Page 1

EA900
ADSL USB Modem
Installation Guide
Microsoft® Windows® 98, 98SE, 2000, Me and XP
Driver Version V5.4.1-1120 / Rev 1.00
For Annex A & Annex B
Page 2

Specification subject to change without notice.
Alcatel is a trademark of Alcatel Microelectronics, All other products or services mentioned
are the trademarks, service marks, or registered service marks of their representative
owners.
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
About This Manual .....................................................................................................1
Preface........................................................................................................................2
The ADSL USB Modem Manual........................................................................2
Chapter 1: Overview................................................................................................3
About ADSL....................................................................................................3
Protocol and Device Driver Selection ................................................................3
Features.........................................................................................................4
Chapter 2: ADSL USB Modem Installation and Software Setup ...........................5
Modem Installation .........................................................................................6
Software Setup...............................................................................................6
Chapter 3: ADSL Control and Status.......................................................................9
Accessing CSA ................................................................................................9
CSA User Screen...........................................................................................10
Chapter 4: Uninstall Software .............................................................................12
Appendix A: Modifying TCP/IP Networking Options...........................................13
RFC 1483 Mode .........................................................................................13
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Windows 98, First and Second Editions...................................13
Windows Me .......................................................................15
Windows 2000......................................................................17
Windows XP..........................................................................19
RFC 2364 / RFC 2516 Mode .....................................................................21
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Windows 98, First and Second Editions...................................21
Windows Me .......................................................................23
Windows 2000......................................................................25
Windows XP..........................................................................27
Appendix B: Connector Pin-out.............................................................................29
Appendix C: Troubleshooting ................................................................................30
Appendix D: Abbreviations....................................................................................31
Appendix E: Government Compliance notices .....................................................33
FCC compliance .........................................................................................33
FCC Class B statement..............................................................................33
DOC compliance information....................................................................34
Austel compliance information ................................................................34
European CTR 21 compliance...................................................................34
Page 4

About This Manual
This manual provides a comprehensive user’s guide and installation manual for ADSL USB
modems. It has been organized in such a way to make it easy to follow by users worldwide.
In order to ensure optimal comprehension, the following list provides brief descriptions of the
formatting styles used throughout this manual.
! Commands: Commands always referred to by using the word “click” before them.
These commands are always shown as bold-faced words. For example, click Next, click
OK, or click Cancel.
! Names of Windows (Dialog Boxes): The names of the windows (also referred to
as dialog boxes) that appear on the PC screen are always referred to in quotes. For
example, the “Setup Complete” window.
! Names of Options in Windows: The names of options to choose from inside the
windows that appear on the PC screen are always referred to in italics. For example,
choose the
Yes, I want to restart my computer now
option from the window.
# Notes: In some cases, preparatory or cautionary information is needed before
proceeding onto the next step in an installation process. This kind of information is
provided in the form of notes, which are always referred to in bold-faced and italicized
letters. For example,
driver must be running. Also, make sure the USB cable is plugged into the
modem.
Note: To access the ADSL Control and Status (CSA), the
1
Page 5

Preface
The ADSL USB Modem Manual
This manual contains information regarding the installation, operation, and configuration of
the ADSL USB Modem. Additionally, it outlines the use of the Control Panel Application.
The following chapters are included in this manual:
Chapter 1: “Overview” offers a brief description of ADSL, protocol and device driver
•
selection, and the features of the ADSL USB Modem.
Chapter 2: “ADSL USB Modem Installation and Software Setup” describes the steps
•
for installing the ADSL USB Modem. The software installation procedure is detailed.
•
Chapter 3: “ADSL Control and Status” describes how to check the performance of
the ADSL USB Modem and the ADSL connection.
Chapter 4: “Uninstall Software” provides the steps for uninstalling the ADSL USB
•
Modem.
2
Page 6

Chapter 1: Overview
About ADSL
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) technology p rovides high-speed d ata access across
regular phone lines (copper wires) by making use of previously u nused frequency ba ndwidth
above the voice band. By placing the ADSL signal above the frequency of the voice signal,
ADSL service is able to coexist on the same line with your telephone service. ADSL is
asymmetric in the sense that it provides a higher data rate in the downstream (receive)
direction than in the upstream (t ransmit) direction. Asymmetric operation is ideal for typical
home and small office use where files and information are downloaded more frequently than
uploaded.
The ADSL USB Modem is capable of supporting the following DSL standards: ANSI T1.413
Issue 2, ITU G.992.1 (G.DMT), ITU G.992.2 (G.lite) and ITU G.992 Annexes A,B and C as
applicable.
Protocol and Device Driver Selection
The ADSL USB Modem can be easily connecte d to a USB port on the PC via a standard USB
cable. The ADSL USB Modem is fully software upgradeable so that new features and
updates may be added by simply loading a new version of the device driver onto your PC.
ADSL USB modems employ ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) framing. ATM is a protocol
that divides packets into small fixed sized cells for rapid transmission over high-speed
networks. The ATM protocol allows various types of traffic (e.g. data, voice, and video) to be
securely and efficiently carried over the same network. ATM is being widely deployed by
telecommunications carriers in their backbone networks. Two type of ATM connections are
possible, PVC (Permanent V irtual Circuit) and SVC (Switched Virtual Circuit).
Several different protocols are used on top of ATM. The protocol required in your
configuration depends on the equipment deployed by your DSL service provider. There are
several possibilities:
1. Bridged/Route d Ethernet/IP over ATM (RFC 1483) – This protocol makes the modem
appear as a local area network (LAN) device to the operating system.
2. Point to Point Protocol (PPP) Over ATM (RFC 2364) - PPP provides session setup, user
authentication (login), and encapsulation for upper layer protocols such as IP
(Internet Protocol). The use of PPP makes the modem appear as a dial modem to
the operating system. Dial- Up Ne tworking is used to establish a connection.
3. Point to Point Protocol (PPP) Over Ethernet (RFC 2516) - PPPoE combines the
Point-to-Point Protocol commonly used in dialup connections, w ith the Ethernet
protocol, which supports multiple users in a local area network. The PPP Protocol
information is encapsulated within an Ethernet frame. The use of PPP makes the
modem appear as a dial modem to the operating system. Dial-Up Networking is used
to establish a connection.
3
Page 7

Features
The ADSL USB Modem provides the following features:
• Compliant with Universal Serial Bus Specification Revision 1.1
• USB bus-powered; an external power supply is not required
• Compatible with all T1.413, G.DMT, and G.lite compliant CO DSLAM eq uipment as well as
the vast majority of deployed ADSL CO equipment
• Software upgradeable
• Includes a Microsoft Windows control panel mo nitoring program for checki ng the status
of the connection
• Provides an RJ-11 connector for connection to the telephone line
• Supports DSL downstream data rates up to 8 Mbps (125 times faster than standard 56K
modems)
• Supports DSL upstream data rates up to 1024 Kbps
4
Page 8

Chapter 2: ADSL USB Modem Installation
and Software Setup
Be sure to follow the instructions provided for your PC’s operating system.
The following information may be required for software installation. Contact you r DSL service
provider before proceeding with software installation.
• Type of Connection to be Installed – RFC 1483 (Bridged/Routed), RFC2364 and
RFC2516 are supported. The choice depends upon your DSL service provider.
• IP Address Settings – the software installation process allows the server to
dynamically assign IP Addr ess settings. If your application requires static setting of
specific address information you will need to know:
IP Address
Subnet Mask (for Bridged Ethernet applications only)
Default Gateway (for Bridged Ethernet applications only)
• Name Server Information – the software installation process allows the server to
dynamically assign Name Server Address setti ngs. If your application requires static
setting of specific address information you will need to know:
Primary DNS Address
Secondary DNS Address
Primary WINS Address
Secondary WINS Address
• ATM Virtual Path ID (VPI)
Note: Required if not using default values for driver type
• ATM Virtual Circuit ID (VCI)
Note: Required if not using default values for driver type
• Encapsulation type
Note: Required if not using default values for driver type
• Modulation type
Note: Required if not using default values for driver type
• User Name & Password (for PPP applications only)
5
Page 9

Modem Installation
1. Insert the rectangular end of the USB cable into the
USB port of your PC.
2. Insert the square end of the USB cable into the USB
port of the Alcatel ADSL USB Modem.
Software Setup
Note: For Windows 98/98SE applications, you may need the Windows 98/98SE CD
ROM to complete the installation.
Before starting the software setup process, close all Windows programs previously running on
your PC.
1. System will
automatically find
a new hardware
after hardware
installation
finished.
Click on Cancel.
(Windows 98/98SE)
(Windows 2000)
(Windows Me)
(Windows XP)
6
Page 10
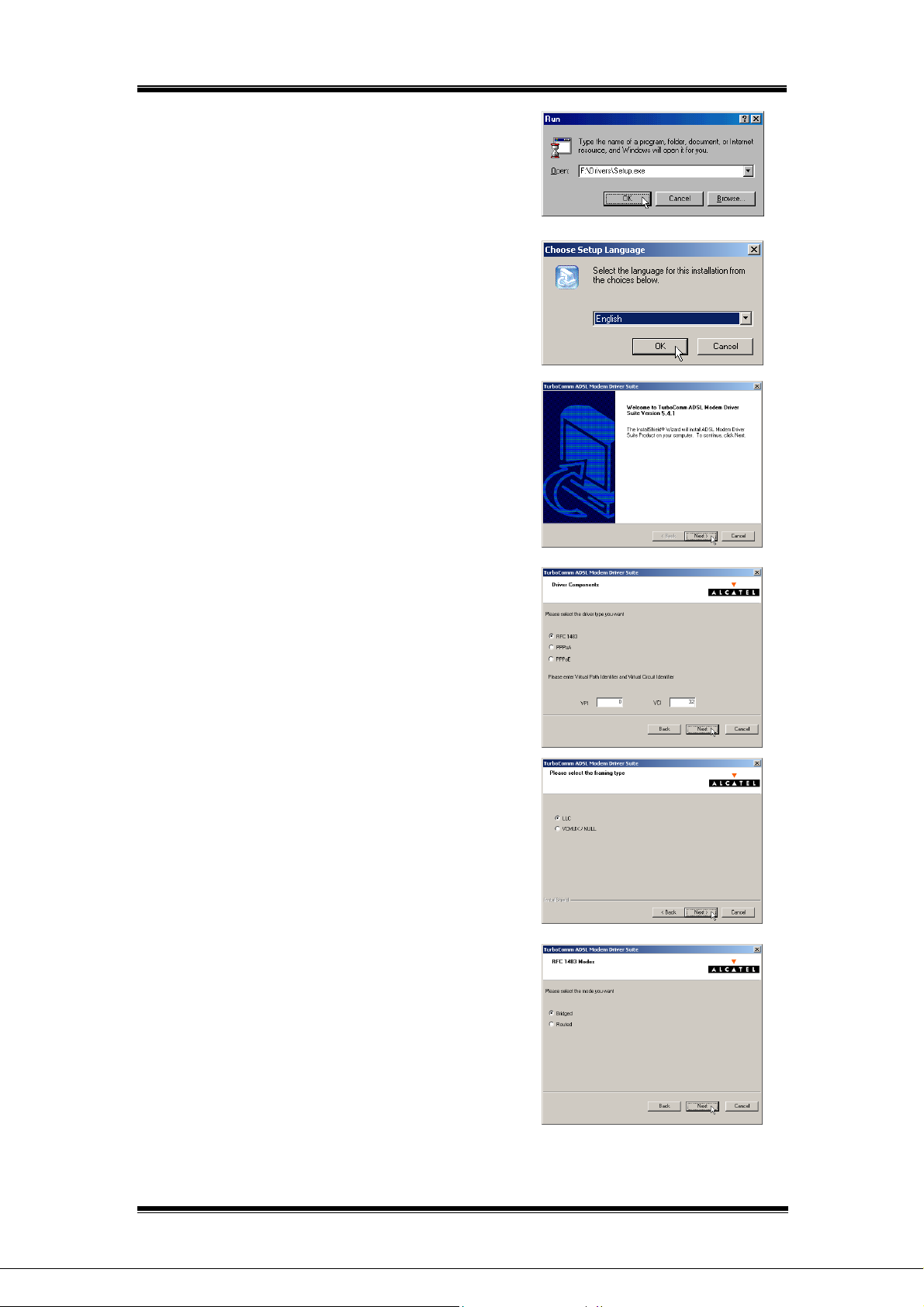
2. Insert the Drivers CD into the CD-ROM drive and
double click Setup.exe to start the installation
procedure. A notification message will appear
indicating that the setup process has begun.
3. Setup program will automatically detects your
windows system’s language version, then displays
corresponding language screen.
If setup program had incorrect detection, please
select corresponding language by yourself.
Then, click on OK.
4. The “Welcome” window provides an opportunity to
quit the setup process to exit all Windows
programs before continuing. If the Windows
programs were previously closed, click on Next.
5. The prompt window allows you to specify your DSL
connection type, ATM Virtual Path ID (VPI) and
ATM Virtual Circuit ID (VCI), which specify by your
ADSL ISP.
Then, click on Next.
6. The prompt window allows you to specify your
framing type of DSL connection, which specify by
your ADSL ISP.
Then, click on Next.
Note: Framing types vary depending upon the
application.
[For RFC1483 connection type only]
7. Please specify your RFC1483 connection mode,
Bridged or Routed.
Then, click on Next.
7
Page 11
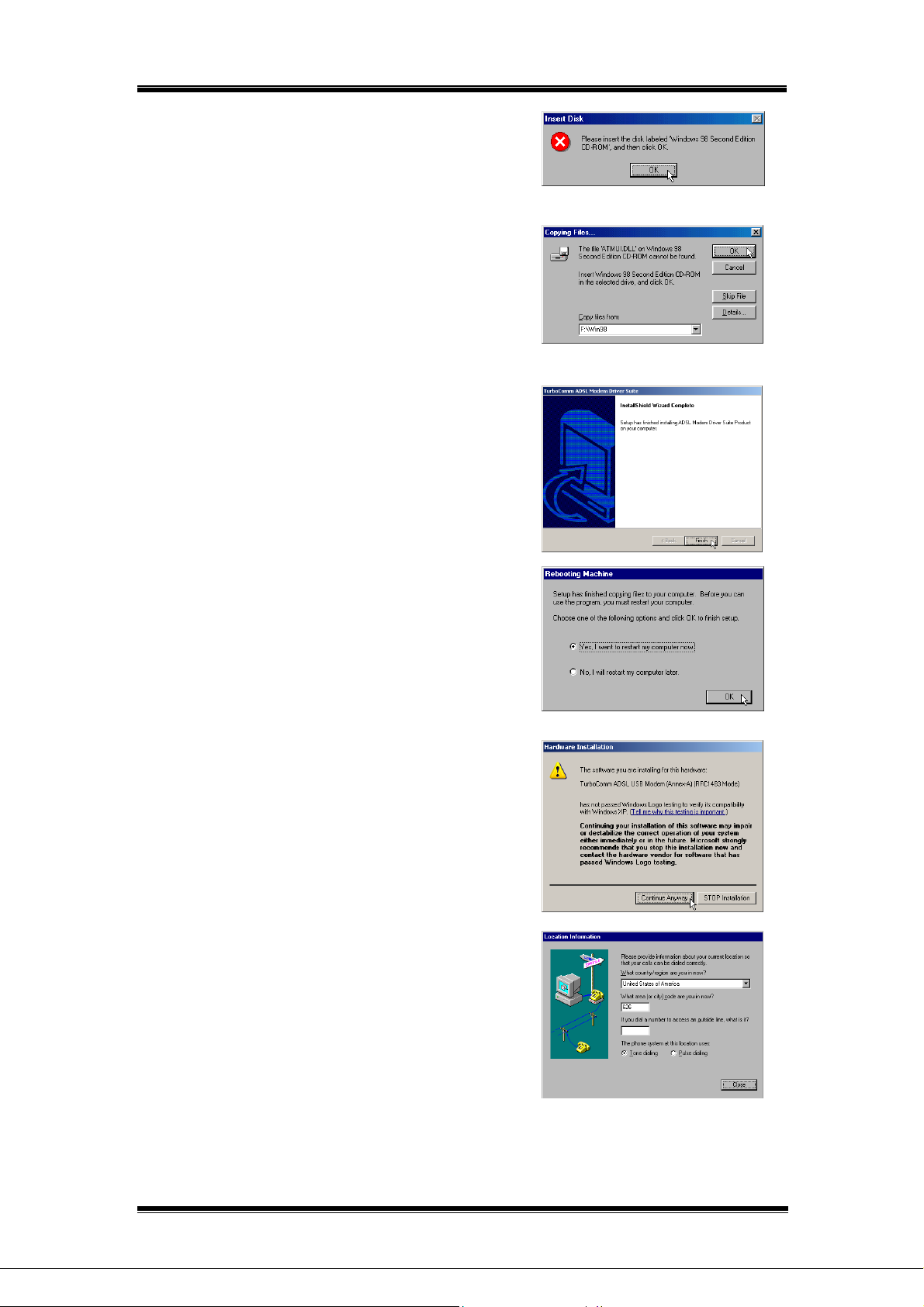
[For Windows 98/98SE only]
8-1. Insert Drivers CD-ROM disc into CD-ROM drive
and then click on OK.
8-2. To specify the directory of Windows 98/98SE like
as “F:\Win98” (“F” is CD-ROM Drive letter), then
click on OK.
9. The shown window indicates the InstallShield
Wizard has completed copying files to your
computer. Click on Finish.
10. The “Rebooting Machine” window indicates
successful completion of the uninstall process.
Choose “Yes, I want to restart my computer now”,
then click on OK.
[For Windows XP applications]
11. After reboot system, the “Software Installation”
windows will appear. Always click on Continue
Anyway.
[For PPPoA / PPPoE applications of Win do ws
98/Me only]
11. After reboot system, the “Location information”
window will appear, then enters your
country/region and telephone number.
Click Close.
8
Page 12

Chapter 3: ADSL Control and Status
ACCESSING CSA
The User Interface to the ADSL Modem is provided by the Control and Status Application
(CSA). You can access the CSA by double-clicking on the CSA icon in the System Tray, located
near the clock on the task bar. The icon, which appears as two monitor screens, also changes
color to indicate the status of the modem (see Table 1. ICON Condition.).
Table 1. ICON Condition
Color Condition
Black The modem is not available.
Red The modem is disconnected.
Blue The modem is waiting for initialization.
Yellow The modem is initializing.
Green The modem is connected and functioning.
CSA
If the
methods:
While connected, the System Tray
about the current ADSL connection. This text appears when the cursor is placed over the icon.
The information displayed is:
icon does not appear in the System Tray, it can be restored by any of the following
• Restart the PC.
• Click the Windows START button, then Programs, ADSL Modem Driver,
and Add CSA Tray Icon.
• Go to the CONTROL PANEL and double-click the ADSL Control and
Status icon.
CSA
icon provides pop-up text that gives information
• bytes transmitted
• bytes received
• connection rate.
9
Page 13

g
g
CSA USER SCREEN
Modem Performance
TRANSMIT AND
RECEIVE
Connection Status
Device Status
The Modem Performance displays performance
information. The primary purpose is to display the
instantaneous throughput rate for both transmit and
receive paths of the modem. This rate is calculated based
on the poll period (generally 2 seconds) and the number
of bytes passed during that time.
The throughput is indicated through two bar graphs, each
provides a maximum rate label indicatin
receive bit rates currently in use. The bar graph displays
peak throughput rates over the last 10-second period.
Basically, the user interface records the instantaneous
throughput for each poll period over the last 10 seconds,
and the peak rate is displayed as the maximum value
achieved over that 10-second period. This value is
indicated on the throughput graph with a vertical red
marker indicating the peak rate.
The user interface displays operational information about
the ADSL modem, relevant when the modem is
connected. When the modem is not connected, all of the
non-averaged operational information are reported as
zero unless otherwise noted. This means that when the
modem is disconnected, these values should immediately
report zero.
The Connection St atus field chan
of the modem connection:
• ADSL link connected
• ADSL link disconnected
The Device Status field changes to indicate the status of
the modem connection:
• ADSL Modem available
the transmit and
es to indicate the status
10
Page 14

Connect/
Disconnect Button
Close Button
Help
About CSA
• ADSL Modem not available
The CONNECT/DISCONNECT button performs the
connection/disconnection operation. If the ADSL Modem
is unavailable, the button is disabled. This occurs when
the ADSL modem driver is disabled or fails to
communicate correctly.
The CLOSE button closes the main interface screen. If the
main window was displayed while the system tray icon
was present, then the application continues to execute hiding the main screen. If for some reason the icon is not
present, however, the application is terminated.
On-line help is available through the HELP screens. Press
the F1 key at the CSA main screen to see the Help table
of contents. This is available from the context menus and
system tray icon menus Help selection.
The ABOUTCSA button displays the product information,
including the version number and date.
11
Page 15

Chapter 4: Uninstall Software
Remove the ADSL Modem drivers by performing the following st eps.
Note: The USB cable should not be unplugged until after the uninstall process has
been completed. For Windows 98 applications, the cable must be unplugged
immediately following Chapter 5 below.
1. From your PC desktop click Start – Programs –
ADSL Modem Driver – Remove ADSL Modem
Driver. A notification message will appear
indicating that the setup process has begun.
2. Setup program will automatically detects your
windows system’s language version, then displays
corresponding language screen.
If setup program had incorrect detection, please
select corresponding language by yourself.
Then, click on OK.
3. A message will be displayed asking you to confirm
the removal of the ADSL modem driver.
Click on Yes from the “Question” window.
4. The “Rebooting Machine” window indicates
successful completion of the uninstall process.
Choose “Yes, I want to restart my computer now”,
then click on OK.
Note: The USB cable must be unplugged before the system is rebooted. For
Windows 98 applications the cable must be unplugged immediately as the
reboot process was begun in Chapter 5 above.
12
Page 16

Appendix A: Modifying TCP/IP Networking
Options
RFC 1483 Mode
Microsoft Windows 98, First and Second Editions
TCP/IP settings are automatically set up during the software installation process. The
following procedure may be used to change TCP/IP settings, if necessary.
1. From the “Control Panel” window (Start –
Settings – Control Panel) double click on the
Network icon.
2. Select
3. From the “IP Address” tab of the “TCP/IP
TCP/IP -> TurboComm ADSL USB
Modem
“Network” window.
Click Properties.
Properties” window, select either the Obtain an IP
address Automatically or Specify an IP Address
option, depending on your network setup. If you
select Specify an IP address, type the IP Address
and Subnet Mask in the spaces provided. Consult
with your network administrator to determine
which option best suits your individual needs.
from the “Configuration” tab of the
13
Page 17

4. The “Gateway” tab allows you to add or remove
gateways. Consult with your network administrator
to determine the appropriate addresses for your
individual needs.
$ To add a new gateway, type the address in the
new gateway field and click Add. The new
gateway will appear in the Installed gateways
list.
$ To remove a previously installed gateway,
highlight the entry to be removed in the
Installed gateways list and click Remove. The
gateway will no longer appear in the Installed
gateways list.
5. Click OK from the “TCP/IP Properties” window.
6. The “Network” window will reappear. Click OK to
end the modifying TCP/IP options session.
7. If you have made changes to TCP/IP properties,
you will be asked to restart/reboot your PC. Click
on Yes, and your PC will restart.
14
Page 18

Microsoft Windows Me
TCP/IP settings are automatically set up during the software installation process. The
following procedure may be used to change TCP/IP settings, if necessary.
1. From the PC desktop, right click the My Network
Places icon and click on Properties.
2. Select
3. From the “IP Address” tab of the “TCP/IP
TCP/IP -> TurboComm ADSL USB
Modem
“Network” window. Click Properties.
Properties” window, select either the
address Automatically
option, depending on your network setup. If you
select
and
with your network administrator to determine
which option best suits your individual needs.
from the “Configuration” tab of the
or
Specify an IP Address
Specify an IP address
Subnet Mask
in the spaces provided. Consult
, type the
Obtain an IP
IP Address
15
Page 19

4. The “Gateway” tab allows you to add or remove
gateways
to determine the appropriate addresses for your
individual needs.
• To add a new gateway, type the address in the
• To remove a previously installed gateway,
.
Consult with your network administrator
new gateway
gateway will appear in the
list.
highlight the entry to be removed in the
gateways
will no longer appear in the
list.
field and click Add. The new
Installed gateways
list and click Remove. The gateway
Installed gateways
Installed
5. Click OK from the “TCP/IP Properties” window.
6. The “Network” window will reappear.
Click OK to end the modifying TCP/IP options
session.
7. If you have made changes to TCP/IP properties,
you will be asked to restart/reboot your PC.
Click Yes, and your PC will restart.
16
Page 20

Microsoft Windows 2000
TCP/IP settings are automatically set up during the software installation process. The
following procedure may be used to change TCP/IP settings, if necessary.
1. From the PC desktop, right click the My Network
Places icon and click on Properties.
2. Right click the Local Area Connection icon from
the “Network and Dial-Up Connections”
window and select “Properties”
Note: The icon name may differ from that
specified above. The ADSL connection icon
will be identified as “TurboComm ADSL USB
Modem” in the Device Name column when
details are viewed from the “Network and
Dial-Up Connection” window (View –
Details).
3. Select
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
“General” tab of the “Local Area Connection”
window. Click Properties.
from the
17
Page 21

4. The “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties” window
is used to modify the IP addresses and DNS Server
addresses:
$ Change the IP address to a user defined
address by selecting
address
left of it) and typing the addresses in the
spaces provided
option (click inside the circle to the
Use the following IP
$ Change the DNS Server addresses to user
defined addresses by selecting
following DNS server addresses
inside the circle to the left of it) and typing the
addresses in the spaces provided.
Note: The Advanced button of the “Inter net
Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties” window may
be used to alter IP settings , DNS server
addresses, WINS addresses, IP security
options, and TCP/IP filtering options.
5. Click OK from the “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties” window.
6. The “Local Area Connection Properties” window will
reappear.
Click OK to end the modifying TCP/IP options
session.
Use the
(click
18
Page 22

Microsoft Windows XP
TCP/IP settings are automatically set up during the software installation process. The
following procedure may be used to change TCP/IP settings, if necessary.
1. From the PC desktop, right click the My Network
Places icon and click on Properties.
2. Right click the Local Area Connection icon from
the Network Connec ti o ns window and click
Properties.
Note: The icon name may differ from that
specified above. The ADSL connection icon
will be identified as “TurboComm ADSL USB
Modem” in the Device Name column when
details are viewed from the “Network and
Dial-Up Connection” window (View –
Details).
3. Select
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
General tab of the Local Area Connection
window. Click on Properties.
from the
19
Page 23

4. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Pr operties
window is used to modify the IP addresses and DNS
Server addresses:
$ Change the IP address to a user defined
address by selecting
address
left of it) and typing the addresses in the
spaces provided
option (click inside the circle to the
Use the following IP
$ Change the DNS Server addresses to user
defined addresses by selecting
following DNS server addresses
inside the circle to the left of it) and typing the
addresses in the spaces provided.
Note: The Advanced button of the “Inter net
Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties” window may
be used to alter IP settings , DNS server
addresses, WINS addresses, IP security
options, and TCP/IP filtering options.
5. Click OK from the “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties” window.
6. The “Local Area Connection Properties” window will
reappear.
Click OK to end the modifying TCP/IP options
session.
Use the
(click
20
Page 24

RFC 2364 / RFC 2516 Mode
Microsoft Windows 98, First and Second Editions
TCP/IP settings are automatically set up during the software installation process. The
following procedure may be used to change TCP/IP settings, if necessary.
1. From your PC desktop, double click the My
Computer icon.
2. From the “My Computer” window, double click the
Dial-Up Networking icon.
3. From the “Dial-Up Networking” window, right click
on the My ADSL ISP icon and click Properties.
Note: The icon name may differ from that
specified above. The ADSL connection icon
will be identified as “TurboComm ADSL USB
Modem” in the Device Name column when
details are viewed from the “Dial-Up
Networking” window (View – Details).
4. From the “Server Types” tab of the “My ADSL ISP”
window, select TCP/IP (marked with a check in
the box to the left) and click TCP/IP Settings.
21
Page 25

5. The “TCP/IP Settings” window is used to modify the
IP address, Name Server addresses and/or default
gateway as follows:
$ Change the IP address to a user defined
address by selecting Specify an IP address
(click inside the circle to the left of it) and
typing the address in the space provided
$ Change the Name Server addresses to user
defined addresses by selecting Specify name
server addresses (click inside the circle to the
left of it) and typing the addresses in the
spaces provided
$ Change the default gateway by leaving the
box blank to the left of Use default gateway
on remote network.
Click OK.
6. The “My ADSL ISP” window will be redisplayed.
Click OK to end the modifying TCP/IP options
session.
22
Page 26

Microsoft Windows Me
TCP/IP settings are automatically set up during the software installation process. The
following procedure may be used to change TCP/IP settings, if necessary.
1. From your PC desktop, open the Dial-Up
Network i ng window (Start - Settings – Dial-Up
Networking).
2. From the “Dial-Up Networking” window, right
click on the My ADSL ISP icon and click on
Properties.
3. From the “Networking” tab of the “My ADSL ISP”
window, select TCP/IP (marked with a check in
the box to the left) and click on TCP/IP
Settings.
23
Page 27

4. The “TCP/IP Settings” window is used to modify
the IP address, Name Server addresses and/or
default gateway as follows:
• Change the IP address to a user defined
address by selecting
Specify an IP add r es s
(click inside the circle to the left of it) and
typing the address in the space provided
• Change the Name Server addresses to u ser
defined addresses by selecting
server addresses
(click inside the circle to
Specify name
the left of it) and typing the addresses in the
spaces provided
• Change the default gateway by leaving the
box blank to the left of
on remote network
Use default gateway
.
Click OK.
5. The “My ADSL ISP” window will be redisplayed.
Click on OK to end the modifying TCP/IP options
session.
24
Page 28

Microsoft Windows 2000
TCP/IP settings are automatically set up during the software installation process. The
following procedure may be used to change TCP/IP settings, if necessary.
1. From your PC desktop, right click the My Network
Places icon and click on Properties.
2. From the “Network and Dial-Up Connections”
window, right click on the My ADSL ISP ico n and
click Properties.
Note: The icon name may differ from that
specified above. The ADSL connection icon
will be identified as “TurboComm ADSL USB
Modem” in the Device Name column when
details are viewed from the “Network and
Dial-Up Connections” window (View –
Details).
3. From “Location Information” window, enter your
country/Region and telephone number, click on
OK.
4. From “Phone And Modem options” window, select
the location from which you are dialing and click
OK.
25
Page 29

5. From the “Networking” tab of the “My ADSL ISP
Properties” window, select
(TCP/IP)
6. The “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties” window
is used to modify the IP address and DNS Server
addresses:
• Change the IP address to a user defined address
by selecting
(click inside the circle to the left of it) and typing
the address in the space provided
and click Properties.
Use the following IP address
Internet Protocol
• Change the DNS Server addresses to user
defined addresses by selecting
following DNS server addresses
the circle to the left of it) and typing the
addresses in the spaces provided.
Use the
(click inside
Note: The “Advanced ” button of the “Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties” window may be
used to alter DNS addresses, WINS addresses
and IP security settings.
7. Click OK from the “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties” window.
8. The “My ADSL ISP Properties” window will reappear.
Click OK to end the modifying TCP/IP options
session.
26
Page 30

Microsoft Windows XP
TCP/IP settings are automatically set up during the software installation process. The
following procedure may be used to change TCP/IP settings, if necessary.
1. From your PC desktop, right click the My
Network Places icon and click on Properties.
2. From the “Network Connections” window, right
click on the My ADSL ISP icon and click on
Properties.
Note: The icon name may differ from that
specified above. The ADSL connection icon
will be identified as “TurboComm ADSL USB
Modem” in the Device Name column when
details are viewed from the “Network and
Dial-Up Connections” window (View –
Details).
3. From “Location Information” window, enter your
country/Region and telephone number, click on
OK.
4. From “Phone And Modem options” window, select
the location from which you are dialing and click
OK.
27
Page 31

5. From the “Networking” tab of the “My ADSL ISP
Properties” window, select
(TCP/IP)
6. The “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties” window
is used to modify the IP address and DNS Server
addresses:
• Change the IP address to a user defined address
and click Properties.
by selecting
(click inside the circle to the left of it) and typing
the address in the space provided
Use the following IP address
Internet Protocol
• Change the DNS Server addresses to user
defined addresses by selecting
following DNS server addresses
the circle to the left of it) and typing the
addresses in the spaces provided.
Use the
(click inside
Note: The “Advanced” button of the
“Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties”
window may be used to alter DNS addresses,
WINS addresses and IP security settings.
7. Click OK from the “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties” window.
8. The “My ADSL ISP Properties” window will reappear.
Click OK to end the modifying TCP/IP options
session.
28
Page 32

Appendix B: Connector Pin-out
The ADSL modem is equipped with a RJ-11 jack for connection to the
ADSL data port. The center two pins, pins 2 and 3, are used for ADSL
data. For the modem to make a proper ADSL connection, the installed
ADSL data port should also use pins 2 and 3 for data. If the ADSL data
port installation uses pins 1 and 4 for data, then a wiring converter will
be required. Do not alter or remove the wiring converter if present.
Consult with your ADSL provider before attempting any wiring changes.
29
Page 33

Appendix C: Troubleshooting
If your internet connection is not working, the following hints may be helpful. After trying
these hints, if you still can not make your connection work, it is recommended that you ask
your service provider for assistance. To run troubleshooting on the system:
Step 1. Is the system tray CSA icon green? If it is not, try a restart of your PC. This may
clear the problem.
Step 2. If this does not correct the problem, make the following checks :
Step a. Is your phone line connected to the wall outlet and to your PC?
Step b. Is the modem connected to the USB port?
Step 3.
Step 4. If the CSA tray icon is still not showing green uninstall the modem (see “Chapter 4.
Step 5. If the system tray CSA icon is green, but you have problems in logging in, or
Step 6. If still experiencing difficulties, contact your service provided for help.
If the CSA icon color does not show green after performing the steps above, it is
recommended to "cleanup" the installation and reinstall. "Cleanup" is a utility that
can be run from the Installation CD. At the Windows Start button, select Run, click
Browse and search for "Cleanup.exe" on the installation CD. Once you run the
utility, it pops up a message for restarting the system. Re-install the modem after a
restart.
Uninstall Software ” on page 12) and re-install.
connecting to, your ISP, running "Cleanup’ and re- installing may solve the problem
(see "Step 3" for details).
30
Page 34

Appendix D: Abbreviations
AAL ATM Adaptation Layer. A function performed during ATM cell processing to adapt
traditional IP or Ethernet traffi c for transmission through an ATM network.
ADSL Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. A method for modulating data to achieve high
bit rates over common twisted-pair copper wire.
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode. A method of networking the uses a fixed length cell
to transmit data (versus a variable length packet). The fixed length cell improved
cell switch performance, hence improves end-to- end data transfer performance.
CBR Constant Bit Rate. This class of service delivers ATM traffic at a consistent rate.
The rate is specified during virtual circuit construction and cannot exceed the
specified value.
CSA Control and Status Application. Basis for this whole document.
GUI Graphical User Interface. The Windows-based interface a user interacts with to
manage and monitor the ADSL modem activity.
LEC Local Exchange Carrier. The business party responsible for delivery of telephone
service to a geographic region.
PDU Protocol Data Unit. Similar to a data packet, a protocol data unit is simply a data
packet that has some protocol processing applied to it.
PVC Permanent Virtual Circuit. A virtual circuit that is defined and exists until explicitly
destroyed.
SAR Segmentation and Reassembly. The process of segmenting AAL PDUs into cells
and reassembling received cells as AAL PDUs.
SVC Switched Virtual Circuit. A virtual circuit that is dynamically created and destroyed
using UNI signaling.
UBR Unspecified Bit Rate. This class of service attempts to deliver ATM traffic in a ‘best
effort’ mode, as long as the amount of bandwidth consumed by the effort does not
exceed a specified peak rate.
UNI User-To-Network Interface. The interface between the user endpoint equipment
and the first ATM switch encountered in the network. The UNI specification suite
(versions 3.0, 3.1, and 4.0) is maintained by the ATM Forum.
VBR Variable Bit Rate. Service class attempts to deliver ATM traffic.
VC Virtual Circuit. A data path setup across an ATM link.
31
Page 35

VCI Virtual Circuit Identifier. A 16-bit value that is included in an ATM cell header to
identify the destination virtual circuit.
VPI Virtual Path Identifier. An 8-bit value that is included in an ATM cell header to
identify the destination virtual path.
32
Page 36

Appendix E: Government compliance notices
FCC compliance
This equipment complies with Part 68 of the FCC Rules. On this equipment is a label that
contains, among other information, the FCC registration number and Ringer Equivalence
Number (REN) for this equipment. You must, upon request, provide this information to your
telephone company.
If your telephone equipment causes harm to the telephone network, the Telephone Company
may discontinue your service temporarily. If possible, they will notify in advance. But, if
advance notice isn’t practical, you will be notified as soon as possible. You will be informed of
your right to file a complaint with the FCC.
Your telephone company may make changes in its facilities, equipment, operations, or
procedures that could affect proper operation of your equipment. If they do, you will be
notified in advance to give you an opportunity to maintain uninterrupted telephone service.
The FCC prohibits this equipment to be connected to party lines or coin-telephone service.
In the event that this equipment should fail to operate properly, disconnect the equipment
from the phone line to determine if it is causing the problem. If the problem is with the
equipment, discontinue use and contact your dealer or vendor.
FCC Class B statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is
no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment
does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one or more of the following measures:
$ Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
$ Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
$ Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
$ Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Notice: 1) Shielded cables, if any, must be used in order to comply with the emission limits.
2) Any change or modification not expressly approved by the Grantee of the
equipment authorization could void the user’ s authority to operate the equipment.
33
Page 37

DOC compliance information
NOTICE: The Canadian Department of Communications label identifies certified equipment.
This certification means that the equipment meets certain telecommunications network
protective, operational and safety requirements. The Department does not guarantee the
equipment will operate to the user’s satisfaction.
Before installing this equipment, users ensure that it is permissible to be connected to the
facilities of the local Telecommunications Company. The equipment must also be installed
using an acceptable method of connection. The customer should be aware that compliance
with the above conditions might not prevent degradation of service in some situations.
Repairs to certified equipment should be made by an authorized Canadian maintenance
facility designated by the supplier. Any repairs or alterations made by the user to this
equipment, or equipment malfunctions, may give the telecommunications company cause to
request the user to disconnect the equipment.
Users should ensure for their own protection that the electrical ground connections of the
power utility, telephone lines and internal metallic water pipe system, if present, are
connected together. This precaution may be particularly important in rural areas.
CAUTION: Users should not attempt to make such connection themselves, but should
contact the appropriate electric inspection authority, or electrician, as appropriate.
NOTICE: The Load Number (LN) assigned to each terminal device denotes the percentage of
the total load to be connected to a telephone loop, which is used by the device, to prevent
overloading.
The termination on a loop may consist of any combination of device subject only to the
requirement that the sum of the Load Numbers of all the devices does not exceed 100.
Austel compliance information
Unit shall be connected to telecommunication network through a line card which meets the
requirements of ACA technical standard TS008.
European CTR 21 compliance
The equipment has been approved in accordance with Council Decision 98/482/EC for
pan-European single terminal connection to the public switched telephone network (PSTN).
However, due to differences between the individual PSTNs provided in different countries, the
approval does not, of itself, give an unconditional assurance of successful operation on every
PSTN network termination point. In the event of problem, you should contact your equipment
supplier in the first instance.
Note: The manufacturer should ensure that the vendor and user of the equipment is clearly
informed of the above information by means of package and /or user manuals of the forms of
user instructions.
34
 Loading...
Loading...