Mitsubishi Electric FR-CC2-H355K, FR-CC2-H400K, FR-CC2-H450K, FR-CC2-H630K, FR-CC2-H500K Instruction Manual
...
INVERTER
F800
FR-F802 (SEPARATED CONVERTER TYPE) INSTRUCTION MANUAL (HARDWARE)
Inverter for fans and pumps
FR-F842-07700(355K) to 12120(560K)
INTRODUCTION
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
PRECAUTIONS FOR USE OF
THE INVERTER
PROTECTIVE FUNCTIONS
PRECAUTIONS FOR
MAINTENANCE AND
INSPECTION
SPECIFICATIONS
1
2
3
4
5
6
Thank you for choosing Mitsubishi Electric inverter.
WARNING
CAUTION
CAUTION
This Instruction Manual describes handling and cautions about the hardware, such as installation and wiring, for the FR-F802
(separated converter type) inverter that are different from the FR-800.
Information about the software, such as basic operations and parameters, is described in the FR-F800 Instruction Manual (Detailed)
in the CD-ROM enclosed with the product. In addition to this manual, read all the relevant instruction manuals on the enclosed CDROM carefully to ensure proper use. Do not use this product until you have a full knowledge of this product's workings, safety
information and instructions.
Please forward this Instruction Manual to the end user.
Fire prevention
Safety instructions
Do not attempt to install, operate, maintain or inspect this
product until you have read the Instruction Manuals and
appended documents carefully. Do not use this product until
you have a full knowledge of this product mechanism, safety
information and instructions.
Installation, operation, maintenance and inspection must be
performed by qualified personnel. Here, qualified personnel
means a person who meets all the following conditions:
A person who possesses a certification in regard with
electric appliance handling, or person took a proper
engineering training. Such training may be available at your
local Mitsubishi Electric office. Contact your local sales
office for schedules and locations.
• A person who can access operating manuals for the
protective devices (for example, light curtain) connected to
the safety control system, or a person who has read these
manuals thoroughly and familiarized themselves with the
protective devices.
In this Instruction Manual, the safety instruction levels are
classified into "WARNING" and "CAUTION".
Incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions, resulting in death
or severe injury.
Incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions, resulting in
medium or slight injury, or may cause
only material damage.
Note that even the level may lead to a
serious consequence depending on conditions. Be sure to
follow the instructions of both levels as they are critical to
personnel safety.
Electric shock prevention
WARNING
Do not remove the front cover or the wiring cover while the power
of this product is ON, and do not run this product with the front
cover or the wiring cover removed as the exposed high voltage
terminals or the charging part of the circuitry can be touched.
Otherwise you may get an electric shock.
Even if power is OFF, do not remove the front cover except for
wiring or periodic inspection as the inside of this product is
charged. Otherwise you may get an electric shock.
Before wiring or inspection, check that the LED display of the
operation panel is OFF. Any person who is involved in wiring or
inspection shall wait for 10 minutes or longer after the power
supply has been cut off, and check that there are no residual
voltage using a tester or the like. The capacitor is charged with
high voltage for some time after power OFF, and it is dangerous.
This product must be earthed (grounded). Earthing (grounding)
must conform to the requirements of national and local safety
regulations and electrical code (NEC section 250, IEC 61140
class 1 and other applicable standards). A neutral-point earthed
(grounded) power supply must be used to be compliant with EN
standard.
Any person who is involved in wiring or inspection of this product
shall be fully competent to do the work.
This product body must be installed before wiring. Otherwise you
may get an electric shock or be injured.
Do not touch the setting dial or keys with wed hands. Doing so
may cause an electric shock.
Do not subject the cables to scratches, excessive stress, heavy
loads or pinching. Doing so may cause an electric shock.
Do not change the cooling fan while power is ON as it is
dangerous.
Do not touch the printed circuit board or handle the cables with
wet hands. Doing so may cause an electric shock.
Before wiring or inspection for a PM motor, confirm that the PM
motor is stopped as a PM motor is a synchronous motor with
high-performance magnets embedded inside and high-voltage is
generated at the motor terminals while the motor is running even
after the power of this product is turned OFF. In an application,
such as fan and blower, that the motor may be driven by the
load, connect a low-voltage manual contactor at the output side
of this product and keep it open during wiring and inspection of
this product. Otherwise you may get an electric shock.
CAUTION
This product must be installed on a nonflammable wall without
any through holes so that nobody touches the heatsink, etc. on
the rear side of this product. Installing it on or near flammable
material may cause a fire.
If this product has become faulty, the product power must be
switched OFF. A continuous flow of large current may cause a
fire.
Be sure to perform daily and periodic inspections as specified in
the Instruction Manual. If this product is used without any
inspection, a burst, breakage, or a fire may occur.
Injury prevention
CAUTION
The voltage applied to each terminal must be as specified in the
Instruction Manual. Otherwise burst, damage, etc. may occur.
The cables must be connected to the correct terminals.
Otherwise burst, damage, etc. may occur.
The polarity (+ and -) must be correct. Otherwise burst, damage,
etc. may occur.
While power is ON or for some time after power-OFF, do not
touch this product as it will be extremely hot. Doing so may
cause a burn.
Additional instructions
The following instructions must be also followed. If this product
is handled incorrectly, it may cause unexpected fault, an injury,
or an electric shock.
CAUTION
Transportation and installation
Any person who is opening a package using a sharp object, such
as a knife or cutter, must wear gloves to prevent injuries caused
by the edge of the sharp object.
This product must be transported in correct method that
corresponds to the weight. Failure to do so may lead to injuries.
Do not stand or place any heavy object on this product.
Do not stack the boxes containing this product higher than the
number recommended.
When carrying this product, do not hold it by the front cover.
Doing so may cause a fall or failure of the product.
During installation, caution must be taken not to drop this product
as doing so may cause injuries.
This product must be installed on the surface that withstands the
weight of the product.
Do not install this product on a hot surface.
The installing orientation of this product must be correct.
This product must be installed on a strong surface securely with
screws so that it does not drop.
Do not install or operate this product if it is damaged or has parts
missing.
Foreign conductive objects must be prevented from entering this
product. That includes screws and metal fragments or other
flammable substance such as oil.
As this product is a precision instrument, do not drop or subject it
to impact.
The surrounding air temperature must be between -10 and
+50°C (non-freezing) for this product at LD (light duty) rating or
between -10 and 40? (non-freezing) for this product at SLD
(super light duty) rating. Otherwise the product may be
damaged.
The ambient humidity must be 95% RH or less (non-condensing)
for this product. Otherwise the product may be damaged. (Refer
to page 17 for details.)
Safety instructions
1
CAUTION
Transportation and installation
The temporary storage temperature (applicable to a short limited
time such as a transportation time) must be between -20 and
+65°C. Otherwise this product may be damaged.
This product must be used indoors (without corrosive gas,
flammable gas, oil mist, dust and dirt). Otherwise the product
may be damaged.
This product must be used at an altitude of 2500 m or less, with
If halogen-based materials (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine,
Wiring
Do not install a power factor correction capacitor, surge absorber,
The output of this product (output terminals U, V, W) must be
Even after the power of this product is turned OFF, a PM motor is
Never connect a PM motor to the commercial power supply.
Test operation
Before starting the test operation, confirm or adjust the
2
2.9 m/s
or less vibration at 10 to 55 Hz (directions of X, Y, Z
axes). Otherwise the product may be damaged. (For installation
at an altitude above 1000 m, consider a 3% reduction in the rated
current per 500 m increase in altitude.)
etc.), included in fumigants to sterilize or disinfect wooden
packages, infiltrate into this product, the product may be
damaged. Prevent residual fumigant components from being
infiltrated into the product when packaging, or use an alternative
sterilization or disinfection method (heat disinfection, etc.). Note
that sterilization or disinfection of wooden package should be
performed before packing the product.
or radio noise filter on the output side of this product. Doing so
may be overheated or burn out.
correctly connected to a motor. Otherwise the motor rotates
inversely.
running for a while and the output terminals U, V, and W of this
product wired to the PM motor hold high voltages all that while.
Before wiring other terminals, be sure that the PM motor is
stopped. Otherwise you may get an electric shock.
Applying the commercial power to the input terminals (U, V, W)
on a PM motor will burn the PM motor. The PM motor must be
applied a power from this product with the output terminals (U, V,
W).
parameter settings. Failure to do so may cause some machines
to make unexpected motions.
WARNING
Usage
Any person must stay away from the equipment after using the
retry function in this product as the equipment will restart
suddenly after the output shutoff of this product.
Depending on the function settings of this product, the product
does not stop its output even when the STOP/RESET key on the
operation panel is pressed. To prepare for it, provide a separate
circuit and switch (to turn OFF the power of this product, or apply
a mechanical brake, etc.) for an emergency stop.
Be sure to turn OFF the start (STF/STR) signal before clearing
the fault as this product will restart the motor suddenly after a
fault clear.
Do not use a PM motor for an application that the motor may be
driven by the load and run at a speed higher than the maximum
motor speed.
&&Use only a three-phase induction motor or PM motor as a
load on this product. &&Connection of any other electrical
equipment to the output of this product may damage the
equipment.
Do not modify this product.
Do not remove any part which is not instructed to be removed in
the Instruction Manuals. Doing so may lead to a failure or
damage of this product.
CAUTION
Usage
The electronic thermal O/L relay function may not be enough for
protection of a motor from overheating. It is recommended to
install an external thermal relay or a PTC thermistor for overheat
protection.
Do not use a magnetic contactor on the input side of this product
for frequent starting/stopping of this product. Otherwise the life of
the product decreases.
Use a noise filter or other means to minimize the electromagnetic
interference with other electronic equipment used nearby this
product.
Appropriate measures must be taken to suppress harmonics.
Otherwise harmonics in power systems generated from this
product may heat/damage a power factor correction capacitor or
a generator.
For a 400 V class motor driven by this product, use an insulation-
enhanced motor, or take measures to suppress surge voltage.
Otherwise surge voltage attributable to the line constants may
occur at the motor terminals, deteriorating the insulation of the
motor.
As all parameters return to their initial values after the Parameter
clear or All parameter clear is performed, the needed parameters
for this product operation must be set again before the operation
is started.
This product can be easily set for high-speed operation.
Therefore, consider all things related to the operation such as the
performance of a motor and equipment in a system before the
setting change.
The stop state of this product by the product's brake function (DC
injection brake function) cannot be held. Install a device to apply
brakes to a motor or equipment in a system for safety.
Before running this product which have been stored and not
been operated for a long period, perform an inspection and a test
operation.
To avoid damage to this product due to static electricity, static
electricity in your body must be discharged before you touch this
product.
Only one PM motor can be connected to a single unit of this
product.
A PM motor must be used under PM motor control. Do not use a
synchronous motor, induction motor, or synchronous induction
motor.
Do not connect a PM motor to this product at a setting for the
induction motor control (initial setting). Do not connect an
induction motor to this product at a setting for PM motor control.
Doing so will cause a failure.
As a process of starting a PM motor, turn ON the power of this
product first, and then close the contactor on the output side of
this product.
Emergency stop
A safety backup such as an emergency brake must be provided
for devices or equipment in a system to prevent hazardous
conditions in case of failure of this product or an external device
controlling this product.
If a breaker on the input side of this product is tripped, the wiring
must be checked for a fault (such as short circuit), and internal
parts of this product for a damage, etc. Identify and remove the
cause of the trip before resetting the tripped breaker (or before
applying the power to this product again).
When any protective function is activated, take an appropriate
corrective action before resetting this product to resume the
operation.
Maintenance, inspection and parts replacement
Do not carry out a megger (insulation resistance) test on the
control circuit of this product. Doing so will cause a failure.
Disposal
This product must be treated as industrial waste.
General instruction
For clarity purpose, illustrations in this Instruction Manual may be
drawn with covers or safety guards removed. Ensure all covers
and safety guards are properly installed prior to starting
operation. For details on the PM motor, refer to the Instruction
Manual of the PM motor.
2
Safety instructions

CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION 7
1.1 Product checking 8
1.2 Inverter component names 9
1.3 About the related manuals 10
2 INSTALLATION AND WIRING 11
2.1 Peripheral devices 12
2.1.1 Inverter and peripheral devices ......................................................................................................................12
2.1.2 Peripheral devices ..........................................................................................................................................14
2.2 Removal and reinstallation of the operation panel and the front covers 15
2.3 Installation of the inverter and enclosure design 17
2.3.1 Inverter installation environment.....................................................................................................................17
2.3.2 Amount of heat generated by the inverter ......................................................................................................19
2.3.3 Cooling system types for inverter enclosure ...................................................................................................20
2.3.4 Inverter installation..........................................................................................................................................21
2.3.5 Protruding the heat sink through a panel ........................................................................................................23
2.4 Terminal connection diagrams 25
2.5 Main circuit terminals 29
2.5.1 Details on the main circuit terminals of the inverter ........................................................................................29
2.5.2 Details on the main circuit terminals of the converter unit (FR-CC2)..............................................................29
2.5.3 Terminal layout of the main circuit terminals, wiring of power supply and the motor......................................30
2.5.4 Applicable cables and wiring length................................................................................................................31
2.5.5 Earthing (grounding) precautions ...................................................................................................................33
2.6 Control circuit 34
2.6.1 Details on the control circuit terminals of the inverter .....................................................................................34
2.6.2 Details on the control circuit terminals of the converter unit (FR-CC2)...........................................................38
2.6.3 Control logic (sink/source) change .................................................................................................................39
2.6.4 Wiring of inverter control circuit ......................................................................................................................41
2.6.5 Wiring precautions ..........................................................................................................................................43
2.6.6 When using separate power supplies for the control circuit and the main circuit ...........................................44
2.6.7 When supplying 24 V external power to the control circuit .............................................................................45
2.6.8 Safety stop function ........................................................................................................................................46
2.7 Communication connectors and terminals 48
2.7.1 PU connector ..................................................................................................................................................48
2.7.2 USB connector................................................................................................................................................49
2.7.3 RS-485 terminal block ....................................................................................................................................50
2.8 Connection of stand-alone option units 51
2.8.1 Connection of the brake unit (FR-BU2) ..........................................................................................................51
2.8.2 Connection of the high power factor converter (FR-HC2) ..............................................................................52
2.8.3 Connection of the power regeneration converter (MT-RC).............................................................................53
CONTENTS
3

3 PRECAUTIONS FOR USE OF THE INVERTER 55
3.1 Electro-magnetic interference (EMI) and leakage currents 56
3.1.1 Leakage currents and precautions .................................................................................................................56
3.1.2 Precautions against inverter-generated EMI .................................................................................................. 59
3.1.3 Converter unit (FR-CC2) built-in EMC filter .................................................................................................... 62
3.2 Power supply harmonics 63
3.2.1 Power supply harmonics ................................................................................................................................63
3.2.2 Harmonic Suppression Guidelines .................................................................................................................64
3.3 Installation of a reactor 66
3.4 Power-OFF and magnetic contactor (MC) 67
3.5 Precautions against deterioration of the 400 V class motor insulation 68
3.6 Checklist before starting operation 69
3.7 Failsafe system which uses the inverter 72
4 PROTECTIVE FUNCTIONS 75
4.1 Inverter fault and alarm indications 76
4.2 Reset method for the protective functions 76
4.3 Check and clear of the faults history 77
4.4 List of fault displays 79
5 PRECAUTIONS FOR
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION 81
5.1 Inspection item 82
5.1.1 Daily inspection .............................................................................................................................................. 82
5.1.2 Periodic inspection .........................................................................................................................................82
5.1.3 Daily and periodic inspection.......................................................................................................................... 83
5.1.4 Checking the inverter and converter modules................................................................................................ 84
5.1.5 Cleaning ......................................................................................................................................................... 85
5.1.6 Replacement of parts .....................................................................................................................................85
5.1.7 &&Removal and reinstallation of the control circuit terminal block................................................................. 87
5.2 Measurement of main circuit voltages, currents and powers 89
5.2.1 Measurement of powers ................................................................................................................................. 91
5.2.2 Measurement of voltages and use of PT........................................................................................................ 91
5.2.3 Measurement of currents ............................................................................................................................... 92
5.2.4 Use of CT and transducer ..............................................................................................................................92
5.2.5 Example of measuring converter unit (FR-CC2) input power factor............................................................... 92
5.2.6 Measurement of converter output voltage (across terminals P and N) ..........................................................92
4
CONTENTS

5.2.7 Measurement of inverter output frequency.....................................................................................................93
5.2.8 Insulation resistance test using megger .........................................................................................................93
5.2.9 Pressure test...................................................................................................................................................93
6 SPECIFICATIONS 95
6.1 Inverter rating 96
6.2 Common specifications 97
6.3 Outline dimension drawings 99
APPENDIX 101
Appendix1 For customers replacing the conventional model with this inverter................................ 102
Appendix2 Comparison with FR-F840 .................................................................................................... 104
Appendix3 Instructions for compliance with the EU Directives........................................................... 105
Appendix4 Instructions for UL and cUL ................................................................................................. 108
Appendix5 Instructions for EAC.............................................................................................................. 110
Appendix 6 Restricted Use of Hazardous Substances in Electronic and Electrical Products........... 111
Appendix 7 Referenced Standard (Requirement of Chinese standardized law).................................. 111
CONTENTS
5

MEMO
6

1 INTRODUCTION
The contents described in this chapter must be read before using
this product.
Always read the instructions before use.
1.1 Product checking......................................................................8
1.2 Inverter component names ......................................................9
1.3 About the related manuals.......................................................10
<Abbreviations>
DU..................................... Operation panel (FR-DU08)
Operation panel ................ Operation panel (FR-DU08) and LCD operation panel (FR-LU08)
Parameter unit .................. Parameter unit (FR-PU07)
PU..................................... Operation panel and parameter unit
Inverter.............................. Mitsubishi Electric inverter FR-F800 series (Separated converter type)
Pr. ..................................... Parameter number (Number assigned to function)
PU operation..................... Operation using the PU (operation panel/parameter unit)
External operation............. Operation using the control circuit signals
Combined operation ......... Combined operation using the PU (operation panel/parameter unit) and External
operation
1
<Notes on descriptions in this Instruction Manual>
• Connection diagrams in this Instruction Manual suppose that the control logic of the input terminal is the sink
logic, unless otherwise specified. (For the control logic, refer to page 39.)
Harmonic Suppression Guidelines
All the models of the inverters used by specific consumers are covered by "the Harmonic Suppression
Guidelines for Consumers Who Receive High Voltage or Special High Voltage". For the details, refer to page 64.
INTRODUCTION
7
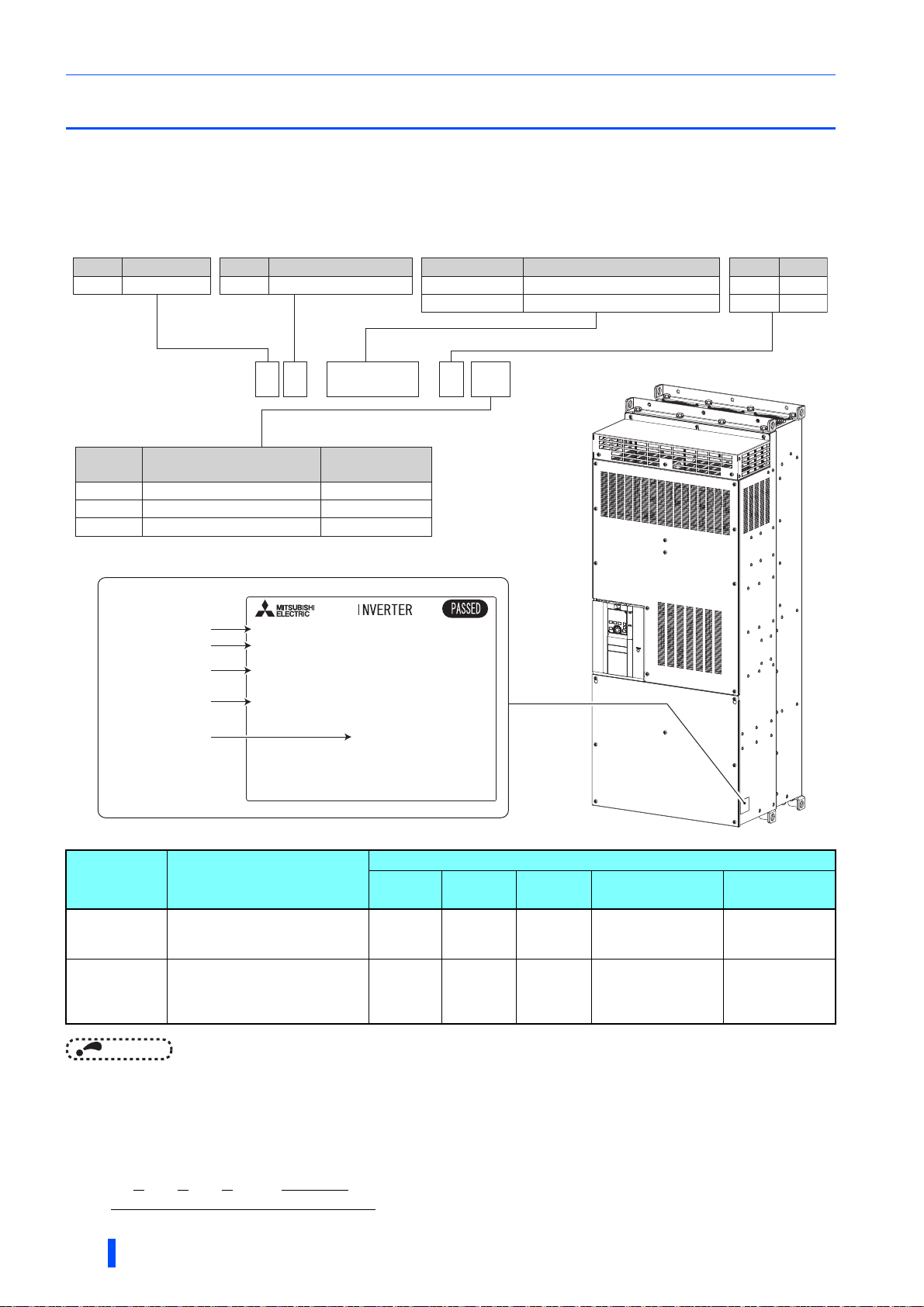
Product checking
NOTE
1.1 Product checking
Unpack the product and check the rating plate and the capacity plate of the inverter to ensure that the model agrees with the
order and the product is intact.
Inverter model
Symbol Voltage class
400 V class
4
F R - F 8 4 2 -
Symbol
-60
-06
Rating plate
Inverter model
Circuit board coating
(conforming to IEC60721-3-3 3C2/3S2)
Input rating
Output rating
SERIAL
Symbol Structure, functionality
Separated converter type
2
07700
Plated conductor
WithoutNone
With
With
02'(/)5)
,1387;;;;;
287387;;;;;
6(5,$/;;;;;;;;;
Without
Without
With
Symbol Description
07700 to 12120
355K to 560K
Inverter SLD rated current (A)
Inverter LD rated capacity (kW)
- 1
Symbol Type
FM
1
2
CA
∗1
Country of origin
Specification differs according to types. Major differences are shown in the table below.
Typ e Monitor output
FM
(terminal FM
equipped model)
CA
(terminal CA
equipped model)
Terminal FM (pulse train output)
Terminal AM (analog voltage output
(0 to 10 VDC))
Terminal CA (analog current output
(0 to 20 mA DC))
Terminal AM (analog voltage output
(0 to 10 VDC))
• In this Instruction Manual, the inverter model name consists of the rated current and the applicable motor capacity.
(Example) FR-F842-07700(355K)
0$'(,1;;;;;
Built-in
EMC filter
OFF Sink logic 60 Hz
ON Source logic 50 Hz
How to read the SERIAL number
Rating plate example
Symbol Year Month Control number
SERIAL
Initial setting
Control
logic
The SERIAL consists of one symbol, two characters indicating the production
year and month, and six characters indicating the control number.
The last digit of the production year is indicated as the Year, and the Month is
indicated by 1 to 9, X (October), Y (November), or Z (December).
Rated
frequency
Pr.19 Base
frequency voltage
9999 (same as the
power supply voltage)
8888 (95% of the
power supply voltage)
Pr.570 Multiple
rating setting
1 (LD rating)
0 (SLD rating)
8
INTRODUCTION
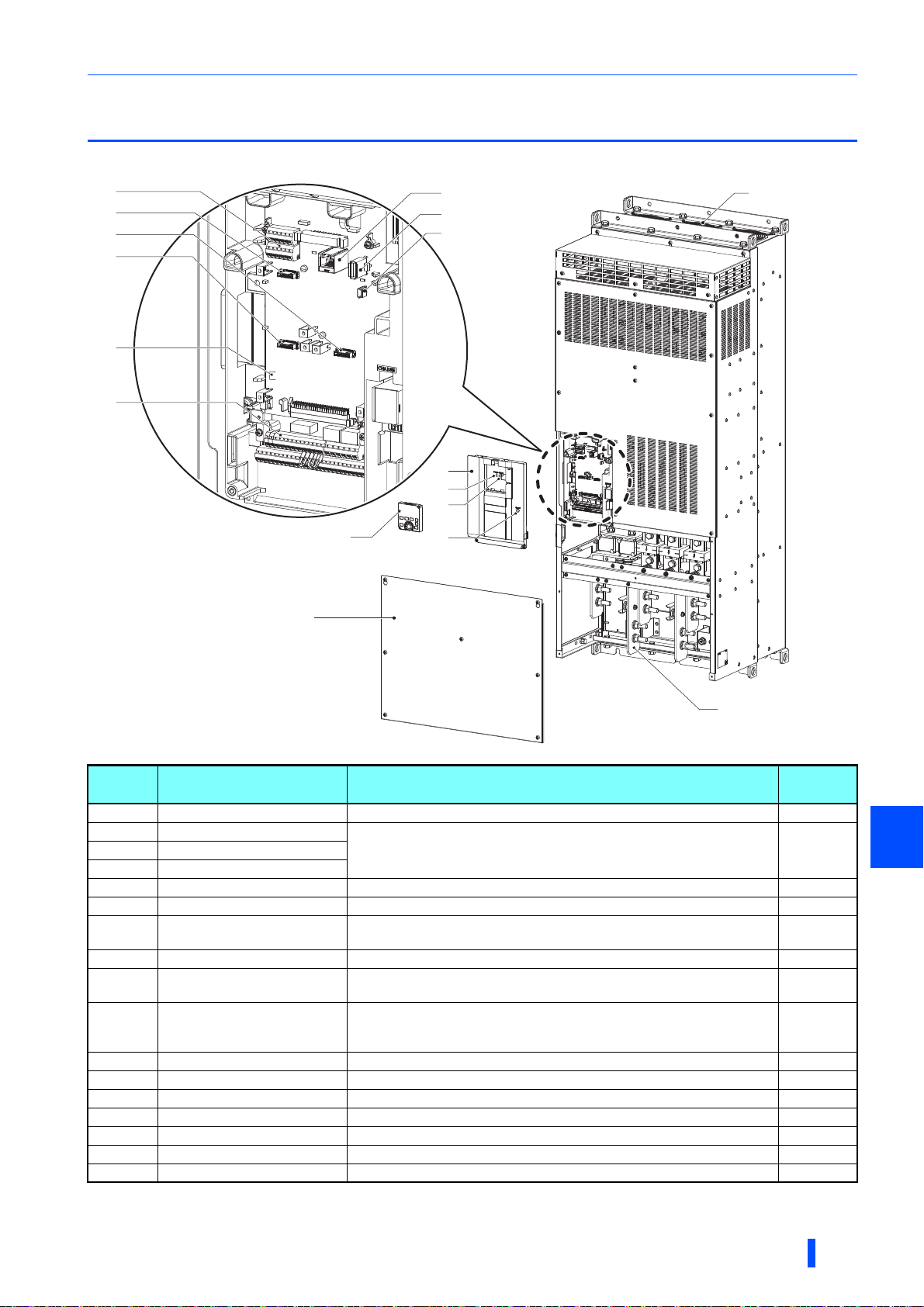
1.2 Inverter component names
(g)
(f)
(e)
(p)
(k)
(m)
(a)
(d)
(b)
(c)
(n)
(l)
(j)
(o)
(h)
(i)
(q)
Component names are as follows.
Inverter component names
Symbol Name Description
(a) RS-485 terminals Enables RS-485, MODBUS RTU, and BACnet communication. 50
(b) Plug-in option connector 1
(c) Plug-in option connector 2
(d) Plug-in option connector 3
(e) Voltage/current input switch Selects between voltage and current for the input via terminals 2 and 4.
(f) Control circuit terminal block Connects cables for the control circuit. 34
(g) PU connector
(h) USB A connector Connects a USB memory device. 49
(i) USB mini B connector
(j) Front cover (upper side)
(k) Power lamp Stays ON while the power is supplied to the control circuit (R1/L11, S1/L21). 30
(l) Alarm lamp Turns ON when the protective function of the inverter is activated. 75
(m) Charge lamp Stays ON while the power is supplied to the main circuit. 30
(n) Operation panel (FR-DU08) Operates and monitors the inverter.
(o) Front cover (lower side) Remove this cover for wiring. 15
(p) Main circuit terminal block Connects cables for the main circuit. 29
(q) Cooling fan Cools the inverter. 86
Refer to the Instruction Manual (Detailed) of the FR-F800.
Connects a plug-in option or a communication option.
Connects the operation panel or the parameter unit. This connector also
enables the RS-485 communication.
Connects a personal computer and enables communication with FR
Configurator2.
Needs to be removed for control circuit wiring, installation of a plug-in
(communication) option, RS-485 terminal wiring, changing of the voltage/
current input switch setting, etc.
Instruction
Manual of
the option
48
49
15
Refer to
page
1
INTRODUCTION
9
About the related manuals
1.3 About the related manuals
The manuals related to the FR-F800 are as follows.
Manual name Manual number
FR-F800 Instruction Manual (Detailed) IB-0600547ENG
FR-CC2 (Converter unit) Instruction Manual IB-0600543ENG
FR Configurator2 Instruction Manual IB-0600516ENG
FR-A800/F800 PLC Function Programming Manual IB-0600492ENG
FR-A800/F800 Safety Stop Function Instruction Manual BCN-A23228-001
10
INTRODUCTION

2 INSTALLATION AND
WIRING
This chapter explains the installation and the wiring of this product.
Always read the instructions before use.
2.1 Peripheral devices ....................................................................12
2.2 Removal and reinstallation of the operation panel and the
front covers ...............................................................................15
2.3 Installation of the inverter and enclosure design ..................17
2.4 Terminal connection diagrams ................................................25
2.5 Main circuit terminals ...............................................................29
2.6 Control circuit ...........................................................................34
2.7 Communication connectors and terminals............................48
2.8 Connection of stand-alone option units .................................51
2
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
11
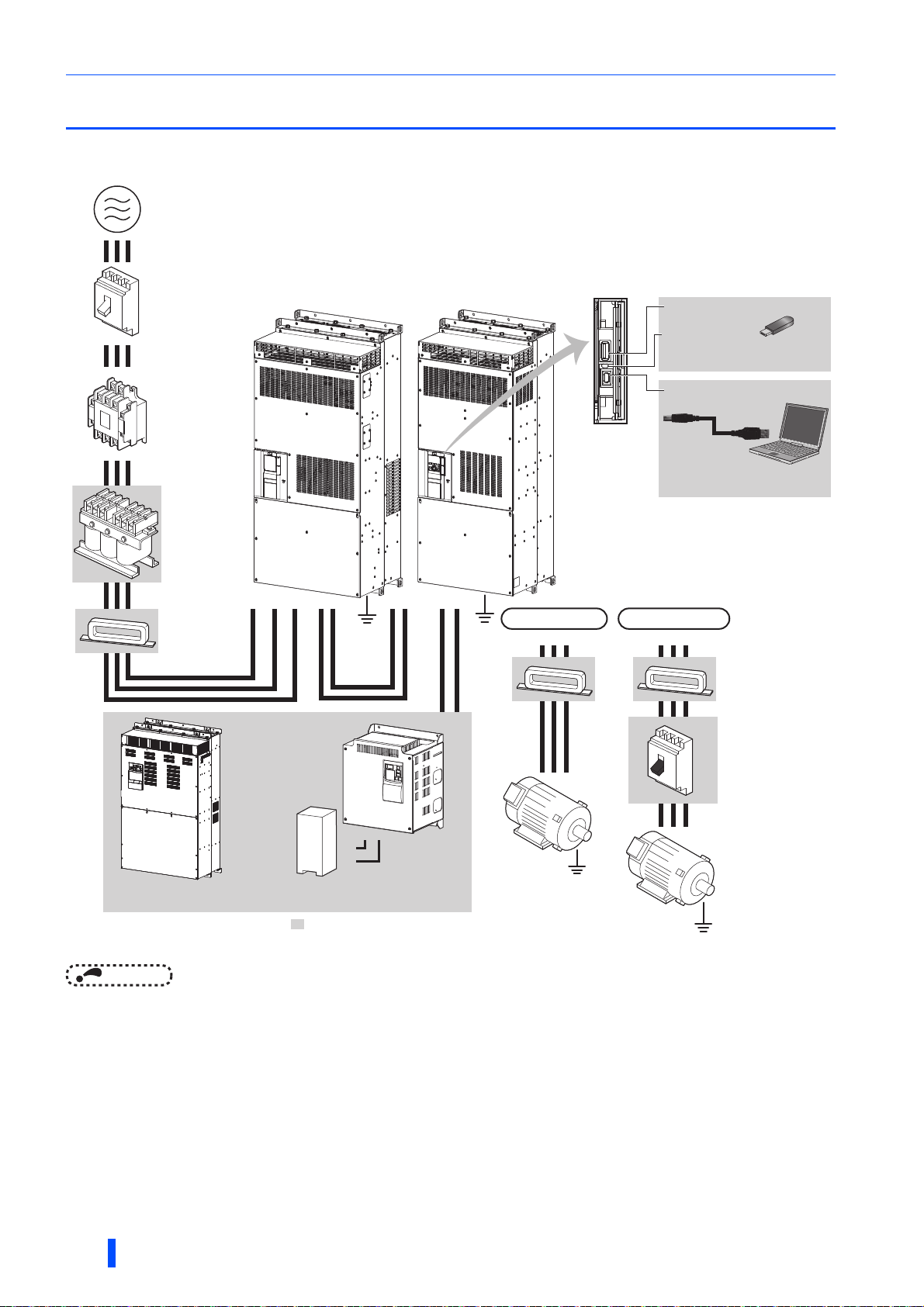
Peripheral devices
NOTE
Earth
(Ground)
R/L1 S/L2T/L3 N/-N/- P/+P/+ N/-P/+
P/+
P/+
PR
PR
: Install these options as required.
UVW
U
Earth (Ground)
VW
(d) Molded case
circuit breaker
(MCCB) or earth
leakage current
breaker (ELB),
fuse
(l) Noise filter
(n) Contactor
Example) No-fuse
switch
(DSN type)
(o) PM motor
(g) Noise filter
(h) High power factor converter
(FR-HC2)
(j) Resistor unit
(MT-BR5)
(i) Brake unit
(FR-BU2)
(e) Magnetic
contactor
(MC)
(a) Inverter
(FR-F802)
(b) Converter unit
(FR-CC2)
(c) Three-phase AC power supply
(k) USB connector
Personal computer
(FR Configurator 2)
USB
USB host
(A connector)
USB device
(Mini B connector)
Communication
status indicator
(LED)(USB host)
Earth
(Ground)
(m) Induction
motor
(f) AC reactor
(FR-HAL)
IM connection
PM connection
Earth
(Ground)
2.1 Peripheral devices
2.1.1 Inverter and peripheral devices
• To prevent an electric shock, always earth (ground) the motor, the inverter, and the converter unit.
• Do not install a power factor correction capacitor or surge suppressor or capacitor type filter on the inverter's output side. Doing
so will cause the inverter to be shut off or the capacitor and surge suppressor to be damaged. If any of the above devices is
connected, immediately remove it. When installing a molded case circuit breaker on the output side of the inverter, contact the
manufacturer of the molded case circuit breaker.
• Electromagnetic wave interference
The input/output (main circuit) of the inverter or the converter unit includes high frequency components, which may interfere
with the communication devices (such as AM radios) used near the inverter or the converter unit. In this case, activating the
EMC filter of the converter unit may minimize interference. (Refer to page 62.)
• For details of options and peripheral devices, refer to the respective Instruction Manual.
• A PM motor cannot be driven by the commercial power supply.
• A PM motor is a motor with permanent magnets embedded inside. High voltage is generated at the motor terminals while the
motor is running. Before closing the contactor at the output side, make sure that the inverter power is ON and the motor is
stopped.
12
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
Peripheral devices
Symbol Name Overview
The life of the inverter and the converter unit is influenced by the
(a) Inverter (FR-F802)
(b) Converter unit (FR-CC2)
(c) Three-phase AC power supply
(d)
(e) Magnetic contactor (MC)
(f) AC reactor (FR-HAL)
(g) Noise filter
(h) High power factor converter (FR-HC2)
(i) Brake unit (FR-BU2)
(j) Resistor unit (MT-BR5)
(k) USB connection
(l) Noise filter
(m) Induction motor Connect a squirrel-cage induction motor. —
(n)
(o) PM motor
Molded case circuit breaker (MCCB),
earth leakage circuit breaker (ELB), or
fuse
Contactor
Example) No-fuse switch (DSN type)
surrounding air temperature.
The surrounding air temperature should be as low as possible within the
permissible range. This must be noted especially when the inverter and the
converter unit installed in an enclosure.
Incorrect wiring may lead to damage of the inverter and the converter unit.
The control signal lines must be kept fully away from the main circuit lines to
protect them from noise.
The converter unit built-in EMC filter can reduce the noise.
Must be within the permissible power supply specifications of the converter
unit.
Must be selected carefully since an inrush current flows in the converter unit
at power ON.
Install this to ensure safety.
Do not use this to start and stop the inverter. Doing so will shorten the life of
the inverter and the converter unit.
Install this to suppress harmonics and to improve the power factor.
An AC reactor (FR-HAL) (option) is required when installing the inverter
near a large power supply system (1000 kVA or more). Under such
condition, the inverter and the converter unit may be damaged if you do not
use a reactor.
Select a reactor according to the applied motor capacity.
Suppresses the noise radiated from the power supply side of the converter
unit.
Suppresses the power supply harmonics significantly. Install these options
as required.
When FR-HC2 is used, FR-CC2 is not required.
Allows the inverter to provide the optimal regenerative braking capability.
Install these options as required.
Connect between the inverter and a personal computer with a USB (ver.
1.1) cable.
Use a USB memory device to copy parameter settings or use the trace
function.
Install this to reduce the electromagnetic noise generated from the inverter
and the converter unit. The noise filter is effective in the range from about
0.5 to 5 MHz.
Connect this for an application where a PM motor is driven by the load even
while the inverter power is OFF. Do not open or close the contactor while
the inverter is running (outputting).
A PM motor can be used. A PM motor cannot be driven by the commercial
power supply.
Refer
to
page
17
25
62
96
14
67
66
59
52
51
49
59
—
—
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
2
13

Peripheral devices
NOTE
MCCB Converter unit
MCCB Converter unit
M
M
INV
INV
2.1.2 Peripheral devices
Selecting the converter unit (FR-CC2)
Select the capacity of the FR-CC2 converter unit according to the connected motor capacity.
Motor
capacity
(kW)
355 H355K - - - 355K 07700 683
400 H400K 355K 07700 770 400K 08660 770
450 H450K 400K 08660 866 450K 09620 866
500 H500K 450K 09620 962 500K 10940 962
560 H560K 500K 10940 1094 560K 12120 1094
630 H630K 560K 12120 1212 - - -
The applicable motor capacity indicated is the maximum capacity applicable for use of the Mitsubishi Electric 4-pole standard motor.
Converter unit
FR-CC2-[ ]
SLD (superlight duty) LD (light duty)
Model
FR-F842-[ ]
Rated current (A)
Selecting the breaker/magnetic contactor
Check the model of the inverter and the converter unit you purchased. Appropriate peripheral devices must be selected
according to the capacity.
Refer to the following table to prepare appropriate peripheral devices.
• 400 V class
Motor
output
(kW)
355 FR-CC2-H355K 800 A S-N600
400 FR-CC2-H400K 900 A S-N800
450 FR-CC2-H450K 1000 A 1000 A rated product
500 FR-CC2-H500K 1200 A 1000 A rated product
560 FR-CC2-H560K 1500 A 1200 A rated product
630 FR-CC2-H630K 2000 A 1400 A rated product
Applicable converter
model
Molded case circuit breaker (MCCB)
or
earth leakage circuit breaker (ELB)
(NF, NV type)
Inverter
Model
FR-F842-[ ]
Rated current (A)
Input-side magnetic contactor
Assumes the use of a Mitsubishi Electric 4-pole standard motor with the power supply voltage
of 400 VAC 50 Hz.
Select an MCCB according to the power supply capacity.
Install one MCCB per converter.
(For the use in the United States or Canada, refer to page 108 to select the appropriate fuse.)
The magnetic contactor is selected based on the AC-1 class. The electrical durability of magnetic contactor is 500,000 times. When the
magnetic contactor is used for emergency stops during motor driving, the electrical durability is 25 times.
If using an MC for emergency stop during driving the motor, select an MC regarding the converter unit input side current as JEM1038-AC-3 class
rated current. When using an MC on the inverter output side for commercial-power supply operation switching using a general-purpose motor,
select an MC regarding the rated motor current as JEM1038-AC-3 class rated current.
• When the converter unit capacity is larger than the motor capacity, select an MCCB and a magnetic contactor according to
the converter unit model, and select cables and reactors according to the motor output.
• When the breaker on the converter unit's input side trips, check for the wiring fault (short circuit), damage to internal parts of
the inverter and the converter unit, etc. The cause of the trip must be identified and removed before turning ON the power of
the breaker.
14
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
Removal and reinstallation of the operation panel and the front covers
(a) (b)
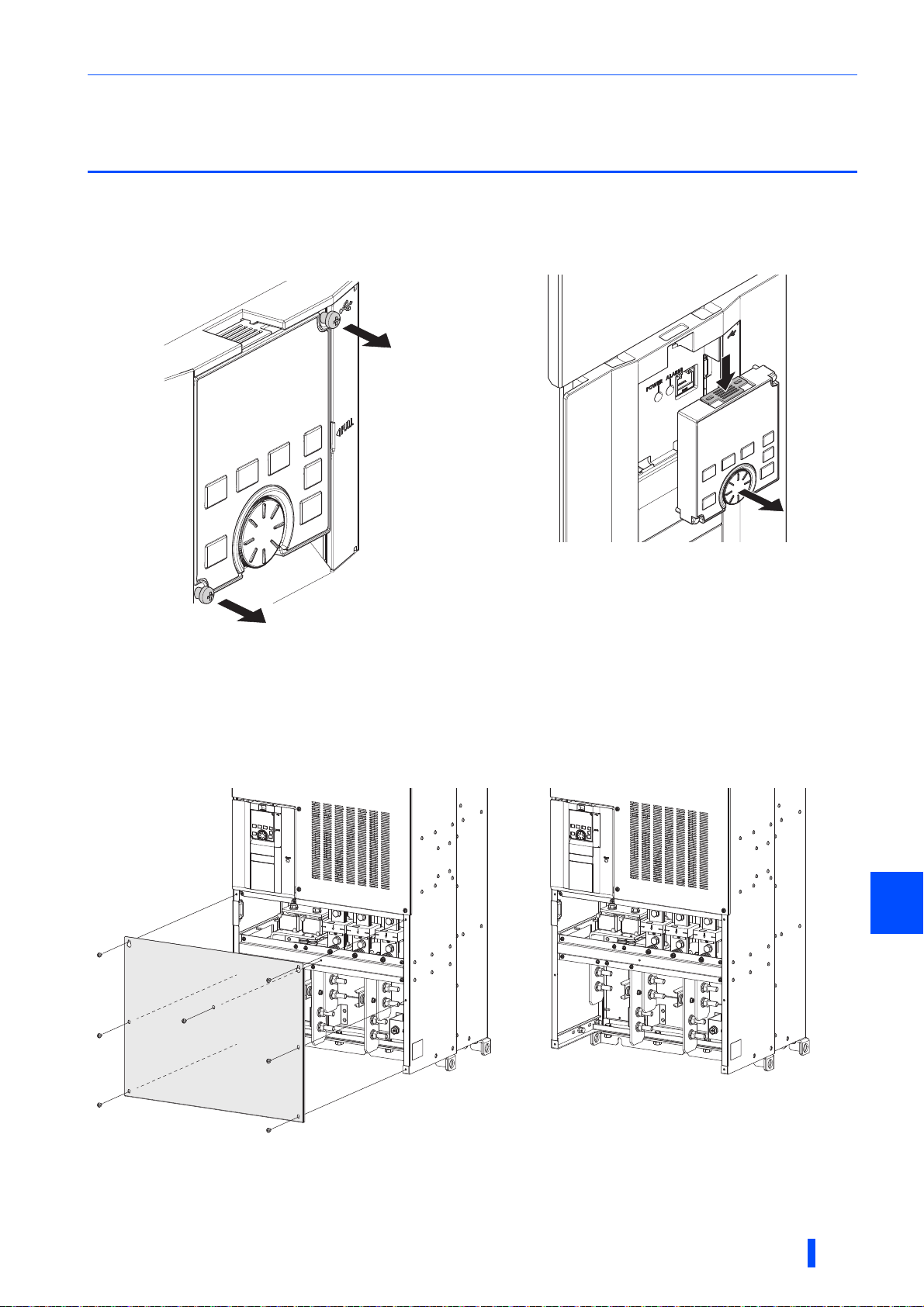
2.2 Removal and reinstallation of the operation
panel and the front covers
Removal and reinstallation of the operation panel
• Loosen the two screws on the operation panel.
(These screws cannot be removed.)
To reinstall the operation panel, align its connector on the back with the PU connector of the inverter, and insert the operation
panel. After confirming that the operation panel is fit securely, tighten the screws. (Tightening torque: 0.40 to 0.45 N·m)
• Press the upper edge of the operation panel while pulling
out the operation panel.
Removal of the front cover (lower side)
(a) When the mounting screws are removed, the front cover (lower side) can be removed. (The number of the mounting screws
differs by the capacity.)
(b) With the front cover (lower side) removed, wiring of the main circuit terminals can be performed.
2
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
15

Removal and reinstallation of the operation panel and the front covers
NOTE
Loosen
Fasten
Fasten
Removal of the front cover (upper side)
(a) (b)
Loosen
Loosen
(a) With the front cover (lower side) removed, loosen the mounting screws on the front cover (upper side). These screws cannot be
removed.
(b) While holding the areas around the installation hooks on the sides of the front cover (upper side), pull out the front cover using its
upper side as a support.
(c) With the front cover (upper side) removed, wiring of the control circuit and the RS-485 terminals, and installation of the plug-in
option can be performed.
(c)
Reinstallation of the front cover
(a)
(a) Insert the upper hooks of the front cover (upper side) into the sockets of the inverter.
(b) Tighten the mounting screws at the lower part of the front cover (upper side).
(c) Fasten the front cover (lower side) with the mounting screws. (The number of the mounting screws differs by the capacity.)
Securely install the front cover (upper side) to the inverter by fixing the hooks on the sides of the cover into place.
(b) (c)
Fasten
Fasten
Fasten
Fasten
16
• When installing the front cover (upper side), fit the connector of the operation panel securely along the guides of the PU
connector.
• Fully make sure that the front cover has been installed securely. Always tighten the mounting screws of the front cover.
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
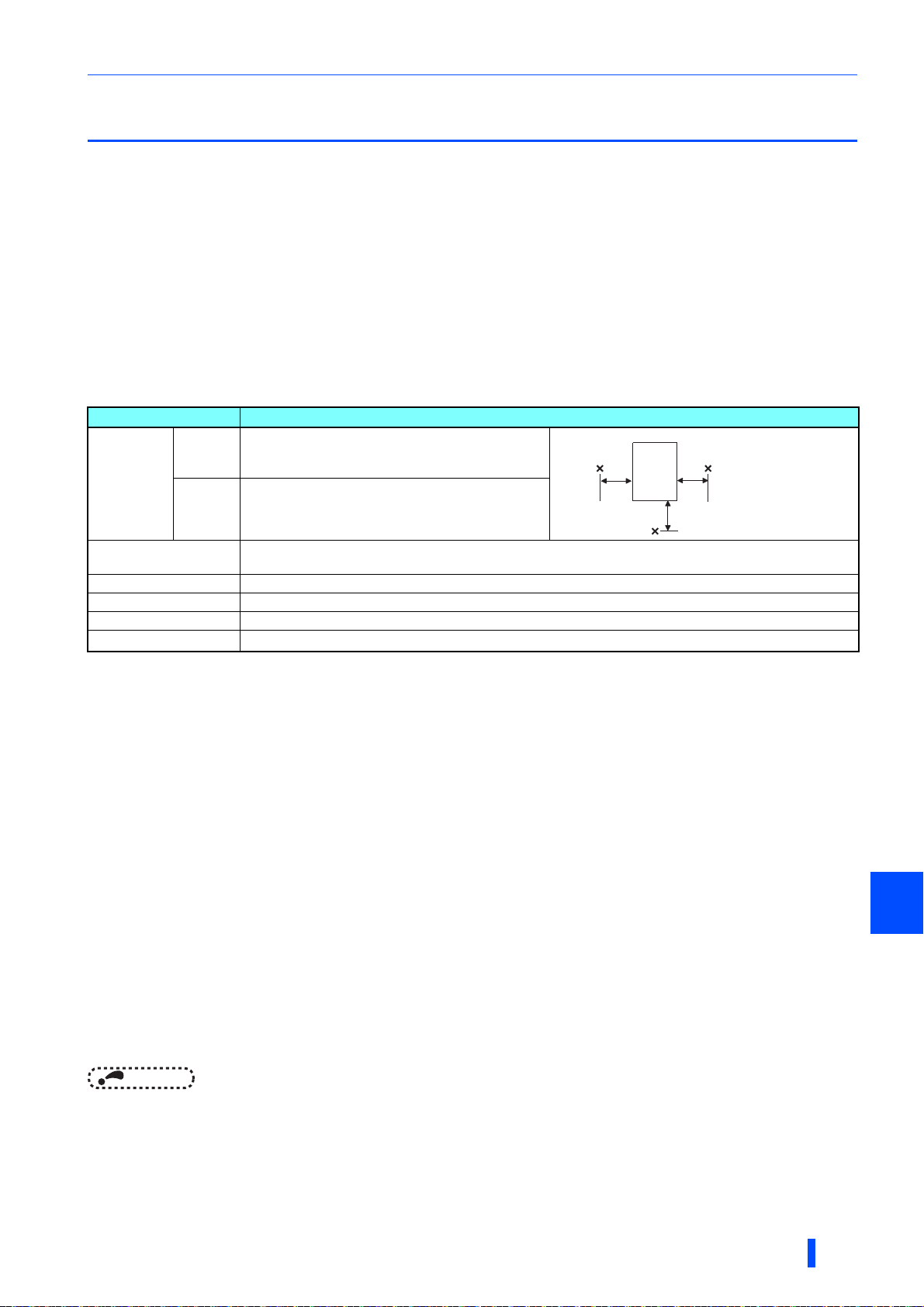
Installation of the inverter and enclosure design
Measurement
position
Measurement
position
Inverter
5 cm 5 cm
5 cm
2.3 Installation of the inverter and enclosure design
When designing or manufacturing an inverter enclosure, determine the structure, size, and device layout of the enclosure by
fully considering the conditions such as heat generation of the contained devices and the operating environment. An inverter
uses many semiconductor devices. To ensure higher reliability and long period of operation, operate the inverter in the
ambient environment that completely satisfies the equipment specifications.
2.3.1 Inverter installation environment
The following table lists the standard specifications of the inverter installation environment. Using the inverter in an
environment that does not satisfy the conditions deteriorates the performance, shortens the life, and causes a failure. Refer to
the following points, and take adequate measures.
Standard environmental specifications of the inverter
Item Description
Surrounding
air
temperature
Ambient humidity
Storage temperature -20 to + 65°C
Atmosphere Indoors (free from corrosive gas, flammable gas, oil mist, dust and dirt)
Altitude Maximum 2500 m
Vibration
LD -10 to +50°C (non-freezing)
SLD -10 to +40°C (non-freezing)
With circuit board coating (conforming to class 3C2/3S2 in IEC 60721-3-3): 95% RH or less (non-condensing)
Without circuit board coating: 90% RH or less (non-condensing)
2
2.9 m/s
or less at 10 to 55 Hz (directions of X, Y, Z axes)
Temperature applicable for a short time, for example, in transit.
For the installation at an altitude above 1000 m, consider a 3% reduction in the rated current per 500 m increase in altitude.
Temperatur e
The permissible surrounding air temperature of the inverter is between -10°C and +50°C (-10°C and +40°C at the SLD rating).
Always operate the inverter within this temperature range. Operation outside this range will considerably shorten the service
lives of the semiconductors, parts, capacitors and others. Take the following measures to keep the surrounding air
temperature of the inverter within the specified range.
(a) Measures against high temperature
• Use a forced ventilation system or similar cooling system. (Refer to page 20.)
• Install the enclosure in an air-conditioned electric chamber.
• Block direct sunlight.
• Provide a shield or similar plate to avoid direct exposure to the radiated heat and wind of a heat source.
• Ventilate the area around the enclosure well.
(b) Measures against low temperature
• Provide a space heater in the enclosure.
• Do not power OFF the inverter. (Keep the start signal of the inverter OFF.)
(c) Sudden temperature changes
• Select an installation place where temperature does not change suddenly.
• Avoid installing the inverter near the air outlet of an air conditioner.
• If temperature changes are caused by opening/closing of a door, install the inverter away from the door.
2
NOTE
Humidity
Operate the inverter within the ambient air humidity of usually 45 to 90% (up to 95% with circuit board coating). Too high
humidity will pose problems of reduced insulation and metal corrosion. On the other hand, too low humidity may cause a spatial
electrical breakdown. The humidity conditions for the insulation distance defined in JEM 1103 standard "Insulation Distance
from Control Equipment" is 45 to 85%.
• For the amount of heat generated by the inverter unit, refer to page 19.
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
17

Installation of the inverter and enclosure design
(a) Measures against high humidity
• Make the enclosure enclosed, and provide it with a hygroscopic agent.
• Provide dry air into the enclosure from outside.
• Provide a space heater in the enclosure.
(b) Measures against low humidity
Air with proper humidity can be blown into the enclosure from outside. Also when installing or inspecting the unit, discharge
your body (static electricity) beforehand, and keep your body away from the parts and patterns.
(c) Measures against condensation
Condensation may occur if frequent operation stops change the in-enclosure temperature suddenly or if the outside air
temperature changes suddenly.
Condensation causes such faults as reduced insulation and corrosion.
• Take the measures against high humidity in (a).
• Do not power OFF the inverter. (Keep the start signal of the inverter OFF.)
Dust, dirt, oil mist
Dust and dirt will cause such faults as poor contacts, reduced insulation and cooling effect due to the moisture-absorbed
accumulated dust and dirt, and in-enclosure temperature rise due to a clogged filter. In an atmosphere where conductive
powder floats, dust and dirt will cause such faults as malfunction, deteriorated insulation and short circuit in a short time.
Since oil mist will cause similar conditions, it is necessary to take adequate measures.
Precautions
• Place the inverter in a totally enclosed enclosure.
Take measures if the in-enclosure temperature rises. (Refer to page 20.)
• Purge air.
Pump clean air from outside to make the in-enclosure air pressure higher than the outside air pressure.
Corrosive gas, salt damage
If the inverter is exposed to corrosive gas or to salt near a beach, the printed board patterns and parts will corrode or the
relays and switches will result in poor contact.
In such places, take the measures given above.
Explosive, flammable gases
As the inverter is non-explosion proof, it must be contained in an explosion-proof enclosure. In places where explosion may
be caused by explosive gas, dust or dirt, an enclosure cannot be used unless it structurally complies with the guidelines and
has passed the specified tests. This makes the enclosure itself expensive (including the test charges). The best way is to
avoid installation in such places and install the inverter in a non-hazardous place.
High altitude
Use the inverter at an altitude of within 2500 m. For use at an altitude above 1000 m, consider a 3% reduction in the rated
current per 500 m increase in altitude.
If it is used at a higher place, it is likely that thin air will reduce the cooling effect and low air pressure will deteriorate dielectric
strength.
Vibration, impact
The vibration resistance of the inverter is up to 2.9 m/s2 at 10 to 55 Hz frequency and 1 mm amplitude for the directions of X,
Y, Z axes. Applying vibration and impacts for a long time may loosen the structures and cause poor contacts of connectors,
even if those vibration and impacts are within the specified values.
Especially when impacts are applied repeatedly, caution must be taken because such impacts may break the installation feet.
Precautions
• Provide the enclosure with rubber vibration isolators.
• Strengthen the structure to prevent the enclosure from resonance.
• Install the enclosure away from the sources of the vibration.
18
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
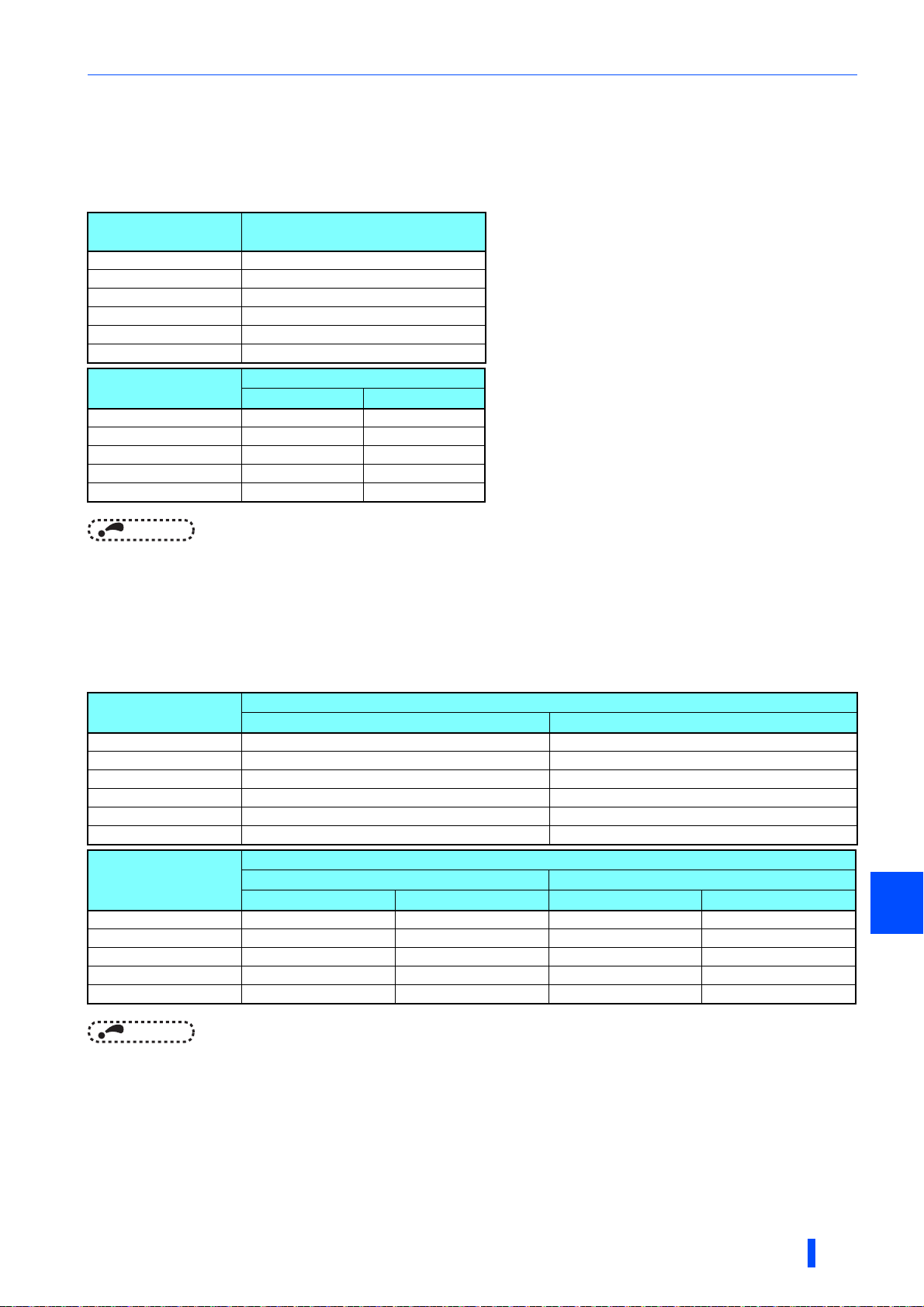
Installation of the inverter and enclosure design
2.3.2 Amount of heat generated by the inverter
Installing the heat sink inside the enclosure
When the heat sink is installed inside the enclosure, the amount of heat generated by the inverter unit and the converter unit is
shown in the following tables.
Converter
FR-CC2-H[]
355K 2600
400K 3050
450K 3400
500K 3800
560K 4400
630K 4920
Inverter
FR-F842-[]
07700(355K) 5800 5050
08660(400K) 6690 5800
09620(450K) 7370 6480
10940(500K) 8600 7340
12120(560K) 9810 8630
Amount of heat generated (W)
Amount of heat generated (W)
SLD LD
NOTE
• The amount of heat generated shown assumes that the output current is the inverter rated current, and the carrier frequency
is 2 kHz.
Protruding the heat sink through a panel
When the heat sink is protruded through a panel, the amount of heat generated by the inverter unit and converter unit is
shown
in the following tables. (For the details on protruding the heat sink through a panel, refer to page 23.)
Converter
FR-CC2-H[]
355K 1820 780
400K 2130 920
450K 2380 1020
500K 2660 1140
560K 3080 1320
630K 3440 1480
Converter
FR-F842-[]
07700(355K) 4060 3530 1740 1520
08660(400K) 4680 4060 2010 1740
09620(450K) 5160 4530 2210 1950
10940(500K) 6020 5140 2580 2200
12120(560K) 6860 6040 2950 2590
Heat sink section (outside of enclosure) Control section (inside of enclosure)
Heat sink section (outside of enclosure) Control section (inside of enclosure)
SLD LD SLD LD
Amount of heat generated (W)
Amount of heat generated (W)
2
NOTE
• The amount of heat generated shown assumes that the output current is the inverter rated current, and the carrier frequency
is 2 kHz.
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
19
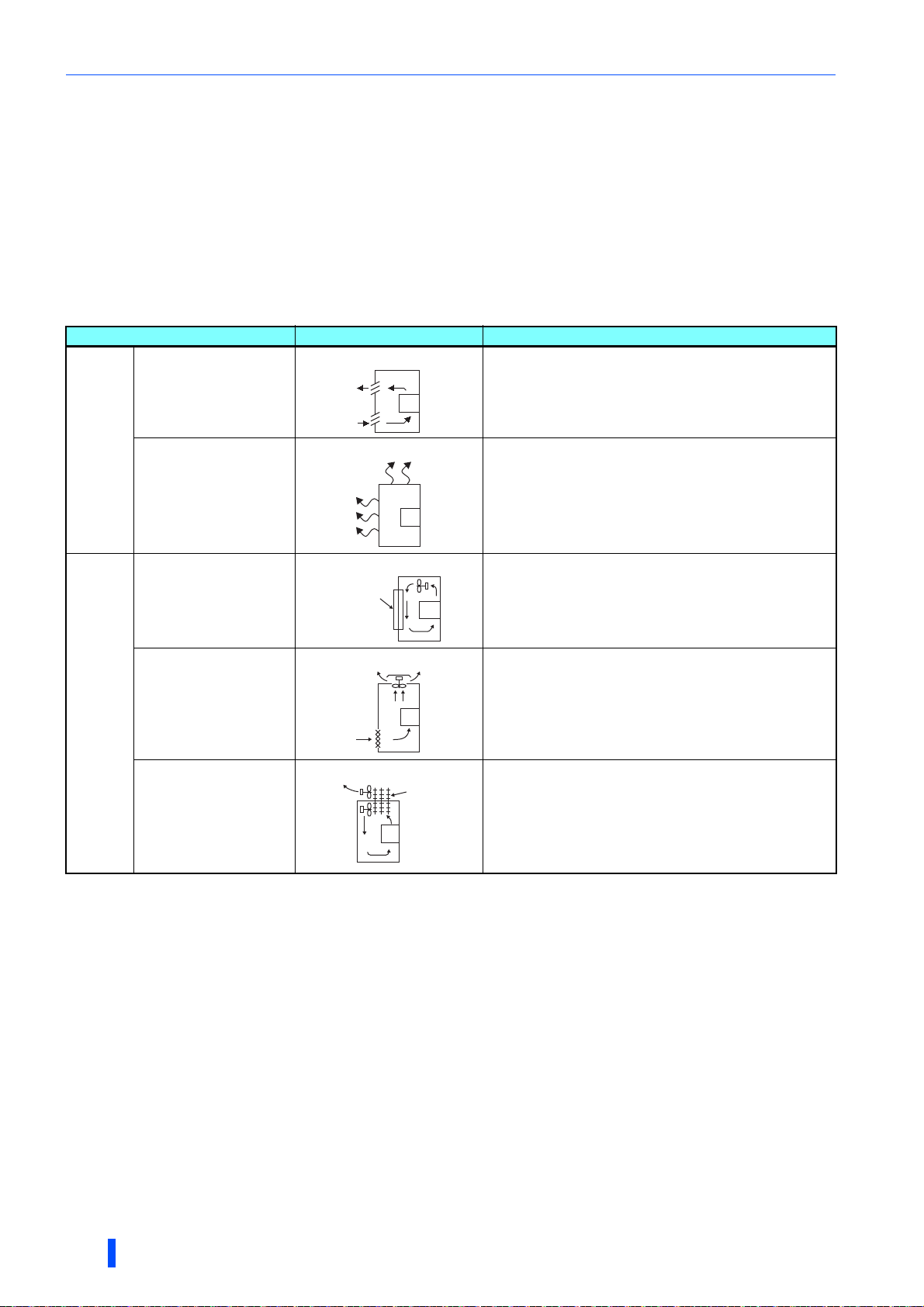
Installation of the inverter and enclosure design
2.3.3 Cooling system types for inverter enclosure
From the enclosure that contains the inverter, the heat of the inverter and other equipment (transformers, lamps, resistors,
etc.) and the incoming heat such as direct sunlight must be dissipated to keep the in-enclosure temperature lower than the
permissible temperatures of the in-enclosure equipment including the inverter.
The cooling systems are classified as follows in terms of the cooling calculation method.
(a) Cooling by natural heat dissipation from the enclosure surface (totally enclosed type)
(b) Cooling by heat sink (aluminum fin, etc.)
(c) Cooling by ventilation (forced ventilation type, pipe ventilation type)
(d) Cooling by heat exchanger or cooler (heat pipe, cooler, etc.)
Cooling system Enclosure structure Comment
Natural
Forced air
Natural ventilation
(enclosed type / open type)
Natural ventilation (totally
enclosed type)
Heat sink cooling
Forced ventilation
Heat pipe This is a totally enclosed for enclosure downsizing.
Heat sink
INV
INV
INV
INV
Heat
pipe
INV
This system is low in cost and generally used, but the
enclosure size increases as the inverter capacity increases.
This system is for relatively small capacities.
Being a totally enclosed type, this system is the most
appropriate for hostile environment having dust, dirt, oil mist,
etc. The enclosure size increases depending on the inverter
capacity.
This system has restrictions on the heat sink mounting
position and area. This system is for relatively small
capacities.
This system is for general indoor installation. This is
appropriate for enclosure downsizing and cost reduction, and
often used.
20
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
2.3.4 Inverter installation
Vertical
Inverter placement
Installation of the inverter and enclosure design
• Install the inverter on a strong surface securely with screws.
• Leave enough clearances and take cooling measures.
• Avoid places where the inverter is subjected to direct sunlight, high temperature and high humidity.
• Install the inverter on a nonflammable wall surface.
• When encasing multiple inverters in an enclosure, install them in parallel as a cooling measure.
• For heat dissipation and maintenance, keep clearance between the inverter and the other devices or enclosure surface.
The clearance below the inverter is required as a wiring space, and the clearance above the inverter is required as a heat
dissipation space.
• When designing or building an enclosure for the inverter, carefully consider influencing factors such as heat generation of
the contained devices and the operating environment.
Clearances (side)Clearances (front)
20 cm or more
5 cm
or more
∗1
Inverter
Vertical
Vertical
10 cm
or more
10 cm
or more
2
Allow clearance.
For replacing the cooling fan, 30 cm or more of space is necessary in front of the inverter. Refer to page 86 for fan replacement.
20 cm or more
Installation orientation of the inverter
Install the inverter on a wall as specified. Do not mount it horizontally or in any other way.
Above the inverter
Heat is blown up from inside the inverter by the small fan built in the unit. Any equipment placed above the inverter should be
heat resistant.
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
21
Installation of the inverter and enclosure design
Arrangement of multiple inverters and converter units
When multiple inverters and converter units are placed in the
same enclosure, generally arrange them horizontally as shown
in the figure on the right.
Do not place multiple products vertically. The exhaust air
temperature of the inverter and the converter unit may be
increased.
When mounting multiple inverters and converter units, fully take
caution not to make the surrounding air temperature of the
inverter and the converter unit higher than the permissible value
by providing ventilation and increasing the enclosure size.
Converter
unit
Converter
unit
Arrangement of multiple inverters and converter units
Inverter
Inverter
Enclosure
Arrangement of the ventilation fan and inverter
Heat generated in the inverter is blown up from the bottom of
the unit as warm air by the cooling fan. When installing a
ventilation fan for that heat, determine the place of ventilation
fan installation after fully considering an air flow. (Air passes
through areas of low resistance. Make an airway and airflow
plates to expose the inverter to cool air.)
Inverter Inverter
Converter
unit
Inverter
<Good example> <Bad example>
Arrangement of the ventilation fan and inverter
22
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
Installation of the inverter and enclosure design
660
Hole
240 240
6-M10 screw
15152015
1550
(Unit: mm)
2.3.5 Protruding the heat sink through a panel
When encasing an inverter to an enclosure, the heat generated in the enclosure can be greatly reduced by protruding the
heat sink of the inverter.
When installing the inverter in a compact enclosure, etc., this installation method is recommended.
Panel cutting
Cut the panel of the enclosure according to the inverter capacity.
FR-F842-07700(355K)
FR-F842-08660(400K)
1515 1270
1300
200
520
Hole
200
FR-F842-09620(450K)
FR-F842-10940(500K)
FR-F842-12120(560K)
6-M10 screw
(Unit: mm)
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
2
23
Installation of the inverter and enclosure design
NOTE
Removal of the rear installation frame
Two installation frames are attached to each of the upper and lower
parts of the inverter. Remove the rear side installation frame on the top
and bottom of the inverter as shown on the right.
Upper installation
frame (rear side)
Lower installation
frame (rear side)
Installation of the inverter in enclosure
Place the inverter in an enclosure so that the inverter's heat sink section protrudes from the hole through the panel of the
enclosure. Fasten the inverter to the panel with screws through holes in the upper and lower installation frames.
Enclosure
Inside of
enclosure
Inverter
Exhaust air
Installation
frame
To avoid interference with small protrusions (finger guard
protective cooling fan covers) on top of the heat sink, the
thickness of the panel of the enclosure should not exceed
10 mm (marked with *1 in the figure below) and the space
around the covers (fans) should be cleared.
Panel of enclosure
Finger guard
10 mm
∗1
140 mm
protective cooling fan cover
6 mm
Cooling
air
185 mm
• As the heat sink section protruded through the panel includes a cooling fan, this type of installation is not suitable for
environment in which the inverter may be exposed to drops of water, oil mist, dust, etc.
• Make sure that screws, debris etc. do not get into the inverter and cooling fan.
Depth dimension of the inverter's heat
sink section protruded through the panel
24
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
R1/L11
S1/L21
PC
Frequency setting signals (Analog)
10E(+10V)
10(+5V)
2
(Analog common)
2
3
1
Auxiliary
input
Terminal 4 input
(Current input)
1
4
Frequency setting
potentiometer
1/2W1kΩ
Running
Up to frequency
Overload
Frequency detection
Open collector output common
Sink/source common
F/C
(FM)
SD
Motor
Relay output 1
(Fault output)
C1
B1
A1
U
V
W
Indicator
(Frequency
meter, etc.)
+-
(-)
(+)
Analog signal output
(0 to ±10VDC)
Earth
(Ground)
AM
5
0 to ±5VDC selectable
0 to ±10VDC
Open collector output
Moving-coil type
1mA full-scale
Calibration
resistor
Main circuit terminal
Control circuit terminal
0 to 5VDC
0 to 10VDC
C2
B2
A2
Relay output 2
Relay output
M
0 to 20mADC
0 to 5VDC
0 to 10VDC
selectable
4 to 20mADC
TXD+
TXD-
RXD+
RXD-
GND
(SG)
Data
transmission
GND
RS-485 terminals
SINK
SOURCE
Connector for plug-in option connection
STF
STR
STP(STOP)
RH
RM
RL
JOG
RT
MRS
X10
RES
AU
CS
SD
RUN
SU
IPF
OL
FU
SE
Data
reception
(+)
(-)
5
VCC
(+)
(-)
5V
Sink logic
Earth (Ground)
N/-
P/+
Initial value
ON
OFF
42
Safety stop signal
Safety monitor output
Safety monitor output common
So (SO)
SOC
Safety stop input (Channel 1)
Shorting
wire
Safety stop input common
Safety stop input (Channel 2)
S1
S2
PC
SD
SIC
+24
SD
Brake unit
(Option)
Jumper
(Permissible load
current 100mA)
connector 1 connector 2
connector 3
24V external power
supply input
Common terminal
24VDC power supply
(Common for external power supply transistor)
Forward rotation start
Reverse rotation start
Start self-holding selection
Middle speed
High speed
Low speed
Jog operation
Second function selection
Reset
Terminal 4 input selection
Control input signals
(No voltage input allowed)
Multi-speed
selection
Contact input common
Main circuit
Control circuit
PU
connector
USB A
connector
USB
mini B
connector
Voltage/current
input switch
selectable
Terminating
resistor
Initial value
Initial value
Output stop
RDA
RDI
Converter
unit
RSO
SE
N/-
P/+
IPF
RDB
FAN
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
OH
RES
SD
PC
+24
C1
B1
A1
24V
24V
Output shutoff
circuit
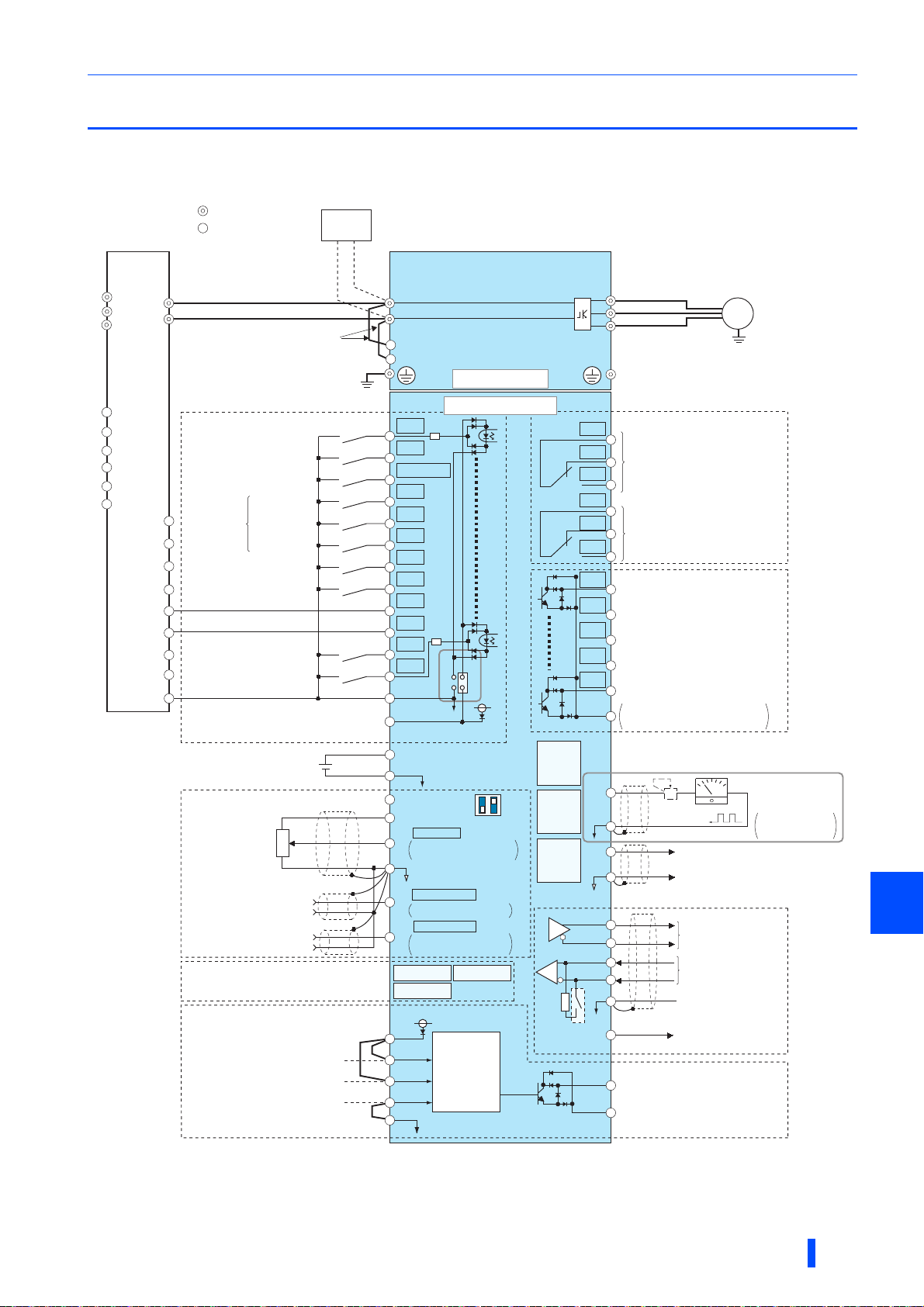
2.4 Terminal connection diagrams
FM type
Terminal connection diagrams
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
2
25
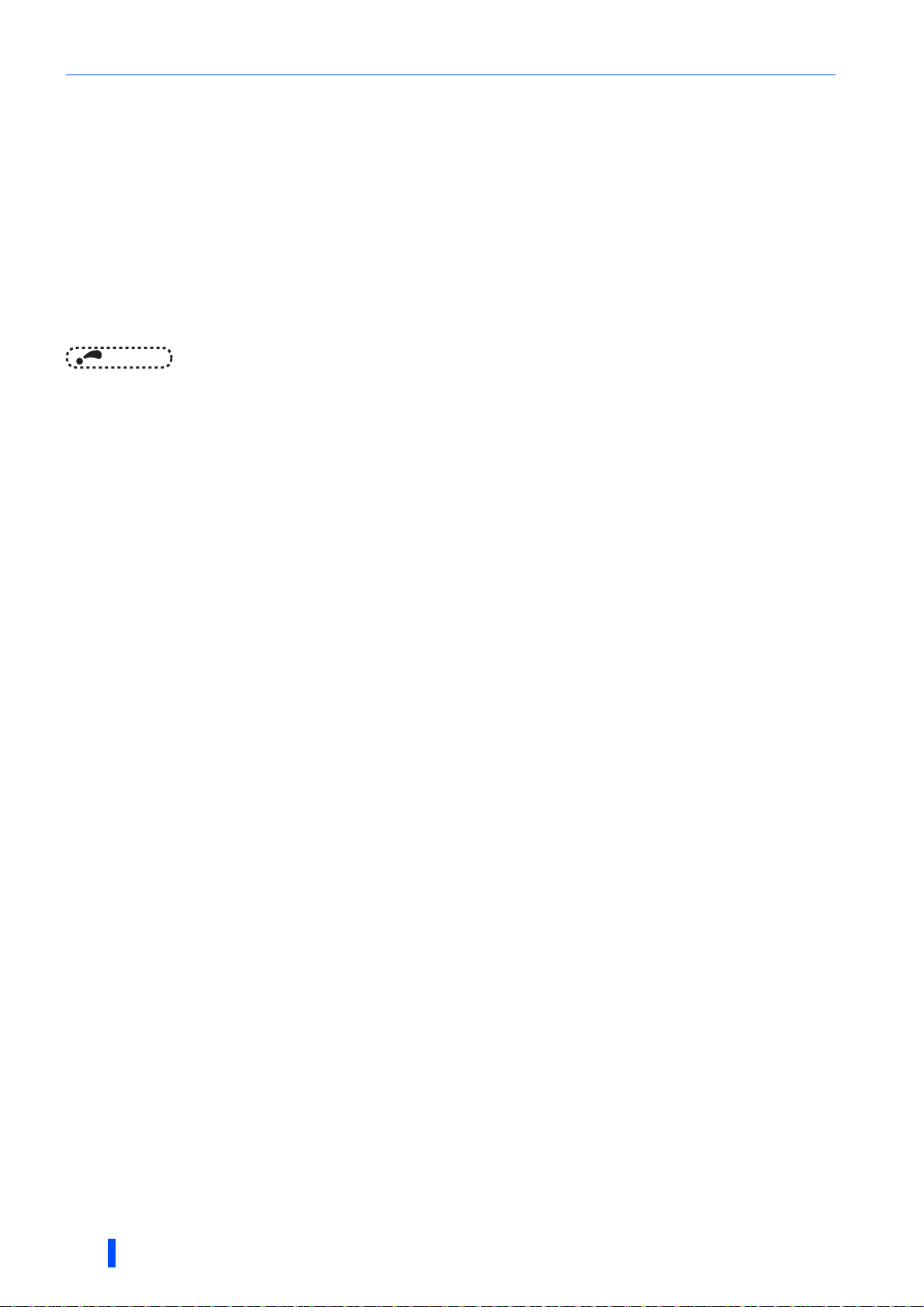
Terminal connection diagrams
NOTE
&&A jumper is installed across terminal R1/L11 and terminal P/+, and across terminal S1/L21 and terminal N/-. When using separate power
supply for the control circuit, remove the jumpers.
The function of these terminals can be changed with the input terminal assignment (Pr.178 to Pr.189).
Terminal JOG is also used as the pulse train input terminal. Use Pr.291 to choose JOG or pulse.
The X10 signal (NC contact input specification) is assigned to the terminal MRS in the initial setting. Set Pr.599 = "0" to change the input
specification of the X10 signal to NO contact.
No function is assigned in the initial setting. Use Pr.186 for function assignment.
Terminal input specifications can be changed by analog input specification switchover (Pr.73, Pr.267). To input a voltage (0 to 5 V/0 to 10 V), set
the voltage/current input switch OFF. To input a current (4 to 20 mA), set the voltage/current input switch ON. Terminals 10 and 2 are also used
as a PTC input terminal (Pr.561).
It is recommended to use 2 W 1 k when the frequency setting signal is changed frequently.
The function of these terminals can be changed with the output terminal assignment (Pr.195, Pr.196).
The function of these terminals can be changed with the output terminal assignment (Pr.190 to Pr.194).
No function is assigned in the initial setting. Use Pr.192 for function assignment.
Terminal FM can be used to output pulse trains as open collector output by setting Pr.291.
Not required when calibrating the scale with the operation panel.
• To prevent a malfunction due to noise, keep the signal cables 10 cm or more away from the power cables. Also, keep the
cables of the main circuit for input and output separated.
• After wiring, wire offcuts must not be left in the inverter.
Wire offcuts can cause an alarm, failure or malfunction. Always keep the inverter clean.
When drilling mounting holes in an enclosure etc., take caution not to allow chips and other foreign matter to enter the
inverter.
• Set the voltage/current input switch correctly. Incorrect setting may cause a fault, failure or malfunction.
26
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
R1/L11
S1/L21
PC
Frequency setting signals (Analog)
10E(+10V)
10(+5V)
2
(Analog common)
2
3
1
Auxiliary
input
Terminal 4 input
(Current input)
1
4
Frequency setting
potentiometer
1/2W1kΩ
Running
Up to frequency
Overload
Frequency detection
Open collector output common
Sink/source common
Motor
Relay output 1
(Fault output)
C1
B1
A1
U
V
W
Earth
(Ground)
0 to ±5VDC selectable
0 to ±10VDC
Open collector output
Main circuit terminal
Control circuit terminal
0 to 5VDC
0 to 10VDC
C2
B2
A2
Relay output 2
Relay output
M
0 to 20mADC
0 to 5VDC
0 to 10VDC
selectable
4 to 20mADC
TXD+
TXD-
RXD+
RXD-
GND
(SG)
Data
transmission
GND
RS-485 terminals
SINK
SOURCE
Connector for plug-in option connection
STF
STR
STP(STOP)
RH
RM
RL
JOG
RT
MRS
X10
RES
AU
CS
SD
RUN
SU
IPF
OL
FU
SE
Data
reception
(+)
(-)
5
VCC
(+)
(-)
5V
Sourse logic
Earth (Ground)
N/-
P/+
Initial value
ON
OFF
42
Safety stop signal
Safety monitor output
Safety monitor output common
So (SO)
SOC
Safety stop input (Channel 1)
Shorting
wire
Safety stop input common
Safety stop input (Channel 2)
S1
S2
PC
SD
SIC
+24
SD
Brake unit
(Option)
Jumper
(Permissible load
current 100mA)
connector 1 connector 2
connector 3
24V external power
supply input
Common terminal
24VDC power supply
Forward rotation start
Reverse rotation start
Start self-holding selection
Middle speed
High speed
Low speed
Jog operation
Second function selection
Reset
Terminal 4 input selection
Control input signals
(No voltage input allowed)
Multi-speed
selection
Contact input common
Main circuit
Control circuit
PU
connector
USB A
connector
USB
mini B
connector
Voltage/current
input switch
selectable
Terminating
resistor
Initial value
Initial value
Output stop
24V
24V
Output shutoff
circuit
Common for external
power supply transistor
(-)
(+)
Analog signal output
(0 to ±10VDC)
(-)
(+)
Analog current output
(0 to 20mADC)
AM
5
F/C
(CA)
RDA
RDI
Converter
unit
RSO
SE
N/-
P/+
IPF
RDB
FAN
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
OH
RES
SD
PC
+24
C1
B1
A1
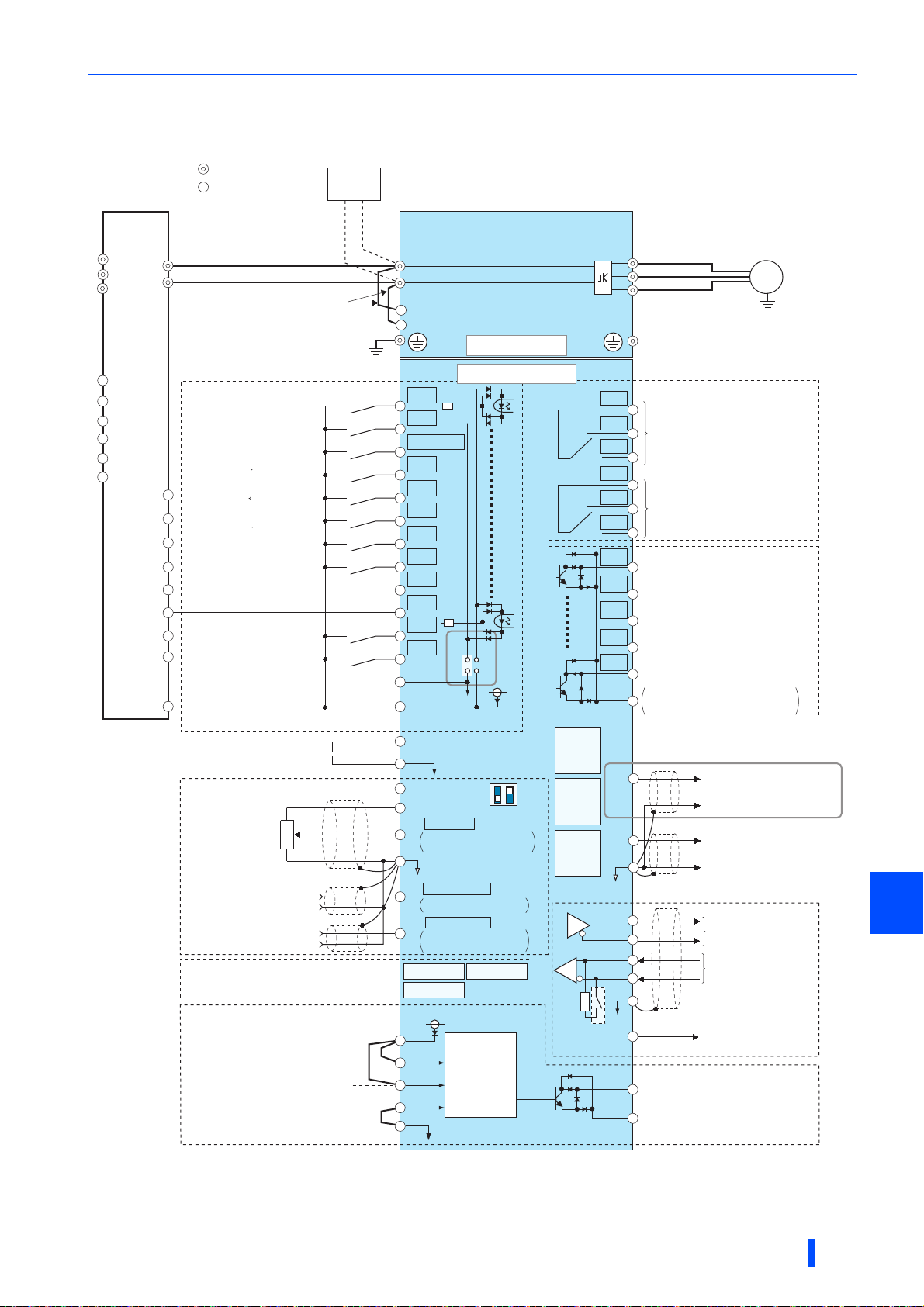
CA type
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
Terminal connection diagrams
2
27
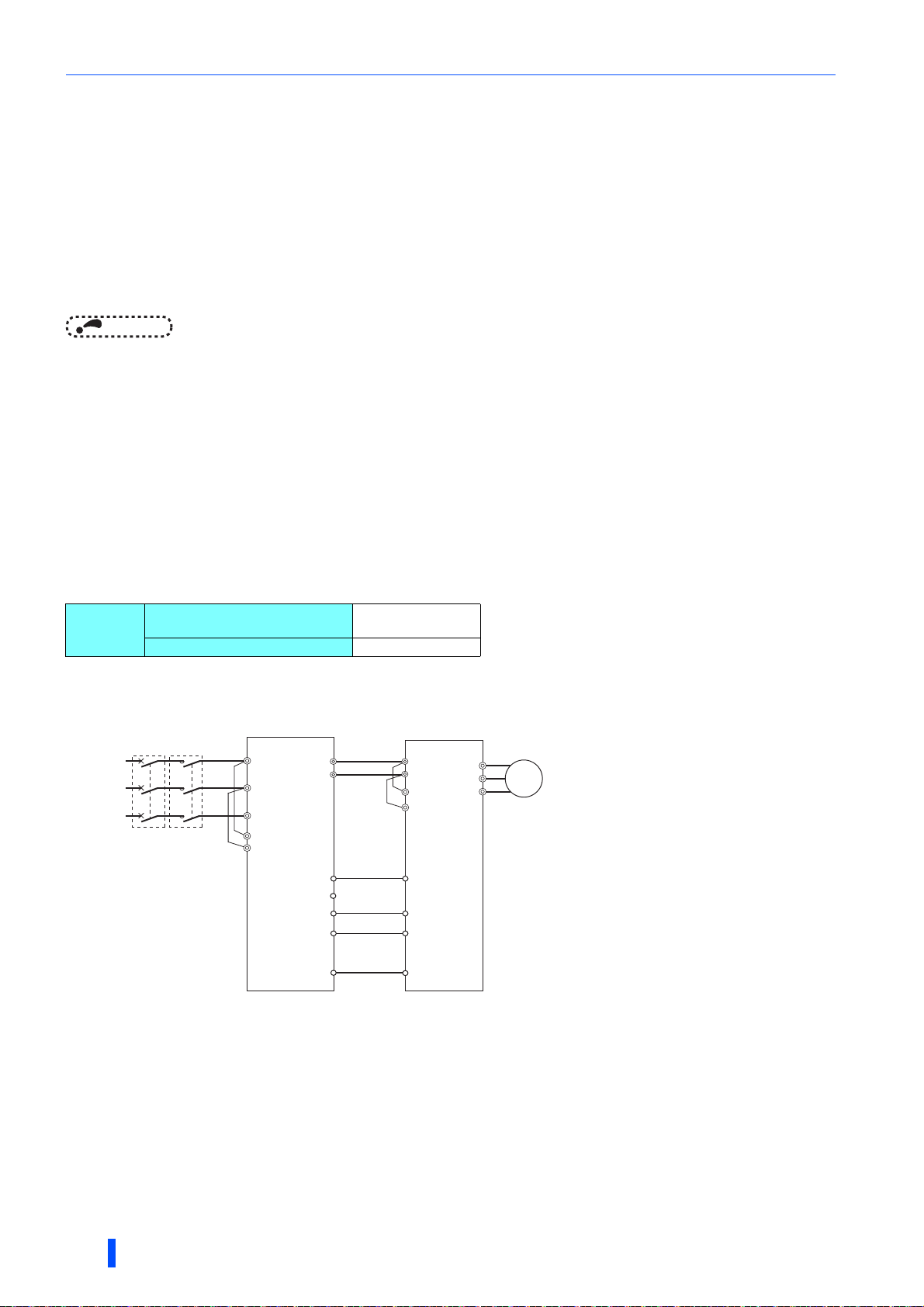
Terminal connection diagrams
NOTE
Inverter
Converter unit
(FR-CC2)
M
R1/L11
S1/L21
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
Power
supply
MCCB
MC
U
V
W
R1/L11
S1/L21
P/+P/+
N/-
N/-
X11
RES
SD
IPF
RSO
SE
MRS(X10)
∗2
RDA
∗4
∗4
∗1
∗3
RDB
&&A jumper is installed across terminal R1/L11 and terminal P/+, and across terminal S1/L21 and terminal N/-. When using separate power
supply for the control circuit, remove the jumpers.
The function of these terminals can be changed with the input terminal assignment (Pr.178 to Pr.189).
Terminal JOG is also used as the pulse train input terminal. Use Pr.291 to choose JOG or pulse.
The X10 signal (NC contact input specification) is assigned to the terminal MRS in the initial setting. Set Pr.599 = "0" to change the input
specification of the X10 signal to NO contact.
No function is assigned in the initial setting. Use Pr.186 for function assignment.
Terminal input specifications can be changed by analog input specification switchover (Pr.73, Pr.267). To input a voltage (0 to 5 V/0 to 10 V), set
the voltage/current input switch OFF. To input a current (4 to 20 mA), set the voltage/current input switch ON. Terminals 10 and 2 are also used
as a PTC input terminal (Pr.561).
It is recommended to use 2 W 1 k when the frequency setting signal is changed frequently.
The function of these terminals can be changed with the output terminal assignment (Pr.195, Pr.196).
The function of these terminals can be changed with the output terminal assignment (Pr.190 to Pr.194).
No function is assigned in the initial setting. Use Pr.192 for function assignment.
• To prevent a malfunction due to noise, keep the signal cables 10 cm or more away from the power cables. Also, keep the
cables of the main circuit for input and output separated.
• After wiring, wire offcuts must not be left in the inverter.
Wire offcuts can cause an alarm, failure or malfunction. Always keep the inverter clean.
When drilling mounting holes in an enclosure etc., take caution not to allow chips and other foreign matter to enter the
inverter.
• Set the voltage/current input switch correctly. Incorrect setting may cause a fault, failure or malfunction.
Connection between the converter unit and the inverter
Perform wiring so that the commands sent from the converter unit are transmitted to the inverter without fail. Incorrect
connection may damage the converter unit and the inverter.
For the wiring length, refer to the table below.
Total wiring
length
Across the terminals P and P and
the terminals N and N
Other control signal cables 30 m or lower
50 m or lower
For the cable gauge of the cable across the main circuit terminals P/+ and N/- (P and P, N and N), refer to page 31.
28
Do not install an MCCB across the terminals P/+ and N/- (across terminals P and P/+ or across N and N/-). Connecting the opposite polarity of
For the terminal used for the X10 signal input, set "10" in any of Pr.178 to Pr.189 (input terminal function selection) to assign the function.
For the terminal used for the X11 signal input, set "11" in any of Pr.178 to Pr.189 (input terminal function selection) to assign the function. For
Always connect the terminal RDA of the converter unit and the terminal MRS (X10) of the inverter, and the terminal SE of the converter unit and
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
terminals N/- and P/+ will damage the inverter.
(The X10 signal is assigned to the terminal MRS in the initial setting.)
For the X10 signal, NC contact input specification is selected in the initial setting. Set Pr.599 = "0" to change the input specification to NO
contact.
RS-485 or any other communication where the start command is only transmitted once, use the X11 signal to save the operation mode at the
time of an instantaneous power failure.
the terminal SD (sink logic) of the inverter. Not connecting these terminals may damage the converter unit.

Main circuit terminals
2.5 Main circuit terminals
2.5.1 Details on the main circuit terminals of the
inverter
Terminal
symbol
U, V, W Inverter output Connect these terminals to a three-phase squirrel cage motor or a PM motor. -
R1/L11,
S1/L21
P/+, N/- Converter unit connection
Terminal name Terminal function description
Connected to the terminals P/+ and N/-. To retain the fault display and fault
output, or to use the converter unit (FR-CC2), remove the jumpers installed
Power supply for the control
circuit
Earth (ground)
across terminals R1/L11 and S1/L21, and supply external power to these
terminals.
The power capacity necessary when separate power is supplied from
terminals R1/L11 and S1/L21 is 80 VA.
Connect the converter unit (FR-CC2), brake unit (FR-BU2), or high power
factor converter (FR-HC2).
For earthing (grounding) the inverter chassis. Be sure to earth (ground) the
inverter.
2.5.2 Details on the main circuit terminals of the
converter unit (FR-CC2)
Terminal
symbol
R/L1,
S/L2,
T/L3
R1/L11,
S1/L21
P/+, N/- Inverter connection Connect to terminals P/+ and N/- of the inverter. 25
Terminal name Terminal function description
Connect these terminals to the commercial power supply. (When the FR-CC2
AC power input
Power supply for the control
circuit
Earth (ground)
converter is connected to the12-phase rectifier power transformer, refer to
the Instruction Manual of the FR-CC2.)
Connected to the AC power supply terminals R/L1 and S/L2. To retain the
fault display and fault output, remove the jumpers across terminals R/L1 and
R1/L11 and across S/L2 and S1/L21, and supply external power to these
terminals.
The power capacity necessary when separate power is supplied from R1/L11
and S1/L21 is 80 VA.
For earthing (grounding) the converter unit chassis. Be sure to earth (ground)
the converter.
Refer
to page
44
25, 51
33
Refer
to page
-
44
33
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
2
29
 Loading...
Loading...