Page 1

G
F
N
J
S
Operating Instruction
Welding machine
Instructions d'utilisation
L’appareil de soudage sous
gaz protecteur
Bruksanvisning
Dekkgass-sveiseapparatet
Käyttökäsikirja
Parhaat onnittelumme tämän
korkealaatuisen
Bruksanvisning
skyddsgassvets
MIG/MAG 140
MIG/MAG 160
115 164 4534 GB/F/N/SF/S 2508 2.1
Page 2

G
F
N
J
S
Great Britain 1.
France 2.
Norge 3.
Suomi/ Finland 4.
Sverige 5.
Retain proof of purchase! You are only entitled to claim warranty against
proof of purchase.
Conservez le reçu d'achat! La garantie ne peut être accordée que sur
présentation de ce reçu.
Oppbevar kvitteringen!
Garantiytelser skjer kun på grunnlag av forelagt kvittering.
Säilytä ostokuitti!
Takuu on voimassa vain kuittia vastaan.
Förvara kvittot!
Garantianspråk erkännes endast mot uppvisande av kvitto.
Page 3
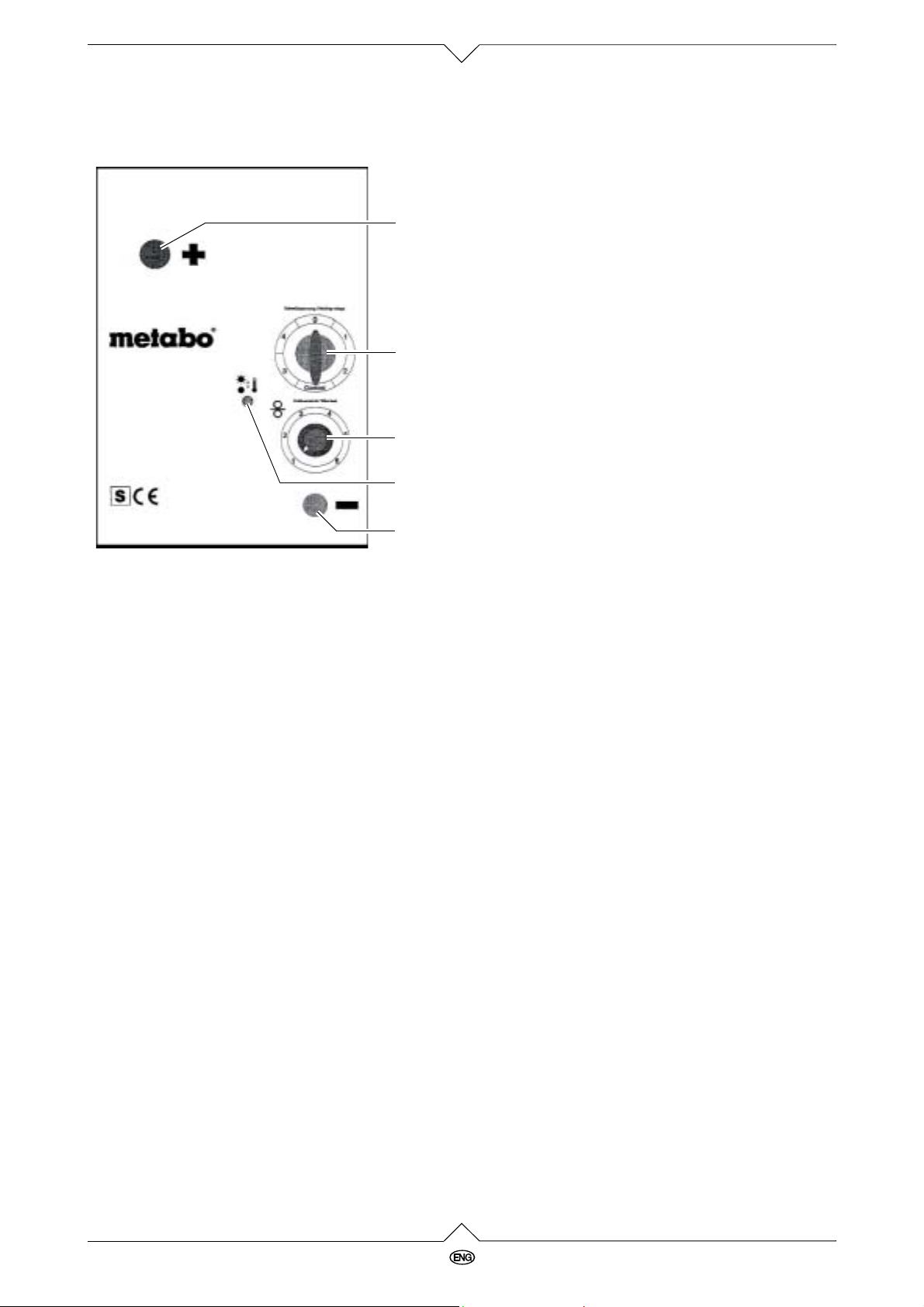
XS00028E.fm
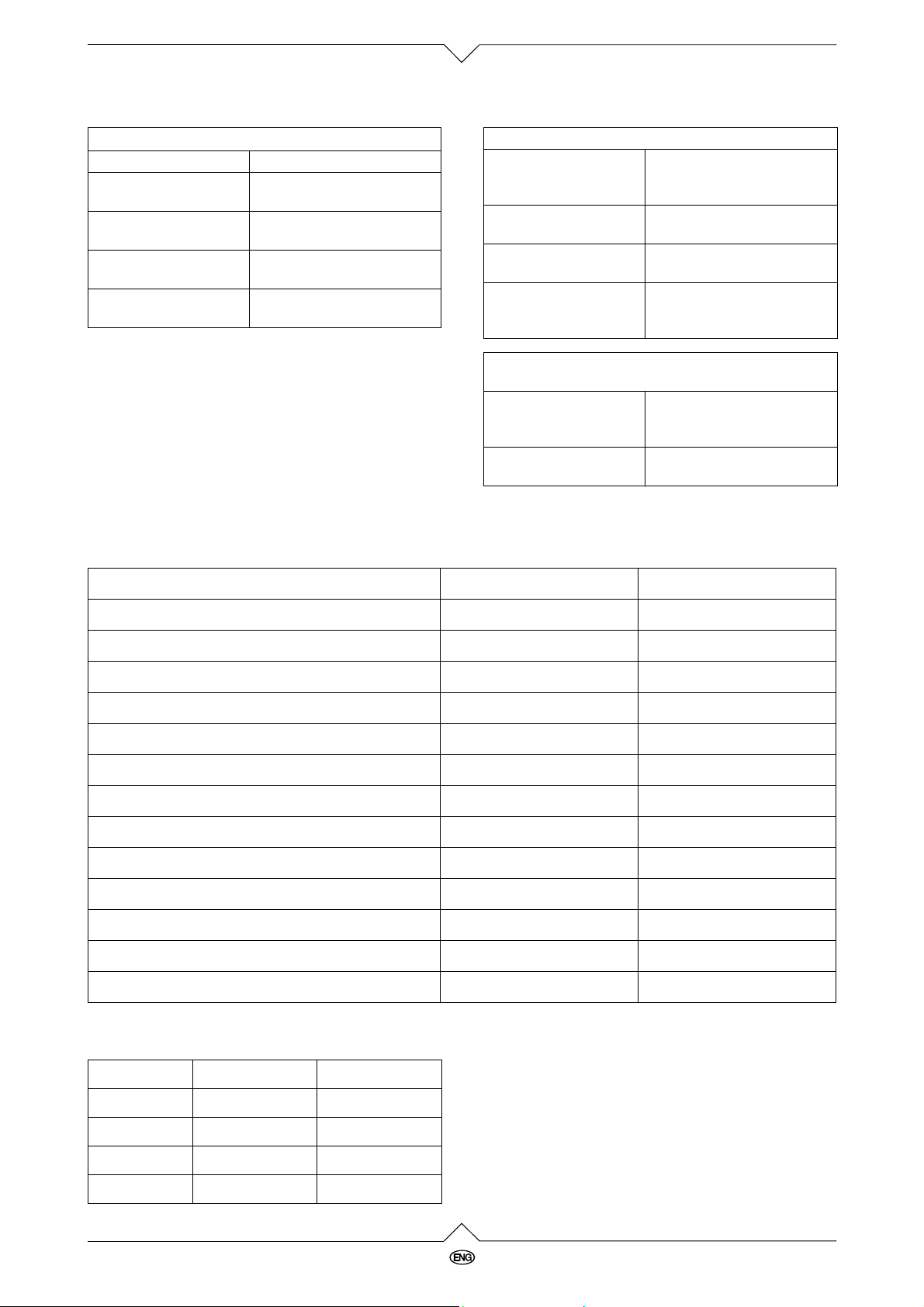
1Great Britain
Operation elements
1
2
3
4
5
1 Connection for torch (+) pole
2 Switch on/off and welding currant
3 Wire feed regulator
4 Overload control light
5 Connection for earth clamp (–) pole
Dear customer,
Congratulations to your purchase of this high-quality
MIG/MAG welding machine.
To ensure your personal safety and for reasons of
appliance safety we ask you to read the instructions
completely before operating this machine and to
observe all points.
Basic Information for the Operator
The MIG/MAG welding machine is a DC welding
power source with integrated wire feed, designed
and manufactured exclusively for MIG and MAG
electric arc welding.
Any other use of this machine involves dangers and
is not permitted.
The welding machine must only be operated on the
mains voltage stated on the machine's rating plate.
Connection to the supply circuit must be made via
an earthed outlet, installed by a qualified electrician.
The supply circuit must be protected by a fuse or
miniature circuit breaker.
Depending on the mains connection conditions at
the point of connection, welding power sources can
cause disturbances to other consumers in the distribution system. Check with your power utility before
connecting to power. (Class A in accordance with
CISPR 11)
Keep the welding machine out of the reach of children.
Please note the hazards associated with the welding process and observe any work and fire prevention regulations.
The welding machine is not suitable for outdoor use
in rain. Store in a dry place.
The unit is not suitable for unfreezing pipes.
Danger!
A
person with a heart condition wearing a pace
maker must contact their doctor before operating this welding machine.
Safety Information and Accident
Prevention Measures
x Keep the welding machine out of the reach of
children.
x Observe all applicable work and fire prevention
regulations when operating this welding
machine. Observe all applicable accident prevention regulations.
x With welding a number of different hazards are
associated, which can pose a danger to health
under certain circumstances.
x When welding always wear a close fitting, dry
overall (preferably fire retardant welders
apparel) unsoiled by combustible substances,
sturdy, insulating boots, headgear and leather
welders gloves.
x Clothing made of synthetic fabrics and shoes
are not suitable.
Dry, insulating gloves worn on both hands protect against electric shock (open-circuit voltage
of the welding current circuit), hazardous rays
(heat and ultra-violet rays) as well as against
glowing metals and slag spatters. The ultra-vio
let radiation causes sunburn-like effects on
unprotected parts of the body.
Fumes – Vapours – Smoke
x During welding hazardous smoke and metal
dust develops. We strongly recommend the
wearing of welding fume respirators, and to weld
only in sufficiently vented rooms, to ensure the
necessary operator protection.
x For enclosed spaces forced ventilation, installed
below the welding area, must be used.
x The material to be welded must be free from hal-
ogen solvents or degreasing agents, to prevent
the generation of toxic vapours.
-
MIG/MAG 140/160
1.1
Page 4

x Metals coated with lead, graphite, cadmium,
zinc, mercury or beryllium, or containing any of
these materials, can generate much smoke dur
ing welding.
x Welding releases ozone, which is a type of oxy-
gen that can lead to irritation or disorder of the
respiratory organs.
x Degreasing agents such as trichlorethylene, tet-
rachloroethylene etc. vaporise during welding
and are chemically converted into phosgene.
Phosgene is poisonous!
UV-Rays
x The arc radiation can cause eye damage and
skin burns.
x For protection against sparks, heat, visible and
invisible rays suitable eye protection gear (welding visor or helmet with standardised filter
lenses to class 10 – 15 of DIN 4647, depending
on welding current) must be worn.
x Do not look into the arc with unprotected eyes
(risk of blinding and burns). The invisible ultraviolet radiation causes, with insufficient eye pro
tection, a very painful conjunctivitis, which
appears only hours later.
x Weld only within the range of visibility of other
persons, who can assist you in an emergency.
x Other persons or helpers near the arc must be
made aware of the hazards, and equipped with
the necessary protective gear.
x Neighbouring workplaces are to be screened off
to provide protection against radiation.
x When welding inside rooms and buildings suffi-
cient ventilation must be ensured.
Fire
Danger!
A
The arc temperature is approx. 2400 °C.
Before starting to weld observe the following information:
x Remove all combustible materials and objects
within a radius of 5 m from the welding point.
x Materials that can not be removed within a 5 m
radius must be protected by covering with sheet
metal, wet cloths etc.
x Any wall openings, cracks and the like must be
covered or sealed respectively, to prevent
uncontrolled flying of sparks.
x Keep fire extinguishing equipment such as fire
extinguisher, water pale etc. at hand.
x Keep in mind that by heat dissipation from the
welding point a fire may be started on covered
parts or in other rooms respectively.
x After completion of the welding work check the
vicinity of the welding point several times within
a period of 6 – 8 hours for heat conduction,
glowing combustion spots, hidden seats of fire
-
etc.
Handling of Shielding Gas Cylinders
x Observe all applicable regulations pertaining to
the handling of gas cylinders. Because of the
dangerously high internal pressure (up to 200
bar) shielding gas cylinders are to be specially
protected against mechanical damage, falling
over or falling down, heating up (max. 50°C),
prolonged radiation by sunlight and heavy frost.
x When the welding machine is equipped with a
gas cylinder too large in size this can cause, on
uneven ground, the welding machine to fall
over. To prevent subsequent damage to the
welding machine or the gas cylinder, use only
proper size gas cylinders (10l / 20l cylinders).
x Have cylinders refilled only by authorised filling
stations.
Electrical Hazards
-
x The connection to power mains and servicing of
the welding machine is to be done in accordance with VDE regulations or other standards
applicable in your area.
x Ensure proper protective bonding of the supply
circuit.
x Ensure proper protective bonding of the work-
bench.
x Any service or maintenance work must only be
carried out by qualified personnel.
x Replace defective or damaged parts of torch or
torch leads without delay.
x The unit must only be connected to an earthed
outlet as a matter of principle. Only connections,
including outlets and extension cables with an
earthed plug, having an earth conductor and
installed by a qualified electrician, are permitted.
x The fuse protection of the supply circuit must be
in accordance with local regulations. According
to these regulations fuses or miniature circuit
breakers respectively, suitable for the conductor
cross section, must be installed. Installation of a
fuse with to high an ampere rating may cause
line fire and subsequent fire damage to the
building.
x Replace damaged torch insulation and welding
cables without delay.
x Replacement of a damaged power cable, plug
etc. and repairs to the electrical components of
the welding machine must be left to a qualified
electrician.
x Welding torches must not be held in an armlock,
or in such way that electricity can run through
the body.
1.2
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 5
x Switch the unit off for longer work breaks.
Unplug when work is completed and before relocating the unit. In case of accidents separate the
welding power source at once from the power
supply.
General Machine Description
The MIG/MAG welding machine consists of a transformer (static characteristic curve), a series-connected silicon rectifier, a welding circuit choke, and
a wire feed unit.
The welding machine is suitable for the welding of
different electrode wires (e.g. steel, see "Technical
Specifications") under a shielding gas cover (CO2,
mixed gas and argon).
The machine is fan cooled and has an overload protection.
Symbols Used
Danger!
Disregard of the following warnings
could cause serious personal injury
or material damage.
6 Manufacturer
7 Machine designation
8 Serial number
9 Standard information – This machine meets
the requirements of the standards mentioned
10 CE mark – This machine conforms to EC
directives as per declaration of conformity
11 Waste disposal symbol – the machine can be
disposed of through the manufacturer
12 Electrical performance data
13 Date of manufacture
Commissioning
Taking out of enclosed parts
All enclosed parts are inside the wire feed compartment and can be taken out after the wire feed compartment cover is removed..
Read operating instructions before
initial operation
Wire feed speed
Do not use in rain.
Welding machine suitable for welding in
environments with an increased electrical hazard.
Excess temperaturer
Information on the name plate:
6
78910
1213
11
Installation Conditions
x The protective gas welding unit must be
installed in a dry environment with sufficient
room for cooling.
x If the unit is placed on an inclined surface it must
be secured against falling: place the unit on a
suitable level support surface.
x The unit is designed for use in covered areas.
Welding outside in the rain is not permitted.
Mains connection
x Check to see that mains voltage matches the
voltage shown on the machine's rating plate.
x Set welding step switch to "0" before plugging
in.
Shielding gas cylinder connection
x Place gas cylinder onto the welding machine's
cylinder rack and secure with the chain to the
cylinder holder at the rear of the unit. Take off
the cylinder cap and open cylinder valve briefly,
facing away from your body.
x Screw pressure reducer to the gas cylinder
valve. Run gas hose from pressure reducer to
gas inlet port of the unit.
x Recommended gas flow rate in draft-free
rooms: 5-10 l/min.
MIG/MAG 140/160
1.3
Page 6
x When using adjustable pressure reducers set
flow rate according to litre scale in the clock with
the T-screw. Turning the T-screw in increases
the gas flow rate, turning it out reduces the gas
flow rate.
x While setting the gas flow rate, the unit must be
switched on and the torch's trigger switch held
down, so the solenoid gas valve is open. To prevent wasting electrode wire swing the wire feed
unit's leaf spring to the side.
Modifications and repairs to pressure reducers are
strictly prohibited due to the hazards involved. Send
faulty pressure reducers to a service centre.
Earth lead connection
Connect earth clamp of the unit's earth cable as
close as possible to the welding point. Ensure good
metal to metal contact.
Hints for Setting and Welding
Techniques
Switching the unit on
The unit is switched on with the combination ON/
OFF – welding step switch. With the switch in the
"0"- position the unit is electrically separated from
the power supply.
The unit is fitted with an embedded temperature
detector, which shuts the unit down in case of an
thermal overload.
The tripping of the thermal overload protector is indicated by the front panel control light. Welding power
source and wire feed are temporarily disabled.
After cooling down the welding power source is
automatically activated again, the control light extinguishes.
Preparation of the welds
The joint section of the workpieces to be welded
must be free of colour, metall covering, dirt, rust,
grease and humidity.
The preparation of the welds is to be done under
observation of all welding techniques regulations.
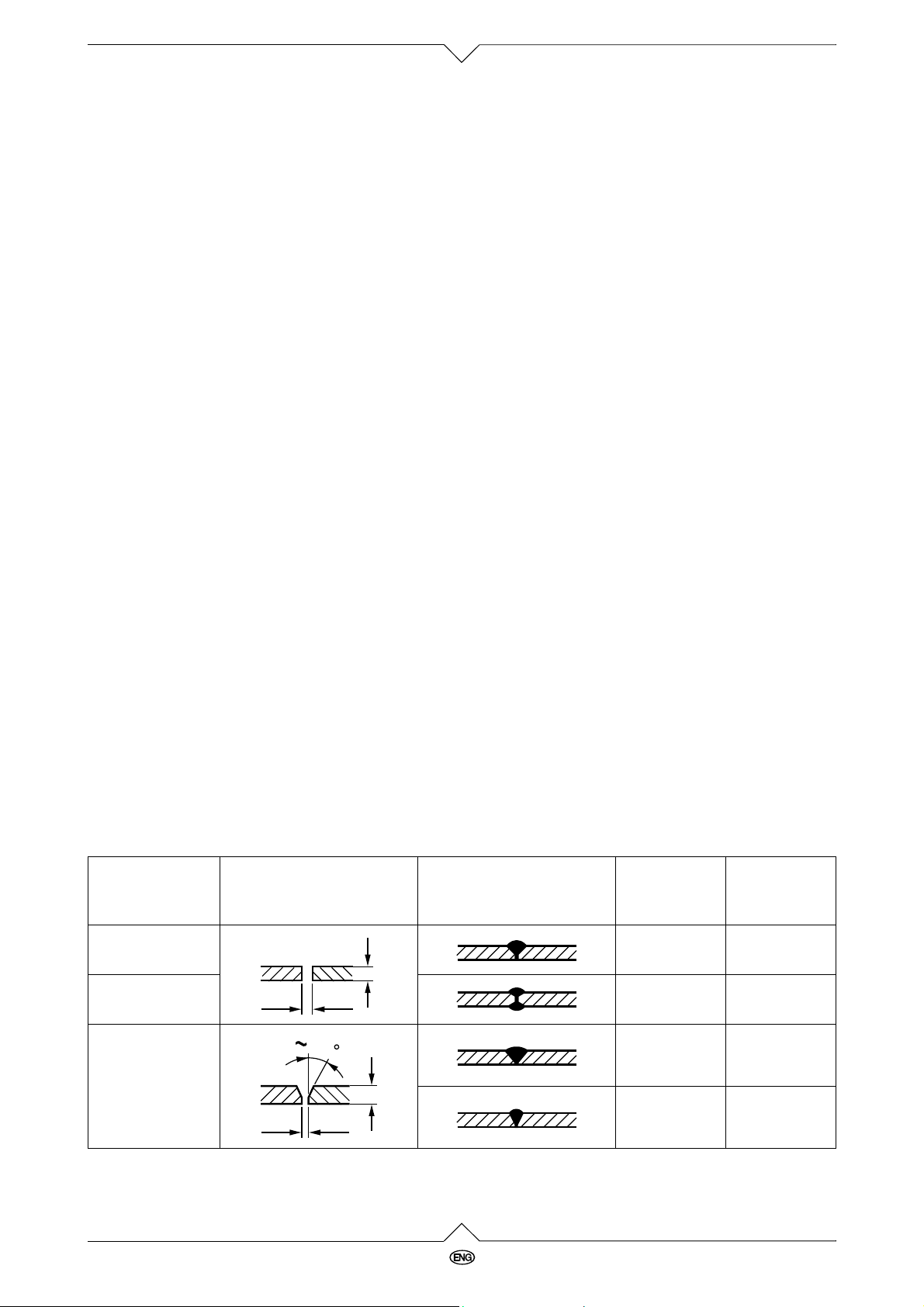
The right joint
The list gives hints for the shaping of the joints.
Form of joint Execution
Setting the welding parameters
After preparation of the welding machine the welding can begin.
To do so, welding voltage and wire feed have to be
matched to suit the welding task. If the wire feed
speed is increased the welding current increases
accordingly.
For every electrode wire diameter and every welding task optimal parameters can be found. They are
recognisable at the typical humming sound of the
arc, amongst other.
If there is too much deviation from the optimal
parameters, a satisfactory welding is not possible.
Platethick-
ness
s (mm)
Gapwidth
b (mm)
I-joint onesided < 1,5
I-joint on both
sides
V-joint
25
s
b
s
b
> 1,5
2 – 4 < 2
3 – 6 < 1
3 – 6 < 1
1.4
0
< 2
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 7
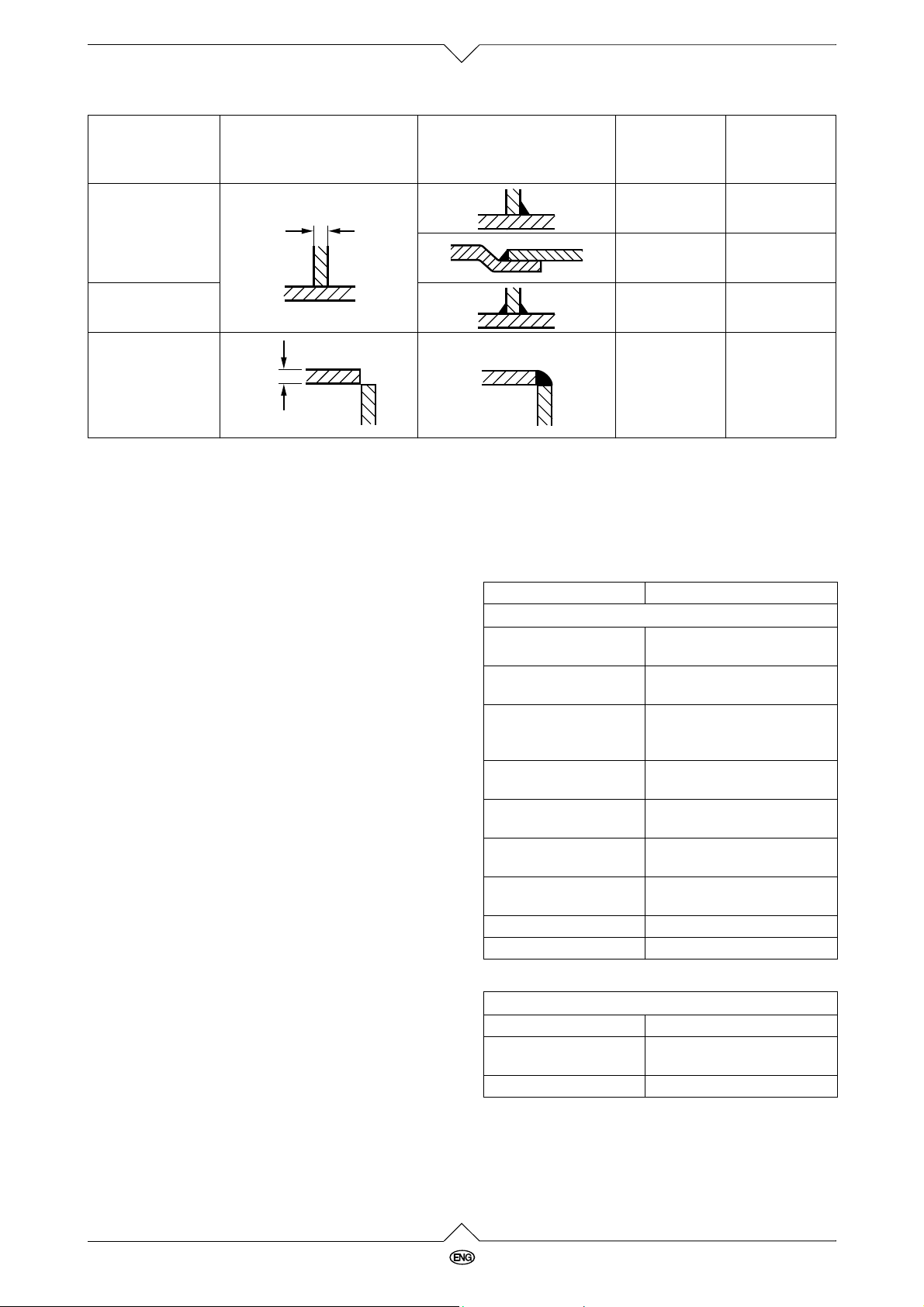
Form of joint Execution
Platethick-
ness
s (mm)
Gapwidth
b (mm)
K-joint
s
Double-K-joint
Cornerjoint
s
Care and Maintenance
The unit is nearly maintenance-free.
Danger – Voltage!
B
Disconnect from power before servicing!
x Check feed roller, pressure roller and wire lead-
in nozzle at regular intervals for dirt build-up,
clean if necessary.
x At appropriate intervals the complete torch
including torch leads should be cleaned, as
rubbed-off parts and dust build-up inside.
x The torch's contact tip is a wearing part. If its ori-
fice has enlarged the contact tip must be
replaced.
x On the inside of the plug-on gas shroud spatters
build up. These have to be removed when nec
essary. An anti-spatter spray eases this job and
keeps spatters from sticking to the shroud.
x Replace damaged cables without delay.
Trouble Shooting
Mechanical faults are mostly indicated by an irregular or completely blocked wire feed. Electrical faults
cause a malfunction of the unit, in part or complete.
> 0,6 –
0,6 – 1,5 –
> 0,6 –
> 1 –
2. Check of fuse for continuity and contact.
3. Visual check for possible shorts or overloads of
windings (discoloring).
Fault, Likely causes Remedy
• Noisy or unstable arc?
Incorrect welding voltage
Too much/too little wire
feed
Earth clamp loose or
high contact resistance
(rust, paint)
Contact tip worn or
-
incorrect diameter
Incorrect gas flow rate
setting
Workpiece not clean in
seam area
Power unit faulty Have machine checked by
Spiral liner dirty Clean or replace
Wire feed faulty See below
Correct with welding step
switch
Correct with wire feed pot
Ensure good contact
between earth clamp and
workpiece
Replace
Correct
Remove paint, rust, grease
etc.
service centre
Danger - Voltage!
B
Electrical fault finding must be left to a qualified electrician.
Further fault finding can proceed according to the
wiring diagram supplied.
Fault find should first start with the unit de-energized, and in the following order:
1. Check of the power supply cable connection
and all other connections on switches, transformer and choke, as well as all plug-and-socket
connections and soldered connections for tightness.
MIG/MAG 140/160
• Excessive spattering
Wire feed rate too high Correct with wire feed pot
Welding voltage too
high
Workpiece not clean Clean
Correct with welding step
switch
1.5
Page 8
• Wire feed motor does not run
No power Check power supply
Welding step switch in
"0" position
Torch trigger switch not
activated
Fuse blown Have replaced by a qualified
Motor faulty Have repaired by service
Set to a welding step
Activate torch trigger switch
electrician
centre
Technical Specification
• No wire feed
Pressure roller loose Increase pressure of leaf
spring with knurled thumb
screw
Wire kinked at wire
feed
Groove in feed roller
worn
Electrode wire stuck to
contact tip
• Machine shuts down, overload control light
comes on
Duty cycle exceeded Let machine cool down,
Power unit faulty Have repaired by service
Adjust wire lead-in nozzle
Replace
Replace contact tip, if wire is
deformed, reduce pressure
of pressure roller
observe duty cycle stated on
nameplate
centre.
MIG/MAG 140 MIG/MAG 160
Power supply 1 x 230 V, 50/60 Hz 1 x 230 V, 50/60 Hz
Power input max. 5,1 kVA 5,3 kVA
Current draw max. 22 A 23 A
Mains fuse, time-lag 16 A 16 A
Open-circuit voltage 17,5 – 28 V 19 – 30 V
Welding current range 30 – 140 A 30 – 160 A
max. Duty cycle (40°C) 4 % 8 %
Welding steps 4 4
Wire feed rate 1,0 – 12 m/min 1,0 – 12 m/min
Electrode wire diameter 0,6 – 0,8 mm 0,6 – 0,8 mm
Protection class IP 21 IP 21
Length x Width x Height 590 x 260 x 420 mm 590 x 260 x 420 mm
Weight 21 kg 26,5 kg
Current setting range
Position MIG / MAG 140 MIG / MAG 160
130A30A
250A60A
380A100A
4140A160A
1.6
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 9
XS0028F.fm
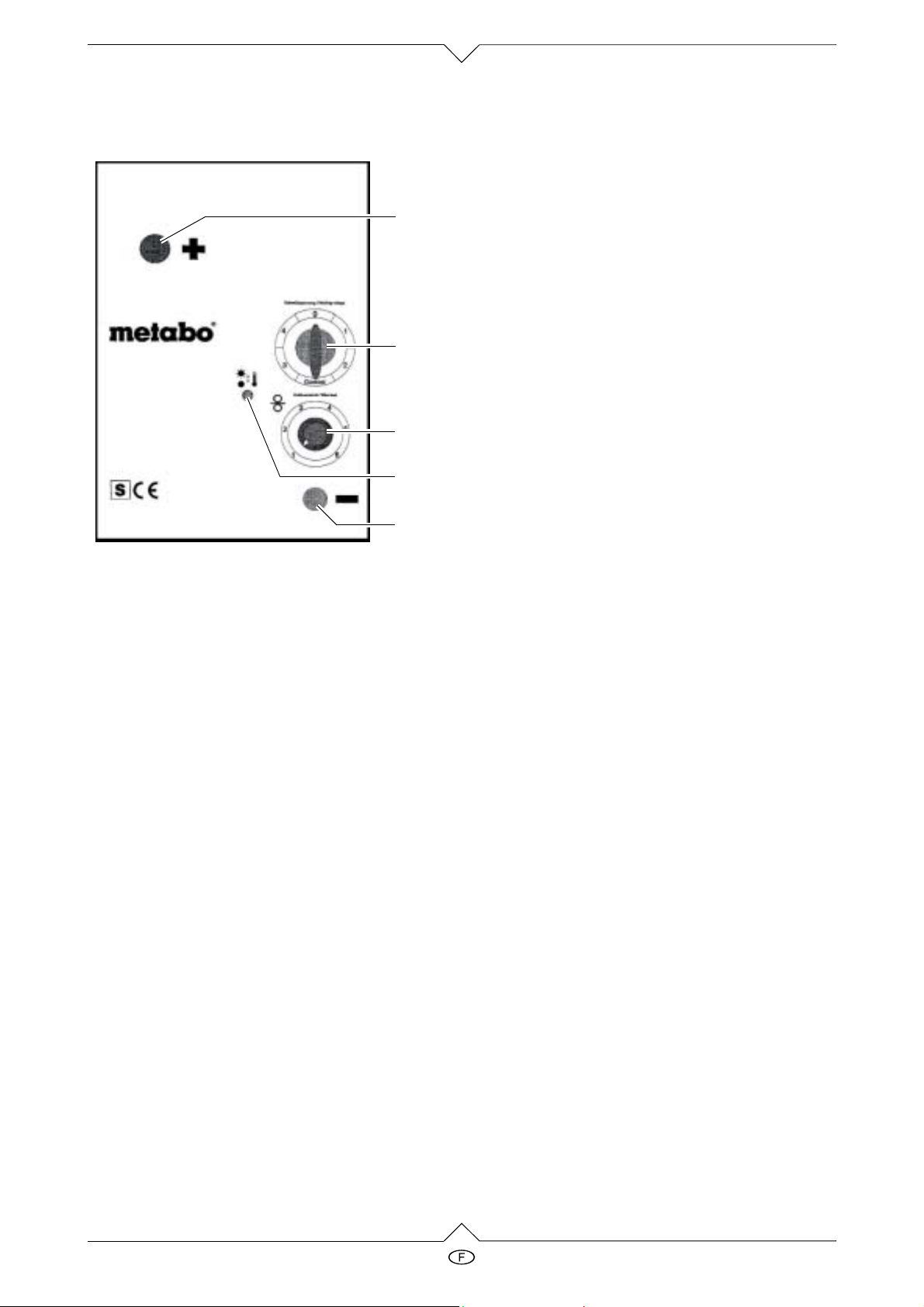
2France
Eléments de commande
1 Branchement chalumeau Pôle (+)
trique des prises de courant doit être protégé par
fusibles ou par interrupteur automatique.
Selon les conditions de branchement sur secteur au
point de jonction, les sources de courant de soudage peuvent entraîner des perturbations dans le sec-
1
2
3
4
5
teur pour d’autres consommateurs. Pour résoudre
ce problème et pour éviter de telles perturbations, il
est nécessaire de se renseigner avant le branche
ment auprès de l’entreprise chargée de l’alimentation en courant. (Classe A selon CISPR 11)
Il faut tenir l’appareil hors de la portée des enfants.
Tenez compte des risques que représentent les travaux de soudage et respectez le règlement du travail ainsi que les consignes de prévention
d’incendie.
L’appareil doit être rangé à l’abri de l’humidité et
n’est pas conçu pour être utilisé dehors, lorsqu’il
pleut.
L'appareil ne convient pas au décongelage de
tubes.
Danger!
A
Les personnes qui portent un stimulateur cardiaque doivent obligatoirement consulter leur
médecin avant de travailler avec l’appareil à
soudage!
-
2 Interrupteur marche/arrêt et courant de
soudage
3 Régulateur d’avancement du fil
4 Indicateur de surcharge
5 Branchement pince à électrodes à la
masse Pôle (–)
Cher client, chère cliente,
nous vous félicitons d’avoir acheté cet appareil de
soudage sous gaz protecteur de haute qualité.
Afin de garantir votre sécurité et la sécurité de
l’appareil, nous vous prions de bien vouloir lire com
plètement et consciencieusement ces instructions
avant la mise en service, et de respecter ces instructions en tous points.
-
Conseils de principe pour l’utilisateur
L’appareil de soudage sous gaz protecteur MIG/
MAG est une source de courant continu avec avancement du fil intégré, conçue et construite uniquement pour le soudage à l’arc MIG, voire MAG.
Toute autre utilisation de l’appareil est soumise à
des risques et donc interdite.
L’appareil ne peut être mis en service que sous la
tension secteur indiquée sur la plaque signalétique.
Le branchement ne peut se faire qu’avec des prises
de courant de sécurité, qui auront été installées par
un spécialiste autorisé en électricité. Le circuit élec-
Conseils de sécurité et mesures
préventives contre les accidents
x L’appareil à soudage sous gaz protecteur doit
être tenu hors de la portée des enfants.
x Lorsque l’on travaille avec l’appareil à soudage
sous gaz protecteur, il faut respecter le règlement du travail ainsi que les consignes de prévention d’incendie en vigueur. Il faut également
respecter les instructions préventives en
vigueur contre les accidents !
x Lors du soudage, différentes sortes de risques
pourraient éventuellement causer des domma
ges à la santé.
x Lors du soudage, il faut porter une combinaison
fermant hermétiquement, ne portant pas de tra
ces de substances qui s’enflamment facilement,
et sèche (mieux encore une combinaison pour
soudeur très résistante aux flammes), des
chaussures robustes, isolantes (bottes), une
protection sur la tête et des gants à fourreau en
cuir.
x Les vêtements en matières synthétiques ainsi
que les chaussures basses ne sont pas adéquats. Des gants isolants aux deux mains protègent des secousses électriques (tension à vide
du circuit électrique de soudage), des radiations
nocives (rayons thermiques et ultraviolets) de
même que des éclaboussures de métal ardent
et de laitier. La radiation ultraviolette a un effet
semblable aux coups de soleil sur les parties du
corps qui ne sont pas protégées.
-
-
MIG/MAG 140/160
2.1
Page 10

Gaz – vapeurs – fumée
x Pendant le soudage, il y a formation de fumée
nocive et de poussière de métal. Nous vous
conseillons d’utiliser des masques de protection
contre la fumée et de veiller à une alimentation
suffisante d’air frais dans les locaux où s’effectue le soudage, afin de garantir la protection
nécessaire du personnel.
x Dans des locaux fermés, il est absolument indis-
pensable d’utiliser des exhausteurs qui devront
être installés en-dessous de la zone de soudage.
x Le matériel que l’on veut souder ne doit pas por-
ter de traces de dégraissants à solution
halogène, pour empêcher la formation de gaz
toxiques.
x Les métaux qui sont recouverts de plomb, de
graphite, de cadmium, de zinc, de mercure ou
de béryllium ou qui contiennent ces matériaux,
sont susceptibles de dégager beaucoup de
fumée au cours du soudage.
x Lors du soudage, il y a dégagement d’ozone. Il
s’agit d’une sorte d’oxygène qui peut entraîner
des irritations ainsi que des maladies des orga
nes respiratoires.
x Les produits solvants de graisse comme le tri-
chloréthylène, le perchloréthylène, etc. s’évaporent pendant le soudage et se transforment, dû
à une modification chimique, en gaz phosgène.
Le gaz phogène est toxique!
Rayons ultraviolets
x Les rayons de l’arc électrique peuvent provo-
quer des blessures aux yeux et des brûlures de
la peau.
x Pour se protéger des étincelles, de la chaleur,
des rayons visibles et invisibles, il faut porter
des protections optiques adéquates (écran pro
tecteur ou coiffe protectrice pourvus de verres
de protection contre les rayons d’échelons 10 à
15 normés DIN 4647, selon la puissance électri
que).
x On ne doit pas regarder l’arc électrique si les
yeux ne sont pas protégés (risque d’éblouissement et de brûlure). Si la protection est insuffisante, la radiation ultraviolette invisible provoquera une conjonctivite douloureuse que l’on ne
remarquera que quelques heures plus tard.
x Pour effectuer le soudage, il est nécessaire
d’avoir à proximité des personnes qui pourront
venir à l’aide immédiatement, en cas d’accident.
x Les personnes ou les assistants qui sont à
proximité de l’arc électrique doivent être informés des dangers existants et être équipés de la
protection adéquate.
x Il est nécessaire de protéger les places de tra-
vail environnantes de la radiation: installer les
écrans de protection en conséquence.
x Lors de travaux de soudage dans des pièces et
des bâtiments, il faut veiller à une bonne circulation de l’air.
Feu
Danger!
A
La température de l’arc électrique s’élève
environ à 2400 °C.
Avant de commencer les travaux de soudage,
veuillez suivre les conseils suivants:
x Dans un rayon de 5 m de l’endroit de soudure, il
faut éloigner toutes les substances et les objets.
x Les substances se trouvant dans un rayon de 5
m et qui ne peuvent pas être éloignées doivent
être protégées correctement: on les recouvre de
tôles d’acier, de linges mouillés, etc.
x Les ouvertures, fentes, orifices dans les murs,
etc., doivent être recouverts ou calfeutrés afin
de les protéger des flammèches incontrôlées.
-
x Les moyens d’extinction tels que les extincteurs
de feu, les seaux à eau, etc., sont à tenir à disposition.
x N’oubliez pas que, dû à la conduction de cha-
leur au point de soudure, un incendie peut se
déclarer sur des objets recouverts ou dans
d’autres pièces.
x Après avoir terminé les travaux de soudage,
assurez-vous à plusieurs reprises dans les 6 – 8
heures qui suivent, qu’il ne reste pas d’endroits
incandescents, de foyers ardents ou de conduc
tion thermique aux environs de l’endroit où le
soudage a eu lieu.
-
Maniement des bouteilles de gaz protec-
-
-
teur
x Pour le maniement des bouteilles de gaz protec-
teur, il faut respecter les consignes de sécurité
en vigueur. Il faut tout particulièrement protéger
les bouteilles de gaz protecteur, à cause de leur
haute pression interne (jusqu’à 200 bar), des
détériorations mécaniques, empêcher qu’elles
ne basculent ou dégringolent. Il faut également
empêcher qu’elles ne se réchauffent (max.
50
°C), ne soient exposées trop longtemps aux
rayons du soleil ou à un gel extrême.
x Lorsque l’on équipe l’appareil MIG/MAG de la
bouteille de gaz protecteur, il faut être conscient
du fait que de trop grandes bouteilles, posées
un sol inégal, peuvent faire basculer l’appareil.
Pour éviter les dommages qui en résulteraient
pour l’appareil, voire pour la bouteille de gaz, on
ne doit utiliser que des bouteilles de taille conve
nable (bouteilles de 10 ou 20 litres).
-
2.2
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 11

x Pour faire remplir ou transvaser les bouteilles, il
faut s’adresser exclusivement aux firmes autorisées
Dangers venant du courant électrique
x Le branchement sur secteur ainsi que l’entretien
du dispositif de gaz protecteur doivent être faits
selon les consignes VDE.
x S’assurer que l’alimentation de courant est cor-
rectement mise à la terre.
x S’assurer que l’établi est correctement mis à la
terre.
x Seul un personnel qualifié peut effectuer l’entre-
tien.
x Les pièces du chalumeau ou du paquet de
tuyaux qui sont défectueuses ou détériorées
doivent être remplacées immédiatement.
x Le branchement de l’appareil ne pourra se faire
qu’à des prises de courant avec contact de mise
à la terre. On doit utiliser uniquement des bran
chements, y compris prises de courant et rallonges équipés de prises de courant de sécurité,
qui auront été installés par un spécialiste autorisé en électricité.
x La protection par fusibles du conducteur d’ame-
née aux prises de courant secteur doit correspondre aux consignes. Selon ces consignes, on
ne peut utiliser que des fusibles ou interrupteurs
automatiques qui correspondent à la section du
conducteur. Si la protection fusibles est trop
forte, il y a risque d’incendie au conducteur ou
risque de dommages suite à un incendie dans le
bâtiment.
x Si l’isolation du chalumeau ou les conducteurs
de soudage sont endommagés, il faut les remplacer immédiatement.
x Seul un spécialiste autorisé en électricité pourra
remplacer une ligne d’alimentation défectueuse,
une prise de courant de sécurité, etc., et effectuer les travaux de réparation de l’appareil à
soudage sous gaz protecteur.
x Il ne faut pas coincer le chalumeau soudeurs
sous le bras. En le tenant, il faut faire attention à
ce que le courant ne puisse passer dans le
corps humain.
x En cas d’une longue interruption du travail, met-
tez l’appareil hors-service. Après avoir fini le travail et avant de changer l’emplacement de
l’appareil, il faut retirer la prise de courant secteur. En cas d’accident, couper aussitôt la
source de courant de soudage du secteur.
courant en silicium intercalé à la suite, et d’un étranglement de la circulation de soudage, de même que
d’un dispositif d’avance d’électrode.
L’appareil est conçu pour le soudage de différentes
électrodes (par exemple l’acier, voir «Détails Techniques»), sous une atmosphère de gaz protecteur
(CO2, gaz mixte et argon.
L’appareil est refroidi par un ventilateur et muni
d’une protection de surcharge.
Symboles figurant sur l'appareil
Danger !
Le non-respect des mises en garde
suivantes peut entraîner des blessures ou des dommages matériels graves.
Avant de mettre en marche l'appareil,
lire les instructions d'utilisation.
-
Indications figurant sur la plaque signalétique :
6
6 Constructeur
7 Nom de l'appareil
Vitesse d'avance du fil
Ne pas utiliser sous la pluie
L'appareil peut être utilisé pour souder
dans un endroit à risque électrique
accru.
Surchauffe
78910
1213
11
Description générale de l’appareil
L’appareil de soudage sous gaz protecteur MIG/
MAG se compose d’un transformateur (Courbe
caractéristique statique) pourvu d’un redresseur de
MIG/MAG 140/160
8 Numéro de série
9 Norme de référence – cet appareil est con-
forme aux exigences de la norme indiquée.
2.3
Page 12

10 Sigle CE – cet appareil est conforme aux
directives européennes comme indiqué
dans la déclaration de conformité.
11 Symbole de mise au rebut – l'appareil peut
être remis au fabricant.
12 Caractéristiques électriques
13 Année de construction
Mise en service
Déballage des pièces jointes
Toutes les pièces jointes se trouvent dans le compartiment d’avance d’électrode et peuvent être retirées, après avoir enlevé la plaque de recouvrement.
Conditions de pose
x L'appareil de soudage sous protection doit être
implanté dans un environnement sec disposant
de suffisamment de place pour la ventilation.
x Quand l'appareil est placé sur une surface en
pente, il doit être empêché de basculer par des
moyens adéquats : placer l'appareil sur un sup
port plan approprié.
x L'appareil est conçu pour être utilisé dans des
locaux abrités. Il ne doit pas être soudé à l'extérieur par temps de pluie.
x Quantité de gaz qui circule – dans les pièces
sans courants d’air - à recommander: 5 – 10
litres par minute.
x Si l’on utilise des détendeurs réglables, il faut
régler la quantité de gaz qui circule selon la graduation en litres, à l’aide de la vis à garrot. Si l’on
visse vers l’intérieur, on augmente la quantité
qui circule. Si l’on vis vers l’extérieur, on diminue
la quantité qui circule.
x Lors du réglage, il faut mettre l’appareil en ser-
vice et l’interrupteur du chalumeau doit être
poussé pour pouvoir ouvrir la vanne magnétique. Pour éviter de consommer trop d’électrode,
on fait pivoter latéralement le ressort à lames de
l’avancement d’électrode.
Les opérations et réparations sur les détendeurs
sont interdits, á cause des dangers que représentent ces opérations. Les détendeurs qui sont défectueux doivent être expédiés à l’atelier prévu dans le
contrat de service après-vente.
Branchement de la pièce de travail
Connecter la borne de la pièce de travail à la ligne
de raccordement de la masse de l’appareil MIG/
MAG directement à côté du point de soudage. Véri
fier que le passage métallique au point de contact
est brillant.
-
Préparation du cordon de soudure
Les pièces de travail à souder ne doivent pas porter
de traces de peinture, couche métallique, pous-
-
sière, rouille, graisse ou humidité à l’endroit du cordon.
La préparation du cordon de soudure doit s’effectuer en respectant les consignes techniques de soudage.
Branchement secteur
x Vérifiez la concordance entre la tension indi-
quée sur la plaque signalétique et la tension de
votre secteur.
x Avant de brancher sur secteur, il faut mettre le
commutateur sélectif de tension secteur sur
zéro.
Branchement de la bouteille de gaz protecteur
x Poser la bouteille de gaz sur le support de bou-
teille de l’appareil et, à l’aide de la chaîne, fixer
la bouteille sur le support de bouteille de la paroi
arrière. Enlever le capuchon de sécurité et
ouvrir brièvement la soupape de la bouteille en
tenant celle-ci éloignée du corps.
x Visser le détendeur sur les tubulures filetées de
la bouteille de gaz. Installer le raccord de tuyau
entre le détendeur et le branchement d’alimentation de gaz de l’appareil MIG/MAG.
2.4
Conseils en matière de réglage et
de technique de soudage
Mise en service de l’appareil
Le réglage de l’appareil se fait à l’aide du commutateur de tension de soudage, combiné à l’interrupteur
Max-Min. Il faut couper l’appareil du secteur lorsque
l’interrupteur Max-Min. est sur zéro.
L’appareil est muni d’un contrôleur de température
qui met l’appareil hors service lors d’une surcharge.
Le déclenchement du contrôleur de température est
signalisé par un voyant lumineux. La source de cou
rant de soudage et l’avance d’électrode sont mis
provisoirement hors service.
Après refroidissement, la source de courant se rallume toute seule; le voyant lumineux s’éteint.
MIG/MAG 140/160
-
Page 13

Réglage des paramètres de soudage
Après préparation de l’appareil, on peut commencer
le soudage.
Pour cela, il faut ajuster les tensions de soudage et
la vitesse d’avance de l’électrode entre elles, en
fonction du travail de soudage à effectuer. Si on
augmente la vitesse d’avance de l’électrode, l’inten
sité du courant augmente également.
-
Pour chaque diamètre d’électrode de soudage et
chaque travail de soudage, on peut trouver les paramètres optimums. On les reconnaît entre autre au
bourdonnement typique émis par l’arc électrique.
Si l’on s’écarte trop des valeurs optimums, il ne sera
pas possible de souder sans défauts.
Le bon cordon de soudure
Dans le tableau, vous pouvez lire les instructions concernant réalisation de la forme de la fente.
Cordon-I d’un
côté
Cordon-I des
deux côtés
Cordon-V
Cordon-K
Cordon double-K
Cordon de coin
Forme de la fente Modèle Epaisseur
de la tôle
s (mm)
s
b
25
s
b
< 1,5
> 1,5
2 – 4 < 2
3 – 6 < 1
3 – 6 < 1
> 0,6 –
s
0,6 – 1,5 –
> 0,6 –
> 1 –
s
Largeur de
fente
b (mm)
0
< 2
MIG/MAG 140/160
2.5
Page 14

Entretien
L’appareil ne nécessite pratiquement pas d’entretien.
Danger – Tension électrique!
B
Avant de procéder à l’entretien de l’appareil
ou à un dépannage, il faut enlever la prise
secteur!
x Vérifier régulièrement la roue d’avancement, le
rouleau de pression et la tuyère d’entrée. S’ils
sont encrassés, il faut les nettoyer.
x A intervalles réguliers, il faut nettoyer le paquet
entier de tuyaux du chalumeau, vu que les
déchets de meulage et la poussière se dépo
sent à l’intérieur.
x La tuyère de contact du chalumeau est une
pièce d’usure perdue. Lorsque son forage est
trop gros, on doit la remplacer.
x Dans les parois intérieures du capuchon à gaz
enfichable du chalumeau, il y a des éclaboussures de métal qui s’incrustent. Si besoin est, il
faut les éliminer. Un agent séparateur facilite ce
travail et empêche que les éclaboussures ne
soient recollées de nouveau.
x Il faut remplacer immédiatement les lignes élec-
triques défectueuses.
Dépannage
On reconnaît dans la plupart des cas une panne
mécanique lorsque l’avance du fil est irrégulière ou
quand il y a un blocage de l’avancement du fil.
Les pannes électriques entraînent l’arrêt partiel ou
complet de l’appareil.
Danger – Tension électrique!
B
Le dépistage des erreurs dans la partie électrique de l’appareil ainsi que tous les travaux
sur les pièces électriques ne pourront être
effectués que par un spécialiste autorisé en
électricité.
En se rapportant au schéma de câblage, il est possible de dépister les autres erreurs.
Le dépistage des erreurs doit se faire d’abord sans
tension et dans l’ordre suivant:
1. Vérification de la stabilité du branchement secteur et des autres branchements aux commutateurs, du transformateur, de l’étranglement ainsi
que des prises de courant embrochables et des
jonctions par brasage.
2. Vérification du passage et du contact des fusibles.
3. Contrôle optique pour détecter éventuellement
les courts-circuits ou la surcharge de bobinages
(décoloration).
Panne, cause Dépannage
• Arc électrique qui vacille, voire instable?
Mauvaise position de
la tension de soudage
Trop / pas assez
d’électrode
Borne de connexion de
la pièce de travail est
lâche ou grande résistance au passage
(rouille, peinture)
Tuyère de contact
-
usée ou diamètre non
adéquat
Réglage de la quantité
de gaz n’est pas correct
La pièce de travail
n’est pas propre au
point du cordon de
soudure
Unité de puissance
défectueuse
Spirale enfichable
encrassée
Problème à l’avancement
• Beaucoup d’éclaboussures lors du soudage?
Trop d’électrode rembobiner le régulateur
Trop de tension de
soudage
Pièce de travail sale Nettoyer
• Le moteur d’avancement ne fonctionne pas?
Pas de tension secteur Contrôler le branchement
Commutateur de tension secteur est sur
zéro
Commutateur de chalumeau n’est pas
actionné
Fusible Faire remplacer par un spé-
Moteur défectueux Déposer à l’atelier de répa-
Corriger sur le commutateur
de tension à échelons
Régler sur le régulateur
d’avance de l’électrode
Etablir un bon contact entre
la pièce de travail et la borne
de connexion de la pièce de
travail
Remplacer
Régler la quantité de gaz
Enlever la peinture, la
rouille, la graisse, etc.
Déposer l’appareil à l’atelier
de réparation
Nettoyer et remplacer
Voir ci-dessous
d’avancement d’électrode
Faire descendre la tension
en diminuant au commutateur
secteur
Régler le degré de tension
Activer le commutateur de
chalumeau
cialiste en électricité autorisé
ration
2.6
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 15
• Pas de transport de l’électrode?
Rouleau de pression
trop lâche
Electrode est pliée à
l’avancement
Rainure de la roue
d’avancement détériorée
Electrode incinérée à
la tuyère de contact
Augmenter la pression de
serrage sur le ressort à
lames à l’aide d’une vis
moletée
Aligner la tuyère d’entrée
Remplacer la roue d’avancement
Remplacer la tuyère de contact, au cas où l’électrode
est déformée. Diminuer la
pression de serrage
• L’appareil s’arrête, le voyant de surcharge
s’allume?
Durée de mise en service est dépassée (ED)
Unité de puissance
défectueuse
Laisser l’appareil refroidir,
respecter ED selon la plaque signalétique
Déposer l’appareil à l’atelier
de réparation.
Détails techniques
MIG/MAG 140 MIG/MAG 160
Tension du secteur 1 x 230 V, 50/60 Hz 1 x 230 V, 50/60 Hz
Courant de ligne de raccordement max. 5,1 kVA 5,3 kVA
Courant de branchement max. 22 A 23 A
Protection par fusibles (à action retardée) 16 A 16 A
Tension en marche à vide 17,5 – 28 V 19 – 30 V
Etendue de réglage 30 – 140 A 30 – 160 A
Durée maximale d’allumage (40°C) 4 % 8 %
Echelons 4 4
Avancement du fil 1,0 – 12 m/min 1,0 – 12 m/min
Diamètre d’électrode 0,6 – 0,8 mm 0,6 – 0,8 mm
Mode de protection IP 21 IP 21
Longueur x largeur x hauteur 590 x 260 x 420 mm 590 x 260 x 420 mm
Poids 21 kg 26,5 kg
Plage de réglage du courant
Position MIG / MAG 140 MIG / MAG 160
130A30A
250A60A
380A100A
4140A160A
MIG/MAG 140/160
2.7
Page 16

XS0028N.fm
3Norge
Betjeningselementer
1
2
3
4
5
1 Tilkopling brenner (+)-pol
2 Av/på- og sveisestrømbryter
3 Innstilling sveisetrådfremtrekk
4 Overbelastningsindikator
5 Tilkopling jordledningskopling (–)-pol
Kjære kunde!
Takk for at du har kjøpt dette dekkgass-sveiseappa-
ratet med høy kvalitet.
For din egen sikkerhet og for apparatsikkerhetens
skyld ber vi deg lese hele denne bruksanvisningen
nøye før du tar apparatet i bruk, og følge alle punk
tene samvittighetsfullt.
styrrelser på nettet for andre apparater. For å
avklare dette spørsmålet og for å unngå forstyrrelser må man før tilkopling innhente opplysninger fra
strømleverandøren. (klasse A ifølge CISPR 11)
Barn må ikke ha tilgang til apparatet.
Det er viktig å være oppmerksom på farene som er
forbundet med sveiseprosessen og å overholde
arbeidsmiljø- og brannforskriftene.
Apparatet må beskyttes mot fuktighet ved oppbevaring og egner seg ikke til bruk utendørs i regnvær.
Apparatet er ikke egnet for opptining av rør.
Fare!
A
Personer med pacemaker bør alltid konsultere lege før sveising!
Sikkerhetsregler og ulykkesforebyggende tiltak
x Dekkgass-sveiseapparatet skal sikres mot barn.
x Ved arbeid med dekkgass-sveiseapparat skal
de aktuelle arbeidsmiljø- og brannvernforskriftene følges. De aktuelle forskriftene for å hindre
ulykker skal følges!
x Ved sveising kan det oppstå forskjellige farer
som under visse omstendigheter kan føre til helseskader.
x Ved sveising bør man ha på seg en tettsittende,
tørr arbeidsdress som ikke er forurenset av lettantennelige stoffer (helst en vanskelig antennelig sveisedress), solid, isolerende skotøy (støvler), hodebekledning og lærhansker med
mansjett.
x Klær av syntetiske materialer og vanlige små-
sko er uegnet. Isolerende hansker på begge
hender beskytter mot elektrisk støt (tomgangs
spenning i sveisestrømkretsen), mot skadelig
stråling (varme og UV-stråler) samt mot glø
dende metall- og slaggsprut. UV-stråling på
-
ubeskyttede kroppsdeler har samme virkning
som solbrenthet.
-
-
Viktige merknader for brukeren
Dekkgass-sveiseapparatet MIG/MAG er en likestrømskilde med integrert trådfremtrekk som er konstruert og bygd utelukkende for hhv. MIG- og MAGlysbuesveising.
All annen bruk av apparatet er forbundet med fare
og skal derfor unngås.
Apparatet skal bare drives med den nettspenningen
som er angitt på typeskiltet. Det må bare tilkoples
jordet stikkontakt som er installert av autorisert elek
troinstallatør. Strømkretsen til stikkontakten må
være sikret med smeltesikring eller vernebryter.
Avhengig av nettilkoplingsbetingelsene på tilkoplingspunktet kan sveisestrømkilden forårsake for-
3.1
-
Gass – damp – røyk
x Under sveisingen utvikles det skadelig røyk og
metallstøv. Vi anbefaler bruk av røykmaske og
at man bare sveiser i tilstrekkelig ventilerte rom
for å sikre den nødvendige beskyttelsen av personalet.
x Ved sveising i lukkede rom er det absolutt
påkrevd å bruke avtrekk som er plassert under
sveisesonen.
x Materialet som skal sveises, må være fritt for
halogenholdige avfettingsmidler for å hindre
dannelsen av giftige gasser.
x Metaller som er belagt med bly, grafitt, kad-
mium, sink, kvikksølv eller beryllium, eller som
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 17

inneholder disse stoffene, kan utvikle kraftig
røyk under sveisingen.
x Ved sveising frigjøres ozon. Det er en form for
oksygen som kan føre til irritasjon og sykdommer i luftveiene.
x Klorholdige fettløsende midler som trikloretylen,
perkloretylen osv. fordamper ved sveising og
gjennomgår en kjemisk forvandling til fosgen.
Fosgen er giftig!
UV-stråler
x Strålene fra lysbuen kan føre til øyeskader og
hudforbrenninger.
x Som vern mot gnister, varme, synlige og usyn-
lige stråler må man bruke egnet øyevern
(beskyttelsesskjold eller beskyttelseshette med
standardiserte strålevernglass trinn 10 til 15
ifølge DIN 4647, avhengig av strømstyrke).
x Man må aldri se inn i lysbuen med ubeskyttede
øyne (fare for å bli blendet og brent). Hvis man
ikke beskytter øynene tilstrekkelig, forårsaker
de usynlige UV-strålene en svært smertefull bin
dehinnebetennelse som først merkes etter noen
timer.
x Sveising må bare skje innenfor synsvidden til
andre personer som kan komme raskt til hjelp i
nødsfall.
x Personer eller hjelpere som befinner seg i nær-
heten av lysbuen, må opplyses om farene og
utstyres med nødvendig beskyttelse.
x Arbeidsplasser i nærheten skal avskjermes på
en egnet måte for å beskyttes mot strålepåvirkning.
x Ved sveisearbeider i rom og bygninger skal det
sørges for tilstrekkelig ventilasjon.
Brann
Fare!
A
Lysbuens temperatur ligger på ca. 2400 °C.
Før sveisearbeidene begynner, må du være oppmerksom på følgende:
x Brennbare stoffer og gjenstander innenfor en
omkrets på 5 m fra sveisestedet må fjernes.
x Stoffer innenfor en omkrets på 5 m, som ikke
kan fjernes, skal dekkes til på en adekvat måte
med stålplater, våte kleder osv.
x Åpninger, sprekker, hull i murer osv. skal dek-
kes til eller tettes igjen for å unngå ukontrollert
gnistregn.
x Slokkemidler som brannslokkere, vannbøtter
osv. skal være i beredskap.
x Vær oppmerksom på at det på grunn av varme-
leding fra sveisestedet også kan oppstå brann
på tildekkede steder eller i andre rom.
x Etter at sveisearbeidene er slutt, må du i løpet
av de neste 6 til 8 timene flere ganger kontrollere sveisestedets omgivelser med hensyn til
gløding, brannsteder, varmeleding osv.
Behandling av dekkgassflasker
x I omgangen med dekkgassflasker skal de aktu-
elle sikkerhetsforskriftene følges. Særlig må
dekkgassflaskene sikres mot mekaniske skader, velting og fall og beskyttes mot oppvarming
(maks. 50 °C), langvarig solbestråling og sterk
kulde på grunn av det farlig høye indre trykket
(opptil 200 bar).
x Når MIG/MAG-apparatet monteres til dekkgass-
flasken, må man være klar over at for store flasker kan føre til at apparatet velter hvis underlaget er ujevnt. For å unngå at det oppstår skader
på apparatet eller gassflasken på denne måten,
bør det bare brukes flaskestørrelser som passer
til apparatet. (10 l- eller 20 l-flasker).
x Etterfylling eller omfylling skal bare foretas av
-
godkjente firmaer.
Farer på grunn av elektrisk strøm
x Tilkopling til nettet og vedlikehold av dekkgass-
anlegget skal utføres forskriftsmessig.
x Sørg for at strømforsyningen er jordet.
x Sørg for at arbeidsbenken er jordet.
x Vedlikehold skal bare utføres av kvalifisert per-
sonale.
x Defekte eller skadede deler på brenner eller
slangepakke skal straks byttes ut.
x Apparatet skal alltid bare koples til stikkontakter
som er jordet. Det er bare tillatt å bruke tilkoplinger inkludert stikkontakter og skjøteledninger
med jordede kontakter som er installert av en
autorisert elektroinstallatør.
x Sikringen av tilførselsledningen til nettkontak-
tene må være i samsvar med forskriftene. Ifølge
disse forskriftene er det bare tillatt å bruke sikringer eller automater som samsvarer med ledningstverrsnittet. Bruk av sikring med for høy
kapasitet kan føre til ledningsbrann eller brannskader på bygning.
x Skadet isolasjon på sveisebrenner og skadede
sveiseledninger skal skiftes ut umiddelbart.
x Bytte av skadet nettledning, stikkontakt osv. og
reparasjoner på dekkgass-sveiseapparatet skal
bare utføres av autorisert elektroinstallatør.
x Sveisebrenneren må ikke klemmes fast under
armen eller holdes slik at det kan gå strøm gjennom kroppen.
x Ved lengre pauser i arbeidet skal apparatet set-
tes ut av drift. Etter at arbeidet er slutt og før
apparatet sskal flyttes, må støpselet trekkes ut
MIG/MAG 140/160
3.2
Page 18

av kontakten. Ved uhell eller ulykker skal sveisestrømkilden umiddelbart skilles fra nettet.
Generell beskrivelse av apparatet
MIG/MAG-dekkgass-sveiseapparatet består av en
transformator (statisk karakteristikk) med silisiumlikeretter og en sveisekretsspole samt en trådfremtrekksenhet.
Apparatet er beregnet på sveising av forskjellige
sveisetråder (f.eks. stål, s. Tekniske data) under en
beskyttende gassatmosfære (CO
og argon).
Apparatet er ventilatorkjølt og utstyrt med overbelastningsvern.
Symboler på apparatet
Fare!
Følgende advarsler må tas til følge
for å unngå store personskader eller
skader på gjenstander
Les bruksanvisningen før apparatet
tas i bruk
Trådmatingshastighet
Skal ikke brukes når det regner
Sveiseapparatet egner seg for sveising i
omgivelser med økt elektrisk fare.
Overtemperatur
Opplysninger på typeskiltet:
6
6 Produsent
7 Apparatbetegnelse
78910
, blandingsgass
2
1213
11
8 Serienummer
9 Normhenvisning – Apparatet oppfyller kra-
vene i h.t. angitt standard
10 CE-merke – Apparatet oppfyller EU-direkti-
vet i h.t. samsvarserklæringen
11 Avhendingssymbol – Apparatet kan avhen-
des via produsenten
12 Elektriske ytelsesdata
13 Produksjonsår
Å ta apparatet i bruk
Uttak av vedlagte deler
Alle vedlagte deler befinner seg i rommet for fremtrekk av sveisetråd, og kan tas ut etter at lokket er
fjernet.
Oppstilling
x Lysbuesveiseapparatet skal plasseres i en tørr
omgivelse med tilstrekkelig frihet for kjøling.
x Når apparatet plasseres på en skrå flate, må
den beskyttes mot å falle over. Plasser apparatet på et egnet, flatt underlag.
x Apparatet er konsipert for bruk i rom med tak.
Når det regner må det ikke sveises utendørs.
Nettilkopling
x Kontroller at spenningen som er angitt på type-
skiltet, stemmer overens med nettspenningen i
strømnettet på stedet.
x Før støpselet settes i kontakten, skal nettspen-
ningsbryteren settes på null.
Tilkopling av dekkgassflasken
x Sett gassflasken på apparatets flaskeoppstil-
lingsplass og fest den til flaskeholderen på bakveggen med kjettingen. Etter at beskyttelseshetten er tatt av, skal flaskeventilen vendes bort
fra kroppen og åpnes et lite øyeblikk.
x Skru trykkreduksjonsventilen på gjengestussen
på gassflasken. Opprett slangeforbindelse mel
lom trykkreduksjonsventilen og gasstilførselstilkoplingen på MIG/MAG-apparatet.
x Anbefalt gassgjennomstrømning i trekkfrie rom:
5 – 10 liter/minutt.
x Hvis det brukes regulerbar trykkreduksjonsven-
til, skal gassgjennomstrømningen stilles inn
etter literskalaen ved hjelp av vingeskrue. Skru
innover for å øke gjennomstrømningen og skru
utover for å redusere den.
-
3.3
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 19

x Mens innstillingen foregår, må apparatet være
slått på og brennerbryteren må være trykt inn,
slik at magnetventilen åpnes. For å unngå unø
dig sveisetrådforbruk, skal bladfjæren i sveisetrådfremtrekket svinges ut til siden.
Det er ikke tillatt å foreta inngrep og reparasjoner på
trykkreduksjonsventiler på grunn av de farene som
er forbundet med dette. Defekte trykkreduksjonsventiler skal sendes inn til serviceverkstedet.
Tilkopling av arbeidsstykket
Klem fast arbeidsstykkeklemmen fra MIG/MAGapparatets jordledning i umiddelbar nærhet av sveisestedet. Pass på at det er metallisk blank overgang
på kontaktstedet.
Forberedelse av sveisefugen
Arbeidsstykkene som skal sveises, skal være frie for
lakk, metallbelegg, smuss, rust, fett og fuktighet.
Forberedelsene av sveisefugen skal gjennomføres i
henhold til de sveisetekniske forskriftene.
Anvisninger om innstilling og om
sveiseteknikk
bryteren. Apparatet er skilt fra nettet når Max-Minbryteren står på null.
-
Apparatet er utstyrt med en temperaturføler som
kopler ut apparatet elektrisk ved overbelastning.
Kontrollampen gir signal når temperaturføleren reagerer. Sveisestrømkilden og sveisetrådfremtrekket
blir forbigående koplet ut.
Etter avkjøling koples strømkilden automatisk inn
igjen; signallampen slukkes.
Innstilling av sveiseparametere
Etter at forberedelsene er gjennomført, kan sveisingen begynne.
Sveisespenning og trådfremtrekkshastighet skal da
tilpasses til hverandre i henhold til sveiseoppgaven.
Hvis trådfremtrekkshastigheten økes, øker strøm
styrken.
Det er mulig å finne optimale parametere for enhver
sveisetråddiameter og enhver sveiseoppgave. De
kan blant annet kjennes igjen på den typisk sum
mende lysbuelyden.
Hvis man avviker for mye fra de optimale verdiene,
er det ikke mulig å få til perfekt sveising.
-
-
Innkopling av apparatet
Innstilling av apparatet skal skje ved hjelp av sveisespenningsbryteren i forbindelse med Max-Min-
Den riktige sveisefugen
I tabellen finner du anvisninger for forming av fuger.
Fugeform Utførelse Platetyk-
kelse
s (mm)
I-fuge ensidig < 1,5
I-fuge tosidig
V-fuge
25
s
b
s
b
> 1,5
2 – 4 < 2
3 – 6 < 1
3 – 6 < 1
Fugbredde
b (mm)
0
< 2
K-fuge
Dobbel K-fuge
MIG/MAG 140/160
s
> 0,6 –
0,6 – 1,5 –
> 0,6 –
3.4
Page 20

Hjørneskjøt
Fugeform Utførelse Platetyk-
kelse
s (mm)
> 1 –
s
Fugbredde
b (mm)
Stell og vedlikehold
Apparatet er for en stor del vedlikeholdsfritt.
Fare – elektrisk spenning!
B
Før ethvert vedlikehold og enhver feilretting
skal støpselet trekkes ut!
x Fremtrekkshjulet, mottrykksrullen og innløpsdy-
sen skal kontrolleres regelmessig med hensyn
til tilsmussing, om nødvendig må de rengjøres.
x Med jevne mellomrom må den komplette bren-
nerslangepakken rengjøres fordi det avsettes
avslitte partikler og støv innvendig.
x Brennerens kontaktdyse er en slitedel. Når hul-
let er blitt for stort, må den byttes.
x På innerveggene i brennerens gasskappe setter
det seg fast små metallpartikler. Disse må evt.
fjernes. Et skillemiddel letter dette arbeidet og
forebygger at splintene kleber seg fast.
x Skadede ledninger må straks skiftes ut.
Feilretting
Mekaniske feil viser seg for det meste ved ujevnt
sveisetrådfremtrekk eller ved at fremtrekket er blok
kert.
Elektriske feil fører til at apparatet faller ut helt eller
delvis.
Fare – elektrisk spenning!
B
Feilsøking i den elektriske delen av apparatet
og alle arbeider på det elektriske anlegget
skal utelukkende foretas av autorisert elektro
installatør.
Videre feilsøking er mulig i henhold til vedlagte koplingsskjema.
Feilsøkingen må først skje når apparatet er i spenningsløs tilstand og i følgende rekkefølge:
1. Det må kontrolleres at nettilkoplingen og de
andre tilkoplingene ved bryterne, trafoen og
drosselen* samt stikkontaktene og loddede forbindelser sitter fast.
2. Kontroll av sikringen med hensyn til passasje og
kontakt.
3. Optisk kontroll med hensyn til evt. kortslutninger
eller overbelastning av viklinger (misfarging).
-
-
Feil, årsak Retting
• Urolig eller ustabil lysbue?
Gal sveisespenningsstilling
For mye / for lite sveisetråd
Arbeidsstykkeklemmen løs eller stor overgangsmotstand (rust,
lakk)
Kontaktdyse slitt eller
gal diameter
Gassmengde galt innstilt
Arbeidsstykket urent i
sømområdet
Effektdel defekt Bring apparatet til service-
Inntrekksspiralen tilsmusset
Feil ved fremtrekket Se nedenfor
• Mye sprut ved sveisingen?
For mye sveisetråd Drei trådfremtrekksregulato-
For høy sveisespenning
Arbeidsstykket urent Rengjør det
• Fremtrekksmotoren går ikke?
Ingen nettspenning Kontroller nettilkoplingen
Nettspenningsbry-
teren står på null
Brennerbryter ikke slått påSlå på brennerbryteren
Sikring La en autorisert elektro-
Motor defekt Bring apparatet til service-
Korriger på spenningstrinnbryteren
Reguler på trådfremtrekksregulatoren
Sørg for at det er god kontakt mellom arbeidsstykket
og arbeidsstykkeklemmen
Bytt den
Still inn gassmengden
Fjern lakk, rust, fett osv.
verksted
Rengjør og skift den
ren tilbake
Still spenningstrinnbryteren
tilbake
Still inn spenningstrinnet
installatør skifte den
verksted
3.5
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 21

• Ingen sveisetrådtransport?
Mottrykksrullen for løs Øk mottrykket på bladfjæren
ved hjelp av fingerskruen
Sveisetråden brukket
av ved fremtrekket
Rille i fremtrekkshjulet
nedslitt
Tråd brent fast på
kontaktdysen
Rett ut innløpsdysen
Bytt fremtrekkshjul
Bytt kontaktdyse, hvis tråden er deformert, reduser
mottrykket
• Apparatet koples ut, overbelastningsindikatoren
lyser?
Innkoplingsvarighet
(ED) overskredet
Effektdel defekt Bring apparatet til service-
La apparatet kjøles ned,
overhold ED iht. typeskiltet
verksted
Tekniske data
MIG/MAG 140 MIG/MAG 160
Tilkoplingsspenning 1 x 230 V, 50/60 Hz 1 x 230 V, 50/60 Hz
Tilkoplingseffekt maks. 5,1 kVA 5,3 kVA
Tilkoplingsstrøm maks. 22 A 23 A
Sikring (treg) 16 A 16 A
Tomgangsspenning 17,5 – 28 V 19 – 30 V
Innstillingsområde 30 – 140 A 30 – 160 A
Maks. innkoplingsvarighet (40°C) 4 % 8 %
Trinn 4 4
Sveisetrådfremtrekk 1,0 – 12 m/min 1,0 – 12 m/min
Elektrodediameter 0,6 – 0,8 mm 0,6 – 0,8 mm
Kapslingsklasse IP 21 IP 21
Lengde x bredde x høyde 590 x 260 x 420 mm 590 x 260 x 420 mm
Vekt 21 kg 26,5 kg
Justeringsområde for strøm
Posisjon MIG / MAG 140 MIG / MAG 160
130A30A
250A60A
380A100A
4140A160A
MIG/MAG 140/160
3.6
Page 22

XS0028B.fm
4Suomi/ Finland
Käyttöohjeet
1
2
3
4
5
1 Hitsauspolttimen liityntä (+) napa
2 Hitsausvirran kytkentä/katkaisu
3 Langansyötön säädin
4 Ylikuormituksen merkkivalo
5 Maadoituspuristimen liityntä (–) napa
Hyvä asiakas
Parhaat onnittelumme tämän korkealaatuisen MIG/
MAG-hitsauskoneen hankinnan johdosta. Taataksemme turvallisuutesi ja laitteen turvallisen käytön,
pyydämme sinua lukemaan käyttöohjeet kokonaan
ennen koneen käyttöä ja noudattamaan kaikkia
kohtia.
Perustietoa käyttäjälle
MIG/MAG hitsauskone on vaihtovirtalähteellä ja
yhdistetyllä langansyöttölaitteella varustettu hitsauskone, joka on tarkoitettu yksinomaan MIG- ja
MAG-kaarihitsaukseen.
Kaikki tämän koneen muu käyttö on vaarallista, eikä
ole sallittua.
Hitsauskonetta tulee käyttää vain koneen arvokilvessä mainitulla pääjännitteellä. Kytkentä verkkoon
tulee tehdä pätevän sähköasentajan asentaman
maadoitetun pistokkeen kautta. Verkko tulee olla
suojattu sulakkeella tai pienoisvirtakytkimellä.
Riippuen virran kytkennästä kytkentäpisteessä hitsausvirtalähde voi aiheuttaa häiriöitä muille virrankuluttajille. Tarkista oma tehonkäyttösi ennen verkkoon kytkeytymistä. (CISPR 11, luokka A)
Pidä hitsauskone lasten ulottumattomissa.
Ota huomioon hitsaukseen liittyvät vaaratekijät ja
noudata kaikkia työhön ja palonestoon liittyviä määräyksiä.
Hitsauskone ei sovellu ulkokäyttöön sateessa. Säilytä kone kuivassa paikassa.
Laite ei sovi putkien sulattamiseen.
Varoitus:
A
henkilön, jolla on sydämentahdistaja, tulee
neuvotella lääkärinsä kanssa ennen tämän
hitsauskoneen käyttöä.
Turvallisuustietoa ja onnettomuuksien torjunnasta
x Pidä hitsauskone lasten ulottumattomissa.
x Noudata kaikkia työsuojelu- ja palontorjuntaoh-
jeita työskennellessäsi tällä hitsauskoneella.
x Noudata kaikkia soveltuvia onnettomuuden
esto-ohjeita. Hitsaukseen liittyy paljon erilaisia
vaaroja, mitkä voivat olla terveysriskejä tietyissä olosuhteissa.
x Käytä hitsatessa aina sopivia, kuivia haalareita
(suositellaan tulenkestäviä hitsaajan haalareita), tukevia eristettyjä saappaita, hitsaajan
maskia ja nahkaisia hitsaajan käsineitä.
x Synteettisistä aineista valmistetut vaatteet ja
kengät eivät ole suositeltavia.
Kuivat, eristävät käsineet molemmissa käsissä
suojaavat sähköiskuilta (hitsausvirtapiirin tyhjäkäyntijännite), vaaralliselta säteilyltä (lämpö- ja
ultraviolettisäteily) sekä hehkuvalta metallilta ja
kuonaroiskeilta. Ultraviolettisäteilystä tulee
auringonpolttovaikutus iholle.
Huurut - höyryt - savu
x Hitsauksen aikana kehittyy vaarallisia savuja ja
metallipölyjä. Hitsaajan työsuojelun takia suo
sittelemme voimakkaasti hitsaushuurujen poistoa ja hitsaamista ainoastaan kunnolla tuuletetuissa tiloissa.
x Suljetuissa tiloissa tulee käyttää tehostettua
tuuletusta, joka sijoitetaan hitsausalueen alapuolelle.
x Hitsattavassa materiaalissa ei saa olla halogee-
niliuottimia tai rasvanpoistoaineita, jottei niistä
muodostuisi myrkyllisiä höyryjä.
x Lyijyllä, grafiitilla, kadmiumilla, sinkillä, elohope-
alla tai berylliumilla päällystetyt tai niitä sisältävät metallit voivat muodostaa paljon savuja hitsauksen aikana.
x Hitsaus muodostaa otsonia, joka voi ärsyttää tai
vioittaa hengityselimiä.
x Rasvanpoistoaineet, kuten trikloorietyleeni, tet-
rakloorietyleeni jne höyrystyvät hitsauksen
aikana ja muuttuvat kemiallisesti fosgeeniksi
(karbonyylikloridi). Fosgeeni on myrkyllistä!
-
4.1
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 23

UV-säteily
x Kaaren säteily voi aiheuttaa silmävaurioita ja
ihon palamista.
x Kipinöiltä, lämmöltä, näkyvältä ja näkymättö-
mältä säteilyltä suojauee käyttää soveltuvaa silmäsuojainta (hitsausmaskia tai kypärää, jossa
on standardinmukainen suodattava suojalasi,
hitsausvirrasta riippuen luokat 10 B 15 DIN 4647
mukaisesti).
x Älä katso suojaamattomin silmin kaareen
(sokeutumis- ja paloriski). Näkymätön ultraviolettisäteily aiheuttaa, jos silmäsuojaus on riittämätön, hyvin kivuliaita, vasta tuntien päästä
ilmeneviä seuraamuksia.
x Hitsaa vain silloin, kun on näköetäisyys muihin,
että voit saada apua hätätilanteessa.
x Avustajien tai muitten lähelläolevien tulee olla
tietoisia vaaroista ja heillä tulee olla tarvittavat
suojavarusteet.
x Viereisten työpaikkojen tulee eristetty toisistaan
säteilysuojaverhoilla.
x Sisällä hitsattaessa tulee olla riittävä tuuletus.
Tulipalo
Varoitus!
A
Kaaren lämpötila on noin 2400 °C.
Ennen hitsauksen aloittamista noudata seuraavaa:
x Poista kaikki palava materiaali ja esineet 5 m
säteellä hitsauspaikasta.
x Materiaali, jota ei voi poistaa 5 m säteellä, tulee
suojata peittämällä se metallilevyillä, märillä
kankailla tms.
x Kaikki seinäaukot, halkeamat jne tulee peittää ja
tiivistää lentäviltä roiskeilta.
x Pidä palotorjuntalaitteet, kuten sammutin, vesi-
astia jne käsillä.
x Pidä mielessä, että palon leviäminen hitsaus-
paikasta voi alkaa peitetyistä osista tai muista
huoneista.
x Hitsaustyön lopettamisen jälkeen tarkista useita
kertoja 6 - 8 tunnin aikana, ettei ympäristössä
ole lämmön johtumista, palavia pisteitä, piilossa
olevat palopesäkkeitä jne.
Suojakaasupullojen käsittely
x Noudata kaasupullojen käsittelyä koskevia
määräyksiä. Vaarallisen korkean paineen
vuoksi (jopa 200 bar) suojakaasupulloja tulee
erityisesti suojata mekaanisilta vaurioilta, putoamiselta tai kaatumiselta, lämpenemiseltä (max.
50 °C), pitkäaikaiselta auringon säteilyltä tai
kovalta pakkaselta.
x Mikäli hitsauskone varustetaan liian suurella
kaasupullolla, siitä tai epätasaisesta perustasta
voi seurata hitsaus- koneen kaatuminen.
Estääksesi tällaisesta johtuvat hitsauskoneen
tai kaasupullon vauriot, käytä ainoastaan sopivan kokoisia kaasupulloja (10l / 20l pulloja).
x Pullojen täyttö tulee tehdä vain valtuutetuilla
täyttöasemilla.
Sähkövaarat
x Hitsauskoneen kytkeminen verkkoon ja huolto
tulee tehdä VDE-säännöksien tai muitten maahan soveltuvien standardien mukaan.
x Varmista kunnollinen syöttöpiirin suojakytkentä.
x Varmista työpenkin suojakytkentä.
x Vain pätevä henkilöstö saa tehdä huolto- tai
kunnossapitotöitä.
x Vaihda vialliset tai vahingoittuneet polttimen
osat tai polttimen johtimet välittömästi.
x Kone saadaan kytkeä periatteessa vain maa-
doitettuun liitäntään. Ainoastaan pätevän sähköasentajan asentamat maadoitetut liittimet, ml.
ulosotot, jatkokaapelit maadoitetuilla pistokkeilla ja maajohtimilla ovat sallittuja.
x Sähkösyötön suojasulakkeen tulee olla paikal-
listen määräyksien mukainen. Näitten määräyksien mukaan tulee asentaa sulakkeet tai pienoiskytkimet johtimen poikkipinnan mukaisesti.
Ampeerimäärältään liian suuren sulakkeen
asentaminen voi aiheuttaa sähkölinjaan palo
vaaran ja rakennukseen palovahinkoja.
x Vaihda vioittunut polttimen eriste tai vioittuneet
hitsauskaapelit välittömästi.
x Vioittuneen voimakaapelin, - tulpan jne vaihta-
minen ja hitsauskoneen sähköisten komponenttien korjaus tulee jättää pätevälle sähköasentajalle.
x Hitsauspoltinta ei tule kiinnittää käteen tai sillä
tavoin että virta voi johtua suoraan hitsaajaan.
Katkaise virta pitempien työkatkoksien ajaksi.
x Kytke kone pois verkosta, kun työ on valmis, tai
kun siirrät konetta. Onnettomuustilanteessa
irroita hitsausvirtalähde heti verkosta.
-
Koneen yleiskuvaus
MIG/MAG-hitsauskone muodostuu muuntajasta,
sarjaan kytketystä piitasasuuntaajasta (staattinen
ominaiskäyrä), hitsausvirran kuristimesta ja langansyöttöyksiköstä.
Hitsauskone sopii erilaisten hitsauslankojen suojakaasuhitsaukseen (mm teräslangan, ks "Tekninen
määrittely") suojakaasun ollessa CO2:ta, seoskaa
sua tai argonia.
Kone on varustettu tuulettimella ja ylikuormasuojalla.
-
MIG/MAG 140/160
4.2
Page 24

Symbolit laitteella
Vaara!
Seuraavien varoitusten laiminlyönti
voi johtaa vakaviin vammoihin.
Lue ohjekirja ennen käyttöönottoa.
Langansyöttönopeus
Älä käytä laitetta sateessa
Hitsauslaite sopii hitsaamiseen ympäristössä, jossa vallitsee tavallista suurempi
sähköinen vaara.
Ylikuumeneminen
Käyttöönotto
Mukana toimitettavat osat
Kaikki mukana toimitettavat osat ovat langansyöttöyksikön sisällä ja voidaan ottaa esille, kun langansyöttöyksikön kansi on irroitettu.
Asennus
x Suojakaasuhitsauslaite tulee sijoittaa kuivaan
ympäristöön, jossa on jäähdytyksen tarvitsema
määrä vapaata tilaa.
x Jos laite sijoitetaan vinolle alustalle, sen kaatu-
minen tulee estää: aseta laite suoran pinnan
muodostavalle kiilamaiselle alustalle.
x Laite on suunniteltu käytettäväksi katetuissa
tiloissa. Ulkona ei saa hitsata sateella.
Tiedot tyyppikilvellä:
6
6 Valmistaja
7 Laitenimitys
8 Sarjanumero
9 Normiohje - Tämä laite täyttää mainitun normin
10 CE-merkki – Tämä laite täyttää EU-direktiivit vaa-
11 Hävityssymboli – Laite voidaan hävittää valmista-
12 Sähköiset tiedot
13 Valmistusvuosi
78910
1213
vaatimukset
timuksenmukaisuusvakuutuksen mukaisesti
jan kautta
11
Verkkoon kytkentä
x Tarkista, että liitäntäjännite vastaa koneen arvo-
kilven jännitettä.
x Aseta koneen hitsauskytkin asentoon "0" ennen
verkkoon kytkemistä.
Suojakaasupullon liitäntä
x Aseta suojakaasupullo hitsauskoneen pulloteli-
neeseen ja lukitse pullo paikalleen koneen takaosassa olevalla ketjulla. Irroita pullon hattu ja
avaa pulloventtiiliiä hiukan poispäin itsestäsi.
x Ruuvaa paineenalennin kaasupullon venttiiliin.
Vedä kaasuletku paineenalentimesta koneen
kaasuliitäntään.
x Suositeltava kaasunvirtaus vedottomassa
tilassa on: 5-10 l/min.
x Käytettäessä säädettävää paineenalenninta
aseta virtaus kellossa olevan virtausasteikon
mukaan T-ruuvilla. Vääntämällä T-ruuvia
sisään kaasunvirtaus lisääntyy ja vääntämällä
sitä ulos virtaus vähenee.
x Säädettäessä kaasunvirtausta, kone tulee olla
kytkettynä päälle ja hitsauspolttimen liipasinta
tulee pitää alaspainettuna, niin että kaasuvent
tiilin solenoidi on auki. Jotta hitsauslankaa ei
kuluisi turhaan, käännä langansyöttöyksikön
lehtijousi sivulle.
Paineenalentimen muutokset ja korjaukset ovat
ehdottomasti kiellettyjä asiaan liittyvien vaarojen
vuoksi. Lähetä vialliset paineenalentimet huoltoon
korjattaviksi.
-
4.3
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 25

Maadoituksen liitäntä
Kiinnitä hitsauskoneen maadoituskaapelin puristin
mahdollisimman lähelle hitsauskohtaa. Varmista
hyvä metallikosketus.
Hitsisauman valmistelu
Hitsisauman alue työkappaleessa tulee olla puhdistettu maalista, metallipinnoitteista, liasta, ruosteesta, rasvasta ja kosteudesta.
Hitsisauman valmistelu tulee tehdä noudattaen hitsin suunnittelumääräyksiä.
Hitsaustekniikan ja koneen säätövihjeitä
Koneen kytkeminen päälle
Kone kytketään päälle yhdistetyllä ON/OFF B hitsauskytkimellä. Kytkimen asennossa "0" kone on sähköisesti irti sähkösyötöstä.
Koneeseen on kytketty lämpötunnistin, joka kytkee
koneen poispäältä lämpötilan noustessa liian korkealle.
Lämpöylikuorma näkyy koneen etupanelissa olevasta merkkivalosta. Hitsausvirtalähde ja langansyöttö eivät toimi. Jäähtymisen jälkeen hitsausvirtalähde ja langansyöttö kytkeytyvät automaattisesti
päälle ja merkkivalo sammuu.
Hitsausarvojen säätö
Hitsauskoneen valmistelujen jälkeen hitsaus voi
alkaa.
Hitsausjännitteen ja langansyöttönopeuden tulee
olla työhön sopivia. Kun langansyöttönopeus kasvaa, kasvaa hitsausvirta vastaavasti.
Jokaista langanhalkaisijaa ja jokaista hitsaustehtävää kohti löytyy optimiarvot. Ne voi tunnistaa mm.
tyypillisestä surisevasta kaaren äänestä.
Mikäli arvot poikkeavat liian paljon optimiarvoista,
hitsaus ei onnistu tyydyttävästi.
Oikea liitos
Allaolevassa taulukossa on informaatiota hitsisauman suunnittelusta.
Hitsisauman muoto Tyyppi Materiaalin
paksuus
s (mm)
1 x I-railo < 1,5
2 x I-railo
V-railo
Piena
25
s
b
s
b
> 1,5
2 – 4 < 2
3 – 6 < 1
3 – 6 < 1
> 0,6 –
s
0,6 – 1,5 –
Kaksoispiena
> 0,6 –
Juuren
avaus
b (mm)
0
< 2
Kulma
MIG/MAG 140/160
> 1 –
s
4.4
Page 26

Hoito ja kunnossapito
Kone on lähes huoltovapaa.
Vaara - jännittellinen
B
Kytke kone irti sähköverkosta ennen huoltoa!
x Tarkista syöttörulla, painerulla ja polttimen lan-
kajohdin-suutin säännöllisin väliajoin, puhdista
mikäli tarpeen.
x Sopivin väliajoin tulee puhdistaa koko hitsaus-
poltin mukaanlukien johtimet, kumiosat ja sisäpuolelle tulevat pölykertymät.
x Polttimen kontaktisuutin on kuluva osa. Reiän
suurennuttua suutin tulee vaihtaa.
x Paikalleen työnnettävään kaasusuuttimeen ker-
tyy roiskeita. Nämä tulee tarvittaessa poistaa.
Roiskeenestospray helpottaa työtä ja estää
roiskeita tarttumasta suuttimeen.
x Vaihda vioittuneet kaapelit välittömästi.
Vianetsintä
Mekaaniset viat ilmenevät useimmiten epäsäännöllisenä tai kokonaan keskeytyvänä langansyöttönä.
Sähköviat aiheuttavat laitteeseen virhetoimintoja,
joko yksittäiseen komponenttiin tai koko laitteeseen.
Vaara - jännittellinen
B
Sähkövikojen etsintä tulee jättää pätevälle
sähköasentajalle.
Se voidaan tehdä mukana olevan sähkökaavion
avulla.
Vikojen etsinnän tulee alkaa virran kytkemisellä pois
koneesta ja sitten seuraavassa järjestyksessä:
1. Tarkista sähkön syöttökaapelin liitäntä ja kaikki
kytkimien liitännät, muuntaja ja kuristin sekä
kaikki pistokkeiden ja tulppien liitännät ja juotet
tujen liitäntöjen tiukkuus.
2. Tarkista sulakkeen johtavuus ja kontakti.
3. Tarkista silmämääräisesti käämien ylikuormitus
tai puutteet (värittyminen).
-
Todennäköinen syy Korjaus
• Äänekäs tai epästabiili kaari
Väärä hitsausjännite Korjaa hitsauskytkimellä
Liikaa/liian vähän lan-
gansyöttöä
Maadoituspuristin löy-
sällä tai suuri vastus
kontaktissa (ruoste,
maali)
Kontaktisuutin kulunut
tai väärä halkaisija
Väärä kaasuvirtauksen
asetus
Työkappale likainen
sauma-alueella
Virtalähde viallinen Tarkastuta kone huollossa
Spiraalijohdin likainen Puhdista tai vaihda
Langansyöttö viallinen Ks alla
• Liiallista roiskuntaa
Liian suuri langansyöttö
Liian korkea jännite Korjaa hitsauskytkimellä
Likainen työkappale Puhdista
• Langansyöttömoottori ei pyöri
Ei virtaa Tarkista virtalähde
Hitsauskytkin "0"
asennossa
Polttimen liipasin ei
päällä
Sulake palanut Anna pätevän sähköasenta-
Moottori viallinen Korjauta huollossa
• Ei langansyöttöä
Painerullat löysällä Lisää lehtijousen painetta
Lanka mutkalla syötössä
Ura syöttörullassa
kulunut
Lanka jumissa kontaktisuuttimessa
Korjaa langansyöttöpotentiometrillä
Varmista hyvä kontakti maadoitus-puristimen ja työkpl:n
välille
Vaihda
Korjaa
Poista maali, ruoste, rasva
jne
Korjaa langansyöttöpotentiometrillä
Aseta hitsausasentoon
Paina liipasinta
jan vaihtaa
pyälletyllä peukalopyörällä
Säädä langan kulku suutti-
messa
Vaihda
Vaihda kontaktisuutin, jos
lanka litistyy, vähennä painerullan painetta
4.5
• Kone sammuu, ylikuormitusvalo palaa
Liiallinen kuormitus Anna koneen jäähtyä, tar-
kista kuormitettavuus arvokilvestä
Virtalähde viallinen Korjauta huollossa
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 27

Tekninen erittely
MIG/MAG 140 MIG/MAG 160
Liitäntäjännite 1 x 230 V, 50/60 Hz 1 x 230 V, 50/60 Hz
Liitetty teho 5,1 kVA 5,3 kVA
Max. virta 22 A 23 A
Pääsulake, hidas 16 A 16 A
Tyhjäkäyntijännite 17,5 – 28 V 19 – 30 V
Hitsausvirta-alue 30 – 140 A 30 – 160 A
Kuormitettavuus (40°C) 4 % 8 %
Hitsausportaat 4 4
Langansyöttönopeus 1,0 – 12 m/min 1,0 – 12 m/min
Langanhalkaisija 0,6 – 0,8 mm 0,6 – 0,8 mm
Suojausluokka IP 21 IP 21
Pituus x Leveys x Korkeus 590 x 260 x 420 mm 590 x 260 x 420 mm
Paino 21 kg 26,5 kg
Virransäätöalue
Taso MIG / MAG 140 MIG / MAG 160
130A30A
250A60A
380A100A
4140A160A
MIG/MAG 140/160
4.6
Page 28

XS0028A.fm
5Sverige
Manöverdon
1
2
3
4
5
1 Anslutning brännare (+) Pol
2 Till/Från och svetsströmbrytare
3 Trådmatarinställning
4 överbelastningsindikering
5 Anslutning jordklämma (–) Pol
Bäste kund!
Vi gratulerar till köpet av denna kraftfulla skyddsgas-
svets.
Läs noggrant igenom hela bruksanvisningen före
start. Detta för att garantera Din egen och svetsens
säkerhet. Tänk på att följa alla punkter i bruksanvis
ningen.
-
Grundläggande tips för användaren
MIG/MAG-skyddsgassvets är en likströmskälla med
integrerad trådmatning, som uteslutande är konstruerad och byggd för MIG- resp MAG-bågssvetsning.
All annan användning av svetsen är förenad med
risker och måste därför undvikas.
Svetsen får endast användas med den nätspänning, som är angiven på märkskylten. Anslutning får
endast ske via skyddsjordad stickkontakt, som har
installerats av behörig elektriker. Stickkontaktens
strömkrets måste vara säkrad genom smältsäkringar eller jordfelsbrytare.
Beroende på nätanslutningsförhållandena vid
anslutningspunkten kan svetsströmkällor orsaka
störningar för andra användare i nätet. För att klara
ut denna fråga och för att undvika störningar, måste
strömleverantören rådfrågas. (Klass A enligt
CISPR° 11)
Svetsen måste skyddas från barn före användning.
Beakta alltid de risker som är förenade med svets-
processen och följ noga arbets- och brandskyddsföreskrifterna.
Förvara svetsen i torrt utrymme. Den är inte lämplig
för användning utomhus vid regn.
Apparaten är inte lämpad för att tina rör.
Fara!
A
Personer med pacemaker måste konsultera
läkare innan svetsningsarbete påbörjas!
Säkerhetsanvisningar och åtgärder för förhindrande av olycksfall
x Svetsen måste skyddas från barn före använd-
ning.
x Vid arbeten med skyddsgassvets måste tillämp-
liga arbets- och brandskyddsföreskrifter beaktas. Likaså måste tillämpliga föreskrifter för förebyggande av olycksfall beaktas!
x Vid svetsning kan olika slags risker uppstå, vilka
ibland kan leda till hälsovådliga skador.
x Vid svetsning bör operatören vara iklädd rena,
torra arbetskläder (eller ännu bättre en svetsoverall av flamsäkert material), stadiga, isolerande skor (stövlar) och kraghandskar av läder.
x Klädespersedlar av syntetiskt material samt låg-
skor är olämpliga. Handskar, som bör användas
på båda händerna, skyddar mot elchock (svets
strömkretsens tomgångsspänning), skadlig
strålning (värme och UV-strålning) samt glö
dande metall och slaggrester. UV-strålning ger
en solbränneliknande effekt på oskyddad hud.
Gaser– ångor – rök
x Under svetsningen utvecklas skadlig rök och
skadligt metalldamm. Vi rekommenderar att rök
skyddsmask alltid används och att svetsning
sker i väl ventilerade utrymmen, för att erforderligt personligt skydd ska kunna garanteras.
x I utrymmen med stillastående luft måste ovillkor-
ligen en utsugningsanordning användas. Denna
placeras lämpligen under svetsområdet.
x Arbetsstycken måste vara fria från halogen-lös-
nings-avfettningsmedel, för att förhindra bildandet av giftiga gaser.
x Metaller, som är överdragna med bly, grafit,
kadmium, zink, kvicksilver eller beryllium eller
som innehåller dessa ämnen, kan framkalla
kraftig rök under svetsningsarbete.
-
-
-
5.1
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 29

x Vid svetsning frisläpps ozon. Detta är ett slags
syre, som kan leda till retningar och skador i
andningsorganen.
x Klorhaltiga fettlösningsmedel såsom triklorety-
len, perkloretylen osv förångas vid svetsning
och genomgår en kemisk förändring till fosgen.
Fosgen är giftigt!
UV-strålar
x Ljusbågens strålar kan leda till ögonskador och
brännskador på huden.
x Till skydd mot gnistor, värme, synliga och osyn-
liga strålar måste passande ögonskydd användas (svetsskärm eller svetshuv med normerat
strålskyddsglas, steg 10 till 15 enligt DIN 4647,
beroende på strömstyrka).
x Titta inte med oskyddade ögon på ljusbågen
(risk för bländning och bränning). Den osynliga
UV-strålningen orsakar vid otillräckligt skydd en
mycket smärtsam bindhinneinflammation, som
inte märks förrän efter några timmar.
x Svetsa endast inom synhåll från andra perso-
ner, som i nödfall kan komma till hjälp.
x Personer eller medhjälpare, som finns i närhe-
ten, måste göras uppmärksamma på riskerna
och förses med nödvändig skyddsutrustning.
x Närliggande arbetsplatser skyddas genom
avskärmning från strålarnas påverkan.
x Vid svetsning inomhus måste alltid tillräcklig luft-
försörjning finnas (till- och frånluft).
Brand
Fara!
A
Ljusbågens temperatur uppgår till ca
2400 °C.
Vidta följande åtgärder innan svetsningsarbetet
påbörjas:
x Brännbara ämnen och föremål tas bort inom en
omkrets av 5 m från svetsstället.
x Ämnen inom en omkrets av 5 m, som inte kan
tas bort, måste skyddas genom passande täckning med plåt, våta dukar osv.
x öppningar, springor osv måste täckas över eller
tätas för att stoppa okontrollerade svetsloppor.
x Släckningsmaterial, såsom eldsläckare eller
vattenhinkar, måste finnas tillgängligt.
x Tänk på att brand kan uppstå på grund av vär-
meöverföring från svetsstället till övertäckta
delar eller till andra utrymmen.
x Kontrollera svetsställets omgivningar efter
avslutat svetsningsarbete. Gör flera kontroller
under 6 till 8 timmar och leta efter glöder, brand
härdar, värmeöverföring osv.
-
Hantering av skyddsgastuber
x Vid hantering av skyddsgastuber måste tillämp-
liga säkerhetsföreskrifter beaktas. Framförallt
måste skyddsgastuberna skyddas mot mekanisk skada, tippning och fall på grund av det
höga innertrycket (upp till 200 bar). De måste
även skyddas mot uppvärmning (max. 50 °C),
längre tids soluppvärmning och stark kyla.
x Vid bestyckning av MIG/MAG-svetsen med
skyddsgastub, måste observeras att för stora
tuber kan orsaka att svetsen välter vid ojämnt
underlag. För att undvika skador på svetsen
eller på gastuben av sådana skäl, bör endast
lämpliga tubstorlekar användas (10 liters- och
20 liters-tuber).
x Påfyllning av tuber får endast utföras av företag
med tillstånd.
Risker genom elström
x Anslutning till nätet ska utföras enl starkströms-
föreskrifterna och underhåll av skyddsgasanläggningen enligt gällande SÄIFS och AFS.
x Kontrollera att strömtillförseln är jordad på kor-
rekt sätt.
x Kontrollera att arbetsbänken är jordad på kor-
rekt sätt.
x Underhåll får endast utföras av därför utbildad
arbetskraft.
x Defekta eller skadade delar på brännaren eller
slangpaketet måste omedelbart bytas.
x Svetsen får endast anslutas till jordat uttag.
Endast jordade anslutningar, inklusive stickkontakter och förlängningskablar, som har installerats av behörig elektriker, får användas.
x Säkring av matningen till nätuttagen måste mot-
svara aktuella föreskrifter. Enligt dessa föreskrifter får endast säkringar eller automatsäkringar användas, som motsvarar kabelns area.
En översäkring kan orsaka brand i kablar, bygg
nad osv.
x Skadad isolering på brännaren och skadade
svetskablar måste genast bytas.
x Byte av en skadad nätkabel, jordad kontakt mm
och reparation av skyddsgassvetsen, får endast
utföras av behörig elektriker.
x Brännaren får inte hållas fast under armen eller
på ett sådant sätt, att strömmen kan passera
genom kroppen.
x Vid längre arbetsuppehåll ska svetsen stängas
av. När arbetet är avslutat och innan svetsen
flyttas måste stickkontakten dras ur. Vid olyckor
måste svetsströmkälllan genast kopplas bort
från nätet.
-
MIG/MAG 140/160
5.2
Page 30
Allmän beskrivning av svetsen
MIG/MAG-skyddsgassvetsen består av en transformator (statisk karakteristik)med efterställd kisellikriktare, en svetskretsdrossel och en trådmatarenhet.
Svetsen är avsedd att användas för svetsning med
olika slags svetstråd (t ex stål, se Tekniska data)
under skyddsgas (CO2, blandgas och argon).
Svetsen är fläktkyld och utrustad med överbelastningsskydd.
Symboler på svetsen
Fara!
Att strunta i följande varningar kan få
allvarliga person- eller materialskador till följd.
Läs igenom bruksanvisningen innan
du börjar använda svetsen
Svetstrådens matningshastighet
Får inte användas vid regn
Svetsen kan användas för svetsning i
områden med ökad risk för elektrisk
ström.
Övertemperatur
10 CE-märkning – Den här apparaten uppfyller kra-
ven för EU-direktiven enligt Förklaringen om överensstämmelse
11 Återvinningssymbol – apparaten kan lämnas till
tillverkaren för återvinning/kassering
12 Elektriska effektdata
13 Byggår
Driftsättning
Urtagning av lösa delar
Alla lösa delar finns i trådmatarfacket och kan tas ur
när täckkåpan har tagits av.
Uppställning av svetsen
x Skyddsgassvetsapparaten skall placeras i torr
omgivning och med tillräcklig utrymme för kylningen.
x Om apparaten placeras på ett lutande underlag
skall den säkras mot tippning: Placera apparaten på en lämplig, plan yta.
x Apparaten koncipierades för användning i
utrymmen under tak. Vid regn får ingen svetsning ske utomhus.
Angivelser på märkplåten:
6
6 Tillverkare
7 Maskinbeteckning
8 Serienummer
9 Normhänvisning – Den här apparaten uppfyller
78910
1213
kraven för nämnda norm
11
Nätanslutning
x Kontrollera att angiven spänning på typskylten
överensstämmer med nätspänningen.
x Innan stickkontakten sticks i, måste nätspän-
ningsomkopplaren ställas på Noll.
Anslutning av skyddsgastuben
x Ställ gastuben i tubstället på svetsen och fäst
den med en kedja vid tubhållaren på baksidan.
Prova funktionen genom att ta av tubventilens
skyddskåpa och släppa ut lite gas i riktning från
operatören.
x Skruva på tryckregulatorn på gastubens gängs-
tos. Anslut slangen mellan tryckregulatorn och
gastillförselanslutningen på MIG/MAG-svetsen.
x Rekommenderat gasflöde i utrymmen utan
genomluftning: 5 – 10 liter/minut.
x Vid användning av inställbar tryckregulator
ställs gasflödet in enligt literskalan med hjälp av
den lettrade skruven. Inskruvning innebär ökat
gasflöde – utskruvning innebär minskat gasflöde.
x Under inställning måste svetsen vara påslagen
och svetskontakten vara intryckt, så att magnet-
5.3
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 31

ventilen öppnas. För att undvika onödig förbrukning av svetstråd, kan trådmatarens bladfjäder
svängas ut åt sidan.
Ingrepp och reparation av tryckregulatorer är inte
tillåtet på grund av därmed sammanhängande risker. En trasig tryckregulator skickas till serviceverkstaden.
Anslutning av arbetsstycket
Jorda jordledningens arbetsstyckeklämma i omedelbar anslutning till svetsstället. Se till att få ordentlig metallkontakt på kontaktstället.
Svetsfogsförberedelse
De arbetsstycken, som ska svetsas, måste vara fria
från färg, metallöverdrag, smuts, rost, fett och fukt i
fogområdet.
Svetsfogsförberedelserna ska genomföras med
hänsyn till svetstekniska föreskrifter.
Anvisningar för inställning och
svetsteknik
Påkoppling av svetsen
Inställning av svetsen görs med svetsspänningsomkopplaren tillsammans med Min-Max-omkopplaren.
Svetsen är inte ansluten till nätet när Min-Maxomkopplaren står på noll.
Svetsen är utrustad med en temperaturvakt, som
stänger av strömmen vid överbelastning.
Aktivering av temperaturvakten indikeras av kontrollampan. Svetsströmkällan och trådmatningen
stängs av tillfälligt.
Efter avkylning slås strömkällan på av sig själv; kontrollampan slocknar.
Inställning av svetsparametrarna
När svetsen har förberetts, kan svetsningen påbörjas.
Därvid måste svetsspänningar och trådmatningshastighet anpassas till varandra beroende på svetsarbete. Vid ökad trådmatningshastighet stiger
strömstyrkan.
Man kan fastställa optimala parametrar för alla
svetstrådsdiametrar och alla svetsuppgifter. De
känns bl a igen på det typiska sjungande ljusbåge
ljudet.
Om man avviker för mycket från optimalvärdena, är
en korrekt svetsning inte möjlig.
-
Korrekt svetsfog
Läs ut anvisningar för utformning av svetsfogen ur tabellen.
Fogform
I-fog ensidig < 1,5
I-fog tvåsidig
s
b
V-fog
25
s
b
K-fog
Utförande Plåttjocklek
s (mm)
> 1,5
2 – 4 < 2
3 – 6 < 1
3 – 6 < 1
> 0,6 –
s
0,6 – 1,5 –
Dubbel-K-fog
> 0,6 –
Fogbredd
b (mm)
0
< 2
MIG/MAG 140/160
5.4
Page 32

Fogform
Utförande Plåttjocklek
s (mm)
Fogbredd
b (mm)
Hörnfog
s
Service och underhåll
Svetsen kräver lite underhåll.
Fara – elspänning!
B
Före underhållsarbete eller avhjälpande av
fel måste stickkontakten dras ur.
x Matarrullen, tryckrullen och inloppsmunstycket
måste regelbundet kontrolleras och vid behov
rengöras.
x Med jämna mellanrum måste hela brännar-
slangpaketet rengöras, eftersom friktionsrester
och damm samlas inuti slangpaketet.
x Brännarens kontaktmunstycke är en förslit-
ningsdetalj. När hålet har blivit för stort, måste
munstycket bytas.
x På innerväggarna i brännarens insticksgaskåpa
fastnar metallsprut. Dessa bör tas bort. Ett
lämpligt svetsspray underlättar detta arbete och
förebygger att sprut fastnar.
x Skadade ledningar måste genast bytas.
Åtgärd av fel
Mekaniska fel visar sig oftast i samband med oregelbunden trådmatning eller genom blockering av
trådmatningen.
Elektriska fel får till följd att svetsen stannar delvis
eller helt och hållet.
Fara – elspänning!
B
Felsökning i svetsens elektriska del och alla
elarbeten får endast utföras av behörig elek
triker.
Vidare felsökning är möjlig enligt bifogat kretsschema.
Felsökning bör först utföras i spänningslöst tillstånd
och i följande ordningsföljd:
1. Kontroll av nätanslutning och övriga anslutningar på omkopplare, transformator och drossel samt att insticksanslutningar och lödställen
sitter ordentligt.
2. Kontroll av säkringens storlek och kontakt.
3. Visuell kontroll av ev kortslutning eller överbelastning av lindningar (missfärgning).
> 1 –
Störning, orsak Åtgärd
• Orolig eller instabil ljusbåge?
Felaktig svetsspännings-inställning
För mycket/för lite tråd Ställ in på trådmatningsin-
Arbetsstyckeklämman
lös eller stort övergångsmotstånd (rost färg)
Kontaktmunstycke slitet
eller fel diameter
Fel gasmängd inställd Ställ in gasmängden
Arbetsstycket förorenat i
fogområdet
Effektdelen trasig Kontakta serviceverkstaden
Insatsspiral smutsig Rengör eller byt spiral
Fel på matningen Se nedan
• Mycket sprut vid svetsningen?
För mycket tråd Vrid tillbaka trådmatningsin-
För mycket svetsspänning
Arbetsstycket smutsigt Rengör arbetsstycket
• Matarmotorn går inte?
Nätspänning saknas Kontrollera nätanslutningen
Nätspänningsom-kopp-
laren står på noll
Svetskontakten inte
intryckt
-
Säkring Låt behörig elektriker byta
Motorn trasig Kontakta serviceverkstaden
• Ingen trådmatning?
Tryckrullen för lös öka anliggningstrycket på
Tråden bockad vid matningen
Ränder på matarrullen
slitna
Tråden har bränt fast i
kontaktmunstycket
• Svetsen stängs av, överbelastningsindikering
lyser?
Intermittens överskriden
Effektdel trasig Kontakta serviceverkstaden
Korrigera på spänningsstegomkopplaren
ställningen
Upprätta god kontakt mellan
arbetsstycke och arbetsstykkeklämma
Byt munstycke
Ta bort färg, rost, fett osv
ställningen
Vrid tillbaka spänningsste-
gomkopplaren
Ställ in spänningssteg
Tryck in svetskontakten
säkringen
bladfjädern med lettrad skruv
Rikta matarmunstycket???
Byt matarrulle
Byt kontaktmunstycke. Om
tråden är deformerad, minska
anliggningstrycket
Låt svetsen svalna, håll
intermittens enligt typskylt
5.5
MIG/MAG 140/160
Page 33

Tekniska data
MIG/MAG 140 MIG/MAG 160
Anslutningsspänning 1 x 230 V, 50/60 Hz 1 x 230 V, 50/60 Hz
Anslutningseffekt max. 5,1 kVA 5,3 kVA
Anslutningsström max. 22 A 23 A
Säkring (trög) 16 A 16 A
Tomgångsspänning 17,5 – 28 V 19 – 30 V
Inställningsområde 30 – 140 A 30 – 160 A
Max intermittens (40 °C) 4 % 8 %
Antal steg 4 4
Trådmatning 1,0 – 12 m/min 1,0 – 12 m/min
Elektroddiameter 0,6 – 0,8 mm 0,6 – 0,8 mm
Skyddsklass IP 21 IP 21
Längd x bredd x höjd
Vikt 21 kg 26,5 kg
590 x 260 x 420 mm 590 x 260 x 420 mm
Ströminställningsområde
Läge MIG / MAG 140 MIG / MAG 160
130A30A
250A60A
380A100A
4140A160A
MIG/MAG 140/160
5.6
 Loading...
Loading...