Mitsubishi M35072-XXXFP Datasheet
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M35072-XXXFP
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS
DESCRIPTION
The M35072-XXXFP is a character pattern display control IC can display on the display monitor. It can display 2 pages (24 characters ✕
12 lines per 1 page) at the same time. It uses a silicon gate CMOS
process and it housed in a 20-pin shrink SOP package .
For M35072-002FP that is a standard ROM version of M35072XXXFP respectively, the character pattern is also mentioned.
FEATURES
Screen composition................ 24 characters 12 lines ✕ 2 pages
•
Number of characters displayed.................. 288 (Max.) ✕ 2 pages
•
Character composition ..................................... 12 ✕ 18 dot matrix
•
Characters available................................ page 0 : 256 characters
•
Character sizes available .................... 4 (vertical) ✕ 2 (horizontal)
•
Display locations available
•
Horizontal direction .............................................. 2007 locations
Vertical direction ..................................................1023 locations
Blinking..................................................................Character units
•
Cycle : division of vertical synchronization signal into 32 or 64
Duty : 25%, 50%, or 75%
Data input .................................. By the 16-bit serial input function
•
Coloring
•
Character color .....................................................Character unit
Background coloring .............................................Character unit
Border (shadow) coloring ........................ 8 colors (RGB output)
Raster coloring ........................................ 8 colors (RGB output)
Blanking Character size blanking
•
Output ports
•
4 shared output ports (toggled between RGB output)
4 dedicated output ports
Display RAM erase function
•
Display input frequency range............... FOSC = 20MHz to 80MHz
•
Horizontal synchronous input frequency
•
........................................................H.sync = 15 kHz to 130 kHz
Display oscillation stop function
•
page 1 : 256 characters
Specified by register
Specified by register
Border size blanking
Matrix-outline blanking
All blanking (all raster area)
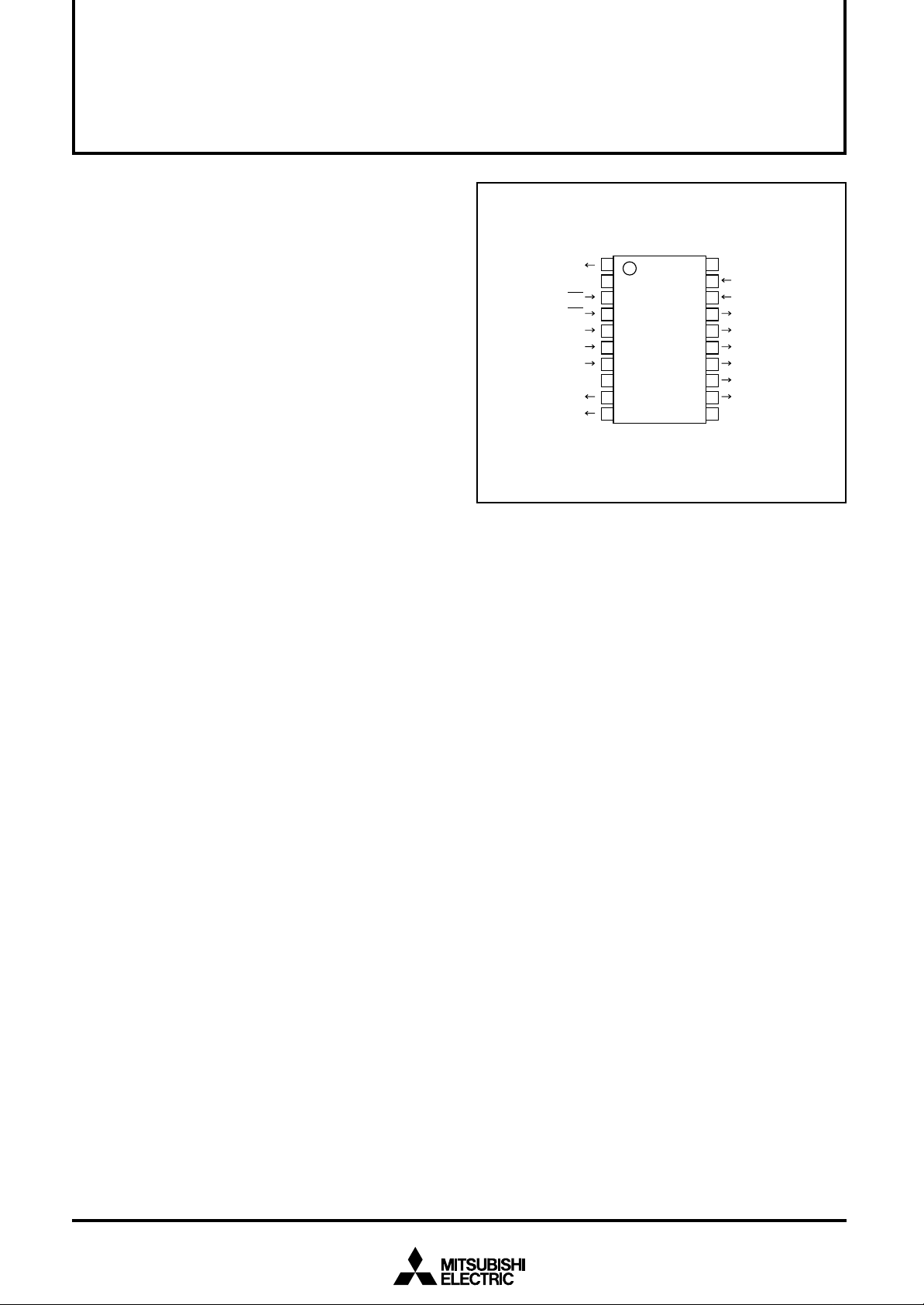
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
CPOUT
V
SS2
AC
CS
SCK
SIN
TCK
V
DD1
P6
P7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
M35072 - XXXFP
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
V
DD2
VERT
HOR
P5/B
P4
P3/G
P2
P1/R
P0/BLNK0
V
SS1
Outline 20P2Q-A
APPLICATION
Liquid crystal display, Plasma display
REV.1.2
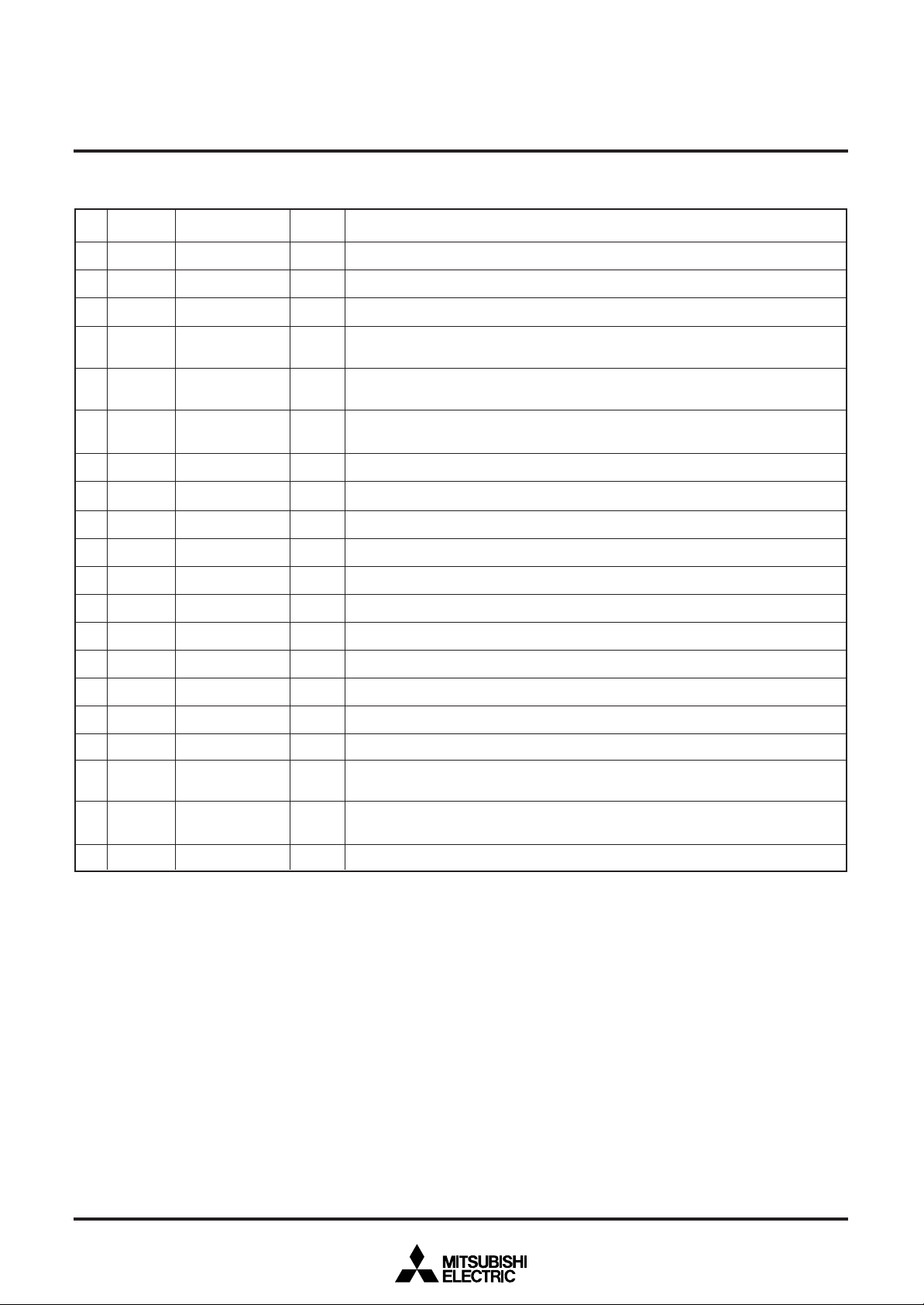
PIN DESCRIPTION
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M35072-XXXFP
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS
Pin
Number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Symbol
CPOUT
VSS2
__
AC
_____
CS
SCK
SIN
TCK
VDD1
P6
P7
VSS1
P0/BLNK0
P1/R
P2
Pin name
Filter output
Earthing pin
Auto-clear input
Chip select input
Serial clock input
Serial data input
External clock
Power pin
Port P6 output
Port P7 output
Earthing pin
Port P0 output
Port P1 output
Port P2 output
Input/
Output
Output
–
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
–
Output
Output
–
Output
Output
Output
Function
Filter output. Connect loop filter to this pin.
Connect to GND.
When “L”, this pin resets the internal IC circuit. Hysteresis input. Built-in pull-up resistor.
This is the chip select input pin, and when serial data transmission is being carried out, it
goes to “L.” Hysteresis input. Built-in pull-up resistor.
_____
When CS pin is “L,” SIN serial data is taken in when SCK rises. Hysteresis input. Built-in
pull-up resistor.
This is the pin for serial input of data and addresses for the display control register and
the display data memory. Hysteresis input. Built-in pull-up resistor.
This is the pin for external clock input.
Please connect to +5V with the power pin.
This is the output port.
This is the output port.
Please connect to GND using circuit earthing pin.
This pin can be toggled between port pin output and BLNK0 signal output.
This pin can be toggled between port pin output and R signal output.
This is the output port.
15
16
17
18
19
20
P3/G
P4
P5/B
HOR
VERT
VDD2
Port P3 output
Port P4 output
Port P5 output
Horizontal synchro-
nous signal input
Vertical synchro-
nous signal input
Power pin
Output
Output
Output
Input
Input
–
This pin can be toggled between port pin output and G signal output.
This is the output port.
This pin can be toggled between port pin output and B signal output.
This pin inputs the horizontal synchronous signal. Hysteresis input.
This pin inputs the vertical synchronous signal. Hysteresis input.
Please connect to +5V with the power pin.
2
4
7
6
8
20
CS
SIN
V
DD1
VDD2
3AC
11VSS1
2VSS2
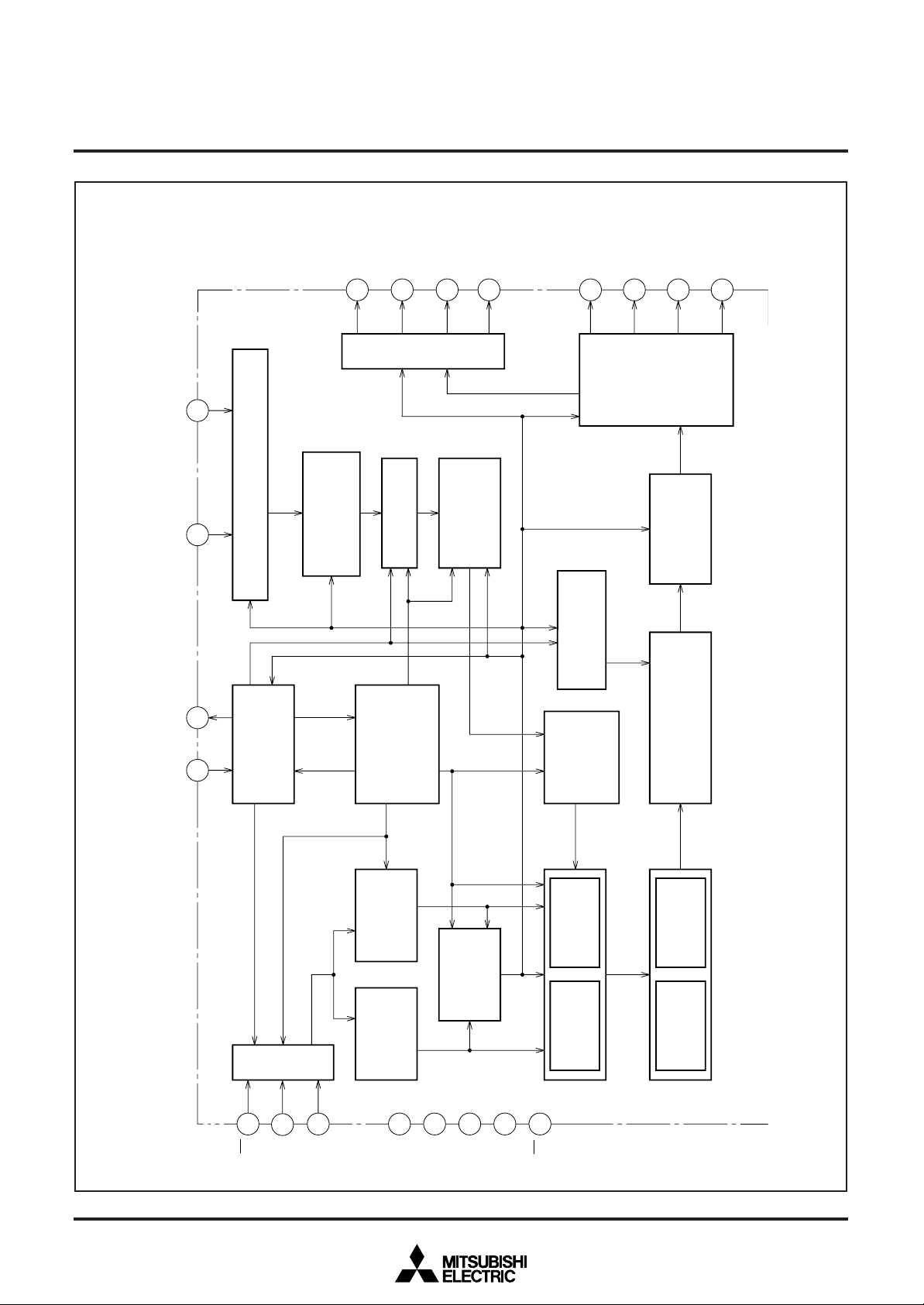
Clock oscillaion
circuit dispay
Timing generator
Polarity switching circuit
Address control
circuit
Data control
circuit
Display control
register
Display RAM0
(page 0)
Display RAM1
(page 1)
Shift register
Blinling circuit
Reading address
control circuit
Display location
detection circuit
H counter
TCK
1
CPOUT
18
HOR
19
12
VERT
Sycnchironous signal
switching circuit
Display control
circuit
Port output
control circuit
P0/BLNK0
13 P1/R
15 P3/G
17 P5/B
14 P2
16 P4
9P6
10 P7
Input control cicuit
Polarity swicthing circuit
Display character
ROM0
(page 0)
Display character
ROM1
(page 1)
SCL 5
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M35072-XXXFP
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS
BLOCK DIAGRAM
3
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M35072-XXXFP
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS
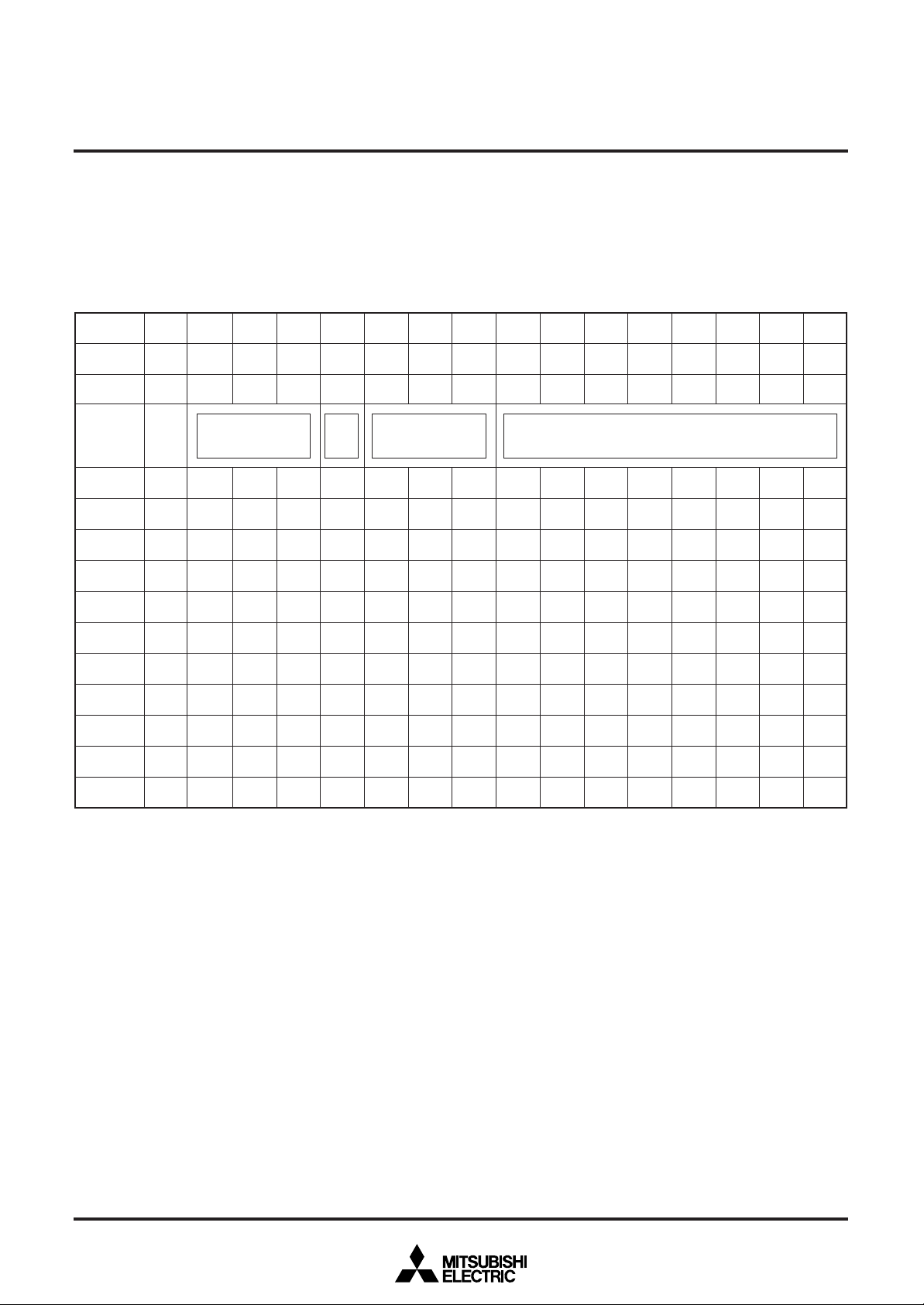
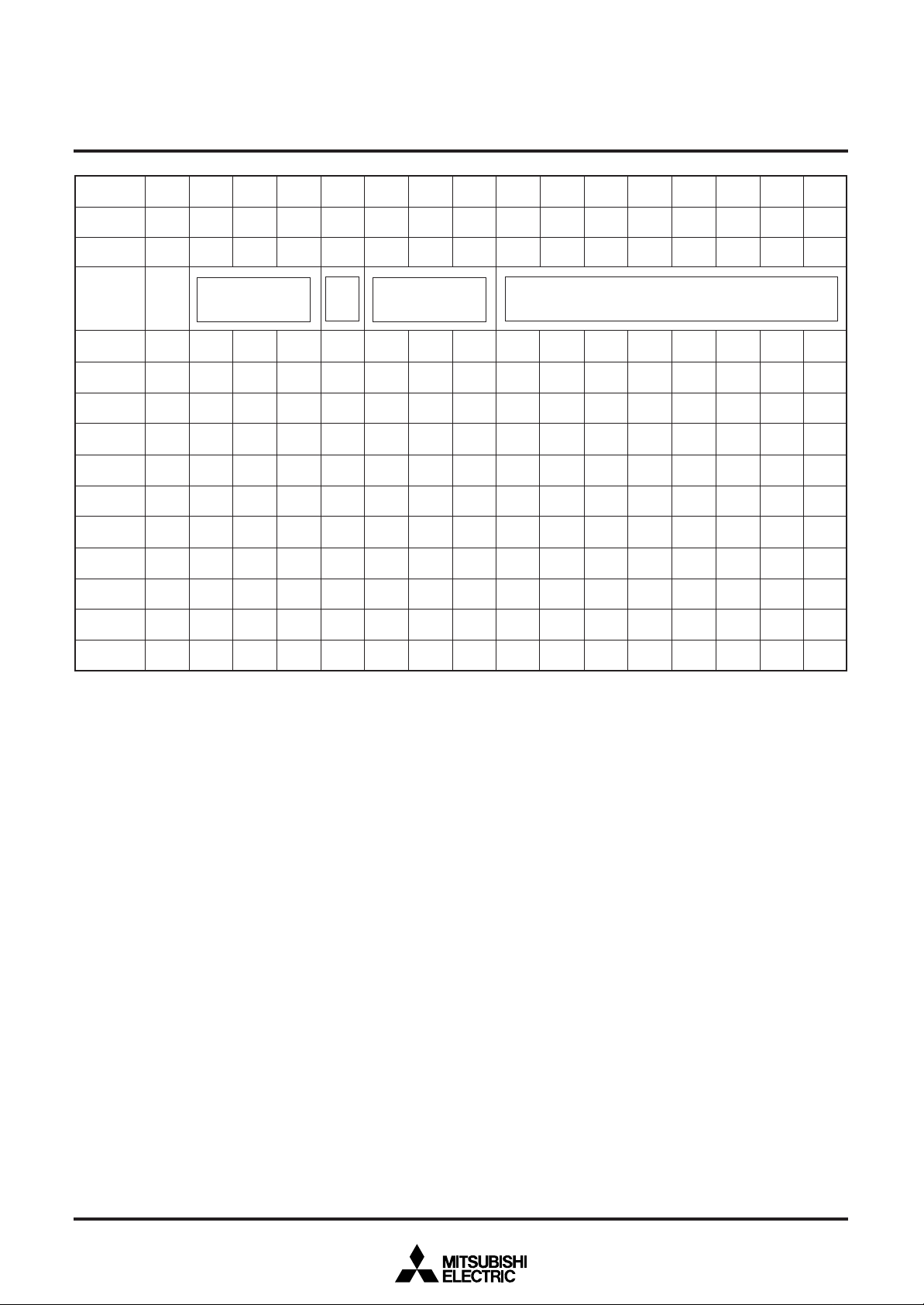
MEMORY CONSTITUTION
Address 00016 to 11F16 are assigned to the display RAM, address
12016 to 12816 are assigned to the display control registers. The internal circuit is reset and all display control registers (address 12016
to 12816) are set to “0” when the AC pin level is “L”. And then, RAM
is not erased and be undefinited. This memory is consisted of 2
Addresses
00016
00116
11E16
11F16
12016
12116
12216
12316
DAF DAE DAD DAC DAB DAA DA9 DA8 DA7 DA6 DA5 DA4 DA3 DA2 DA1 DA0
0 BB BG BR BLINK B G R C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
0 BB BG BR BLINK B G R C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
………
………
0 BB BG BR BLINK B G R C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
0 BB BG BR BLINK B G R C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
0 EXCK0 VJT DIVS1 DIVS0 DIV10 DIV9 DIV8 DIV7 DIV6 DIV5 DIV4 DIV3 DIV2 DIV1 DIV0
0 RSEL0 PTD7 PTD6 PTD5 PTD4 PTD3 PTD2 PTD1 PTD0 PTC5 PTC4 PTC3 PTC2 PTC1 PTC0
0
RSEL1
0 EXCK1 TEST3 TEST2 TEST1 TEST0 VP9 VP8 VP7 VP6 VP5 VP4 VP3 VP2 VP1 VP0
__
Background
coloring
SPACE2 SPACE1 SPACE0
Blink-
ing
Character color
HP10 HP9 HP8 HP7 HP6 HP5 HP4 HP3 HP2 HP1 HP0
pages : page 0 memory and page 1 memory (their addresses are
common), page controlled by DAF bit of each address when writing
data. For detail, see “Data input”. Memory constitution is shown in
Figure 1 and 2.
Character code
12416
12516
12616
12716
12816
Fig. 1 Memory constitution (page 0 memory)
0 TEST9 TEST5 TEST4 DSP11 DSP10 DSP9 DSP8 DSP7 DSP6 DSP5 DSP4 DSP3 DSP2 DSP1 DSP0
0
TEST10 VSZ1H1 VSZ1H0 VSZ1L1
0
TEST13 VSZ2H1 VSZ2H0 VSZ2L1 VSZ2L0 V18SZ1 V18SZ0
0
MODE0 TEST12 HSZ20 TEST11
0
MODE1 BLINK2 BLINK1 BLINK0
VSZ1L0
V1SZ1 V1SZ0 LIN9 LIN8 LIN7 LIN6 LIN5 LIN4 LIN3 LIN2
LIN17 LIN16 LIN15 LIN14 LIN13 LIN12 LIN11 LIN10
HSZ10
BETA14
TEST8 TEST7 TEST6 FB FG FR RB RG RR
DSPON
STOP
RAMERS
SYAD BLK1 BLK0 POLH POLV
VMASK
B/F BCOL
4
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M35072-XXXFP
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS
Addresses
00016
00116
………
11E16
11F16
12016
12116
12216
12316
12416
12516
12616
12716
DAF DAE DAD DAC DAB DAA DA9 DA8 DA7 DA6 DA5 DA4 DA3 DA2 DA1 DA0
1 BB BG BR BLINK B G R C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
1 BB BG BR BLINK B G R C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
………
1 BB BG BR BLINK B G R C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
1 BB BG BR BLINK B G R C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
1–––––––––––––––
1–––––––––––––––
1–
1 – TEST3 TEST2 TEST1 TEST0 VP9 VP8 VP7 VP6 VP5 VP4 VP3 VP2 VP1 VP0
1 – – TEST4 DSP11 DSP10 DSP9 DSP8 DSP7 DSP6 DSP5 DSP4 DSP3 DSP2 DSP1 DSP0
1–
1–
1–
Background
coloring
SPACE2 SPACE1 SPACE0
VSZ1H1 VSZ1H0 VSZ1L1 VSZ1L0
VSZ2H1 VSZ2H0 VSZ2L1 VSZ2L0 V18SZ1 V18SZ0
TEST12
HSZ20
Blink-
ing
TEST11
Character color
HP10 HP9 HP8 HP7 HP6 HP5 HP4 HP3 HP2 HP1 HP0
V1SZ1 V1SZ0 LIN9 LIN8 LIN7 LIN6 LIN5 LIN4 LIN3 LIN2
HSZ10
BETA14
TEST8 TEST7 TEST6 FB FG FR RB RG RR
Character code
LIN17 LIN16 LIN15 LIN14 LIN13 LIN12 LIN11 LIN10
12816
Fig. 2 Memory constitution (page 1 memory)
Note: Page 0 and page 1 registers are found in their respective pages. For example, HP10 to HP0 of the page 0 memory sets the horizontal
display start position of page 0, whereas HP10 to HP0 (same register name) of the page 1 memory sets the horizontal display start
position of page 1. Also, registers common to both page 0 and page 1 are found only in the page 0 memory. For example, PTC0 is the
control register of the P0 pin and is found only in the page 0 memory.
1–
BLINK2 BLINK1 BLINK0 DSPON TEST13
RAMERS
SYAD BLK1 BLK0 ––––BCOL
5
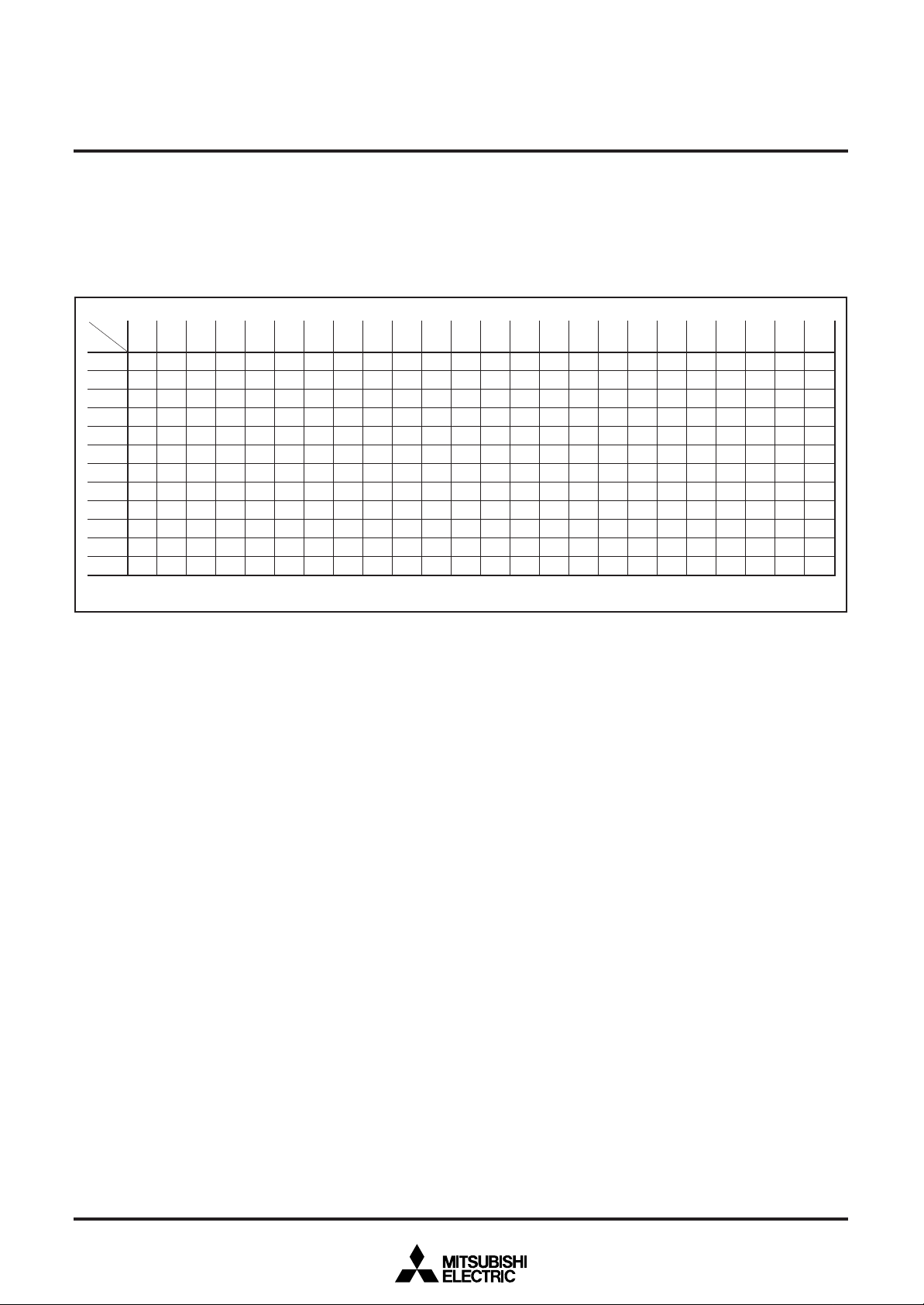
SCREEN CONSTITUTION
The screen lines and rows are determined from each address of
the display RAM (page 0 and page 1 are common). The screen
constitution is shown in Figure 3.
Row
Line
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 101112131415161718192021222324
0001600116002160031600416005160061600716008160091600A1600B1600C1600D1600E1600F1601016011160121601316014160151601616017
1
2
018160191601A1601B1601C1601D1601E1601F160201602116022160231602416025160261602716028160291602A1602B1602C1602D1602E1602F
3
0301603116032160331603416035160361603716038160391603A1603B1603C1603D1603E1603F1604016041160421604316044160451604616047
4
048160491604A1604B1604C1604D1604E1604F160501605116052160531605416055160561605716058160591605A1605B1605C1605D1605E1605F
5
0601606116062160631606416065160661606716068160691606A1606B1606C1606D1606E1606F1607016071160721607316074160751607616077
6
078160791607A1607B1607C1607D1607E1607F160801608116082160831608416085160861608716088160891608A1608B1608C1608D1608E1608F
7
0901609116092160931609416095160961609716098160991609A1609B1609C1609D1609E1609F160A0160A1160A2160A3160A4160A5160A6160A7
8
0A8160A9160AA160AB160AC160AD160AE160AF160B0160B1160B2160B3160B4160B5160B6160B7160B8160B9160BA160BB160BC160BD160BE160BF
9
0C0160C1160C2160C3160C4160C5160C6160C7160C8160C9160CA160CB160CC160CD160CE160CF160D0160D1160D2160D3160D4160D5160D6160D7
10
0D8160D9160DA160DB160DC160DD160DE160DF160E0160E1160E2160E3160E4160E5160E6160E7160E8160E9160EA160EB160EC160ED160EE160EF
11
0F0160F1160F2160F3160F4160F5160F6160F7160F8160F9160FA160FB160FC160FD160FE160FF1610016101161021610316104161051610616107
12
108161091610A1610B1610C1610D1610E1610F161101611116112161131611416115161161611716118161191611A1611B1611C1611D1611E1611F
✽ The hexadecimal numbers in the boxes show the display RAM address.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M35072-XXXFP
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
Fig. 3 Screen constitution
6
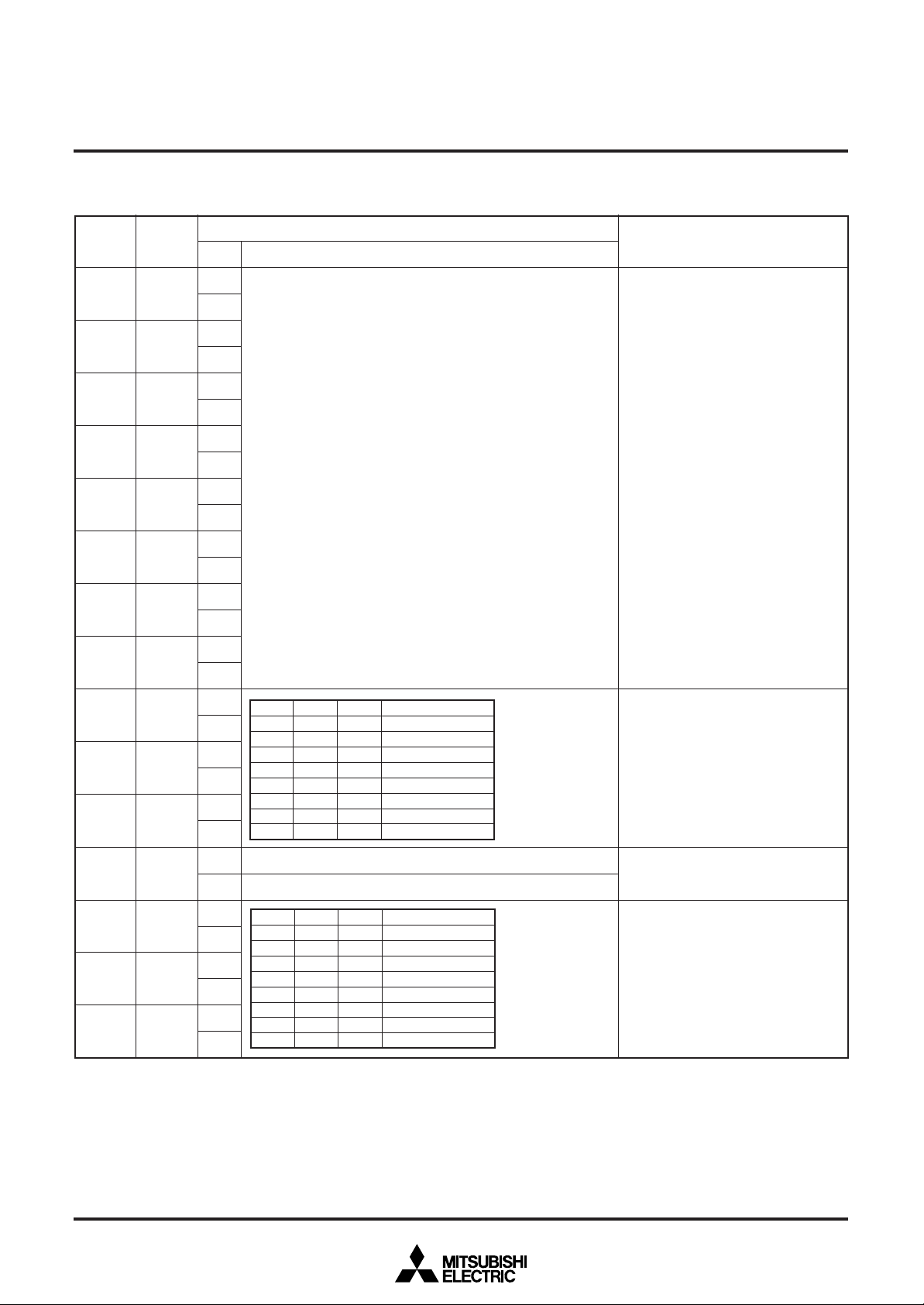
DISPLAY RAM
Address 00016 to 11F16
DA
Register
0
1
2
C0
C1
C2
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS
Contents
Status
0
Set the displayed ROM character code.
1
0
To write data into page 0 (Note 2), select the data from the ROM
characters (256 types) for page 0 and set the character code. To
1
write data into page 1, do the same from the ROM characters (256
types) for page 1.
0
1
Function
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M35072-XXXFP
Remarks
Set display character
3
C3
1
0
0
4
C4
1
0
5
C5
1
0
6
C6
1
0
7
C7
1
8
R
1
0
0
9
G
1
0
A
B
1
Do not blink.
B
C
BLINK
BR
0
1
Blinking
0
BB
1
0
D
BG
1
0
E
BB
1
Notes 1. The display RAM is undefined state at the AC pin.
G
B
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
R
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
Color
Black
Red
Green
Yellow
Blue
Magenta
Cyan
White
Set character color (character unit)
Set blinking
See register BLINK2 to BLINK0 (address12816)
BR
BG
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
____
Color
Black
Red
Green
Yellow
Blue
Magenta
Cyan
White
Set character background
(character unit)
2. The display RAM consists of 2 pages, page 0 and page 1 (common address). The page in which data is written is controlled by the
DAF bit. When set to "0", data is written into page 0, whereas when set to "1", data is written into page 1.
7
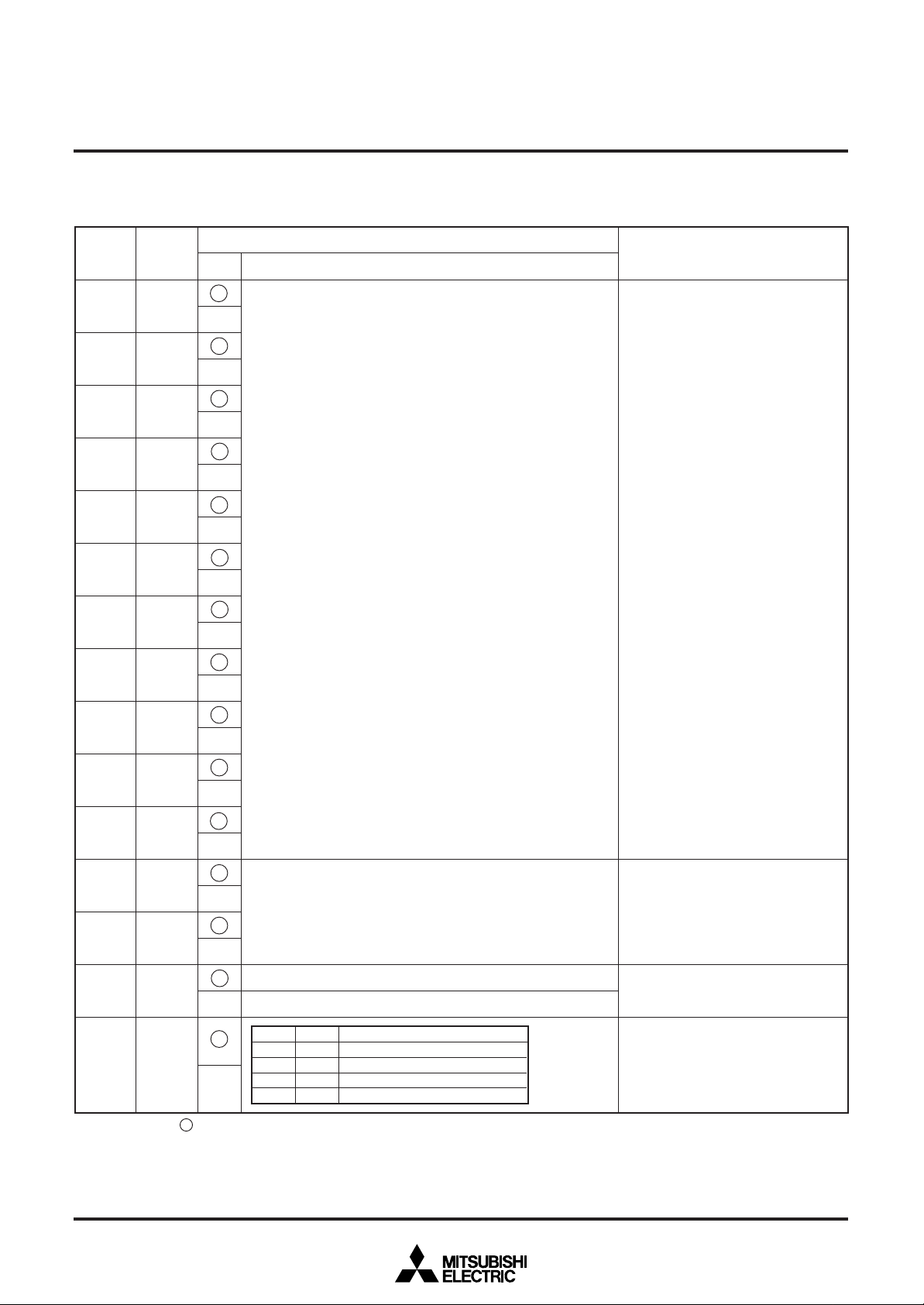
REGISTERS DESCRIPTION
(1) Address 12016
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M35072-XXXFP
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS
DA
Register
Status
0
0
1
2
DIV0
(Note 3)
DIV1
(Note 3)
DIV2
(Note 3)
Set external clock frequency division value of horizontal oscillation
1
frequency.
0
1
0
10
N1 =
(DIVn × 2n)
Σ
n = 0
N1 : division value
1
0
3
DIV3
(Note 3)
1
0
4
DIV4
(Note 3)
1
Function
Set display frequency by division value
setting.
For details, see REGISTER
SUPPLYMENTARY DESCRIPTION
(1).
Also, set the display frequency range by
registers DIVS0, DIVS1(address
12016), RSEL0(address 12116) and
RSEL1(address 12216) in accordance
with the display frequency.
Any of this settings above is required
only when EXCK1 = 1, EXCK0 = 1.
Remarks
0
Contents
5
DIV5
(Note 3)
1
0
6
DIV6
(Note 3)
1
0
7
DIV7
(Note 3)
1
0
8
DIV8
(Note 3)
1
9
DIV9
(Note 3)
1
0
0
A
B
DIV10
(Note 3)
DIVS0
(Note 3)
1
0
For setting, see REGISTER SUPPLYMENTARY DESCRIPTION
(2).
1
Set display frequency range.
0
C
D
E
Notes 1. The mark around the status value means the reset status by the "L" level is input to AC pin.
DIVS1
(Note 3)
VJT
(Note 3)
EXCK0
(Note 3)
1
0
It is used to "0", normally.
1
Alleviates continuous vertical jitters.
EXCK1
0
1
EXCK0
0
0
0
1
1
External synchronous (external clock)
1
0
1
External synchronous (internal clock)
Display clock input
Do not set
Do not set
Display clock setting
See REGISTER SUPPLYMENTARY
DESCRIPTION (1)
EXCK1 : address12316
____
2. The page in which data is written is controlled by the DAF bit. When set to "0", data is written into page 0, whereas when set to "1",
data is written into page 1.
3. Registers marked with (Note 3) are found only in page 0, therefore the register value does not change when the DAF bit is set to "1".
8
(2) Address 12116
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M35072-XXXFP
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS
DA
Register
Status
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
PTC0
(Note 3)
PTC1
(Note 3)
PTC2
(Note 3)
PTC3
(Note 3)
PTC4
(Note 3)
PTC5
(Note 3)
PTD0
(Note 3)
P0 output (port P0).
0
BLNK0 output.
1
P1 output (port P1).
0
R signal output.
1
P2 output (port P2).
0
Can not be used.
1
P3 output (port P3).
0
G signal output.
1
P4 output (port P4).
0
Can not be used.
1
P5 output (port P5).
0
B signal output.
1
“L” output or negative polarity output (BLNK0 output).
0
“H” output or positive polarity output (BLNK0 output).
1
Function
P0 pin output control.
P1 pin output control.
P2 pin output control.
P3 pin output control.
P4 pin output control.
P5 pin output control.
P0 pin data control.
Remarks
Contents
“L” output or negative polarity output (R signal output).
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
PTD1
(Note 3)
PTD2
(Note 3)
PTD3
(Note 3)
PTD4
(Note 3)
PTD5
(Note 3)
PTD6
(Note 3)
PTD7
(Note 3)
RSEL0
(Note 3)
0
“H” output or positive polarity output (R signal output).
1
“L” output.
0
“H” output.
1
“L” output or negative polarity output (G signal output).
0
“H” output or positive polarity output (G signal output).
1
“L” output.
0
“H” output.
1
“L” output or negative polarity output (B signal output).
0
“H” output or positive polarity output (B signal output).
1
“L” output.
0
“H” output.
1
0
“L” output.
1
“H” output.
0
For setting, see REGISTER SUPPLYMENTARY DESCRIPTION
(2).
1
Notes 1. The mark around the status value means the reset status by the "L" level is input to AC pin.
P1 pin data control.
P2 pin data control.
P3 pin data control.
P4 pin data control.
P5 pin data control.
P6 pin data control.
P7 pin data control.
Set display frequency range.
____
2. The page in which data is written is controlled by the DAF bit. When set to "0", data is written into page 0, whereas when set to "1",
data is written into page 1.
3. Registers marked with (Note 3) are found only in page 0, therefore the register value does not change when the DAF bit is set to "1".
9
(3) Address 12216
DA
Register
0
1
2
HP0
HP1
HP2
Status
0
1
0
1
0
1
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS
Contents
Function
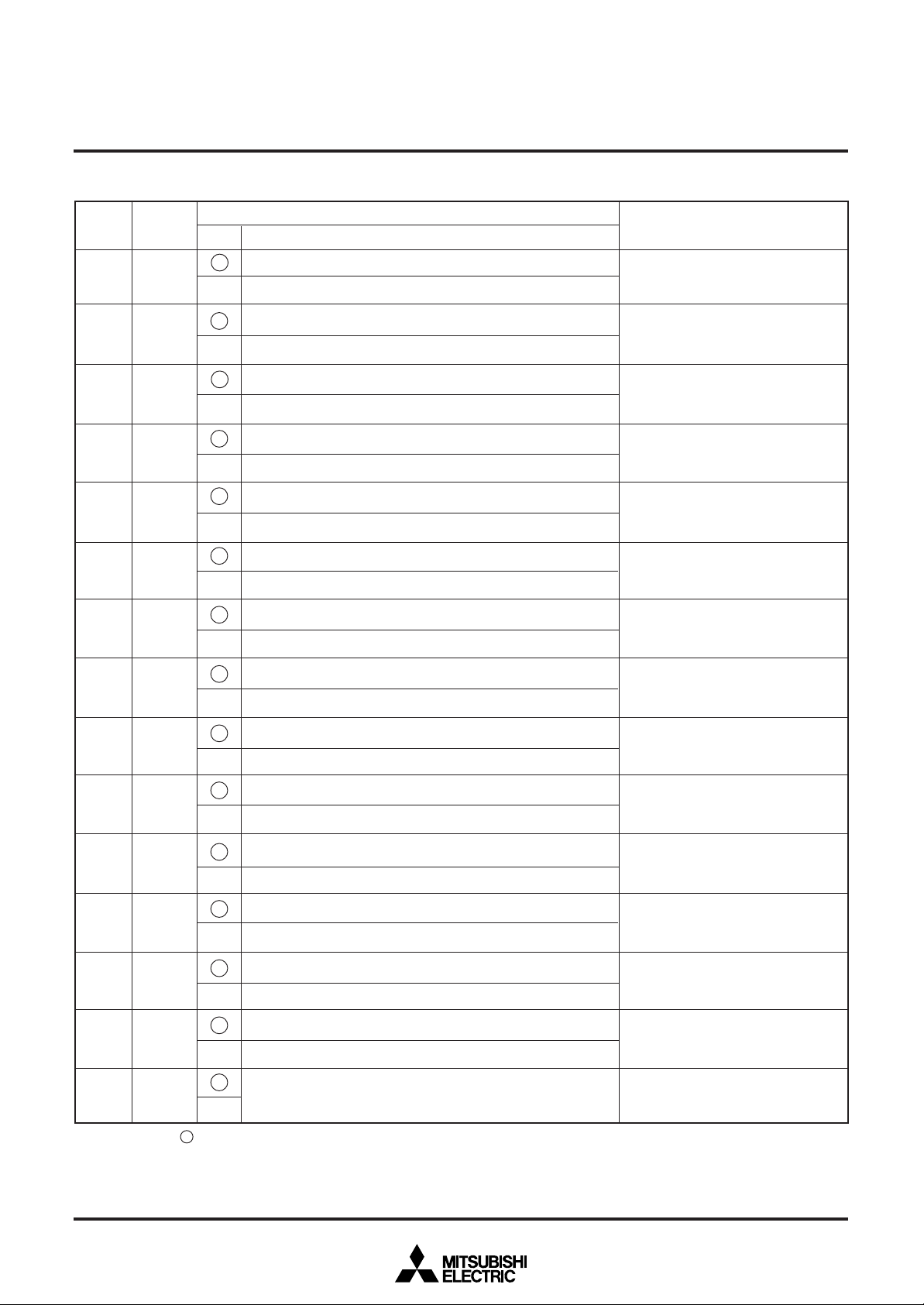
If HS is the horizontal display start location,
HS = T × 2nHPn + 6)
T : Period of display frequency
2007 settings are possible.
10
(Σ
n = 0
HOR
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M35072-XXXFP
Remarks
Horizontal display start location is
specified using the 11 bits from HP10
to HP0.
HP10 to HP0 = (000000000002) and
(000001001112) setting is forbidden.
3
HP3
1
0
0
VS
4
HP4
1
HS
*
5
HP5
0
VERT
1
0
6
HP6
Display area
HS* (shown left) shows horizontal
display start location that is register B/F
(address 12816) = 0 is set.
1
0
7
HP7
1
0
8
HP8
1
0
9
HP9
1
0
A
HP10
1
B
SPACE0
1
0
0
C
SPACE1
1
0
D
SPACE2
E
RSEL1
(Note 3)
1
(S) represents one line worth of spac
0
For setting, see REGISTER SUPPLYMENTARY DESCRIPTION
(2).
1
SPACE
2
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
1
1
1
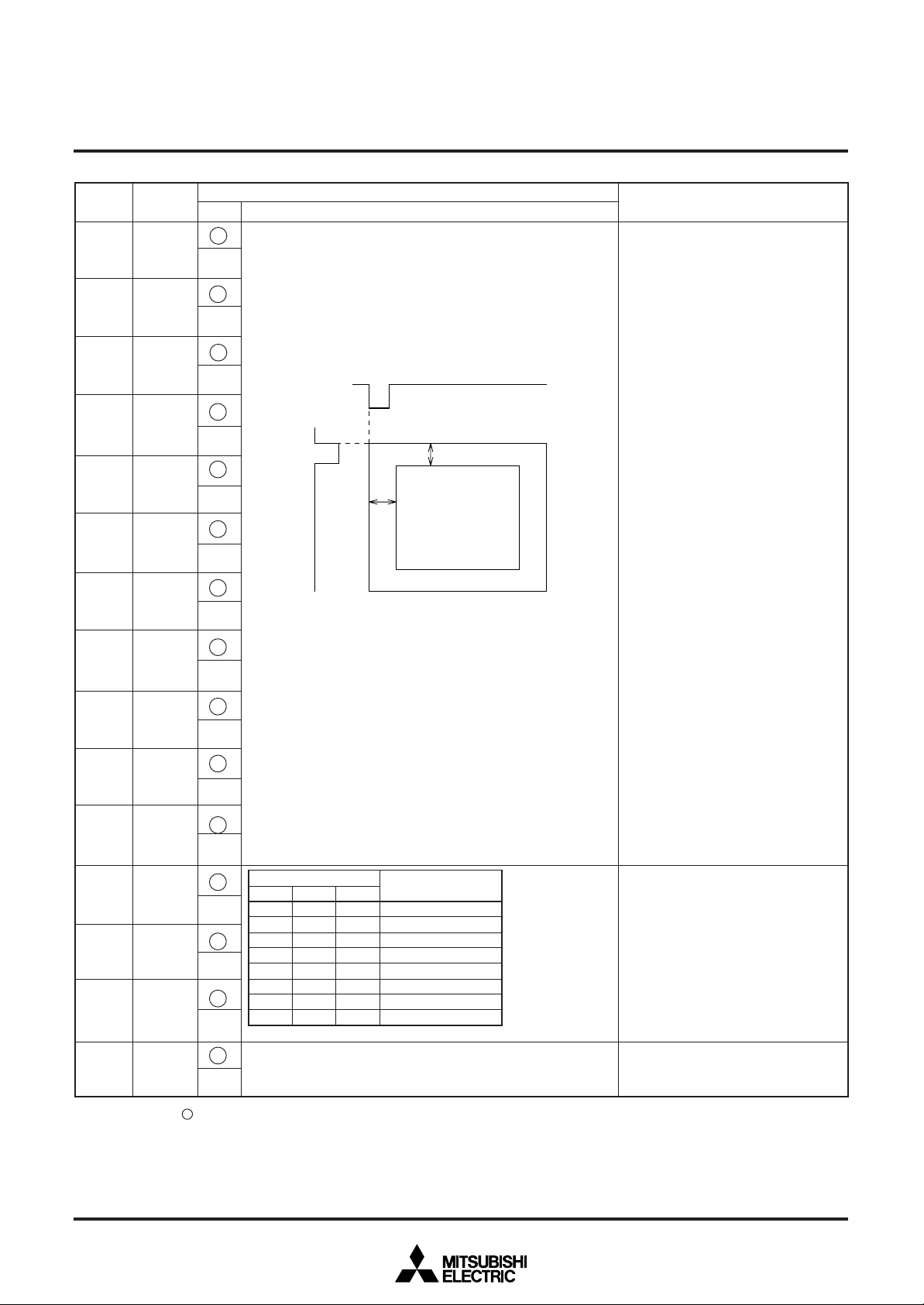
Number of Lines and Space
<(S) represents space>
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
1 (S) 10 (S) 1
2 (S) 8 (S) 2
3 (S) 6 (S) 3
4 (S) 4 (S) 4
5 (S) 2 (S) 5
6 (S) 6
6 (S)(S) 6
12
Notes 1. The mark around the status value means the reset status by the "L" level is input to AC pin.
Leave one line worth of space in the vertical direction.
For example, 6 (S) 6 indicates two sets
of 6 lines with a line of spaces between
lines 6 and 7.
A line is 18 × N horizontal scan lines.
N is determined by the character size in
the vertical direction
Set display frequency range.
____
2. The page in which data is written is controlled by the DAF bit. When set to "0", data is written into page 0, whereas when set to "1",
data is written into page 1.
3. Registers marked with (Note 3) are found only in page 0, therefore the register value does not change when the DAF bit is set to
"1".
__
10
(4) Address 12316
DA
Register
0
1
2
VP0
VP1
VP2
Contents
Status
0
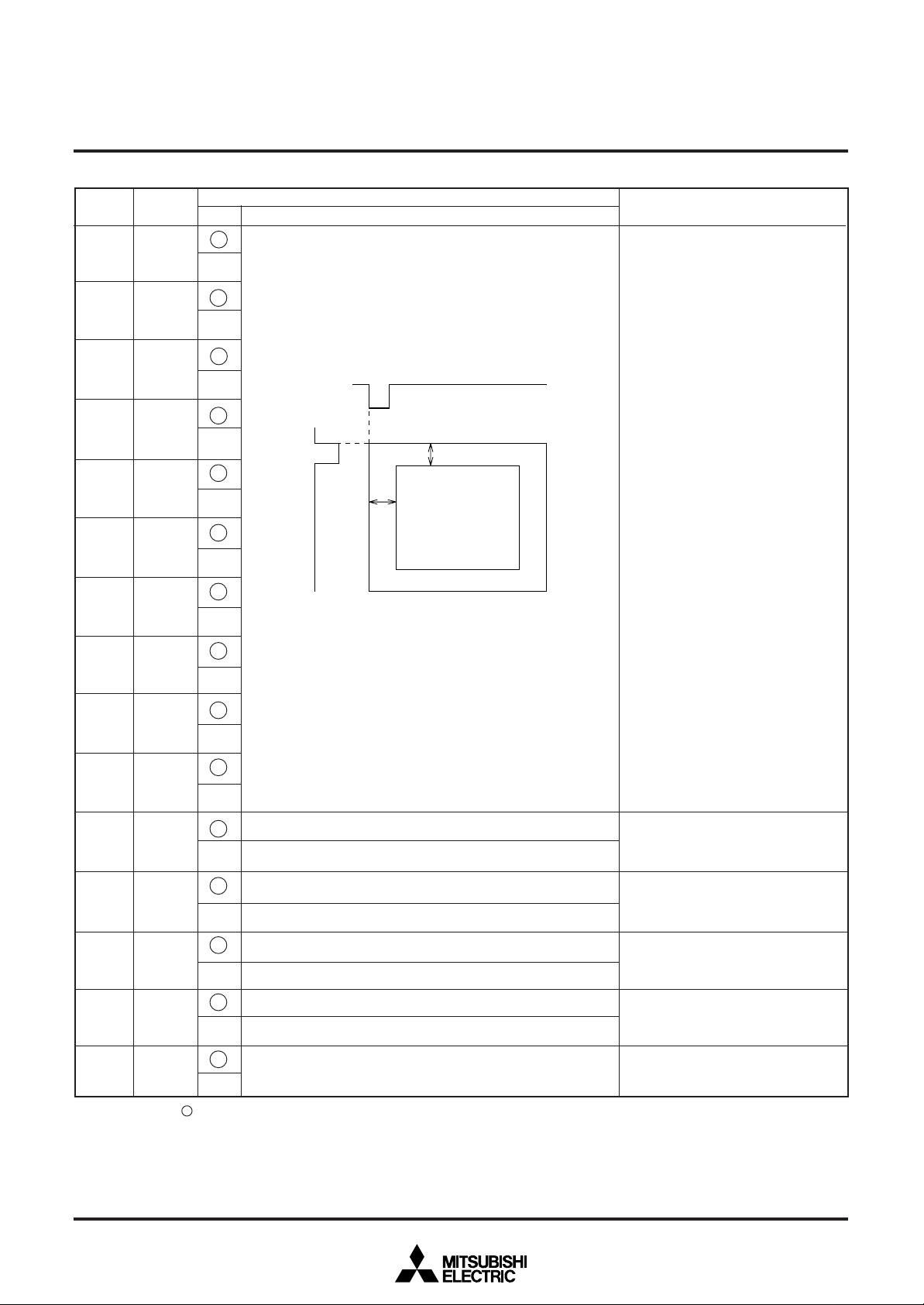
If VS is the vertical display start location,
1
VS = H × 2nVPn
0
H: Cycle with the horizontal synchronizing pulse
1
1023 settings are possible.
9
Σ
n = 0
Function
0
1
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M35072-XXXFP
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS
Remarks
The vertical start location is specified
using the 10 bits from VP9 to VP0.
VP9 to VP0 = (00000000002) setting is
forbidden.
HOR
3
4
5
6
VP3
VP4
VP5
VP6
0
1
VS
0
1
0
VERT
1
0
HS
*
Display area
HS* (shown left) shows horizontal
display start location that is register B/F
(address 12816) = 0 is set.
__
1
7
VP7
0
1
8
VP8
0
1
9
VP9
0
1
It should be fixed to "0".
A
TEST0
(Note 3)
0
Can not be used.
1
It should be fixed to "0".
B
C
D
E
TEST1
(Note 3)
TEST2
(Note 3)
TEST3
(Note 3)
EXCK1
(Note 3)
Notes 1. The mark around the status value means the reset status by the "L" level is input to AC pin.
0
Can not be used.
1
It should be fixed to "0".
0
Can not be used.
1
0
It should be fixed to "0".
1
Can not be used.
0
For setting, see Register EXCK0 (address 12016).
1
Display clock setting
____
2. The page in which data is written is controlled by the DAF bit. When set to "0", data is written into page 0, whereas when set to "1",
data is written into page 1.
3. Registers marked with (Note 3) are found only in page 0, therefore the register value does not change when the DAF bit is set to
"1".
11
(5) Address 12416
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M35072-XXXFP
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS
DA
Register
0
1
DSP0
DSP1
Status
0
1
0
The display mode (blanking mode) for line n on the display
screen is set line-by-line, using DSPn (n = 0 to 11).
The display mode is determined by the combination of registers
BLK1 and BLK0 (address 12816). Settings are given below.
Contents
Function
Remarks
Sets the display mode of line 1.
Sets the display mode of line 2.
1
2
DSP2
0
1
3
DSP3
0
BLK1
0
0
1
1
BLK0
0
1
0
1
DSPn= “0”
Matrix-outline border
Character
Border
Matrix-outline
DSPn= “1”
Matrix-outline
Border
Matrix-outline
Character
(At register BCOL = “0”)
Sets the display mode of line 3.
Sets the display mode of line 4.
1
0
4
DSP4
For detail, see DISPLAY FORM1(1).
Sets the display mode of line 5.
1
5
DSP5
0
Sets the display mode of line 6.
1
6
DSP6
0
Sets the display mode of line 7.
1
7
DSP7
0
Sets the display mode of line 8.
1
8
DSP8
0
Sets the display mode of line 9.
1
9
DSP9
0
Sets the display mode of line 10.
1
A
DSP10
0
Sets the display mode of line 11.
1
B
DSP11
0
Sets the display mode of line 12.
1
It should be fixed to “0”.
C
TEST4
D
TEST5
(Note 3)
E
TEST9
(Note 3)
Notes 1. The mark around the status value means the reset status by the "L" level is input to AC pin.
0
Can not be used.
1
It should be fixed to “0”.
0
1
Can not be used.
0
Can not be used.
1
It should be fixed to “1”.
____
2. The page in which data is written is controlled by the DAF bit. When set to "0", data is written into page 0, whereas when set to "1",
data is written into page 1.
3. Registers marked with (Note 3) are found only in page 0, therefore the register value does not change when the DAF bit is set to "1".
12
 Loading...
Loading...