicates error status of the QD64D2.
ON: Error at 1 CH or more.
OFF: All channels in normal operation
Indicates fuse status of external coincidence output part.
ON: Blown fuse detected
OFF: Blown fuse not detected
Indicates input status of A- phase pulse terminal.
ON: Pulse ON
OFF: Pulse OFF
Indicates input status of B- phase pulse terminal.
ON: Pulse ON
OFF: Pulse OFF
Indicates subtraction status of a count.
ON: During subtraction
OFF: During addition
A connector for connecting an encoder and controller
For terminal layout, refer to Section 3.5.
A01
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
8
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
4.3 Part Names
TROUBLESHOOTING
4 - 3
Page 56

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
OPERATION
POINT
Even if the fuse of the external coincidence output part is blown, the FUSE LED
does not turn ON unless a voltage is applied to the external coincidence output
power supply terminal.
(1) Connectors for external wiring
Purchase the connector for the QD64D2 separately.
The following tables show the recommended connector types and crimp tool.
(a) Connector types
Table 4.3 Connector types
Typ e Model
Soldering type, straight out A6CON1
Crimp type, straight out A6CON2
Soldering type, usable for both straight out and
diagonal out
A6CON4
* The A6CON3 connector (pressure welding type, straight out) cannot be used for the QD64D2.
(b) Connector crimp tool
Table 4.4 Connector crimp tool
Type Model Applicable wire size Contact
Crimp tool FCN-363T-T005/H AWG28 to 24
FUJITSU COMPONENT
LIMITED
4 - 4
4.3 Part Names
Page 57

PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
4
OPERATION
4.4 Wiring
1
This section describes wiring an encoder and controller to the QD64D2.
4.4.1 Wiring precautions
One of the conditions to maximize the QD64D2 functions and make the system highreliable, the external wiring has to be laid so that the QD64D2 becomes less subject to
noise.
This section describes the precautions on external wiring.
(1) Inputting a signal of different voltage may result in a malfunction or
mechanical failure.
(2) For 1-phase input, always perform pulse input wiring on the phase A
side.
(3) When pulse status noise is input, the QD64D2 may miscount.
(4) Take the following measures against noise for high-speed pulse input.
(a) Always use a shielded twisted pair cable and ground it on the QD64D2 side.
(b) Wire the shielded twisted pair cables so as not to be in parallel with wires causing
much noise such as power lines or I/O wires while keeping a distance of at least
150 mm (5.91 inch) between such wires. Also install the shielded twisted pair
cables as short as possible.
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
(5) The following diagram shows an example of wiring for measures against
Inverter
Terminal
block
Install I/O wires at least
150 mm (5.91 inch)
away from the high
voltage equipment such
as relay and inverter.
(Apply this wiring in a
control panel as well.)
AC
motor
noise.
Programmable
controller
Terminal
block
Figure 4.3 Example of wiring for measures against noise
QD64D2
Ground the shielded twisted pair cable on the QD64D2 side, and install
the cable as short as possible.
Avoid using a solenoid valve and inductive load together in the same
metallic pipe. If a sufficient distance cannot be secured with high voltage
cable due to such as duct wiring, use CVVS or other shielded cable for the
high voltage cable.
Make the distance between the encoder and relay box as
Relay box
Cart
Encoder
short as possible.
If the distance is long, a voltage drop may occur. Therefore,
check that the voltages while the encoder is in
operation/stop are within the rated voltage at the terminal
block of the relay box using the measure such as a
synchronoscope.
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
4.4 Wiring
4.4.1 Wiring precautions
TROUBLESHOOTING
4 - 5
Page 58

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
OPERATION
(6) Take the following measures to conform the wiring to the EMC and Low
Voltage Directives.
(a) Ground the shielded twisted pair cables to a control panel with the AD75CK cable
clamp (manufactured by Mitsubishi Electric Corporation)
In a control panel
QD64D2
20cm (7.87inch)
AD75CK
to 30cm (11.81inch)
Figure 4.4 AD75CK cable clamp
For the AD75CK, refer to the following manual.
AD75CK-type Cable Clamping Instruction Manual
(b) The power supply line connecting to the external coincidence output power supply
module should be 10m or less long.
(c) Keep the length of the cable connected to the external devices of the QD64D2 to
30m or less.
4 - 6
4.4 Wiring
4.4.1 Wiring precautions
Page 59

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
OPERATION
4.4.2 Example of wiring the module and an encoder
Alphanumeric characters in parentheses of QD64D2 terminal parts indicate CH2 terminal
numbers.
(1) Example of wiring with a line driver (AM26LS31 equivalent) encoder
1
OVERVIEW
2
QD64D2
Phase A
Phase B
27k
Digital
isolator
Digital
isolator
Line
receiver
Line
receiver
External
power supply
1/10W
27k
1/10W
27k
1/10W
27k
1/10W
4.7k
1/10W
4.7k
1/10W
4.7k
1/10W
4.7k
1/10W
PULSE
COM
VCC
PULSE
100
1/2W
PULSE
PULSE
100
1/2W
PULSE
0V
A+
B19(A19)
B18(A18)
A-
B+
B17(A17)
B16(A16)
B-
B15/A15
Shield
twisted pair cable
twisted pair cable
Shield
Shielded
Shielded
A
A
E
B
B
E
VCC
0V
Figure 4.5 Example of wiring with a line driver (AM26LS31 equivalent) encoder
Encoder
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
4.4 Wiring
4.4.2 Example of wiring the module and an encoder
4 - 7
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 60

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
OPERATION
4.4.3 Example of wiring a controller and an external input terminal
Alphanumeric characters in parentheses of QD64D2 terminal parts indicate CH2 terminal
numbers.
(1) Example of wiring with a controller (sink loading type)
QD64D2
Controller
Preset
Latch counter
QD64D2
Shielded
twisted pair cable
Shielded
twisted pair cable
OUT
+24V
E
OUT
+24V
E
24VDC
1k
1/10W
1k
1/10W
10k
PRST
1/3W
B12(A12)
B13(A13)
PRST COM
10k
LATCH
1/3W
B08(A08)
B09(A09)
LATCH COM
Shield
Shield
Figure 4.6 Example of wiring with a controller (sink loading type)
(2) Example of wiring with a controller (source loading type)
Controller
4 - 8
Preset
Latch counter
1k
1/10W
1k
1/10W
10k
PRST
1/3W
B12(A12)
B13(A13)
PRST COM
10k
LATCH
1/3W
B08(A08)
B09(A09)
LATCH COM
twisted pair cable
Shield
twisted pair cable
Shield
Figure 4.7 Example of wiring with a controller (source loading type)
4.4 Wiring
4.4.3 Example of wiring a controller and an external input terminal
Shielded
Shielded
OUT
GND
E
OUT
GND
E
24VDC
Page 61

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
OPERATION
4.4.4 Example of wiring with an external output terminal
When using coincidence output No. 1 terminal (EQU1) and coincidence output No. 2
terminal (EQU2), external power supply of 10.2 to 30VDC is required.
Figure 4.8 shows wiring example.
Alphanumeric characters in parentheses of QD64D2 terminal parts indicate CH2 terminal
numbers.
(1) Example of wiring with an external output terminal (sink output type)
1
OVERVIEW
2
QD64D2
EQU1
B05(A05)
EQU2
B04(A04)
FUSE
12/24V
0V
B03/A03
B02/A02
To blown fuse
detection circuit
Figure 4.8 Example of wiring with an external output terminal (sink output type)
Load
Load
10.2 to
30VDC
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
4.4 Wiring
4.4.4 Example of wiring with an external output terminal
4 - 9
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 62
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
4
OPERATION
4.5 Intelligent Function Module Switch Setting
This section describes the intelligent function module switch setting.
The switch setting is made on the [I/O assignment] screen of GX Developer.
(1) Intelligent function module switch setting
The switch has five switches and is set at 16-bit data.
When the switch setting is not made, the default values of the switches from 1 to 5 are
0.
Table 4.5 Intelligent function module switches
Setting item Setting value Default
1) Pulse input mode
H: 1 multiple of 1 phase
1)
Reserved:
Fixed to 0
Switch 1
(CH1)
0
1H: 2 multiples of 1 phase
2H: CW/CCW
3H: 1 multiple of 2 phases
H: 2 multiples of 2 phases
4
5H: 4 multiples of 2 phases
b8b11
2)
Reserved:
Fixed to 0
b12b15
3)
2) Counter format
0H : Linear counter
1H : Ring counter
0000
H
Switch 2
(CH2)
Switch 3 Reserved: Fixed to 0
Switch 4 Reserved: Fixed to 0
Switch 5 Reserved: Fixed to 0
Same as for the switch 1 0000
Reserved:
Fixed to 0
3) Counter value comparison
function election
H : Coincidence output function
0
1H : Continuous comparison
function
H
4 - 10
4.5 Intelligent Function Module Switch Setting
Page 63

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
OPERATION
1
(Example) Target channel: channel 1, pulse input mode setting: 1 multiple of 2
phases, counter format: ring counter, and counter value comparison function
selection: continuous comparison function
Set the switch 1 = 1103
H.
POINT
The reserved bits in Table 4.5 are for system use, not for users.
Therefore, always fix them to 0. If used (changed from 0 to 1) by a user, the
functions of the QD64D2 are not guaranteed.
(2) Details of the intelligent function module switch setting
Table 4.6 Details of the intelligent function module switch setting
Setting item Description Reference
Set the pulse input mode for each channel.
Pulse input mode
Counter format Set the counter format for each channel.
Counter value comparison
function selection
When setting 6H to FH, a switch setting error (error code:
810) occurs.
Set the counter value comparison function for each
channel.
Section 5.1.1
Section 5.2.1
Section 5.2.2
Section 5.3.1
Section 5.3.2
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
4.5 Intelligent Function Module Switch Setting
4 - 11
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 64

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
OPERATION
(3) Operating procedure
Set the switches on the [I/O assignment] screen of GX Developer.
(a) [I/O assignment] screen
Make the following settings to the slot to which the QD64D2 is mounted.
[Type]: Select [Intelli].
[Model name]: Input the model of the module.
[Points]: Select [32points].
[Start XY]: Input the start I/O number of the QD64D2.
Figure 4.9 Setting example of [I/O assignment]
(b) [Switch setting for I/O and intelligent function module] screen
Click the on the [I/O assignment] screen to display the screen below and
set the switches from 1 to 5.
Entering the values in hexadecimal make the setting easier.
Change [Input format] to [HEX.] and enter values.
Figure 4.10 [Switch setting for I/O and intelligent function module] screen
POINT
Since [Error time output mode] and [H/W error time PLC operation mode] on the
[Switch setting for I/O and intelligent function module] screen are disabled to the
QD64D2, the settings are unnecessary.
4 - 12
4.5 Intelligent Function Module Switch Setting
Page 65

5
FUNCTIONS
CHAPTER5 FUNCTIONS
This chapter describes functions of the QD64D2.
5.1 Pulse Input and Count Methods
5.1.1 Types of the pulse input method
1
OVERVIEW
2
Pulse input
method
1 multiple of 1 phase
2 multiples of 1
phase
The pulse input method has six types as shown on Table 5.1.
This chapter describes I/O numbers (X/Y) of channel 1 only.
For I/O numbers (X/Y) of channel 2, refer to Section 3.3.1.
Set the count method with the intelligent function module switch setting of GX Developer
(refer to Section 4.5).
Table 5.1 Types of the pulse input method
Count timing
For addition count
For subtraction
count
For addition count
For subtraction
count
A
B
(and subtraction count
command (Y05))
A
B
(or subtraction count
command (Y05))
A
B
(and subtraction count
command (Y05))
A
B
(or subtraction count
command (Y05))
Counts on the rising edge ( ) of A.
B and the subtraction count command (Y05) are OFF.
Counts on the falling edge ( ) of A.
B or the subtraction count command (Y05) is ON.
Counts on the rising ( ) and falling ( ) edges of A.
B and the subtraction count command (Y05) are OFF.
Counts on the rising ( ) and falling ( ) edges of A.
B or the subtraction count command (Y05) is ON.
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
CW/CCW
1 multiple of 2
phases
For addition count
For subtraction
count
For addition count
For subtraction
count
A
B
A
B
A
B
A
B
Counts on the rising edge ( ) of A.
B is OFF.
A is OFF.
Counts on the rising edge ( ) of B.
When B is OFF, counts on the rising edge ( ) of A.
When B is OFF, counts on the falling edge ( ) of A.
5.1 Pulse Input and Count Methods
5.1.1 Types of the pulse input method
5 - 1
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 66

5
Pulse input
method
FUNCTIONS
Table 5.1 Types of the pulse input method (continued)
Count timing
2 multiples of 2
phases
4 multiples of 2
phases
For addition count
For subtraction
count
For addition count
For subtraction
count
POINT
When performing control with phase B pulse input or the subtraction count
command (Y05) at 1-phase pulse input, always turn OFF the unused signals.
If either of phase B pulse input or the subtraction count command (Y05) is ON,
subtraction count is performed at phase A pulse input.
A
B
A
B
A
B
A
B
When B is OFF, counts on the rising edge ( ) of A.
When B is ON, counts on the falling edge ( ) of A.
When B is ON, counts on the rising edge ( ) of A.
When B is OFF, counts on the falling edge ( ) of A.
When B is OFF, counts on the rising edge ( ) of A.
When B is ON, counts on the falling edge ( ) of A.
When A is ON, counts on the rising edge ( ) of B.
When A is OFF, counts on the falling edge ( ) of B.
When B is ON, counts on the rising edge ( ) of A.
When B is OFF, counts on the falling edge ( ) of A.
When A is OFF, counts on the rising edge ( ) of B.
When A is ON, counts on the falling edge ( ) of B.
5 - 2
5.1 Pulse Input and Count Methods
5.1.1 Types of the pulse input method
Page 67

5
FUNCTIONS
5.2 Selecting a Counter Format
The counter format has the following two types.
Select a counter format using the intelligent function module switch setting of GX
Developer. (Refer to Section 4.5.)
• Linear counter
• Ring counter
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
8
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
5.2 Selecting a Counter Format
5.1.1 Types of the pulse input method
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 3
Page 68

5
FUNCTIONS
5.2.1 Selecting the linear counter
(1) Linear counter operation
(a) For the linear counter, the counting is executed within the range of -2147483648
to 2147483647.
Present value
0
Subtraction
Overflow
Figure 5.1 Operation image of the linear counter
(b) The following functions can be used in combination.
• Counter value comparison function (Coincidence output function, continuous
comparison function)
• Coincidence detection interrupt function
• Preset function
• Latch counter function
Overflow
+2147483647
Addition
-2147483648
(2) Overflow error
(a) If the present value (Un\G12 and 13) exceeds the range of -2147483648 to
2147483647, an overflow error occurs.
(b) The following are processed at the overflow error.
• The counting stops. Even if a pulse is input at this status, the present value
(Un\G12 and 13) remains at -2147483648 or 2147483647.
• "1" is stored in the overflow detection flag (Un\G16).
• The error occurrence (X0D) turns ON, and the error code 100 is stored in the
error code (Un\G18).
5 - 4
(c) The overflow error can be cleared by setting the present value (Un\12 and 13)
within the range of -2147483648 to 2147483647 using the preset function.
When the overflow error is cleared, "0" is stored in the overflow detection flag
(Un\G16) and the counting can be restarted.
However, the error occurrence (X0D) remains ON and the stored value of the
error code (Un\G18) is held even after presetting.
Turn ON the error reset command (Y0D) to reset the error.
5.2 Selecting a Counter Format
5.2.1 Selecting the linear counter
Page 69

5
FUNCTIONS
1
5.2.2 Selecting the ring counter
(1) Ring counter operation
(a) For the ring counter, the counting is executed repeatedly within the range set by
the ring counter lower limit value (Un\G0 and 1) and the ring counter upper limit
value (Un\G2 and 3).
Overflow error does not occur.
Present value
+2147483647
Ring counter upper limit value (Un\G2 and 3)
0
Subtraction
Figure 5.2 Operation image of the ring counter
(b) The following functions can be used in combination.
• Counter value comparison function (Coincidence output function, continuous
comparison function)
• Coincidence detection interrupt function
• Preset function
• Latch counter function
Addition
Ring counter lower limit value (Un\G0 and 1)
-2147483648
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
5.2 Selecting a Counter Format
5.2.2 Selecting the ring counter
5 - 5
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 70

5
Range 1
+ 2147483647
Ring counter upper
limit value
FUNCTIONS
(2) Count range of the ring counter
(a) Count range is the following three types shown in Table 5.2
Count range
• Count range is determined by the ring counter lower limit value (Un\G0 and
1), the ring counter upper limit value (Un\G2 and 3) and the present value
(Un\G12 and 13).
• Range 1 and 2 in Table 5.2 are examples with the following setting.
Ring counter lower limit value (Un\G0 and 1) = -50000
Ring counter upper limit value (Un\G2 and 3) = 100000
Table 5.2 Count range of the ring counter
Setting condition
Ring counter lower
limit value
(Un\G0 and 1)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Ring counter upper
limit value
()()()
(Un\G2 and 3)
Ring counter lower
limit value
- 2147483648
Range 2
+ 2147483647
Ring counter upper
limit value
Ring counter lower
limit value
- 2147483648
Range 3
+ 2147483647
Ring counter upper
limit value
Ring counter lower
limit value
Subtraction
Count range
Subtraction
Count range
-2147483648 to -50000
100001 to 2147483647
Subtraction
-50000 to 99999
Addition
Addition
Addition
and
Ring counter lower
limit value
(()
(Un\G0 and 1)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
()
or
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
() ()
Ring counter lower
limit value
()
(Un\G0 and 1)
Ring counter upper
limit value
(Un\G2 and 3)
Ring counter lower
limit value
()
(Un\G0 and 1)
Ring counter upper
limit value
(Un\G2 and 3)
Ring counter upper
limit value
()
(Un\G2 and 3)
)
5 - 6
- 2147483648
Count range
-2147483648 to 2147483647
5.2 Selecting a Counter Format
5.2.2 Selecting the ring counter
The present value (Un\G12 and 13) is not included in the setting condition.
Page 71

5
FUNCTIONS
(b) Setting method of the count range
(c) When the ring counter lower limit value (Un\G0 and 1) and the ring counter upper
1) Select a count range from range 1 to 3.
2) Preset the present value (Un\G12 and 13) in accordance with the setting
condition. (Only when using a range 1 or 2)
• Set the preset value setting (Un\G4 and 5).
• Turn from OFF to ON the preset command (Y04), or turn ON the preset
input terminal (PRST) for external input.
3) Set a count range for the ring counter.
• Set the ring counter lower limit value (Un\G0 and 1) and the ring counter
upper limit value (Un\G2 and 3).
• Turn from OFF to ON the count enable command (Y06).
limit value (Un\G2 and 3) are set as shown below and turn from OFF to ON the
count enable command (Y06), a ring counter upper/lower limit value setting error
(Error code: 500) occurs.
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
POINT
Ring counter
lower limit value
()
(Un\G0 and 1)
• The present value (Un\G12 and 13) can be preset during counting.
However, the changes for the ring counter lower limit value (Un\G0 and 1)
and the ring counter upper limit value (Un\G2 and 3) become valid only
after turning from OFF to ON the count enable command (Y06).
• When changing the count range by the preset, to avoid miss-counting,
always turn OFF the count enable command (Y06) before changing it.
Ring counter
upper limit value
()
(Un\G2 and 3)
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
5.2 Selecting a Counter Format
5.2.2 Selecting the ring counter
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 7
Page 72

5
FUNCTIONS
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
The counter value comparison function compares the present value (Un\G12 and 13) to a
comparison point, and outputs the comparison result by the input signal (X01 to X06) or
the external output (EQU1 and EQU2).
The counter value comparison function has the following two types.
Select a counter value comparison function using the intelligent function module switch
setting. (Refer to Section 4.5.)
• Coincidence output function
• Continuous comparison function
5 - 8
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
Page 73

5
FUNCTIONS
5.3.1 Using the coincidence output function
Each channel has No.1 and No.2 comparison points. Each point individually compares to
the present value (Un\G12 and 13) and outputs the comparison result. (Refer to Table
5.3.)
One comparison point can be set for each No.1 and No.2.
Table 5.3 Coincidence output function
Signal and external output terminal used to output the
Comparison point
Input signal (X) External output
•Counter value large No.1 (X01)
Coincidence output No.1 point setting (Un\G6
No.1
to 7)
Coincidence output No.1 point setting (Un\G8
No.2
to 9)
In this section, I/O numbers (X/Y) and buffer memory addresses are listed for channel 1
and coincidence output No.1. For I/O numbers and buffer memory addresses used for
channel 2 and coincidence output No.2, refer to Section 3.3.1 and Section 3.4.1.
•Counter value coincidence
No.1 (X02)
•Counter value small (X03)
•Counter value large No.2 (X04)
•Counter value coincidence
No.2 (X05)
•Counter value small No.2 (X06)
comparison result
Coincidence output No.1
terminal (EQU1)
Coincidence output No.2
terminal (EQU2)
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
(1) Operation of coincidence output function
At the point where the coincidence
output No.1 point change request
(Un\G10) changes from "1" (Change
request) to "0" (No change request),
the comparison between the value set
in the coincidence output No.1 point
setting (Un\G6 and 7) (1000) and the
present value (Un\G12 and 13) starts.
Count enable command
(Y06)
Coincidence output
enable command
(Y03)
Coincidence output No.1
point change request
(Un\G10)
Coincidence output
No.1 point setting
(Un\G6 and 7)
Counter value small No.1
(X03)
Counter value coincidence No.1
(X02)
Coincidence output
No.1 terminal
(EQU1)
Coincidence signal
No.1 reset command
(Y01)
Counter value large No.1
(X01)
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
1
0
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
OPERATION
5
3)
1)
FUNCTIONS
1)1000
0
2)
t*1
4)
4)
4)
6)
t*1
5)
6
7
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
Configurator-CT)
Present value (Un\G12 and 13)
0
1
999
Figure 5.3 Operation example of the coincidence output function
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.1 Using the coincidence output function
1000
1001
*1 t 2ms
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 9
Page 74

5
FUNCTIONS
Table 5.4 Details of operation example of the coincidence output function
Number Description
With the following procedures, start the coincidence detection using the value
set in the coincidence output No.1 point setting (Un\G6 and 7).
(1) Write "1000" for the coincidence output No.1 point setting (Un\G6 and 7).
*1
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
(2) Write "1" (Change request) for the coincidence output No.1 point change
request (Un\G10).
(3) The setting value becomes valid when "1" (Change requet) turns to "0" (No
change request).
When the present value (Un\G12 and 13) is smaller than the coincidence output
No.1 point setting (Un\G6 and 7), the counter value small No.1 (X03) turns ON.
When outputting from the coincidence output No.1 terminal (EQU1) of external
device connector, turn ON the coincidence output enable command (Y03).
At the time, the coincidence output No.2 terminal (EQU2) is also enabled.
When the present value (Un\G12 and 13) is equal to the coincidence output
No.1 point setting (Un\G6 and 7), the counter value small No.1 (X03) turns OFF
and the counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) turns ON.
When the present value (Un\G12 and 13) is larger than the coincidence output
No.1 point setting (Un\G6 and 7), the counter value large No.1 (X01) turns ON.
The counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) remains ON until resetting it.
Turn ON the coincidence signal No.1 reset command (Y01) to reset the counter
value coincidence No.1 (X02). If the counter value coincidence No.1 (X02)
remains ON, the counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) cannot be output next
time.
* 1 If the operation in 1) is not executed, comparison with the values stored in the coincidence output
No.1 point setting (Un\G6 and 7) and the coincidence output No.2 point setting (Un\G8 and 9) is
not executed.
5 - 10
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.1 Using the coincidence output function
Page 75

5
FUNCTIONS
POINT
(1) At immediately after the power-on or resetting the programmable controller
CPU, the relation of the present value and the coincidence output point
setting is the following: "Present value = Coincidence output point setting = 0".
Therefore, the counter value coincidence (X02, X05, X12, and X15) of
channels that use the coincidence output function turns ON.
For channels that use the coincidence output function, always execute the
following procedures from 1 to 3.
For the programming method of the following procedures, refer to Section 7.3
and Section 7.4.
Procedure 1:
Set the following buffer memories and make sure that the coincidence output
point settings are other than "0"
Buffer memory address to be set Setting value
CH1 coincidence output No.1 point setting (Un\G6 and 7)
CH1 coincidence output No.2 point setting (Un\G8 and 9)
CH2 coincidence output No.1 point setting (Un\G206 and 207)
CH2 coincidence output No.2 point setting (Un\G208 and 209)
CH1 coincidence output No.1 point change request (Un\G10)
CH1 coincidence output No.2 point change request (Un\G11)
CH2 coincidence output No.1 point change request (Un\G210)
CH2 coincidence output No.2 point change request (Un\G211)
Procedure 2:
Turn from OFF to ON then OFF the following signals to turn OFF the counter
value coincidence (X02, X05, X12, and X15).
Other than "0"
1
1
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
Signals to be turned OFF ON OFF
CH1 coincidence signal No.1 reset command (Y01)
CH1 coincidence signal No.2 reset command (Y02)
CH2 coincidence signal No.1 reset command (Y11)
CH2 coincidence signal No.2 reset command (Y12)
*1 Make sure that ON time is longer than 2ms.
Procedure 3 (Only for external output):
After checking that the counter value coincidence (X02, X05, X12, and X15) is
OFF, turn ON the coincidence output enable (Y03 and Y13).
(2) Even if the coincidence signal No.1 reset command (Y01) is turned from ON
to OFF while the present value is equal to the coincidence output point
setting, the counter value coincidence (X02) and the coincidence output No.1
terminal (EQU1) turn ON again.
(3) When the counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) is turned from OFF to ON by
the coincidence detection process of the QD64D2, there may be cases where
the counter value large No.1 (X01) or the counter value small No.1 (X03)
turns ON.
*1
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.1 Using the coincidence output function
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 11
Page 76

5
FUNCTIONS
(2) Wiring check for the coincidence output No.1 terminal (EQU1) and the
coincidence output No.2 terminal (EQU2)
For the coincidence output function, the wiring cannot be checked with the
coincidence output test function (refer to Section 5.3.3).
Check the wiring referring to the following procedures.
Wiring check for the coincidence output No.1 terminal (EQU1) of channel 1 is
indicated below.
1) Set the same value for the coincidence output No.1 point setting (Un\G6 and 7)
and the present value (Un\G12 and 13).
2) Write "1" (Change request) for the coincidence output No.1 point change
request (Un\G10).
If the setting is other than "1", the value after changing the coincidence output
No.1 point setting (Un\G6 and 7) is not reflected, and the comparison is
performed with the value before change.
3) Turn ON or OFF the coincidence output enable command (Y03).
Note that in the case where the coincidence output No.1 point setting (Un\G6
and 7) is equal to the coincidence output No.2 point setting (Un\G8 and 9),
when the coincidence output enable command (Y03) is turned ON or OFF, the
coincidence output No.2 terminal (EQU2) also turns ON.
5 - 12
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.1 Using the coincidence output function
Page 77

5
FUNCTIONS
5.3.2 Using the continuous comparison function
Each channel has No.1 and No.2 comparison points. Each point individually compares to
the present value (Un\G12 and 13) and outputs the comparison result (refer to Table 5.5).
16 comparison points can be set for each No.1 and No.2.
Without rewriting the comparison point in the middle of the control, multiple coincidence
detections can be executed easily.
Table 5.5 Continuous comparison function
Signal and external output terminal used to output the
Comparison point
Input signal (X) External output
Continuous comparison No.1 point 1 setting
(Un\G54 and 55)
No.1
Continuous comparison No.1 point 16 setting
(Un\G84 and 85)
Continuous comparison No.2 point 1 setting
(Un\G104 and 105)
No.2
Continuous comparison No.2 point 16 setting
(Un\G134 and 135)
to
to
•Counter value large No.1 (X01)
•Counter value coincidence
No.1 (X02)
•Counter value small No.1 (X03)
•Counter value large No.2 (X04)
•Counter value coincidence
No.2 (X05)
•Counter value small No.2 (X06)
comparison result
Coincidence output No.1
terminal (EQU1)
Coincidence output No.2
terminal (EQU2)
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
In this section, I/O numbers (X/Y) and buffer memory addresses are listed for channel 1
and continuous comparison No.1. For I/O numbers and buffer memory addresses used for
channel 2 and continuous comparison No.2, refer to Section 3.3.1 and Section 3.4.1.
(1) Usage sequence of the continuous comparison No.1 point n setting
(Un\G54 to 85) and the continuous comparison No.2 point n setting
(Un\G104 to 135)
By the magnitude correlation of the following buffer memories, an order and range of
the continuous comparison points as comparison targets can be specified.
A: Continuous comparison No.1 start point setting (Un\G50)
B: Continuous comparison No.1 repeat point setting (Un\G51)
(a) When A < B
Example: A = 5, B = 10
567 8910
(b) When A > B
Example: A = 10, B = 3
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
10 11 12 16 1 2 3
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.2 Using the continuous comparison function
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 13
Page 78

5
FUNCTIONS
(c) When A = B
Example: A = 5, B = 5
5
After coincidence detection with the continuous comparison No.1 point 16 setting
(Un\G84 and 85) is completed, the comparison target returns to the continuous
comparison No.1 point 1 setting (Un\G54 and 55) again.
When temporarily stopping the continuous comparison, turn OFF the count enable
command (Y06) and so on, so that the present value (Un\G12 and 13) does not
change.
POINT
When restarting the continuous comparison function after stopping the function,
the comparison starts from the point set by the continuous comparison No.1 start
point setting (Un\G50).
5 - 14
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.2 Using the continuous comparison function
Page 79
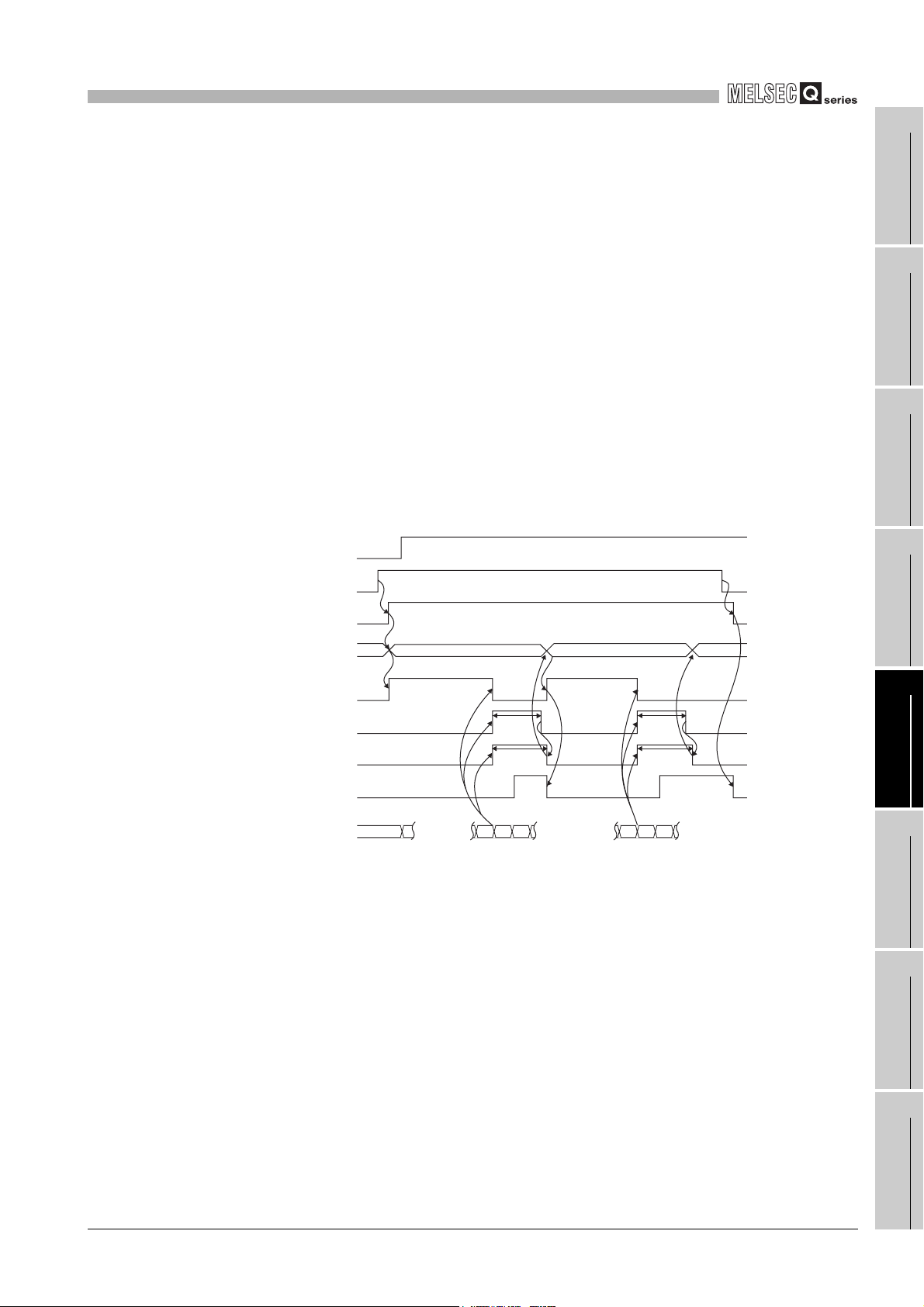
5
FUNCTIONS
(2) Operation of the continuous comparison function
Setting example for comparing between point 1 (1000) and point 2
(21000) repeatedly using the continuous comparison No.1 is indicated
below.
(a) Initial setting
Write the following values beforehand. *1
Continuous comparison No.1 start point setting (Un\G50) = 1
Continuous comparison No.1 repeat point setting (Un\G51) = 2
Continuous comparison No.1 ON time setting (Un\G52) = 1ms
Continuous comparison No.1 point 1 setting (Un\G54 and 55) = 1000
Continuous comparison No.1 point 2 setting (Un\G56 and 57) = 21000
* 1 The continuous comparison point can be set up to 16 points each. Beforehand, set all points to be
used. (Refer to Section 3.4.1)
If the settings of buffer memories for the continuous comparison No.1 start point setting (Un\G50)
and so on are improper, an error (Error code 201 to 222) occurs and the continuous comparison
cannot be started.
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
(b) Operation diagram
Count enable command
(Y06)
Continuous comparison
No.1 execution command
(Y09)
During continuous
comparison No.1 execution
(X09)
Continuous comparison No.1
point monitor during comparison
Coincidence output No.1 terminal
Counter value coincidence No.1
(Un\G86)
Counter value small No.1
(X03)
(EQU1)
(X02)
Counter value large No.1
(X01)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Figure 5.4 Operation example of the continuous comparison function
ON
OFF
1)
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
2)
021
1
3)
*1
t1
4)
t2 t2
*1 *1
1
0
999
1000 1001
*1 t1 = Continuous comparison No.1 ON time setting (Un\G52)
*2 t1<t2< (t1+1ms)
t1
20999 21000
*1
21001
6)
PROCEDURES AND
5)
4
5
6
7
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
Configurator-CT)
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.2 Using the continuous comparison function
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 15
Page 80

5
FUNCTIONS
Table 5.6 Details of operation example of the continuous comparison function
Number Description
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
[Execution request]
Turn ON the continuous comparison No.1 execution command (Y09).
[Continuous comparison start]
When the continuous comparison is ready, first comparison target will be the
continuous comparison No.1 point 1 setting (Un\G54 and 55) because "1" is set
in the continuous comparison No.1 start point setting (Un\G50).
When "1" is stored in the continuous comparison No.1 point monitor during
comparison (Un\G86), the during continuous comparison No.1 execution (X09)
turns ON and the continuous comparison starts.
[At counter value coincidence]
When the present value (Un\G12 and 13) is equal to the continuous comparison
No.1 point 1 setting, the following are processed.
1) The counter value small No.1 (X03) turns OFF and the counter value
coincidence No.1 (X02) and the coincidence output No.1 terminal (EQU1)
turn ON.
2) A coincidence detection interrupt to the programmable controller CPU is
generated.
[Process after the continuous comparison ON time setting]
After a set time of the continuous comparison No.1 ON time setting (Un\G52)
elapses, the coincidence output No.1 terminal (EQU1) turns OFF.
•Comparison target will be the continuous comparison No.1 point 2 setting
(Un\G56 and 57).
•"2" is stored in the continuous comparison No.1 point monitor during
comparison (Un\G86).
•The counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) turns OFF.
When OFF of the coincidence output No.1 terminal (EQU1) is detected, the
following are processed.
(After that, the comparison is repeated with the continuous comparison No.1
point 2 setting (Un\G56 and 57) and the continuous comparison No.1 point 1
setting (Un\G54 and 55) until the continuous comparison No.1 execution
command (Y09) is turned OFF. )
•Comparison target will be the continuous comparison No.1 point 1 setting
(Un\G54 and 55).
•"1" is stored in the continuous comparison No.1 point monitor during
comparison (Un\G86).
•The counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) turns OFF.
[Complete process]
When the coninuous comparison No.1 execution command (Y09) is turned OFF,
the following are processed and the during continuous comparison No.1
execution (X09) turns OFF.
•The counter value small No.1 (X03) turns OFF.
•The counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) turns OFF.
•The counter value large No.1 (X01) turns OFF.
The continuous comparison No.1 point monitor during comparison (Un\G86) is
held until the during continuous comparison No.1 execution (X09) turns ON.
5 - 16
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.2 Using the continuous comparison function
Page 81

5
FUNCTIONS
POINT
(1) When the count value coincides with the comparison point, an external output
is performed. Therefore, do not connect anything to the unused coincidence
output terminal (EQU).
(2) When the counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) is turned from OFF to ON by
the coincidence detection process of the QD64D2, there may be cases where
the counter value large No.1 (X01) or the counter value small No.1 (X03)
turns ON.
(3) If the continuous comparison No.1 execution command (Y09) is turned OFF
while outputting from the coincidence output No.1 terminal (EQU1), the output
stops regardless of the set time of the continuous comparison No.1 ON time
setting (Un\G52).
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
8
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.2 Using the continuous comparison function
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 17
Page 82

5
FUNCTIONS
(3) When comparing with 17 points or more of the continuous comparison
point setting
For the QD64D2, settable continuous comparison No.1 point n setting (Un\G54 to 85)
is up to 16 points each. Therefore, when comparing with 17 points or more, execute
the following procedures.
(a) Initial setting
Set the following and turn from OFF to ON the continuous comparison No.1
execution command (Y09).
• Continuous comparison No.1 start point setting (Un\G50) = 1
• Continuous comparison No.1 repeat point setting (Un\G51) = 16
*1
*1
• Set the continuous comparison points for point 1 through point 16 in the
following buffer memories.
Continuous comparison No.1 point 1 setting (Un\G54 and 55) to
Continuous comparison No.1 point 16 setting (Un\G84 and 85)
* 1 When starting from point 2 or later, set a value that is "Start point setting -1" for the repeat point
setting.
Example) When start point = 6, repeat point = 5
When starting from point 16, set the following.
Start point = 16, Repeat point = 1
Continuous comparison
No.1 point monitor
during comparison
(Un\G86)
Continuous comparison
No.1 point monitor
during comparison
(Un\G86)
(b) Rewriting data during comparison
Set the following when the continuous comparison No.1 point monitor during
comparison (Un\G86) becomes "2".
• Continuous comparison No.1 point setting (Un\G54 and 55) = Continuous
comparison point setting for the 17th point
After that, rewrite the data at every point change.
1234
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
No.1 point 1 setting
(Un\G54 and 55) to
the setting for
the 17th point.
Figure 5.5 Rewriting data during comparison
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
No.1 point 2 setting
(Un\G56 and 57) to
the setting for the
18th point.
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
No.1 point 3 setting
(Un\G58 and 59) to
the setting for
the 19th point.
After that, repeat
setting until the end point.
When the point monitor is "1", rewrite the point 16 setting.
15 16 1 2
5 - 18
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
No.1 point 14 setting
(Un\G80 and 81).
Figure 5.6 When the point monitor is "1"
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
No.1 point 15 setting
(Un\G82 and 83).
No.1 point 16 setting
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.2 Using the continuous comparison function
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
(Un\G84 and 85).
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
No.1 point 1 setting
(Un\G54 and 55).
Page 83

5
FUNCTIONS
Continuous comparison
No.1 point monitor
during comparison
(Un\G86)
(c) Process after completion of comparison at end point
1) When repeatedly comparing from the 1st point
Set the following after setting all continuous comparison point settings for the
17th point and later.
• Continuous comparison No.1 point n setting (Un\G54 to 85) of
(Continuous comparison No.1 point monitor during comparison (Un\G86)
-1) = Continuous comparison point setting of the 1st point and later
Figure 5.7 is the example when comparing with 19 points.
Comparison end point
3456
After that, repeat
setting until the end point.
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
No.1 point 2 setting
(Un\G56 and 57) to
the setting for the
18th point.
Figure 5.7 When repeatedly comparing from the 1st point
2) When stopping the continuous comparison
Turn from ON to OFF the continuous comparison No.1 execution command
(Y09) under the following condition.
Figure 5.8 is the example when comparing with 19 points.
Continuous comparison
No.1 point monitor
during comparison
(Un\G86)
Figure 5.8 When stopping the continuous comparison
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
No.1 point 3 setting
(Un\G58 and 59) to
the setting for the
19th point.
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
No.1 point 4 setting
(Un\G60 and 61) to
the setting for the
1st point.
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
No.1 point 5 setting
(Un\G62 and 63) to
the setting for the
2nd point.
• (Continuous comparison No.1 point monitor during comparison (Un\G86)
-1) = Comparison end point
Comparison end point
Comparison end point + 1
*2
234
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
No.1 point 2 setting
(Un\G56 and 57) to
the setting for the
18th point.
*1 When the present value may coincide with the comparison point of the
(comparison end point + 1) before stopping the continuous comparison, store
a value which does not perform a coincidence output (for example: -1) to the
(comparison end point + 1) before completing the coincidence detection at
the comparison end point.
*2 In the case of the comparison end point is 16, turn from ON to OFF the
execution command when the point monitor changes to 1.
Rewrite the
continuous
comparison
No.1 point 3 setting
(Un\G58 and 59) to
the setting for the
19th point.
Turn from OFF to ON
the continuous
comparison No.1
execution command
(Y09). *1
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.2 Using the continuous comparison function
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 19
Page 84

5
FUNCTIONS
Table 5.7 shows the example of continuous comparison point setting for 19 points.
Table 5.7 Example of continuous comparison point setting
Continuous
comparison
order
1 100 Continuous comparison No.1 point 1 setting
2 110 Continuous comparison No.1 point 2 setting
3 120 Continuous comparison No.1 point 3 setting
4 130 Continuous comparison No.1 point 4 setting
5 140 Continuous comparison No.1 point 5 setting
6 150 Continuous comparison No.1 point 6 setting
7 160 Continuous comparison No.1 point 7 setting
8 170 Continuous comparison No.1 point 8 setting
9 180 Continuous comparison No.1 point 9 setting
10 190 Continuous comparison No.1 point 10 setting
11 200 Continuous comparison No.1 point 11 setting
12 210 Continuous comparison No.1 point 12 setting
13 220 Continuous comparison No.1 point 13 setting
14 230 Continuous comparison No.1 point 14 setting
15 240 Continuous comparison No.1 point 15 setting
16 250 Continuous comparison No.1 point 16 setting
17 260 Continuous comparison No.1 point 1 setting
18 270 Continuous comparison No.1 point 2 setting
19 280 Continuous comparison No.1 point 3 setting
---- -1
Continuous
comparison
point setting
Target continuous comparison No.1 point n setting
Continuous comparison No.1 point 4 setting
(Set "-1" so that the coincidence output is not performed
when the continuous comparison function is stopped. )
5 - 20
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.2 Using the continuous comparison function
Page 85

5
FUNCTIONS
(4) Continuous comparison No.m point n setting interval
For the interval of the continuous comparison No.m point n setting, set the values to
satisfy the following conditions 1 and 2.
(a) Condition 1:
1
OVERVIEW
2
Interval of (Continuous comparison
No.m point n setting)
(Continuous comparison No.m
()
ON time setting [ms])
1[ms]
Input pulse speed [pps]
1000
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
(b) Condition 2 (Applies only when the derating of external coincidence output is less
than 100% (Refer to Section 3.1.2)):
Interval of (Continuous comparison
No.m point n setting)
SPECIFICATIONS
Continuous comparison No.m
ON time setting [ms]
(
For example, when "Continuous comparison No.1 ON time setting" = 10[ms], "ON
ratio" = 50[%], "Input pulse speed" = 4[Mpps] = 4000000[pps], interval of the
continuous comparison No.1 point n setting (Un\G54 to 85) is the following.
Condition 1:
Interval of (Continuous comparison
No.1 point n setting (Un\G54 to 85))
Condition 2:
Interval of (Continuous comparison
No.1 point n setting (Un\G54 to 85))
100[%]
ON ratio [%]
10[ms] 1[ms]
(
44000
10[ms]
(
80000
)
100[%]
Input pulse speed [pps]
)
50[%]
)
1000
4000000[pps]
1000
4000000[pps]
1000
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
(To satisfy the conditions 1 and 2, set the value of condition 2.)
Interval of the continuous comparison No.1 point n setting (Un\G54 to 85) 80000
POINT
"1ms" in the above condition 1 is a time for the comparison target change in the
QD64D2. Always set the sequence program to satisfy the condition 1.
When the count value is coincided within the time, the QD64D2 may not detect
the coincidence depending on the timing of the count value coincidence and the
comparison target change.
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.2 Using the continuous comparison function
5 - 21
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 86

5
FUNCTIONS
5.3.3 Using the coincidence output test function
Use the coincidence output test function to check the wiring of the coincidence output No.1
terminal (EQU1) and the coincidence output No.2 terminal (EQU2) when selecting the
continuous comparison function.
When using the continuous comparison function, the coincidence output No.1 terminal
(EQU1) and the coincidence output No.2 terminal (EQU2) automatically turn OFF.
Therefore, check the wiring using the coincidence output test function.
(1) Operation of coincidence output test function
Coincidence output No.1 test command
(Y0B)
ON
OFF
1) 2)
Coincidence output No.1 terminal
External I/O status monitor. b4
Figure 5.9 Operation example of the coincidence output test function
Number Description
1)
2)
(EQU1)
(Un\G17)
Table 5.8 Details of operation example of coincidence output test function
When the coincidence output No.1 test command (Y0B) is turned ON, the
following are executed.
•The coincidence output No.1 terminal (EQU1) turns ON.
•Bit 4 (Coincidence output No.1 output status) of the external I/O status monitor
(Un\G17) turns ON.
When the coincidence output No.1 test command (Y0B) is turned OFF, the
following are executed.
•The coincidence output No.1 terminal (EQU1) turns OFF.
•Bit 4 (Coincidence output No.1 output status) of the external I/O status monitor
(Un\G17) turns OFF.
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
(2) Execution condition of the coincidence output test function
5 - 22
(a) Before executing the coincidence output test function, check that the following
signals are all OFF.
• Count enable command (Y06)
• Continuous comparison No.1 execution command (Y09)
• During continuous comparison No.1 execution (X09)
• Continuous comparison No.2 execution command (Y0A)
• During continuous comparison No.2 execution (X0A)
If the coincidence output test is attempted while any of the above signal is ON, the
coincidence output No.m test output not possible warning (Warning code: 31 and
32) occurs.
(b) Counting cannot be started while the coincidence output test command is ON.
Do not turn ON the count enable command (Y06).
If it is turned ON, a count enable execution not possible error (Error code: 300)
occurs.
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.3 Using the coincidence output test function
Page 87

5
FUNCTIONS
(c) Do not turn ON the continuous comparison execution command while the
POINT
coincidence output test command is ON.
If the continuous comparison execution command is turned ON while the test
command is ON, a continuous comparison No.m execution not possible error
(Error code: 311 and 312) occurs.
• Even if the coincidence output No.1 test command (Y0B) and the
coincidence output No.2 test command (Y0C) are turned ON, the counter
value coincidence No.1 (X02) and the counter value coincidence No.2
(X05) do not turn ON/OFF. (Coincidence detection interrupt also does not
occur.)
• The coincidence output test function cannot be used when selecting the
coincidence output function.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
8
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.3 Using the coincidence output test function
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 23
Page 88

5
FUNCTIONS
5.3.4 Coincidence detection interrupt function
Use the coincidence detection interrupt function to request an interrupt to the
programmable controller CPU when a coincidence is detected, and start up the interrupt
program.
(a) Up to 16-point interrupt factors (SI) are allowed for a single MELSEC-Q series
intelligent function module.
As shown in Table 5.9, the QD64D2 has 4-point interrupt factors (SI) for
coincidence detection.
Table 5.9 List of interrupt factors
SI No. Interrupt factor
0
1
2
3
4 to 15 Reserved
Channel 1: Coincidence detection of coincidence output No.1 point setting or continuous
comparison No.1 point m setting
Channel 1: Coincidence detection of coincidence output No.2 point setting or continuous
comparison No.2 point m setting
Channel 2: Coincidence detection of coincidence output No.1 point setting or continuous
comparison No.1 point m setting
Channel 2: Coincidence detection of coincidence output No.2 point setting or continuous
comparison No.2 point m setting
I/O signals
Internal processing
of the programmable
controller CPU
Timing of interrupt signal generation
Counter value
coincidence No.1
(X02)
Coincidence signal
No.1 reset command
(Y01)
Interrupt request
Interrupt request clear
Program processing in the
programmable controller CPU
*1 The coincidence signal No.1 reset command (Y01) is only used for the coincidence output function.
For the continuous comparison function, the counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) automatically
turns OFF after elapsing the set time of the continuous comparison No.1 ON time setting (Un\G52).
Figure 5.10 Timing of interrupt signal generation
Interrupt program processing
*1
(b) It takes approximately 150 s from when the QD64D2 detects a coincidence until
it requests an interrupt to the programmable controller CPU.
(c) Select [PLC parameter] - [PLC system] - [Intelligent function module setting] -
[Interrupt pointer settings] to set the interrupt factors (SI) of the QD64D2 and
interrupt pointers of the programmable controller CPU.
5 - 24
1) [PLC side] [Interrupt pointer start No.]
Set the start interrupt pointer number of the programmable controller CPU.
Setting range: 50 to 255
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.4 Coincidence detection interrupt function
Page 89

5
FUNCTIONS
1
2) [PLC side] [Interrupt pointer No. of module]
Set the number of interrupt factors (SI).
Setting range: 1 to 4
3) [Intelli. module side] [Start I/O No.]
Set the start I/O number of the QD64D2.
Setting range: 0000 to 0FE0(
4) [Intelli. module side] [Start SI No.]
Set the start interrupt factor (SI) of the QD64D2.
Setting range: 0 to 3
The following shows a setting example where SI 0 to 3 of the QD64D2 in the slot
of start I/O No.20 are assigned to interrupt pointers I50 to I53.
H)
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
Figure 5.11 Interrupt pointer setting example (GX Developer screen)
(d) The following two methods are available for using particular SI numbers only.
1) Using the interrupt pointer setting with parameters
According to the setting in the [Intelligent function module interrupt pointer
setting] dialog box, only the interrupt factors starting from the [Start SI No.] and
equivalent to the number set at [Interrupt pointer No. of module] are used.
For example, if the [Start SI No.] and [Interrupt pointer No. of module] are set to
1 and 2 respectively, only SI 1 and 2 will be used.
The interrupt function is not used if the interrupt pointer setting with parameters
has not been made.
2) Using the IMASK instruction from the sequence program
With the IMASK instruction, whether to enable or disable (interrupt mask) the
interrupt program execution can be set to each interrupt pointer number.
For details of the IMASK instruction, refer to the following manual.
MELSEC-Q/L Programming Manual (Common Instruction)
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.4 Coincidence detection interrupt function
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 25
Page 90

5
FUNCTIONS
POINT
• Coincidence detection interrupt occurs at the rising edge (OFF ON) of
the counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) or the counter value
coincidence No.2 (X05). Therefore, next interrupt request does not occur
unless the counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) and the counter value
coincidence No.2 (X05) are reset and turned OFF.
• When using the coincidence output function, the counter value
coincidence No.1 (X02) and the counter value coincidence No.2 (X05)
turns ON immediately after the power-on or resetting the programmable
controller CPU; however, a coincidence detection interrupt does not
occur.
For resetting method of the counter value coincidence No.1 (X02) and the
counter value coincidence No.2 (X05), refer to Section 5.3.1.
5 - 26
5.3 Using the Counter Value Comparison Function
5.3.4 Coincidence detection interrupt function
Page 91

5
FUNCTIONS
5.4 Using the Preset Function
Use the preset function to rewrite the present value (Un\G12 and 13) to any value (preset
value) and start counting pulses from the value.
The following two methods are available for presetting.
• Turn ON the preset command (Y04) by the sequence program.
• Turn ON the preset input terminal (PRST) of external input.
In (1) and (2) below, I/O numbers (X/Y) and buffer memory addresses are listed for
channel 1. For I/O numbers and buffer memory addresses used for channel 2 , refer to
Section 3.3.1 and Section 3.4.1.
(1) Operation when turning ON the preset command (Y04) by the sequence
program
Turn ON the preset command (Y04) by the sequence program to execute preset.
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
Count enable command
(Y06)
Counter input pulse
Preset value setting
(Un\G4 and 5)
Preset command
(Y04)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Figure 5.12 Operation example of the preset function by the sequence program
Table 5.10 Details of operation example of the preset function by the sequence program
Number Description
1)
2)
ON
OFF
1)1)
0
ON
OFF
0
Write any value in the preset value setting (Un\G4 and 5) of the QD64D2 in 32-
bit binary format.
At the rising edge (OFF ON) of the preset command (Y04), the preset value
setting (Un\G4 and 5) is stored in the present value (Un\G12 and 13).
The preset can be executed regardless of the ON/OFF status of the count
enable command (Y06).
1000
1001
20001000
t*t*
2)2)
to
1067106610651002
20012000
2002 2003 2004 2005
*t 2ms
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
5.4 Using the Preset Function
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 27
Page 92

5
FUNCTIONS
(2) Operation when presetting by the external control signal
Apply ON voltage to the preset input terminal (PRST) for external input to execute
preset. Operation example is indicated in Figure 5.13.
Count enable command
(Y06)
Counter input pulse
Preset value setting
(Un\G4 and 5)
Preset command
(Y04)
Preset input terminal
(PRST)
External preset
request detection
(X08)
External preset request
detection reset command
(Y08)
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
1)
1000
t*
0
1000
Figure 5.13 Operation example of the preset function by external control signal
Table 5.11 Details of operation example of the preset function by external control signal
Number Description
1)
Write any value in the preset value setting (Un\G4 and 5) of the QD64D2 in 32-
bit binary format.
When the preset input terminal (PRST) is turned from OFF to ON, the preset
2)
value setting (Un\G4 and 5) is stored in the present value (Un\G12 and 13).
The preset can be executed regardless of ON/OFF status of the count enable
command (Y06).
While the external preset request detection (X08) is ON, the preset cannot be
3)
executed by turning ON the preset command (Y04) or the preset input terminal
(PRST).
When the external preset request detection reset command (Y08) is turned ON
4)
and the external preset request detection (X08) turns OFF, the preset can be
executed.
1)
20000
t*t*
2)2) 2)
to to
10671066106510021001
20012000
t*
3)
3)
4)
t*
2023 2024 2025 2000 2001
*t 2ms
5 - 28
POINT
When the external preset request detection (X08) is OFF, both the preset
command (Y04) and the preset input terminal (PRST) are valid.
5.4 Using the Preset Function
Page 93

5
FUNCTIONS
5.5 Using the Latch Counter Function
The latch counter function latches the present value (Un\G12 and 13) to the latch count
value (Un\G14 and 15).
The following two methods are available for latch operation.
• Turn ON the latch counter execution command (Y07) by the sequence program.
• Turn ON the latch counter input terminal (LATCH) of external input.
In (1) below, I/O numbers (X/Y) and buffer memory addresses are listed for channel 1. For
I/O numbers and buffer memory addresses used for channel 2 , refer to Section 3.3.1 and
Section 3.4.1.
(1) Operation of the latch counter function
Count enable command
(Y06)
ON
OFF
150
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
4)
SPECIFICATIONS
4
130
Present value
(Un\G12 and 13)
Latch counter
execution command
(Y07)
Latch counter
input terminal
(LATCH)
Latch count value
(Un\G14 and 15)
100
50
0
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
150
100
50
0
100
50
0
1)
t*
2)
0
Figure 5.14 Operation example of the latch counter function
1) 3)
t*
50
3)
100
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
OPERATION
5
1)
FUNCTIONS
6
t*
t*
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
Configurator-CT)
130
7
PROGRAMMING
8
*t 2ms
5.5 Using the Latch Counter Function
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 29
Page 94

5
FUNCTIONS
Table 5.12 Details of operation example of the latch counter function
Number Description
When the latch counter execution command (Y07) is turned from OFF to ON,
1)
2)
3)
4)
the present value (Un\G12 and 13) is stored in the latch count value (Un\G14
and 15).
When the latch counter input terminal (LATCH) is turned from OFF to ON, the
present value (Un\G12 and 13) is stored in the latch count value (Un\G14 and
15).
While the latch counter execution command (Y07) or the latch counter input
terminal (LATCH) is ON, the latch counter function cannot be executed.
The latch counter function can be executed regardless of ON/OFF status of the
count enable command (Y06).
5 - 30
5.5 Using the Latch Counter Function
Page 95

5
FUNCTIONS
5.6 Response Delay Time
In the QD64D2, a response delays due to the cause indicated in (a) and (b) below.
1
(a) Scan time of the sequence program
It affects the delay of I/O signal.
Use the direct access input (DX) or the direct access output (DY) to minimize the
delay.
(b) Control cycle (1ms) of the QD64D2
Up to 2ms (1 control cycle 2) of delay occurs until the QD64D2 reads out the
output signal and buffer memory updated by the sequence program and
completes processing.
Update timing of the I/O signal and buffer memory varies within the range of a
control cycle.
For example, the following is the maximum delay time until the QD64D2 executes the latch
counter function and updates the latch count value after the latch counter execution
command (Y07) is turned ON by the sequence program.
Maximum delay time [ms] = [Time of (a)] + [Maximum time of (b)]
= Sequence program scan time + 2 [ms]
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
5.6 Response Delay Time
5 - 31
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 96

6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-CT)
CHAPTER6 UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-CT)
6.1 Utility Package Functions
Table 6.1 shows the functions of the utility package.
Table 6.1 Utility package (GX Configurator-CT) functions list
Function Description Reference
(1) Make the initial settings for each channel to operate the QD64D2.
Set the values of the items where initial settings are required.
• CH Ring counter lower limit
• CH Ring counter upper limit
• CH Preset value setting
• CH Coincidence output No.1 point setting
• CH Coincidence output No.2 point setting
• CH Coincidence output No.1 point change request
• CH Coincidence output No.2 point change request
Initial setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.1 start point setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.1 repeat point setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.1 ON time setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.1 point n setting (n: 1 to 16)
• CH Continuous comparison No.2 start point setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.2 repeat point setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.2 ON time setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.2 point n setting (n: 1 to 16)
Section 6.4
Auto refresh
(2) Data with initial settings are registered to programmable controller CPU parameters and are
automatically written to the QD64D2 when the programmable controller CPU is in RUN.
(1) Set the buffer memory of the QD64D2 to which auto refresh is to be performed for each
channel.
• CH Present value
• CH Latch count value
• CH Overflow detection flag
• CH External I/O status monitor
• CH Error code
• CH Warning code
• CH Continuous comparison No.1 point monitor during comparison
• CH Continuous comparison No.2 point monitor during comparison
(2) The values stored in the QD64D2 buffer memory with auto refresh setting are automatically
read when the programmable controller CPU executes the END instruction.
Section 6.5
6 - 1
6.1 Utility Package Functions
Page 97

6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-CT)
Table 6.1 Utility package (GX Configurator-CT) functions list
Function Description Reference
(1) Monitors/tests the following buffer memories and I/O signals of the QD64D2.
• Y device
• CH Ring counter lower limit
• CH Ring counter upper limit
• CH Preset value setting
• CH Coincidence output No.1 point setting
• CH Coincidence output No.2 point setting
• CH Coincidence output No.1 point change request
• CH Coincidence output No.2 point change request
• CH Continuous comparison No.1 start point setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.1 repeat point setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.1 ON time setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.1 point n setting (n: 1 to 16)
Monitor/Test
• CH Continuous comparison No.2 start point setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.2 repeat point setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.2 ON time setting
• CH Continuous comparison No.2 point n setting (n: 1 to 16)
(2) Monitors the following buffer memories of the QD64D2.
• X device
• CH Present value
• CH Latch count value
• CH Overflow detection flag
• CH External I/O status monitor
• CH Error code
• CH Warning code
• CH Continuous comparison No.1 point monitor during comparison
• CH Continuous comparison No.2 point monitor during comparison
Section 6.6
1
2
SYSTEM
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
6.1 Utility Package Functions
6 - 2
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
PROGRAMMING
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 98

6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-CT)
6.2 Installing and Uninstalling the Utility Package
For how to install or uninstall the utility package, refer to "Method of installing the
MELSOFT Series" included in the utility package.
6.2.1 Handling precautions
The following explains the precautions on using the utility package.
(1) For safety
Since the utility is add-in software for GX Developer, read "SAFETY PRECAUTIONS"
and the basic operating procedures in the GX Developer Operating Manual.
(2) About installation
GX Configurator-CT is add-in software for GX Developer Version 4 or later.
Therefore, GX Configurator-CT must be installed on the personal computer that has
already GX Developer Version 4 or later installed.
(3) Screen error of [Intelligent function module utility]
Insufficient system resource may cause the screen to be displayed inappropriately
while using the Intelligent function module utility.
If this occurs, close the Intelligent function module utility, GX Developer (program,
comments, etc.), and other applications, and then start GX Developer and Intelligent
function module utility again.
(4) To start the [Intelligent function module utility]
(a) In GX Developer, select "QCPU (Q mode)" for [PLC series] and specify a project.
If any other than "QCPU (Q mode)" is selected for [PLC series], or if no project is
specified, the [Intelligent function module utility] will not start.
(b) Multiple [Intelligent function module utility] can be started.
However, [Open parameters] and [Save parameters] operations under [Intelligent
function module parameter] are allowed for one [Intelligent function module utility]
only. Only the [Monitor/test] operation is allowed for the other utilities.
(5) Switching between two or more Intelligent function module utilities
When two or more Intelligent function module utility screens cannot be displayed side
by side, select a screen to be displayed on the top of others using the task bar.
6 - 3
(6) Number of parameters that can be set in GX Configurator-CT
When multiple intelligent function modules are mounted, set the parameters within the
maximum number of settable parameters shown on the next page.
6.2 Installing and Uninstalling the Utility Package
6.2.1 Handling precautions
Page 99

6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-CT)
Table 6.2 Maximum number of settable parameters using GX Configurator
When intelligent function modules
are mounted to:
Q00J/Q00/Q01CPU 512 256
Q02/Q02H/Q06H/Q12H/Q25HCPU 512 256
Q02PH/Q06PH/Q12PH/Q25PHCPU 512 256
Q12PRH/Q25PRHCPU 512 256
Q00UJ/Q00U/Q01UCPU 512 256
Q02UCPU 2048 1024
Q03UD/Q04UDH/Q06UDH/Q10UDH/
Q13UDH/Q20UDH/Q26UDH/
Q03UDE/Q04UDEH/Q06UDEH/
Q10UDEH/Q13UDEH/Q20UDEH/
Q26UDEHCPU
Q50UDEH/Q100UDEHCPU Use prohibited Use prohibited
MELSECNET/H remote I/O station 512 256
Maximum number of parameter settings
Initial setting Auto refresh setting
4096 2048
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
For example, if multiple intelligent function modules are mounted to the remote I/O
station, configure the settings in GX Configurator so that the number of parameters
set for all the intelligent function modules does not exceed the limit of the remote I/O
station. Calculate the total number of parameter settings separately for the initial
setting and for the auto refresh setting.
The number of parameters that can be set for one module in GX Configurator-CT is
as shown below.
Table 6.3 Number of settable parameters per module
Target module Initial setting Auto refresh setting
QD64D2 6 (fixed) 16 (Max.)
Example) Counting the number of parameter settings in Auto refresh setting
This one row is counted as one
setting.
Blank rows are not counted.
Count up all the setting items on this
screen, and add the total to the
number of settings for other intelligent
function modules to get a grand total.
Figure 6.1 Numeration for the number of parameters set in Auto refresh setting
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
5
6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX
7
SPECIFICATIONS
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
Configurator-CT)
6.2 Installing and Uninstalling the Utility Package
6.2.1 Handling precautions
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
6 - 4
Page 100

6
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-CT)
6.2.2 Operating environment
This section explains the operating environment of the personal computer that runs GX
Configurator-CT.
Item Description
Installation (Add-in) target
Computer
CPU
Required
memory
Hard disk
*3
space
Display
For installation 65 MB or more
For operation 10 MB or more
Table 6.4 Operating environment of the personal computer
*1
Add-in to GX Developer Version 4 (English version) or later.
Windows -based personal computer
Refer to Table 6.5 "Operating system and performance required for personal
computer".
800 600 dots or more resolution
Microsoft Windows 95 Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows 98 Operating System (English version)
*4
*2
Basic software
Microsoft Windows Millennium Edition Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows NT Workstation Operating System Version 4.0 (English
version)
Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows XP Professional Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows XP Home Edition Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows Vista Home Basic Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows Vista Home Premium Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows Vista Business Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows Vista Enterprise Operating System (English version)
* 1 Install GX Configurator-CT in GX Developer Version 4 or higher in the same language.
GX Developer (English version) and GX Configurator-CT (Japanese version) cannot be used in
combination, and GX Developer (Japanese version) and GX Configurator-CT (English version)
cannot be used in combination.
* 2 GX Configurator-CT is not applicable to GX Developer Version 3 or earlier.
* 3 At least 15GB is required for Windows Vista .
* 4 Resolution of 1024 X 768 dots or more is recommended for Windows Vista .
6 - 5
6.2 Installing and Uninstalling the Utility Package
6.2.2 Operating environment
 Loading...
Loading...