Mitsubishi M37280MK-XXXSP, M37280MF-XXXSP, M37280EKSP Datasheet

PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
1. DESCRIPTION
The M37280MF–XXXSP and M37280MK-XXXSP are single-chip
microcomputers designed with CMOS silicon gate technology. They
have a OSD function and a data slicer function, so it is useful for a
channel selection system for TV with a closed caption decoder.
The feautures of the M37280EKSP is similar to those of the
M37280MK-XXXSP except that the chip has a built-in PROM which
can be written electrically . The difference between M37280MK-XXXSP
and M37280MF-XXXSP are the ROM size and RAM size. Accordingly, the following descriptions will be for the M37280MK-XXXSP.
2. FEATURES
●Number of basic instructions .................................................... 71
●Memory size
ROM ..................... 60K bytes (M37280MF-XXXSP)
80K bytes (M37280MK-XXXSP,
M37280EKSP)
RAM .....................1024 bytes (M37280MF-XXXSP)
1472 bytes (M37280MK-XXXSP,
M37280EKSP)
ROM correction memory............................ 64 bytes
●Minimum instruction execution time
.........................................0.5 µs (at 8 MHz oscillation frequency)
●Power source voltage ................................................. 5 V ± 10 %
●Subroutine nesting ............................................. 128 levels (Max.)
●Interrupts ....................................................... 19 types, 16 vectors
●8-bit timers .................................................................................. 6
●Programmable I/O ports (Ports P0, P1, P2, P30, P31) ............. 26
●Input ports (Ports P40–P46, P63, P64, P70–P72) ...................... 12
●Output ports (Ports P32, P47, P5, P60–P62, P65–P67) .............. 16
●12 V withstand ports ................................................................... 8
●LED drive ports ........................................................................... 2
●Serial I/O ............................................................8-bit ✕ 1 channel
●Multi-master I2C-BUS interface .............................. 1 (2 systems)
●A-D converter (8-bit resolution)....................................8 channels
●PWM output circuit......................................................... 8-bit ✕ 8
●Power dissipation
In high-speed mode .........................................................165 mW
(at VCC = 5.5V, 8 MHz oscillation frequency, CRT on, and Data
slicer on)
In low-speed mode .........................................................0.33 mW
(at VCC = 5.5V, 32 kHz oscillation frequency)
●ROM correction function
●Closed caption data slicer
●OSD function
Display characters .... 32 characters ✕ 16 lines + RAM font (1 character)
Kinds of characters ......... 510 kinds + 62 kinds +1 kind
(Coloring unit) (a character) (a dot) (a dot)
Triple layer function.......................................................................
2 layers selected from CC/CDOSD/OSD mode + RAM font layer
Character display area.............. CC/CDOSD mode: 16 ✕ 26 dots
Kinds of character sizes.................... CC mode/RAM font: 4 kinds
Kinds of character colors ..............................................................
64 colors (4 adjustment levels for each R, G, B)
Coloring unit............ dot, character, character background, raster
Blanking output OUT1, OUT2
Display position
Horizontal: 256 levels Vertical :1024 levels
(RAM font can be set independently)
Attribute ........................................................................................
CC mode: smooth italic, underline, flash, automatic solid space
OSD mode: border, shadow
Window/Blank function
(CC/OSD mode)(CDOSD mode)(RAM font)
OSD mode/RAM font: 16 ✕ 20 dots
OSD/CDOSD mode: 14 kinds
3. APPLICA TION
TV with a closed caption decoder
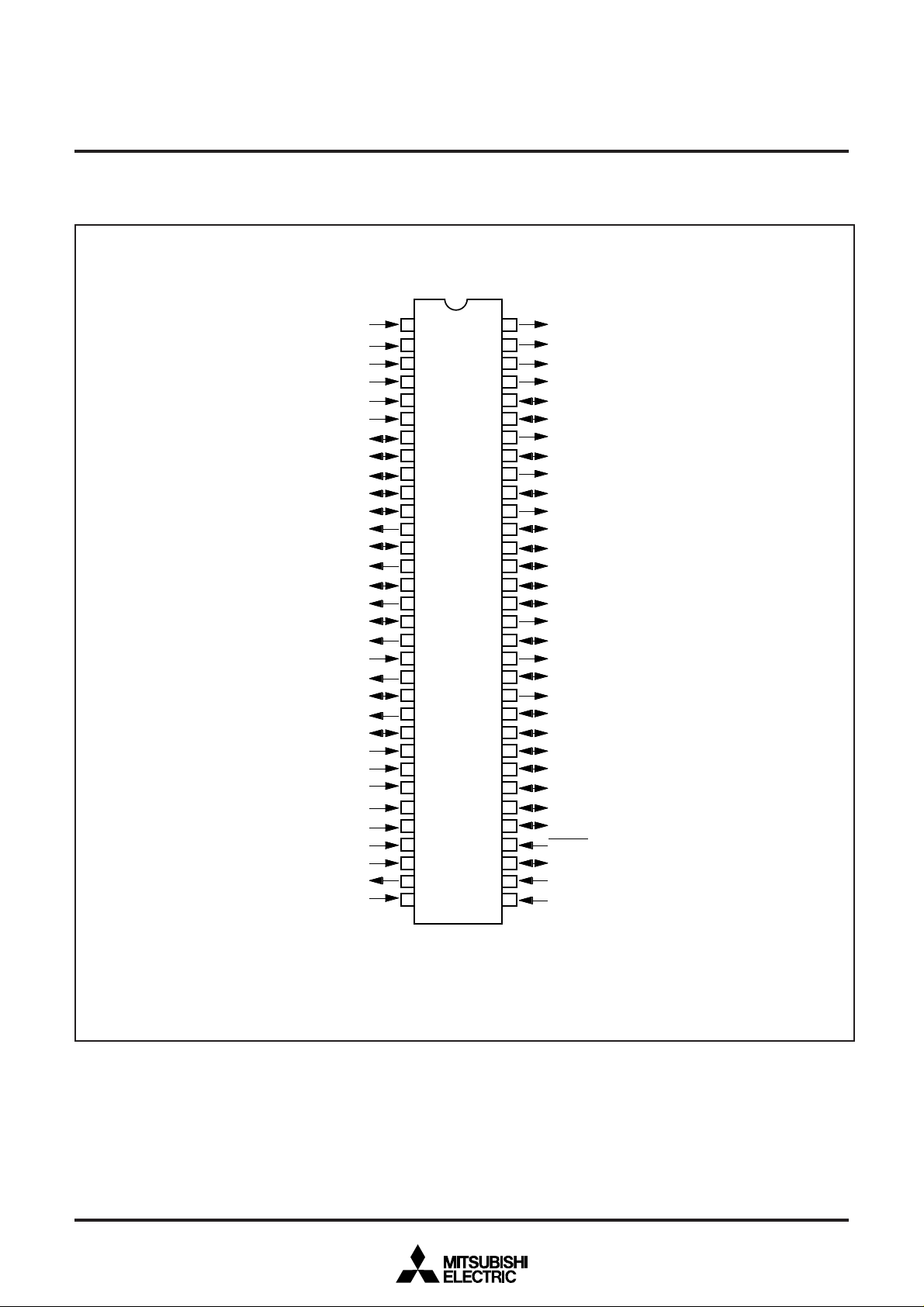
4. PIN CONFIGURATION
Refer to page 3.
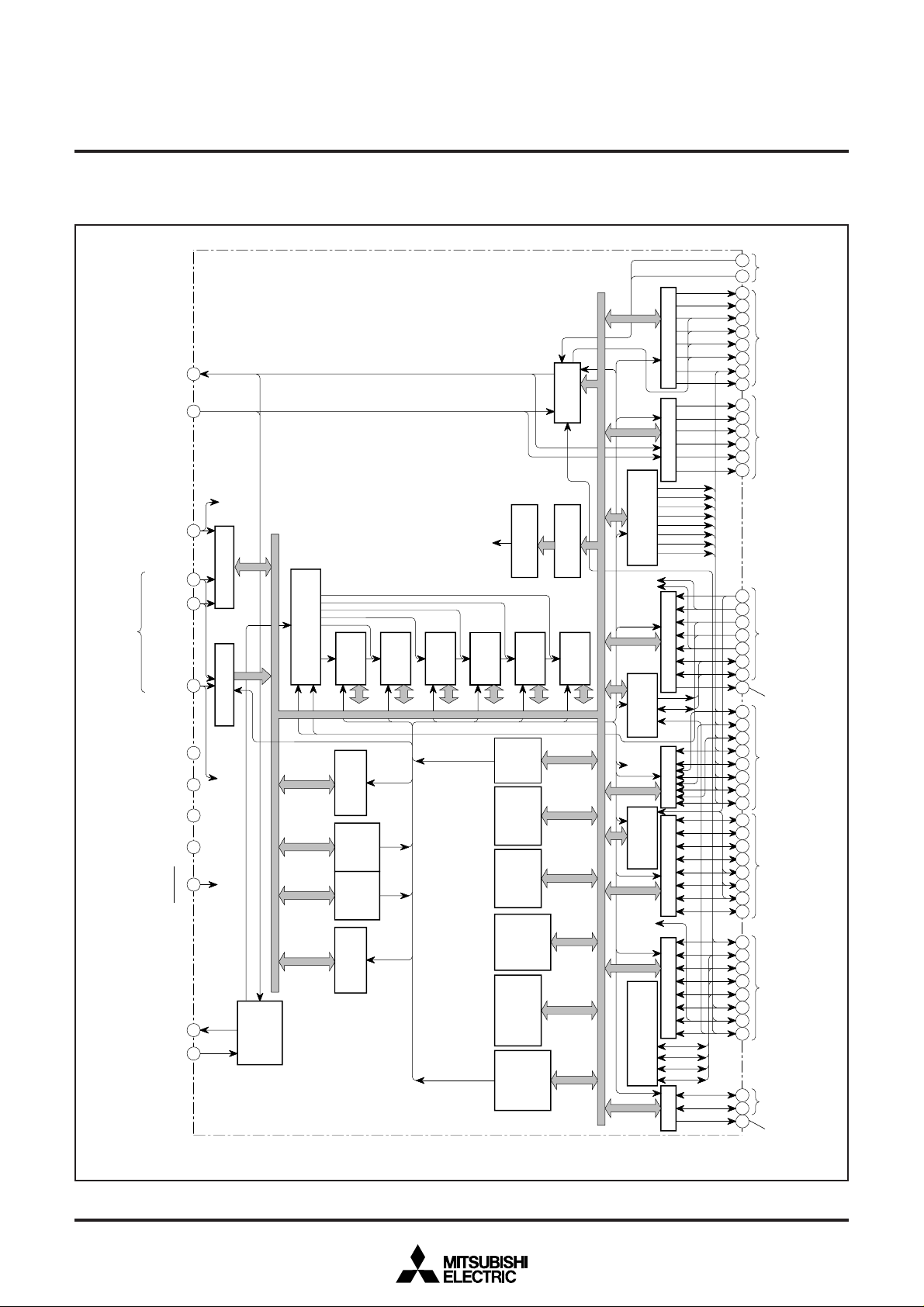
5. BLOCK DIAGRAM
Refer to page 4.
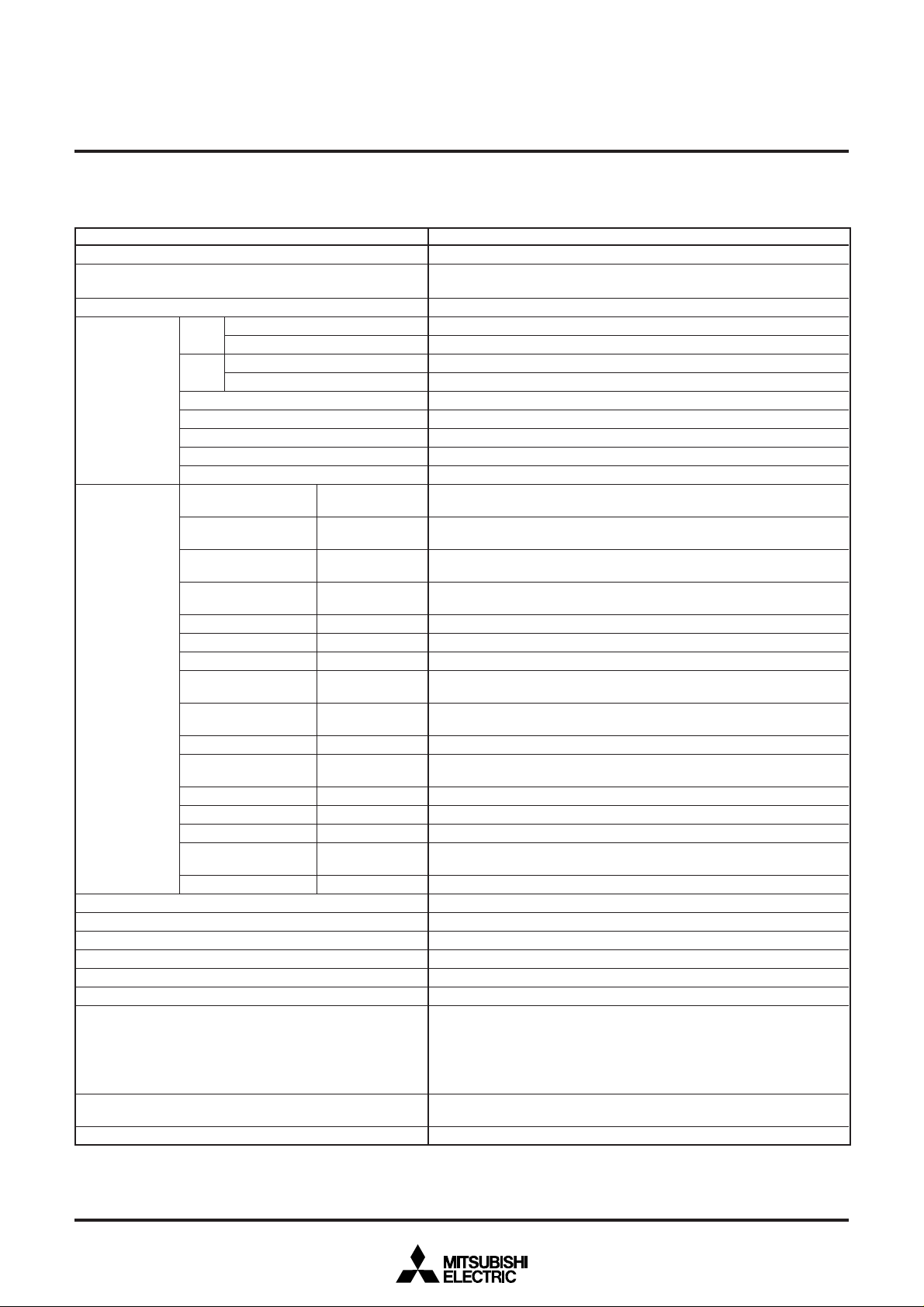
6. PERFORMANCE OVERVIEW
Refer to pages 5 and 6.
7. PIN DESCRIPTION
Refer to pages 7 to 11.
Rev. 1.0

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
8. PIN CONFIGURATION ................................................................................................................................................................................... 3
9. FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM .................................................................................................................................................................. 4
10. PERFORMANCE OVERVIEW...................................................................................................................................................................... 5
11. PIN DESCRIPTION....................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
12. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION.................................................................................................................................................................... 12
12.1 CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU) ........................................................................................................................................... 12
12.2 MEMORY ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 13
12.3 INTERRUPTS .................................................................................................................................................................................. 21
12.4 TIMERS............................................................................................................................................................................................ 26
12.5 SERIAL I/O....................................................................................................................................................................................... 30
12.6 MULTI-MASTER I2C-BUS INTERFACE .......................................................................................................................................... 33
12.7 PWM OUTPUT CIRCUIT ................................................................................................................................................................. 46
12.8 A-D CONVERTER............................................................................................................................................................................ 50
12.9 ROM CORRECTION FUNCTION .................................................................................................................................................... 54
12.10 DATA SLICER ................................................................................................................................................................................ 55
12.11 OSD FUNCTIONS.......................................................................................................................................................................... 66
13. SOFTWARE RUNAWAY DETECT FUNCTION ......................................................................................................................................... 117
14. RESET CIRCUIT........................................................................................................................................................................................118
15. CLOCK GENERATING CIRCUIT............................................................................................................................................................... 119
15.1 OSCILLATION CONTROL..............................................................................................................................................................119
16. DISPLAY OSCILLATION CIRCUIT ........................................................................................................................................................... 122
17. AUTO-CLEAR CIRCUIT............................................................................................................................................................................ 122
18. ADDRESSING MODE ............................................................................................................................................................................... 122
19. MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS ..................................................................................................................................................................... 122
20. PROGRAMMING NOTES......................................................................................................................................................................... 122
21. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS ............................................................................................................................................................ 123
22. RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS........................................................................................................................................ 123
23. ELECTRIC CHARACTERISTICS ............................................................................................................................................................. 124
24. ANALOG R, G, B OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS.................................................................................................................................... 126
25. A-D CONVERETER CHARACTERISTICS ............................................................................................................................................... 126
26. MULTI-MASTER I2C-BUS BUS LINE CHARACTERISTICS .................................................................................................................... 127
27. DATA REQUIRED FOR MASK ORDERS ................................................................................................................................................. 128
28. PROM PROGRAMMING METHOD.......................................................................................................................................................... 128
29. MASK CONFIRMATION FORM................................................................................................................................................................ 129
30. MARK SPECIFICATION FORM................................................................................................................................................................ 135
31. APPENDIX ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 136
32. PACKAGE OUTLINE ................................................................................................................................................................................ 176
M37280EKSP
Rev. 1.0
2
PRELIMINARY
7
4
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
8. PIN CONFIGURATION
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
HSYNC
VSYNC
P40AD4
1/INT2
P4
P42/TIM2
P43/TIM3
P24/AD3
5/AD2
P2
P26/AD1
P27/AD5
P00/PWM
P50/PWM
P01/PWM5
P47
P02/PWM6
P51
P17/SIN/R0
P32
P44/INT1
P56
P45/SOUT
P57
P46/SCLK
AVCC
HLF/AD6
P72/(SIN)
P71/VHOLD
P70/CVIN
CNVSS
XIN
XOUT
VSS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
M37280EKSP
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
P52/R/R1
64
P53/G/G1
63
4/B/B1
P5
62
P55/OUT1
61
P04/PWM0
60
P05/PWM1
59
0
P6
58
57
P06/PWM2
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
P61
P07/PWM3
P62
P20
P21
P22
P23
P10/OUT2
P65
P1
1/SCL1
P66
P12/SCL2
P67
P1
3/SDA1
P14/SDA2
5/G0
P1
P16/INT3/B0
P03/PWM7
P30/AD7
P31/AD8
RESET
4/OSC2/XCOUT
P6
P63/OSC1/XCIN
VCC
M37280MF-XXXSP, M37280MK-XXXSP,
Fig. 8.1 Pin Configuration (Top View)
Rev. 1.0
Outline 64P4B
3
PRELIMINARY
Clock input
Clock output
XINX
OUT
Reset input
AVCCVCCVSSCNVSSPins for data slicer
Clock output for OSD/
sub-clock output
Input ports P6
3
, P6
4
OSC1
OSC2
Clock input for
OSD/sub-clock input
P1 (8)
Multi-master
I
2
C-BUS interface
P3 (3)
SDA1
SCL2
SCL1
SDA2
P2 (8)
P0 (8)
P4 (8)
S
IN
S
CLK
S
OUT
SI/O (8)
P6 (8)
INT1
INT2
PWM6
PWM5
PWM4
PWM3
PWM2
PWM1
PWM0
P5 (8)
OUT1
B
G
R
H
SYNC
V
SYNC
A-D
converter
8-bit
PWM circuit
8-bit
arithmetic
and
logical unit
Accumulator
A (8)
Timer 6
T6 (8)
Timer 5
T5 (8)
Timer 4
T4 (8)
Timer 3
T3 (8)
Timer 2
T2 (8)
Timer 1
T1 (8)
Timer count source
selection circuit
TIM2
Data slicer
Instruction
register (8)
Instruction
decoder
Control signal
OSD circuit
Processor
status
register
PS (8)
Stack
pointer
S (8)
Index
register
Y (8)
Index
register
X (8)
ROM
Program
counter
PC
L
(8)
Progam
counter
PC
H
(8)
RAM
Data bus
Clock
generating
circuit
303136
RESET
243332
29
CV
IN
282725
26
V
HOLD
RVCO
HLF
34
35
Address bus
361740414243454749109875051525355575960391513112321196543616263642
1
I/O ports
P3
0
, P3
1
I/O port P1
I/O port P2
I/O port P0
Input ports P4
0
–P4
6
Output port P5
Sync
signal input
Output port P4
7
20
2216125658
44
Output ports
P6
0
–P6
2
, P6
5
–P4
7
14
18
Output port
P3
2
INT3
PWM7
374854
46
Input ports P7
0 –
P7
2
A-D converter
SI/O
P7 (3)
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
9. FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Fig. 9.1 Functional Block Diagram of M37280
4
Rev. 1.0
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
10. PERFORMANCE OVERVIEW
Table 10.1 Performance Overview
Parameter
Number of basic instructions
Instruction execution time
Clock frequency
Memory size
Input/Output
ports
Serial I/O
Multi-master I2C-BUS interface
A-D converter
PWM output circuit
Timers
Subroutine nesting
Interrupt
Clock generating circuit
Data slicer
ROM
M37280MF-XXXSP
M37280MK-XXXSP, M37280EKSP
RAM
M37280MF-XXXSP
M37280MK-XXXSP, M37280EKSP
ROM correction memory
OSD ROM (character font)
OSD ROM (color dot font)
OSD RAM (SPRITE)
OSD RAM (character)
P00–P02, P04–P07
P03
P10, P15–P17
P11–P14
P2
P30, P31
P32
P40–P44
P45, P46
P47
P50, P51, P56, P57
P52–P55
P60–P62, P65–P67
P63
P64
P70–P72
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Functions
71
0.5 µs (the minimum instruction execution time, at 8 MHz oscillation frequency)
8 MHz (maximum)
60K bytes
80K bytes
1024 bytes
1472 bytes
64 bytes
20400 bytes
9672 bytes
120 bytes
1536 bytes
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Output
Input
Input
Output
Output
Output
Output
Input
Input
Input
7-bit ✕ 1 (N-channel open-drain output structure, can be used as 8-bit PWM
output pins)
1-bit ✕ 1 (CMOS input/output structure, can be used as 14-bit PWM output
pin)
4-bit ✕ 1 (CMOS input/output structure, can be used as OSD output pin,
INT input pin, serial input pin)
4-bit ✕ 1 (N-channel open-drain output structure, can be used as multimaster I2C-BUS interface)
8-bit ✕ 1 (CMOS input/output structure, can be used as A-D input pins)
2-bit ✕ 1 (CMOS input/output structure, can be used as A-D input pins)
1-bit ✕ 1 (N-channel open-drain output structure)
5-bit ✕ 1 (can be used as A-D input pins, INT input pins, external clock input
pins)
2-bit ✕ 1 (N-channel open-drain output structure when serial I/O is used,
can be used as serial I/O pins)
1-bit ✕ 1 (N-channel open-drain output structure)
4-bit ✕ 1 (N-channel open-drain output structure, can be used as PWM
output pin)
4-bit ✕ 1 (CMOS output structure, can be used as OSD output pins)
6-bit ✕ 1 (N-channel open-drain output structure)
1-bit ✕ 1 (can be used as sub-clock input pin, OSD clock input pin)
1-bit ✕ 1 (CMOS output structure when LC is oscillating, can be used as
sub-clock output pin, OSD clock output pin)
3-bit ✕ 1 (can be used as data slicer input/output, serial input pin)
8-bit ✕ 1
1 (2 systems)
8 channels (8-bit resolution)
8-bit ✕ 8
8-bit timer ✕ 6
128 levels (maximum)
<19 types>
External interrupt ✕ 3, Internal timer interrupt ✕ 6, Serial I/O interrupt ✕ 1,
OSD interrupt ✕ 1, Multi-master I2C-BUS interface interrupt ✕ 1,
Data slicer interrupt ✕ 1, f(XIN)/4096 interrupt ✕ 1, SPRITE OSD interrupt
✕ 1, VSYNC interrupt ✕ 1, A-D conversion interrupt ✕ 1, BRK instruction
interrupt ✕ 1
2 built-in circuits (externally connected to a ceramic resonator or a quartzcrystal oscillator)
Built in
Rev. 1.0
5
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
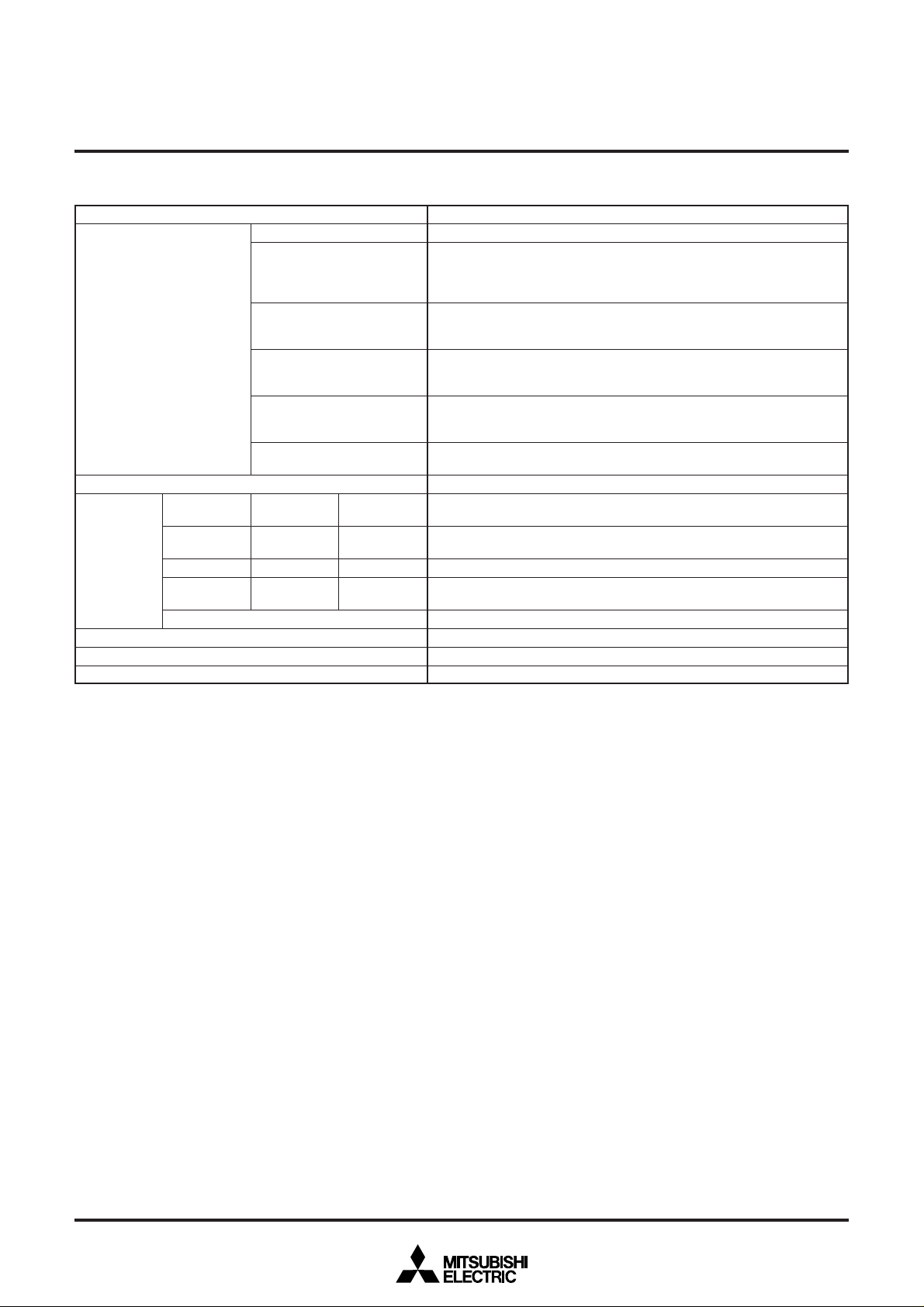
Table 10.2 Performance Overview
Parameter
OSD function
Power source voltage
Power
dissipation
Operating temperature range
Device structure
Package
In high-speed
mode
In low-speed
mode
In stop mode
Number of display characters
Character display area
Kinds of characters
Kinds of character sizes
Kinds of character colors
Display position (horizontal,
vertical)
OSD ON
(Analog output)
OSD ON
(Digital output)
OSD OFF
OSD OFF
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Functions
Data slicer
ON
Data slicer
OFF
Data slicer OFF
Data slicer
OFF
32 characters ✕ 16 lines
CC mode: 16 ✕ 26 dots (dot structure: 16 ✕ 20 dots)
OSD mode: 16 ✕ 20 dots
EXOSD mode: 16 ✕ 26 dots
SPRITE display: 16 ✕ 20 dots
CC/OSD mode: 510 kinds
CDOSD mode: 62 kinds
SPRITE display: 1 kind
CC mode: 2 kinds
OSD/CDOSD mode: 14 kinds
SPRITE display: 8 kinds
CC/CDOSD mode: 8 kinds (R, G, B, OUT1, OUT2))
OSD mode: 15 kinds (R, G, B, OUT1, OUT2)
SPRITE display: 8 kinds (R, G, B, OUT1)
256 levels (horizontal) ✕ 1024 levels (vertical)
SPRITE display: 2048 ✕ 1024
5V ± 10%
275 mW typ. ( at oscillation frequency f(XIN) = 8 MHz, fOSC = 27 MHz)
165 mW typ. ( at oscillation frequency f(XIN) = 8 MHz, fOSC = 27 MHz )
82.5 mW typ. ( at oscillation frequency f(XIN) = 8 MHz)
0.33 mW typ. ( at oscillation frequency f(XCIN) = 32 kHz, f(XIN) = stop)
0.055 mW ( maximum )
–10 °C to 70 °C
CMOS silicon gate process
64-pin shrink plastic molded DIP
Rev. 1.0
6
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
11. PIN DESCRIPTION
Table 11.1 Pin Description
Pin Name Functions
VCC,
AVCC,
VSS
CNVSS
RESET
XIN
XOUT
P00/
PWM4–
P02/PWM6,
P03/PWM7,
P04/
PWM0–
P07/PWM3
P10/OUT2,
P11/SCL1,
P12/SCL2,
P13/SDA1,
P14/SDA2,
P15/G0,
P16/INT3/
B0,
P17/SIN/R0
P20–P23
P24/AD3–
P26/AD1,
P27/AD5
P30/AD7,
P31/AD8
P32
P40/AD4,
P41/INT2,
P42/TIM2,
P43/TIM3,
P44/INT1,
P45/SOUT,
P46/SCLK
P47
Power source
CNVSS
Reset input
Clock input
Clock output
I/O port P0
8-bit PWM output
I/O port P1
OSD output
Multi-master
I2C-BUS interface
External interrupt
input
Serial I/O data
input
I/O port P2
Analog input
I/O port P3
Analog input
Output port P3
Input port P4
Analog input
External interrupt
input
External clock input
Serial I/O data
output
Serial I/O
synchronous clock
input/output
Output port P4
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
Input/
Output
Apply voltage of 5 V ± 10 % (typical) to VCC and AVCC, and 0 V to VSS.
Input
Input
Input
Output
I/O
Output
I/O
Output
Output
Input
Input
I/O
Input
I/O
Input
Output
Input
Input
Input
Input
Output
I/O
Output
Connected to VSS.
To enter the reset state, the reset input pin must be kept at a LOW for 2 µs or more (under
normal VCC conditions).
If more time is needed for the quartz-crystal oscillator to stabilize, this LOW condition should
be maintained for the required time.
This chip has an internal clock generating circuit. To control generating frequency, an external ceramic resonator or a quartz-crystal oscillator is connected between pins XIN and XOUT.
If an external clock is used, the clock source should be connected to the XIN pin and the
XOUT pin should be left open.
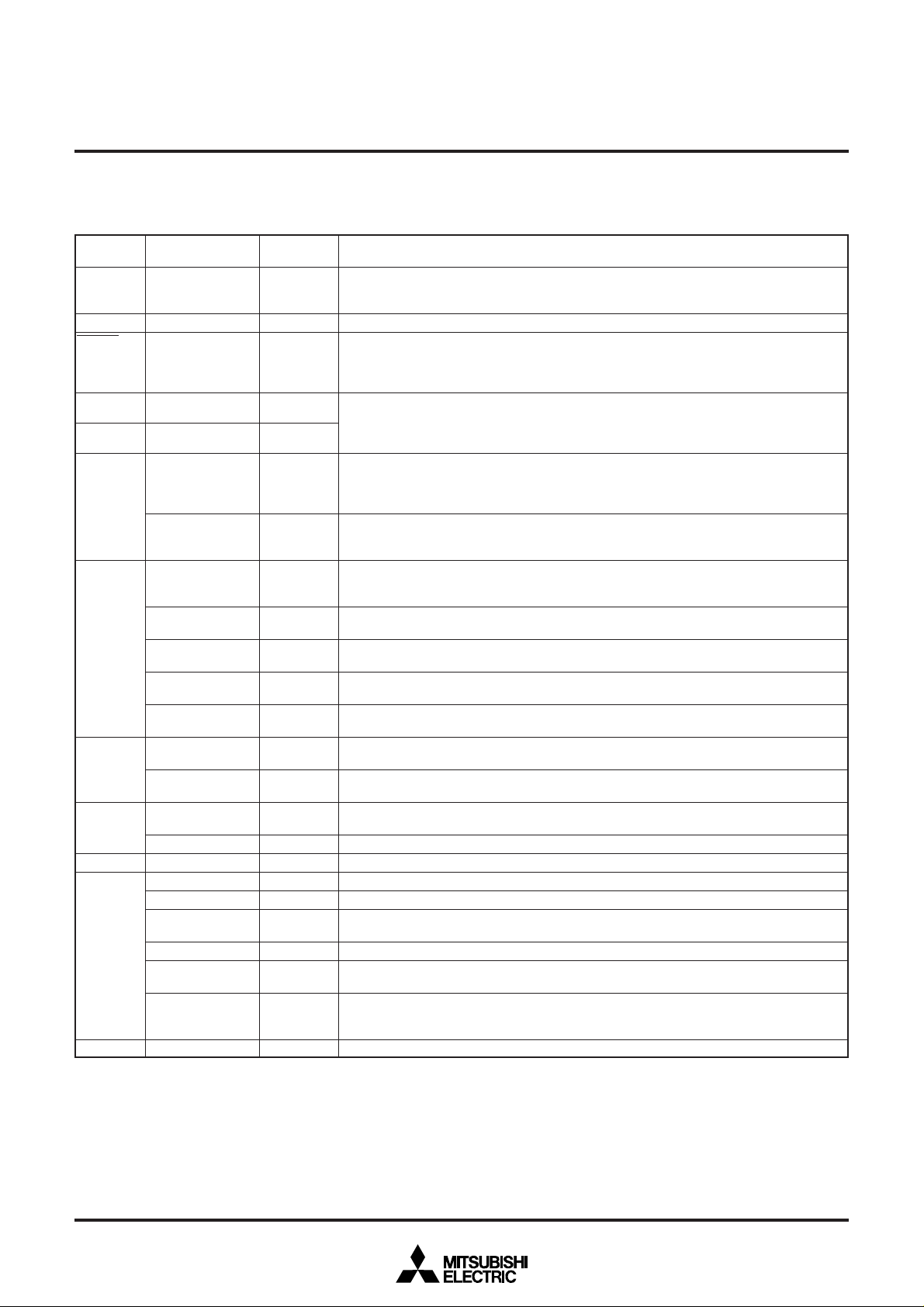
Port P0 is an 8-bit I/O port with direction register allowing each I/O bit to be individually
programmed as input or output. At reset, this port is set to input mode. The output structure
of P03 is CMOS output, that of P00–P02 and P04–P07 are N-channel open-drain output. See
notes at end of Table for full details of port P0 functions.
Pins P00–P03 and P04–P07 are also used as 8-bit PWM output pins PWM4–PWM7 and
PWM0–PWM3 respectively. The output structure of PWM0–PWM6 is N-channel open-drain
output. And the output structure of PWM7 is CMOS output.
Port P1 is an 8-bit I/O port and has basically the same functions as port P0. The output
structure of P10 and P15–P17 is CMOS output, that of P11–P14 is N-channel open-drain
output.
Pin P10, P15–P17 are also used as OSD output pins OUT2, G0, B0, R0, respectively. The
output structure is CMOS output.
Pin P11–P14 are used as SCL1, SCL2, SDA1 and SDA2 respectively, when multi-master
I2C-BUS interface is used. The output structure is N-channel open-drain output.
Pin P16 is also used as extemal interrupt input pin INT3.
Pin P17 is also used as serial I/O data input pin SIN.
Port P2 is an 8-bit I/O port and has basically the same functions as port P0. The output
structure is CMOS output.
Pins P24–P26, P27 are also used as analog input pins AD3–AD1, AD5 respectively.
Ports P30 and P31 are 2-bit I/O ports and have basically the same functions as port P0. The
output structure is CMOS output.
Pins P30, P31 are also used as analog input pins AD7, AD8 respectively.
Ports P32 is a 1-bit output port. The output structure is N-channel open-drain output.
Ports P40–P46 are a 7-bit input port.
Pin P40 is also used as analog input pin AD4.
Pins P41, P44 are also used as external interrupt input pins INT2, INT1.
Pins P42 and P43 are also used as external clock input pins TIM2, TIM3 respectively.
Pin P45 is used as serial I/O data output pin SOUT. The output structure is N-channel open-
drain output.
Pin P46 is used as serial I/O synchronous clock input/output pin SCLK. The output structure
is N-channel open-drain output.
Port P47 is a 1-bit output port. The output structure is N-channel open-drain output.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280EKSP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Rev. 1.0
7
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
Table 11.2 Pin Description (continued)
Pin Name Functions
P50/PWM7,
P51,
P52/R/R1,
P53/G/G1,
P54/B/B1,
P55/OUT1,
P56, P5
P60–P62,
P65–P67
P63/OSC1/
XCIN,
P64/OSC2/
XCOUT
P70/CVIN,
P71/VHOLD,
P72/(SIN)
HLF/AD6
HSYNC
VSYNC
Output port P5
PWM output
OSD output
7
Output port P6
Input port P6
Clock input for OSD
Clock output for OSD
Sub-clock output
Sub-clock input
Input port P7
Input for data
slicer
Serial I/O data input
Analog input
HSYNC input
VSYNC input
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
Input/
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Input
Input
Output
Output
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
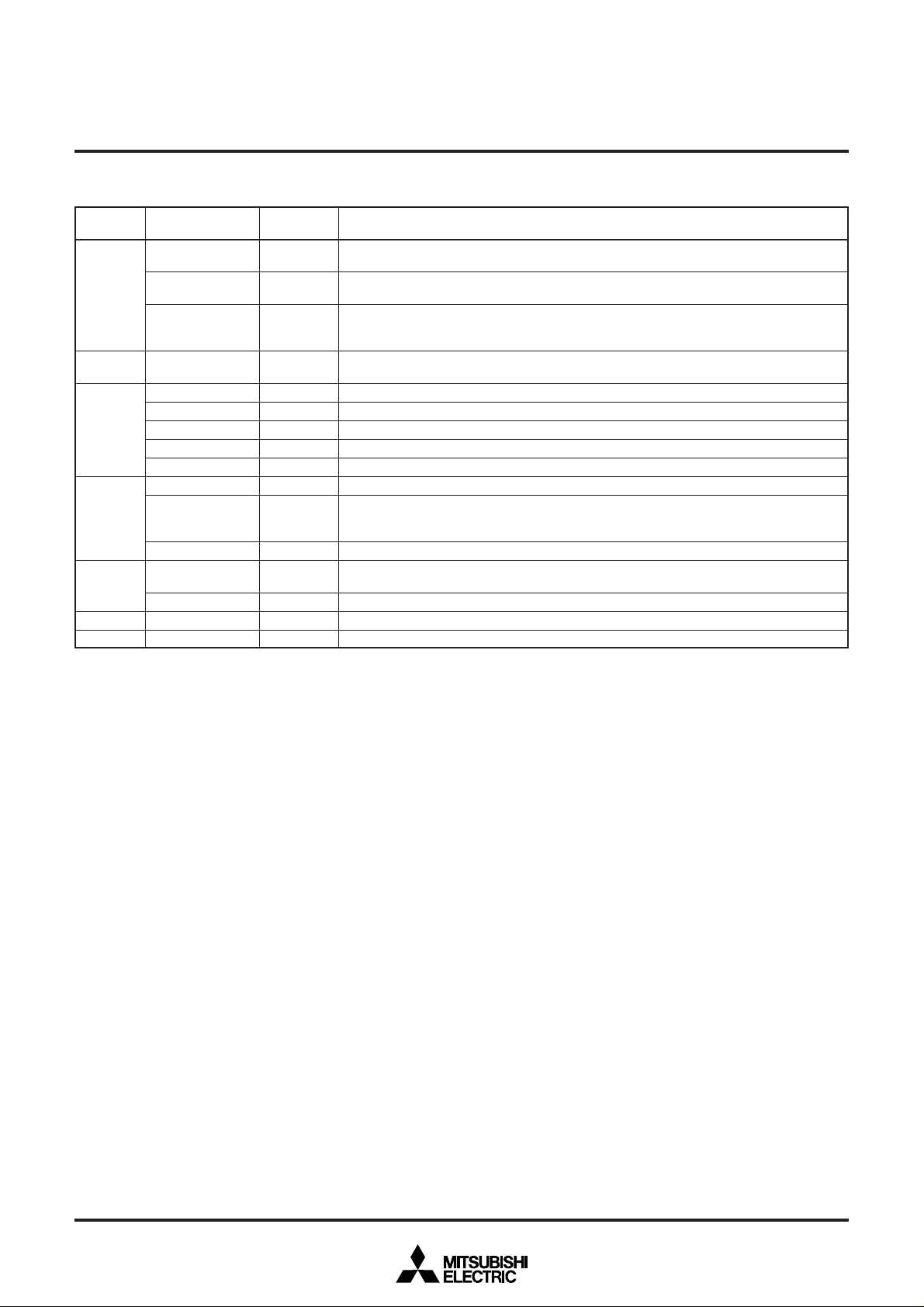
Port P5 is a 4-bit output port. The output structure of P50, P51, P56 and P57 is N-channel
open-drain output, that of P52–P55 is CMOS output.
Pin P50 is also used as 8-bit PWM output pin PWM7. The output structure is N-channel
open-drain output.
Pins P52–P55 are also used as OSD output pins R/R1, G/G1, B/B1, OUT1 respectively. At
R, G, B output, the output structure is analog output. At R1, G1, B1 and OUT1 output, the
output structure is CMOS output.
Ports P60–P62 and P65–P67 are 6-bit output ports. The output structure is N-channel opendrain output.
Ports P63 and P64 are 2-bit input port.
Pin P63 is also used as OSD clock input pin OSC1.
Pin P64 is also used as OSD clock output pin OSC2. The output structure is CMOS output.
Pin P64 is also used as sub-clock output pin XCOUT. The output structure is CMOS output.
Pin P63 is also used as sub-clock input pin XCIN.
Ports P70–P72 are 3-bit input port.
Pins P70, P71 are also used as data slicer input pins CVIN, VHOLD respectively . When using
data slicer, input composite video signal through a capacitor. Connect a capacitor between
VHOLD and VSS.
Pins P72 is also used as serial I/O data input pin SIN.
When using data slicer , connect a filter using of a capacitor and a resistor between HLF and
VSS.
This is an analog input pin AD6 .
This is a horizontal synchronous signal input for OSD.
This is a vertical synchronous signal input for OSD.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280EKSP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Note : As shown in the memory map (Figure 12.2.1), port P0 is accessed as a memory at address 00C016 of zero page. Port P0 has the port P0 direction register
(address 00C116 of zero page) which can be used to program each bit as an input (“0”) or an output (“1”). The pins programmed as “1” in the direction register
are output pins. When pins are programmed as “0,” they are input pins. When pins are programmed as output pins, the output data are written into the port
latch and then output. When data is read from the output pins, the output pin level is not read but the data of the port latch is read. This allows a previouslyoutput value to be read correctly even if the output “L” voltage has risen, for example, because a light emitting diode was directly driven. The input pins float,
so the values of the pins can be read. When data is written into the input pin, it is written only into the port latch, while the pin remains in the floating state.
Rev. 1.0
8
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
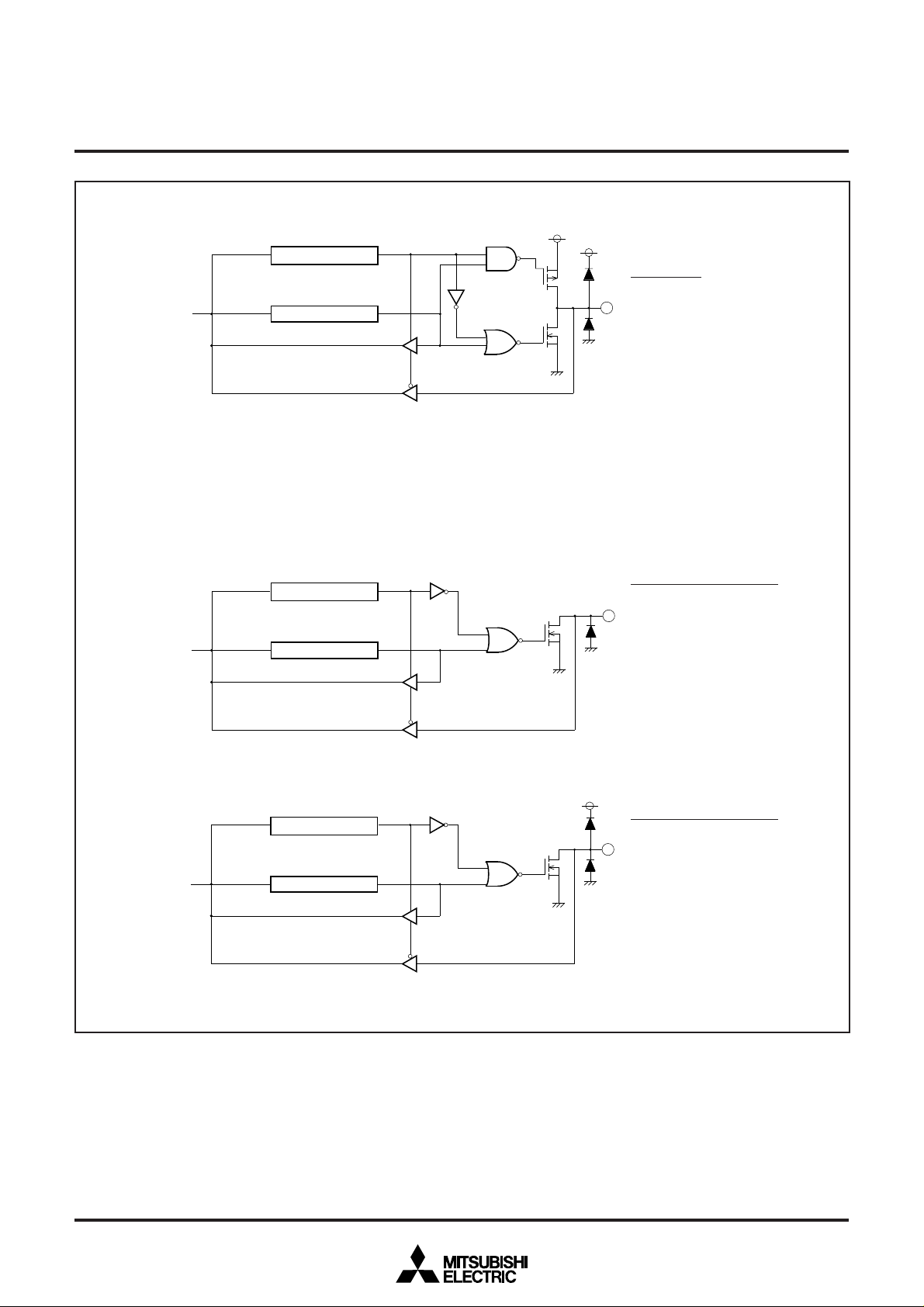
Ports P03, P10, P15–P17, P2, P30, P31
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Data bus
Ports P0
Data bus
0–P02, P04–P07
Direction register
Port latch
Direction register
Port latch
CMOS output
Ports P03, P10, P15–P17,
P2, P3
0, P31
Note : Each port is also used as follows :
P0
0 : PWM7
P1
0 : OUT2
P1
5 : G0
P1
6 : INT3/B0
P1
7 : SIN/R0
P2
4–P26 : AD3–AD1
P2
7 : AD5
P3
0 : AD7
P3
1 : AD8
N-channel open-drain output
0–P02, P04–P07
Ports P0
Note : Each port is also used as follows :
P0
0–P02 : PWM4–PWM6
P0
4–P07 : PWM0–PWM3
Ports P11–P14
Data bus
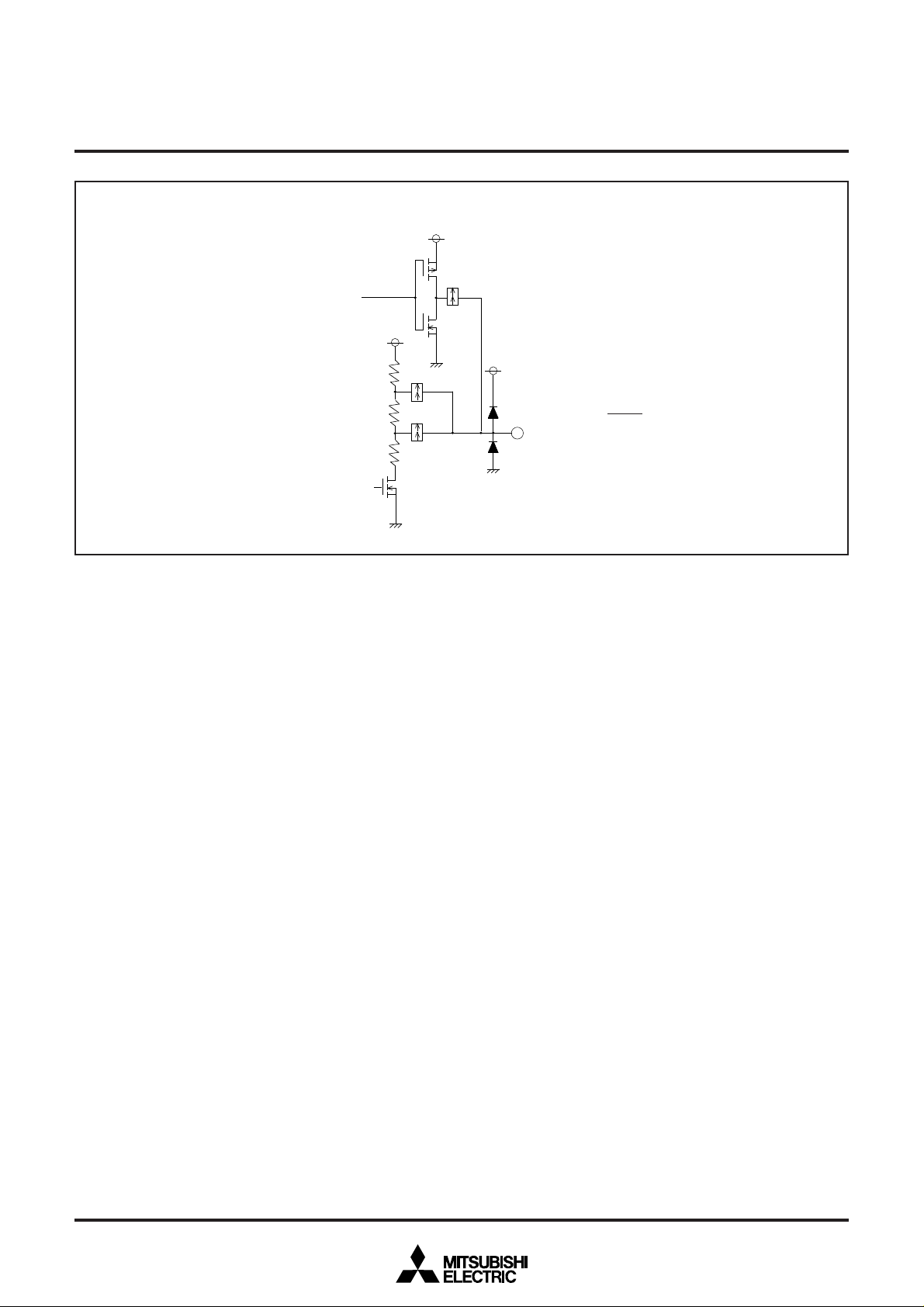
Fig. 11.1 I/O Pin Block Diagram (1)
Rev. 1.0
Direction register
Port latch
N-channel open-drain output
Port P11-P14
Note : Each port is also used as follows :
P1
1 : SCL1
P1
2 : SCL2
P1
3 : SDA1
P1
4 : SDA2
9
PRELIMINARY
t
t
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
S
OUT
, S
CLK
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
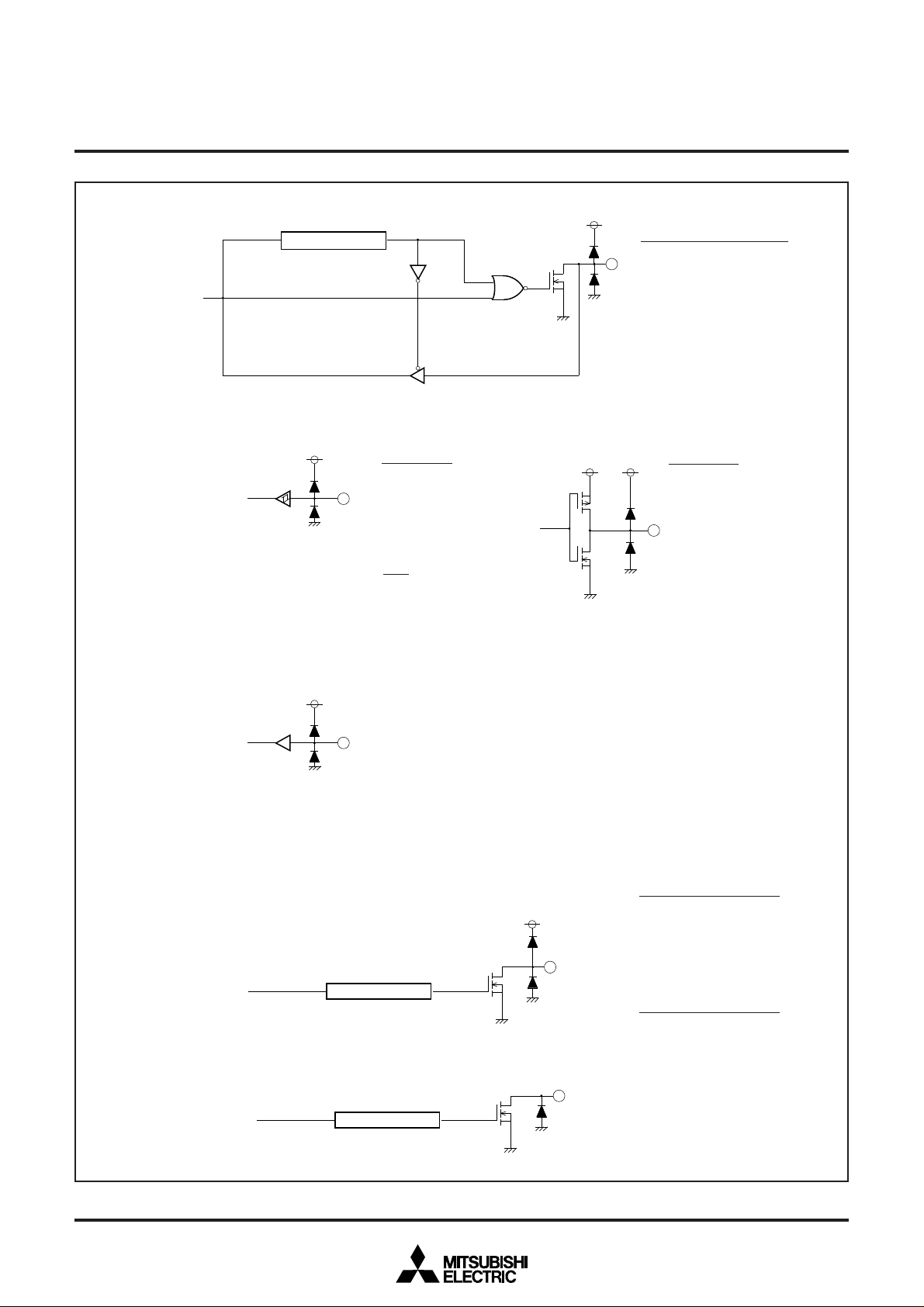
Data bus
H
SYNC
Ports P4
, V
SYNC
Internal circui
0
–P4
4
Direction register
Port P5
5
Schmidt input
SYNC, VSYNC
H
Internal circui
Input
Ports P40–P44
Note : Each port is also used as below :
P4
0 : AD4
P4
1 : INT2
P4
2 : TIM2
P4
3 : TIM3
P4
4 : INT1
N-channel open-drain output
Ports P45, P46
Note : Each pin is also used
as follows :
P4
5 : SOUT
P46 : SCLK
CMOS output
Port P5
5
Note : Port P55 is also used
as pin OUT1.
Data bus
Ports P32, P47, P51, P56, P57,
P6
Port P5
0
–P62, P65–P6
Data bus
0
Data bus
7
Ports latch
Ports latch
N-chanel open drain output
Ports P3
2, P47, P51, P56, P57,
P6
0–P62, P65–P67
N-chanel open drain output
Port P5
0
Note : Port P50 is also used
as pin PWM7.
Fig. 11.2 I/O Pin Block Diagram (2)
10
Rev. 1.0
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Ports P52–P5
Fig. 11.3 I/O Pin Block Diagram (3)
4
Internal circuit
Output
Ports P5
2–P54
Note : Each port is also used
as below :
P5
2 : R/R1
P5
3 : G/G1
P5
4 : B/B1
Rev. 1.0
11
PRELIMINARY
0
B
After reset
W
2
4
0
e
s
(CM0, CM1)
bit (CM2) (See note)
age
00516
0
WRWRWRWRW
selection bit (CM5)
GH d
e
7
0
W
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
12. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
12.1. CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
This microcomputer uses the standard 740 Family instruction set.
Refer to the table of 740 Family addressing modes and machine
instructions or the SERIES 740 <Software> User’s Manual for details on the instruction set.
Machine-resident 740 Family instructions are as follows:
The FST, SLW instruction cannot be used.
The MUL, DIV, WIT and STP instructions can be used.
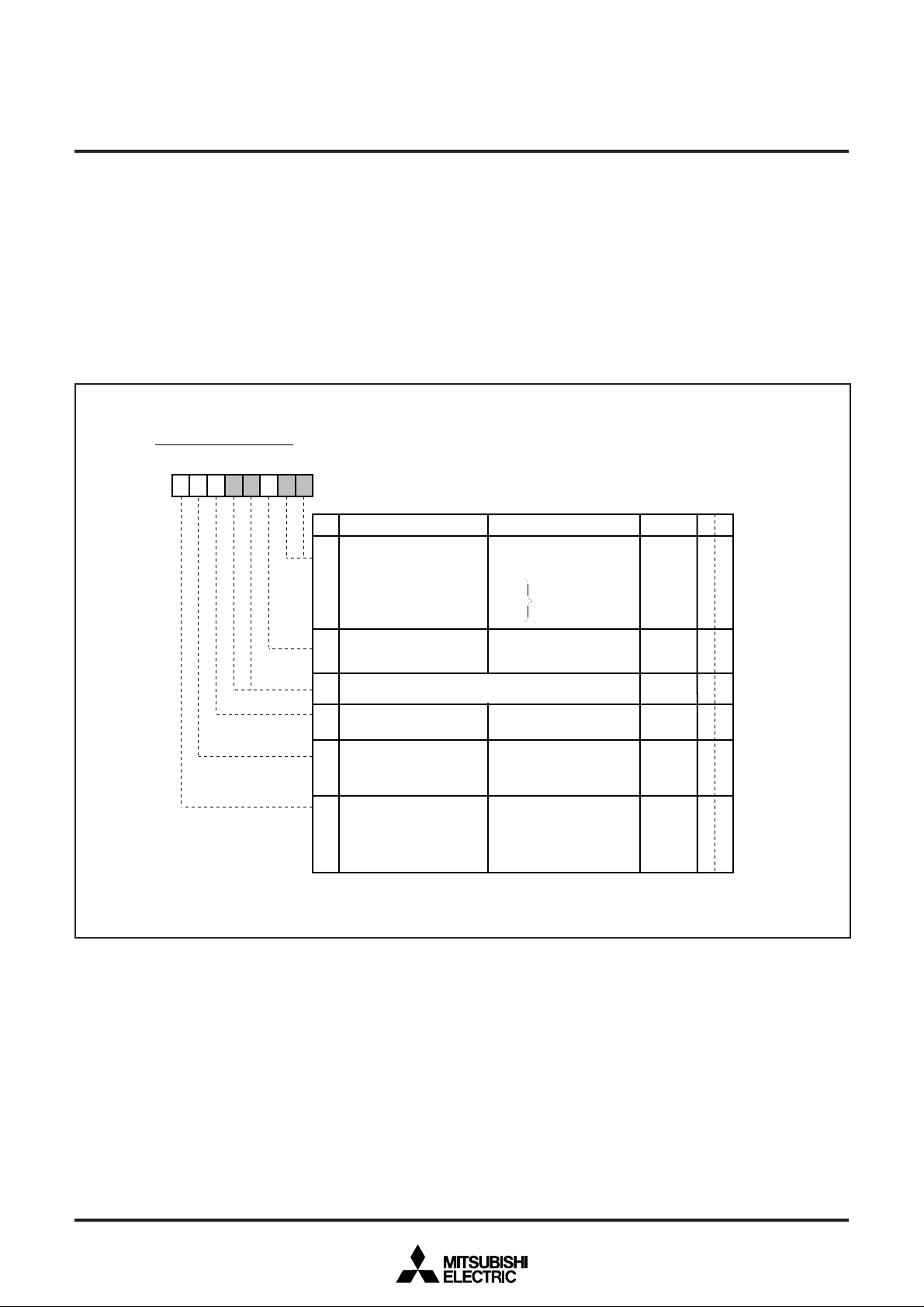
CPU Mode Register
b7b6b5b4b3b2b1b
1
1
CPU mode register (CM) [Address 00FB16]
Nam
Processor mode bits
0, 1
Stack page selection
3,
Fix these bits to “1.”
12.1.1 CPU Mode Register
The CPU mode register contains the stack page selection bit and
internal system clock selection bit. The CPU mode register is allocated at address 00FB16.
Function
b1 b0
0 0: Single-chip mode
0 1:
1 0: Not available
1 1:
0: 0 page
1: 1 p
R
R
1
1
Fig. 12.1.1 CPU Mode Register
XCOUT drivability
Main Clock (XIN–XOUT)
stop bit
(CM6)
Internal system clock
selection bit
(CM7)
Note: This bit is set to “1” after the reset release.
0: LOW drive
1: HI
0: Oscillating
1: Stopped
0: XIN–XOUT selected
(high-speed mode)
1: X
CIN–XCOUT selected
(low-speed mode)
riv
R
12
Rev. 1.0
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
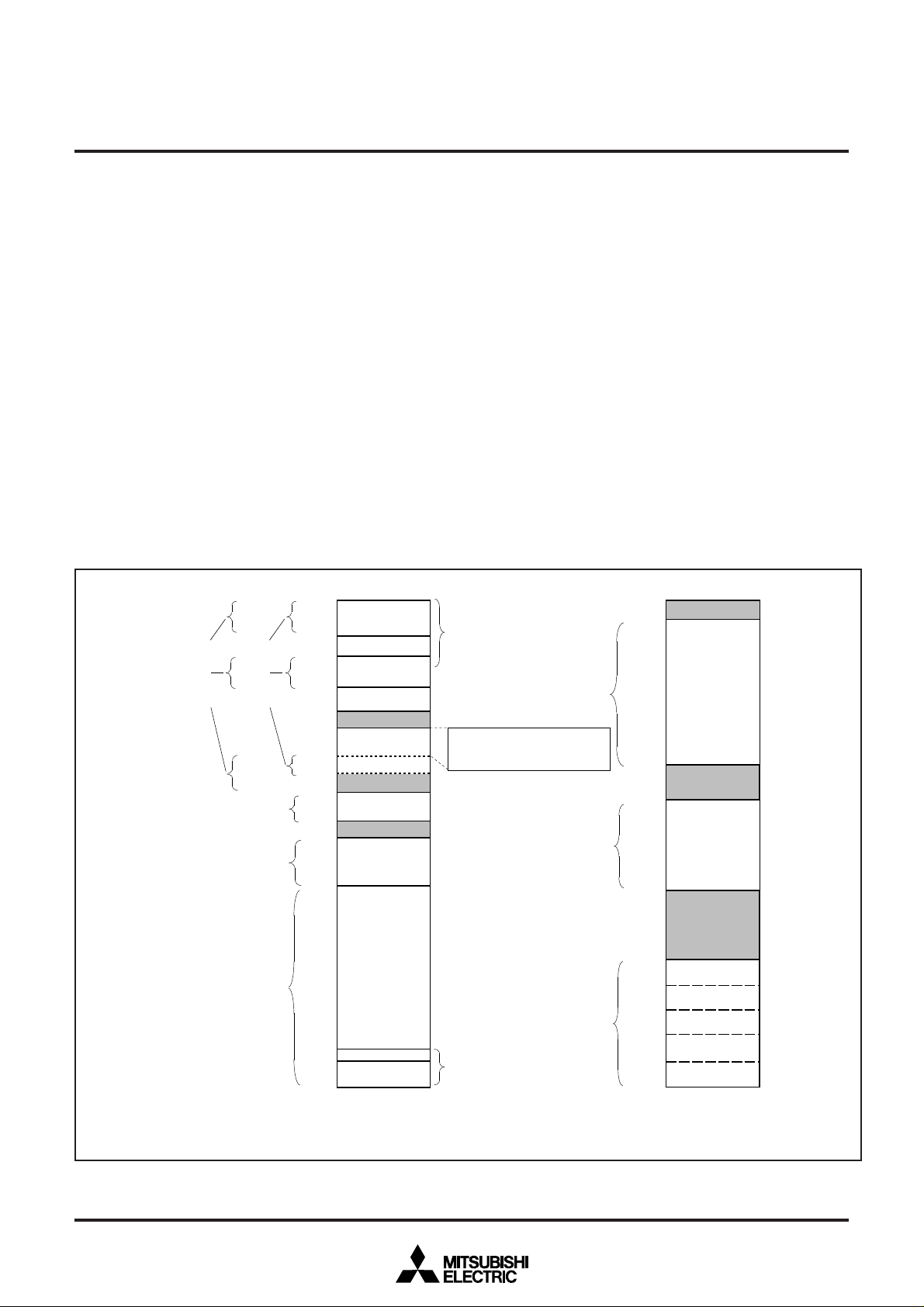
12.2 MEMORY
12.2.1 Special Function Register (SFR) Area
The special function register (SFR) area in the zero page contains
control registers such as I/O ports and timers.
12.2.2 RAM
RAM is used for data storage and for stack area of subroutine calls
and interrupts.
12.2.3 ROM
The M37280MF-XXXSP has 60K-byte program area. The M37280MK
-XXXSP has 56K-byte program area and 24K-byte data-dedicated
area. For the M37280EKSP, the two area (60K, 24K + 56K) can be
swithed each other by setting the bank control register.
12.2.4 OSD RAM
RAM for display is used for specifying the character codes and colors to display.
12.2.5 OSD ROM
ROM for display is used for storing character data.
0000
16
00BF
16
00C0
RAM
(1472 bytes)
for
M37280MK-XXXSP
and M37280EKSP
OSD RAM (SPRITE)
OSD RAM (character)
RAM
(1024 bytes)
for
M37280MF-
XXXSP
(120 bytes)
(See note 1)
(1536 bytes)
(See note 2)
00FF
0100
0200
0258
02C0
02FF
0300
053F
06FF
0700
07A7
0800
0FFF
1000
16
SFR1 area
16
16
16
SFR2 area
16
Not used
16
16
16
16
Not used
16
16
16
Not used
16
16
16
12.2.6 Interrupt Vector Area
The interrupt vector area contains reset and interrupt vectors.
12.2.7 Zero Page
The 256 bytes from addresses 000016 to 00FF16 are called the zero
page area. The internal RAM and the special function registers (SFR)
are allocated to this area.
The zero page addressing mode can be used to specify memory and
register addresses in the zero page area. Access to this area with
only 2 bytes is possible in the zero page addressing mode.
12.2.8 Special Page
The 256 bytes from addresses FF0016 to FFFF16 are called the special page area. The special page addressing mode can be used to
specify memory addresses in the special page area. Access to this
area with only 2 bytes is possible in the special page addressing
mode.
12.2.9 ROM Correction Memory (RAM)
This is used as the program area for ROM correction.
10000
16
Not used
10800
157FF
18000
1ACFF
16
16
Not used
16
16
Zero page
OSD ROM
(character font)
(20400 bytes)
ROM correction memory (64 bytes)
Block 1 : addresses 02C0
Block 2 : addresses 02E0
16 to
02DF
16 to
02FF
OSD ROM
(color dot font)
(9672 bytes)
16
16
Fig. 12.2.1 Memory Map
Rev. 1.0
ROM
(60K bytes)
FF00
FFDE
FFFF
16
16
16
Interrupt vector area
1B000
Expansion ROM
(20K bytes)
for
M37280MK-XXXSP
Special page
Notes 1: Refer to Table 12.11.3 OSD RAM (SPRITE).
and M37280EKSP
2: Refer to Tables 12.11.4 and 2.11.5 OSD RAM (character).
1C000
1D000
1E000
1F000
1FFFF
Not used
16
Bank 11
16
Bank 12
16
Bank 13
16
Bank 14
16
Bank 15
16
13
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
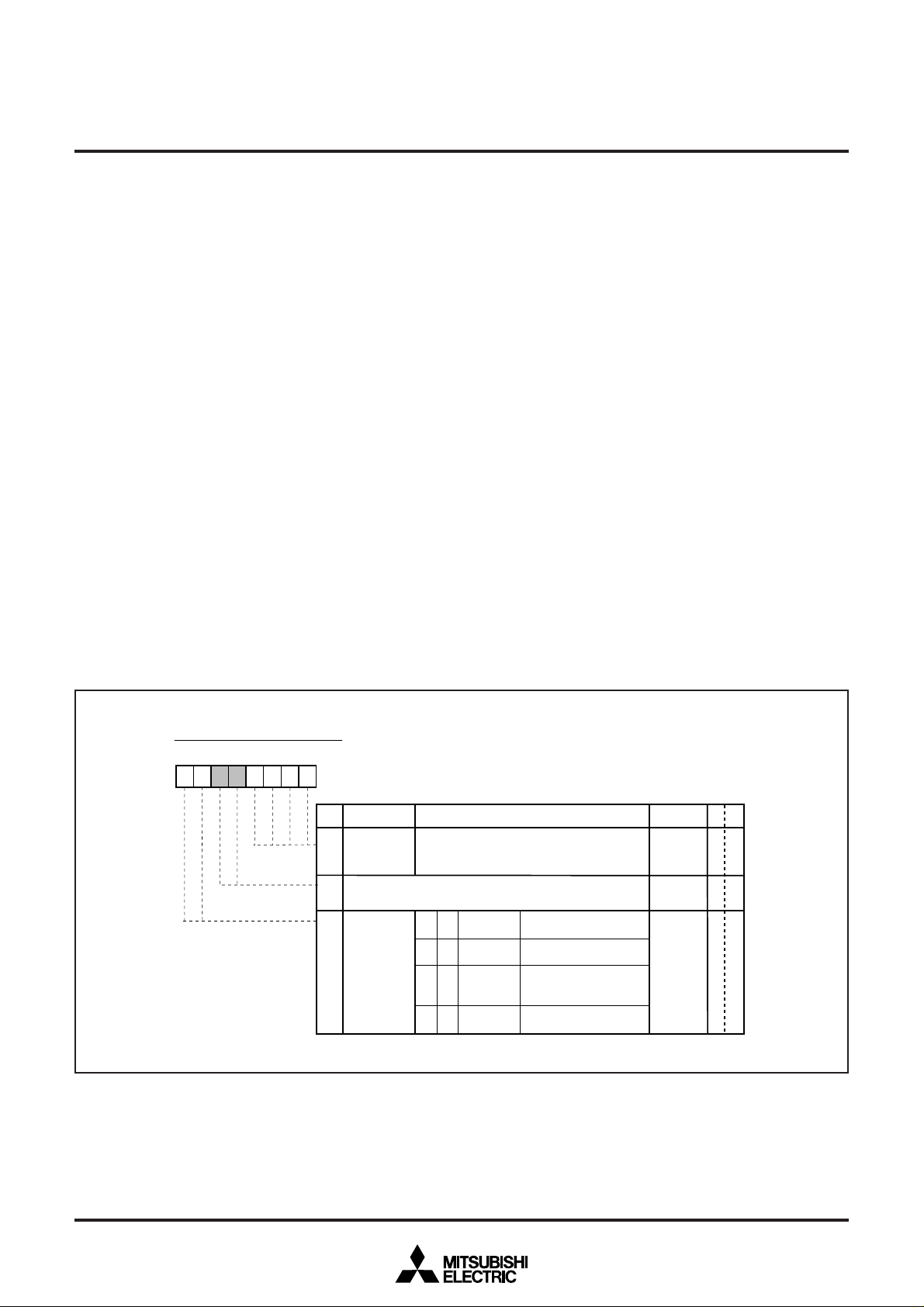
12.2.10 Expansion ROM (only M37280MKXXXSP/M37280EKSP)
The M37280MK-XXXSP/M37280EKSP can use 5-bank (total 20K
bytes) expansion ROM (4K bytes each bank) by setting the bank
register.
The expansion ROM is assigned to address 1B00016 to 1FFFF16.
The contents of each bank in the expansion ROM are read by setting
the bank register and accessing addresses 100016 to 1FFF16. As the
expansion ROM is not programmable, use it as data-dedicated area.
When using the expansion ROM area, the internal ROM at addresses
100016 to 1FFF16 (extra area) is not also programmable.
Notes 1: When using the expansion ROM (BK7 = “1”), the ROM correction
function do not operate for addresses 1000
2:When using the emulator MCU (M37280ERSS), as addresses 1000
to FFFF16 can be emulated by setting bit 7 of the bank control register to “0,” the expansion ROM cannot be used. Addresses 2000
FFFF
16 can be emulated by setting it to “1.” The data in specified
area by the bank selection bits can be read by accessing addresses
1000
16 to 1FFF16.
3:When using the emulator MCU, the expansion ROM and the extra
area cannot be emulated by setting bit 7 of the bank control register
to “1.” Therefore, write the data to this area before using.
4:For the M37280MK-XXXSP, fix bit 7 of the bank control register to
“1.” For M37280MF-XXXSP, fix the address 00ED
16 to 1FFF16.
16 to
16 to “0016.”
16
Bank Control Register
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
00
Fig. 12.2.2 Bank Control Register
Bank control register (BK) [Address 00ED
B Name Functions
0
Bank
to
selection bits
3
(BK0 to BK3)
Fix these bits to “0”.
4, 5
6, 7 Bank control
bits
(BK6, BK7)
Bank number is selected (bank 11 to 15)
Bank ROM Address 1000
b6
b7
0
✕
10
11
Not used
Used
Used
access
Read out from extra area
(programmable)
Read out the data
from area specified by
the bank selection bits
Read out from extra area
(data-dedicated)
16]
16 level
After reset R
0RW
0RW
0RW
W
14
Rev. 1.0
PRELIMINARY
)
)
)
(P1)
)
)
)
)
)
r
)
)
)
)
)
)
(P7)
(
)
(
)
OUT1
OUT2
OC16
OC17
OC14
OC15
OC12
OC13
OC10
OC11
BC10
BC11
BC12
BC13
BC14
BC15
BC16
BC20
BC21
BC22
BC23
BC24
BC25
BC26
BC30
BC31
BC32
BC33
BC34
BC35
BC36
BC40
BC41
BC42
BC43
BC44
BC45
BC46
BC50
BC51
BC52
BC53
BC54
BC55
BC56
BC60
BC61
BC62
BC63
BC64
BC65
BC66
BC70
BC71
BC72
BC73
BC74
BC75
BC76
BC80
BC81
BC82
BC83
BC84
BC85
BC86
BC90
BC91
BC92
BC93
BC94
BC95
BC96
BC100
BC101
BC102
BC103
BC104
BC105
BC106
BC110
BC111
BC112
BC113
BC114
BC115
BC116
BC120
BC121
BC122
BC123
BC124
BC125
BC126
HP16
HP17
HP14
HP15
HP12
HP13
HP10
HP11
T3CS
BC130
BC131
BC132
BC133
BC134
BC135
BC136
BC140
BC141
BC142
BC143
BC144
BC145
BC146
BC150
BC151
BC152
BC153
BC154
BC155
BC156
BC160
BC161
BC162
BC163
BC164
BC165
BC166
P6IM
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
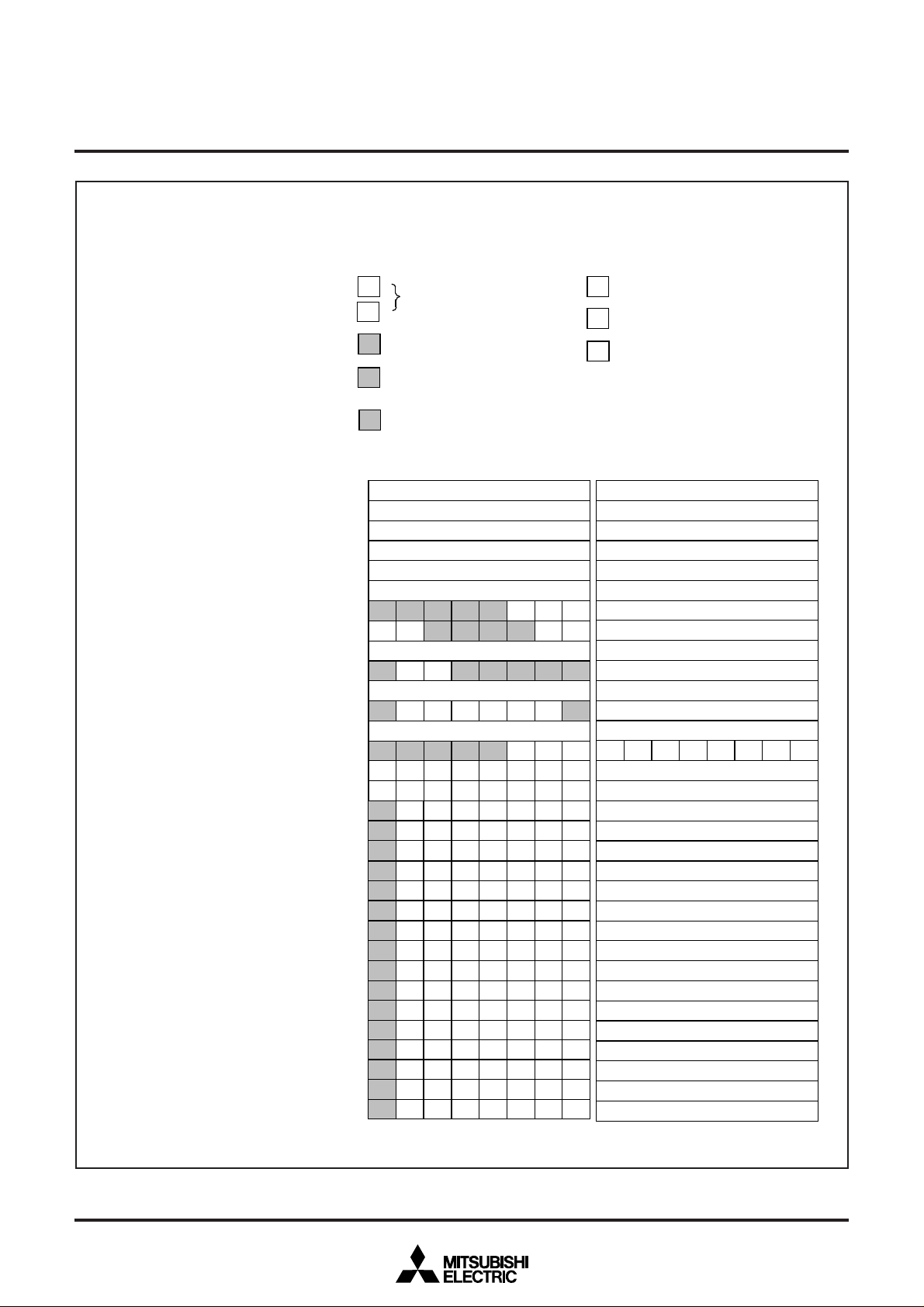
■ SFR1 area (addresses C016 to DF16)
Bit allocation
:
Name
:
: No function bit
: Fix to this bit to “0”
0
: Fix to this bit to “1”
1
Address
C016
C116
C216
C316
C416
C516
C616
C716
C816
C916
CA16
CB16
CC16
CD16
CE16
CF16
D016
D116
D216
D316
D416
D516
D616
D716
D816
D916
DA16
DB16
DC16
DD16
DE16
DF16
Registe
Port P0 (P0
Port P0 direction register (D0
Port P1
Port P1 direction register (D1
Port P2 (P2
Port P2 direction register (D2
Port P3 (P3
Port P3 direction register (D3
Port P4 (P4
Port P4 direction register (D4
Port P5 (P5
OSD port control register (PF
Port P6 (P6
Port P7
OSD control register 1 (OC 1
Horizontal position register (HP
Block control register 1 (BC1)
Block control register 2 (BC2)
Block control register 3 (BC
Block control register 4 (BC
Block control register 5 (BC
Block control register 6 (BC
Block control register 7 (BC
Block control register 8 (BC8)
Block control register 9 (BC
Block control register 10 (BC
Block control register 11 (BC
Block control register 12 (BC
Block control register 13 (BC13)
Block control register 14 (BC
Block control register 15 (BC
Block control register 16 (BC
)
3
)
4
)
5
)
6
)
7
)
9
10
11
12
14
15
16
b7 b0 b7 b0
0
)
)
)
)
)
)
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
State immediately after reset
: “0” immediately after reset
Function bit
do not write to “1”
do not write to “0”
Bit allocation State immediately after reset
RGB
R0GB
2BIT
0
: “1” immediately after reset
1
: Indeterminate immediately
?
after reset
?
0016
?
00
?
0016
?
0016
?
0
0016
?
0016
?
00?00??0
0016
0016
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
16
Fig. 12.2.3 Memory Map of Special Function Register 1 (SFR1) (1)
Rev. 1.0
15
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
Data slicer control register 1 (DSC1)
A-D conversion register (AD)
A-D control register (ADCON)
Timer mode register 1 (TM1)
Timer mode register 2 (TM2)
I2C clock control register (S2)
Interrupt request register 1 (IREQ1)
Interrupt request register 2 (IREQ2)
Interrupt control register 1 (ICON1)
Interrupt control register 2 (ICON2)
Data slicer control register 2 (DSC2)
r
(
)
State immediately after reset
(
)
TM20
TM21
TM22
TM23
TM24
TM10
TM11
TM12
TM13
TM14
OSDR
OSDE
TM25
TM15
TM16
TM17
TM26
TM27?SAD0
SAD1
SAD2
SAD3
SAD4
SAD5
SAD6
BSEL0
BSEL1
CCR0
CCR1
CCR2
CCR3
CCR4ACK
R
TM56R
TM56E
TM56S
ADIN0
ADIN1
ADIN2
ADVREF
ADSTR
10BIT
DSC10
DSC11
DSC12
DSC20
DSC23
DSC24
DSC25
CRD3
CRD4
CRD5
CRD6
CRD7
DPS3
DPS4
DPS5
DPS6
DPS7
CPS0
CPS3
CPS4
CPS5
CPS1
CPS2
CPS6
CPS7
CDH10
CDH13
CDH14
CDH15
CDH11
CDH12
CDH16
CDH17
CDL10
CDL13
CDL14
CDL15
CDL11
CDL12
CDL16
CDL17
FAST
E
ACK
CDH20
CDH23
CDH24
CDH25
CDH21
CDH22
CDH26
CDH27
CDL20
CDL23
CDL24
CDL25
CDL21
CDL22
CDL26
CDL27
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
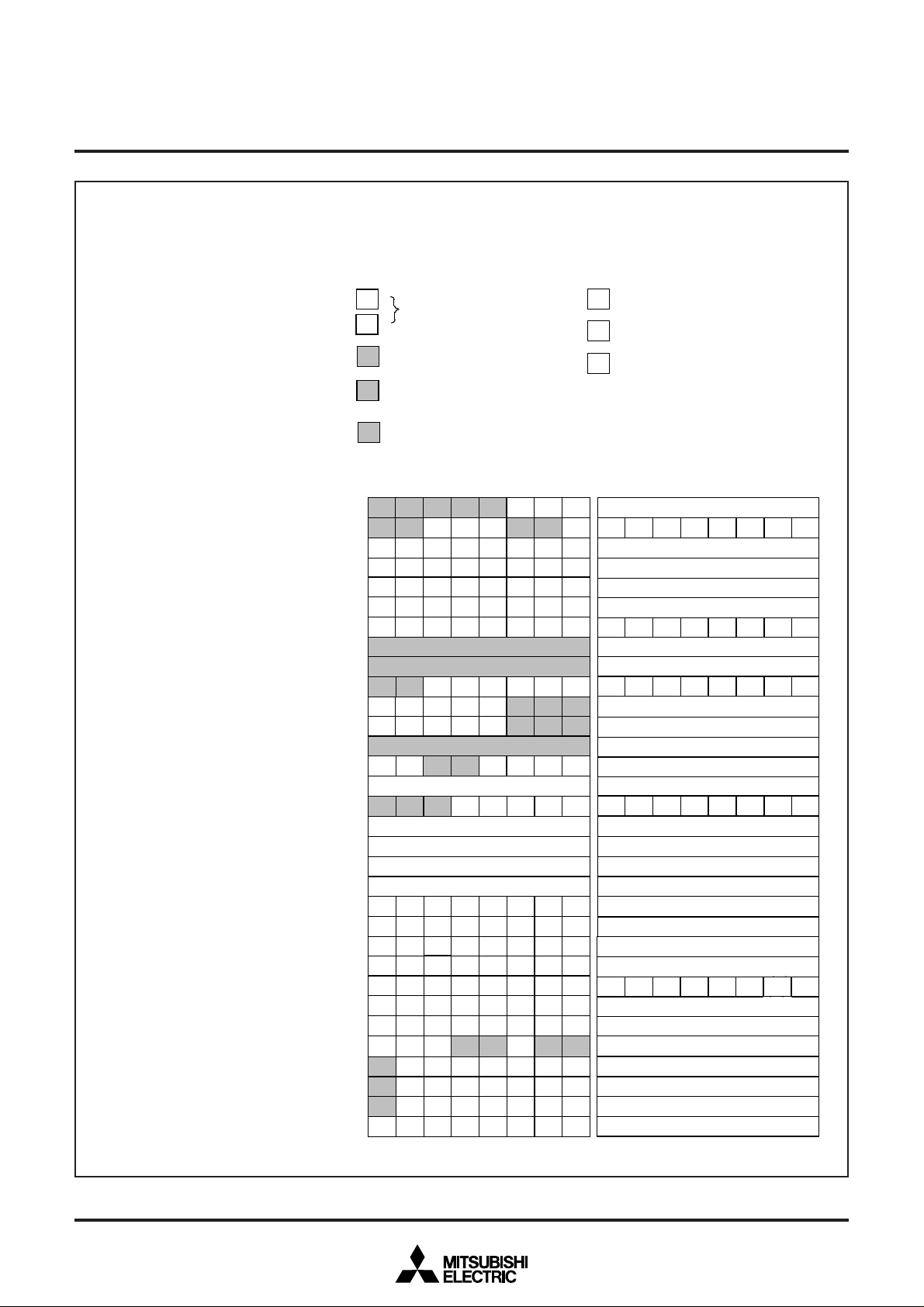
■ SFR1 area (addresses E016 to FF16)
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
Bit allocation
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280EKSP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Address
E016
E116
E216
E316
E416
E516
E616
E716
E816
E916
EA16
EB16
EC16
ED16
EE16
EF16
F016
F116
F216
F316
F416
F516
F616
F716
F816
F916
FA16
FB16
FC16
FD16
FE16
FF16
Registe
Caption data register 1 (CD1)
Caption data register 2 (CD2)
Caption data register 3 (CD3)
Caption data register 4 (CD4)
Caption Position register (CPS)
Data slicer test register 2
Data slicer test register 1
Sync signal counter register (HC)
Clock run-in detect register (CRD)
Data clock position register (DPS)
Bank control register (BK)
Timer 1 (T1)
Timer 2 (T2)
Timer 3 (T3)
Timer 4 (T4)
I2C data shift register (S0)
I2C address register (S0D)
I2C status register (S1)
I2C control register (S1D)
CPU mode register (CM)
:
Function bit
:
Name
: No function bit
: Fix to this bit to “0”
0
do not write to “1”
: Fix to this bit to “1”
1
do not write to “0”
Bit allocation
b7
0
00
0
00
0
CM7 CM5CM6
BIT
ADR
ADE
0
SAD
MOD
VSCR
IN2RIICR
VSCE
b0
00
0
0016
0016
HC0HC3HC4HC5 HC1HC2
0
10
BK0BK3 BK1BK2BK6BK7
D1D2D3D4D5D6D7 D0
RBW
LRBAD0AASALPINBBTRXMST
BC0BC1BC2ESOALS
CK
CKEIICE
CM2
SIOR
00
TM1RTM2RTM3RTM4R
DSR
TM1ETM2ETM3ETM4E
IN1EDSESIOEIN2E
101
CK0 IN1R
: “0” immediately after reset
0
: “1” immediately after reset
1
: Indeterminate immediately
?
after reset
State immediately after reset
b7
0016
0?0? 0 ???
0016
0016
0016
0016
0000?00 0
0016
0016
??00??? ?
0016
0916
?
0016
?
000?001 0
FF16
0716
FF16
0716
0016
0016
0016
00 0 010 0?
0016
0016
3C16
0016
0016
0016
0016
b0
Fig. 12.2.4 Memory Map of Special Function Register 1 (SFR2) (2)
16
Rev. 1.0
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
Interrupt input polarity register (IP)
)
)
Clock control register (CS)
(
)
)
)
)
I/O polarity control register (PC)
r
(
)
(
)
)
g
)
ROM correction address 1 (high-order)
ROM correction enable register (RCR)
ROM correction address 2 (high-order)
ROM correction address 2 (low-order)
ROM correction address 1 (low-order)
0
5PW6PN3
INT3
AD/INT3
AD/INT3
INT3
AD/INT3
INT3
AD/INT3
INT3
AD/INT3
INT3
AD/INT3
TB20
TB21
BB20
BB21
0
OC30
OC31
OC32
BB17
BB16
BB15
BB14
BB13
BB12
BB11
BB10
TB17
TB16
TB15
TB14
TB13
TB12
TB11
TB10
OC27
OC25
OC24
OC23
OC12
OC21
OC20
OC33
OC34
INT3
AD/INT3
OC26
RCR0
RCR1
OC35
OC36
OC37
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
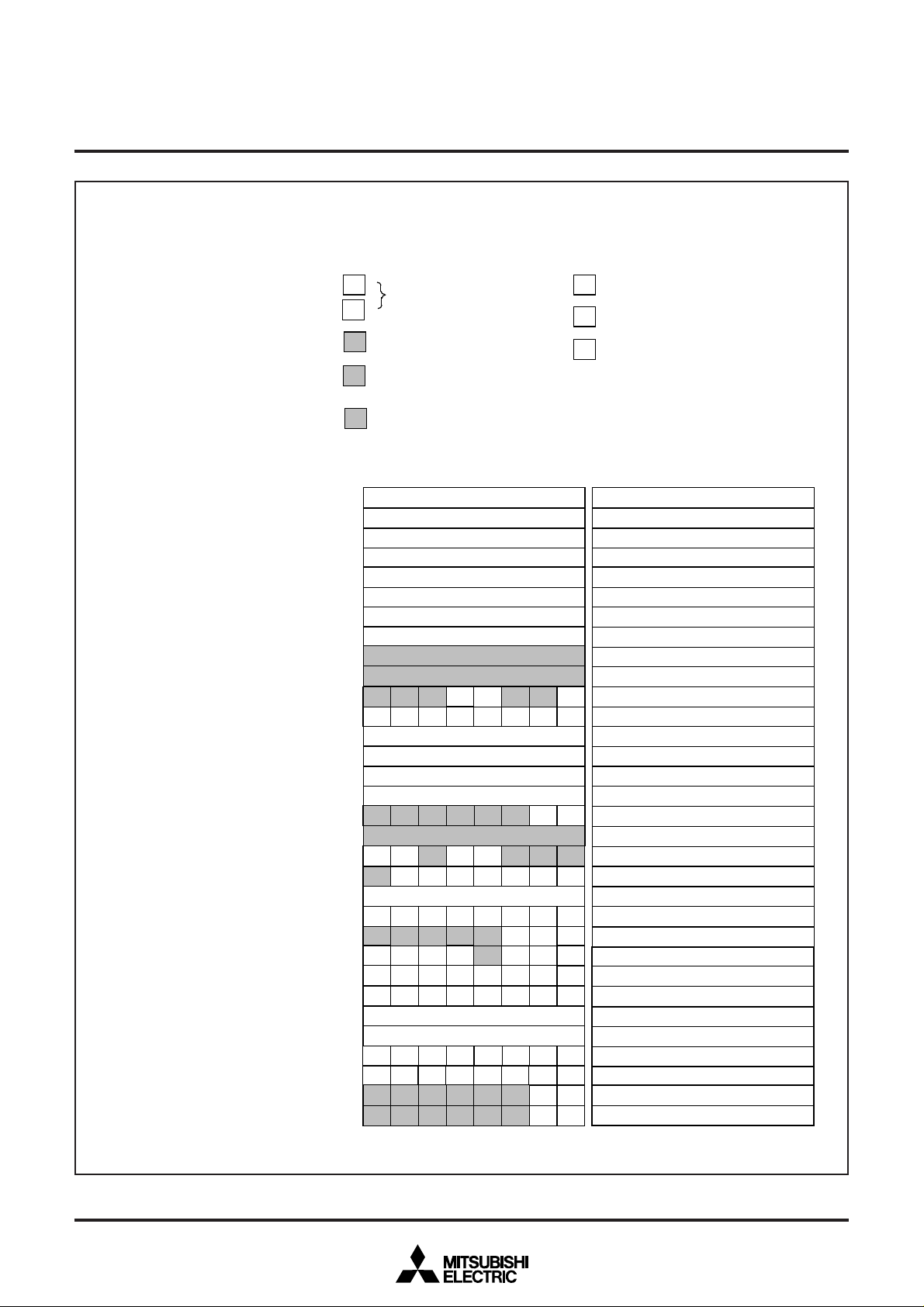
■ SFR2 area (addresses 20016 to 21F16)
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
Bit allocation
:
Function bit
Name
:
: No function bit
: Fix to this bit to “0”
0
do not write to “1”
: Fix to this bit to “1”
1
do not write to “0”
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280EKSP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
State immediately after reset
: “0” immediately after reset
0
: “1” immediately after reset
1
: Indeterminate immediately
?
after reset
Address Registe
2001
2011
2021
2031
2041
2051
2061
2071
PWM0 register (PWM0
PWM1 register (PWM1
PWM2 register (PWM2
PWM3 register (PWM3
PWM4 register (PWM4
PWM5 register (PWM5
PWM6 register (PWM6
PWM7 register (PWM7
2081
2091
20A1
20B1
PWM mode register 1 (PN
PWM mode register 2 (PW
20C16
20D16
20E1
20F1
2101
2111
Test register
2121
2131
2141
2151
Serial I/O mode register (SM
Serial I/O register (SIO
OSD control re
2161
2171
2181
2191
21A1
21B1
21C16
21D16
21E1
21F1
Raster color register (RC
OSD control register 3(OC3)
Timer 5 (TM5
Timer 6
TM6
Top border control register 1 (TB1)
Bottom border control register 1 (BB1)
Top border control register 1 (TB2)
Bottom border control register 1 (BB2)
ister 2(OC2
b7 b0 b7 b0
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
Bit allocation State immediately after reset
PW7
PN4
PN
PW
PW1PW2PW3PW4PW
0016
0016
0016
0016
0016
0016
SEL
SEL
SEL
SEL
POL
POL3
POL
SM6
POL
00
0016
POL2POL1
RE1RE2RE3RE5
0016
0016
RE1RE2RE3RE5
SM0RE1RE2RE3SM4RE5
SM1SM2SM3SM5
0016
0016
?
0016
SEL
SEL
SEL
0
00
POL
POL
POL
0
RC3RC4
RE1RE2
CS0CS1CS2
PC0RE1RE2RE3PC4RE5
PC1PC2PC5PC6PC7
RC0RE1RE2RE3RE5
RC1RC2
RE1RE2RE3
0016
8016
0016
0016
0716
FF16
?
?
?
?
Fig. 12.2.5 Memory Map of Special Function Register 2 (SFR2) (1)
Rev. 1.0
17
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
Vertical position register 1
(VP111)
Vertical position register 13(VP13)
Vertical position register 17 (VP17)
Vertical position register 15(VP15)
Vertical position register 16 (VP16)
Vertical position register 11(VP11)
Vertical position register 12(VP12)
Vertical position register 19 (VP19)
Vertical position register 1
(VP110)
Vertical position register 14(VP14)
Vertical position register 1
(VP112)
Vertical position register 18 (VP18)
Vertical position register 23 (VP23)
Vertical position register 27 (VP27)
Vertical position register 25 (VP25)
Vertical position register 26 (VP26)
Vertical position register 21 (VP21)
Vertical position register 29 (VP29)
Vertical position register 2
(VP210)
Vertical position register 24 (VP24)
Vertical position register 2
(VP212)
Vertical position register 28 (VP28)
Vertical position register 22 (VP22)
Vertical position register 2
(VP211)
r
State immediately after reset
(
)
Vertical position register 2
(VP214)
Vertical position register 2
(VP213)
Vertical position register 2
(VP216)
Vertical position register 2
(VP215)
Vertical position register 1
(VP113)
Vertical position register 1
(VP114)
Vertical position register 1
(VP115)
Vertical position register 1
(VP116)
VP112
VP113
VP114
VP115
VP116
VP117
VP122
VP123
VP124
VP125
VP126
VP127
VP132
VP133
VP134
VP135
VP136
VP137
VP142
VP143
VP144
VP145
VP146
VP147
VP152
VP153
VP154
VP155
VP156
VP157
VP162
VP163
VP164
VP165
VP166
VP167
VP172
VP173
VP174
VP175
VP176
VP177
VP182
VP183
VP184
VP185
VP186
VP187
VP192
VP193
VP194
VP195
VP196
VP197
VP1102
VP1103
VP1104
VP1105
VP1106
VP1107
VP1112
VP1113
VP1114
VP1115
VP1116
VP1117
VP111
VP121
VP131
VP141
VP151
VP161
VP171
VP181
VP191
VP1101
VP1111
VP1121
VP1122
VP1123
VP1124
VP1125
VP1126
VP1127
VP210
VP211
VP220
VP221
VP230
VP231
VP240
VP241
VP250
VP251
VP260
VP261
VP270
VP271
VP280
VP281
VP290
VP291
VP2100
VP2101
VP2110
VP2111
VP2120
VP2121
VP110
VP120
VP130
VP140
VP150
VP160
VP170
VP180
VP190
VP1100
VP1110
VP1120
VP2130
VP2131
VP2140
VP2141
VP2150
VP2151
VP2160
VP2161
VP1142
VP1143
VP1144
VP1145
VP1146
VP1147
VP1152
VP1153
VP1154
VP1155
VP1156
VP1157
VP1162
VP1163
VP1164
VP1165
VP1166
VP1167
VP1140
VP1150
VP1160
VP1141
VP1151
VP1161
VP1131
VP1132
VP1133
VP1134
VP1135
VP1136
VP1137
VP1130
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
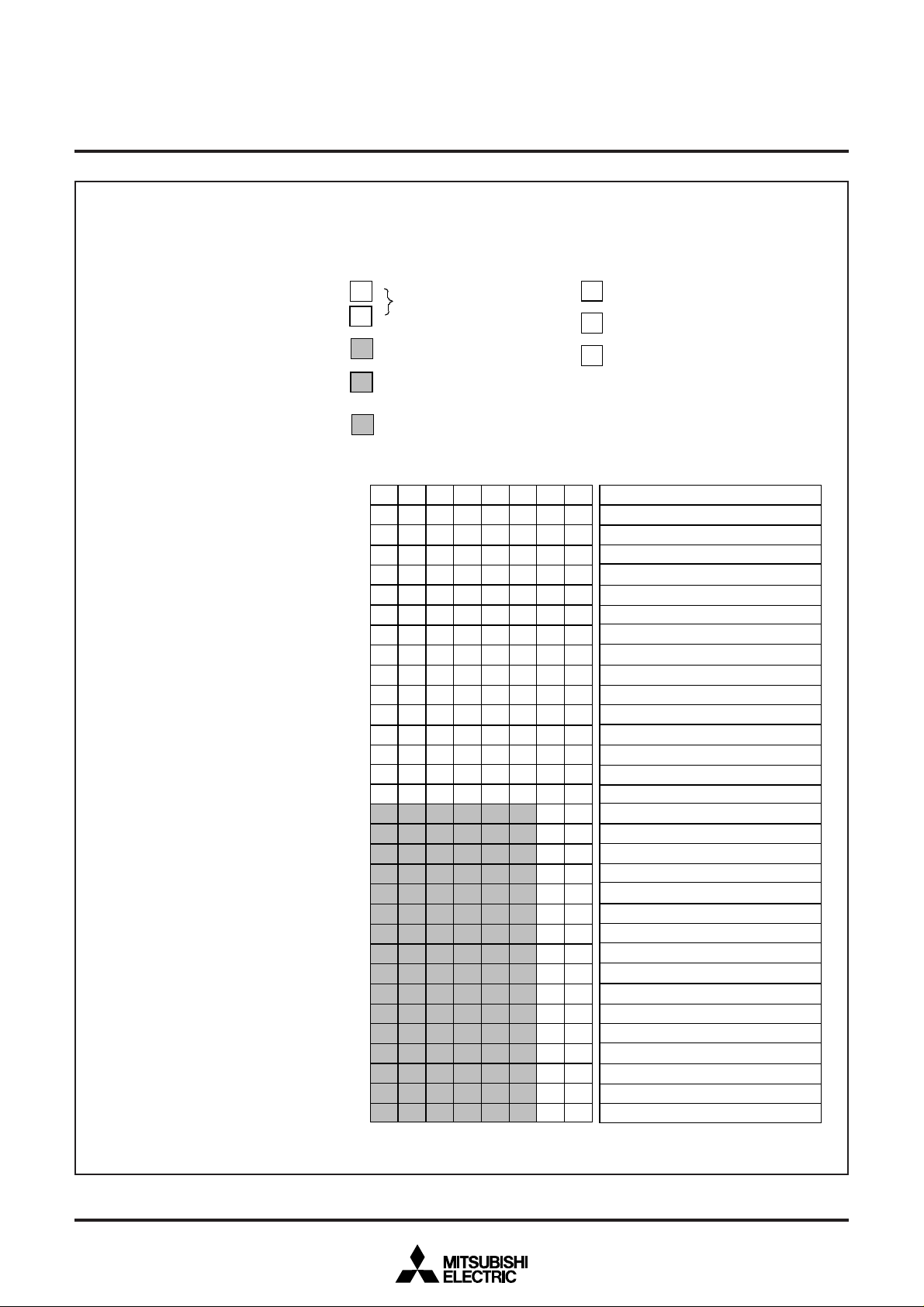
■ SFR2 area (addresses 22016 to 23F16)
Address
22016
22116
22216
22316
22416
22516
22616
22716
22816
22916
22A16
22B16
22C16
22D16
22E16
22F16
23016
23116
23216
23316
23416
23516
23616
23716
23816
23916
23A16
23B16
23C16
23D16
23E16
23F16
Registe
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
Bit allocation
:
Function bit
:
Name
: No function bit
: Fix to this bit to “0”
0
(do not write to “1”)
: Fix to this bit to “1”
1
do not write to “0”
Bit allocation
b7 b0 b7 b0
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280EKSP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
: “0” immediately after reset
0
: “1” immediately after reset
1
: Indeterminate immediately
?
after reset
State immediately after reset
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
Fig. 12.2.6 Memory Map of Special Function Register 2 (SFR2) (2)
18
Rev. 1.0

M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
State immediately after reset
r
CR12
CR13
CR14
CR15
CR16
CR22
CR23
CR24
CR25
CR26
CR32
CR33
CR34
CR35
CR36
CR42
CR43
CR44
CR45
CR46
CR52
CR53
CR54
CR55
CR56
CR62
CR63
CR64
CR65
CR66
CR72
CR73
CR74
CR75
CR76
CR92
CR93
CR94
CR95
CR96
CR102
CR103
CR104
CR105
CR106
CR112
CR113
CR114
CR115
CR116
CR11
CR21
CR31
CR41
CR51
CR61
CR71
CR91
CR101
CR111
CR121
CR122
CR123
CR124
CR125
CR126
CR10
CR20
CR30
CR40
CR50
CR60
CR70
CR90
CR100
CR110
CR120
CR142
CR143
CR144
CR145
CR146
CR152
CR153
CR154
CR155
CR156
CR140
CR150
CR141
CR151
CR131
CR132
CR133
CR134
CR135
CR136
CR130
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
■ SFR2 area (addresses 24016 to 25816)
Address
24016
24116
24216
24316
24416
24516
24616
24716
24816
24916
24A16
24B16
24C16
24D16
24E16
24F16
25016
25116
25216
25316
25416
25516
25616
25716
25816
Registe
Color pallet register 1 (CR1)
Color pallet register 2 (CR2)
Color pallet register 3 (CR3)
Color pallet register 4 (CR4)
Color pallet register 5 (CR5)
Color pallet register 6 (CR6)
Color pallet register 7 (CR7)
Color pallet register 9 (CR9)
Color pallet register10 (CR10)
Color pallet register 11 (CR11)
Color pallet register 12 (CR12)
Color pallet register 13 (CR13)
Color pallet register 14 (CR14)
Color pallet register 15 (CR15)
Left border control register 1 (LB1)
Left border control register 2 (LB2)
Right border control register 1 (RB1)
Right border control register 2 (RB2)
SPRITE vertical position register 1 (VS1)
SPRITE vertical position register 2 (VS2)
SPRITE horizontal position register 1 (HS1)
SPRITE horizontal position register 2 (HS2)
SPRITE OSD control register (SC)
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
Bit allocation
:
Function bit
:
Name
: No function bit
: Fix to this bit to “0”
0
(do not write to “1”)
: Fix to this bit to “1”
1
(do not write to “0”)
Bit allocation
b7 b0 b7 b0
LB12LB13LB14LB15LB16LB17
VS12VS13VS14VS15VS16VS17
HS12HS13HS14HS15HS16HS17
HS22
SC2SC3SC4SC5
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280EKSP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
: “0” immediately after reset
0
: “1” immediately after reset
1
: Indeterminate immediately
?
after reset
State immediately after reset
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
LB10LB11
LB20LB21LB22
RB10RB11RB12RB13RB14RB15RB16RB17
RB20RB21RB22
VS10VS11
VS20VS21
HS10HS11
HS20HS21
SC0SC1
0116
0016
FF16
0716
?
0016
?
???00000
0016
Fig. 12.2.7 Memory Map of Special Function Register 2 (SFR2) (3)
Rev. 1.0
19
PRELIMINARY
Name
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Bit allocation
:
Function bit
:
: No function bit
: Fix to this bit to “0”
0
?
(do not write to “1”)
: Fix to this bit to “1”
1
(do not write to “0”)
Register
b7
Processor status register (PS)
Program counter (PCH)
Program counter (PCL)
Fig. 12.2.8 Internal State of Processor Status Register and Program Counter at Reset
Bit allocation State immediately after reset
b0
b7
I ZCDBTVN???????
State immediately after reset
: “0” immediately after reset
0
: “1” immediately after reset
1
: Indeterminate immediately
after reset
1
Contents of address FFFF16
Contents of address FFFE16
b0
Rev. 1.0
20
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
12.3 INTERRUPTS
Interrupts can be caused by 19 different sources consisting of 3 external, 14 internal, 1 software, and reset. Interrupts are vectored interrupts with priorities as shown in Table 12.3.1. Reset is also included in the table because its operation is similar to an interrupt.
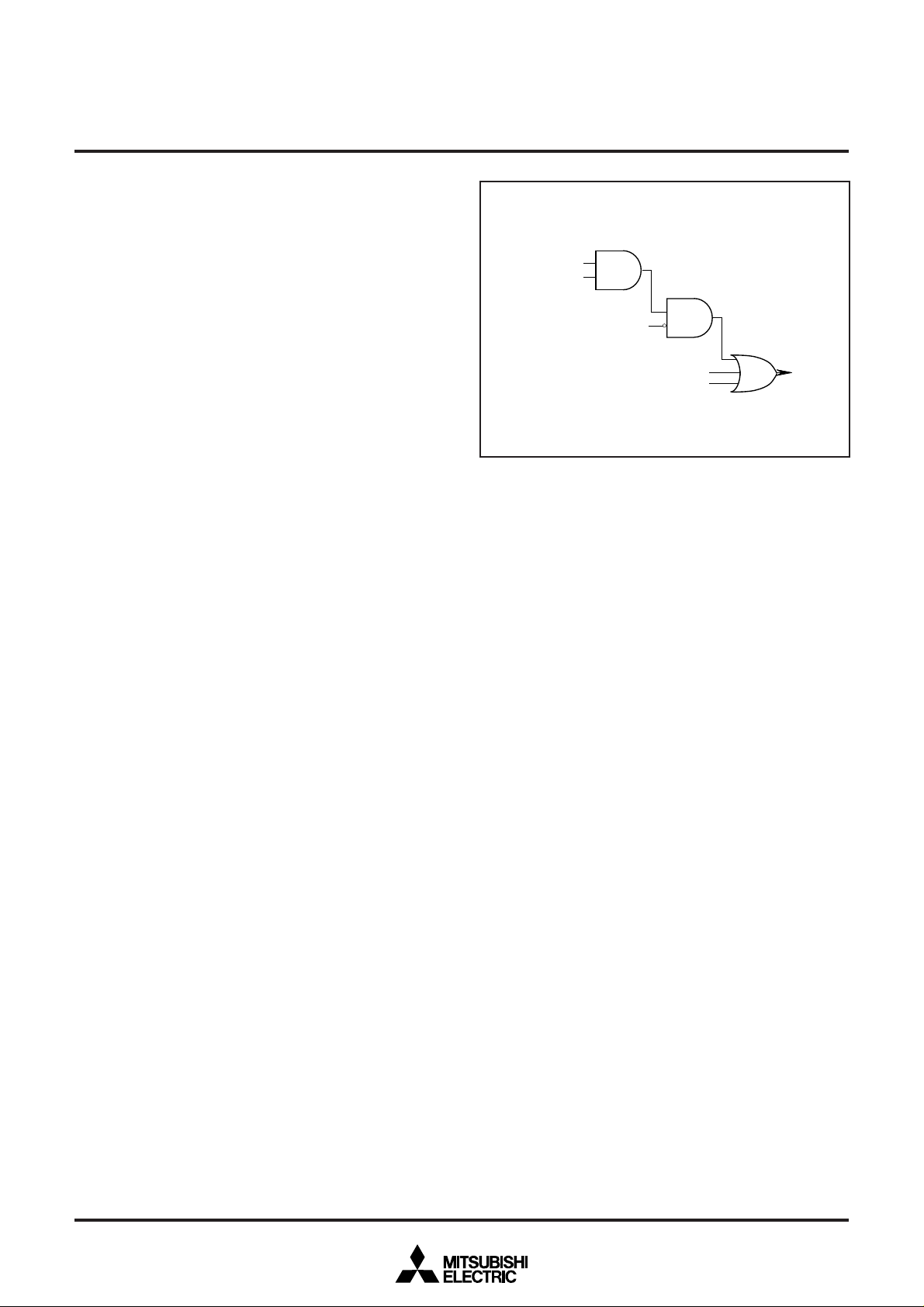
When an interrupt is accepted,
① The contents of the program counter and processor status regis
ter are automatically stored into the stack.
➁ The interrupt disable flag I is set to “1” and the corresponding
interrupt request bit is set to “0.”
➂ The jump destination address stored in the vector address enters
the program counter.
Other interrupts are disabled when the interrupt disable flag is set to
“1.”
All interrupts except the BRK instruction interrupt have an interrupt
request bit and an interrupt enable bit. The interrupt request bits are
in interrupt request registers 1 and 2 and the interrupt enable bits are
in interrupt control registers 1 and 2. Figures 12.3.2 to 12.3.6 show
the interrupt-related registers.
Interrupts other than the BRK instruction interrupt and reset are accepted when the interrupt enable bit is “1,” interrupt request bit is “1,”
and the interrupt disable flag is “0.” The interrupt request bit can be
set to “0” by a program, but not set to “1.” The interrupt enable bit can
be set to “0” and “1” by a program.
Reset is treated as a non-maskable interrupt with the highest priority.
Figure 12.3.1 shows interrupt control.
12.3.1 Interrupt Causes
(1) VSYNC and OSD Interrupts
The VSYNC interrupt is an interrupt request synchronized with
the vertical sync signal.
The OSD interrupt occurs after character block display to the
CRT is completed.
(2) INT1, INT2 Interrupts
The INT1 and INT2 interrupts are external interrupt inputs, the
system detects that the level of a pin changes from LOW to HIGH
or from HIGH to LOW, and generates an interrupt request. The
input active edge can be selected by bits 3 and 4 of the interrupt
input polarity register (address 021216) : when this bit is “0,” a
change from LOW to HIGH is detected; when it is “1,” a change
from HIGH to LOW is detected. Note that both bits are cleared to
“0” at reset.
(3) Timer 1 to 4 Interrupts
An interrupt is generated by an overflow of timer 1, 2, 3 or 4.
Table 12.3.1 Interrupt Vector Addresses and Priority
Priority
Reset
1
OSD interrupt
2
INT1 interrupt
3
Data slicer interrupt
4
Serial I/O interrupt
5
Timer 4 • SPRITE OSD interrupt
6
f(XIN)/4096 interrupt
7
VSYNC interrupt
8
Timer 3 interrupt
9
Timer 2 interrupt
10
Timer 1 interrupt
11
A-D convertion • INT3 interrupt
12
INT2 interrupt
13
Multi-master I2C-BUS interface interrupt
14
Timer 5 • 6 interrupt
15
BRK instruction interrupt
16
Note : Switching a source during a program causes an unnecessary interrupt occurs. Accordingly, set a source at initializing of program.
Interrupt Source
Vector Addresses
FFFF16, FFFE16
FFFD16, FFFC16
FFFB16, FFFA16
FFF916, FFF816
FFF716, FFF616
FFF516, FFF416
FFF316, FFF216
FFF116, FFF016
FFEF16, FFEE16
FFED16, FFEC16
FFEB16, FFEA16
FFE916, FFE816
FFE716, FFE616
FFE516, FFE416
FFE316, FFE216
FFDF16, FFDE16
Remarks
Non-maskable
Active edge selectable
Software switch by software (See note)
Active edge selectable
Software switch by software (See note)/
When selecting INT3 interrupt, active edge selectable.
Active edge selectable
Software switch by software (See note)
Non-maskable (software interrupt)
Rev. 1.0
21
PRELIMINARY
t
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
(4) Serial I/O Interrupt
This is an interrupt request from the clock synchronous serial I/O
function.
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
(5) f(XIN)/4096 • SPRITE OSD Interrupt
The f (XIN)/4096 interrupt occurs regularly with a f(XIN)/4096 period. Set bit 0 of the PWM mode register 1 to “0.”
The SPRITE OSD interrupt occurs at the completion of SPRITE
display.
Since f(XIN)/4096 interrupt and SPRITE OSD interrupt share the
same vector, an interrupt source is selected by bit 5 of the SPRITE
OSD control register (address 025816).
(6) Data Slicer Interrupt
An interrupt occurs when slicing data is completed.
(7) Multi-master I2C-BUS Interface Interrupt
This is an interrupt request related to the multi-master I2C-BUS
interface.
(8) A-D Conversion • INT3 Interrupt
The A-D conversion interrupt occurs at the completion of A-D
conversion.
The INT3 is an external input,the system detects that the level of
a pin changes from LOW to HIGH or from HIGH to LOW, and
generates an interrupt request. The input active edge can be
selected by bit 6 of the interrupt input polarity register (address
021216) : when this bit is “0,” a change from LOW to HIGH is
detected; when it is “1,” a change from HIGH to LOW is detected.
Note that this bit is cleared to “0” at reset.
Since A-D conversion interrupt and the INT3 interrupt share the
same vector, an interrupt source is selected by bit 7 of the interrupt interval determination control register (address 021216).
Interrupt request bi
Interrupt enable bit
Interrupt disable flag I
Fig. 12.3.1 Interrupt Control
BRK instruction
Reset
Interrupt
request
(9) Timer 5 • 6 Interrupt
An interrupt is generated by an overflow of timer 5 or 6. Their
priorities are same, and can be switched by software.
(10) BRK Instruction Interrupt
This software interrupt has the least significant priority. It does
not have a corresponding interrupt enable bit, and it is not affected by the interrupt disable flag I (non-maskable).
Rev. 1.0
22
PRELIMINARY
After reset
0 : No interrupt request issued
)
q
)
q
)
q
)
(
)
q
)
A-D conversion • INT3
0 : No interrupt request issued
0 : No interrupt request issued
0 : No interrupt request issued
0 : No interrupt request issued
0 : No interrupt request issued
0 : No interrupt request issued
,
After reset
q
)
0 : No interrupt request issued
q
)
q
)
q
)
5
0 : No interrupt request issued
0 : No interrupt request issued
0 : No interrupt request issued
✽
✽
W
f(XIN)/4096 • SPRITE OSD
0 : No interrupt request issued
2
0 : No interrupt request issued
6
q
)
0 : No interrupt request issued
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
Interrupt Request Register 1
b7b6 b5b4b3 b2b1b0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
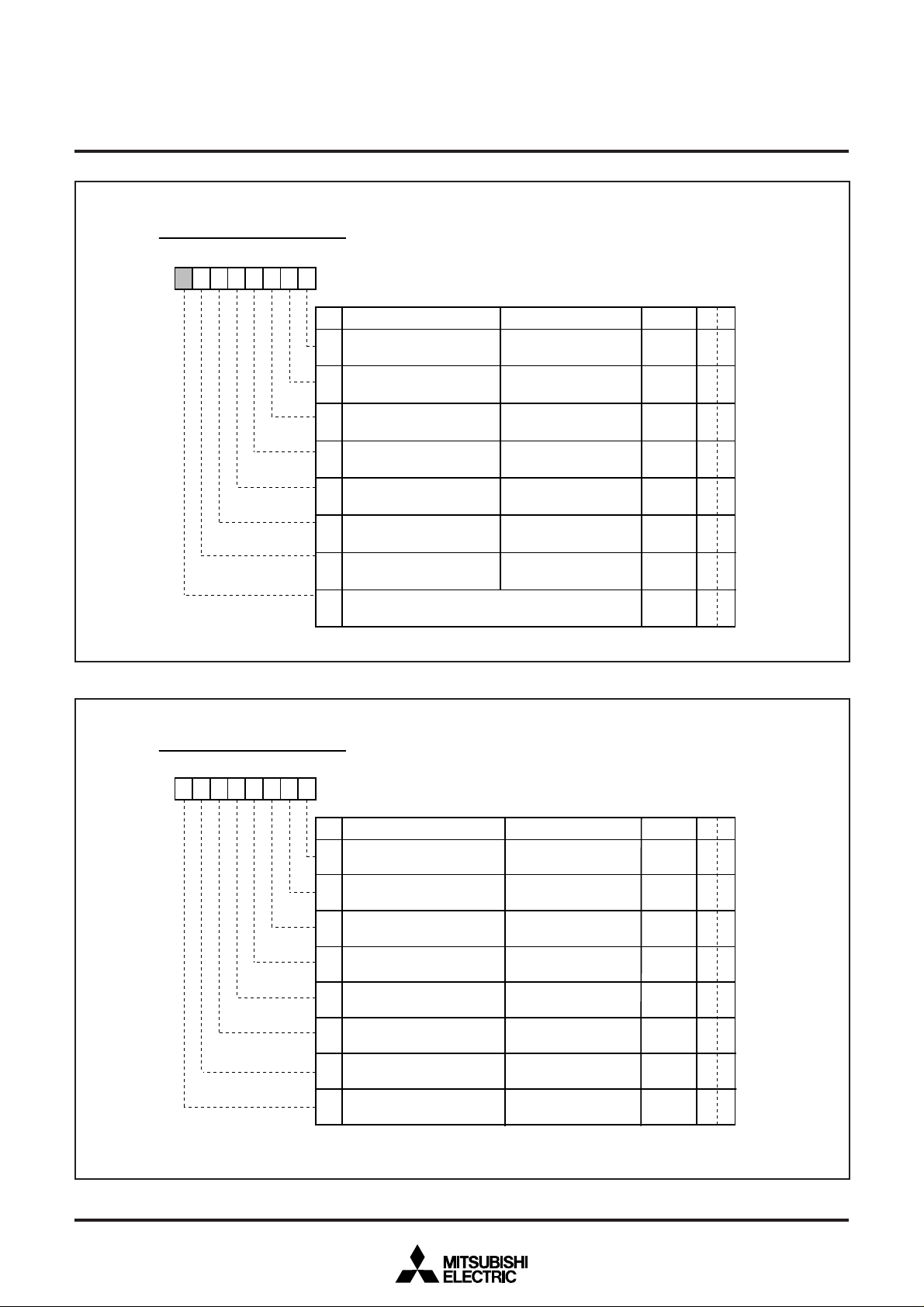
Interrupt request register 1 (IREQ1) [Address 00FC
16]
Fig. 12.3.2 Interrupt Request Register 1
Interrupt Request Register 2
B Name Functions
Timer 1 interrupt
0
request bit (TM1R
Timer 2 interrupt
1
re
uest bit (TM2R
Timer 3 interrupt
2
uest bit (TM3R
re
Timer 4 interrupt
3
re
uest bit (TM4R
OSD interrupt request
4
bit
OSDR
SYNC interrupt
V
5
re
uest bit (VSCR
6
interrupt request bit (ADR)
Nothing is assigned. This bit is a write disable bit.
7
When this bit is read out
✽: “0” can be set by software, but “1” cannot be set.
1 : Interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
the value is “0.”
RW
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
✽
R
✽
R
✽
R
✽
R
✽
R
✽
R
✽
R
—
R
b7 b6b5b4b3 b2b1b0
0
Fig. 12.3.3 Interrupt Request Register 2
Interrupt request register 2 (IREQ2) [Address 00FD
B Name Functions
INT1 interrupt
0
uest bit (IN1R
re
Data slicer interrupt
1
re
uest bit (DSR
Serial I/O interrupt
2
uest bit (SIOR
re
1 : Interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
3
interrupt request bit (CKR)
INT2 interrupt
4
uest bit (IN2R
re
Multi-master I
C-BUS
interrupt request bit (IICR)
1 : Interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
Timer 5 • 6 interrupt
uest bit (TM56R
re
Fix this bit to “0.”
7
1 : Interrupt request issued
✽: “0” can be set by software, but “1” cannot be set.
16
]
RW
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
✽
R
✽
R
✽
R
R
✽
R
R
✽
R
R
Rev. 1.0
23
PRELIMINARY
After reset
(
)
0 : Interrupt disabled
(
)
(
)
(
)
0 : Interrupt disabled
0 : Interrupt disabled
0 : Interrupt disabled
7
,
(
)
0 : Interrupt disabled
5
(
)
0 : Interrupt disabled
6
A-D conversion • INT3
0 : Interrupt disabled
After reset
(
)
0 : Interrupt disabled
(
)
(
)
(
)
0 : Interrupt disabled
0 : Interrupt disabled
0 : Interrupt disabled
f(XIN)/4096 • SPRITE OSD
0 : Interrupt disabled
5
0 : Interrupt disabled
6
(
)
0 : Interrupt disabled
7
(
)
0 : Timer 5
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
Interrupt Control Register 1
b7b6 b5b4b3 b2b1b0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Interrupt control register 1 (ICON1) [Address 00FE
16]
Fig. 12.3.4 Interrupt Control Register 1
Interrupt Control Register 2
b7b6 b5b4b3 b2b1b0
B Name Functions
Timer 1 interrupt
0
enable bit
Timer 2 interrupt
1
enable bit
Timer 3 interrupt
2
enable bit
Timer 4 interrupt
3
enable bit
OSD interrupt enable bit
4
OSDE
VSYNC interrupt enable
bit
interrupt enable bit (ADE)
Nothing is assigned. This bit is a write disable
bit. When this bit is read out
Interrupt control register 2 (ICON2) [Address 00FF
TM1E
TM2E
TM3E
TM4E
VSCE
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Interrupt enabled
the value is “0.”
0
0
0
0
0
0RW
0RW
0
16]
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
R—
Fig. 12.3.5 Interrupt Control Register 2
24
B Name Functions
INT1 interrupt
0
enable bit
Data slicer interrupt
1
enable bit
Serial I/O interrupt
2
enable bit
3
interrupt enable bit (CKE)
INT2 interrupt enable
4
bit
IN2E
Multi-master I2C-BUS interface
interrupt enable bit (IICE)
Timer 5 • 6 interrupt
enable bit
Timer 5 • 6 interrupt
switch bit
IN1E
DSE
SIOE
TM56E
TM56S
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Interrupt enabled
1 : Timer 6
RW
0
RW
0
RW
0
RW
0
RW
0
RW
0RW
0RW
0RW
Rev. 1.0
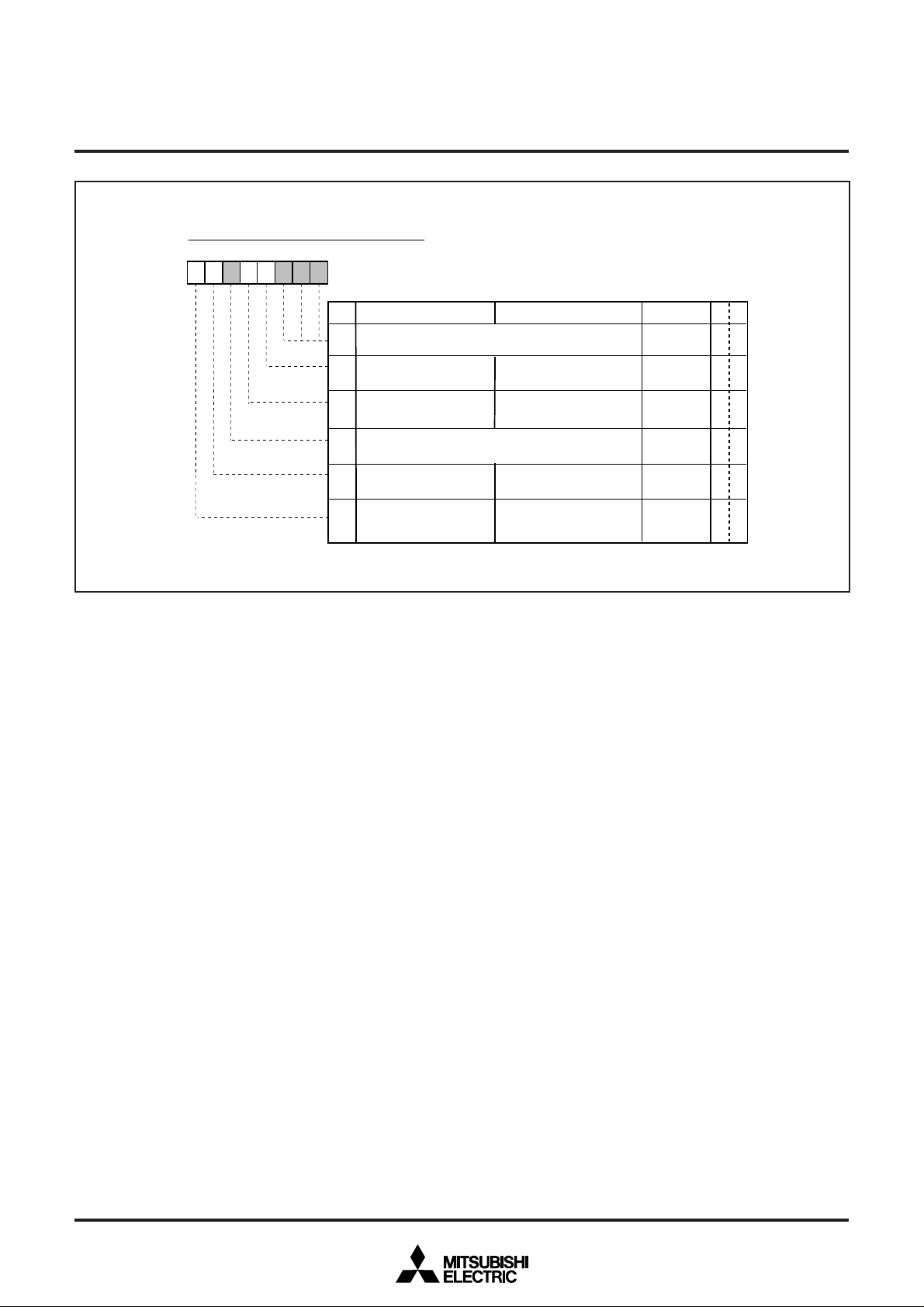
PRELIMINARY
e
s
R
W
0 to 2
R
RWRWR
W
R
W
R
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
Interrupt Input Polarity Register
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Interrupt input polarity register (IP) [Address 0212
16]
Fig. 12.3.6 Interrupt Input Polarity Register
B Nam
Nothing is assigned. These bits are write disable bits.
When these bits are read out, the values are “0.”
3
INT1 polarity switch bit
(POL1)
INT2 polarity switch bit
4
(POL2)
5
Nothing is assigned. This bit is write disable bit.
When this bit is read out, the value is “0.”
6
INT3 polarity switch bit
(POL3)
7 A-D conversion • INT3
interrupt source selection
bit (AD/INT3SEL)
0 : Positive polarity
1 : Negative polarity
0 : Positive polarity
1 : Negative polarity
0 : Positive polarity
1 : Negative polarity
0 : INT3 interrupt
1 : A-D conversion interrupt
Function
After reset
0
0
0
0
0
0
—
—
Rev. 1.0
25

PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
12.4 TIMERS
This microcomputer has 6 timers: timer 1, timer 2, timer 3, timer 4,
timer 5, and timer 6. All timers are 8-bit timers with the 8-bit timer
latch. The timer block diagram is shown in Figure 12.4.3.
All of the timers count down and their divide ratio is 1/(n+1), where n
is the value of timer latch. By writing a count value to the corresponding timer latch (addresses 00F016 to 00F316 : timers 1 to 4, addresses
021A16 and 021B16 : timers 5 and 6), the value is also set to a timer ,
simultaneously.
The count value is decremented by 1. The timer interrupt request bit
is set to “1” by a timer overflow at the next count pulse, after the
count value reaches “0016”.
12.4.1 Timer 1
Timer 1 can select one of the following count sources:
• f(XIN)/16 or f(XCIN)/16
• f(XIN)/4096 or f(XCIN)/4096
• External clock from the P42/TIM2 pin
The count source of timer 1 is selected by setting bits 5 and 0 of
timer mode register 1 (address 00F416). Either f(XIN) or f(XCIN) is
selected by bit 7 of the CPU mode register.
Timer 1 interrupt request occurs at timer 1 overflow.
12.4.2 Timer 2
Timer 2 can select one of the following count sources:
• f(XIN)/16 or f(XCIN)/16
• Timer 1 overflow signal
• External clock from the TIM2 pin
The count source of timer 2 is selected by setting bits 4 and 1 of
timer mode register 1 (address 00F416). Either f(XIN) or f(XCIN) is
selected by bit 7 of the CPU mode register. When timer 1 overflow
signal is a count source for the timer 2, the timer 1 functions as an 8bit prescaler.
Timer 2 interrupt request occurs at timer 2 overflow.
12.4.3 Timer 3
Timer 3 can select one of the following count sources:
• f(XIN)/16 or f(XCIN)/16
• f(XCIN)
• External clock from the TIM3 pin
The count source of timer 3 is selected by setting bit 0 of timer mode
register 2 (address 00F516) and bit 6 at address 00C716. Either f(XIN)
or f(XCIN) is selected by bit 7 of the CPU mode register.
Timer 3 interrupt request occurs at timer 3 overflow.
12.4.5 Timer 5
Timer 5 can select one of the following count sources:
• f(XIN)/16 or f(XCIN)/16
• Timer 2 overflow signal
• Timer 4 overflow signal
The count source of timer 3 is selected by setting bit 6 of timer mode
register 1 (address 00F416) and bit 7 of timer mode register 2 (address 00F516). When overflow of timer 2 or 4 is a count source for
timer 5, either timer 2 or 4 functions as an 8-bit prescaler. Either
f(XIN) or f(XCIN) is selected by bit 7 of the CPU mode register.
Timer 5 interrupt request occurs at timer 5 overflow.
12.4.6 Timer 6
Timer 6 can select one of the following count sources:
• f(XIN)/16 or f(XCIN)/16
• Timer 5 overflow signal
The count source of timer 6 is selected by setting bit 7 of timer mode
register 1 (address 00F416). Either f(XIN) or f(XCIN) is selected by bit
7 of the CPU mode register. When timer 5 overflow signal is a count
source for timer 6, timer 5 functions as an 8-bit prescaler.
Timer 6 interrupt request occurs at timer 6 overflow.
At reset, timers 3 and 4 are connected by hardware and “FF16” is
automatically set in timer 3; “0716” in timer 4. The f(XIN)✽ /16 is selected as the timer 3 count source. The internal reset is released by
timer 4 overflow in this state and the internal clock is connected.
At execution of the STP instruction, timers 3 and 4 are connected by
hardware and “FF16” is automatically set in timer 3; “0716” in timer 4.
However, the f(XIN)✽ /16 is not selected as the timer 3 count source.
So set both bit 0 of timer mode register 2 (address 00F516) and bit 6
at address 00C716 to “0” before execution of the STP instruction
(f(XIN)✽ /16 is selected as the timer 3 count source). The internal
STP state is released by timer 4 overflow in this state and the internal clock is connected.
As a result of the above procedure, the program can start under a
stable clock.
✽ : When bit 7 of the CPU mode register (CM7) is “1,” f(XIN) becomes
f(XCIN).
The structure of timer-related registers is shown in Figures 12.4.1
and 12.4.2.
12.4.4 Timer 4
Timer 4 can select one of the following count sources:
• f(XIN)/16 or f(XCIN)/16
• f(XIN)/2 or f(XCIN)/2
• f(XCIN)
The count source of timer 3 is selected by setting bits 1 and 4 of
timer mode register 2 (address 00F516). Either f(XIN) or f(XCIN) is
selected by bit 7 of the CPU mode register. When timer 3 overflow
signal is a count source for the timer 4, the timer 3 functions as an 8bit prescaler.
Timer 4 interrupt request occurs at timer 4 overflow.
26
Rev. 1.0
PRELIMINARY
After reset
234
0: f(XIN)/16 or f(X
)/16 (Note)
0: f(XIN)/16 or f(X
)/16 (See note)
5
0: f(XIN)/4096 or f(X
)/4096 (See note)
6
7
0: f(XIN)/16 or f(X
)/16 (See note)
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
Timer Mode Register 1
b7b6 b5b4b3 b2b1b0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Timer mode register 1 (TM1) [Address 00F4
16]
B
0
1
Note: Either f(XIN) or f(XCIN) is selected by bit 7 of the CPU mode register.
Name Functions
Timer 1 count source
selection bit 1 (TM10)
Timer 2 count source
selection bit 1 (TM11)
Timer 1 count
stop bit (TM12)
Timer 2 count stop bit
(TM13)
Timer 2 count source
selection bit 2 (TM14)
Timer 1 count source
selection bit 2 (TM15)
Timer 5 count source
selection bit 2 (TM16)
Timer 6 internal count
source selection bit
(TM17)
1: Count source selected by bit 5 of TM1
0: Count source selected by bit 4 of TM1
1: External clock from TIM2 pin
0: Count start
1: Count stop
0: Count start
1: Count stop
1: Timer 1 overflow
1: External clock from TIM2 pin
0: Timer 2 overflow
1: Timer 4 overflow
1: Timer 5 overflow
CIN
CIN
CIN
CIN
R
0
0
0
0
0
0WR
0WR
0WR
W
WR
WR
WR
WR
WR
Fig. 12.4.1 Timer Mode Register 1
Rev. 1.0
27
PRELIMINARY
After reset
0
4
0
230
005
0
6
0
W
7
0: f(XIN)/16 or f(X
)/16 (See note)
b0
(b6 at address 00C716)
External clock from TIM3 pin
b4 b1
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
Timer Mode Register 2
b7b6 b5b4b3 b2b1b0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Timer mode register 2 (TM2) [Address 00F5
16]
B
0
Timer 3 count source
selection bit (TM20)
1,
Timer 4 count source
selection bits
(TM21, TM24)
Timer 3 count stop bit
(TM22)
Timer 4 count stop bit
(TM23)
Timer 5 count stop bit
(TM25)
Timer 6 count stop bit
(TM26)
Timer 5 count source
selection bit 1
(TM27)
Note: Either f(XIN) or f(XCIN) is selected by bit 7 of the CPU mode register.
Name Functions
0 0 : f(XIN)/16 or f(XCIN)/16 (See note)
1 0: f(X
01:
11 :
0 0 : Timer 3 overflow signal
0 1 : f(X
1 0 : f(X
1 1 : f(X
0: Count start
1: Count stop
0: Count start
1: Count stop
0: Count start
1: Count stop
0: Count start
1: Count stop
1: Count source selected by bit 6
CIN)
IN)/16 or f(XCIN)/16 (See note)
IN)/2 or f(XCIN)/2 (See note)
CIN)
CIN
of TM1
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
R
Fig. 12.4.2 Timer Mode Register 2
28
Rev. 1.0
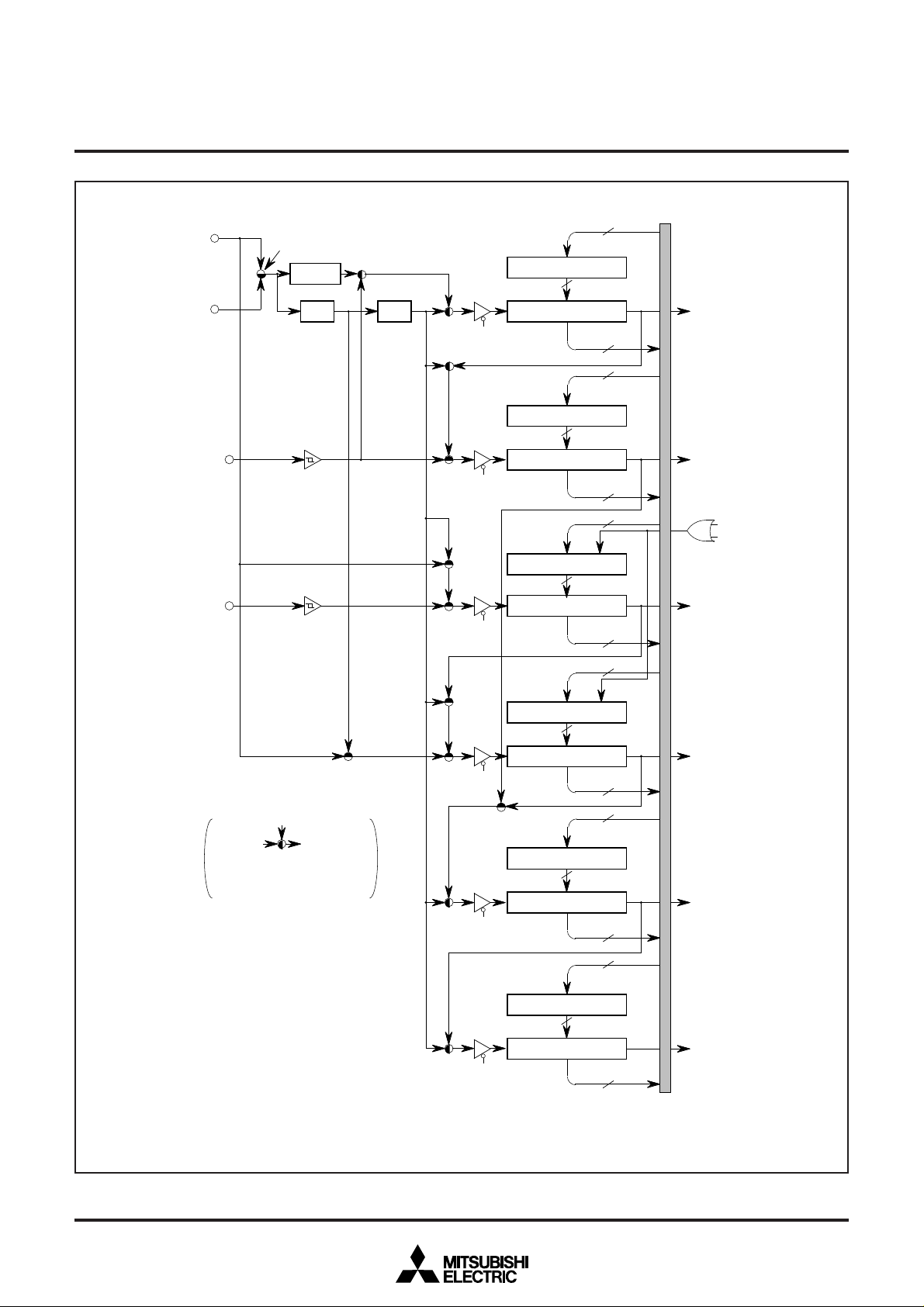
PRELIMINARY
2
3
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
X
CIN
X
IN
TIM
CM7
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Data bus
8
1/4096
1/2
TM15
1/8
TM10
TM12
TM14
TM11
TM13
Timer 1 latch (8)
8
Timer 1 (8)
Timer 2 latch (8)
8
Timer 2 (8)
Timer 1
interrupt request
8
8
Timer 2
interrupt request
8
TIM
Selection gate : Connected to
black side at
reset
TM1 : Timer mode register 1
TM2 : Timer mode register 2
T3CS : Timer 3 count source
switch bit (address 00C7
CM : CPU mode register
TM21
8
FF
16
T3CS
TM20
TM22
TM21
TM24
TM23
TM27
TM25
16
)
TM16
Timer 3 latch (8)
8
Timer 3 (8)
Timer 4 latch (8)
8
Timer 4 (8)
Timer 5 latch (8)
8
Timer 5 (8)
8
8
07
16
8
8
8
8
Reset
STP instruction
Timer 3
interrupt request
Timer 4
interrupt request
Timer 5
interrupt request
Timer 6 latch (8)
8
TM17
TM26
Notes 1: HIGH pulse width of external clock inputs TIM2 and TIM3 needs 4 machine cycles or more.
2: When the external clock source is selected, timers 1, 2, and 3 are counted at a rising edge of input signal.
3: In the stop mode or the wait mode, external clock inputs TIM2 and TIM3 cannot be used.
Timer 6 (8)
8
Timer 6
interrupt request
Fig. 12.4.3 Timer Block Diagram
Rev. 1.0
29
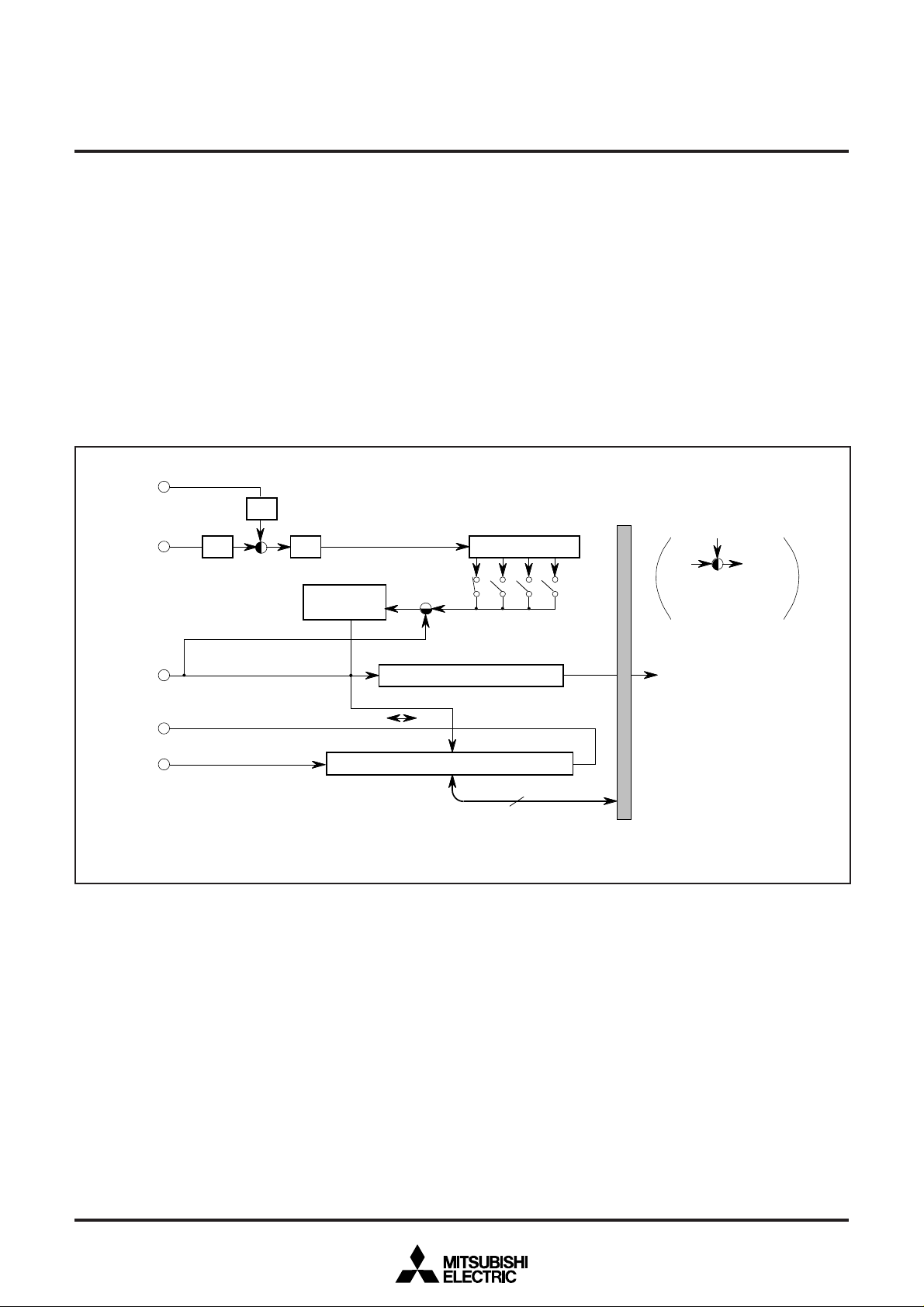
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some paramentic limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37280MF–XXXSP, M37280MK–XXXSP
M37280EKSP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
12.5 SERIAL I/O
This microcomputer has a built-in serial I/O which can either transmit
or receive 8-bit data serially in the clock synchronous mode.
The serial I/O block diagram is shown in Figure 12.5.1. The synchronous clock I/O pin (SCLK), and data output pin (SOUT) also function
as port P4, data input pin (SIN) also functions as ports P1 and P7.
Bit 2 of the serial I/O mode register (address 021316) selects whether
the synchronous clock is supplied internally or externally (from the
SCLK pin). When an internal clock is selected, bits 1 and 0 select
whether f(XIN) or f(XCIN) is divided by 8, 16, 32, or 64. To use SOUT
and SCLK pins for serial I/O, set the corresponding bits of the port P4
direction register (address 00C916) to “0.” To use SIN pin for serial
I/O, set the corresponding bit of the port P1 direction register (address 00C316) to “0.”
XCIN
1/2
IN
X
SCLK
1/2
CM7
1/2
Synchronous
circuit
SM2
Serial I/O counter (8)
The operation of the serial I/O is described below. The operation of
the serial I/O differs depending on the clock source; external clock or
internal clock.
Data bus
Frequency divider
1/2
1/81/4 1/16
SM1
SM0
Selection gate: Connect to
CM : CPU mode register
SM : Serial I/O mode register
Serial I/O
interrupt request
black side at
reset.
SOUT
SIN
Note : When the data is set in the serial I/O register (address 021416), the register functions as the serial I/O shift register.
Fig. 12.5.1 Serial I/O Block Diagram
SM5 : LSB
MSB
Serial I/O shift register (8)
(Note)
(Address 021416)
8
30
Rev. 1.0
 Loading...
Loading...