Page 1

Page 2
High reliability is realized!
Equipped with small class highest level of function/performance!!
Features
•
Standard
•
specifications
1
5
(1) (1)
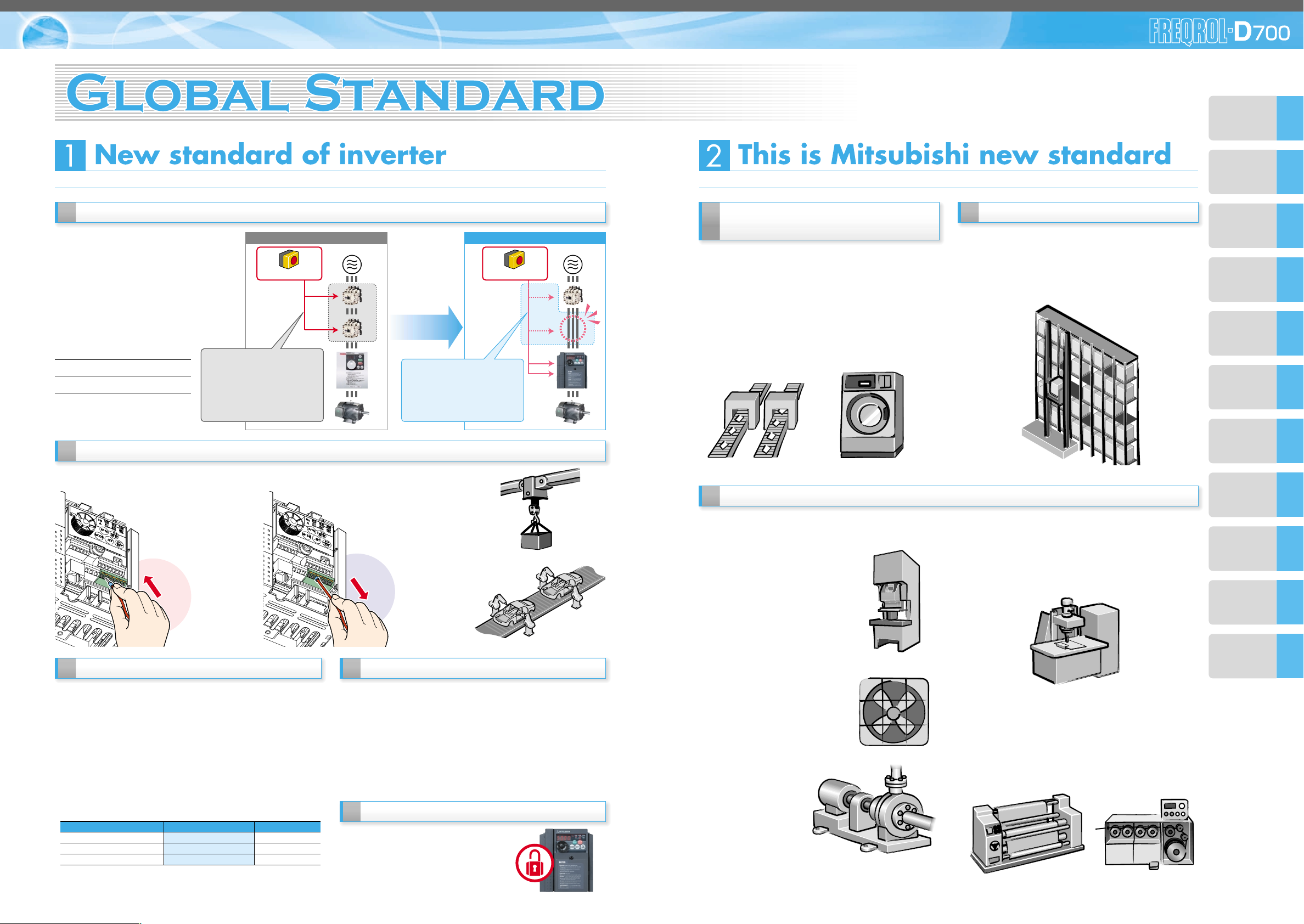
Safety stop function
The FR-D700 series is compliant to the EU
Machinery Directive without the addition of
previously required external devices.
Operation of an external Emergency
Stop device results in a highly reliable
immediate shutoff of the D700's output to
the motor.
This safety stop function conforms to the
following standards.
For conventional modelFor conventional model...
EN954-1 (ISO13849-1) Category 3
IEC60204-1 Stop Categor y 0
(2)
Spring clamp terminal (control circuit terminal)
Highly reliable and easy wiring is realized by the incorporation of spring clamp terminals.*
*: Main circuit terminal is screw terminal.
Easy wiring
•
Wiring is completed only
by inserting wires treated
with bar terminal (max,
diameter 1.5mm)
Capable of wiring without
a bar terminal.
(3) (4)
Long-life design
The design life of the cooling fan has been extended to 10
•
*1
. The life of the fan can be further extended utilizing the
years
it’s ON/OFF.
The longevity of the capacitors has been extended to 10
•
years by the adoption of a capacitor with a specification of
5000 hours and 105˚C surrounding air temperature
*1: Surrounding air temperature : annual average 40˚C (free from corrosive gas,
flammable gas, oil mist, dust and dirt) Since the design life is a calculated value, it is
not a guaranteed value.
*2: Output current : 80% of the inverter rated current
Life indication of critical components
•
Components
Cooling fan
Main circuit smoothing capacitor
Printed board smoothing capacitor
*3: Excerpts from "Periodic check of the transistorized inverter" of JEMA (Japan Electrical
Manufacturerís Association)
Guideline of the FR-D700 Life
For conventional model...
Two MCs are necessary
Two MCs are necessaryTwo MCs are necessary
•High cost
•Maintenance of two MCs is
necessary
•Installation space is necessary
10 years
10 years
10 years
Provided by the user (present) FR-D700
Emergency stop
Safety function
is equipped
•
Magnetic contactor (MC)
•
Emergency stop wiring
Only one MC is enough Only one MC is enough
Only one MC is enough
with safety stop function!
with safety stop function!with safety stop function!
•Cost reduction
•Maintenance of one MC
•Installation space is reduced
High reliability
•
Spring structure in terminal contact
section inside prevents contact fault
by vibration.
Maintenance is unnecessary
•
Screw retightening is unnecessary.
Emergency stop
(example: hoist)
(example: automobile production line)
Most advanced life check
Degrees of deterioration of main circuit capacitor, control
•
circuit capacitor, and inrush current limit circuit can be
monitored.
Trouble can be avoided with the self-diagnostic alarm*4 that is
•
*1,*2
.
Guideline of JEMA
2 to 3 years
5 years
5 years
output when the life span is near.
*4: If any one of main circuit capacitor, control circuit capacitor, inrush current restriction
circuit or cooling fan reaches the output level, an alarm is output. Capacity of the main
circuit capacitor can be measured by setting parameter at a stop and turning the
power from off to on. Measuring the capacity enables alarm to be output.
The cooling fan outputs alarm by using fan speed detection.
(5)
Password function
*3
Registering 4-digit password can limit
parameter read/write.
It is effective for parameter setting
protection.
150%/1Hz high starting torque by general
-purpose magnetic flux vector control
General-purpose magnetic flux vector control and auto
tuning function are available.
It ensures operation that requires high starting torque,
such as transfer machine including conveyer, hoist, lift,
etc., washing machine, and agitators.
High torque 150%/1Hz and 200%/3Hz are realized
•
Auto tuning
•
Many kinds of motors can be optimally controlled with
Mitsubishi original "non-rotation " auto tuning function.
(R1 constants tuning)
(example: conveyer)
(3)
Enhanced function
New functions and useful functions from superior models
support all sorts of applications.
Regeneration avoidance function
•
For a pressing machine and
fan rotated faster than the set
speed due to the effect of
another fan, a trip can be
made less likely to occur by
automatically increasing
frequency at regeneration.
Optimum excitation control
•
This control enables the motor
efficiency to its optimum. More
energy saving is possible in
applications with variable load
torque characteristic such as
fan and pump.
(example:
industrial washing machine)
(example: pressing machine)
(example: air-conditioning fan)
(example: pump)
(2)
Brake resistor can be connected
A brake transistor is built-in to the 0.4K or more.
Connecting an optional brake resistor increases
regeneration capability.
It is useful for deceleration time reduction of a machine
with a large inertia, such as fan, and operation of lift, etc.
(example: automated storage)
Power failure-time deceleration-to-stop function
•
The motor can be decelerated to a stop when a power
failure or undervoltage occurred to prevent the motor
from coasting.
For fail-safe of machine tool, etc., it is effective to stop
the motor when a power failure has occurred.
(example: spindle)
Dancer control
•
Entering position detection signal of dancer roll to use
PID control enables tension control by dancer roll.
Traverse function
•
Traverse function for wind-up drum of spinning
machine and wiredrawing machine prevents
unevenness and deformation at thread winding.
(example: textile machine) (example: wiredrawing machine)
Outline
•
dimension
drawings
Terminal connection
•
diagram
Terminal specification
•
explanation
Operation panel
•
Parameter unit
•
Parameter list
•
Protective
•
functions
Option and
•
peripheral devices
Precautions for
•
operation/selection
Precautions for peripheral
•
device selection
FR-D700 Series
•
Specification
Difference List
Warranty
•
International
•
FA Center
1 2
7
11
13
16
23
24
27
32
33
Page 3
(1) (1) (2)
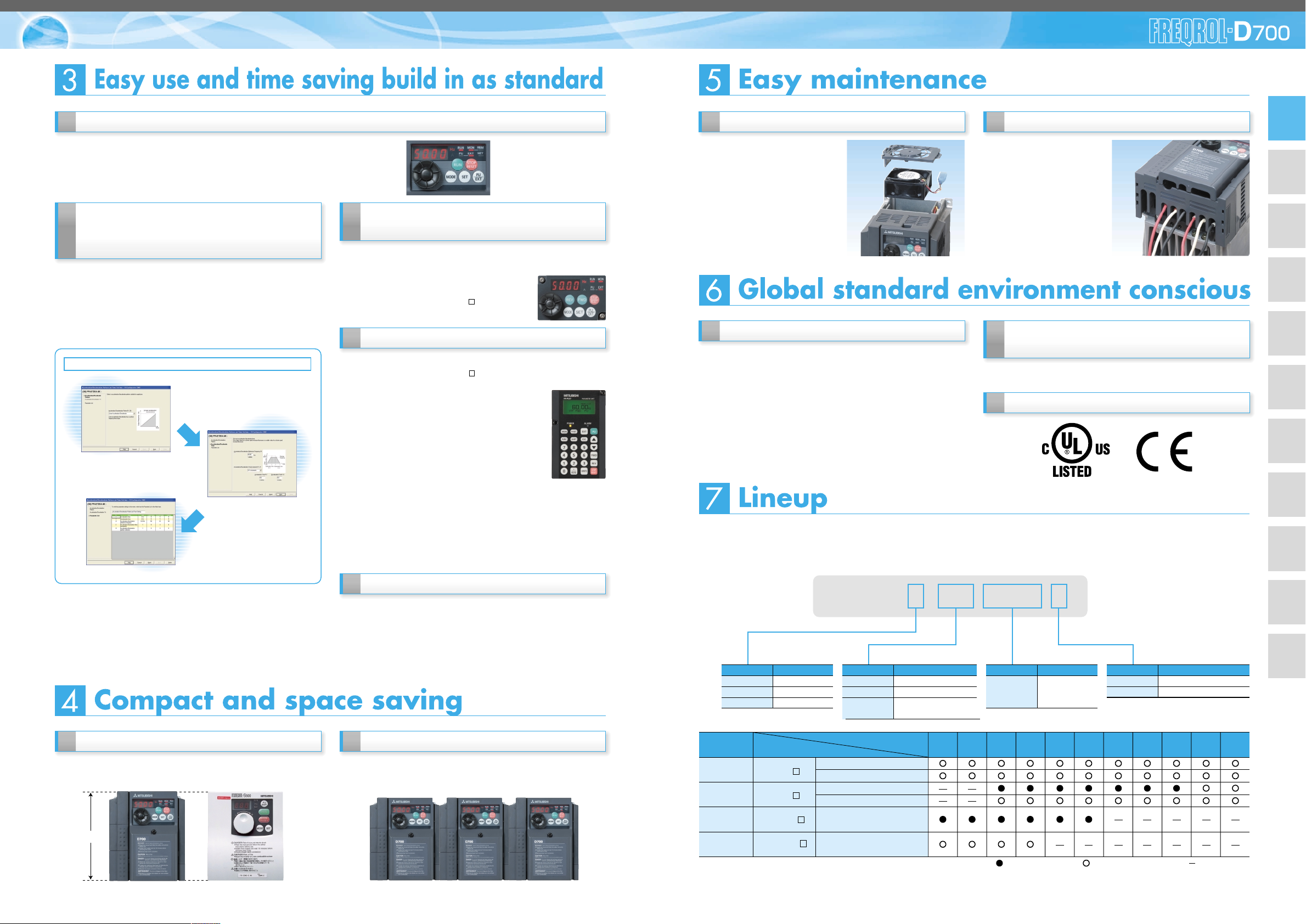
Quick setup with the setting dial
Mitsubishi inverter has a setting dial of course.
The scrolling speed of the dial was made to variable for more
•
improved operability.
The nonslip setting dial is easier to turn.
•
Easy replacement of cooling fan
A cooling fan is provided on top
of the inverter of all capacities
requiring a cooling fan (1.5K or
more).
A cooling fan can be easily
(2) (3)
Setting is easily done from a personal
computer using the FR Configurator
(option) (available soon)
Connecting a personal computer and the inverter via RS-485
communication realizes setting with wizard (interactive) function
of the FR Configurator (inverter setup software).
In addition, a parameter setting can be converted from the FRS500 series to the FR-D700 series by "convert" function.
Displays monitor data in waveform. [Graph]
Setting wizard function (example: acceleration/deceleration time setting)
Enclosure surface operation panel
FR-PA07 (option)
Optional enclosure surface operation panel (FR-PA07) can be
connected. In addition, an operation panel for the FR-E500
series can be connected.
The operation panel of the inverter can not be removed.
A parameter unit connection cable (FR-CB20 ) is
separately necessary.
(4)
Parameter unit FR-PU07 (option)
An optional parameter unit (FR-PU07) can be connected as well.
A parameter unit connection cable (FR-CB20 ) is separately necessary.
Setting such as direct input method with a numeric
•
keypad, operation status indication, and help
function are usable.
replaced without disconnecting
main circuit wires.
(1)
RoHS Directive compliant
Human and environment-friendly inverter in compliant with
RoHS Directive.
RoHS Directive requires member nations must guarantee that new electrical and electronic
equipment sold in the market after July 1, 2006 do not contain lead, cadmium, mercury,
hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyl (PBB) and polybrominated diphenyl ether
(PBDE) flame retardants
<G> mark indicating RoHS Directive compliance is printed on the package.
Eight languages can be displayed.
Parameter setting values of maximum of three
•
Acceleration/deceleration
pattern setting
inverters can be stored.
A battery pack type (FR-PU07BB(-L)) allows
•
parameter setting and parameter copy without
powering on the inverter. (available soon)
To use a parameter unit with battery pack (FR-PU07BB)
Acceleration/deceleration
time setting
Parameter list display
•
outside Japan, order a “FR-PU07BB-L” (parameter unit type
indicated on the package has L at the end).
Since enclosed batteries may conflict with laws in countries to
be used (new EU Directive on batteries and accumulators, etc.),
batteries are not enclosed with an FR-PU07BB except Japan.
(5)
Enhanced communication function
Modbus and Mitsubishi inverter protocol
•
The lineup of three phase 200V/400V class goes to 15K.
For the FR-D700 series, North American (NA), EU (EC), and Chinese (CHT) specifications also are supported.
*: This catalog explains based on the Japanese specifications.
Consult our sales office for specifications of each country.
FR-D740 -0.4K-
Supports Modbus RTU
Communication speed of RS-485 has been improved
(communication at 38.4kbps is available)
"Multi command mode" has been added to Mitsubishi inverter protocol
(data processing time of the inverter has been reduced to 1/4)
Symbol
1
2
4
Voltage
100V class
200V class
400V class
Symbol
None
S
W
Number of Power Phases
Three-phase input
Single-phase input
Single-phase input
(double voltage output)
Combed shaped wiring cover
Since a cover can be fitted
after wiring, wiring work is
easily done.
(3)
EMC filter integrated model
(to be released)
The lineup of EMC filter integrated models.
(3)
Complies with UL, cUL,EN (LVD) standards
Symbol
0.1K to 15K
Inverter Capacity
Indicate capacity
"kW".
Symbol
None
C
Protective Structure
Enclosed-type structure IP20
Totally enclosed structure IP40
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
(1) (2)
Easily replaceable compact body
Installation size is the same as that of the FR-S500 series which
is the smallest model of the Mitsubishi inverter.
128mm
3 4
FR-D740-0.4K FR-S540E-0.4K
Side by side installation saves space
Space can be saved by side by side no clearance installation*.
*: Use the inverter at the surrounding air temperature of 40˚C or less.
Power
Supply
Three phase
200V
Three phase
400V
Single phase
200V
*
Single phase
100V *
*: Output of the single-phase 200V and single-phase 100V input models is three-phase 200V.
Inverter Type
FR-D720- K
FR-D740- K
FR-D720S- K
FR-D710W- K
Totally-enclosed structure (IP40)
Totally-enclosed structure (IP40)
Inverter Capacity
Enclosed structure (IP20)
Enclosed structure (IP20)
Enclosed structure (IP20)
Enclosed structure (IP20)
0.1 0.2 0.4 0.75 1.5 2.2 3.7 5.5 7.5
11 15
:Available models :Models to be released :Not available
Page 4

Standard specifications
Rating
z Three-phase 400V power supply
Model FR-D740-K(-C)∗6 0.4 0.75 1.5 2.2 3.7 5.5 7.5
Model FR-D740--NA 012 022 036 050 080 120 160
Model FR-D740--EC 012 022 036 050 080 120 160
Model FR-D740-K-CHT 0.4 0.75 1.5 2.2 3.7 5.5 7.5
Applicable motor capacity (kW)∗1 0.4 0.75 1.5 2.2 3.7 5.5 7.5
Rated capacity (kVA)∗2 1.2 2.0 3.0 4.6 7.2 9.1 13.0
Rated current (A) 1.2 2.2 3.6 5.0 8.0 12.0 16.0
Overload current rating∗3 150% 60s, 200% 0.5s (inverse-time characteristics)
Output
Voltage∗4 Three-phase 380 to 480V
Rated input voltage/frequency Three-phase 380 to 480V 50Hz/60Hz
Permissible AC voltage fluctuation 325 to 528V 50Hz/60Hz
Permissible frequency fluctuation ±5%
Power supply capacity (kVA)∗5 1.52.54.55.59.512 17
Power supply
Protective structure (JEM1030) Enclosed type (IP20). IP40 for totally enclosed structure series.
Cooling system Self-cooling Forced air cooling
Approximate mass (kg) 1.2 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 3.1 3.1
∗1 The applicable motor capacity indicated is the maximum capacity applicable for use of the Mitsubishi 4-pole standard motor.
∗2 The rated output capacity indicated assumes that the output voltage is 440V.
∗3 The % value of the overload current rating indicated is the ratio of the overload current to the inverter's rated output current. For repeated duty, allow time for
the inverter and motor to return to or below the temperatures under 100% load.
∗4 The maximum output voltage does not exceed the power supply voltage. The maximum output voltage can be changed within the setting range. However,
the pulse voltage value of the inverter output side voltage remains unchanged at about that of the power supply.
∗5 The power supply capacity varies with the value of the power supply side inverter impedance (including those of the input reactor and cables).
∗6 Totally enclosed structure series ends with -C.
2
z Single-phase 200V power supply
Model FR-D720S-K 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.75 1.5 2.2
Model FR-D720S--NA 008 014 025 042 070 100
Model FR-D720S--EC 008 014 025 042 070 100
Model FR-D720S-K-CHT 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.75 1.5 2.2
Applicable motor capacity (kW)∗1 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.75 1.5 2.2
Rated capacity (kVA)∗2 0.3 0.5 1.0 1.6 2.8 3.8
Rated current (A) 0.8 1.4 2.5 4.2 7.0 10.0
Overload current rating∗3 150% 60s, 200% 0.5s (inverse-time characteristics)
Output
Voltage∗4 Three-phase 200 to 240V
Rated input voltage/frequency Single-phase 200 to 240V 50Hz/60Hz
Permissible AC voltage fluctuation 170 to 264V 50Hz/60Hz
Permissible frequency fluctuation ±5%
Power supply capacity (kVA)∗5 0.5 0.9 1.5 2.3 4.0 5.2
Power supply
Protective structure (JEM1030) Enclosed type (IP20).
Cooling system Self-cooling Forced air cooling
Approximate mass (kg) 0.5 0.6 0.9 1.1 1.5 1.9
∗1 The applicable motor capacity indicated is the maximum capacity applicable for use of the Mitsubishi 4-pole standard motor.
∗2 The rated output capacity indicated assumes that the output voltage is 230V.
∗3 The % value of the overload current rating indicated is the ratio of the overload current to the inverter's rated output current. For repeated duty, allow time for
the inverter and motor to return to or below the temperatures under 100% load.
∗4 The maximum output voltage does not exceed the power supply voltage. The maximum output voltage can be changed within the setting range. However,
the pulse voltage value of the inverter output side voltage remains unchanged at about that of the power supply.
∗5 The power supply capacity varies with the value of the power supply side inverter impedance (including those of the input reactor and cables).
2
5
Page 5
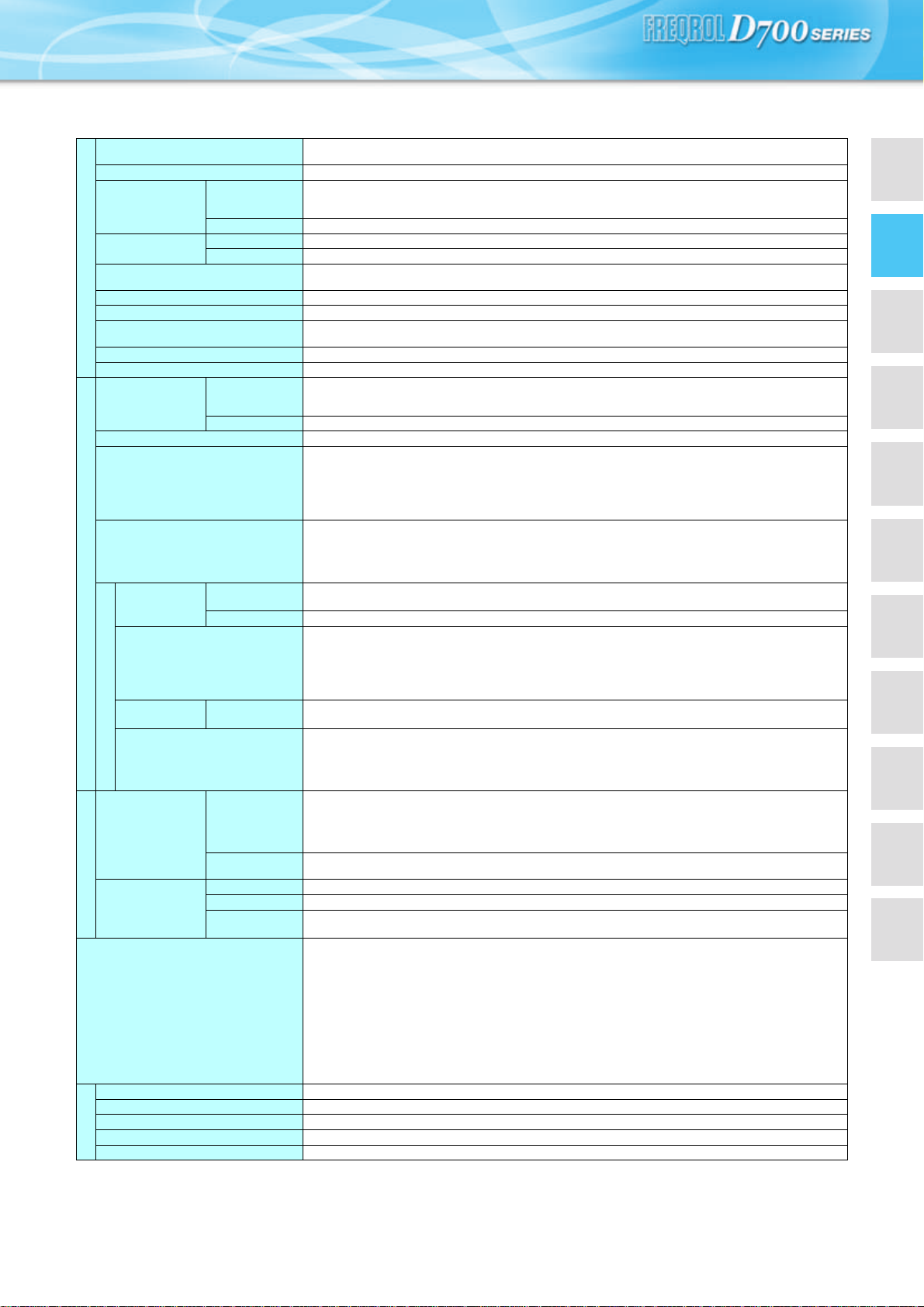
Common specifications
Control method
Output frequency range
Frequency setting
Analog input
resolution
Digital input
Frequency
accuracy
Analog input
Digital input
Voltage/frequency characteristics
Starting torque
Torque boost
Control specifications
Acceleration/deceleration time setting
DC injection brake
Stall prevention operation level
Frequency setting
Analog input
signal
Digital input
Start signal
Input signal
Operational functions
Output signal
points
Open collector
output
Relay output
Operation specifications
Operating status
For meter
Output signal
Output points
Pulse output
For meter
Operation panel
Operating status
Parameter unit
(FR-PU07)
Indication
Additional display
by the parameter
unit (FR-PU04/FRPU07) only
Fault definition
Operating status
Fault definition
Interactive
guidance
Protective/warning function
Surrounding air temperature
Ambient humidity
Storage temperature∗1
Atmosphere
Altitude/vibration
Environment
∗1 Temperatures applicable for a short time, e.g. in transit.
∗2 As the 0.75K or less is not provided with the cooling fan, this alarm does not function.
∗3 When using the inverters at the surrounding air temperature of 40°C or less, the inverters can be installed closely attached (0cm clearance).
∗4 This protective function does not function in the initial status.
∗5 This protective function is available with the three-phase power input specification model only.
Soft-PWM control/high carrier frequency PWM control (V/F control, general-purpose magnetic flux vector control,
optimum excitation control can be selected)
0.2 to 400Hz
0.06Hz/60Hz (terminal2, 4: 0 to 10V/10bit)
0.12Hz/60Hz (terminal2, 4: 0 to 5V/9bit)
0.06Hz/60Hz (terminal4: 0 to 20mA/10bit)
0.01Hz
Within ±1% of the max. output frequency (25°C ±10°C)
Within 0.01% of the set output frequency
Base frequency can be set from 0 to 400Hz
Constant torque/variable torque pattern can be selected
150% or more (at 1Hz)...when general-purpose magnetic flux vector control and slip compensation is set
Manual torque boost
0.1 to 3600s (acceleration and deceleration can be set individually), linear or S-pattern acceleration/deceleration
mode can be selected.
Operation frequency (0 to 120Hz), operation time (0 to 10s), operation voltage (0 to 30%) variable
Operation current level can be set (0 to 200% adjustable), whether to use the function or not can be selected
Two po in ts
Terminal 2: 0 to 10V, 0 to 5V can be selected
Terminal 4: 0 to 10V, 0 to 5V, 4 to 20mA can be selected
Entered from operation panel and parameter unit. Frequency setting increments is selectable
Forward and reverse rotation or start signal automatic self-holding input (3-wire input) can be selected.
Five points
You can select from among multi-speed selection, remote setting, second function selection, terminal 4 input
selection, JOG operation selection, PID control valid terminal, external thermal input, PU-external operation
switchover, V/F switchover, output stop, start self-holding selection, traverse function selectiom, forward rotation,
reverse rotation command, inverter reset, PU-NET operation switchover, external-NET operation switchover,
command source switchover, inverter operation enable signal, and PU operation external interlock
Maximum/minimum frequency setting, frequency jump operation, external thermal relay input selection, automatic
restart after instantaneous power failure operation, forward/reverse rotation prevention, remote setting, second
function, multi-speed operation, regeneration avoidance, slip compensation, operation mode selection, offline
auto tuning function, PID control, computer link operation (RS-485), optimum excitation control, power failure
stop, speed smoothing control, Modbus-RTU
One point
One point
You can select from among inverter operation, up-to-frequency, overload alarm, output frequency detection,
regenerative brake prealarm, electronic thermal relay function prealarm, inverter operation ready, output current
detection, zero current detection, PID lower limit, PID upper limit, PID forward/reverse rotation output, fan
alarm∗2, heatsink overheat pre-alarm, deceleration at an instantaneous power failure, PID control activated, PID
output interruption, during retry, life alarm, current average value monitor, remote output, alarm output, fault
output, fault output 3, and maintenance timer alarm
MAX 2.4kHz: one point
You can select from among output frequency, motor current (steady), output voltage, frequency setting, converter
output voltage, regenerative brake duty, electronic thermal relay function load factor, output current peak value,
converter output voltage peak value, reference voltage output, motor load factor, PID set point, PID measured
value, output power, PID deviation, Motor thermal load factor, Inverter thermal load factor
Pulse train output (1440 pulses/s/full scale)
You can select from among output frequency, motor current (steady), output voltage, frequency setting,
cumulative energization time, actual operation time, converter output voltage, regenerative brake duty, electronic
thermal relay function load factor, output current peak value, converter output voltage peak value, motor load
factor, PID set point, PID measured value, PID deviation, inverter I/O terminal monitor, output power, cumulative
power, motor thermal load factor, inverter thermal load factor, PTC thermistor resistance.
Fault definition is displayed when the fault occurs and the past 8 fault definitions (output voltage/current/
frequency/cumulative energization time right before the fault occurs) are stored
Not used
Output voltage/current/frequency/cumulative energization time immediately before the fault occurs
Function (help) for operation guide
<Protective functions>
Overcurrent during acceleration, overcurrent during constant speed, overcurrent during deceleration, overvoltage
during acceleration, overvoltage during constant speed, overvoltage during deceleration, inverter protection
thermal operation, motor protection thermal operation, heatsink overheat, input phase failure ∗4 ∗5, output side
earth (ground) fault overcurrent at start∗4, output phase failure, external thermal relay operation ∗4, PTC
thermistor operation∗4, parameter error, PU disconnection, retry count excess ∗4, CPU fault, brake transistor
alarm, inrush resistance overheat, analog input error, stall prevention operation, output current detection value
exceeded
<Warning functions>
Fan alarm∗2, overcurrent stall prevention, overvoltage stall prevention, PU stop, parameter write error,
regenerative brake prealarm ∗4, electronic thermal relay function prealarm, maintenance output ∗4, undervoltage,
operation panel lock, password locked, inverter reset
-10°C to +50°C (non-freezing) (-10°C to +40°C for totally-enclosed structure feature) ∗3
90%RH maximum (non-condensing)
-20°C to +65°C
Indoors (without corrosive gas, flammable gas, oil mist, dust and dirt etc.)
Maximum 1000m above sea level, 5.9m/s 2 or less
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
6
Page 6
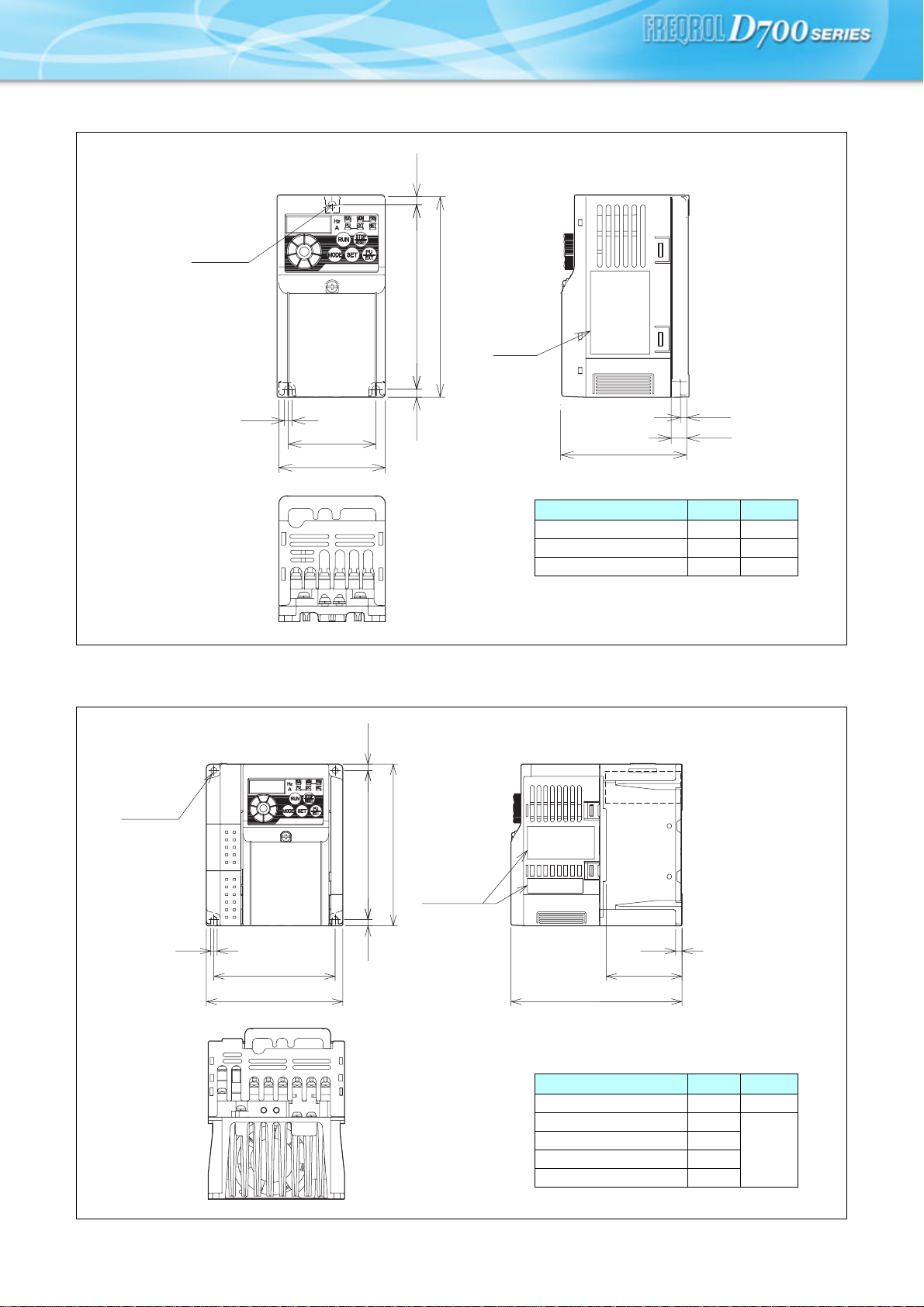
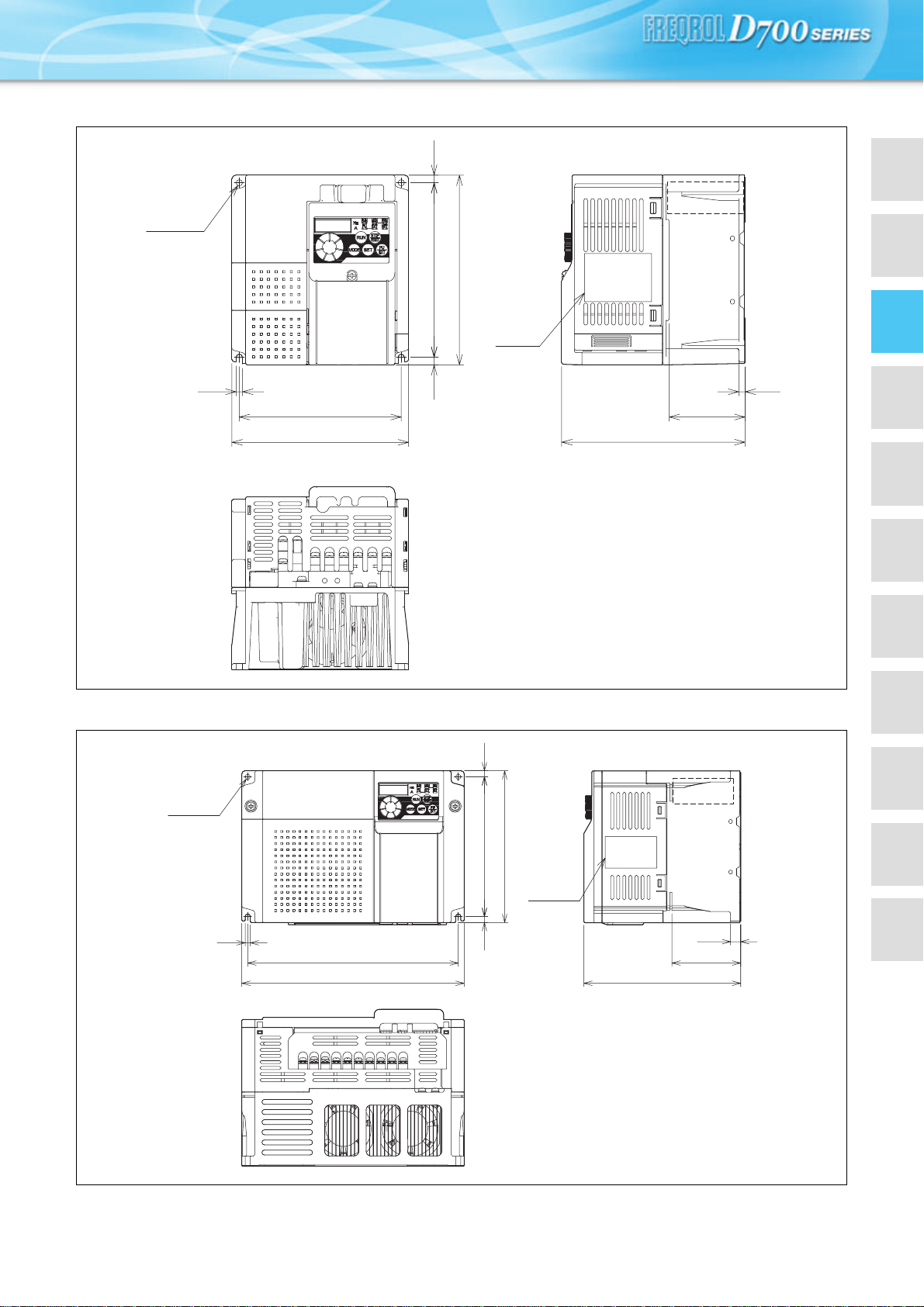
Outline Dimension Drawings
zFR-D720S-0.1K to 0.75K
1-φ5 hole
128
Rating
plate
zFR-D740-0.4K to 3.7K
zFR-D720S-1.5K
2-φ5 hole
5
56
68
5 118 5
D
Inverter Type
4
D1
D D1
FR-D720S-0.1K, 0.2K 80.5 10
FR-D720S-0.4K 142.5 42
FR-D720S-0.75K 162.5 62
(Unit: mm)
FAN
*
128
118
Rating
plate
5
96
108
5 5
D
∗ FR-D740-0.4K, 0.75K are not provided with the cooling fan.
Inverter Type
5
D1
D D1
FR-D740-0.4K, 0.75K 129.5 54
FR-D740-1.5K 135.5
FR-D740-2.2K 155.5
FR-D740-3.7K 165.5
60
FR-D720S-1.5K 155.5
(Unit: mm)
7
Page 7
zFR-D720S-2.2K
2-φ5 hole
FeaturesOptions
FAN
Standard
138 66
150
Specifications
zFR-D740-5.5K, 7.5K
Rating
plate
5
128
140
145
60
5
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
(Unit: mm)
6
2-φ5 hole
FAN
1386
150
Rating
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
plate
155
10
68
Warranty
FA Center
International
5
208
220
(Unit: mm)
8
Page 8
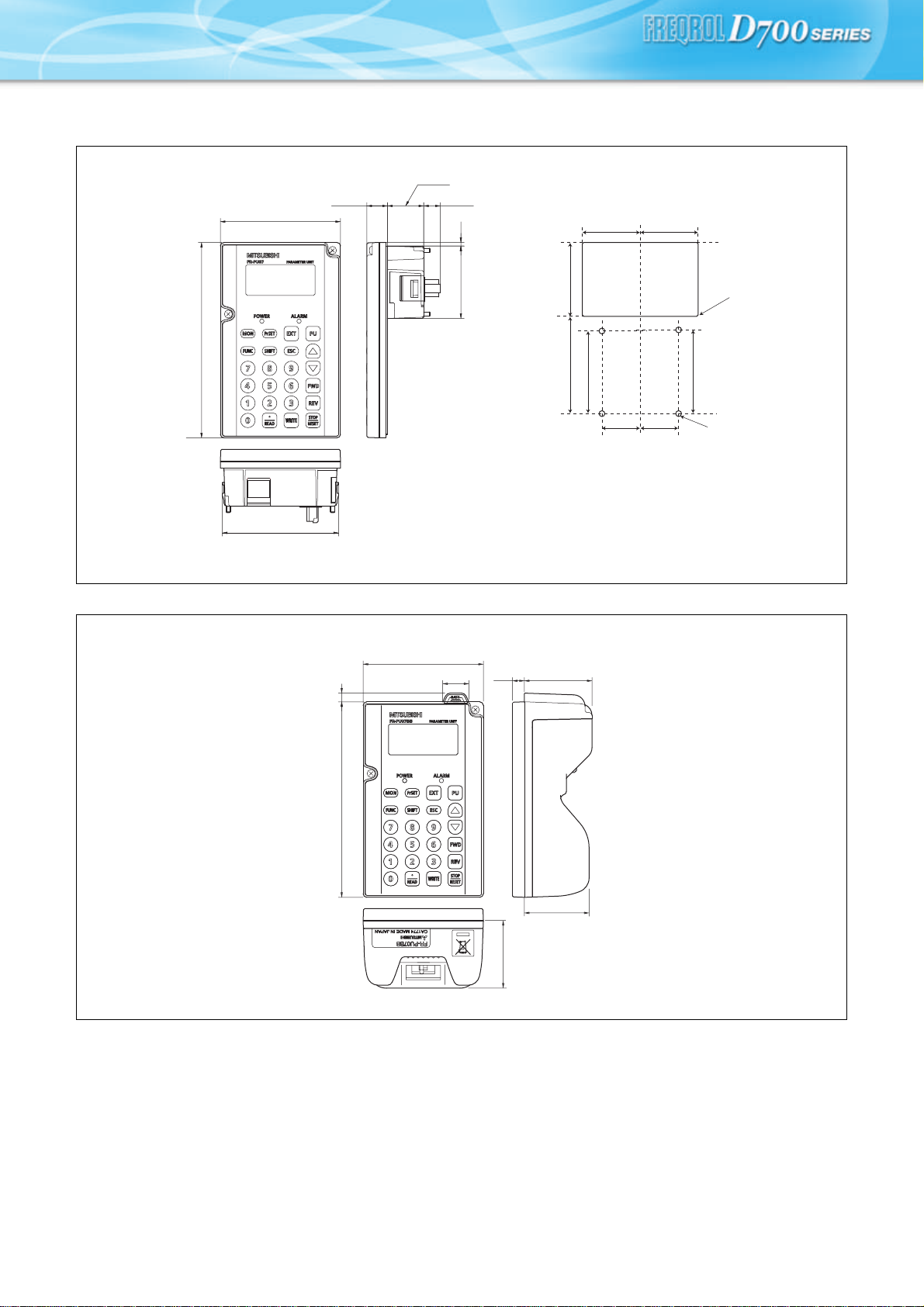
zParameter unit (option) (FR-PU07)
<Outline drawing> <Panel cut dimension drawing>
83
*1
135
(14.2)
*1
25.05
*1
*1
(11.45)
2.5
50
40
51
67
56.8
40
Air-bleeding
hole
4-R1
57.8
80.3
∗1 When installing the FR-PU07 on the enclosure, etc., remove screws or fix the screws to the FR-PU07 with M3 nuts.
∗2 Select the installation screw whose length will not exceed the effective depth of the installation screw hole.
Parameter unit (option) (FR-PU07BB (-L))
z
6
135
<
Outline drawing>
83
8.2
18
46.7
26.5
26.5
4-φ4 hole
(
Effective depth of the
installation screw hole 5.0)
M3 screw *2
(Unit: mm)
44.7
46.7
∗ Select the installation screw whose length will not exceed the effective depth of the installation screw hole.
(Unit: mm)
9
Page 9
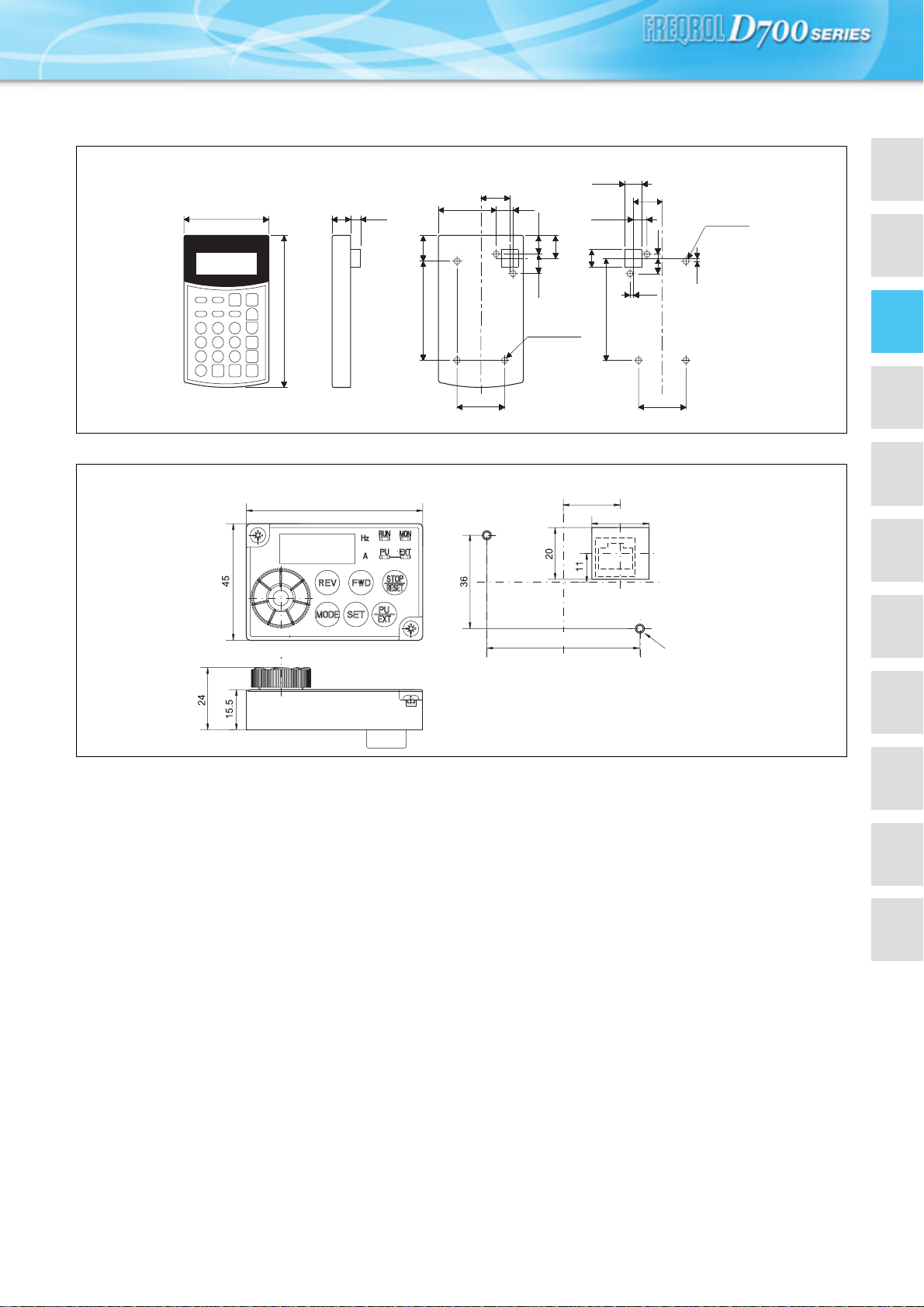
zParameter unit (option) (FR-PU04)
w
<
Outline drawing><Panel cut dimension drawing>
72 15 10.5
21.5
125
80
Select the installation screws whose length will not exceed the effective depth of the installation screw hole.
zEnclosure surface operation panel (option) (FR-PA07)
Outline drawing><Panel cut dimension drawing>
<
68
48
40
24
13
18.5
20
14.5
5-M3 screw
Effective
depth
of the
installation
screw hole
17
4.5
22
16.5
11.75
81.5
23.75
5-φ4 hole
FeaturesOptions
1.5
13
1.25
1.5
40
(Unit: mm)
22
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
59
2-M3 scre
Functions
Protective
(Unit: mm)
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
10
Page 10
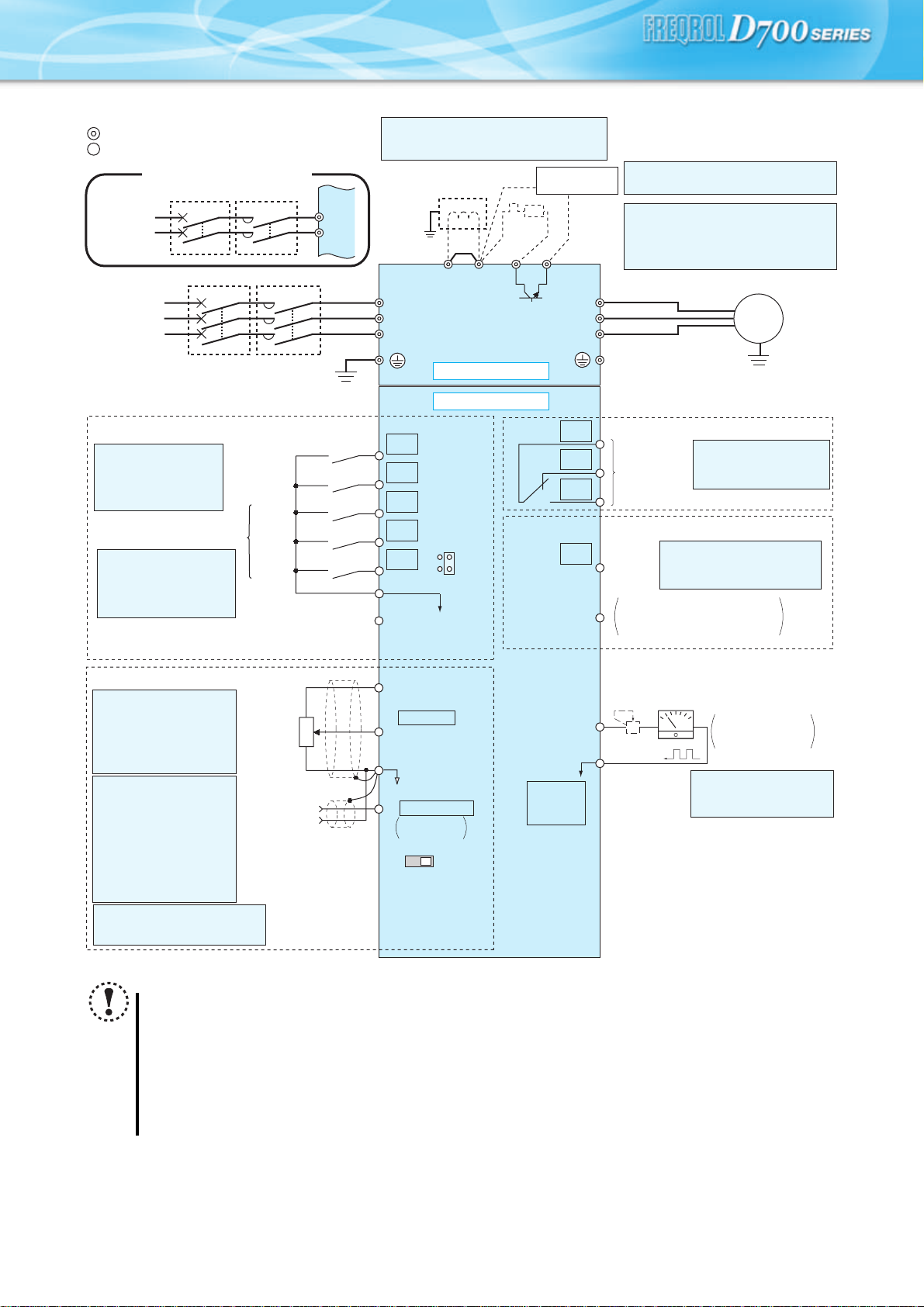
Terminal Connection Diagram
Source logic
Main circuit terminal
Control circuit terminal
Single-phase power input
MCCB MC
Single-phase
AC power
supply
MCCB MC
Three-phase
AC power
supply
Earth
(Ground)
Control input signals (No voltage input allowed)
Terminal functions vary
with the input terminal
assignment (Pr. 178 to
Pr. 182)
Multi-speed selection
*2 When using terminals PC-
SD as a 24VDC power
supply, take care not to
short across terminals
PC-SD.
(Common for external power supply transistor)
Forward
rotation start
Reverse
rotation start
High
speed
Middle
speed
Low
speed
Contact input common
24VDC power supply
Contact input common
R/L1
S/L2
*1. DC reactor (FR-HEL)
When connecting a DC reactor, remove the
jumper across P1-P/+
*1
Earth
(Ground)
Jumper
P1 P/+
*7
PR
*6
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
Main circuit
Control circuit
STF
STR
RH
RM
PC
RL
SD
*2
SINK
SOURCE
R
N/-
Brake unit
(Option)
W
C
B
A
RUN
SE
*6 A brake transistor is not built-in to the
FR-D720S-0.1K and 0.2K.
*7 Brake resistor (FR-ABR, MRS)
Install a thermal relay to prevent an
overheat and burnout of the brake resistor.
(The brake resistor can not be connected
to the FR-D720S-0.1K and 0.2K.)
U
V
Relay output
Terminal functions vary
Relay output
(Fault output)
by Pr. 192 A,B,C terminal
function selection
Open collector output
Terminal functions vary by
Running
Pr. 190 RUN terminal function
selection
Open collector output common
Sink/source common
Motor
IM
Earth (Ground)
Frequency setting signals (Analog)
*3 Terminal input specifications
can be changed by analog
input specifications
switchover (Pr. 73).
Terminal 10 and terminal 2
are used as PTC input
terminal (Pr. 561).
*4 Terminal input
specifications can be
changed by analog input
specifications switchover
(Pr. 267). Set the
voltage/current input
switch in the "V" position
to select voltage input (0
to 5V/0 to10V) and "I"
(initial value) to select
current input (4 to 20mA).
*5 It is recommended to use 2W1kΩ
when the frequency setting signal
is changed frequently.
Frequency
setting
potentiometer
1/2W1kΩ
*5
Terminal 4
input
(Current
input)
Note
y To prevent a malfunction caused by noise, separate the signal cables more than 10cm from the power cables.
y After wiring, wire offcuts must not be left in the inverter.
Wire offcuts can cause an alarm, failure or malfunction. Always keep the inverter clean. When drilling mounting holes
in an enclosure etc., take care not to allow chips and other foreign matter to enter the inverter.
y To ensure safety, for single-phase power input specification model, connect the power input to the inverter via a
magnetic contactor and earth leakage circuit breaker or moulded case circuit breaker, and use the magnetic
contactor to switch power on-off.
y The output of the single-phase power input specification is three-phase 200V.
3
2
1
(+)
(-)
10(+5V)
2 0 to 5VDC
(0 to 10VDC)
*3
5(Analog common)
4 4 to 20mADC
0 to 5VDC
0 to 10VDC
*4
PU
connector
Calibration resistor
FM
*8
SD
Indicator
+
(Frequency meter, etc.)
-
*8 It is not necessary when
calibrating the indicator
from the operation panel.
Moving-coil type
1mA full-scale
VI
Voltage/current
input switch
*4
11
Page 11

Terminal Specification Explanation
Typ e
Ter min al
Symbol
R/L1, S/L2,
T/L3
∗
Terminal Name Description
AC power input
U, V, W Inverter output
P/+, PR
Brake resistor
P/+, N/- Brake unit connection
Main circuit
P/+, P1 DC reactor connection
Earth (Ground)
STF Forward rotation start
STR Reverse rotation start
RH, RM, RL Multi-speed selection
Contact input common
(sink) (initial setting)
SD
External transistor
common (source)
24VDC power supply
Contact input
PC
External transistor
(sink) (initial setting)
Contact input common
24VDC power supply
10
Control circuit/input signal
2
4
Frequency setting
Frequency setting
Frequency setting
Frequency setting
Frequency setting
PTC thermistor input
PTC
5
10
2
thermistor
A, B, C
Relay
RUN Inverter running
SE
Open collector
Open collector
output common
FM For meter
Control circuit/output signal
Pulse
— PU connector
Communication
S1
connection
common
common
(source)
power supply
(voltage)
(current)
common
Relay output
(fault output)
Connect to the commercial power supply. Keep these terminals open when using the high power
factor converter (FR-HC) or power regeneration common converter (FR-CV).
∗ When using single-phase power input, terminals are R/L1 and S/L2.
Connect a three-phase squirrel-cage motor.
Connect a brake transistor (MRS, FR-ABR) across terminals P/+-PR.
(The brake resistor can not be connected to the FR-D720S-0.1K and 0.2K)
Connect the brake unit (FR-BU2), power regeneration common converter (FR-CV) or high power
factor converter (FR-HC).
Remove the jumper across terminals P/+-P1 and connect a DC reactor.
For earthing (grounding) the inverter chassis. Must be earthed (grounded).
Turn on the STF signal to start forward rotation and turn it off to stop.
Turn on the STR signal to start reverse rotation and turn it off to stop.
Multi-speed can be selected according to the combination of RH, RM and RL signals.
Common terminal for contact input terminal (sink logic) and terminal FM.
When connecting the transistor output (open collector output), such as a programmable controller,
when source logic is selected, connect the external power supply common for transistor output to this
terminal to prevent a malfunction caused by undesirable currents.
Common output terminal for 24VDC 0.1A power supply (PC terminal).
Isolated from terminals 5 and SE.
When connecting the transistor output (open collector output), such as a programmable controller,
when sink logic is selected, connect the external power supply common for transistor output to this
terminal to prevent a malfunction caused by undesirable currents.
Common terminal for contact input terminal (source logic).
Can be used as 24VDC 0.1A power supply.
Used as power supply when connecting potentiometer for frequency setting
(speed setting) from outside of the inverter.
Inputting 0 to 5VDC (or 0 to 10V) provides the maximum output
frequency at 5V (10V) and makes input and output proportional.
Use Pr. 73 to switch between input 0 to 5VDC (initial setting) and 0
to 10VDC input.
Inputting 0 to 20mADC (or 0 to 5V / 0 to 10V) provides the
maximum output frequency at 20mA makes input and output
proportional. This input signal is valid only when the AU signal is on
(terminal 2 input is invalid). Use Pr. 267 to switch from among input
4 to 20mA (initial setting), 0 to 5VDC and 0 to 10VDC. Set the
voltage/current input switch in the "V" position to select voltage
input (0 to 5V/0 to 10V).
Common terminal for the frequency setting signals (terminals 2 or 4). Do not earth (ground).
For connecting PTC thermistor output.
When PTC thermistor protection is valid (Pr. 561 ≠ "9999"), terminal
2 is not available for frequency setting.
1 changeover contact output indicates that the inverter fault occurs.
Fault: discontinuity across B-C (continuity across A-C), Normal: continuity across B-C (discontinuity
across A-C) Contact capacity 230VAC 0.3A (power factor = 0.4) 30VDC 0.3A
Switched low when the inverter output frequency is equal to or
higher than the starting frequency (initial value 0.5Hz). Switched
high during stop or DC injection brake operation.
(Low indicates that the open collector output transistor is on
(conducts). High indicates that the transistor is off (does not conduct))
Common terminal of terminal RUN and FU.
Select one e.g. output frequency from monitor items. (Not output
during inverter reset.) The output signal is proportional to the
magnitude of the corresponding monitoring item.
With the PU connector, RS-485 communication can be made.
· Conforming standard: EIA-485 (RS-485)
· Transmission format: Multi-drop link
· Communication speed: 4800 to 38400bps
· Overall extension: 500m
When the STF and STR signals
are turned on simultaneously,
the stop command is given.
5VDC
permissible load
current 10mA
Input resistance 10kΩ ± 1kΩ
Permissible maximum voltage
20VDC
Voltage input:
Input resistance 10kΩ ± 1kΩ
Permissible maximum voltage
20VDC
Current input:
Input resistance 233Ω ± 5
Maximum permissible current 30mA.
Adaptive PTC thermistor
resistance:
100Ω to 30kΩ
Permissible load 24VDC
(Maximum 27VDC) 0.1A
(a voltage drop is 3.4V maximum
when the signal is on)
Permissible load current 1mA
1440 pulses/s at 60Hz
Ω
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
S2
SO
Terminal for inverter
manufacturer setting
SC
Keep these open. Otherwise, the inverter may be damaged.
Do not remove wires for shorting across terminal S1 and SC, across terminal S2 and SC. If one of these wires is removed, the
inverter cannot be operated.
Note
y Set Pr. 267
a voltage with voltage/current input switch in "I" position (current input is selected) or a current with switch in "V" position
(voltage input is selected) could cause component damage of the inverter or analog circuit of output device
y The inverter will be damaged if power is applied to the inverter output terminals (U, V, W). Never perform such wiring.
y indicates that terminal functions can be selected using Pr. 178 to Pr. 182, Pr. 190, Pr. 192 (I/O terminal function selection).
y Terminal names and terminal functions are those of the factory set.
and a voltage/current input switch correctly, then input an analog signal in accordance with the setting. Applying
s.
12
Page 12

Explanation of the Operation Panel
The operation panel cannot be removed from the inverter.
Operation mode indication
PU: Lit to indicate PU operation mode.
EXT: Lit to indicate external operation
mode.
NET: Lit to indicate network operation
mode.
PU, EXT: Lit to indicate external/PU
combined operation mode 1, 2.
Unit indication
Hz: Lit to indicate frequency.
(Flickers when the set frequency
monitor is displayed.)
A: Lit to indicate current.
(Both "Hz" and "A" turn off when other
than the above is displayed.)
Monitor (4-digit LED)
Shows the frequency, parameter number,
etc.
Setting dial
(Setting dial: Mitsubishi inverter dial)
Used to change the frequency setting
and parameter values.
Press to display the following.
y Displays the set frequency in the
monitor mode
y Currently set value is displayed during
calibration
y Displays the order in the faults history
mode
Mode switchover
Used to change each setting mode.
Pressing simultaneously changes
the operation mode.
Pressing for a while (2s) can lock
operation.
Determination of each setting
If pressed during operation, monitor
changes as below;
Running frequency
Operating status display
Lit or flicker during inverter operation. ∗
∗ On: Indicates that forward rotation
operation is being performed.
Slow flickering (1.4s cycle):
Reverse rotation operation
Fast flickering (0.2s cycle):
When was pressed or the start
command was given, but the operation
can not be made.
y When the frequency command is less
than the starting frequency.
y When the MRS signal is input.
Parameter setting mode
Lit to indicate parameter setting mode.
Monitor indication
Lit to indicate monitoring mode.
Stop operation
Used to stop Run command.
Fault can be reset when protective
function is activated (fault).
Operation mode switchover
Used to switch between the PU and
external operation mode.
When using the external operation mode
(operation using a separately connected
frequency setting potentiometer and start
signal), press this key to light up the EXT
indication.
(Press simultanesouly (0.5s) or
change
Pr. 79
setting to change to combined
mode .)
PU: PU operation mode
EXT: External operation mode
Cancels PU stop also.
Start command
The rotation direction can be selected by
setting Pr. 40.
13
Output current
Output voltage
Page 13

Basic operation of the operation panel
Operation mode switchover
At powering on (external operation mode)
PU operation mode
(output frequency monitor)
PU Jog operation mode
Value change
Output current monitor
STOP
(Example)
and frequency flicker.
Frequency setting has been
written and completed!!
Output voltage monitor
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Parameter setting mode
Parameter settingFaults history Monitor/frequency setting
Value change
Parameter clear All parameter
clear
[Operation for displaying faults history]
Past eight faults can be displayed.
(The latest fault is ended by ".".)
When no fault history exists, is displayed.
Display the
current setting
(Example)
Parameter and a setting value
flicker alternately.
Parameter write is completed!!
Faults history clear
Initial value
change list
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
14
Page 14

Explanations of Parameter unit
180.0S
180.0S
e
Reading
Verifying
Parameter unit (FR-PU07), parameter unit with battery pack (FR-PU07BB(-L) (available soon))
y The parameter unit is a convenient tool for inverter setting
such as direct input method with a numeric keypad,
operation status indication, and help function.
Eight languages can be displayed.
y Parameter setting values of maximum of three inverters can
be stored.
y
With the FR-PU07BB(-L), parameter check and setting
change can be made without connecting a power supply to the
inverter. Use AA nickel hydride batteries, AA alkali batteries, or
AC adapter separately available as power supply.
y To use a parameter unit with battery pack (FR-PU07BB)
outside Japan, order a "FR-PU07BB-L" (parameter unit type
indicated on the package has L at the end). Since enclosed
batteries may conflict with laws in countries to be used (new
EU Directive on batteries and accumulators, etc.), batteries
are not enclosed with an FR-PU07BB except Japan.
y Since the shape is specially designed for portable use, it is
easy to work with the FR-PU07BB(-L) in hand.
y The parameter unit connection cable FR-CB20 is required
for connecting to the inverter.
POWER lamp
Lit when the power turns on.
FR-PU07 FR-PU07BB(-L)
Monitor
Liquid crystal display
(16 characters 4 lines with backlight)
Interactive parameter setting
Trouble shooting guidance
Monitor (frequency, current, power, etc.)
ALARM lamp
Lit to indicate an inverter alarm
occurrence.
Operation keys
(Refer to the table on the right)
Key Description
Use for parameter setting
Press to choose the parameter setting mode.
First priority monitor is displayed.
In the initial setting, the output frequency is displayed.
Operation cancel key
Used to display the function menu.
A variety of functions can be used on the function menu.
Used to shift to the next item in the setting or monitoring mode.
Used to enter a frequency, parameter number or set value.
to
Inverter operates in the external operation mode.
Used to select the PU operation mode to display the frequency
setting screen.
y Used to keep on increasing or decreasing the running
frequency. Hold down to vary the frequency.
y Press either of these keys on the parameter setting mode
screen to change the parameter setting value sequentially.
y
On the selecting screen, these keys are used to move the cursor.
y Hold down and press either of these keys to advance
or return the display screen one page.
Forward rotation command key.
Reverse rotation command key.
y Stop command key.
y Used to reset the inverter when an alarm occurs.
y Used to write a set value in the setting mode.
y Used as a clear key in the all parameter clear or alarm history
clear mode.
y Used as a decimal point when entering numerical value.
y Used as a parameter number read key in the setting mode.
y Used as an item select key on the menu screen such as
parameter list or monitoring list.
y Used as an alarm definition display key in the alarm history
display mode.
y
Used as a command voltage read key in the calibration mode.
zMonitor: Merely pressing calls 6 different monitor screens in sequence.
Top two monitor types of
Switch power
on or press
READ:List
0.00Hz
--- STOP EXT
Output frequency monitor
READ:List
0.00A
--- STOP EXT
Output current monitor
READ:List
0.0
V
--- STOP EXT
Output voltage monitor
ALARM HISTORY
<READ>
Alarm history
monitor
OTHERS
<READ>
Selective monitor
(Running speed, motor torque, etc.
from 16 different monitors)
0.00Hz
0.00A
0.0V
--- STOP EXT
3-step monitor
the first priority monitor,
output frequency, output
current and output voltage
are displayed in line
zParameter setting: When changing 5s to 180s as the Pr. 8 Deceleration time setting
Freq Set
SET 0.00Hz
0~400Hz
SETTING MODE
0~9:Set Pr.NO.
Select Oper
SETTING MODE
Pr.NO.
8
<READ>
8 Dec.T1
5.0S
0~3600
8 Dec.T1
5.0S
180S
0~3600
8 Dec.T1
180.0S
180.0S
Completed
9 Set THM
2.55A
0~500
zPr. List: Displays the parameters list.
You can select the parameter from the list to read and write the parameter setting.
1 MONITOR
2 PU Oper
3 Pr.List
4 Pr.Clear
1 MONITOR
2 PU Oper
3 Pr.List
4 Pr.Clear
Using , move the
cursor to "3 Pr. List".
1 Setting Mode
2 Pr.List
3 Set Pr.List
4 Def.Pr.List
1 Setting Mode
2 Pr.List
3 Set Pr.List
4 Def.Pr.List
Using , move the
cursor to "2 Pr. List".
0 Trq Bst1
1 Max.F1
2 Min.F1
3 VFbaseF1
0 Trq Bst1
6.0%
0~30
Parameter setting mod
zMultiple copies: You can read the parameter settings of the inverter into the FR-PU07 and store the settings of maximum
three inverters. You can also copy the stored parameter settings to another inverter of the same series.
Select the "READ".
1 MONITOR
2 PU Oper
3 Pr.List
4 Pr.Clear
9 S/W
10 Selectop
11 Option
12 PRCpy set
Select "12 PRCpy set".
1 Copy area 1
2 Copy area 2
3 Copy area 3
Select the copy area.
Copy area 1
1 Read VFD
2 Write VFD
3 Verifing
Read "1 Read VFD".
Select the "WRITE".
Copy area 1
1 Read VFD
2 Write VFD
3 Verifing
Select "2 Write VFD".
Select the "Verifying".
Copy area 1
1 Read VFD
2 Write VFD
3 Verifing
Select "3 Verifing".
Name:012
:Select Char
READ:Decide Char
WRITE:DecideName
Give a name.
012
Area 1 to VFD
WRITE:Executing
ESC:Cancel
012
Verify Area 1
WRITE:Executing
ESC:Cancel
012
Overwrite area 1
WRITE:Executing
ESC:Cancel
Write.
Param Copy
Writing
Completed
Please Reset
Param Copy
Verifying
Please Wait
Param Copy
Reading
Completed
15
Page 15

Parameter List
For simple variable-speed operation of the inverter, the initial setting of the parameters may be used as they are. Set the
necessary parameters to meet the load and operational specifications. Parameter setting, change and check can be made
from the operation panel. For details of parameters, refer to the instruction manual.
This catalog explains based on the Japanese specifications.
POINT
Only simple mode parameter can be displayed using
displayed with the initial setting. Set
z Simple mode parameter
Pr. 160 Extended function display selection
Pr. 160 Extended function display selection
as required.
. (All parameters are
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Parameter
Number
Name
Setting
Range
Minimum
Setting
Increments
0 Torque boost 0 to 30% 0.1% 6%/4%/3%∗
1 Maximum frequency 0 to 120Hz 0.01Hz 120Hz
2 Minimum frequency 0 to 120Hz 0.01Hz 0Hz
3 Base frequency 0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
4
5
6
Multi-speed setting
(high speed)
Multi-speed setting
(middle speed)
Multi-speed setting (low
speed)
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 30Hz
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 10Hz
7 Acceleration time 0 to 3600s 0.1s 5s/10s∗
8 Deceleration time 0 to 3600s 0.1s 5s/10s∗
9
79
125
126
160
Electronic thermal O/L
relay
Operation mode
selection
Terminal 2 frequency
setting gain frequency
Terminal 4 frequency
setting gain frequency
Extended function
display selection
0 to 500A 0.01A
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6,
7
10
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
0, 9999 1 9999
Initial
Val ue
Rated
inverter
current
Application
Set when you want to increase a
starting torque or when the motor
with a load will not rotate, resulting in
an alarm [OL] and a trip [OC1].
∗ Initial values differ according to the
inverter capacity. (0.75K or less/1.5K
to 3.7K/5.5K, 7.5K)
Set when the maximum output
frequency need to be limited.
Set when the minimum output
frequency need to be limited.
Set when the rated motor
frequency is 50Hz.
Check the motor rating plate.
Set when changing the preset
speed in the parameter with a
terminal.
Acceleration/deceleration time can
be set.
∗ Initial values differ according to the
inverter capacity. (3.7K or less/5.5K,
7.5K)
The inverter protects the motor
from overheat.
Set the rated motor current.
Select the start command location
and frequency command location.
Frequency for the maximum value
of the potentiometer (5V initial
value) can be changed.
Frequency for the maximum
current input (20mA initial value)
can be changed.
Parameter which can be read from
the operation panel and parameter
unit can be restricted.
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
16
Page 16

z Extended mode parameter
REMARKS
y indicates simple mode parameters.
y The shaded parameters in the table allow its setting to be changed during operation even if "0" (initial value) is set in Pr. 77
Parameter write selection.
Func-
Parameter
tion
0 Torque boost 0 to 30% 0.1% 6/4/3% ∗1
1 Maximum frequency 0 to 120Hz 0.01Hz 120Hz
2 Minimum frequency 0 to 120Hz 0.01Hz 0Hz
3 Base frequency 0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
4 Multi-speed setting (high speed) 0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
5 Multi-speed setting (middle speed) 0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 30Hz
6 Multi-speed setting (low speed) 0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 10Hz
7 Acceleration time 0 to 3600s 0.1s 5/10s ∗2
Basic functions
8 Deceleration time 0 to 3600s 0.1s 5/10s ∗2
9 Electronic thermal O/L relay 0 to 500A 0.01A
10 DC injection brake operation frequency 0 to 120Hz 0.01Hz 3Hz
11 DC injection brake operation time 0 to 10s 0.1s 0.5s
brake
DC injection
— 13 Starting frequency 0 to 60Hz 0.01Hz 0.5Hz
— 14 Load pattern selection 0 to 3 1 0
JOG
— 17 MRS input selection 0, 2, 4 1 0
— 18 High speed maximum frequency 120 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 120Hz
— 19 Base frequency voltage 0 to 1000V, 8888, 9999 0.1V 9999
12 DC injection brake operation voltage 0 to 30% 0.1% 4%
15 Jog frequency 0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 5Hz
16 Jog acceleration/deceleration time 0 to 3600s 0.1s 0.5s
operation
Name Setting Range
Minimum
Setting
Increments
Initial
Val ue
Rated
inverter
current
Customer
Setting
20
Acceleration/
deceleration time
22 Stall prevention operation level 0 to 200% 0.1% 150%
Stall
Multi-speed
— 29
— 30 Regenerative function selection 0, 1, 2 1 0
Frequency jump
— 37 Speed display 0, 0.01 to 9998 0.001 0
— 40 RUN key rotation direction selection 0, 1 1 0
Frequency
23
prevention
24 Multi-speed setting (speed 4) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
25 Multi-speed setting (speed 5) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
26 Multi-speed setting (speed 6) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
setting
27 Multi-speed setting (speed 7) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
31 Frequency jump 1A 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
32 Frequency jump 1B 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
33 Frequency jump 2A 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
34 Frequency jump 2B 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
35 Frequency jump 3A 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
36 Frequency jump 3B 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
41 Up-to-frequency sensitivity 0 to 100% 0.1% 10%
42 Output frequency detection 0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 6Hz
43
detection
Acceleration/deceleration reference
frequency
Stall prevention operation level
compensation factor at double speed
Acceleration/deceleration pattern
selection
Output frequency detection for reverse
rotation
1 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
0 to 200%, 9999 0.1% 9999
0, 1, 2 1 0
0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
17
Page 17

Func-
Parameter
tion
44 Second acceleration/deceleration time 0 to 3600s 0.1s 5/10s ∗2
45 Second deceleration time 0 to 3600s, 9999 0.1s 9999
46 Second torque boost 0 to 30%, 9999 0.1% 9999
47 Second V/F (base frequency) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
48
Second functions
51 Second electronic thermal O/L relay 0 to 500A, 9999 0.01A 9999
52 DU/PU main display data selection
54 FM terminal function selection
55 Frequency monitoring reference 0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
Monitor functions
56 Current monitoring reference 0 to 500A 0.01A
57 Restart coasting time 0, 0.1 to 5s, 9999 0.1s 9999
Name Setting Range
Second stall prevention operation
current
Minimum
Setting
Increments
Initial
Val ue
0 to 200%, 9999 0.1% 9999
0, 5, 8 to 12, 14, 20,
23 to 25, 52 to 55, 61,
10
62, 64, 100
1 to 3, 5, 8 to 12, 14, 21,
24, 52, 53, 61, 62
1 1
Rated
inverter
current
Customer
Setting
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
restart
Automatic
58 Restart cushion time 0 to 60s 0.1s 1s
functions
— 59 Remote function selection 0, 1, 2, 3 1 0
— 60 Energy saving control selection 0, 9 1 0
— 65 Retry selection 0 to 5 1 0
— 66
Stall prevention operation reduction
starting frequency
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
67 Number of retries at fault occurrence 0 to 10, 101 to 110 1 0
Retry
68 Retry waiting time 0.1 to 600s 0.1s 1s
69 Retry count display erase 0 1 0
— 70 Special regenerative brake duty 0 to 30% 0.1% 0%
— 71 Applied motor
0, 1, 3, 13, 23, 40, 43,
50, 53
10
— 72 PWM frequency selection 0 to 15 1 1
— 73 Analog input selection 0, 1, 10, 11 1 1
— 74 Input filter time constant 0 to 8 1 1
— 75
Reset selection/disconnected PU
detection/PU stop selection
0 to 3, 14 to 17 1 14
— 77 Parameter write selection 0, 1, 2 1 0
— 78 Reverse rotation prevention selection 0, 1, 2 1 0
— 79 Operation mode selection 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7 1 0
80 Motor capacity 0.1 to 7.5kW, 9999 0.01kW 9999
82 Motor excitation current 0 to 500A, 9999 0.01A 9999
83 Motor rated voltage 0 to 1000V 0.1V
200V/
400V
84 Rated motor frequency 10 to 120Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
Motor constants
90 Motor constant (R1) 0 to 50Ω , 9999 0.001Ω 9999
96 Auto tuning setting/status 0, 11, 21 1 0
117 PU communication station number 0 to 31 (0 to 247) 1 0
118 PU communication speed 48, 96, 192, 384 1 192
119 PU communication stop bit length 0, 1, 10, 11 1 1
120 PU communication parity check 0, 1, 2 1 2
121 Number of PU communication retries 0 to 10, 9999 1 1
122 PU communication check time interval 0, 0.1 to 999.8s, 9999 0.1s 0
123 PU communication waiting time setting 0 to 150ms, 9999 1 9999
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
Instructions
∗6
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
124 PU communication CR/LF selection 0, 1, 2 1 1
PU connector communication
— 125
— 126
Terminal 2 frequency setting gain
frequency
Terminal 4 frequency setting gain
frequency
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
18
Page 18

Func-
Parameter
tion
127
128 PID action selection 0, 20, 21, 40 to 43 1 0
129 PID proportional band 0.1 to 1000%, 9999 0.1% 100%
130 PID integral time 0.1 to 3600s, 9999 0.1s 1s
131 PID upper limit 0 to 100%, 9999 0.1% 9999
132 PID lower limit 0 to 100%, 9999 0.1% 9999
PID operation
133 PID action set point 0 to 100%, 9999 0.01% 9999
134 PID differential time 0.01 to 10.00s, 9999 0.01s 9999
145 PU display language selection 0 to 7 1 0
PU
— 146 ∗5 Built-in potentiometer switching 0, 1 1 1
150 Output current detection level 0 to 200% 0.1% 150%
151
Current
— 156 Stall prevention operation selection 0 to 31, 100, 101 1 0
— 157 OL signal output timer 0 to 25s, 9999 0.1s 0s
— 160 Extended function display selection 0, 9999 1 9999
— 161
152 Zero current detection level 0 to 200% 0.1% 5%
detection
153 Zero current detection time 0 to 1s 0.01s 0.5s
PID control automatic switchover
frequency
Output current detection signal delay
time
Frequency setting/key lock operation
selection
Name Setting Range
0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
0 to 10s 0.1s 0s
0, 1, 10, 11 1 0
Minimum
Setting
Increments
Initial
Val ue
Customer
Setting
162
functions
165
Automatic restart
166
167
Current detection
—168
— 169
170 Watt-hour meter clear 0, 10, 9999 1 9999
Cumulative
Input terminal function
171 Operation hour meter clear 0, 9999 1 9999
monitor clear
178 STF terminal function selection
179 STR terminal function selection
180 RL terminal function selection
assignment
181 RM terminal function selection 1 1
182 RH terminal function selection 1 2
Automatic restart after instantaneous
power failure selection
Stall prevention operation level for
restart
Output current detection signal
retention time
Output current detection operation
selection
Parameter for manufacturer setting. Do not set.
0, 1, 10, 11 1 1
0 to 200% 0.1% 150%
0 to 10s, 9999 0.1s 0.1s
0, 1 1 0
0 to 5, 7, 8, 10, 12,
14, 16, 18, 24, 25,
60, 62, 65 to 67, 9999
0 to 5, 7, 8, 10, 12,
14, 16, 18, 24, 25,
61, 62, 65 to 67, 9999
0 to 5, 7, 8, 10, 12,
14, 16, 18, 24, 25,
62, 65 to 67, 9999
160
1 61
10
19
Page 19

Func-
tion
Parameter
Name Setting Range
Minimum
Setting
Increments
0, 1, 3, 4, 7, 8, 11 to 16,
25, 26, 46, 47, 64, 70,
90, 91, 93, 95, 96, 98,
99, 100, 101, 103,
190 RUN terminal function selection
104, 107, 108,
1 0
111 to 116, 125, 126,
146, 147, 164, 170,
190, 191, 193, 195,
196, 198, 199, 9999
0, 1, 3, 4, 7, 8, 11 to 16,
25, 26, 46, 47, 64, 70,
90, 91, 95, 96, 98, 99,
192 A,B,C terminal function selection
Output terminal function assignment
100, 101, 103, 104,
107, 108, 111 to 116,
125, 126, 146, 147, 164,
170, 190, 191, 195, 196,
199
198, 199, 9999
232 Multi-speed setting (speed 8) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
233 Multi-speed setting (speed 9) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
234 Multi-speed setting (speed 10) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
235 Multi-speed setting (speed 11) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
236 Multi-speed setting (speed 12) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
237 Multi-speed setting (speed 13) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
238 Multi-speed setting (speed 14) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
Multi-speed setting
239 Multi-speed setting (speed 15) 0 to 400Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 9999
— 240 Soft-PWM operation selection 0, 1 1 1
— 241 Analog input display unit switchover 0, 1 1 0
— 244 Cooling fan operation selection 0, 1 1 1
245 Rated slip 0 to 50%, 9999 0.01% 9999
Slip
246 Slip compensation time constant 0.01 to 10s 0.01s 0.5s
compensation
247
Constant-power range slip
compensation selection
0, 9999 1 9999
— 249 Earth (ground) fault detection at start 0, 1 1 0
0 to 100s,
— 250 Stop selection
1000 to 1100s,
0.1s 9999
8888, 9999
— 251 Output phase loss protection selection 0, 1 1 1
255 Life alarm status display (0 to 15) 1 0
256 Inrush current limit circuit life display (0 to 100%) 1% 100%
257 Control circuit capacitor life display (0 to 100%) 1% 100%
258 Main circuit capacitor life display (0 to 100%) 1% 100%
259 Main circuit capacitor life measuring 0, 1 (2, 3, 8, 9) 1 0
Life diagnosis
— 260 PWM frequency automatic switchover 0, 1 1 0
Initial
Val ue
Customer
Setting
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
261 Power failure stop selection 0, 1, 2 1 0
stop
Power failure
— 267 Terminal 4 input selection 0, 1, 2 1 0
— 268 Monitor decimal digits selection 0, 1, 9999 1 9999
— 269 Parameter for manufacturer setting. Do not set.
— 295 Magnitude of frequency change setting
0, 0.01, 0.10, 1.00,
10.00
0.01 0
296 Password lock level 1 to 6, 101 to 106, 9999 1 9999
1000 to 9999 (0 to 5,
9999)
1 9999
Password
297 Password lock/unlock
function
— 298 Frequency search gain 0 to 32767, 9999 1 9999
—299
Rotation direction detection selection
at restarting
0, 1, 9999 1 0
Warranty
20
FA Center
International
Page 20

Func-
Parameter
tion
RS-485 communication
constant
Second motor
Output
Remote
— 502
Minimum
Name Setting Range
Setting
Increments
338
339
340 Communication startup mode selection 0, 1, 10 1 0
342
343 Communication error count — 1 0
450 Second applied motor 0, 1, 9999 1 9999
495 Remote output selection 0, 1, 10, 11 1 0
496 Remote output data 1 0 to 4095 1 0
503 Maintenance timer 0 (1 to 9998) 1 0
Communication operation command
source
Communication speed command
source
Communication EEPROM write
selection
Stop mode selection at communication
error
0, 1 1 0
0, 1, 2 1 0
0, 1 1 0
0, 1, 2 1 0
Initial
Val ue
Customer
Setting
504
Maintenance
549 Protocol selection 0, 1 1 0
551
Communication
555 Current average time 0.1 to 1s 0.1s 1s
556 Data output mask time 0 to 20s 0.1s 0s
time monitor
Current average
— 561 PTC thermistor protection level 0.5 to 30kΩ , 9999 0.01Ω 9999
— 563 Energization time carrying-over times (0 to 65535) 1 0
— 564 Operating time carrying-over times (0 to 65535) 1 0
— 571 Holding time at a start 0 to 10s, 9999 0.1s 9999
PID
— 611 Acceleration time at a restart 0 to 3600s, 9999 0.1s 9999
— 653 Speed smoothing control 0 to 200% 0.1% 0
—665
557
575 Output interruption detection time 0 to 3600s, 9999 0.1s 1s
576 Output interruption detection level 0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 0Hz
operation
577 Output interruption cancel level 900 to 1100% 0.1% 1000%
Maintenance timer alarm output set
time
PU mode operation command source
selection
Current average value monitor signal
output reference current
Regeneration avoidance frequency
gain
0 to 9998, 9999 1 9999
2, 4, 9999 1 9999
0 to 500A 0.01A
0 to 200% 0.1% 100
Rated
inverter
current
21
functions
Protective
function
Regeneration avoidance
872 ∗7 Input phase loss protection selection 0, 1 1 0
882
883
885
886 Regeneration avoidance voltage gain 0 to 200% 0.1% 100%
Regeneration avoidance operation
selection
Regeneration avoidance operation
level
Regeneration avoidance compensation
frequency limit value
0, 1, 2 1 0
300 to 800V 0.1V
0 to 10Hz, 9999 0.01Hz 6Hz
400VDC/
780VDC
∗6
Page 21

Func-
tion
Parameter
Name Setting Range
Minimum
Setting
Increments
Initial
Val ue
Customer
Setting
888 Free parameter 1 0 to 9999 1 9999
Free
889 Free parameter 2 0 to 9999 1 9999
parameter
— 891
C0
(900)
C2
(902)
C3
(902)
125
(903)
C4
(903)
C5
(904)
C6
(904)
126
(905)
Calibration parameters
C7
(905)
C22
(922) ∗4∗5
C23
(922) ∗4∗5
C24
(923) ∗4∗5
C25
(923)
990 PU buzzer control 0, 1 1 1
PU
991 PU contrast adjustment 0 to 63 1 58
Pr.CL Parameter clear 0, 1 1 0
ALLC All parameter clear 0, 1 1 0
Cumulative power monitor digit shifted
times
FM terminal calibration — — —
∗5
Terminal 2 frequency setting bias
frequency
∗5
Terminal 2 frequency setting bias 0 to 300% 0.1% 0%
∗5
Terminal 2 frequency setting gain
frequency
∗5
Terminal 2 frequency setting gain 0 to 300% 0.1% 100%
∗5
Terminal 4 frequency setting bias
frequency
∗5
Terminal 4 frequency setting bias 0 to 300% 0.1% 20%
∗5
Terminal 4 frequency setting gain
frequency
∗5
Terminal 4 frequency setting gain 0 to 300% 0.1% 100%
∗5
Frequency setting voltage bias
frequency (built-in potentiometer)
Frequency setting voltage bias (built-in
potentiometer)
Frequency setting voltage gain
frequency (built-in potentiometer)
Frequency setting voltage gain (built-in
potentiometer)
∗4∗5
0 to 4, 9999 1 9999
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 0Hz
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 0Hz
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 0
0 to 300% 0.1% 0
0 to 400Hz 0.01Hz 60Hz
0 to 300% 0.1% 100%
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Er.CL Faults history clear 0, 1 1 0
Clear parameters
Pr.CH Initial value change list — — —
Initial value change list
∗1 Differ according to capacities.
6%: 0.75K or less
4%: 1.5K to 3.7K
3%: 5.5K, 7.5K
∗2 Differ according to capacities.
5s: 3.7K or less
10s: 5.5K, 7.5K
∗3 Differ according to capacities.
6%: 0.1K, 0.2K
4%: 0.4K to 7.5K
∗4 Set this parameter when calibrating the operation panel built-in potentiometer for the FR-E500 series operation panel (PA02) connected with
cable.
∗5 The parameter number in parentheses is the one for use with the operation panel (PA02) for the FR-E500 series or parameter unit (FR-PU04/
FR-PU07).
∗6 The initial value differs according to the voltage class. (200V class, 400V class)
∗7 Available only for the three-phase power input specification model.
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
22
Page 22

Protective Functions
When a fault occurs, the inverter trips and the PU display automatically changes to any of the following fault or alarm indications.
Function Name Description Display
Operation panel lock Appears when operation was tried during operation panel lock.
Password locked Appears when a password restricted parameter is read/written.
∗2
Parameter write error
Error message
Inverter reset Appears when the RES signal is on.
Stall prevention (overcurrent) Appears during overcurrent stall prevention.
Stall prevention (overvoltage)
Regenerative brake prealarm ∗7
Electronic thermal relay function prealarm
∗3
Warnings
PU stop
Maintenance signal output ∗7
Undervoltage Appears when the main circuit power became low voltage.
Fan fault
∗4
Alarms
Overcurrent trip during acceleration
Overcurrent trip during constant speed
Overcurrent trip during deceleration
or stop
Regenerative overvoltage trip during
acceleration
Regenerative overvoltage trip during
constant speed
Regenerative overvoltage trip during
deceleration or stop
Inverter overload trip
(electronic thermal relay function)
Motor overload trip
(electronic thermal relay function)
Fin overheat Appears when the heatsink overheated.
Input phase loss ∗7 ∗8
Stall prevention
Brake transistor alarm detection
∗5
Fault
Output side earth (ground) fault
overcurrent at start ∗7
Output phase loss Appears if one of the three phases on the inverter output side opened.
External thermal relay operation∗6 ∗7 Appears when the external thermal relay connected to the OH signal was activated.
PTC thermistor operation ∗7
Parameter storage device fault Appears when operation of the element where parameters stored became abnormal. (control board)
PU disconnection
Retry count excess ∗7 Appears when the operation was not restarted within the set number of retries.
CPU fault Appears during the CPU and peripheral circuit errors occurred.
Output current detection value
exceeded ∗7
Inrush current limit circuit fault Appears when the resistor of the inrush current limit circuit overheated.
Analog input fault
∗1 Resetting the inverter initializes the internal thermal integrated data of the electronic thermal relay function.
∗2 The error message shows an operational error. The inverter output is not shut off.
∗3 Warnings are messages given before fault occur. The inverter output is not shut off.
∗4 Alarms warn the operator of failures with output signals. The inverter output is not shut off.
∗5 When faults occur, the protective functions are activated to inverter trip and output the fault signals.
∗6 The external thermal operates only when the OH signal is set in Pr. 178 to Pr. 182 (input terminal function selection).
∗7 This protective function does not function in the initial status.
∗8 This protective function is available with the three-phase power input specification model only.
Appears when an error occurred during parameter writing.
Appears during overvoltage stall prevention. Appears while the regeneration avoidance function is activated.
Appears if the regenerative brake duty reaches or exceeds 85% of the
value. If the regenerative brake duty reaches 100%, a regenerative overvoltage (E. OV_) occurs.
Appears when the electronic thermal O/L relay has reached 85% of the specified value.
Appears when on the operation panel was pressed during external operation.
Appears when the cumulative energization time has exceeded the maintenance output timer set value.
Appears when the cooling fan remains stopped when operation is required or when the speed has
decreased.
Appears when an overcurrent occurred during acceleration.
Appears when an overcurrent occurred during constant speed operation.
Appears when an overcurrent occurred during deceleration and at a stop.
Appears when an overvoltage occurred during acceleration.
Appears when an overvoltage occurred during constant speed operation.
Appears when an overvoltage occurred during deceleration and at a stop.
Appears when the electronic thermal relay function for inverter element protection was activated.
Appears when the electronic thermal relay function for motor protection was activated.
∗1
Appears if one of the three phases on the inverter input side opened. It may function if phase-to-
phase voltage of the three-phase power input becomes largely unbalanced.
Appears when the output frequency drops to 1Hz as a result of deceleration due to the excess motor load.
This function stops the inverter output if an alarm occurs in the brake circuit, e.g. damaged brake
transistors. In this case, the inverter must be powered off immediately.
Appears when an earth (ground) fault occurred on the inverter's output side. (detects only at a start)
Appears when resistance of PTC thermistor connected between terminal 2 and terminal 10 is more
than the value set in Pr. 561 PTC thermistor protection level.
Appears when a communication error between the PU and inverter occurred, the communication
interval exceeded the permissible time during the RS-485 communication with the PU connector, or
communication errors exceeded the number of retries during the RS-485 communication.
Appears when output current exceeded the output current detection level set by the parameter.
Appears when voltage is input (7.3V or more for 5s or more) with the terminal 4 set to current input.
Pr. 70 Special regenerative brake duty
to
23
Page 23

Option and Peripheral Devices
Option list
By fitting the following options to the inverter, the inverter is provided with more functions.
Name Type Applications, Specifications, etc.
Parameter unit (8 languages)
Parameter unit with battery pack FR-PU07BB(-L)
Enclosure surface operation panel FR-PA07
Parameter unit connection cable FR-CB20
AC reactor FR-HAL
DC reactor FR-HEL
Radio noise filter FR-BIF(H) For radio noise reduction (connect to the input side)
Line noise filter
Brake resistor MRS type For increasing the regenerative braking capability (permissible duty 3%ED)
High-duty brake resistor FR-ABR
Brake unit
Resistor unit
Discharging resistor
Stand-alone shared
Power regeneration common
converter
Stand-alone reactor dedicated for
the FR-CV
High power factor converter FR-HC
Surge voltage suppression filter
DIN rail attachment FR-UDA01 to 03 Attachment for installation on DIN rail
Manual controller FR-AX
DC tach. follower FR-AL For synchronous operation (1.5VA) by external signal (0 to 5V, 0 to 10V DC)∗
Three speed selector FR-AT
Motorized speed setter FR-FK
Ratio setter FR-FH For ratio operation. The ratios of five inverters can be set (3VA)∗
Speed detector FR-FP For tracking operation by a pilot generator (PG) signal (3VA)∗
Master controller FR-FG
speed controller
Soft starter FR-FC
FR series manual controller/
Deviation detector FR-FD
Preamplifier FR-FA Used as an A/V converter or arithmetic amplifier (3VA)∗
Pilot generator QVAH-10 For tracking operation. 70V/35VAC 500Hz (at 2500r/min)
Deviation sensor YVGC-500W-NS
Frequency setting potentiometer WA2W 1kΩ For frequency setting. Wire-wound 2W 1kΩ type B characteristic
Analog frequency meter
×
60mm)
(64mm
Others
Calibration resistor RV24YN 10kΩ For frequency meter calibration. Carbon film type B characteristic
FR Configurator SW3(VFD setup
software)
∗ Rated power consumption. The power supply specifications of the FR series manual controllers and speed controllers are 200VAC 50Hz, 220V/220VAC 60Hz,
and 115VAC 60Hz.
FR-PU07
FR-PU04
FR- BSF01
FR- BLF
FR-BU2
FR-BR
GZG, GRZG type
FR-CV
FR-CVL
FR-ASF
FR-BMF
YM206NRI 1mA
FR-SW3-SETUPWE
Interactive parameter unit with LCD display
This parameter unit enables parameter setting without connecting the inverter
to power supply.
This operation panel enables inverter operation and monitoring of frequency,
etc. from the enclosure surface
Cable for connection of operation panel or parameter unit
indicates a cable length. (1m, 3m, 5m)
For harmonic current reduction and inverter input power factor improvement
(total power factor approx. 88%)
For harmonic current reduction and inverter input power factor improvement
(total power factor approx. 93%)
For line noise reduction
For increasing the regenerative braking capability (permissible duty 10%/
6%ED)
For increasing the braking capability of the inverter (for high-inertia load or
negative load)
Brake unit, electrical-discharge resistor and resistor unit are used in
combination
Unit which can return motor-generated braking energy back to the power
supply in common converter system
The high power factor converter switches the converter section on/off to
reshape an input current waveform into a sine wave, greatly suppressing
harmonics. (Used in combination with the standard accessory.)
Filter for suppressing surge voltage on motor
For independent operation. With frequency meter, frequency potentiometer and
start switch.
For three speed switching, among high, middle and low speed operation
(1.5VA)∗
For remote operation. Allows operation to be controlled from several places
(5VA)∗
Master controller (5VA) for parallel operation of multiple (maximum 35)
inverters.∗
For soft start and stop. Enables acceleration/deceleration in parallel operation
(3VA)∗
For continuous speed control operation. Used in combination with a deviation
sensor or synchro (5VA)∗
For continuous speed control operation (mechanical deviation detection)
Output 90VAC/90ºC
Dedicated frequency meter (graduated to 120Hz). Moving-coil type DC
ammeter
Supports an inverter startup to maintenance.
Applicable
Inverter
Shared among
all models
Shared among
all models
(Available soon)
Shared among
all models
According to
capacities
Shared among
all models
For the 0.4K or
more
According to
capacities
400V: According
to capacities
400V: For the
5.5K or more
Compatible with
the 3.7K or less
Shared among
all models
Shared among
all models
(Available soon)
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
24
Page 24

Peripheral devices/cable size list
Moulded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)∗1
or Earth Leakage Current Breaker (ELB)∗2
Reactor connection Reactor connection
Inverter type
Motor
Output
(kW)
Without With Without With
FR-D740-0.4K 0.4 30AF 5A 30AF 5A S-N10 S-N10 2 2
FR-D740-0.75K 0.75 30AF 5A 30AF 5A S-N10 S-N10 2 2
FR-D740-1.5K 1.5 30AF 10A 30AF 10A S-N10 S-N10 2 2
FR-D740-2.2K 2.2 30AF 15A 30AF 10A S-N10 S-N10 2 2
FR-D740-3.7K 3.7 30AF 20A 30AF 15A S-N10 S-N10 2 2
FR-D740-5.5K 5.5 30AF 30A 30AF 20A S-N20 S-N11, S-N12 3.5 2
Three-phase 400V
FR-D740-7.5K 7.5 30AF 30A 30AF 30A S-N20 S-N20 3.5 3.5
FR-D720S-0.1K 0.1 30AF 5A 30AF 5A S-N10 S-N10 2 2
FR-D720S-0.2K 0.2 30AF 5A 30AF 5A S-N10 S-N10 2 2
FR-D720S-0.4K 0.4 30AF 10A 30AF 5A S-N10 S-N10 2 2
FR-D720S-0.75K 0.75 30AF 15A 30AF 10A S-N10 S-N10 2 2
FR-D720S-1.5K 1.5 30AF 30A 30AF 15A S-N10 S-N10 2 2
Single-phase 200V
FR-D720S-2.2K 2.2 30AF 40A 30AF 30A S-N20, S-N21 S-N10 3.5 2
∗1 Select an MCCB according to the inverter power supply capacity.
Install one MCCB per inverter.
∗2 For installations in the United States or Canada, use the class T type fuse certified by the UL and cUL.
∗3 Magnetic contactor is selected based on the AC-1 class. The electrical durability of magnetic contactor is 500,000 times. When the magnetic contactor is
used for emergency stop during motor driving, the electrical durability is 25 times.
When using the MC for emergency stop during motor driving or using on the motor side during commercial-power supply operation, select the MC with
class AC-3 rated current for the motor rated current.
∗4 When using single-phase power input, terminals are R/L1 and S/L2.
Magnetic
Contactor (MC)∗3
HIV Cables, etc.
(mm2)
R/L1,
S/L2,
T/L3∗4
MCCB INV
MCCB INV
U, V, W
IM
IM
Note
y When the inverter capacity is larger than the motor capacity, select an MCCB and a magnetic contactor according to
the inverter type and cable and reactor according to the motor output.
y When the breaker on the inverter primary side trips, check for the wiring fault (short circuit), damage to internal parts
of the inverter, etc. Identify the cause of the trip, then remove the cause and power on the breaker.
25
Page 25

Selecting the rated sensitivity current for the earth leakage current breaker
-
W
When using the earth leakage current breaker with the
inverter circuit, select its rated sensitivity current as follows,
independently of the PWM carrier frequency.
y Breaker designed for harmonic and surge suppression
Rated sensitivity current I∆n≥10×(Ig1+Ign+Igi+Ig2+Igm)
y Standard breaker
Rated sensitivity current I∆n≥10×{Ig1+Ign+Igi+3X(Ig2+Igm)}
Ig1, Ig2: Leakage currents in wire path during commercial power supply
operation
Ign : Leakage current of inverter input side noise filter
Igm : Leakage current of motor during commercial power supply operation
Igi : Leakage current of inverter unit
Example of leakage current of
cable path per 1km during the
commercial power supply operation
when the CV cable is routed in
metal conduit
(200V 60Hz)
120
100
80
60
40
20
Leakage currents (mA)
0
2 3.5
8142230386080
5.5
Cable size (mm2)
Example of leakage current per 1km during
the commercial power supply operation
when the CV cable is routed in metal conduit
(Three-phase three-wire delta
connection 400V60Hz)
120
100
80
60
40
20
leakage currents (mA)
0
2 3.5
8142230386080
5.5
Cable
For " " connection, the amount of leakage current is appox.1/3 of the above value.
size (mm2)
100
100
150
150
Example of leakage current
of three-phase induction motor
during the commercial
power supply operation
(200V 60Hz)
1.0
0.7
0.5
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.07
0.05
0.03
Leakage currents (mA)
0.02
0.1 0.2
0.75
2.2
0.4
Motor capacity (kW)
Example of leakage current of three
phase induction motor during the
commercial power supply operation
(Totally-enclosed fan-cooled
type motor 400V60Hz)
2. 0
1. 0
0. 7
0. 5
0. 3
0. 2
leakage currents (mA)
0. 1
1.5 3.7
Motor capacity (kW)
5.5 11
1.5
3.7
7.5
7.5 15
2.2
11 2 05.5
20
15
Example
2 ×
5.5mm
5m 5.5mm
ELB
Noise
filter
Inverter
Ig1 Ign
Igi
(Note) 1 Install the earth leakage breaker (ELB) on the input side of the inverter.
2 In the connection earthed-neutral system, the sensitivity current is blunt
against an earth (ground) fault in the inverter output side. Earthing (Grounding)
must conform to the requirements of national and local safety regulations and
electrical codes. (NEC section 250, IEC 536 class 1 and other applicable
standards)
2 ×
60m
IM
Ig2 Igm
3φ
400V
2.2k
zSelection example
(in the case of the above figure (400V class
Breaker Designed for
Leakage current
Ig1 (mA)
Leakage current
Ign (mA)
Leakage current Igi
(mA)
Leakage current
Ig2 (mA)
Motor leakage
current Igm (mA)
Total leakage
current (mA)
Rated sensitivity
current (mA) (≥ Ig ×
10)
Harmonic and Surge
Suppression
1
×
66 ×
3
0 (without noise filter)
1
×
66 ×
3
2.79 6.15
30 100
Standard Breaker
5m
1000m
1
60m
1000m
0.36
connection))
= 0.11
= 1.32
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
26
Page 26

Precautions for Operation/Selection
Precautions for use of the inverter
Safety Precautions
z To operate the inverter correctly and safely, be sure to read the
"instruction manual" before starting operation.
z This product has not been designed or manufactured for use
with any equipment or system operated under life-threatening
conditions.
z Please contact our sales office when you are considering using
this product in special applications such as passenger mobile,
medical, aerospace, nuclear, power or undersea relay
equipment or system.
z Although this product is manufactured under strict quality
control, safety devices should be installed when a serious
accident or loss is expected by a failure of this product.
z The load used should be a three-phase induction motor only.
Operation
z A magnetic contactor (MC) provided on the input side should
not be used to make frequent starts and stops. It could cause
the inverter to fail.
z However, at this time, the motor cannot be brought to a sudden
stop. Hence, provide a mechanical stopping/holding mechanism
for the machine/equipment which requires an emergency stop.
z It will take time for the capacitor to discharge after shutoff of the
inverter power supply. When accessing the inverter for
inspection, wait for at least 10 minutes after the power supply
has been switched off, and check to make sure that there are no
residual voltage using a tester or the like.
Installation
z Avoid hostile environment where oil mist, fluff, dust particles,
etc. are suspended in the air, and install the inverter in a clean
place or put it in an ingress-protected "enclosed" enclosure.
When placing the inverter in an enclosure, determine the
cooling system and panel dimensions so that the surrounding
air temperature of the inverter is within the permissble value.
(refer to page 6 for the specified value)
z Do not install the inverter on wood or other combustible material
as it will be hot partly.
z Install the inverter in the vertical orientation.
Setting
z The inverter can be operated as fast as a maximum of 400Hz by
parameter setting. Therefore, incorrect setting can cause a
danger. Set the upper limit using the maximum frequency limit
setting function.
z A setting higher than the initial value of DC injection brake
operation voltage or operation time can cause motor overheat
(electronic thermal relay error).
z Do not set Pr. 70 Special regenerative brake duty except for using
the optional brake resistor. This function is used to protect the
brake resistor from overheating. Do not set the value exceeding
permissible duty of the brake resistor.
Wiring
z Application of power to the output terminals (U, V, W) of the
inverter will damage the inverter. Therefore, fully check the
wiring and sequence to ensure that wiring is correct, etc. before
powering on.
z The terminals P/+, PR, P1, N/- are provided for connection of a
dedicated option. Connect only a dedicated option. Do not short
the frequency setting power supply terminal 10 and common
terminal 5 or the terminal PC and terminal SD.
Power supply
z When the inverter is connected
under a large-capacity power
transformer (500kVA or more
transformer) or when a power
capacitor is to be switched over,
an excessive peak current may
flow in the power input circuit,
damaging the inverter.
To prevent this, always install an optional AC reactor (FR-HAL).
z If a surge voltage occurs in the power supply system, this surge
energy may flow into the inverter, causing the inverter to display
overvoltage protection (E.OV) and come to an inverter trip. To
prevent this, always install an optional AC reactor (FR-HAL).
Power
supply
system
capacity
(kVA)
1500
1000
500
0
Range
requiring
installation
of the reactor
Wiring length (m)
10
27
Page 27

Precautions for selection
Inverter capacity selection
z When operating a special motor or more than one motor in
parallel with a single inverter, select the inverter capacity so that
1.1 times the total rated motor current is less than the rated
output current of the inverter.
Starting torque of the motor
z The start and acceleration characteristics of the motor driven by
the inverter are restricted by the overload current rating of that
inverter. Generally the torque characteristic is less than when
the motor is started by a commercial power supply. If torque
boost adjustment or general-purpose magnetic flux vector
control cannot provide enough torque when a large starting
torque is necessary, select the inverter of one rank higher
capacity or increase the capacities of both the motor and
inverter.
Acceleration/deceleration times
z The acceleration/deceleration time of the motor depends on the
motor-generated torque, load torque and moment of inertia of
the load (J).
z When the stall prevention function is activated during
acceleration/deceleration, increase the acceleration/
deceleration time as the actual time may become longer.
z To decrease the acceleration/deceleration time, increase the
torque boost value (setting of a too large value may activate the
stall prevention function at a start, longer the acceleration time),
use the general-purpose magnetic flux vector control or
increase the inverter and motor capacities. To decrease the
deceleration time, it is necessary to add optional brake resistor
FR-ABR (for the 0.4K or more), the brake unit (FR-BU2), power
regeneration common converter (FR-CV), or a similar device to
absorb braking energy.
Power transfer mechanism
(reduction gear, belt, chain, etc.)
z When an oil-lubricated gear box, speed change/reduction gear
or similar device is used in the power transfer system, note that
continuous operation at low speed only may deteriorate oil
lubrication, causing seizure. When performing fast operation at
higher than 60Hz, fully note that such operation will cause
strength shortage due to the noise, life or centrifugal force of the
power transfer mechanism.
Instructions for overload operation
z When performing operation of frequent start/stop of the inverter,
rise/fall in the temperature of the transistor element of the
inverter will repeat due to a repeated flow of large current,
shortening the life from thermal fatigue. Since thermal fatigue is
related to the amount of current, the life can be increased by
reducing current at locked condition, starting current, etc.
Decreasing current may increase the life. However, decreasing
current will result in insufficient torque and the inverter may not
start. Therefore, choose the inverter which has enough
allowance for current.
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
28
Page 28

Precautions for Peripheral Device Selection
Installation and selection of moulded case circuit breaker
Install a moulded case circuit breaker (MCCB) on the power
receiving side to protect the wiring of the inverter input side. For
MCCB selection, refer to page 25 since it depends on the inverter
power supply side power factor (which changes depending on the
power supply voltage, output frequency and load). Especially for a
completely electromagnetic MCCB, one of a slightly large capacity
must be selected since its operation characteristic varies with
harmonic currents. (Check it in the data of the corresponding
breaker.) As an earth leakage current breaker, use the Mitsubishi
earth leakage current breaker designed for harmonics and surge
suppression. (Refer to page 26)
When installing a moulded case circuit breaker on the output side
of the inverter, contact each manufacturer for selection of the
moulded case circuit breaker.
Handling of the inverter input side magnetic contactor
z For operation via external terminal (terminal STF or STR used),
provide an input side MC to prevent an accident caused by a
natural restart at power recovery after a power failure, such as
an instantaneous power failure, and to ensure safety for
maintenance work. Do not use this magnetic contactor to make
frequent starts and stops. (The switching life of the inverter input
circuit is about 1,000,000 times.) For parameter unit operation,
an automatic restart after power failure is not made and the MC
cannot be used to make a start. Note that the primary side MC
may be used to make a stop but the regenerative brake specific
to the inverter does not operate and the motor is coasted to a
stop.
z Installation of a magnetic contactor on the primary side is
recommended. Since when cycle operation or heavy-duty
operation is performed with an optional brake resistor
connected, overheat and burnout of the electrical-discharge
resistor can be prevented if a regenerative brake transistor is
damaged due to insufficient heat capacity of the electricaldischarge resistor and excess regenerative brake duty. In this
case, shut-off the magnetic contactor when fault occurs and
inverter trips.
Handling of the inverter output side magnetic contactor
Switch the magnetic contactor between the inverter and motor
only when both the inverter and motor are at a stop. When the
magnetic contactor is turned on while the inverter is operating,
overcurrent protection of the inverter and such will activate. When
an MC is provided for switching to the commercial power supply,
for example, switch it on/off after the inverter and motor have
stopped.
Thermal relay installation
The inverter has an electronic thermal relay function to protect the
motor from overheating. However, when running multiple motors
with one inverter or operating a multi-pole motor, provide a thermal
relay (OCR) between the inverter and motor. In this case, set the
electronic thermal relay function of the inverter to 0A. And for the
setting of the thermal relay, add the line-to line leakage current
(refer to page 30) to the current value on the motor rating plate.
For low-speed operation where the cooling capability of the motor
reduces, it is recommended to use a thermal relay protector
incorporated motor.
Measuring instrument on the output side
When the inverter-to-motor wiring length is large, especially in the
400V class, small-capacity models, the meters and CTs may
generate heat due to line-to-line leakage current. Therefore,
choose the equipment which has enough allowance for the current
rating.
Disuse of power factor improving capacitor (power capacitor)
The power factor improving capacitor and surge suppressor on the
inverter output side may be overheated or damaged by the
harmonic components of the inverter output. Also, since an
excessive current flows in the inverter to activate overcurrent
protection, do not install a capacitor or surge suppressor. For
power factor improvement, use a DC reactor.
Wire thickness and wiring distance
When the wiring length between the inverter and motor is long,
use thick wires so that the voltage drop of the main circuit cable is
2% or less especially at low frequency output. (A selection
example for the wiring distance of 20m is shown on page 25)
Especially at a long wiring distance, the maximum wiring length
should be within the length in the table below since the overcurrent
protection function may be misactivated by the influence of a
charging current due to the stray capacitances of the wiring.
(The overall wiring length for connection of multiple motors should
be within the value in the table below.)
Pr. 72 Setting
(carrier frequency)
1 or less
2 to 15
0.1K 0.2K 0.4K 0.75K 1.5K 2.2K
200V 200m 200m 300m 500m 500m 500m —
400V — — 200m 200m 300m 500m 500m
200V 30m 100m 200m 300m 500m 500m —
400V — — 30m 100m 200m 300m 500m
When using the automatic restart after instantaneous power failure
function with wiring length exceeding below, select "without
frequency search" (Pr.162 = "1, 11").
Motor Capacity
Wiring Length 20m 50m 100m
0.1K 0.2K 0.4K or more
Use the recommended connection cable when connecting the
parameter unit.
For remote operation via analog signal, wire the control cable
between the operation box or operation signal and inverter within
30m and away from the power circuits (main circuit and relay
sequence circuit) to prevent induction from other devices.
When using the external potentiometer instead of the parameter
unit to set the frequency, use a shielded or twisted cable, and do
not earth (ground) the shield, but connect it to terminal 5 as shown
below.
(3)
(2)
(1)
Frequency setting
potentiometer
Twisted
cable
10
2
5
Shielded cable
(3)
(2)
(1)
Frequency setting
potentiometer
3.7K or
more
10
2
5
29
Page 29

Earth (Ground)
When the inverter is run in the low acoustic noise mode, more
leakage currents occur than in the non-low acoustic noise mode
due to high-speed switching operation. Be sure to earth (ground)
the inverter and motor before use. In addition, always use the
earth (ground) terminal of the inverter to earth (ground) the
inverter. (Do not use the case and chassis)
Noise
When performing low-noise operation at higher carrier frequency,
electromagnetic noise tends to increase. Therefore, refer to the
following measure example and consider taking the measures.
Depending on the installation condition, the inverter may be
affected by noise in a non-low noise (initial) status.
z The noise level can be reduced by decreasing the carrier
frequency (Pr. 72).
z As measures against AM radio broadcasting noise, radio noise
filter FR-BIF produces an effect.
z As measures against sensor malfunction, line noise filter FR-
BSF01, FR-BLF produces an effect.
z As measures against induction noise from the power cable of
the inverter, an effect is produced by putting a distance of 30cm
(at least 10cm) or more and using a twisted pair shielded cable
as a signal cable. Do not earth (ground) shield but connect it to
signal common cable.
Noise reduction examples
Install common mode filter
on inverter input side.
Install capacitor type FR-BIF filter
on inverter input side.
FR- BLF
FR- BSF01
Inverter
power
supply
Separate inverter and power
line by more than 30cm (at
least 10cm) from sensor circuit.
Control
power
supply
Do not earth (ground)
enclosure directly.
Do not earth (ground) control cable.
Enclosure
FRBSF01
for sensor
Decrease
carrier frequency
FR-
Inverter
BSF01
FRBIF
Power
supply
Do not earth (ground) shield but
connect it to signal common cable.
Install common mode filter
on inverter output side.
IM
Use 4-core cable for motor
power cable and use one
cable as earth (ground) cable.
Use a twisted pair shielded cable
Sensor
Motor
FR- BLF
FR- BSF01
Leakage currents
Capacitances exist between the inverter I/O cables, other cables
and earth and in the motor, through which a leakage current flows.
Since its value depends on the static capacitances, carrier
frequency, etc., low acoustic noise operation at the increased
carrier frequency of the inverter will increase the leakage current.
Therefore, take the following measures. Select the earth leakage
current breaker according to its rated sensitivity current,
independently of the carrier frequency setting. (Refer to page 26)
To-earth (ground) leakage currents
Type Influence and Measures
y Leakage currents may flow not only into the inverter's
own line but also into the other line through the earth
(ground) cable, etc. These leakage currents may
operate earth (ground) leakage circuit breakers and
earth leakage relays unnecessarily.
z Countermeasures
Influence and
measures
Undesirable
current path
Line leakage current
Type Influence and Measures
Influence and
measures
y If the carrier frequency setting is high, decrease the Pr.
72 PWM frequency selection setting.
Note that motor noise increases. Select Pr. 240 Soft-
PWM operation selection to make the sound inoffensive.
y By using earth leakage circuit breakers designed for
harmonic and surge suppression in the inverter's own
line and other line, operation can be performed with the
carrier frequency kept high (with low noise).
Power
supply
NV1
Leakage
breaker
NV2
Leakage
breaker
Inverter
Motor
C
C
Motor
C
• This leakage current flows via a static capacitance
between the inverter output cables.
• The external thermal relay may be operated
unnecessarily by the harmonics of the leakage current.
When the wiring length is long (50m or more) for the
400V class model, the external thermal relay is likely to
operate unnecessarily because the ratio of the leakage
current to the rated motor current increases.
z Countermeasures
• Use Pr.9 Electronic thermal O/L relay.
• If the carrier frequency setting is high, decrease the Pr.
72 PWM frequency selection setting.
Note that motor noise increases. S elect Pr. 240 Soft-PWM
operation selection to make the sound inoffensive.
To ensure that the motor is protected against line-to-
line leakage currents, it is recommended to use a
temperature sensor to directly detect motor
temperature.
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
Undesirable
current path
Power
supply
MCCB MC
Inverter
Line-to-line leakage currents path
Thermal relay
Line-to-line static
capacitances
Motor
IM
30
Page 30

zHarmonic suppression guideline
Harmonic currents flow from the inverter to a power receiving point
via a power transformer. The harmonic suppression guideline was
established to protect other consumers from these outgoing
harmonic currents.
The three-phase 200V input specifications 3.7kW or less are
previously covered by "Harmonic suppression guideline for
household appliances and general-purpose products" and other
models are covered by "Harmonic suppression guideline for
consumers who receive high voltage or special high voltage".
However, the transistorized inverter has been excluded from the
target products covered by "Harmonic suppression guideline for
household appliances and general-purpose products" in January
2004 and "Harmonic suppression guideline for household
appliances and general-purpose products" was repealed on
September 6, 2004.
All capacity and all models of general-purpose inverter used by
specific consumers are covered by "Harmonic suppression
guideline for consumers who receive high voltage or special high
voltage".
y "Harmonic suppression guideline for consumers who receive high
voltage or special high voltage"
This guideline sets forth the maximum values of harmonic currents
outgoing from a high-voltage or especially high-voltage consumer
who will install, add or renew harmonic generating equipment. If any
of the maximum values is exceeded, this guideline requires that
consumer to take certain suppression measures.
Users who use models other than the target models are not covered
by the guideline. However, we ask to connect an AC reactor or a DC
reactor as before to the users who are not covered by the guideline.
For compliance to the harmonic suppression guideline for
consumers who receive high voltage or special high voltage
zCalculation of outgoing harmonic current
Outgoing harmonic current = fundamental wave current (value converted
from received power voltage) × operation ratio × harmonic content
yOperation ratio: Operation ratio = actual load factor operation
time ratio during 30 minutes
yHarmonic content: Found in Table.
Table 1: Harmonic Contents (Values at the fundamental current of 100%)
Reactor 5th 7th 11th 13th 17th 19th 23rd 25th
Not used 65 41 8.5 7.7 4.3 3.1 2.6 1.8
Used (AC side) 38 14.5 7.4 3.4 3.2 1.9 1.7 1.3
Used (DC side) 30 13 8.4 5.0 4.7 3.2 3.0 2.2
Used (AC, DC sides)
Table 2: Rated Capacities and Outgoing Harmonic Currents for Inverter Drive
Rated
Current [A]
Applied
400V 5th 7th 11 th 13th 17th 19th 23rd 25th
Motor kW
0.81 49 0.57 31.85 20.09 4.165 3.773 2.107 1.519 1.274 0.882
0.4
1.37 83 0.97 53.95 34.03 7.055 6.391 3.569 2.573 2.158 1.494
0.75
2.75 167 1.95 108.6 68.47 14.20 12.86 7.181 5.177 4.342 3.006
1.5
3.96 240 2.81 156.0 98.40 20.40 18.48 10.32 7.440 6.240 4.320
2.2
6.50 394 4.61 257.1 161.5 33.49 30.34 16.94 12.21 10.24 7.092
3.7
9.55 579 6.77 376.1 237.4 49.22 44.58 24.90 17.95 15.05 10.42
5.5
12.8 776 9.07 504.4 318.2 65.96 59.75 33.37 24.06 20.18 13.97
7.5
28 9.1 7.2 4.1 3.2 2.4 1.6 1.4
Outgoing Harmonic Current Converted from
(No reactor, 100% operation ratio)
Rated Capacity (kVA)
Fundamental Wave Current
Converted from 6.6kV (mA)
6.6kV (mA)
Input
Power
Supply
Three-phase
400V
Tar get
Capacity
All
capacities
Countermeasures
Make a judgment based on "Harmonic
suppression guideline for consumers who
receive high voltage or special high voltage"
issued by the Japanese Ministry of Economy,
Trade and Industry (formerly Ministry of
International Trade and Industry) in
September 1994 and take measures if
necessary. For calculation method of power
supply harmonics, refer to materials below.
Reference materials
y "Harmonic suppression measures of the
inverter"
Jan. 2004 Japan Electrical Manufacturer's
Association
y "Calculation method of harmonic current of
the general-purpose inverter used by
specific consumers"
JEM-TR201 (revised in Dec. 2003): Japan
Electrical Manufacturer's Association
Japan Electrical Manufacturer's Association
31
Page 31

FR-D700 Series Specification Difference List
Item
Applicable Capacity
Typ e
Main Circuit Terminal
Name
AC Power Input
Three-phase Input
Single-phase Input
Brake Unit
Connection
Control Terminal Logic
Initial Setting
Control Terminal
Contact Input Common
Ter mina l
Initial Setting
Monitor Output
Terminal For Indicator
Parameter
Pr.3, Pr.4, Pr.20,
Pr.55, Pr.66, Pr.84,
Pr.125, Pr.126, Pr.903,
Pr.905, Pr.923
Initial Value
Pr.19 Initial Value
Pr.145 Initial Value
Pr.160 Initial Value
Pr.249 Initial Value
Indicator Output
Terminal Function
Traverse Function
Pr.592 to Pr.597
Japanese Specification
FR-D740-0.4K to 7.5K
FR-D720S-0.1K to 2.2K
Type : Rated capacity (kW)
NA Specification EC Specification CHT Specification
FR-D740-012 to 160-NA
FR-D720S-008 to 100-NA
Type : Rated current value
FR-D740-012 to 160-EC
FR-D720S-008 to 100-EC
Type : Rated current value
FR-D740-0.4K to 7.5K-CHT
FR-D720S-0.1K to 2.2K-CHT
Type : Rated capacity (kW)
R, S, T L1, L2, L3
R, S L1, N
P, N +, -
Sink logic Sink logic Source logic Sink logic
SD SD PC SD
FM (Digital output) AM (Analog output) AM (Analog output) AM (Analog output)
60Hz 60Hz 50Hz 50Hz
9999 9999 8888 9999
0111
9999 0 9999 9999
0011
Pr.54 FM terminal function
selection,
Pr.900 FM terminal
calibration
Pr.158 AM terminal function
selection,
Pr.901 AM terminal
calibration
Pr.158 AM terminal function
selection,
Pr.901 AM terminal
calibration
Pr.158 AM terminal function
selection,
Pr.901 AM terminal
calibration
Without Without With With
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
32
Page 32

Warranty
1. Gratis warranty period and coverage
[Gratis warranty period]
Note that an installation period of less than one year after installation in your company or your customer's premises or a
period of less than18 months (counted from the date of production) after shipment from our company, whichever is shorter,
is selected.
[Coverage]
(1) Diagnosis of failure
As a general rule, diagnosis of failure is done on site by the customer.
However, Mitsubishi or Mitsubishi service network can perform this service for an agreed upon fee upon the customer's
request.
There will be no charges if the cause of the breakdown is found to be the fault of Mitsubishi.
(2) Breakdown repairs
There will be a charge for breakdown repairs, exchange replacements and on site visits for the following four conditions,
otherwise there will be a charge.
1)Breakdowns due to improper storage, handling, careless accident, software or hardware design by the customer.
2)Breakdowns due to modifications of the product without the consent of the manufacturer.
3)Breakdowns resulting from using the product outside the specified specifications of the product.
4)Breakdowns that are outside the terms of warranty.
Since the above services are limited to Japan, diagnosis of failures, etc. are not performed abroad.
If you desire the after service abroad, please register with Mitsubishi. For details, consult us in advance.
2. Exclusion of opportunity loss from warranty liability
Regardless of the gratis warranty term, compensation to opportunity losses incurred to your company or your customers by
failures of Mitsubishi products and compensation for damages to products other than Mitsubishi products and other
services are not covered under warranty.
3. Repair period after production is discontinued
Mitsubishi shall accept product repairs for seven years after production of the product is discontinued.
4. Terms of delivery
In regard to the standard product, Mitsubishi shall deliver the standard product without application settings or adjustments
to the customer and Mitsubishi is not liable for on site adjustment or test run of the product.
33
Page 33

International FA Center
r
UK FA Center
European FA Center
Central and Eastern Europe
FA Center
Beijing FA Center
Tianjin FA Center
Shanghai FA Center
Guangzhou FA Center
Hong Kong FA Center
ASEAN FA Center
Korean
FA Center
Taiwan FA Center
Thailand FA Center
North American FA Cente
FeaturesOptions
Standard
Specifications
Outline
Drawings
Dimension
Diagram
Explanation
Terminal Connection
Terminal Specification
Parameter unit
Operation panel
List
Parameter
zNorth American FA Center
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC AUTOMATION, INC.
500 Corporate Woods Parkway, Vernon Hills, IL60061 U.S.A
TEL. +1-847-478-2100 FAX. +1-847-478-0327
zTaiwan FA Center
SETSUYO ENTERPRISE CO., LTD.
6F No.105, Wu Kung 3rd RD, Wu-Ku Hsiang Taipei Hsien,
248, Taiwan
TEL. +886-2-2299-2499 FAX. +886-2-2299-2509
zKorean FA Center
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC AUTOMATION KOREA CO., LTD.
B1F,2F, 1480-6, Gayang-Dong, Gangseo-Gu, Seoul, 157-200,
Korea
TEL. +82-2-3660-9607 FAX. +82-2-3664-0475
zBeijing FA Center
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC AUTOMATION (SHANGHAI) LTD.
BEIJING OFFICE
9F Office Tower 1, Henderson Center, 18 Jianguomennei
Avenue, Dongcheng District, Beijing, China 100005
TEL. +86-10-6518-8830 FAX. +86-10-6518-8030
zTianjin FA Center
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC AUTOMATION (SHANGHAI) LTD.
TIANJIN OFFICE
B-2 801/802, Youyi Building, No.50 Youyi Road, Hexi District,
Tianjin, China 300061
TEL +86-22-2813-1015 FAX. +86-22-2813-1017
zShanghai FA Center
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC AUTOMATION (SHANGHAI) LTD.
4/F Zhi Fu Plazz, No.80 Xin Chang Road, Shanghai, China
200003
TEL. +86-21-6121-2460 FAX. +86-21-6121-2424
zASEAN FA Center
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC ASIA PTE, LTD.
307 Alexandra Road #05-01/02, Mitsubishi Electric Building,
Singapore 159943
TEL. +65-6470-2480 FAX. +65-6476-7439
zHong Kong FA Center
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC AUTOMATION (Hong Kong) LTD.
10th Floor, Manulife Tower, 169 Electric Road, North Point, Hong Kong
TEL.+852-2887-8870 FAX. +852-2887-7984
zEuropean FA Center
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC EUROPE B. V. GERMAN BRANCH
Gothaer Strasse 8, D-40880 Ratingen, Germany
TEL. +49-2102-486-0 FAX. +49-2102-486-1120
zUK FA Center
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC EUROPE B. V. UK BRANCH
Travellers Lane, Hatfield, Hertfordshire, AL10 8XB, UK.
TEL. +44-1707-276100 FAX. +44-1707-278695
zThailand FA Center
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC AUTOMATION (THAILAND) CO., LTD.
Bang-Chan Industrial Estate No.111, Soi Serithai 54,
T.Kannayao, A.Kannayao, Bangkok 10230
TEL. +66-2-906-3238 FAX. +66-2-906-3239
zGuangzhou FA Center
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC AUTOMATION (SHANGHAI) LTD.
GUANGZHOU OFFICE
Rm.1609, North Tower, The Hub Center, No.1068, Xing Gang
East Road, Haizhu District, Guangzhou, China 510335
TEL. +86-20-8923-6713 FAX. +86-20-8923-6715
zCentral and Eastern Europe FA Center
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC EUROPE B.V. CZECH BRANCH
Avenir Business Park, Radlicka 714/113a,158 00 Praha 5, Czech
Republic
TEL. +420-251-551-470 FAX. +420-251-551-471
Functions
Protective
Instructions
Specification
Difference List
FR-D700 Series
Warranty
FA Center
International
34
 Loading...
Loading...