Page 1

Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live
Migration
White Paper
Published: August 09
This is a preliminary document and may be changed substantially prior to final commercial release of the software described herein.
The information contained in this document represents the current view of Microsoft Corporation on the issues discussed as of the date of publication. Because
Microsoft must respond to changing market conditions, it should not be interpreted to be a commitment on the part of Microsoft, and Microsoft cannot guarantee
the accuracy of any information presented after the date of publication.
This white paper is for informational purposes only. MICROSOFT MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, IN THIS
DOCUMENT.
Complying with all applicable copyright laws is the responsibility of the user. Without limiting the rights under copyright, no part of this document may be
reproduced, stored in, or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or
otherwise), or for any purpose, without the express written permission of Microsoft Corporation.
Microsoft may have patents, patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights covering subject matter in this document. Except as
expressly provided in any written license agreement from Microsoft, the furnishing of this document does not give you any license to these patents, trademarks,
copyrights, or other intellectual property.
© 2009 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
The example companies, organizations, products, domain names, e-mail addresses, logos, people, places, and events depicted herein are fictitious. No
association with any real company, organization, product, domain name, e-mail address, logo, person, place, or event is intended or should be inferred.
Microsoft, SharePoint, Windows Server, and the Windows logo are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or
other countries.
All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
Page 2
Table of Contents
Business Value of Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ and Live Migration ................................................. 3
Overview of Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Features.......................................................................... 4
Dynamic VM storage ............................................................................................................................. 4
Enhanced Processor Support ................................................................................................................ 4
Enhanced Networking Support ............................................................................................................. 5
Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) .............................................................................................................. 5
Live Migration ....................................................................................................................................... 5
Live Migration Overview ........................................................................................................................... 5
Live Migration Compared to Quick Migration ...................................................................................... 6
Live Migration Architecture ...................................................................................................................... 6
Requirements ........................................................................................................................................ 7
Live Migration Scenarios ......................................................................................................................... 13
Physical Computer Maintenance ........................................................................................................ 13
Dynamic Datacenter ........................................................................................................................... 15
Green IT ............................................................................................................................................... 16
Deploying Live Migration ........................................................................................................................ 17
Managing Live Migration ........................................................................................................................ 18
Summary ..................................................................................................................................................... 18
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #2
Page 3
Business Value of Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™
For More Information:
http://www.microsoft.com/windowsserver2008/en/us/hyperv-R2.aspx
“We expect to consolidate an
additional 75 servers using
Hyper-V, which will lead to a
cost savings of more than
$325,000 annually. By the
time we hit our fifth virtual
machine, we’ve usually paid
for the host. Long term, we
will be able to reduce our total
data center holdings by 75
percent—from nearly 400
servers to fewer than 100
servers.”
-Robert McShinsky, Senior
Systems Administrator
Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical
Center
and Live Migration
Today’s IT departments are under increasing pressure to manage and support expanding computer
resources while at the same time reducing costs. Server virtualization, which lets multiple operating
systems run concurrently on the same physical server, has become a broadly accepted method to meet
these requirements. By converting under-utilized physical
servers into virtual machines that run on a single physical
server, organizations can reduce space, power and hardware
costs in the data center. Because virtual machines are
generally much faster to recover in a disaster than physical
computers are, virtualization also increases server uptime
and reliability.
To help customers adopt virtualization easily, Microsoft has
developed a next-generation server virtualization solution as
a feature of Microsoft® Windows Server® 2008 R2. HyperVTM is a virtualization platform that out of the box provides
reliable and scalable platform capabilities along with a single
set of integrated management tools to manage both
physical and virtual resources.
Windows Server 2008 R2 adds powerful enhancements to
Hyper-V including increased availability, improved
management, and simplified deployments. The new version
of Hyper-V also includes an exciting feature called Live
Migration – the ability to move virtual servers across
physical hosts in the datacenter with no perceived downtime for users, so IT can restructure the datacenter as
business needs demand without stopping important work streams.
Live Migration provides the highest uptime for virtual machines and enables a dynamic IT infrastructure.
The feature facilitates hardware maintenance and upgrades, manual failover, and the consolidation of
workloads on fewer servers. With this level of automation in the data center, businesses save on IT costs
related to labor, power, cooling and maintenance.
This whitepaper details Live Migration architecture, scenarios, deployment and management. It also
highlights other valuable new features available in Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V that help
businesses maximize resources and reduce costs. These features include Dynamic VM Storage,
Enhanced Processor Support, Enhanced Networking Support and Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV).
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #3
Page 4

Overview of Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™
Features
Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ builds on the architecture and feature set of Windows Server®
2008 Hyper-V™ by adding multiple new features that significantly enhance product flexibility. The
adoption of virtualization in the enterprise has led to increased flexibility in deployment and life cycle
management of applications. IT professionals have deployed and used virtualization to consolidate
workloads reducing server sprawl. Additionally they can deploy virtualization with clustering
technologies to provide a robust IT infrastructure with high availability and disaster recovery. Even so,
customers are looking for higher flexibility. Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ provides greater
flexibility with live migration. Live migration is integrated with Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ and
Microsoft® Hyper-V™ Server 2008 R2. With Hyper-V™ live migration, you can move running VMs from
one Hyper-V™ physical host to another, without any disruption or perceived loss of service. IT
professionals are increasingly looking to use live migration to create a dynamic and flexible IT
environment which can respond to emerging business needs. Live migration provides the core
technology required for dynamic load balancing, virtual machine (VM) placement, high availability for
virtualized workloads during physical computer maintenance, and reduced datacenter power
consumption.
Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ adds valuable new features to those provided by the first version
of Hyper-V™. For example, by using live migration in Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™, running VMs
can be migrated from one physical computer to another. Storage can be added or removed from a VM
while it is running. In addition, Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ takes better advantage of physical
computer hardware with greater processor support and deeper support for physical computer
hardware. This paper provides an overview of the new features in Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™
and detailed information on live migration.
Dynamic VM storage
Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ supports hot plug-in and hot removal of storage. By supporting the
addition or removal of Virtual Hard Drive (VHD) files and pass-through disks while a VM is running,
Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ makes it possible to quickly reconfigure VMs to meet changing
requirements. This feature allows the addition and removal of both VHD files and pass-through disks to
existing SCSI controllers of VMs.
Note: Hot add and removal of storage requires the Hyper-V™ Integration Services supplied with
Windows Server® 2008 R2 to be installed in the guest operating system.
Enhanced Processor Support
Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ supports up to 32 logical processor cores. The increased processor
support makes it possible to run even more demanding workloads on a single physical computer, or
consolidate more workloads to a single physical computer.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #4
Page 5

Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ also supports Second-Level Address Translation (SLAT) and CPU
Core Parking. SLAT uses special CPU functionality available in Intel processors that support Extended
Page tables and AMD processors that support Rapid Virtualization Indexing to carry out some VM
memory management functions that reduce the overhead of translating guest physical address to real
physical addresses. This significantly reduces Hypervisor CPU time and saves memory for each VM,
allowing the physical computer to do more work while utilizing fewer system resources. CPU Core
Parking enables power savings by scheduling VM execution on only some of a server’s CPU cores and
placing the rest in a sleep state.
Enhanced Networking Support
In Windows Server 2008 R2 there are three new networking features that improve the performance of
networking in the virtualization environment. Support for Jumbo frames, previously available in nonvirtual environments, has been extended to be available in VMs. This feature enables virtual machines
to use Jumbo Frames up to 9014 bytes in size if the underlying physical network supports it. Supporting
Jumbo frames reduces the network stack overhead incurred per byte and increases throughput. In
addition, there is also a significant reduction of CPU utilization due to the fewer number of calls from
the network stack to the network driver.
TCP Chimney, which allows the offloading of TCP/IP processing to the network hardware, has also been
extended to work in the virtual world. TCP Chimney improves VM performance by allowing the VM to
offload network processing to hardware, especially with networks over 1 Gigabit. This feature is
especially beneficial for roles involving large amounts of data transfer such as the file server role.
The Virtual Machine Queue (VMQ) feature allows physical computer Network Interface Cards (NICs) to
use DMA to place the contents of packets directly into VM memory, increasing I/O performance.
Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV)
With Windows Server® 2008 R2, Hyper-V™ is able to use CSV storage to simplify and enhance shared
storage usage. CSV enables multiple Windows Servers to access SAN storage with a single consistent
namespace for all volumes on all hosts. Multiple hosts can access the same Logical Unit Number (LUN)
on SAN storage. CSV enables faster live migrations and easier storage management for Hyper-V™ when
used in a cluster configuration. Cluster Shared Volumes is available as part of the Windows Failover
Clustering feature of Windows Server® 2008 R2.
Live Migration
One of the most highly anticipated new features in Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ is live
migration. The remainder of this document describes the live migration feature of Windows Server®
2008 R2 Hyper-V™ in detail, including information on how live migration moves running VMs , describes
several scenarios where live migration is particularly useful, and the requirements for implementing live
migration.
Live Migration Overview
As stated earlier, live migration is integrated with Windows Server 2008® R2 Hyper-V™ and Microsoft®
Hyper-V™ Server 2008 R2. With Hyper-V™ live migration, you can move running VMs from one HyperV™ physical host to another without any disruption of service or perceived downtime.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #5
Page 6

Since Hyper-V™ live migration can move running virtual machines without downtime, it will facilitate
greater flexibility and value:
Provides better agility: Datacenters with multiple Hyper-V™ physical hosts will be able to move
running VMs to the best physical computer for performance, scaling, or optimal consolidation
without impacting users.
Reduces costs and increase productivity: Datacenters with multiple Hyper-V™ physical hosts
will be able to service those systems in a more controlled fashion, scheduling maintenance
during regular business hours. Live migration makes it possible to keep VMs online, even during
maintenance, increasing productivity for both users and server administrators. Datacenters will
be also able to reduce power consumption by dynamically increasing consolidation ratios and
powering off un-used physical hosts during times of lower demand.
Live Migration Compared to Quick Migration
Quick Migration is a feature of both Windows Server® 2008 Hyper-V™ and Windows Server® 2008 R2
Hyper-V™. Live migration and Quick Migration both move running VMs from one Hyper-V™ physical
computer to another, the primary difference is that Quick Migration saves, moves and restores a VM
which results in some downtime. The live migration process uses a different mechanism for moving the
running VM to the new physical computer. This process will be explained in greater detail in the Live
Migration Architecture section of this document. Below is a summary of the live migration process:
1. All VM memory pages are transferred from the source Hyper-V™ physical host to the destination
Hyper-V™ physical host. While this is occurring, any VM modifications to its memory pages are
tracked.
2. ™Pages that were modified while step 1 was occurring are transferred to the destination
physical computer.
3. The storage handle for the VM’s VHD files are moved to the destination physical computer.
4. The destination VM is brought online on the destination Hyper-V™ server.
Live migration produces significantly less downtime for the VM being migrated. This makes live
migrations the preferred migration type when users must have uninterrupted access to the migrating
VM. Because a live migration will complete in less time than the TCP timeout for the migrating VM,
users will not experience any outage for the migrating VM during steps 3 and 4 of the migration.
Note: Windows Server® 2008 Hyper-V™ supports Quick Migration. Windows Server® 2008 R2 Hyper-V™
supports both Quick Migration and live migration.
Live Migration Architecture
Hyper-V™ live migration is designed to move running VMs with no impact on VM availability to users.
By pre-copying the memory of the migrating VM to the destination physical host, live migration
minimizes the amount of transfer time of the VM A live migration is deterministic, meaning that the
administrator, or script, that initiates the live migration can control which computer is the destination
for the live migration. The guest operating system in the migrating VM is unaware that the migration is
happening, so no special configuration for the guest operating system is needed.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #6
Page 7

Requirements
Hyper-V™ live migration has very similar requirements to Hyper-V™ Quick Migration. For organizations
already using quick migration, the shift to using live migration should be simple. The physical hosts that
will participate in live migration must be configured with Microsoft Failover Clustering Services as a
Failover Cluster and must use shared storage. In addition, the physical hosts must use the same
processor type. For example, to use live migration to move a VM from one Hyper-V™ physical host to
another, both physical hosts must use processor(s) from the same manufacturer. It should be noted
that there are no differences in storage requirements between Quick Migration and live migration.
Below is a complete list of the requirements for Hyper-V™ live migration:
Hyper-V™ live migration is supported on the following editions of Windows Server 2008 R2:
o Windows Server 2008 R2 x64 Enterprise Edition
o Windows Server 2008 R2 x64 Datacenter Edition
Live migration is also supported on Microsoft® Hyper-V™ Server 2008 R2.
Microsoft Failover Clustering must be configured on all physical hosts that will use live migration
Failover Clustering supports up to 16 nodes per cluster
The cluster should be configured with a dedicated network for the live migration traffic
Physical host servers must use a processor or processors from the same manufacturer
Physical hosts must be configured on the same TCP/IP subnet
Physical hosts must have access to shared storage
Recommendations and Notes:
A clustered shared volume is recommended for VM storage in a cluster where live migration will
be used.
One live migration can be active between any two cluster nodes at any time. This means that a
cluster will support number_of_nodes/2 simultaneous live migrations. For example, a 16-node
cluster will support 8 simultaneous live migrations with no more than one live migration session
active from every node of the cluster.
A dedicated 1 Gigabit Ethernet connection is recommended for the live migration network
between cluster nodes to transfer the large number of memory pages typical for a virtual
machine.
The cluster configurations that have been validated by vendors can be found through the listings
in the FCCP program under the heading of The Microsoft Support Policy for Windows Server
2008 Failover Clusters at this URL: http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-
US;943984
How Live Migration Works
The live migration process is designed to move a running VM from the source physical host to a
destination physical host as quickly as possible. A live migration is initiated by an administrator through
one of the methods listed below. The speed at which the process completes is partially dependent on
the hardware used for the source and destination physical computers, as well as the network capacity.
There are three methods by which a live migration can be initiated:
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #7
Page 8

Using the Failover Cluster Management console, an administrator can initiate a live migration.
If Virtual Machine Manager is managing physical hosts that are configured to support live
migration, the Virtual Machine Manager administration console can be used to initiate a live
migration.
A WMI or PowerShell script can be used to initiate a live migration.
Any guest operating system supported by Hyper-V™ will work with the live migration process
After a live migration is initiated, the following process occurs:
1. Live migration setup
In the first stage of a live migration (Figure 1 below), the source physical host creates a TCP
connection with the destination physical host. This connection is used to transfer the VM
configuration data to the destination physical host. A skeleton VM is set up on the destination
physical host and memory is allocated to the destination VM.
Figure 1 – Live Migration Setup
2. Memory pages are transferred from the source node to the destination node
In the second stage of a live migration (Figure 2 below), the memory assigned to the migrating
VM is copied over the network to the destination physical host. This memory is referred to as
the working set of the migrating VM. A page of memory is 4 kilobytes in size.
For example, suppose that a VM named NYC-SVR2 which is configured with 1024MB of RAM is
migrating to another Hyper-V™ physical host. The entire 1024MB of RAM assigned to this VM
comprises the working set of NYC-SVR2. The utilized pages within the NYC-SVR2 working set are
copied to the destination Hyper-V™ physical computer.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #8
Page 9

In addition to copying the working set of NYC-SVR2 to the destination physical host, Hyper-V™
on the source physical host monitors the pages in the working set for NYC-SVR2. As memory
pages are modified by NYC-SVR2, they are tracked and marked as being modifed. The list of
modified pages is simply the list of memory pages NYC-SVR2 has modified after the copy of its
working set has begun.
During this phase of the migration, the migrating VM continues to run. Hyper-V™ iterates the
memory copy process several times, each time a smaller number of modified pages will need to
be copied to the destination physical computer.
After the working set is copied to the destination physical host, the next stage of the live
migration begins.
Figure 2 – Memory Pages Transferred
3. C memory pages are transferred
A final memory copy process copies the remaining modified memory pages for NYC-SVR2 to the
destination physical host. The source physical host transfers the register and device state of the
VM to the destination physical host.
During this stage of the live migration, the network bandwidth available between the source and
destination physical hosts is critical to the speed of the live migration. For this reason, 1 Gigabit
Ethernet is recommended. The faster the source physical host can transfer the modified pages
from the migrating VMs working set, the more quickly the live migration will complete.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #9
Page 10
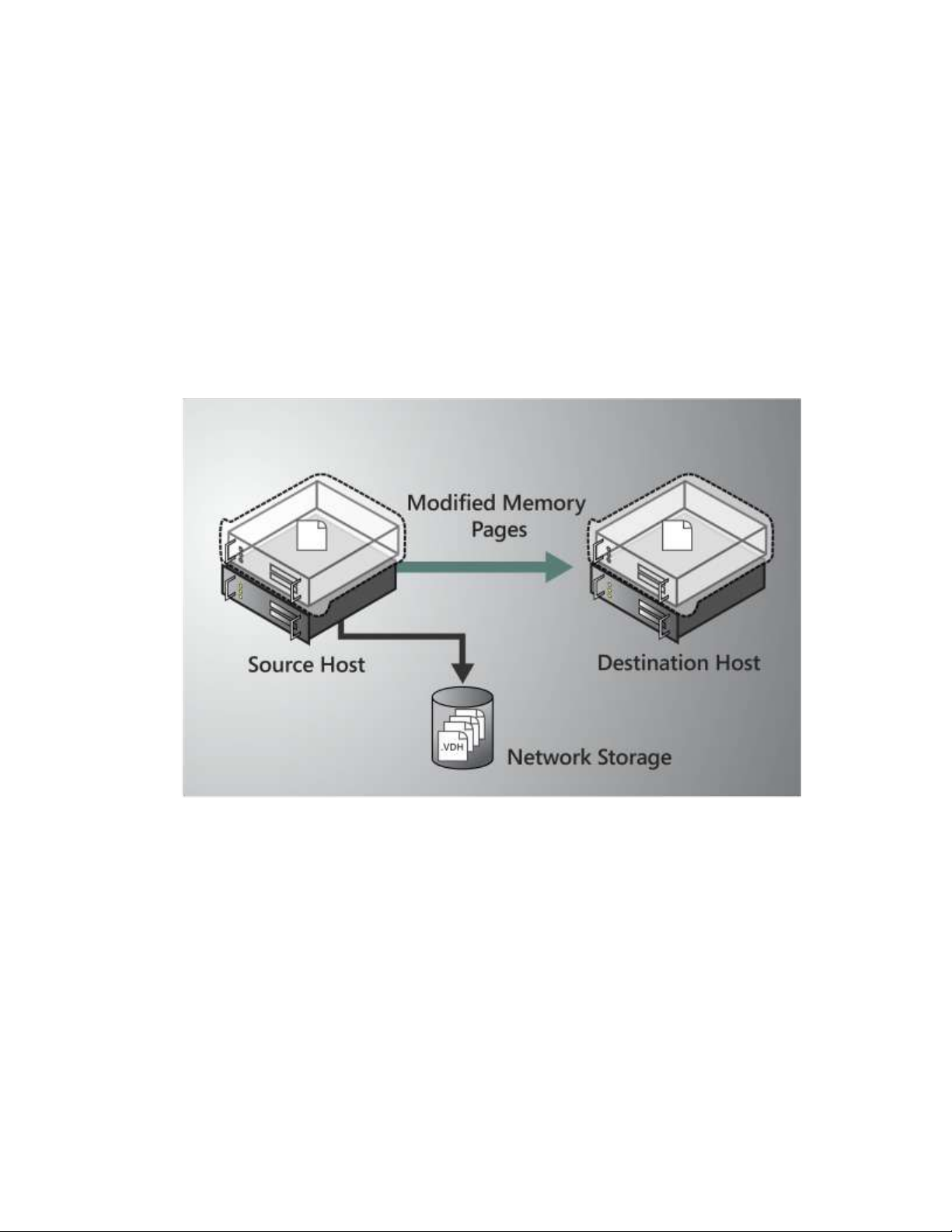
It is important to note that the number of pages to be transferred in this stage is dictated by
how actively the VM is accessing and modifying memory pages. The more modified pages the
longer the VM migration process will be to allow for all pages to be transferred to the
destination physical host.
After the modified memory pages have been completly copied to the destination physical host,
the destination physical host has an up-to-date working set for NYC-SVR2. This means that the
working set for NYC-SVR2 is present on the destination physical host in the exact state it was in
when NYC-SVR2 began the migration process.
Note: The live migration process may be cancelled at any point before this stage of the
migration.
Figure 3 – Modified Pages Transferred
4. Move the storage handle from source to destination
In the fourth stage of a live migration (Figure 4 below), control of the storage associated with
NYC-SVR2, such as any VHD files or pass-through disks, is transferred to the destination physical
host.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #10
Page 11

Figure 4 – Storage Handle Moved
5. The VM is brought online on the destination server
In the fifth stage of a live migration (Figure 5 below), the destination server now has the up-todate working set for NYC-SVR2 as well as access to any storage used by NYC-SVR2. At this point
NYC-SVR2 is resumed.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #11
Page 12

Figure 5 – VM Resumed
6. Network cleanup occurs
In the final stage of a live migration, the migrated VM is running on the destination server. At
this point a message is sent to the physical network switch which causes it to re-learn the MAC
addresses of the migrated VM so that network traffic to and from NYC-SVR2 can use the correct
switch port.
The live migration process will complete in less time than the TCP timeout interval for the VM being
migrated. TCP timeout intervals vary based on network topology and other factors. The following
variables may affect live migration speed:
The number of modified pages on the VM to be migrated: the larger number of modified pages,
the longer the VM will remain in a migrating state
Network available bandwidth between source and destination physical computers
Hardware configuration of source and destination physical computers
Load on source and destination physical hosts
Available bandwidth (network or Fiber Channel) between Hyper-V™ physical hosts and shared
storage
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #12
Page 13

Live Migration Scenarios
Hyper-V™ live migration increases flexibility for many applications and uses of Hyper-V™, but the
following usage scenarios are interesting examples of how live migration provides real-world benefits.
Physical Computer Maintenance
Physical computer security updates, software servicing, and hardware maintenance are very significant
considerations in any server virtualization scenario. Because a single physical host running Hyper-V™
can host multiple VMs, any downtime required to update the physical computer can affect all the VMs
running on that physical computer. Because the security of the VMs running on the physical host is
partially dependent on the security of the physical host’s operating system, keeping physical hosts
updated and secured is especially important.
Hyper-V™ live migration brings two primary benefits to the server maintenance scenario. The ability to
migrate a running VM from one Hyper-V™ physical host to another with no downtime means that VMs
can be migrated away from a Hyper-V™ physical host before it is serviced. After the physical host is
serviced and possibly rebooted, VMs can be migrated back to the physical computer. All of this can
happen with no impact on VM availability. In addition, because physical host maintenance can be
carried out with no impact on VM availability, this maintenance can occur during normal business hours.
Finally, because Hyper-V™ operations including live migration can be scripted using the Hyper-V’s WMI
interface, many physical host maintenance operations can be automated. System management tools
that can make script or WMI calls, such as Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager, can be
configured to work with live migration.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #13
Page 14

Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #14
Page 15

Figure 3 – Physical Host Maintenance
Dynamic Datacenter
With Hyper-V™ live migration, organizations can implement dynamic IT environments. Dynamic IT
environments facilitate server provisioning based on actual utilization and service demand rather than
on less flexible criteria, such as expected demand. The management logic of the dynamic IT
environment assigns virtual machines to Hyper-V™ physical hosts according to actual utilization and
demand.
For example, if the IT environment hosts a Web-based application and the number of simultaneous
requests to the Web site increases, Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) can
automatically provide one or more additional Web servers. When provisioning these Web servers,
Virtual Machine Manager takes into account the workload on the current physical hardware. If the IT
environment load continues to increase, Virtual Machine Manager can switch on additional physical
hosts and start up more virtual machines to meet the load.
As the load fluctuates, virtual machines can be transferred between physical hosts to keep hardware
utilization rates high. Unused physical hosts can then be turned off, which reduces both power
consumption and cooling requirements, and therefore helps minimize running costs. Mismatches
between physical host capacity and VM demands can be more easily addressed because no downtime is
required to move a VM to a physical host with more available processing capacity. If the physical host
performance or usage changes after a VM is placed on that server, the VM can easily be migrated to a
server with more free capacity. Virtual Machine Manager can be used to easily report on current
physical host utilization and to help select ideal candidates for the VM in question.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #15
Page 16
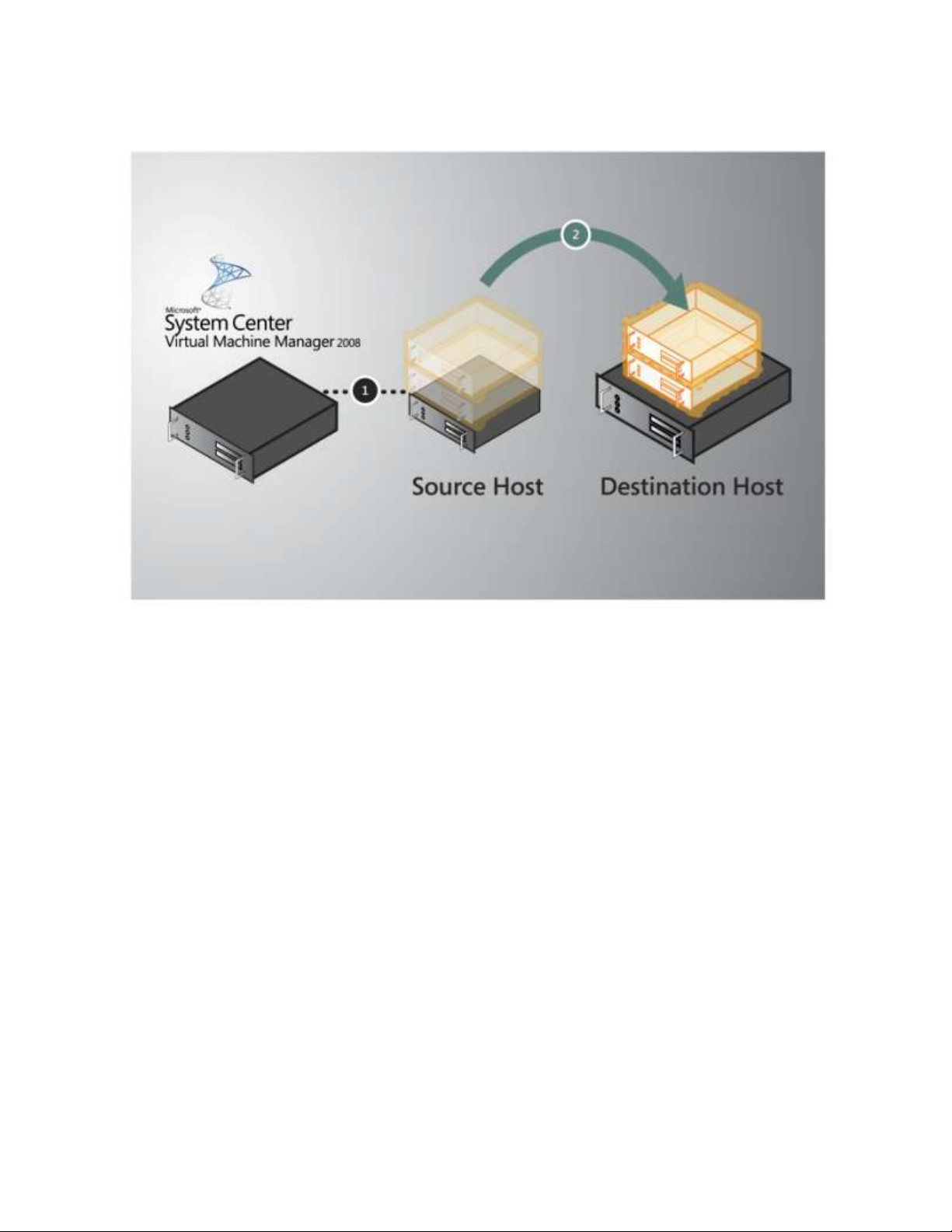
Figure 4 – Workload Moved to a More Powerful Server
Green IT
As much as 33% of the power consumed by many datacenters goes towards cooling and other
supporting infrastructure requirements. The agile load balancing approach enabled by Hyper-V™ live
migration can be extended to reduce power consumption in the datacenter. Datacenters with
fluctuating loads can use script automation and live migration to increase the virtual machine
consolidation ratio during low demand times. With fewer physical host servers running more VMs each,
the un-used physical host can be powered off to reduce electricity and cooling demand. In anticipation
of periods of greater demand (such as daily peak usage, quarter end, or yearend processing), the offline
physical host can be powered back on and the VM load can be redistributed using live migration.
The Hyper-V™ live migration feature is integrated with Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ and no
separate licensing or product installation is involved. In fact, any configuration which worked with Quick
Migration and also includes processors of the same type will support live migration.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #16
Page 17
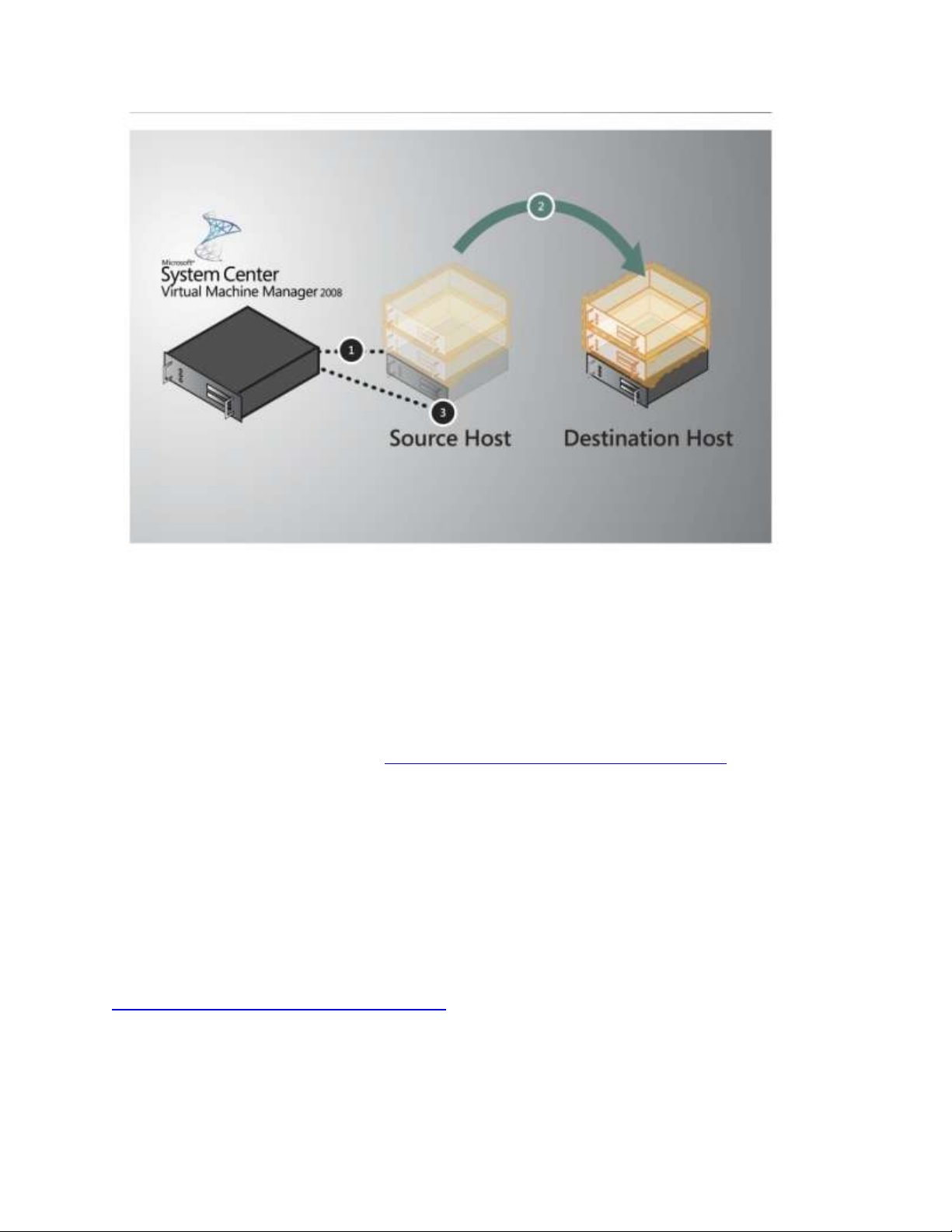
Figure 5 – Increasing Consolidation Ratio
Deploying Live Migration
Because Windows Server 2008 has eased the configuration process for Failover Clustering, deploying
live migration is easy. First, complete the planning necessary to determine how many cluster nodes you
will implement. Next, ensure that the physical host and shared storage meet Microsoft’s requirements
for usage in a Failover Cluster. See the Microsoft Failover Cluster Configuration Program for more
information. The process involves the following high-level steps:
1. Configure Windows Server 2008 R2 Failover Clustering.
2. Connect both physical hosts to networks and storage
3. Install Hyper-V™ and Failover Clustering on both physical hosts
4. Enable Cluster Shared Volumes
5. Make the Virtual Machines highly available
6. Test a Live Migration
For detailed, step-by-step instructions see the deploying live migration whitepaper at this URL:
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139667
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #17
Page 18

Managing Live Migration
Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2008 R2 adds significant value to organizations that
use Hyper-V™ live migration. The virtual machine management and reporting functions of Virtual
Machine Manager can be used in conjunction with live migration to reduce the effort needed to manage
a virtualized datacenter. Virtual Machine Manager used in conjunction with live migration can increase
an organizations’ ability to respond to changing usage levels and requirements. Virtual Machine
Manager is also very useful when managing disparate Hyper-V™ physical hosts in an organization, such
as Hyper-V™ physical hosts located in remote sites.
When Virtual Machine Manager manages a Hyper-V™ host that is configured for high availability, Virtual
Machine Manager is able to initiate Quick Migrations or live migrations from within the Virtual Machine
Manager management console. This provides a single management tool for all VM management tasks,
including live migrations.
Because the Virtual Machine Manager administration console can optionally output PowerShell scripts
for every task an administrator uses the console for, future iterations of common tasks can easily be
automated with minimal programming skill required. Of course this extends to live migrations as well.
Using Virtual Machine Manager to initiate a live migration moves a running VM to another physical host
with no downtime, and also produces the PowerShell script that can initiate that same task in the future
or be easily modified to initiate live migration on a different VM or different source and destination
physical host pair.
Virtual Machine Manager offers comprehensive reporting on virtualization physical host utilization and
VM placement. These reports can be used in the decision making process for placement of new VMs or
migrations of existing VMs. Especially in a very dense environment like many datacenters or very
dispersed environment like remote sites, good information about virtualization performance can be vital
in meeting uptime and availability requirements. Virtual Machine Manager easily provides the
information required to manage multiple Hyper-V™ physical hosts or VMs effectively. Because HyperV™ live migration makes it so easy to move VMs from one physical host to another, obtaining good
information about Hyper-V™ physical hosts in the environment is especially important.
Summary
The live migration feature of Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ greatly increases the flexibility of
Hyper-V™. The ability to move running VMs between Hyper-V™ physical hosts with no downtime for
users not only makes it easier to maintain physical host, it also opens up new possibilities for
dynamically scaling server resources to efficiently meet changing demands. Live migration makes it
possible to perform maintenance on Hyper-V™ servers without scheduling a maintenance window for
running VMs. When demand on a VM changes, you can migrate it to a more powerful server with no
downtime, or if demand has decreased you can migrate it to a server where the consolidation ratio is
higher to conserve electricity usage. Hyper-V™ live migration makes it possible to use VMs with less
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #18
Page 19

effort and greater flexibility than before. These benefits translate to time and money savings in almost
any Hyper-V™ server virtualization usage.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ Live Migration Page #19
 Loading...
Loading...