Page 1

MITEL – SIPCoE
Technical
Configuration Notes
Configure the MCD 6.0 for use
with the Commend SIP
Doorphone
SIP CoE 13-4940-00251
Page 2

NOTICE
The information contained in this document is believed to be accurate in all respects but
is not warranted by Mitel Networks™ Corporation (MITEL
®
). The information is subject to
change without notice and should not be construed in any way as a commitment by Mitel
or any of its affiliates or subsidiaries. Mitel and its affiliates and subsidiaries assume no
responsibility for any errors or omissions in this document. Revisions of this document or
new editions of it may be issued to incorporate such changes.
No part of this document can be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means electronic or mechanical - for any purpose without written permission from Mitel Networks
Corporation.
TRADEMARKS
Mitel is a trademark of Mitel Networks Corporation.
Windows and Microsoft are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other product names mentioned in this document may be trademarks of their respective
companies and are hereby ack nowledge d.
Mitel Technical Configuration Notes – Configure the MCD for use with the Commend SIP
Doorphone
February 2012, 13-4940-00251
®,™ Trademark of Mitel Networks Corporation
© Copyright 2013, Mitel Networks Corporation
All rights reserved
ii
Page 3

Table of Contents
OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................... 1
Interop History.................................................................................................................... 1
Interop Status .................................................................................................................... 1
Software & Hardware Setup ............................................................................................... 1
Tested Features ................................................................................................................. 2
Resiliency .......................................................................................................................... 3
Device Limitations .............................................................................................................. 4
Network Topology .............................................................................................................. 5
CONFIGURATION NOTES ....................................................................................... 6
3300 ICP Configuration Notes ............................................................................................ 6
Network Requirements .................................................................................................................... 6
Assumptions for the 3300 ICP Programming .................................................................................. 6
Licensing and Option Select ion – SIP Licensing ............................................................................ 7
Multiline IP Set Configuration .......................................................................................................... 8
Class of Service Assignment .......................................................................................................... 9
SIP Device Capabilities ................................................................................................................. 10
Station Attributes ........................................................................................................................... 12
COMMEND DOORPHONE CONFI GURATION NOTES ......................................... 13
Accessing Commend Doorphone ..................................................................................... 13
Mitel Resiliency Configurations ..................................................................................................... 17
iii
Page 4

Page 5

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Overview
This document provides a reference to Mitel Authorized Solutions Providers for
configuring the Mitel 3300 ICP to host the Commend SIP Doorphone. The different
devices can be configured in various configurations depending on your VoIP solution.
This document covers a basic setup with required option setup.
Interop History
Version Date Reason
1
February 27, 2012 Interop with Mitel 3300 12.0.0.49 and Commend SIP Doorphone
Interop Sta tus
The Interop of the Commend SIP Doorphone has been given a Certification status. This
device will be included in the SIP CoE Reference Guide. The status the Commend SIP
doorphone achieved is:
The most common certification which means the device/service has
been tested and/or validated by the Mitel SIP CoE team. Product
support will provide all necessary support related to the interop, but
issues unique or specific to the 3rd party will be referred to the 3rd party
as appropriate.
Software & Hardware Setup
This was the test setup to generate a basic SIP call between Commend SIP door phone
and the 3300 ICP.
Manufacturer Variant Software Version
Mitel 3300 ICP – Mxe Platform 12.0.0.49
Mitel MBG – Teleworker V7.1.31.0
Mitel 5330 SIP Sets SIP (05.02.00.15)
Mitel 5320 IP Sets Minet (05.02.00.15)
Commend WS800P SIP Doorphone
GE Wireline Analog Set n/a
Firmware: 3.0 Build: 259
Page 6
13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
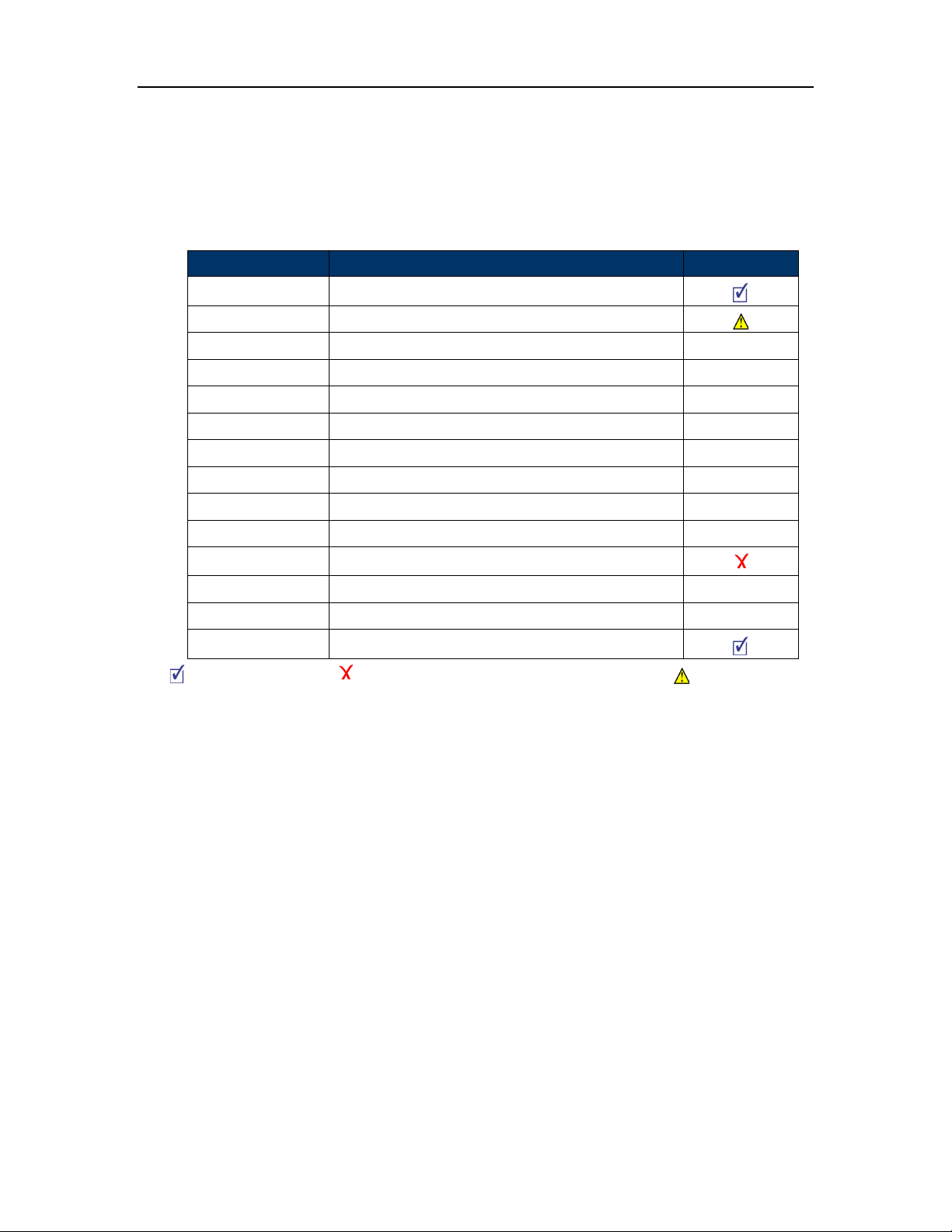
Tested Features
This is an overview of the features tested during the Interop test cycle and not a detailed
view of the test cases. Please see the SIP Line Side Interoperability Test Pans for
detailed test cases.
Feature Feature Description Issues
Basic Call Making and receiving a call
DTMF Signal Sending DTMF after call setup (i.e. mailbox password)
Call Hold Putting a call on hold N/S
Music-on-Hold The sounds played to other party which is held N/S
Call Transfer Transferring a call to another destination N/S
Call Forward Forwarding a call to another destination N/S
Conference Conferencing multiple calls together N/S
Redial Last Number Redial N/S
MWI Message Waiting Indication N/S
Dynamic Extension Personal Ring Group configuration N/S
Resiliency Basic calls through a Secondary SIP proxy
T.38 Fax Fax Messages N/S
Video Video Capabilities N/S
Teleworker Mitel remote connectivity with Teleworker
- No issues found - Issues found, cannot recommend to use - Issues found
2
Page 7

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Resiliency
The following table lists the scenarios of resilience supported by this device when
connected to the MCD 6.0 on the 3300 ICP.
Device Scenario 1 Scenario 2 Scenario 3 Scenario 4
Commend
doorphone
Not Supported Not Supported Not Supported
- No issues found - Issues found, cannot recommend use - Issues found
Note: Refer to list of device limitations and known issues later in the document for
recommendations.
The various scenarios are described below. The scenario names are a convenience for
understanding this section of the configuration guide.
Scenario 1: Resiliency is achieved by utilizing the ability of DNS servers to provide
multiple IP addresses against a single FQDN. This is generally achieved by using DNS
SRV or A records. This scenario requires nothing from a SIP Endpoint except that it
supports standard DNS behavior.
Scenario 2: The device has inherent knowledge of the primary and secondary 3300 ICPs
and will switch between them if a SIP request (REGISTER, INVITE, or SUBSCRIBE)
times out. Behavior will be characterized based on whether the device returns to primary
ICP and when this occurs. This scenario has some dependency on user action in order
to detect a failure, especially if configured with a long registration expiry time, so the
chance of a user experiencing a long delay making a call goes up.
Scenario 3: The behavior of the device is the same as that of scenario 2, except that the
device will “ping" the currently active server with an OPTIONS request. If the OPTIONS
request times out, the device will switch to the alternate server for all future requests.
The intent of this scenario is to provide much faster failure detection by the device. This
will allow devices to failover to their alternate ICP much more quickly, and much more
unnoticeably. (If the device can detect a failure of the primary ICP, and can failover
immediately, the chance that the user even notices a lack of service falls dramatically.)
Scenario 4: The device will support a new SIP header designed specifically for
resiliency. The P-Alternate-Server header must be included in a 200 OK or 301 Mov ed
Permanently response. This header will include data that designates the potential
servers and which server the UA must use.
Page 8

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Recommendation:
Device Limitations
This is a list of problems or not supported features when the Commend SIP Doorphone is
connected to the Mitel 3300 ICP.
Feature Problem Description
De-registration
All Call Features
DTMF
Codec Support
Resiliency
Miscellaneous
Not supported. The Commend SIP Doorphone has no means on the
client to de-register.
Recommendation: Contact your local Commend reseller for further
details
The Commend SIP Doorphone has only a single call button to initiate
outbound calls to a pre-provisioned DN, and therefore cannot support
call features.
Recommendation: Contact your local Commend reseller for further
details
For In-Band DTMF on SIP to SIP calls, you could hear the played
tones on the Commend SIP Doorphone, but the tones would not
activate the door relay.
use RFC2833
The Commend 8028 does not support G729
Recommendation: Use G711 or G722 codec.
Not supported – The Commend Doorphone does not switch to
secondary MCD when the primary MCD is not available.
Recommendation: Contact your local Commend reseller for further
details
The Commend SIP Doorphone dos not support non-preferred
Provisionial Response (PRACK or no PRACK) and did not maintain
long calls through Session Timer resets (neither UPDATE nor reINVITE).
4
Recommendation: Contact your local Commend reseller for further
details
Page 9

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Network Topology
This diagram shows how the testing network is configured for reference.
Page 10

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Configuration Notes
This section is a description of how the SIP Interop was configured. These notes should
give a guideline as to how a device can be configured in a customer environment and
how the Commend doorphone was configured in our test environment.
We recommend that the Commend doorphone is configured in Device Based mode. You
will configure the Device Based mode in the SIP Device Capabilities Form as described
in this section.
Disclaimer: Although Mitel has attempted to setup the interop testing facility as
closely as possible to a customer premise environment, implementation setup
could be different onsite. YOU MUST EXER CISE YOUR OWN DUE DILIGENCE IN
REVIEWING, planning, implementing, and testing a customer configuration.
3300 ICP Configuration Notes
The following steps show how to program a 3300 ICP to connect with the Commend
doorphone.
Network Requirements
• There must be adequate bandwidth to support the voice over IP. As a guide, the
Ethernet bandwidth is approx 85 Kb/s per G.711 voice session and 29 Kb/s per
G.729 voice session (assumes 20ms packetization). As an example, for 20
simultaneous SIP sessions, the Ethernet bandwidth consumption will be approx 1.7
Mb/s for G.711 and 0.6Mb/s. Almost all Enterprise LAN networks can support this
level of traffic without any special engineering. Please refer to the 3300 Engineering
guidelines for further information.
• For high quality voice, the network connectivity must support a voice-quality grade of
service (packet loss <1%, jitter < 30ms, one-way delay < 80ms).
Assumptions for the 3300 ICP Pr og r am ming
• The SIP signaling connection uses UDP on Port 5060.
6
Page 11

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Licensing and Option Selection – SIP Licensing
Ensure that the 3300 ICP is equipped with enough IP Users licenses for the connection
of SIP end points. This can be verified within the License and Option Selection form. See
Figure 1.
Figure 1 – License and Option Selection
Page 12

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Multiline IP Set Configuration
On the Mitel 3300 ICP, a SIP device can be programmed either in the User Configuration
form or the Multiline IP Set Configuration form and are programmed as a “Generic SIP
Phone”. Enterprise Manager can also be used to provision where this application is
installed.
The User PIN is the SIP authentication password and the Number is the Directory
Number (DN is a telephone number). The Number and User PIN must match the
information in the Commend doorphone’s settings. All other field names should be
programmed according to the site requirements or left at default. See an example in
Figure 2.
8
Figure 2 – Multiline IP Set Configuration
Page 13

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Class of Service Assignment
The Class of Service Options form is used to create or edit the Class of Service and
specify its options. Classes of Service, identified by Class of Service numbers, are
referenced by the Station Attributes form for the SIP device.
Many different options may be required for your site deployment, but the options below
are required to be changed from the default for a Generic SIP De vice to wor k with the
3300 ICP. (See example in Figure 3)
Under General tab:
Navigate to section Campon and ensure:
• Auto Campon Timer is blanked (no value)
Navigate to section HCI and ensure:
• HCI/CTI/TAPI Call Control Allowed set to Yes
• HCI/CTI/TAPI Monitor Allowed set to Yes
Navigate to section Trunk and ensure:
• Public Network Access via DPNSS set to Yes
Figure 3 – Class of Service
Page 14

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
SIP Device Capabilities
This form provides configuration options that can be applied to various types of SIP
devices. The association between the SIP device and the form is similar to how the Class
of Service options work. The SIP Device Capabilities number provides a SIP profile that
can be applied to particular SIP devices to allow for alternate capabilities as
recommended through the Mitel interop process.
In the SIP Device Capabilities form, program a SIP Device Capabilities Number for the
Commend doorphone. Ensure that “Enable Dig it Col le c tion in Bus y Or Alerti ng State” is
set to ‘Yes’.
10
Figure 4 – SIP Device Capabilities - Basic
Page 15

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Settings for the Timers are important part for the SIP devices configuration.
Set Registration Period, Subscription Period and Session Timer according to the site
requirements. Ensure that the time periods for Registration and Subscription are
matching those configured in Commend doorphone. See an example in Figure 5.
The settings on all other tabs of SIP Device Capabilities form remain unchanged, at their
default values.
Figure 5 – SIP Device Capabilities – Timers
Page 16

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Station Attributes
Use the Station Attributes form to assign the previously configured Class of Service and
SIP Device Capability number to each of the Commend doorphones in the 3300 ICP.
This form utilizes Range Programming.
Select the Commend doorphone device number then select Change. Enter the previously
configured SIP Device Capability number and Class of Service for Day, Night 1 & Night 2.
See an example in Figure 6 below.
12
Figure 6 – Station Attributes
Page 17

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Commend doorphone Configuration Notes
The following steps show how to program the Commend doorphone to interconnect with the
3300ICP.
The configuration settings below are the main reference points and by any means could not be
considered as the comprehensive configuration instructions.
We strongly recommend contacting the phones’ manufacturer Commend International GmbH
website http://www.commend.com/sip for more detailed instructions and manuals.
Accessing Commend Doorphone
In our test environment, we configured Commend doorphone through the web interface.
The SIP stations are delivered ex works with a standard IP address, via which the web interface
of the station can be accessed:
IP address 192.168.1.200
Subnet mask 255.255.255.0
If the station can not be used in the local network (LAN) with this IP address, then the following
procedure is recommended:
Establish connection between PC and SIP station via a hub (or switch) or via a direct
connection cable.
The PC must be in the same subnet as the SIP station.
This means, an appropriate IP address of that subnet range (e.g. 192.168.1.199) has to be
allocated to the PC temporar il y.
Note: When connecting the SIP station with this IP-address to the local network (LAN), it is
essential to make sure that this IP-address does not already exist in the network! Take a note of
IP address assigned to the phone, e.g. 192.168.101.131.
After entering the IP address, a login dialogue appears where following data has to be entered:
User name factory default: admin
Password factor y default: commend
Page 18

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
14
Figure 7 – Commend SIP Doorphone
Page 19

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Figure 8 – Initial Configuration
Page 20

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
16
Figure 9 – Initial Configuration
Page 21

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
Mitel Resiliency Configurations
Resiliency behavior tested as in Scen ario 1, configure the parameter for Domain server as
shown in Figure 11.
In this example,
sipint4sipint2 is the FQDN name of the primary 192.168.101.11 SIP Pr oxy (3300 ICP) using DNS
SRV or A records to get the secondary 192.168.101.20 (i.e. Alternati ve) SIP pr oxy (3300 ICP).
NOTE: Before configuring this parameter, make sure that DNS server correctly resolves the
names of the SIP proxy to IP addresses! The order, in which the SIP proxies IP addresses are
resolved, is also important! To check it, use the command in command shell:
nslookup sipint4sipint2.sipcoe.mitel.com
Server: ad-sip-interop.sipcoe.mitel.com
Address: 192.168.101.200
Name: sipint4sipint2.sipcoe.mitel.com
Addresses: 192.168.101.11, 192.168.101.20
In this example, 192.168.101.11 is the IP address of primary SIP Proxy (3300 ICP) and
192.168.101.20 is the IP address of the secondary (i.e. Alternative) SIP proxy (3300 ICP).
NOTE: Although FQDNs could be set for the primary and secondary PBXs’ addresses, we
recommend using of IP addresses. The site’s DNS server can be inaccessible in case of the
network failure. That’s why, for better reliability, the use of IP addresses is more preferable.
Do not forget to click Apply to submit the settings to Commend doorphone to force the phone to
reset and load new settings.
Page 22

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
18
Figure 10 – Scenario 1 resiliency
Page 23

13-4940-00251 Commend SIP Doorphone
 Loading...
Loading...